⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
NS-Net: Decoupling CLIP Semantic Information through NULL-Space for Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Jiazhen Yan, Fan Wang, Weiwei Jiang, Ziqiang Li, Zhangjie Fu
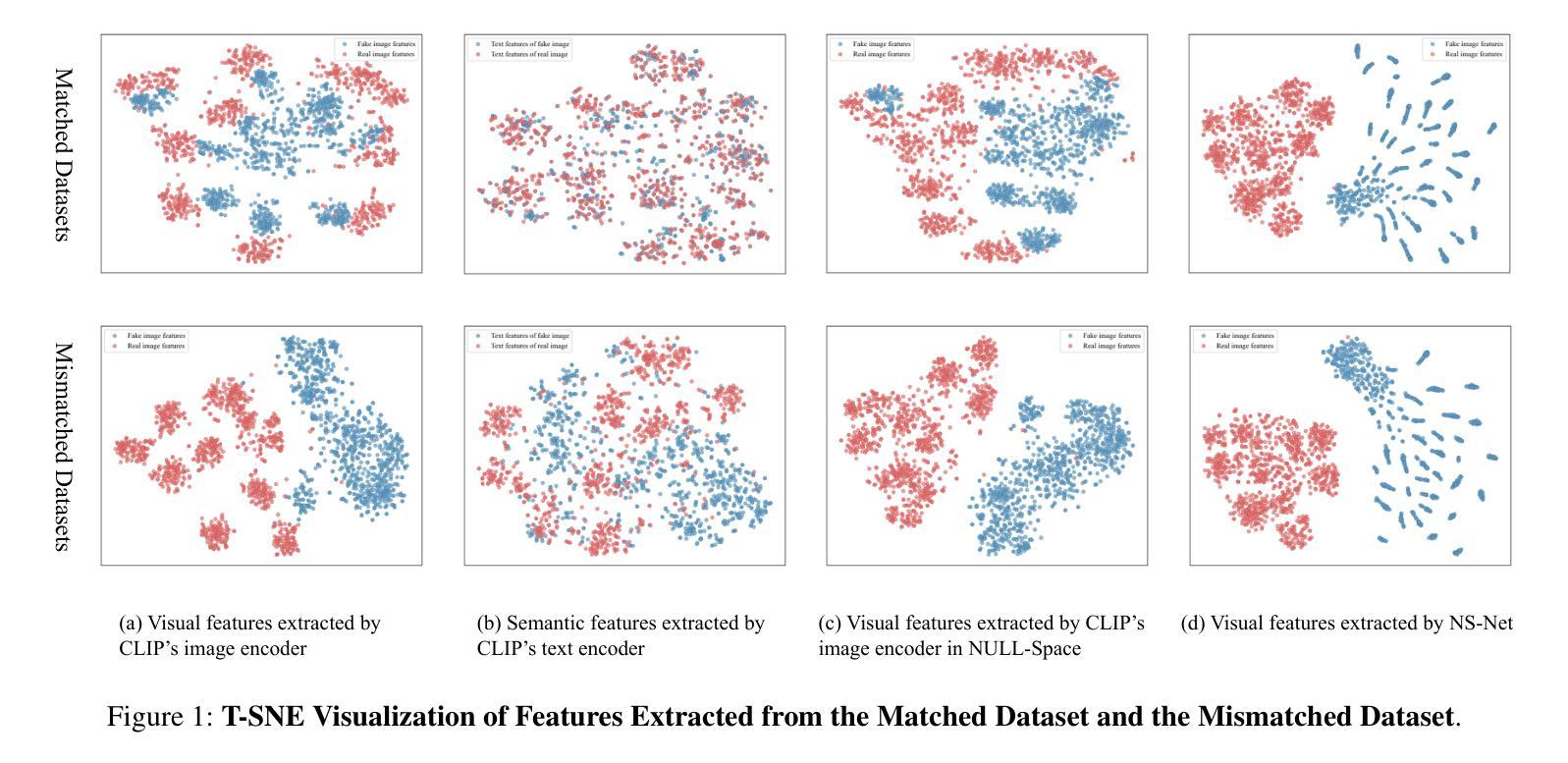
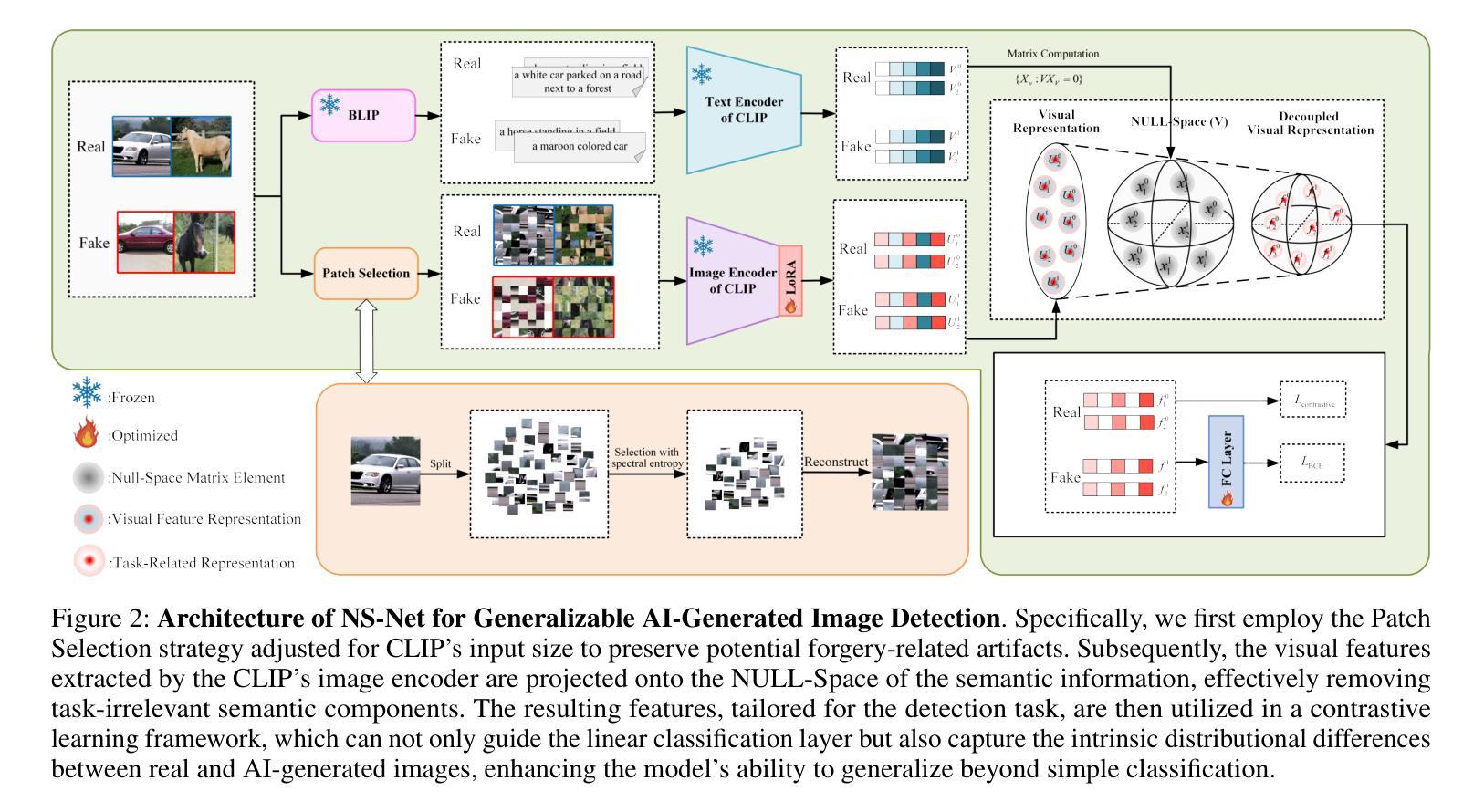
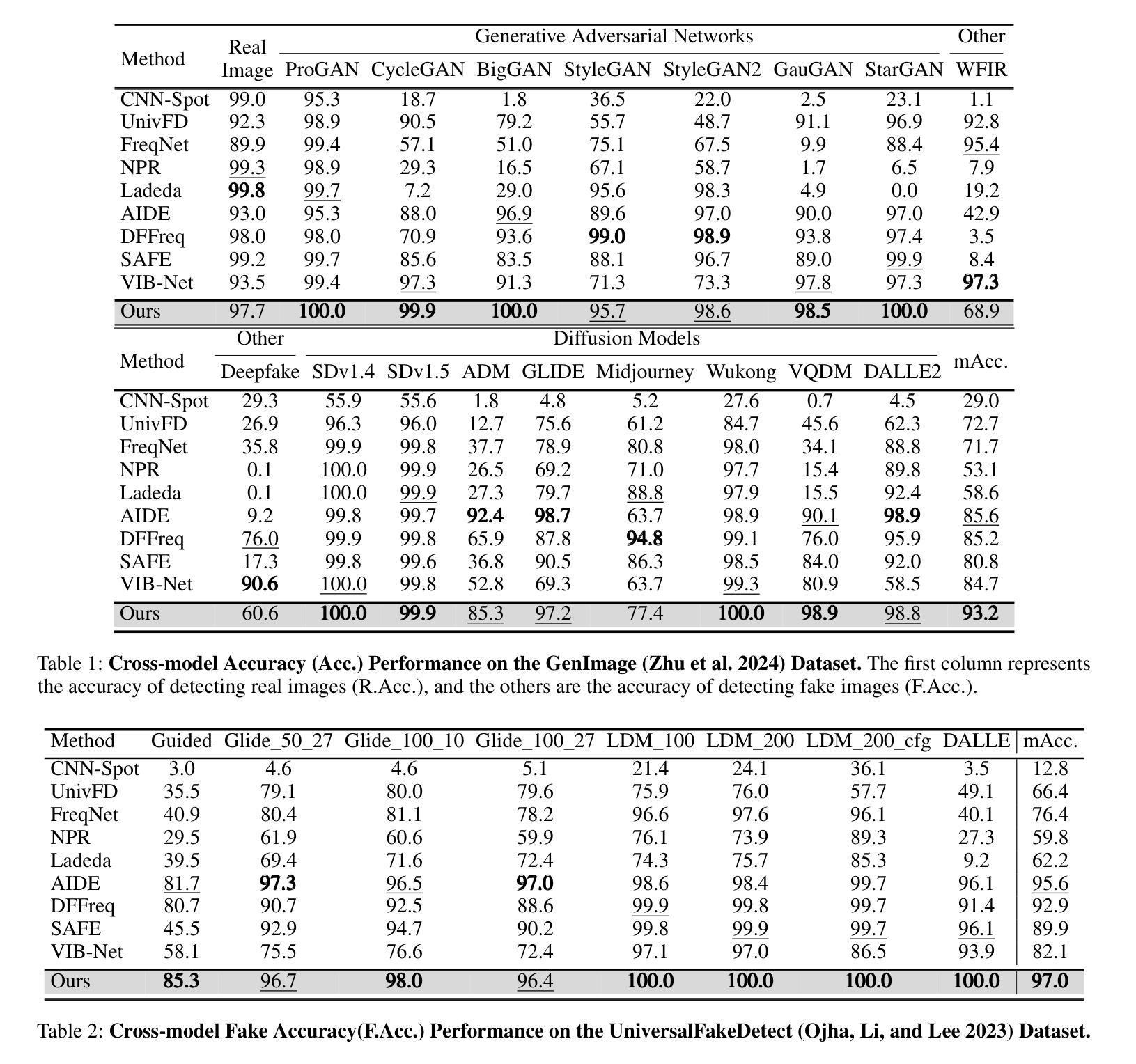
The rapid progress of generative models, such as GANs and diffusion models, has facilitated the creation of highly realistic images, raising growing concerns over their misuse in security-sensitive domains. While existing detectors perform well under known generative settings, they often fail to generalize to unknown generative models, especially when semantic content between real and fake images is closely aligned. In this paper, we revisit the use of CLIP features for AI-generated image detection and uncover a critical limitation: the high-level semantic information embedded in CLIP’s visual features hinders effective discrimination. To address this, we propose NS-Net, a novel detection framework that leverages NULL-Space projection to decouple semantic information from CLIP’s visual features, followed by contrastive learning to capture intrinsic distributional differences between real and generated images. Furthermore, we design a Patch Selection strategy to preserve fine-grained artifacts by mitigating semantic bias caused by global image structures. Extensive experiments on an open-world benchmark comprising images generated by 40 diverse generative models show that NS-Net outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving a 7.4% improvement in detection accuracy, thereby demonstrating strong generalization across both GAN- and diffusion-based image generation techniques.
生成模型(如GAN和扩散模型)的快速发展促进了高度逼真的图像的创作,引发了安全敏感领域对其误用的日益关注。尽管现有的检测器在已知的生成设置下表现良好,但它们往往无法推广到未知的生成模型,尤其是在真实和虚假图像之间的语义内容紧密对齐时。本文重新审视了使用CLIP特性进行AI生成图像检测,并发现了一个关键限制:CLIP视觉特征中嵌入的高级语义信息妨碍了有效的辨别。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了NS-Net,这是一个新的检测框架,它利用零空间投影来解耦CLIP视觉特征中的语义信息,然后通过对比学习来捕捉真实和生成图像之间的内在分布差异。此外,我们设计了一种Patch Selection策略,通过缓解全局图像结构引起的语义偏差来保留细微的伪迹。在由40种不同的生成模型生成的开放世界基准测试上的广泛实验表明,NS-Net优于现有的最先进方法,检测准确率提高了7.4%,从而证明了对基于GAN和扩散的图像生成技术的强大泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高性能的生成模型,如GAN和扩散模型,能生成高度逼真的图像,但在安全敏感领域的应用引发了滥用担忧。现有检测器在已知生成环境下表现良好,但在未知生成模型上泛化能力较差,尤其是真实和虚假图像语义内容紧密对齐时。本文重新审视了CLIP特性在AI生成图像检测中的应用,并发现了关键局限:CLIP视觉特征中嵌入的高级语义信息阻碍了有效鉴别。为此,我们提出NS-Net,一种利用零空间投影来解耦CLIP视觉特征中的语义信息的新颖检测框架,并通过对比学习捕捉真实和生成图像之间的内在分布差异。此外,我们设计了一个Patch Selection策略,通过减轻全局图像结构引起的语义偏差来保留细微特征。在由40种不同生成模型生成的开放世界基准测试上的广泛实验表明,NS-Net优于现有最先进的检测方法,检测准确率提高了7.4%,在GAN和扩散图像生成技术中均表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型如GAN和扩散模型的快速发展推动了高度逼真图像的生成,引发了安全敏感领域滥用的担忧。
- 现有检测器在已知生成环境下表现良好,但在未知生成模型上泛化能力差。
- CLIP特性在AI生成图像检测中存在关键局限:高级语义信息阻碍了有效鉴别。
- NS-Net框架通过零空间投影解耦CLIP视觉特征中的语义信息,并采用对比学习捕捉真实和生成图像的差异。
- NS-Net采用Patch Selection策略来保留细微特征,减轻全局图像结构的语义偏差。
- NS-Net在由多种生成模型构成的开放世界基准测试上表现出卓越性能,检测准确率显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

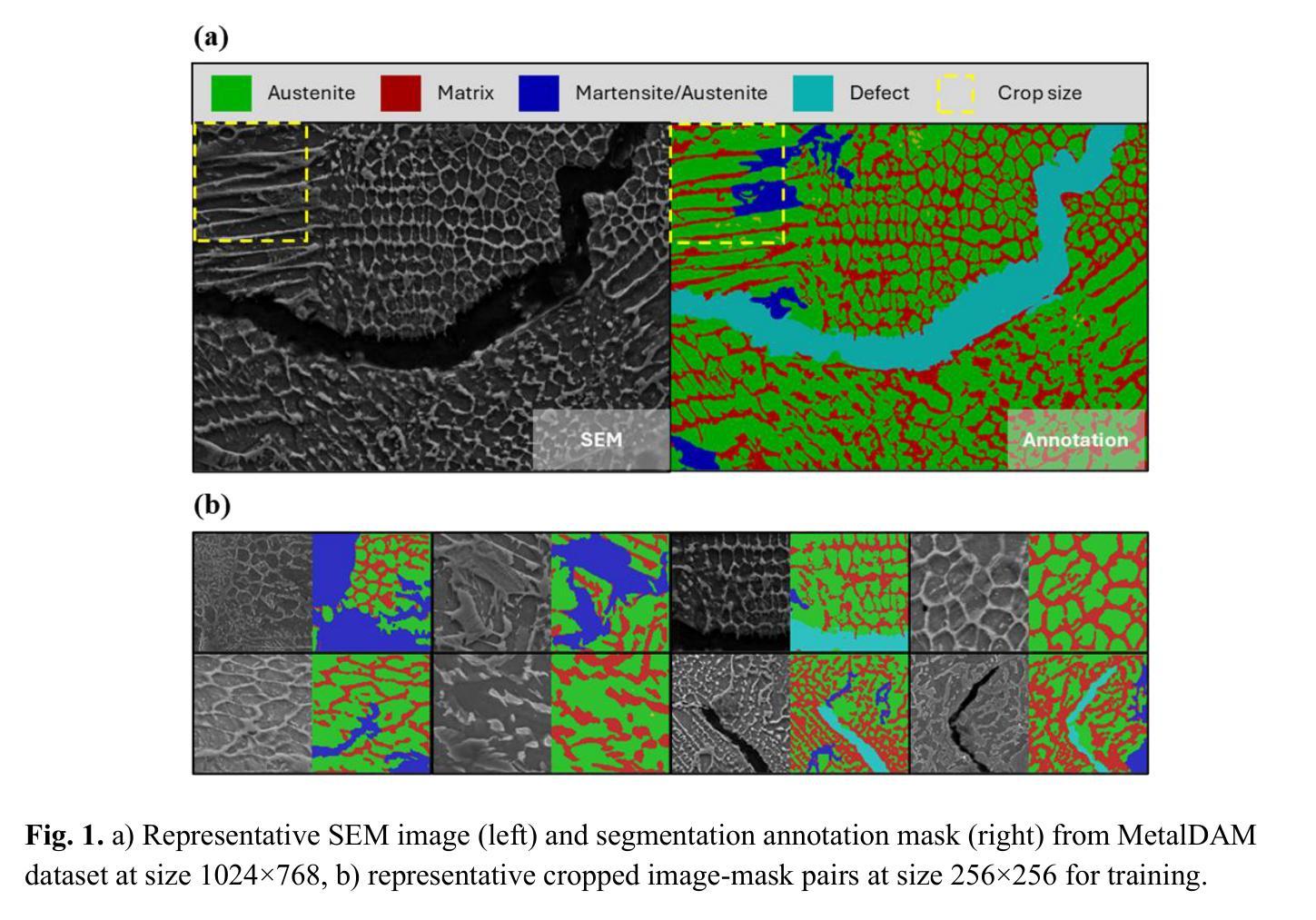
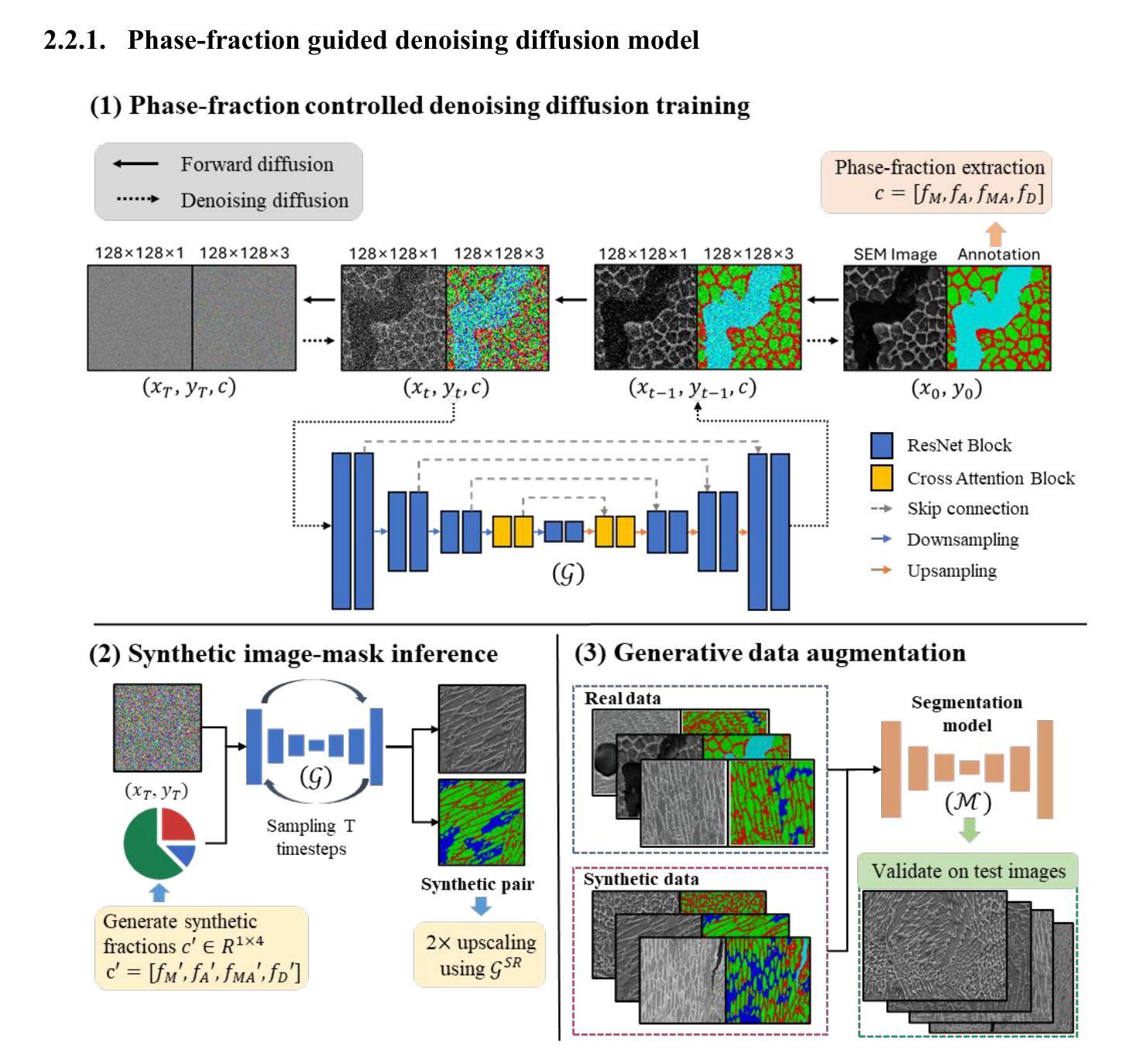
Phase-fraction guided denoising diffusion model for augmenting multiphase steel microstructure segmentation via micrograph image-mask pair synthesis
Authors:Hoang Hai Nam Nguyen, Minh Tien Tran, Hoheok Kim, Ho Won Lee
The effectiveness of machine learning in metallographic microstructure segmentation is often constrained by the lack of human-annotated phase masks, particularly for rare or compositionally complex morphologies within the metal alloy. We introduce PF-DiffSeg, a phase-fraction controlled, one-stage denoising diffusion framework that jointly synthesizes microstructure images and their corresponding segmentation masks in a single generative trajectory to further improve segmentation accuracy. By conditioning on global phase-fraction vectors, augmented to represent real data distribution and emphasize minority classes, our model generates compositionally valid and structurally coherent microstructure image and mask samples that improve both data diversity and training efficiency. Evaluated on the MetalDAM benchmark for additively manufactured multiphase steel, our synthetic augmentation method yields notable improvements in segmentation accuracy compared to standard augmentation strategies especially in minority classes and further outperforms a two-stage mask-guided diffusion and generative adversarial network (GAN) baselines, while also reducing inference time compared to conventional approach. The method integrates generation and conditioning into a unified framework, offering a scalable solution for data augmentation in metallographic applications.
机器学习在金属学显微结构分割中的应用效果通常受到人为注释相掩膜缺乏的制约,特别是在金属合金中的稀有或成分复杂的形态中更是如此。我们引入了PF-DiffSeg,这是一种受相分数控制的一阶段去噪扩散框架,它在一个单一的生成轨迹中合成显微结构图像及其相应的分割掩膜,以进一步提高分割精度。通过以全局相分数向量为条件,辅以代表真实数据分布并强调少数类,我们的模型生成了成分有效和结构连贯的显微结构图像和掩膜样本,提高了数据多样性和训练效率。在MetalDAM基准测试上对增材制造的多相钢进行评估,与标准增强策略相比,我们的合成增强方法在分割准确性方面取得了显著的改进,特别是在少数类中更为明显,并且优于两阶段的掩膜引导扩散和生成对抗网络(GAN)基线,同时减少了与传统方法的推理时间。该方法将生成和条件整合到一个统一的框架中,为金属学应用中的数据增强提供了可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PF-DiffSeg的新型机器学习技术,用于改进金属学显微结构分割的准确性。通过采用相位控制扩散框架,该技术可在单一生成轨迹中合成显微结构图像及其对应的分割掩膜,从而提高分割精度。该技术通过增强少数类别的数据分布来表示真实数据分布,并生成成分有效和结构连贯的显微结构图像和掩膜样本,提高数据多样性和训练效率。在MetalDAM基准测试上,该技术合成扩充方法在分割准确度上实现了显著的改进,特别是少数类别的准确度提高显著,并且优于两阶段掩膜引导扩散和生成对抗网络(GAN)基线方法,同时降低了推理时间。该技术将生成和条件整合到一个统一的框架中,为金属学应用中的数据扩充提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- PF-DiffSeg技术通过合成显微结构图像及其对应的分割掩膜,提高了金属学显微结构分割的准确性。
- 该技术采用相位控制扩散框架,为数据扩充提供了一个有效的解决方案。
- PF-DiffSeg能够增强少数类别的数据分布,从而提高数据多样性和训练效率。
- 在MetalDAM基准测试中,PF-DiffSeg显著提高了分割准确度,特别是针对少数类别。
- 与其他方法相比,PF-DiffSeg降低了推理时间。
- PF-DiffSeg将生成和条件整合到一个统一的框架中,具有良好的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图