⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-06 更新
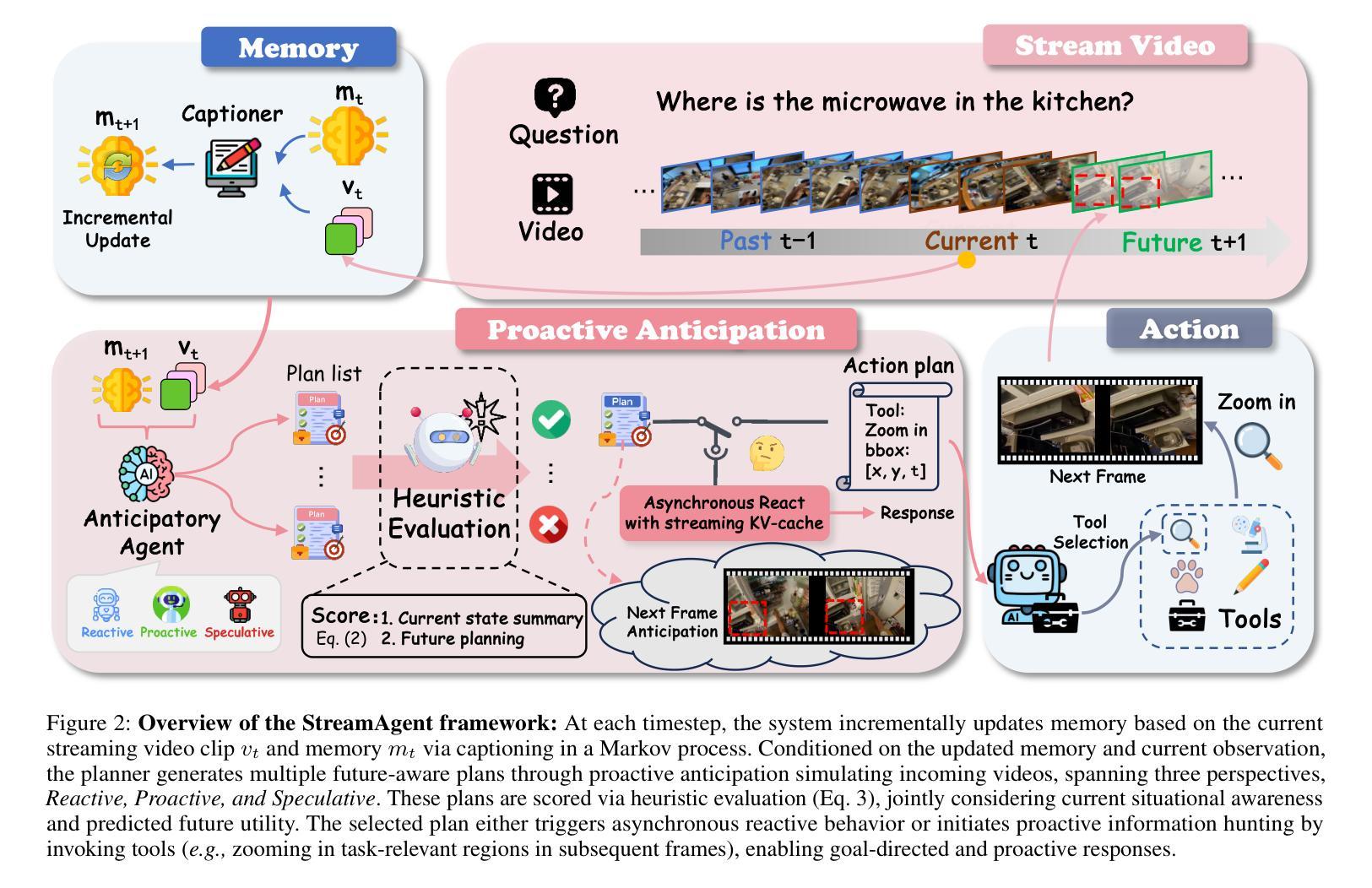
Glioblastoma Overall Survival Prediction With Vision Transformers
Authors:Yin Lin, iccardo Barbieri, Domenico Aquino, Giuseppe Lauria, Marina Grisoli, Elena De Momi, Alberto Redaelli, Simona Ferrante
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive and common brain tumors, with a median survival of 10-15 months. Predicting Overall Survival (OS) is critical for personalizing treatment strategies and aligning clinical decisions with patient outcomes. In this study, we propose a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) approach for OS prediction using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images, exploiting Vision Transformers (ViTs) to extract hidden features directly from MRI images, eliminating the need of tumor segmentation. Unlike traditional approaches, our method simplifies the workflow and reduces computational resource requirements. The proposed model was evaluated on the BRATS dataset, reaching an accuracy of 62.5% on the test set, comparable to the top-performing methods. Additionally, it demonstrated balanced performance across precision, recall, and F1 score, overcoming the best model in these metrics. The dataset size limits the generalization of the ViT which typically requires larger datasets compared to convolutional neural networks. This limitation in generalization is observed across all the cited studies. This work highlights the applicability of ViTs for downsampled medical imaging tasks and establishes a foundation for OS prediction models that are computationally efficient and do not rely on segmentation.
胶质母细胞瘤是最具侵袭性和最常见的脑肿瘤之一,中位生存期为10-15个月。预测总体生存期(OS)对于个性化治疗方案和使临床决策与病人结果相一致至关重要。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种利用磁共振成像(MRI)图像进行总体生存期预测的新型人工智能(AI)方法,利用视觉转换器(ViTs)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需进行肿瘤分割。与传统的做法不同,我们的方法简化了工作流程,降低了计算资源要求。所提出模型在BRATS数据集上进行了评估,在测试集上达到了62.5%的准确率,与表现最好的方法相当。此外,它在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面表现出平衡的性能,在这些指标上超越了最佳模型。数据集的大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,与卷积神经网络相比,ViT通常需要更大的数据集。所有引用的研究都观察到了这种泛化限制。这项工作强调了ViTs在下采样医学成像任务中的适用性,并为计算效率高且不需要依赖分割的总体生存期预测模型奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures, EMBC2025
Summary
该研究利用人工智能和磁共振成像(MRI)图像提出一种新的预测生存期方法,利用Vision Transformer直接提取图像隐藏特征,无需肿瘤分割。此方法简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源需求,在BRATS数据集上达到了测试集准确率62.5%,且在精确度、召回率和F1得分方面表现均衡。但数据集大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,这需要更大的数据集来支持。此研究展示了ViT在医学成像任务中的适用性,并为计算效率高且无需依赖分割的生存预测模型奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 利用Vision Transformer (ViT) 直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征进行生存期预测。
- 无需肿瘤分割,简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源需求。
- 在BRATS数据集上进行了评估,达到了较高的准确率(62.5%),并与顶级方法具有竞争力。
- 模型在精确度、召回率和F1得分方面表现均衡。
- 数据集大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,需要更大的数据集来提升性能。
- 研究展示了ViT在医学成像任务中的适用性。
点此查看论文截图

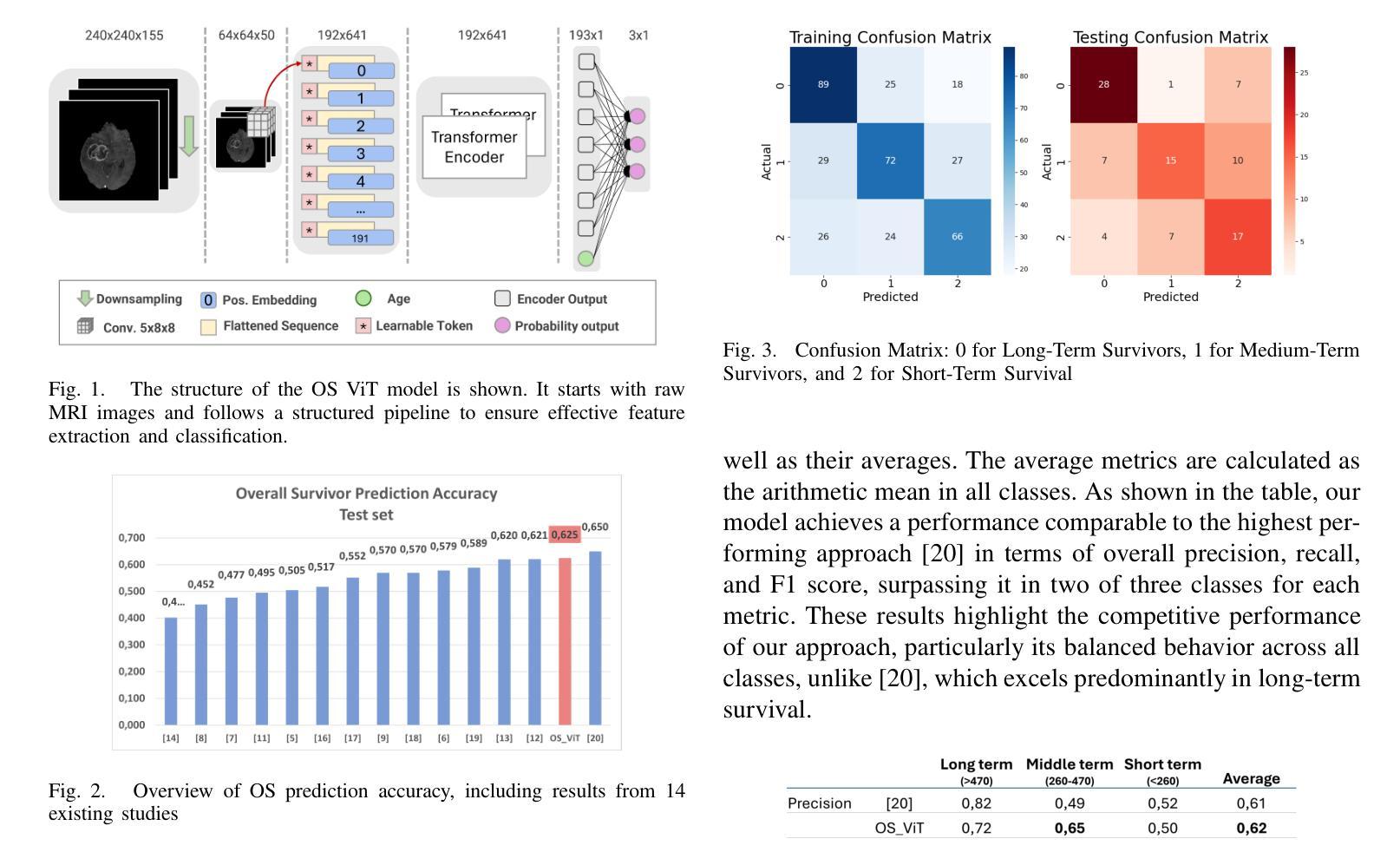
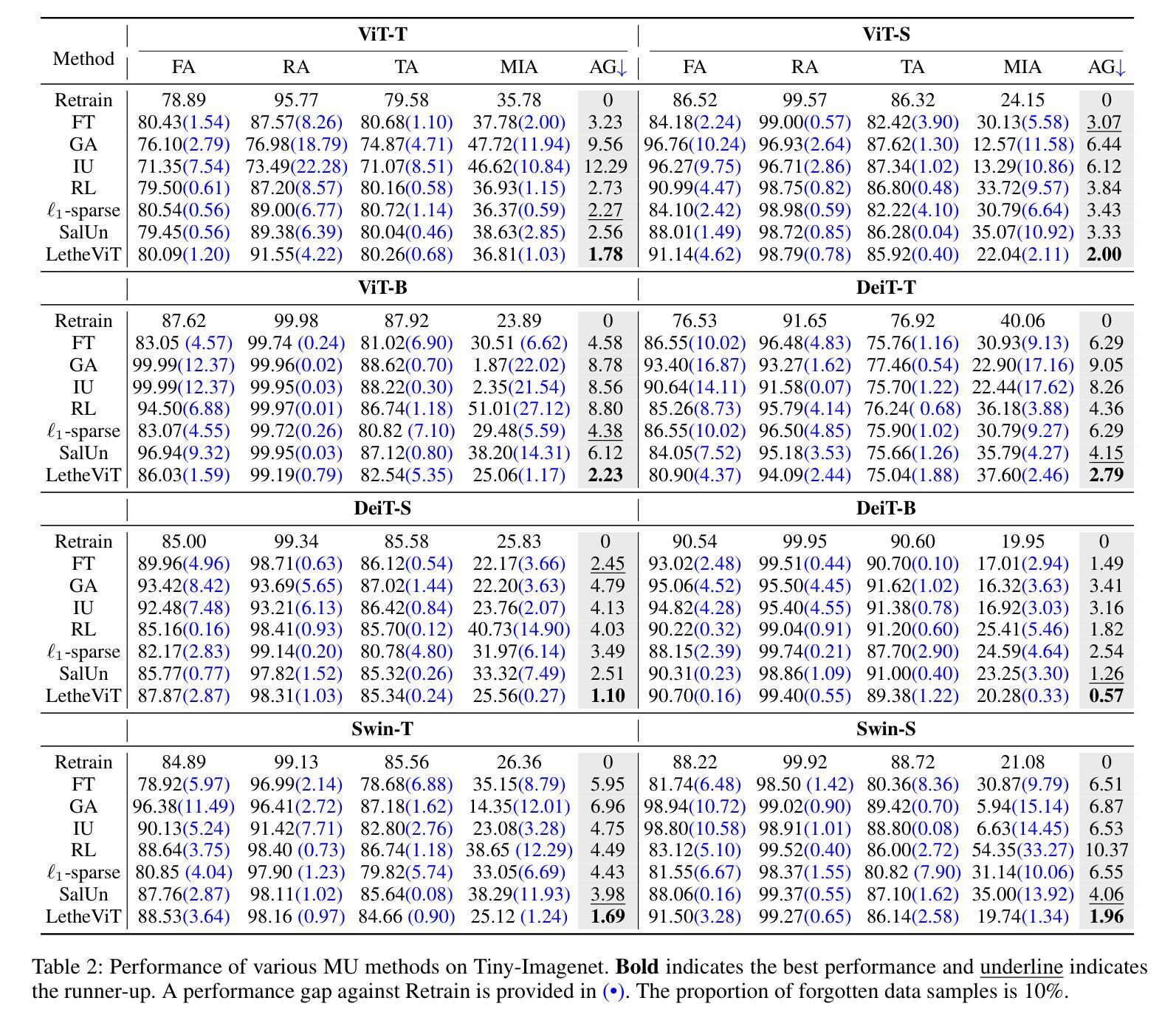
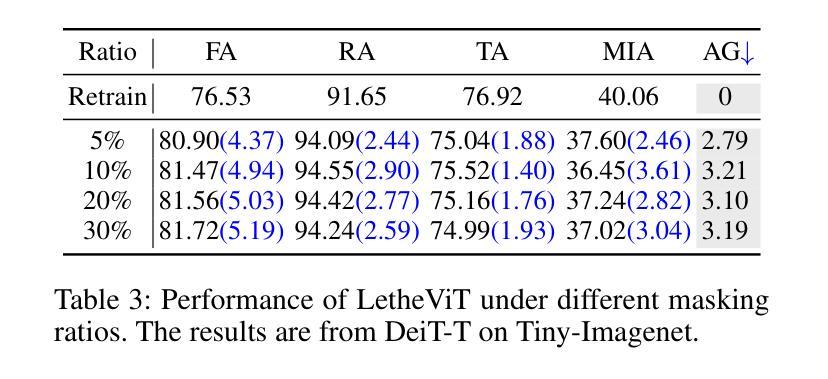
LetheViT: Selective Machine Unlearning for Vision Transformers via Attention-Guided Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yujia Tong, Tian Zhang, Jingling Yuan, Yuze Wang, Chuang Hu
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have revolutionized computer vision tasks with their exceptional performance. However, the introduction of privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA has brought new challenges to them. These laws grant users the right to withdraw their data, necessitating not only the deletion of data but also the complete removal of its influence from trained models. Machine unlearning emerges as a critical solution, with exact unlearning being computationally prohibitive and approximate methods offering a more practical approach. This work addresses the particularly challenging scenario of random data forgetting in ViTs, where the model must forget specific samples while retaining others, even within the same class. We first reveal the core characteristics of ViTs through selective masking experiments: when high-attention areas are masked, the model retains its recognition capability but significantly weakens its memorization ability. Based on the above insights, we propose LetheViT, a contrastive unlearning method tailored for ViTs. LetheViT uses masked image inputs to generate positive logits and original image inputs to generate negative logits, guiding the model to forget specific details while retaining the general cl category outlines. Experimental results demonstrate that LetheViT achieves state-of-the-art performance, effectively balancing privacy compliance with model efficacy.
视觉Transformer(ViT)以其卓越性能彻底改变了计算机视觉任务。然而,GDPR和CCPA等隐私法规的出台给它们带来了新的挑战。这些法律赋予用户收回其数据的权利,这不仅要求删除数据,还要求从已训练的模型中完全消除其影响。机器遗忘作为一种关键的解决方案而出现,精确遗忘在计算上是禁止的,而近似方法提供了更实用的方法。本文解决了ViT中随机数据遗忘这一特别具有挑战性的场景,其中模型必须遗忘特定样本而保留其他样本,即使在同一类中也是如此。我们首先通过选择性掩码实验揭示了ViT的核心特征:当高注意力区域被掩码时,模型的识别能力得以保留,但记忆能力会显著减弱。基于上述见解,我们提出了针对ViT的对比遗忘方法LetheViT。LetheViT使用掩码图像输入生成正向逻辑值,使用原始图像输入生成负向逻辑值,引导模型遗忘特定细节,同时保留一般类别轮廓。实验结果表明,LetheViT达到了最先进的性能,有效地平衡了隐私合规与模型效率之间的关系。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉转换器(ViTs)在计算机视觉任务中具有出色的性能,但隐私法规的引入带来了新的挑战。用户有权撤回数据,要求不仅删除数据,还要从已训练的模型中完全消除其影响。机器遗忘作为一种关键解决方案出现,精确遗忘计算量大,近似方法更实用。本研究解决了ViTs中随机数据遗忘这一特别具有挑战性的场景,模型必须忘记特定样本而保留其他样本,即使在同一类别内也是如此。通过选择性掩蔽实验,我们揭示了ViTs的核心特征:当高注意力区域被掩蔽时,模型的识别能力得以保留,但记忆能力显著减弱。基于此,我们提出了针对ViTs的对比遗忘方法LetheViT。LetheViT使用掩蔽图像输入生成正对数,原始图像输入生成负对数,引导模型忘记特定细节,同时保留一般类别轮廓。实验结果表明,LetheViT实现了最先进的性能,有效平衡了隐私合规性和模型有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉转换器(ViTs)在计算机视觉任务中具有卓越性能。
- 隐私法规如GDPR和CCPA为数据撤回设置了用户权利,对ViTs提出新挑战。
- 机器遗忘是应对这些挑战的关键解决方案。
- 通过选择性掩蔽实验揭示了ViTs的核心特征:高注意力区域的掩蔽会导致模型识别能力保留但记忆能力减弱。
- 提出了针对ViTs的对比遗忘方法LetheViT。
- LetheViT利用正负对数引导模型忘记特定细节,同时保留类别轮廓。
点此查看论文截图

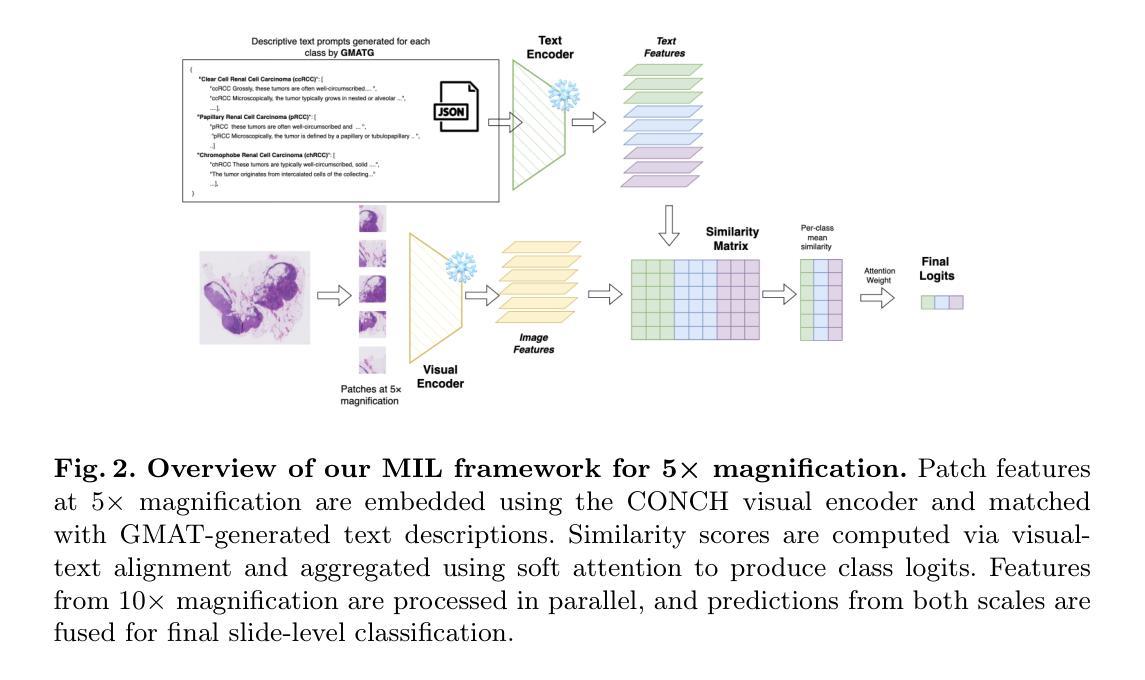
GMAT: Grounded Multi-Agent Clinical Description Generation for Text Encoder in Vision-Language MIL for Whole Slide Image Classification
Authors:Ngoc Bui Lam Quang, Nam Le Nguyen Binh, Thanh-Huy Nguyen, Le Thien Phuc Nguyen, Quan Nguyen, Ulas Bagci
Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) is the leading approach for whole slide image (WSI) classification, enabling efficient analysis of gigapixel pathology slides. Recent work has introduced vision-language models (VLMs) into MIL pipelines to incorporate medical knowledge through text-based class descriptions rather than simple class names. However, when these methods rely on large language models (LLMs) to generate clinical descriptions or use fixed-length prompts to represent complex pathology concepts, the limited token capacity of VLMs often constrains the expressiveness and richness of the encoded class information. Additionally, descriptions generated solely by LLMs may lack domain grounding and fine-grained medical specificity, leading to suboptimal alignment with visual features. To address these challenges, we propose a vision-language MIL framework with two key contributions: (1) A grounded multi-agent description generation system that leverages curated pathology textbooks and agent specialization (e.g., morphology, spatial context) to produce accurate and diverse clinical descriptions; (2) A text encoding strategy using a list of descriptions rather than a single prompt, capturing fine-grained and complementary clinical signals for better alignment with visual features. Integrated into a VLM-MIL pipeline, our approach shows improved performance over single-prompt class baselines and achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art models, as demonstrated on renal and lung cancer datasets.
多实例学习(MIL)是全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的领先方法,能够高效分析吉像素病理切片。最近的研究将视觉语言模型(VLM)引入到MIL管道中,通过基于文本的类描述而不是简单的类名来融入医学知识。然而,当这些方法依赖于大型语言模型(LLM)来生成临床描述或使用固定长度的提示来表示复杂的病理学概念时,VLM的有限令牌容量通常限制了编码类信息的表达性和丰富性。此外,仅由LLM生成的临床描述可能缺乏领域基础和专业医学细节,导致与视觉特征的对齐效果不佳。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个视觉语言MIL框架,其中包含两个关键贡献:(1)基于病理学教科书构建的多代理描述生成系统,利用专业代理(如形态学、空间上下文)来生成准确和多样的临床描述;(2)使用一系列描述而不是单个提示的文本编码策略,捕获精细且具有补充性的临床信号,以更好地与视觉特征对齐。在我们的视觉语言MIL管道中,与单提示类基线相比,我们的方法显示出更高的性能,并且在肾脏和肺癌数据集上取得了与最新模型相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在整張鏡片影像(WSI)分類方面,多重實例學習(MIL)是主流方法。最近的研究將視覺語言模型(VLM)引入MIL流程,以通過基於文本的類別描述融入醫學知識,而非僅僅使用類別名稱。然而,當這些方法依賴大型語言模型(LLM)來生成複雜病理學概念時,受限於其標記能力與表示方法,它們往往無法充分表現與類別信息相匹配的細微差別。此外,僅由LLM生成的描述可能缺乏特定於特定领域的精緻性,導致與視覺特徵對準不佳。為解決這些問題,我們提出了一個具有兩個關鍵貢獻的視覺語言MIL框架:一是基于病理解剖學教材和多個專門代理的複雜描述生成系統;二是使用一系列描述而非單一提示的文本編碼策略,以捕捉細微的診斷訊息,以改善與視覺特徵的對準。實驗證明,此新方法在單個提示類別基準的基礎上提升了性能,並在肺腫瘤和腎腫瘤數據集上取得了先進成果。
Key Takeaways
- 多重實例學習(MIL)在整張鏡片影像(WSI)分類中佔有重要地位。
- 視覺語言模型(VLM)被引入MIL流程以融入醫學知識,通過基於文本的類別描述而非僅僅使用類別名稱。
- 大型語言模型(LLM)在生成複雜病理概念時存在局限,不能充分捕捉細微差別和特定領域的精緻性。
- 提出了一個新的視覺語言MIL框架,包括基於病理解剖學教材和多個專門代理的描述生成系統以及使用一系列描述來改善與視覺特徵對準的文本編碼策略。
- 新方法提升性能於單個提示類別基準之上並在特定數據集上取得顯著成果。
- 此方法能夠提高診斷準確性和效率,有望改善病理學家的日常工作流程。
点此查看论文截图

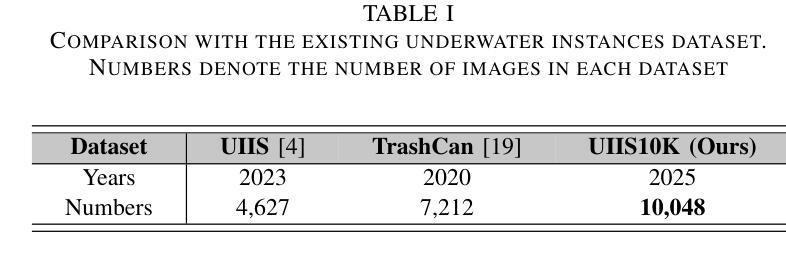
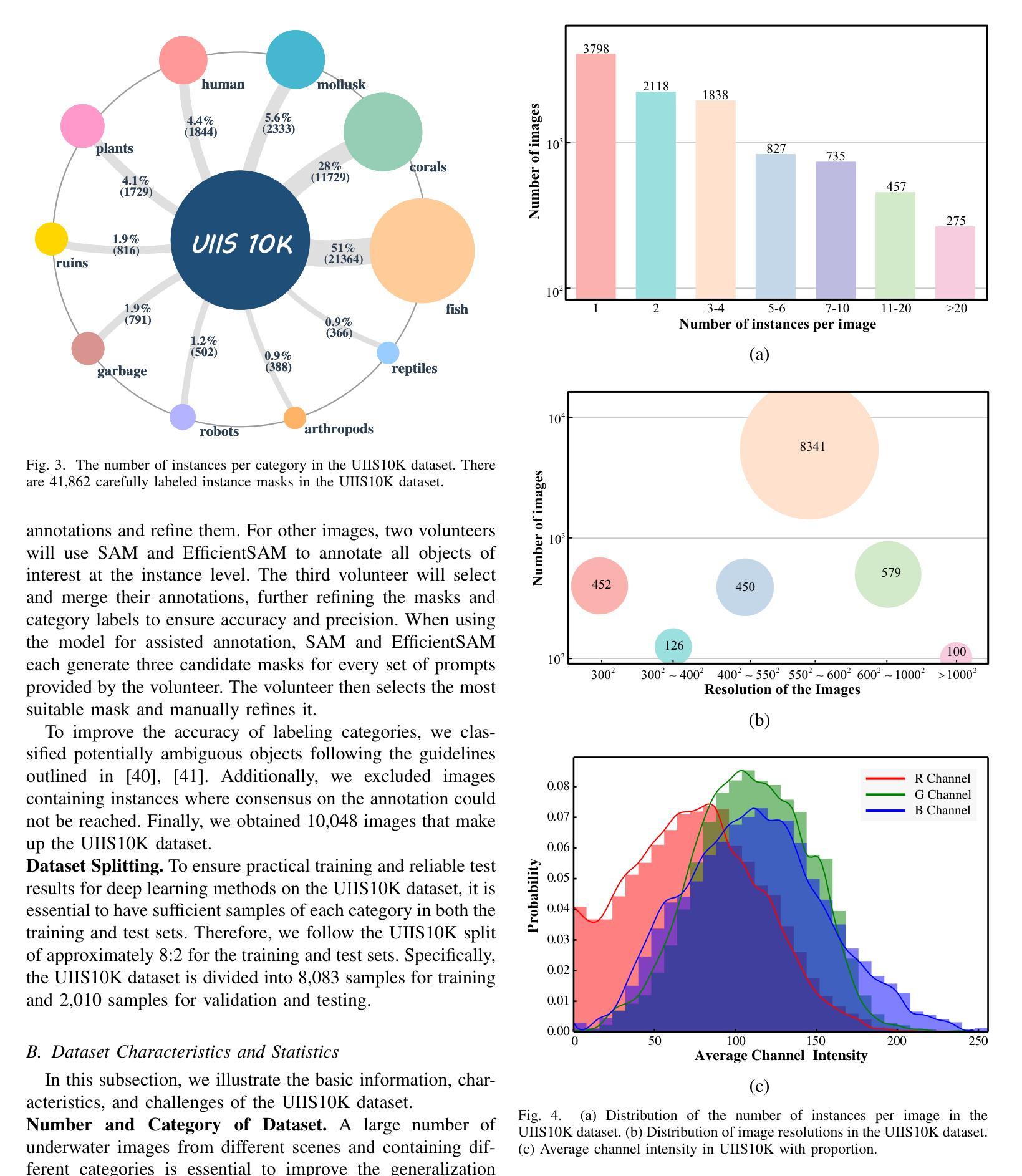
Taming SAM for Underwater Instance Segmentation and Beyond
Authors:Hua Li, Shijie Lian, Zhiyuan Li, Runmin Cong, Chongyi Li
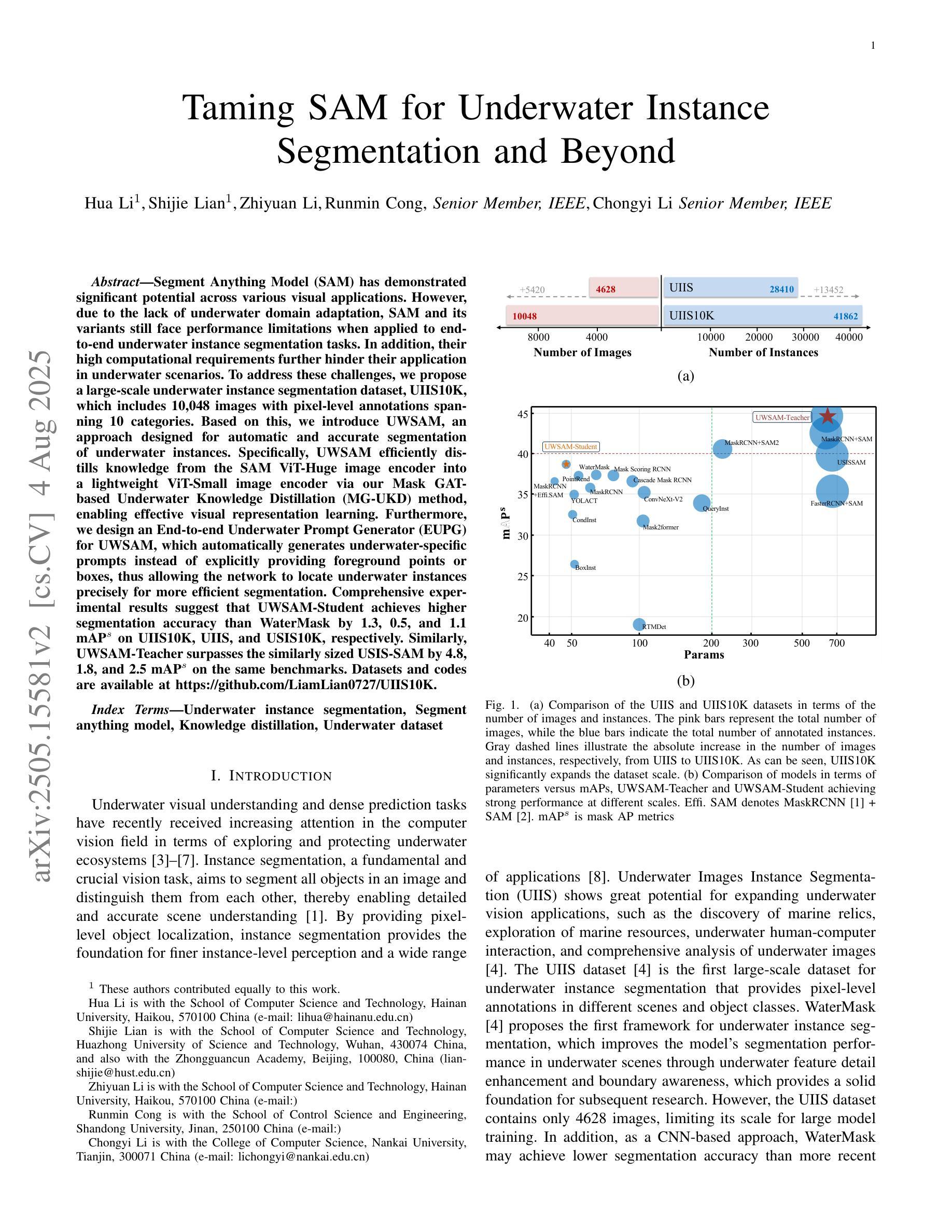
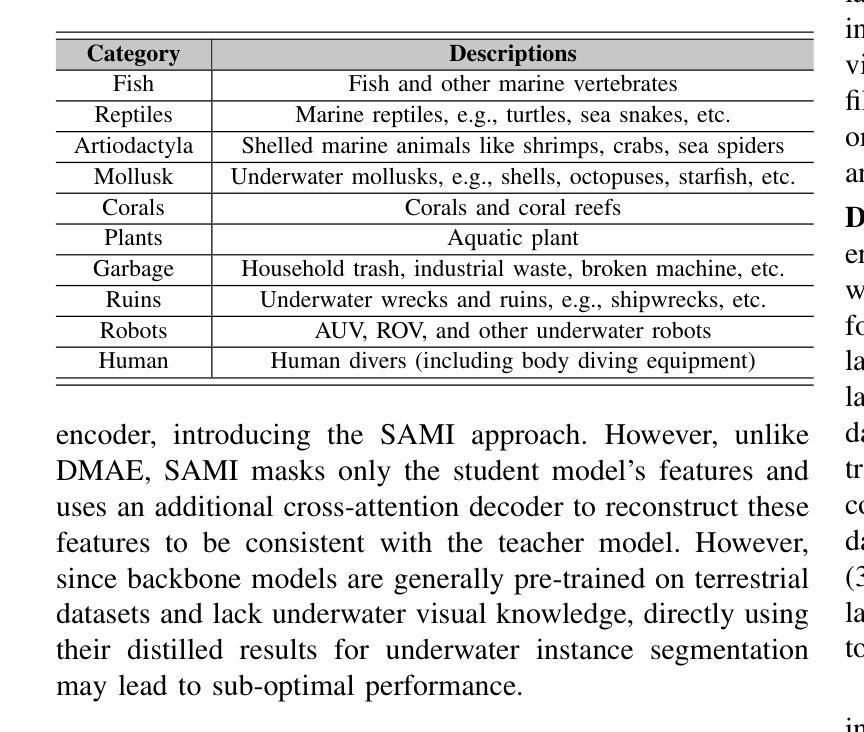
With recent breakthroughs in large-scale modeling, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated significant potential in a variety of visual applications. However, due to the lack of underwater domain expertise, SAM and its variants face performance limitations in end-to-end underwater instance segmentation tasks, while their higher computational requirements further hinder their application in underwater scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a large-scale underwater instance segmentation dataset, UIIS10K, which includes 10,048 images with pixel-level annotations for 10 categories. Then, we introduce UWSAM, an efficient model designed for automatic and accurate segmentation of underwater instances. UWSAM efficiently distills knowledge from the SAM ViT-Huge image encoder into the smaller ViT-Small image encoder via the Mask GAT-based Underwater Knowledge Distillation (MG-UKD) method for effective visual representation learning. Furthermore, we design an End-to-end Underwater Prompt Generator (EUPG) for UWSAM, which automatically generates underwater prompts instead of explicitly providing foreground points or boxes as prompts, thus enabling the network to locate underwater instances accurately for efficient segmentation. Comprehensive experimental results show that our model is effective, achieving significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on multiple underwater instance datasets. Datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K.
随着大规模建模技术的最新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中面临性能限制,而它们较高的计算要求进一步阻碍了在水下场景中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一个大规模的水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,其中包含10,048张具有10类像素级注释的图像。接着,我们介绍了UWSAM,这是一个为自动和准确水下实例分割而设计的高效模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器蒸馏知识到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器,从而实现有效的视觉表示学习。此外,我们为UWSAM设计了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),它会自动生成水下提示,而不是明确地提供前景点或盒子作为提示,从而使网络能够准确地定位水下实例,以实现有效的分割。综合实验结果表明,我们的模型是有效的,在多个水下实例数据集上实现了对最先进方法的显著性能改进。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对大型建模的突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在多种视觉应用中显示出巨大潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中的性能受限。为此,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张带10类像素级注释的图像。同时,我们引入了专为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的UWSAM模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器蒸馏知识到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器,实现有效的视觉表征学习。此外,我们还为UWSAM设计了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),能够自动生成水下提示,而非显式提供前景点或框作为提示,使网络能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效分割。实验结果证实,我们的模型在多个水下实例数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉应用中的潜力巨大,但在水下实例分割任务中面临性能限制。
- 缺乏水下领域的专业知识是SAM及其变体面临性能挑战的主要原因。
- UIIS10K数据集的提出是为了解决这一挑战,包含大量带像素级注释的水下图像。
- UWSAM模型专为水下实例分割设计,通过知识蒸馏和视觉表征学习提升性能。
- UWSAM采用基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,提高编码器的效率。
- 端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG)能够自动生成水下提示,提高网络定位水下实例的准确性。
- 实验结果显示,UWSAM在多个水下实例数据集上的性能显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

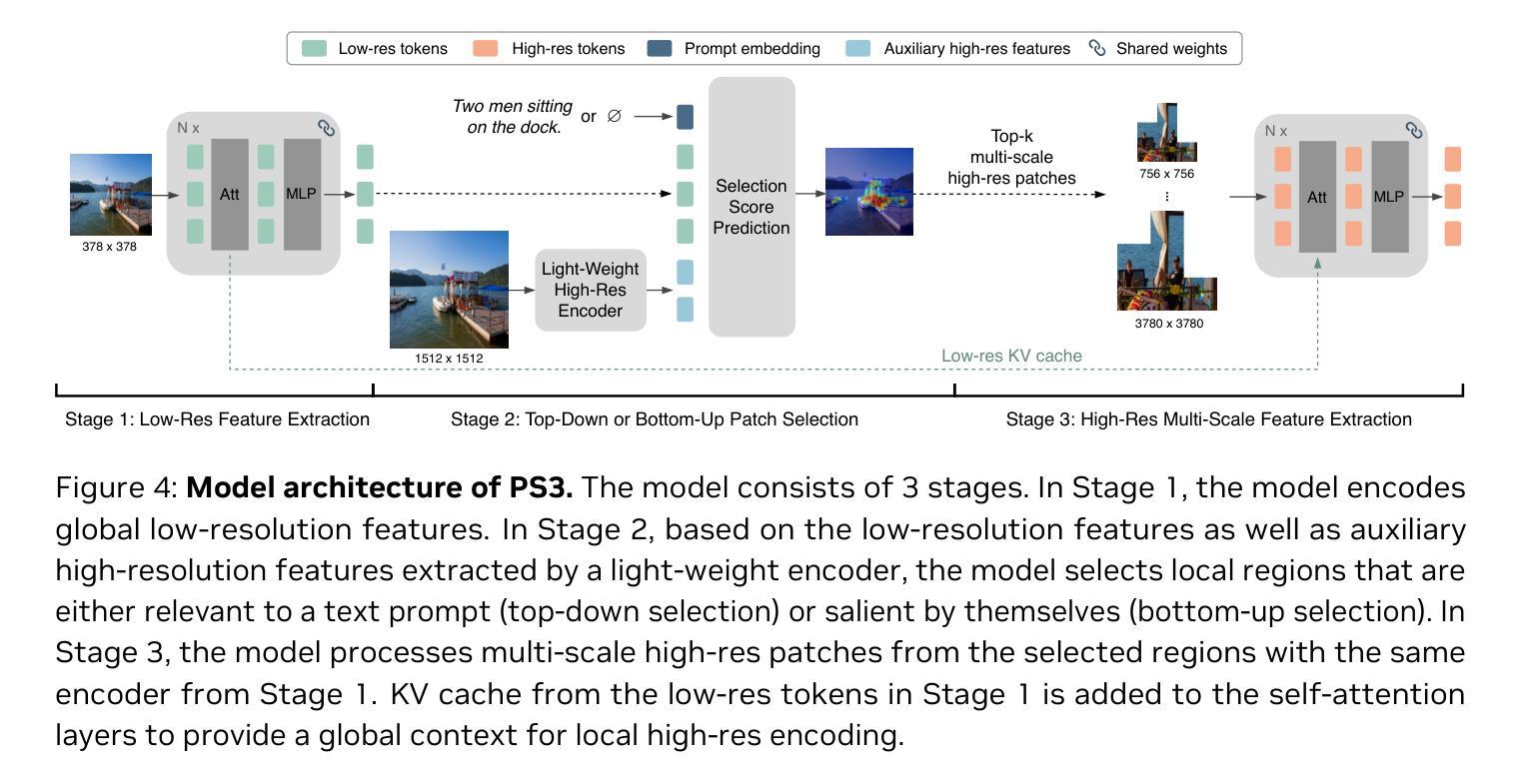
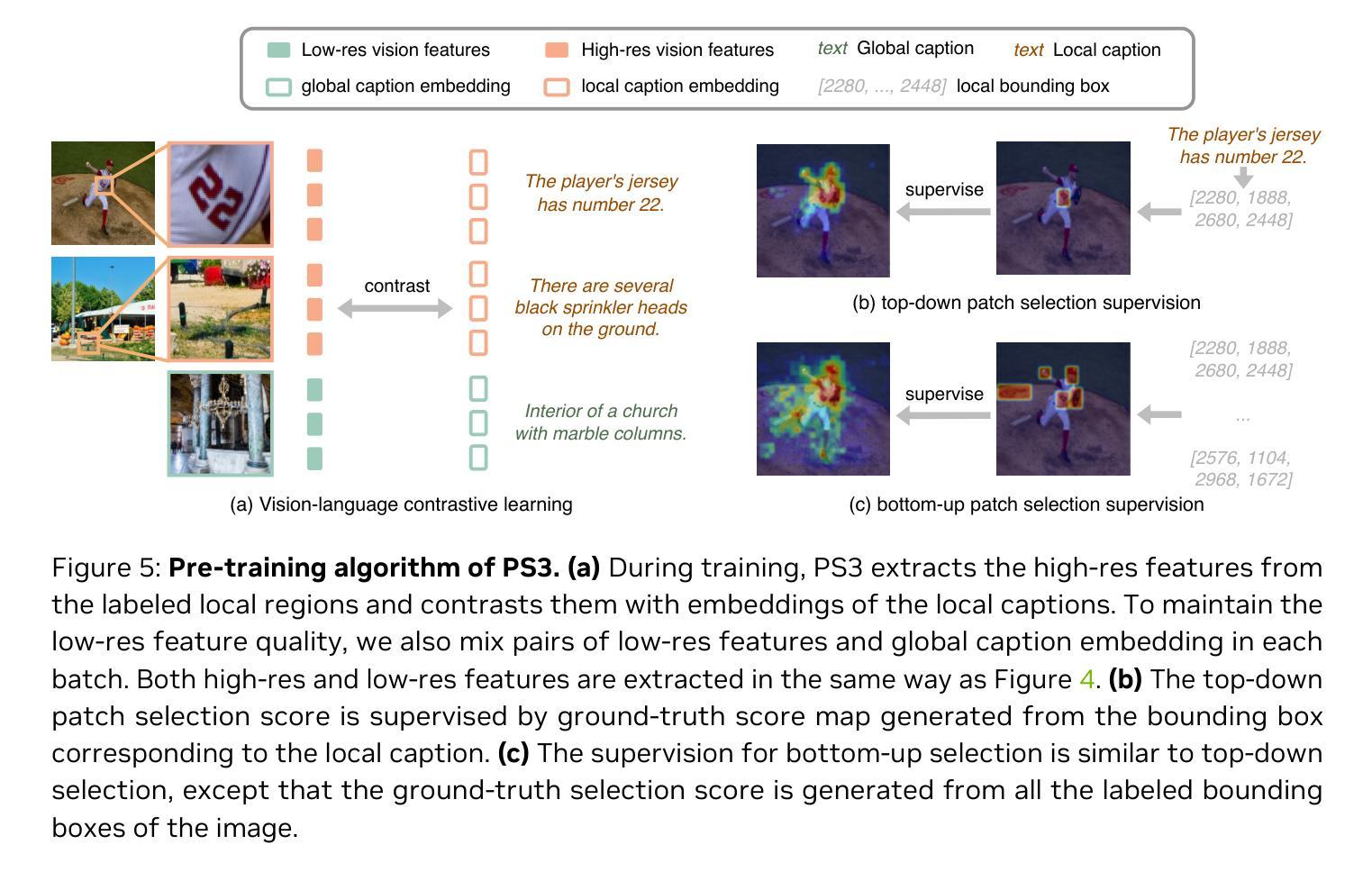
Scaling Vision Pre-Training to 4K Resolution
Authors:Baifeng Shi, Boyi Li, Han Cai, Yao Lu, Sifei Liu, Marco Pavone, Jan Kautz, Song Han, Trevor Darrell, Pavlo Molchanov, Hongxu Yin
High-resolution perception of visual details is crucial for daily tasks. Current vision pre-training, however, is still limited to low resolutions (e.g., 378 x 378 pixels) due to the quadratic cost of processing larger images. We introduce PS3 that scales CLIP-style vision pre-training to 4K resolution with a near-constant cost. Instead of contrastive learning on global image representation, PS3 is pre-trained by selectively processing local regions and contrasting them with local detailed captions, enabling high-resolution representation learning with greatly reduced computational overhead. The pre-trained PS3 is able to both encode the global image at low resolution and selectively process local high-resolution regions based on their saliency or relevance to a text prompt. When applying PS3 to multi-modal LLM (MLLM), the resulting model, named VILA-HD, significantly improves high-resolution visual perception compared to baselines without high-resolution vision pre-training such as AnyRes and S^2 while using up to 4.3x fewer tokens. PS3 also unlocks appealing scaling properties of VILA-HD, including scaling up resolution for free and scaling up test-time compute for better performance. Compared to state of the arts, PS3 and VILA-HD outperform previous vision encoders (e.g., SigLIP2 and Perception Encoder) and MLLMs (e.g., NVILA and Qwen2.5-VL) respectively across multiple benchmarks and achieve better efficiency than latest token pruning approaches. Finally, we find current benchmarks do not require 4K-resolution perception, which motivates us to propose 4KPro, a new benchmark of image QA at 4K resolution, on which VILA-HD outperforms all previous MLLMs, including a 16.1% improvement over GPT-4o and a 7.5% improvement and 1.67x speedup over Qwen2.5-VL.
视觉细节的分辨率感知对于日常任务至关重要。然而,当前的视觉预训练仍然受限于低分辨率(例如,378 x 378像素),这是因为处理更大图像的成本是二次方的。我们引入了PS3,它以近恒定的成本将CLIP风格的视觉预训练扩展到4K分辨率。与全局图像表示的对比学习不同,PS3通过选择性处理局部区域并为它们提供局部详细字幕来进行预训练,从而能够以大大降低的计算开销实现高分辨率表示学习。预训练的PS3既能够编码低分辨率的全局图像,又能根据局部高分辨率区域的显著性或其与文本提示的相关性来选择性处理这些区域。将PS3应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时,所得模型(名为VILA-HD)与没有高分辨率视觉预训练的基准模型(如AnyRes和S^2)相比,显著提高了高分辨率视觉感知能力。同时,与基准模型相比,VILA-HD使用的令牌数最多减少了4.3倍。PS3还解锁了VILA-HD的吸引人的可扩展属性,包括免费提高分辨率和在测试时增加计算以提高性能。与最前沿技术相比,PS3和VILA-HD分别在多个基准测试中优于先前的视觉编码器(如SigLIP2和感知编码器)和多模态大型语言模型(如NVILA和Qwen2.5-VL),并且在最新的令牌修剪方法中也实现了更高的效率。最后,我们发现当前基准测试不需要4K分辨率的感知,这促使我们提出一个新的4K分辨率图像问答基准测试4KPro。在此基准测试中,VILA-HD超越了所有先前的MLLM,包括对GPT-4o的16.1%改进和对Qwen2.5-VL的7.5%改进以及1.67倍的加速。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://nvlabs.github.io/PS3
Summary
高解析度视觉细节感知对日常任务至关重要。当前视觉预训练受限于低分辨率(例如378 x 378像素),处理更大图像的成本为二次方成本。本文介绍了PS3,它将CLIP风格的视觉预训练扩展到4K分辨率,同时保持近乎恒定的成本。PS3通过选择性处理局部区域并将它们与局部详细字幕进行对比来进行预训练,从而实现高分辨率表示学习并大大降低了计算开销。预训练的PS3能够根据文本提示对局部高解析度区域进行编码,并选择性地处理这些区域。将PS3应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时,产生的模型VILA-HD显著提高了高分辨率视觉感知能力,与使用低分辨率视觉预训练的基准模型相比,如AnyRes和S^2,其使用的令牌数量减少了高达4.3倍。PS3还开启了VILA-HD的吸引人的可扩展属性,包括免费提高分辨率和在测试时增加计算以提高性能。相较于最新技术和现有的大型语言模型,PS3与VILA-HD在多个基准测试中表现出色。最后,当前基准测试不需要4K分辨率感知功能,为此本文提出了一个新的图像问答基准测试4KPro,在测试中VILA-HD表现优于所有先前的大型语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视觉预训练受限于低分辨率,PS3方法能够扩展CLIP风格的视觉预训练至高分辨率。
- PS3通过选择性处理局部区域并对比,降低计算成本并实现高分辨率表示学习。
- VILA-HD模型利用PS3预训练提高高分辨率视觉感知能力,相较于基准模型使用更少令牌数量。
- VILA-HD通过扩大分辨率和测试时增加计算实现良好的性能提升。
- 对比最新技术和现有大型语言模型,PS3与VILA-HD在多个基准测试中表现优越。
- 当前基准测试不需要4K分辨率感知功能,为此提出新的图像问答基准测试4KPro。
点此查看论文截图



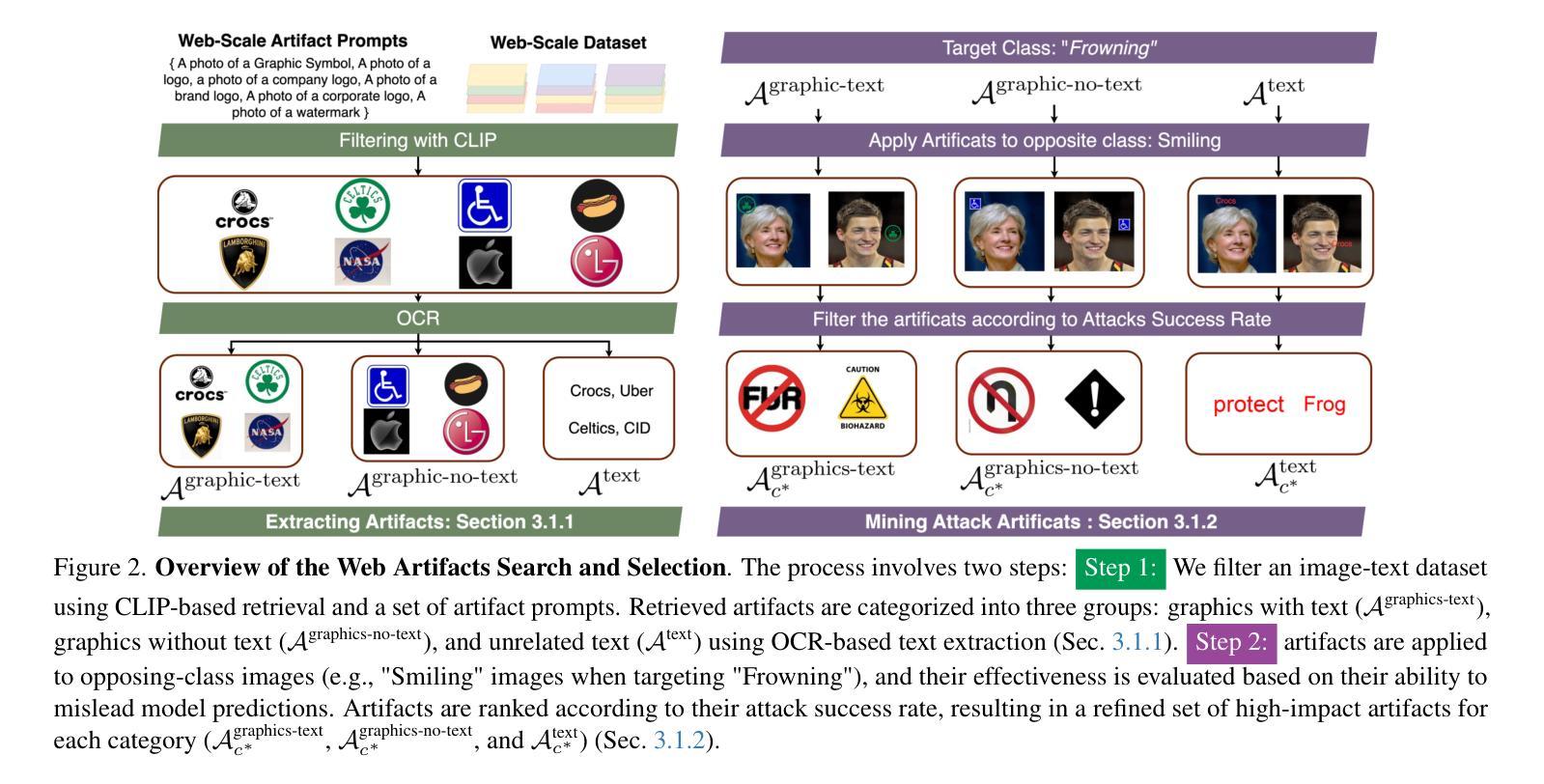
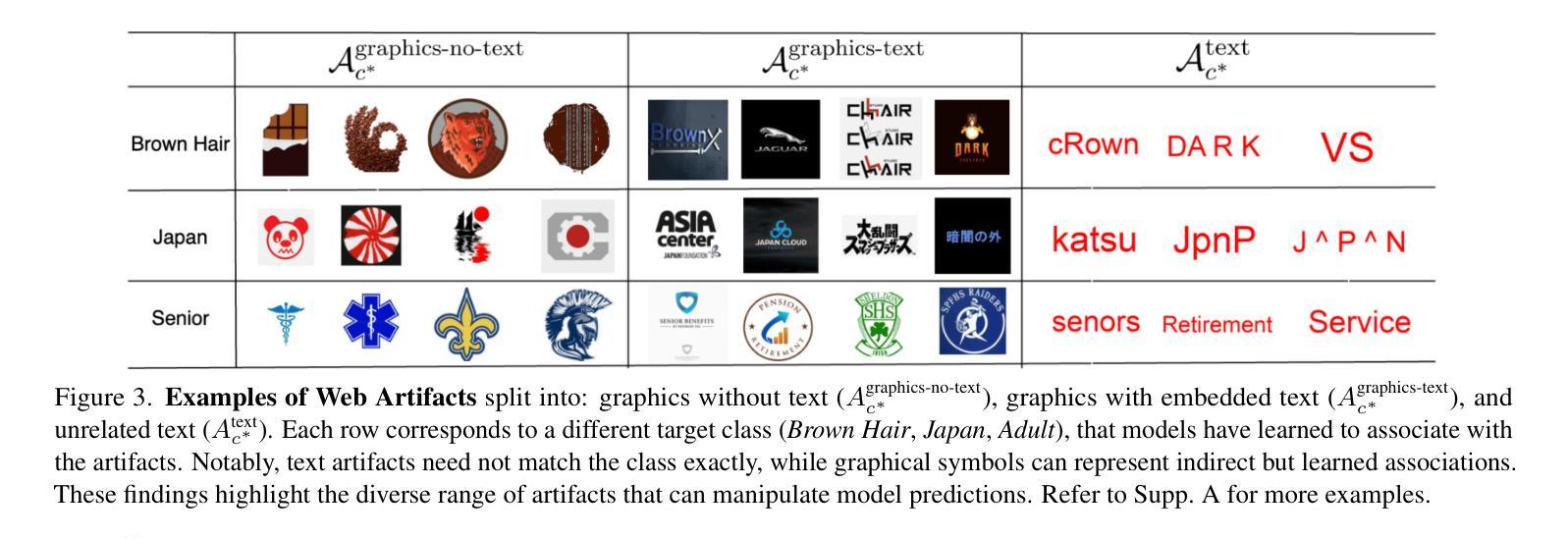
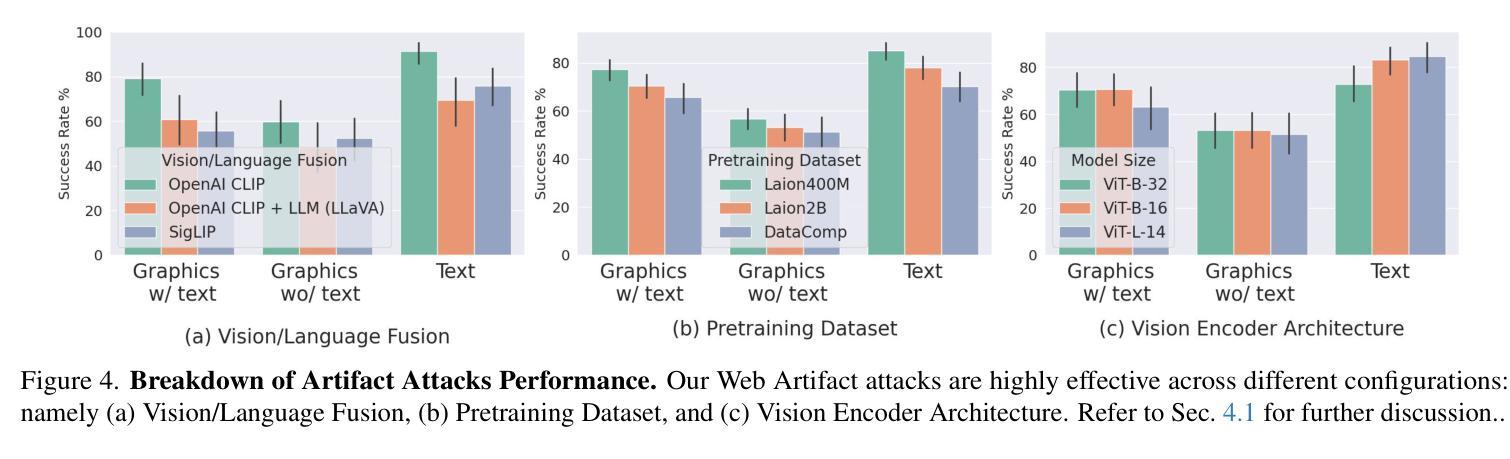
Web Artifact Attacks Disrupt Vision Language Models
Authors:Maan Qraitem, Piotr Teterwak, Kate Saenko, Bryan A. Plummer
Vision-language models (VLMs) (e.g. CLIP, LLaVA) are trained on large-scale, lightly curated web datasets, leading them to learn unintended correlations between semantic concepts and unrelated visual signals. These associations degrade model accuracy by causing predictions to rely on incidental patterns rather than genuine visual understanding. Prior work has weaponized these correlations as an attack vector to manipulate model predictions, such as inserting a deceiving class text onto the image in a “typographic” attack. These attacks succeed due to VLMs’ text-heavy bias-a result of captions that echo visible words rather than describing content. However, this attack has focused solely on text that matches the target class exactly, overlooking a broader range of correlations, including non-matching text and graphical symbols, which arise from the abundance of branding content in web-scale data. To address this gap, we introduce “artifact-based” attacks: a novel class of manipulations that mislead models using both non-matching text and graphical elements. Unlike typographic attacks, these artifacts are not predefined, making them simultaneously harder to defend against and more challenging to find. We address this by framing artifact attacks as a search problem and demonstrate their effectiveness across five datasets, with some artifacts reinforcing each other to reach 100% attack success rates. These attacks transfer across models with up to 90% effectiveness, making it possible to attack unseen models. To defend against these attacks, we extend prior work’s artifact aware prompting to the graphical setting. We see a moderate reduction of success rates of up to 15% relative to standard prompts, suggesting a promising direction for enhancing model robustness. Code: https://github.com/mqraitem/Web-Artifact-Attacks
视觉语言模型(如CLIP、LLaVA)是在大规模、轻度整理的网页数据集上进行训练的,这导致它们学会了语义概念和无关视觉信号之间的意外关联。这些关联使模型预测依赖于偶然的模式,而非真正的视觉理解,从而降低了模型的准确性。之前的工作已经利用这些关联作为攻击向量来操纵模型预测,例如在图像中插入欺骗性类别文本,进行“排版”攻击。这些攻击之所以成功,是因为视觉语言模型存在重文本偏置——描述语倾向于重复可见词汇,而非描述内容。然而,这种攻击主要集中于与目标类别完全匹配的文本,忽略了更广泛的关联,包括非匹配文本和图形符号,这些关联源于网页数据中品牌内容的丰富性。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了“基于工件”的攻击:一种新型操纵方法,使用非匹配文本和图形元素来误导模型。与排版攻击不同,这些工件不是预先定义的,因此同时更难防御和查找。我们通过将工件攻击构建为搜索问题来解决这一问题,并在五个数据集上证明了其有效性,某些工件会相互加强以达到100%的攻击成功率。这些攻击在高达90%的有效性下跨模型进行转移,使得攻击未知模型成为可能。为了防御这些攻击,我们将先前工作的工件感知提示扩展到图形设置。我们看到相对于标准提示,成功率的适度降低高达15%,这表明是增强模型稳健性的一个有前途的方向。代码:https://github.com/mqraitem/Web-Artifact-Attacks
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
该文本主要介绍了视觉语言模型(VLMs)面临的新型攻击方式。这些攻击通过利用模型学习到的意外关联,使用非匹配文本和图形元素来误导模型。新的“artifact-based”攻击方法利用网页数据中丰富的品牌内容产生的广泛关联,比传统攻击更具隐蔽性和挑战性。针对这种新型攻击,论文提出了将其视为搜索问题的方法,并在五个数据集上验证了其有效性。同时,论文还尝试通过扩展先前工作的提示方法来防御这些攻击,取得了一定的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)易受新型攻击影响,这些攻击利用模型学习到的意外关联来误导预测。
- “artifact-based”攻击是一种新型攻击方式,利用非匹配文本和图形元素,比传统攻击更具隐蔽性和挑战性。
- 这种新型攻击方法通过在五个数据集上的实验验证,且攻击效果可跨模型转移,达到高达100%的成功率。
- 单纯的防御方法对于对抗这种新型攻击效果有限,需要探索更有效的防御手段。
- 论文提出了一种将artifact attack视为搜索问题的方法,为解决这类问题提供了新的思路。
- 扩展的提示方法对于防御这种新型攻击有一定的效果,但需要进一步研究和改进以提高防御能力。
点此查看论文截图