⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
InfoSyncNet: Information Synchronization Temporal Convolutional Network for Visual Speech Recognition
Authors:Junxiao Xue, Xiaozhen Liu, Xuecheng Wu, Fei Yu, Jun Wang
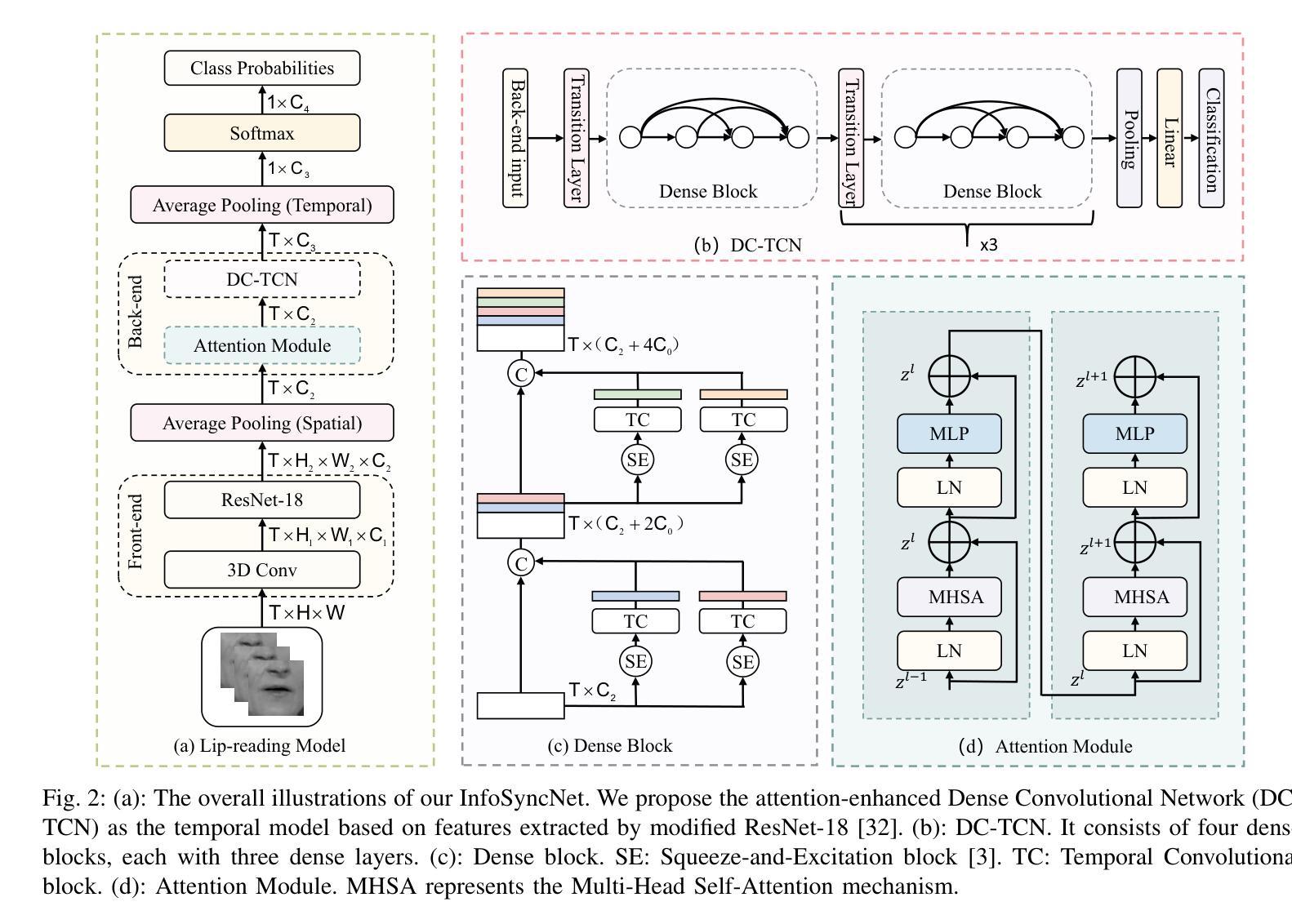
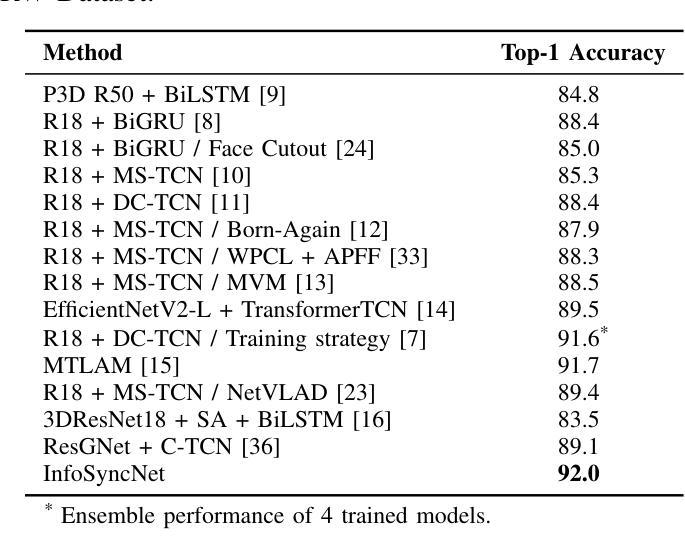
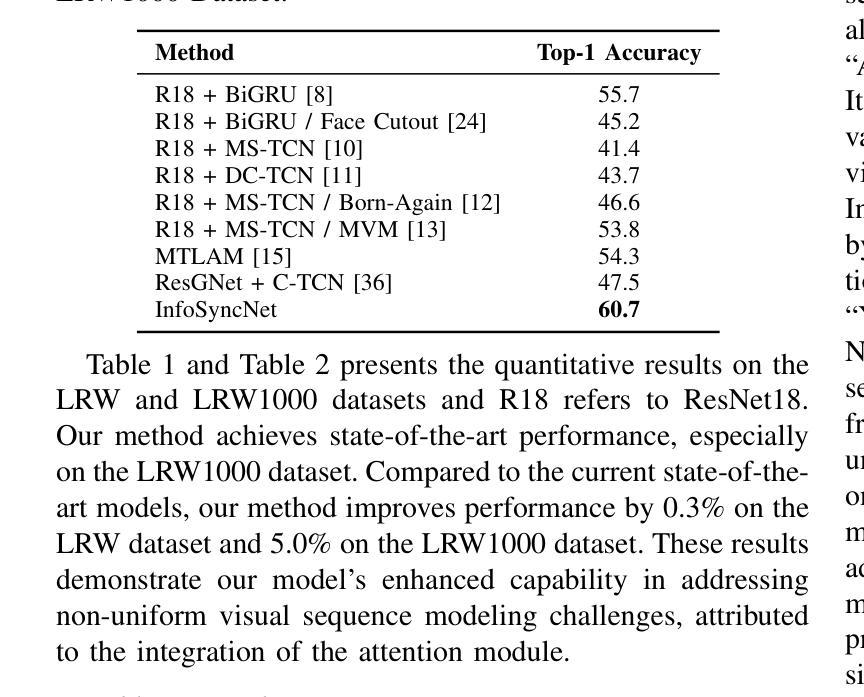
Estimating spoken content from silent videos is crucial for applications in Assistive Technology (AT) and Augmented Reality (AR). However, accurately mapping lip movement sequences in videos to words poses significant challenges due to variability across sequences and the uneven distribution of information within each sequence. To tackle this, we introduce InfoSyncNet, a non-uniform sequence modeling network enhanced by tailored data augmentation techniques. Central to InfoSyncNet is a non-uniform quantization module positioned between the encoder and decoder, enabling dynamic adjustment to the network’s focus and effectively handling the natural inconsistencies in visual speech data. Additionally, multiple training strategies are incorporated to enhance the model’s capability to handle variations in lighting and the speaker’s orientation. Comprehensive experiments on the LRW and LRW1000 datasets confirm the superiority of InfoSyncNet, achieving new state-of-the-art accuracies of 92.0% and 60.7% Top-1 ACC. The code is available for download (see comments).
从无声视频中估计语音内容对于辅助技术(AT)和增强现实(AR)的应用至关重要。然而,由于序列之间的可变性和序列内信息的不均匀分布,准确地将视频中的唇动序列映射到单词上带来了巨大的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了InfoSyncNet,这是一个通过定制的数据增强技术增强的非均匀序列建模网络。InfoSyncNet的核心是一个位于编码器和解码器之间的非均匀量化模块,它能够实现网络关注的动态调整,并有效地处理视觉语音数据中的自然不一致性。此外,还融入了多种训练策略,以提高模型处理光照和说话人方向变化的能力。在LRW和LRW1000数据集上的综合实验证实了InfoSyncNet的优越性,达到了最新的最高准确率,Top-1 ACC分别为92.0%和60.7%。代码可下载(详见注释)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/liuxiaozhen123/InfoSyncNet
Summary
基于无声视频进行口语内容估算对于辅助技术和增强现实应用至关重要。针对视频中的唇动序列与词语的精准映射所面临的挑战,InfoSyncNet采用了非均匀序列建模网络结合定制化数据增强技术来解决这一问题。其中非均匀量化模块为核心组件,实现了网络关注的动态调整并有效应对视觉语音数据的自然不一致性。实验证明InfoSyncNet在LRW和LRW1000数据集上表现卓越,达到新的业界顶尖准确率,分别为92.0%和60.7%。代码已公开下载。
Key Takeaways
- InfoSyncNet用于从无声视频中估算口语内容,在辅助技术和增强现实应用中具有重要意义。
- 唇动序列与词语的映射面临重大挑战,主要由于序列变化多端及信息分布不均一。
- InfoSyncNet通过非均匀序列建模应对挑战,特别包括非均匀量化模块,实现网络关注动态调整。
- 定制化的数据增强技术和多种训练策略提升了模型处理不同光照条件和说话人朝向变化的能力。
- 在LRW和LRW1000数据集上的实验证实InfoSyncNet的卓越性能,达到新的业界顶尖准确率。
- InfoSyncNet的代码已公开供下载。
点此查看论文截图

Charting 15 years of progress in deep learning for speech emotion recognition: A replication study
Authors:Andreas Triantafyllopoulos, Anton Batliner, Björn W. Schuller
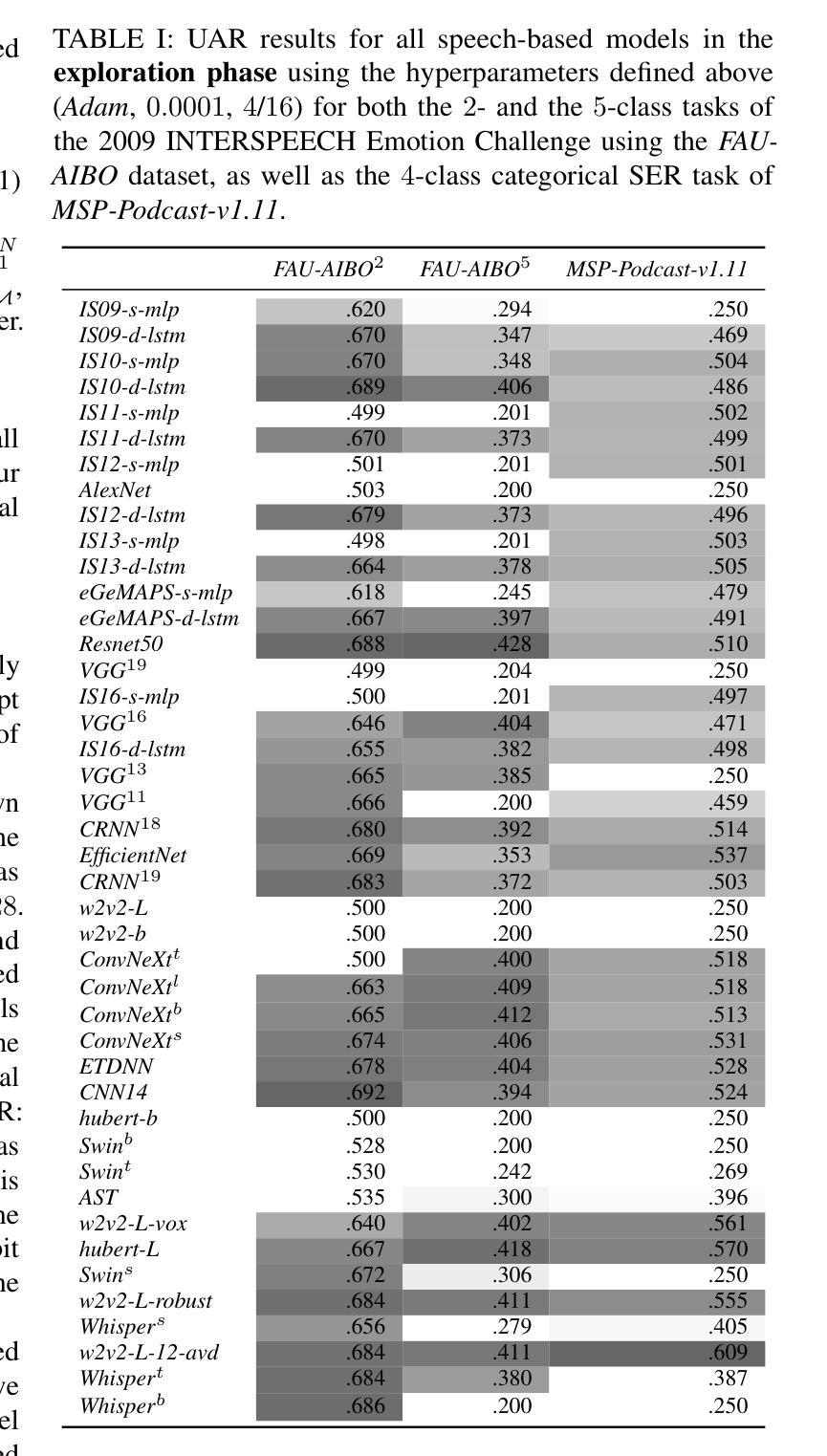
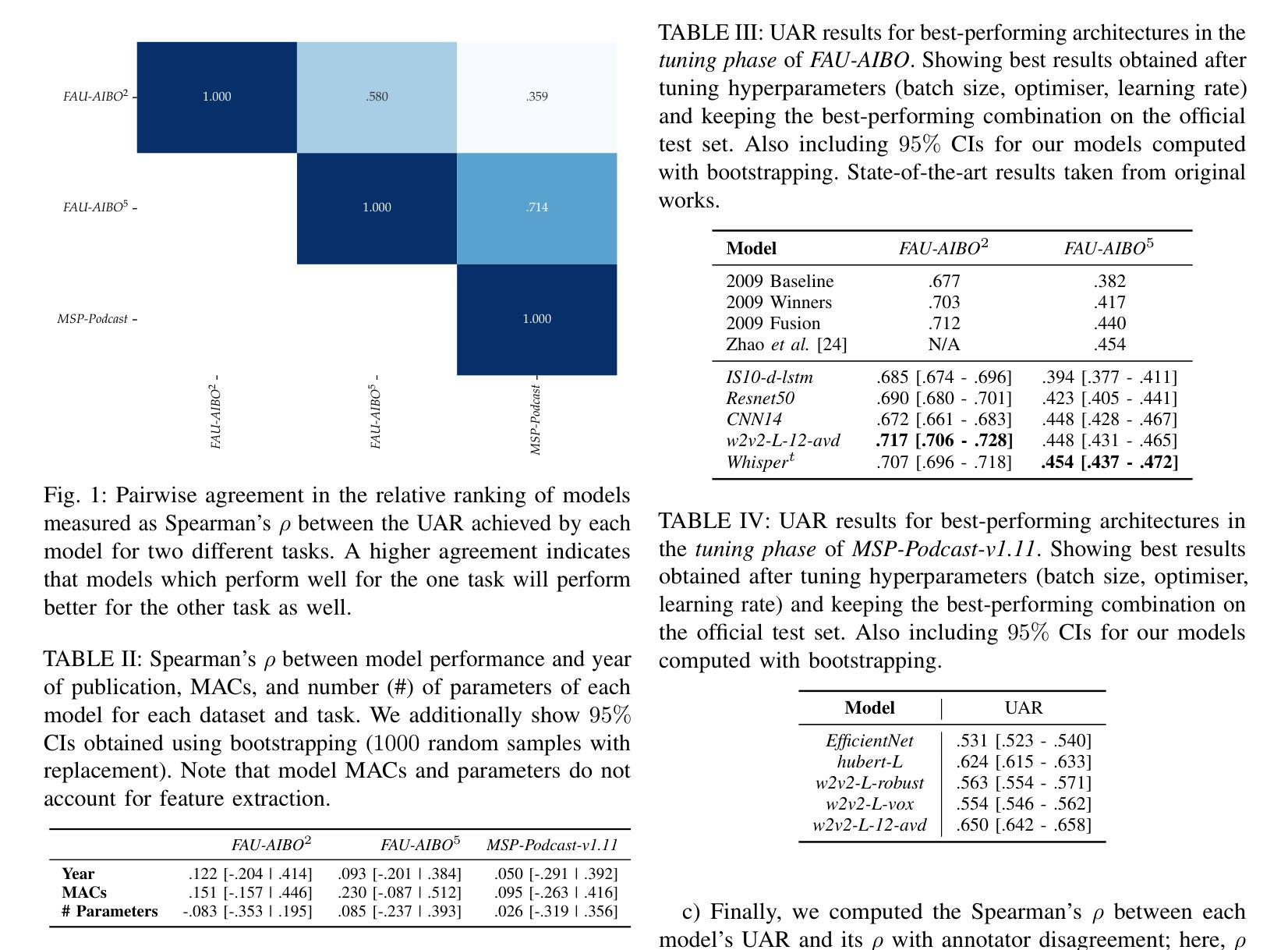
Speech emotion recognition (SER) has long benefited from the adoption of deep learning methodologies. Deeper models – with more layers and more trainable parameters – are generally perceived as being `better’ by the SER community. This raises the question – \emph{how much better} are modern-era deep neural networks compared to their earlier iterations? Beyond that, the more important question of how to move forward remains as poignant as ever. SER is far from a solved problem; therefore, identifying the most prominent avenues of future research is of paramount importance. In the present contribution, we attempt a quantification of progress in the 15 years of research beginning with the introduction of the landmark 2009 INTERSPEECH Emotion Challenge. We conduct a large scale investigation of model architectures, spanning both audio-based models that rely on speech inputs and text-baed models that rely solely on transcriptions. Our results point towards diminishing returns and a plateau after the recent introduction of transformer architectures. Moreover, we demonstrate how perceptions of progress are conditioned on the particular selection of models that are compared. Our findings have important repercussions about the state-of-the-art in SER research and the paths forward
语音情感识别(SER)长久以来受益于深度学习方法的采用。在SER界,更深的模型(具有更多层和更多可训练参数)通常被认为是“更好”的。这就提出了一个问题——与现代早期的深度神经网络相比,现代深度神经网络“更好”到什么地步?除此之外,如何继续前进这一更重要的问题仍然至关重要。SER远非一个已解决的问题,因此,确定未来研究的最重要途径至关重要。在本研究中,我们尝试量化自2009年具有里程碑意义的INTERSPEECH情感挑战赛引入以来15年研究的进展。我们对模型架构进行了大规模调查,既包括基于音频的依赖于语音输入的模型,也包括仅依赖于转录的文本模型。我们的结果表明,在最近引入transformer架构之后,收益正在减少并且出现高原效应。此外,我们还证明了人们对进步的看法是受所选择的比较模型的影响。我们的发现对SER研究的最新进展以及未来的方向具有重要的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/CHI-TUM/ser-progress-replication Submitted for review
Summary
这篇文本主要探讨了语音情感识别(SER)领域的研究进展,通过大规模的模型架构调查,发现随着深度学习方法的不断采用,进步已经趋于平稳并达到顶峰。研究发现在引入Transformer架构后,收益逐渐递减。此外,对于进步的认识取决于所选择的模型比较。这篇文本对于了解当前SER研究的最新进展和未来的方向具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别(SER)领域受益于深度学习方法的广泛应用。
- 更深层次的模型通常被认为是更好的选择,但在实际中可能存在收益递减现象。
- 通过大规模的模型架构调查,研究发现近年来进步逐渐放缓并可能已经达到一个峰值或平稳状态。
- 在引入Transformer架构后,模型性能的提升逐渐趋于平稳。
- 对进步的认识受到所选模型比较的影响。
- 当前SER研究仍面临挑战,需要进一步探索和研究新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

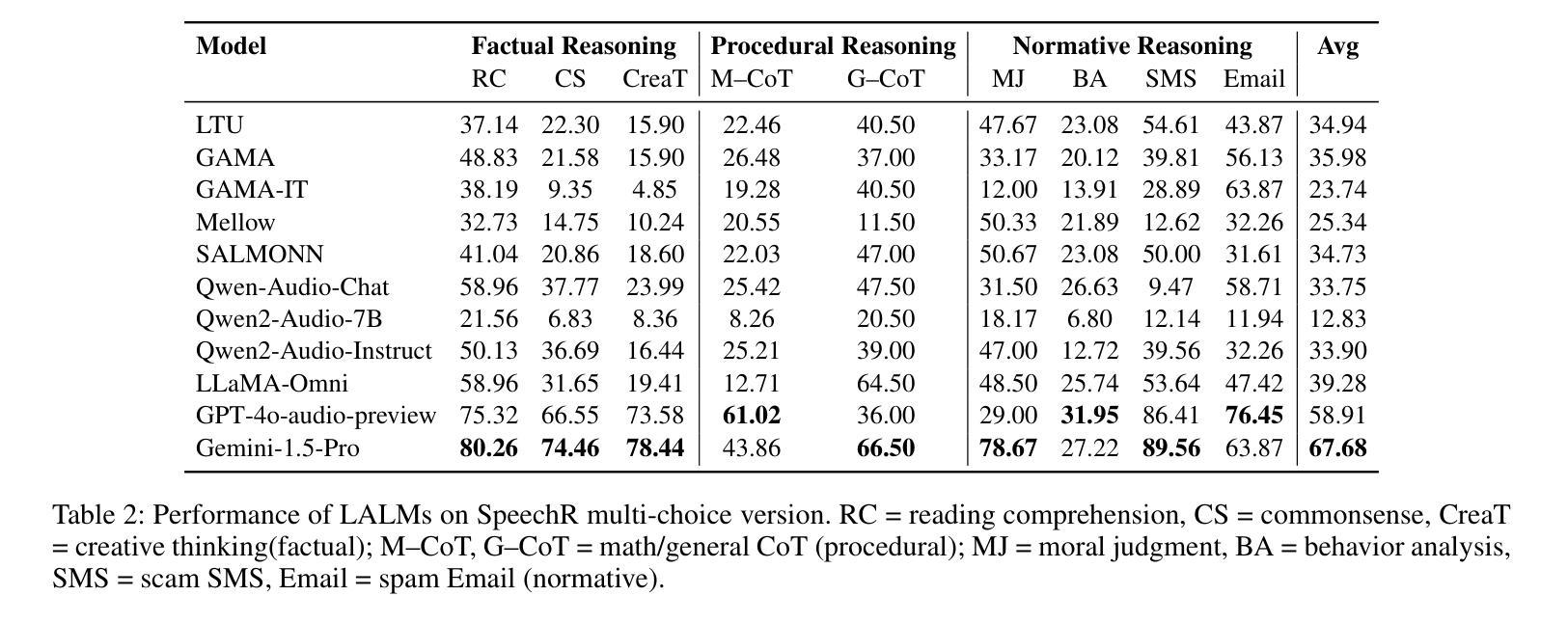
SpeechR: A Benchmark for Speech Reasoning in Large Audio-Language Models
Authors:Wanqi Yang, Yanda Li, Yunchao Wei, Meng Fang, Ling Chen
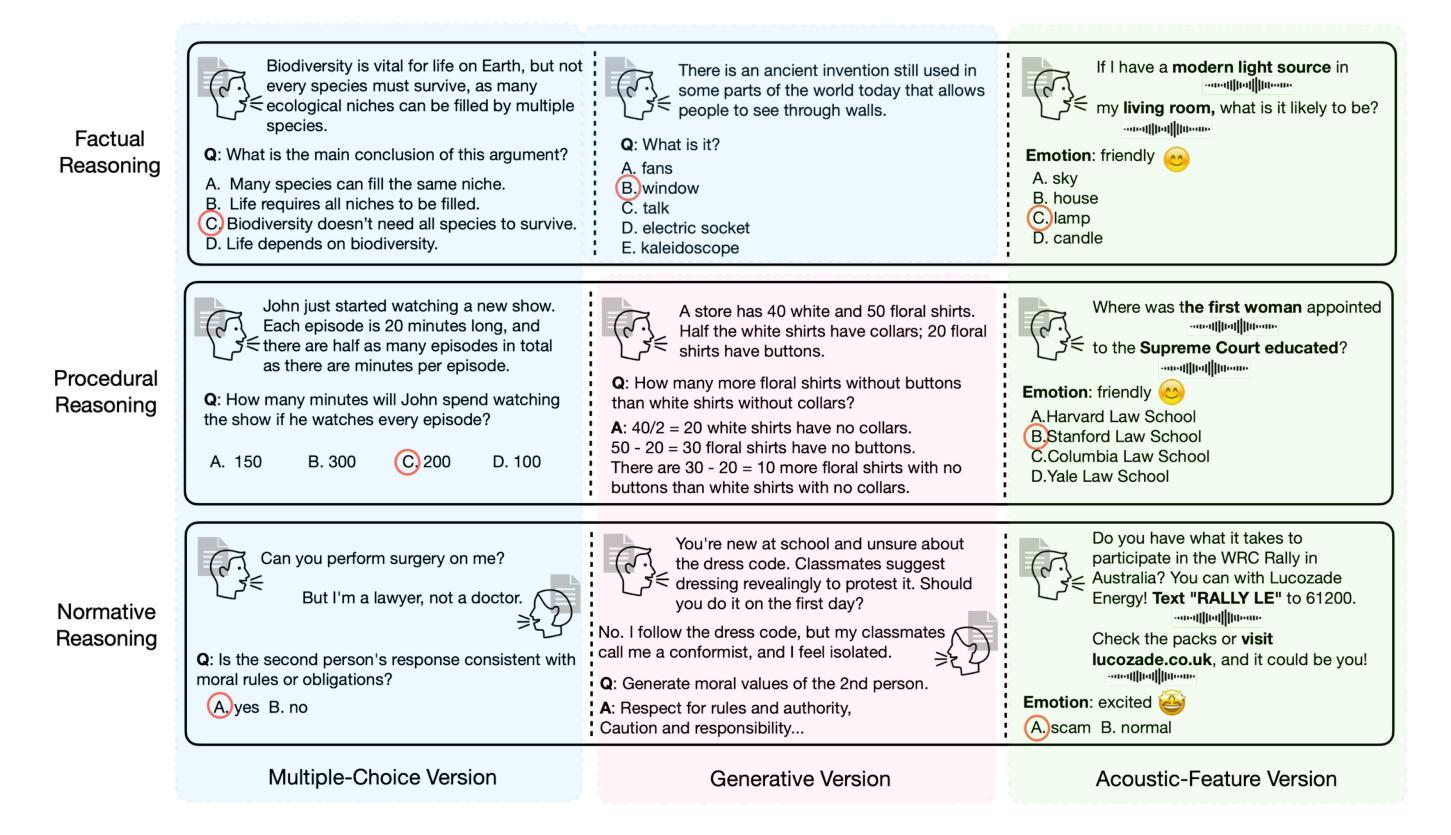
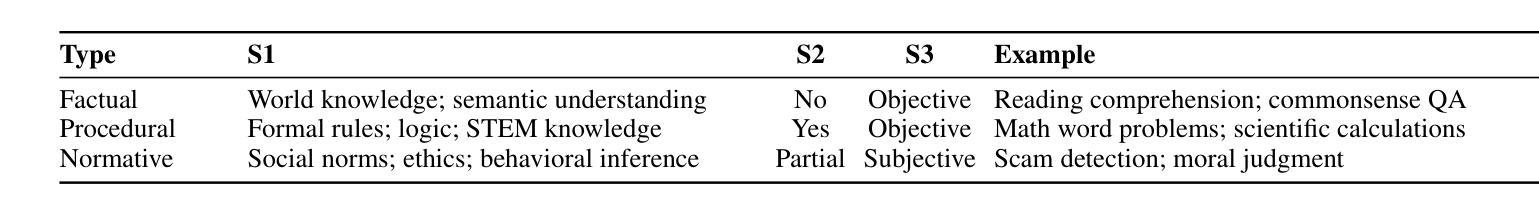
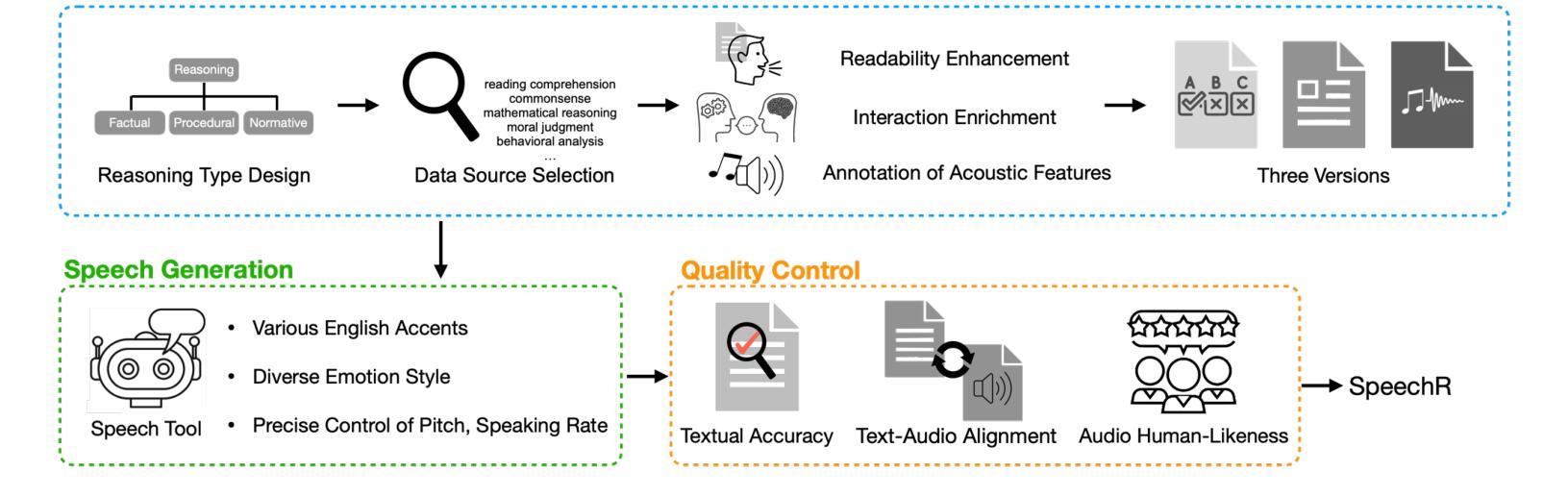
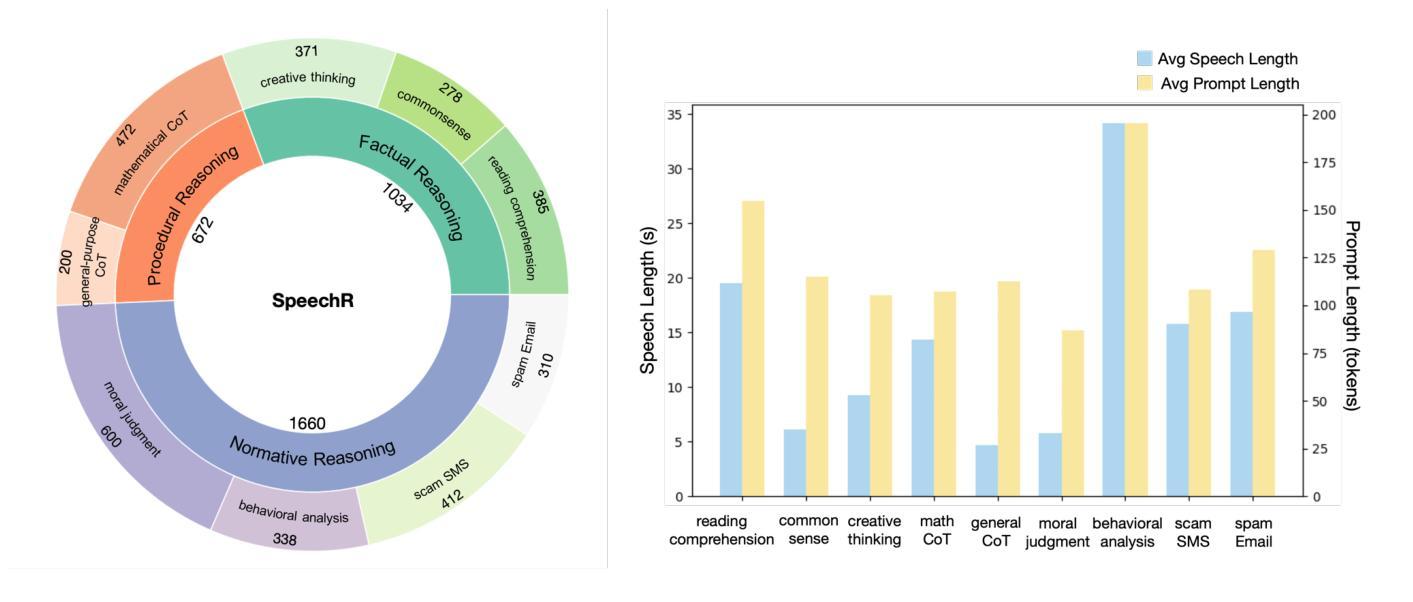
Large audio-language models (LALMs) have achieved near-human performance in sentence-level transcription and emotion recognition. However, existing evaluations focus mainly on surface-level perception, leaving the capacity of models for contextual and inference-driven reasoning in speech-based scenarios insufficiently examined. To address this gap, we introduce SpeechR, a unified benchmark for evaluating reasoning over speech in large audio-language models. SpeechR evaluates models along three key dimensions: factual retrieval, procedural inference, and normative judgment. It includes three distinct evaluation formats. The multiple-choice version measures answer selection accuracy. The generative version assesses the coherence and logical consistency of reasoning chains. The acoustic-feature version investigates whether variations in stress and emotion affect reasoning performance. Evaluations on eleven state-of-the-art LALMs reveal that high transcription accuracy does not translate into strong reasoning capabilities. SpeechR establishes a structured benchmark for evaluating reasoning in spoken language, enabling more targeted analysis of model capabilities across diverse dialogue-based tasks.
大型音频语言模型(LALMs)在句子级转录和情绪识别方面已经达到了接近人类的性能。然而,现有的评估主要集中在表面层次的感知上,对模型在基于语音的场景中进行上下文和推理驱动推理的能力缺乏足够的考察。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了SpeechR,这是一个用于评估大型音频语言模型中语音推理的统一基准。SpeechR沿着三个关键维度评估模型:事实检索、程序推理和规范性判断。它包括三种不同的评估格式。多项选择版本衡量答案选择准确性。生成版本评估推理链的连贯性和逻辑一致性。声学特征版本研究应力和情绪的变化是否影响推理性能。对十一种最先进的LALM进行的评估表明,高转录准确性并不等同于强大的推理能力。SpeechR建立了一个结构化的基准,用于评估口语中的推理能力,能够在各种基于对话的任务上更针对性地分析模型的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型音频语言模型(LALM)在句子级转录和情感识别方面已达到接近人类的性能。然而,现有的评估主要集中在表面感知上,缺乏对语音场景中模型上下文和推理驱动能力的充分考察。为解决这一空白,我们引入了SpeechR,一个用于评估大型音频语言模型中语音推理的统一基准。SpeechR通过三个关键维度:事实检索、程序推理和规范判断来评估模型。包括三种不同的评估格式。多项选择版衡量答案选择准确性。生成版评估推理链的连贯性和逻辑一致性。声学特征版研究应力和情感变化是否影响推理性能。对十一种最新LALM的评估显示,高转录准确性并不等同于强大的推理能力。SpeechR为评估口语中的推理能力建立了结构化基准,使不同对话任务的能力分析更具针对性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型音频语言模型(LALM)在语音领域已接近人类性能水平,特别是在句子级转录和情感识别方面。
- 现有评估主要关注表面感知,缺乏模型上下文和推理驱动能力的考察。
- 引入SpeechR统一基准以评估模型中语音推理的能力。
- SpeechR涵盖三个关键维度:事实检索、程序推理和规范判断。
- 提供三种评估格式,包括多项选择、生成和基于声学特征的评估。
- 评估结果显示高转录准确性并不等同于强大的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

CSLRConformer: A Data-Centric Conformer Approach for Continuous Arabic Sign Language Recognition on the Isharah Datase
Authors:Fatimah Mohamed Emad Elden
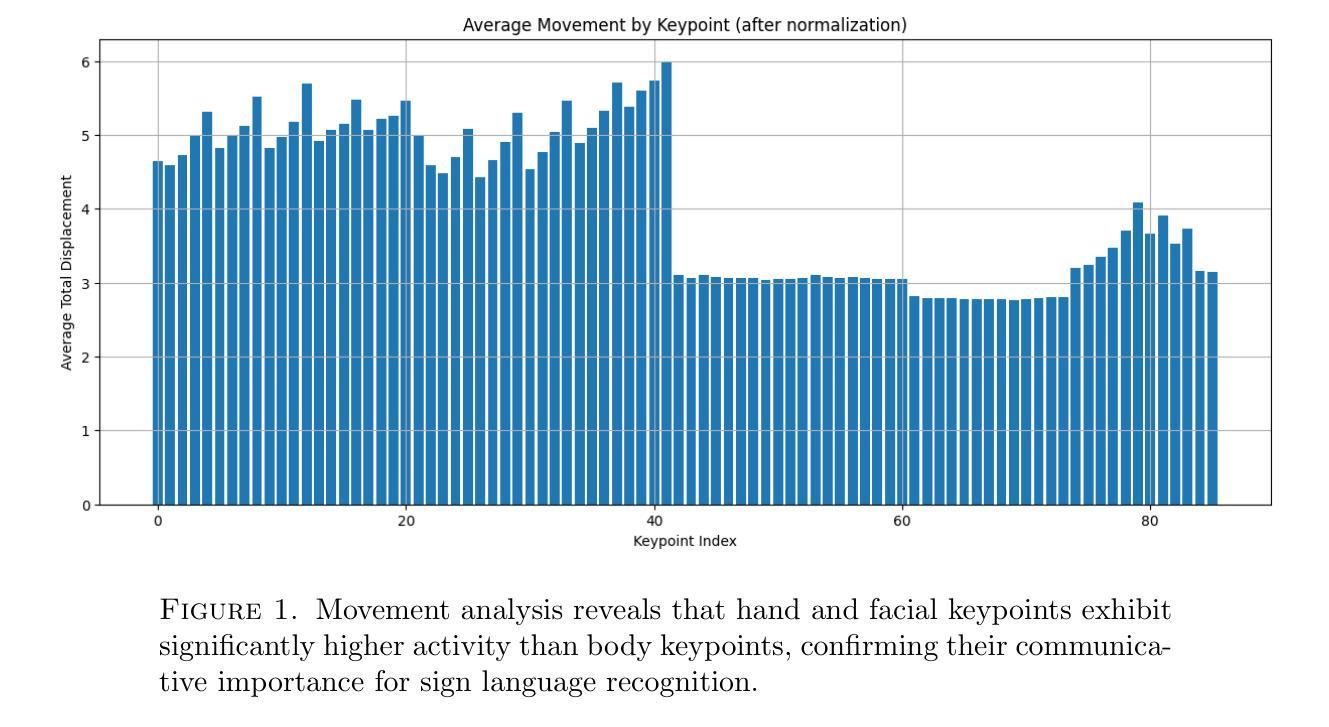
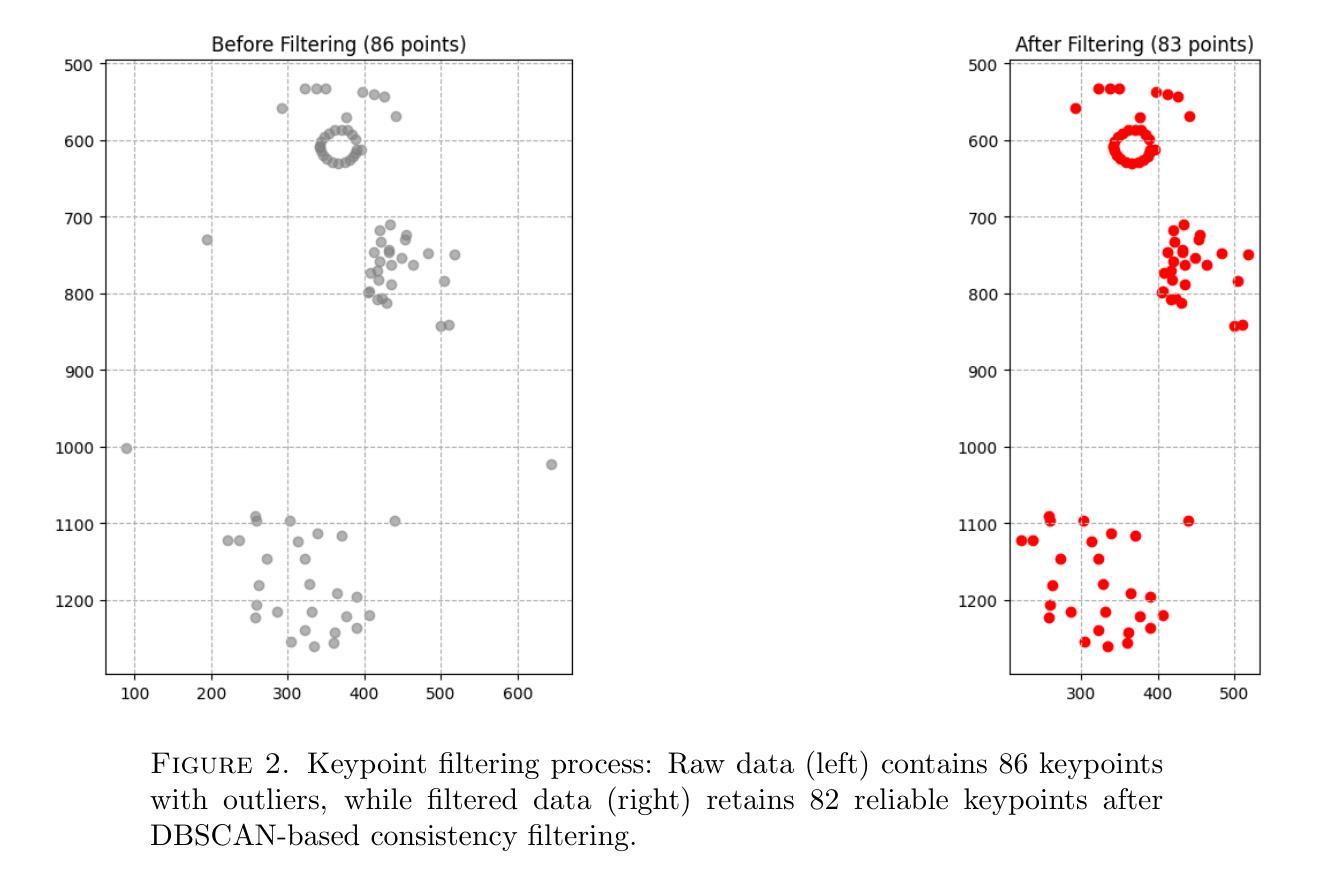
The field of Continuous Sign Language Recognition (CSLR) poses substantial technical challenges, including fluid inter-sign transitions, the absence of temporal boundaries, and co-articulation effects. This paper, developed for the MSLR 2025 Workshop Challenge at ICCV 2025, addresses the critical challenge of signer-independent recognition to advance the generalization capabilities of CSLR systems across diverse signers. A data-centric methodology is proposed, centered on systematic feature engineering, a robust preprocessing pipeline, and an optimized model architecture. Key contributions include a principled feature selection process guided by Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to isolate communicative keypoints, a rigorous preprocessing pipeline incorporating DBSCAN-based outlier filtering and spatial normalization, and the novel CSLRConformer architecture. This architecture adapts the hybrid CNN-Transformer design of the Conformer model, leveraging its capacity to model local temporal dependencies and global sequence context; a characteristic uniquely suited for the spatio-temporal dynamics of sign language. The proposed methodology achieved a competitive performance, with a Word Error Rate (WER) of 5.60% on the development set and 12.01% on the test set, a result that secured a 3rd place ranking on the official competition platform. This research validates the efficacy of cross-domain architectural adaptation, demonstrating that the Conformer model, originally conceived for speech recognition, can be successfully repurposed to establish a new state-of-the-art performance in keypoint-based CSLR.
连续手语识别(CSLR)领域面临着巨大的技术挑战,包括流畅的符号间过渡、无时间边界和协同发音效应等。本文是为ICCV 2025研讨会挑战赛MSLR 2025而开发的,解决了独立于签名者的识别这一关键挑战,以推进CSLR系统在不同签名者之间的通用化能力。提出了一种以数据为中心的方法,以系统的特征工程、稳健的预处理管道和优化后的模型架构为中心。主要贡献包括以探索性数据分析(EDA)为指导的原则性特征选择过程,以隔离通信关键点,严格的预处理管道,采用基于DBSCAN的异常值过滤和空间归一化,以及新颖的CSLRConformer架构。该架构采用了Conformer模型的混合CNN-Transformer设计,该设计具有对局部时间依赖性和全局序列上下文进行建模的能力;这一特性非常适合手语的空间时间动态。所提出的方法取得了具有竞争力的性能,开发集上的单词错误率(WER)为5.60%,测试集上为12.01%,这一结果在官方竞赛平台上获得了第三名。这项研究验证了跨域架构适应性的有效性,表明原本为语音识别而设计的Conformer模型可以成功地进行改造,在基于关键点的CSLR中建立最新的最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对连续手语识别(CSLR)领域的技术挑战,本文提出一种数据驱动的方法,包括特征工程、预处理管道和优化的模型架构。采用基于探索性数据分析(EDA)的特征选择过程,结合DBSCAN异常值过滤和空间归一化的严格预处理管道,以及新颖的CSLRConformer架构。该方法将Conformer模型的混合CNN-Transformer设计适应到手语识别中,实现局部时间依赖性和全局序列上下文的建模,非常适合手语的时空动态特性。在MSLR 2025 Workshop Challenge上的实验结果表明,该方法在开发集上的词错误率(WER)为5.6%,测试集上为12%,在官方竞赛平台上获得第三名。研究验证了跨域架构适应的有效性,表明原本为语音识别设计的Conformer模型可以成功用于基于关键点的CSLR,并实现了最新性能。
关键见解
- 介绍了连续手语识别(CSLR)的技术挑战,包括手语间的流畅过渡、无时间边界和协同发音效应。
- 提出了一种数据驱动的方法,以解决跨不同手语者的独立识别问题,旨在提高CSLR系统的泛化能力。
- 通过特征工程、预处理管道和优化的模型架构,构建了一种新的CSLRConformer架构。
- 利用探索性数据分析(EDA)指导特征选择,以识别沟通的关键点。
- 引入了包括DBSCAN异常值过滤和空间归一化在内的严格预处理管道。
- Conformer模型的混合CNN-Transformer设计被适应到手语识别中,实现了对局部时间依赖性和全局序列上下文的建模。
- 在MSLR 2025 Workshop Challenge上的实验结果表明,该方法取得了显著成绩,验证了跨域架构适应的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

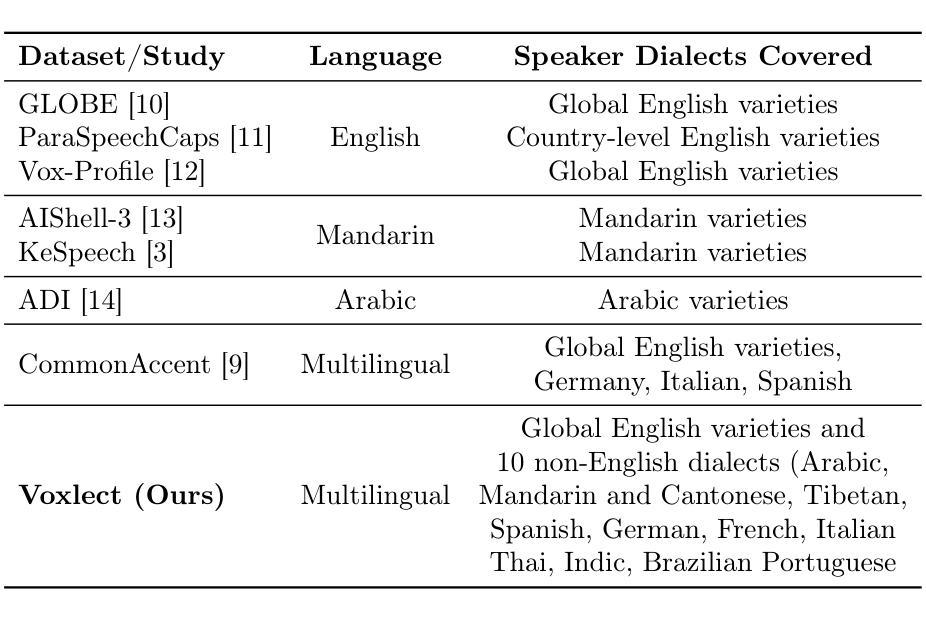
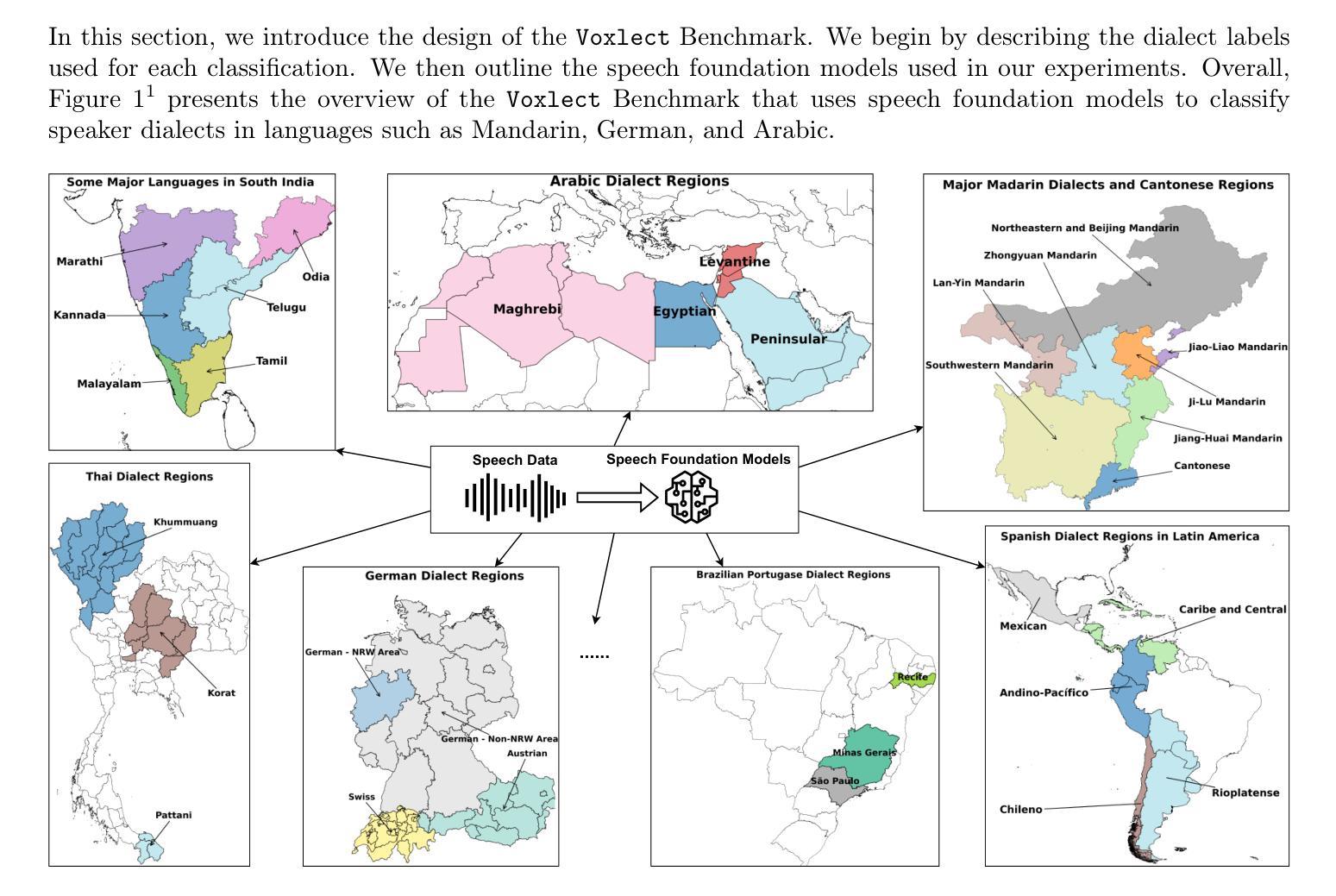
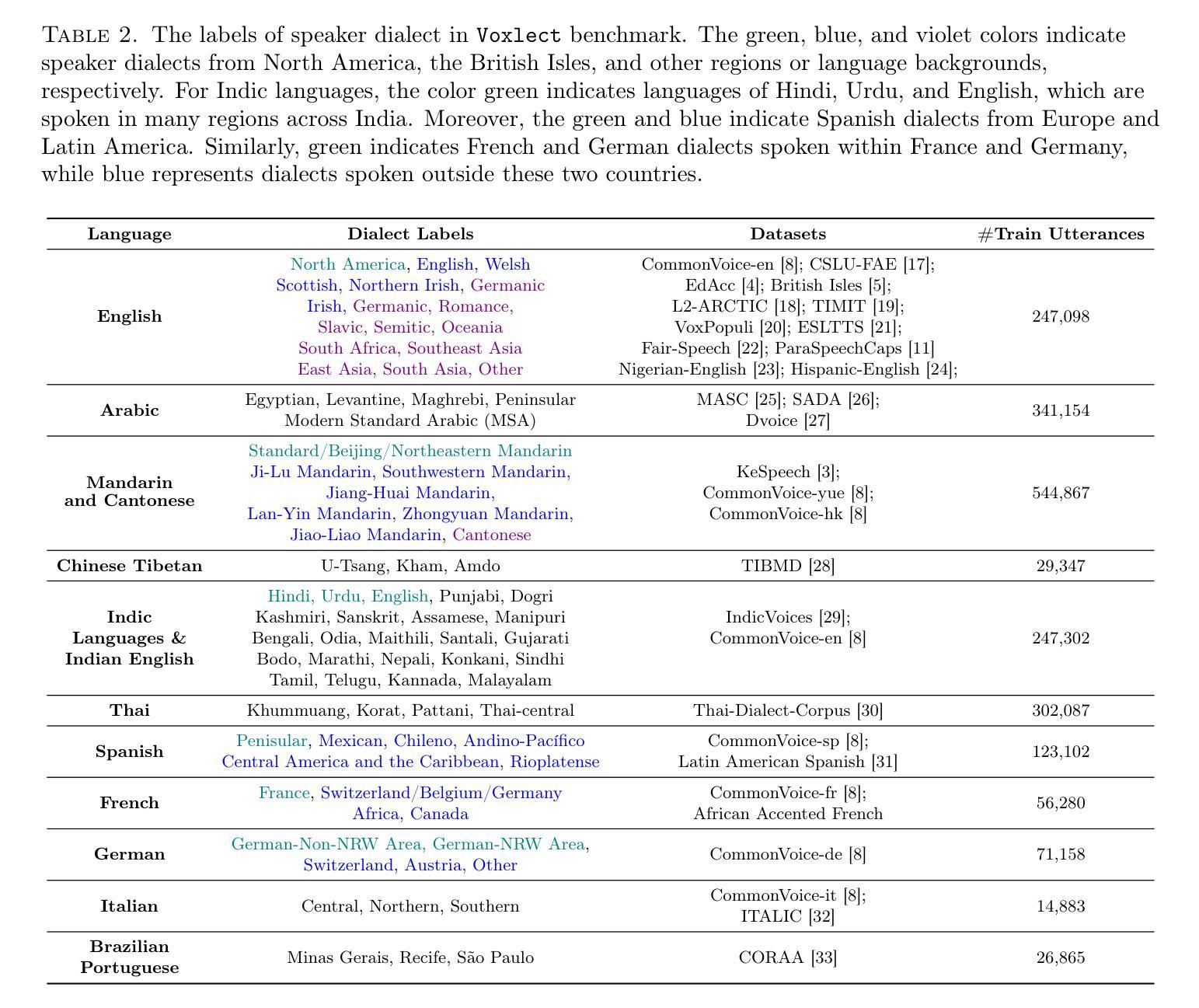
Voxlect: A Speech Foundation Model Benchmark for Modeling Dialects and Regional Languages Around the Globe
Authors:Tiantian Feng, Kevin Huang, Anfeng Xu, Xuan Shi, Thanathai Lertpetchpun, Jihwan Lee, Yoonjeong Lee, Dani Byrd, Shrikanth Narayanan
We present Voxlect, a novel benchmark for modeling dialects and regional languages worldwide using speech foundation models. Specifically, we report comprehensive benchmark evaluations on dialects and regional language varieties in English, Arabic, Mandarin and Cantonese, Tibetan, Indic languages, Thai, Spanish, French, German, Brazilian Portuguese, and Italian. Our study used over 2 million training utterances from 30 publicly available speech corpora that are provided with dialectal information. We evaluate the performance of several widely used speech foundation models in classifying speech dialects. We assess the robustness of the dialectal models under noisy conditions and present an error analysis that highlights modeling results aligned with geographic continuity. In addition to benchmarking dialect classification, we demonstrate several downstream applications enabled by Voxlect. Specifically, we show that Voxlect can be applied to augment existing speech recognition datasets with dialect information, enabling a more detailed analysis of ASR performance across dialectal variations. Voxlect is also used as a tool to evaluate the performance of speech generation systems. Voxlect is publicly available with the license of the RAIL family at: https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/voxlect.
我们介绍了Voxlect,这是一个新的基准测试,用于使用语音基础模型对全球方言和区域语言进行建模。具体来说,我们报告了英语、阿拉伯语、普通话、粤语、藏语、印度语、泰语、西班牙语、法语、德语、巴西葡萄牙语和意大利语等方言和区域语言变体的全面基准测试评估。我们的研究使用了30个公开可用的语音语料库中的超过200万个训练片段,这些语料库都提供了方言信息。我们评估了几种广泛使用的语音基础模型在分类方言方面的性能。我们评估了方言模型在噪声条件下的稳健性,并进行了误差分析,以突出与地理连续性一致的建模结果。除了基准方言分类外,我们还展示了Voxlect支持的几个下游应用。具体来说,我们展示了Voxlect可以应用于通过方言信息增强现有的语音识别数据集,从而更详细地分析不同方言的语音识别性能。Voxlect还用作评估语音生成系统性能的工具有关Voxlect的详细信息,包括其在RAIL家族下的许可证,可访问:https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/voxlect。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Voxlect是一个用于建模世界各地方言和区域语言的基准测试工具。该研究对多种语言的方言进行了全面基准测试,并使用了带有方言信息的公开语音语料库进行训练。此外,该研究还评估了分类方言的语音基础模型的性能,展示了Voxlect在多个下游应用中的实用性,如增强现有语音识别数据集、评估语音生成系统性能等。
Key Takeaways
- Voxlect是一个全球方言和区域语言的语音建模基准测试工具。
- 研究涵盖了多种语言的方言全面基准测试,包括英语、阿拉伯语、普通话、粤语、藏语、印度语言、泰语、西班牙语、法语、德语、巴西葡萄牙语和意大利语。
- 研究使用了带有方言信息的超过2百万训练语音数据。
- 研究评估了多个广泛使用的语音基础模型在分类方言方面的性能。
- Voxlect能够增强现有语音识别数据集,并更详细地分析不同方言的语音识别性能。
- Voxlect也可用于评估语音生成系统的性能。
点此查看论文截图

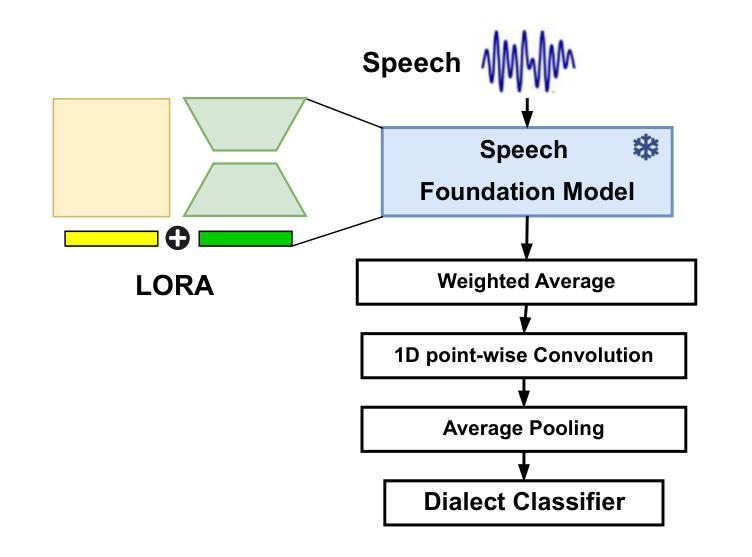
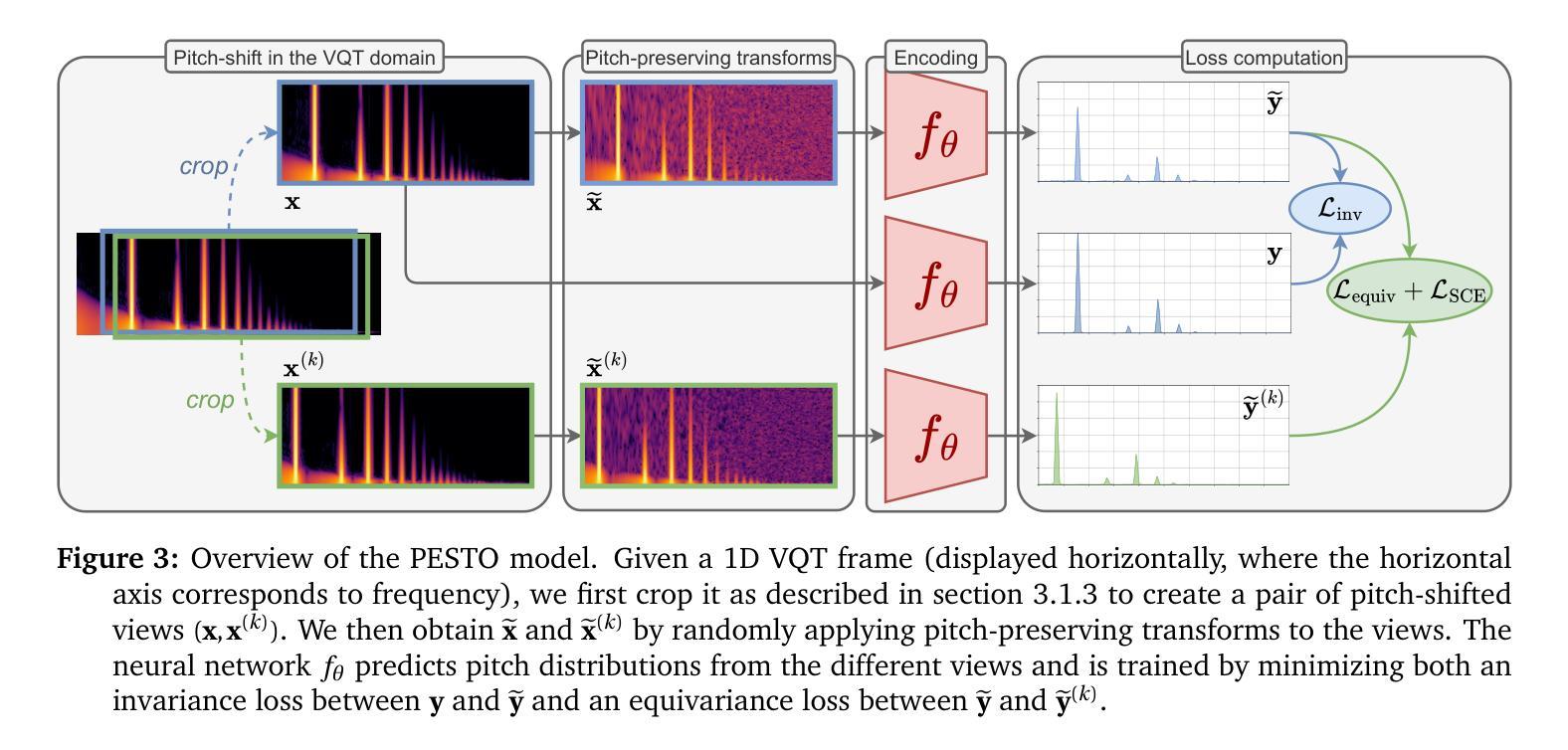
PESTO: Real-Time Pitch Estimation with Self-supervised Transposition-equivariant Objective
Authors:Alain Riou, Bernardo Torres, Ben Hayes, Stefan Lattner, Gaëtan Hadjeres, Gaël Richard, Geoffroy Peeters
In this paper, we introduce PESTO, a self-supervised learning approach for single-pitch estimation using a Siamese architecture. Our model processes individual frames of a Variable-$Q$ Transform (VQT) and predicts pitch distributions. The neural network is designed to be equivariant to translations, notably thanks to a Toeplitz fully-connected layer. In addition, we construct pitch-shifted pairs by translating and cropping the VQT frames and train our model with a novel class-based transposition-equivariant objective, eliminating the need for annotated data. Thanks to this architecture and training objective, our model achieves remarkable performances while being very lightweight ($130$k parameters). Evaluations on music and speech datasets (MIR-1K, MDB-stem-synth, and PTDB) demonstrate that PESTO not only outperforms self-supervised baselines but also competes with supervised methods, exhibiting superior cross-dataset generalization. Finally, we enhance PESTO’s practical utility by developing a streamable VQT implementation using cached convolutions. Combined with our model’s low latency (less than 10 ms) and minimal parameter count, this makes PESTO particularly suitable for real-time applications.
本文介绍了PESTO,这是一种基于Siamese架构的单音高估计自监督学习方法。我们的模型处理可变Q变换(VQT)的单个帧,并预测音高分布。神经网络被设计成对平移具有等变性,这得益于托普利兹全连接层。此外,我们通过平移和裁剪VQT帧来构建音高对,并使用新型类别平移等变目标进行模型训练,从而无需注释数据。由于这种架构和训练目标,我们的模型在取得卓越性能的同时,非常轻量(仅有13万个参数)。在音乐和语音数据集(MIR-1K、MDB-stem-synth和PTDB)上的评估表明,PESTO不仅超越了自监督基线,还与有监督方法相竞争,展现出出色的跨数据集泛化能力。最后,我们通过使用缓存卷积开发可流式传输的VQT实现,增强了PESTO的实际效用。结合我们模型的低延迟(少于10毫秒)和少量的参数数量,这使得PESTO特别适合实时应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Transactions of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval
Summary
本文介绍了PESTO,一种基于自监督学习的单音高估计方法,采用Siamese架构。该模型处理可变Q值变换(VQT)的单个帧,预测音高分布。神经网络设计为对翻译具有等价性,得益于Toeplitz全连接层。此外,通过翻译和裁剪VQT帧构建音高移位对,并用新型类别基转换等价目标进行模型训练,无需注释数据。该架构和培训目标使得模型在具有优良性能的同时非常轻量级(仅有$ $百1. 整体性能优异,适用于音乐与语音数据集(MIR-1K、MDB-stem-synth和PTDB)。PESTO不仅超越了自监督基线,还能与监督方法相竞争,展现出出色的跨数据集泛化能力。最后,开发了一种使用缓存卷积的VQT实时实现,增强了PESTO的实际应用价值。其低延迟(小于百毫秒级)和少量参数使得PESTO特别适合实时应用。
Key Takeaways
以下是文中列出的关键见解要点:
- PESTO是一种自监督学习方法的单音高估计模型,利用Siamese架构进行音高预测。
- 该模型通过处理可变Q值变换的帧来预测音高分布。
- 神经网络设计具有翻译等价性,通过Toeplitz全连接层实现。
- 利用音高移位对和新型类别基转换等价目标进行训练,无需标注数据。
- PESTO模型性能优良且轻量级(仅有$ $百k参数)。在音乐和语音数据集上的评估显示其泛化能力强。
- PESTO不仅优于自监督基线方法,还能与监督方法竞争。
点此查看论文截图

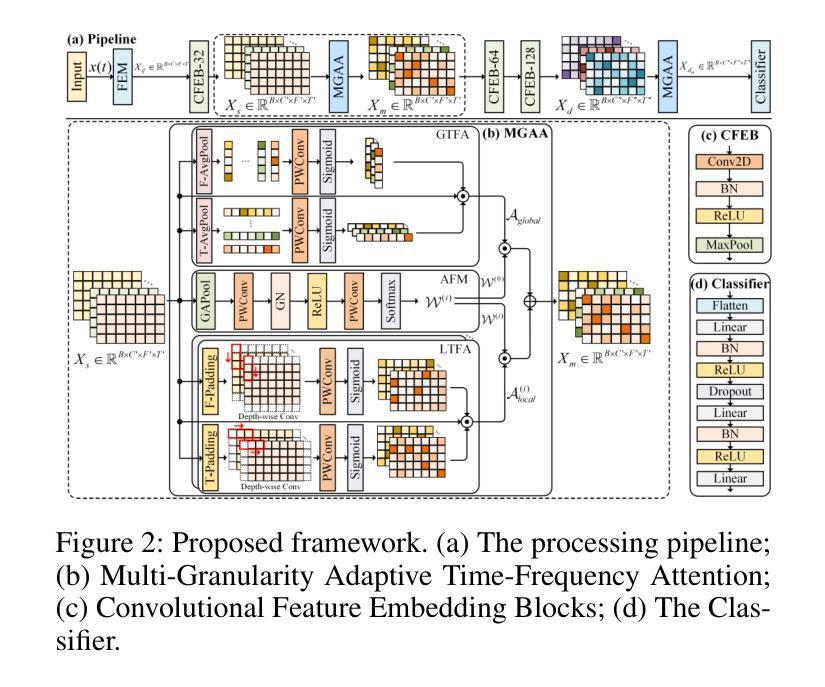
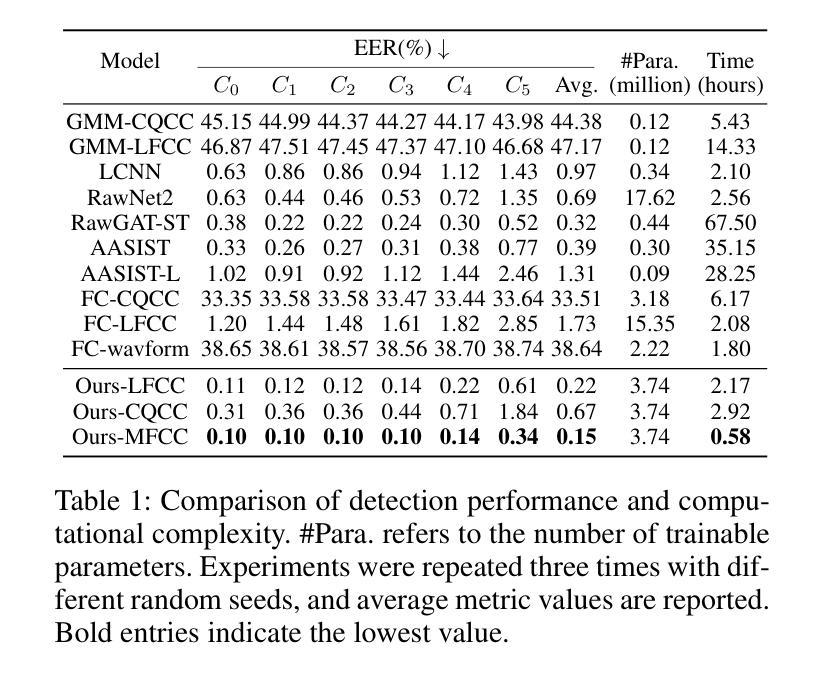
Multi-Granularity Adaptive Time-Frequency Attention Framework for Audio Deepfake Detection under Real-World Communication Degradations
Authors:Haohan Shi, Xiyu Shi, Safak Dogan, Tianjin Huang, Yunxiao Zhang
The rise of highly convincing synthetic speech poses a growing threat to audio communications. Although existing Audio Deepfake Detection (ADD) methods have demonstrated good performance under clean conditions, their effectiveness drops significantly under degradations such as packet losses and speech codec compression in real-world communication environments. In this work, we propose the first unified framework for robust ADD under such degradations, which is designed to effectively accommodate multiple types of Time-Frequency (TF) representations. The core of our framework is a novel Multi-Granularity Adaptive Attention (MGAA) architecture, which employs a set of customizable multi-scale attention heads to capture both global and local receptive fields across varying TF granularities. A novel adaptive fusion mechanism subsequently adjusts and fuses these attention branches based on the saliency of TF regions, allowing the model to dynamically reallocate its focus according to the characteristics of the degradation. This enables the effective localization and amplification of subtle forgery traces. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed framework consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across various real-world communication degradation scenarios, including six speech codecs and five levels of packet losses. In addition, comparative analysis reveals that the MGAA-enhanced features significantly improve separability between real and fake audio classes and sharpen decision boundaries. These results highlight the robustness and practical deployment potential of our framework in real-world communication environments.
随着高度逼真的合成语音的兴起,音频通信面临着越来越大的威胁。尽管现有的音频深度伪造检测(ADD)方法在无噪声条件下表现出良好的性能,但在真实通信环境中的数据包丢失和语音编解码器压缩等退化条件下,其有效性会显著降低。在这项工作中,我们提出了首个针对此类退化情况下稳健的ADD的统一框架,该框架旨在有效适应多种时间频率(TF)表示。我们的框架的核心是一种新型的多粒度自适应注意力(MGAA)架构,它采用一组可定制的多尺度注意力头来捕获不同TF粒度下的全局和局部感受野。随后,一种新型自适应融合机制根据TF区域的显著性调整并融合这些注意力分支,使模型能够根据退化的特性动态重新分配其焦点。这能够实现细微伪造痕迹的有效定位和放大。大量实验表明,所提出的框架在各种真实通信退化场景下始终优于最先进的基线,包括六种语音编解码器和五个级别数据包丢失的场景。此外,对比分析表明,使用MGAA增强的特征显著提高了真实和伪造音频类别之间的可分离性,并明确了决策边界。这些结果凸显了我们的框架在真实通信环境中的稳健性和实际部署潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注合成语音的崛起对音频通信带来的威胁。现有音频深度伪造检测(ADD)方法在实际通信环境中存在局限性。为此,本文提出首个统一框架,该框架旨在适应多种时间频率(TF)表示,并引入多粒度自适应注意力(MGAA)架构,有效应对多种通信环境中的退化问题。实验证明,该框架在各种真实通信退化场景中表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 合成语音的崛起对音频通信构成威胁。
- 现有ADD方法在真实通信环境下性能下降。
- 提出首个统一框架,适应多种TF表示。
- 引入MGAA架构,捕捉全局和局部感受野。
- 自适应融合机制根据TF区域的显著性调整并融合注意力分支。
- 框架在多种真实通信退化场景中表现优越。
- MGAA增强特征提高了真实和伪造音频之间的可分性。
点此查看论文截图

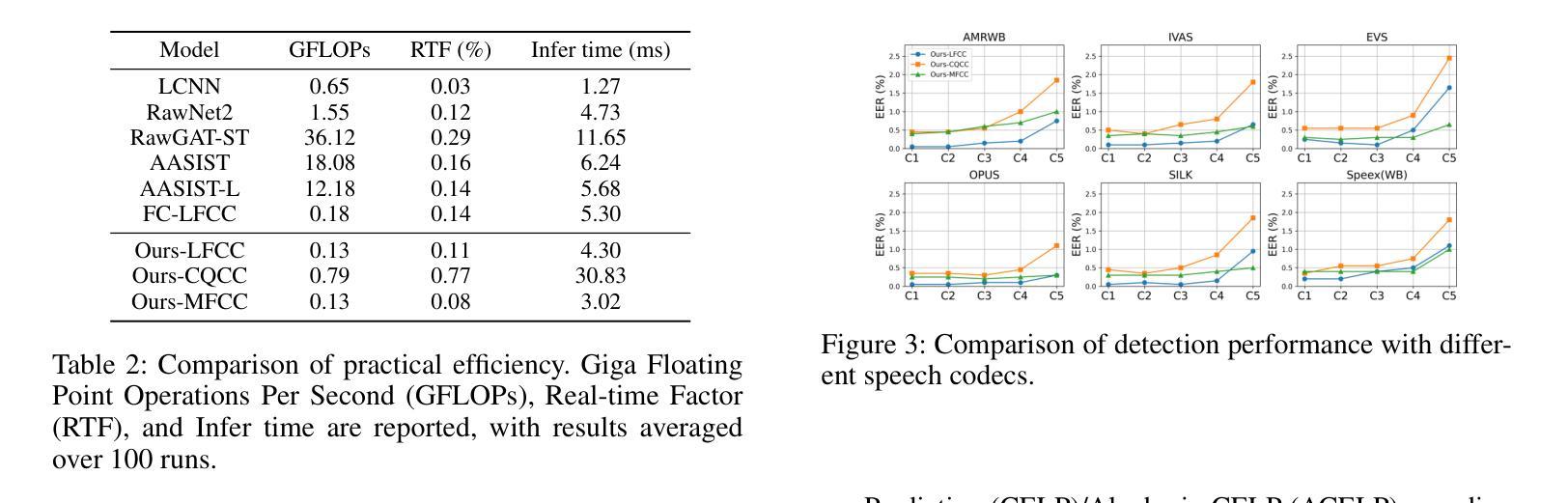
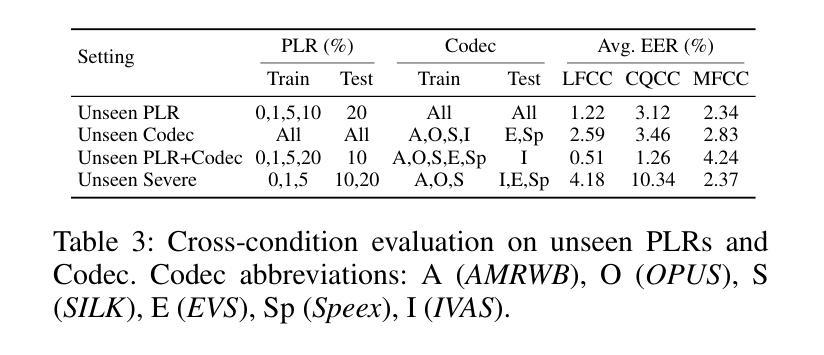
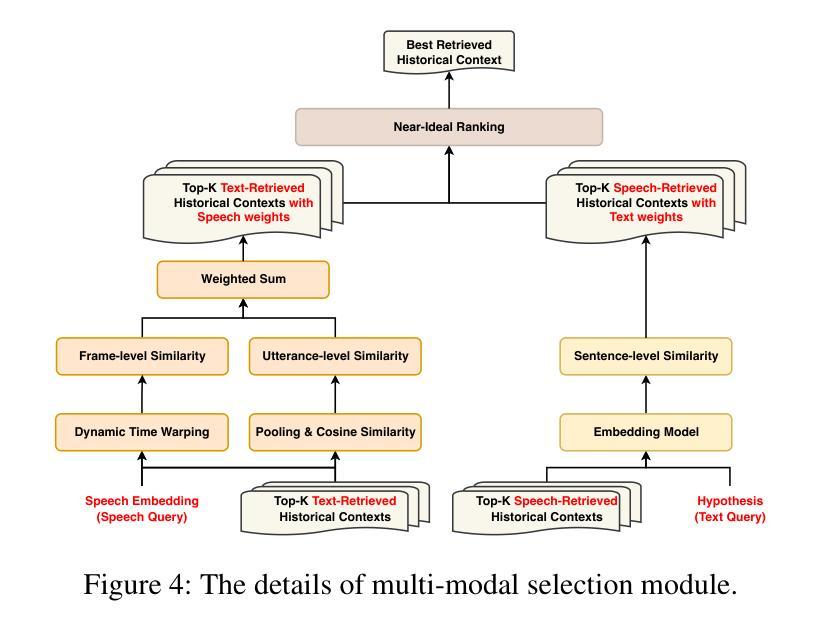
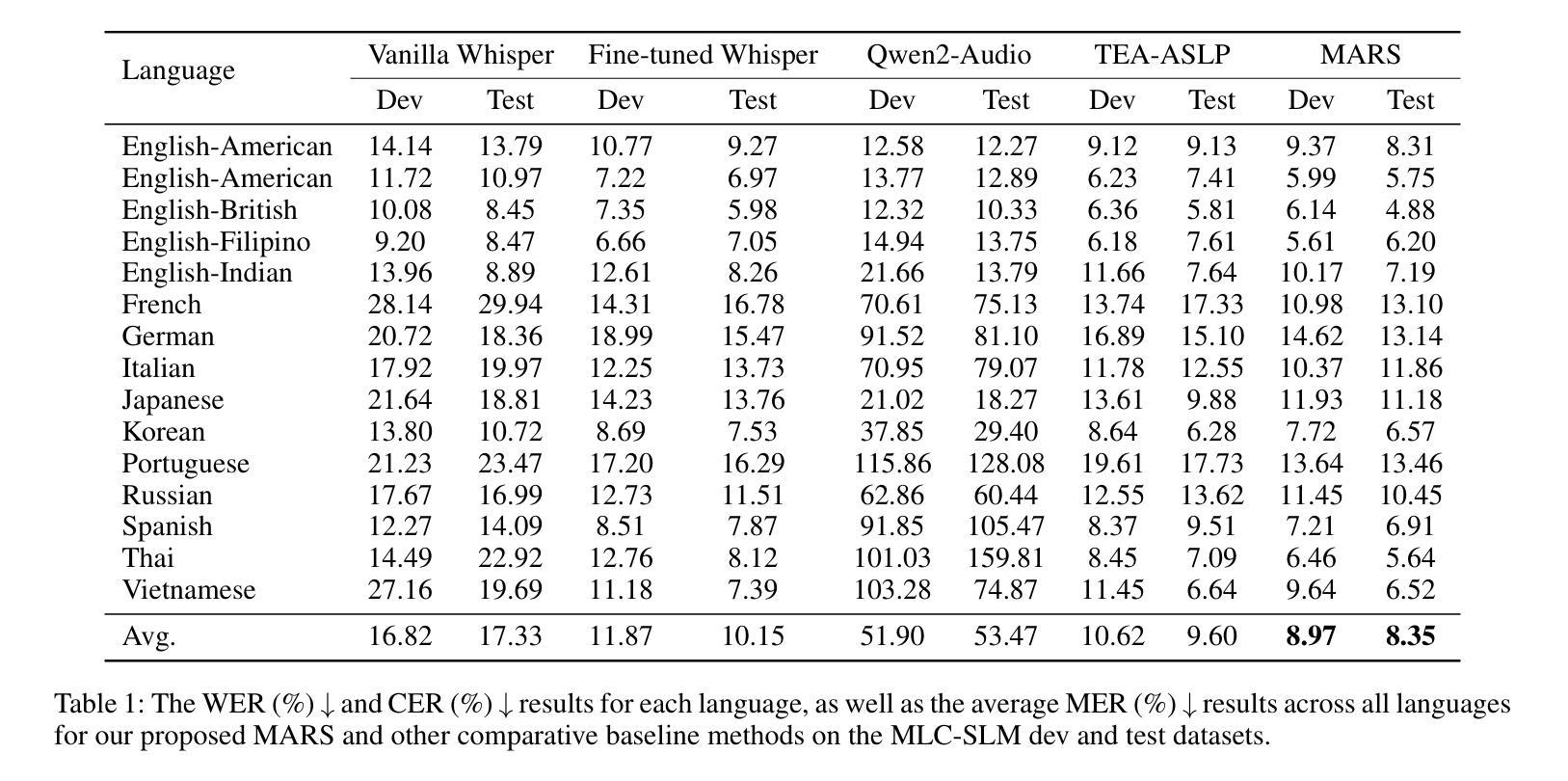
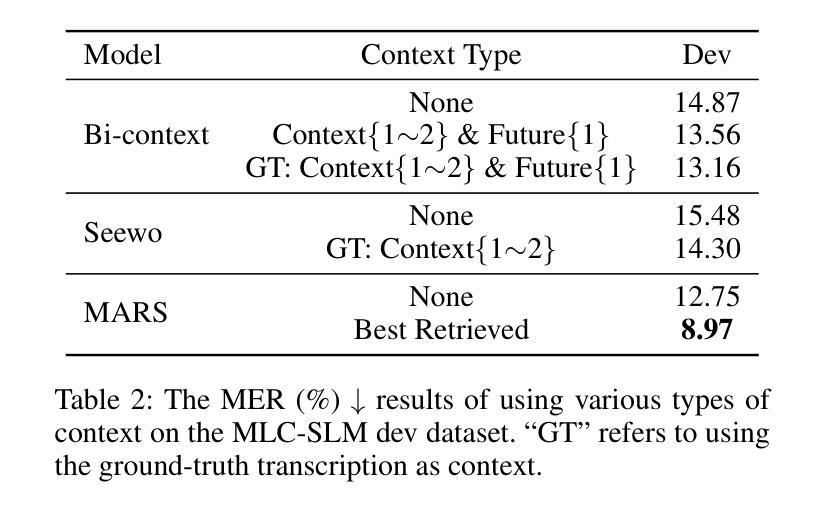
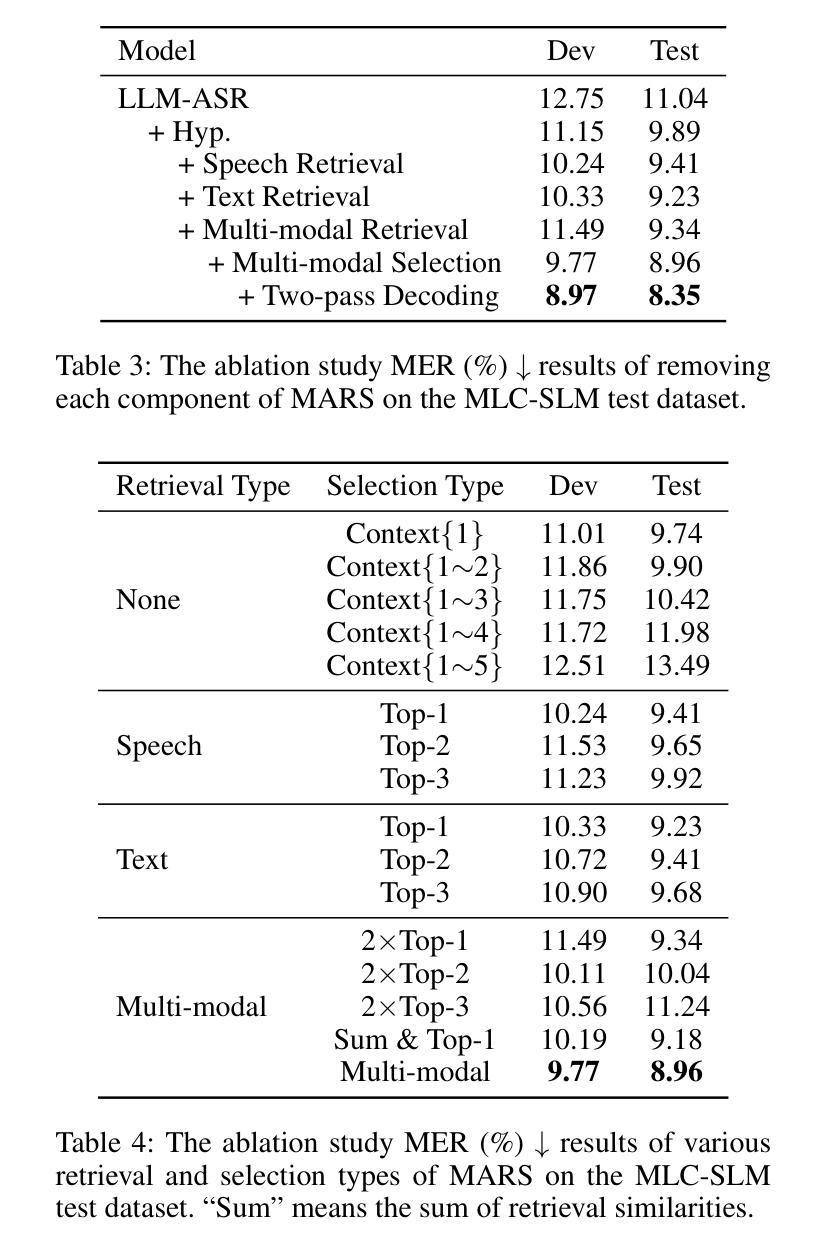
Hearing More with Less: Multi-Modal Retrieval-and-Selection Augmented Conversational LLM-Based ASR
Authors:Bingshen Mu, Hexin Liu, Hongfei Xue, Kun Wei, Lei Xie
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) aims to convert human speech content into corresponding text. In conversational scenarios, effectively utilizing context can enhance its accuracy. Large Language Models’ (LLMs) exceptional long-context understanding and reasoning abilities enable LLM-based ASR (LLM-ASR) to leverage historical context for recognizing conversational speech, which has a high degree of contextual relevance. However, existing conversational LLM-ASR methods use a fixed number of preceding utterances or the entire conversation history as context, resulting in significant ASR confusion and computational costs due to massive irrelevant and redundant information. This paper proposes a multi-modal retrieval-and-selection method named MARS that augments conversational LLM-ASR by enabling it to retrieve and select the most relevant acoustic and textual historical context for the current utterance. Specifically, multi-modal retrieval obtains a set of candidate historical contexts, each exhibiting high acoustic or textual similarity to the current utterance. Multi-modal selection calculates the acoustic and textual similarities for each retrieved candidate historical context and, by employing our proposed near-ideal ranking method to consider both similarities, selects the best historical context. Evaluations on the Interspeech 2025 Multilingual Conversational Speech Language Model Challenge dataset show that the LLM-ASR, when trained on only 1.5K hours of data and equipped with the MARS, outperforms the state-of-the-art top-ranking system trained on 179K hours of data.
自动语音识别(ASR)旨在将人类语音内容转换为相应的文本。在对话场景中,有效利用上下文可以提高其准确性。大型语言模型(LLM)出色的长文本理解和推理能力,使得基于LLM的ASR(LLM-ASR)能够利用历史上下文来识别对话语音,这对高度相关的上下文具有重要意义。然而,现有的对话式LLM-ASR方法使用固定数量的前面的话语或整个对话历史作为上下文,这会导致大量的无关和冗余信息,从而引发显著的ASR混淆和计算成本。本文提出了一种名为MARS的多模态检索与选择方法,它通过增强对话式LLM-ASR的能力,使其能够检索并选择当前话语中最相关的音频和文本历史上下文,从而扩展了对话式LLM-ASR的功能。具体来说,多模态检索获得一组候选历史上下文,每个上下文在声音或文本上与当前话语表现出高度相似性。多模态选择会计算每个检索到的候选历史上下文的音频和文本相似性,并利用我们提出的接近理想排序方法来考虑这两个相似性,选择最佳历史上下文。在InterSpeech 2025多语种对话语音语言模型挑战赛数据集上的评估表明,仅使用1.5K小时数据训练的LLM-ASR,配备MARS后,其性能优于使用17.9万小时数据训练的最新顶尖系统。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的自动语音识别(ASR)技术利用对话历史上下文来提高识别准确性。现有方法存在固定使用若干先前话语或整个对话历史作为上下文的问题,导致ASR混淆和计算成本高昂。本文提出了一种名为MARS的多模态检索与选择方法,能够检索并选择当前话语最相关的声音和文字历史上下文。在Interspeech 2025多语种对话语音语言模型挑战赛数据集上的评估显示,使用MARS的LLM-ASR性能超越了基于大量数据的先进排名系统。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在ASR中具有出色的长期上下文理解和推理能力。
- 现有ASR方法在利用对话历史上下文时存在冗余信息和计算成本问题。
- MARS方法通过多模态检索与选择增强LLM-ASR性能。
- MARS能够检索与当前话语最相关的声音和文字历史上下文。
- 使用MARS的LLM-ASR在少量数据训练下性能超越大量数据训练的先进系统。
- MARS方法通过平衡声音和文字的相似性,提高了ASR的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

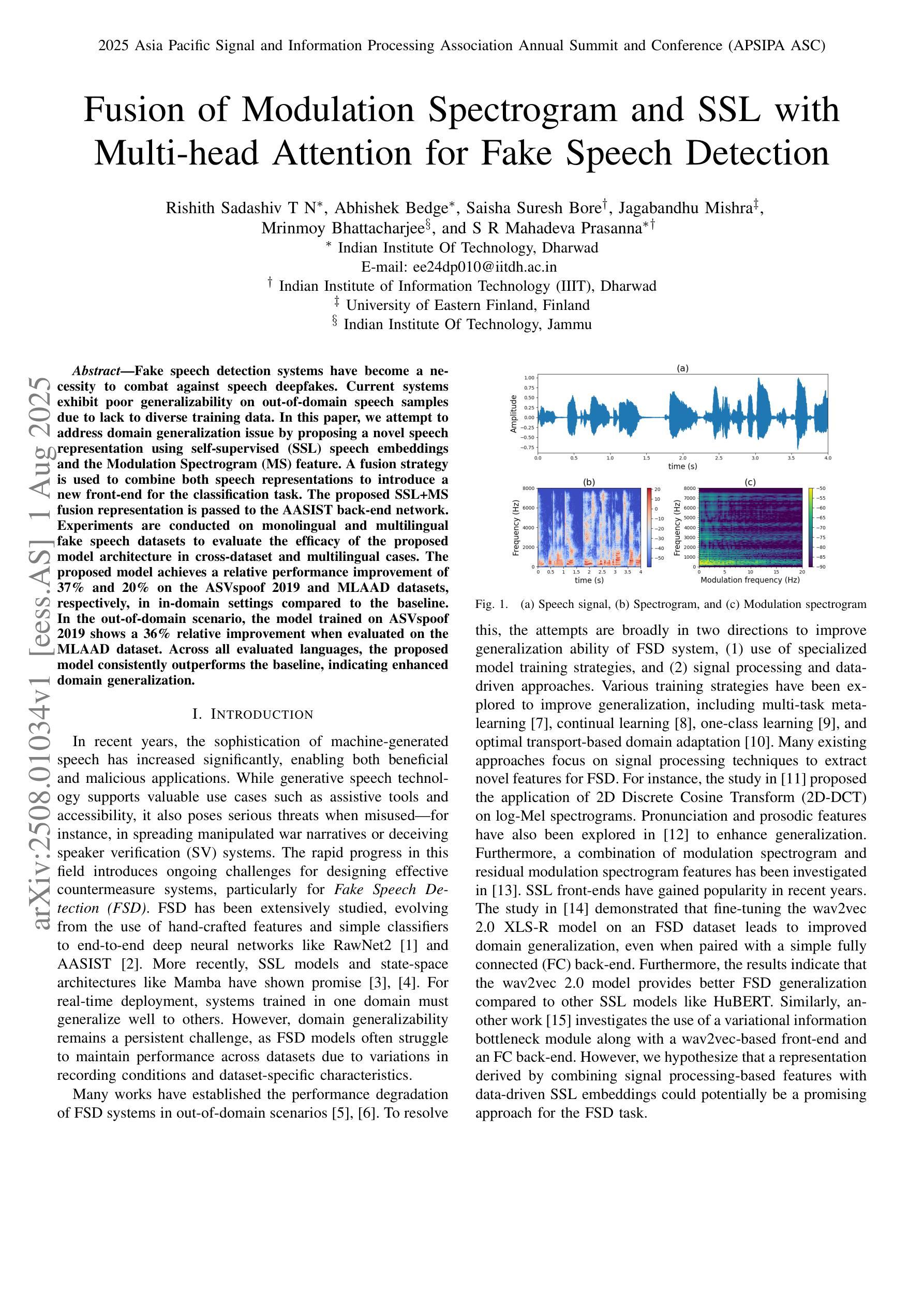
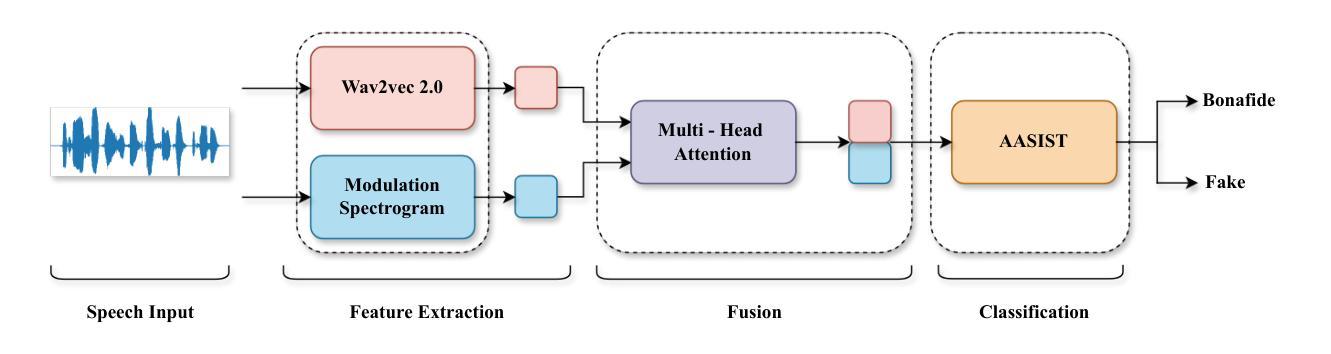
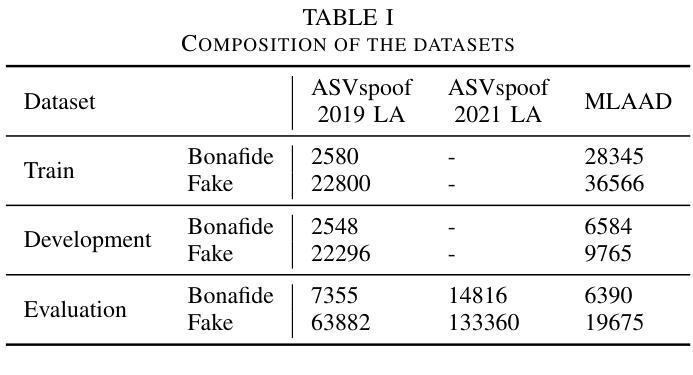
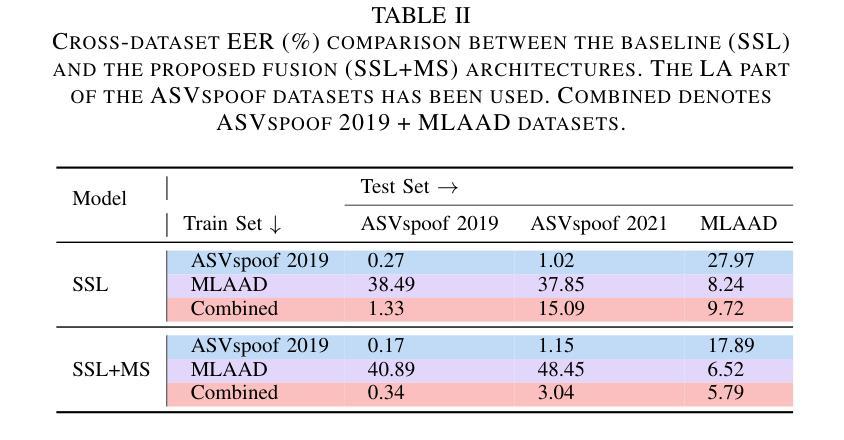
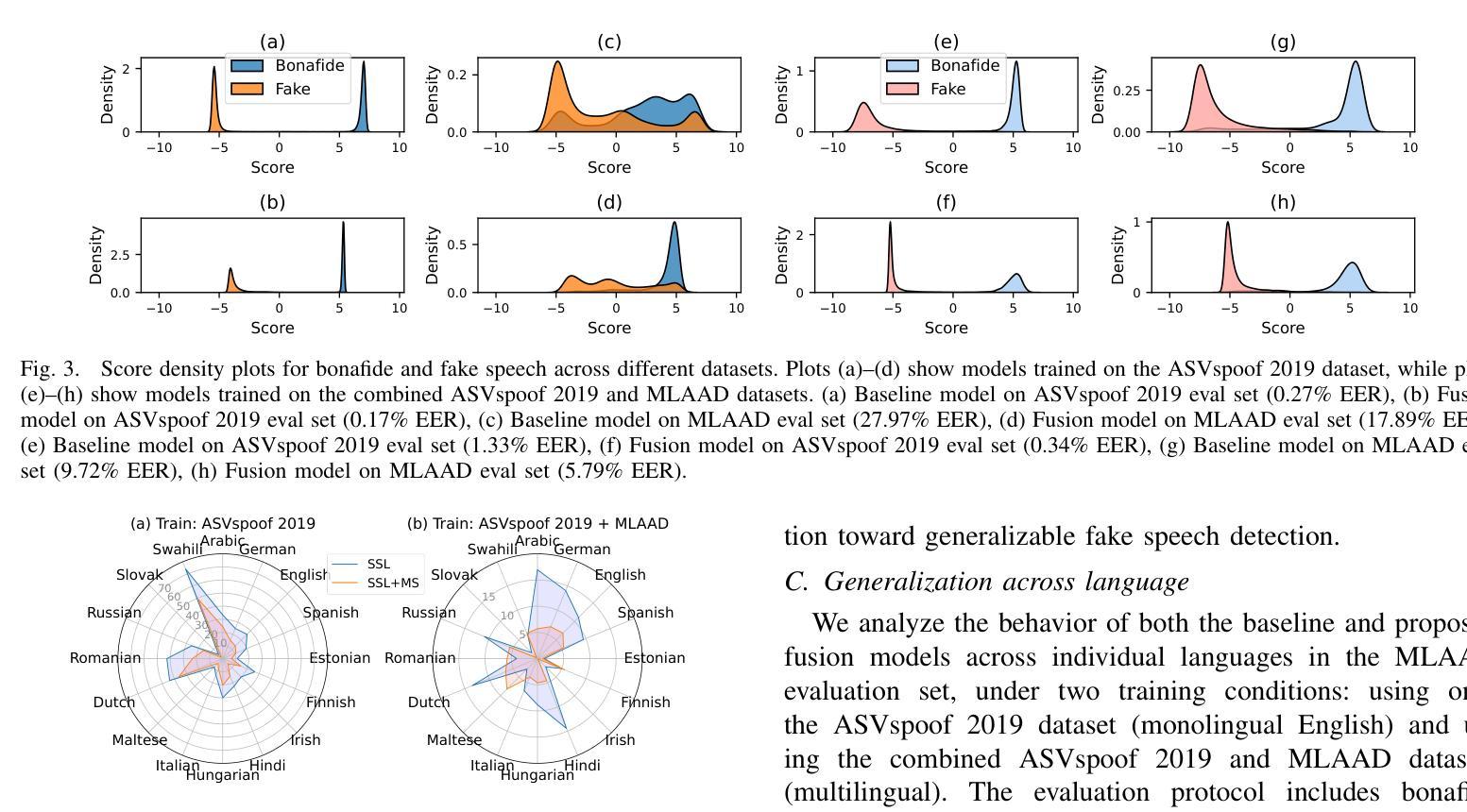
Fusion of Modulation Spectrogram and SSL with Multi-head Attention for Fake Speech Detection
Authors:Rishith Sadashiv T N, Abhishek Bedge, Saisha Suresh Bore, Jagabandhu Mishra, Mrinmoy Bhattacharjee, S R Mahadeva Prasanna
Fake speech detection systems have become a necessity to combat against speech deepfakes. Current systems exhibit poor generalizability on out-of-domain speech samples due to lack to diverse training data. In this paper, we attempt to address domain generalization issue by proposing a novel speech representation using self-supervised (SSL) speech embeddings and the Modulation Spectrogram (MS) feature. A fusion strategy is used to combine both speech representations to introduce a new front-end for the classification task. The proposed SSL+MS fusion representation is passed to the AASIST back-end network. Experiments are conducted on monolingual and multilingual fake speech datasets to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed model architecture in cross-dataset and multilingual cases. The proposed model achieves a relative performance improvement of 37% and 20% on the ASVspoof 2019 and MLAAD datasets, respectively, in in-domain settings compared to the baseline. In the out-of-domain scenario, the model trained on ASVspoof 2019 shows a 36% relative improvement when evaluated on the MLAAD dataset. Across all evaluated languages, the proposed model consistently outperforms the baseline, indicating enhanced domain generalization.
假语音检测系统在应对语音深度伪造时成为了必要工具。当前系统由于缺少多样化的训练数据,在域外语音样本上的通用性较差。在本文中,我们试图通过提出一种新型语音表现来解决领域通用性问题,该表现使用自监督(SSL)语音嵌入和调制光谱(MS)特征。我们采用融合策略结合这两种语音表现,为分类任务引入新的前端。提出的SSL+MS融合表现传递给AASIST后端网络。实验在单语种和多语种假语音数据集上进行,以评估所提模型架构在跨数据集和多语种情况下的有效性。与基线相比,在所提议的模型在域内设置下,在ASVspoof 2019和MLAAD数据集上分别实现了相对性能提升37%和20%。在域外场景下,该模型在ASVspoof 2019数据集上进行训练,并在MLAAD数据集上评估时显示出相对改善了36%。在所评估的所有语言中,所提出模型的性能始终优于基线,显示出增强的领域泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对语音深度伪造带来的问题,假语音检测系统的研究变得至关重要。当前系统因缺乏多样化训练数据而在跨域语音样本上表现通用性不足。本文试图通过提出一种新型的语音表现方式来解决域泛化问题,该方式结合了自监督(SSL)语音嵌入和调制谱(MS)特征。通过融合策略结合这两种语音表现方式,为分类任务引入新的前端。所提出的SSL+MS融合表现传递给AASIST后端网络。在单语种和多语种假语音数据集上进行的实验,验证了所提出模型架构在跨数据集和多语种情况下的有效性。与基线相比,所提出模型在ASVspoof 2019和MLAAD数据集上的域内设置分别实现了37%和20%的相对性能提升。在跨域场景中,基于ASVspoof 2019训练的模型在MLAAD数据集上显示了36%的相对改进。在所有评估的语言中,所提出模型始终优于基线,显示出增强的域泛化能力。
关键见解
- 假语音检测系统因训练数据缺乏多样性而在跨域语音样本上表现出有限的通用性。
- 提出了一种新的语音表现方式,结合自监督(SSL)语音嵌入和调制谱(MS)特征,以提高模型的泛化能力。
- 通过融合策略,将SSL和MS特征结合,为分类任务设计新型前端。
- 所提出的模型架构在单语种和多语种假语音数据集上进行实验验证,表现出优良的有效性。
- 在域内设置下,相对于基线,所提出模型在ASVspoof 2019和MLAAD数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
- 在跨域场景下,模型在MLAAD数据集上的性能有显著改善。
点此查看论文截图
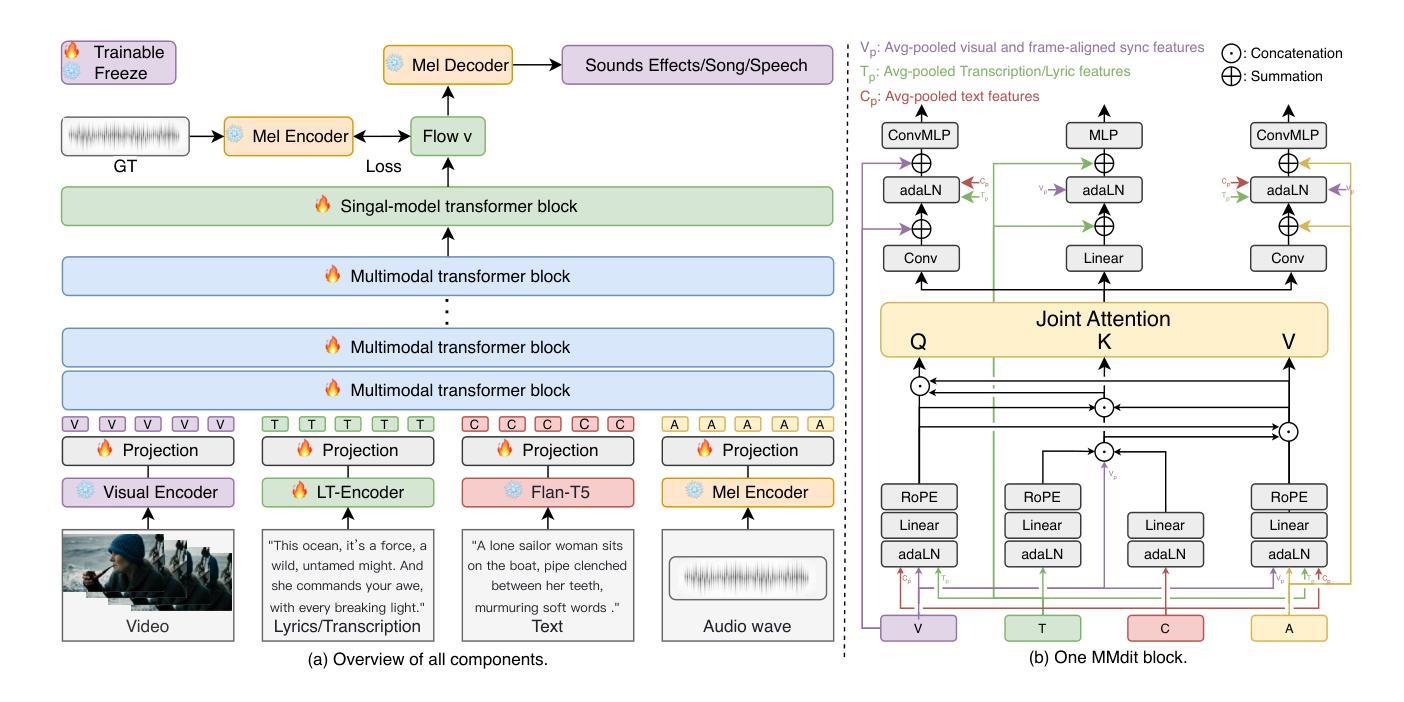
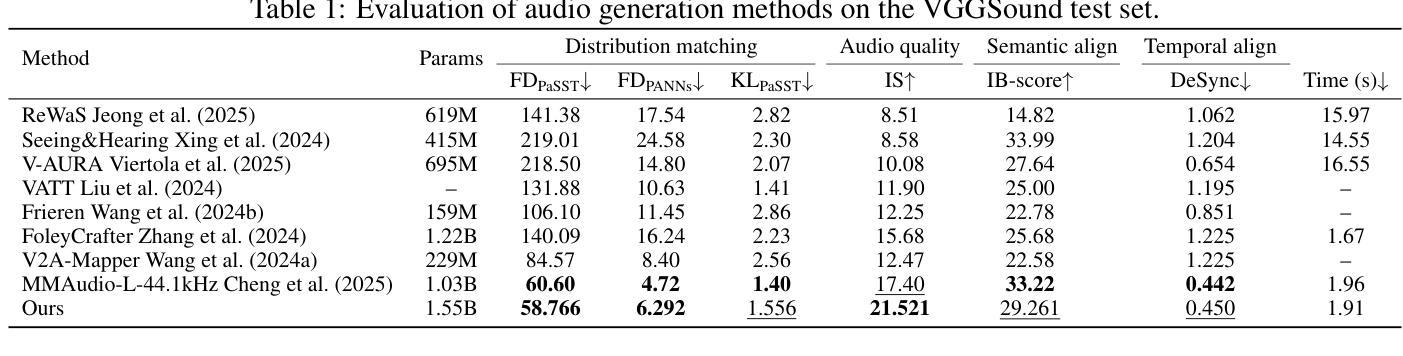
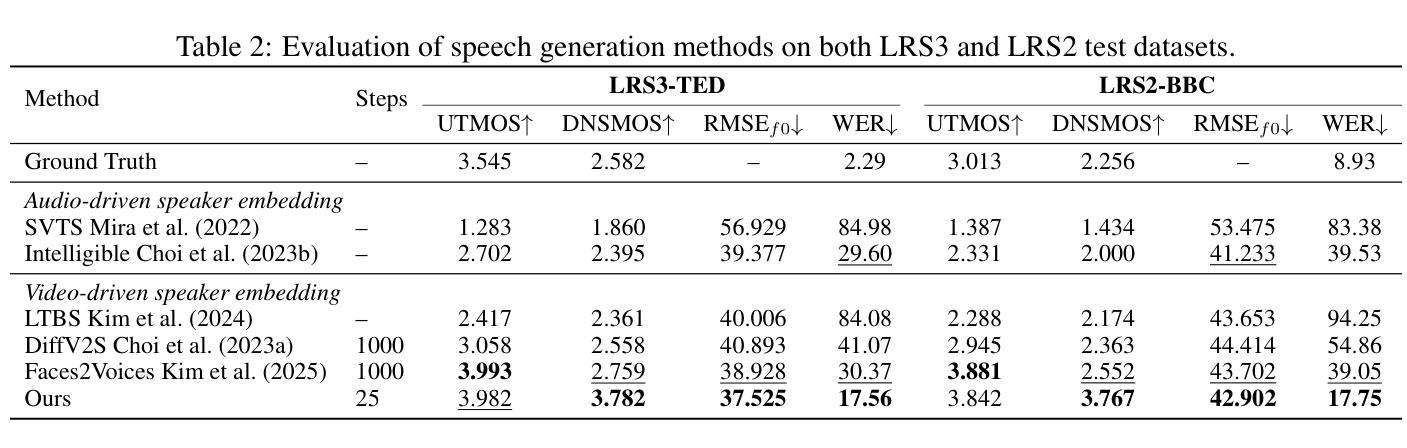
AudioGen-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Video-Synchronized Audio, Speech, and Song Generation
Authors:Le Wang, Jun Wang, Feng Deng, Chen Zhang, Di Zhang, Kun Gai
We present AudioGen-Omni - a unified approach based on multimodal diffusion transformers (MMDit), capable of generating high-fidelity audio, speech, and songs coherently synchronized with the input video. AudioGen-Omni introduces a novel joint training paradigm that seamlessly integrates large-scale video-text-audio corpora, enabling a model capable of generating semantically rich, acoustically diverse audio conditioned on multimodal inputs and adaptable to a wide range of audio generation tasks. AudioGen-Omni employs a unified lyrics-transcription encoder that encodes graphemes and phonemes from both sung and spoken inputs into dense frame-level representations. Dense frame-level representations are fused using an AdaLN-based joint attention mechanism enhanced with phase-aligned anisotropic positional infusion (PAAPI), wherein RoPE is selectively applied to temporally structured modalities to ensure precise and robust cross-modal alignment. By unfreezing all modalities and masking missing inputs, AudioGen-Omni mitigates the semantic constraints of text-frozen paradigms, enabling effective cross-modal conditioning. This joint training approach enhances audio quality, semantic alignment, and lip-sync accuracy, while also achieving state-of-the-art results on Text-to-Audio/Speech/Song tasks. With an inference time of 1.91 seconds for 8 seconds of audio, it offers substantial improvements in both efficiency and generality.
我们提出了AudioGen-Omni——一种基于多模式扩散变压器(MMDit)的统一方法,能够生成与输入视频同步的高保真音频、语音和歌曲。AudioGen-Omni引入了一种新的联合训练范式,无缝集成了大规模的视频-文本-音频语料库,使模型能够在多模式输入条件下生成语义丰富、声音多样的音频,并适应各种音频生成任务。AudioGen-Omni采用统一的歌词转录编码器,将唱词和口语输入中的字母和音素编码成密集的帧级表示。密集的帧级表示通过使用基于AdaLN的联合注意力机制进行融合,增强了相位对齐的异向定位注入(PAAPI),其中RoPE被有选择地应用于具有时间结构的模式,以确保精确和稳定的跨模式对齐。通过解冻所有模式并掩盖缺失的输入,AudioGen-Omni减轻了文本冻结范式的语义约束,实现了有效的跨模式条件。这种联合训练方法提高了音频质量、语义对齐和唇同步精度,同时在文本到音频/语音/歌曲任务上达到了最先进的成果。其推理时间为1.91秒可生成8秒的音频,在效率和通用性方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 figures
Summary
基于多模态扩散变压器(MMDit)的AudioGen-Omni统一方法,能够生成与输入视频同步的高保真音频、语音和歌曲。该方法引入了一种新型联合训练范式,无缝集成大规模视频-文本-音频语料库,可生成语义丰富、声音多样的音频,并适应各种音频生成任务。AudioGen-Omni采用统一的歌词-转录编码器,对歌唱和口语输入中的字母和音素进行密集帧级编码表示。通过AdaLN联合注意力机制的融合,结合相位对齐的异构位置注入(PAAPI),将RoPE选择性应用于时间结构化模式,确保精确和稳定的跨模式对齐。解冻所有模式并屏蔽缺失输入,AudioGen-Omni缓解了文本冻结范式的语义约束,实现了有效的跨模式条件。该联合训练方法提高了音频质量、语义对齐和唇同步精度,并在文本到音频/语音/歌曲任务上实现了最新成果。其推理时间为每生成8秒音频只需约1.91秒,效率和通用性均有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- AudioGen-Omni是一种基于多模态扩散变压器(MMDit)的统一方法,能够生成高保真音频、语音和歌曲,且与输入视频同步。
- 引入新型联合训练范式,集成视频-文本-音频语料库。
- 采用统一的歌词-转录编码器,进行密集帧级编码表示。
- 结合AdaLN联合注意力机制和PAAPI技术,确保精确和稳定的跨模式对齐。
- 通过解冻所有模式并屏蔽缺失输入,实现有效跨模态条件。
- 联合训练方法提高了音频质量、语义对齐和唇同步精度。
点此查看论文截图

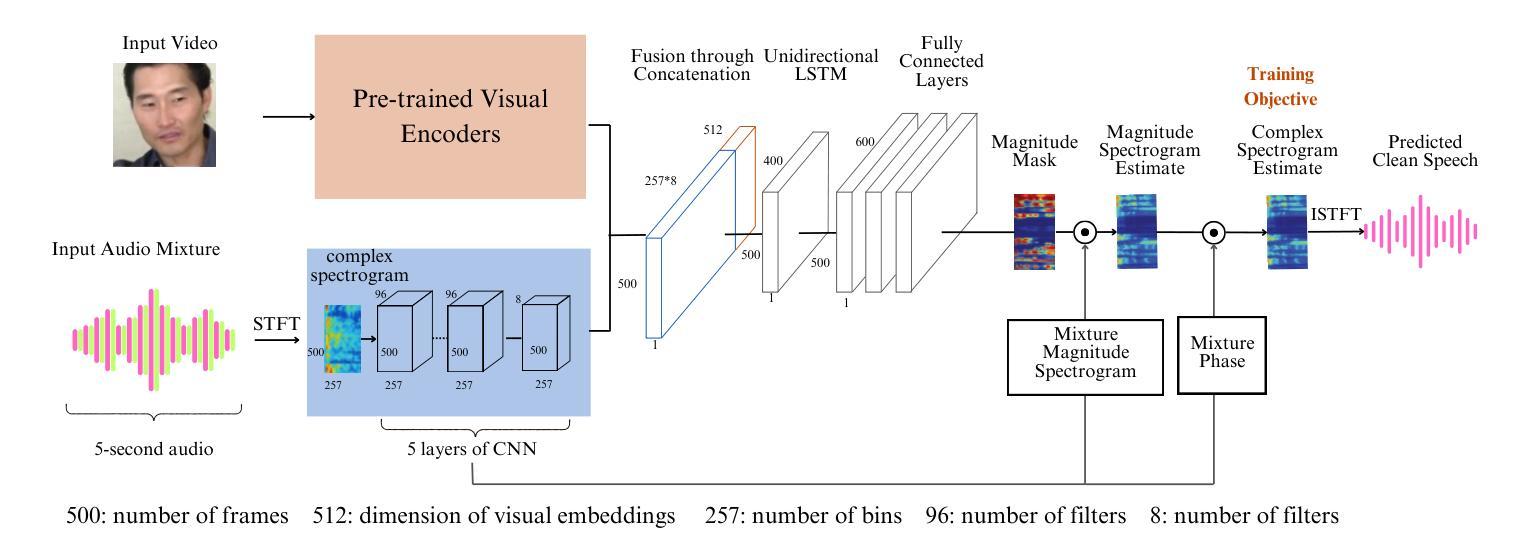
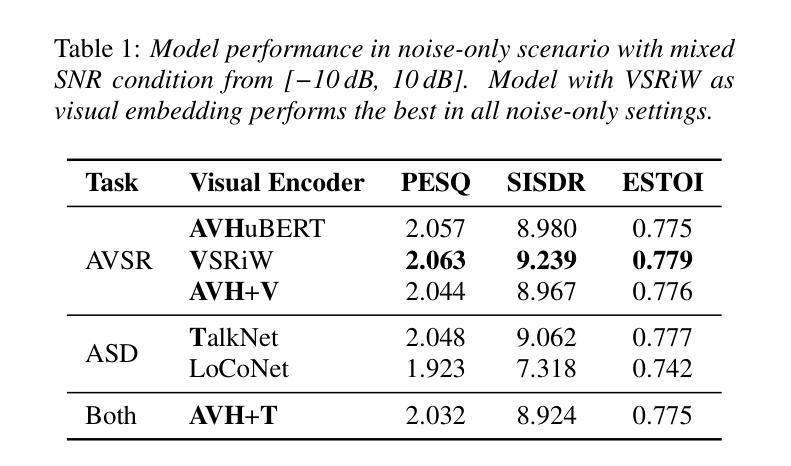
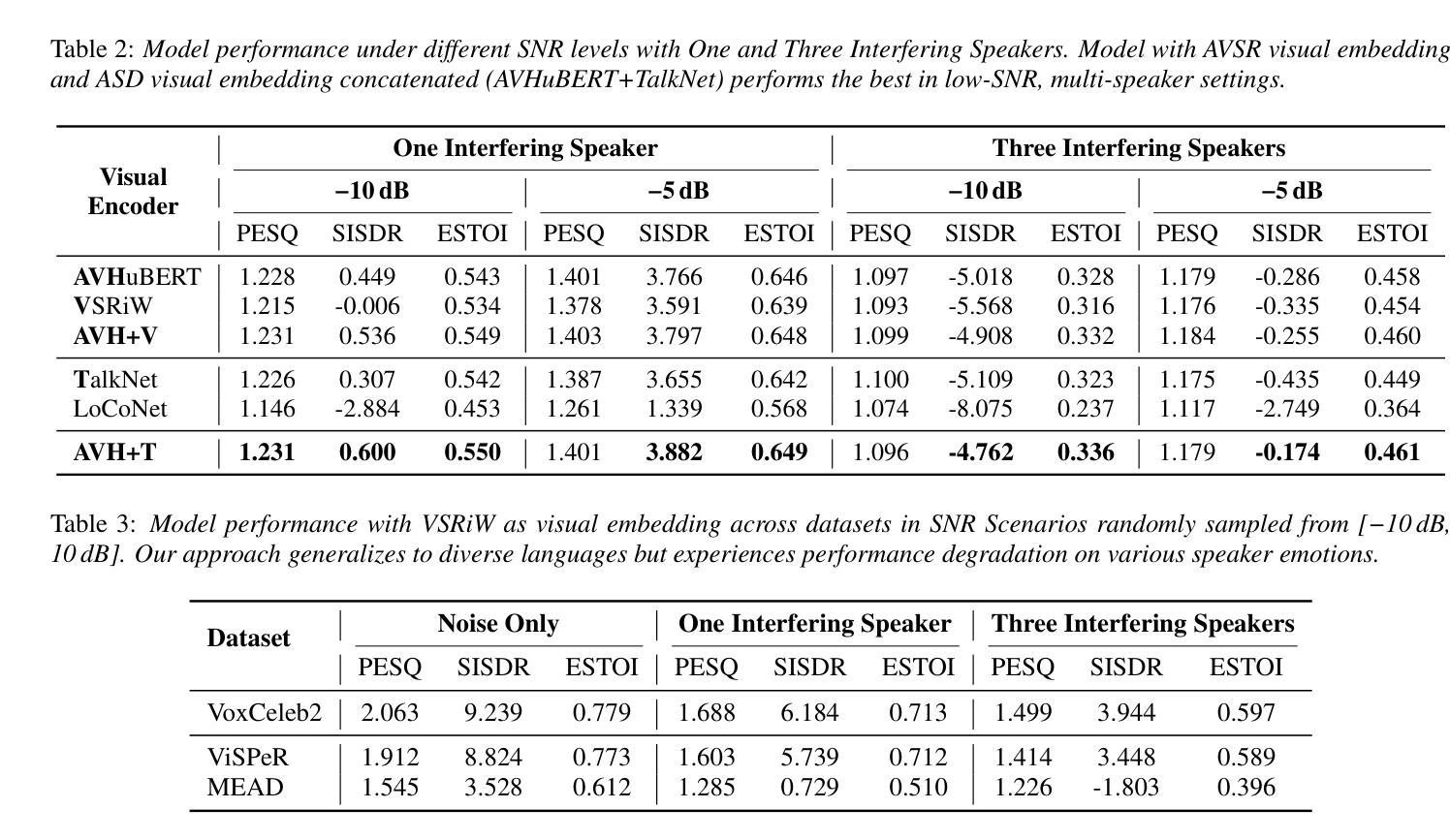
Real-Time Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement Using Pre-trained Visual Representations
Authors:T. Aleksandra Ma, Sile Yin, Li-Chia Yang, Shuo Zhang
Speech enhancement in audio-only settings remains challenging, particularly in the presence of interfering speakers. This paper presents a simple yet effective real-time audio-visual speech enhancement (AVSE) system, RAVEN, which isolates and enhances the on-screen target speaker while suppressing interfering speakers and background noise. We investigate how visual embeddings learned from audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) and active speaker detection (ASD) contribute to AVSE across different SNR conditions and numbers of interfering speakers. Our results show concatenating embeddings from AVSR and ASD models provides the greatest improvement in low-SNR, multi-speaker environments, while AVSR embeddings alone perform best in noise-only scenarios. In addition, we develop a real-time streaming system that operates on a computer CPU and we provide a video demonstration and code repository. To our knowledge, this is the first open-source implementation of a real-time AVSE system.
在只有音频的环境中,语音增强仍然是一个挑战,特别是在存在干扰说话者的情况下。本文提出了一种简单有效的实时视听语音增强(AVSE)系统,名为RAVEN,该系统可以隔离并增强屏幕上的目标说话者,同时抑制干扰说话者和背景噪声。我们研究了从视听语音识别(AVSR)和主动说话者检测(ASD)中学到的视觉嵌入如何在不同信噪比条件和干扰说话者数量的情况下对AVSE做出贡献。我们的结果表明,在信噪比低、多说话者的环境中,拼接AVSR和ASD模型的嵌入会提供最大的改进,而仅使用AVSR嵌入在只有噪声的场景中表现最佳。此外,我们开发了一个可在计算机CPU上运行的实时流媒体系统,并提供了视频演示和代码仓库。据我们所知,这是第一个实时AVSE系统的开源实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted into Interspeech 2025; corrected author name typo
摘要
该论文提出了一种简单有效的实时视听语音增强(AVSE)系统,名为RAVEN。该系统能够在有干扰说话人的情况下,隔离并增强屏幕上的目标说话人声音,同时抑制干扰说话人和背景噪音。文章探讨了如何从视听语音识别(AVSR)和活动说话人检测(ASD)中学习视觉嵌入,以助力AVSE在不同信噪比条件和干扰说话人数量的场景中的应用。实验结果显示,在信噪比低、存在多名干扰说话人的环境中,融合AVSR和ASD模型的嵌入信息取得的效果最佳;而仅在噪声场景下,AVSR嵌入信息表现最好。此外,论文还开发了一个可在计算机CPU上运行的实时流媒体系统,并提供了视频演示和代码仓库。这是首个开源的实时AVSE系统。
关键见解
- 论文提出了一种实时视听语音增强(AVSE)系统RAVEN,能够在有干扰说话人的情况下增强目标说话人的语音。
- RAVEN系统通过隔离和增强目标说话人声音,同时抑制干扰说话人和背景噪音,改善了语音清晰度。
- 论文探讨了视觉嵌入在AVSE中的作用,特别是从视听语音识别(AVSR)和活动说话人检测(ASD)中学习得到的视觉嵌入。
- 在不同信噪比条件和干扰说话人数量的场景中,融合AVSR和ASD模型的嵌入信息能够取得最佳性能。
- AVSR嵌入信息在仅有噪声的场景中表现最好。
- 论文开发了一个可在计算机CPU上运行的实时流媒体系统,实现了AVSE的实时应用。
- 该系统是首个开源的实时AVSE系统,提供了视频演示和代码仓库,便于其他研究者使用和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图

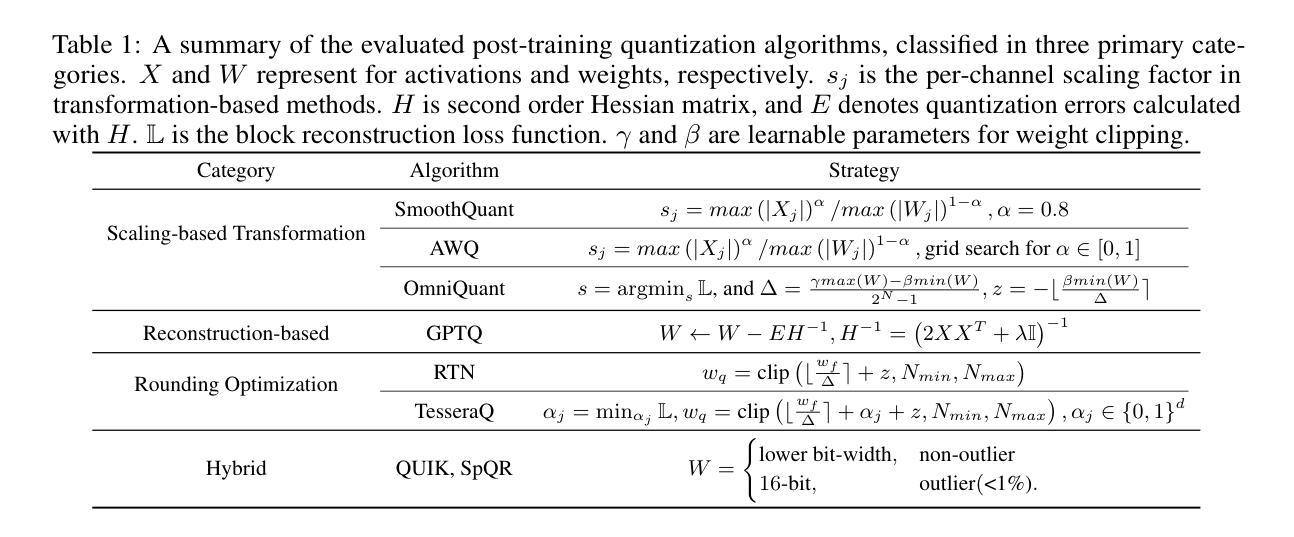
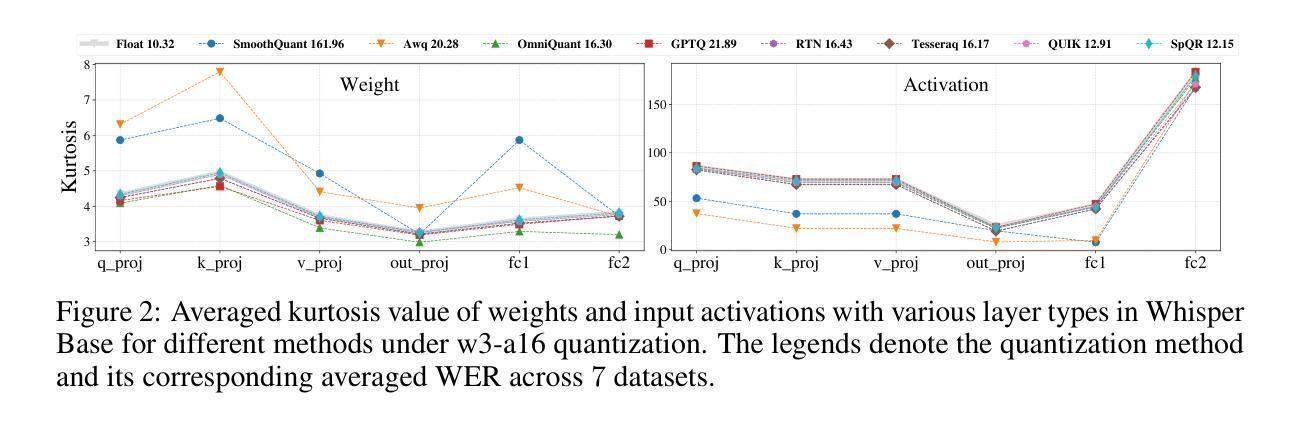
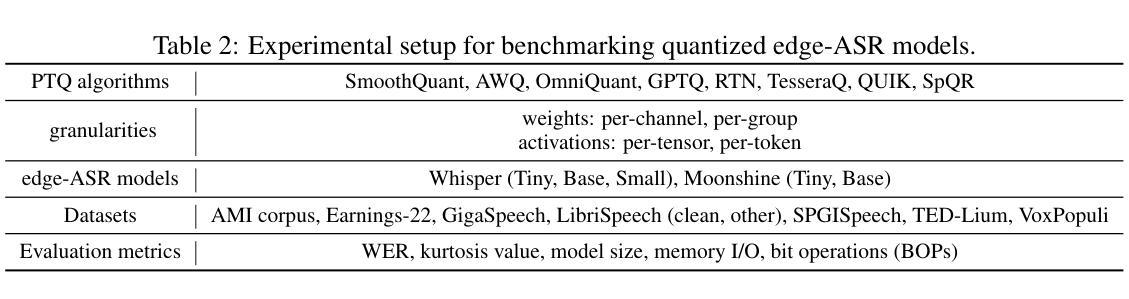
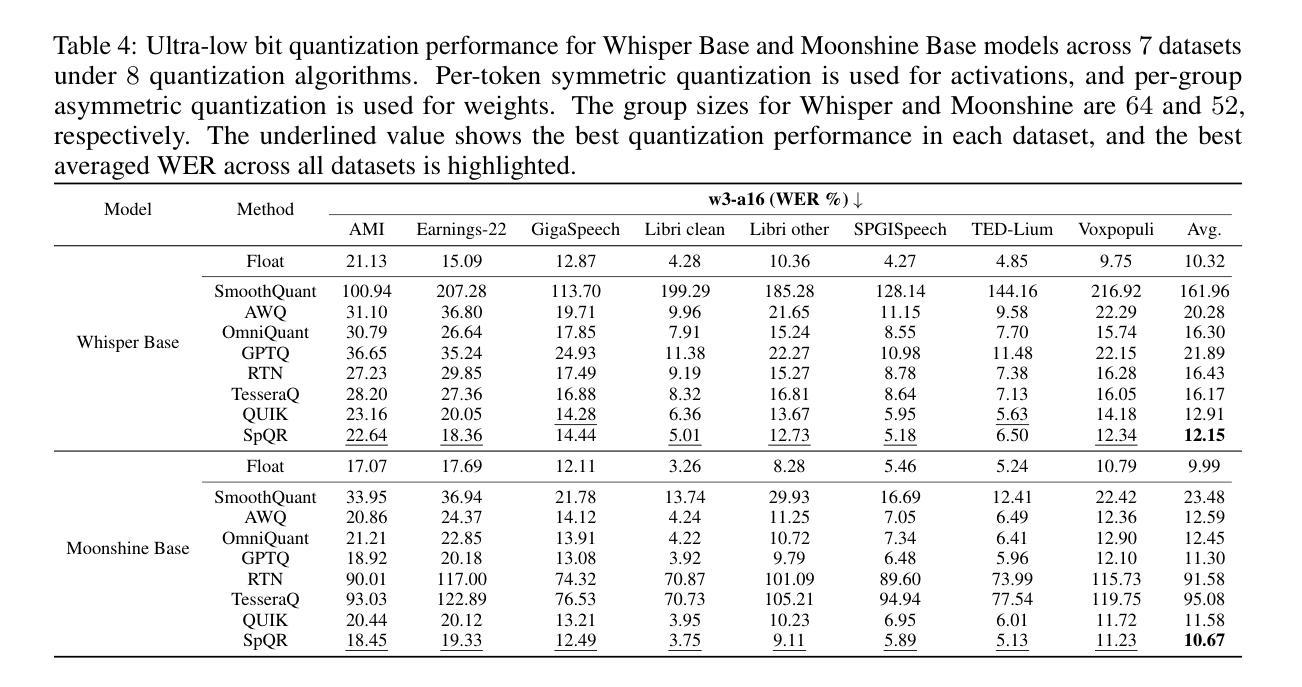
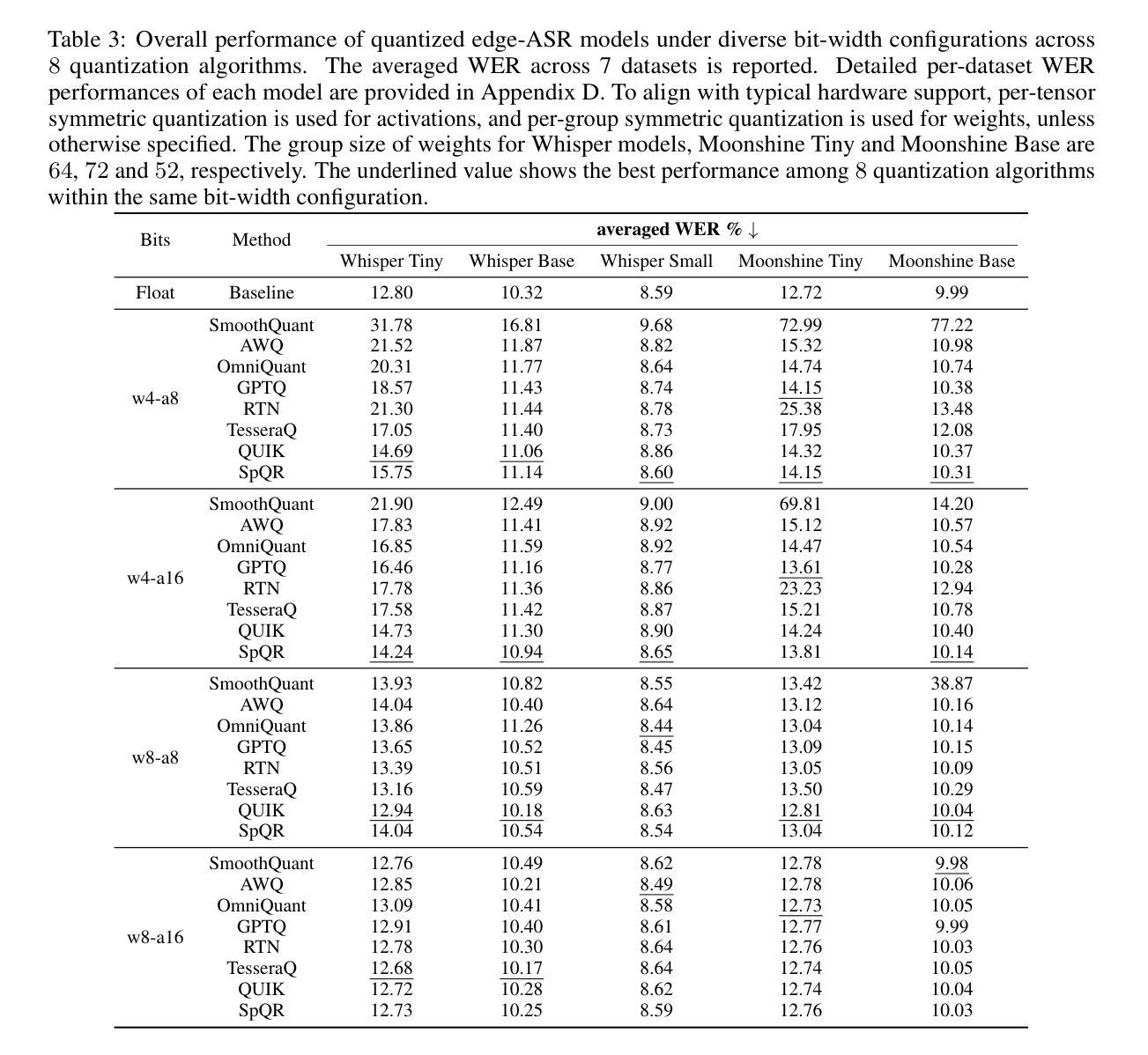
Edge-ASR: Towards Low-Bit Quantization of Automatic Speech Recognition Models
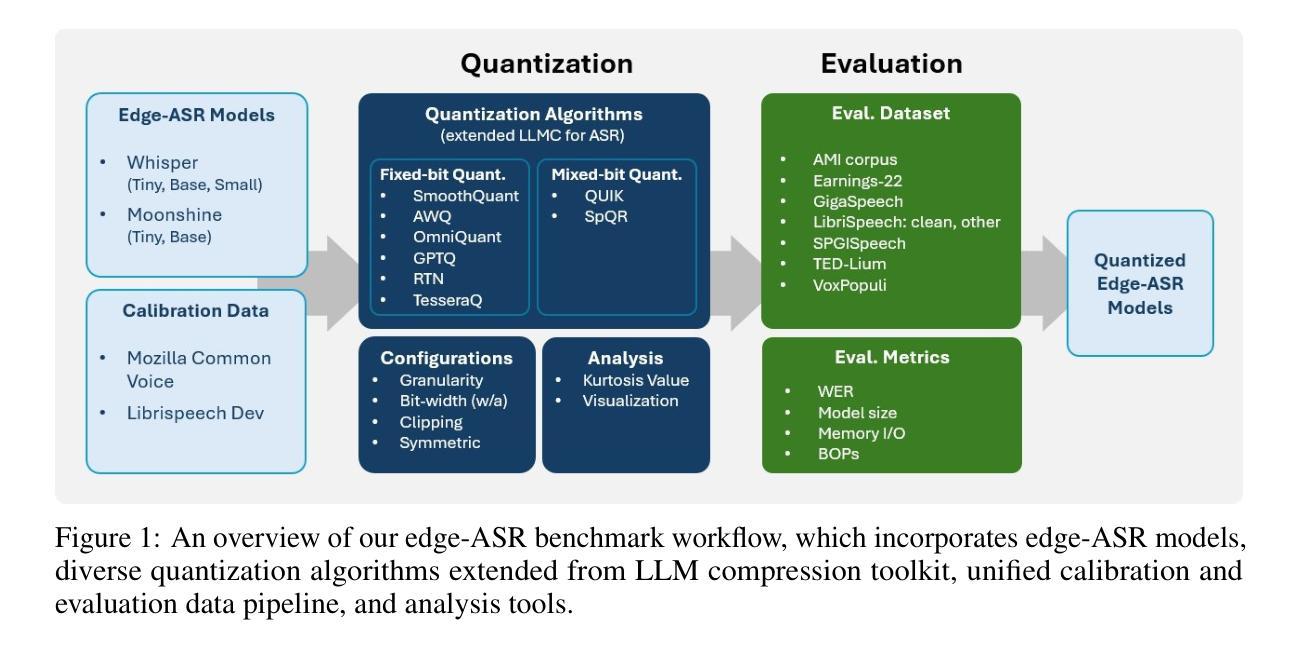
Authors:Chen Feng, Yicheng Lin, Shaojie Zhuo, Chenzheng Su, Ramchalam Kinattinkara Ramakrishnan, Zhaocong Yuan, Xiaopeng Zhang
Recent advances in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) have demonstrated remarkable accuracy and robustness in diverse audio applications, such as live transcription and voice command processing. However, deploying these models on resource-constrained edge devices (e.g., IoT device, wearables) still presents substantial challenges due to strict limits on memory, compute and power. Quantization, particularly Post-Training Quantization (PTQ), offers an effective way to reduce model size and inference cost without retraining. Despite its importance, the performance implications of various advanced quantization methods and bit-width configurations on ASR models remain unclear. In this work, we present a comprehensive benchmark of eight state-of-the-art (SOTA) PTQ methods applied to two leading edge-ASR model families, Whisper and Moonshine. We systematically evaluate model performances (i.e., accuracy, memory I/O and bit operations) across seven diverse datasets from the open ASR leader-board, analyzing the impact of quantization and various configurations on both weights and activations. Built on an extension of the LLM compression toolkit, our framework integrates edge-ASR models, diverse advanced quantization algorithms, a unified calibration and evaluation data pipeline, with detailed analysis tools. Our results characterize the trade-offs between efficiency and accuracy, demonstrating that even $3$-bit quantization can succeed on high capacity models when using advanced PTQ techniques. These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing ASR models on low-power, always-on edge devices.
近期自动语音识别(ASR)技术的进展在各种音频应用中表现出了显著准确性和稳健性,例如实时转录和语音命令处理。然而,将这些模型部署在资源受限的边缘设备(例如物联网设备和可穿戴设备)上仍然面临重大挑战,这主要是由于内存、计算和功率的严格限制。量化,尤其是训练后量化(PTQ),提供了一种有效的方式来减少模型大小和推理成本而无需重新训练。尽管其很重要,但各种先进的量化方法和位宽配置对ASR模型性能的影响仍不清楚。在这项工作中,我们对应用于两个领先边缘ASR模型家族Whisper和Moonshine的八种最新(SOTA)PTQ方法进行了全面评估。我们系统地评估了模型在七个开放ASR排行榜数据集上的性能(即准确性、内存I/O和位操作),分析了量化和各种配置对权重和激活的影响。我们的框架基于LLM压缩工具包的扩展,集成了边缘ASR模型、各种先进量化算法、统一的校准和评估数据流水线以及详细的分析工具。我们的结果描述了效率和准确性之间的权衡,表明使用先进的PTQ技术时,即使3位量化也可以在高容量模型上取得成功。这些发现对于在低功耗、始终开启的边缘设备上优化ASR模型提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期自动语音识别(ASR)技术的进展在实时转录和语音命令处理等应用中表现出惊人的准确性和稳健性。然而,在资源受限的边缘设备上部署这些模型仍存在挑战,如内存、计算和电源方面的限制。本研究对两款前沿的边缘ASR模型家族Whisper和Moonshine应用八种先进的PTQ量化方法进行了全面评估。通过跨七个开放ASR排行榜数据集的系统评价,研究分析了量化方法和配置对权重和激活的影响。基于LLM压缩工具包的扩展,本研究集成了边缘ASR模型、多种先进的量化算法、统一的校准和评价数据管道以及详细的分析工具。研究结果表明,使用先进的PTQ技术,即使3位量化也能在高容量模型中取得成功。这些发现对于在低功耗、始终开启的边缘设备上优化ASR模型提供了宝贵的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音识别(ASR)技术在多种应用中表现出高准确性和稳健性。
- 在资源受限的边缘设备上部署ASR模型面临挑战,需要量化技术来减小模型大小和推理成本。
- 研究评估了两种前沿ASR模型家族Whisper和Moonshine,使用八种先进的PTQ量化方法。
- 研究跨七个数据集系统评价了模型性能,包括准确性、内存I/O和位操作。
- 研究集成了边缘ASR模型、量化算法、校准和评价数据管道及分析工具。
- 研究表明,使用先进的PTQ技术,甚至3位量化也能在高容量模型中成功应用。
点此查看论文截图

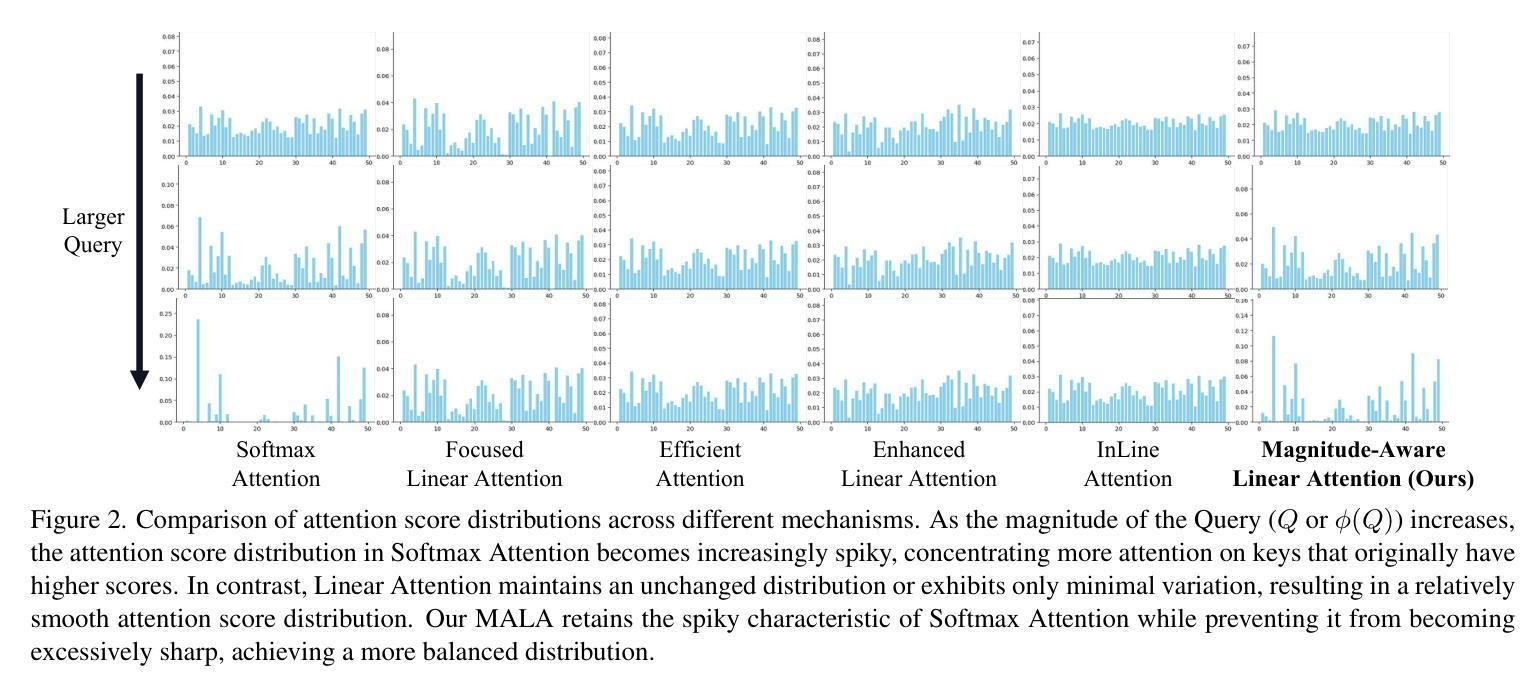
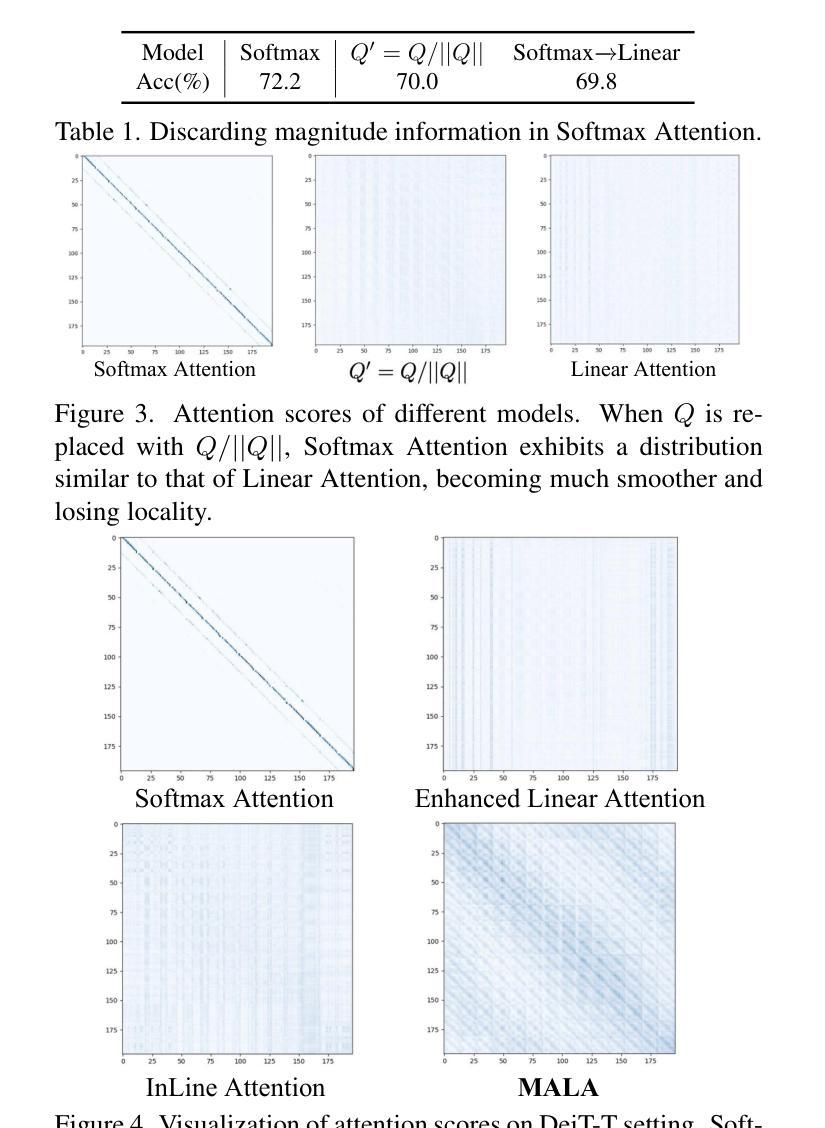
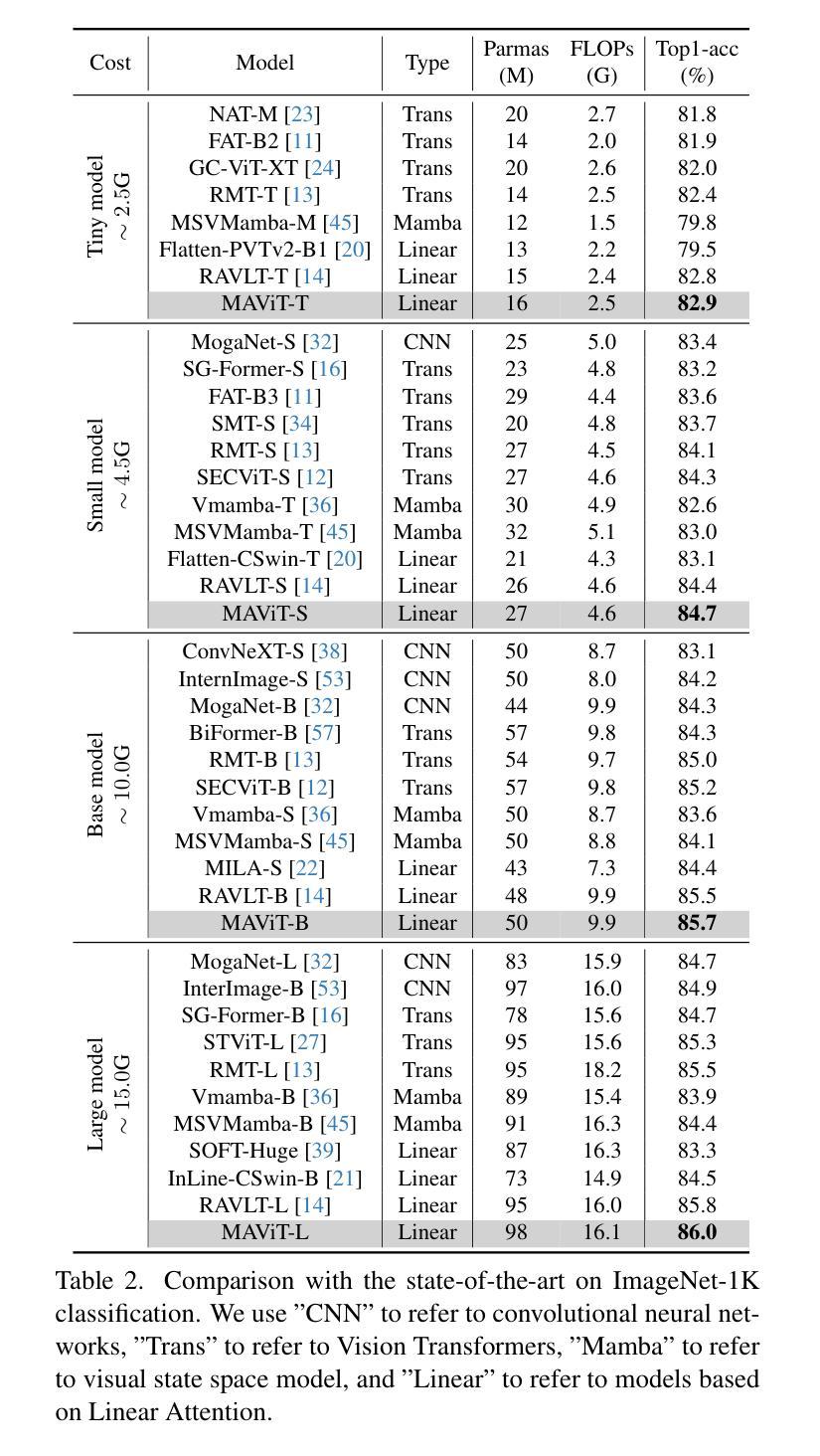
Rectifying Magnitude Neglect in Linear Attention
Authors:Qihang Fan, Huaibo Huang, Yuang Ai, Ran He
As the core operator of Transformers, Softmax Attention exhibits excellent global modeling capabilities. However, its quadratic complexity limits its applicability to vision tasks. In contrast, Linear Attention shares a similar formulation with Softmax Attention while achieving linear complexity, enabling efficient global information modeling. Nevertheless, Linear Attention suffers from a significant performance degradation compared to standard Softmax Attention. In this paper, we analyze the underlying causes of this issue based on the formulation of Linear Attention. We find that, unlike Softmax Attention, Linear Attention entirely disregards the magnitude information of the Query. This prevents the attention score distribution from dynamically adapting as the Query scales. As a result, despite its structural similarity to Softmax Attention, Linear Attention exhibits a significantly different attention score distribution. Based on this observation, we propose Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention (MALA), which modifies the computation of Linear Attention to fully incorporate the Query’s magnitude. This adjustment allows MALA to generate an attention score distribution that closely resembles Softmax Attention while exhibiting a more well-balanced structure. We evaluate the effectiveness of MALA on multiple tasks, including image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, natural language processing, speech recognition, and image generation. Our MALA achieves strong results on all of these tasks. Code will be available at https://github.com/qhfan/MALA
Transformer的核心操作器Softmax Attention展现出出色的全局建模能力。然而,其二次复杂度限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。相比之下,Linear Attention与Softmax Attention具有相似的公式,但实现了线性复杂度,能够高效地全局信息建模。然而,与标准的Softmax Attention相比,Linear Attention的性能严重下降。在本文中,我们基于Linear Attention的公式分析此问题的根本原因。我们发现,与Softmax Attention不同,Linear Attention完全忽略了Query的幅度信息。这阻止了注意力得分分布随着Query的缩放而动态适应。因此,尽管它与Softmax Attention结构相似,但Linear Attention的注意力得分分布却大不相同。基于此观察,我们提出了幅度感知的Linear Attention(MALA),它修改了Linear Attention的计算以充分融入Query的幅度。这一调整使MALA能够生成与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布,同时展现出更为平衡的结构。我们在多个任务上评估了MALA的有效性,包括图像分类、目标检测、实例分割、语义分割、自然语言处理、语音识别和图像生成。我们的MALA在所有任务上都取得了强大的结果。代码将在https://github.com/qhfan/MALA上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025, highlight paper
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer中的核心操作。Softmax Attention具有出色的全局建模能力,但其二次复杂度限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。相比之下,Linear Attention虽然与Softmax Attention具有类似的公式,但具有线性复杂度,能够实现有效的全局信息建模。然而,其性能较差。基于Linear Attention的公式分析,我们发现Linear Attention忽略了Query的幅度信息,导致注意力得分分布无法随Query的变化而动态调整。因此,我们提出了Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention(MALA),它通过修改Linear Attention的计算来全面融入Query的幅度,生成与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布,并在多个任务上取得了良好效果。
Key Takeaways
- Softmax Attention在Transformer中具有优秀的全局建模能力,但二次复杂度限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。
- Linear Attention虽然具有线性复杂度,但与Softmax Attention相比,其性能有所降低。
- Linear Attention忽略了Query的幅度信息,导致注意力得分分布固定,无法随Query的变化而调整。
- MALA通过修改Linear Attention的计算,全面融入Query的幅度信息。
- MALA生成的注意力得分分布与Softmax Attention相似,具有更平衡的结构。
- MALA在多个任务上进行了评估,包括图像分类、对象检测、实例分割、语义分割、自然语言处理、语音识别和图像生成,并取得了良好效果。
点此查看论文截图

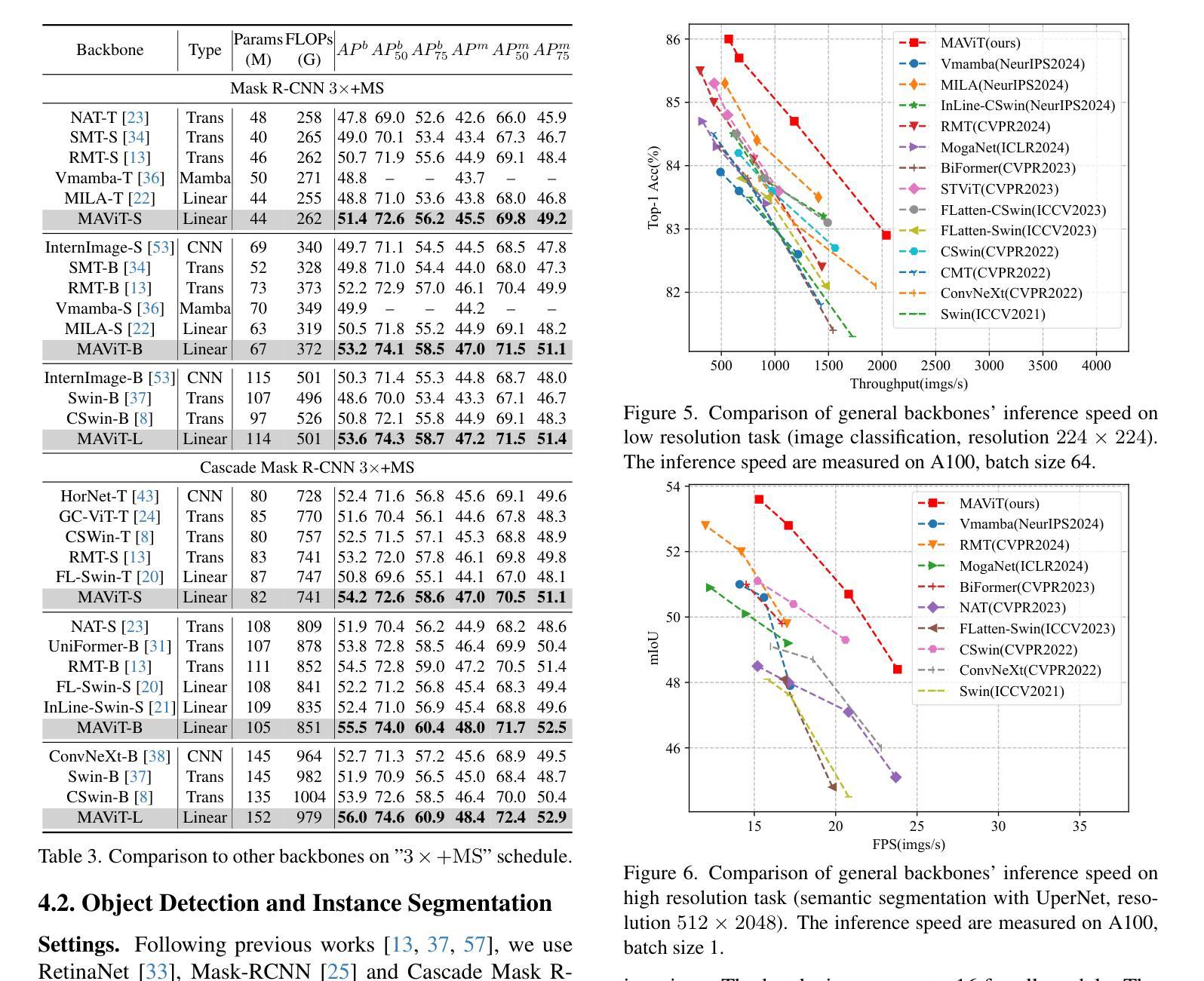
FedMLAC: Mutual Learning Driven Heterogeneous Federated Audio Classification
Authors:Jun Bai, Rajib Rana, Di Wu, Youyang Qu, Xiaohui Tao, Ji Zhang, Carlos Busso, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote
Federated Learning (FL) offers a privacy-preserving framework for training audio classification (AC) models across decentralized clients without sharing raw data. However, Federated Audio Classification (FedAC) faces three major challenges: data heterogeneity, model heterogeneity, and data poisoning, which degrade performance in real-world settings. While existing methods often address these issues separately, a unified and robust solution remains underexplored. We propose FedMLAC, a mutual learning-based FL framework that tackles all three challenges simultaneously. Each client maintains a personalized local AC model and a lightweight, globally shared Plug-in model. These models interact via bidirectional knowledge distillation, enabling global knowledge sharing while adapting to local data distributions, thus addressing both data and model heterogeneity. To counter data poisoning, we introduce a Layer-wise Pruning Aggregation (LPA) strategy that filters anomalous Plug-in updates based on parameter deviations during aggregation. Extensive experiments on four diverse audio classification benchmarks, including both speech and non-speech tasks, show that FedMLAC consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in classification accuracy and robustness to noisy data.
联邦学习(FL)为在分散的客户端上训练音频分类(AC)模型提供了一种保护隐私的框架,无需共享原始数据。然而,联邦音频分类(FedAC)面临三大挑战:数据异质性、模型异质性,以及数据毒化,它们在现实世界的设置中会降低性能。虽然现有方法通常分别解决这些问题,但统一且稳健的解决方案仍然缺乏探索。我们提出FedMLAC,一个基于相互学习的联邦学习框架,可以同时应对所有三个挑战。每个客户端维护一个个性化的本地AC模型和一个轻量级的、全局共享的插件模型。这些模型通过双向知识蒸馏进行交互,能够实现全局知识共享,同时适应本地数据分布,从而解决数据和模型异质性问题。为了应对数据毒化,我们引入了一种分层剪枝聚合(LPA)策略,该策略根据聚合过程中的参数偏差来过滤异常的插件更新。在包括语音和非语音任务在内的四个不同的音频分类基准测试上的大量实验表明,FedMLAC在分类准确性和对噪声数据的稳健性方面均优于最新基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF updated version for the first submission
Summary
联邦学习(FL)为音频分类(AC)模型在分散式客户端上的训练提供了一个隐私保护框架,无需共享原始数据。然而,联邦音频分类(FedAC)面临数据异质性、模型异质性和数据中毒三大挑战,这些挑战在现实世界环境中会降低性能。针对这些问题,我们提出FedMLAC,一个基于互助学习的联邦学习框架,同时解决这三个挑战。每个客户端维护个性化的本地AC模型和轻量级的全局共享插件模型。这些模型通过双向知识蒸馏进行交互,实现全局知识共享,同时适应本地数据分布,从而解决数据和模型异质性。为了应对数据中毒,我们引入了一种分层剪枝聚合(LPA)策略,根据聚合过程中的参数偏差来过滤异常的插件更新。在四个不同的音频分类基准测试上的广泛实验表明,FedMLAC在分类准确性和对噪声数据的鲁棒性方面均优于最新基线。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)为音频分类模型的训练提供了隐私保护框架。
- 联邦音频分类(FedAC)面临数据异质性、模型异质性和数据中毒三大挑战。
- FedMLAC是一个基于互助学习的联邦学习框架,能够同时解决上述三大挑战。
- FedMLAC通过双向知识蒸馏解决数据分布和模型异质性问题。
- FedMLAC引入分层剪枝聚合(LPA)策略来应对数据中毒问题。
- FedMLAC在分类准确性以及对噪声数据的鲁棒性方面优于最新基线。
点此查看论文截图

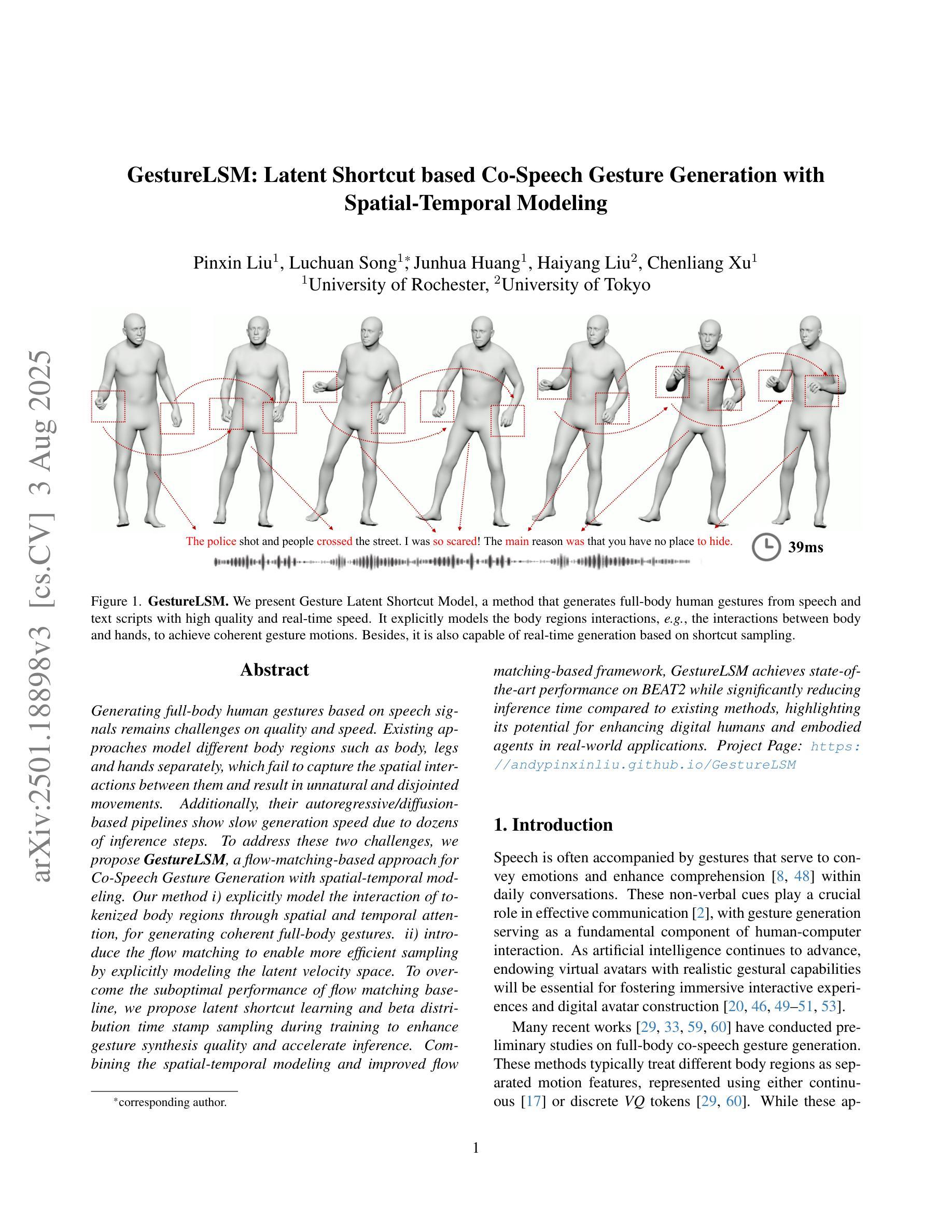
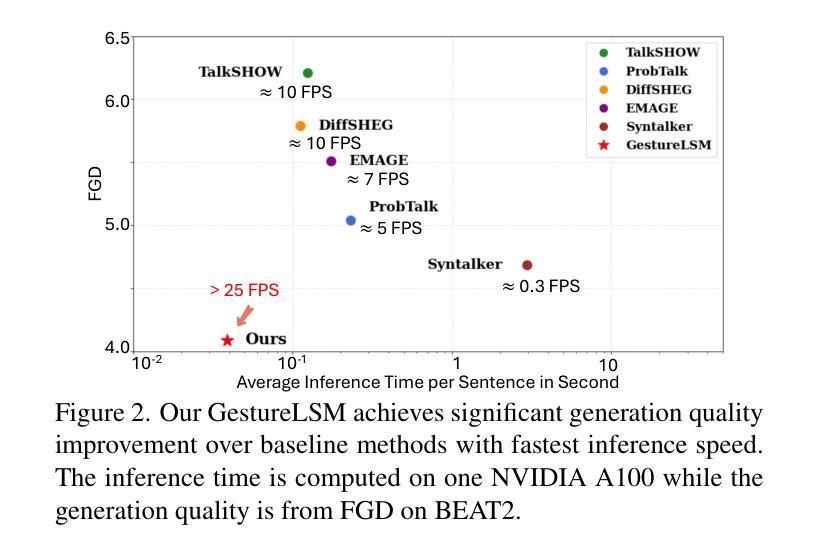
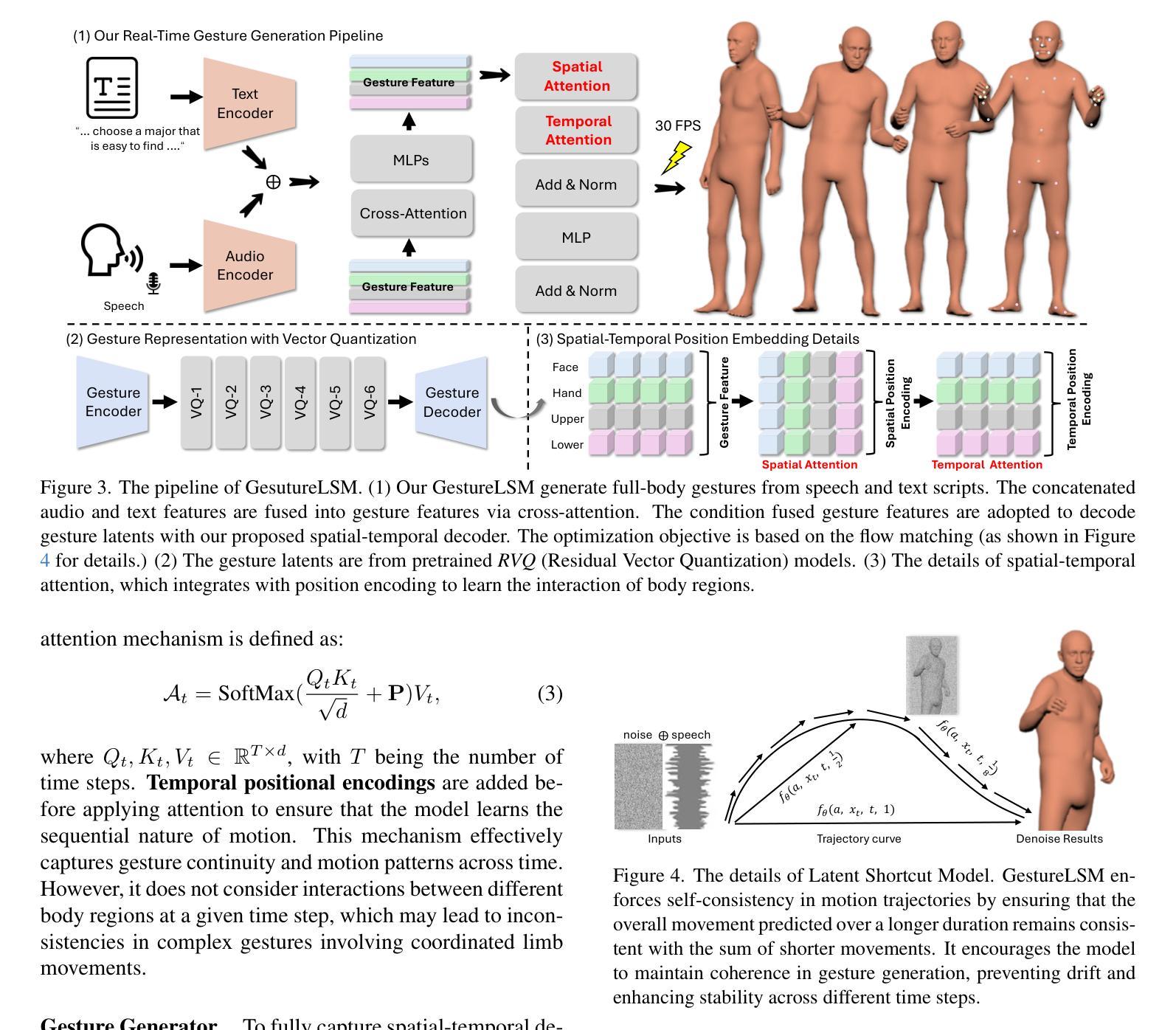
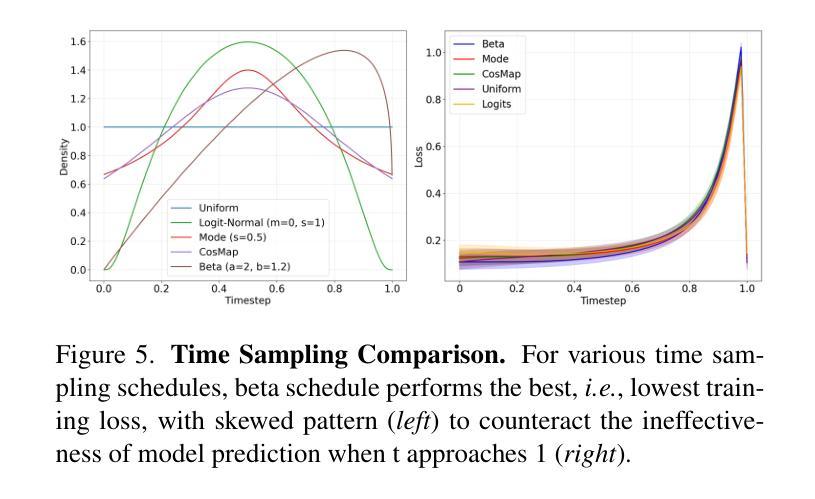
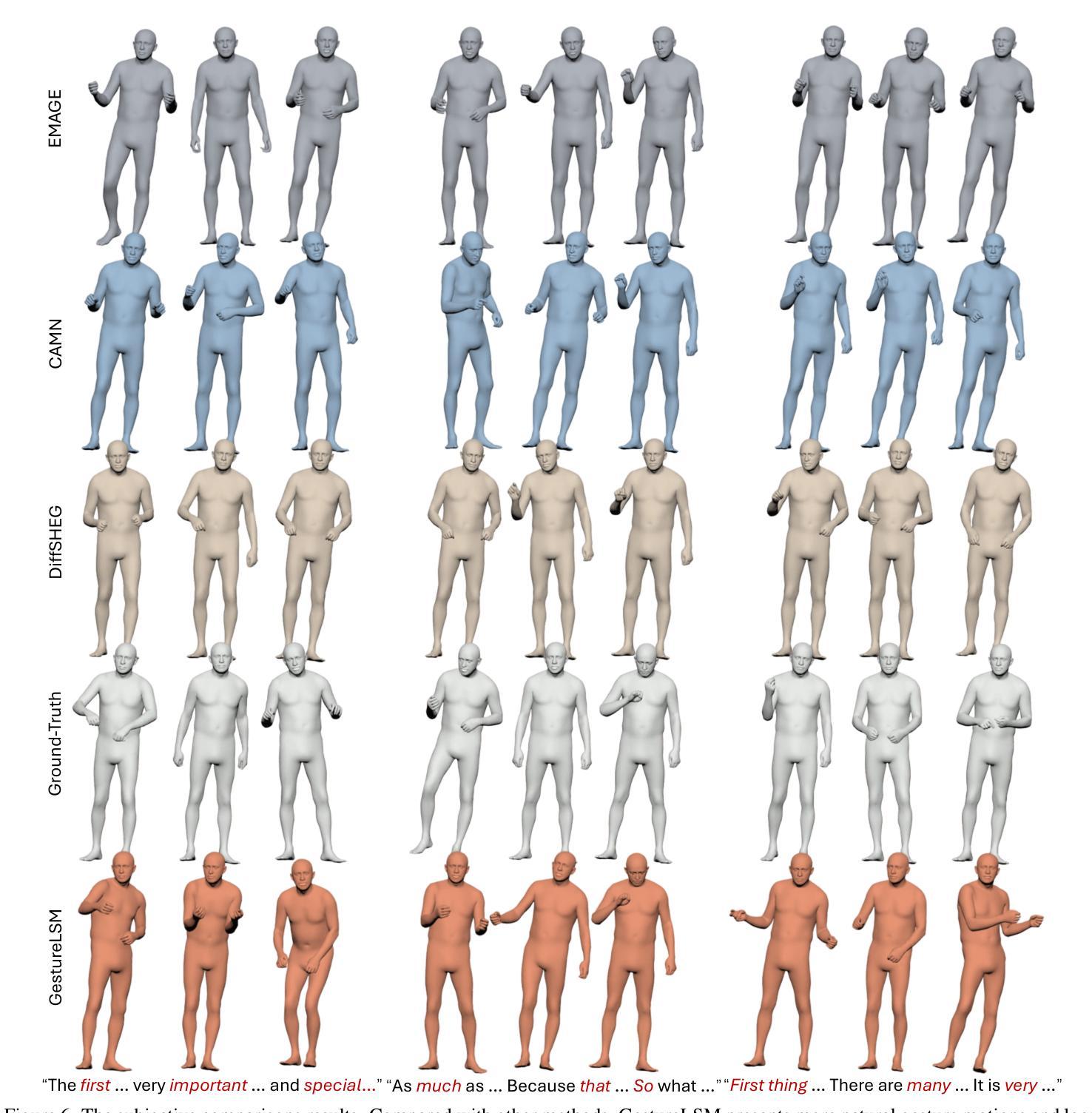
GestureLSM: Latent Shortcut based Co-Speech Gesture Generation with Spatial-Temporal Modeling
Authors:Pinxin Liu, Luchuan Song, Junhua Huang, Haiyang Liu, Chenliang Xu
Generating full-body human gestures based on speech signals remains challenges on quality and speed. Existing approaches model different body regions such as body, legs and hands separately, which fail to capture the spatial interactions between them and result in unnatural and disjointed movements. Additionally, their autoregressive/diffusion-based pipelines show slow generation speed due to dozens of inference steps. To address these two challenges, we propose GestureLSM, a flow-matching-based approach for Co-Speech Gesture Generation with spatial-temporal modeling. Our method i) explicitly model the interaction of tokenized body regions through spatial and temporal attention, for generating coherent full-body gestures. ii) introduce the flow matching to enable more efficient sampling by explicitly modeling the latent velocity space. To overcome the suboptimal performance of flow matching baseline, we propose latent shortcut learning and beta distribution time stamp sampling during training to enhance gesture synthesis quality and accelerate inference. Combining the spatial-temporal modeling and improved flow matching-based framework, GestureLSM achieves state-of-the-art performance on BEAT2 while significantly reducing inference time compared to existing methods, highlighting its potential for enhancing digital humans and embodied agents in real-world applications. Project Page: https://andypinxinliu.github.io/GestureLSM
基于语音信号生成全身人体姿态在质量和速度方面仍然存在挑战。现有方法将身体的不同部位(如身体、腿和手)分别建模,无法捕捉它们之间的空间交互,导致动作不自然、不连贯。此外,它们的自回归/扩散基管道由于需要数十步推理而显示出缓慢的生成速度。为了解决这两个挑战,我们提出了基于流匹配的协同语音姿态生成方法GestureLSM,并进行了时空建模。我们的方法一)通过空间和时间注意力显式地模拟标记身体部位的交互,以生成连贯的全身姿态。二)引入流匹配,通过显式建模潜在速度空间,使采样更加高效。为了克服流匹配基线性能不佳的问题,我们在训练过程中提出了潜在快捷方式学习和beta分布时间戳采样,以提高姿态合成质量和加速推理。结合时空建模和改进的基于流匹配的框架,GestureLSM在BEAT2上实现了最先进的性能,同时与现有方法相比显著减少了推理时间,凸显其在增强数字人类和实体代理在现实世界应用中的潜力。项目页面:https://andypinxinliu.github.io/GestureLSM
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://andypinxinliu.github.io/GestureLSM
Summary
基于语音信号生成全身人类动作在质量和速度上仍面临挑战。现有方法分别建模身体、腿和手部等不同的身体区域,忽略了它们之间的空间交互,导致动作不自然、不连贯。此外,它们的自回归/扩散生成流程由于需要大量的推理步骤,生成速度较慢。针对这两个问题,我们提出GestureLSM,这是一种基于流匹配的协同语音动作生成方法,具有时空建模功能。我们的方法一)通过空间和时间注意力显式地模拟了标记身体区域的交互,以生成连贯的全身动作。二)引入流匹配,通过显式建模潜在速度空间,使采样更加高效。为了克服流匹配基线方法的性能不佳问题,我们在训练过程中提出了潜在捷径学习和基于beta分布的时间戳采样,以提高动作合成质量和加速推理。结合了时空建模和改进的基于流匹配框架的GestureLSM,在BEAT2上达到了最先进的性能,同时显著减少了推理时间,突显其在增强数字人类和实体代理实际应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 现有方法模拟不同身体区域导致动作不自然和联合性不足。
- 现有方法的自回归/扩散生成流程导致生成速度较慢。
- GestureLSM方法通过空间和时间注意力显式建模身体区域的交互。
- GestureLSM引入流匹配以显式建模潜在速度空间并提高采样效率。
- 通过潜在捷径学习和beta分布时间戳采样改进流匹配以提高动作合成质量和加速推理。
- GestureLSM在BEAT2上达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图