⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
From Pixels to Pathology: Restoration Diffusion for Diagnostic-Consistent Virtual IHC
Authors:Jingsong Liu, Xiaofeng Deng, Han Li, Azar Kazemi, Christian Grashei, Gesa Wilkens, Xin You, Tanja Groll, Nassir Navab, Carolin Mogler, Peter J. Schüffler
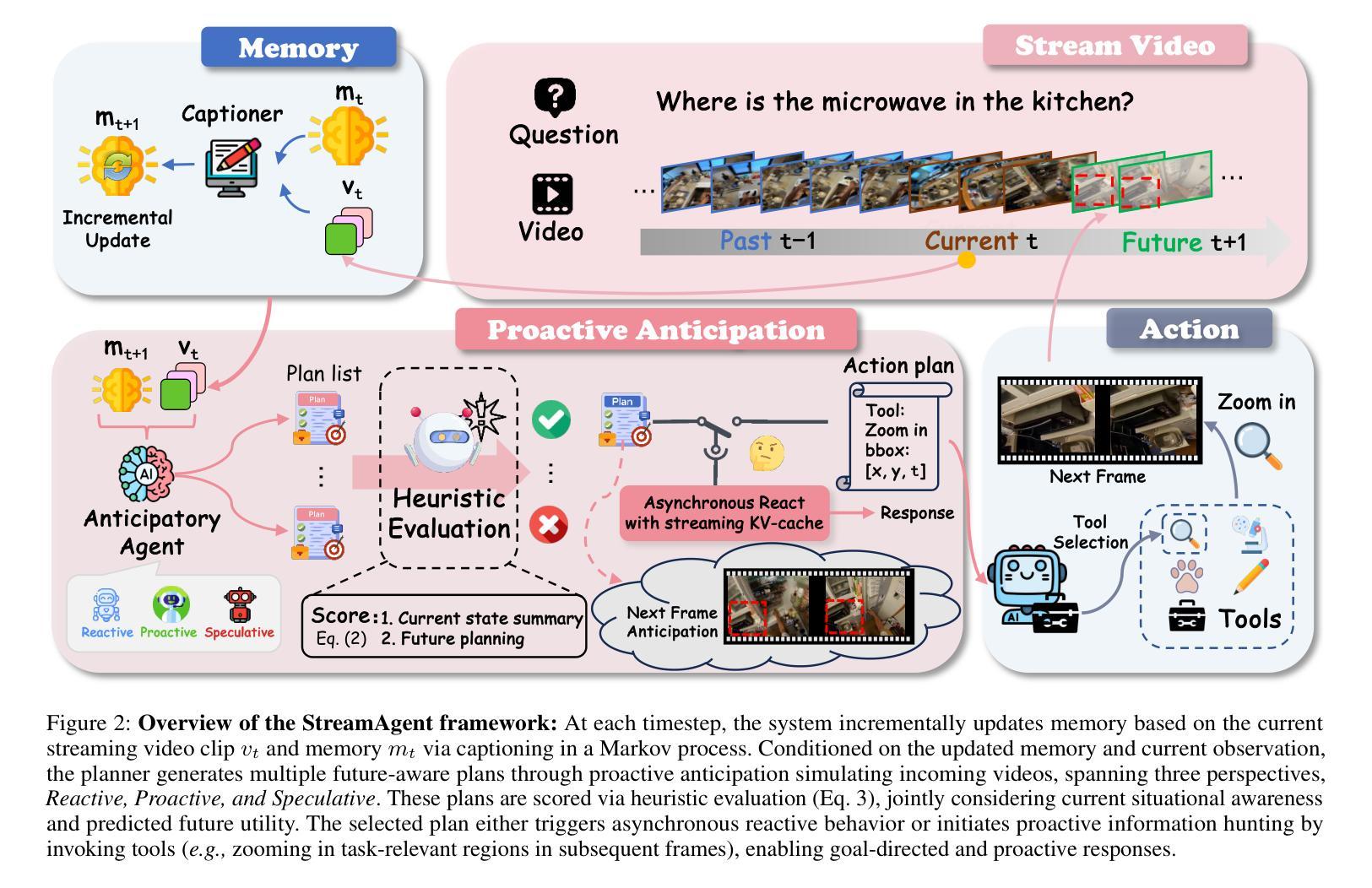
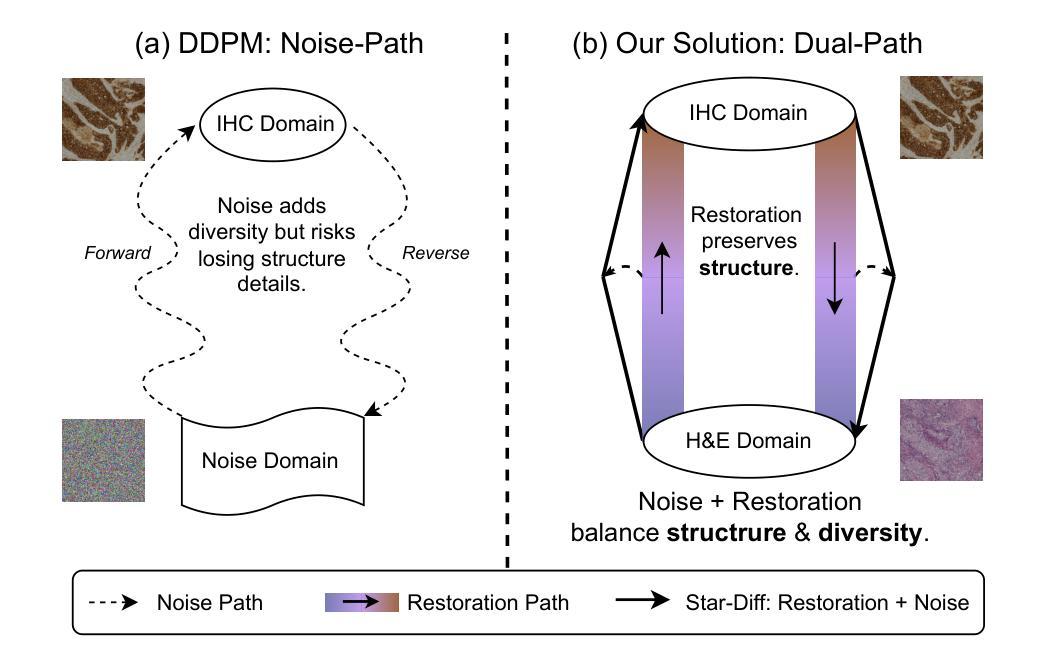
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the clinical standard for assessing tissue morphology, but it lacks molecular-level diagnostic information. In contrast, immunohistochemistry (IHC) provides crucial insights into biomarker expression, such as HER2 status for breast cancer grading, but remains costly and time-consuming, limiting its use in time-sensitive clinical workflows. To address this gap, virtual staining from H&E to IHC has emerged as a promising alternative, yet faces two core challenges: (1) Lack of fair evaluation of synthetic images against misaligned IHC ground truths, and (2) preserving structural integrity and biological variability during translation. To this end, we present an end-to-end framework encompassing both generation and evaluation in this work. We introduce Star-Diff, a structure-aware staining restoration diffusion model that reformulates virtual staining as an image restoration task. By combining residual and noise-based generation pathways, Star-Diff maintains tissue structure while modeling realistic biomarker variability. To evaluate the diagnostic consistency of the generated IHC patches, we propose the Semantic Fidelity Score (SFS), a clinical-grading-task-driven metric that quantifies class-wise semantic degradation based on biomarker classification accuracy. Unlike pixel-level metrics such as SSIM and PSNR, SFS remains robust under spatial misalignment and classifier uncertainty. Experiments on the BCI dataset demonstrate that Star-Diff achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in both visual fidelity and diagnostic relevance. With rapid inference and strong clinical alignment,it presents a practical solution for applications such as intraoperative virtual IHC synthesis.
苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色是评估组织形态的临床标准,但它缺乏分子水平的诊断信息。相比之下,免疫组织化学(IHC)为生物标志物表达提供了关键的见解,例如乳腺癌分级中的HER2状态,但其成本高昂且耗时时,限制了其在时间敏感的临床工作流程中的应用。为了解决这一差距,从H&E到IHC的虚拟染色已成为一种有前途的替代方案,但面临两个核心挑战:(1)合成图像与错位IHC真实值的公平评估不足;(2)在翻译过程中保持结构完整性和生物变异性。为此,我们在工作中提出了涵盖生成和评估的端到端框架。我们介绍了Star-Diff,这是一种结构感知染色恢复扩散模型,它将虚拟染色重新表述为图像恢复任务。通过结合残差和基于噪声的生成路径,Star-Diff在建模现实生物标志物变异性的同时保持了组织结构。为了评估生成IHC补丁的诊断一致性,我们提出了语义保真度分数(SFS),这是一种基于临床分级任务的指标,它根据生物标志物分类准确性对分类语义退化进行量化。与SSIM和PSNR等像素级指标不同,SFS在空间错位和分类器不确定性下保持稳健性。在BCI数据集上的实验表明,Star-Diff在视觉保真度和诊断相关性方面达到了最新水平。凭借其快速推理和强大的临床对齐能力,它为术中虚拟IHC合成等应用提供了实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了H&E染色在临床组织形态评估中的局限性,以及免疫组织化学(IHC)在提供分子水平诊断信息方面的作用。为解决二者在成本和效率上的不足,虚拟染色技术成为了一个有前途的替代方案。但虚拟染色面临的核心挑战是缺乏与虚拟图像对应的公正评价及翻译过程中的结构完整性和生物学变异性的保留。本文提出了一种涵盖生成和评估的端到端框架,并介绍了Star-Diff模型,该模型将虚拟染色重新定义为图像恢复任务,同时通过结合残差和噪声生成路径来保持组织结构并模拟真实的生物标志物变化。为了评估生成的IHC图像的诊断一致性,本文提出了语义保真度评分(SFS),这是一种基于生物标志物分类准确率的临床分级任务驱动度量。实验表明,Star-Diff在视觉保真度和诊断相关性方面达到最佳效果,可为术中虚拟IHC合成等应用提供实际解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- H&E染色在临床组织形态评估中缺乏分子水平诊断信息。
- 免疫组织化学(IHC)为生物标志物表达提供重要见解,但成本高昂且耗时而难以在临床工作流程中广泛应用。
- 虚拟染色技术作为替代方案正在兴起,但面临公正评价和保留结构完整性与生物学变异性的挑战。
- 提出了一个涵盖生成和评估的端到端框架来解决上述问题。
- 介绍了一种结构感知染色恢复扩散模型Star-Diff,将虚拟染色视为图像恢复任务。
- 为评估生成的IHC图像的诊断一致性,引入了语义保真度评分(SFS)。SFS克服了像素级度量在空对错位和分类器不确定性下的不稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

Is Uncertainty Quantification a Viable Alternative to Learned Deferral?
Authors:Anna M. Wundram, Christian F. Baumgartner
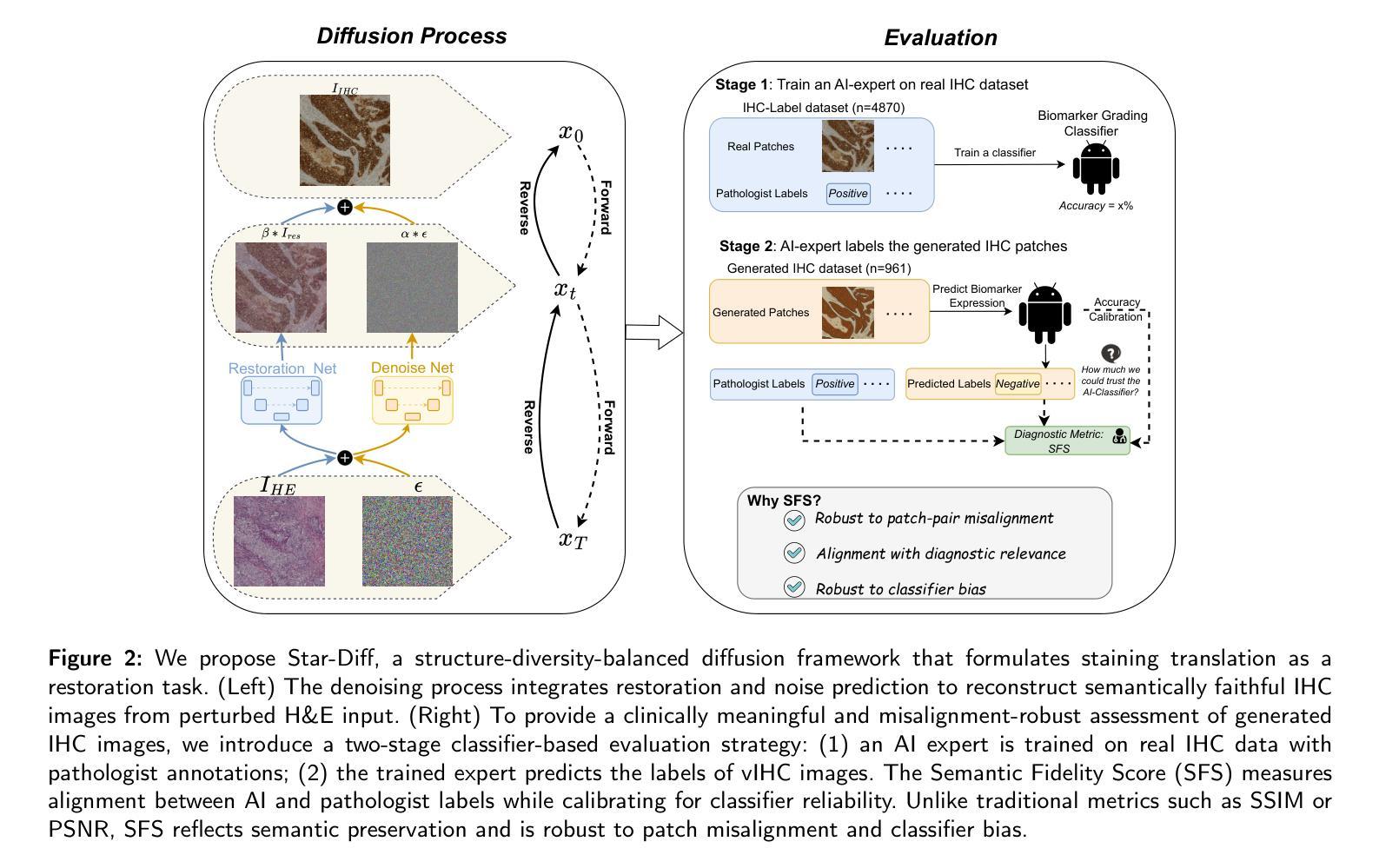
Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds the potential to dramatically improve patient care. However, it is not infallible, necessitating human-AI-collaboration to ensure safe implementation. One aspect of AI safety is the models’ ability to defer decisions to a human expert when they are likely to misclassify autonomously. Recent research has focused on methods that learn to defer by optimising a surrogate loss function that finds the optimal trade-off between predicting a class label or deferring. However, during clinical translation, models often face challenges such as data shift. Uncertainty quantification methods aim to estimate a model’s confidence in its predictions. However, they may also be used as a deferral strategy which does not rely on learning from specific training distribution. We hypothesise that models developed to quantify uncertainty are more robust to out-of-distribution (OOD) input than learned deferral models that have been trained in a supervised fashion. To investigate this hypothesis, we constructed an extensive evaluation study on a large ophthalmology dataset, examining both learned deferral models and established uncertainty quantification methods, assessing their performance in- and out-of-distribution. Specifically, we evaluate their ability to accurately classify glaucoma from fundus images while deferring cases with a high likelihood of error. We find that uncertainty quantification methods may be a promising choice for AI deferral.
人工智能(AI)具有改善病人护理的巨大潜力。然而,它并非无所不能,因此需要人类-AI协作以确保安全实施。人工智能安全的一个方面是,当它们可能自主错误分类时,模型能够将决策权转交给人类专家。最近的研究集中在通过优化代理损失函数来学习推迟决策的方法,该损失函数能在预测类别标签或推迟决策之间找到最佳平衡。然而,在临床翻译过程中,模型经常面临数据迁移等挑战。不确定性量化方法旨在估计模型对其预测的信心。然而,它们也可以作为一种不依赖于从特定训练分布中学习的推迟策略。我们假设,开发用于量化不确定性的模型比经过监督训练的学习延迟模型对输入中的非预期分布更加稳健。为了验证这一假设,我们在大型眼科数据集上进行了广泛的评估研究,对学过延迟模型和已有的不确定性量化方法进行了考察,评估其在预期分布内和预期分布外的性能。具体来说,我们评估了它们在准确分类眼底图像中的青光眼的同时,推迟可能出现错误的案例的能力。我们发现不确定性量化方法可能是AI延期策略的另一种有前景的选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as an oral presentation at MICCAI UNSURE 2025
Summary
人工智能(AI)可改善患者护理,但非万能,需人机协作确保安全实施。AI模型在自主决策时,需具备向人类专家请求协助的能力。最新研究聚焦于通过优化替代损失函数来学习推迟决策的方法,以在预测类别或推迟决策之间找到最佳平衡。但在临床翻译中,模型常面临数据偏移等挑战。不确定性量化方法旨在估算模型的预测信心,也可用作不依赖于特定训练分布的推迟策略。我们假设,与通过监督方式训练的延迟决策模型相比,开发用于量化不确定性的模型对异常输入更具鲁棒性。为验证此假设,我们在大型眼科数据集上进行了一项全面评估研究,对比了延迟决策模型与不确定性量化方法,评估其在内外视角下的表现,特别是从眼底图像准确分类青光眼的能力。我们发现不确定性量化方法在AI决策中颇具前景。
Key Takeaways
- AI在改善患者护理方面具有潜力,但存在缺陷,需人机协作确保安全实施。
- AI模型应具备在自主决策时向人类专家请求协助的能力。
- 最新研究通过优化替代损失函数来学习推迟决策方法,以找到预测类别和推迟决策的平衡。
- 临床翻译中,模型面临数据偏移等挑战。
- 不确定性量化方法旨在估算模型的预测信心,也能作为推迟决策的策略。
- 与监督训练的延迟决策模型相比,不确定性量化模型对异常输入更具鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

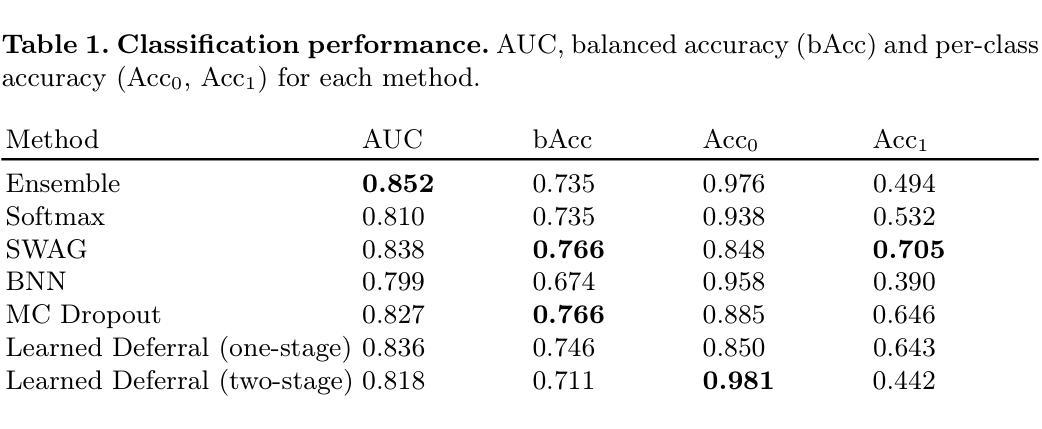
Whole-body Representation Learning For Competing Preclinical Disease Risk Assessment
Authors:Dmitrii Seletkov, Sophie Starck, Ayhan Can Erdur, Yundi Zhang, Daniel Rueckert, Rickmer Braren
Reliable preclinical disease risk assessment is essential to move public healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive identification and prevention. However, image-based risk prediction algorithms often consider one condition at a time and depend on hand-crafted features obtained through segmentation tools. We propose a whole-body self-supervised representation learning method for the preclinical disease risk assessment under a competing risk modeling. This approach outperforms whole-body radiomics in multiple diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD), type 2 diabetes (T2D), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Simulating a preclinical screening scenario and subsequently combining with cardiac MRI, it sharpens further the prediction for CVD subgroups: ischemic heart disease (IHD), hypertensive diseases (HD), and stroke. The results indicate the translational potential of whole-body representations as a standalone screening modality and as part of a multi-modal framework within clinical workflows for early personalized risk stratification. The code is available at https://github.com/yayapa/WBRLforCR/
可靠的临床前疾病风险评估对于推动公共医疗从被动治疗转向主动识别和预防至关重要。然而,基于图像的预测算法通常每次只考虑一种状况,并且依赖于通过分割工具获得的手动特征。我们提出了一种基于竞争风险建模的临床前疾病风险评估全身自监督表示学习方法。该方法在多疾病方面的表现优于全身放射组学,包括心血管疾病(CVD)、2型糖尿病(T2D)、慢性阻塞性肺病(COPD)和慢性肾脏病(CKD)。模拟临床前筛查情景,然后与心脏MRI相结合,进一步提高了对心血管疾病分组(缺血性心脏病(IHD)、高血压疾病(HD)和中风)的预测准确性。结果表明,全身表现为一种独立的筛查方式以及临床工作流程中的多模态框架的一部分,在早期个性化风险评估中具有转化潜力。代码可在https://github.com/yayapa/WBRLforCR/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在公共卫生领域,早期疾病风险评估已从被动治疗转向主动识别和预防。我们提出了一种基于竞争风险建模的全身自我监督表示学习方法,用于早期疾病风险评估,该方法优于多种疾病的全身放射学方法。结合模拟早期筛查情景和心脏MRI,该方法能更精确地预测心血管疾病的多个亚组。该方法的翻译潜力既可作为独立的筛查方式,也可作为临床工作流程中的多模态框架的一部分,用于早期个性化的风险评估分层。相关代码可在[yayapa/WBRLforCR/]上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 早期疾病风险评估对公共卫生领域至关重要,已经转向主动识别和预防。
- 提出的全身自我监督表示学习方法基于竞争风险建模,用于早期疾病风险评估。
- 该方法在多种疾病上的表现优于全身放射学方法。
- 结合模拟早期筛查情景和心脏MRI,能更精确地预测心血管疾病的亚组。
- 该方法具有作为独立筛查方式和多模态框架内临床工作流程中的一部分的翻译潜力。
点此查看论文截图

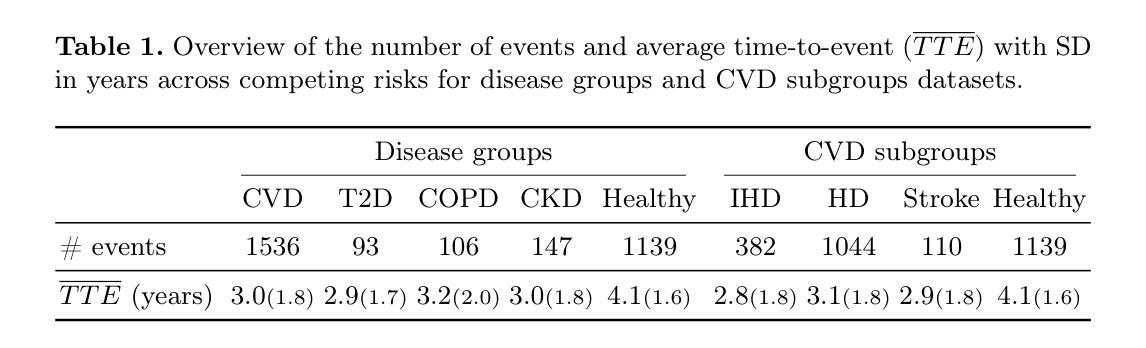
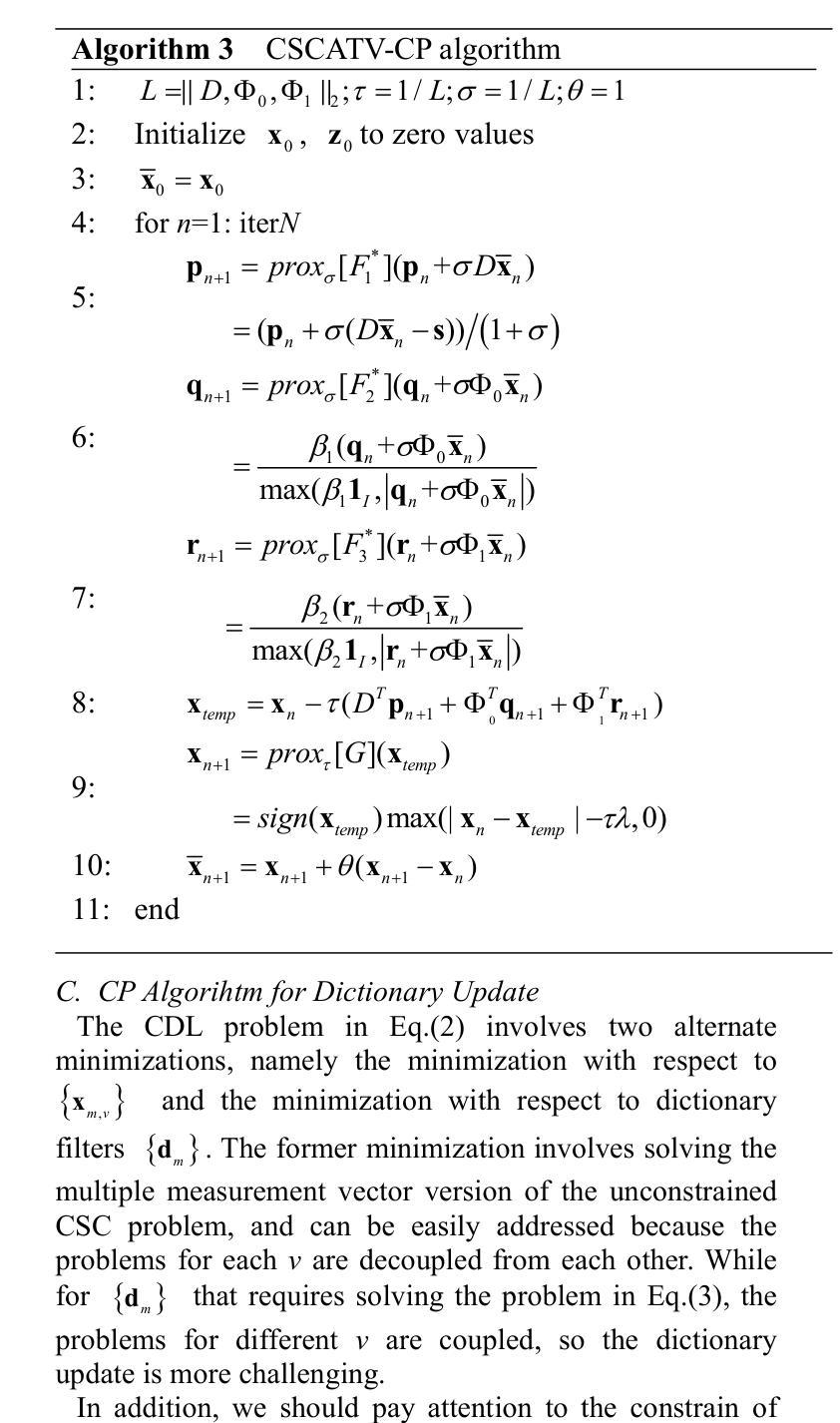
Efficient Chambolle-Pock based algorithms for Convoltional sparse representation
Authors:Yi Liu, Junjing Li, Yang Chen, Haowei Tang, Pengcheng Zhang, Tianling Lyu, Zhiguo Gui
Recently convolutional sparse representation (CSR), as a sparse representation technique, has attracted increasing attention in the field of image processing, due to its good characteristic of translate-invariance. The content of CSR usually consists of convolutional sparse coding (CSC) and convolutional dictionary learning (CDL), and many studies focus on how to solve the corresponding optimization problems. At present, the most efficient optimization scheme for CSC is based on the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). However, the ADMM-based approach involves a penalty parameter that needs to be carefully selected, and improper parameter selection may result in either no convergence or very slow convergence. In this paper, a novel fast and efficient method using Chambolle-Pock(CP) framework is proposed, which does not require extra manual selection parameters in solving processing, and has faster convergence speed. Furthermore, we propose an anisotropic total variation penalty of the coefficient maps for CSC and apply the CP algorithm to solve it. In addition, we also apply the CP framework to solve the corresponding CDL problem. Experiments show that for noise-free image the proposed CSC algorithms can achieve rival results of the latest ADMM-based approach, while outperforms in removing noise from Gaussian noise pollution image.
近期,卷积稀疏表示(CSR)作为一种稀疏表示技术,因其平移不变性特性在图像处理领域越来越受到关注。CSR的内容通常包括卷积稀疏编码(CSC)和卷积字典学习(CDL),许多研究集中于解决相应的优化问题。目前,CSC的最优化方案基于交替方向乘子法(ADMM)。然而,基于ADMM的方法涉及一个需要仔细选择的惩罚参数,不适当的参数选择可能导致不收敛或收敛非常慢。本文提出了一种使用Chambolle-Pock(CP)框架的快速高效方法,该方法在求解过程中不需要额外的人工选择参数,并且具有更快的收敛速度。此外,我们为CSC提出了系数图的各向异性总变差惩罚,并应用CP算法来解决它。另外,我们还应用CP框架来解决相应的CDL问题。实验表明,对于无噪声图像,所提出的CSC算法可以达到与最新的基于ADMM的方法相当的结果,而在去除高斯噪声污染图像中的噪声方面表现更佳。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
卷积稀疏表示(CSR)因其平移不变性在图像处理领域受到越来越多的关注。本文提出了一种基于Chambolle-Pock(CP)框架的快速高效方法,无需额外手动选择参数,解决了卷积稀疏编码(CSC)和卷积字典学习(CDL)的优化问题,并具有更快的收敛速度。对于无噪声图像,所提出的CSC算法可达到与最新ADMM方法相当的结果,并且在去除高斯噪声污染图像方面的表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积稀疏表示(CSR)在图像处理中因其平移不变性而受到关注。
- 现有的卷积稀疏编码(CSC)优化主要依赖于交替方向法乘数(ADMM),但存在参数选择问题。
- 本文提出了一种基于Chambolle-Pock(CP)框架的方法,解决CSC和CDL的优化问题,无需额外手动选择参数。
- CP方法具有更快的收敛速度。
- 对于无噪声图像,基于CP的CSC算法性能与ADMM相当。
- 该方法在去除高斯噪声污染图像方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


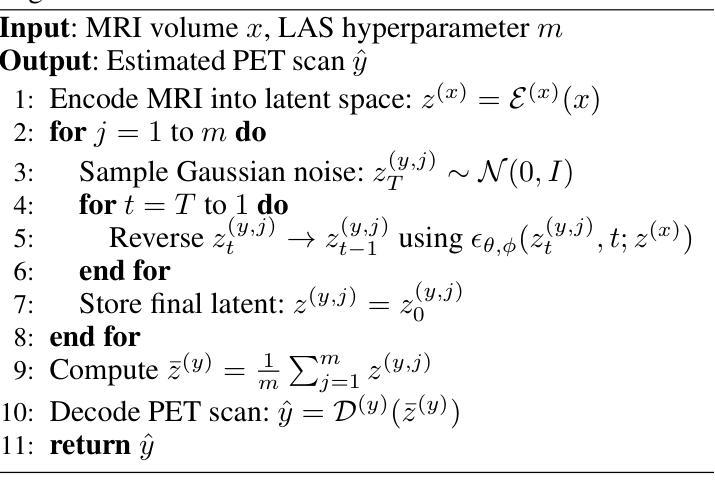
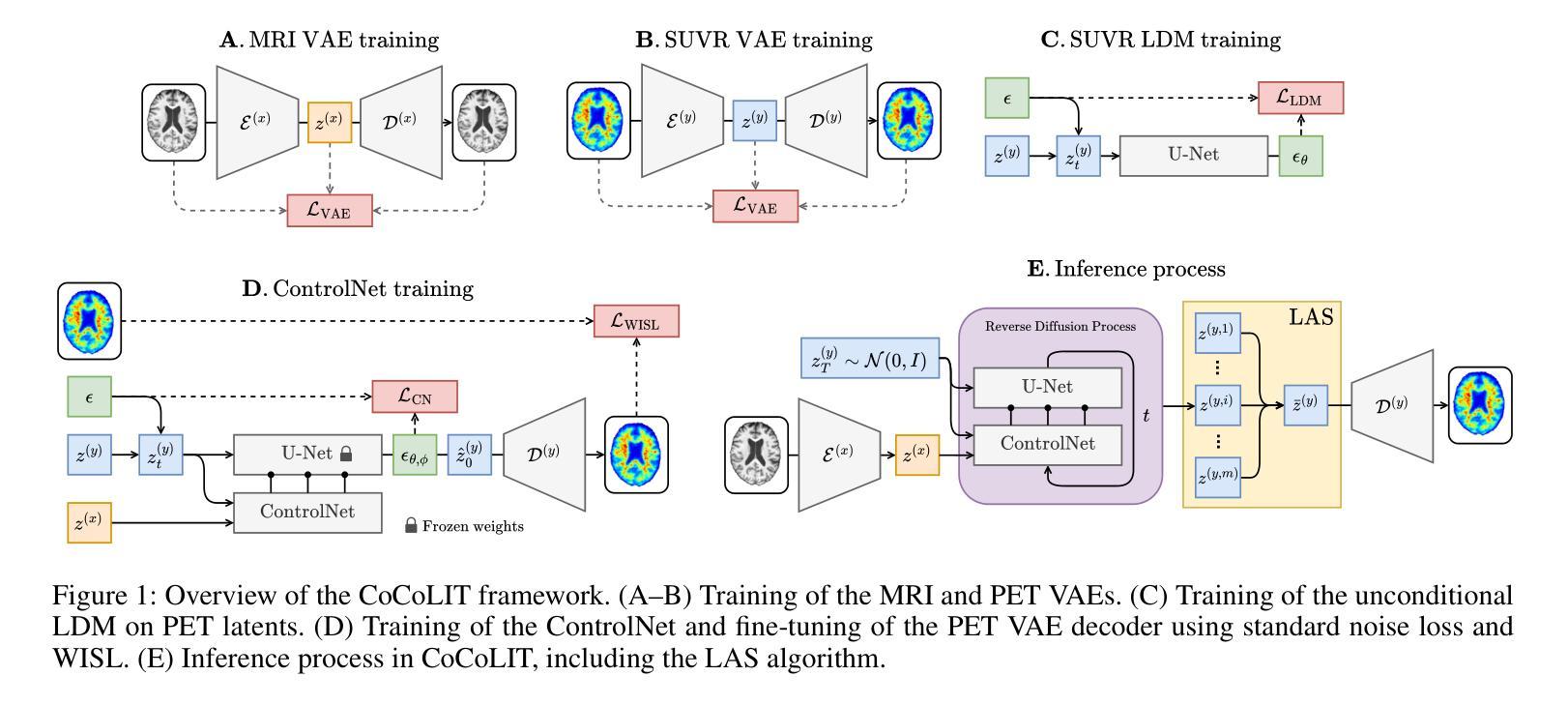
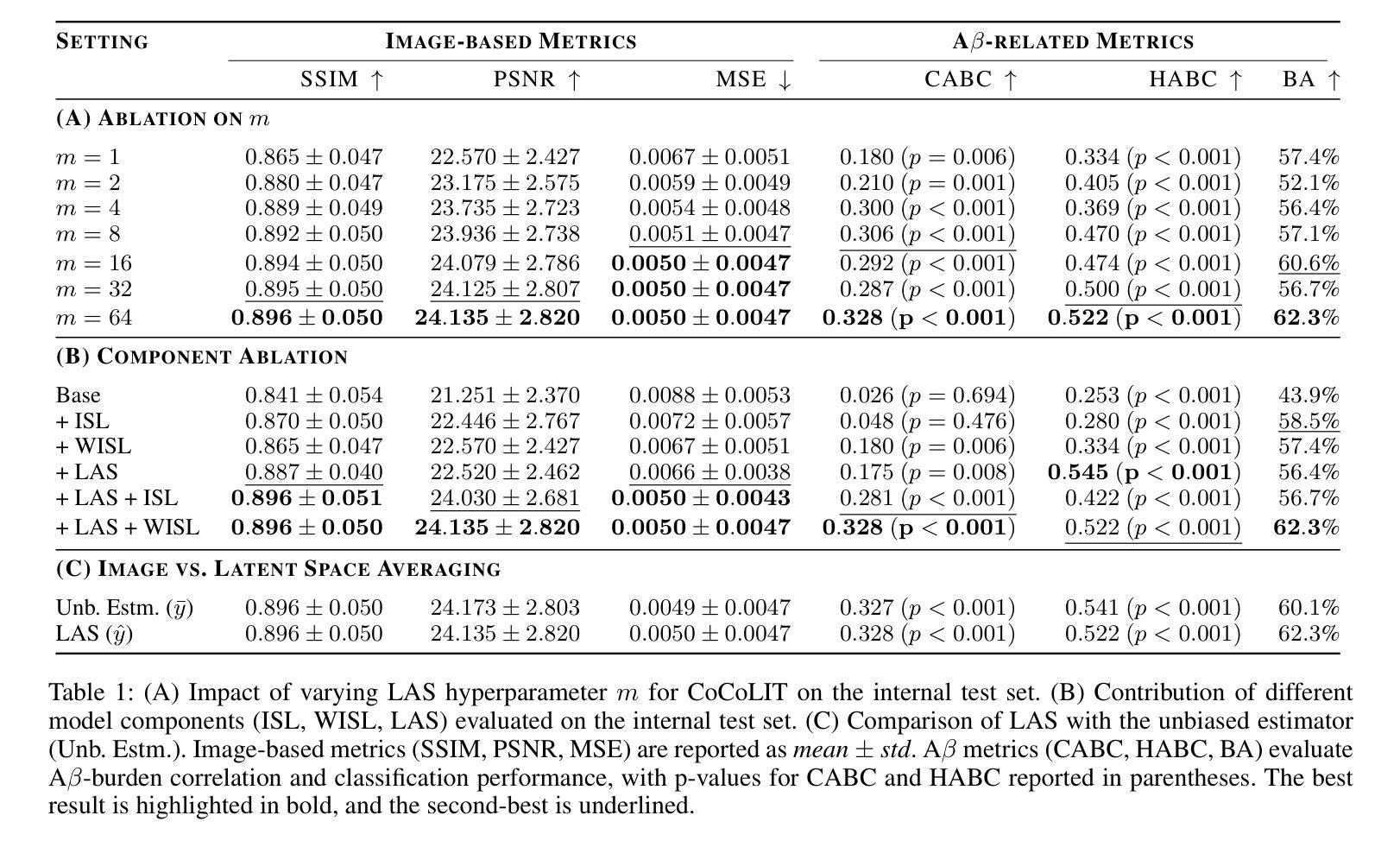
CoCoLIT: ControlNet-Conditioned Latent Image Translation for MRI to Amyloid PET Synthesis
Authors:Alec Sargood, Lemuel Puglisi, James H. Cole, Neil P. Oxtoby, Daniele Ravì, Daniel C. Alexander
Synthesizing amyloid PET scans from the more widely available and accessible structural MRI modality offers a promising, cost-effective approach for large-scale Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) screening. This is motivated by evidence that, while MRI does not directly detect amyloid pathology, it may nonetheless encode information correlated with amyloid deposition that can be uncovered through advanced modeling. However, the high dimensionality and structural complexity of 3D neuroimaging data pose significant challenges for existing MRI-to-PET translation methods. Modeling the cross-modality relationship in a lower-dimensional latent space can simplify the learning task and enable more effective translation. As such, we present CoCoLIT (ControlNet-Conditioned Latent Image Translation), a diffusion-based latent generative framework that incorporates three main innovations: (1) a novel Weighted Image Space Loss (WISL) that improves latent representation learning and synthesis quality; (2) a theoretical and empirical analysis of Latent Average Stabilization (LAS), an existing technique used in similar generative models to enhance inference consistency; and (3) the introduction of ControlNet-based conditioning for MRI-to-PET translation. We evaluate CoCoLIT’s performance on publicly available datasets and find that our model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both image-based and amyloid-related metrics. Notably, in amyloid-positivity classification, CoCoLIT outperforms the second-best method with improvements of +10.5% on the internal dataset and +23.7% on the external dataset. The code and models of our approach are available at https://github.com/brAIn-science/CoCoLIT.
通过将从更广泛且更容易获取的机构MRI模式合成的淀粉样蛋白PET扫描,提供了一个有前景且经济实惠的大规模筛选阿尔茨海默病(AD)的方法。这是由证据驱动的,虽然MRI不会直接检测淀粉样蛋白病理,但它仍然可以编码与淀粉样沉积相关的信息,这些信息可以通过先进的建模来揭示。然而,三维神经成像数据的高维度和结构复杂性对现有MRI到PET转换方法构成了重大挑战。在较低维度的潜在空间中建模跨模态关系可以简化学习任务并更有效地实现转换。因此,我们提出了CoCoLIT(ControlNet控制的潜在图像翻译),这是一个基于扩散的潜在生成框架,包含三个主要创新点:(1)一种新颖的有权图像空间损失(WISL),可以提高潜在表示学习和合成质量;(2)对潜在平均稳定化(LAS)的理论和实证分析,这是一种用于增强推理一致性的现有技术,用于类似的生成模型;(3)引入基于ControlNet的条件进行MRI到PET的翻译。我们在公开数据集上评估了CoCoLIT的性能,发现我们的模型在基于图像和淀粉样相关指标上均显著优于最新方法。值得注意的是,在淀粉样阳性分类方面,CoCoLIT在内部数据集上较第二名提高了+10.5%,在外部数据集上提高了+23.7%。我们的方法的代码和模型可在https://github.com/brAIn-science/CoCoLIT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过合成淀粉样蛋白PET扫描与更广泛且可访问的结构性MRI模式,为大规模阿尔茨海默病筛查提供了一个有前景且经济实惠的方法。虽然MRI不能直接检测淀粉样病理,但它可能编码与淀粉样沉积相关的信息,可通过高级建模来揭示。CoCoLIT(ControlNet控制的潜在图像翻译)是一个基于扩散的潜在生成框架,包含三个主要创新点:新型加权图像空间损失(WISL)提高了潜在表示学习和合成质量;对潜在平均稳定化(LAS)的理论和实证分析;以及用于MRI到PET翻译的基于ControlNet的条件技术。在公开数据集上评估CoCoLIT的性能,发现该模型在图像和淀粉样相关指标上均显著优于现有方法。在淀粉样阳性分类中,CoCoLIT比第二名的方法高出+10.5%(内部数据集)和+23.7%(外部数据集)。我们的方法和模型代码可在https://github.com/brAIn-science/CoCoLIT获取。
Key Takeaways
- 利用MRI模态合成淀粉样蛋白PET扫描为阿尔茨海默病筛查提供成本效益高的方法。
- MRI可能编码与淀粉样沉积相关的信息,可通过高级建模揭示。
- CoCoLIT框架包含三个主要创新点:WISL、LAS分析和基于ControlNet的条件技术。
- CoCoLIT在公开数据集上的性能显著优于现有方法。
- 在淀粉样阳性分类中,CoCoLIT有显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

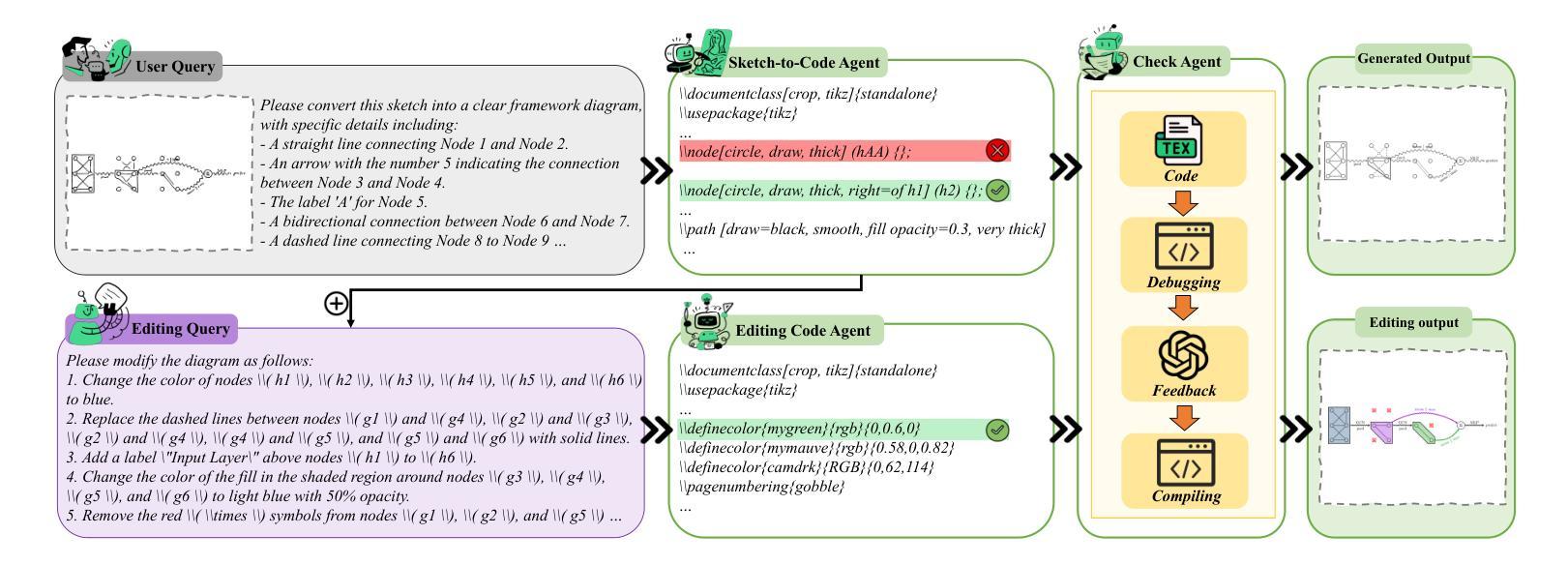
SketchAgent: Generating Structured Diagrams from Hand-Drawn Sketches
Authors:Cheng Tan, Qi Chen, Jingxuan Wei, Gaowei Wu, Zhangyang Gao, Siyuan Li, Bihui Yu, Ruifeng Guo, Stan Z. Li
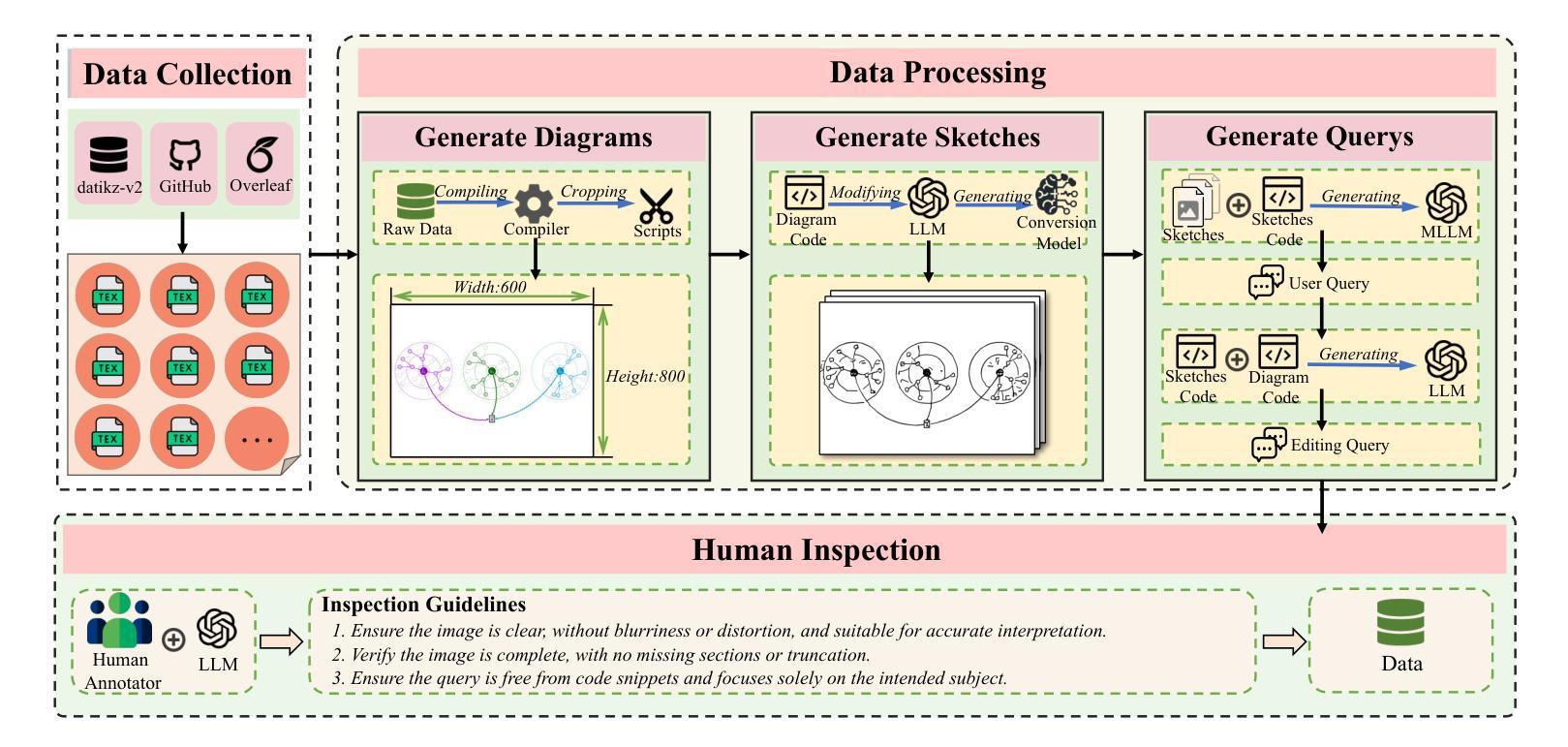
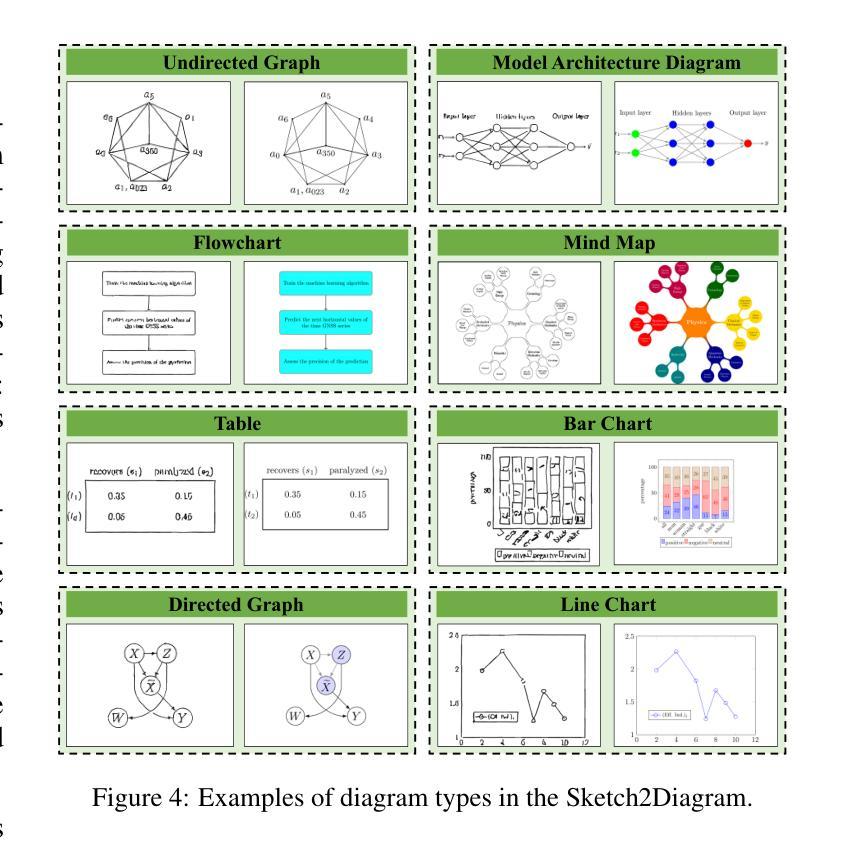
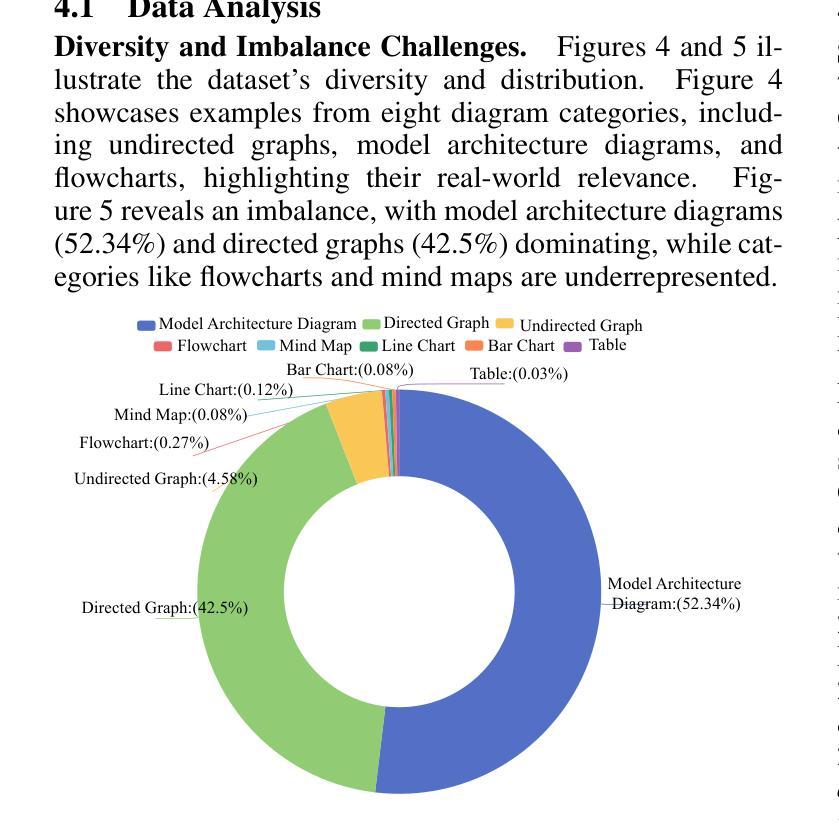
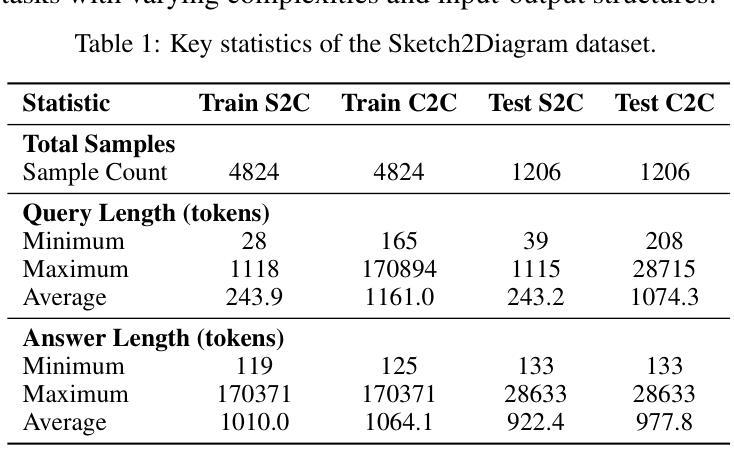
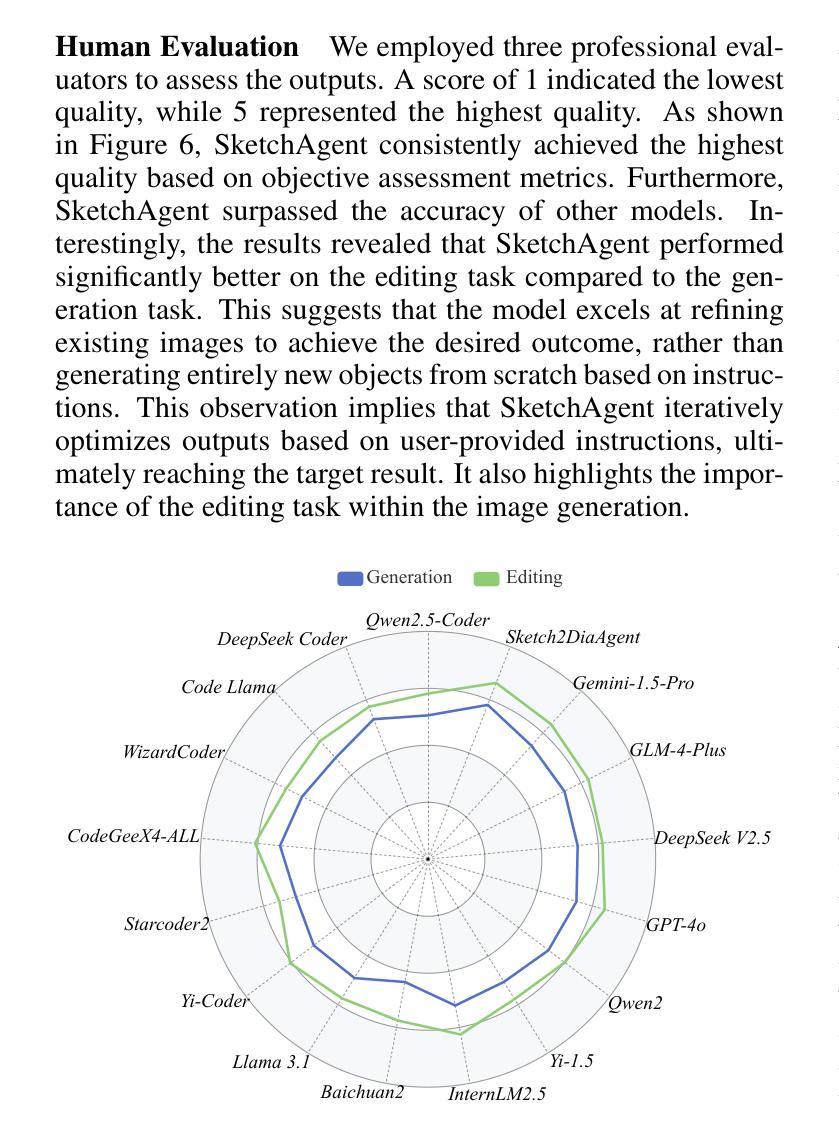
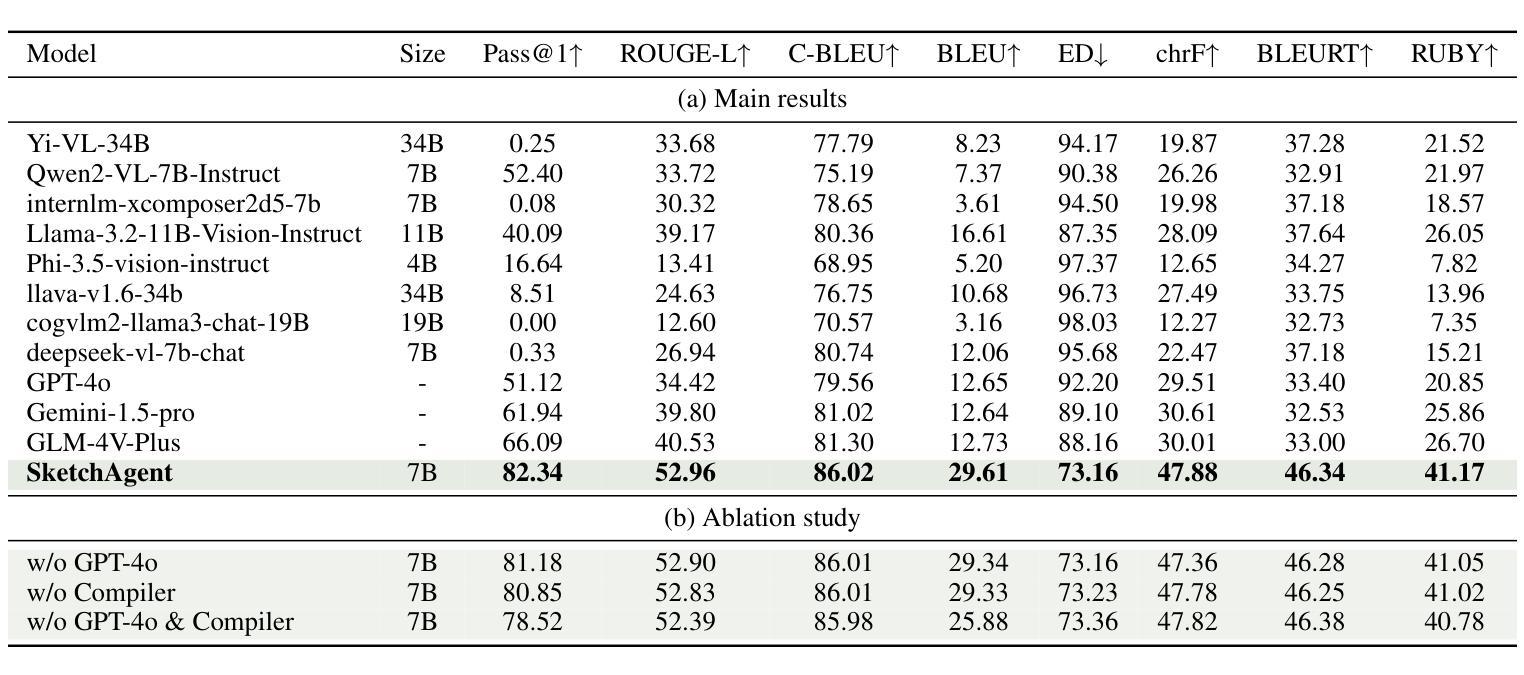
Hand-drawn sketches are a natural and efficient medium for capturing and conveying ideas. Despite significant advancements in controllable natural image generation, translating freehand sketches into structured, machine-readable diagrams remains a labor-intensive and predominantly manual task. The primary challenge stems from the inherent ambiguity of sketches, which lack the structural constraints and semantic precision required for automated diagram generation. To address this challenge, we introduce SketchAgent, a multi-agent system designed to automate the transformation of hand-drawn sketches into structured diagrams. SketchAgent integrates sketch recognition, symbolic reasoning, and iterative validation to produce semantically coherent and structurally accurate diagrams, significantly reducing the need for manual effort. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we propose the Sketch2Diagram Benchmark, a comprehensive dataset and evaluation framework encompassing eight diverse diagram categories, such as flowcharts, directed graphs, and model architectures. The dataset comprises over 6,000 high-quality examples with token-level annotations, standardized preprocessing, and rigorous quality control. By streamlining the diagram generation process, SketchAgent holds great promise for applications in design, education, and engineering, while offering a significant step toward bridging the gap between intuitive sketching and machine-readable diagram generation. The benchmark is released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/DiagramAgent/Sketch2Diagram-Benchmark.
手绘草图是一种自然且高效的思想捕捉和传达媒介。尽管在可控自然图像生成方面取得了重大进展,但将手绘草图转换为结构化、机器可读的图表仍然是一项劳动密集型且以手动操作为主的任务。主要挑战源于草图本身的模糊性,草图缺乏结构约束和语义精度,无法实现自动化图表生成。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了SketchAgent,这是一个多代理系统,旨在自动将手绘草图转换为结构化图表。SketchAgent集成了草图识别、符号推理和迭代验证,以产生语义连贯、结构准确的图表,从而大大减少了对手动操作的需求。为了评估我们的方法的有效性,我们提出了Sketch2Diagram Benchmark,这是一个包含八种不同图表类别的综合数据集和评估框架,如流程图、有向图、模型架构等。数据集包含超过6000个高质量示例,具有标记符号级别的注释、标准化预处理和严格的质量控制。通过简化图表生成过程,SketchAgent在设计、教育和工程等领域的应用前景广阔,同时为直观的草图和机器可读的图表生成之间搭建了桥梁。该基准测试已在https://huggingface.co/datasets/DiagramAgent/Sketch2Diagram-Benchmark发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025
Summary
手绘草图是一种自然且高效的思想表达与传递媒介。尽管自然图像生成技术取得了显著进展,但将手绘草图转化为结构化、机器可读的图表仍是一项劳动密集型、以手动为主的任务。SketchAgent多主体系统的出现解决了这一问题,该系统将手绘草图自动转化为结构化图表,过程中涉及草图识别、符号推理和迭代验证。为评估方法的有效性,我们推出了Sketch2Diagram Benchmark基准测试,涵盖流程图、有向图、模型架构等八个类别的图表,包含6000多个高质量样本,具备标记化预处理和严格的质量控制。SketchAgent简化了图表生成流程,在设计、教育和工程领域具有广泛应用前景,也为直观草图和机器可读图表生成之间搭建了桥梁。详情访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 手绘草图作为思想和创意的表达方式,在思想交流和传递中具有重要意义。
- 将手绘草图转化为机器可读的图表是一项复杂的任务,需要高效的自动化工具。
- SketchAgent多主体系统通过结合草图识别、符号推理和迭代验证,实现了手绘草图到结构化图表的自动化转化。
- Sketch2Diagram Benchmark基准测试为评估此类方法的性能提供了标准数据集和评估框架。
- 该基准测试涵盖多个类别的图表,样本质量高,具备严格的质量控制。
- SketchAgent简化了图表生成流程,提高了效率,具有广泛的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

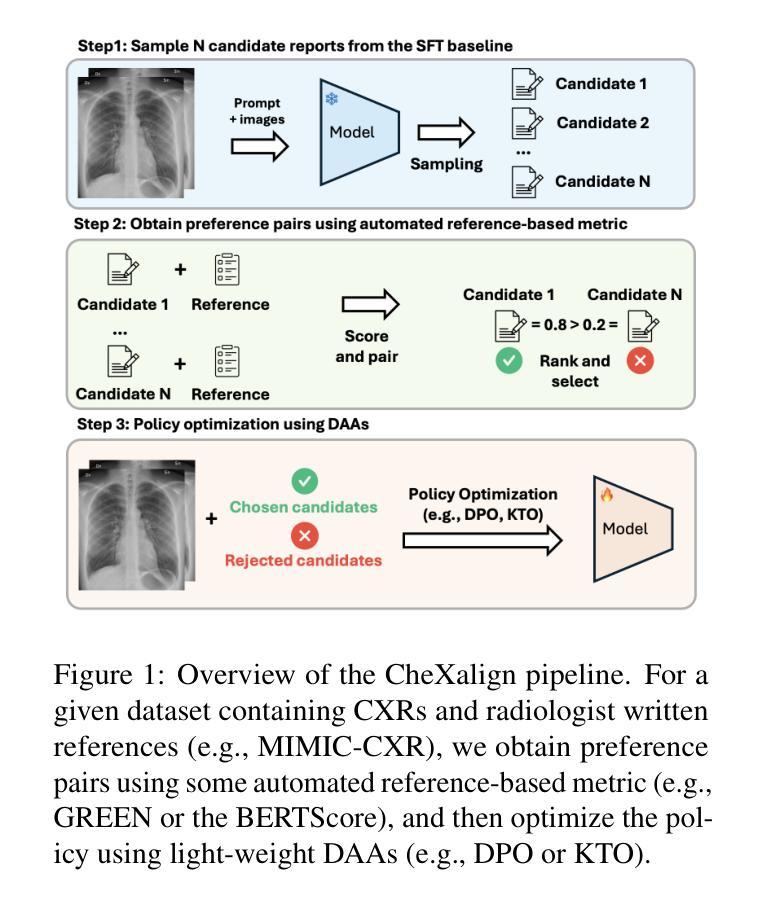
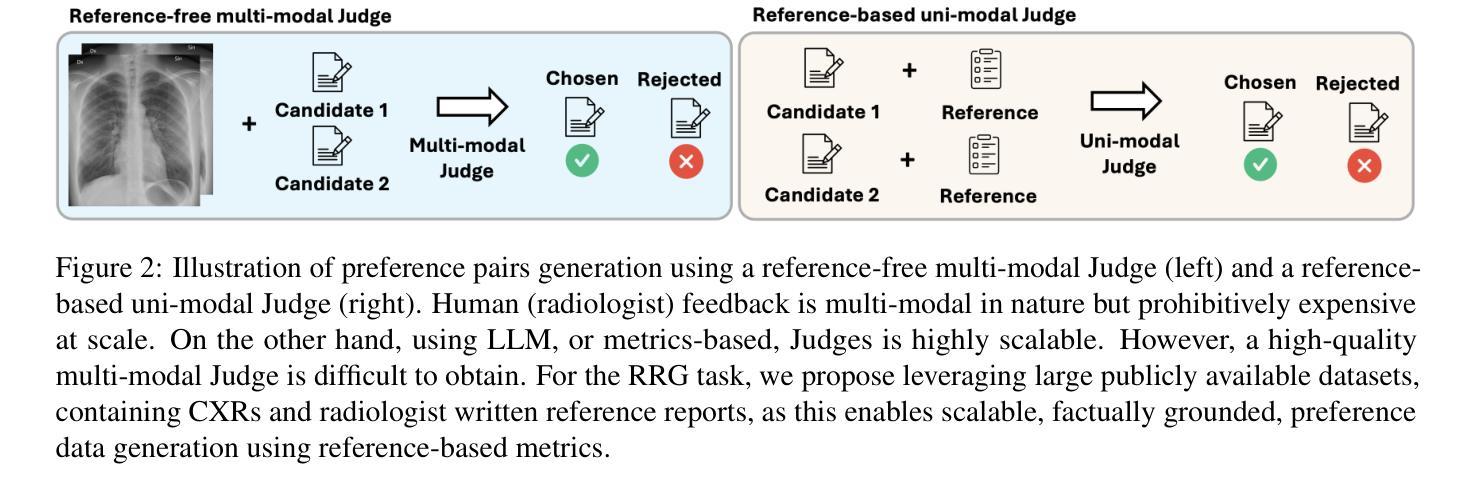
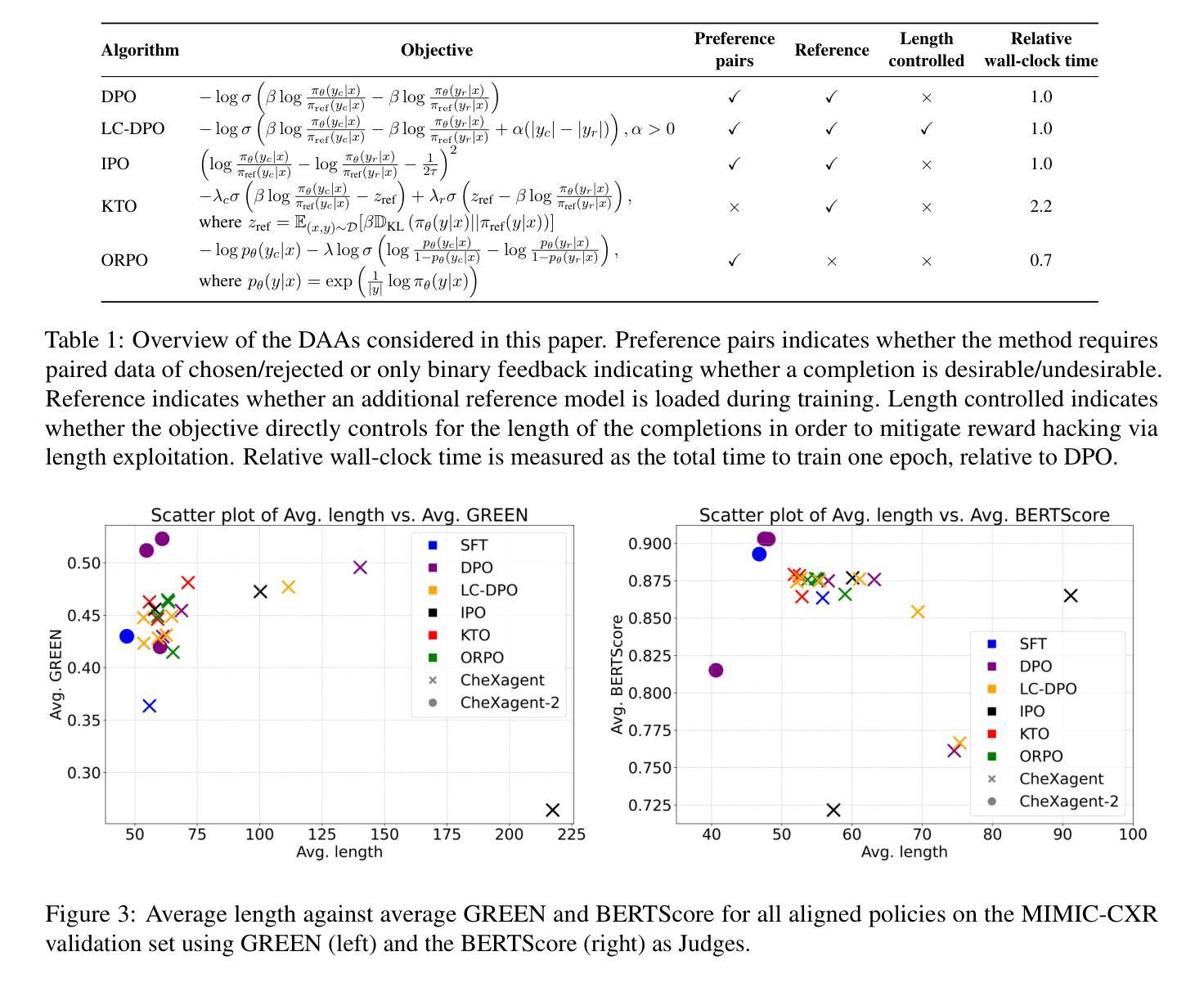
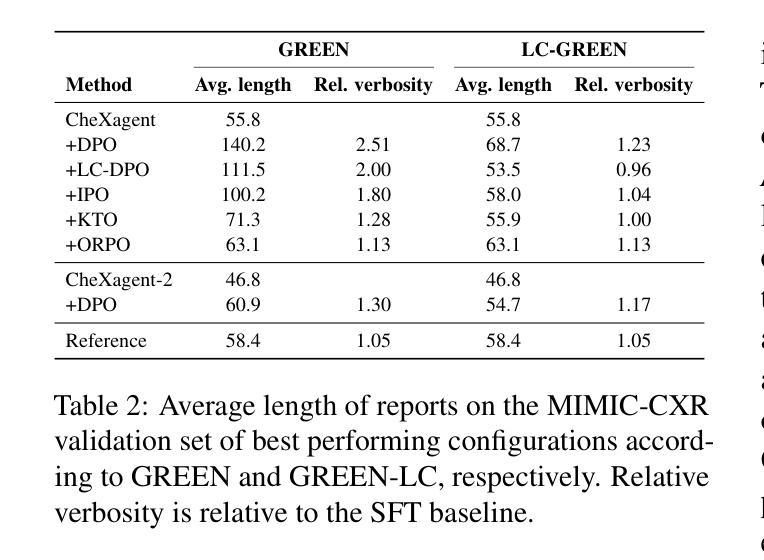
CheXalign: Preference fine-tuning in chest X-ray interpretation models without human feedback
Authors:Dennis Hein, Zhihong Chen, Sophie Ostmeier, Justin Xu, Maya Varma, Eduardo Pontes Reis, Arne Edward Michalson, Christian Bluethgen, Hyun Joo Shin, Curtis Langlotz, Akshay S Chaudhari
Radiologists play a crucial role in translating medical images into actionable reports. However, the field faces staffing shortages and increasing workloads. While automated approaches using vision-language models (VLMs) show promise as assistants, they require exceptionally high accuracy. Most current VLMs in radiology rely solely on supervised fine-tuning. Meanwhile, additional preference fine-tuning in the post-training pipeline has become standard practice in the general domain. The challenge in radiology lies in the prohibitive cost of obtaining radiologist feedback at scale. To address this challenge, we propose an automated pipeline for preference feedback, focusing on chest X-ray radiology report generation (RRG). Specifically, our method leverages publicly available datasets containing pairs of images and radiologist-written reference reports with reference-based metrics, or Judges, eliminating the need for additional radiologist feedback. We investigate reward overoptimization via length exploitation in this setting and introduce a length-controlled version of the GREEN score. Our best-performing setup achieves state-of-the-art CheXbert scores on the MIMIC-CXR dataset for the RRG task while on average maintaining robust performance across six additional image perception and reasoning tasks.
放射科医生在将医学图像转化为可操作报告方面扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,该领域面临着人员短缺和工作量增加的问题。虽然使用视觉语言模型的自动化方法作为助理显示出潜力,但它们需要极高的准确性。当前大多数放射科的视觉语言模型仅依赖于监督微调。同时,在训练后的管道中进行额外的偏好微调已成为通用领域的标准做法。放射学中的挑战在于大规模获取放射科医生反馈的禁止成本。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种自动化偏好反馈管道,专注于胸部X射线放射报告生成。具体来说,我们的方法利用公开可用的数据集,其中包含图像和放射科医生编写的参考报告对,以及基于参考的度量或评判,消除了对额外放射科医生反馈的需求。我们研究了这一环境下的长度利用导致的奖励过度优化问题,并引入了长度控制的GREEN评分版本。我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集上的放射报告生成任务上实现了最先进的CheXbert分数,同时在另外六个图像感知和推理任务上保持了稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025
Summary
本文探讨了放射科医生在将医学图像转化为可操作报告方面的重要作用,同时指出该领域面临人员短缺和工作量增加的问题。虽然使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的自动化方法显示出潜力,但它们需要极高的准确性。文章提出了一种针对胸部X射线放射学报告生成(RRG)的自动化管道,利用公开数据集和基于参考的度量标准,消除对额外放射科医生反馈的需求。同时,文章还探讨了长度优化问题,并引入了一种控制长度的GREEN评分版本。最佳设置方案在MIMIC-CXR数据集上的RRG任务中实现了最先进的CheXbert分数,同时在六个额外的图像感知和推理任务中保持了稳健的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 放射科医生在将医学图像转化为操作报告方面起关键作用,但面临人员短缺和工作量增加的挑战。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在放射学中有应用潜力,但需达到极高准确性。
- 当前大多数放射学中的VLMs仅依赖于监督微调。
- 在一般领域中,偏好微调已成为标准做法。
- 放射学中的挑战在于大规模获取放射科医生反馈的昂贵成本。
- 提出一种自动化管道进行偏好反馈,专注于胸部X射线放射学报告生成(RRG),利用公开数据集和基于参考的度量标准。
点此查看论文截图