⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
Inference-time Scaling for Diffusion-based Audio Super-resolution
Authors:Yizhu Jin, Zhen Ye, Zeyue Tian, Haohe Liu, Qiuqiang Kong, Yike Guo, Wei Xue
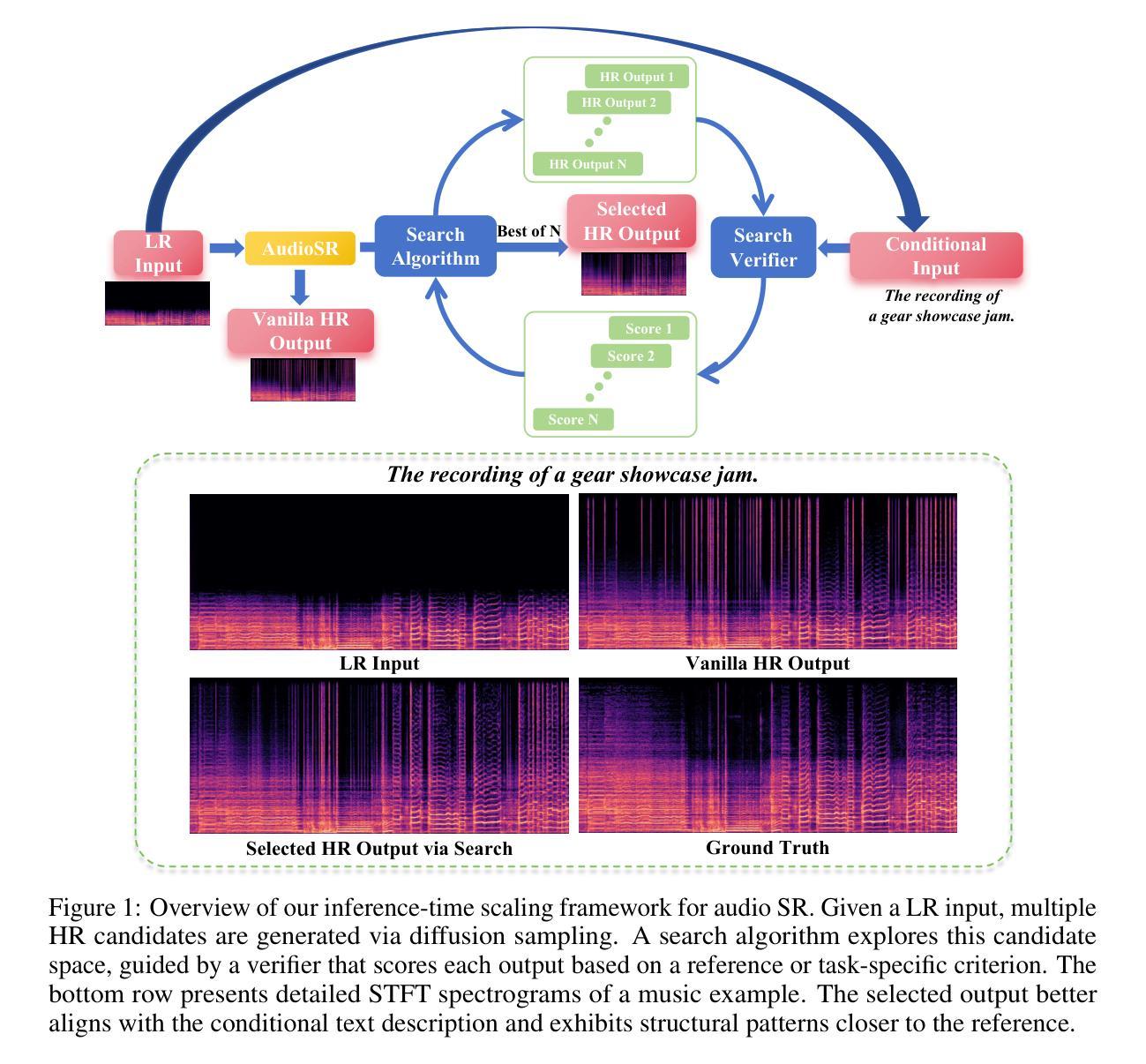
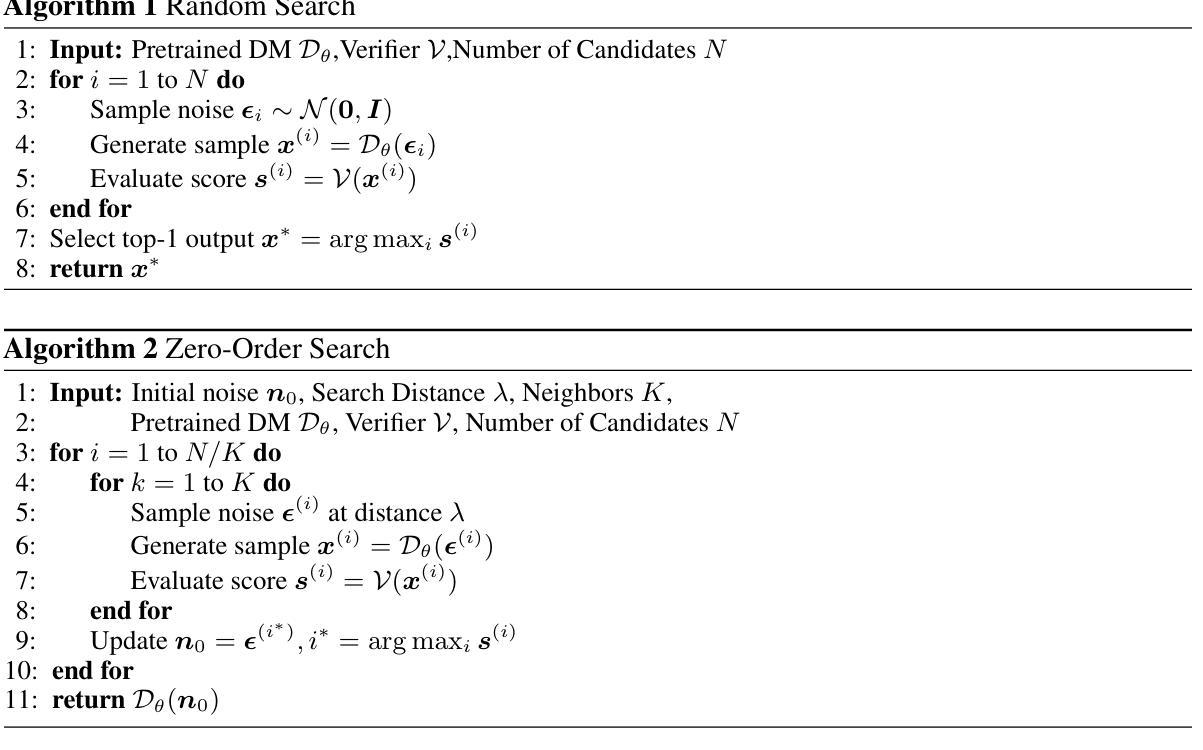
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in generative tasks, including audio super-resolution (SR). In many applications like movie post-production and album mastering, substantial computational budgets are available for achieving superior audio quality. However, while existing diffusion approaches typically increase sampling steps to improve quality, the performance remains fundamentally limited by the stochastic nature of the sampling process, leading to high-variance and quality-limited outputs. Here, rather than simply increasing the number of sampling steps, we propose a different paradigm through inference-time scaling for SR, which explores multiple solution trajectories during the sampling process. Different task-specific verifiers are developed, and two search algorithms, including the random search and zero-order search for SR, are introduced. By actively guiding the exploration of the high-dimensional solution space through verifier-algorithm combinations, we enable more robust and higher-quality outputs. Through extensive validation across diverse audio domains (speech, music, sound effects) and frequency ranges, we demonstrate consistent performance gains, achieving improvements of up to 9.70% in aesthetics, 5.88% in speaker similarity, 15.20% in word error rate, and 46.98% in spectral distance for speech SR from 4kHz to 24kHz, showcasing the effectiveness of our approach. Audio samples are available at: https://racerk.github.io/tt-scale-audiosr/.
扩散模型在生成任务中取得了显著的成功,包括音频超分辨率(SR)。在许多应用程序中,如电影后期制作和专辑制作,我们拥有大量的计算预算来实现卓越的音频质量。然而,尽管现有的扩散方法通常通过增加采样步骤来提高质量,但性能仍然受到采样过程随机性的根本限制,导致高方差和质量有限的输出。在这里,我们提出了一种不同的范式,即通过对SR进行推理时间缩放,而不是简单地增加采样步骤。在采样过程中探索多个解决方案轨迹。开发了不同的任务特定验证器,并介绍了两种搜索算法,包括用于SR的随机搜索和零阶搜索。通过验证器算法组合主动引导高维解空间的探索,我们能够实现更稳健和更高质量的输出。通过对各种音频领域(语音、音乐、音效)和频率范围的广泛验证,我们证明了性能的一致提升,在美学上提升了高达9.70%,演讲者相似性提升5.88%,词错误率降低15.20%,语音SR的频谱距离在4kHz至24kHz范围内提升46.98%,展示了我们的方法的有效性。音频样本可在:https://racerk.github.io/tt-scale-audiosr/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在生成任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括音频超分辨率(SR)。尽管现有扩散方法通过增加采样步骤来提高质量,但采样过程的随机性根本限制了性能,导致高方差和质量受限的输出。本研究提出了一种新的范式——基于推理时间的缩放进行SR,该范式在采样过程中探索多个解决方案轨迹。开发了不同的任务特定验证器,并引入了两种搜索算法,包括随机搜索和零阶搜索用于SR。通过验证器算法组合,主动引导高维解空间的探索,实现更稳健和更高质量的输出。在多种音频领域和频率范围进行了广泛验证,证明我们的方法有效,实现了美学上的提升达9.7%,说话人相似性提升5.88%,单词错误率降低15.2%,语音SR从4kHz到24kHz的频谱距离提升达46.98%。相关音频样本可在链接中找到:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成任务包括音频超分辨率上表现出显著成功。
- 现有扩散方法通过增加采样步骤来提高质量,但存在根本性限制。
- 提出新的基于推理时间的缩放范式进行SR,探索采样过程中的多个解决方案轨迹。
- 开发了任务特定验证器和两种搜索算法用于SR。
- 通过验证器算法组合主动引导高维解空间探索,提升输出质量和稳健性。
- 在多个音频领域和频率范围进行广泛验证,证明方法有效。
点此查看论文截图

AgentTTS: Large Language Model Agent for Test-time Compute-optimal Scaling Strategy in Complex Tasks
Authors:Fali Wang, Hui Liu, Zhenwei Dai, Jingying Zeng, Zhiwei Zhang, Zongyu Wu, Chen Luo, Zhen Li, Xianfeng Tang, Qi He, Suhang Wang
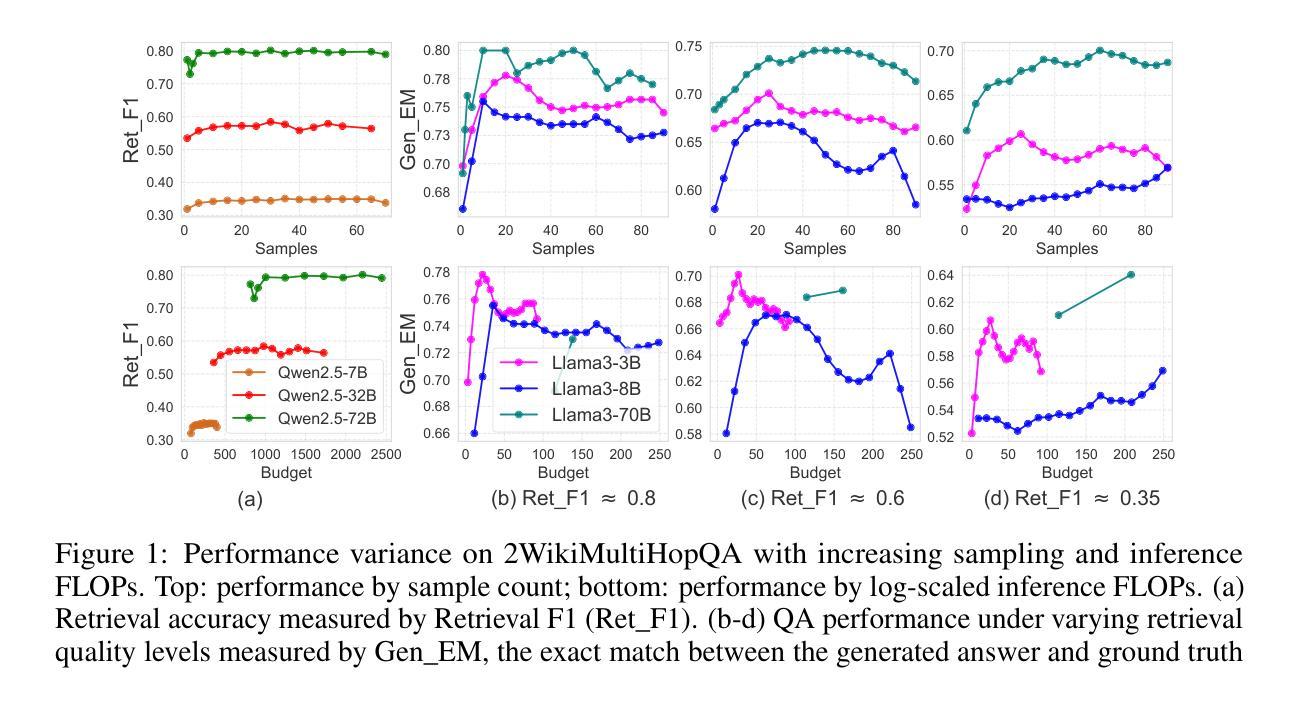
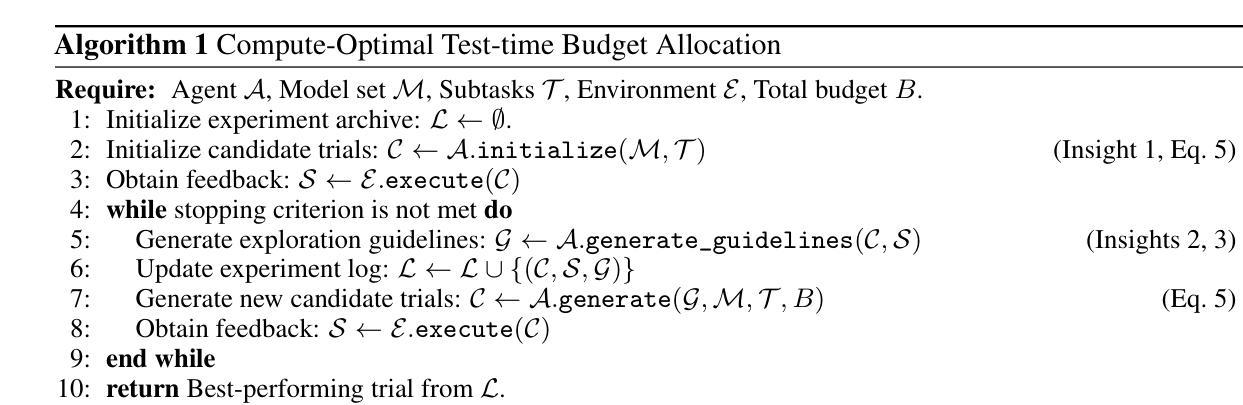
Test-time scaling (TTS) enhances the performance of large language models (LLMs) by allocating additional compute resources during inference. However, existing research primarily investigates TTS in single-stage tasks; while many real-world problems are multi-stage complex tasks, composed of a sequence of heterogeneous subtasks with each subtask requires LLM of specific capability. Therefore, we study a novel problem: the test-time compute-optimal scaling in multi-stage complex tasks, aiming to select suitable models and allocate budgets per subtask to maximize overall performance. TTS in multi-stage tasks introduces two fundamental challenges: (i) The combinatorial search space of model and budget allocations, combined with the high cost of inference, makes brute-force search impractical. (ii) The optimal model and budget allocations across subtasks are interdependent, increasing the complexity of the compute-optimal search. To address this gap, we conduct extensive pilot experiments on four tasks across six datasets, deriving three empirical insights characterizing the behavior of LLMs in multi-stage complex tasks. Informed by these insights, we propose AgentTTS, an LLM-agent-based framework that autonomously searches for compute-optimal allocations through iterative feedback-driven interactions with the execution environment. Experimental results demonstrate that AgentTTS significantly outperforms traditional and other LLM-based baselines in search efficiency, and shows improved robustness to varying training set sizes and enhanced interpretability.
测试时缩放(TTS)通过推理过程中的额外计算资源分配,提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。然而,现有研究主要调查单一阶段的TTS任务,而许多现实世界的问题是多阶段复杂任务,由一系列具有特定能力的异构子任务组成。因此,我们研究了一个新问题:在多阶段复杂任务中实现测试时计算最优缩放,旨在选择适当的模型并为每个子任务分配预算,以最大限度地提高整体性能。多阶段任务中的TTS带来了两个基本挑战:(i)模型和预算分配的组合搜索空间,结合推理的高成本,使得暴力搜索不切实际。(ii)各子任务之间的最佳模型和预算分配是相互依赖的,增加了计算最优搜索的复杂性。为了弥补这一空白,我们在四个任务、六个数据集上进行了广泛的试点实验,得出了三个描述LLM在多阶段复杂任务中行为的经验见解。根据这些见解,我们提出了AgentTTS,这是一个基于LLM代理的框架,它通过与执行环境的迭代反馈驱动交互,自主寻找计算最优分配。实验结果表明,AgentTTS在搜索效率方面显著优于传统和其他LLM基线,在提高对不同训练集大小的鲁棒性方面表现出更好的性能,并增强了可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文探讨了测试时缩放(TTS)在多阶段复杂任务中的应用,通过为不同子任务分配适当的模型和预算来优化计算资源,从而提高大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。针对多阶段任务中的TTS面临的挑战,提出了AgentTTS框架,通过与环境进行反馈驱动的交互,实现计算最优分配。实验结果表明,AgentTTS在搜索效率、对训练集大小变化的稳健性以及可解释性方面均优于传统和其他LLM基线。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放(TTS)技术用于提高大型语言模型(LLM)在多阶段复杂任务中的性能。
- 多阶段任务中的TTS面临模型与预算分配的组合搜索空间挑战以及跨子任务的优化分配互依赖性问题。
- 通过实验获得三个实证见解,描述了LLM在多阶段复杂任务中的行为特征。
- 提出了AgentTTS框架,这是一个基于LLM代理的框架,通过与环境进行反馈驱动的交互,实现计算最优分配。
- AgentTTS显著提高了搜索效率,并对训练集大小的变化表现出更强的稳健性。
- AgentTTS还增强了可解释性。
点此查看论文截图