⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
MedSynth: Realistic, Synthetic Medical Dialogue-Note Pairs
Authors:Ahmad Rezaie Mianroodi, Amirali Rezaie, Niko Grisel Todorov, Cyril Rakovski, Frank Rudzicz
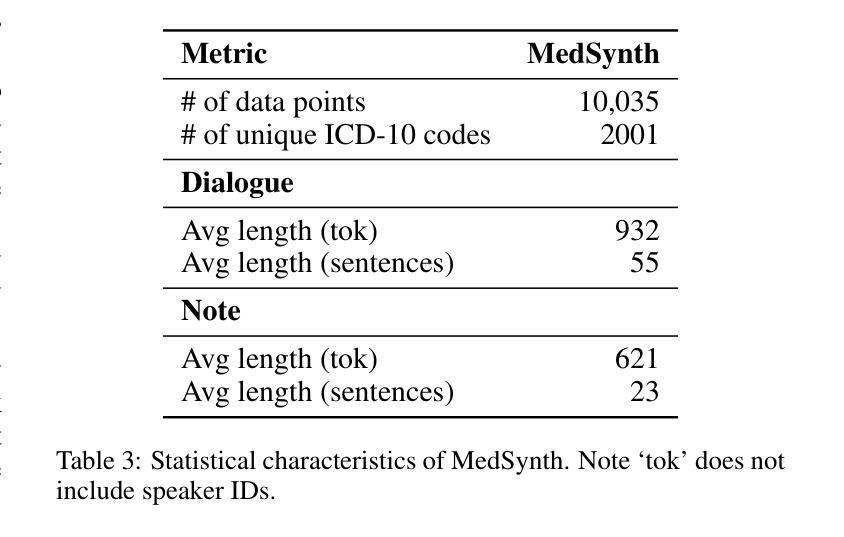
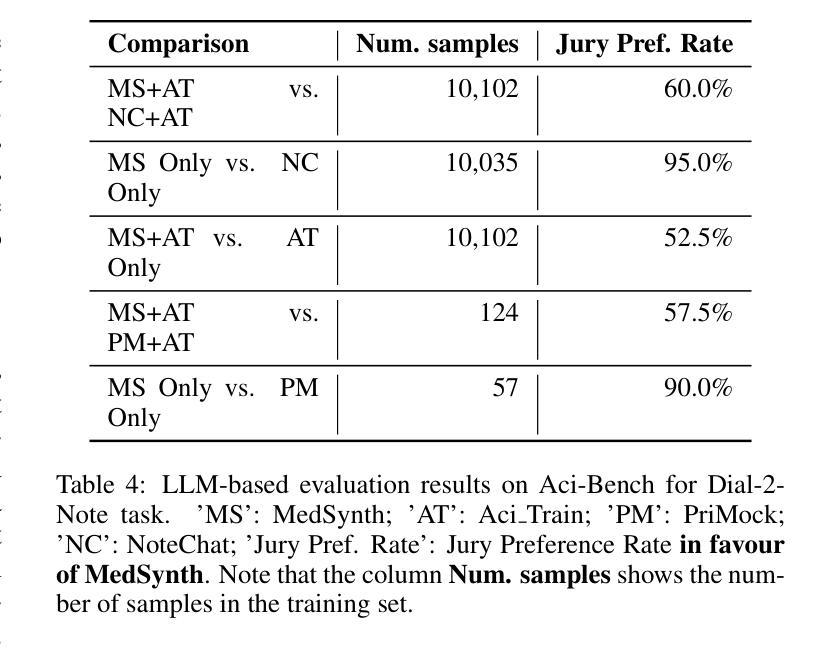
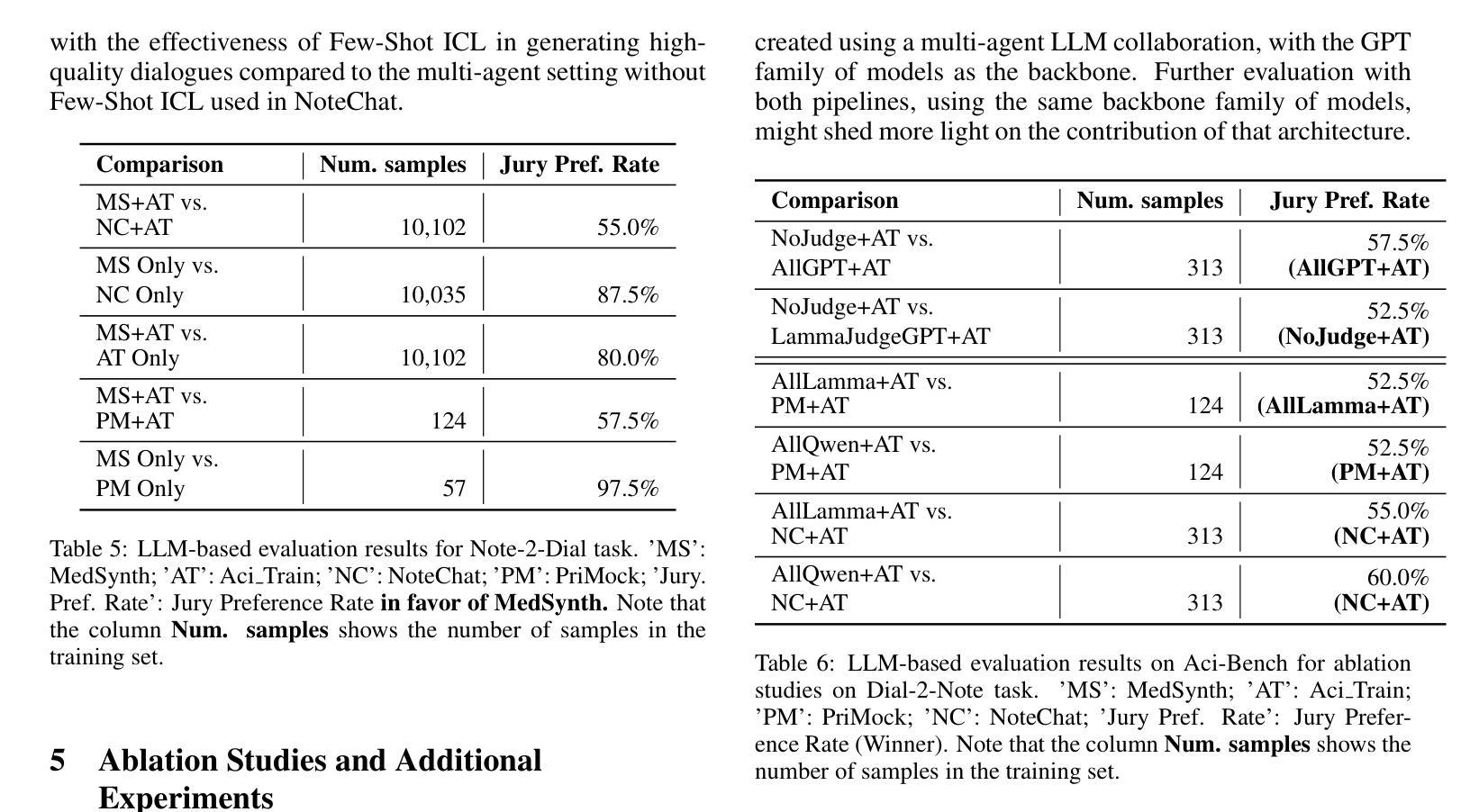
Physicians spend significant time documenting clinical encounters, a burden that contributes to professional burnout. To address this, robust automation tools for medical documentation are crucial. We introduce MedSynth – a novel dataset of synthetic medical dialogues and notes designed to advance the Dialogue-to-Note (Dial-2-Note) and Note-to-Dialogue (Note-2-Dial) tasks. Informed by an extensive analysis of disease distributions, this dataset includes over 10,000 dialogue-note pairs covering over 2000 ICD-10 codes. We demonstrate that our dataset markedly enhances the performance of models in generating medical notes from dialogues, and dialogues from medical notes. The dataset provides a valuable resource in a field where open-access, privacy-compliant, and diverse training data are scarce. Code is available at https://github.com/ahmadrezarm/MedSynth/tree/main and the dataset is available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Ahmad0067/MedSynth.
医学专家在记录临床诊疗过程方面花费了大量时间,这无疑增加了他们的工作压力,甚至可能导致职业倦怠。为解决这一问题,开发用于医学文档记录的自动化工具至关重要。我们推出了MedSynth——一个合成医学对话和笔记的新数据集,旨在推动对话到笔记(Dial-2-Note)和笔记到对话(Note-2-Dial)任务的发展。该数据集基于疾病分布的深入分析,包含超过1万个对话-笔记对,涵盖了超过2000个ICD-10代码。我们证明,该数据集显著提高了从对话生成医学笔记和从医学笔记生成对话的模型性能。在该领域,公开访问、符合隐私规定和多样化的训练数据十分稀缺,该数据集具有重要的参考价值。相关代码可在https://github.com/ahmadrezarm/MedSynth/tree/main找到,数据集可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/Ahmad0067/MedSynth获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages excluding references and appendices
Summary
本文介绍了为解决医生记录临床遭遇所花费的时间和职业倦怠问题,推出了一种名为MedSynth的新型数据集。该数据集包含超过一万对对话笔记,涵盖了超过两千个ICD-10代码,旨在推进对话到笔记(Dial-2-Note)和笔记到对话(Note-2-Dial)的任务。该数据集提高了模型生成医疗对话和笔记的性能,为缺乏开放访问、隐私合规和多样化训练数据的领域提供了有价值的资源。
Key Takeaways
- 医生和临床记录相关的挑战:医生花费大量时间记录临床遭遇,这增加了职业倦怠的问题。
- MedSynth数据集的介绍:这是一个新型数据集,包含超过一万对合成医疗对话和笔记。
- 数据集与任务的关联:数据集旨在推进对话到笔记(Dial-2-Note)和笔记到对话(Note-2-Dial)的任务。
- 数据集的构成:该数据集涵盖了超过两千个ICD-10代码,基于疾病分布进行广泛分析。
- 模型性能的提升:MedSynth数据集显著提高了模型在生成医疗对话和笔记方面的性能。
- 数据集的贡献:为缺乏开放访问、隐私合规和多样化训练数据的领域提供了有价值的资源。
点此查看论文截图

REACT: A Real-Time Edge-AI Based V2X Framework for Accident Avoidance in Autonomous Driving System
Authors:Fengze Yang, Bo Yu, Yang Zhou, Xuewen Luo, Zhengzhong Tu, Chenxi Liu
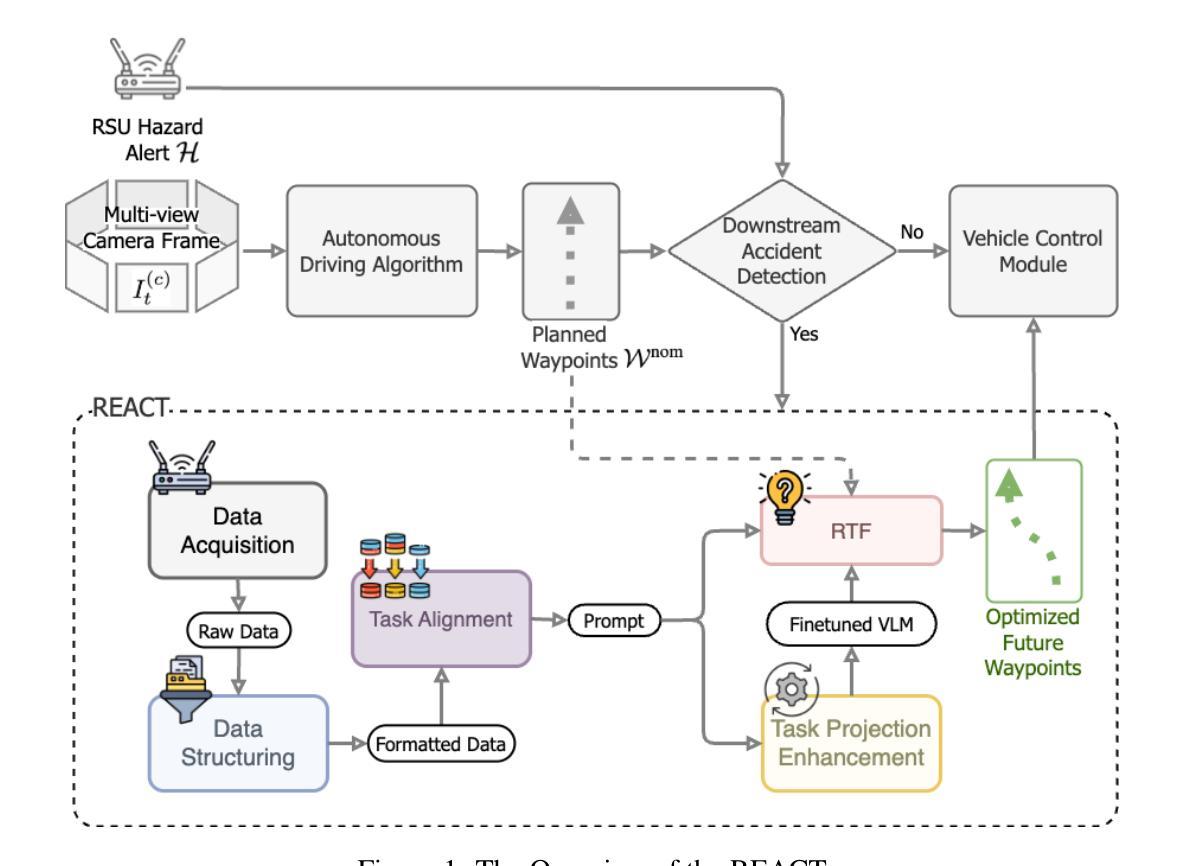
Collisions caused by human error are the most common type of multi-vehicle crash, highlighting the critical need for autonomous driving (AD) systems to leverage cooperative perception through Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication. This capability extends situational awareness beyond the limitations of onboard sensors. However, current transformer-based V2X frameworks suffer from limited generalization, shallow contextual reasoning, and reliance on mono-modal inputs. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer enhanced reasoning and multimodal integration but typically fall short of real-time performance requirements in safety-critical applications. This paper presents REACT, a real-time, V2X-integrated trajectory optimization framework built upon a fine-tuned lightweight VLM. REACT integrates a set of specialized modules that process multimodal inputs into optimized, risk-aware trajectories. To ensure real-time performance on edge devices, REACT incorporates edge adaptation strategies that reduce model complexity and accelerate inference. Evaluated on the DeepAccident benchmark, REACT achieves state-of-the-art performance, a 77% collision rate reduction, a 48.2% Video Panoptic Quality (VPQ), and a 0.57-second inference latency on the Jetson AGX Orin. Ablation studies validate the contribution of each input, module, and edge adaptation strategy. These results demonstrate the feasibility of lightweight VLMs for real-time edge-based cooperative planning and showcase the potential of language-guided contextual reasoning to improve safety and responsiveness in autonomous driving.
由人为错误导致的碰撞是最常见的多车事故类型,这凸显了自动驾驶(AD)系统利用车辆对一切(V2X)通信进行协同感知的紧迫需求。这种能力超越了车载传感器的局限,扩展了态势感知。然而,基于变压器的V2X框架存在通用性有限、上下文推理浅显以及依赖单一模态输入的问题。视觉语言模型(VLM)提供了增强的推理和多模态集成,但在安全关键应用的实时性能要求方面通常表现不足。本文提出了REACT,一个基于精细调整过的轻量级VLM的实时、V2X集成轨迹优化框架。REACT集成了一系列专业模块,将多模态输入转化为优化的、具有风险意识的轨迹。为了确保在边缘设备上的实时性能,REACT采用了边缘适应策略,降低了模型复杂度并加速了推理。在DeepAccident基准测试上,REACT达到了最先进的性能,碰撞率降低了77%,视频全景质量(VPQ)达到48.2%,在Jetson AGX Orin上的推理延迟为0.57秒。消融研究验证了每个输入、模块和边缘适应策略的贡献。这些结果证明了轻量级VLM用于实时边缘协同规划的可行性,并展示了语言引导上下文推理在改善自动驾驶安全性和响应能力方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 tables, 7 figures
Summary
本文探讨了人类误差导致的碰撞在多车事故中的普遍性问题,强调了自动驾驶(AD)系统通过车辆对一切(V2X)通信利用合作感知的重要性。然而,现有的基于转换器的V2X框架存在通用性有限、上下文推理浅以及依赖单一模态输入的问题。本文提出了REACT,一个基于精细调整轻量级视觉语言模型(VLM)的实时、V2X集成轨迹优化框架。REACT集成了专门处理多模态输入的模块,生成优化后的风险感知轨迹。为了确保在边缘设备上的实时性能,REACT融入了边缘适配策略,以降低模型复杂性和加速推理。在DeepAccident基准测试中,REACT达到了业界领先的表现,实现了77%的碰撞率降低、48.2%的视频全景质量(VPQ)以及0.57秒的推理延迟。
Key Takeaways
- 人类误差是导致多车辆碰撞最常见的原因,强调自动驾驶系统中合作感知的重要性。
- 当前基于转换器的V2X框架存在局限性,包括有限的通用性、较浅的上下文推理和对单一模态输入的依赖。
- 提出的REACT框架是一个实时的、V2X集成的轨迹优化系统,基于精细调整的轻量级VLM。
- REACT通过集成处理多模态输入的专门模块,生成优化后的风险感知轨迹。
- 为了在边缘设备上实现实时性能,REACT采用了边缘适配策略。
- 在DeepAccident基准测试中,REACT表现出卓越性能,包括碰撞率降低77%,VPQ达到48.2%,推理延迟为0.57秒。
点此查看论文截图

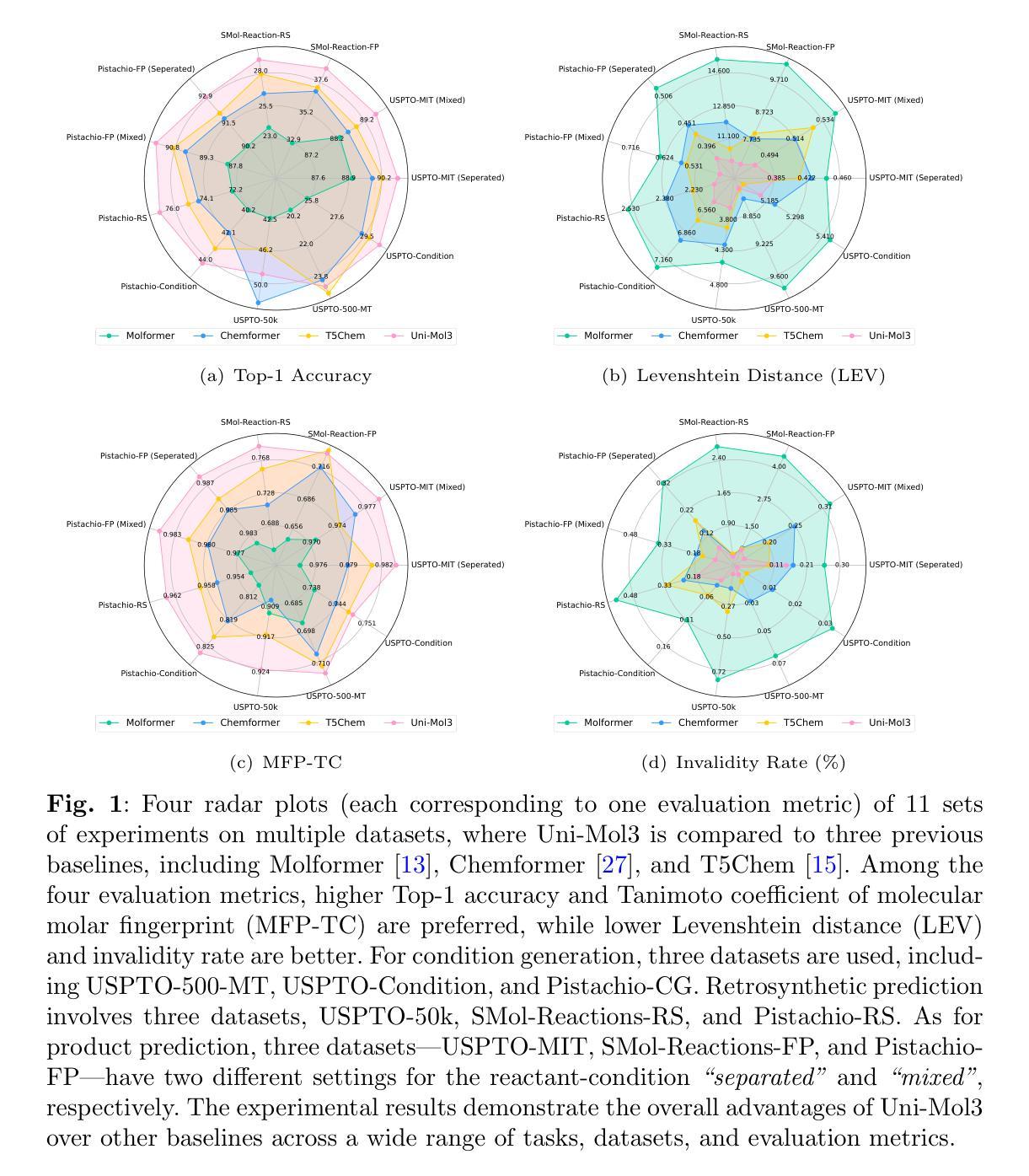
Uni-Mol3: A Multi-Molecular Foundation Model for Advancing Organic Reaction Modeling
Authors:Lirong Wu, Junjie Wang, Zhifeng Gao, Xiaohong Ji, Rong Zhu, Xinyu Li, Linfeng Zhang, Guolin Ke, Weinan E
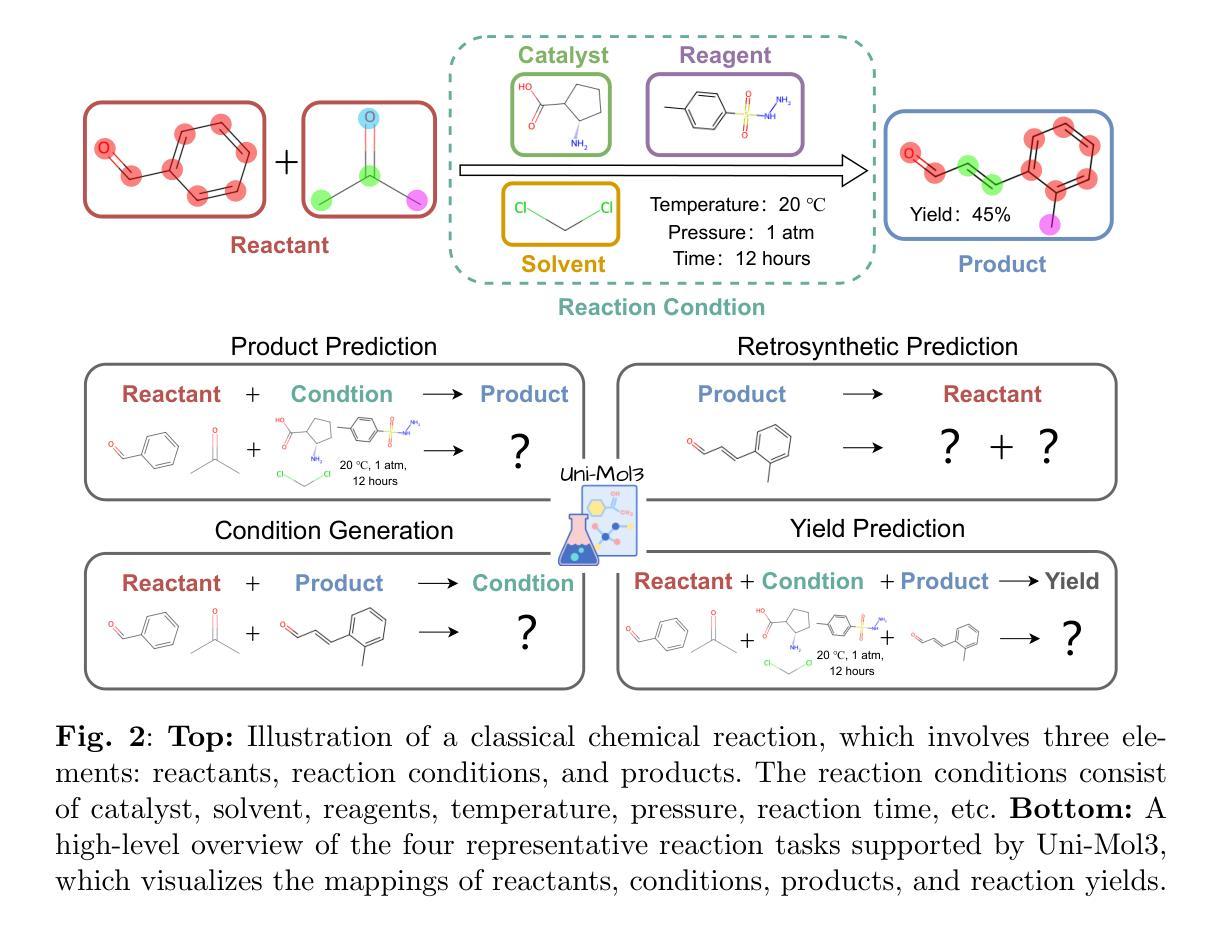
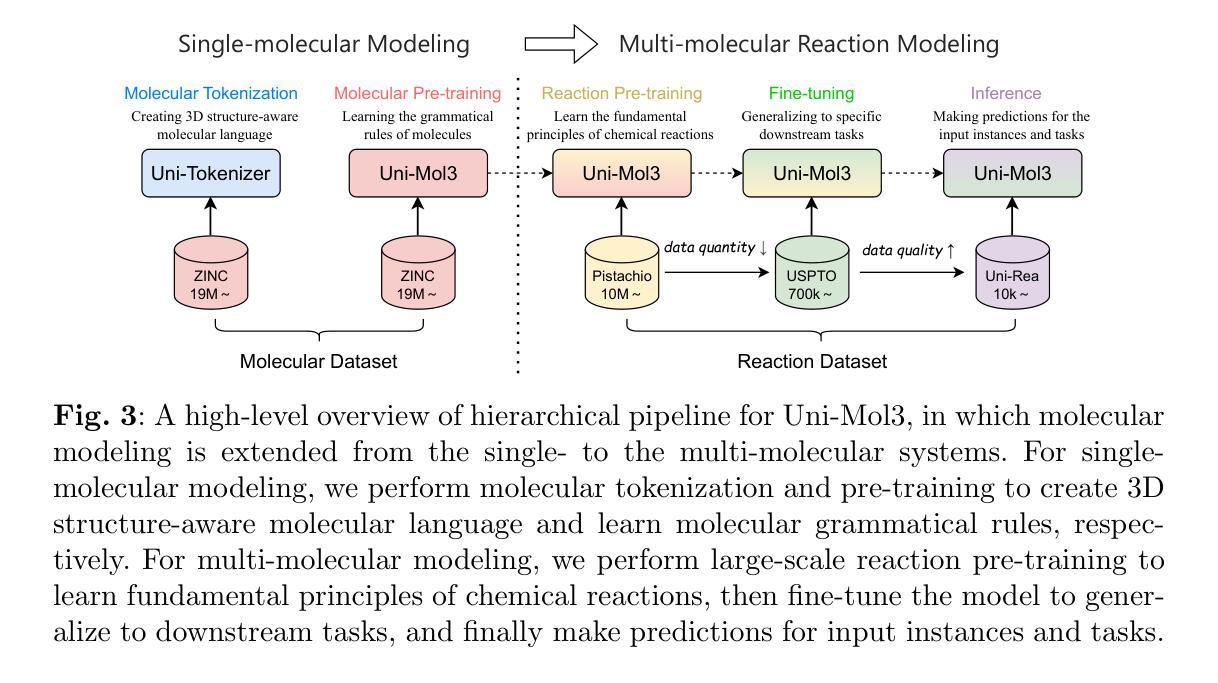
Organic reaction, the foundation of modern chemical industry, is crucial for new material development and drug discovery. However, deciphering reaction mechanisms and modeling multi-molecular relationships remain formidable challenges due to the complexity of molecular dynamics. While several state-of-the-art models like Uni-Mol2 have revolutionized single-molecular representation learning, their extension to multi-molecular systems, where chemical reactions inherently occur, has been underexplored. This paper introduces Uni-Mol3, a novel deep learning framework that employs a hierarchical pipeline for multi-molecular reaction modeling. At its core, Uni-Mol3 adopts a multi-scale molecular tokenizer (Mol-Tokenizer) that encodes 3D structures of molecules and other features into discrete tokens, creating a 3D-aware molecular language. The framework innovatively combines two pre-training stages: molecular pre-training to learn the molecular grammars and reaction pre-training to capture fundamental reaction principles, forming a progressive learning paradigm from single- to multi-molecular systems. With prompt-aware downstream fine-tuning, Uni-Mol3 demonstrates exceptional performance in diverse organic reaction tasks and supports multi-task prediction with strong generalizability. Experimental results across 10 datasets spanning 4 downstream tasks show that Uni-Mol3 outperforms existing methods, validating its effectiveness in modeling complex organic reactions. This work not only ushers in an alternative paradigm for multi-molecular computational modeling but also charts a course for intelligent organic reaction by bridging molecular representation with reaction mechanism understanding.
有机反应是现代化学工业的基础,对于新材料开发和药物发现至关重要。然而,由于分子动力学的复杂性,解析反应机制和模拟多分子关系仍然是巨大的挑战。虽然最先进的模型如Uni-Mol2已经实现了单分子表示学习革命,但其在多分子系统中的应用探索不足,而化学反应本质上就是发生在多分子系统中。本文介绍了Uni-Mol3,这是一种新型深度学习框架,采用分层管道进行多分子反应建模。Uni-Mol3的核心是采用多尺度分子标记器(Mol-Tokenizer),它将分子的三维结构和其他特征编码成离散标记,创建了一种三维感知分子语言。该框架创新地结合了两种预训练阶段:分子预训练学习分子语法和反应预训练捕捉基本反应原理,形成了从单分子系统到多分子系统的渐进学习范式。通过提示感知的下游微调,Uni-Mol3在多种有机反应任务中表现出卓越性能,支持多任务预测并具有强大的泛化能力。跨越10个数据集、涵盖4个下游任务的实验结果表明,Uni-Mol3优于现有方法,验证了其在建模复杂有机反应中的有效性。这项工作不仅为计算多分子建模提供了替代范式,而且通过连接分子表示和反应机制理解,为智能有机反应指明了方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文介绍了一种新型深度学习框架Uni-Mol3,用于多分子反应建模。它采用分级管道,结合分子预训练和反应预训练,实现了从单分子系统到多分子系统的渐进学习。通过促进下游微调,Uni-Mol3在不同有机反应任务中表现出卓越性能,并支持多任务预测,具有强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- Uni-Mol3是一个用于多分子反应建模的新型深度学习框架。
- 它采用分级管道来处理复杂的有机反应机制。
- Uni-Mol3引入了一种名为Mol-Tokenizer的多尺度分子令牌化技术,能够将分子的三维结构和其他特征编码成离散令牌。
- 该框架结合了分子预训练和反应预训练两个阶段,形成了一种从单分子系统到多分子系统的渐进学习模式。
- Uni-Mol3具有出色的性能表现,支持多任务预测并展示强大的泛化能力。
- 通过跨十个数据集的实验验证,Uni-Mol3在多个下游任务上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

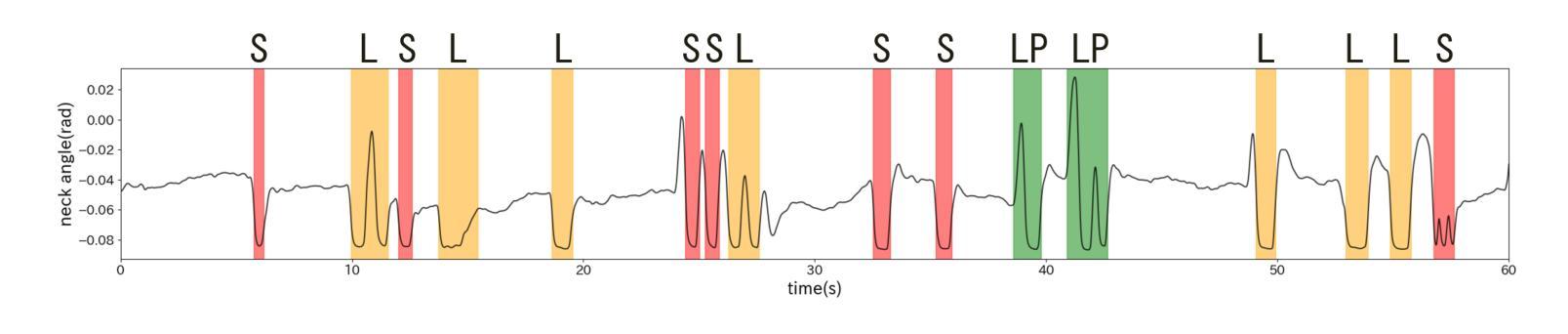
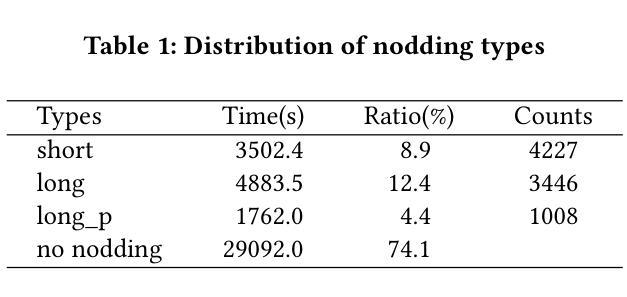
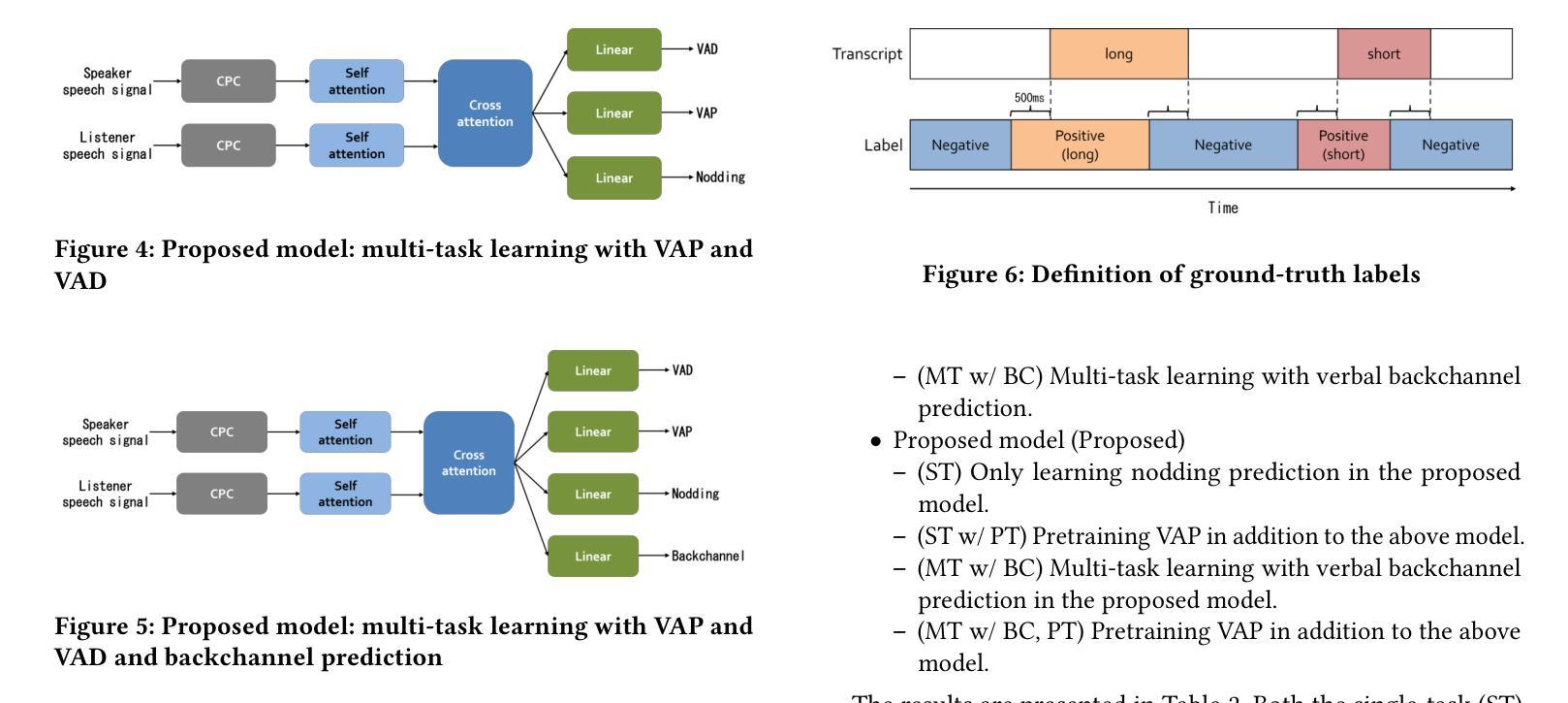
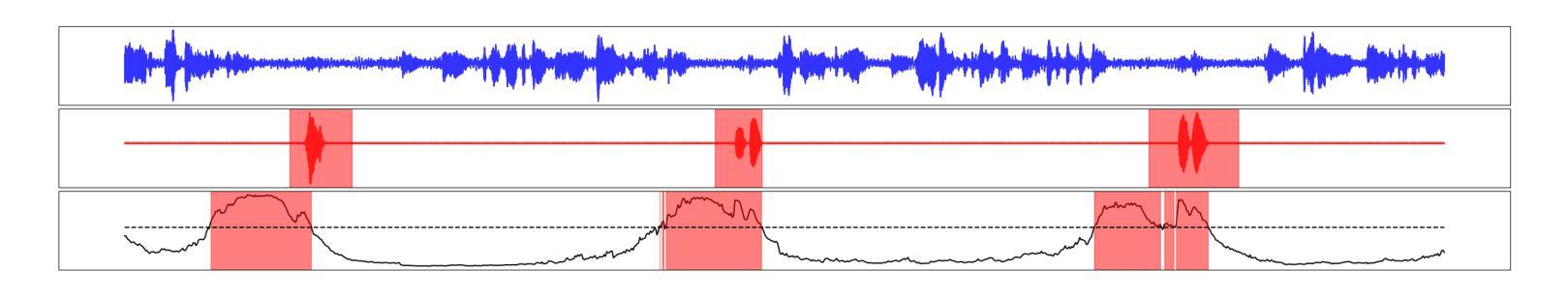
Real-time Generation of Various Types of Nodding for Avatar Attentive Listening System
Authors:Kazushi Kato, Koji Inoue, Divesh Lala, Keiko Ochi, Tatsuya Kawahara
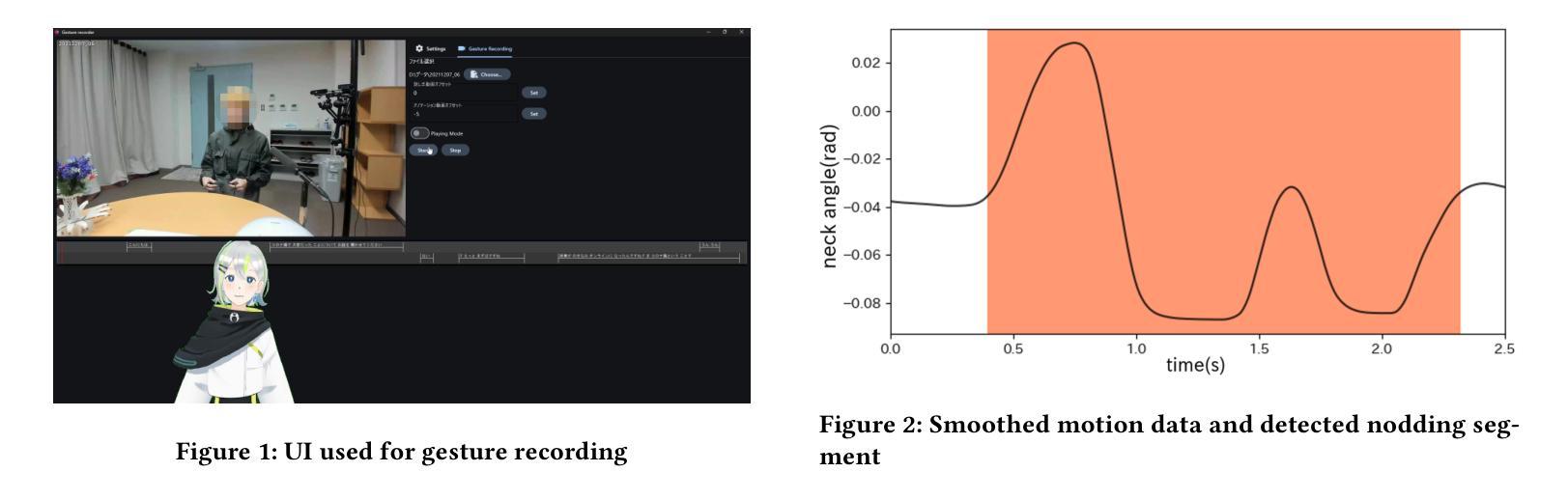
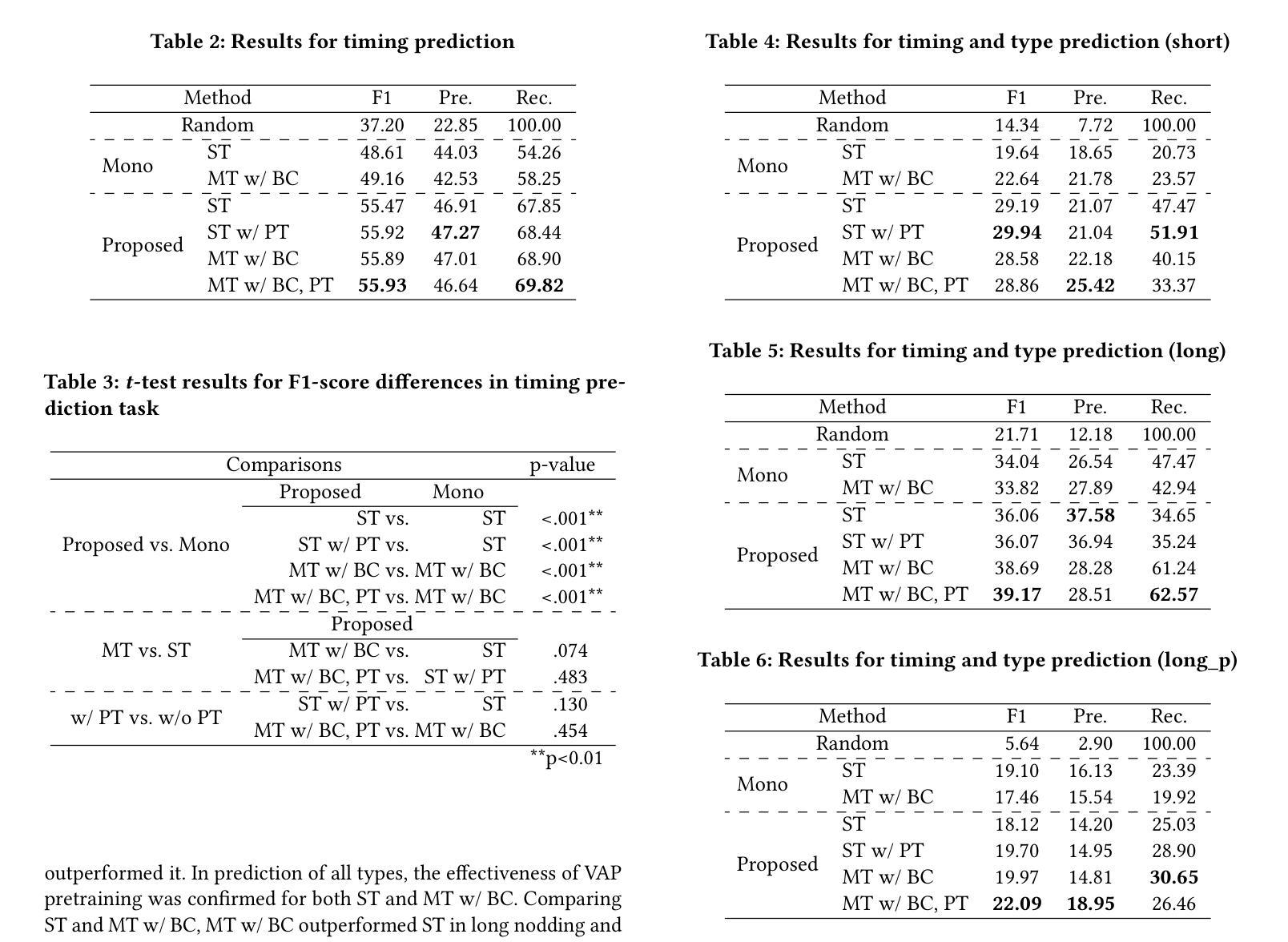
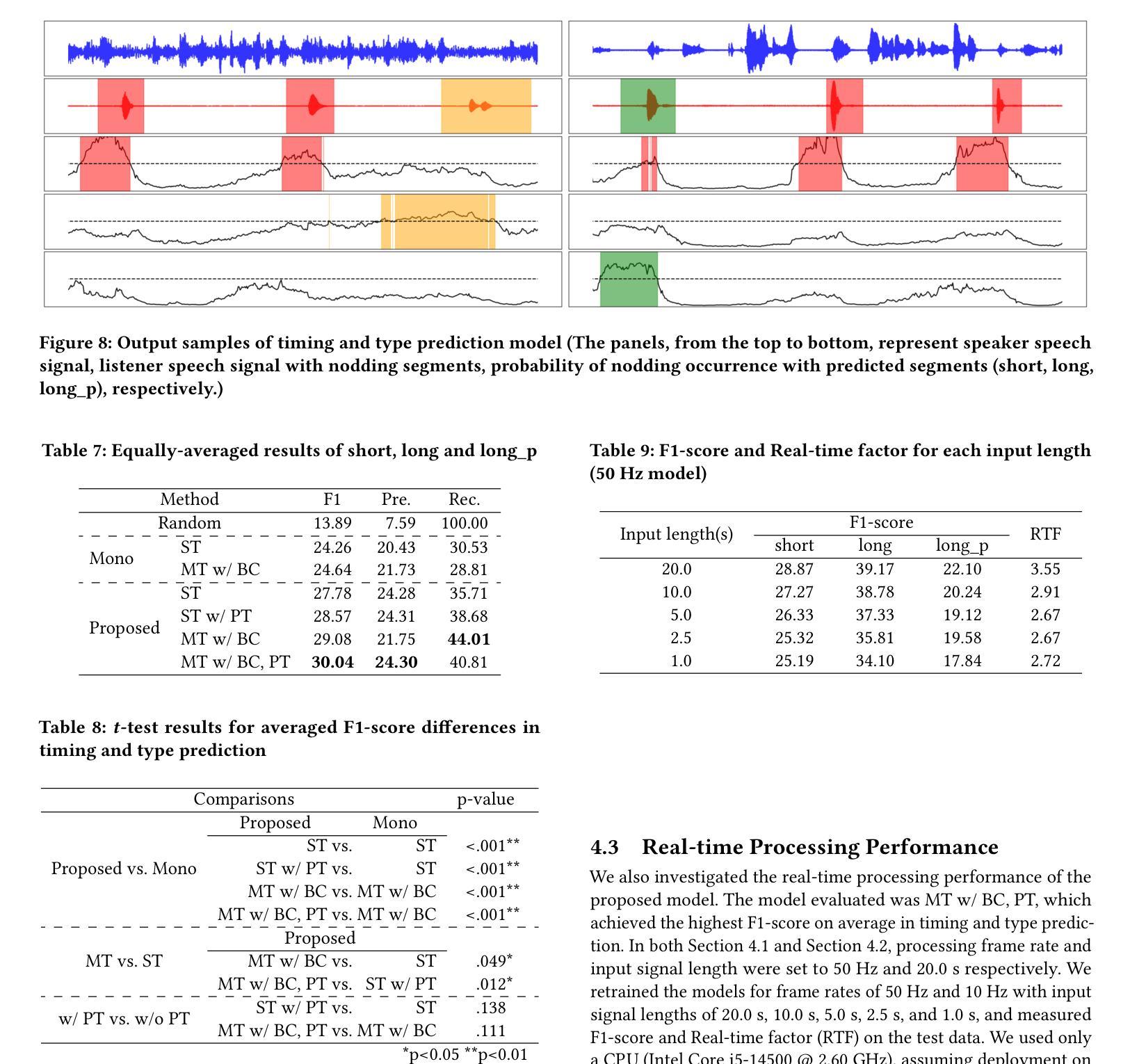
In human dialogue, nonverbal information such as nodding and facial expressions is as crucial as verbal information, and spoken dialogue systems are also expected to express such nonverbal behaviors. We focus on nodding, which is critical in an attentive listening system, and propose a model that predicts both its timing and type in real time. The proposed model builds on the voice activity projection (VAP) model, which predicts voice activity from both listener and speaker audio. We extend it to prediction of various types of nodding in a continuous and real-time manner unlike conventional models. In addition, the proposed model incorporates multi-task learning with verbal backchannel prediction and pretraining on general dialogue data. In the timing and type prediction task, the effectiveness of multi-task learning was significantly demonstrated. We confirmed that reducing the processing rate enables real-time operation without a substantial drop in accuracy, and integrated the model into an avatar attentive listening system. Subjective evaluations showed that it outperformed the conventional method, which always does nodding in sync with verbal backchannel. The code and trained models are available at https://github.com/MaAI-Kyoto/MaAI.
在人机对话中,非言语信息如点头和面部表情与言语信息一样重要,口语对话系统也被期望能够表达这样的非言语行为。我们专注于点头,它在倾听系统中起着关键作用,并提出一种能够实时预测其时机和类型的模型。所提出的模型基于语音活动投影(VAP)模型,该模型可以从听众和说话者的音频来预测语音活动。我们将其扩展到预测连续实时点头的各种类型,不同于传统模型。此外,所提出的模型结合了多任务学习与言语反馈预测,并在一般对话数据上进行预训练。在预测时机和类型任务中,多任务学习的有效性得到了显著证明。我们证实了降低处理速率可以在不显著降低准确性的情况下实现实时操作,并将该模型集成到虚拟角色专注倾听系统中。主观评估表明,它优于传统方法,后者总是与言语反馈同步点头。相关代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/MaAI-Kyoto/MaAI中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 27th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI ‘25), Long paper
Summary
本文关注人类对话中的非言语信息,特别是点头行为在倾听系统中的作用。提出了一种实时预测点头时机和类型的模型,该模型基于语音活动投影(VAP)模型,能够预测听者和说话者的语音活动,并扩展至连续实时预测多种点头行为。通过多任务学习和语音回馈预测,以及一般对话数据的预训练,该模型在预测时效性和类型方面表现出显著效果。模型已集成至虚拟形象倾听系统中,主观评估显示其性能优于传统方法。
Key Takeaways
- 非言语信息如点头和面部表情在对话中至关重要,因此,对话系统也需要表达这些非言语行为。
- 提出了一种基于语音活动投影(VAP)模型的实时点头预测模型。
- 模型能够连续实时预测多种点头行为。
- 通过多任务学习和语音回馈预测,增强了模型的预测能力。
- 模型经过一般对话数据的预训练,提高了准确性。
- 降低处理速率可实现模型的实时操作,且不影响准确性。
点此查看论文截图

Listening to the Unspoken: Exploring “365” Aspects of Multimodal Interview Performance Assessment
Authors:Jia Li, Yang Wang, Wenhao Qian, Zhenzhen Hu, Richang Hong, Meng Wang
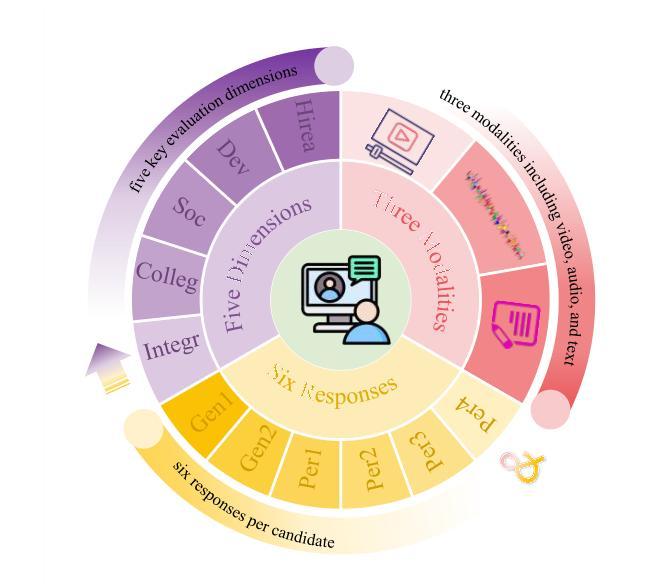
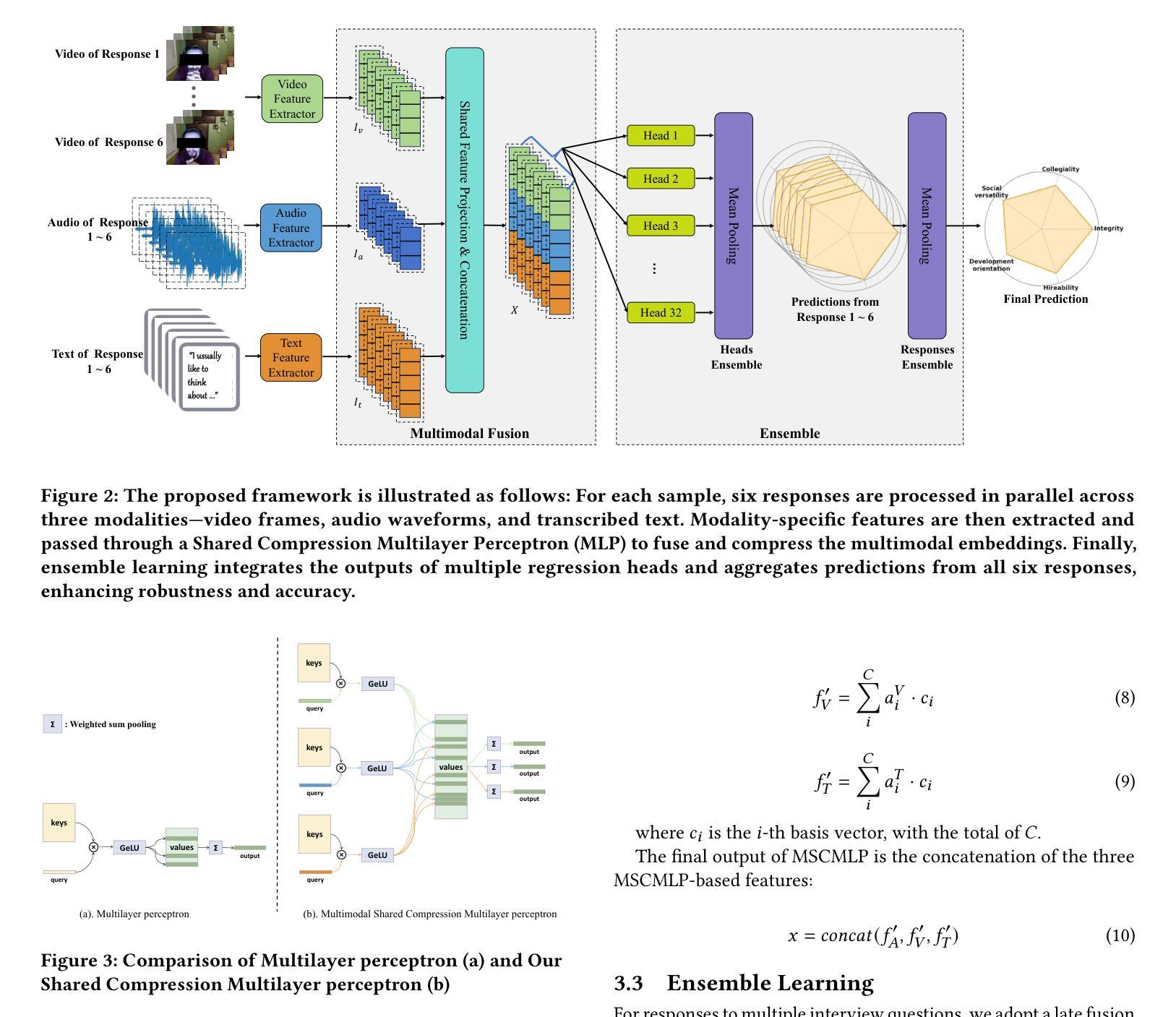
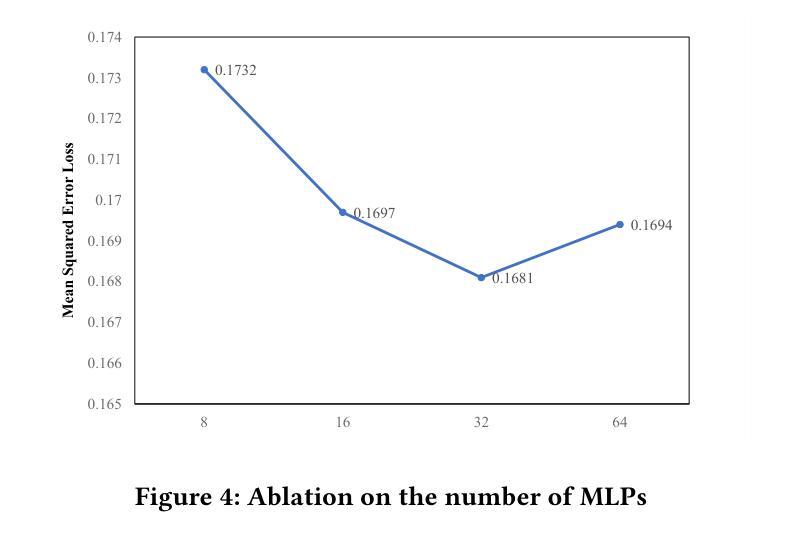
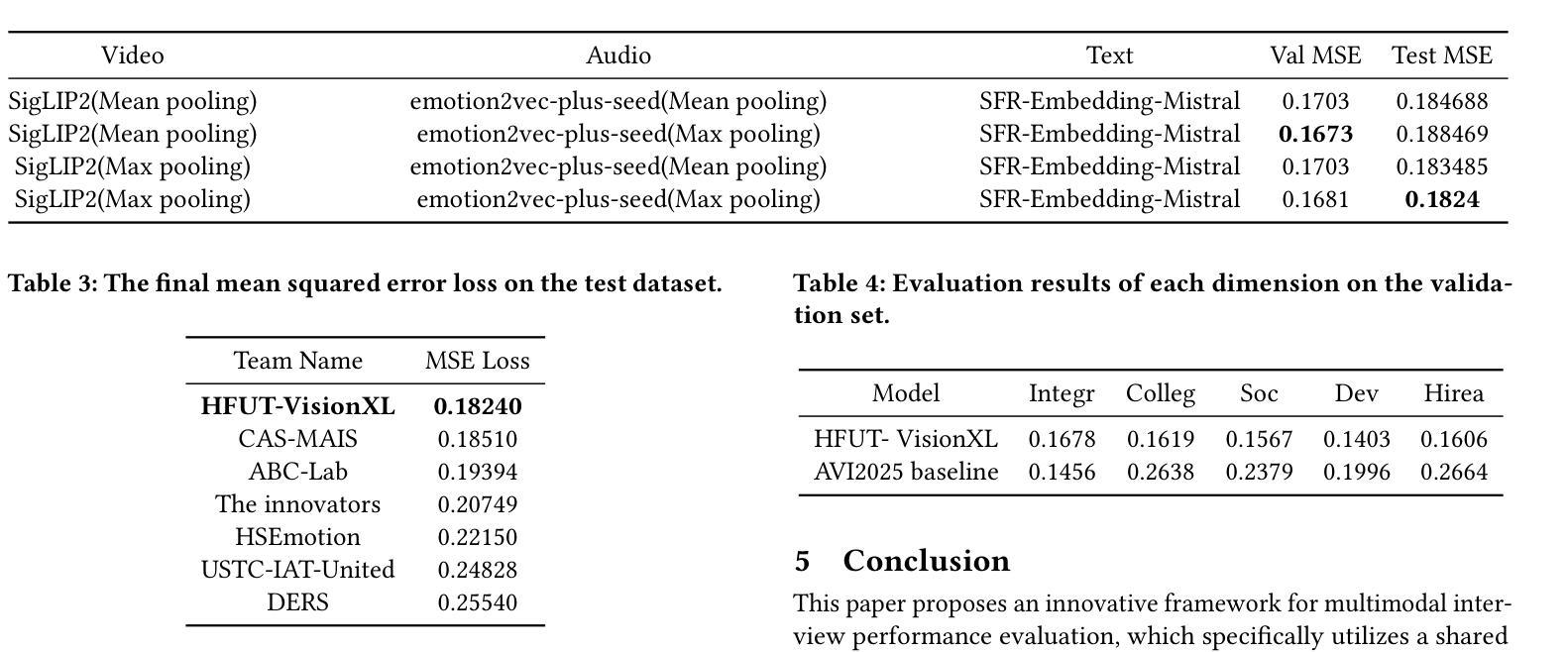
Interview performance assessment is essential for determining candidates’ suitability for professional positions. To ensure holistic and fair evaluations, we propose a novel and comprehensive framework that explores ``365’’ aspects of interview performance by integrating \textit{three} modalities (video, audio, and text), \textit{six} responses per candidate, and \textit{five} key evaluation dimensions. The framework employs modality-specific feature extractors to encode heterogeneous data streams and subsequently fused via a Shared Compression Multilayer Perceptron. This module compresses multimodal embeddings into a unified latent space, facilitating efficient feature interaction. To enhance prediction robustness, we incorporate a two-level ensemble learning strategy: (1) independent regression heads predict scores for each response, and (2) predictions are aggregated across responses using a mean-pooling mechanism to produce final scores for the five target dimensions. By listening to the unspoken, our approach captures both explicit and implicit cues from multimodal data, enabling comprehensive and unbiased assessments. Achieving a multi-dimensional average MSE of 0.1824, our framework secured first place in the AVI Challenge 2025, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness in advancing automated and multimodal interview performance assessment. The full implementation is available at https://github.com/MSA-LMC/365Aspects.
面试绩效评估对于确定候选人是否适合专业职位至关重要。为了确保全面公平的评估,我们提出了一种新型的综合框架,通过整合视频、音频和文本三种模式,候选人的六种回应,以及五个关键评估维度,来探索面试表现的“365”方面。该框架使用特定于模式的特征提取器来编码异质数据流,然后通过共享压缩多层感知器进行融合。此模块将多模式嵌入压缩到统一的潜在空间,促进特征的有效交互。为了提高预测的稳健性,我们采用了两级集成学习策略:(1)独立回归头预测每个响应的分数;(2)使用平均池化机制对响应的预测进行汇总,以产生五个目标维度的最终分数。通过倾听“未说出口的话”,我们的方法能够从多模式数据中捕获明确和隐含的线索,从而实现全面客观的评估。我们的框架在2025年AVI挑战赛中取得第一名,实现了多维度平均MSE为0.1824,证明了其在推进自动化和多模式面试绩效评估中的有效性和稳健性。完整实现可访问https://github.com/MSA-LMC/365Aspects。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, ACM MM 2025. github:https://github.com/MSA-LMC/365Aspects
Summary
本文主要提出了一个全新的综合框架,用于通过视频、音频和文本三种模式,对候选人在面试中的表现进行全方位的评估。该框架融合了多种技术,包括特定模态特征提取器、共享压缩多层感知器等,旨在从六个回应和五个关键评价维度全面评价候选人的面试表现。该框架在AVI Challenge 2025中获得了第一名,证明了其有效性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个全新的综合框架,用于评估面试表现。
- 该框架融合了视频、音频和文本三种模式的数据。
- 框架包括特定模态特征提取器、共享压缩多层感知器等关键组件。
- 该框架考虑了六个回应和五个关键评价维度。
- 采用了两级集成学习策略,以提高预测稳健性。
- 该框架在AVI Challenge 2025中获得了第一名。
点此查看论文截图