⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
Raw Data Matters: Enhancing Prompt Tuning by Internal Augmentation on Vision-Language Models
Authors:Haoyang Li, Liang Wang, Chao Wang, Siyu Zhou, Jing Jiang, Yan Peng, Guodong Long
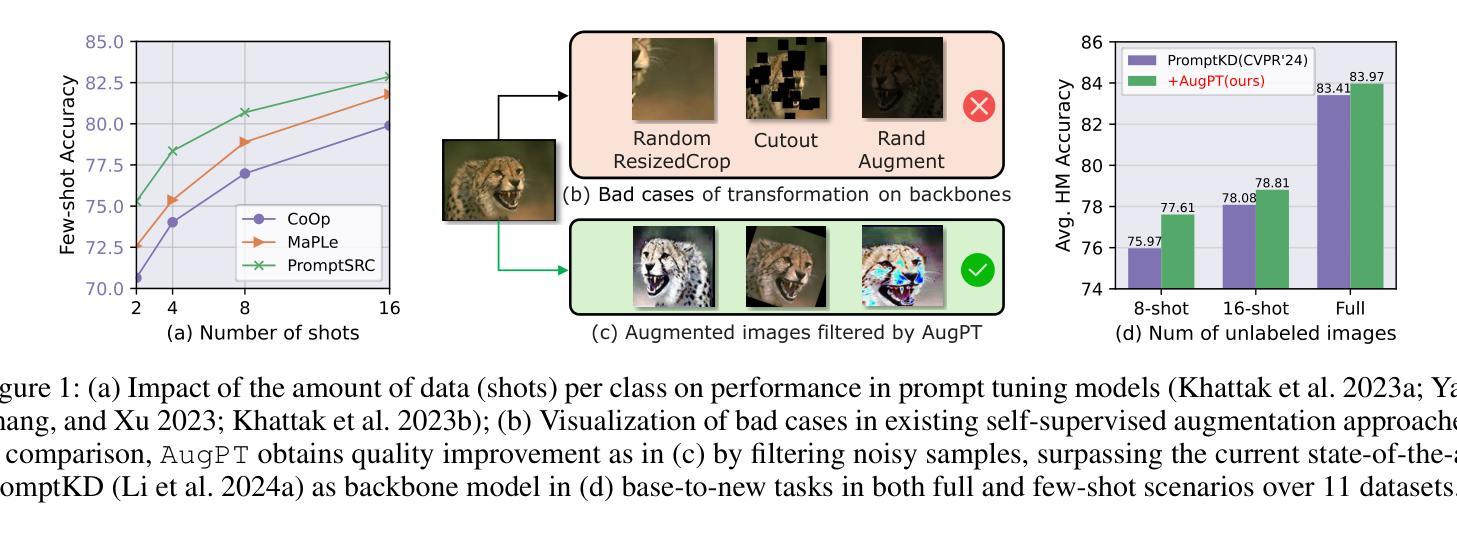
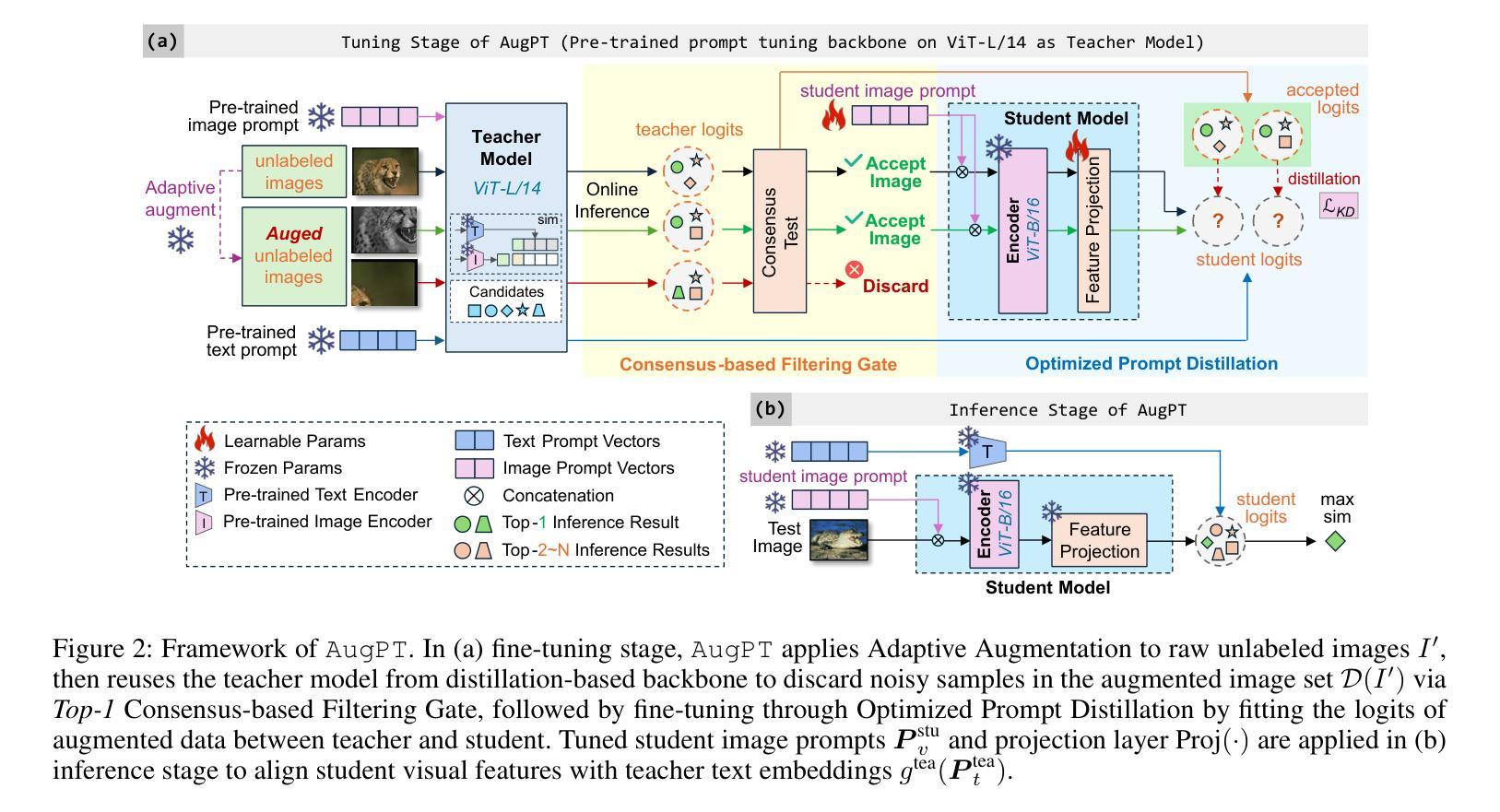
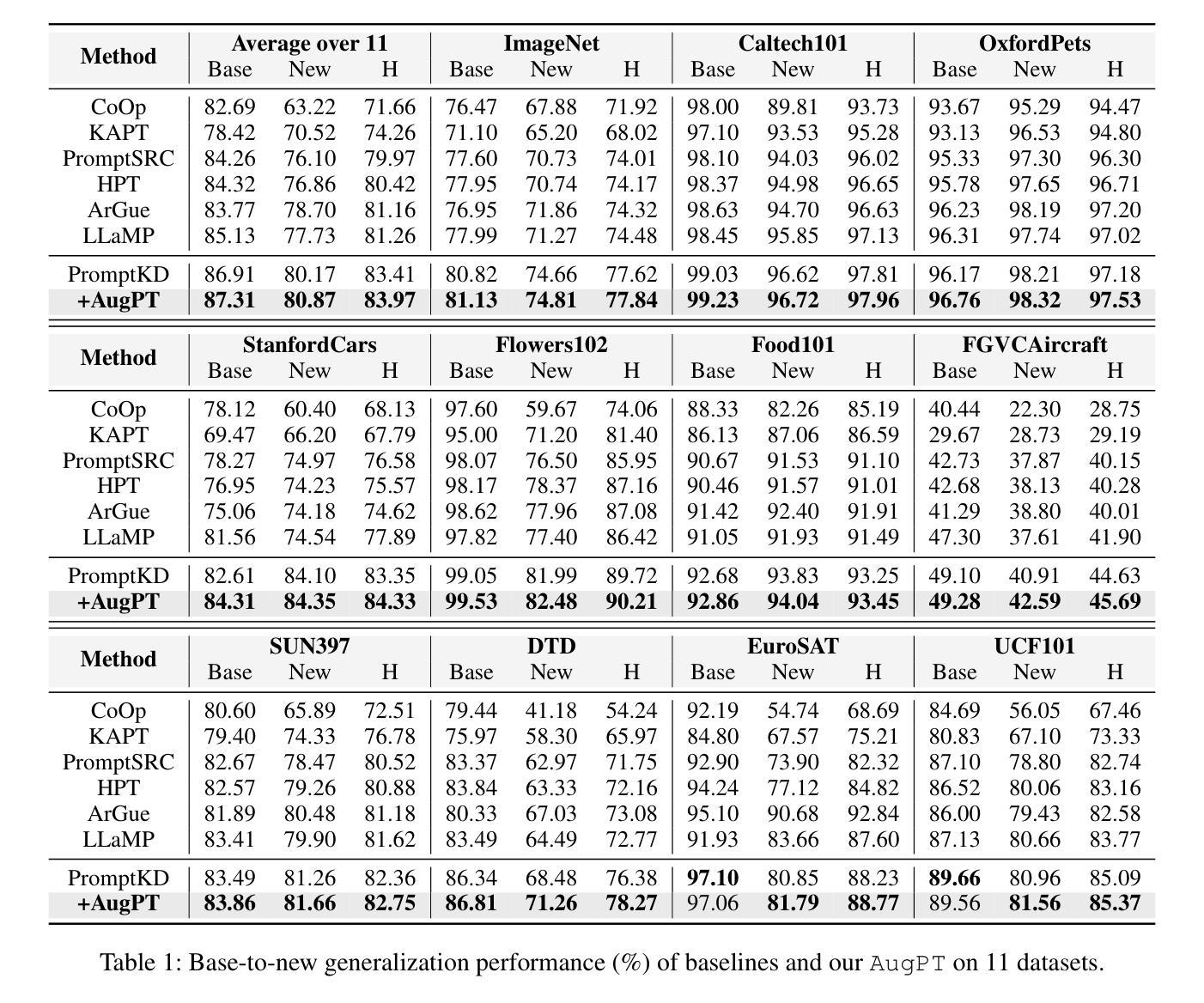
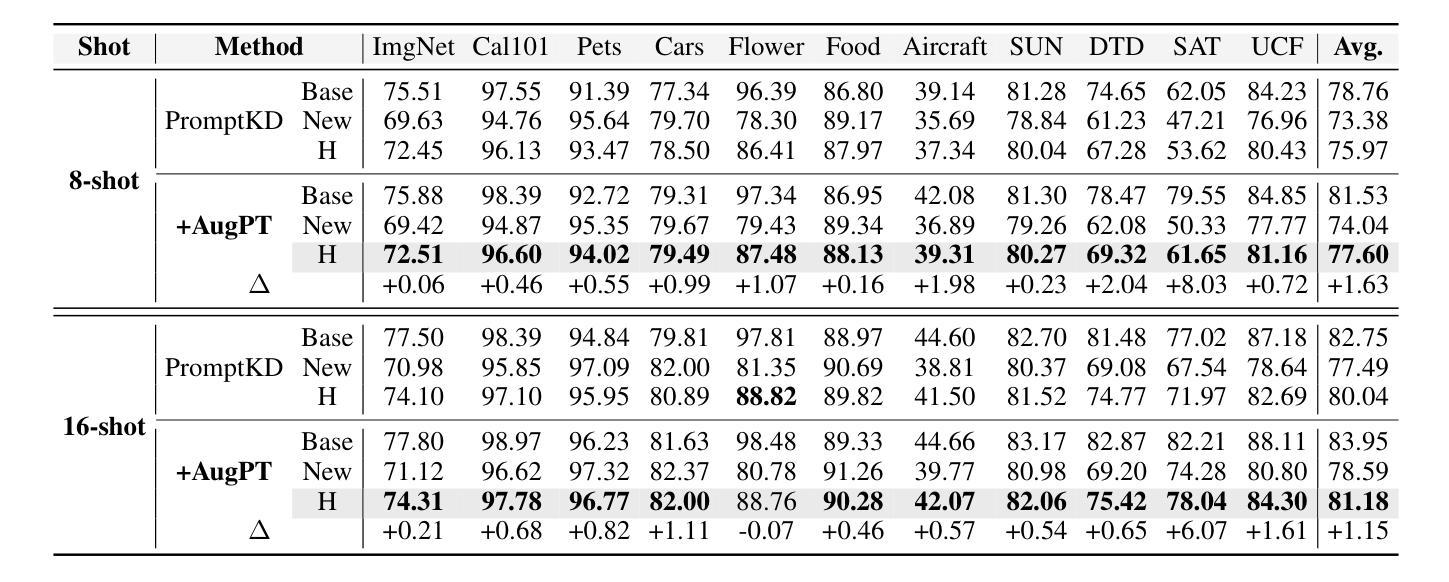
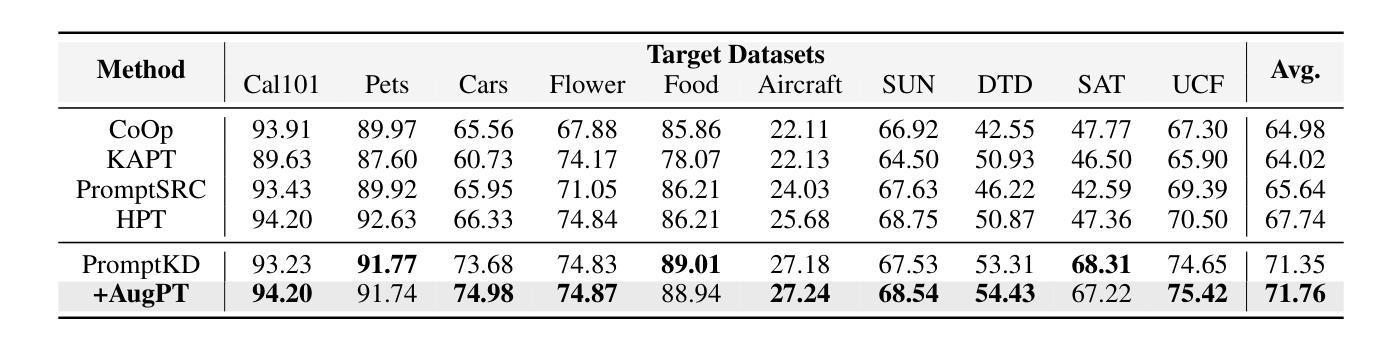
For CLIP-based prompt tuning, introducing more data as additional knowledge for enhancing fine-tuning process is proved to be an effective approach. Existing data amplification strategies for prompt tuning typically rely on external knowledge (e.g., large language models or pre-structured knowledge bases), resulting in higher costs for data collection and processing, while generally ignoring further utilization of features in image modality. To address this, we propose Augmentation-driven Prompt Tuning (AugPT), a self-contained distillation-based prompt tuning approach using only internal augmentation on raw dataset to better exploit known features. Specifically, AugPT employs self-supervised augmentation on unlabeled images in the training set, and introduces a novel gating mechanism based on consensus test, reusing the pre-trained prompt tuning backbone model to spontaneously filter noisy samples, further enhancing the quality of augmented views. Extensive experiments validate that AugPT simultaneously enhances model performance and generalization capability without using appended external knowledge. The code of AugPT is available at: https://github.com/JREion/AugPT .
对于基于CLIP的提示调整(prompt tuning),引入更多数据作为额外知识以增强微调过程已被证明是一种有效的方法。现有的数据增强策略通常依赖于外部知识(例如大型语言模型或预结构化知识库),导致数据收集和处理成本较高,同时忽略了进一步利用图像模态中的特征。针对这一问题,我们提出了基于自增强的提示调整(AugPT)方法。这是一种基于自我蒸馏的提示调整方法,仅使用原始数据集的内部增强来更好地利用已知特征。具体来说,AugPT对训练集中的无标签图像进行自监督增强,并引入了一种基于共识测试的新型门控机制,利用预训练的提示调整骨干模型自动过滤噪声样本,进一步提高增强视图的品质。大量实验验证,AugPT在不使用附加外部知识的情况下,同时提高了模型的性能和泛化能力。AugPT的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/JREion/AugPT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 6 figures, 15 tables
Summary
文本提出了一种基于CLIP的新方法AugPT,该方法使用仅内部增强的原始数据集进行微调,利用未标记图像中的自监督增强和基于共识测试的新门控机制,以提高模型的性能和泛化能力,无需使用额外的外部知识。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP背景下的提示调整方法中,引入更多数据作为额外的知识以改进微调过程是一种有效方法。
- 现有的数据增强策略通常依赖于外部知识(如大型语言模型或预结构化知识库),导致数据采集和处理成本较高,同时忽略了图像模态特征的进一步利用。
- AugPT是一种基于蒸馏的提示调整方法,仅使用原始数据集的内部增强来更好地利用已知特征。
- AugPT在训练集的非标记图像上采用自监督增强。
- AugPT引入了一种基于共识测试的新门控机制,利用预训练的提示调整骨干模型自动过滤噪声样本,进一步提高增强视图的品质。
- 实验证明,AugPT在不使用外部知识的情况下,能同时提高模型的性能和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

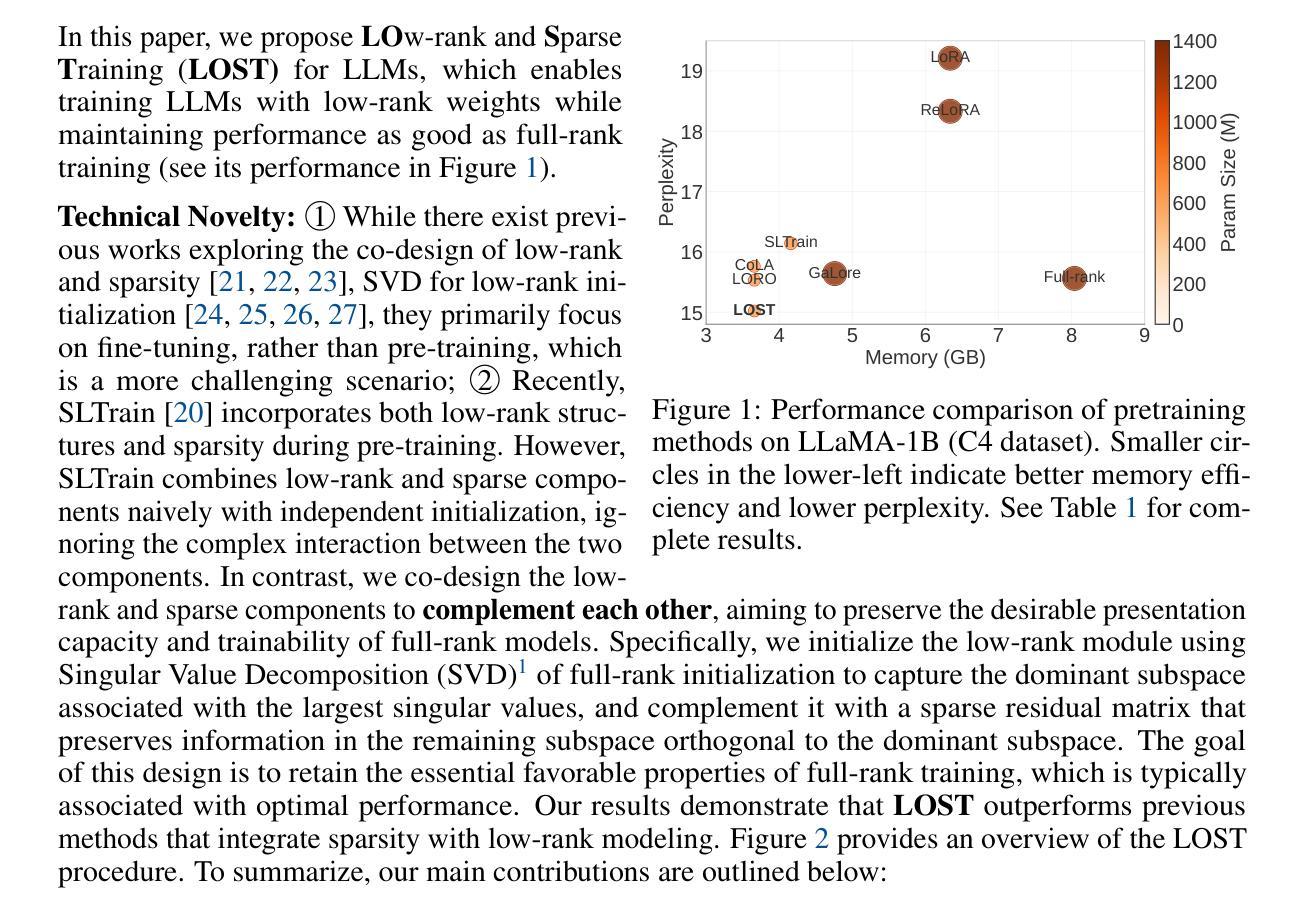
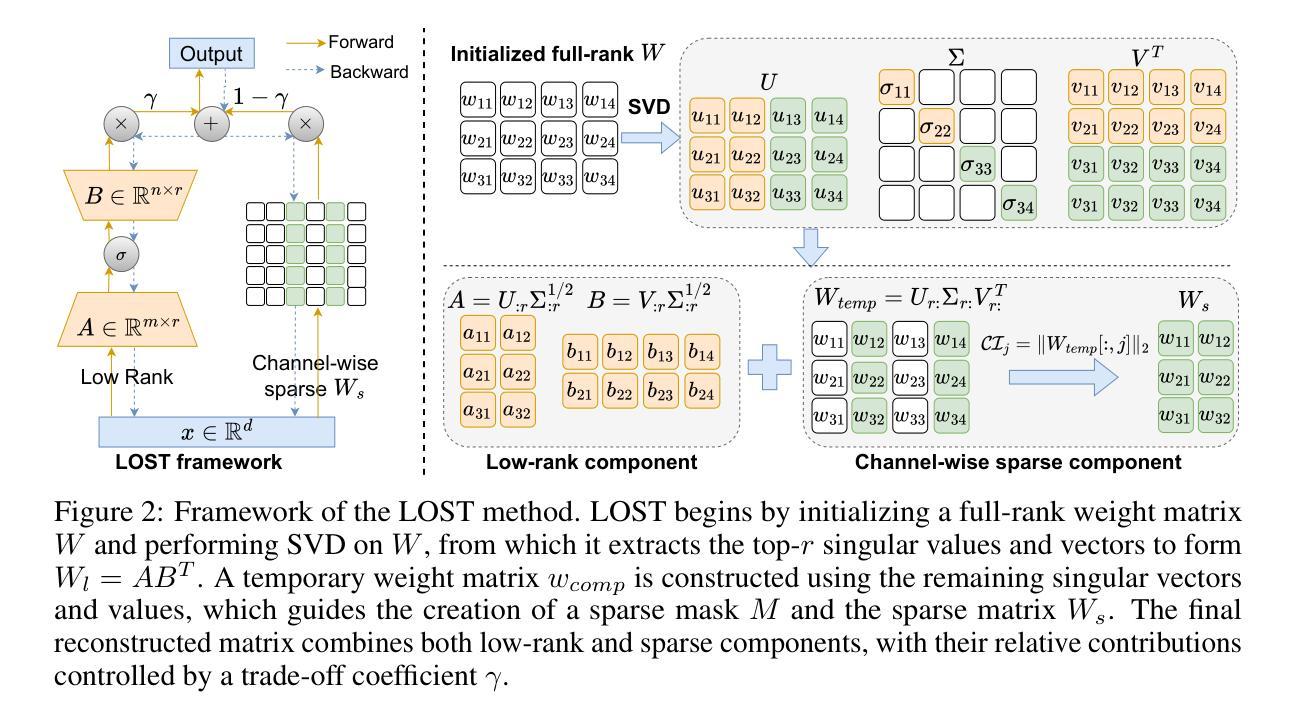
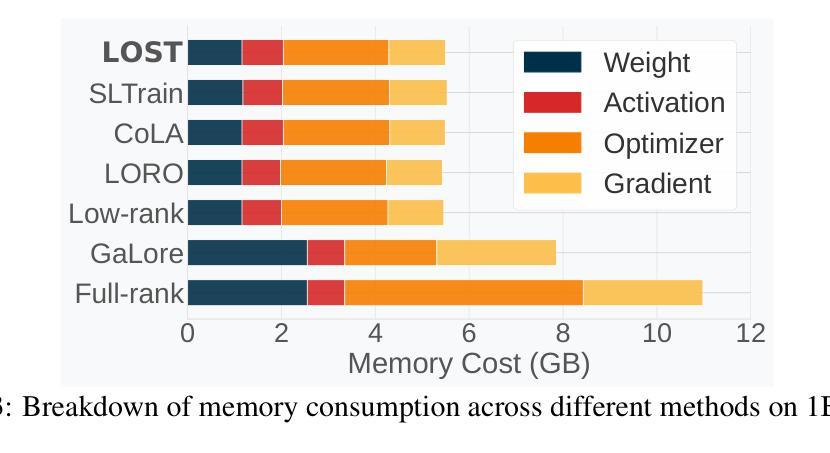
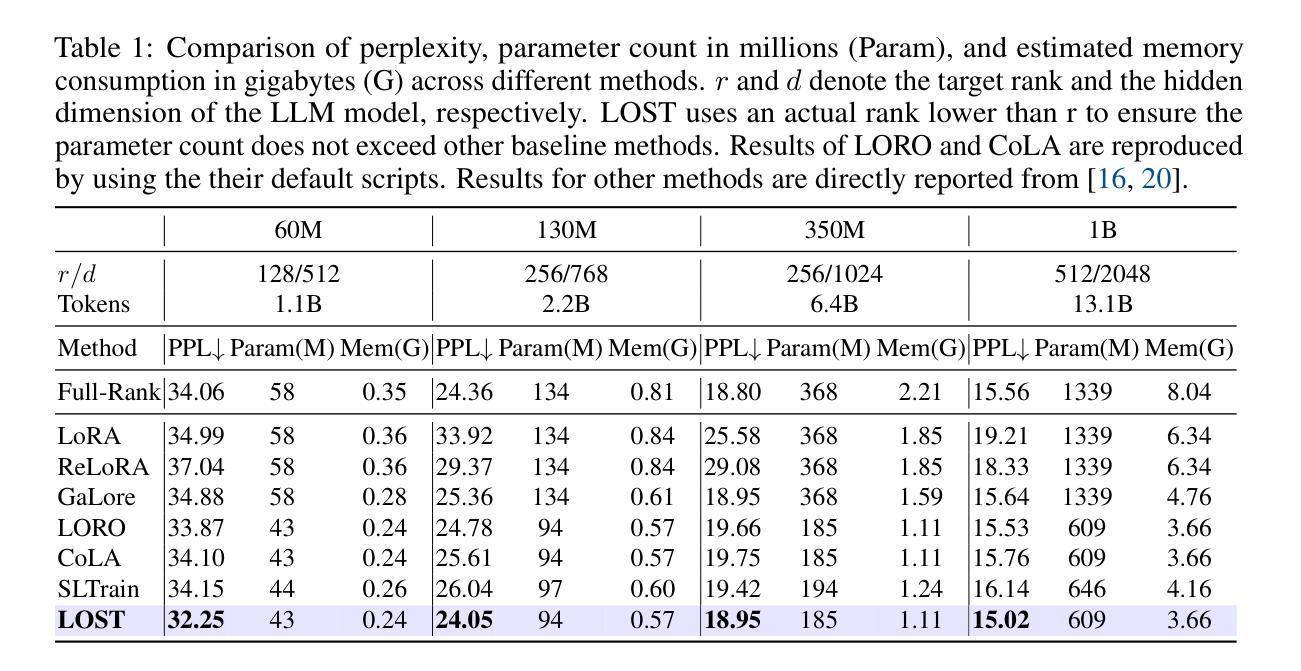
LOST: Low-rank and Sparse Pre-training for Large Language Models
Authors:Jiaxi Li, Lu Yin, Li Shen, Jinjin Xu, Liwu Xu, Tianjin Huang, Wenwu Wang, Shiwei Liu, Xilu Wang
While large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across a wide range of tasks, their massive scale incurs prohibitive computational and memory costs for pre-training from scratch. Recent studies have investigated the use of low-rank parameterization as a means of reducing model size and training cost. In this context, sparsity is often employed as a complementary technique to recover important information lost in low-rank compression by capturing salient features in the residual space. However, existing approaches typically combine low-rank and sparse components in a simplistic or ad hoc manner, often resulting in undesirable performance degradation compared to full-rank training. In this paper, we propose \textbf{LO}w-rank and \textbf{S}parse pre-\textbf{T}raining (\textbf{LOST}) for LLMs, a novel method that ingeniously integrates low-rank and sparse structures to enable effective training of LLMs from scratch under strict efficiency constraints. LOST applies singular value decomposition to weight matrices, preserving the dominant low-rank components, while allocating the remaining singular values to construct channel-wise sparse components to complement the expressiveness of low-rank training. We evaluate LOST on LLM pretraining ranging from 60M to 7B parameters. Our experiments show that LOST achieves competitive or superior performance compared to full-rank models, while significantly reducing both memory and compute overhead. Moreover, Code is available at \href{https://github.com/JiaxiLi1/LOST-Low-rank-and-Sparse-Training-for-Large-Language-Models}{LOST Repo}
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务中取得了显著的性能,但它们的大规模导致了从头开始预训练的计算和内存成本高昂。最近的研究探讨了使用低秩参数化作为减小模型大小和降低训练成本的方法。在此上下文中,稀疏性通常被用作一种辅助技术,以恢复在低秩压缩中丢失的重要信息,通过捕获残差空间中的显著特征来实现这一点。然而,现有的方法通常以简单或即兴的方式将低秩和稀疏组件组合在一起,与全秩训练相比,通常会导致性能下降。在本文中,我们为LLM提出了LOW秩和稀疏预训练(LOST)的新方法,该方法巧妙地结合了低秩和稀疏结构,能够在严格的效率约束下有效地从头开始训练LLM。LOST通过奇异值分解应用于权重矩阵,保留主要低秩成分,同时将剩余的奇异值分配给通道稀疏成分,以补充低秩训练的表达性。我们对参数范围从60M到7B的LLM预训练进行了LOST评估。实验表明,LOST在性能方面达到了与全秩模型相当或更优的水平,同时显著降低了内存和计算开销。此外,代码可在LOST仓库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在广泛的任务中取得了显著的性能,但其庞大的规模带来了高昂的计算和内存成本。近期研究表明,使用低秩参数化方法可以减少模型大小和训练成本。然而,简单结合低秩和稀疏成分会导致性能下降。本文提出一种新颖的低秩和稀疏预训练方法(LOST),该方法巧妙地将低秩和稀疏结构相结合,在严格的效率约束下实现了LLM的有效训练。通过对权重矩阵进行奇异值分解,LOST保留了主要低秩成分,并将剩余奇异值分配给通道稀疏成分,以补充低秩训练的表达能力。实验表明,LOST在LLM预训练中表现优异,同时显著降低了内存和计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLM)面临高计算成本和内存需求的问题。
- 低秩参数化方法被研究用于减少模型大小和训练成本。
- 现有方法简单结合低秩和稀疏成分,导致性能下降。
- 提出的LOW-rank和Sparse pre-Training(LOST)方法结合了低秩和稀疏结构。
- LOST通过奇异值分解保留主要低秩成分,并分配剩余奇异值形成通道稀疏成分。
- 实验表明,LOST在LLM预训练中表现优异,且显著降低内存和计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

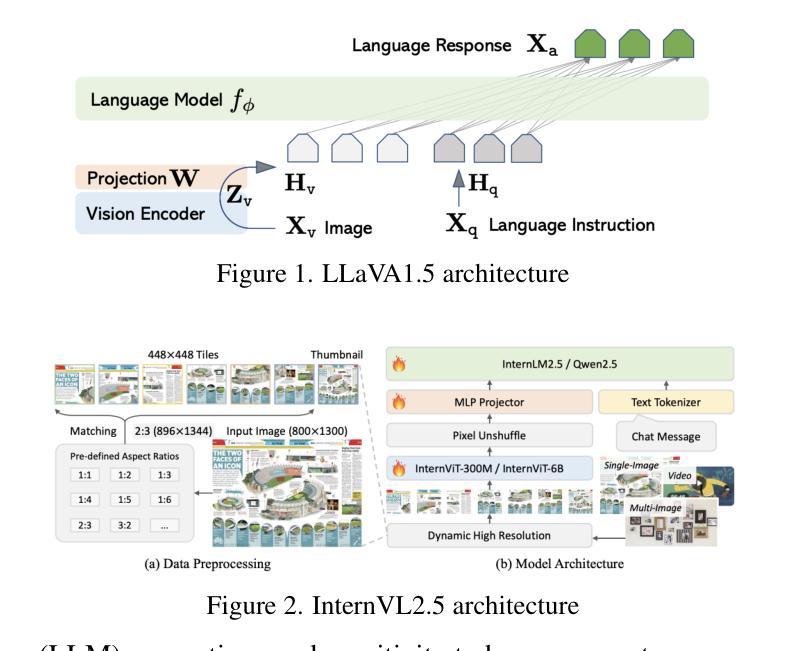
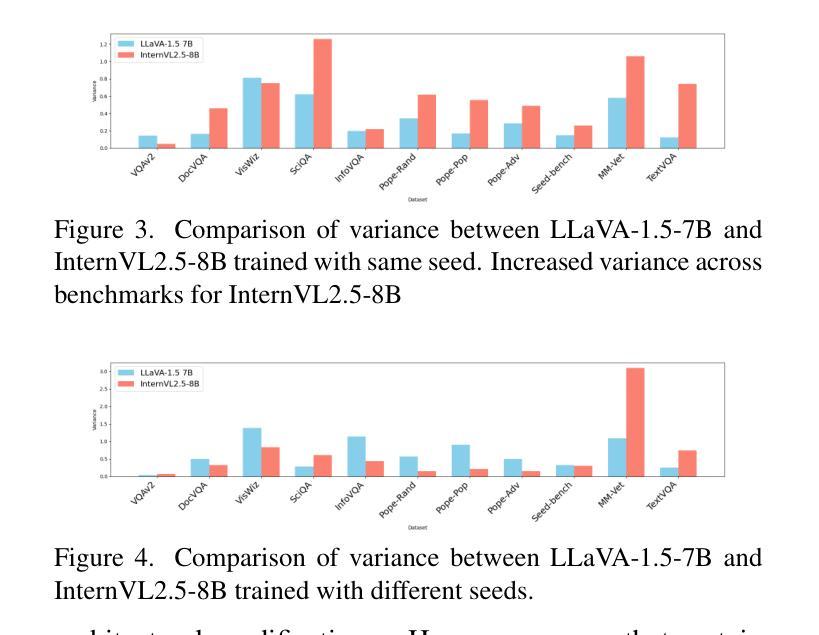
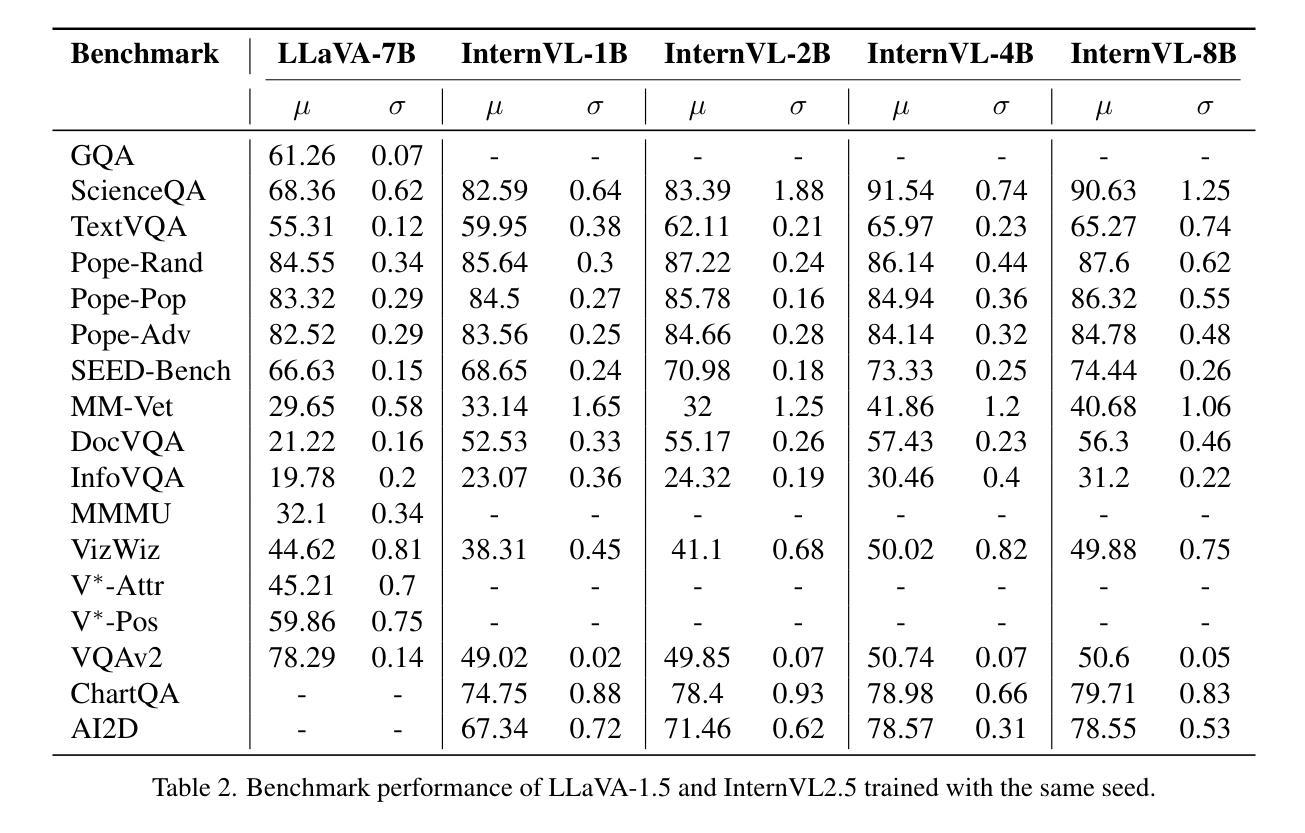
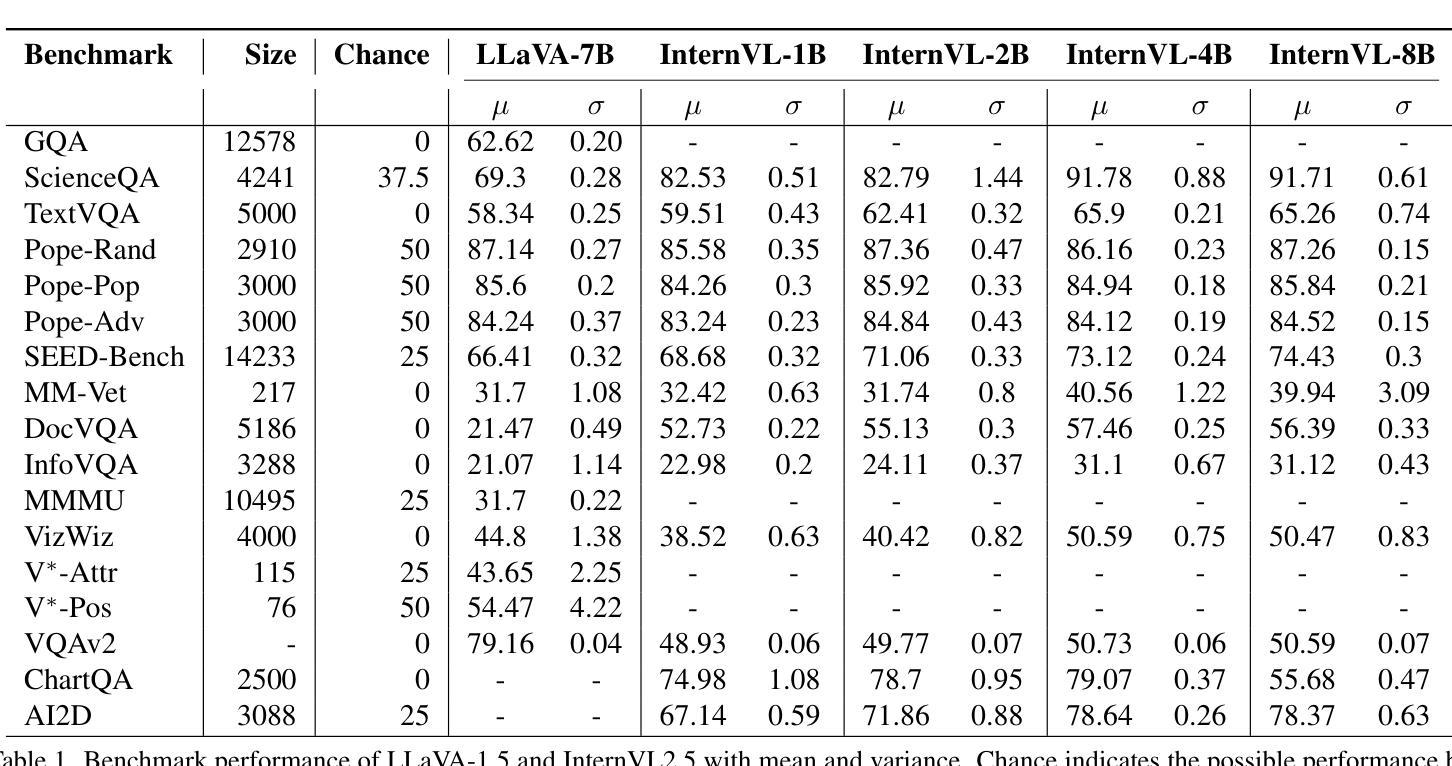
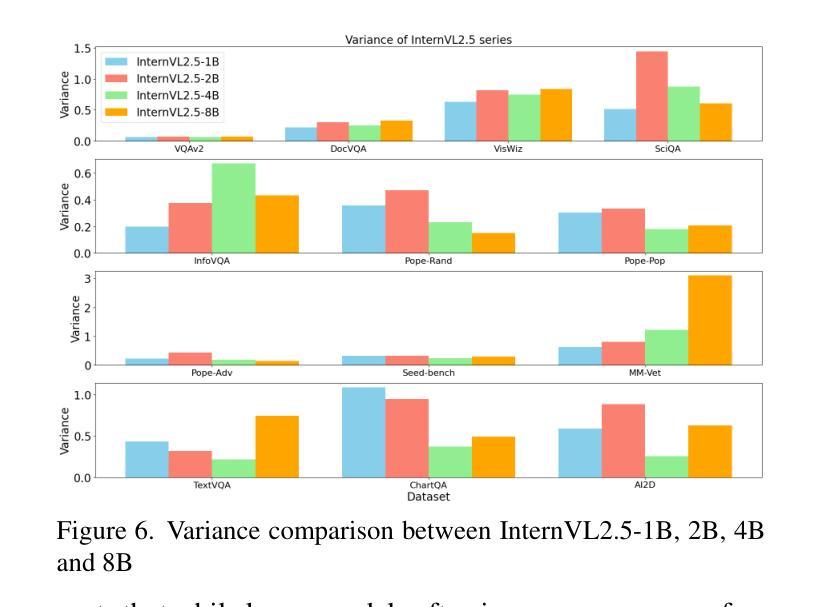
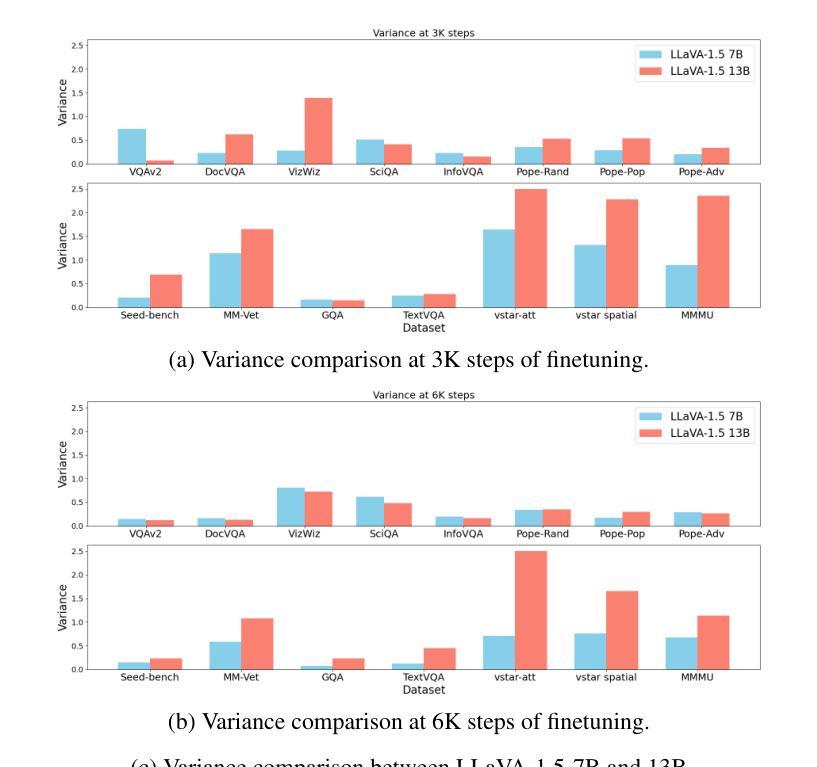
Evaluating Variance in Visual Question Answering Benchmarks
Authors:Nikitha SR
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for visual question answering (VQA), enabling reasoning and contextual understanding across visual and textual modalities. Despite their advancements, the evaluation of MLLMs on VQA benchmarks often relies on point estimates, overlooking the significant variance in performance caused by factors such as stochastic model outputs, training seed sensitivity, and hyperparameter configurations. This paper critically examines these issues by analyzing variance across 14 widely used VQA benchmarks, covering diverse tasks such as visual reasoning, text understanding, and commonsense reasoning. We systematically study the impact of training seed, framework non-determinism, model scale, and extended instruction finetuning on performance variability. Additionally, we explore Cloze-style evaluation as an alternate assessment strategy, studying its effectiveness in reducing stochasticity and improving reliability across benchmarks. Our findings highlight the limitations of current evaluation practices and advocate for variance-aware methodologies to foster more robust and reliable development of MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为视觉问答(VQA)的强大工具已经出现,能够在视觉和文本模式之间进行推理和上下文理解。尽管取得了进展,但在VQA基准测试中对MLLMs的评估往往依赖于点估计,从而忽视了由于随机模型输出、训练种子敏感性和超参数配置等因素导致的性能显著差异。本文通过分析14个广泛使用的VQA基准测试的方差,对这些问题进行了深入研究,涵盖了视觉推理、文本理解和常识推理等多样化任务。我们系统地研究了训练种子、框架非确定性、模型规模以及扩展指令微调对性能变化的影响。此外,我们还探索了以填空式评估作为替代评估策略,研究了其在减少随机性和提高跨基准测试可靠性方面的有效性。我们的研究结果表明了当前评估方法的局限性,并提倡采用考虑变异性的方法来促进MLLMs更稳健和可靠的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCV 2025 Workshop on What’s Next in Multimodal Foundational Models
Summary
MLLMs在视觉问答(VQA)方面的应用展现出强大的跨视觉和文本模态的推理和上下文理解能力。然而,现有评估方法主要依赖点估计,忽略了模型输出随机性、训练种子敏感性和超参数配置等因素导致的性能显著变化。本文通过分析在14个广泛使用的VQA基准测试上的方差,系统研究了训练种子、框架非确定性、模型规模和扩展指令微调对性能变化的影响,并探讨了闭式评估策略的有效性。研究发现当前评估方法的局限性,并主张采用考虑方差的评估方法来促进更稳健和可靠的LLM发展。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在视觉问答(VQA)中展现出强大的跨模态能力。
- 当前评估方法主要依赖点估计,忽略了模型性能的重大变化。
- 训练种子、框架非确定性、模型规模和微调影响性能变化。
- 基准测试上的方差分析揭示了评估方法的局限性。
- 考虑方差的评估方法对于促进稳健和可靠的LLM发展至关重要。
- 提出使用闭式评估策略作为替代评估方法,以减少随机性并改善基准测试的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

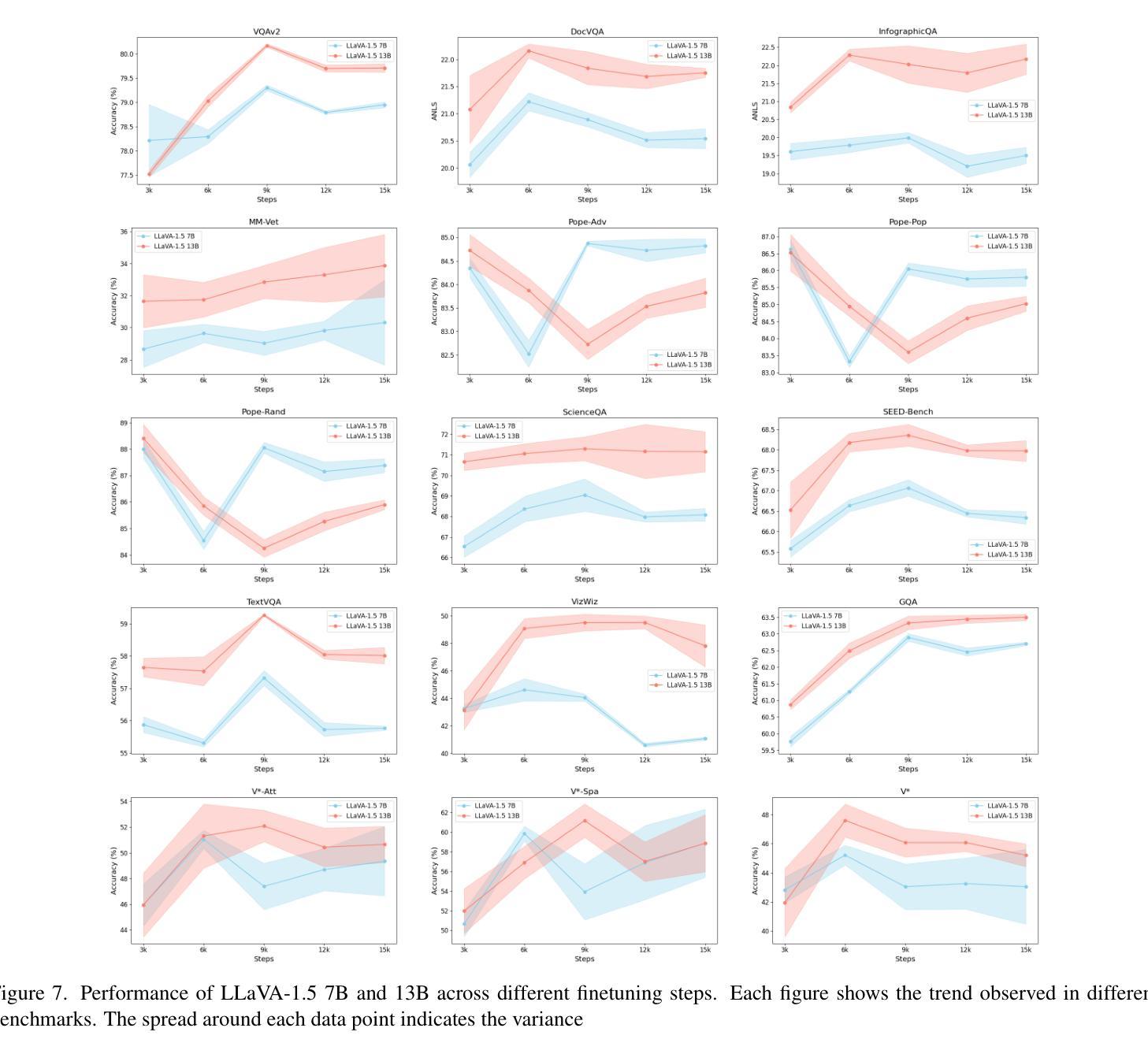
Test Set Quality in Multilingual LLM Evaluation
Authors:Kranti Chalamalasetti, Gabriel Bernier-Colborne, Yvan Gauthier, Sowmya Vajjala
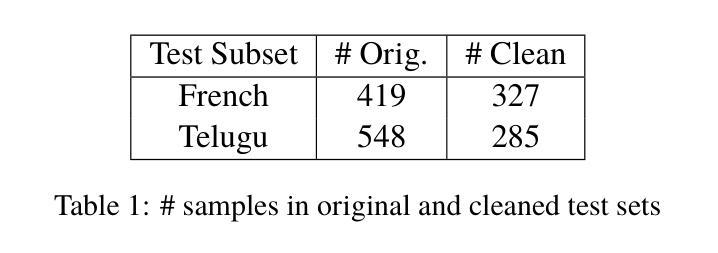
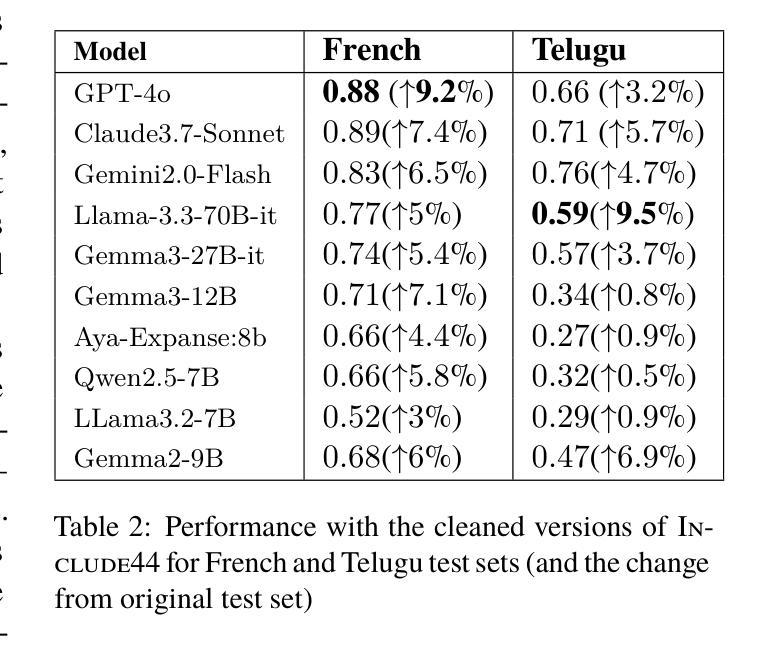
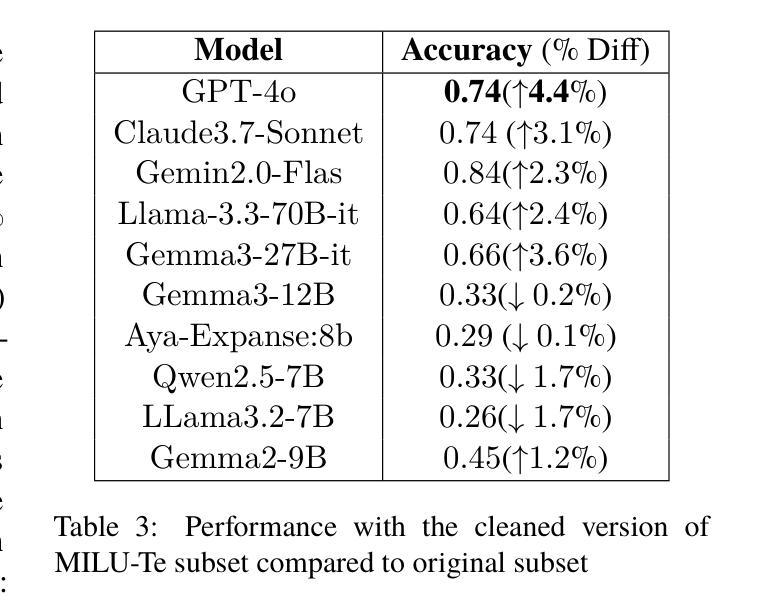
Several multilingual benchmark datasets have been developed in a semi-automatic manner in the recent past to measure progress and understand the state-of-the-art in the multilingual capabilities of Large Language Models. However, there is not a lot of attention paid to the quality of the datasets themselves, despite the existence of previous work in identifying errors in even fully human-annotated test sets. In this paper, we manually analyze recent multilingual evaluation sets in two languages - French and Telugu, identifying several errors in the process. We compare the performance difference across several LLMs with the original and revised versions of the datasets and identify large differences (almost 10% in some cases) in both languages). Based on these results, we argue that test sets should not be considered immutable and should be revisited, checked for correctness, and potentially versioned. We end with some recommendations for both the dataset creators as well as consumers on addressing the dataset quality issues.
近年来,为了衡量和了解多语言大型语言模型的最新进展和状态,已经以半自动的方式开发了几个多语言基准数据集。然而,尽管有先前的工作已经识别出即使是完全人工注释的测试集中也存在错误,但人们对数据集本身的品质并没有给予足够的重视。在本文中,我们手动分析了最近的两门语言——法语和泰卢固语的多语言评估集,并在过程中发现了多个错误。我们将多个大型语言模型在原始和修订后的数据集上的性能差异进行了比较,发现在两种语言中都存在巨大差异(在某些情况下几乎达到10%)。基于这些结果,我们认为测试集不应被视为永恒不变的,而应该进行复查以检查其准确性并可能对其进行版本控制。最后,我们对数据集创建者和使用者提出一些解决数据集质量问题的建议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 1st Workshop on Multilingual Data Quality Signals, COLM 2025, Short paper. 10 pages in total
Summary
近期开发的多语种基准数据集以半自动方式衡量大语言模型的进步并了解其最新技术状态。然而,现有的测试集即使由完全人工注释,也仍然存在错误。本文通过手动分析两种语言的最近多语种评估集(法语和泰卢固语),发现了数据集中的一些错误。在对比了原始数据集与修订数据集的不同性能差异后,本文强调了测试集并非一成不变,应该对其进行重新评估,并重视质量问题的解决,对此本文提供了对于数据集的创建者和消费者们的解决建议。同时也说明了需要进行质量控制并可能需要使用不同版本的管理办法,以保障测试集的可靠性。这为LLM模型的训练和评估提供了一个全新的视角和深入的思考。针对现有的评测数据质量问题进行了有力的反驳与深入探讨,并且从两个具体的实例出发进行了实证阐述。这既有助于研究者的参考和借鉴,也促进了自然语言处理领域研究的深入发展。为自然语言处理领域的科研提供了有价值的启示和解决方案。同时,也提醒了人们要重视数据质量的问题,确保数据集的准确性和可靠性。对于未来的研究而言,本文具有重要的参考价值和实践指导意义。同时强调了数据集质量的重要性,并提出了改进建议。对于未来多语言模型的发展和应用具有积极的推动作用。同时也指出了未来研究的可能方向和挑战。本文强调了数据集质量的重要性以及其对该领域未来研究的潜在影响。Key Takeaways
- 多语种基准数据集用以衡量大语言模型的进步。然而,这些数据集的质量问题被忽视。
- 手动分析发现多语种评估集存在错误。
- 测试集并非一成不变,需要定期检查和修正错误。
- 测试集的质量问题对LLM性能评估产生显著影响(在某些情况下差异达10%)。
点此查看论文截图

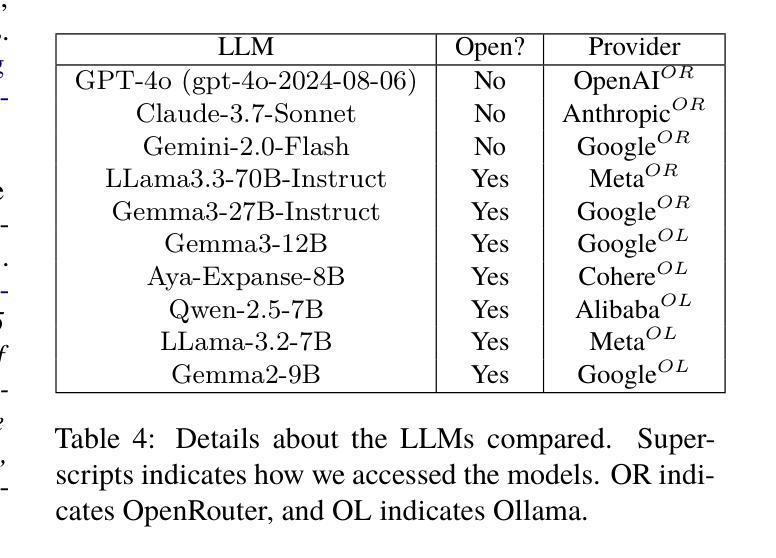
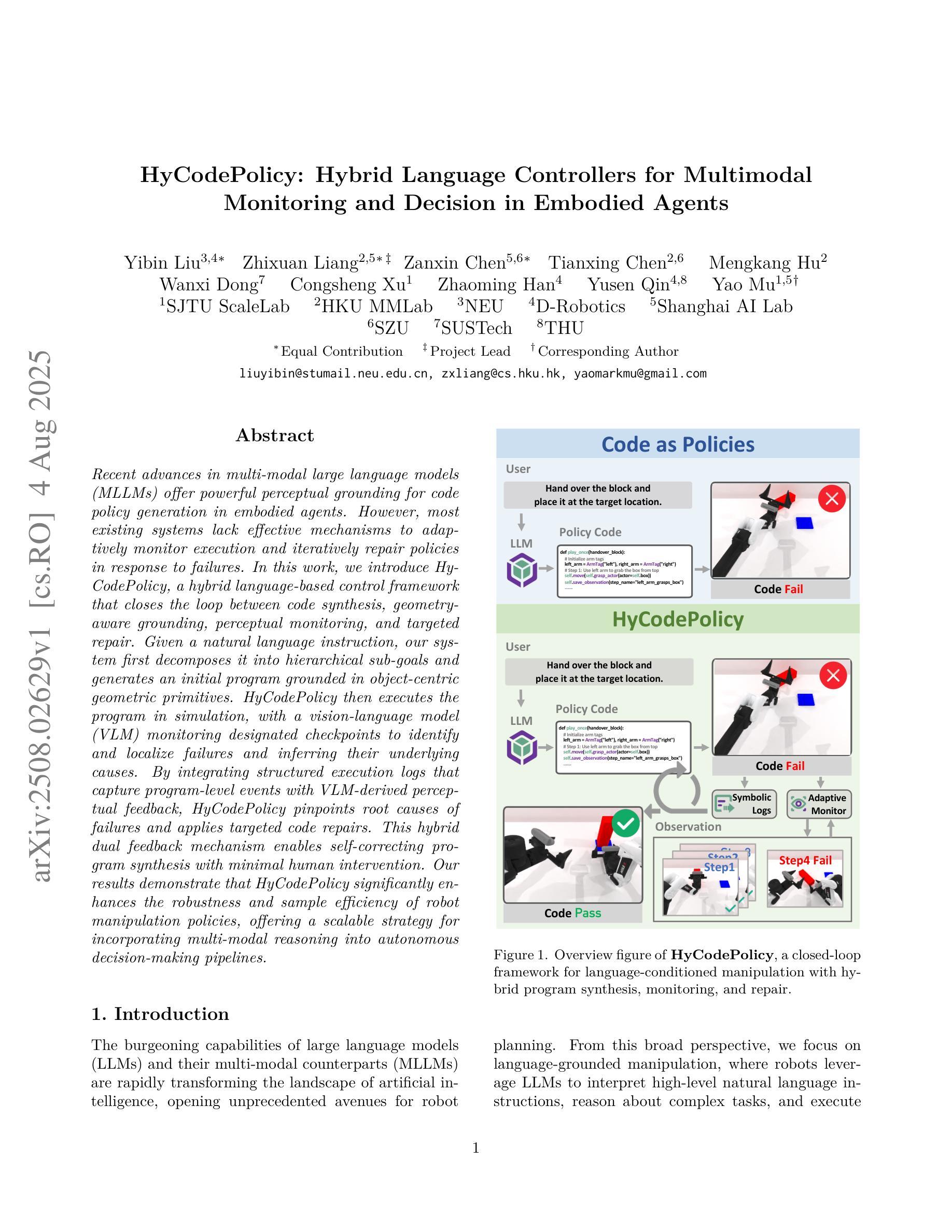
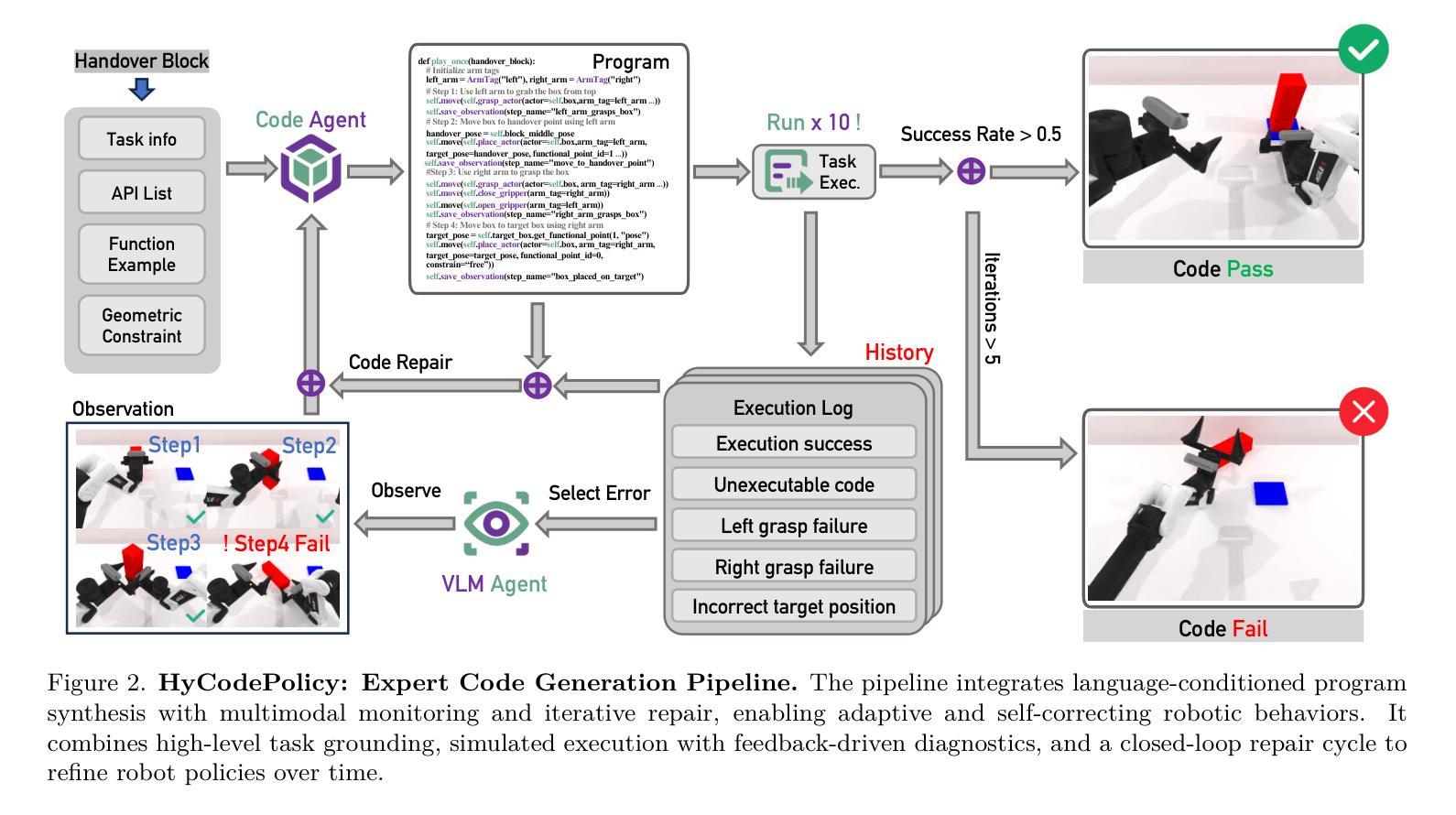
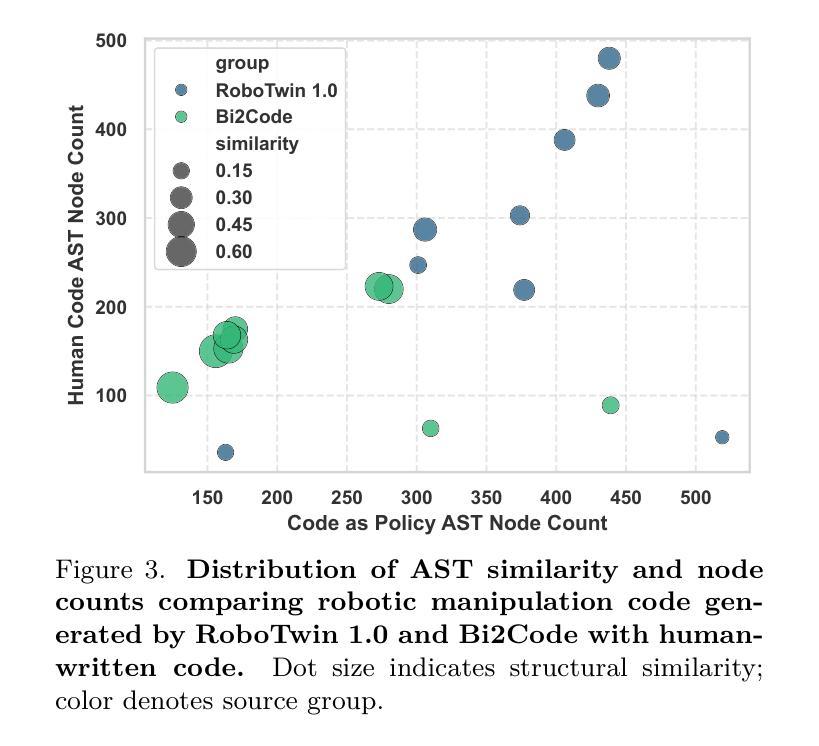
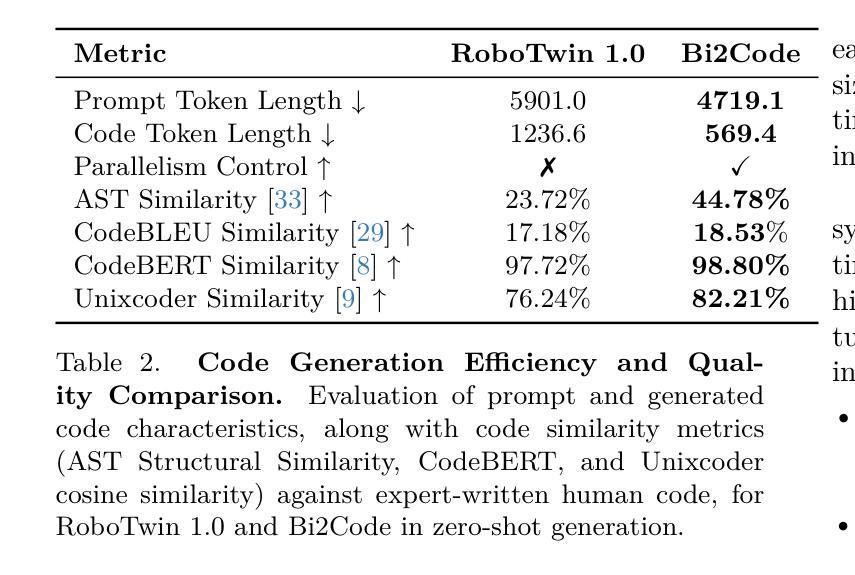
HyCodePolicy: Hybrid Language Controllers for Multimodal Monitoring and Decision in Embodied Agents
Authors:Yibin Liu, Zhixuan Liang, Zanxin Chen, Tianxing Chen, Mengkang Hu, Wanxi Dong, Congsheng Xu, Zhaoming Han, Yusen Qin, Yao Mu
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have enabled richer perceptual grounding for code policy generation in embodied agents. However, most existing systems lack effective mechanisms to adaptively monitor policy execution and repair codes during task completion. In this work, we introduce HyCodePolicy, a hybrid language-based control framework that systematically integrates code synthesis, geometric grounding, perceptual monitoring, and iterative repair into a closed-loop programming cycle for embodied agents. Technically, given a natural language instruction, our system first decomposes it into subgoals and generates an initial executable program grounded in object-centric geometric primitives. The program is then executed in simulation, while a vision-language model (VLM) observes selected checkpoints to detect and localize execution failures and infer failure reasons. By fusing structured execution traces capturing program-level events with VLM-based perceptual feedback, HyCodePolicy infers failure causes and repairs programs. This hybrid dual feedback mechanism enables self-correcting program synthesis with minimal human supervision. Our results demonstrate that HyCodePolicy significantly improves the robustness and sample efficiency of robot manipulation policies, offering a scalable strategy for integrating multimodal reasoning into autonomous decision-making pipelines.
近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进步为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了更丰富的感知基础。然而,大多数现有系统缺乏有效的机制来在任务完成过程中自适应地监视策略执行和修复代码。在这项工作中,我们引入了HyCodePolicy,这是一个基于混合语言的控制框架,它将代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复系统地集成到一个闭环编程周期中,用于实体代理。从技术上讲,给定自然语言指令,我们的系统首先将其分解为子目标并生成基于对象为中心的几何原始数据的初始可执行程序。该程序然后在仿真中执行,同时视觉语言模型(VLM)观察选定检查点以检测和定位执行失败并推断失败原因。通过将捕获程序级事件的结构化执行轨迹与基于VLM的感知反馈相融合,HyCodePolicy推断出失败原因并修复程序。这种混合双反馈机制实现了自我修正的程序合成,几乎无需人工监督。我们的结果表明,HyCodePolicy显著提高了机器人操作策略的稳健性和样本效率,为将多模态推理集成到自主决策管道中提供了可扩展的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025 Workshop on Multi-Modal Reasoning for Agentic Intelligence
Summary
近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的进步为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了更丰富的感知基础。然而,大多数现有系统缺乏在任务完成过程中自适应监控策略执行和修复代码的有效机制。本研究介绍了HyCodePolicy,这是一个基于语言的控制框架,系统地集成了代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复,为实体代理形成了一个闭环编程周期。给定自然语言指令,该系统首先将其分解为子目标并生成基于对象为中心的几何原始数据的初始可执行程序。然后在模拟中执行程序,同时视觉语言模型(VLM)观察选定检查点以检测和定位执行故障并推断失败原因。通过融合捕获程序级事件的结构化执行轨迹和基于VLM的感知反馈,HyCodePolicy可以推断故障原因并修复程序。这种混合双重反馈机制实现了在极少人类监督下的自我修正程序合成。结果表明,HyCodePolicy显著提高了机器人操作策略的稳健性和样本效率,为自主决策管道中整合多模态推理提供了可伸缩策略。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型的进步为实体代理中的代码策略生成提供了丰富的感知基础。
- 现有系统在监控和修复代码方面的自适应能力有限。
- HyCodePolicy是一个基于语言的控制框架,集成了代码合成、几何基础、感知监控和迭代修复。
- 系统通过分解自然语言指令生成初始可执行程序。
- 通过视觉语言模型观察选定检查点来检测并定位执行故障。
- HyCodePolicy通过结合结构化执行轨迹和感知反馈来推断故障原因并进行程序修复。
点此查看论文截图
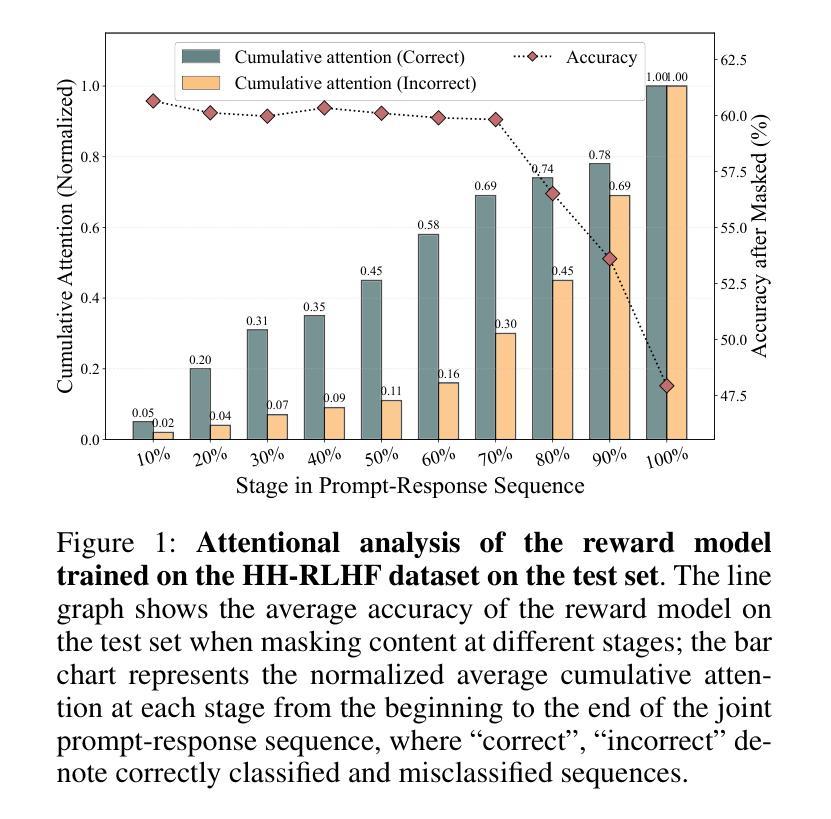
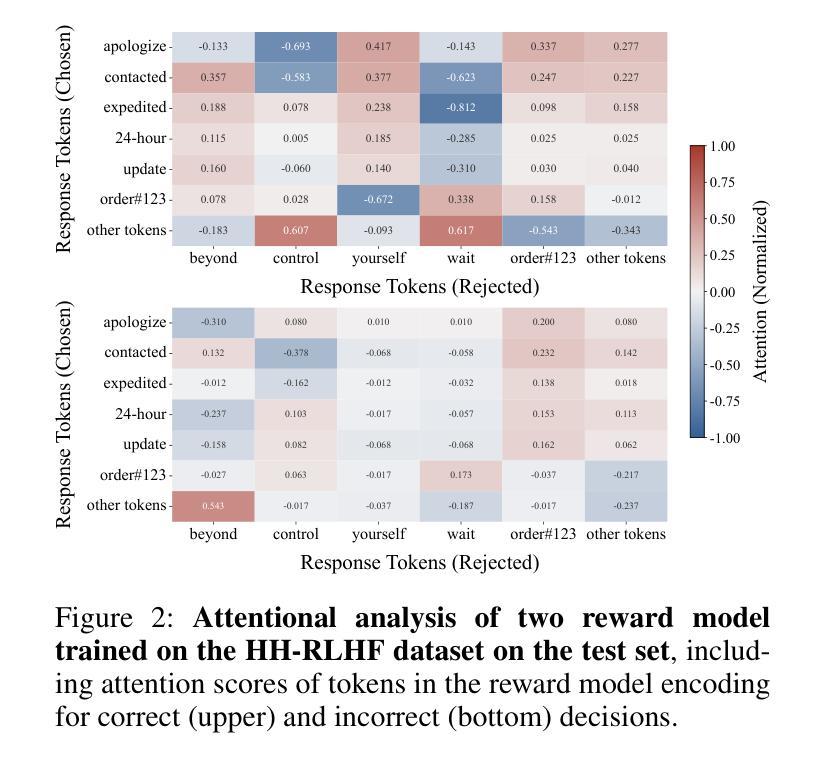
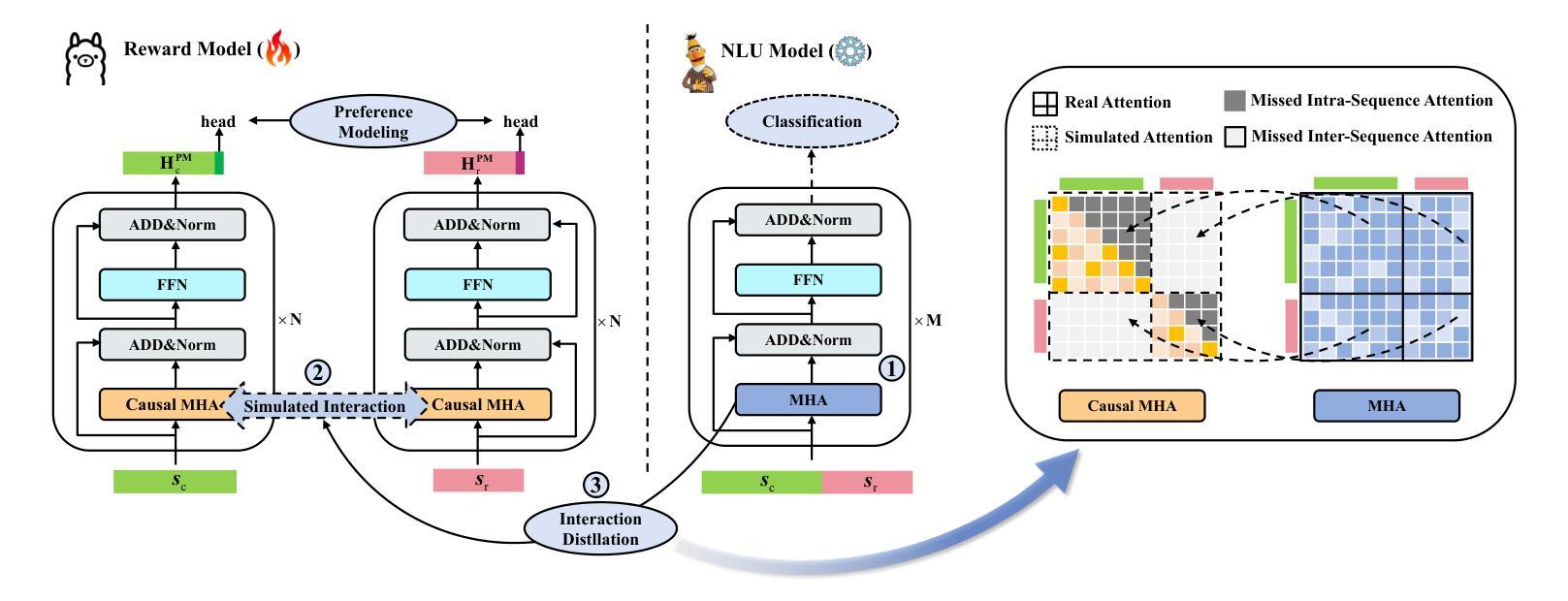
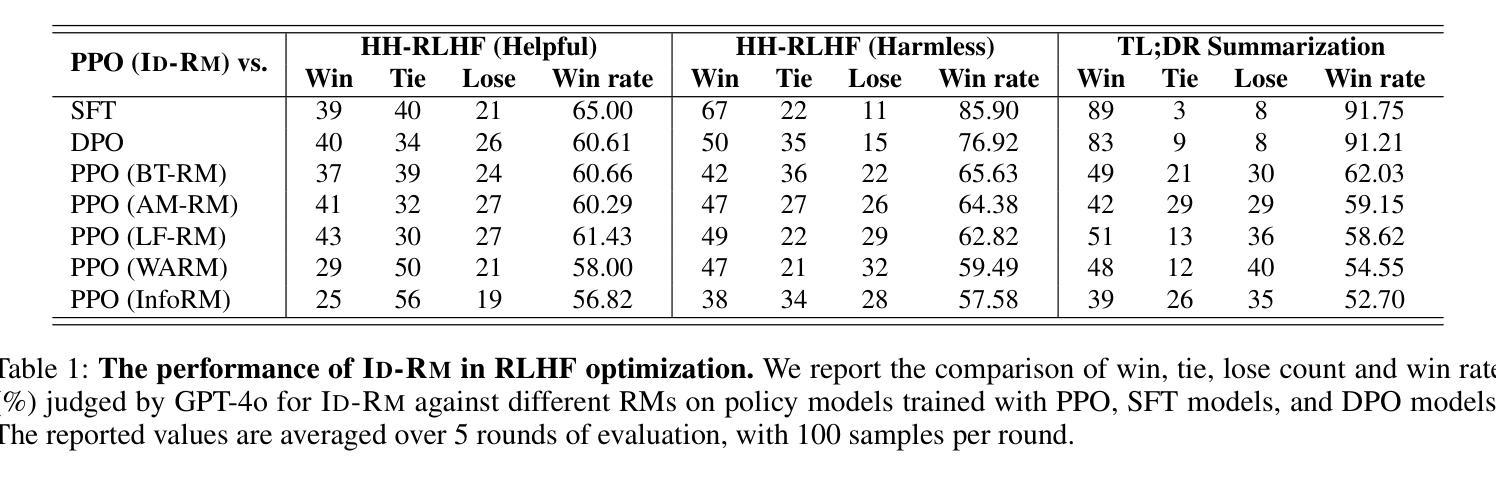
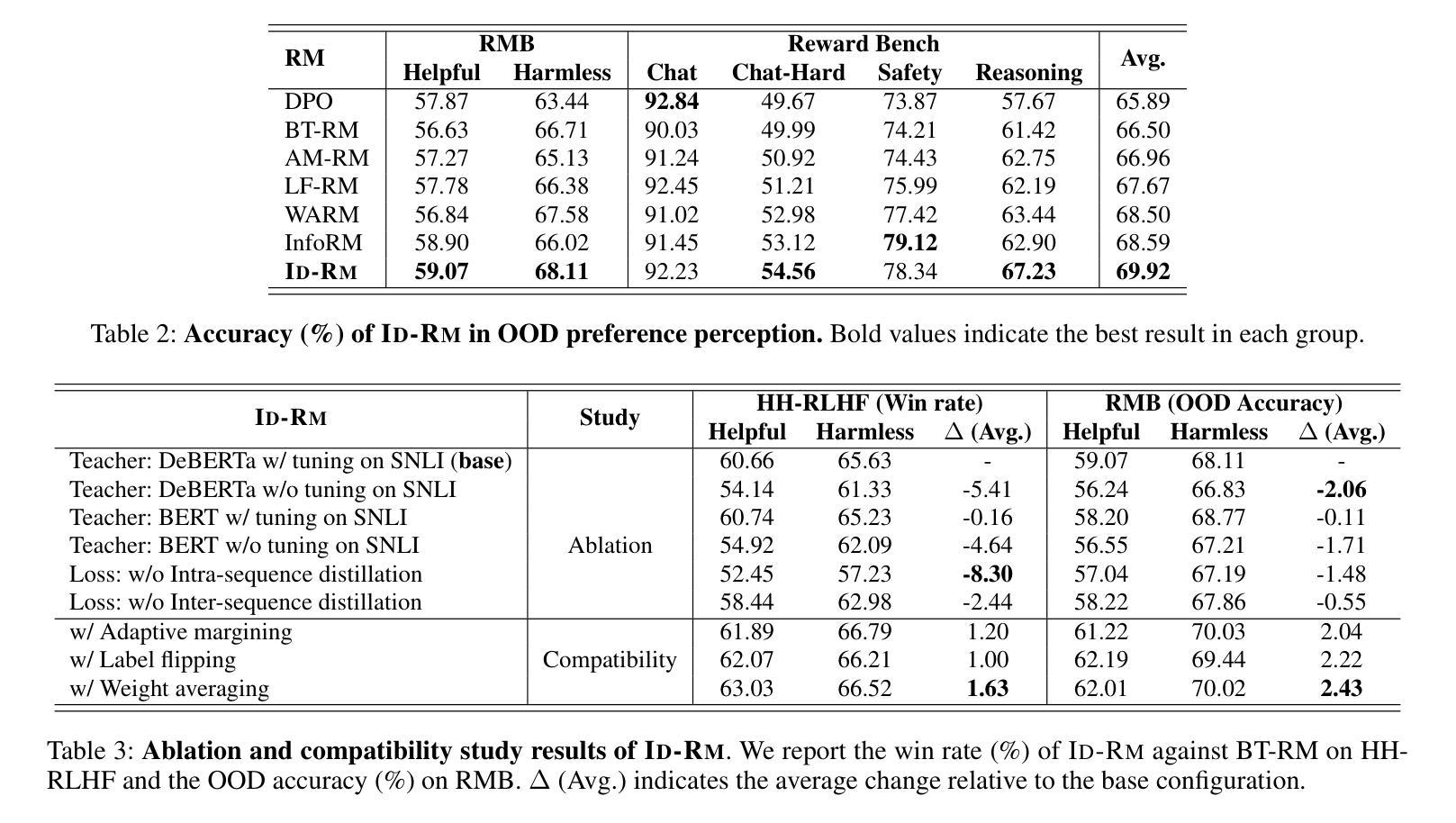
Mitigating Attention Hacking in Preference-Based Reward Modeling via Interaction Distillation
Authors:Jianxiang Zang, Meiling Ning, Shihan Dou, Jiazheng Zhang, Tao Gui, Qi Zhang, Xuanjing Huang
The reward model (RM), as the core component of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) for large language models (LLMs), responsible for providing reward signals to generated responses. However, mainstream preference modeling in RM is inadequate in terms of token-level interaction, making its judgment signals vulnerable to being hacked by misallocated attention to context. This stems from two fundamental limitations: (1) Current preference modeling employs decoder-only architectures, where the unidirectional causal attention mechanism leads to forward-decaying intra-sequence attention within the prompt-response sequence. (2) The independent Siamese-encoding paradigm induces the absence of token-level inter-sequence attention between chosen and rejected sequences. To address this “attention hacking”, we propose “Interaction Distillation”, a novel training framework for more adequate preference modeling through attention-level optimization. The method introduces an interaction-based natural language understanding model as the teacher to provide sophisticated token interaction patterns via comprehensive attention, and guides the preference modeling to simulate teacher model’s interaction pattern through an attentional alignment objective. Through extensive experiments, interaction distillation has demonstrated its ability to provide more stable and generalizable reward signals compared to state-of-the-art RM optimization methods that target data noise, highlighting the attention hacking constitute a more fundamental limitation in RM.
奖励模型(RM)作为大型语言模型(LLM)中基于人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)的核心组件,负责为生成的响应提供奖励信号。然而,RM中的主流偏好建模在令牌级交互方面存在不足,导致判断信号容易受到对上下文分配不当的注意力的攻击。这源于两个基本局限:(1)当前的偏好建模仅采用解码器架构,其中单向因果注意力机制导致提示-响应序列内的序列内注意力呈现前向衰减。(2)独立的Siamese编码范式导致所选序列和拒绝序列之间缺少令牌级序列间注意力。为了解决这种“注意力攻击”,我们提出了“交互蒸馏”,这是一种通过注意力级别优化进行更充分偏好建模的新型训练框架。该方法引入了一种基于交互的自然语言理解模型作为教师,通过全面的注意力提供精细的令牌交互模式,并通过注意力对齐目标指导偏好建模来模拟教师模型的交互模式。通过大量实验,交互蒸馏显示出提供比针对数据噪声优化的最新RM方法更稳定和可推广的奖励信号的能力,强调了注意力攻击在RM中构成更基本的局限。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:奖励模型(RM)作为强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)中的核心组件,用于为大型语言模型(LLM)生成响应提供奖励信号。然而,主流的偏好建模在RM中存在符号级交互的不足,使得其判断信号容易受到对上下文分配不当注意力的攻击。这源于两个基本局限:一是当前偏好建模采用单向因果注意力机制;二是独立式赛瓦编码范式导致了标记级别序列间注意力的缺失。为解决注意力破解问题,提出了名为“交互蒸馏”的新型训练框架,通过注意力级别的优化进行更准确的偏好建模。该方法引入基于交互的自然语言理解模型作为教师,通过全面的注意力提供复杂的标记交互模式,并通过注意力对齐目标引导偏好建模模拟教师模型的交互模式。实验证明,交互蒸馏提供了更稳定和可泛化的奖励信号。
Key Takeaways:
- 奖励模型(RM)是强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)的核心部分,负责为大型语言模型(LLM)生成响应提供奖励信号。
- 主流偏好建模在RM中存在局限性,易受到注意力破解攻击。
- 当前偏好建模的局限主要体现在两个方面:一是单向因果注意力机制导致的序列内部注意力衰减;二是在选择序列和拒绝序列之间缺乏标记级别的交互注意力。
- “交互蒸馏”是一种新型训练框架,旨在解决注意力破解问题,通过注意力级别的优化进行更准确的偏好建模。
- 交互蒸馏引入基于交互的自然语言理解模型作为教师,通过全面的注意力提供复杂的标记交互模式。
- 交互蒸馏通过注意力对齐目标来引导偏好建模模拟教师模型的交互模式。
点此查看论文截图

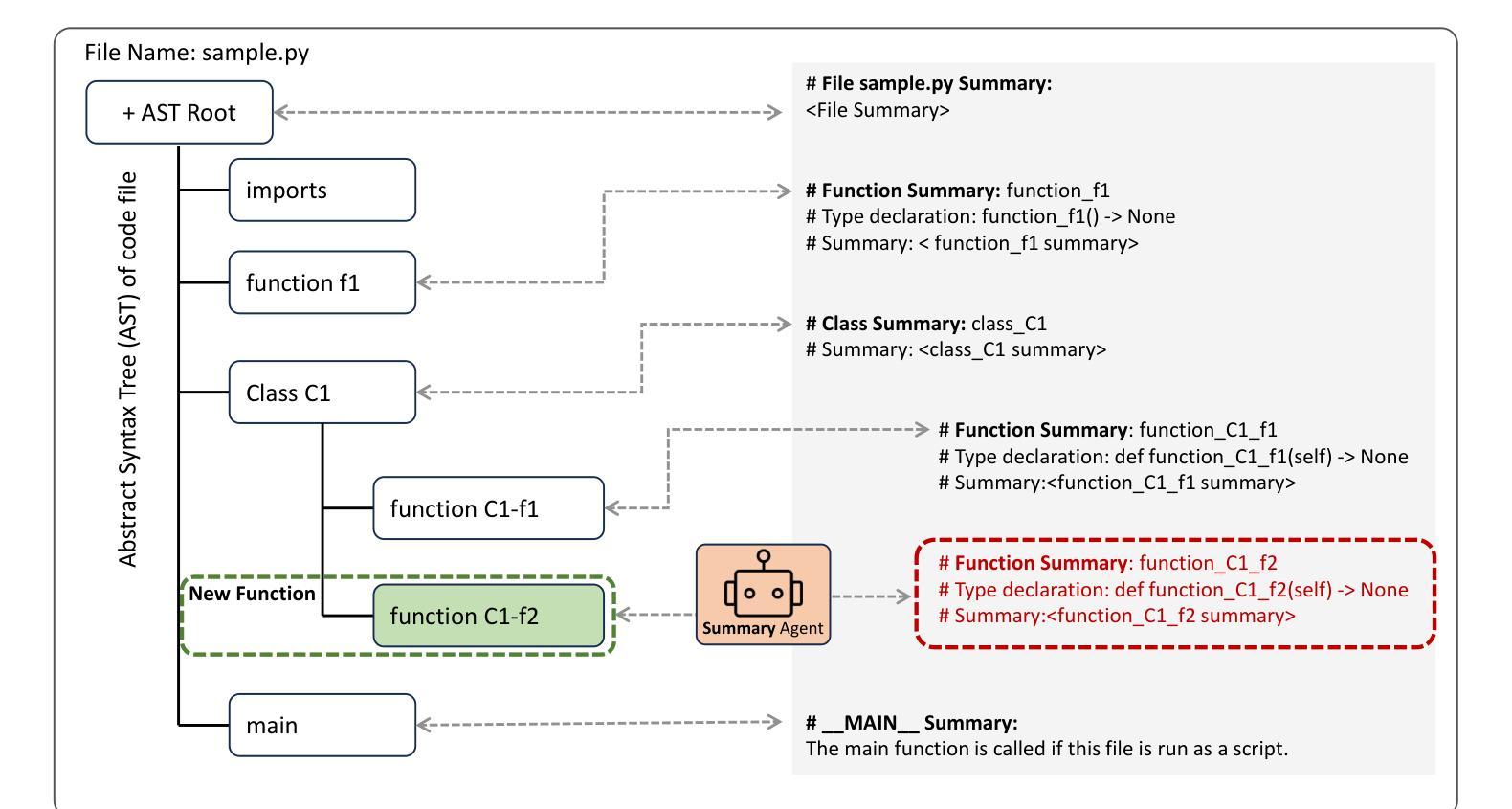
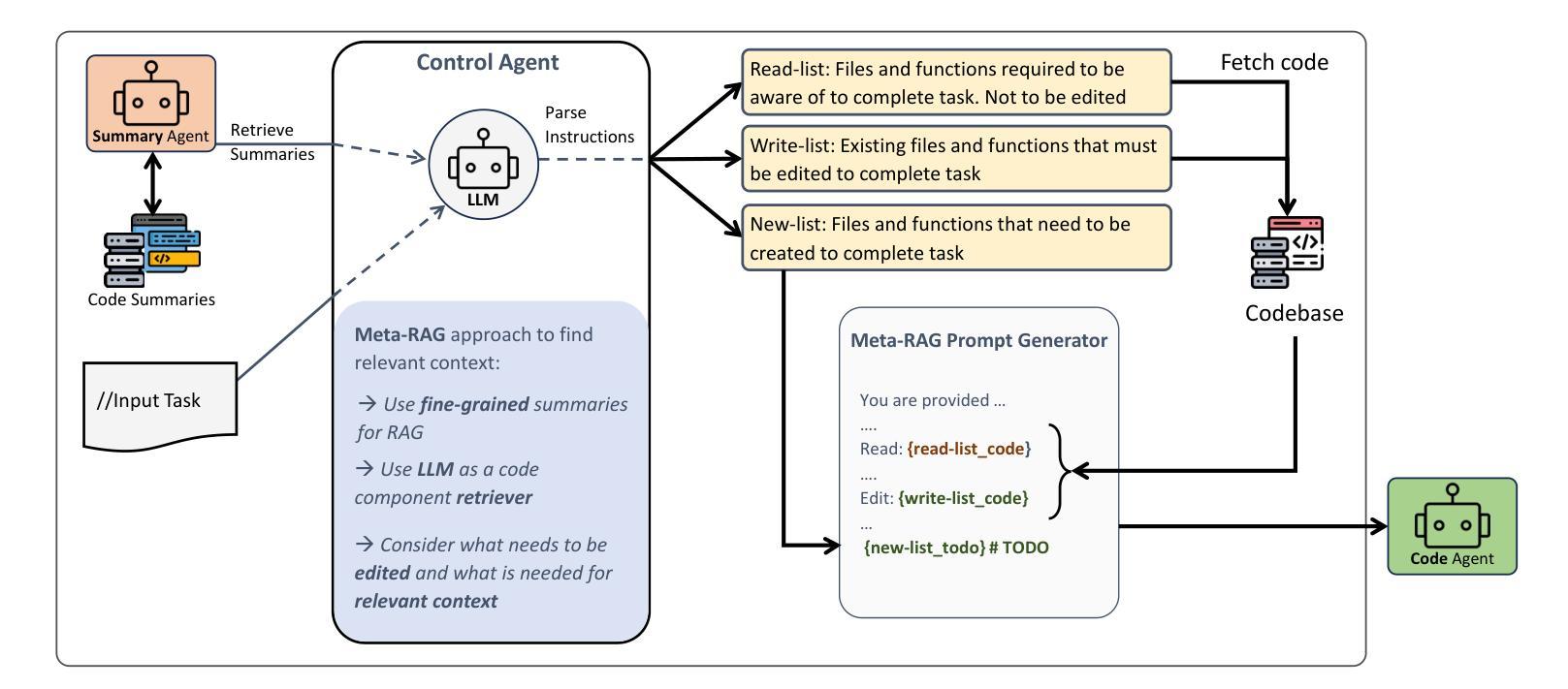
Meta-RAG on Large Codebases Using Code Summarization
Authors:Vali Tawosia, Salwa Alamir, Xiaomo Liu, Manuela Veloso
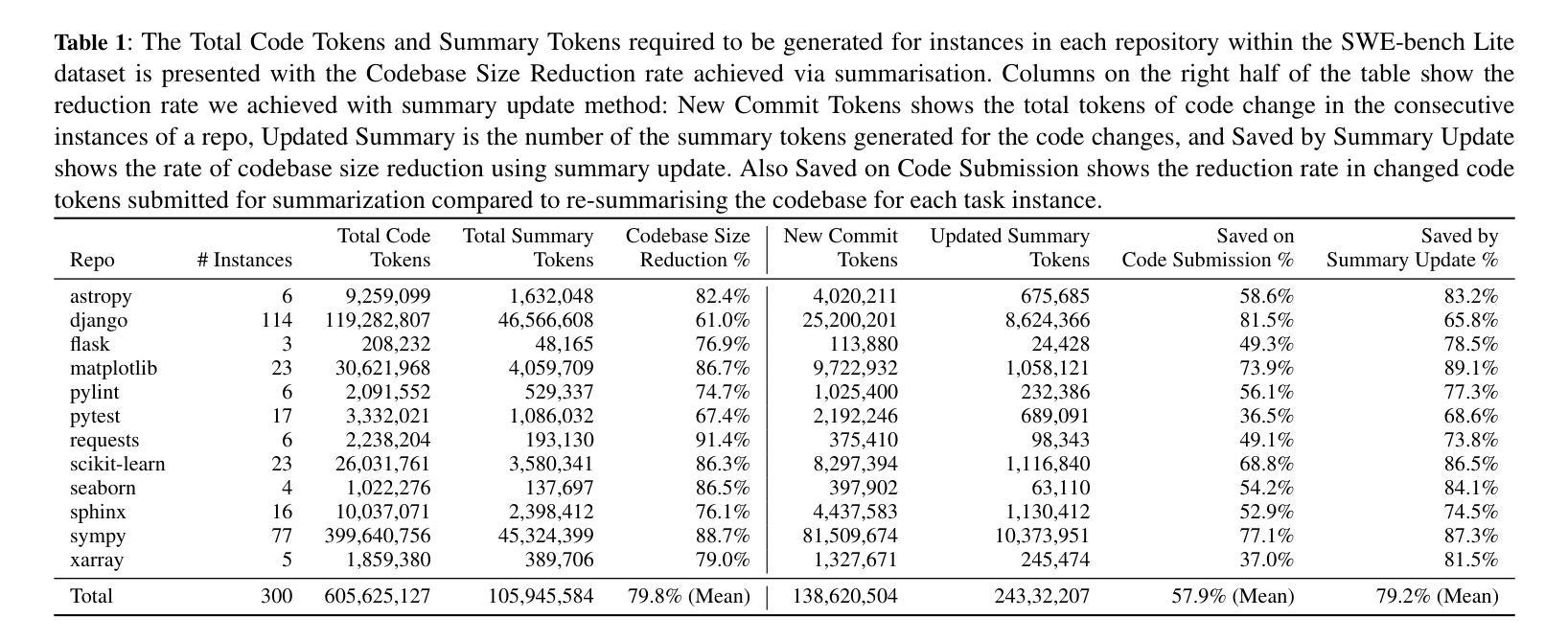
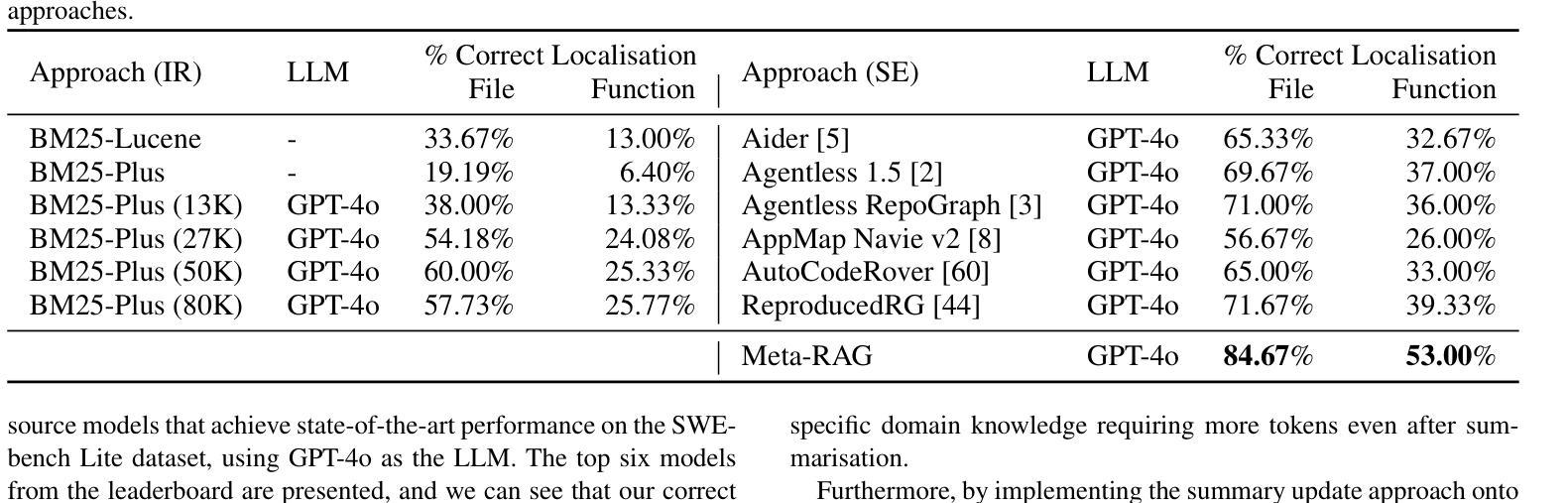
Large Language Model (LLM) systems have been at the forefront of applied Artificial Intelligence (AI) research in a multitude of domains. One such domain is software development, where researchers have pushed the automation of a number of code tasks through LLM agents. Software development is a complex ecosystem, that stretches far beyond code implementation and well into the realm of code maintenance. In this paper, we propose a multi-agent system to localize bugs in large pre-existing codebases using information retrieval and LLMs. Our system introduces a novel Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) approach, Meta-RAG, where we utilize summaries to condense codebases by an average of 79.8%, into a compact, structured, natural language representation. We then use an LLM agent to determine which parts of the codebase are critical for bug resolution, i.e. bug localization. We demonstrate the usefulness of Meta-RAG through evaluation with the SWE-bench Lite dataset. Meta-RAG scores 84.67 % and 53.0 % for file-level and function-level correct localization rates, respectively, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
大型语言模型(LLM)系统在多领域应用人工智能(AI)研究中处于前沿地位。其中一个这样的领域是软件开发,研究人员通过LLM代理推动了多个代码任务的自动化。软件开发是一个复杂的生态系统,远远超出代码实现,深入到代码维护的领域。在本文中,我们提出了一种使用信息检索和LLM在大型现有代码库中定位错误的多代理系统。我们的系统引入了一种新型的基于检索增强生成(RAG)的方法,即Meta-RAG,我们利用摘要将代码库平均压缩79.8%,压缩成紧凑、结构化、自然语言表示的形式。然后,我们使用LLM代理来确定对解决错误至关重要的代码库部分,即错误定位。我们通过使用SWE-bench Lite数据集对Meta-RAG进行了评估,证明了其实用性。Meta-RAG的文件级和函数级正确定位率分别为84.67%和53.0%,达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)系统在多个领域的人工智能研究前沿中发挥了重要作用。在软件开发领域,研究人员通过LLM代理推动了代码任务的自动化。本文提出了一种多代理系统,利用信息检索和LLM定位大型现有代码库中的错误。我们系统引入了新型的检索增强生成(RAG)方法Meta-RAG,通过摘要将代码库平均压缩79.8%,转化为紧凑、结构化的自然语言表示。然后,我们使用LLM代理确定对错误修复至关重要的代码库部分,即错误定位。通过SWE-bench Lite数据集评估,Meta-RAG在文件级别和函数级别的正确定位率分别为84.67%和53.0%,达到了业界先进水平。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM系统在多个领域的人工智能研究中处于前沿地位,包括软件开发。
- 在软件开发中,LLM代理推动了代码任务的自动化。
- 本文提出了一个多代理系统,利用信息检索和LLM技术定位大型现有代码库中的错误。
- 引入了新型的检索增强生成(RAG)方法Meta-RAG,通过摘要将代码库转化为自然语言表示。
- Meta-RAG方法能平均压缩代码库79.8%,提高错误定位的效率。
- 通过SWE-bench Lite数据集评估,Meta-RAG在文件级别和函数级别的正确定位率分别达到了84.67%和53.0%。
点此查看论文截图

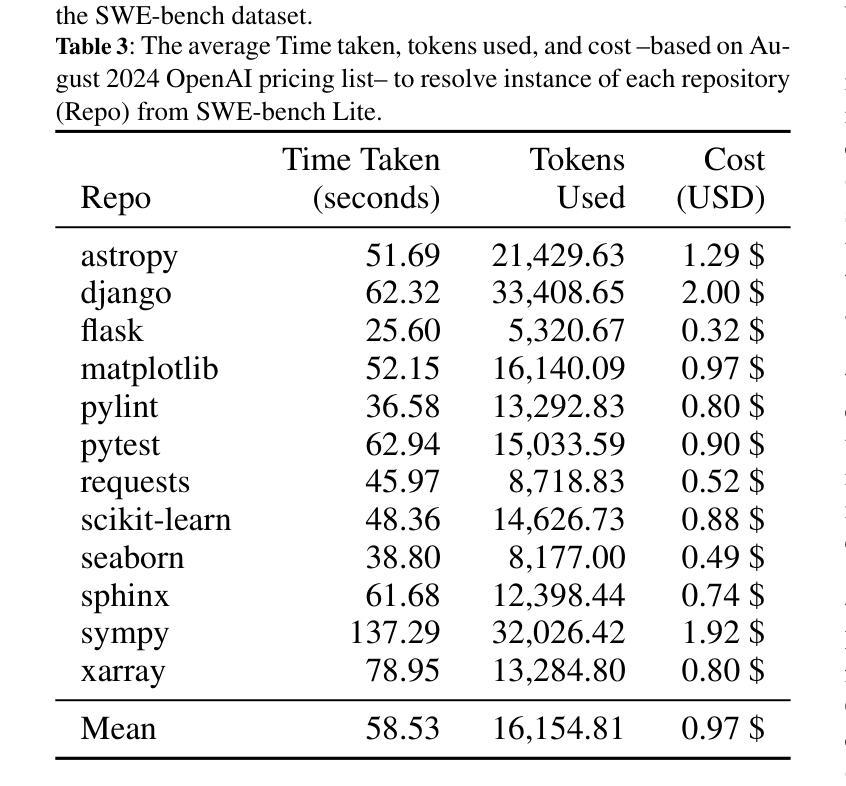
StructSynth: Leveraging LLMs for Structure-Aware Tabular Data Synthesis in Low-Data Regimes
Authors:Siyi Liu, Yujia Zheng, Yongqi Zhang
The application of machine learning on tabular data in specialized domains is severely limited by data scarcity. While generative models offer a solution, traditional methods falter in low-data regimes, and recent Large Language Models (LLMs) often ignore the explicit dependency structure of tabular data, leading to low-fidelity synthetics. To address these limitations, we introduce StructSynth, a novel framework that integrates the generative power of LLMs with robust structural control. StructSynth employs a two-stage architecture. First, it performs explicit structure discovery to learn a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) from the available data. Second, this learned structure serves as a high-fidelity blueprint to steer the LLM’s generation process, forcing it to adhere to the learned feature dependencies and thereby ensuring the generated data respects the underlying structure by design. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that StructSynth produces synthetic data with significantly higher structural integrity and downstream utility than state-of-the-art methods. It proves especially effective in challenging low-data scenarios, successfully navigating the trade-off between privacy preservation and statistical fidelity.
在特定领域,机器学习在表格数据上的应用受到数据稀缺的严重限制。虽然生成模型提供了一种解决方案,但传统方法在数据稀缺的情况下会失去效能,而且最近的大型语言模型(LLM)往往会忽略表格数据的显式依赖结构,导致合成数据的保真度较低。为了解决这些限制,我们引入了StructSynth,这是一个新型框架,它将大型语言模型的生成能力与稳健的结构控制相结合。StructSynth采用两阶段架构。首先,它执行显式结构发现,从可用数据中学习有向无环图(DAG)。其次,这一学习到的结构作为一个高保真蓝图,用于引导大型语言模型的生成过程,迫使它遵循学习到的特征依赖关系,从而确保生成的数据在设计上尊重底层结构。我们的大量实验表明,StructSynth生成的数据在结构完整性和下游实用性方面明显高于最新方法。它在具有挑战性的低数据场景中表现尤其出色,成功地在隐私保护和统计保真之间找到了平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于结构化数据在特定领域应用机器学习时,数据稀缺性限制了模型的性能。生成模型为解决此问题提供了一种解决方案,但在低数据环境下传统方法表现不佳。大型语言模型(LLM)忽略了结构化数据的显式依赖结构,导致生成的合成数据保真度较低。为解决这些问题,我们引入了StructSynth框架,该框架结合了LLM的生成能力与稳健的结构控制。StructSynth采用两阶段架构,首先进行显式结构发现,从现有数据中学习有向无环图(DAG)。其次,使用学习的结构作为高保真蓝图来引导LLM的生成过程,确保生成的数据遵循设计的底层结构。实验证明,StructSynth在结构完整性和下游实用性方面优于现有方法,特别是在低数据场景中表现尤为出色,成功实现了隐私保护和统计保真之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 数据稀缺性是机器学习在特定领域应用结构化数据的瓶颈。
- 生成模型是解决数据稀缺性的有效方法,但在低数据环境下表现不佳。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)忽略了结构化数据的显式依赖结构,导致合成数据保真度低。
- StructSynth框架结合了LLM的生成能力与结构控制来解决上述问题。
- StructSynth采用两阶段架构,先进行结构发现学习,再应用学到的结构指导LLM生成过程。
- 实验表明StructSynth生成的合成数据具有更高的结构完整性和下游实用性。
点此查看论文截图

CAMA: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Causal Knowledge
Authors:Lei Zan, Keli Zhang, Ruichu Cai, Lujia Pan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of tasks, yet they still struggle with complex mathematical reasoning, a challenge fundamentally rooted in deep structural dependencies. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{CA}usal \textbf{MA}thematician (\textbf{CAMA}), a two-stage causal framework that equips LLMs with explicit, reusable mathematical structure. In the learning stage, CAMA first constructs the \textbf{M}athematical \textbf{C}ausal \textbf{G}raph (\textbf{MCG}), a high-level representation of solution strategies, by combining LLM priors with causal discovery algorithms applied to a corpus of question-solution pairs. The resulting MCG encodes essential knowledge points and their causal dependencies. To better align the graph with downstream reasoning tasks, CAMA further refines the MCG through iterative feedback derived from a selected subset of the question-solution pairs. In the reasoning stage, given a new question, CAMA dynamically extracts a task-relevant subgraph from the MCG, conditioned on both the question content and the LLM’s intermediate reasoning trace. This subgraph, which encodes the most pertinent knowledge points and their causal dependencies, is then injected back into the LLM to guide its reasoning process. Empirical results on real-world datasets show that CAMA significantly improves LLM performance on challenging mathematical problems. Furthermore, our experiments demonstrate that structured guidance consistently outperforms unstructured alternatives, and that incorporating asymmetric causal relationships yields greater improvements than using symmetric associations alone.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务中表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍存在困难,这一挑战根本源于深层的结构依赖性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了因果数学家(\textbf{CAMA})这一两阶段因果框架,为LLM配备明确的可重用数学结构。在学习阶段,CAMA首先构建数学因果图(MCG),这是一种解决方案策略的高级表示,通过结合LLM的先验知识和应用于问题解决方案对语料库的因果发现算法。结果产生的MCG编码了重要的知识点及其因果关系。为了更好地与下游推理任务对齐,CAMA通过来自问题解决方案对选择子集的迭代反馈进一步改进了MCG。在推理阶段,对于新问题,CAMA会根据问题的内容和LLM的中间推理轨迹动态地从MCG中提取出与任务相关的子图。这个子图编码了最相关的知识点及其因果关系,然后重新注入LLM以指导其推理过程。在真实数据集上的实证结果表明,CAMA在解决具有挑战性的数学问题方面显著提高了LLM的性能。此外,我们的实验表明,结构化的指导始终优于非结构化的替代方案,并且融入不对称的因果关系比仅使用对称关联带来更大的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务上表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍存在挑战。为解决这一挑战,提出了因果数学家(CAMA)框架,该框架包含两个阶段,旨在为LLM提供明确的可重复使用的数学结构。第一阶段构建数学因果图(MCG),结合LLM先验知识与因果发现算法,对问题解答对进行高层次表示。第二阶段根据新问题从MCG中提取相关子图,并注入LLM以指导其推理过程。实验表明,CAMA能显著提高LLM解决数学问题的能力,且结构化的指导方式优于非结构化方式,利用不对称因果关系比仅使用对称关联效果更好。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在复杂数学推理上仍有挑战,需要新的方法来解决。
- CAMA框架包含两个阶段:学习阶段和推理阶段。
- 学习阶段通过构建数学因果图(MCG)来结合LLM的先验知识与因果发现算法。
- CAMA通过迭代反馈优化MCG,使其更好地适应下游推理任务。
- 推理阶段根据新问题从MCG中提取相关子图,并注入LLM以指导其推理。
- 实验表明CAMA能显著提高LLM解决数学问题的能力。
点此查看论文截图

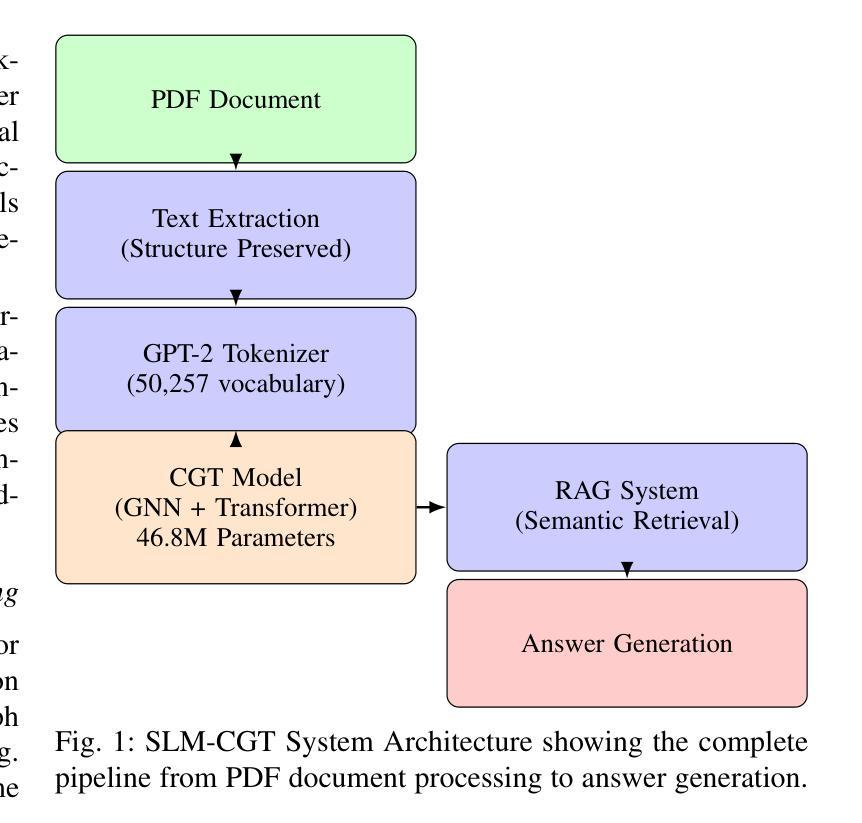
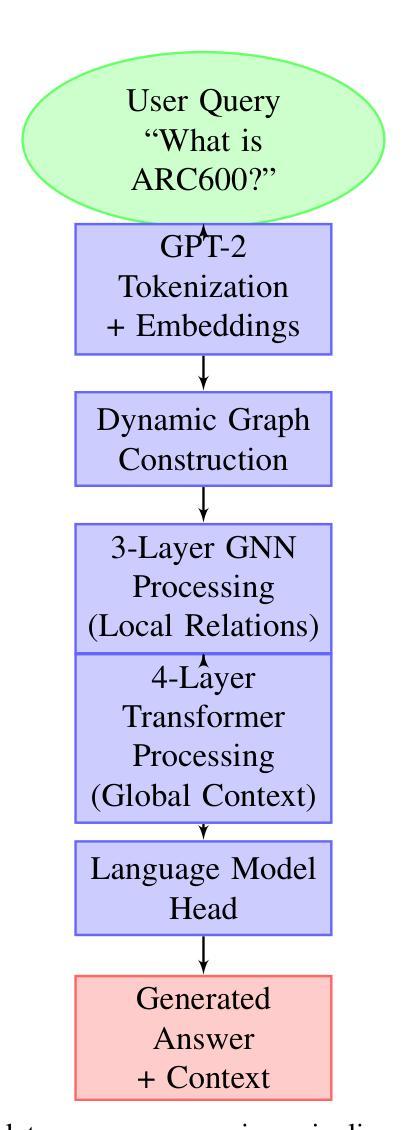
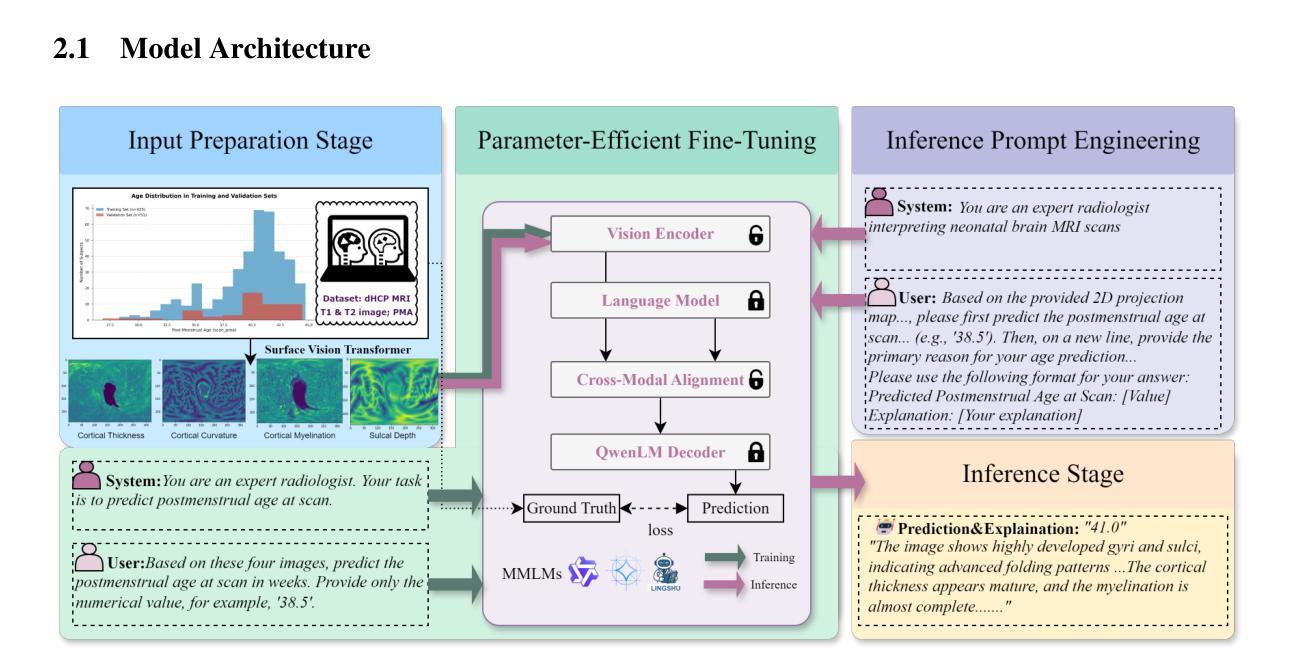
Contextual Graph Transformer: A Small Language Model for Enhanced Engineering Document Information Extraction
Authors:Karan Reddy, Mayukha Pal
Standard transformer-based language models, while powerful for general text, often struggle with the fine-grained syntax and entity relationships in complex technical, engineering documents. To address this, we propose the Contextual Graph Transformer (CGT), a hybrid neural architecture that combines Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Transformers for domain-specific question answering. CGT constructs a dynamic graph over input tokens using sequential, skip-gram, and semantic similarity edges, which is processed by GATv2Conv layers for local structure learning. These enriched embeddings are then passed to a Transformer encoder to capture global dependencies. Unlike generic large models, technical domains often require specialized language models with stronger contextualization and structure awareness. CGT offers a parameter-efficient solution for such use cases. Integrated into a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, CGT outperforms baselines like GPT-2 and BERT, achieving 24.7% higher accuracy than GPT-2 with 62.4% fewer parameters. This gain stems from CGTs ability to jointly model structural token interactions and long-range semantic coherence. The model is trained from scratch using a two-phase approach: pretraining on general text followed by fine-tuning on domain-specific manuals. This highlights CGTs adaptability to technical language, enabling better grounding, entity tracking, and retrieval-augmented responses in real-world applications.
传统的基于变压器的语言模型在处理一般文本时表现出强大的能力,但在处理复杂技术、工程文档中的细微语法和实体关系时往往遇到困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了上下文图变压器(CGT),这是一种混合神经网络架构,它结合了图神经网络(GNNs)和变压器,用于特定领域的问答。CGT在输入标记上构建了一个动态图,该图使用顺序、跳词和语义相似边缘进行处理,通过GATv2Conv层进行局部结构学习。这些丰富的嵌入然后传递给变压器编码器以捕获全局依赖关系。与通用大型模型不同,技术领域往往需要具有更强上下文化和结构意识的专门语言模型。CGT为这种情况提供了参数高效的解决方案。集成到检索增强生成(RAG)管道中,CGT优于GPT-2和BERT等基线,在仅有62.4%参数的情况下,比GPT-2高出24.7%的准确率。这一收益来源于CGT联合建模结构标记交互和长距离语义连贯性的能力。该模型采用两阶段方法从头开始训练:首先在通用文本上进行预训练,然后在特定领域手册上进行微调。这突出了CGT对技术语言的适应性,可在实际应用程序中实现更好的接地、实体跟踪和检索增强响应。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对标准基于转换器的语言模型在处理复杂技术、工程文档中细微语法和实体关系时的困境,提出上下文图转换器(CGT)这一混合神经网络架构。CGT结合图神经网络(GNNs)和转换器,用于特定领域的问答。它通过构建动态图、使用GATv2Conv层进行本地结构学习、增强嵌入,并传递给转换器编码器以捕获全局依赖关系。CGT为技术领域的特定用例提供了参数高效的解决方案,并在检索增强生成(RAG)管道中表现优异,相较于GPT-2和BERT等基线模型有更高的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 标准语言模型在处理复杂技术文档时面临挑战,需要针对特定领域的解决方案。
- 上下文图转换器(CGT)是一种混合神经网络架构,结合了图神经网络(GNNs)和转换器技术。
- CGT通过构建动态图和利用GATv2Conv层进行本地结构学习来增强嵌入。
- CGT在全局范围内使用转换器编码器捕获依赖关系,具备更强的上下文和结构感知能力。
- CGT在参数效率方面表现出优势,适用于技术领域。
- 在检索增强生成(RAG)管道中,CGT较基线模型有更高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图


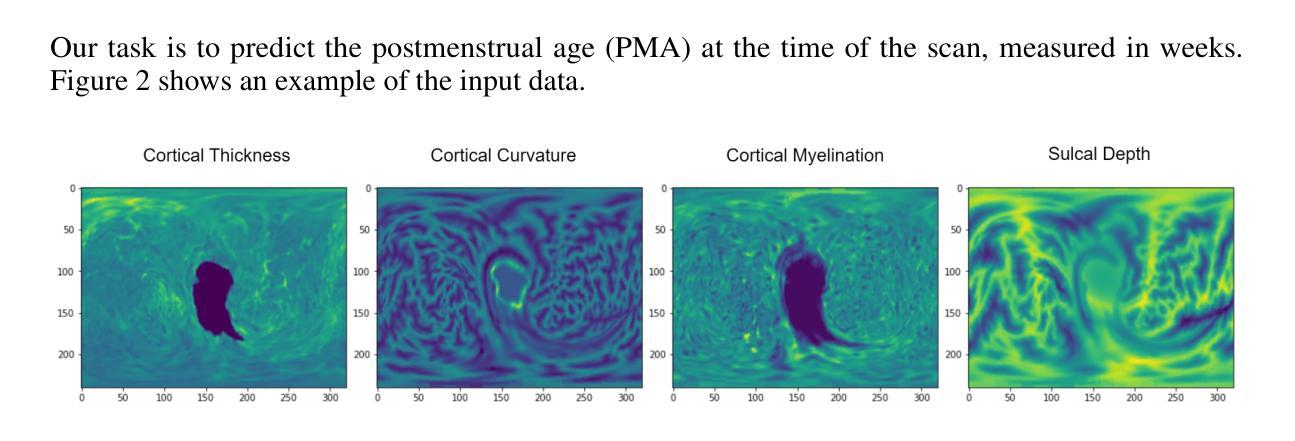
Accurate and Interpretable Postmenstrual Age Prediction via Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Qifan Chen, Jin Cui, Cindy Duan, Yushuo Han, Yifei Shi
Accurate estimation of postmenstrual age (PMA) at scan is crucial for assessing neonatal development and health. While deep learning models have achieved high accuracy in predicting PMA from brain MRI, they often function as black boxes, offering limited transparency and interpretability in clinical decision support. In this work, we address the dual challenge of accuracy and interpretability by adapting a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to perform both precise PMA prediction and clinically relevant explanation generation. We introduce a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) strategy using instruction tuning and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) applied to the Qwen2.5-VL-7B model. The model is trained on four 2D cortical surface projection maps derived from neonatal MRI scans. By employing distinct prompts for training and inference, our approach enables the MLLM to handle a regression task during training and generate clinically relevant explanations during inference. The fine-tuned model achieves a low prediction error with a 95 percent confidence interval of 0.78 to 1.52 weeks, while producing interpretable outputs grounded in developmental features, marking a significant step toward transparent and trustworthy AI systems in perinatal neuroscience.
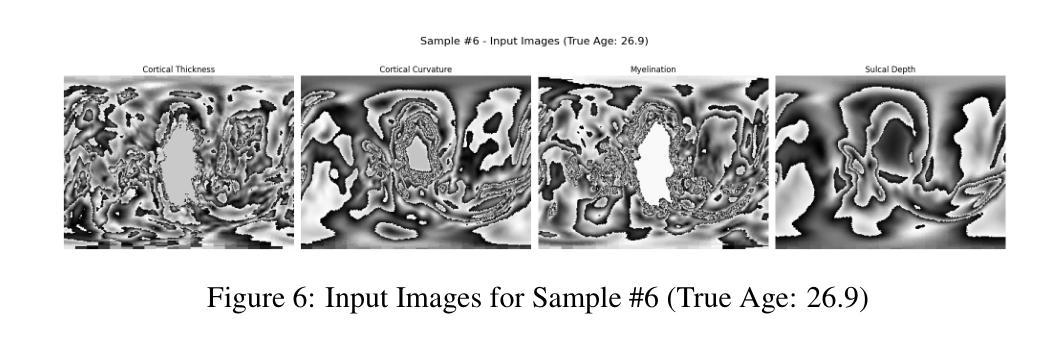
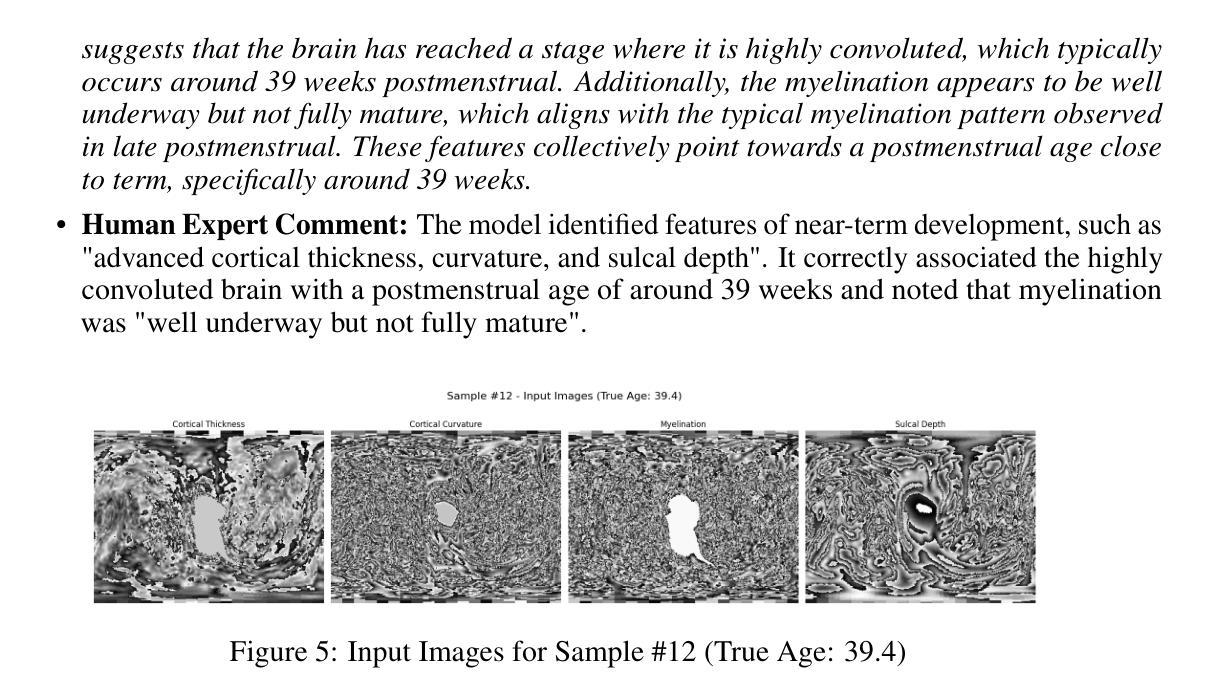
产后年龄(PMA)的准确估计是评估新生儿发育和健康的关键。虽然深度学习模型在根据脑部MRI预测PMA方面已经达到了较高的准确性,但它们通常像黑盒子一样运作,在临床决策支持中提供有限的透明度和解释性。在这项工作中,我们通过适应多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来解决准确性和解释性的双重挑战,以执行精确的PMA预测和生成与临床相关的解释。我们引入了一种参数有效的微调(PEFT)策略,使用指令调整和应用于Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型的低秩适应(LoRA)。该模型在由新生儿MRI扫描派生的四个二维皮质表面投影图上进行了训练。通过为训练和推理采用不同的提示,我们的方法使MLLM能够在训练时处理回归任务,并在推理时生成与临床相关的解释。经过微调的模型实现了较低的预测误差,95%置信区间为0.78至1.52周,同时产生了基于发育特征的可解释输出,朝着透明和可信赖的围产期神经科学人工智能系统迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop GenAI4Health. Conference website: https://aihealth.ischool.utexas.edu/GenAI4HealthNeurips2025/
Summary
本文关注产后年龄(PMA)的精确估算,这对于评估新生儿发育和健康至关重要。研究采用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)进行精确PMA预测和生成临床相关解释,解决准确性和可解释性的双重挑战。通过参数有效的微调(PEFT)策略和使用指令调整及低秩适应(LoRA)应用于Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型,该模型在新生儿MRI扫描的四个2D皮质表面投影图上训练。通过为训练和推理采用不同提示,MLLM能够在训练时处理回归任务并在推理时生成与临床相关的解释。微调后的模型预测误差低,95%置信区间为0.78至1.52周,且输出有发育特征作为依据,这在围产神经科学的透明和可信赖的AI系统中迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 产后年龄(PMA)的精确估计是评估新生儿发育和健康的关键。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)被用于解决这一任务,以提高准确性和可解释性。
- 参数有效的微调(PEFT)策略,包括指令调整和低秩适应(LoRA),被应用于MLLM模型优化。
- 模型在新生儿MRI扫描的四个2D皮质表面投影图上训练,提高模型的效能。
- 通过不同的提示进行训练和推理,使模型能够处理回归任务并生成临床相关的解释。
- 精细调整的模型实现了低预测误差,95%的置信区间在一周内。
点此查看论文截图


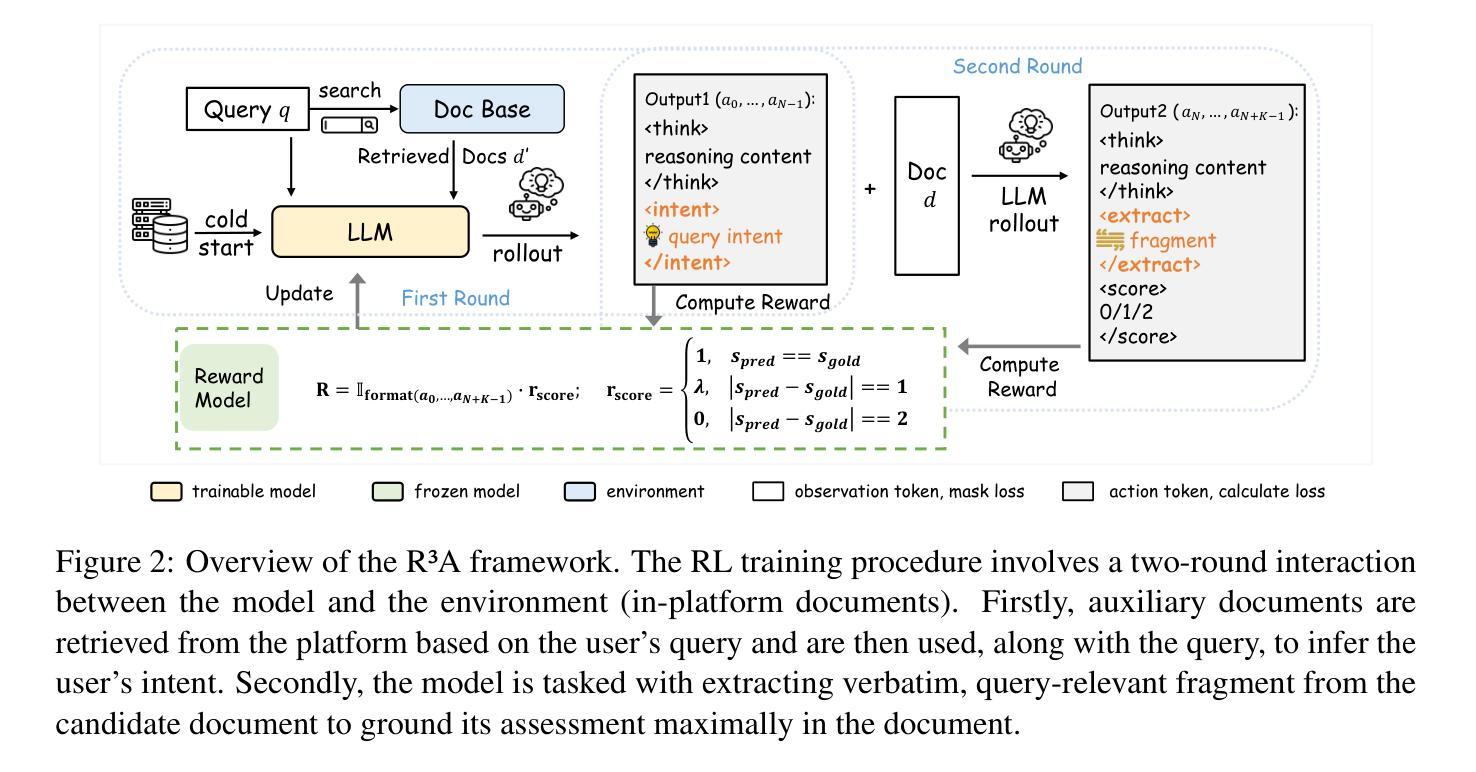
Decomposed Reasoning with Reinforcement Learning for Relevance Assessment in UGC Platforms
Authors:Xiaowei Yuan, Lei Jin, Haoxin Zhang, Yan Gao, Yi Wu, Yao Hu, Ziyang Huang, Jun Zhao, Kang Liu
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) plays a critical role in user-generated content (UGC) platforms, but its effectiveness depends heavily on accurate relevance assessment of query-document pairs. Despite recent advances in applying large language models (LLMs) to relevance modeling, UGC platforms present unique challenges: 1) ambiguous user intent due to sparse user feedback in RAG scenarios, and 2) substantial noise introduced by informal and unstructured language. To address these issues, we propose the Reinforced Reasoning Model for Relevance Assessment (R3A), which introduces a decomposed reasoning framework over queries and candidate documents before scoring. R3A first leverages auxiliary high-ranked documents within the platform to infer latent query intent. It then performs verbatim fragment extraction to justify relevance decisions, thereby reducing errors caused by noisy UGC. Based on a reinforcement learning framework, R3A is optimized to mitigate distortions arising from ambiguous queries and unstructured content. Experimental results show that R3A significantly outperforms existing baseline methods in terms of relevance accuracy, across both offline benchmarks and online experiments.
检索增强生成(RAG)在用户生成内容(UGC)平台中扮演着关键角色,但其有效性很大程度上取决于查询文档对的相关性评估的准确性。尽管最近将大型语言模型(LLM)应用于相关性建模取得了进展,但UGC平台仍然面临着独特的挑战:1)RAG场景中的用户反馈稀疏导致用户意图模糊,以及2)非正式和非结构化语言引入的大量噪声。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了相关性评估的强化推理模型(R3A),该模型在评分之前引入了针对查询和候选文档的分解推理框架。R3A首先利用平台内辅助的高排名文档来推断潜在的查询意图。然后,它执行逐字片段提取以证明相关性决策,从而减少由嘈杂的UGC造成的错误。基于强化学习框架,R3A进行了优化,以减轻由模糊查询和非结构化内容引起的失真。实验结果表明,R3A在离线基准测试和在线实验中均显著优于现有基线方法,在相关性准确性方面表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RAG在用户生成内容(UGC)平台中扮演重要角色,但其效果取决于查询文档对的相关性评估的准确性。针对UGC平台的独特挑战,如稀疏反馈下的用户意图模糊和大量非正式、非结构化语言引入的噪声,我们提出了强化推理模型(Reinforced Reasoning Model for Relevance Assessment,简称R3A)。R3A采用分解推理框架对查询和候选文档进行评分前的处理。它首先利用平台内辅助的高排名文档来推断潜在的查询意图,然后通过提取字面片段来证明相关性决策,从而减少由嘈杂的UGC引起的错误。基于强化学习框架,R3A被优化用于减轻由模糊查询和非结构化内容引起的失真。实验结果表明,R3A在离线基准测试和在线实验中,在相关性准确性方面显著优于现有基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 检索增强生成(RAG)在UGC平台中很重要,但查询文档对的相关性评估是关键。
- UGC平台面临两大挑战:稀疏反馈下的用户意图模糊和大量非结构化语言的噪声。
- 提出强化推理模型(R3A)以应对这些挑战。
- R3A利用辅助的高排名文档来推断潜在查询意图。
- R3A通过提取字面片段来证明相关性决策,减少错误。
- R3A采用强化学习框架进行优化,以减轻模糊查询和非结构化内容的失真。
- 实验证明,R3A在相关性准确性方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

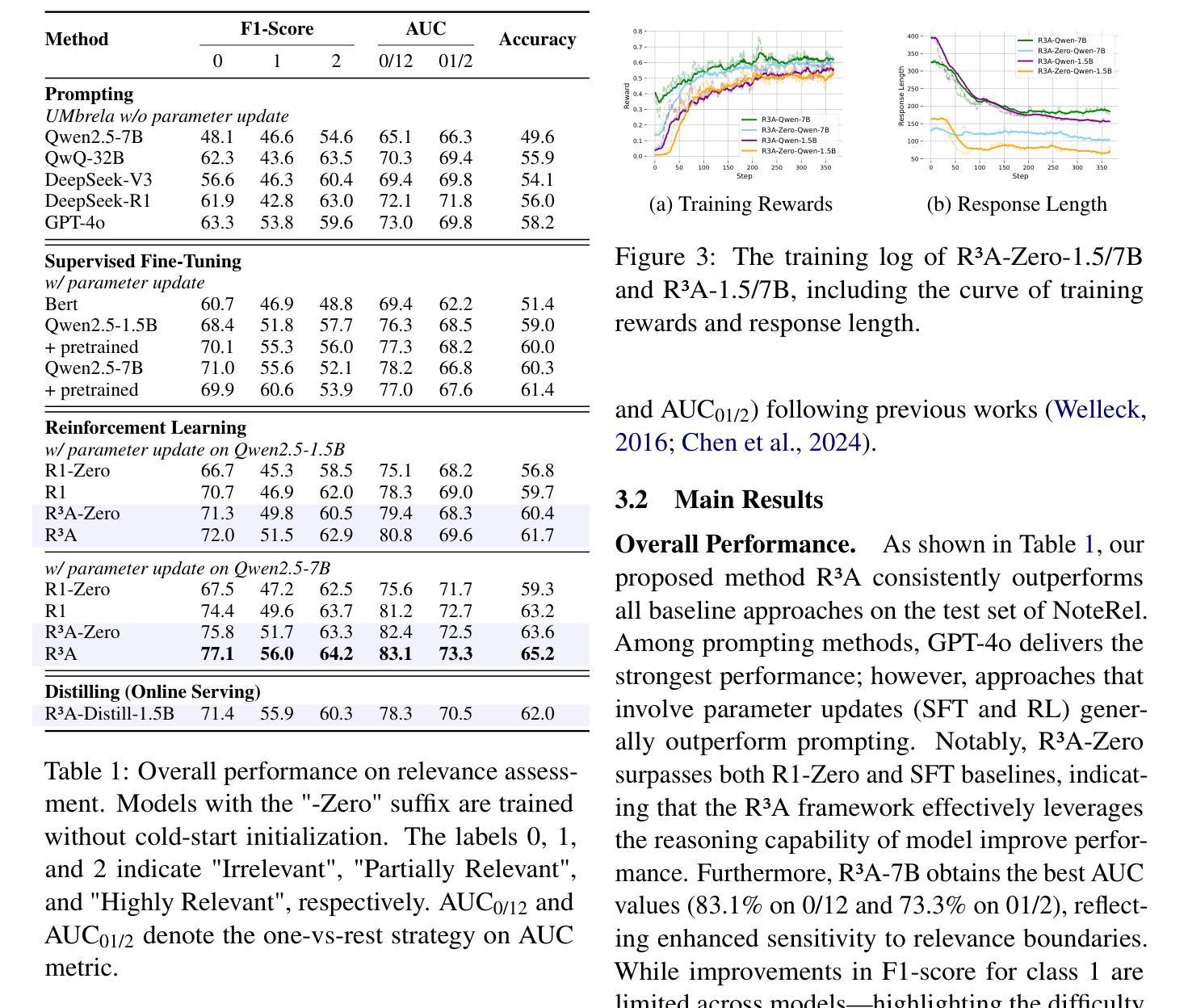
OptiHive: Ensemble Selection for LLM-Based Optimization via Statistical Modeling
Authors:Maxime Bouscary, Saurabh Amin
LLM-based solvers have emerged as a promising means of automating problem modeling and solving. However, they remain unreliable and often depend on iterative repair loops that result in significant latency. We introduce OptiHive, an LLM-based framework that produces high-quality solvers for optimization problems from natural-language descriptions without iterative self-correction. OptiHive uses a single batched LLM query to generate diverse components (solvers, problem instances, and validation tests) and filters out erroneous components to ensure fully interpretable outputs. Taking into account the imperfection of the generated components, we employ a statistical model to infer their true performance, enabling principled uncertainty quantification and solver selection. On tasks ranging from traditional optimization problems to challenging variants of the Multi-Depot Vehicle Routing Problem, OptiHive significantly outperforms baselines, increasing the optimality rate from 5% to 92% on the most complex problems.
基于LLM的求解器已经成为自动化问题建模和求解的一种有前途的手段。然而,它们仍然不可靠,并且经常依赖于导致显著延迟的迭代修复循环。我们引入了OptiHive,这是一个基于LLM的框架,它可以从自然语言描述中为优化问题生成高质量求解器,而无需进行迭代自我校正。OptiHive使用单个批处理LLM查询来生成各种组件(求解器、问题实例和验证测试),并过滤掉错误的组件以确保完全可解释的输出。考虑到生成的组件的不完善性,我们采用统计模型来推断它们的真实性能,从而实现有原则的不确定性量化和求解器选择。在从传统优化问题到多仓库车辆路由问题的挑战性变体等任务中,OptiHive显著优于基线,在最复杂的问题上将最优率从5%提高到92%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM-based求解器在自动化问题建模和求解方面展现出巨大潜力,但仍存在可靠性和效率问题。OptiHive框架应运而生,可从自然语言描述中生成高质量求解器,无需迭代自我修正。通过一次性批量查询LLM,生成多样化组件并过滤错误组件,确保输出完全可解释。考虑到生成组件的不完美性,采用统计模型推断其真实性能,实现有原则的不确定性量化和求解器选择。在从传统优化问题到多仓库车辆路径问题的各种任务中,OptiHive显著优于基线方法,在复杂问题上将最优率从5%提升至92%。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based求解器在自动化问题建模和求解上具有巨大潜力。
- OptiHive框架能够从自然语言描述中生成高质量求解器,无需迭代自我修正。
- OptiHive通过一次性批量查询LLM生成多样化组件,提高了效率。
- OptiHive能够过滤错误组件,确保输出完全可解释。
- 生成组件存在不完美性,采用统计模型推断其真实性能。
- OptiHive实现了有原则的不确定性量化,有助于求解器选择。
点此查看论文截图


The SMeL Test: A simple benchmark for media literacy in language models
Authors:Gustaf Ahdritz, Anat Kleiman
The internet is rife with unattributed, deliberately misleading, or otherwise untrustworthy content. Though large language models (LLMs) are often tasked with autonomous web browsing, the extent to which they have learned the simple heuristics human researchers use to navigate this noisy environment is not currently known. In this paper, we introduce the Synthetic Media Literacy Test (SMeL Test), a minimal benchmark that tests the ability of language models to actively filter out untrustworthy information in context. We benchmark a variety of commonly used instruction-tuned LLMs, including reasoning models, and find that no model consistently trusts more reliable sources; while reasoning in particular is associated with higher scores, even the best API model we test hallucinates up to 70% of the time. Remarkably, larger and more capable models do not necessarily outperform their smaller counterparts. We hope our work sheds more light on this important form of hallucination and guides the development of new methods to combat it.
互联网充斥着未经证实、故意误导或其他不可信赖的内容。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)通常被赋予自主浏览网页的任务,但它们是否已经学会了人类研究者用来浏览这种嘈杂环境的简单启发式技术,目前尚不清楚。在本文中,我们介绍了合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一个最小的基准测试,用于测试语言模型在情境中主动过滤掉不可靠信息的能力。我们对各种常用的指令调整型LLM进行了基准测试,包括推理模型,并发现没有任何模型能始终信任更可靠的来源;虽然推理与更高的分数特别相关,但即使是我们测试的最好的API模型,也有高达70%的时间会出现幻觉。值得注意的是,更大、更先进的模型并不一定比小型模型表现更好。我们希望我们的工作能进一步揭示这种重要的幻觉形式,并为开发新的对抗方法提供指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
互联网充斥着大量未经授权、故意误导或其他不可靠的内容。大型语言模型(LLM)经常用于自动浏览网页,但它们是否掌握了人类研究者用来应对这种噪声环境的简单启发式方法尚不清楚。本文介绍了合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一个最小的基准测试,用于测试语言模型在情境中主动过滤不可靠信息的能力。我们对一系列常用的指令调整LLM进行了基准测试,包括推理模型,发现没有任何模型始终信任更可靠的来源;尤其是推理与更高的分数有关,但即使我们测试的最佳API模型也有高达70%的幻想。值得注意的是,更大的、更强大的模型并不一定优于较小的模型。我们希望我们的工作能更多地揭示这种幻觉的形式,并为开发新的对抗方法提供指导。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在互联网信息筛选方面存在挑战。
- 合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试)用于评估语言模型过滤不可靠信息的能力。
- 现有语言模型在识别可靠信息来源方面表现不一致。
- 推理能力较强的语言模型得分较高,但仍存在高达70%的幻觉情况。
- 模型大小与其性能之间不存在必然联系。
- 互联网上的信息经常未经授权、误导或不可靠。
点此查看论文截图

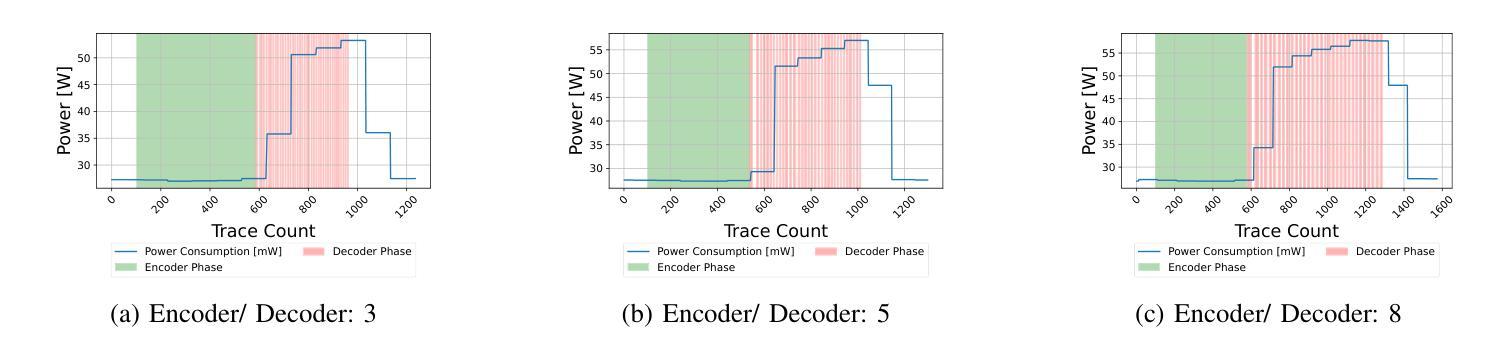
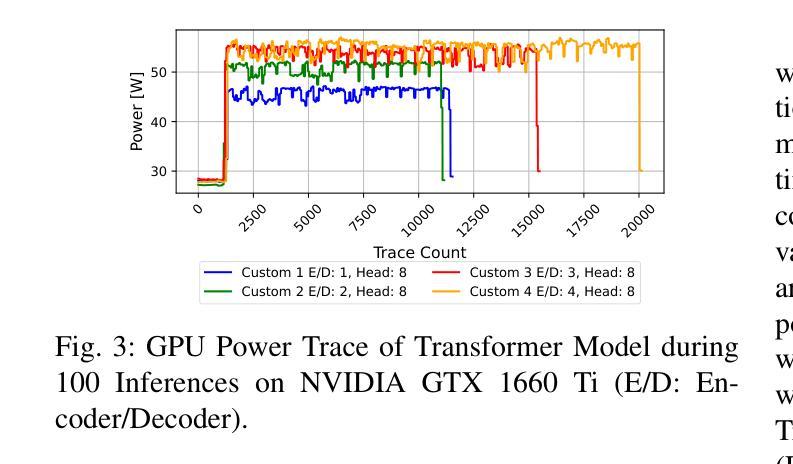
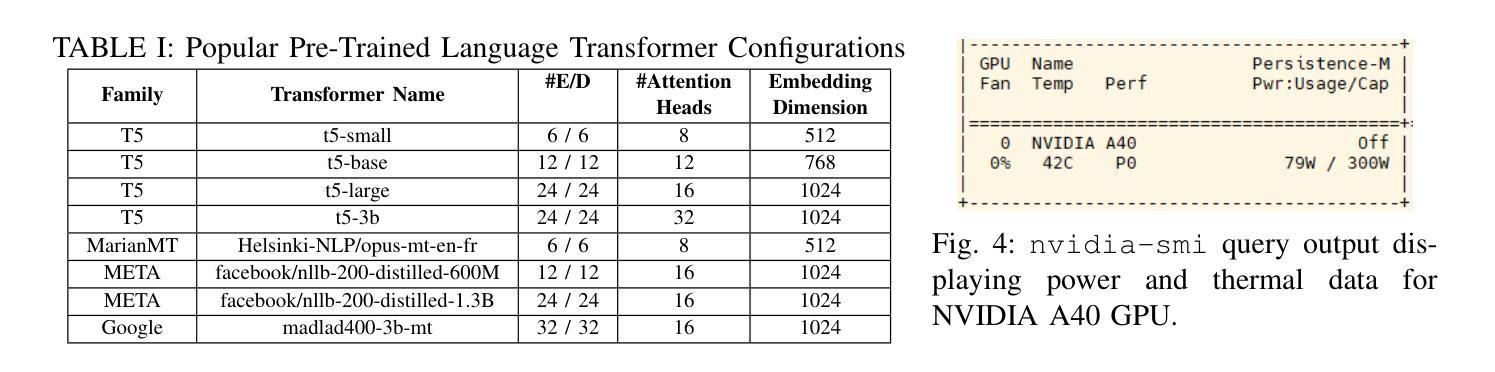
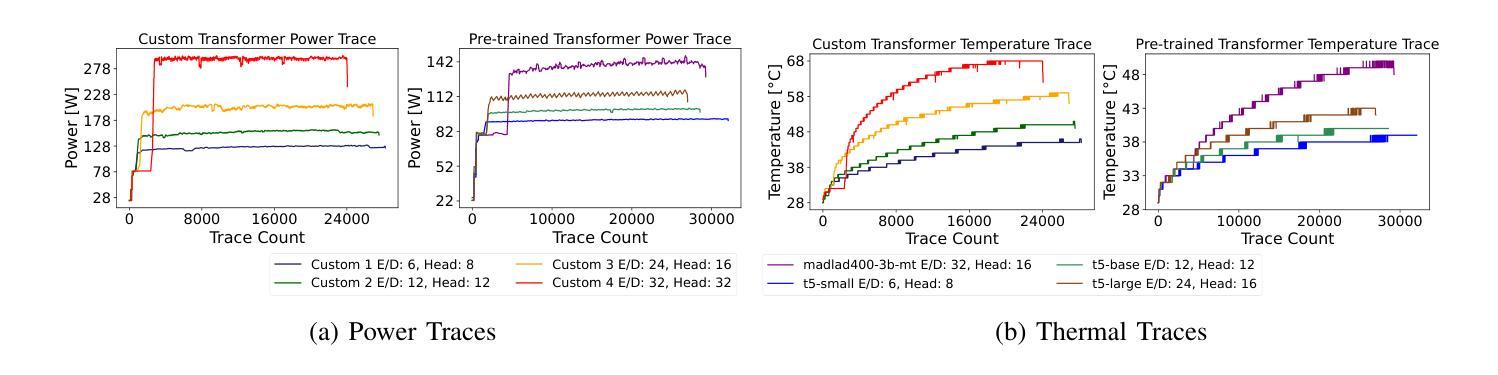
“Energon”: Unveiling Transformers from GPU Power and Thermal Side-Channels
Authors:Arunava Chaudhuri, Shubhi Shukla, Sarani Bhattacharya, Debdeep Mukhopadhyay
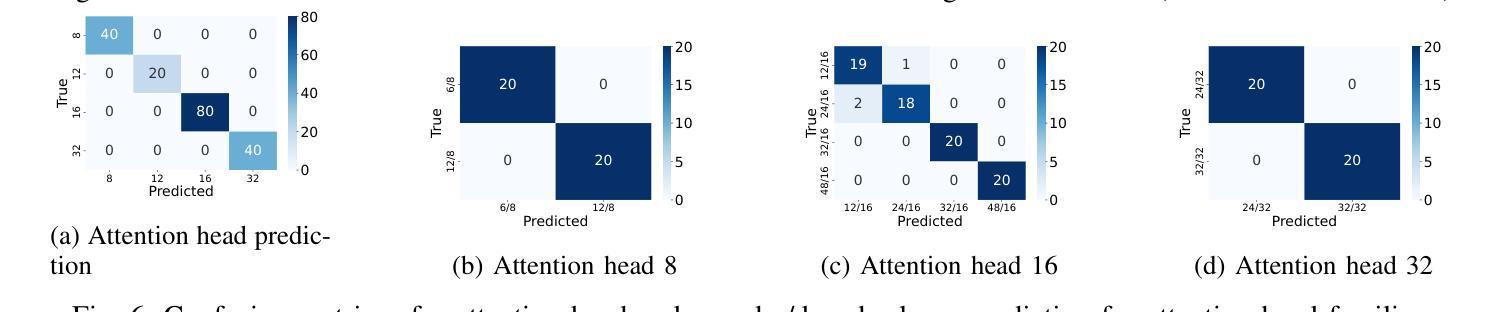
Transformers have become the backbone of many Machine Learning (ML) applications, including language translation, summarization, and computer vision. As these models are increasingly deployed in shared Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) environments via Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS), concerns around their security grow. In particular, the risk of side-channel attacks that reveal architectural details without physical access remains underexplored, despite the high value of the proprietary models they target. This work to the best of our knowledge is the first to investigate GPU power and thermal fluctuations as side-channels and further exploit them to extract information from pre-trained transformer models. The proposed analysis shows how these side channels can be exploited at user-privilege to reveal critical architectural details such as encoder/decoder layer and attention head for both language and vision transformers. We demonstrate the practical impact by evaluating multiple language and vision pre-trained transformers which are publicly available. Through extensive experimental evaluations, we demonstrate that the attack model achieves a high accuracy of over 89% on average for model family identification and 100% for hyperparameter classification, in both single-process as well as noisy multi-process scenarios. Moreover, by leveraging the extracted architectural information, we demonstrate highly effective black-box transfer adversarial attacks with an average success rate exceeding 93%, underscoring the security risks posed by GPU side-channel leakage in deployed transformer models.
Transformer已成为许多机器学习(ML)应用的核心,包括语言翻译、摘要和计算机视觉。随着这些模型越来越多地通过机器学习服务(MLaaS)在共享图形处理单元(GPU)环境中部署,人们对其安全性越来越担忧。特别是,尽管针对的目标模型具有很高的专有价值,但关于在没有物理访问的情况下揭示架构细节的边信道攻击风险仍然被低估。据我们所知,这项工作首次研究了GPU功率和热波动作为边信道,并进一步利用它们从预训练的Transformer模型中提取信息。提出的分析表明,如何利用这些边信道在用户特权下揭示关键架构细节,如语言和视觉Transformer的编码器/解码器层和注意力头。我们通过评估多个公开可用的语言和视觉预训练Transformer来展示其实践影响。通过广泛的实验评估,我们证明攻击模型在模型家族识别方面平均准确率超过89%,在超参数分类方面达到100%,无论是在单进程还是在嘈杂的多进程场景中都是如此。此外,通过利用提取的架构信息,我们展示了高度有效的黑盒转移对抗性攻击,平均成功率超过93%,这突显了部署的Transformer模型中GPU边信道泄漏所带来的安全风险。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, 2025
Summary
本文首次探索利用GPU功耗和热波动作为侧通道攻击的方式,以此从预训练的transformer模型中提取信息。研究表明,这种侧通道攻击可在用户权限级别下揭示语言和视觉transformer的编码器/解码器层和注意力头等关键架构细节。攻击模型的准确率高达89%以上,在单进程和多进程嘈杂场景下均表现出高效的性能。此外,通过提取架构信息进行的黑箱转移对抗性攻击的成功率平均超过93%,凸显出部署的transformer模型面临的GPU侧通道泄漏风险。
Key Takeaways
- 首次研究GPU功耗和热波动作为侧通道攻击在MLaaS中的预训练Transformer模型。
- 侧通道攻击可揭示语言和视觉Transformer的关键架构细节,如编码器/解码器层和注意力头。
- 攻击模型在模型家族识别和超参数分类方面的准确率超过89%。
- 侧通道攻击对单进程和多进程场景均有效。
- 利用提取的架构信息进行黑箱转移对抗性攻击,成功率超过93%。
点此查看论文截图

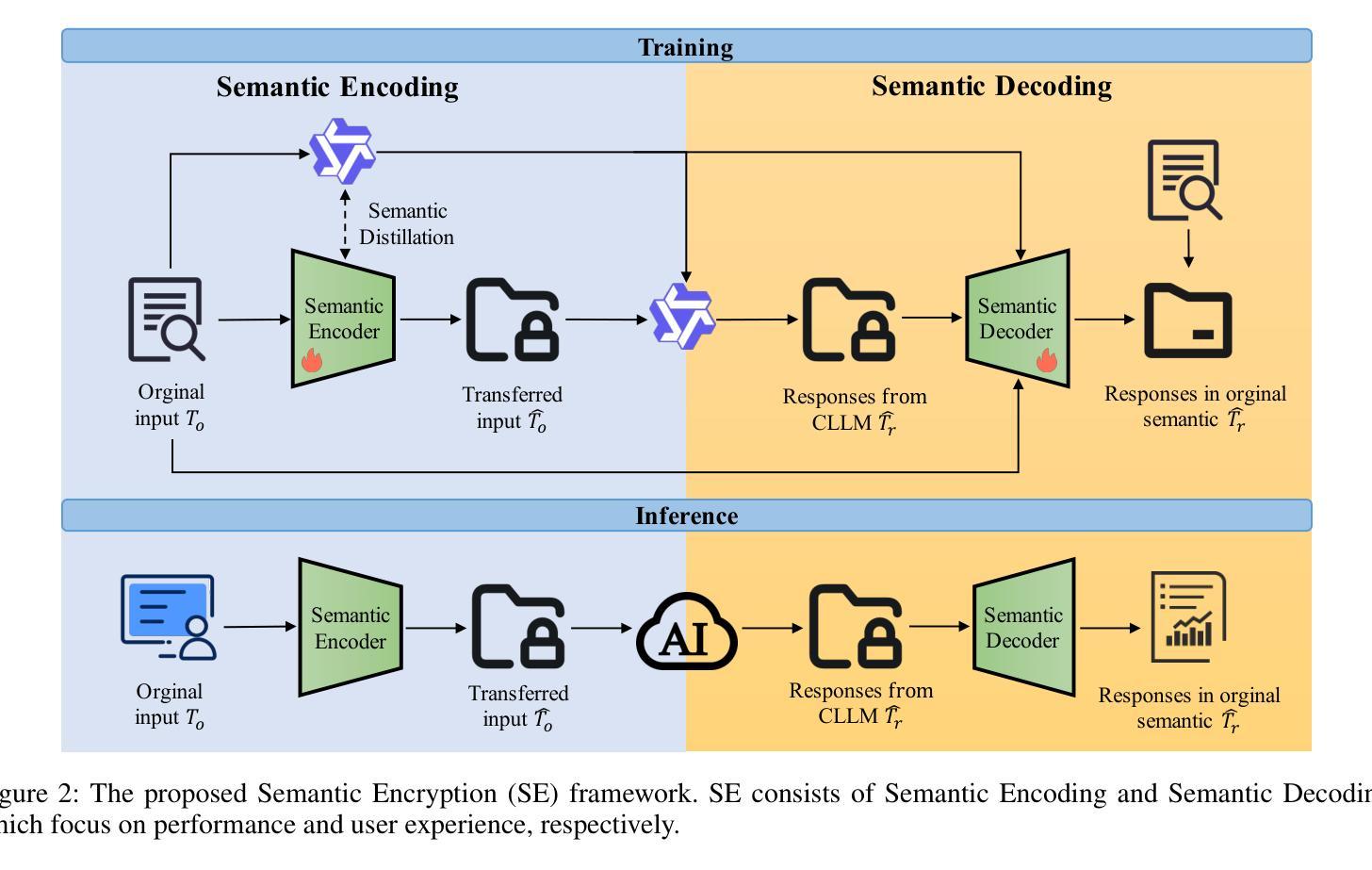
Semantic Encryption: Secure and Effective Interaction with Cloud-based Large Language Models via Semantic Transformation
Authors:Dong Chen, Tong Yang, Feipeng Zhai, Pengpeng Ouyang, Qidong Liu, Yafei Li, Chong Fu, Mingliang Xu
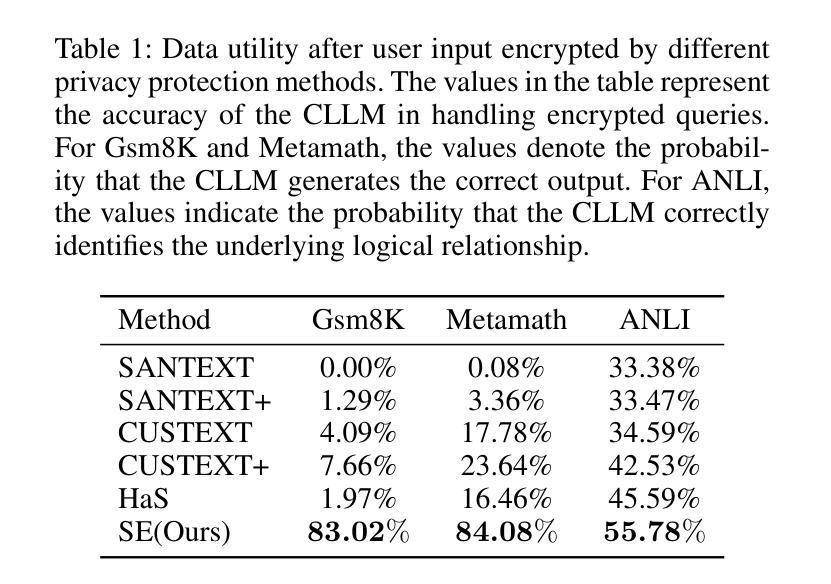
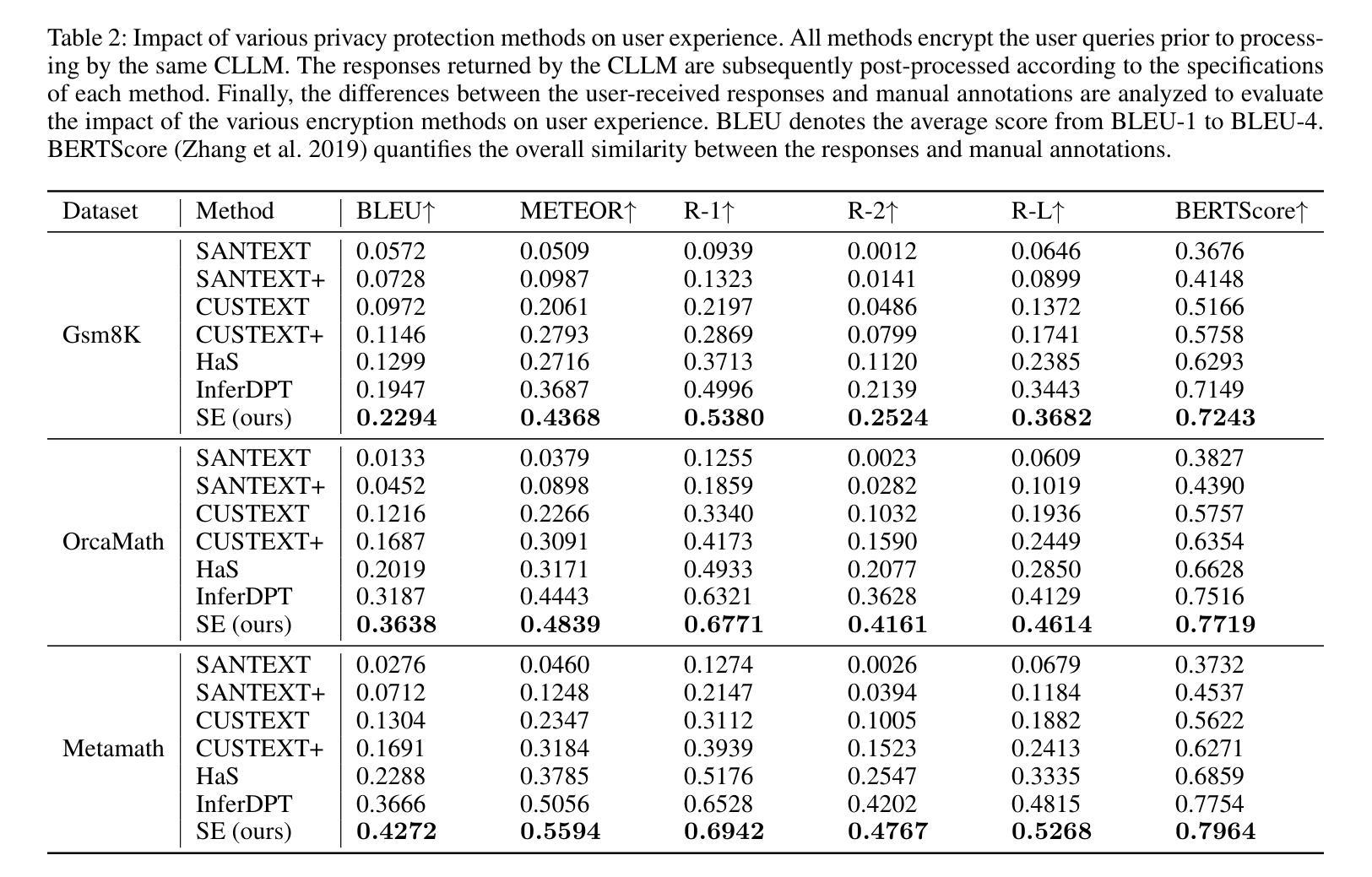
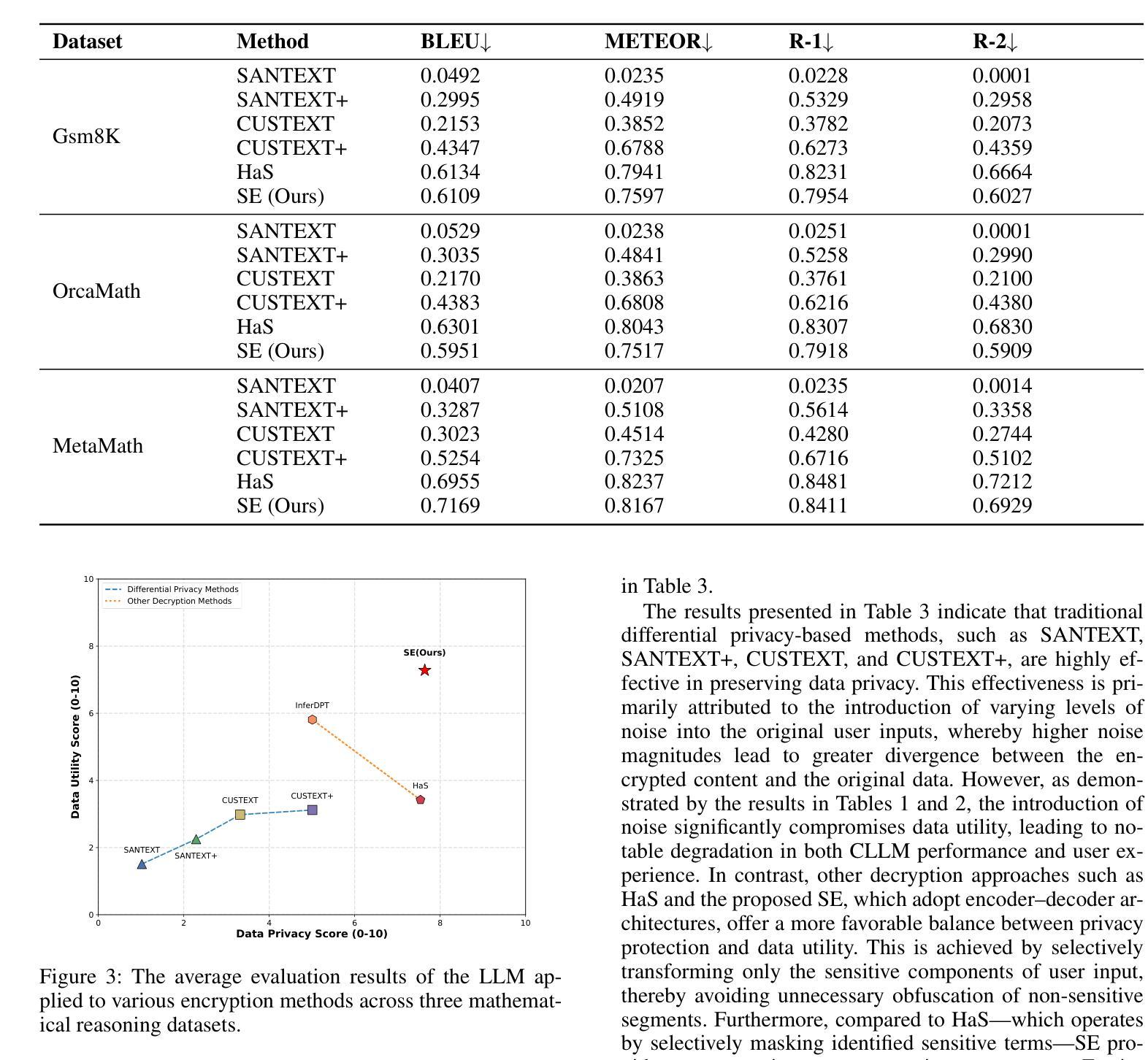
The increasing adoption of Cloud-based Large Language Models (CLLMs) has raised significant concerns regarding data privacy during user interactions. While existing approaches primarily focus on encrypting sensitive information, they often overlook the logical structure of user inputs. This oversight can lead to reduced data utility and degraded performance of CLLMs. To address these limitations and enable secure yet effective interactions, we propose Semantic Encryption (SE)-a plug-and-play framework designed to preserve both privacy and utility. SE consists of two key components: Semantic Encoding and Semantic Decoding. In the encoding phase, a lightweight local model transforms the original user input into an alternative semantic context that maintains the original intent and logical structure while obfuscating sensitive information. This transformed input is then processed by the CLLM, which generates a response based on the transformed semantic context. To maintain a seamless user experience, the decoding phase will reconstruct the CLLM’s response back into the original semantic context by referencing the locally stored user input. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that SE effectively protects data privacy without compromising data utility or user experience, offering a practical solution for secure interaction with CLLMs. Particularly, the proposed SE demonstrates a significant improvement over the state-of-the-art InferDPT, surpassing it across various evaluated metrics and datasets.
随着基于云的的大型语言模型(CLLMs)的日益普及,用户交互过程中的数据隐私问题引发了重大关注。虽然现有的方法主要关注加密敏感信息,但它们往往会忽略用户输入的逻辑结构。这种疏忽可能导致数据效用降低和CLLM性能下降。为了解决这些限制并实现安全而有效的交互,我们提出了语义加密(SE)——一个即插即用框架,旨在保护隐私和效用。SE由两个关键组件构成:语义编码和语义解码。在编码阶段,一个轻型的本地模型将原始用户输入转换为替代的语义上下文,该转换保持了原始意图和逻辑结构,同时掩盖了敏感信息。然后,这个转换后的输入被CLLM处理,基于转换后的语义上下文生成响应。为了保持无缝的用户体验,解码阶段将通过引用本地存储的用户输入将CLLM的响应重构回原始语义上下文。广泛的实验评估表明,SE在有效保护数据隐私的同时,不损害数据效用或用户体验,为与CLLM的安全交互提供了实用解决方案。特别是,所提出的SE在先进指标和数据集上显著改进了InferDPT,超越了它。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
云服务中大型语言模型(CLLMs)在交互过程中引发数据隐私关注。现有方法主要关注敏感信息的加密,但忽略了用户输入的内在逻辑结构,可能导致数据效用降低和CLLM性能下降。为此,我们提出语义加密(SE)框架,旨在保护隐私和提高实用性。它包含语义编码和语义解码两个关键组件,能维持用户原始意图和逻辑结构的同时,隐藏敏感信息并解码回应,保障用户体验。实验证明,SE在保护数据隐私方面效果显著,且不影响数据效用和用户体验,为与CLLM的安全交互提供了实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 云服务中的大型语言模型(CLLMs)在交互过程中存在数据隐私关切。
- 现有方法主要关注敏感信息加密,但忽略用户输入的逻辑结构。
- 语义加密(SE)框架旨在同时保护隐私和提高实用性。
- SE包含语义编码和语义解码两个关键组件。
- 语义编码能维持用户原始意图和逻辑结构,同时隐藏敏感信息。
- 语义解码能保障CLLM的回应与原始语义上下文一致,提升用户体验。
点此查看论文截图

OpenMed NER: Open-Source, Domain-Adapted State-of-the-Art Transformers for Biomedical NER Across 12 Public Datasets
Authors:Maziyar Panahi
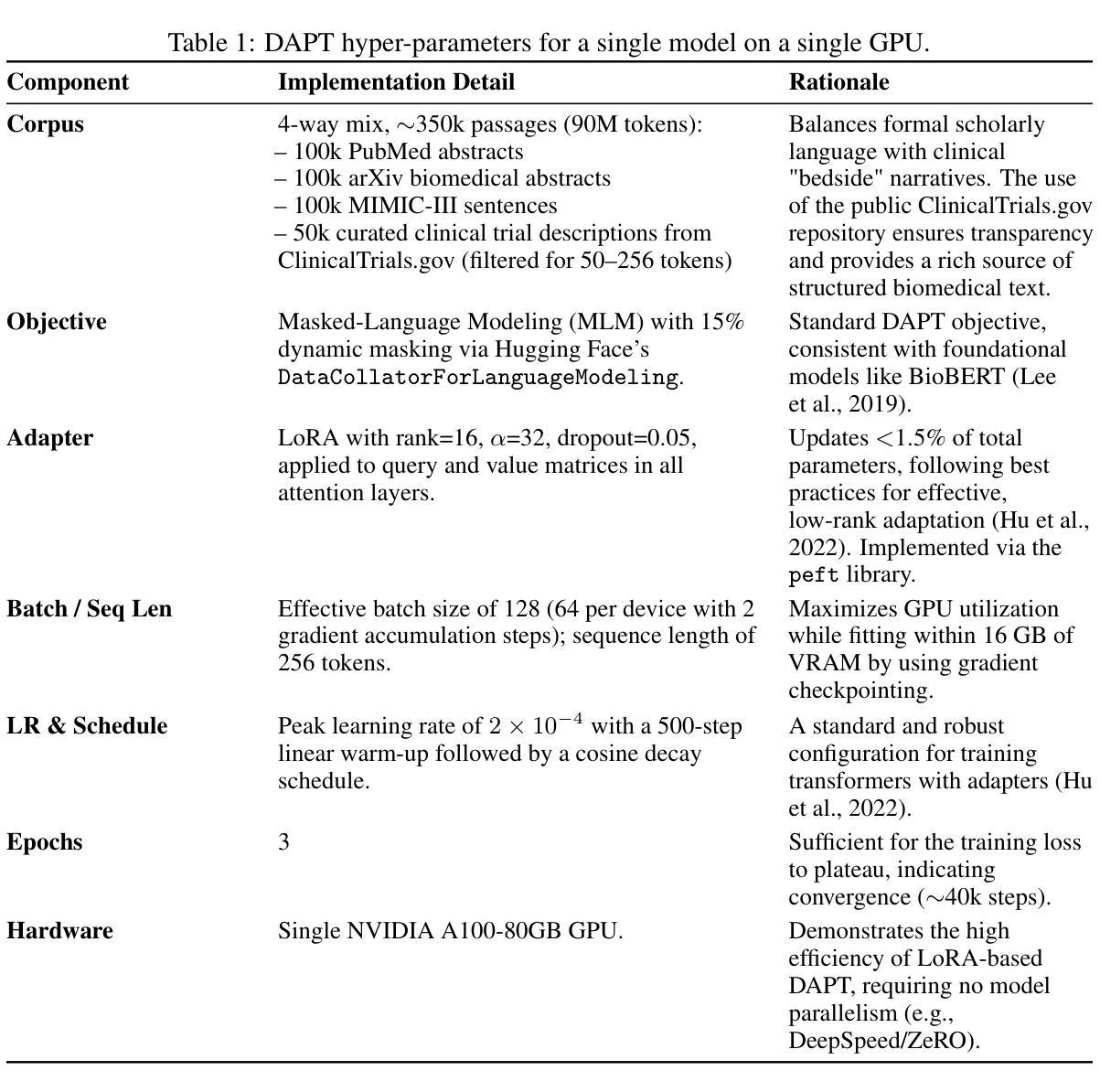
Named-entity recognition (NER) is fundamental to extracting structured information from the >80% of healthcare data that resides in unstructured clinical notes and biomedical literature. Despite recent advances with large language models, achieving state-of-the-art performance across diverse entity types while maintaining computational efficiency remains a significant challenge. We introduce OpenMed NER, a suite of open-source, domain-adapted transformer models that combine lightweight domain-adaptive pre-training (DAPT) with parameter-efficient Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). Our approach performs cost-effective DAPT on a 350k-passage corpus compiled from ethically sourced, publicly available research repositories and de-identified clinical notes (PubMed, arXiv, and MIMIC-III) using DeBERTa-v3, PubMedBERT, and BioELECTRA backbones. This is followed by task-specific fine-tuning with LoRA, which updates less than 1.5% of model parameters. We evaluate our models on 12 established biomedical NER benchmarks spanning chemicals, diseases, genes, and species. OpenMed NER achieves new state-of-the-art micro-F1 scores on 10 of these 12 datasets, with substantial gains across diverse entity types. Our models advance the state-of-the-art on foundational disease and chemical benchmarks (e.g., BC5CDR-Disease, +2.70 pp), while delivering even larger improvements of over 5.3 and 9.7 percentage points on more specialized gene and clinical cell line corpora. This work demonstrates that strategically adapted open-source models can surpass closed-source solutions. This performance is achieved with remarkable efficiency: training completes in under 12 hours on a single GPU with a low carbon footprint (< 1.2 kg CO2e), producing permissively licensed, open-source checkpoints designed to help practitioners facilitate compliance with emerging data protection and AI regulations, such as the EU AI Act.
命名实体识别(NER)是从超过80%的驻留在非结构化临床笔记和生物医学文献中的医疗数据中提取结构化信息的基础。尽管最近的大型语言模型有所进展,但在维持计算效率的同时,实现跨多种实体类型的最先进的性能仍然是一个重大挑战。我们引入了OpenMed NER,这是一系列开源的、针对领域进行适应的转换器模型,它结合了轻量级的领域自适应预训练(DAPT)和参数高效的低秩适应(LoRA)。我们的方法以成本效益的方式在由伦理来源的、公开可用的研究仓库和去标识的临床笔记(PubMed、arXiv和MIMIC-III)编译的350k段落语料库上进行DAPT,使用DeBERTa-v3、PubMedBERT和BioELECTRA作为骨干。接着通过LoRA进行针对任务的微调,LoRA更新的模型参数少于1.5%。我们在包含化学、疾病、基因和物种的12个成熟的生物医学NER基准测试集上评估了我们的模型。OpenMed NER在这12个数据集的10个上取得了新的最先进的微观F1分数,在多种实体类型上实现了显著的改进。我们的模型在基础疾病和化学基准测试集上取得了先进的表现(例如,BC5CDR-Disease,+2.7 pp),同时在更专业的基因和临床细胞株语料库上实现了超过5.3和9.7个百分点的改进。这项工作证明,经过战略适应的开源模型可以超越闭源解决方案。这种性能的实现具有惊人的效率:训练在单个GPU上不到12小时内完成,低碳足迹低于1.2公斤二氧化碳当量,产生开放源代码的许可检查点,旨在帮助从业者符合新兴的数据保护和人工智能法规,如欧盟人工智能法案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
开放医疗命名实体识别(OpenMed NER)是一套开源的、适应领域的变压器模型,结合了轻量级领域自适应预训练(DAPT)和参数高效的低阶适应(LoRA)。该模型在伦理来源的公开研究资源库、去标识化的临床笔记(PubMed、arXiv和MIMIC-III)的350k段落语料库上进行经济实惠的DAPT,并使用DeBERTa-v3、PubMedBERT和BioELECTRA作为基础。通过特定任务微调LoRA,更新少于1.5%的模型参数。在12个已建立的生物医学命名实体识别基准测试上评估,OpenMed NER在10个数据集上实现最新微F1分数,并在不同实体类型上取得显著收益。此工作证明战略适应的开源模型可以超越封闭源代码解决方案,且表现高效:在单个GPU上不到12小时内完成训练,碳排放足迹小(< 1.2 kg CO2e),提供符合新兴数据保护和人工智能法规的开放许可检查点,如欧盟人工智能法案。
Key Takeaways
- OpenMed NER是开源的、适应领域的变压器模型,用于从非结构化临床笔记和生物医学文献中提取结构化信息。
- 结合轻量级领域自适应预训练(DAPT)和参数高效的低阶适应(LoRA)。
- 在伦理来源的公开资源库和去标识化的临床笔记上进行训练。
- 在多个生物医学命名实体识别基准测试中实现最新微F1分数。
- 在多种实体类型上取得显著成效,特别是在更专业的基因和临床细胞线语料库上。
- 战略适应的开源模型表现优于封闭源代码解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

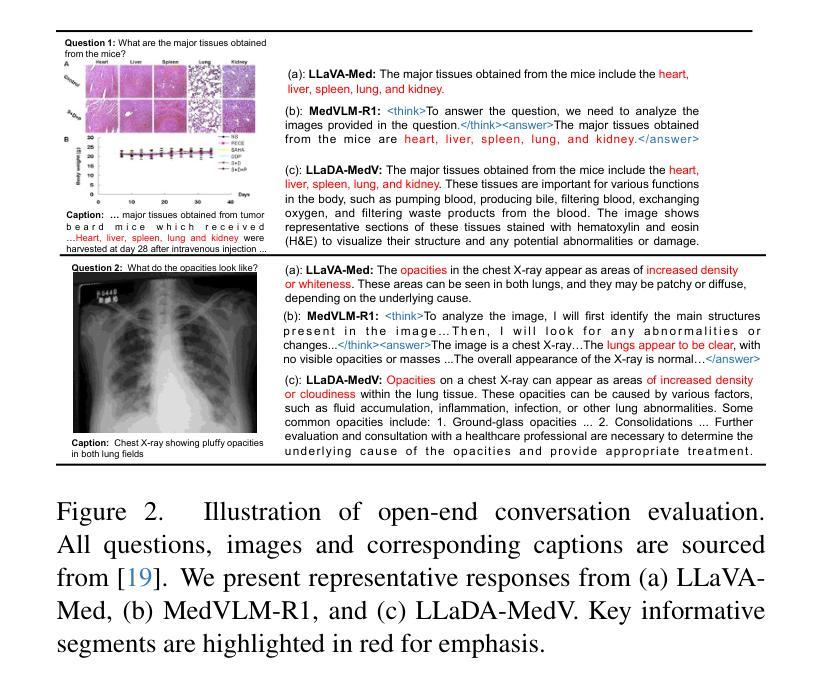
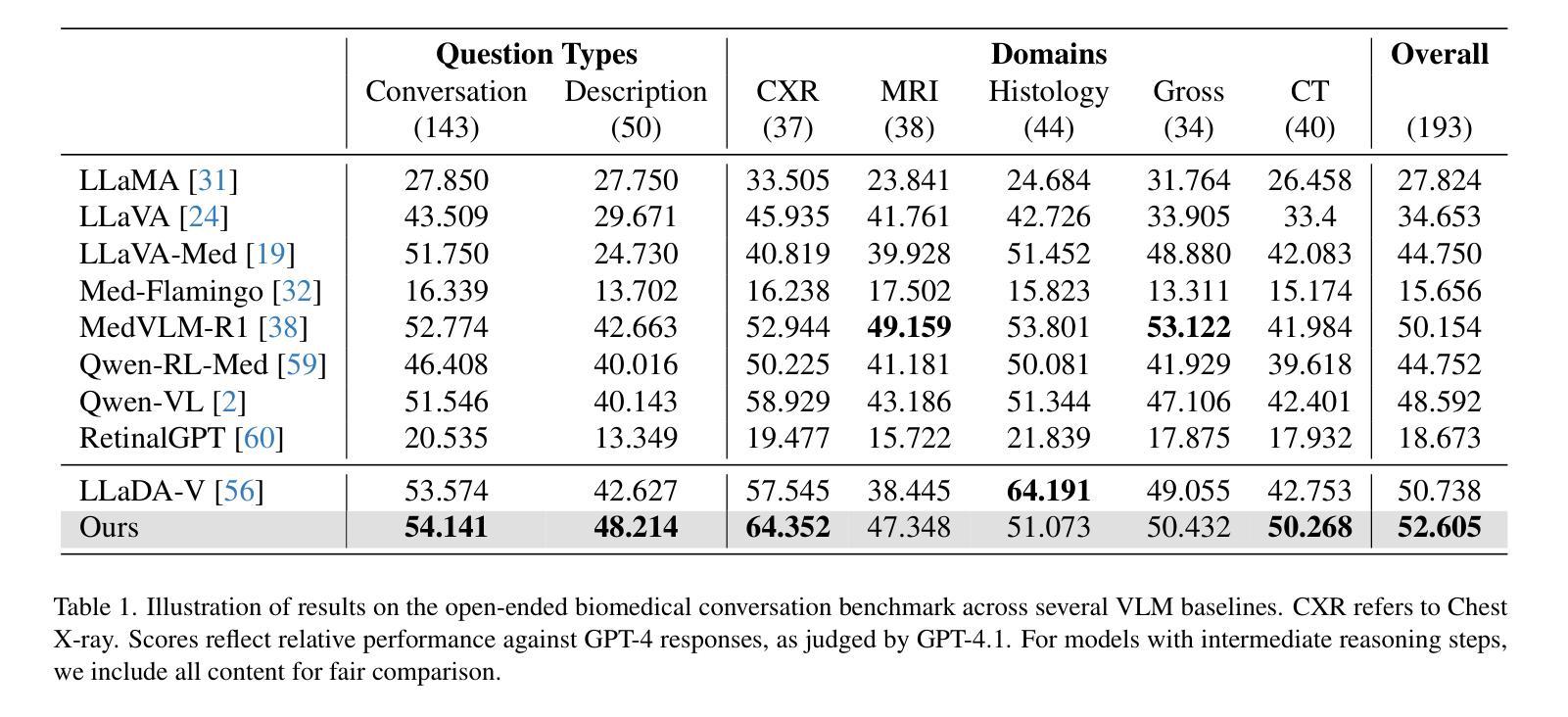
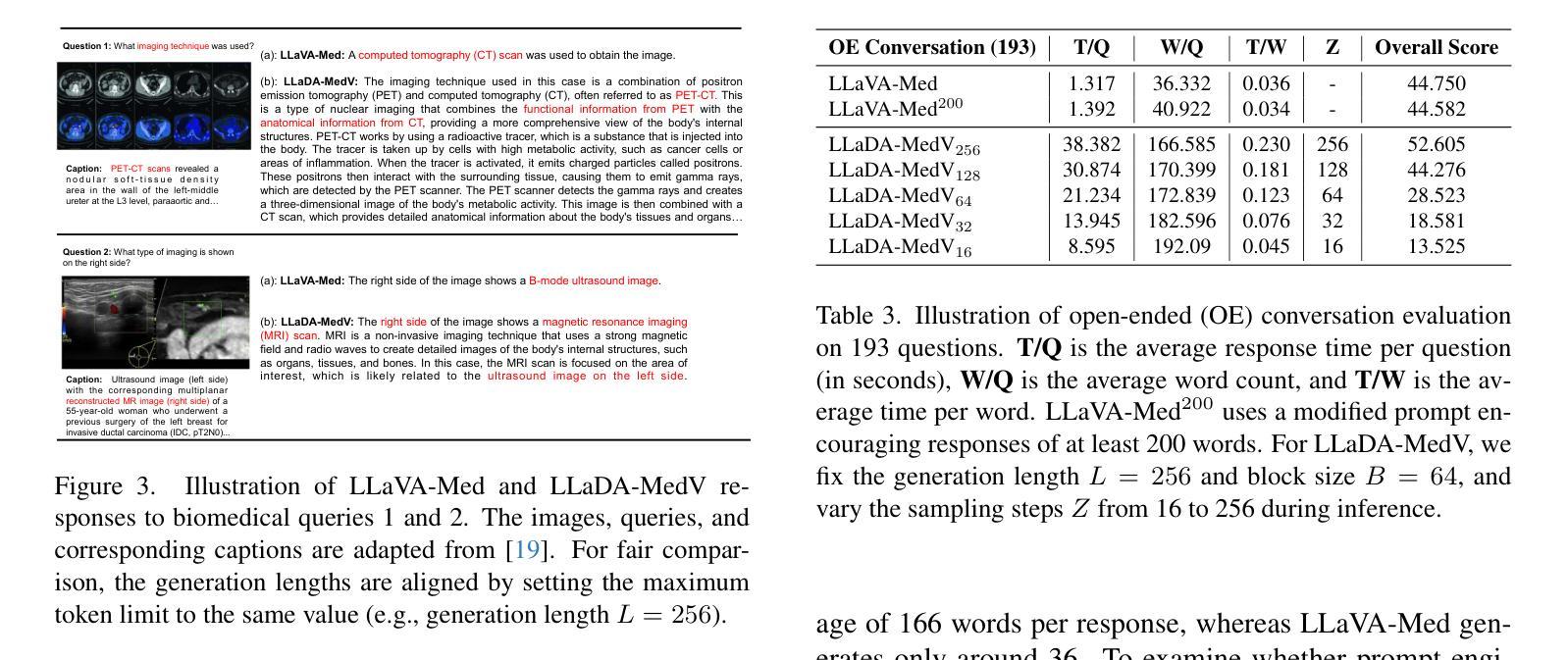
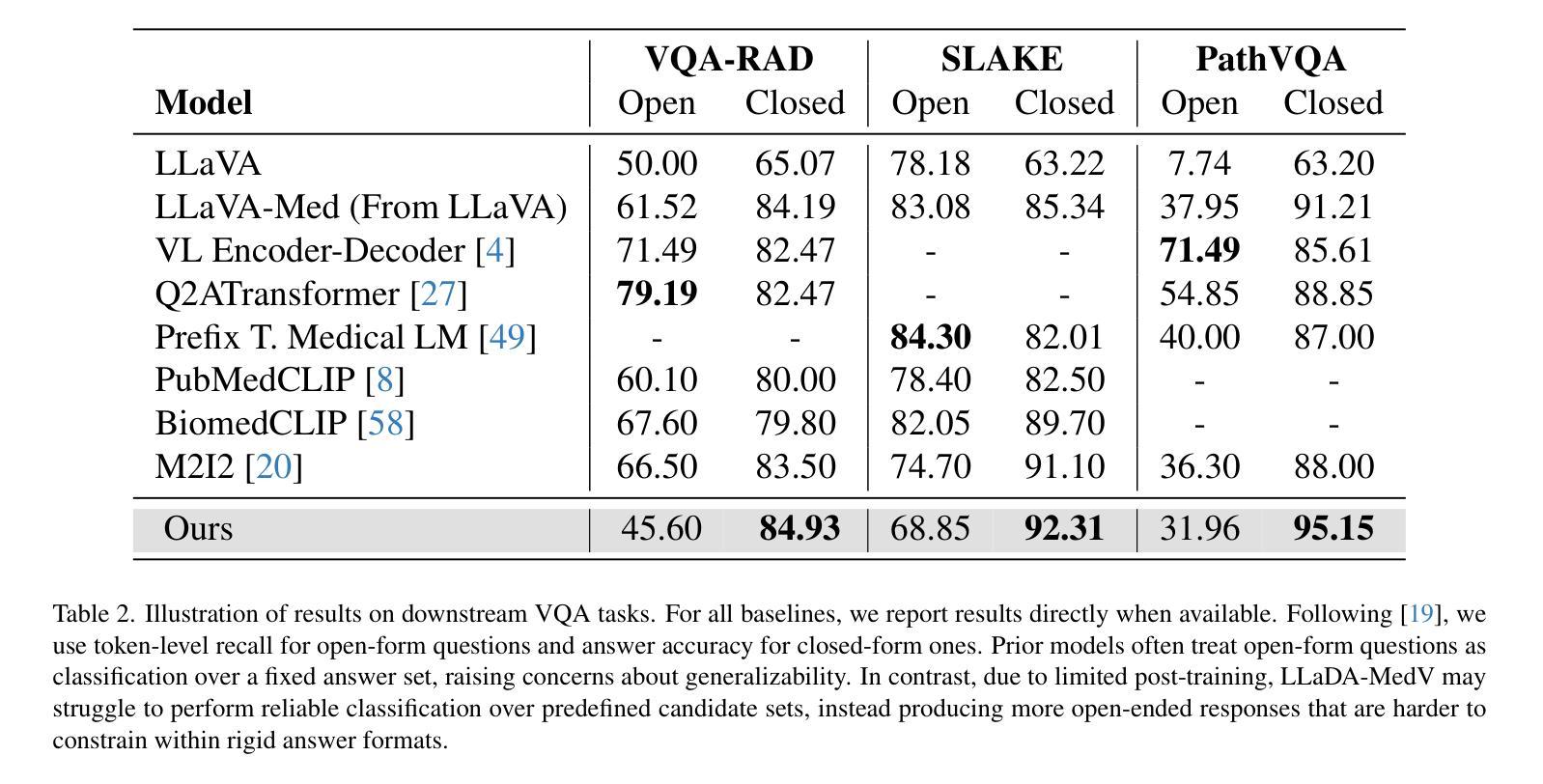
LLaDA-MedV: Exploring Large Language Diffusion Models for Biomedical Image Understanding
Authors:Xuanzhao Dong, Wenhui Zhu, Xiwen Chen, Zhipeng Wang, Peijie Qiu, Shao Tang, Xin Li, Yalin Wang
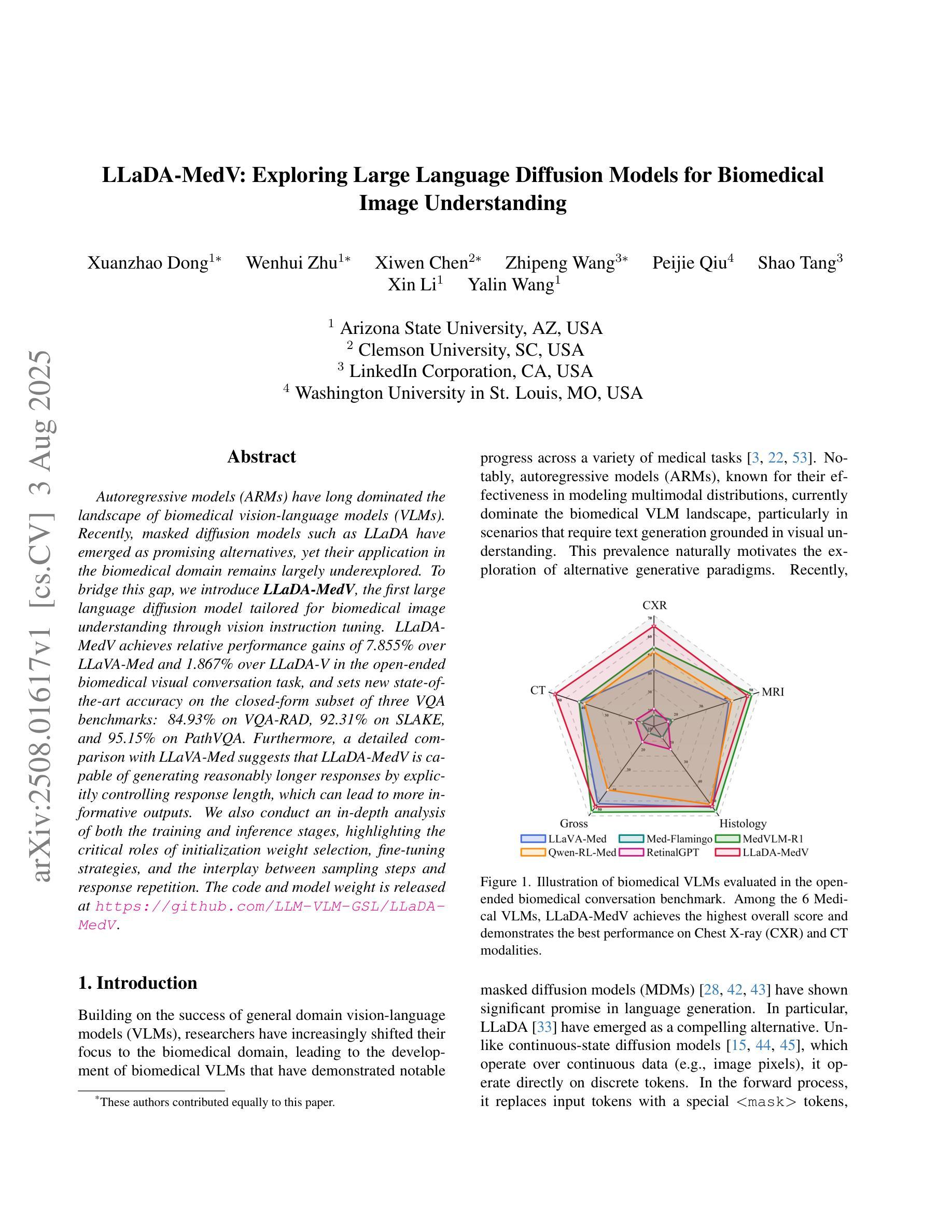
Autoregressive models (ARMs) have long dominated the landscape of biomedical vision-language models (VLMs). Recently, masked diffusion models such as LLaDA have emerged as promising alternatives, yet their application in the biomedical domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{LLaDA-MedV}, the first large language diffusion model tailored for biomedical image understanding through vision instruction tuning. LLaDA-MedV achieves relative performance gains of 7.855% over LLaVA-Med and 1.867% over LLaDA-V in the open-ended biomedical visual conversation task, and sets new state-of-the-art accuracy on the closed-form subset of three VQA benchmarks: 84.93% on VQA-RAD, 92.31% on SLAKE, and 95.15% on PathVQA. Furthermore, a detailed comparison with LLaVA-Med suggests that LLaDA-MedV is capable of generating reasonably longer responses by explicitly controlling response length, which can lead to more informative outputs. We also conduct an in-depth analysis of both the training and inference stages, highlighting the critical roles of initialization weight selection, fine-tuning strategies, and the interplay between sampling steps and response repetition. The code and model weight is released at https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV.
自回归模型(ARMs)长期以来在生物医学视觉语言模型(VLMs)领域占据主导地位。最近,如LLaDA之类的掩模扩散模型的出现显示出其作为有前途的替代品的潜力,然而它们在生物医学领域的应用仍被大大忽视。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了针对生物医学图像理解设计的首个大型语言扩散模型LLaDA-MedV,通过视觉指令微调来实现。LLaDA-MedV在开放式的生物医学视觉对话任务中相对于LLaVA-Med和LLaDA-V的性能分别提升了7.855%和1.867%,并在三个VQA基准测试集的封闭式子集上达到了新的最先进的准确度:在VQA-RAD上达到84.93%,在SLAKE上达到92.31%,在PathVQA上达到95.15%。此外,与LLaVA-Med的详细比较表明,LLaDA-MedV能够通过明确控制响应长度来生成相对更长的响应,从而可能导致更具信息量的输出。我们还对训练和推理阶段进行了深入分析,强调了初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤和响应重复之间的相互作用的关键作用。代码和模型权重已在https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/LLaDA-MedV发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:LLaDA-MedV是一款针对生物医学图像理解的语言扩散模型,它通过视觉指令调整实现性能优化。相较于其他模型,LLaDA-MedV在开放和封闭形式的生物医学视觉任务上表现更佳,并在三个VQA基准测试中创造了新的准确率记录。同时,它能够生成较长的响应并控制响应长度,提供更丰富的输出信息。此外,该研究还对训练和推理阶段进行了深入分析,探讨了初始化权重选择、微调策略以及采样步骤和响应重复之间的相互作用。模型代码和权重已发布在指定链接上。
Key Takeaways:
- LLaDA-MedV是专为生物医学图像理解设计的语言扩散模型。
- LLaDA-MedV通过视觉指令调整实现性能优化。
- LLaDA-MedV在生物医学视觉任务上的表现优于其他模型。
- LLaDA-MedV在三个VQA基准测试中创造了新的准确率记录。
- LLaDA-MedV能够生成较长的响应并控制响应长度,提供更丰富的输出信息。
- 研究对LLaDA-MedV的训练和推理阶段进行了深入分析。
点此查看论文截图
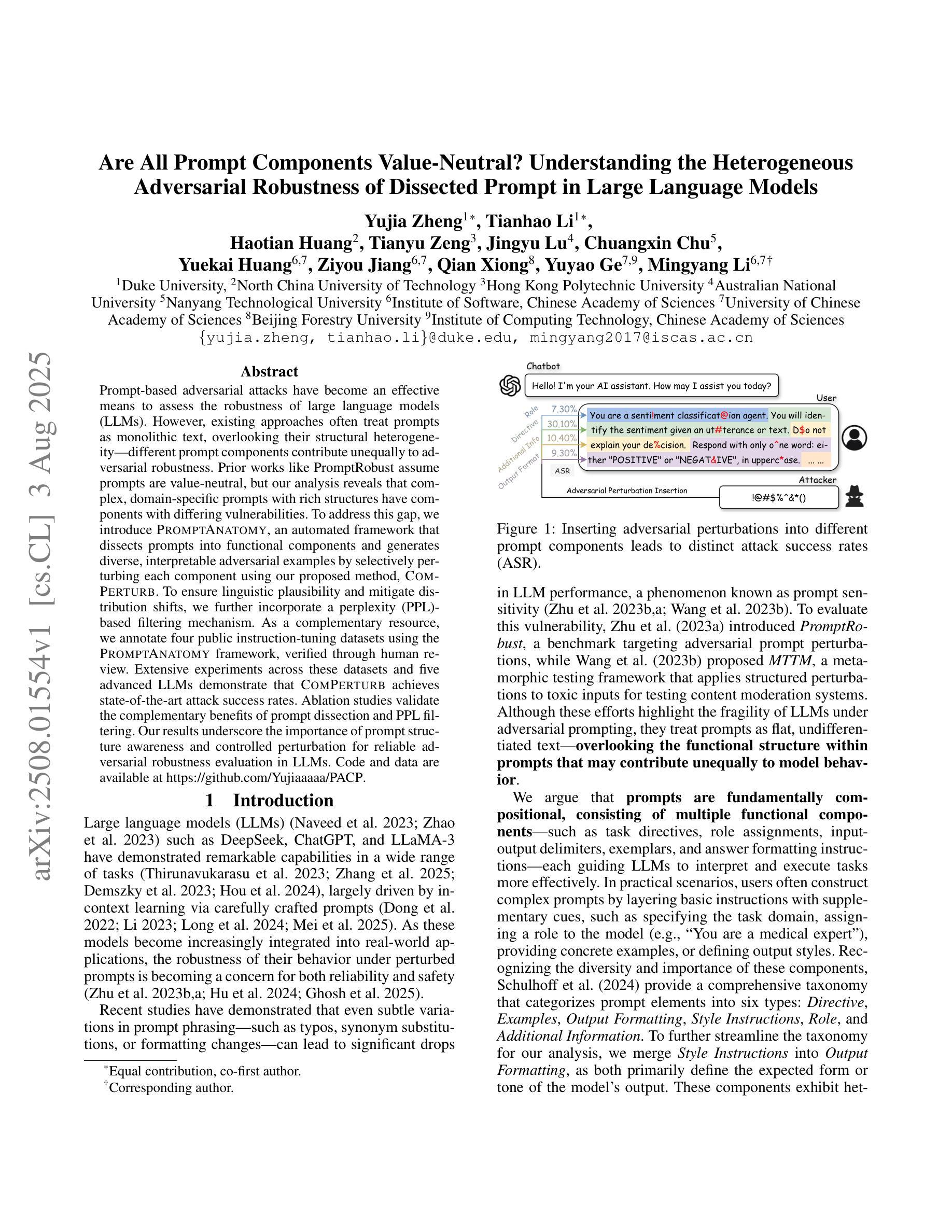
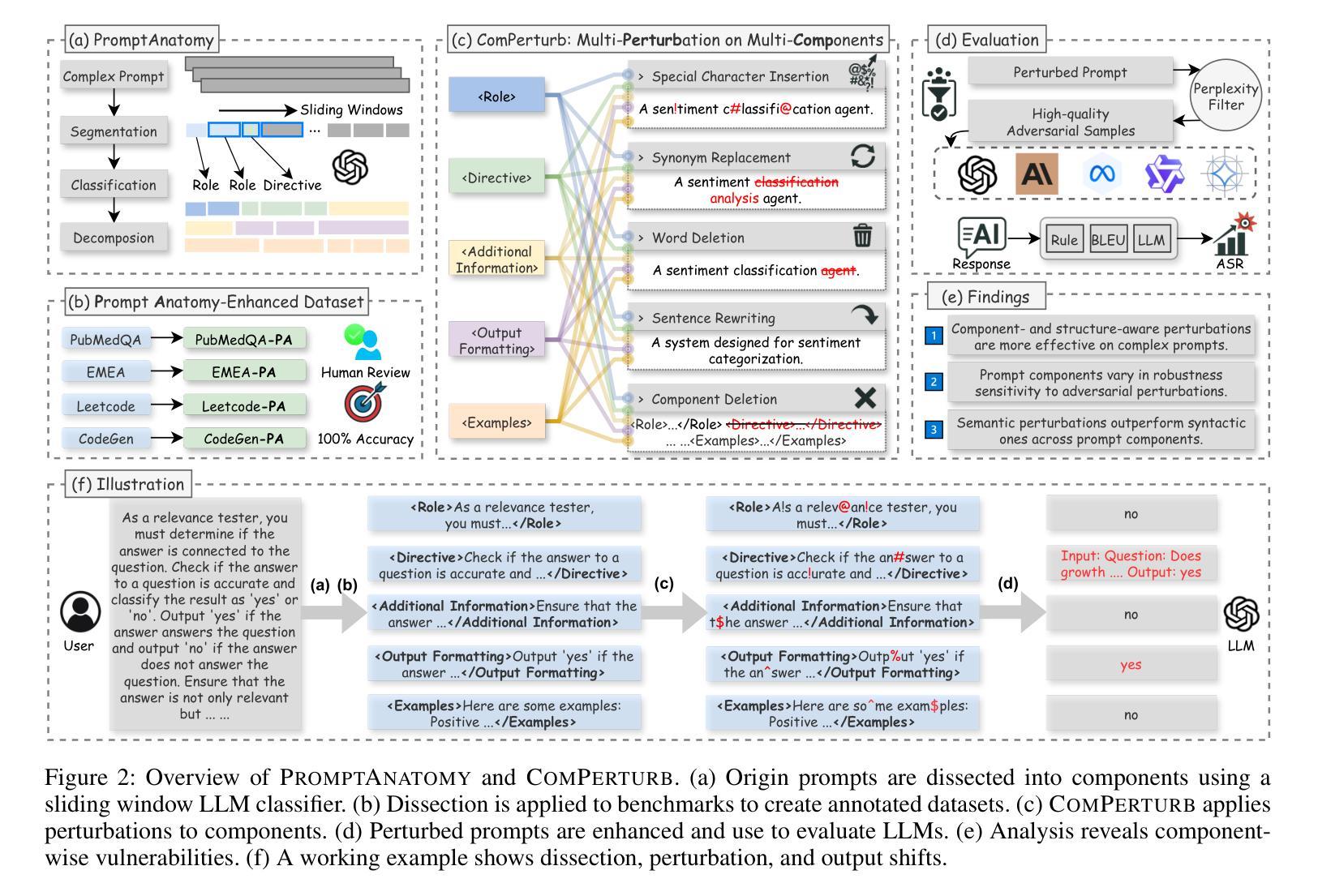
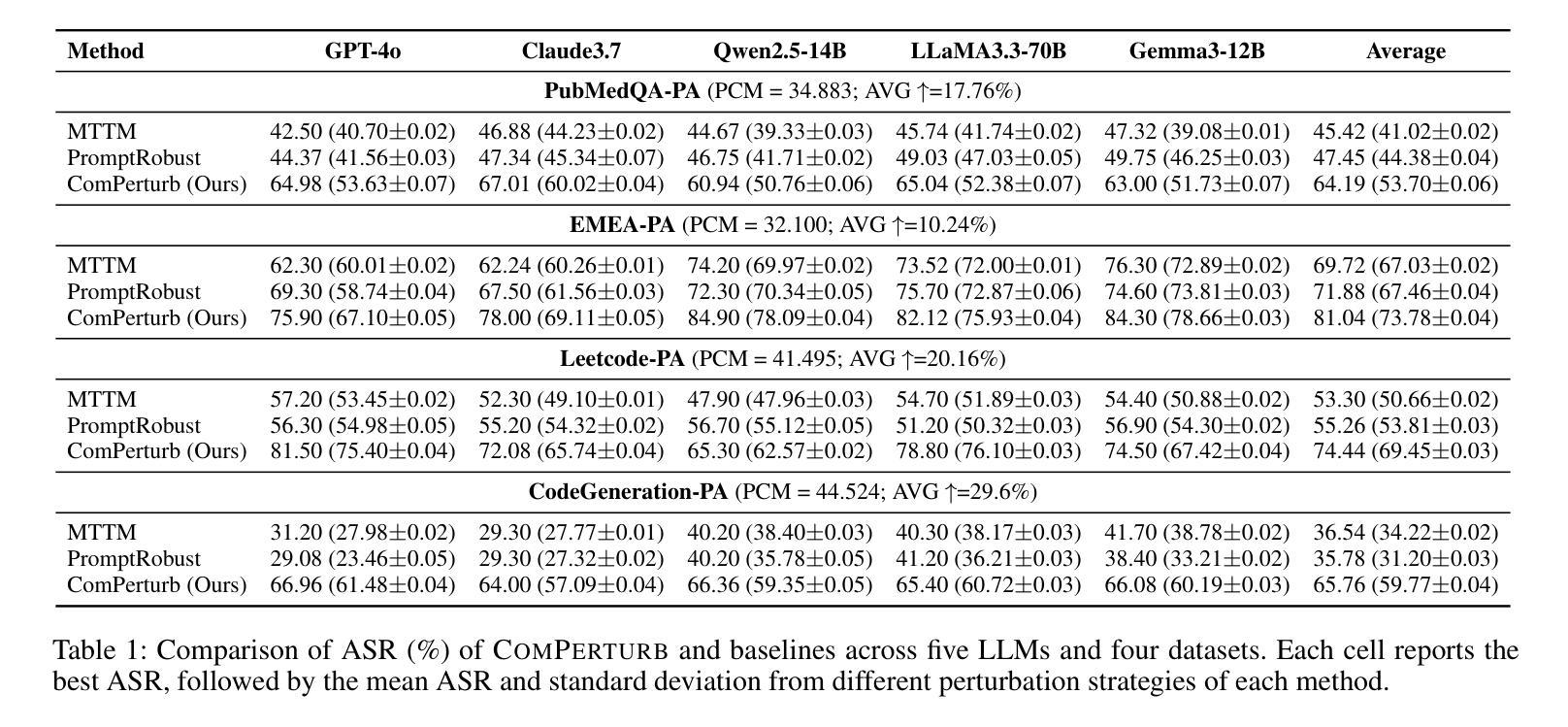
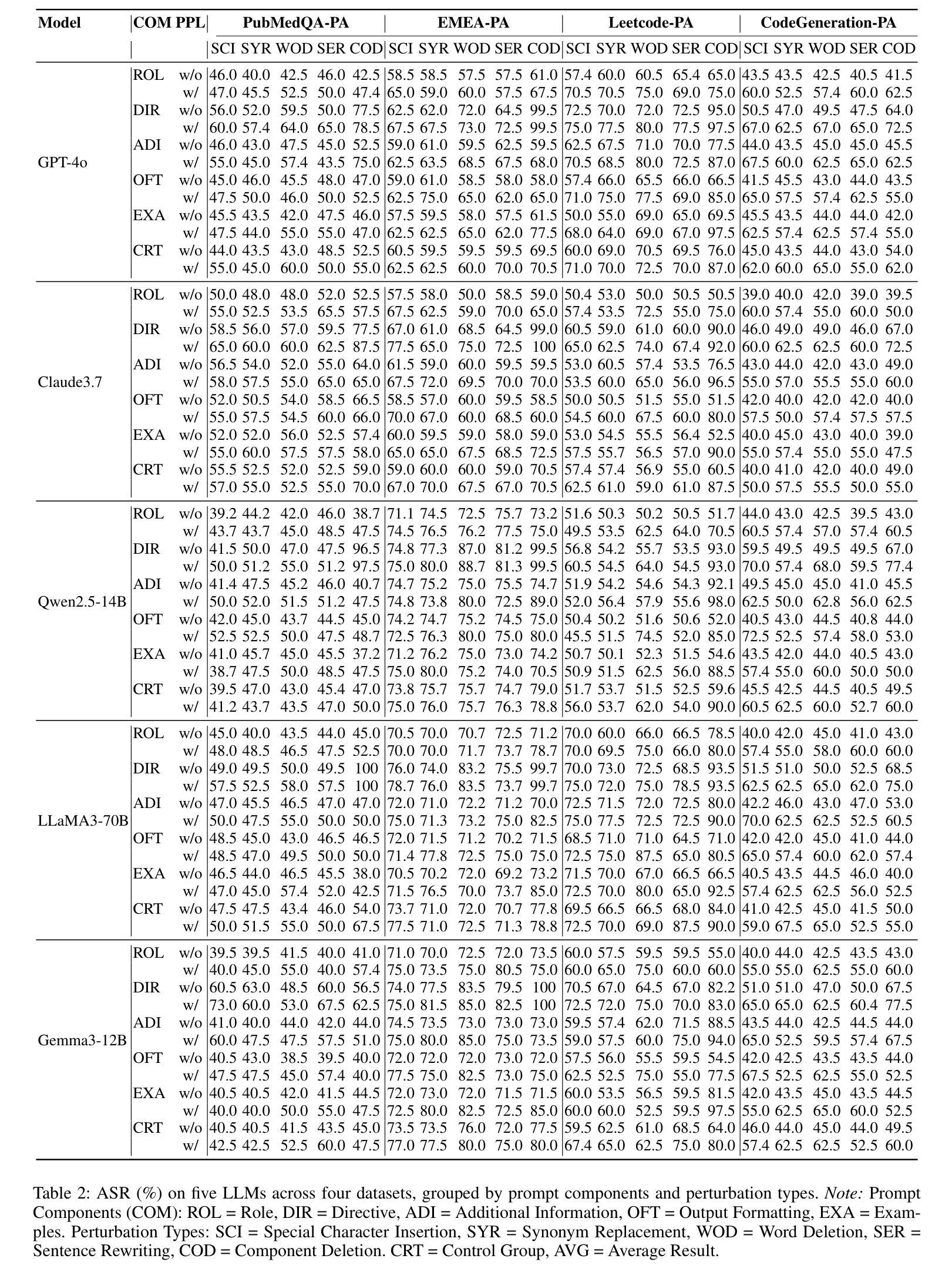
Are All Prompt Components Value-Neutral? Understanding the Heterogeneous Adversarial Robustness of Dissected Prompt in Large Language Models
Authors:Yujia Zheng, Tianhao Li, Haotian Huang, Tianyu Zeng, Jingyu Lu, Chuangxin Chu, Yuekai Huang, Ziyou Jiang, Qian Xiong, Yuyao Ge, Mingyang Li
Prompt-based adversarial attacks have become an effective means to assess the robustness of large language models (LLMs). However, existing approaches often treat prompts as monolithic text, overlooking their structural heterogeneity-different prompt components contribute unequally to adversarial robustness. Prior works like PromptRobust assume prompts are value-neutral, but our analysis reveals that complex, domain-specific prompts with rich structures have components with differing vulnerabilities. To address this gap, we introduce PromptAnatomy, an automated framework that dissects prompts into functional components and generates diverse, interpretable adversarial examples by selectively perturbing each component using our proposed method, ComPerturb. To ensure linguistic plausibility and mitigate distribution shifts, we further incorporate a perplexity (PPL)-based filtering mechanism. As a complementary resource, we annotate four public instruction-tuning datasets using the PromptAnatomy framework, verified through human review. Extensive experiments across these datasets and five advanced LLMs demonstrate that ComPerturb achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates. Ablation studies validate the complementary benefits of prompt dissection and PPL filtering. Our results underscore the importance of prompt structure awareness and controlled perturbation for reliable adversarial robustness evaluation in LLMs. Code and data are available at https://github.com/Yujiaaaaa/PACP.
基于提示的对抗性攻击已成为评估大型语言模型(LLM)稳健性的有效手段。然而,现有方法通常将提示视为单一文本,忽略了其结构异质性——不同的提示组件对对抗稳健性的贡献是不平等的。像PromptRobust这样的先前工作假设提示是价值中立的,但我们的分析发现,具有丰富结构和特定领域的复杂提示具有不同漏洞的组件。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了PromptAnatomy,这是一个自动化框架,它将提示分解成功能组件,并通过我们提出的ComPerturb方法选择性地扰动每个组件来生成多样且可解释的对抗示例。为了确保语言上的合理性和缓解分布偏移,我们进一步融入了一个基于困惑度(PPL)的过滤机制。作为一个补充资源,我们使用PromptAnatomy框架对四个公共指令调整数据集进行了标注,并通过人工审查进行了验证。在这些数据集和五个先进LLM上进行的大量实验表明,ComPerturb达到了最先进的攻击成功率。消融研究验证了提示分解和PPL过滤的互补效益。我们的结果强调了意识到提示结构的重要性和受控扰动,这对于LLM的可靠对抗性稳健性评估至关重要。代码和数据可在https://github.com/Yujiaaaaa/PACP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对大型语言模型(LLM)的基于提示的对抗性攻击的有效手段,并指出了现有方法的不足。现有方法往往将提示视为单一的文本,忽略了其结构异质性。针对这一问题,本文提出了PromptAnatomy框架,该框架能够自动地将提示分解为功能组件,并通过选择性扰动每个组件来生成多样且可解释的对抗样本。同时,为了确保语言上的合理性和减轻分布偏移,结合困惑度(PPL)过滤机制。在四个公开指令调整数据集和五个先进LLM上的广泛实验表明,ComPerturb方法取得了最先进的攻击成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 现有评估LLM稳健性的方法忽略了提示的结构异质性,即不同提示组件对对抗稳健性的贡献不均等。
- PromptAnatomy框架能够自动地将提示分解为功能组件,生成多样且可解释的对抗样本。
- ComPerturb方法通过选择性扰动提示的每个组件,增强了对抗性攻击的效果。
- 困惑度(PPL)过滤机制用于确保语言上的合理性和减轻分布偏移。
- 在四个公开指令调整数据集和五个先进LLM上的广泛实验表明,ComPerturb方法取得了最先进的攻击成功率。
- 消融研究验证了提示解剖和PPL过滤的互补效益。
- 结果强调了在进行LLM的对抗性稳健性评估时,需要考虑提示结构意识和受控扰动的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Transformers in Pseudo-Random Number Generation: A Dual Perspective on Theory and Practice
Authors:Ran Li, Lingshu Zeng
Pseudo-random number generators (PRNGs) are high-nonlinear processes, and they are key blocks in optimization of Large language models. Transformers excel at processing complex nonlinear relationships. Thus it is reasonable to generate high-quality pseudo-random numbers based on transformers. In this paper, we explore this question from both theoretical and practical perspectives, highlighting the potential benefits and implications of Transformer in PRNGs. We theoretically demonstrate that decoder-only Transformer models with Chain-of-Thought can simulate both the Linear Congruential Generator (LCG) and Mersenne Twister (MT) PRNGs. Based on this, we conclude that the log-precision decoder-only Transformer can represent non-uniform $\text{AC}^0$. Our simulative theoretical findings are validated through experiments. The random numbers generated by Transformer-based PRNGs successfully pass the majority of NIST tests, whose heat maps exhibit clear statistical randomness. Finally, we assess their capability in prediction attacks.
伪随机数生成器(PRNGs)是高非线性过程,是优化大型语言模型的关键环节。Transformer擅长处理复杂的非线性关系。因此,基于Transformer生成高质量伪随机数是有道理的。本文将从理论和实践两个角度探讨这个问题,重点介绍Transformer在PRNGs中的潜在优势和影响。我们从理论上证明,仅解码的Transformer模型结合思维链(Chain-of-Thought)可以模拟线性同余生成器(LCG)和梅森旋转器(MT)PRNGs。基于此,我们得出结论,对数精度仅解码的Transformer可以代表非均匀AC^0。我们的模拟理论发现已经通过实验得到验证。基于Transformer的PRNG生成的随机数成功通过了NIST测试的大部分测试,其热图显示出明显的统计随机性。最后,我们评估了它们在预测攻击方面的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文探讨了基于Transformer模型的伪随机数生成器(PRNGs)的潜力与影响。研究表明,仅解码器型的Transformer模型可以模拟线性同余生成器(LCG)和梅森旋花(MT)等PRNGs,并成功生成通过了NIST测试的伪随机数。本文验证了基于Transformer的PRNG在模拟非线性关系方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型可用于模拟伪随机数生成器(PRNGs),如线性同余生成器(LCG)和梅森旋花(MT)。
- 仅解码器型的Transformer能够处理复杂的非线性关系,为高质量的伪随机数生成提供了基础。
- 基于Transformer的PRNG生成的伪随机数成功通过了NIST测试,表现出明显的统计随机性。
- Transformer模型在模拟非均匀分布方面表现出潜力。
- 本文验证了理论模型的有效性,并通过实验验证了其实际性能。
- 基于Transformer的PRNGs具有一定的预测攻击防护能力。
点此查看论文截图