⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
MicroMix: Efficient Mixed-Precision Quantization with Microscaling Formats for Large Language Models
Authors:Wenyuan Liu, Haoqian Meng, Yilun Luo, Peng Zhang, Xindian Ma
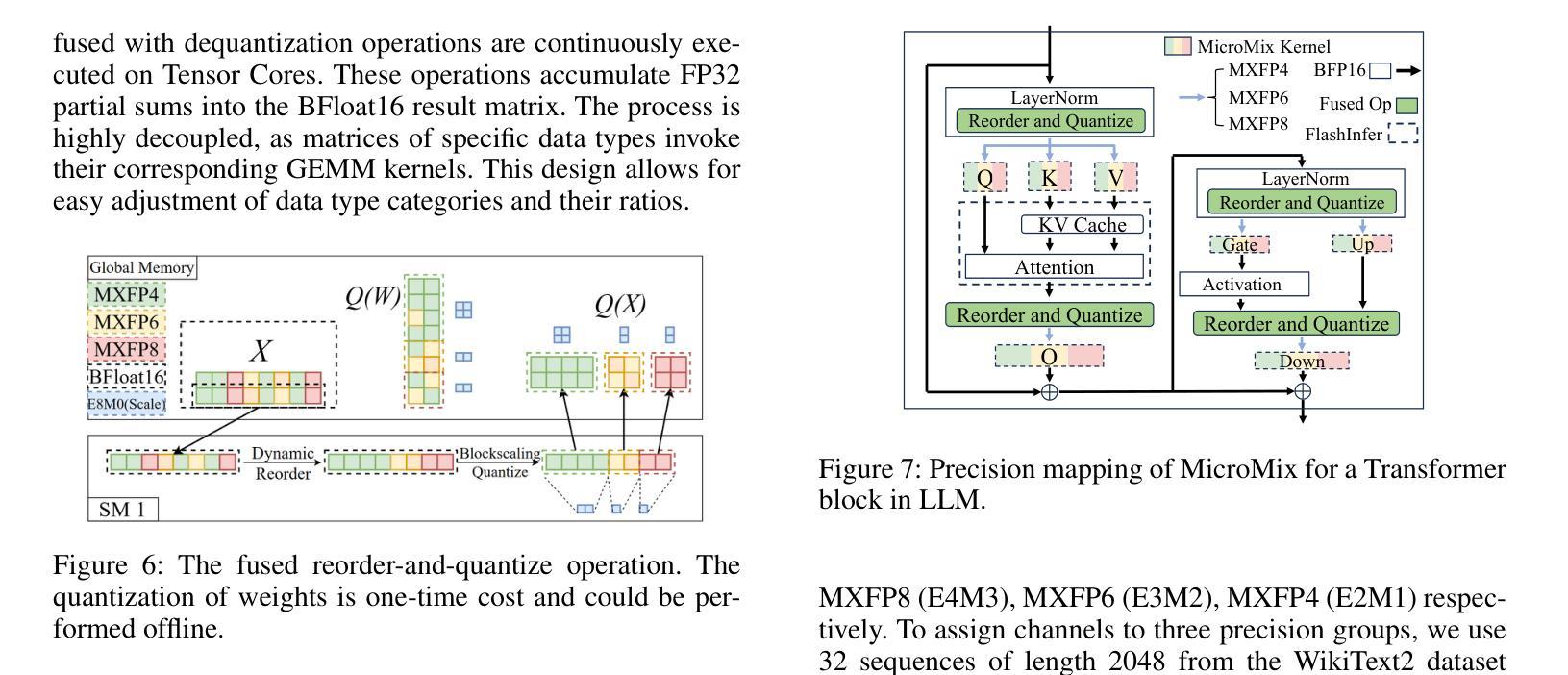
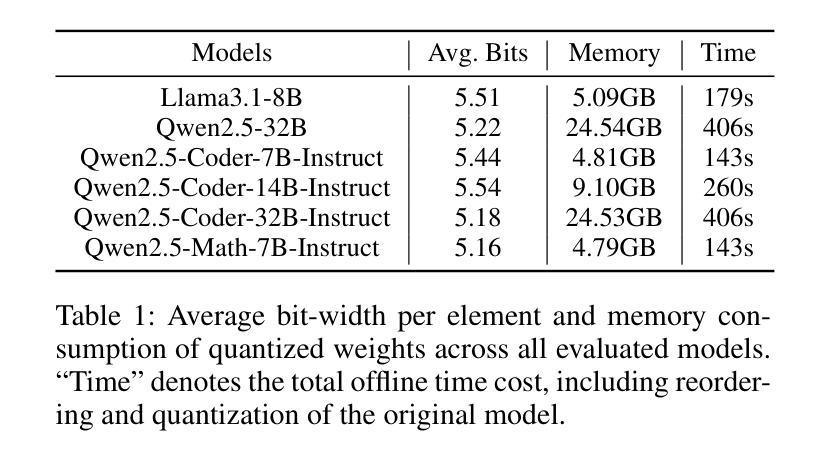
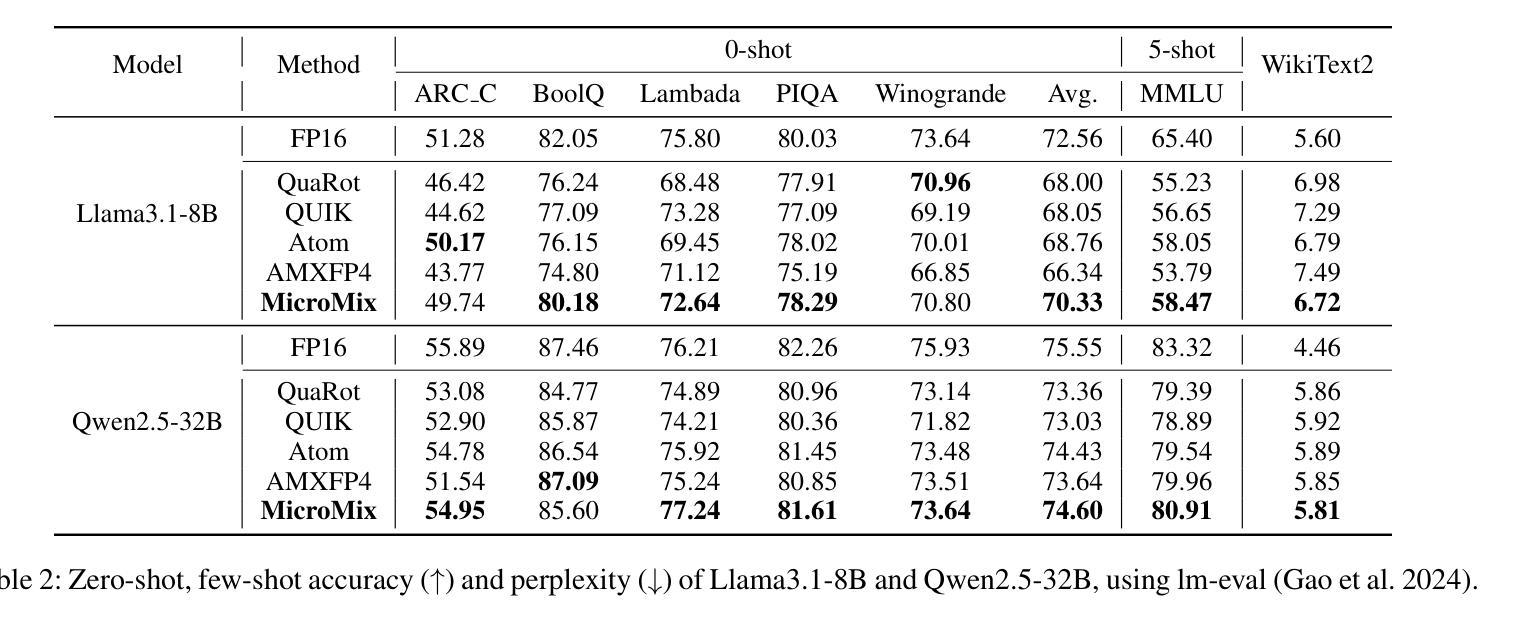
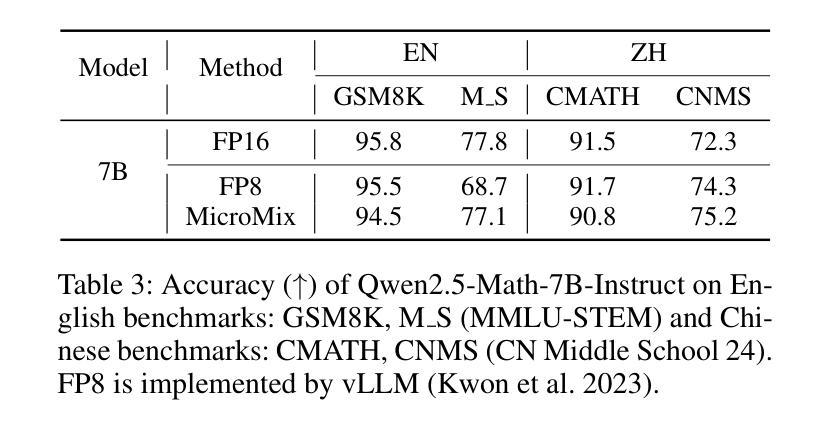
Quantization significantly accelerates inference in large language models (LLMs) by replacing original high-precision matrices with low-precision counterparts. Recent advances in weight-activation quantization have primarily focused on mapping both weights and activations to the INT4 format. Although the new FP4 Tensor Cores in NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture offer up to 4x speedup over FP16, existing INT4-based kernels fail to fully exploit this capability due to mismatched data formats. To bridge this gap, we propose MicroMix, a co-designed mixed-precision quantization algorithm and matrix multiplication kernel based on Microscaling (MX) data formats. Tailored for the Blackwell architecture, the MicroMix kernel supports arbitrary combinations of MXFP4, MXFP6, and MXFP8 channels, and produces BFloat16 outputs. To achieve a favorable trade-off between accuracy and efficiency for each linear layer, we introduce quantization thresholds that identify activation elements where lower-precision formats (MXFP4 or MXFP6) incur excessive quantization error. Our algorithm selectively allocates higher-precision channels to preserve accuracy while maintaining compute efficiency. MicroMix achieves competitive or superior performance across diverse downstream tasks, including zero-shot and few-shot learning, language modeling, code generation, and mathematical reasoning. On both consumer-grade (RTX 5070Ti laptop) and server-grade (RTX 5090) GPUs, our kernel delivers at least 20% faster execution than TensorRT-FP8. Furthermore, when applied to various Llama and Qwen models, MicroMix consistently improves prefill latency and memory efficiency across a range of batch sizes compared to TensorRT baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/lwy2020/MicroMix.
量化通过用低精度矩阵替换原始的高精度矩阵,从而显著加速大语言模型(LLM)的推断。权重激活量化的最新进展主要集中在将权重和激活映射到INT4格式上。尽管NVIDIA Blackwell架构中的新型FP4 Tensor Cores比FP16提供高达4倍的加速,但由于数据格式不匹配,现有的基于INT4的核无法充分利用这一功能。为了弥合这一鸿沟,我们提出了MicroMix,这是一种共同设计的混合精度量化算法和基于Microscaling(MX)数据格式的矩阵乘法核。针对Blackwell架构进行定制,MicroMix核支持MXFP4、MXFP6和MXFP8通道的任意组合,并产生BFloat16输出。为了在每个线性层之间实现准确性和效率之间的平衡,我们引入了量化阈值,以确定在激活元素中,使用较低精度格式(MXFP4或MXFP6)会导致过多的量化误差的位置。我们的算法有选择地分配较高精度的通道以保留准确性并保持计算效率。MicroMix在包括零样本和少样本学习、语言建模、代码生成和数学推理在内的各种下游任务中取得了具有竞争力或出色的性能。无论是在消费者级(RTX 5070Ti笔记本电脑)还是服务器级(RTX 5090)GPU上,我们的核的执行速度至少比TensorRT-FP8快20%。此外,当应用于各种Llama和Qwen模型时,与TensorRT基准相比,MicroMix在各种批次大小的情况下始终改进了预填充延迟和内存效率。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lwy2020/MicroMix找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
摘要
量化通过使用低精度矩阵替代原始的高精度矩阵,显著加速了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理速度。最近关于权重激活量化的进展主要集中在将权重和激活映射到INT4格式上。尽管NVIDIA的Blackwell架构中的新型FP4 Tensor Cores比FP16提供了高达4倍的速度提升,但由于数据格式不匹配,现有的INT4内核无法充分利用此功能。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了MicroMix,这是一种针对Blackwell架构的混合精度量化算法和基于Microscaling(MX)数据格式的矩阵乘法内核。MicroMix内核支持MXFP4、MXFP6和MXFP8通道的任意组合,并产生BFloat16输出。为了针对每个线性层实现准确性和效率之间的平衡,我们引入了量化阈值来识别在较低精度格式(MXFP4或MXFP6)下出现过大量化误差的激活元素。我们的算法有选择地为保留准确性分配较高精度通道的同时保持计算效率。MicroMix在包括零样本和少样本学习、语言建模、代码生成和数学推理等不同的下游任务中实现了具有竞争力的性能甚至更出色的性能。无论是在消费者级(RTX 5070Ti笔记本电脑)还是服务器级(RTX 5090)GPU上,我们的内核的执行速度都比TensorRT-FP8至少快20%。此外,当应用于各种Llama和Qwen模型时,与TensorRT基线相比,MicroMix在跨不同批次大小的情况下始终提高了预填充延迟和内存效率。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lwy2020/MicroMix找到。
关键见解
- 量化能显著加速大型语言模型的推理过程。
- 当前INT4内核无法完全利用NVIDIA Blackwell架构中的FP4 Tensor Cores的优势。
- MicroMix是一种针对Blackwell架构的混合精度量化算法和矩阵乘法内核。
- MicroMix支持多种数据格式组合,并产生BFloat16输出。
- 通过引入量化阈值,MicroMix实现了线性层之间的准确性和效率平衡。
- MicroMix在多种下游任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括零样本和少样本学习等。
点此查看论文截图


OccamVTS: Distilling Vision Models to 1% Parameters for Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Sisuo Lyu, Siru Zhong, Weilin Ruan, Qingxiang Liu, Qingsong Wen, Hui Xiong, Yuxuan Liang
Time series forecasting is fundamental to diverse applications, with recent approaches leverage large vision models (LVMs) to capture temporal patterns through visual representations. We reveal that while vision models enhance forecasting performance, 99% of their parameters are unnecessary for time series tasks. Through cross-modal analysis, we find that time series align with low-level textural features but not high-level semantics, which can impair forecasting accuracy. We propose OccamVTS, a knowledge distillation framework that extracts only the essential 1% of predictive information from LVMs into lightweight networks. Using pre-trained LVMs as privileged teachers, OccamVTS employs pyramid-style feature alignment combined with correlation and feature distillation to transfer beneficial patterns while filtering out semantic noise. Counterintuitively, this aggressive parameter reduction improves accuracy by eliminating overfitting to irrelevant visual features while preserving essential temporal patterns. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that OccamVTS consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance with only 1% of the original parameters, particularly excelling in few-shot and zero-shot scenarios.
时间序列预测在多种应用中具有根本重要性。最近的方法利用大型视觉模型(LVMs)通过视觉表示来捕捉时间序列的模式。我们发现,虽然视觉模型提高了预测性能,但其99%的参数对时间序列任务是不必要的。通过跨模态分析,我们发现时间序列与低级别的纹理特征相符,而与高级别的语义特征不符,这可能会损害预测准确性。我们提出了OccamVTS,这是一个知识蒸馏框架,仅从大型视觉模型中提取关键的1%预测信息到轻量级网络中。使用预训练的大型视觉模型作为特权教师,OccamVTS采用金字塔风格的特征对齐,结合相关性和特征蒸馏来转移有益的模式,同时过滤掉语义噪声。这种减少参数的激进做法出人意料地提高了准确性,它通过消除对无关视觉特征的过度拟合同时保留关键的时间模式来提高准确性。在多个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,OccamVTS始终达到了最新的技术水平,仅使用原始参数的百分之一,尤其在小样和零样本场景中表现尤为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期方法利用大型视觉模型(LVMs)捕捉时间序列的临时模式来进行预测。研究发现,虽然视觉模型能提高预测性能,但其99%的参数对时间序列任务来说是冗余的。本文提出一种名为OccamVTS的知识蒸馏框架,该框架能从LVMs中提取仅1%的预测信息到轻量级网络中。借助预训练的LVM作为特权教师网络,OccamVTS采用金字塔风格的特征对齐结合相关性和特征蒸馏来转移有益模式,同时过滤掉语义噪声。通过减少参数,OccamVTS提高了准确性,因为去除了对无关视觉特征的过度拟合,同时保留了关键的时间模式。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,OccamVTS在仅使用原始参数的1%的情况下持续取得卓越性能,尤其在小样尺寸和零样本场景中表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVMs)能有效捕捉时间序列的临时模式,但大部分参数对时间序列任务是冗余的。
- 知识蒸馏框架OccamVTS能从LVM中提取关键预测信息到轻量级网络。
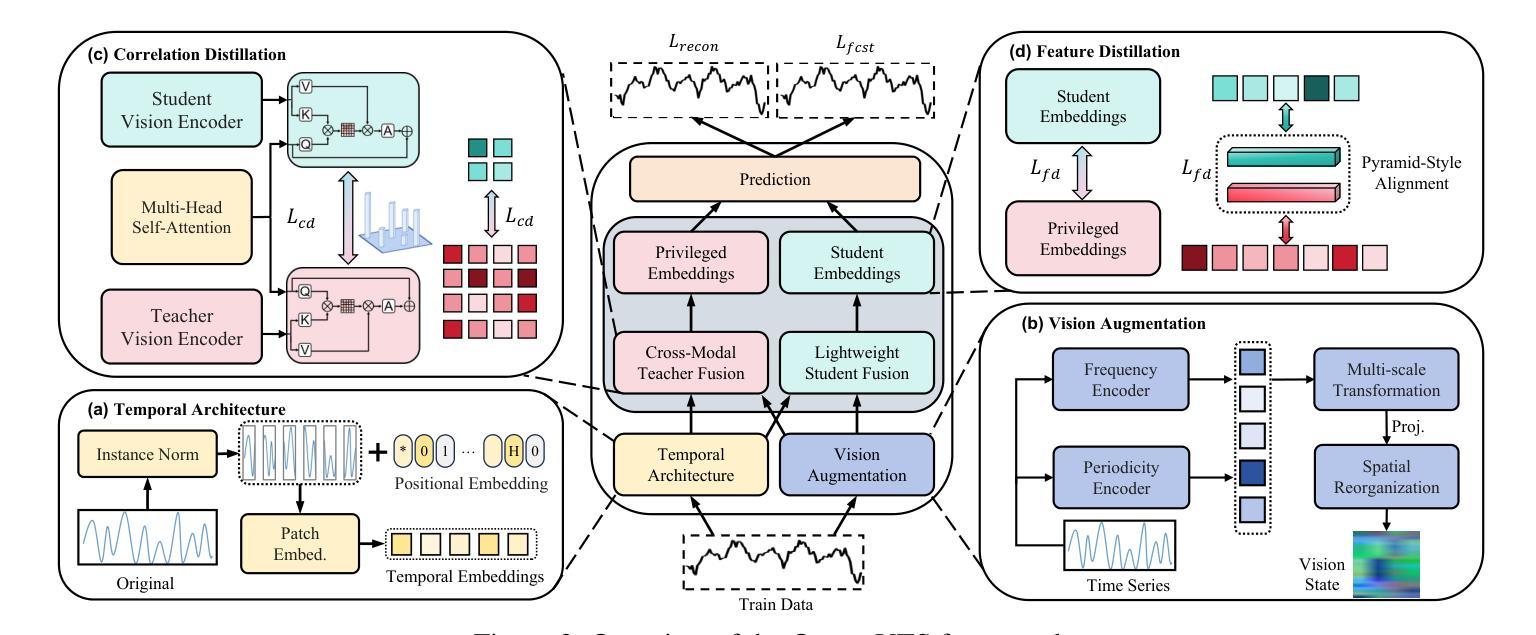
- OccamVTS采用金字塔风格的特征对齐结合相关性和特征蒸馏来转移有益模式并过滤语义噪声。
- 通过减少参数,OccamVTS提高了预测准确性,通过消除对无关特征的过度拟合并保留关键时间模式。
- 实验表明,OccamVTS在多个基准数据集上取得了卓越性能,尤其是小样尺寸和零样本场景下的表现突出。
- 研究发现时间序列与低级别纹理特征有关,而与高级语义关联不大,后者可能损害预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图

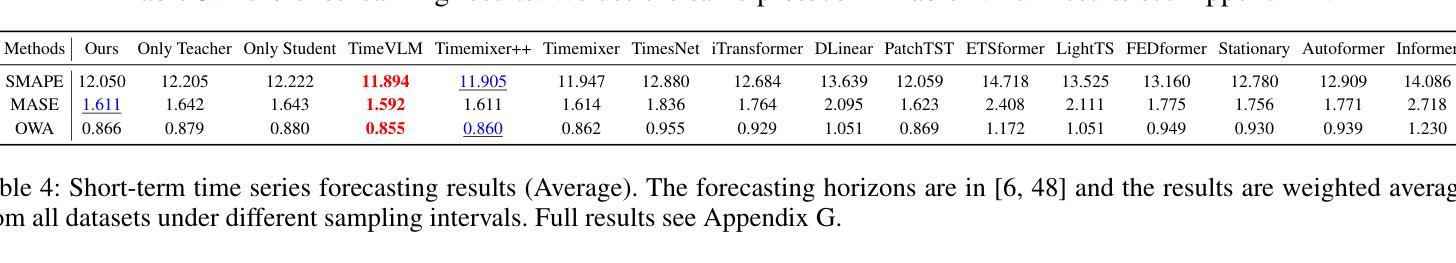
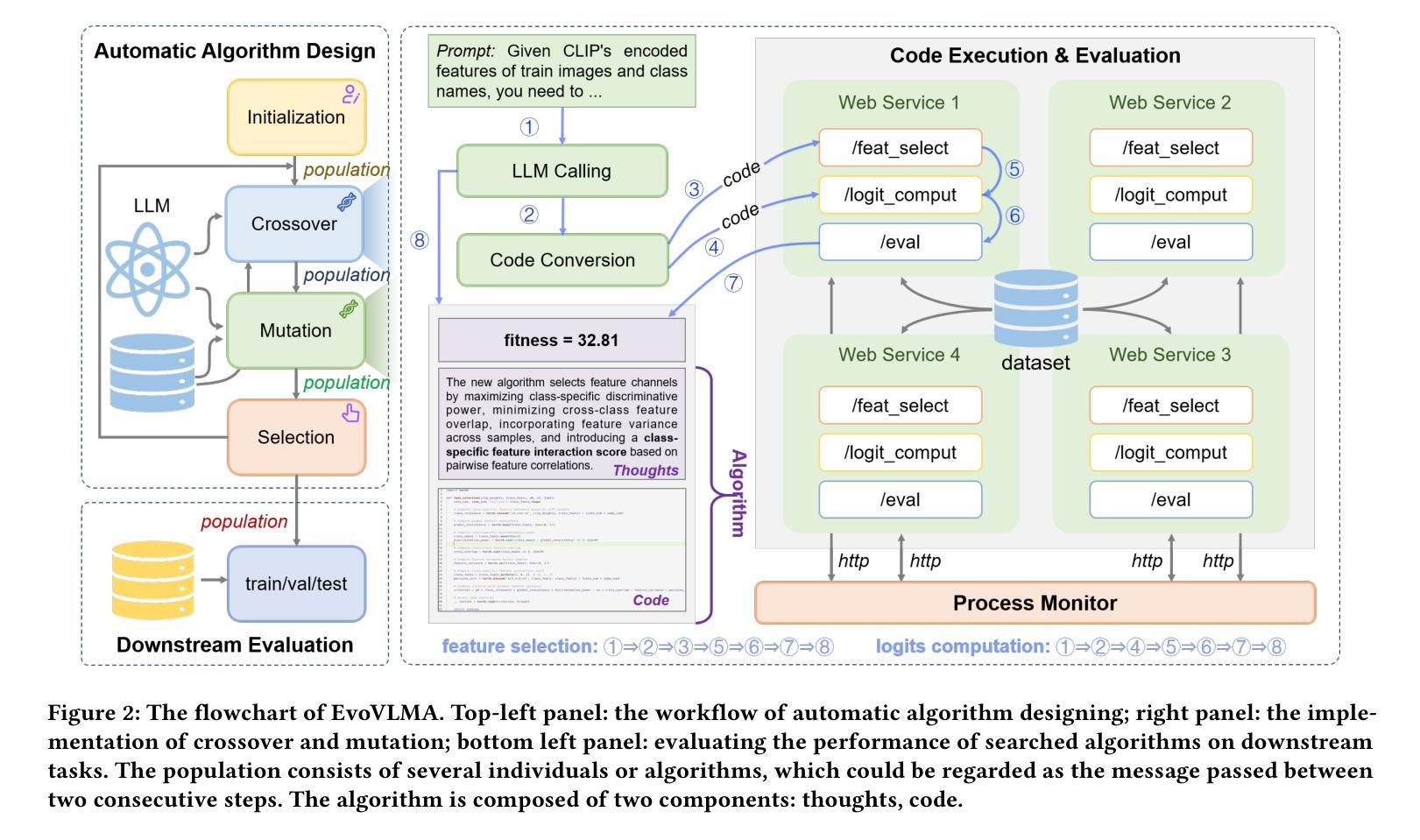
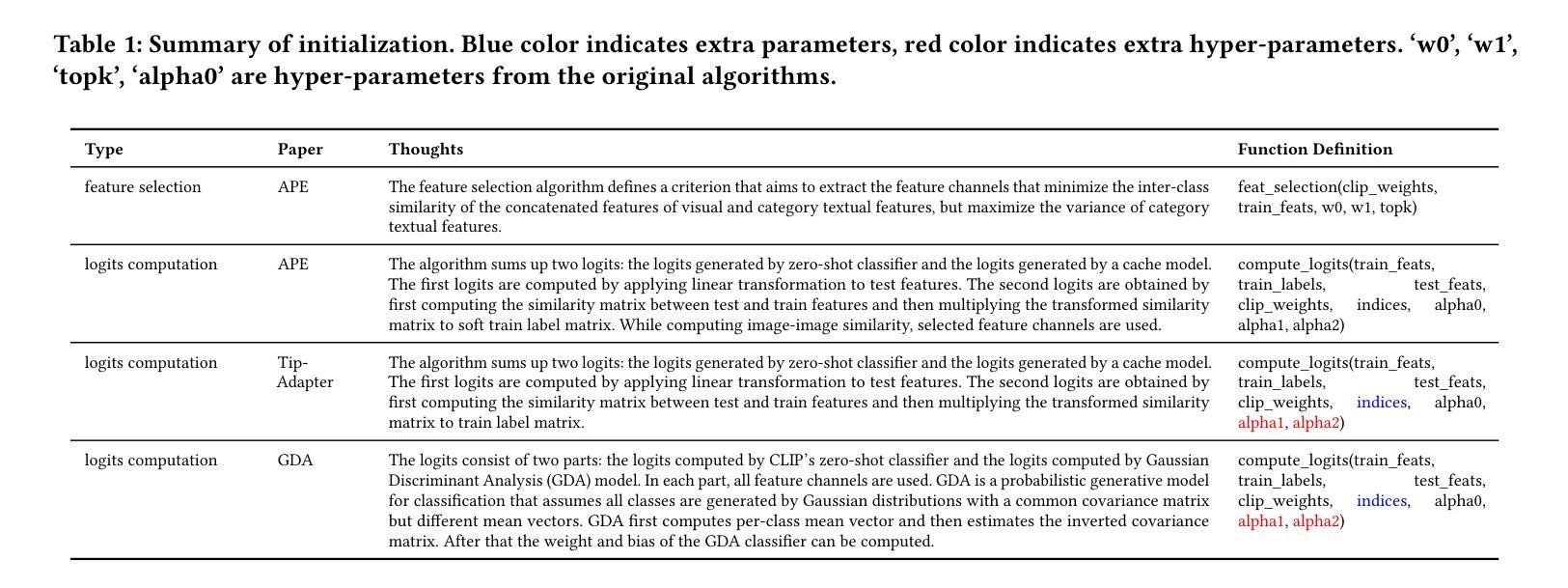
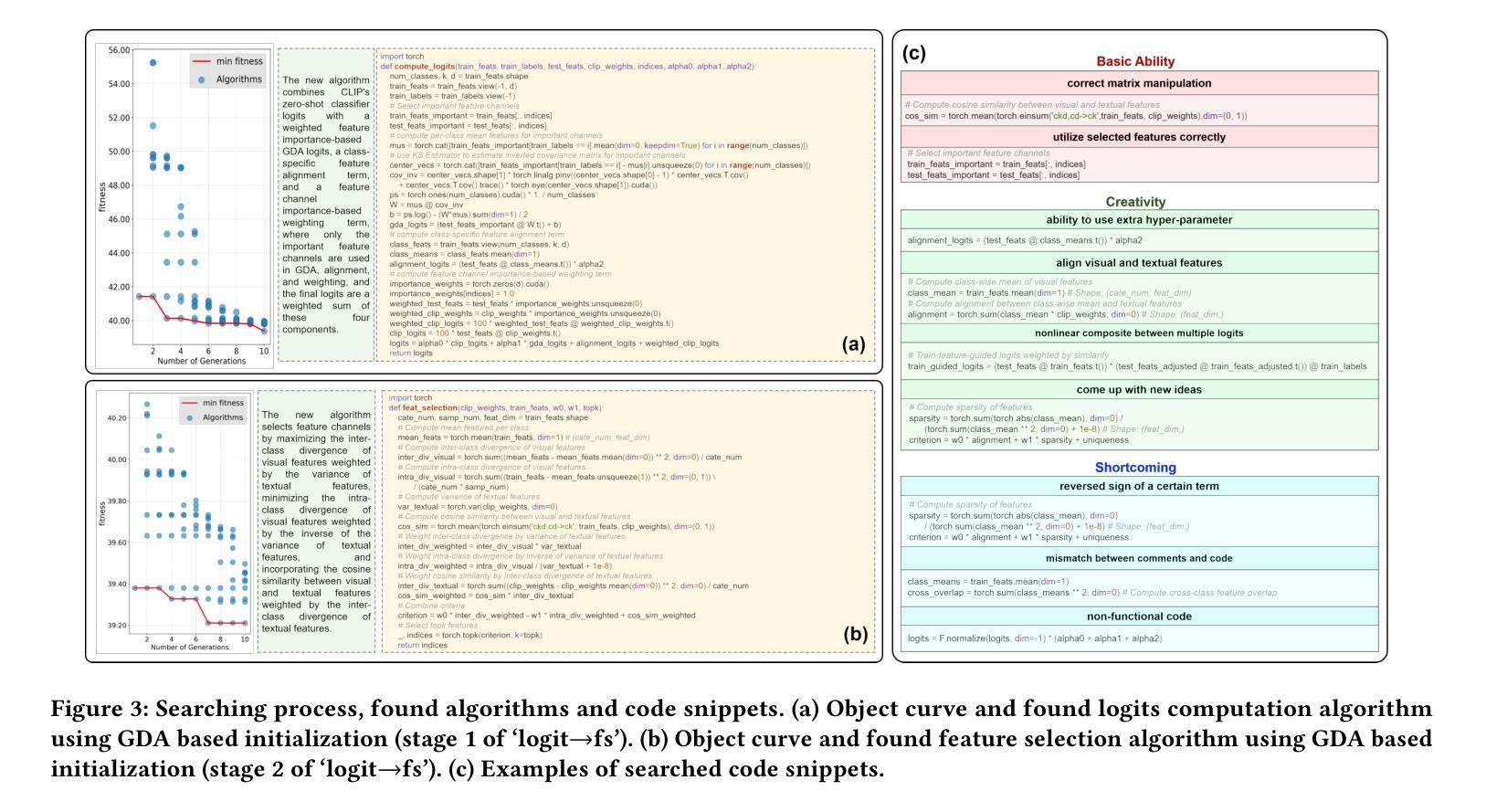
EvoVLMA: Evolutionary Vision-Language Model Adaptation
Authors:Kun Ding, Ying Wang, Shiming Xiang
Pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been exploited in various Computer Vision tasks (e.g., few-shot recognition) via model adaptation, such as prompt tuning and adapters. However, existing adaptation methods are designed by human experts, requiring significant time cost and experience. Inspired by recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) based code generation, we propose an Evolutionary Vision-Language Model Adaptation (EvoVLMA) method to automatically search training-free efficient adaptation algorithms for VLMs. We recognize feature selection and logits computation as the key functions in training-free VLM adaptation, and propose a two-stage LLM-assisted evolutionary algorithm for optimizing these parts in a sequential manner, effectively addressing the challenge posed by the expansive search space through a divide-and-conquer strategy. Besides, to enhance the stability and efficiency of searching process, we propose low-precision code conversion, web based code execution and process monitoring, leading to a highly effective automatic algorithm design system. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the algorithms found by EvoVLMA can obtain promising results compared to previous manually-designed ones. More specifically, in the 8-shot image classification setting, the classical APE algorithm can be improved by 1.91 points in recognition accuracy. This research opens new possibilities for automating the optimization of adaptation algorithms of pre-trained multimodal models. Code is available at: https://github.com/kding1225/EvoVLMA
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过各种模型适配方法已在各种计算机视觉任务(例如,小样本识别)中得到应用,如提示调整和适配器等。然而,现有的适配方法是由人类专家设计的,需要大量的时间和经验。受基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代码生成的最新进展的启发,我们提出了一种进化视觉语言模型适配(EvoVLMA)方法,可自动搜索无需训练的VLMs的高效适配算法。我们认识到特征选择和逻辑计算是无需训练的VLM适配中的关键功能,并提出了一种两阶段的LLM辅助进化算法,按序优化这些部分,通过分而治之的策略有效地解决了由巨大的搜索空间带来的挑战。此外,为了提高搜索过程的稳定性和效率,我们提出了低精度代码转换、基于网络的代码执行和进程监控,从而建立了一个高效自动的算法设计系统。大量实验表明,与以前的手动设计算法相比,EvoVLMA找到的算法可以获得有前景的结果。更具体地说,在8次射击的图像分类设置中,经典APE算法的识别准确率可以提高1.91个点。这项研究为自动优化预训练多模态模型的适配算法开辟了新的可能性。代码可用在:https://github.com/kding1225/EvoVLMA
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by ACM Multimedia 2025 (ACM MM 2025)
Summary
本文提出了基于进化算法的自动视觉语言模型适应方法(EvoVLMA),用于为预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在无需训练的情况下进行高效的模型适应。EvoVLMA识别了特征选择和计算logits作为关键任务,采用两阶段LLM辅助进化算法来优化这些部分。通过代码转换、基于网络的代码执行和过程监控等技术,提高了搜索过程的稳定性和效率。实验表明,该方法相对于手动设计的方法获得较好效果,如通过进化算法改进的APE算法在少样本图像分类任务上的准确度提升达到了约近二十个点。这开创了自动优化预训练多模态模型自适应算法的新可能。更多细节请参见文中描述及GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/kding1225/EvoVLMA。
Key Takeaways
- EvoVLMA是一种基于进化算法的自动视觉语言模型适应方法,适用于预训练的视觉语言模型在各种计算机视觉任务中的自适应问题。
- EvoVLMA通过识别特征选择和计算logits作为关键任务并采用两阶段LLM辅助进化算法进行优化,有效解决了训练自适应模型的搜索空间问题。
- 引入了低精度代码转换、基于网络的代码执行和过程监控等技术来提高搜索过程的稳定性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

Instruction-based Time Series Editing
Authors:Jiaxing Qiu, Dongliang Guo, Brynne Sullivan, Teague R. Henry, Tom Hartvigsen
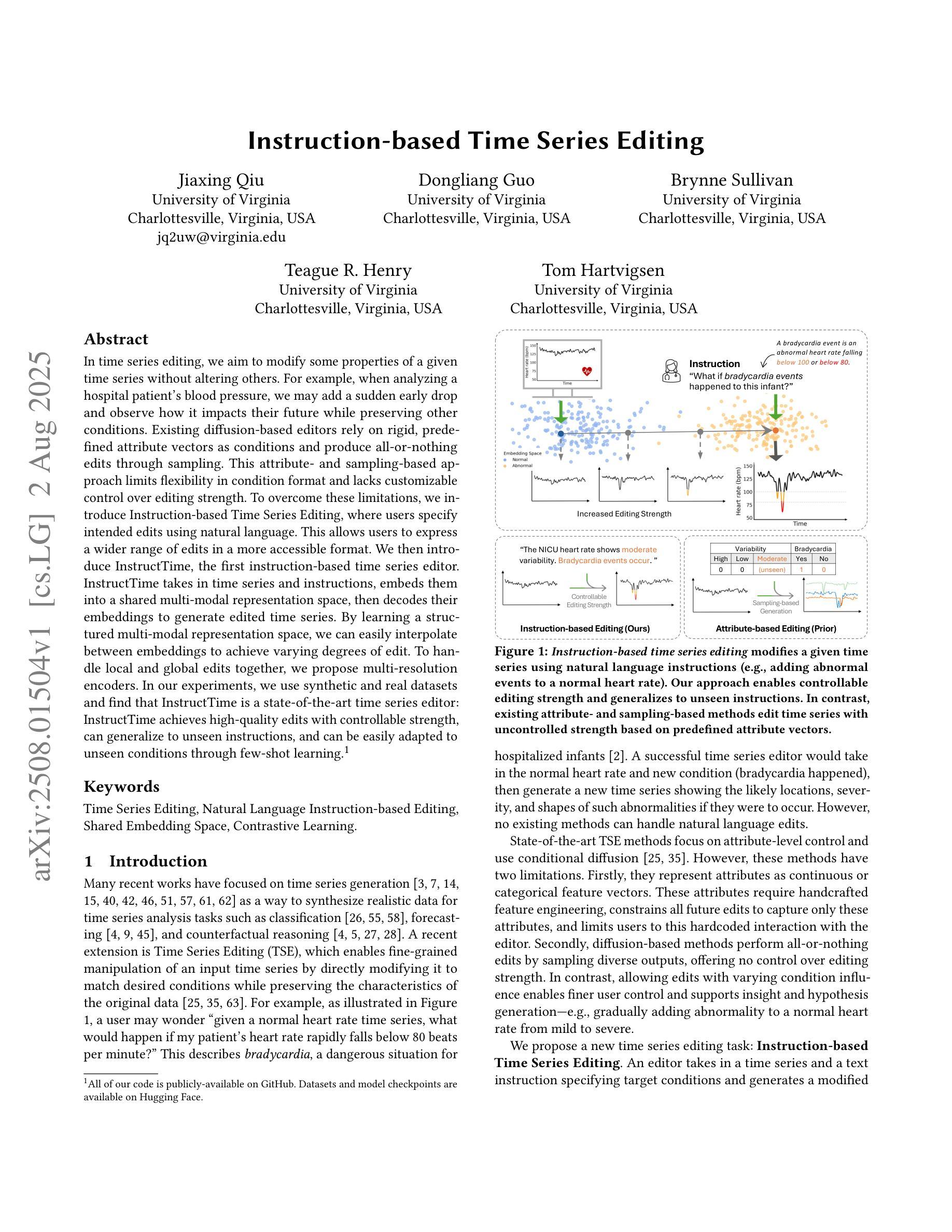
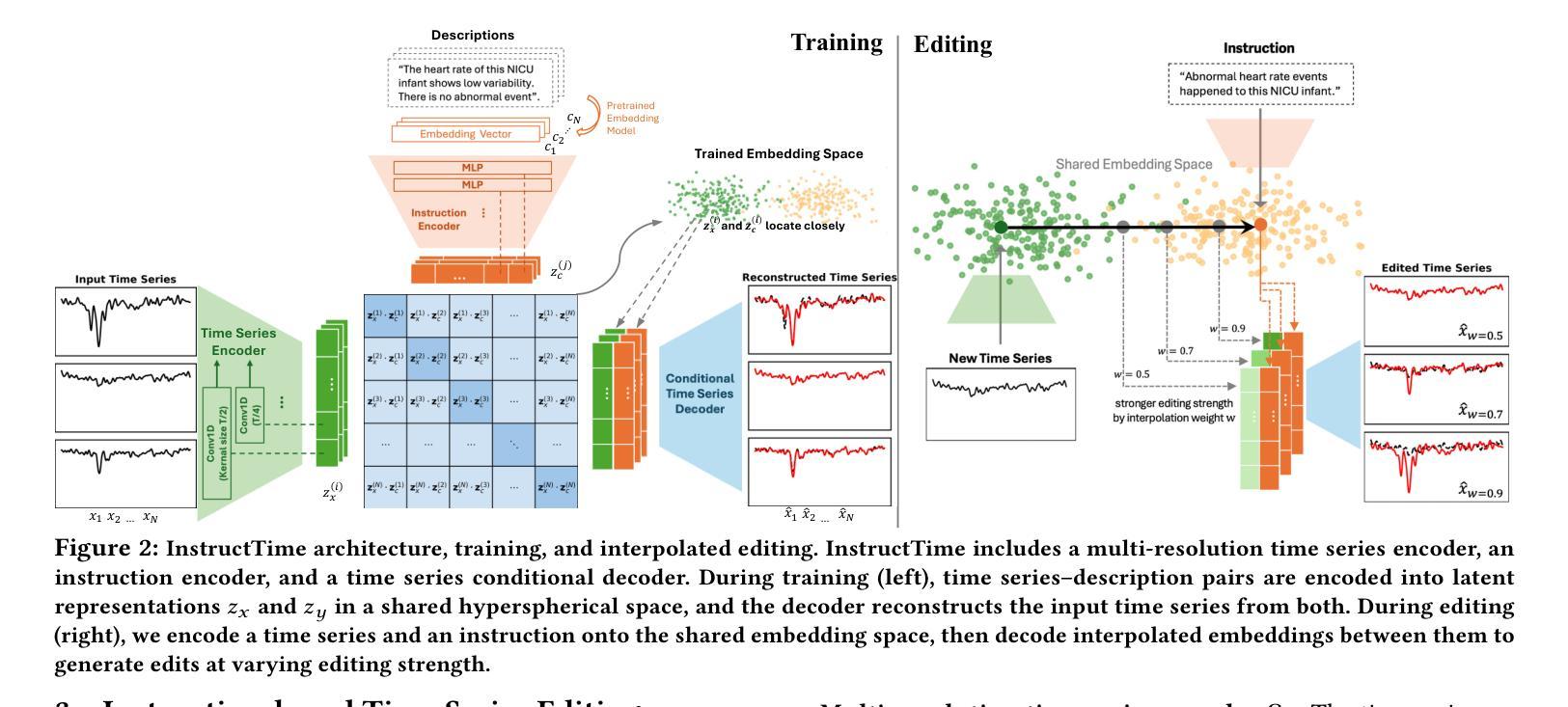
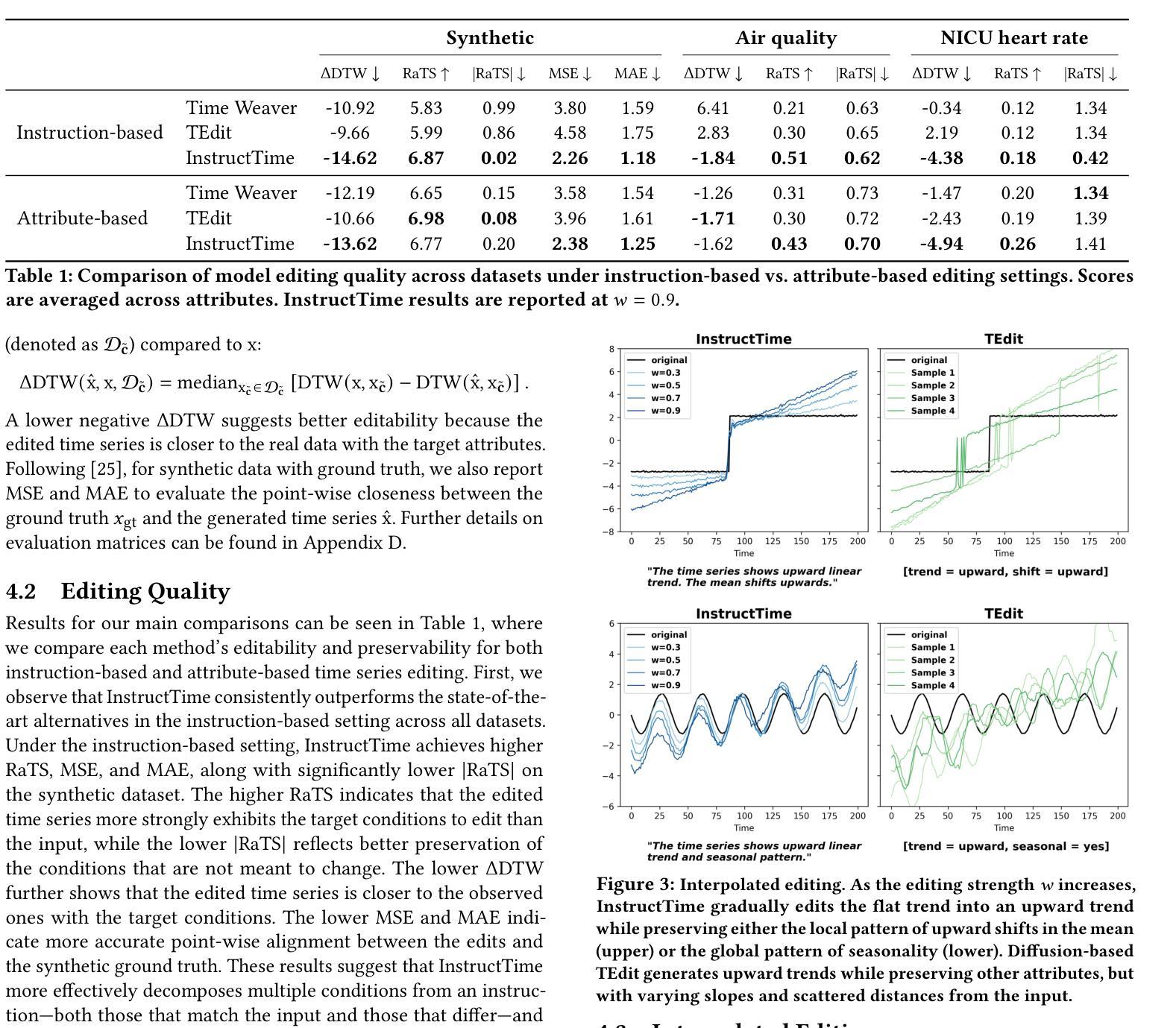
In time series editing, we aim to modify some properties of a given time series without altering others. For example, when analyzing a hospital patient’s blood pressure, we may add a sudden early drop and observe how it impacts their future while preserving other conditions. Existing diffusion-based editors rely on rigid, predefined attribute vectors as conditions and produce all-or-nothing edits through sampling. This attribute- and sampling-based approach limits flexibility in condition format and lacks customizable control over editing strength. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Instruction-based Time Series Editing, where users specify intended edits using natural language. This allows users to express a wider range of edits in a more accessible format. We then introduce InstructTime, the first instruction-based time series editor. InstructTime takes in time series and instructions, embeds them into a shared multi-modal representation space, then decodes their embeddings to generate edited time series. By learning a structured multi-modal representation space, we can easily interpolate between embeddings to achieve varying degrees of edit. To handle local and global edits together, we propose multi-resolution encoders. In our experiments, we use synthetic and real datasets and find that InstructTime is a state-of-the-art time series editor: InstructTime achieves high-quality edits with controllable strength, can generalize to unseen instructions, and can be easily adapted to unseen conditions through few-shot learning.
在时间序列编辑中,我们的目标是对给定的时间序列的某些属性进行修改,而不改变其他属性。例如,在分析医院患者的血压时,我们可能会增加一个突然的早期下降,并观察它如何影响未来,同时保持其他状况不变。现有的基于扩散的编辑器依赖于僵硬的预定义属性向量作为条件,并通过采样进行全有或全无的编辑。这种基于属性和采样的方法限制了条件格式灵活性,并缺乏对编辑强度的可定制控制。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了基于指令的时间序列编辑,用户可以使用自然语言指定预期的编辑内容。这允许用户以更可访问的格式表达更广泛的编辑内容。然后我们推出了InstructTime,第一个基于指令的时间序列编辑器。InstructTime接收时间序列和指令,将它们嵌入到共享的多模式表示空间中,然后解码它们的嵌入以生成编辑后的时间序列。通过学习结构化的多模式表示空间,我们可以轻松地在嵌入之间进行插值以实现不同程度的编辑。为了同时处理局部和全局编辑,我们提出了多分辨率编码器。在我们的实验中,我们使用合成和真实数据集发现InstructTime是先进的时间序列编辑器:InstructTime能够实现高质量且可控强度的编辑,可以推广到未见过的指令,并且可以通过小样本学习轻松适应未见过的条件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时间序列编辑旨在修改时间序列的某些属性而不改变其他属性。现有基于扩散的编辑器依赖于预设的属性向量作为条件,并通过采样进行全有或全无的编辑,这限制了条件格式的灵活性和编辑强度的可定制控制。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了基于指令的时间序列编辑方法,用户可以使用自然语言指定预期的编辑。我们然后介绍了InstructTime,这是一个基于指令的时间序列编辑器。它采用时间序列和指令,将它们嵌入到共享的多模式表示空间中,然后解码它们的嵌入以生成编辑后的时间序列。通过学习结构化的多模式表示空间,我们可以轻松地在嵌入之间进行插值以实现不同程度的编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列编辑旨在修改时间序列的特定属性,同时保持其他属性不变。
- 现有基于扩散的编辑器有局限性,如条件格式不灵活和编辑强度不可定制。
- 引入基于指令的时间序列编辑方法,允许用户以自然语言指定预期的编辑。
- InstructTime是首个基于指令的时间序列编辑器,采用多模式表示空间进行编辑。
- InstructTime通过嵌入和解码机制实现高质量且可控的编辑强度。
- InstructTime能够处理局部和全局编辑的结合,提出了多分辨率编码器。
点此查看论文截图
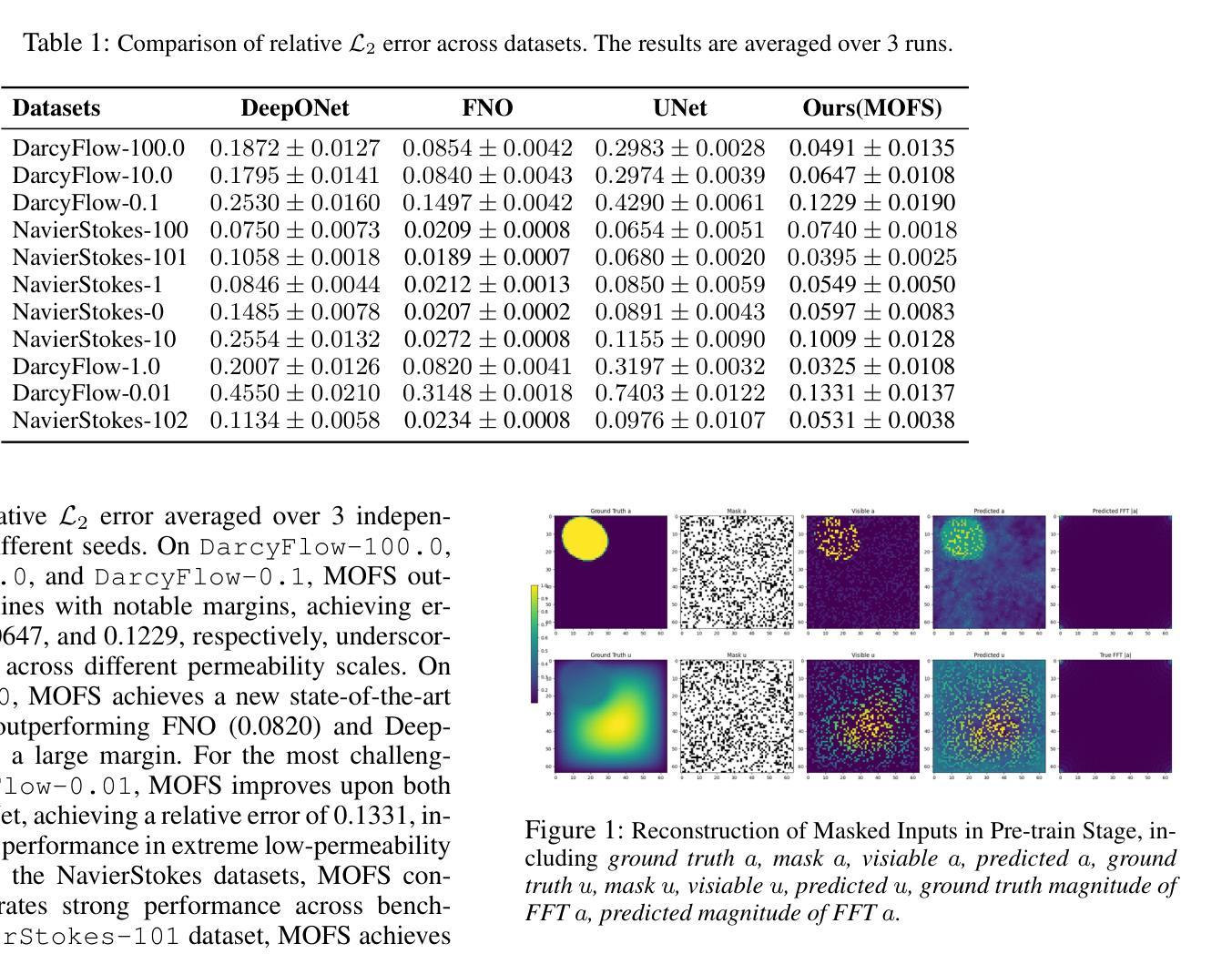
Multi-Operator Few-Shot Learning for Generalization Across PDE Families
Authors:Yile Li, Shandian Zhe
Learning solution operators for partial differential equations (PDEs) has become a foundational task in scientific machine learning. However, existing neural operator methods require abundant training data for each specific PDE and lack the ability to generalize across PDE families. In this work, we propose MOFS: a unified multimodal framework for multi-operator few-shot learning, which aims to generalize to unseen PDE operators using only a few demonstration examples. Our method integrates three key components: (i) multi-task self-supervised pretraining of a shared Fourier Neural Operator (FNO) encoder to reconstruct masked spatial fields and predict frequency spectra, (ii) text-conditioned operator embeddings derived from statistical summaries of input-output fields, and (iii) memory-augmented multimodal prompting with gated fusion and cross-modal gradient-based attention. We adopt a two-stage training paradigm that first learns prompt-conditioned inference on seen operators and then applies end-to-end contrastive fine-tuning to align latent representations across vision, frequency, and text modalities. Experiments on PDE benchmarks, including Darcy Flow and Navier Stokes variants, demonstrate that our model outperforms existing operator learning baselines in few-shot generalization. Extensive ablations validate the contributions of each modality and training component. Our approach offers a new foundation for universal and data-efficient operator learning across scientific domains.
学习偏微分方程(PDEs)的解决方案算子已成为科学机器学习中的一项基础任务。然而,现有的神经算子方法针对每种特定偏微分方程需要大量训练数据,且缺乏跨偏微分方程家族的泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了MOFS:一种统一的多模态框架,用于多算子的少样本学习,旨在仅使用少数几个示例来泛化到看不见的偏微分方程算子。我们的方法集成了三个关键组件:(i)多任务自监督预训练共享傅里叶神经算子(FNO)编码器,以重建掩蔽的空间场并预测频谱;(ii)从输入-输出场的统计摘要中得出的文本条件算子嵌入;(iii)带有门控融合和跨模态基于梯度的注意力的记忆增强多模态提示。我们采用两阶段训练模式,首先学习对可见算子的提示条件推理,然后应用端到端对比微调,以对齐视觉、频率和文本模态的潜在表示。在包括达西流和Navier-Stokes变体的PDE基准测试上的实验表明,我们的模型在少样本泛化方面优于现有的算子学习基准测试。广泛的消融研究验证了每种模态和培训组件的贡献。我们的方法为跨科学领域的通用和数据高效算子学习提供了新的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一个研究团队提出了MOFS:一种统一的多模态少样本学习框架,旨在通过少量示例实现对未见过的PDE算符进行泛化。该研究集成了三项关键技术,包括多任务自监督预训练共享傅里叶神经网络(FNO)编码器、基于文本条件的算符嵌入以及增强记忆的多模态提示与门控融合和跨模态梯度注意力机制。实验表明,该模型在PDE基准测试中表现优于现有算符学习基准,实现了跨科学领域的通用和高效算符学习。
Key Takeaways
- 研究团队引入了MOFS框架,实现了对PDE算符的少样本学习泛化。
- MOFS框架集成了多任务自监督预训练的傅里叶神经网络编码器,用于重建掩膜空间场和预测频谱。
- 算符嵌入通过基于文本条件的统计摘要实现,将输入-输出字段的信息融入模型。
- 框架采用增强记忆的多模态提示技术,包括门控融合和跨模态梯度注意力机制。
- 采用两阶段训练范式,先学习已知算符的提示条件推理,然后通过端到端对比微调实现跨视觉、频率和文本模态的潜在表示对齐。
- 实验证明MOFS在PDE基准测试中表现优异,优于现有算符学习基准。
点此查看论文截图

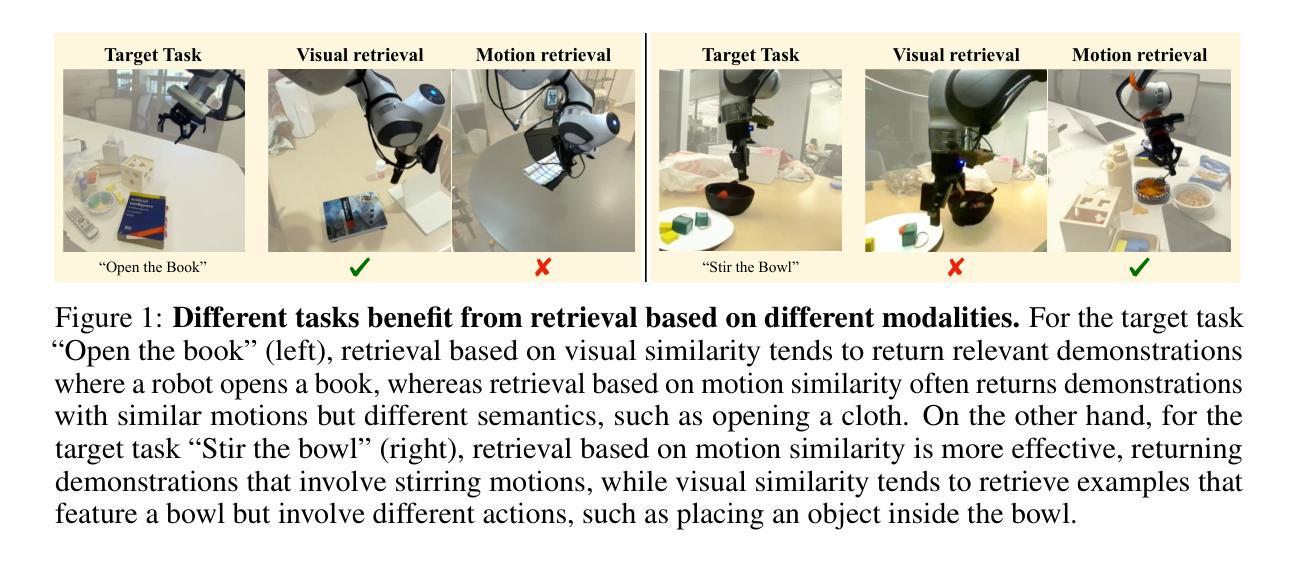
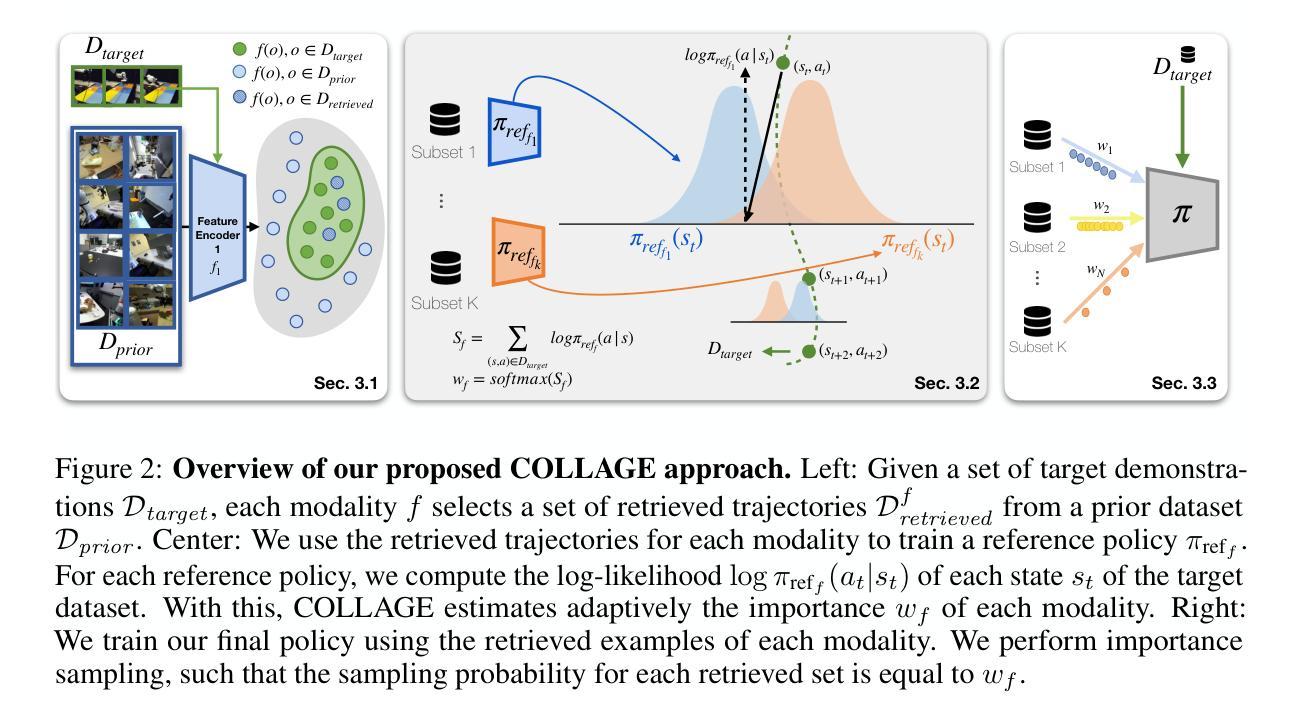
COLLAGE: Adaptive Fusion-based Retrieval for Augmented Policy Learning
Authors:Sateesh Kumar, Shivin Dass, Georgios Pavlakos, Roberto Martín-Martín
In this work, we study the problem of data retrieval for few-shot imitation learning: selecting data from a large dataset to train a performant policy for a specific task, given only a few target demonstrations. Prior methods retrieve data using a single-feature distance heuristic, assuming that the best demonstrations are those that most closely resemble the target examples in visual, semantic, or motion space. However, this approach captures only a subset of the relevant information and can introduce detrimental demonstrations, e.g., retrieving data from unrelated tasks due to similar scene layouts, or selecting similar motions from tasks with divergent goals. We present COLLAGE, a method for COLLective data AGgrEgation in few-shot imitation learning that uses an adaptive late fusion mechanism to guide the selection of relevant demonstrations based on a task-specific combination of multiple cues. COLLAGE follows a simple, flexible, and efficient recipe: it assigns weights to subsets of the dataset that are pre-selected using a single feature (e.g., appearance, shape, or language similarity), based on how well a policy trained on each subset predicts actions in the target demonstrations. These weights are then used to perform importance sampling during policy training, sampling data more densely or sparsely according to estimated relevance. COLLAGE is general and feature-agnostic, allowing it to combine any number of subsets selected by any retrieval heuristic, and to identify which subsets provide the greatest benefit for the target task. In extensive experiments, COLLAGE outperforms state-of-the-art retrieval and multi-task learning approaches by 5.1% in simulation across 10 tasks, and by 16.6% in the real world across 6 tasks, where we perform retrieval from the large-scale DROID dataset. More information at https://robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu/COLLAGE .
在这项工作中,我们研究了小样模仿学习的数据检索问题:从大型数据集中选择数据来训练针对特定任务的性能策略,而只有少数目标演示样本。以前的方法使用单一特征距离启发式进行数据存储检索,假设最佳的演示是那些在视觉、语义或运动空间中最接近目标示例的演示。然而,这种方法只捕获了部分相关信息,并可能引入有害的演示,例如由于场景布局相似而从无关任务中检索数据,或从目标不同的任务中选择相似的动作。我们提出了COLLAGE,这是一种小样模仿学习中的集体数据聚合方法。它使用自适应的后期融合机制,根据针对特定任务的多个线索组合来指导相关演示的选择。COLLAGE遵循简单、灵活和高效的配方:它为使用单一特征(例如外观、形状或语言相似性)预先选择的数据集子集分配权重,基于在每个子集上训练的策略对目标演示的预测效果。然后,这些权重被用于在策略训练期间执行重要性采样,根据估计的相关性更密集或更稀疏地采样数据。COLLAGE是通用的,与特征无关,可以组合任何数量由任何检索启发式选择的子集,并确定哪些子集对目标任务提供最大的好处。在广泛的实验中,与最新检索和多任务学习方法相比,COLLAGE在模拟的10个任务上提高了5.1%的性能,在现实世界的6个任务上提高了16.6%的性能,我们从大规模DROID数据集中进行检索。更多信息请访问:https://robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu/COLLAGE。(注:该网址可能无法直接访问)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 2025. Project page: https://robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu/COLLAGE
摘要
本文研究了少样本模仿学习中的数据检索问题,即如何从大规模数据集中选择数据来训练针对特定任务的性能策略,仅给出少量的目标演示。本文提出了一种方法COLLAGE,使用自适应的后期融合机制,基于特定任务的多个线索组合来指导相关演示的选择。COLLAGE简单、灵活、高效,为数据集子集分配权重,基于每个子集训练的策略对目标演示的预测效果。这些权重用于在策略训练期间执行重要性采样,根据估计的相关性更密集或更稀疏地采样数据。在与最先进的检索和多任务学习方法进行的广泛实验中,COLLAGE在模拟的10个任务中提高了5.1%的性能,在现实世界的6个任务中提高了16.6%的性能,这些实验均从大规模DROIS数据集中进行检索。
关键见解
- 研究了少样本模仿学习中的数据检索问题,关注于从大规模数据集中选择相关数据来训练任务特定策略。
- 提出了COLLAGE方法,采用自适应后期融合机制,结合多种线索来选择相关的演示数据。
- COLLAGE简单、灵活、高效,能根据子集对目标演示的预测性能为数据集子集分配权重。
- COLLAGE采用重要性采样,根据估计的相关性调整数据采样密度。
- COLLAGE可与其他任何检索启发式方法结合,可识别对目标任务最有益的子集。
- 在模拟的10个任务和现实世界的6个任务实验中,COLLAGE方法显著优于现有方法。
- COLLAGE方法从大规模DROIS数据集中进行检索,展示了其在实际应用中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


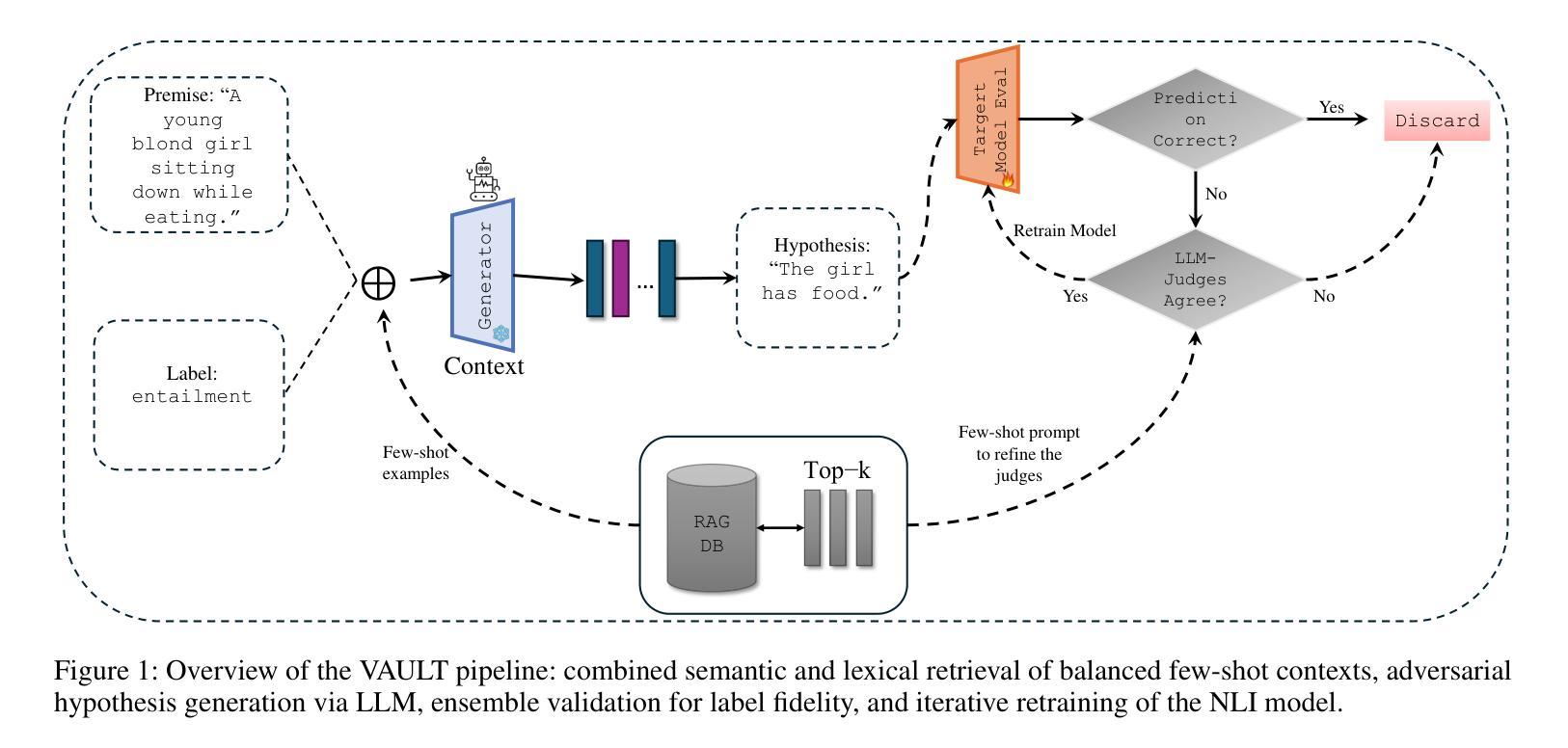
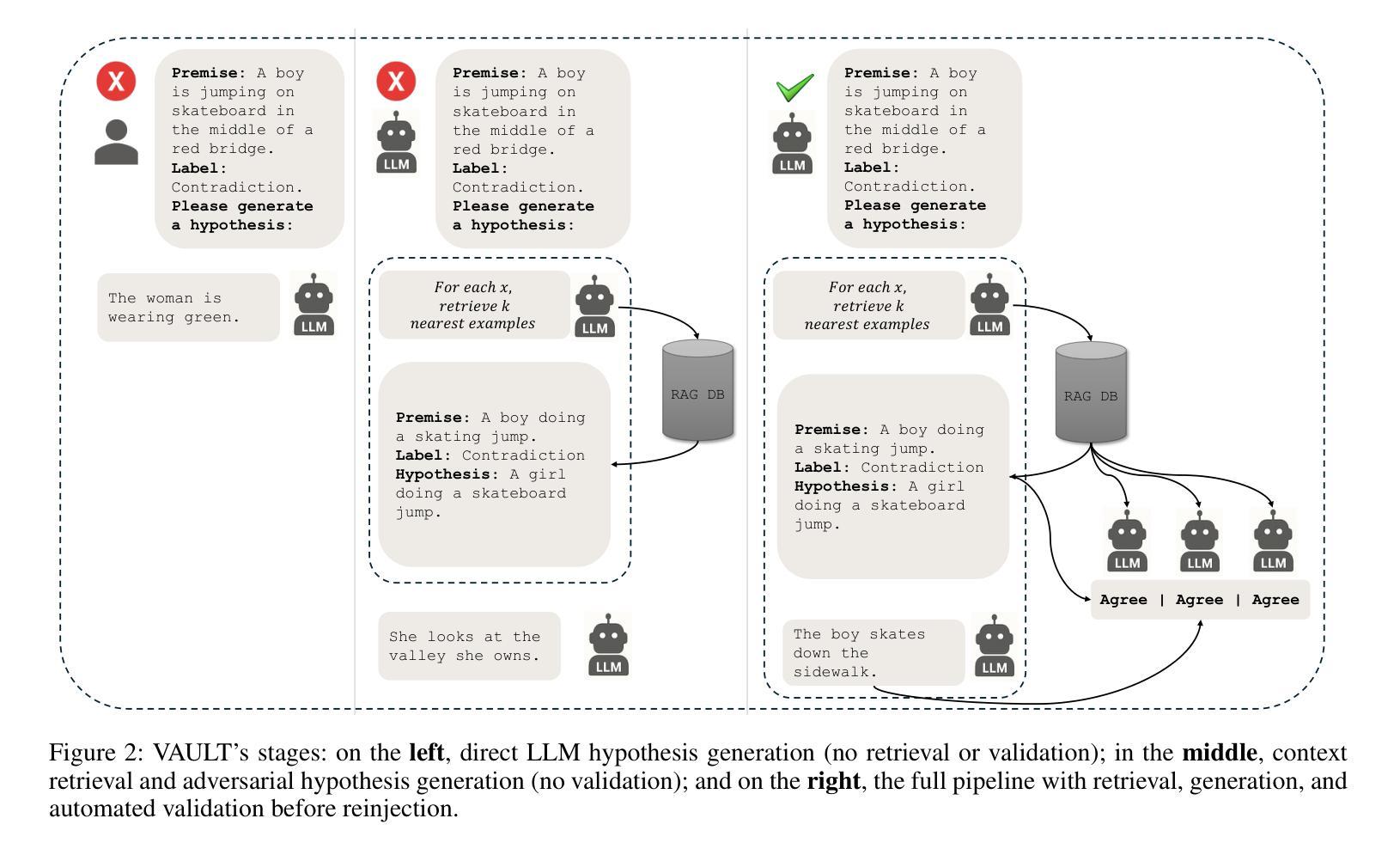
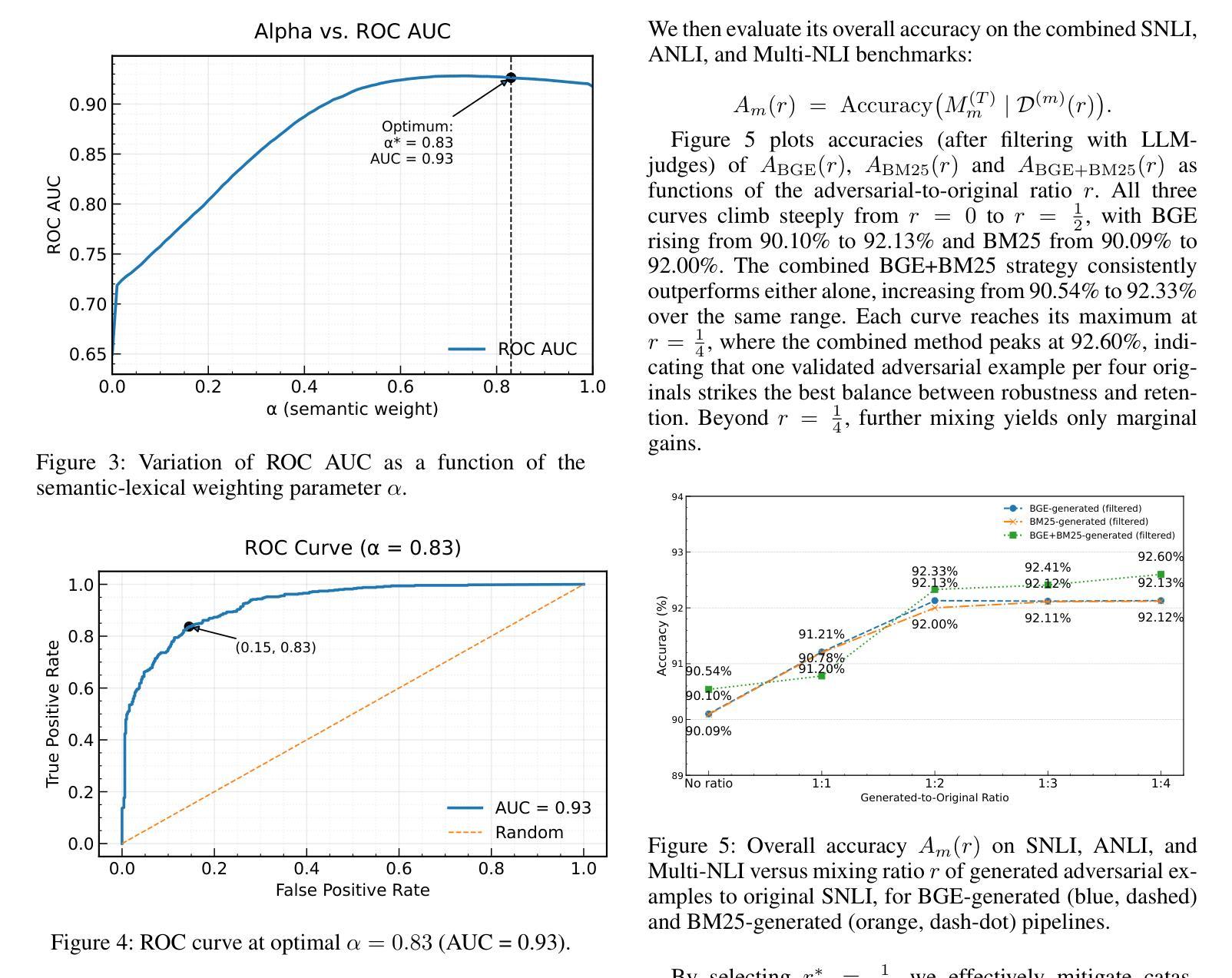
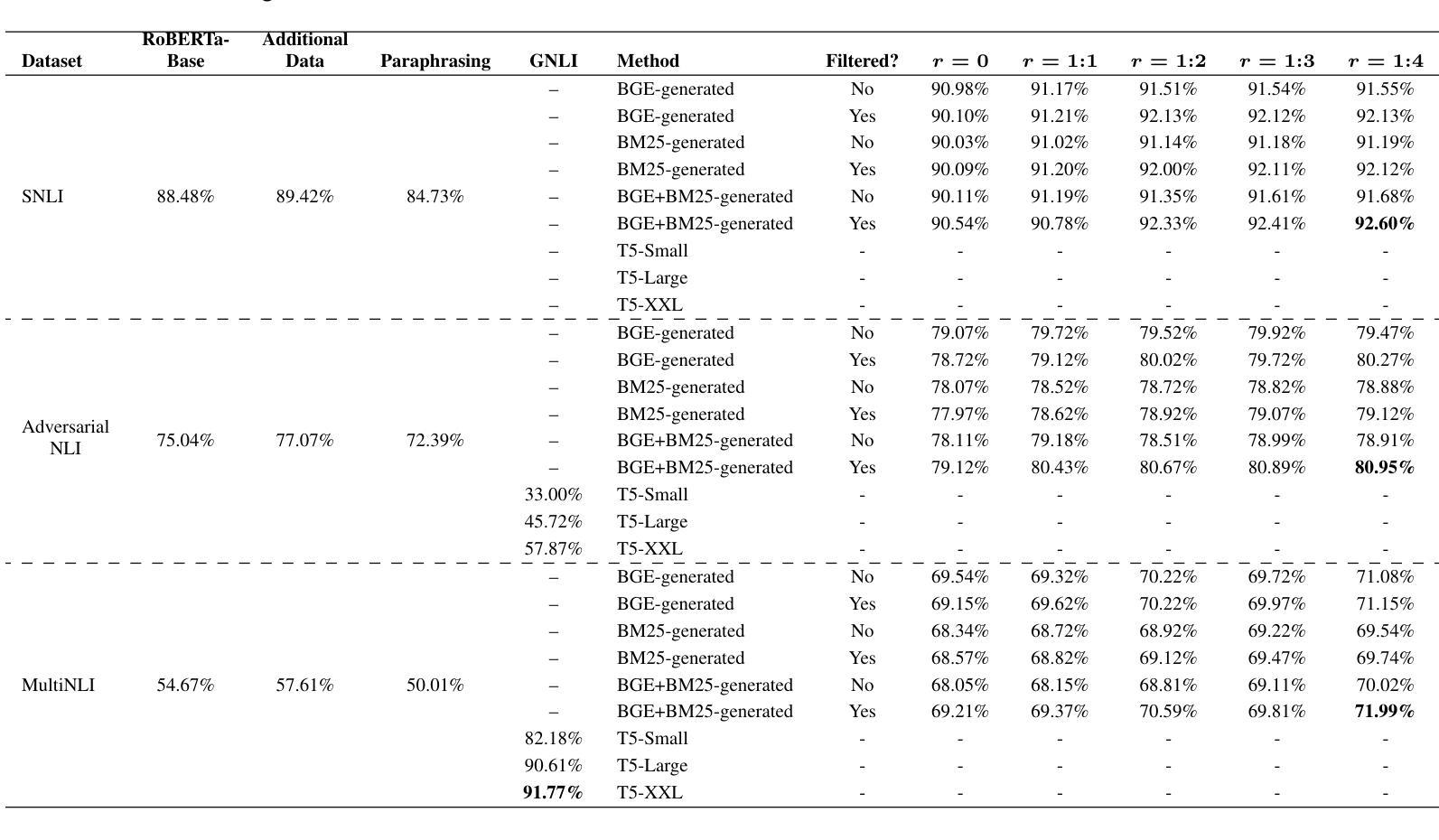
VAULT: Vigilant Adversarial Updates via LLM-Driven Retrieval-Augmented Generation for NLI
Authors:Roie Kazoom, Ofir Cohen, Rami Puzis, Asaf Shabtai, Ofer Hadar
We introduce VAULT, a fully automated adversarial RAG pipeline that systematically uncovers and remedies weaknesses in NLI models through three stages: retrieval, adversarial generation, and iterative retraining. First, we perform balanced few-shot retrieval by embedding premises with both semantic (BGE) and lexical (BM25) similarity. Next, we assemble these contexts into LLM prompts to generate adversarial hypotheses, which are then validated by an LLM ensemble for label fidelity. Finally, the validated adversarial examples are injected back into the training set at increasing mixing ratios, progressively fortifying a zero-shot RoBERTa-base model.On standard benchmarks, VAULT elevates RoBERTa-base accuracy from 88.48% to 92.60% on SNLI +4.12%, from 75.04% to 80.95% on ANLI +5.91%, and from 54.67% to 71.99% on MultiNLI +17.32%. It also consistently outperforms prior in-context adversarial methods by up to 2.0% across datasets. By automating high-quality adversarial data curation at scale, VAULT enables rapid, human-independent robustness improvements in NLI inference tasks.
我们介绍了VAULT,这是一种全自动对抗性RAG管道,它通过三个阶段系统地发现和解决NLI模型的弱点:检索、对抗性生成和迭代重训。首先,我们通过嵌入前提,实现语义(BGE)和词汇(BM25)相似性平衡进行少量检索。接下来,我们将这些上下文组合成LLM提示,生成对抗性假设,然后通过LLM集合验证标签的忠实度。最后,经过验证的对抗性实例以不断增加的混合比例注入训练集,逐步加强零样本RoBERTa基础模型。在标准基准测试中,VAULT将RoBERTa基础准确率从SNLI的88.48%提高到92.6%,ANLI的准确率从75.04%提高到80.95%,MultiNLI的准确率从54.67%提高到71.99%。它还持续优于先前的上下文对抗方法,跨数据集最高达2.0%。通过大规模自动化高质量对抗数据收集,VAULT能够在NLI推断任务中实现快速、无需人工参与的稳健性提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:我们提出了VAULT这一全自动的对抗性RAG流程,用于系统发现和改进自然语言理解模型(NLI)中的弱点。VAULT包括三个阶段:检索、对抗性生成和迭代重训练。通过嵌入前提实现平衡少量检索,利用语义和词汇相似性生成LLM提示以产生对抗性假设,通过LLM集合验证标签可信度。最后,将验证过的对抗性实例以不同混合比例注入训练集,逐步强化零样本RoBERTa基础模型。在标准基准测试中,VAULT提高了RoBERTa基础模型的准确率。此外,VAULT能够自动化大规模高质量对抗数据的整理,实现无需人工参与的NLI推理任务稳健性快速改进。
Key Takeaways:
- VAULT是一个全自动的对抗性RAG流程,用于提升自然语言理解模型的稳健性。
- VAULT包括三个主要阶段:检索、对抗性生成和迭代重训练。
- VAULT通过嵌入前提实现平衡少量检索,并利用语义和词汇相似性生成对抗性假设。
- LLM集合被用于验证标签可信度。
- VAULT将验证过的对抗性实例注入训练集,逐步强化模型。
- VAULT在标准基准测试中表现出卓越的性能提升效果。
点此查看论文截图

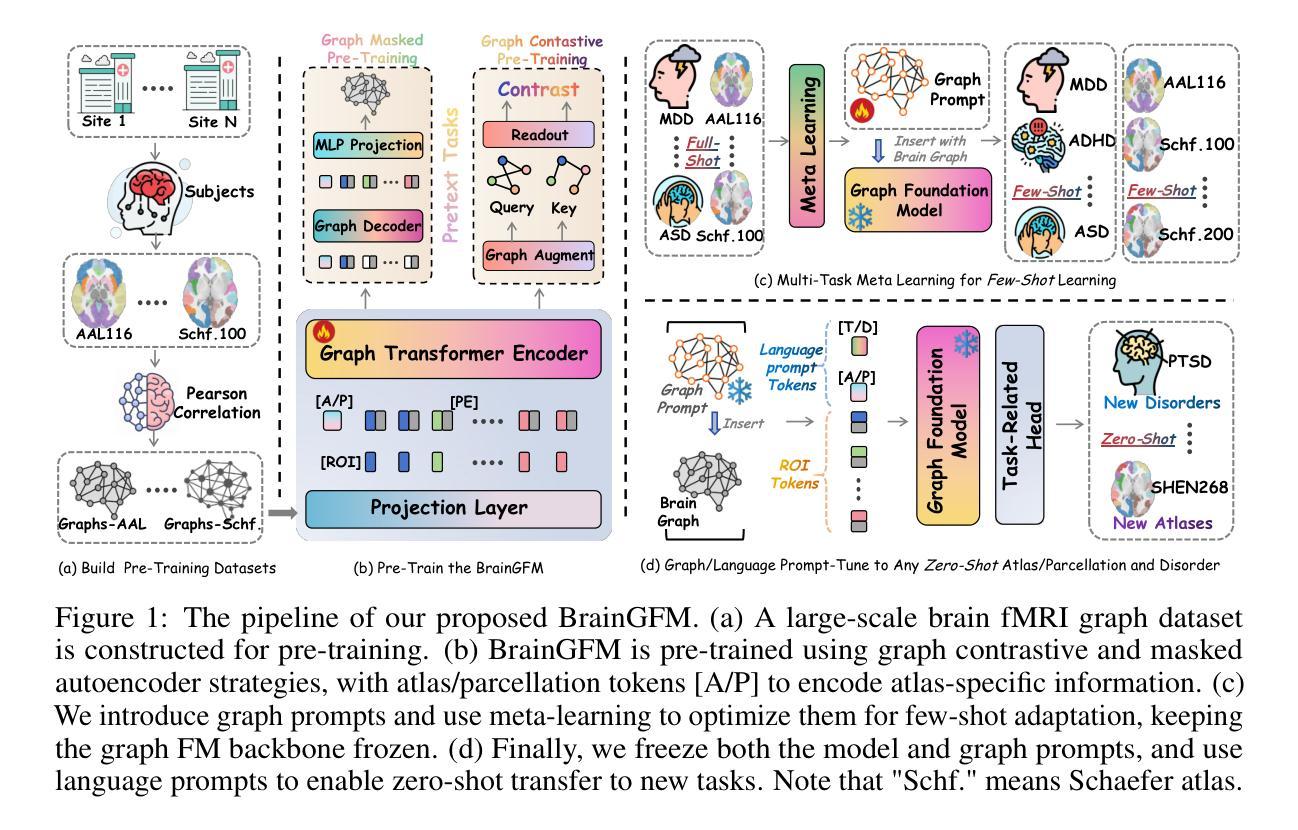
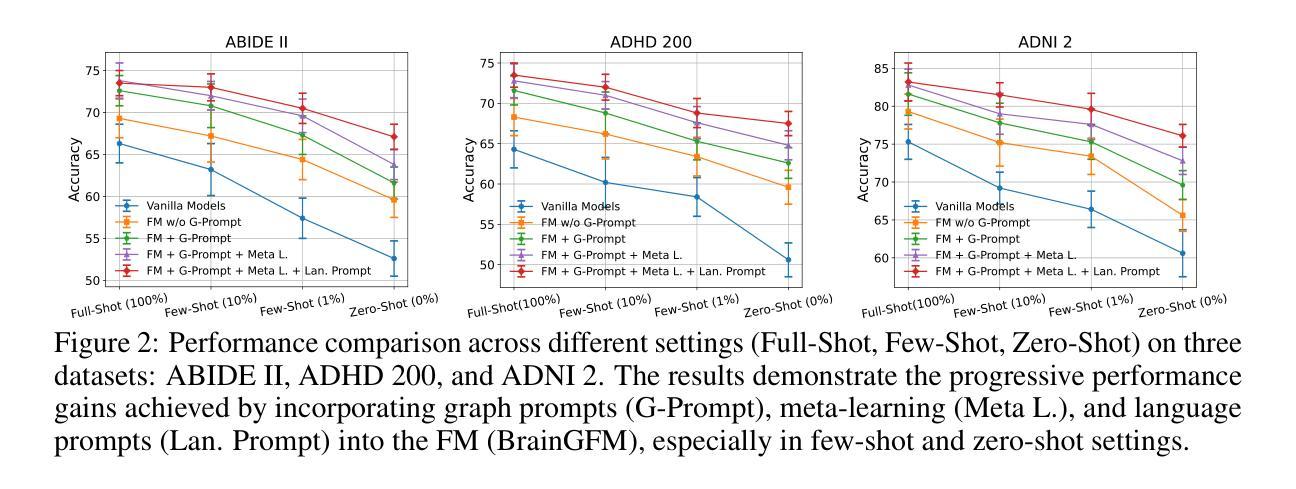
A Brain Graph Foundation Model: Pre-Training and Prompt-Tuning for Any Atlas and Disorder
Authors:Xinxu Wei, Kanhao Zhao, Yong Jiao, Lifang He, Yu Zhang
As large language models (LLMs) continue to revolutionize AI research, there is a growing interest in building large-scale brain foundation models to advance neuroscience. While most existing brain foundation models are pre-trained on time-series signals or connectome features, we propose a novel graph-based pre-training paradigm for constructing a brain graph foundation model. In this paper, we introduce the Brain Graph Foundation Model, termed BrainGFM, a unified framework that leverages graph contrastive learning and graph masked autoencoders for large-scale fMRI-based pre-training. BrainGFM is pre-trained on a diverse mixture of brain atlases with varying parcellations, significantly expanding the pre-training corpus and enhancing the model’s ability to generalize across heterogeneous fMRI-derived brain representations. To support efficient and versatile downstream transfer, we integrate both graph prompts and language prompts into the model design, enabling BrainGFM to flexibly adapt to a wide range of atlases, neurological and psychiatric disorders, and task settings. Furthermore, we employ meta-learning to optimize the graph prompts, facilitating strong generalization to previously unseen disorders under both few-shot and zero-shot learning conditions via language-guided prompting. BrainGFM is pre-trained on 27 neuroimaging datasets spanning 25 common neurological and psychiatric disorders, encompassing 2 types of brain atlases (functional and anatomical) across 8 widely-used parcellations, and covering over 25,000 subjects, 60,000 fMRI scans, and a total of 400,000 graph samples aggregated across all atlases and parcellations. The code is available at: https://github.com/weixinxu666/BrainGFM
随着大型语言模型(LLM)继续引领人工智能研究的革命,建立大规模脑基础模型以推动神经科学发展的兴趣日益浓厚。尽管大多数现有的脑基础模型都是基于时间序列信号或连接组特征进行预训练的,但我们提出了一种基于图的新型预训练范式来构建脑图基础模型。在本文中,我们介绍了Brain Graph Foundation Model(BrainGFM),这是一个统一框架,利用图对比学习和图掩码自动编码器进行大规模基于fMRI的预训练。BrainGFM在具有不同分割的多种脑图谱混合数据上进行预训练,显著扩展了预训练语料库,提高了模型在不同异构图MRI衍生的脑表示中的泛化能力。为了支持高效且通用的下游迁移,我们将图提示和语言提示集成到模型设计中,使BrainGFM能够灵活地适应各种图谱、神经和精神疾病以及任务设置。此外,我们采用元学习来优化图提示,通过语言引导提示,在少样本学习和零样本学习条件下实现对以前未见过的疾病的强大泛化。BrainGFM在27个神经成像数据集上进行预训练,涵盖25种常见的神经和精神疾病,包括两种类型的脑图谱(功能和结构)跨越8种广泛使用的分割方法,涉及超过25,000名受试者、60,000次fMRI扫描和总计40万张跨所有图谱和分割方法的图样本。代码可在以下网址获取:https://github.com/weixinxu666/BrainGFM 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30pages
Summary
本文介绍了BrainGFM模型,这是一种基于图对比学习和图掩码自编码器的统一框架,用于大规模基于fMRI的预训练。BrainGFM利用多种脑图谱和分割方法,扩展了预训练语料库,增强了模型对异构图像的泛化能力。模型结合了图提示和语言提示,能够适应不同的脑图谱、神经和精神障碍以及任务设置。通过元学习优化图提示,BrainGFM在少样本和无样本学习条件下对未见过的疾病进行语言引导提示,具有良好的泛化能力。该模型在涵盖多种常见神经和精神障碍的27个神经成像数据集上进行预训练。
Key Takeaways
- BrainGFM是一个基于图对比学习和图掩码自编码器的脑图基础模型。
- 它使用多样化的脑图谱进行大规模基于fMRI的预训练。
- 模型能够适应多种不同的脑图谱和分割方法,增强其在异构图像上的泛化能力。
- 结合了图提示和语言提示,BrainGFM可灵活应用于各种脑图谱、神经和精神障碍以及任务设置。
- 通过元学习优化图提示,BrainGFM在少样本和无样本学习条件下表现出良好的泛化性能。
- 该模型在涵盖多种常见神经和精神障碍的多个神经成像数据集上进行预训练。
点此查看论文截图

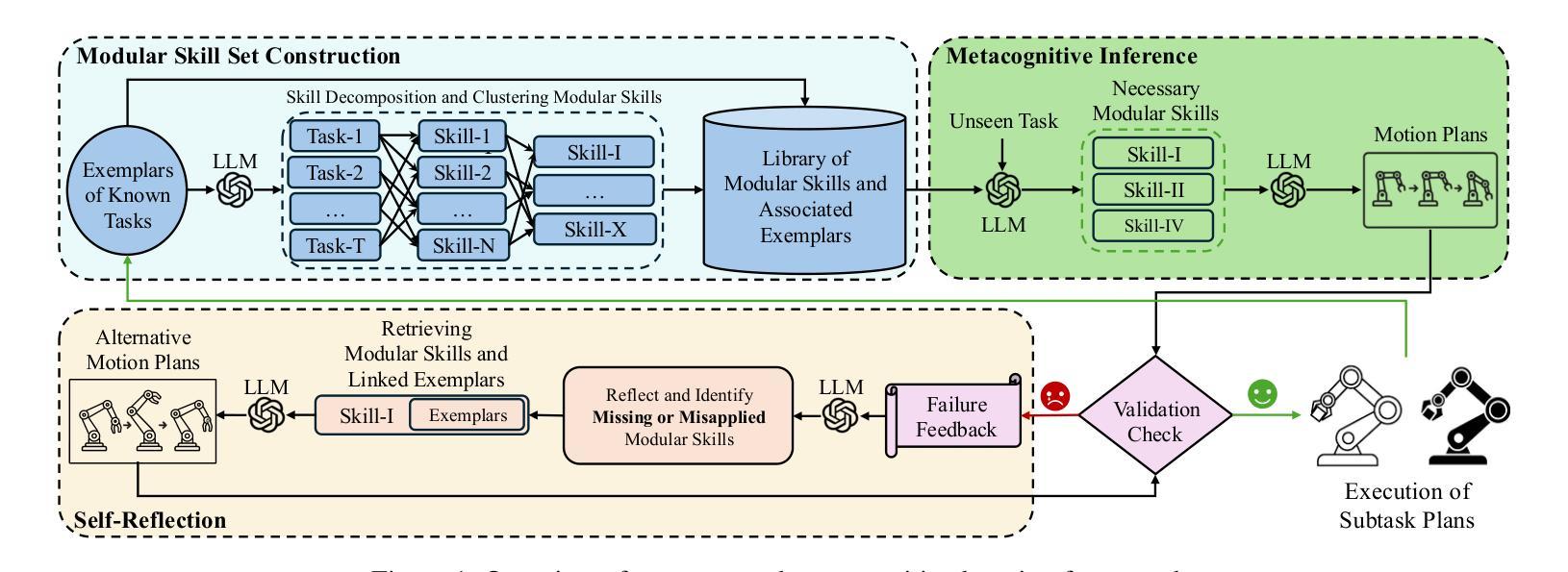
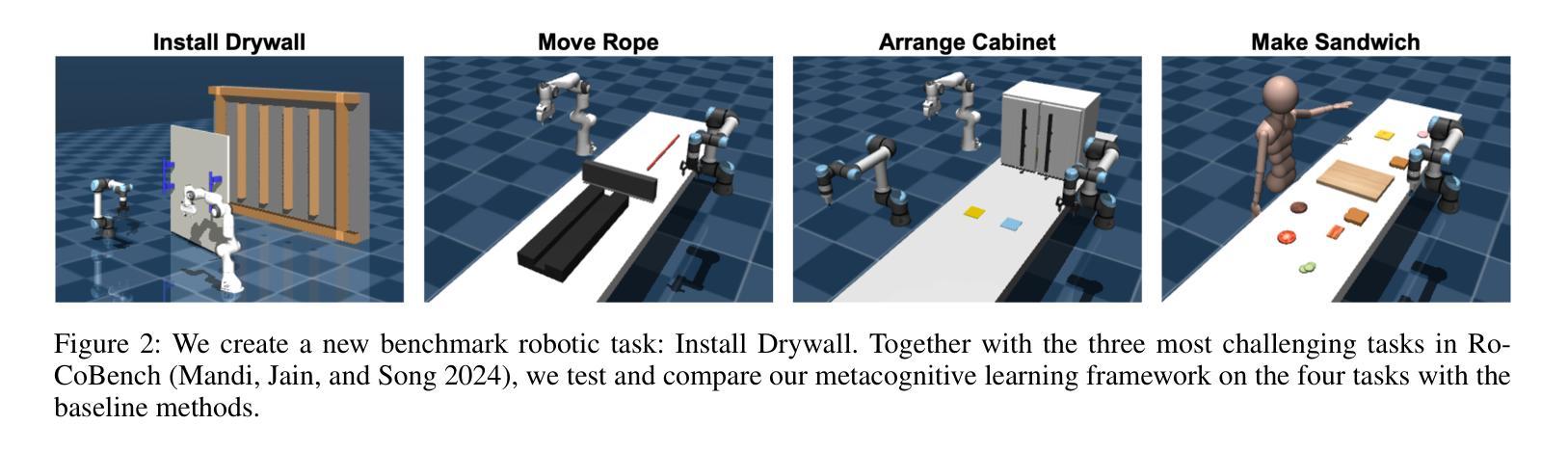
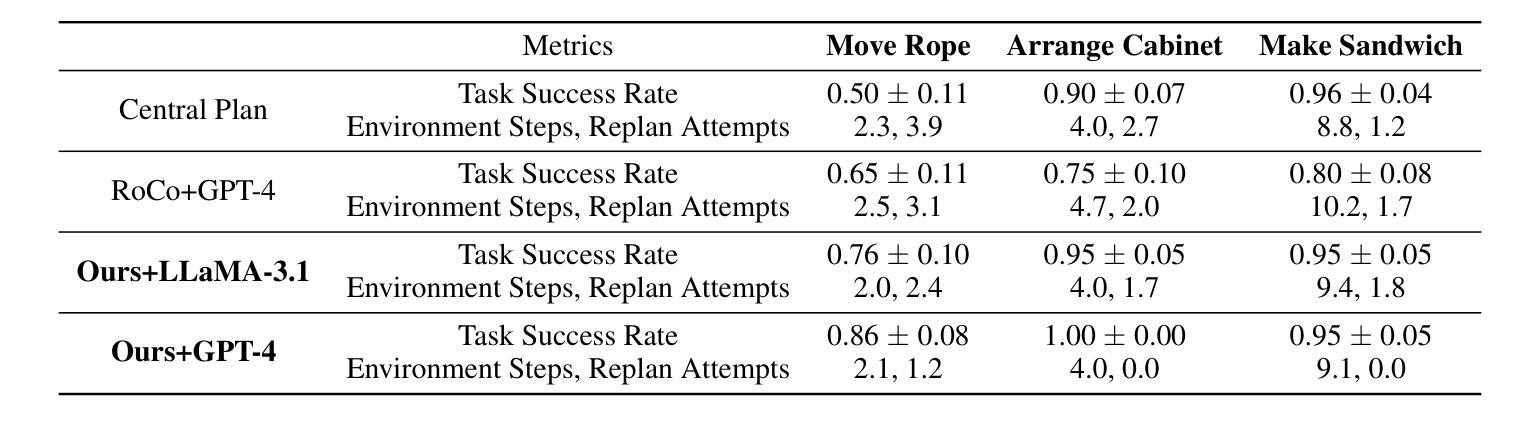
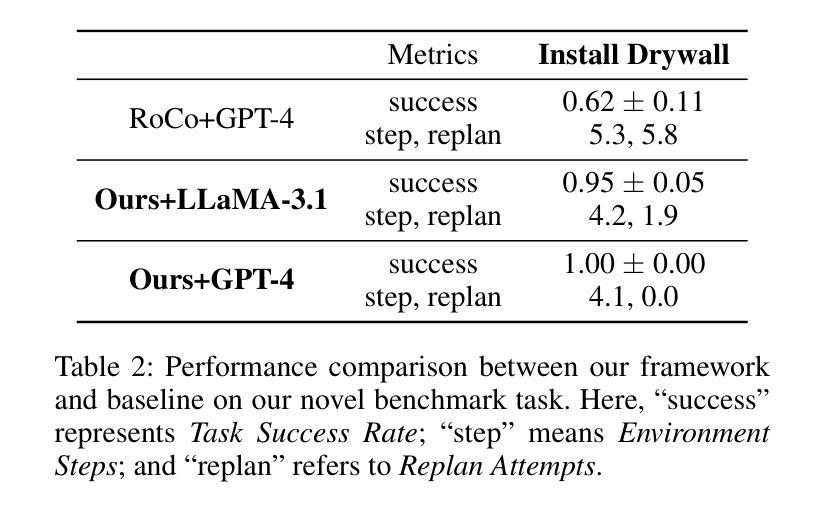
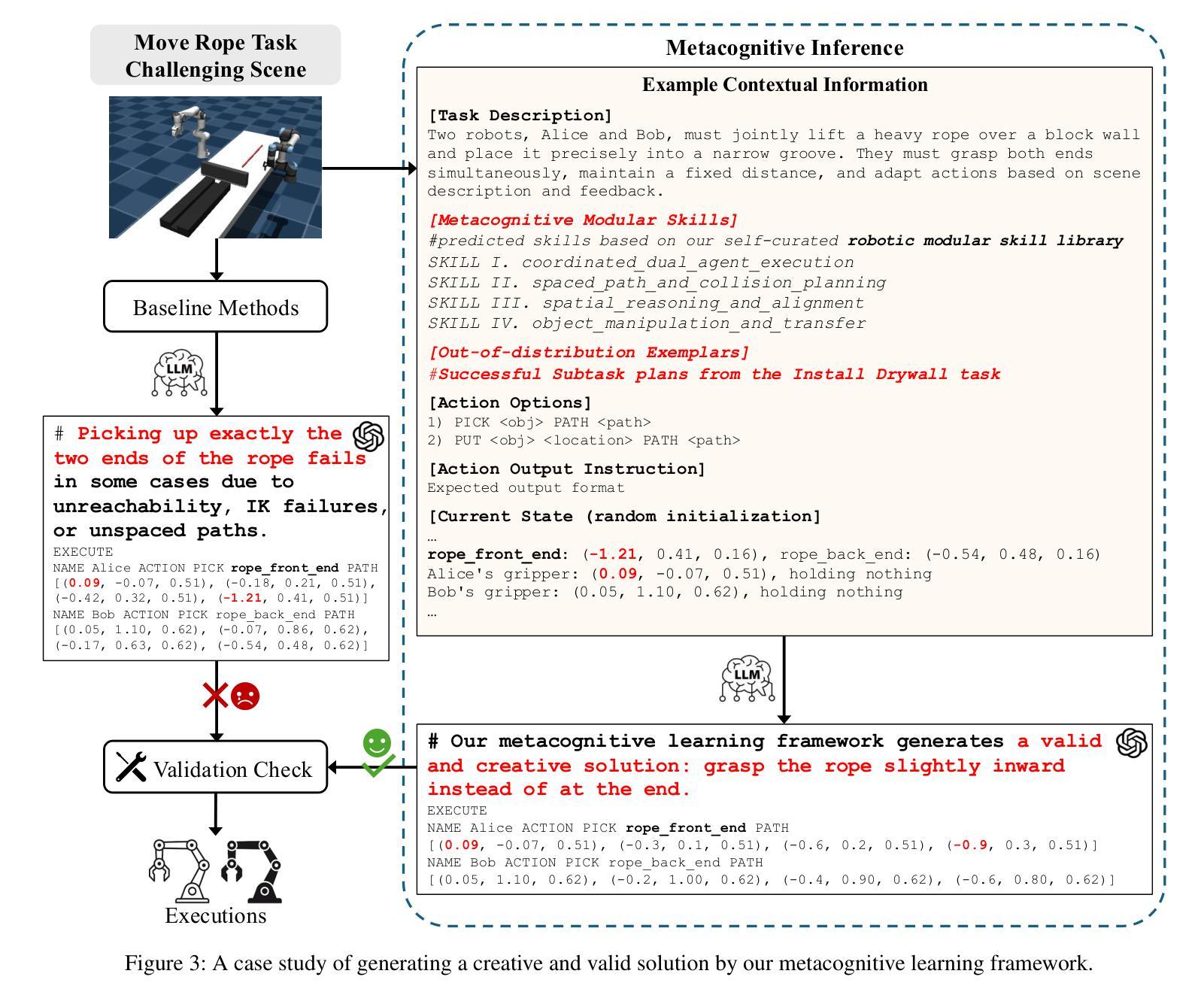
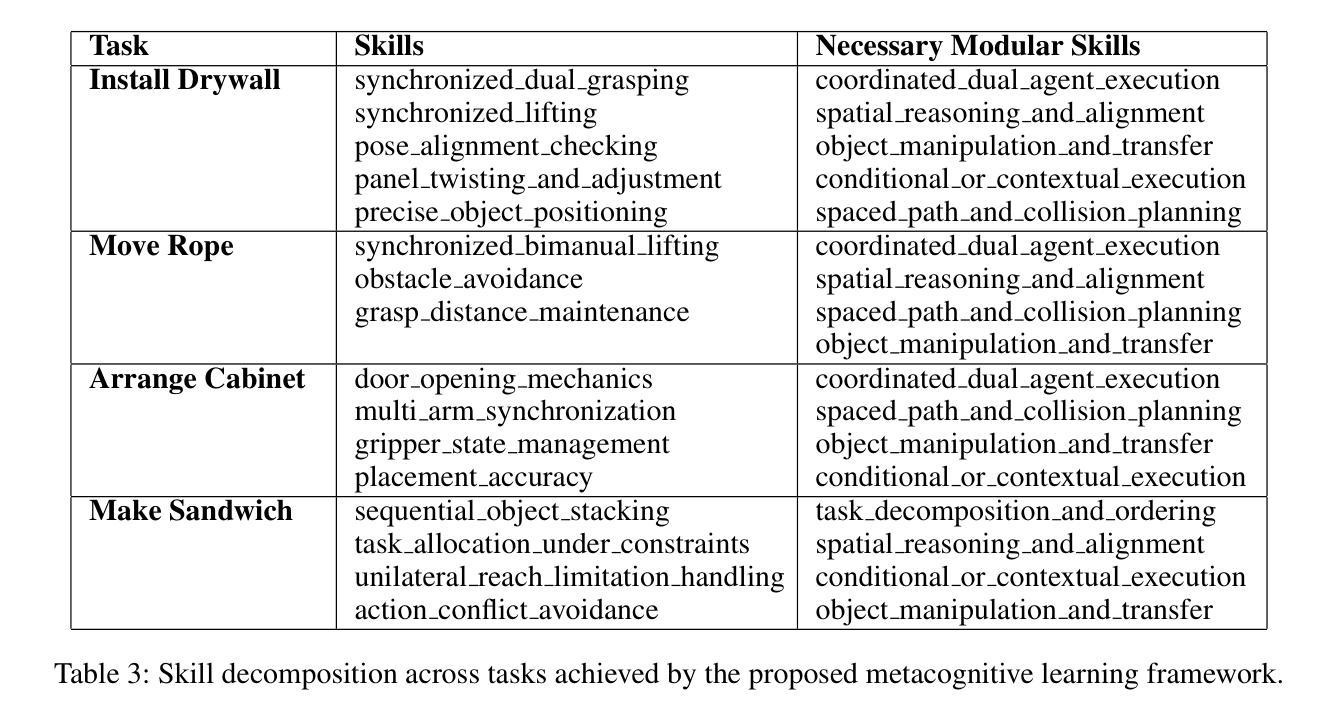
Think, Reflect, Create: Metacognitive Learning for Zero-Shot Robotic Planning with LLMs
Authors:Wenjie Lin, Jin Wei-Kocsis, Jiansong Zhang, Byung-Cheol Min, Dongming Gan, Paul Asunda, Ragu Athinarayanan
While large language models (LLMs) have shown great potential across various domains, their applications in robotics remain largely limited to static prompt-based behaviors and still face challenges in complex tasks under zero-shot or few-shot settings. Inspired by human metacognitive learning and creative problem-solving, we address this limitation by exploring a fundamental question: Can LLMs be empowered with metacognitive capabilities to reason, reflect, and create, thereby enhancing their ability to perform robotic tasks with minimal demonstrations? In this paper, we present a framework that integrates metacognitive learning into LLM-powered multi-robot collaboration. The system equips the LLM-powered robotic agents with a skill decomposition and self-reflection mechanism that identifies modular skills from prior tasks, reflects on failures in unseen task scenarios, and synthesizes effective new solutions. We propose a more challenging robotic benchmark task and evaluate our framework on the existing benchmark and the novel task. Experimental results show that our metacognitive learning framework significantly outperforms existing baselines. Moreover, we observe that the framework can generate solutions that differ from the ground truth yet still successfully complete the tasks. These findings support our hypothesis that metacognitive learning can foster creativity in robotic planning.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在各个领域表现出了巨大的潜力,但它们在机器人领域的应用仍然主要局限于基于静态提示的行为,并且在零样本或小样例设置下执行复杂任务时仍面临挑战。我们受到人类元认知学习和创造性解决问题的启发,通过探索一个基本问题来解决这一局限性:能否为LLM赋予元认知能力,使其能够推理、反思和创造,从而提高它们在少量演示情况下执行机器人任务的能力?在本文中,我们提出了一个将元认知学习融入LLM驱动的多机器人协作的框架。该系统为LLM驱动的机器人代理配备了技能分解和自我反思机制,该机制能够从先前任务中识别模块化技能,反思未见任务场景中的失败,并合成有效的新解决方案。我们提出了一个更具挑战性的机器人基准任务,并在现有基准测试和新型任务上评估了我们的框架。实验结果表明,我们的元认知学习框架显著优于现有基准测试。此外,我们观察到该框架能够生成与标准答案不同但仍能成功完成任务的解决方案。这些发现支持我们的假设,即元认知学习可以促进机器人规划中的创造力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型在机器人领域的应用仍然局限于静态提示行为,并在零样本或少样本环境下的复杂任务中面临挑战。本文受人类元认知学习和创造性解决问题的启发,探索了一个基本问题:能否为大语言模型赋予元认知能力进行推理、反思和创新,从而提升其在少量演示下的机器人任务执行能力?本文提出了一个将元认知学习整合到语言模型驱动的机器人协作框架中。该框架为语言模型驱动的机器人配备了技能分解和自我反思机制,可以从先前的任务中识别模块化技能,反思在未见的任务场景中的失败,并合成有效的解决方案。实验结果表明,该元认知学习框架显著优于现有基线,并能生成与真实答案不同但仍能成功完成任务的解决方案。这支持了我们的假设:元认知学习可以促进机器人规划中的创造力。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型在机器人领域的应用受限于静态提示行为,尤其在复杂任务的零样本或少样本环境下存在挑战。
- 本文探索了使大语言模型具备元认知能力的可能性,以进行推理、反思和创新。
- 提出的框架将元认知学习整合到语言模型驱动的机器人协作中。
- 框架配备了技能分解和自我反思机制,识别模块化技能,反思失败并合成新解决方案。
- 实验表明,该元认知学习框架优于现有基线。
- 框架能够生成与真实答案不同但仍能成功完成任务的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

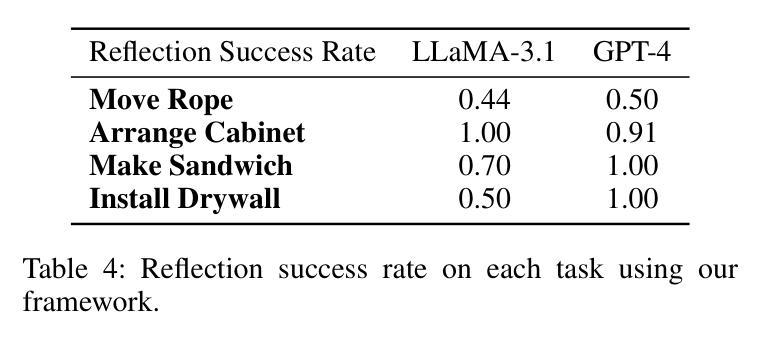
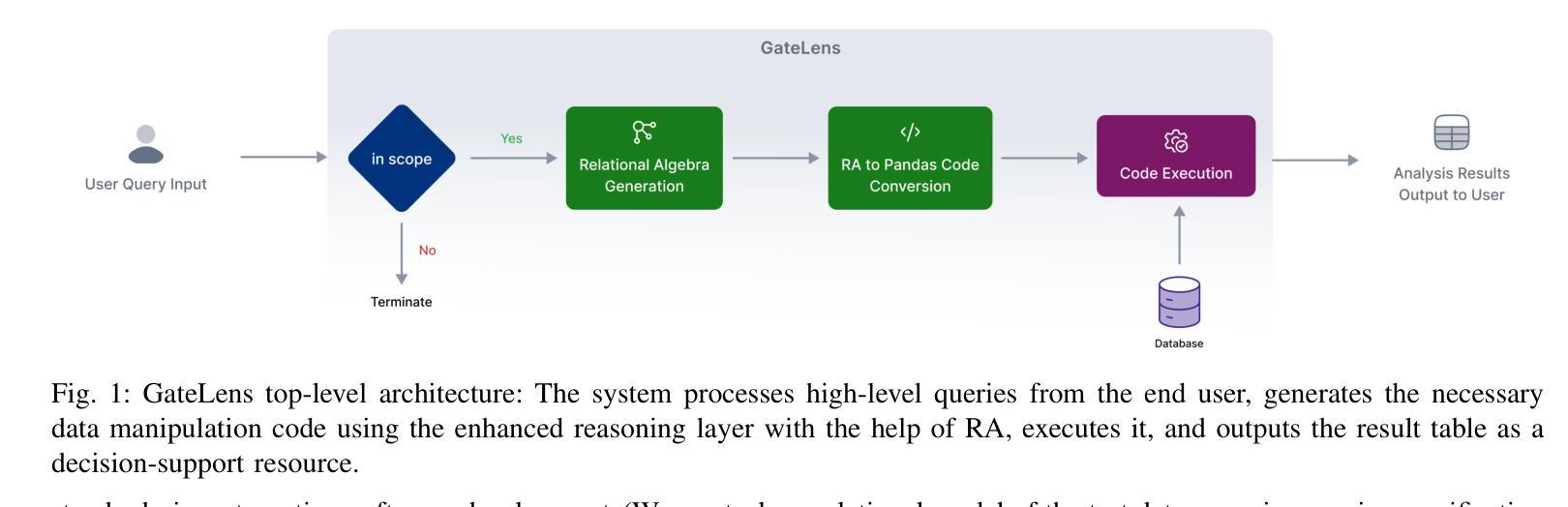
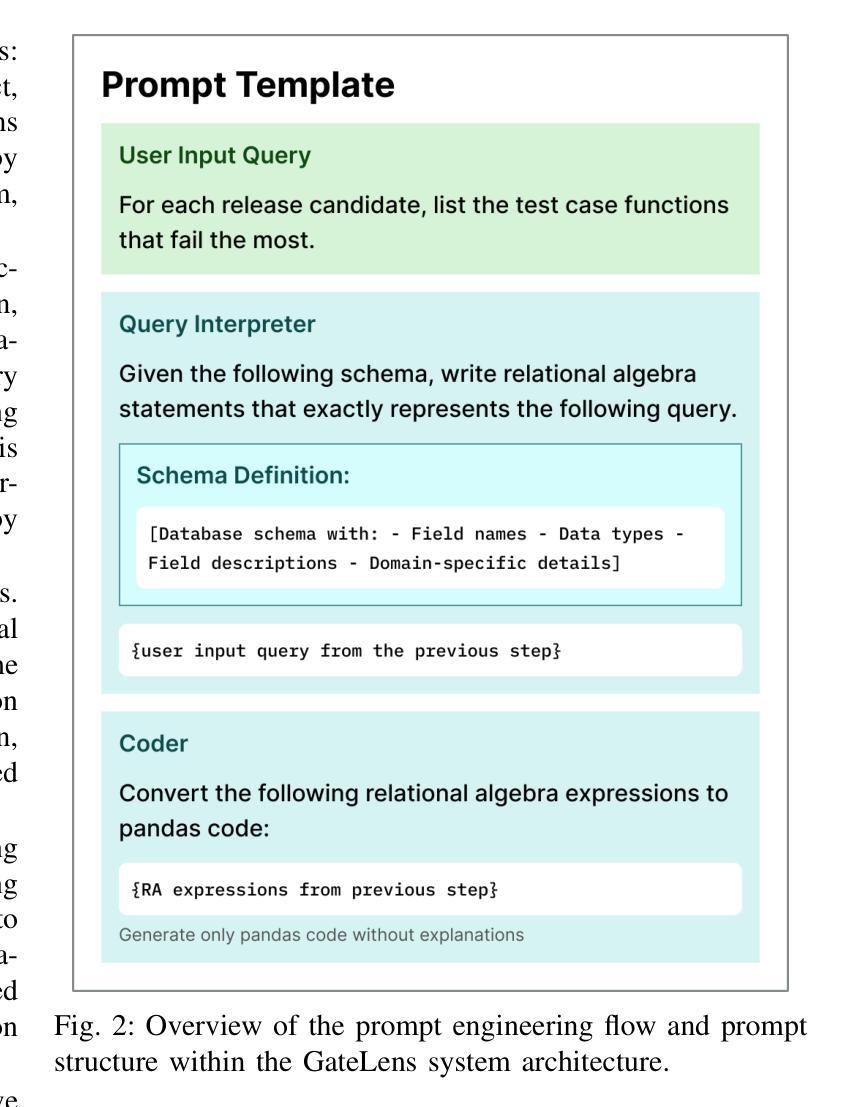
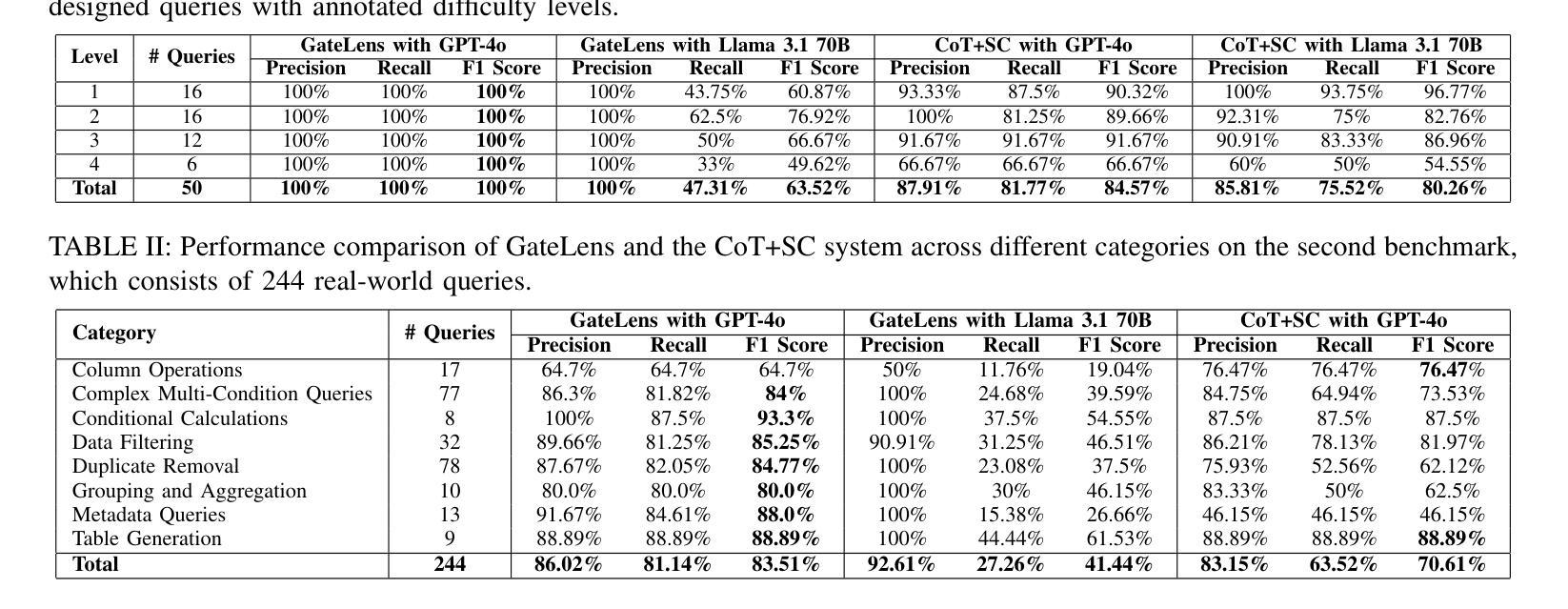
GateLens: A Reasoning-Enhanced LLM Agent for Automotive Software Release Analytics
Authors:Arsham Gholamzadeh Khoee, Shuai Wang, Yinan Yu, Robert Feldt, Dhasarathy Parthasarathy
Ensuring reliable software release decisions is critical in safety-critical domains such as automotive manufacturing. Release validation relies on large tabular datasets, yet manual analysis is slow, costly, and error-prone. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promising automation potential, they face challenges in analytical reasoning, structured data handling, and ambiguity resolution. This paper introduces GateLens, an LLM-based system for analyzing tabular data in the automotive domain. GateLens translates natural language queries into Relational Algebra (RA) expressions and generates optimized Python code. Unlike traditional multi-agent or planning-based systems that can be slow, opaque, and costly to maintain, GateLens emphasizes speed, transparency, and reliability. Experimental results show that GateLens outperforms the existing Chain-of-Thought (CoT) + Self-Consistency (SC) based system on real-world datasets, particularly in handling complex and ambiguous queries. Ablation studies confirm the essential role of the RA layer. Industrial deployment shows over 80% reduction in analysis time while maintaining high accuracy across test result interpretation, impact assessment, and release candidate evaluation. GateLens operates effectively in zero-shot settings without requiring few-shot examples or agent orchestration. This work advances deployable LLM system design by identifying key architectural features-intermediate formal representations, execution efficiency, and low configuration overhead-crucial for safety-critical industrial applications.
在汽车行业等安全关键领域,确保可靠的软件发布决策至关重要。发布验证依赖于大型表格数据集,但手动分析速度缓慢、成本高昂且易出错。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)提供了有前景的自动化潜力,但在分析推理、结构化数据处理和歧义解决方面面临挑战。本文介绍了GateLens,一个基于LLM用于分析汽车领域表格数据的系统。GateLens将自然语言查询翻译成关系代数(RA)表达式,并生成优化的Python代码。与传统的多代理或基于规划的系统相比,这些系统可能速度较慢、不透明且维护成本高昂,GateLens强调速度、透明度和可靠性。实验结果表明,在真实数据集上,GateLens优于现有的基于思维链(CoT)和自我一致性(SC)的系统,特别是在处理复杂和模糊查询方面。消融研究证实了RA层的关键作用。工业部署显示,在分析时间方面减少了80%以上,同时在测试结果解读、影响评估和发布候选评估等方面保持了高准确性。GateLens在零样本设置下运行有效,无需少量样本或代理编排。这项工作通过识别关键架构特征——中间正式表示、执行效率和低配置开销,来推进可部署的LLM系统设计,对于安全关键的工业应用至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了GateLens系统,一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的汽车领域表格数据分析系统。该系统将自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式并生成优化的Python代码,具有快速、透明和可靠的特点。相较于传统系统,它在处理复杂和模糊查询时表现出优势,并能在工业部署中大幅减少分析时间同时保持高精度。
Key Takeaways
- 汽车制造业中,软件发布的可靠性决策至关重要。
- 释放验证依赖于大型表格数据集,但手动分析是缓慢、昂贵和易出错的。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化潜力方面具有前景,但在分析推理、结构数据处理和歧义解决方面面临挑战。
- GateLens系统介绍:利用LLM分析汽车领域的表格数据,将自然语言查询转化为关系代数表达式,并生成优化的Python代码。
- GateLens强调速度、透明度和可靠性,优于传统多代理或基于规划的系统。
- 实验结果表明,GateLens在真实数据集上优于现有的Chain-of-Thought(CoT)+ Self-Consistency(SC)系统,特别是在处理复杂和模糊查询方面。
- 工业化部署显示,分析时间减少了80%以上,同时在测试结果解读、影响评估和发布候选评估方面保持了高精度。
点此查看论文截图

PRIMAL: Physically Reactive and Interactive Motor Model for Avatar Learning
Authors:Yan Zhang, Yao Feng, Alpár Cseke, Nitin Saini, Nathan Bajandas, Nicolas Heron, Michael J. Black
We formulate the motor system of an interactive avatar as a generative motion model that can drive the body to move through 3D space in a perpetual, realistic, controllable, and responsive manner. Although human motion generation has been extensively studied, many existing methods lack the responsiveness and realism of real human movements. Inspired by recent advances in foundation models, we propose PRIMAL, which is learned with a two-stage paradigm. In the pretraining stage, the model learns body movements from a large number of sub-second motion segments, providing a generative foundation from which more complex motions are built. This training is fully unsupervised without annotations. Given a single-frame initial state during inference, the pretrained model not only generates unbounded, realistic, and controllable motion, but also enables the avatar to be responsive to induced impulses in real time. In the adaptation phase, we employ a novel ControlNet-like adaptor to fine-tune the base model efficiently, adapting it to new tasks such as few-shot personalized action generation and spatial target reaching. Evaluations show that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. We leverage the model to create a real-time character animation system in Unreal Engine that feels highly responsive and natural. Code, models, and more results are available at: https://yz-cnsdqz.github.io/eigenmotion/PRIMAL
我们将交互式角色的运动系统建模为一个生成运动模型,该模型能够驱动角色在三维空间中以持续、真实、可控和响应迅速的方式移动。尽管人类运动生成已经得到了广泛的研究,但许多现有方法缺乏真实人类运动的响应性和真实性。受基础模型最新进展的启发,我们提出了PRIMAL模型,该模型采用两阶段学习范式。在预训练阶段,模型从大量亚秒级运动片段中学习身体动作,为构建更复杂的动作提供了一个生成基础。这种训练是完全无监督的,无需注释。给定推理过程中的单帧初始状态,预训练模型不仅生成无界限、真实、可控的运动,还使角色能够实时响应产生的脉冲。在适应阶段,我们采用类似ControlNet的适配器对基础模型进行微调,使其适应新任务,如小样本人格化动作生成和空间目标达成。评估表明,我们提出的方法优于最新基线。我们利用该模型在Unreal Engine中创建了一个实时角色动画系统,感觉非常响应且自然。代码、模型和更多结果请访问:https://yz-cnsdqz.github.io/eigenmotion/PRIMAL
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV’25 camera ready; main paper and appendix; 19 pages in total
Summary
本文介绍了一种交互式角色的运动系统,该系统采用生成运动模型的方式,使角色能够在三维空间中实现持久、真实、可控和响应迅速的动作。系统采用两阶段学习法,首先在大量无标注的子秒级运动片段上进行预训练,为复杂动作生成提供基础;然后在推理阶段通过控制网络适配器进行微调,适应新任务如个性化动作生成和空间目标达到等。实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,并在Unreal Engine中实现了实时响应和自然动画的角色系统。
Key Takeaways
- 交互式角色的运动系统通过生成运动模型实现角色的持久、真实、可控和响应迅速的动作。
- 系统采用两阶段学习法,先进行预训练学习基础动作,然后进行微调适应新任务。
- 预训练阶段使用大量无标注的子秒级运动片段,为复杂动作生成提供基础。
- 控制网络适配器用于在推理阶段进行微调,适应个性化动作生成和空间目标达到等任务。
- 该方法优于现有技术,提供了更真实的角色运动生成。
- 系统在Unreal Engine中实现了实时响应和自然动画的角色系统。
点此查看论文截图

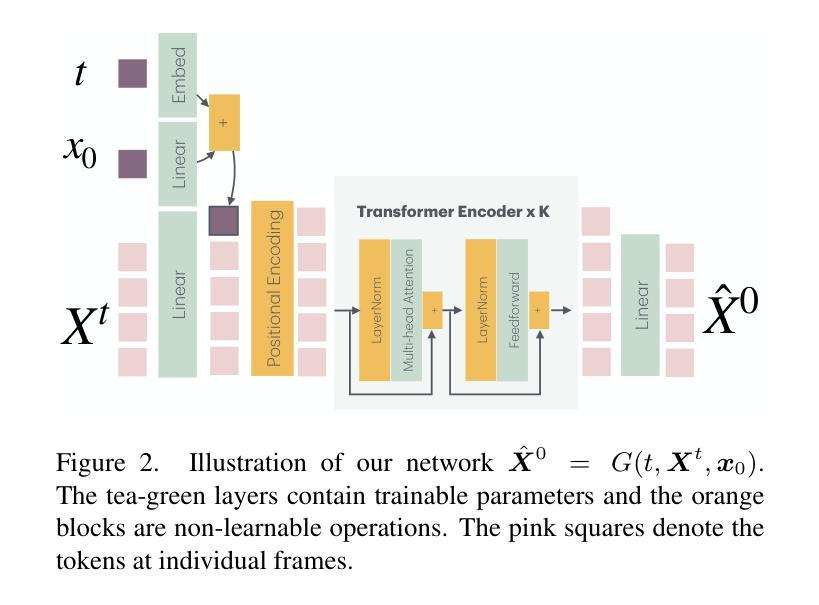
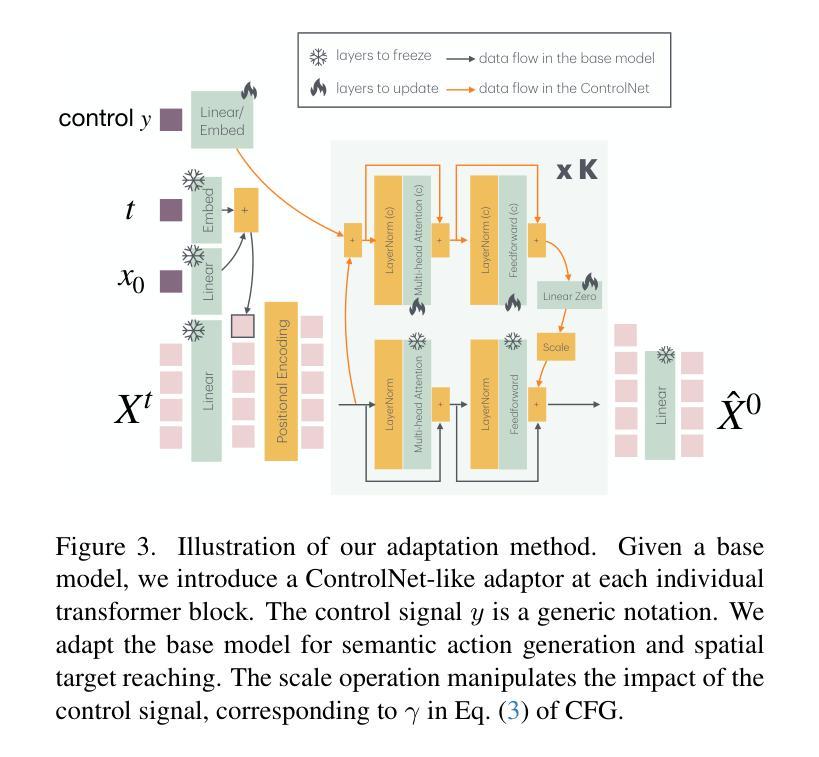
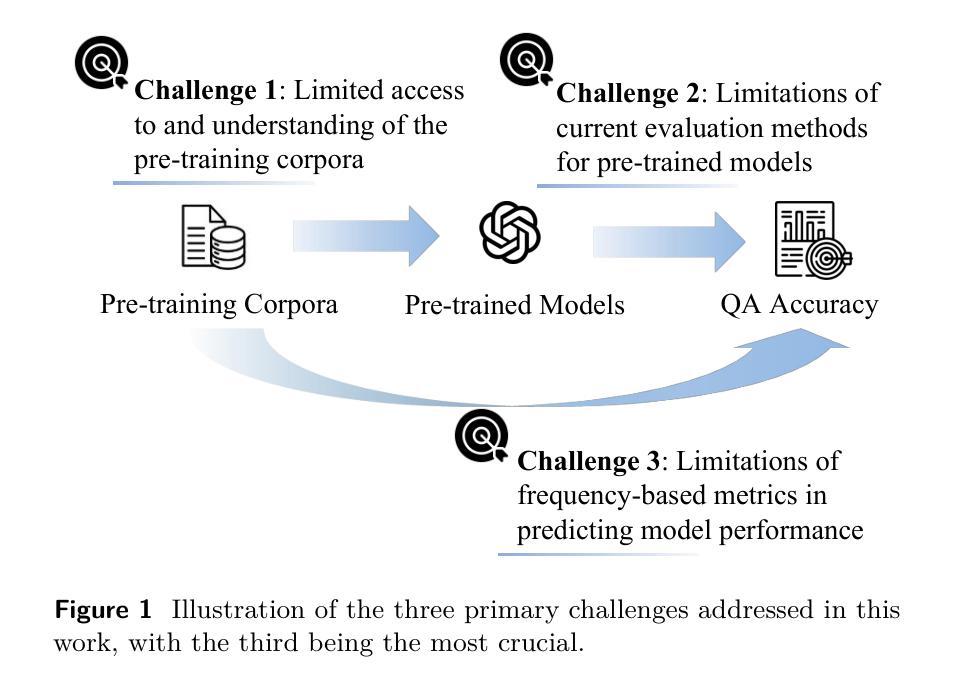
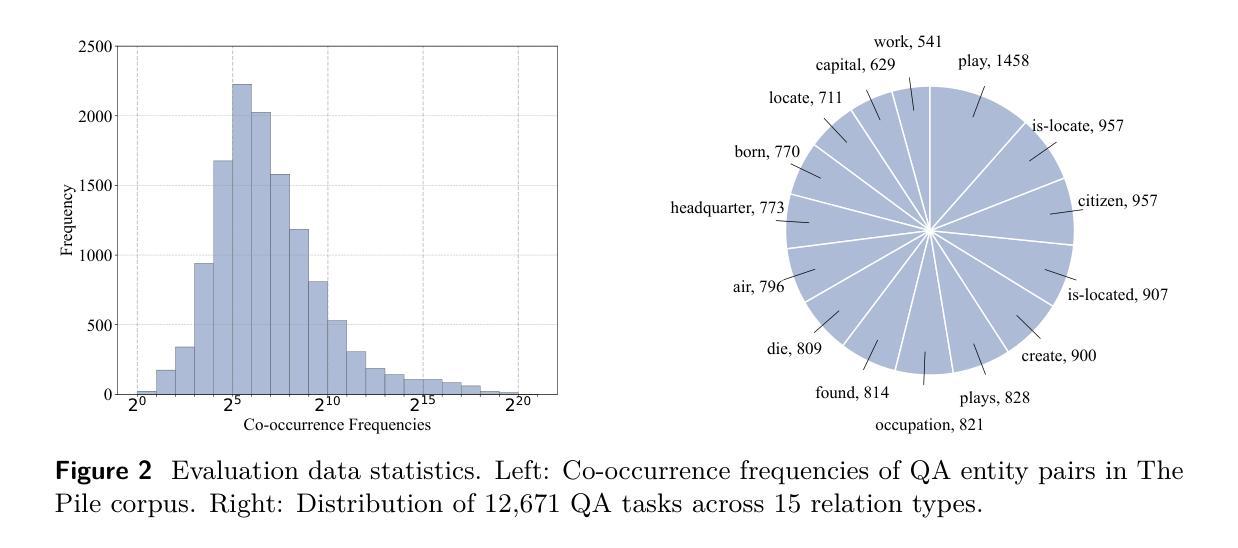
Beyond Scaling: Measuring and Predicting the Upper Bound of Knowledge Retention in Language Model Pre-Training
Authors:Changhao Jiang, Ming Zhang, Junjie Ye, Xiaoran Fan, Yifei Cao, Jiajun Sun, Zhiheng Xi, Shihan Dou, Yi Dong, Yujiong Shen, Jingqi Tong, Baoyu Fan, Zhen Wang, Tao Liang, Zhihui Fei, Mingyang Wan, Guojun Ma, Qi Zhang, Tao Gui, Xuanjing Huang
The GPT-4 technical report highlights the possibility of predicting model performance on downstream tasks using only pre-training signals, though detailed methodologies are absent. Such predictive capabilities are essential for resource-efficient pre-training and the construction of task-aligned datasets. In this paper, we aim to predict performance in closed-book question answering (QA), a vital downstream task that directly reflects a model’s internalized knowledge without the help of external tools. We address three primary challenges: (1) limited access to and understanding of pre-training corpora, (2) limitations of current evaluation methods for pre-trained models, and (3) limitations of frequency-based metrics in predicting model performance. In response, we conduct large-scale retrieval and semantic analysis across the pre-training corpora of 21 publicly available and 3 custom-trained large language models. We then develop a multi-template QA evaluation framework incorporating paraphrased question variants. Building on these foundations, we propose Size-dependent Mutual Information (SMI), an information-theoretic metric that linearly correlates pre-training data characteristics, model size, and QA accuracy, without requiring additional training. Experimental results show that SMI outperforms co-occurrence-based baselines, achieving $R^2 > 0.75$ on models with over one billion parameters. Theoretical analysis further suggests an upper bound of around 80% QA accuracy under optimal pre-training, reflecting intrinsic memory limitations and motivating the use of retrieval or few-shot methods in later stages.
GPT-4技术报告强调了仅使用预训练信号预测模型在下游任务上性能的可行性,虽然缺乏详细的方法论。这种预测能力对于资源高效的预训练和任务对齐数据集的构建至关重要。本文旨在预测封闭式问答(QA)中的性能,这是一个重要的下游任务,能够直接反映模型的内部知识,无需外部工具的帮助。我们解决了三个主要挑战:(1)对预训练语料库的有限访问和了解,(2)当前预训练模型评估方法的局限性,(3)基于频率的指标在预测模型性能方面的局限性。为此,我们对21个公开可用的和3个自定义训练的大型语言模型的预训练语料库进行了大规模检索和语义分析。然后,我们开发了一个多模板QA评估框架,该框架结合了改述问题变体。在此基础上,我们提出了Size-dependent Mutual Information(SMI),这是一种信息理论指标,它线性地关联预训练数据特性、模型大小与问答准确性,无需额外的训练。实验结果表明,SMI优于基于共现的基线,在具有超过十亿参数的模型上实现了R²> 0.75。理论分析进一步表明,在最佳预训练情况下,QA准确率的上限约为80%,这反映了内在的存储限制,并激励在后期使用检索或小样方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在预测大型预训练语言模型在封闭问答任务中的性能。研究团队通过对多个预训练语料库的语义分析,提出了基于信息理论的度量标准——Size-dependent Mutual Information(SMI)。该度量标准能够反映预训练数据特性、模型大小与问答准确度的关系,无需额外训练。实验结果显示,SMI相较于基于共现的基线方法表现更优,在百亿参数以上的模型上达到R²大于0.75的效果。此外,理论分析结果指出,在最佳预训练条件下,QA准确率的上限约为80%,这反映了内在的记忆限制并鼓励后续阶段使用检索或小样方法。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4技术报告强调了仅使用预训练信号预测模型在下游任务中性能的可能性。
- 针对资源高效的预训练和任务对齐数据集的建设,预测能力至关重要。
- 在封闭问答任务中预测模型性能是一大挑战,该任务直接反映模型的内部知识且无需外部工具帮助。
- 研究团队通过大规模检索和语义分析多个预训练语料库来应对挑战。
- 提出了Size-dependent Mutual Information(SMI)这一信息理论度量标准,能够线性关联预训练数据特性、模型大小与问答准确度。
- 实验结果显示SMI相较于共现基线有更好的表现,并在百亿参数以上的模型上取得较高准确性。
点此查看论文截图

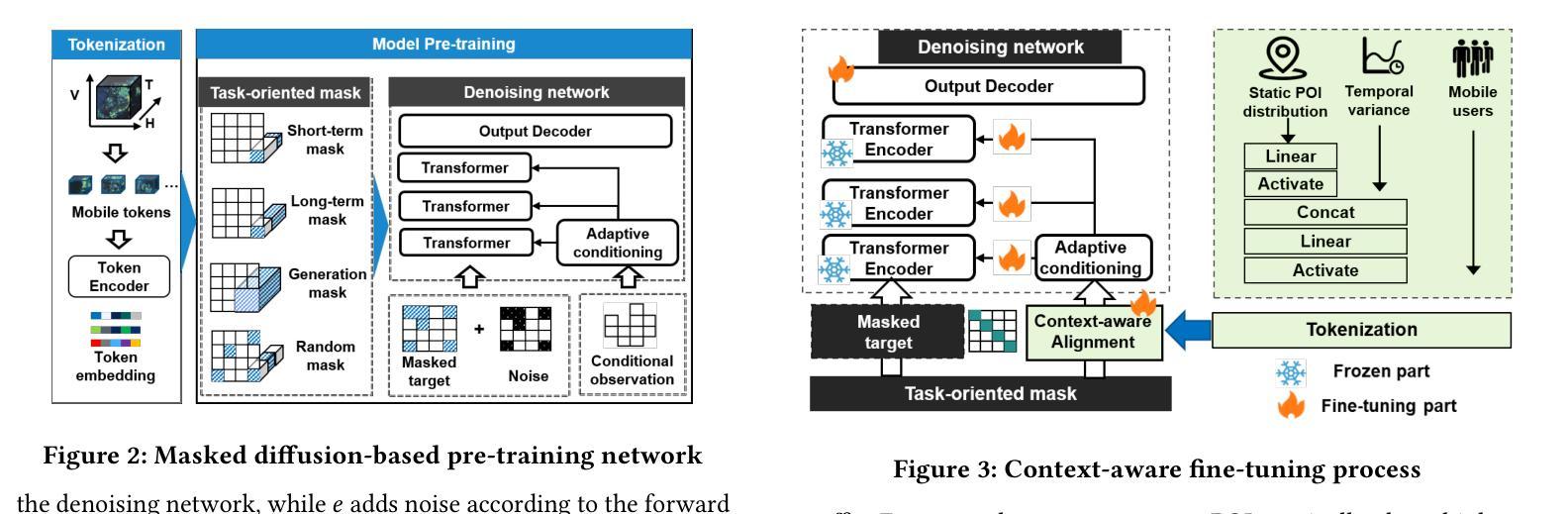
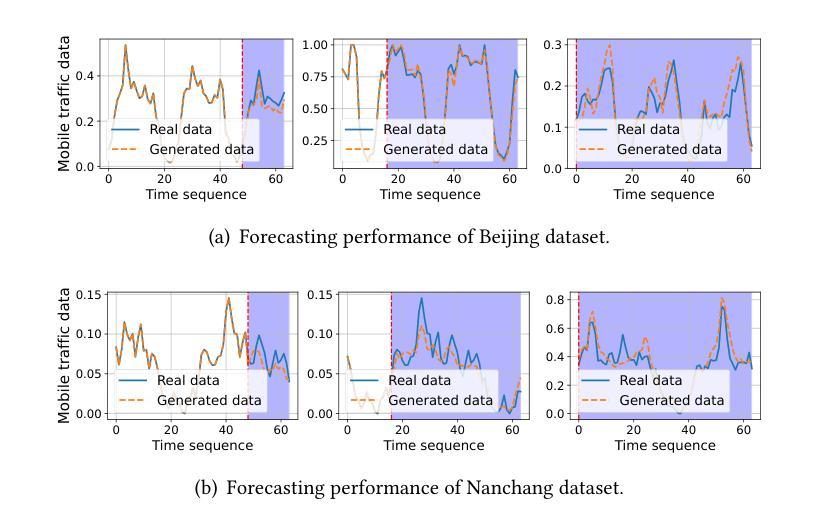
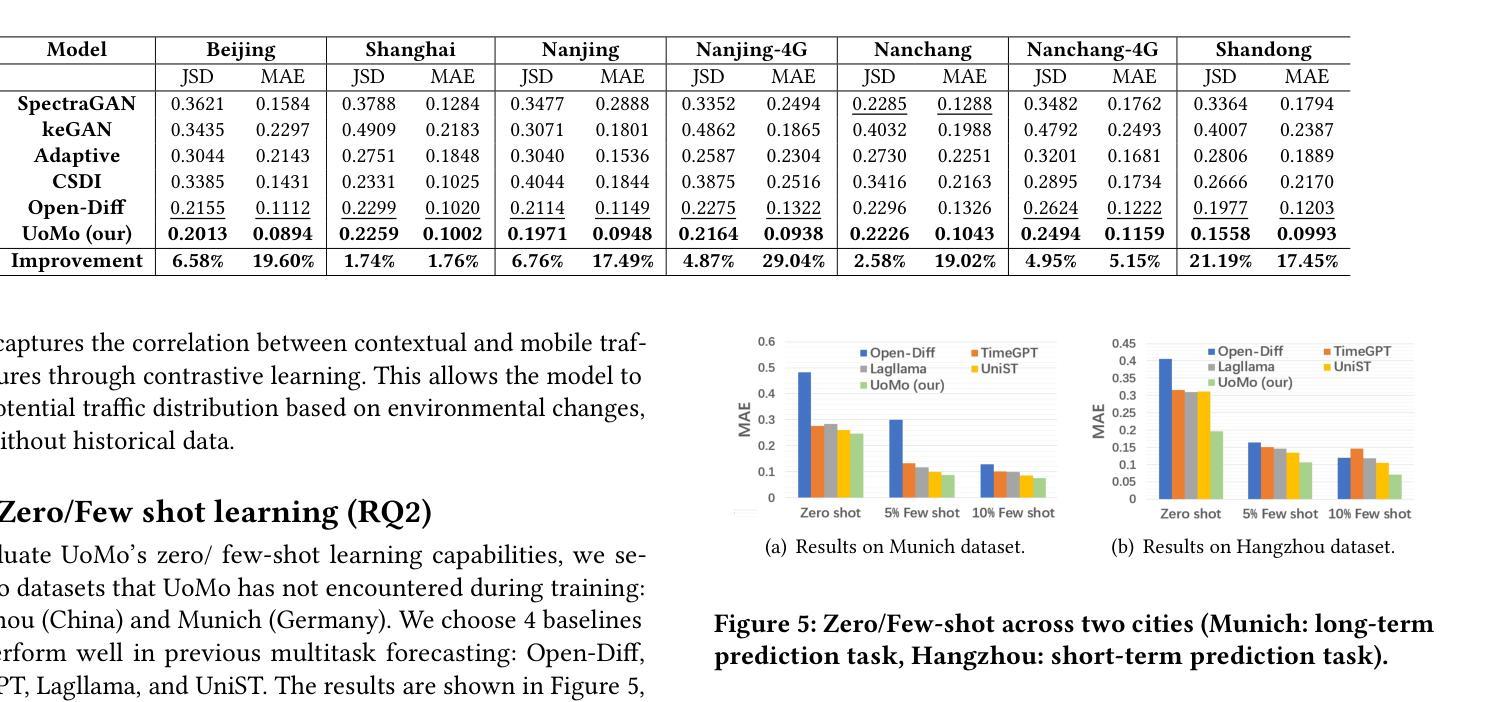
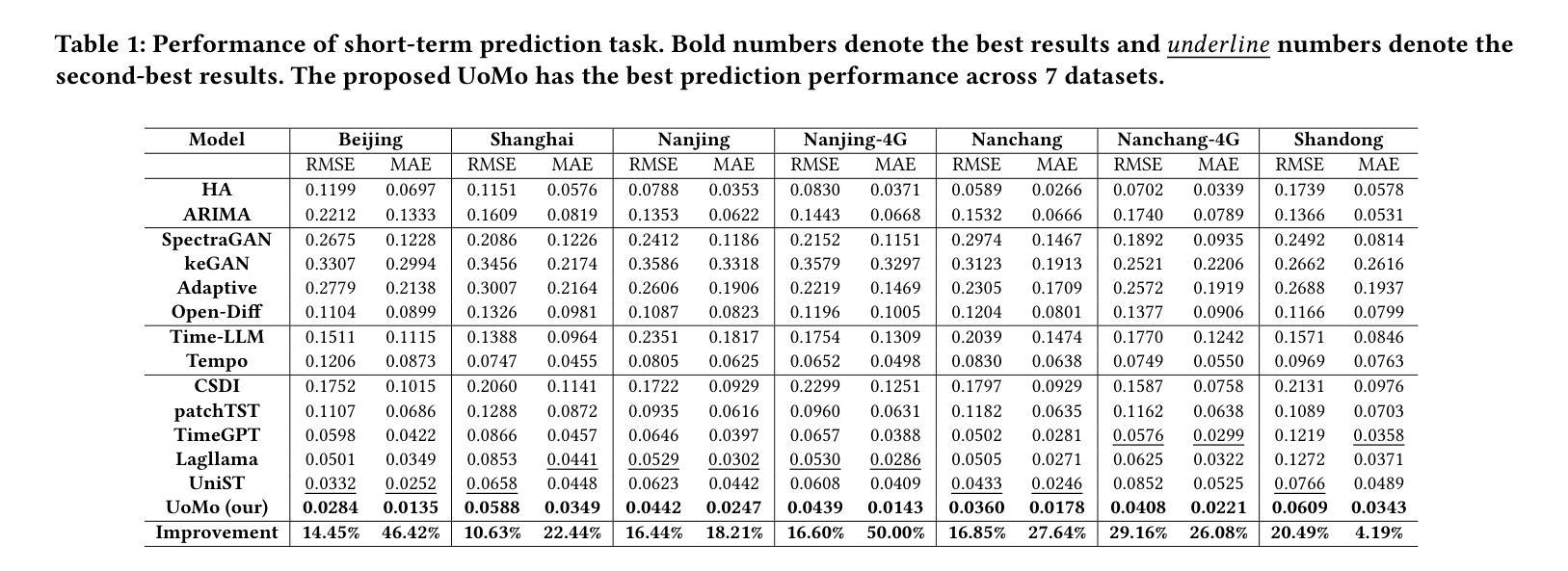
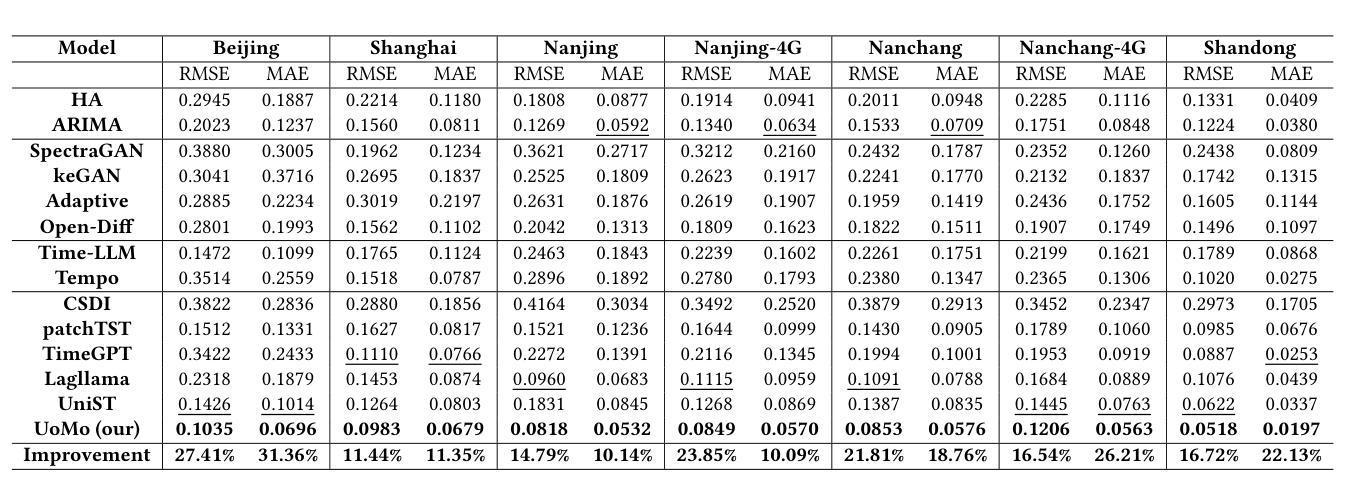
UoMo: A Foundation Model for Mobile Traffic Forecasting with Diffusion Model
Authors:Haoye Chai, Shiyuan Zhang, Xiaoqian Qi, Baohua Qiu, Yong Li
Mobile traffic forecasting allows operators to anticipate network dynamics and performance in advance, offering substantial potential for enhancing service quality and improving user experience. However, existing models are often task-oriented and are trained with tailored data, which limits their effectiveness in diverse mobile network tasks of Base Station (BS) deployment, resource allocation, energy optimization, etc. and hinders generalization across different urban environments. Foundation models have made remarkable strides across various domains of NLP and CV due to their multi-tasking adaption and zero/few-shot learning capabilities. In this paper, we propose an innovative Foundation model for Mo}bile traffic forecasting (FoMo), aiming to handle diverse forecasting tasks of short/long-term predictions and distribution generation across multiple cities to support network planning and optimization. FoMo combines diffusion models and transformers, where various spatio-temporal masks are proposed to enable FoMo to learn intrinsic features of different tasks, and a contrastive learning strategy is developed to capture the correlations between mobile traffic and urban contexts, thereby improving its transfer learning capability. Extensive experiments on 9 real-world datasets demonstrate that FoMo outperforms current models concerning diverse forecasting tasks and zero/few-shot learning, showcasing a strong universality.
移动流量预测使运营商能够提前预测网络动态和性能,为提高服务质量和改善用户体验提供了巨大潜力。然而,现有模型通常是面向任务的,并且使用定制数据进行训练,这限制了它们在基站部署、资源配置、能源优化等多样化的移动网络任务中的有效性,并阻碍了它们在不同城市环境中的泛化能力。由于其在多任务适应和零/少样本学习能力方面的优势,基础模型在NLP和计算机视觉的不同领域取得了显著的进步。在本文中,我们提出了一种创新的移动流量预测基础模型(FoMo),旨在处理短期/长期预测和跨多个城市进行分布生成的多样化预测任务,以支持网络规划和优化。FoMo结合了扩散模型和变压器,提出了各种时空掩码,使FoMo能够学习不同任务的内蕴特征,并开发了一种对比学习策略来捕捉移动流量和城市上下文之间的相关性,从而提高其迁移学习能力。在9个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,FoMo在多样化的预测任务和零/少样本学习上优于当前模型,展示了强大的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2025
Summary
移动流量预测有助于运营商提前预测网络动态和性能,对提高服务质量和用户体验有巨大潜力。然而,现有模型往往针对特定任务并使用特定数据进行训练,这在多样化的移动网络任务(如基站部署、资源分配、能源优化等)中限制了其有效性,并阻碍了其在不同城市环境中的泛化能力。本文提出了一种创新的移动流量预测基础模型(FoMo),旨在处理短期/长期预测和跨多个城市的分布生成的多样化预测任务,以支持网络规划和优化。FoMo结合了扩散模型和转换器,通过提出各种时空掩码来使模型学习不同任务的内蕴特征,并开发了一种对比学习策略来捕捉移动流量和城市环境之间的相关性,从而提高了其迁移学习能力。在9个真实数据集上的广泛实验表明,FoMo在多样化的预测任务和零/少样本学习上优于当前模型,展示了强大的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 移动流量预测对于网络运营商来说非常重要,有助于他们提前了解网络动态和性能。
- 现有模型在多样化的移动网络任务中受限于特定任务和数据的训练,影响了其在不同城市环境中的泛化能力。
- 本文提出了一种创新的移动流量预测基础模型(FoMo),旨在处理多种预测任务,包括短期和长期预测,以及跨多个城市的分布生成。
- FoMo结合了扩散模型和转换器,通过时空掩码和对比学习策略来捕捉移动流量和城市环境之间的相关性。
- 对比学习策略有助于提高模型的迁移学习能力。
- 在多个真实数据集上的实验表明,FoMo在多样化的预测任务和零/少样本学习上表现出强大的通用性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图


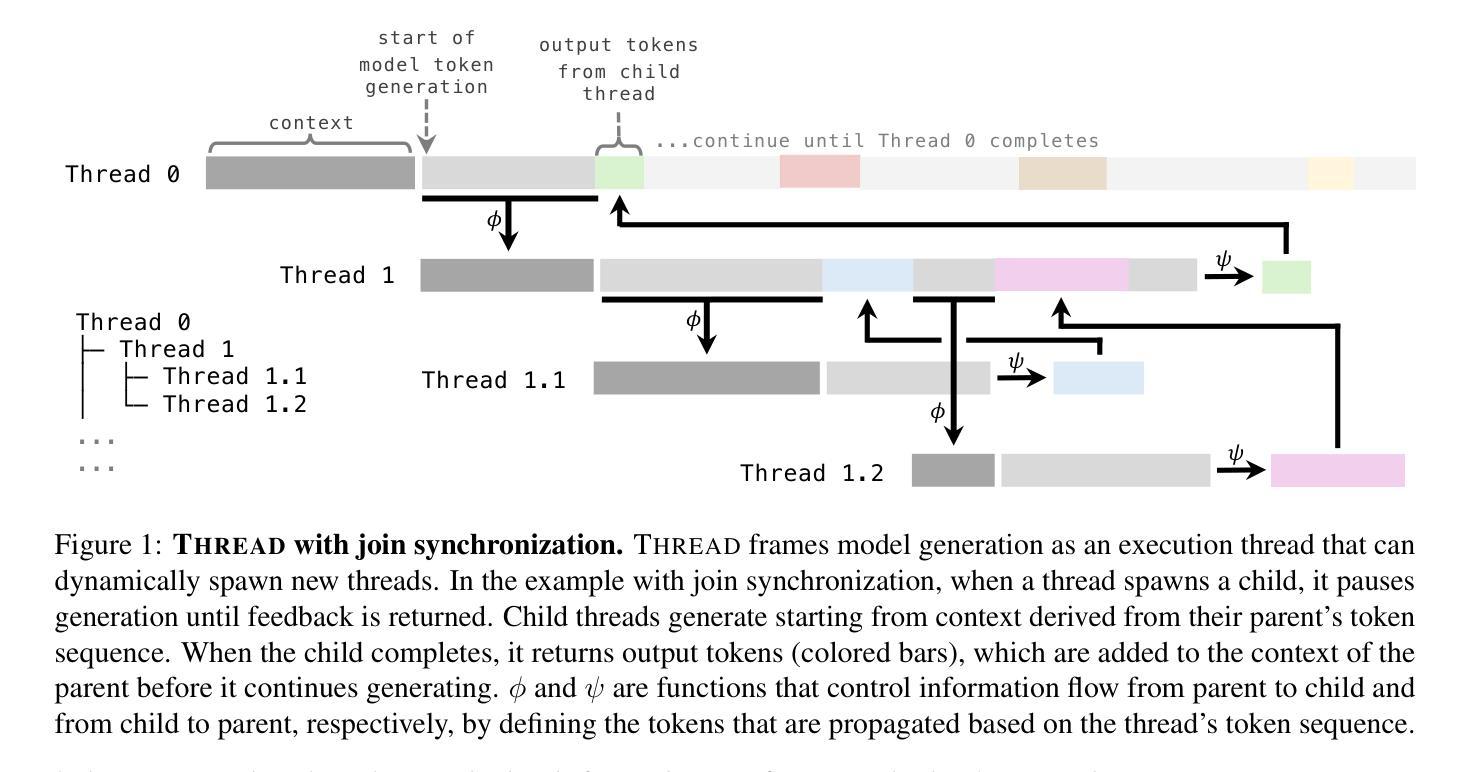
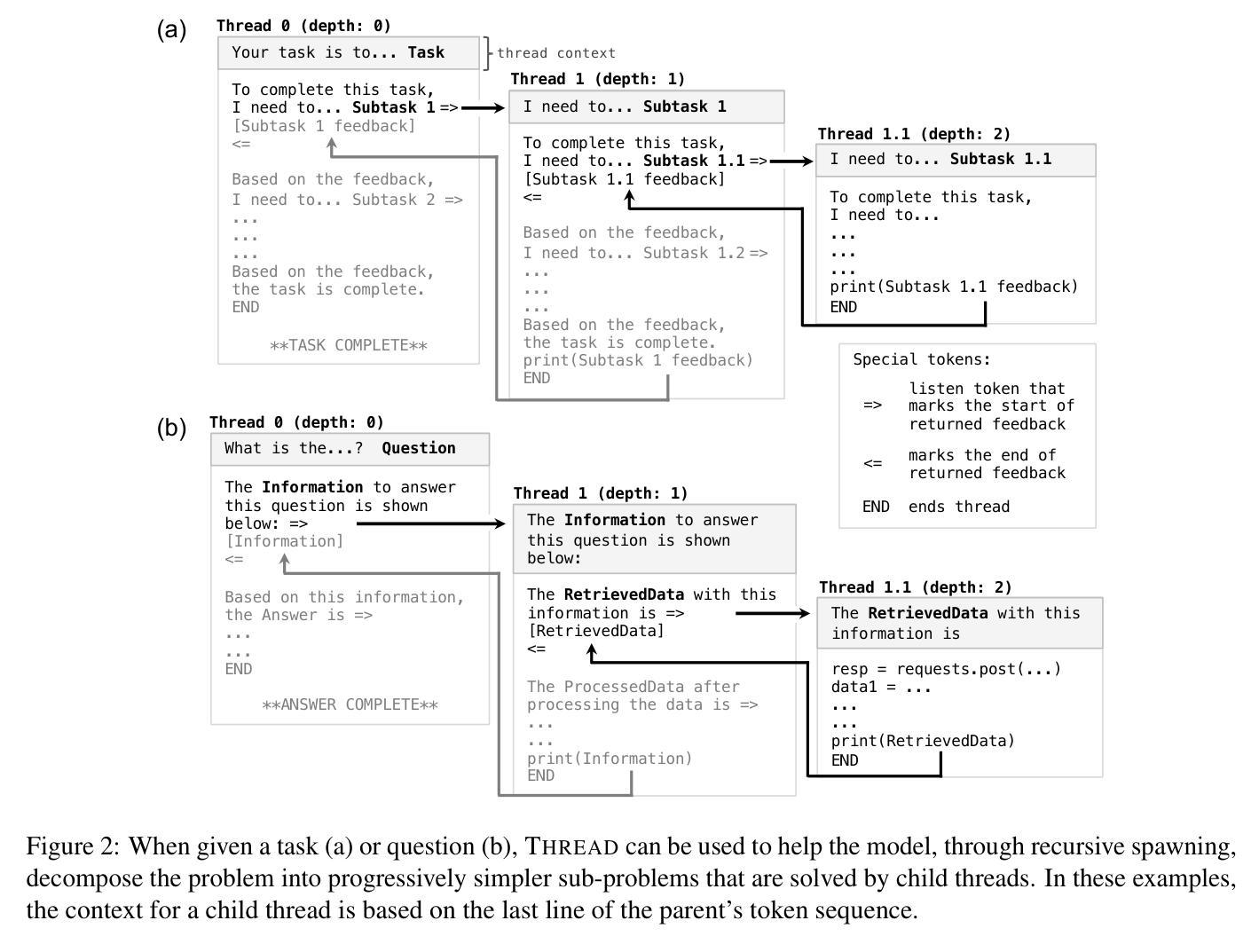
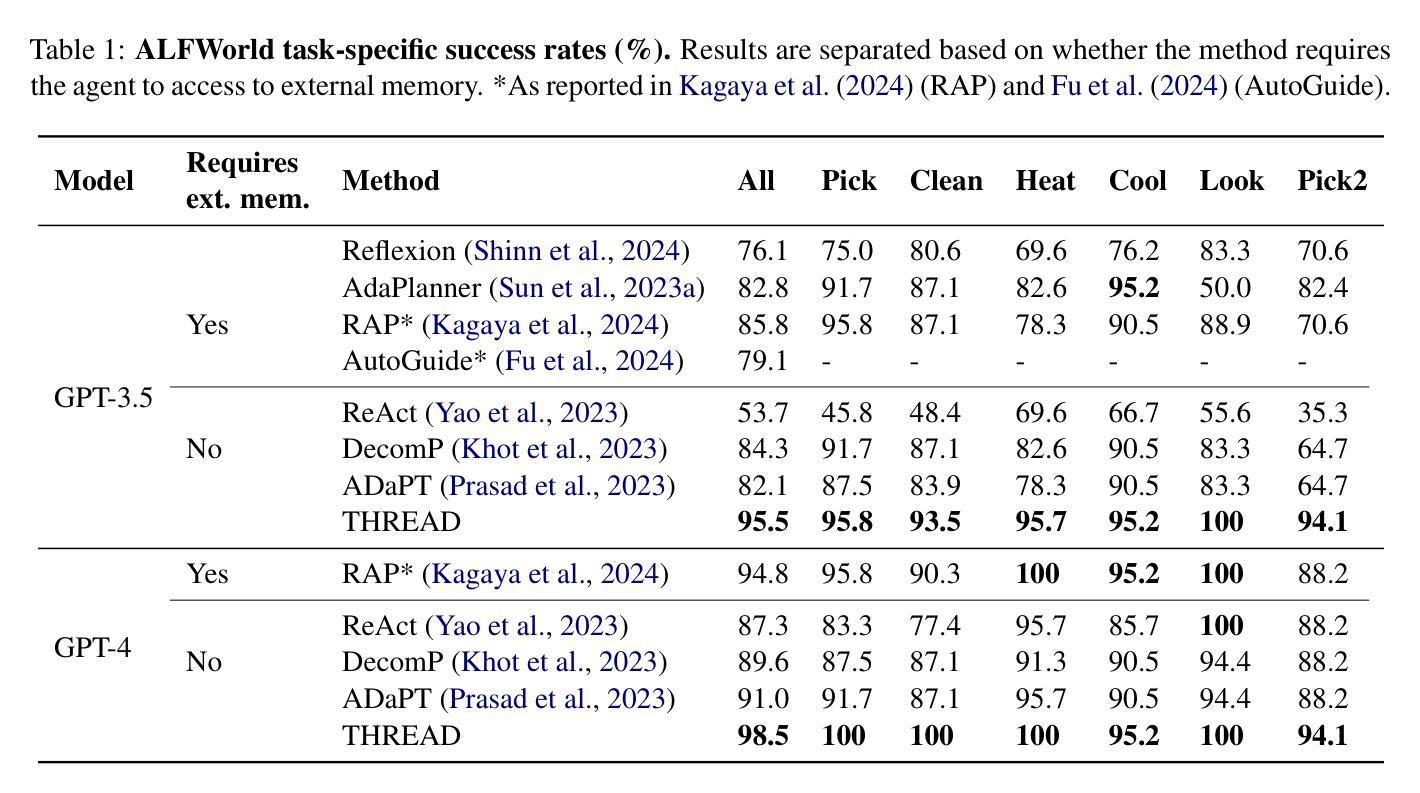
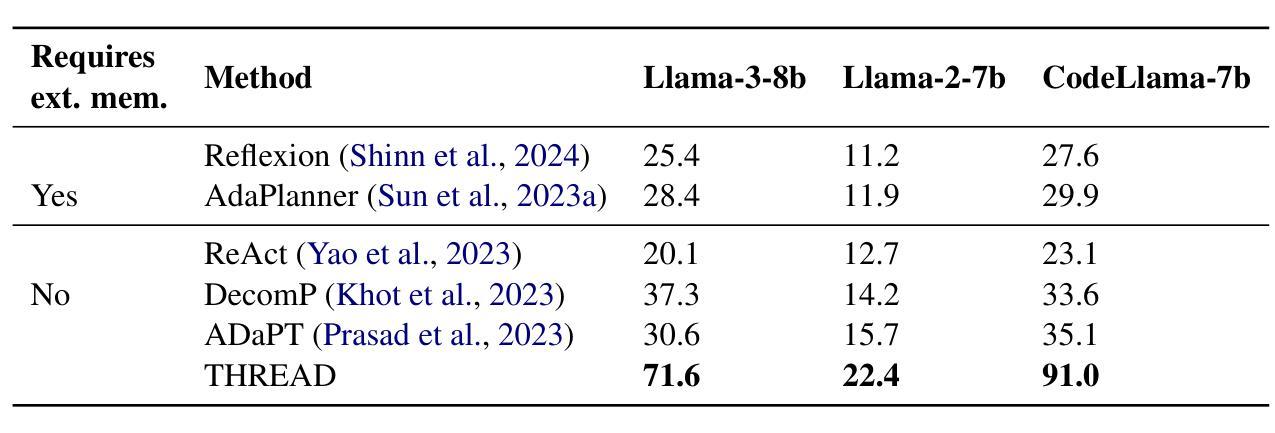
THREAD: Thinking Deeper with Recursive Spawning
Authors:Philip Schroeder, Nathaniel Morgan, Hongyin Luo, James Glass
Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities across diverse settings, but still struggle as the length and complexity of the context increases. To address this challenge, we propose Thinking Recursively and Dynamically (ThReaD). THREAD frames model generation as a thread of execution that, based on the context, can run to completion or dynamically spawn new threads. By spawning, threads can offload work (e.g., thinking, retrieving information) to child threads, which only return tokens needed for the parent thread to do its work. In effect, this enables the model to adapt, as needed, the amount of intermediate work used to produce tokens. We apply THREAD in the settings of LLM task solving and question answering, where the dynamic threading allows the model to recursively decompose the given task or question into progressively simpler sub-problems that can be solved by separate child threads. We test THREAD, implemented using a few-shot learning approach, on diverse benchmarks for agent tasks and data-grounded question answering. THREAD achieves state-of-the-art performance with GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 on these benchmarks, including ALFWorld, TextCraft, and WebShop, along with two new benchmarks, DataCommons QA and MIMIC-III ICU QA. In addition, THREAD outperforms existing frameworks by 10% to 50% absolute points with smaller models, including Llama-3-8b and CodeLlama-7b.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种场景中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但随着上下文长度和复杂性的增加,它们仍然面临挑战。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了递归动态思考(Thread)。Thread将模型生成构建为执行线程,可以根据上下文运行到完成或动态生成新线程。通过生成线程,可以将工作(如思考、检索信息)委派给子线程,子线程只返回父线程完成工作所需的令牌。实际上,这允许模型根据需要适应用于产生令牌的中间工作量。我们在LLM任务解决和问答场景中应用了Thread,其中动态线程允许模型将给定的任务或问题递归地分解为可以单独由子线程解决的越来越简单的子问题。我们使用少量样本学习的方法实现了Thread,并在多种基准测试上对代理任务和基于数据的问题回答进行了测试。Thread在包括ALFWorld、TextCraft、WebShop以及两个新基准测试DataCommons QA和MIMIC-III ICU QA在内的多个基准测试中实现了与GPT-4和GPT-3.5的最先进性能。此外,对于较小的模型,包括Llama-3-8b和CodeLlama-7b等,Thread在绝对得分上较现有框架高出10%至50%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种场景下表现出强大的能力,但在处理复杂和长文本时仍面临挑战。为解决这一问题,本文提出了递归动态思考(Thinking Recursively and Dynamically,简称ThReaD)框架。该框架将模型生成视为执行线程,能够根据上下文运行至完成或动态生成新线程。新线程的生成可以卸下工作(如思考、获取信息)并将其分配给子线程,仅返回父线程完成工作所需的标记。在大型语言模型任务解决和问答场景中,动态线程使得模型能够递归地将给定任务或问题分解为更简单的子问题,这些子问题可以由单独的子线程解决。本研究在多种基准测试中验证了Thread框架的有效性,包括代理任务和基于数据的问题回答。Thread框架实现了在GPT-4和GPT-3.5上的最新性能,并在多个基准测试中超越现有框架,绝对点数提高了10%至50%。即使是较小的模型,如Llama-3-8b和CodeLlama-7b也能取得显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂和长文本处理时存在挑战。
- ThReaD框架将模型生成视为执行线程,能动态调整工作负载。
- ThReaD通过动态生成子线程来分解复杂任务或问题。
- ThReaD框架在多个基准测试中表现优异,包括ALFWorld、TextCraft、WebShop等。
- ThReaD实现了在GPT-4和GPT-3.5上的最新性能。
- ThReaD框架在小型模型上也有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

Continual Adversarial Defense
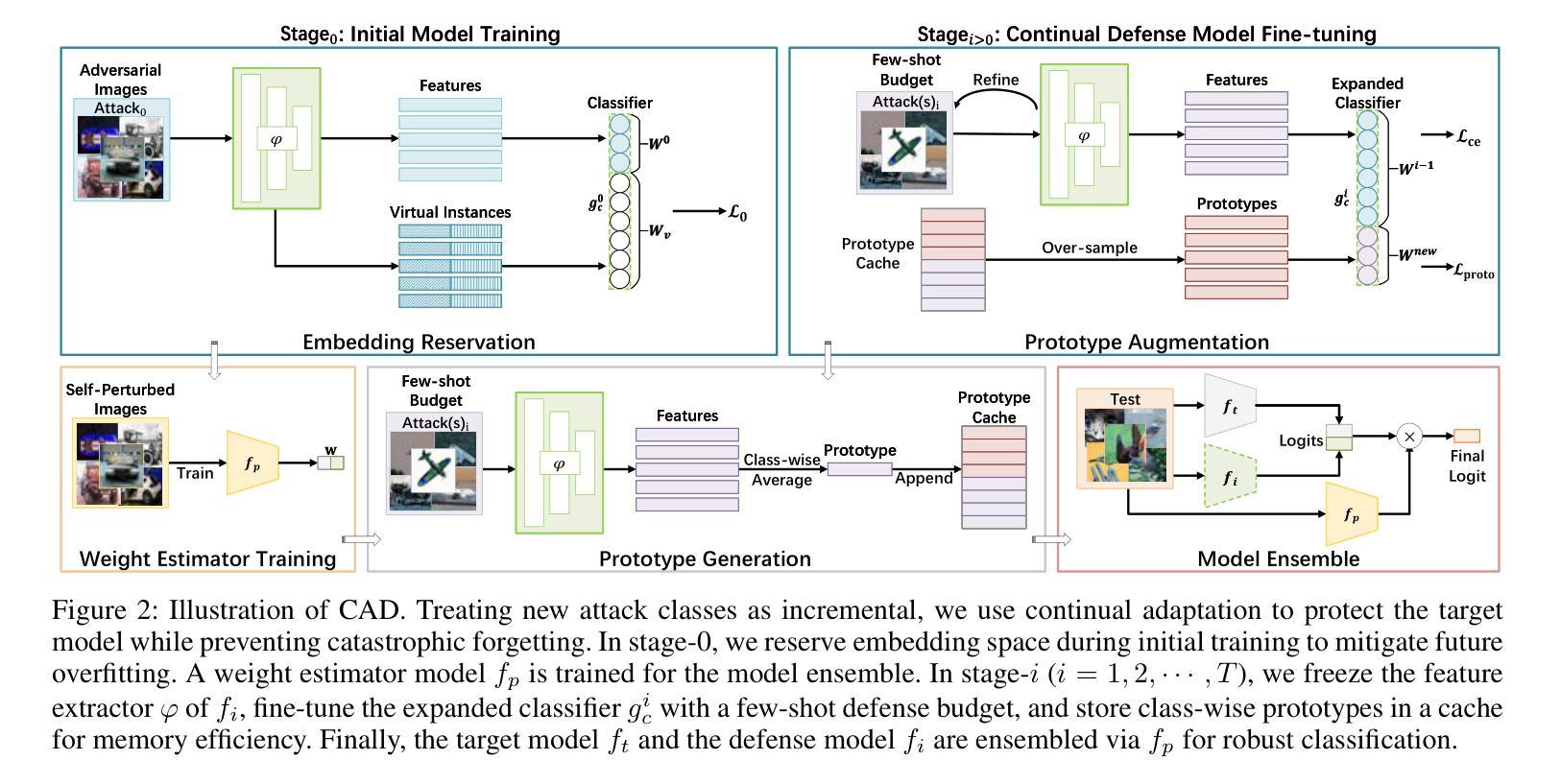
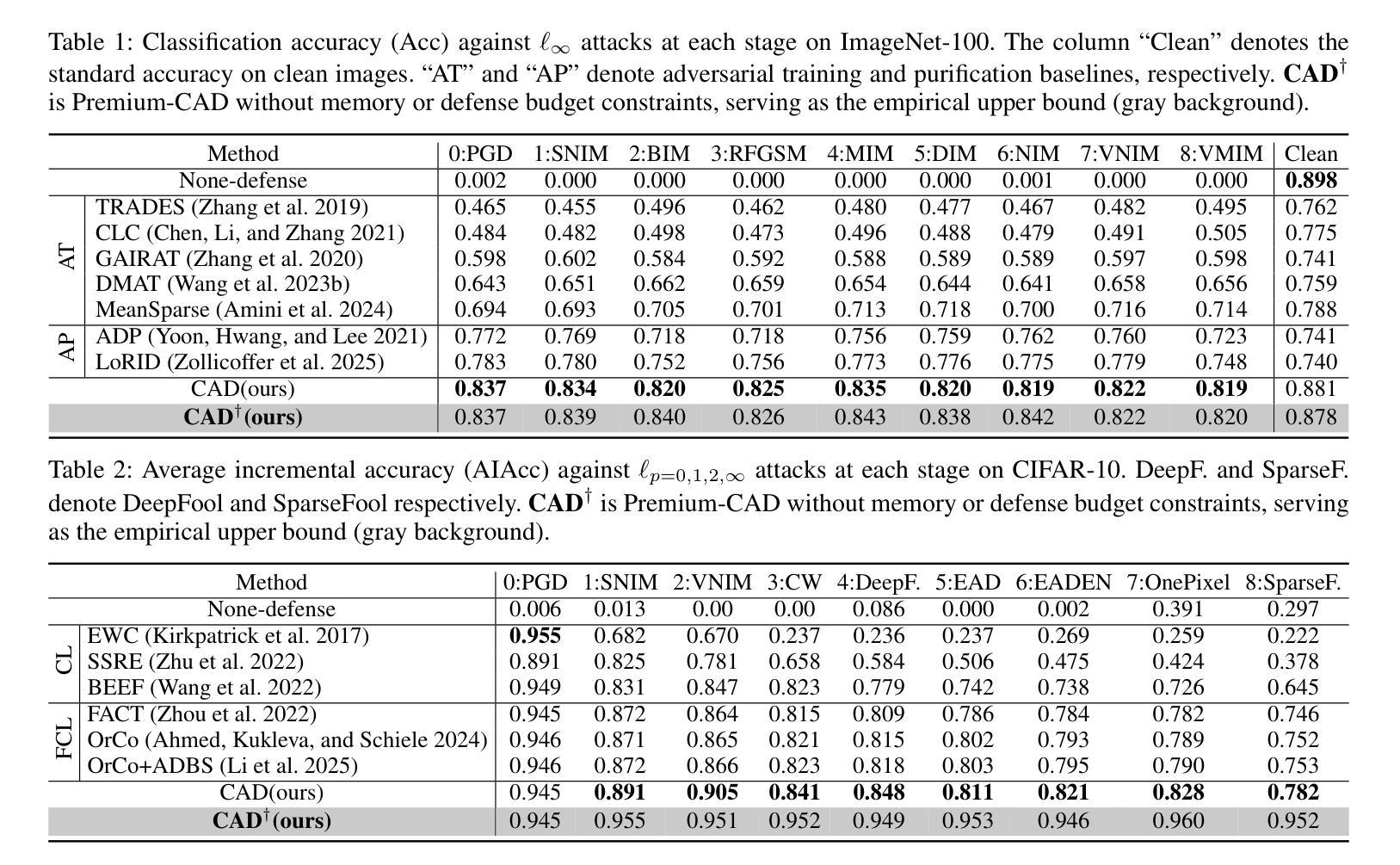
Authors:Qian Wang, Hefei Ling, Yingwei Li, Qihao Liu, Ruoxi Jia, Ning Yu
In response to the rapidly evolving nature of adversarial attacks against visual classifiers, numerous defenses have been proposed to generalize against as many known attacks as possible. However, designing a defense method that generalizes to all types of attacks is unrealistic, as the environment in which the defense system operates is dynamic. Over time, new attacks inevitably emerge that exploit the vulnerabilities of existing defenses and bypass them. Therefore, we propose a continual defense strategy under a practical threat model and, for the first time, introduce the Continual Adversarial Defense (CAD) framework. CAD continuously collects adversarial data online and adapts to evolving attack sequences, while adhering to four practical principles: (1) continual adaptation to new attacks without catastrophic forgetting, (2) few-shot adaptation, (3) memory-efficient adaptation, and (4) high classification accuracy on both clean and adversarial data. We explore and integrate cutting-edge techniques from continual learning, few-shot learning, and ensemble learning to fulfill the principles. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach against multi-stage adversarial attacks and demonstrate significant improvements over a wide range of baseline methods. We further observe that CAD’s defense performance tends to saturate as the number of attacks increases, indicating its potential as a persistent defense once adapted to a sufficiently diverse set of attacks. Our research sheds light on a brand-new paradigm for continual defense adaptation against dynamic and evolving attacks.
针对视觉分类器所面临的不断进化的对抗性攻击,已经提出了许多防御策略来应对尽可能多的已知攻击。然而,设计一个能够应对所有类型攻击的防御方法是不现实的,因为防御系统所处的环境是动态的。随着时间的推移,新的攻击不可避免地会出现,利用现有防御的漏洞并绕过它们。因此,我们在实用的威胁模型下提出了持续的防御策略,并首次引入了持续对抗性防御(CAD)框架。CAD持续在线收集对抗性数据,并适应不断变化的攻击序列,同时遵循四个实用原则:(1)不断适应新攻击而不会发生灾难性遗忘,(2)快速适应,(3)内存高效适应,以及(4)在干净和对抗性数据上都具有高分类准确率。我们探索并整合了终身学习、快速学习和集成学习的前沿技术来实现这些原则。大量实验验证了我们对多阶段对抗性攻击的有效性,并在一系列基准方法上取得了显著改进。我们进一步观察到,随着攻击数量的增加,CAD的防御性能趋于饱和,这表明一旦适应足够多样化的攻击集,其作为持久防御的潜力。我们的研究为应对动态和不断演变的攻击的持续防御适应提供了新的范例。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
面对视觉分类器不断演变的对抗性攻击,尽管已有多种防御策略提出,旨在应对尽可能多的已知攻击,但设计一种能应对所有类型攻击的防御方法是不可行的。因此,我们提出了一个实际的威胁模型下的持续防御策略,并首次引入了持续对抗性防御(CAD)框架。该框架能够持续在线收集对抗性数据,并适应不断变化的攻击序列,同时遵循四个实用原则:1)适应新攻击而不遗忘旧知识;2)小样本适应;3)内存高效适应;4)在干净和对抗性数据上实现高分类准确率。我们通过集成最新技术,如持续学习、小样本学习和集成学习来实现这些原则。实验证明,我们的方法能有效应对多阶段对抗性攻击,并在多种基线方法上取得了显著改进。随着攻击数量的增加,CAD的防御性能趋于饱和,这表明其在适应足够多样化的攻击后具有持久防御的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗攻击的不断演变使得设计一种能应对所有攻击的防御方法变得不切实际。
- 引入持续对抗性防御(CAD)框架来应对动态变化的攻击。
- CAD框架能持续在线收集对抗性数据并适应攻击序列的变化。
- CAD遵循四个实用原则:适应新攻击、小样本适应、内存高效适应和高分类准确率。
- 通过集成持续学习、小样本学习和集成学习的最新技术来实现这些原则。
- 实验证明CAD能有效应对多阶段对抗性攻击并显著改进基线方法。
点此查看论文截图