⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
X-SAM: From Segment Anything to Any Segmentation
Authors:Hao Wang, Limeng Qiao, Zequn Jie, Zhijian Huang, Chengjian Feng, Qingfang Zheng, Lin Ma, Xiangyuan Lan, Xiaodan Liang
Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in broad knowledge representation, yet they are inherently deficient in pixel-level perceptual understanding. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) represents a significant advancement in visual-prompt-driven image segmentation, it exhibits notable limitations in multi-mask prediction and category-specific segmentation tasks, and it cannot integrate all segmentation tasks within a unified model architecture. To address these limitations, we present X-SAM, a streamlined Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) framework that extends the segmentation paradigm from \textit{segment anything} to \textit{any segmentation}. Specifically, we introduce a novel unified framework that enables more advanced pixel-level perceptual comprehension for MLLMs. Furthermore, we propose a new segmentation task, termed Visual GrounDed (VGD) segmentation, which segments all instance objects with interactive visual prompts and empowers MLLMs with visual grounded, pixel-wise interpretative capabilities. To enable effective training on diverse data sources, we present a unified training strategy that supports co-training across multiple datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that X-SAM achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of image segmentation benchmarks, highlighting its efficiency for multimodal, pixel-level visual understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/wanghao9610/X-SAM.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在广泛的知识表示方面表现出强大的能力,但它们在像素级别的感知理解方面存在固有缺陷。尽管Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉提示驱动的图像分割方面取得了重大进展,但在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割任务方面仍存在显著局限性,且无法将所有分割任务整合到统一的模型架构中。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了X-SAM,一个简化的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)框架,它将分割范式从“分割任何事物”扩展到“任何分割”。具体来说,我们引入了一种新型统一框架,为MLLM提供更先进的像素级别感知理解能力。此外,我们提出了一个新的分割任务,称为Visual GrounDed(VGD)分割,它通过交互式的视觉提示对所有实例对象进行分割,并为MLLM提供视觉接地、像素级的解释能力。为了能够在多样化的数据源上进行有效训练,我们提出了一种支持跨多个数据集联合训练的统一训练策略。实验结果证明,X-SAM在广泛的图像分割基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,突显了其在多模态、像素级别的视觉理解方面的效率。相关代码可通过https://github.com/wanghao9eav技术联盟组织长瞄准低成本多模式演示新技术端科研方向以便申请科研项目基金**简明扼要摘要提炼。**研究了大型语言模型在图像分割领域的局限性,并提出了一个简化的多模态大型语言模型框架X-SAM来解决这些问题。该框架引入了新型统一框架和Visual GrounDed分割任务来提升模型的像素级别感知理解能力。实验结果证明了X-SAM的有效性,并且强调了其在多模态视觉理解方面的潜力。代码已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
大语言模型(LLMs)具有广泛的知识表示能力,但在像素级感知理解方面存在固有缺陷。Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉提示驱动图像分割方面取得了显著进展,但在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割任务方面存在局限性,且无法将所有分割任务集成到统一模型架构中。为解决这些问题,我们提出了X-SAM,一个简化的多模态大语言模型(MLLM)框架,将分割范式从“分割任何事物”扩展到“任何分割”。我们引入了一个新颖的统一框架,为MLLM提供更先进的像素级感知理解。此外,我们提出了名为Visual GrounDed(VGD)分割的新分割任务,通过交互式视觉提示对所有实例对象进行分割,并为MLLM提供视觉基础、像素级的解释能力。为在多样数据源上进行有效训练,我们提出了一种支持跨多个数据集联合训练的统一训练策略。实验结果表明,X-SAM在广泛图像分割基准测试中达到最新性能,证明其在多模态、像素级视觉理解方面的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在像素级感知理解方面存在缺陷。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉提示驱动图像分割方面有所突破,但仍存在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割的任务局限性。
- X-SAM是一个多模态大语言模型(MLLM)框架,旨在解决SAM的局限性,实现从“分割任何事物”到“任何分割”的扩展。
- X-SAM引入了一个新颖的统一框架,增强了MLLM的像素级感知理解能力。
- 提出了Visual GrounDed(VGD)分割任务,通过交互式视觉提示对所有实例对象进行分割,增强MLLM的视觉基础、像素级解释能力。
- X-SAM采用统一训练策略,支持跨多个数据集的有效训练。
- 实验结果表明,X-SAM在图像分割基准测试中表现优异,具备多模态、像素级视觉理解的效率。
点此查看论文截图

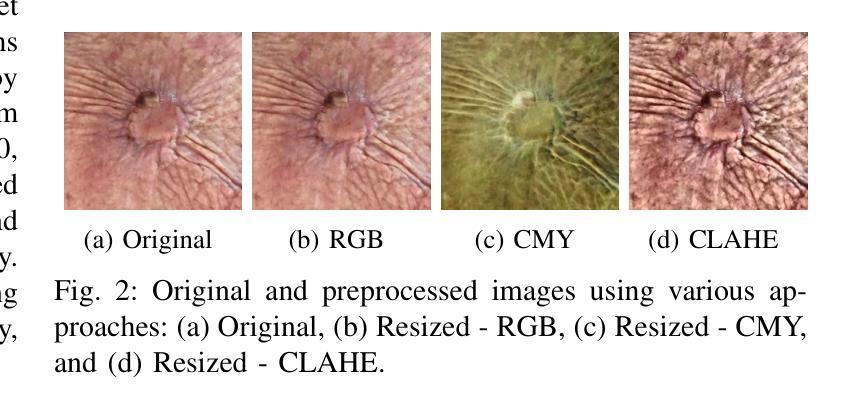
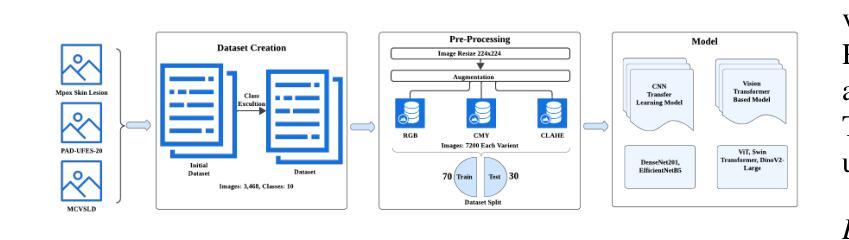
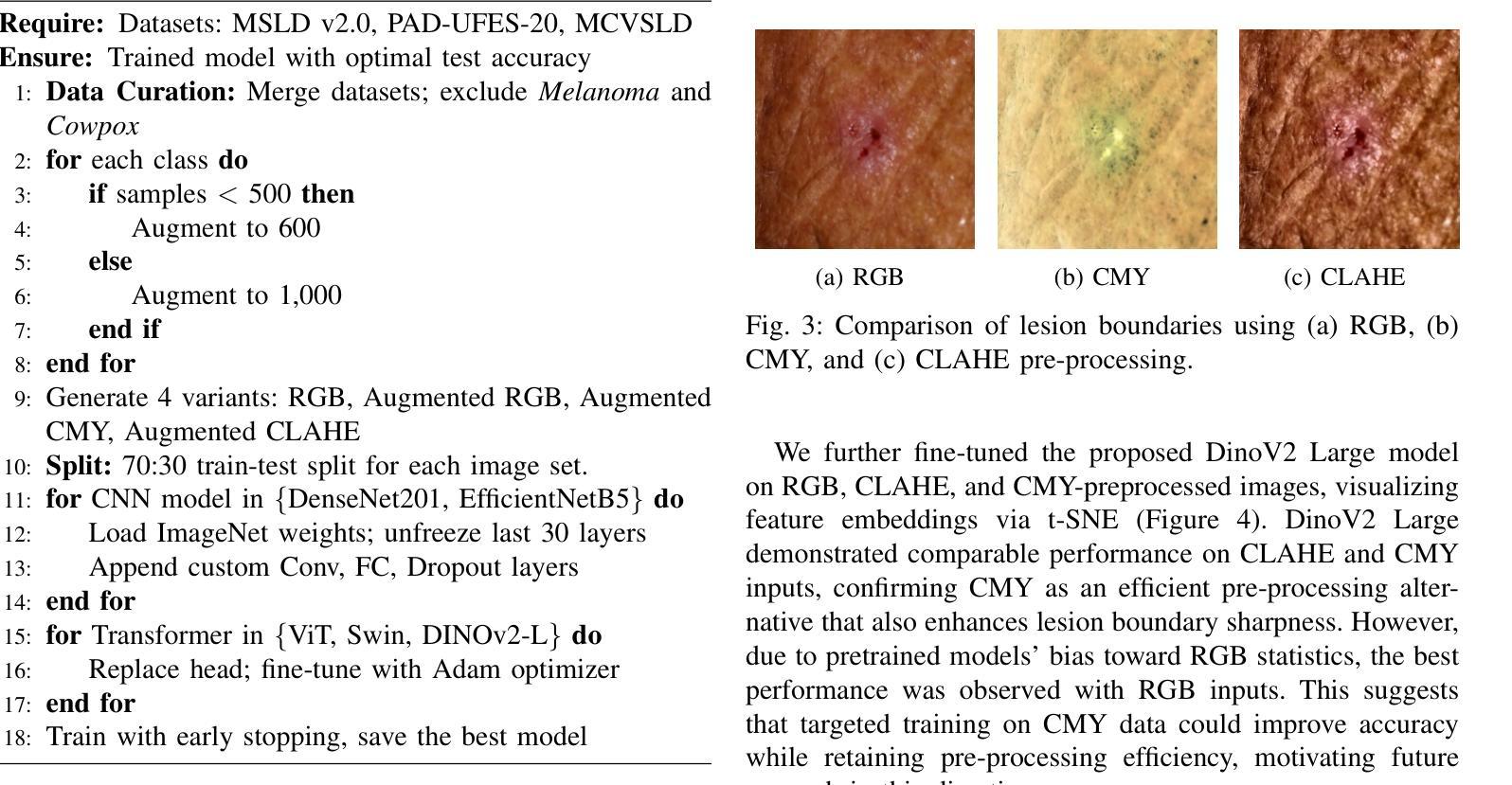
Visual Bias and Interpretability in Deep Learning for Dermatological Image Analysis
Authors:Enam Ahmed Taufik, Abdullah Khondoker, Antara Firoz Parsa, Seraj Al Mahmud Mostafa
Accurate skin disease classification is a critical yet challenging task due to high inter-class similarity, intra-class variability, and complex lesion textures. While deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems have shown promise in automating dermatological assessments, their performance is highly dependent on image pre-processing and model architecture. This study proposes a deep learning framework for multi-class skin disease classification, systematically evaluating three image pre-processing techniques: standard RGB, CMY color space transformation, and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE). We benchmark the performance of pre-trained convolutional neural networks (DenseNet201, Efficient-NetB5) and transformer-based models (ViT, Swin Transformer, DinoV2 Large) using accuracy and F1-score as evaluation metrics. Results show that DinoV2 with RGB pre-processing achieves the highest accuracy (up to 93%) and F1-scores across all variants. Grad-CAM visualizations applied to RGB inputs further reveal precise lesion localization, enhancing interpretability. These findings underscore the importance of effective pre-processing and model choice in building robust and explainable CAD systems for dermatology.
精确的皮肤疾病分类是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务,因为存在类间相似性高、类内变化大以及病变纹理复杂的问题。虽然基于深度学习的计算机辅助诊断(CAD)系统在自动化皮肤科评估方面显示出潜力,但其性能高度依赖于图像预处理和模型架构。本研究提出了一种用于多类皮肤疾病分类的深度学习框架,系统评估了三种图像预处理技术:标准RGB、CMY颜色空间转换和对比度受限自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)。我们使用预训练的卷积神经网络(DenseNet201、Efficient-NetB5)和基于transformer的模型(ViT、Swin Transformer、DinoV2 Large),以准确率和F1分数作为评估指标,对它们进行了基准测试。结果表明,使用RGB预处理的DinoV2获得了最高准确率(高达93%)和F1分数。应用于RGB输入的Grad-CAM可视化进一步揭示了精确的病变定位,提高了可解释性。这些发现强调了有效预处理和模型选择在构建用于皮肤病的稳健且可解释的CAD系统方面的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted in the 4th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing and Media Computing (ICIPMC) 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于深度学习的多类皮肤病分类问题,探讨了不同的图像预处理技术,包括标准RGB、CMY色彩空间转换和Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization(CLAHE)。研究使用了预训练的卷积神经网络(DenseNet201、Efficient-NetB5)和基于transformer的模型(ViT、Swin Transformer、DinoV2 Large),以准确度和F1分数为评价指标。结果表明,使用RGB预处理的DinoV2模型在准确度和F1分数上表现最佳(高达93%)。Grad-CAM可视化进一步揭示了精确的病变定位,增强了模型的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在皮肤病分类中具有潜力,但面临类间相似度高、类内变异复杂和病变纹理多样等挑战。
- 有效的图像预处理技术对于提高深度学习模型的性能至关重要。
- 本研究测试了多种图像预处理技术,包括标准RGB、CMY色彩空间转换和CLAHE。
- 预训练的卷积神经网络和基于transformer的模型在皮肤病分类中表现出良好的性能。
- DinoV2模型使用RGB预处理在准确度和F1分数上达到最高表现。
- Grad-CAM可视化有助于精确病变定位,提高模型的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

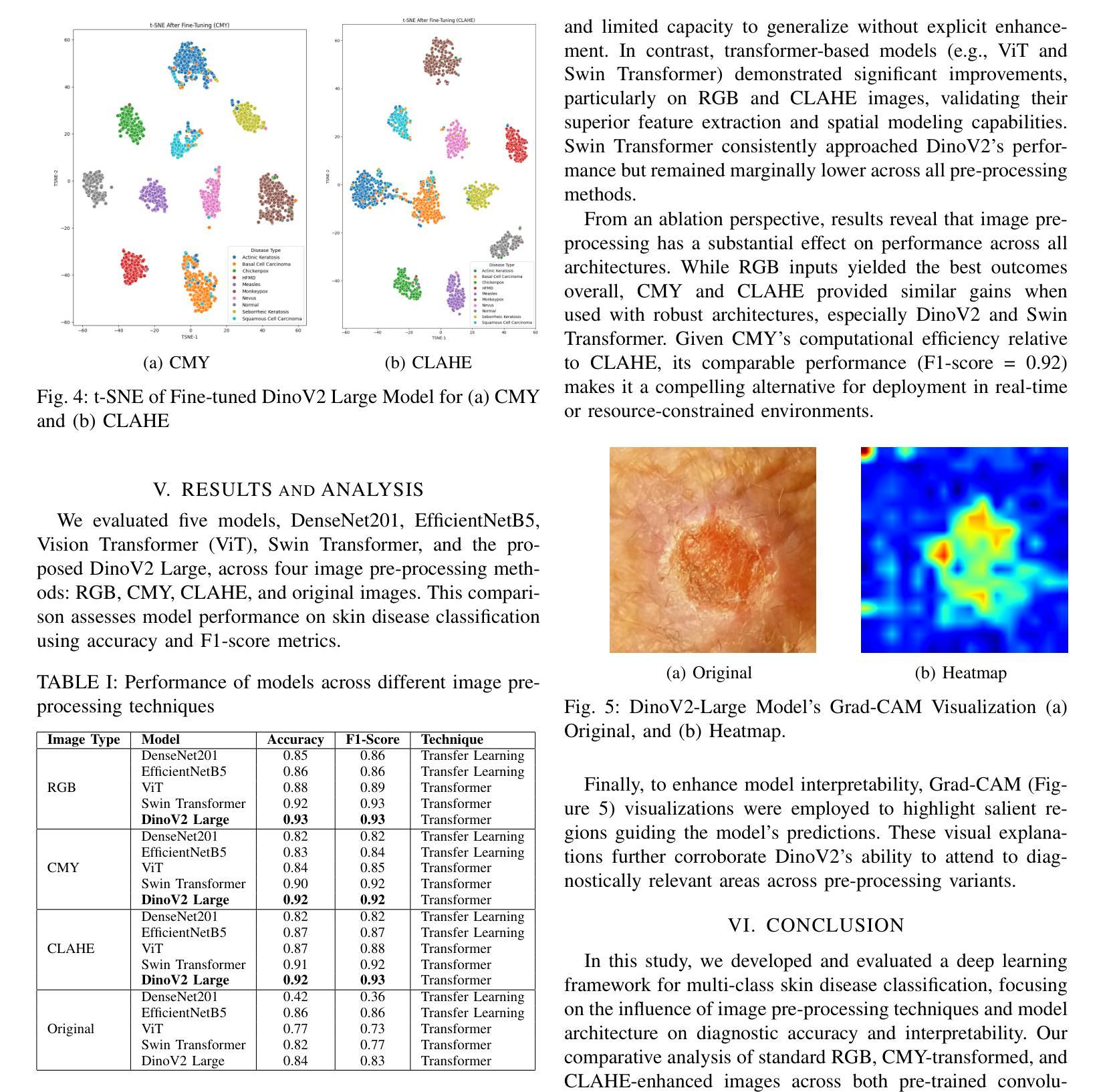
DDTracking: A Deep Generative Framework for Diffusion MRI Tractography with Streamline Local-Global Spatiotemporal Modeling
Authors:Yijie Li, Wei Zhang, Xi Zhu, Ye Wu, Yogesh Rathi, Lauren J. O’Donnell, Fan Zhang
This paper presents DDTracking, a novel deep generative framework for diffusion MRI tractography that formulates streamline propagation as a conditional denoising diffusion process. In DDTracking, we introduce a dual-pathway encoding network that jointly models local spatial encoding (capturing fine-scale structural details at each streamline point) and global temporal dependencies (ensuring long-range consistency across the entire streamline). Furthermore, we design a conditional diffusion model module, which leverages the learned local and global embeddings to predict streamline propagation orientations for tractography in an end-to-end trainable manner. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation across diverse, independently acquired dMRI datasets, including both synthetic and clinical data. Experiments on two well-established benchmarks with ground truth (ISMRM Challenge and TractoInferno) demonstrate that DDTracking largely outperforms current state-of-the-art tractography methods. Furthermore, our results highlight DDTracking’s strong generalizability across heterogeneous datasets, spanning varying health conditions, age groups, imaging protocols, and scanner types. Collectively, DDTracking offers anatomically plausible and robust tractography, presenting a scalable, adaptable, and end-to-end learnable solution for broad dMRI applications. Code is available at: https://github.com/yishengpoxiao/DDtracking.git
本文介绍了DDTracking,这是一种新型的深度生成框架,用于将扩散磁共振成像(dMRI)的流线传播建模为条件去噪扩散过程。在DDTracking中,我们引入了一个双路径编码网络,该网络对局部空间编码进行联合建模(捕获每条流线点的精细结构细节),并建模全局时间依赖性(确保整个流线的远程一致性)。此外,我们设计了一个条件扩散模型模块,该模块利用学习到的局部和全局嵌入来预测流线传播方向,以进行端到端的可训练 tractography。我们在多种独立获取的dMRI数据集上进行了全面评估,包括合成数据和临床数据。在具有基准真实值(ISMRM Challenge和TractoInferno)的两个公认基准上的实验表明,DDTracking在总体上大大优于当前最先进的tractography方法。此外,我们的结果表明,DDTracking在不同数据集上具有强大的泛化能力,涵盖各种健康状况、年龄组、成像协议和扫描仪类型。总之,DDTracking提供了解剖上合理且稳健的tractography,为广泛的dMRI应用提供了可扩展、可适应和端到端的可学习解决方案。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/yishengpoxiao/DDtracking.git 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version. The content may be updated in the future
Summary
本文提出DDTracking,一种用于扩散MRI轨迹追踪的新型深度生成框架。它将流线传播表述为条件去噪扩散过程,引入双路径编码网络,同时建模局部空间编码和全局时间依赖性。通过条件扩散模型模块,利用学习和全局嵌入预测流线传播方向,实现端对端训练。在多种独立获取的dMRI数据集上的综合评估表明,DDTracking显著优于当前最先进的轨迹追踪方法,具有强大的泛化能力,适用于广泛的dMRI应用。
Key Takeaways
- DDTracking是一个用于扩散MRI轨迹追踪的深度生成框架。
- 流线传播被表述为条件去噪扩散过程。
- 引入双路径编码网络,同时建模局部空间编码和全局时间依赖性。
- 条件扩散模型模块利用学习和全局嵌入预测流线传播方向。
- DDTracking在多种dMRI数据集上进行了综合评估,包括合成和临床数据。
- DDTracking显著优于当前最先进的轨迹追踪方法。
点此查看论文截图

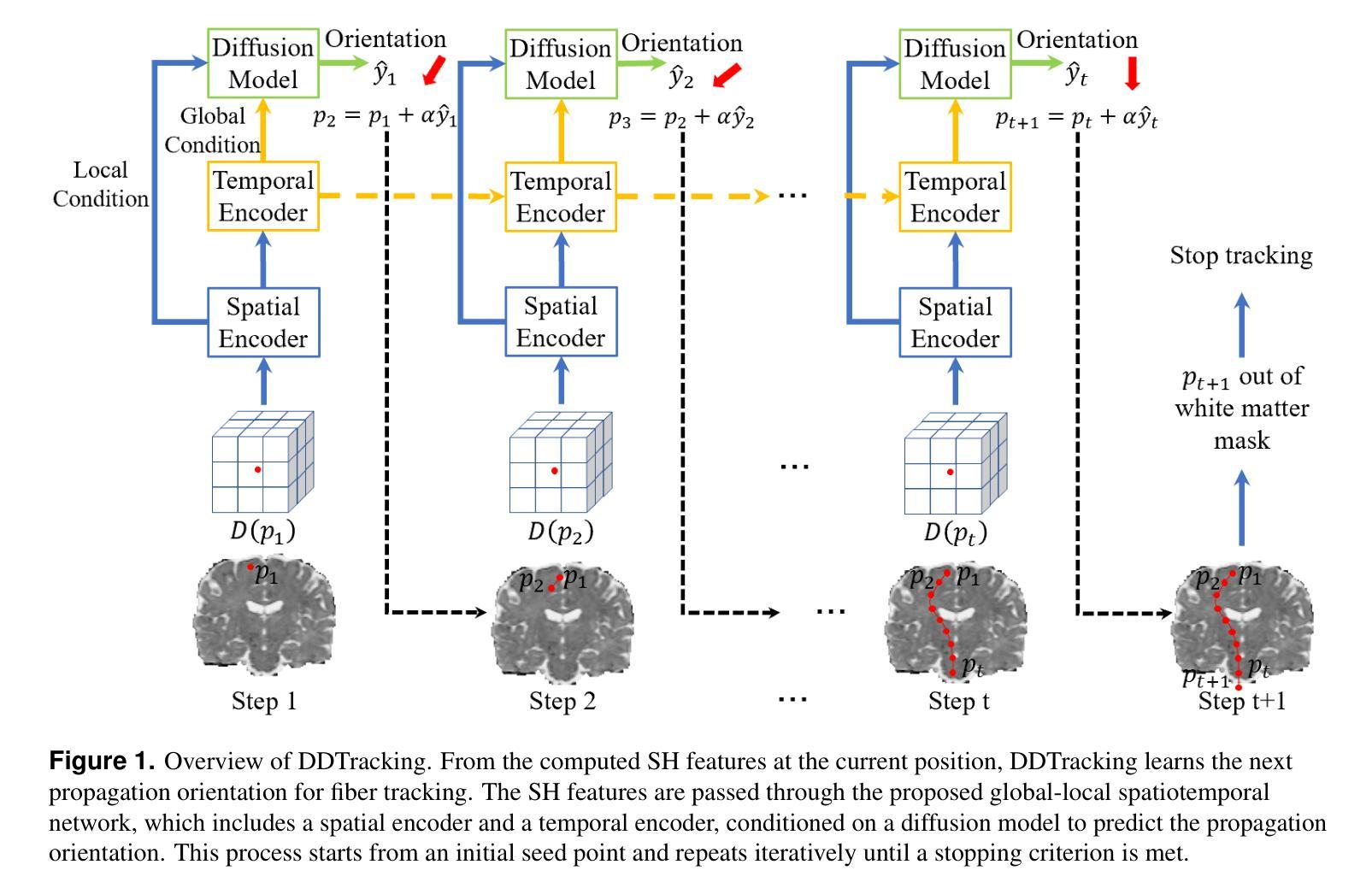
Augmentation-based Domain Generalization and Joint Training from Multiple Source Domains for Whole Heart Segmentation
Authors:Franz Thaler, Darko Stern, Gernot Plank, Martin Urschler
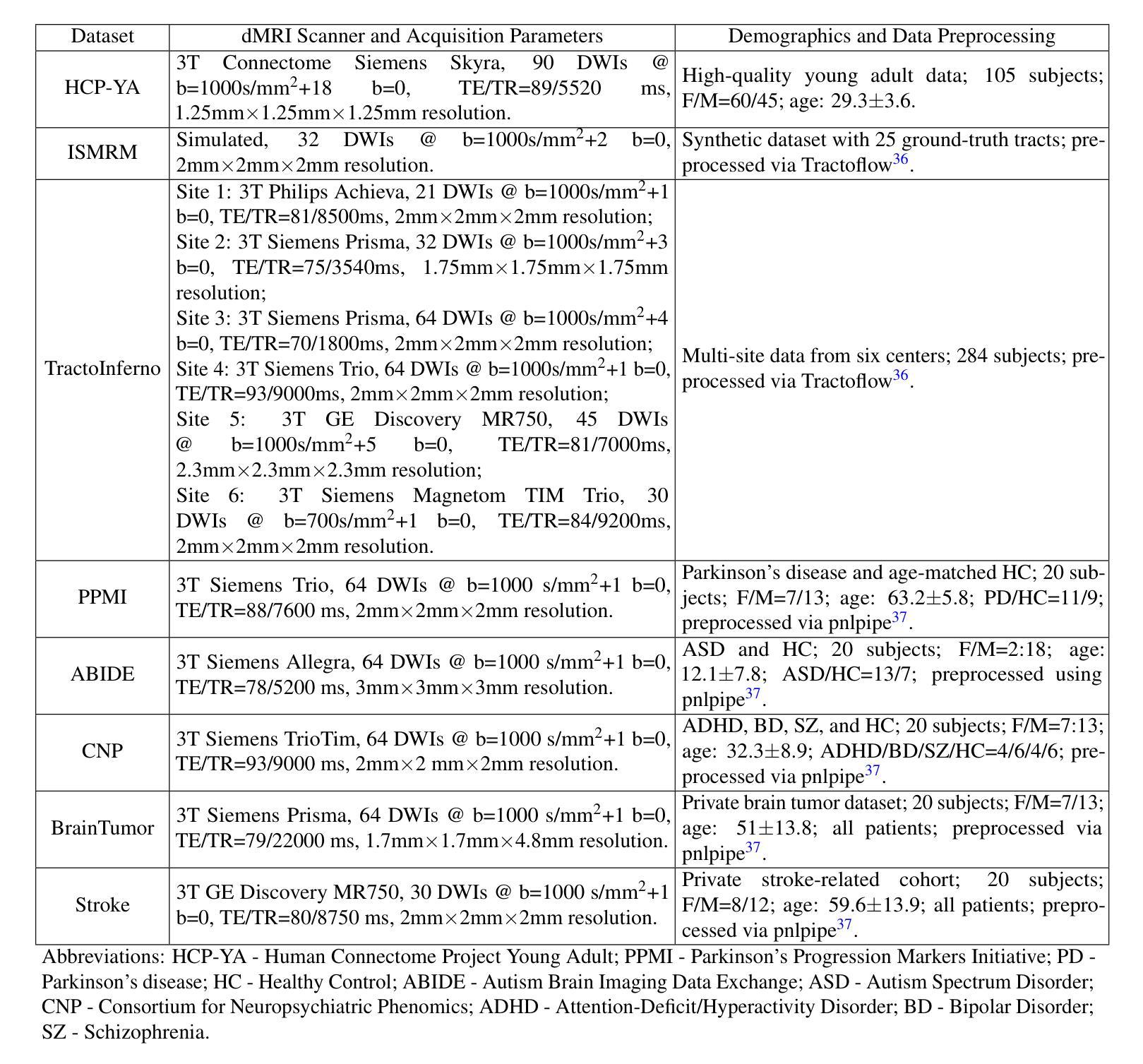
As the leading cause of death worldwide, cardiovascular diseases motivate the development of more sophisticated methods to analyze the heart and its substructures from medical images like Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance (MR). Semantic segmentations of important cardiac structures that represent the whole heart are useful to assess patient-specific cardiac morphology and pathology. Furthermore, accurate semantic segmentations can be used to generate cardiac digital twin models which allows e.g. electrophysiological simulation and personalized therapy planning. Even though deep learning-based methods for medical image segmentation achieved great advancements over the last decade, retaining good performance under domain shift – i.e. when training and test data are sampled from different data distributions – remains challenging. In order to perform well on domains known at training-time, we employ a (1) balanced joint training approach that utilizes CT and MR data in equal amounts from different source domains. Further, aiming to alleviate domain shift towards domains only encountered at test-time, we rely on (2) strong intensity and spatial augmentation techniques to greatly diversify the available training data. Our proposed whole heart segmentation method, a 5-fold ensemble with our contributions, achieves the best performance for MR data overall and a performance similar to the best performance for CT data when compared to a model trained solely on CT. With 93.33% DSC and 0.8388 mm ASSD for CT and 89.30% DSC and 1.2411 mm ASSD for MR data, our method demonstrates great potential to efficiently obtain accurate semantic segmentations from which patient-specific cardiac twin models can be generated.
作为全世界的主要死亡原因,心血管疾病促使了更精细的方法的发展,用于从计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振(MR)等医学图像中分析心脏及其子结构。表示整个心脏的重要心脏结构的语义分割对于评估患者特定的心脏形态和病理非常有用。此外,准确的语义分割可用于生成心脏数字孪生模型,这可以进行例如电生理模拟和个性化治疗计划。尽管基于深度学习的医学图像分割方法在过去十年中取得了巨大进步,但在领域迁移(即当训练和测试数据来自不同的数据分布时)的情况下保持良好的性能仍然是一个挑战。为了在对训练时有域知识的领域上表现良好,我们采用了(1)平衡联合训练方法,该方法平等地利用来自不同源域的CT和MR数据。此外,为了缓解仅在测试时遇到的领域迁移问题,我们依赖于(2)强大的强度和空间增强技术来极大地多样化可用的训练数据。我们提出的整个心脏分割方法是一个五重集成方法,其中包含我们的贡献,在MR数据上取得了最佳性能,并且在与仅使用CT数据训练的模型相比时,对于CT数据也达到了类似最佳性能。我们的方法在CT数据上达到了93.33%的DSC和0.8388毫米的ASSD,在MR数据上达到了89.30%的DSC和1.2411毫米的ASSD,显示出从准确的语义分割中有效获得患者特定心脏孪生模型的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the MICCAI Challenge on Comprehensive Analysis and Computing of Real-World Medical Images 2024, 12 pages
摘要
本文关注心血管疾病的医学图像分析,特别是心脏结构的语义分割。文章介绍了使用先进的深度学习技术,结合计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振(MR)数据,进行心脏结构分割的研究。该研究通过平衡联合训练方法和强度与空间增强的技术,提高了模型在不同领域数据上的表现。提出的全心脏分割方法取得了优异的性能,特别是在磁共振数据上,并展示了生成个性化心脏双胞胎模型的潜力。
关键见解
- 心血管疾病是全球主要死亡原因,促使开发从医学图像(如CT和MR)分析心脏及其子结构的更先进方法。
- 心脏结构的语义分割有助于评估患者特定的心脏形态和病理。
- 深度学习在医学图像分割方面取得了重大进展,但在领域转移(即训练数据和测试数据来自不同分布)的情况下保持性能仍然是一个挑战。
- 通过平衡联合训练方法和强度与空间增强技术,该研究提高了模型在已知和未知领域数据上的表现。
- 提出的全心脏分割方法,特别是在磁共振数据上,性能卓越,与仅使用CT数据训练的模型相比具有竞争力。
- 该方法具有生成患者特异性心脏双胞胎模型的潜力,这对于个性化治疗规划和电生理模拟具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图


Conditional Fetal Brain Atlas Learning for Automatic Tissue Segmentation
Authors:Johannes Tischer, Patric Kienast, Marlene Stümpflen, Gregor Kasprian, Georg Langs, Roxane Licandro
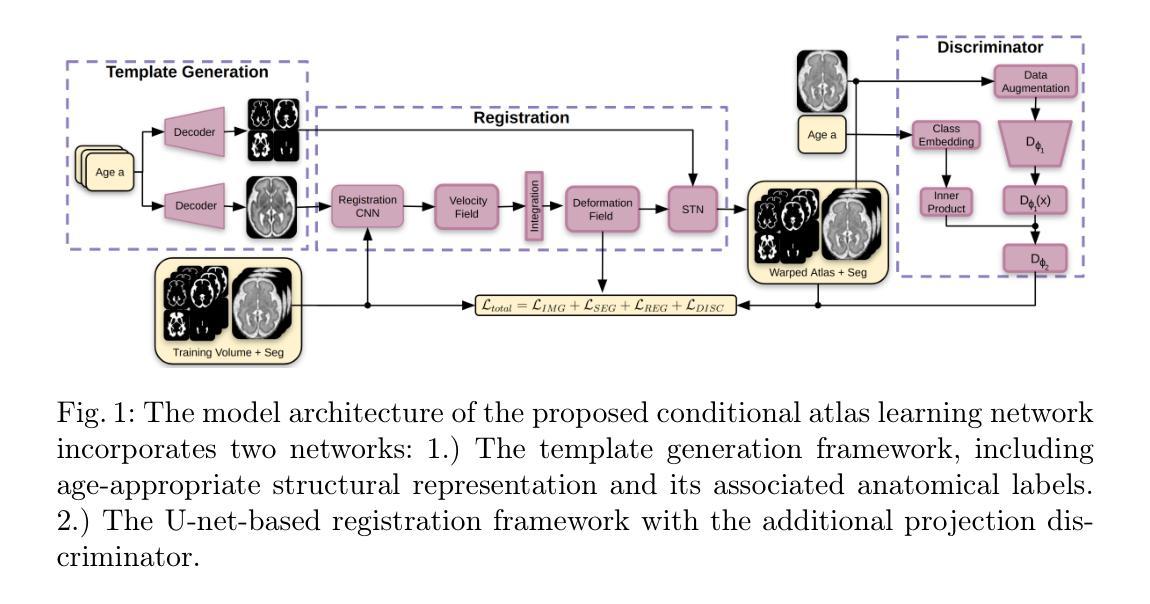
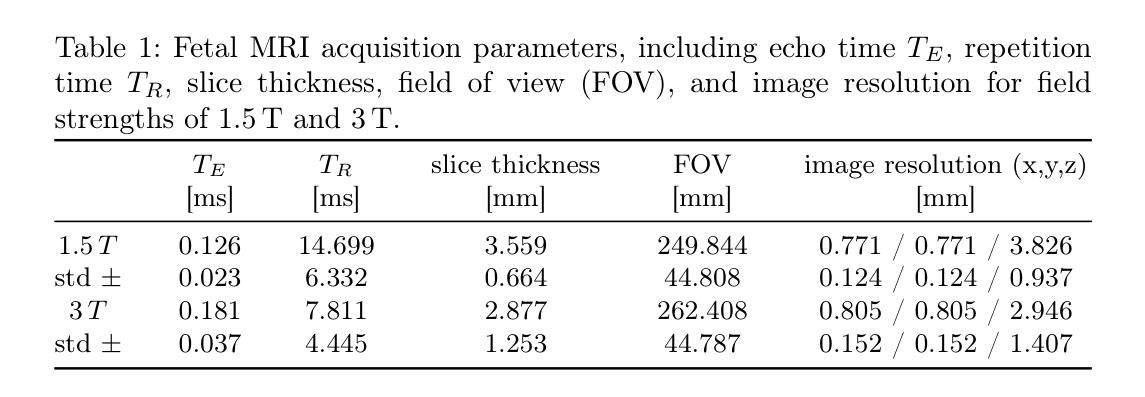
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the fetal brain has become a key tool for studying brain development in vivo. Yet, its assessment remains challenging due to variability in brain maturation, imaging protocols, and uncertain estimates of Gestational Age (GA). To overcome these, brain atlases provide a standardized reference framework that facilitates objective evaluation and comparison across subjects by aligning the atlas and subjects in a common coordinate system. In this work, we introduce a novel deep-learning framework for generating continuous, age-specific fetal brain atlases for real-time fetal brain tissue segmentation. The framework combines a direct registration model with a conditional discriminator. Trained on a curated dataset of 219 neurotypical fetal MRIs spanning from 21 to 37 weeks of gestation. The method achieves high registration accuracy, captures dynamic anatomical changes with sharp structural detail, and robust segmentation performance with an average Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 86.3% across six brain tissues. Furthermore, volumetric analysis of the generated atlases reveals detailed neurotypical growth trajectories, providing valuable insights into the maturation of the fetal brain. This approach enables individualized developmental assessment with minimal pre-processing and real-time performance, supporting both research and clinical applications. The model code is available at https://github.com/cirmuw/fetal-brain-atlas
胎儿脑部磁共振成像(MRI)已成为研究脑发育的关键工具。然而,由于脑部成熟的差异性、成像协议的不确定性以及妊娠期年龄(GA)的估算不确定,其评估仍然具有挑战性。为了克服这些问题,脑图谱提供了一个标准化的参考框架,通过在一个共同的坐标系中对图谱和受试者进行对齐,从而便于进行跨受试者之间的客观评估和比较。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型深度学习框架,用于生成连续、年龄特定的胎儿脑图谱,以进行实时胎儿脑组织分割。该框架结合了一个直接注册模型和一个条件鉴别器。该框架在由21至37周妊娠的神经典型胎儿MRI组成的精选数据集上进行训练。该方法实现了高注册精度,能够捕捉动态解剖结构变化并显示尖锐的结构细节,并且在六种脑组织上实现了平均Dice相似系数(DSC)为86.3%的稳健分割性能。此外,生成的图谱的体积分析揭示了详细的神经典型生长轨迹,为胎儿脑部成熟提供了宝贵的见解。这种方法能够实现个性化的发育评估,具有最小的预处理和实时性能,既支持研究也支持临床应用。模型代码可从https://github.com/cirmuw/fetal-brain-atlas获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, MICCAI Workshop on Perinatal Imaging, Placental and Preterm Image analysis
Summary
该文本介绍了基于深度学习的新型胎儿脑图谱生成框架,旨在用于胎儿脑组织分割和个体化发育评估。此框架结合了直接注册模型和条件判别器,可实现高效准确的注册、精细的解剖结构捕捉以及稳健的分割性能。同时,通过生成的图谱可详细了解胎儿神经系统的正常发育轨迹。此外,模型具有简洁快速的实时性能,可用于临床和研究应用。
Key Takeaways
- 胎儿脑MRI成像已成为研究脑发育的关键工具,但评估仍然具有挑战性。
- 脑图谱提供了一个标准化的参考框架,有助于客观评估和比较不同受试者之间的数据。
- 新型深度学习框架结合了直接注册模型和条件判别器,用于生成连续、特定年龄的胎儿脑图谱。
- 该框架实现了高注册精度和精细的结构细节捕捉,平均Dice相似系数(DSC)为86.3%。
- 通过生成的图谱,可详细了解胎儿神经系统的正常发育轨迹。
点此查看论文截图

TotalRegistrator: Towards a Lightweight Foundation Model for CT Image Registration
Authors:Xuan Loc Pham, Gwendolyn Vuurberg, Marjan Doppen, Joey Roosen, Tip Stille, Thi Quynh Ha, Thuy Duong Quach, Quoc Vu Dang, Manh Ha Luu, Ewoud J. Smit, Hong Son Mai, Mattias Heinrich, Bram van Ginneken, Mathias Prokop, Alessa Hering
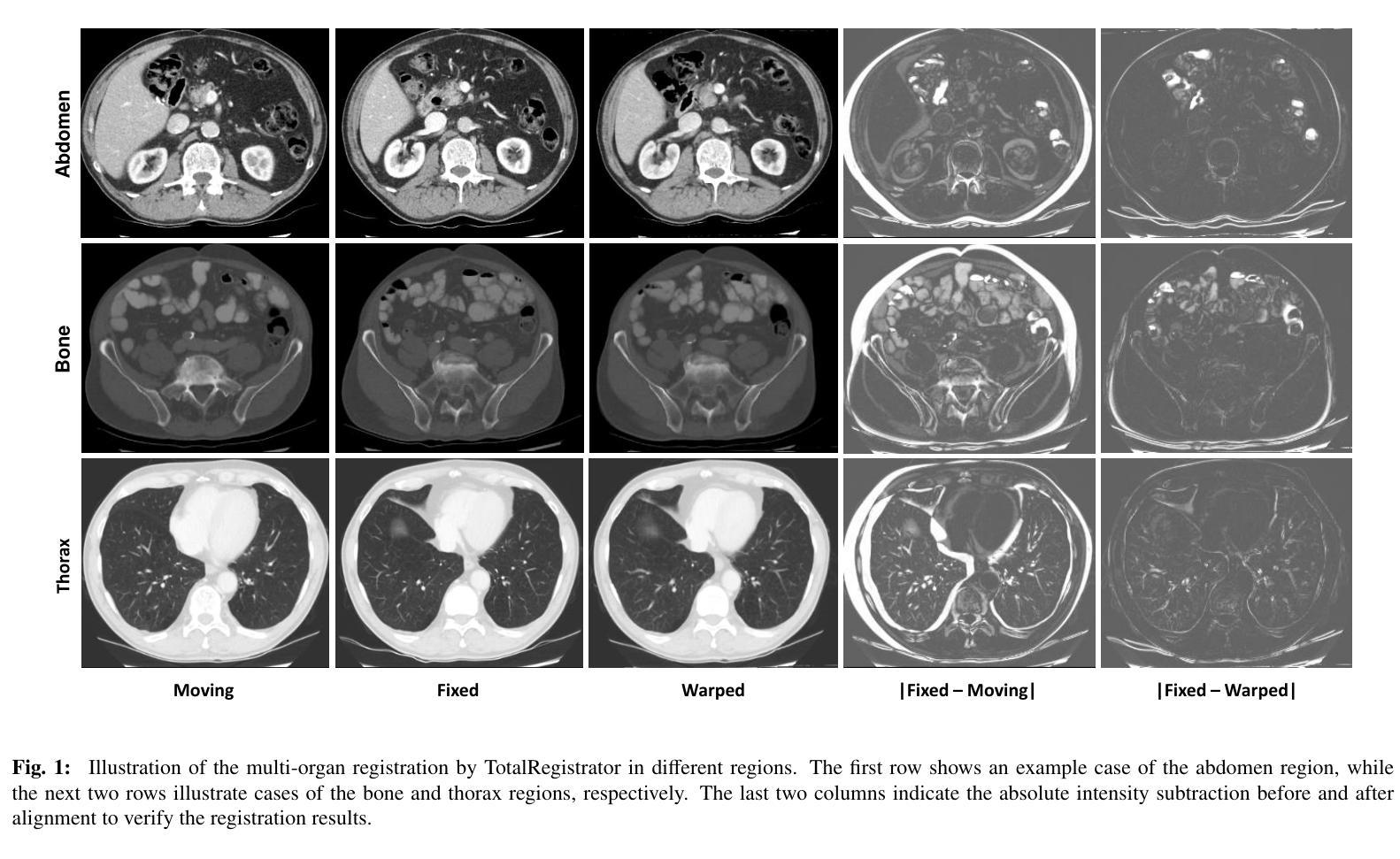
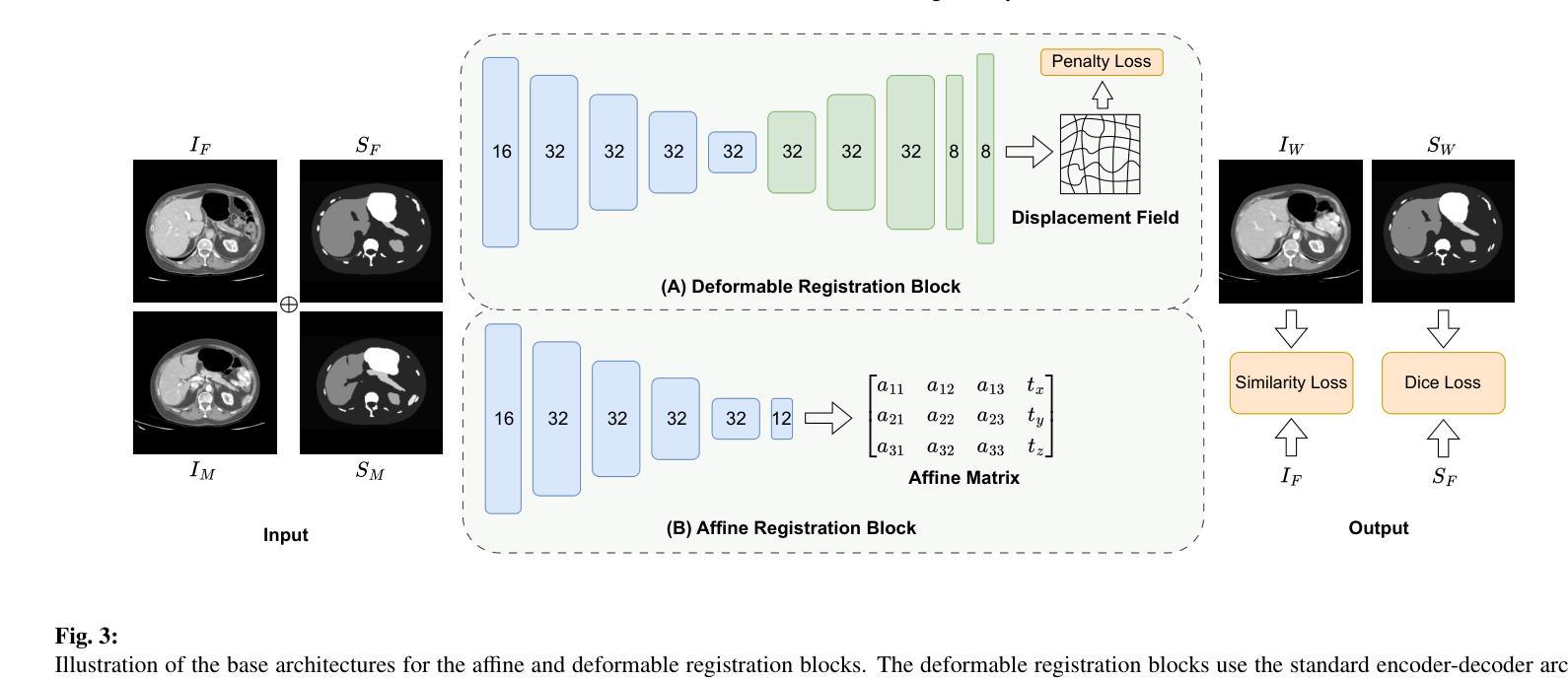
Image registration is a fundamental technique in the analysis of longitudinal and multi-phase CT images within clinical practice. However, most existing methods are tailored for single-organ applications, limiting their generalizability to other anatomical regions. This work presents TotalRegistrator, an image registration framework capable of aligning multiple anatomical regions simultaneously using a standard UNet architecture and a novel field decomposition strategy. The model is lightweight, requiring only 11GB of GPU memory for training. To train and evaluate our method, we constructed a large-scale longitudinal dataset comprising 695 whole-body (thorax-abdomen-pelvic) paired CT scans from individual patients acquired at different time points. We benchmarked TotalRegistrator against a generic classical iterative algorithm and a recent foundation model for image registration. To further assess robustness and generalizability, we evaluated our model on three external datasets: the public thoracic and abdominal datasets from the Learn2Reg challenge, and a private multiphase abdominal dataset from a collaborating hospital. Experimental results on the in-house dataset show that the proposed approach generally surpasses baseline methods in multi-organ abdominal registration, with a slight drop in lung alignment performance. On out-of-distribution datasets, it achieved competitive results compared to leading single-organ models, despite not being fine-tuned for those tasks, demonstrating strong generalizability. The source code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/DIAGNijmegen/oncology_image_registration.git.
图像配准是临床实践中对纵向和多阶段CT图像进行分析的基本技术。然而,大多数现有方法都是针对单器官应用而定制的,限制了它们在其它解剖区域的应用。本研究提出了TotalRegistrator,这是一种图像配准框架,它采用标准UNet架构和一种新的场分解策略,能够同时对准多个解剖区域。该模型轻量级,只需11GB的GPU内存即可进行训练。为了训练和评估我们的方法,我们构建了一个大规模纵向数据集,包含来自同一患者在不同时间点采集的695个全身(胸腹盆)配对CT扫描。我们将TotalRegistrator与一种通用的经典迭代算法和一种最新的图像配准基础模型进行了比较。为了进一步评估其鲁棒性和通用性,我们在三个外部数据集上评估了我们的模型:来自Learn2Reg挑战的公共胸部和腹部数据集,以及来自合作医院的私人多阶段腹部数据集。在内部数据集上的实验结果表明,在多数器官腹部配准方面,所提出的方法通常超过了基线方法,但在肺对齐方面的性能略有下降。在超出分布的数据集上,尽管没有进行针对这些任务的微调,但它仍然取得了与领先的单器官模型竞争的结果,显示出强大的泛化能力。源代码将在以下网址公开提供:https://github.com/DIAGNijmegen/oncology_image_registration.git。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
图像配准是临床实践中分析纵向和多阶段CT图像的基本技术。然而,大多数现有方法都是针对单器官应用的,限制了它们在其他解剖区域的推广。本研究提出了TotalRegistrator,这是一种图像配准框架,采用标准UNet架构和新型场域分解策略,能够同时对准多个解剖区域。该模型轻量级,仅需11GB的GPU内存进行训练。为了训练和评估我们的方法,我们构建了一个大规模纵向数据集,包含来自不同时间点采集的695例全身(胸腹盆)配对CT扫描。我们将TotalRegistrator与通用的经典迭代算法和最近的图像配准基础模型进行了比较。为了进一步评估其稳健性和通用性,我们在三个外部数据集上评估了我们的模型:来自Learn2Reg挑战的公共胸部和腹部数据集,以及来自合作医院的私人多阶段腹部数据集。在内部数据集上的实验结果表明,在多数器官腹部配准方面,所提出的方法总体上超过了基线方法,但在肺对齐性能方面略有下降。在外部数据集上,尽管未针对这些任务进行微调,但与领先的单一器官模型相比,它取得了具有竞争力的结果,显示出强大的泛化能力。源代码将公开在:https://github.com/DIAGNijmegen/oncology_image_registration.git。
关键见解
- TotalRegistrator是一种多解剖区域图像配准框架,基于标准UNet架构和新颖场域分解策略。
- 该框架能够同时进行多区域配准,展示了强大的性能。
- 通过大规模纵向数据集进行训练和评估,包含来自不同时间点的全身CT扫描。
- TotalRegistrator在多数器官腹部配准方面优于基线方法。
- 在未针对特定任务微调的情况下,该模型在外部数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。
- TotalRegistrator在肺对齐性能方面略有不足,但仍具有潜力进行进一步优化。
- 源代码将公开供公众访问,以便进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

3D Mapping of Static Magnetic Field Magnitude and AxialComponents around a total body 3T MRI clinical scanner
Authors:Francesco Girardello, Maria Antonietta D’Avanzo, Massimo Mattozzi, Victorian Michele Ferro, Giuseppe Acri, Valentina Hartwig
Objective. The technology employed in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems has evolved continuously, resulting in MRI scanners with stronger static magnetic fields (SMF) B0, faster and stronger gradient magnetic fields, and more powerful radiofrequency transmission coils. The most well-known hazard associated with an MRI environment is the projectile effect due to Spatial Field Gradient (SFG). Furthermore, movement through the SFG generates a time-varying magnetic field, which in turn induces a voltage in body tissues. This has the potential to result in a range of physiological symptoms, including headache, nausea, vertigo, phosphenes, numbness, tingling, loss of proprioception, and balance disturbances. Approach. The methodology outlined in this study provides a comprehensive and reliable approach to creating a 3D map of the SMF (fringe field) around a clinical MRI facility. The methodology involves measuring the unperturbed B field, including magnitude and axial components, in specific points and subsequently performing a mathematical procedure involving fitting and interpolation. Main results. Fringe field magnitude and axial components 3D maps are presented for a 3T whole-body MRI scanner for clinical application located in a hospital facility. Significance. The map obtained could be used for a number of purposes, including the evaluation of hazard. This could be achieved by using digital tools to create a simulation of all types of MRI workers movements within the facility. The map could also be used for the training and education of MRI operators, with a view to establishing best practices. The estimation of magnetic field axial components represents a valuable enhancement, as these data can be used to calculate induced electric fields during rotational movements, such as those of the head or torso.
目标:磁共振成像(MRI)系统所采用的技术不断发展,导致MRI扫描仪的静态磁场(SMF)B0更强、梯度磁场更快更强,射频传输线圈的性能也更强大。与MRI环境相关的最知名的危害是由于空间场梯度(SFG)引起的投射效应。此外,通过SFG的移动会产生时变磁场,进而在人体组织中感应出电压。这可能会导致一系列生理症状,包括头痛、恶心、眩晕、眼冒金星、麻木、刺痛、失去位置感和平衡失调。
方法:本研究中概述的方法提供了一个全面可靠的方法来创建临床MRI设施周围SMF(边缘场)的3D地图。该方法涉及测量特定点的未受干扰的B场,包括幅度和轴向分量,随后进行涉及拟合和插值的数学程序。
主要结果:针对位于医院设施的用于临床应用的3T全身MRI扫描仪,呈现了边缘场幅度和轴向分量的3D地图。
意义:所获得的地图可用于多种用途,包括危险评估。这可以通过使用数字工具模拟MRI设施内所有类型的工人移动来实现。该地图也可用于MRI操作员的培训和教育,目的是建立最佳实践。估计磁场轴向分量是一个有价值的增强,因为这些数据可用于计算旋转运动(如头部或躯干)期间感应的电场。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了磁共振成像(MRI)系统的技术进步,包括更强的静态磁场(SMF)B0、更快的梯度磁场和更强大的射频传输线圈的应用。重点阐述了因空间场梯度(SFG)而产生的项目射效应和随时间变化的磁场对人体的影响,并可能引发一系列生理症状。研究了一种为临床MRI设施周围创建SMF(边缘场)三维地图的可靠方法,并对结果进行了介绍。此地图可应用于评估危害、训练和教育MRI操作人员等。
Key Takeaways
- MRI技术不断进步,包括更强的静态磁场(SMF)、更快的梯度磁场和更强大的射频传输线圈的应用。
- 空间场梯度(SFG)导致的项目射效应是MRI环境中最为人知的风险。
- 人体通过SFG产生的随时间变化的磁场会在体内感应出电压,可能导致一系列生理症状。
- 研究提供了一种为临床MRI设施周围创建SMF(边缘场)三维地图的可靠方法。
- 该方法包括测量未受干扰的B场(包括大小和轴向分量)在特定点,然后进行数学拟合和插值过程。
- 获得了适用于医院设施中用于临床应用的3T全身MRI扫描仪的边缘场大小和轴向分量的三维地图。
点此查看论文截图

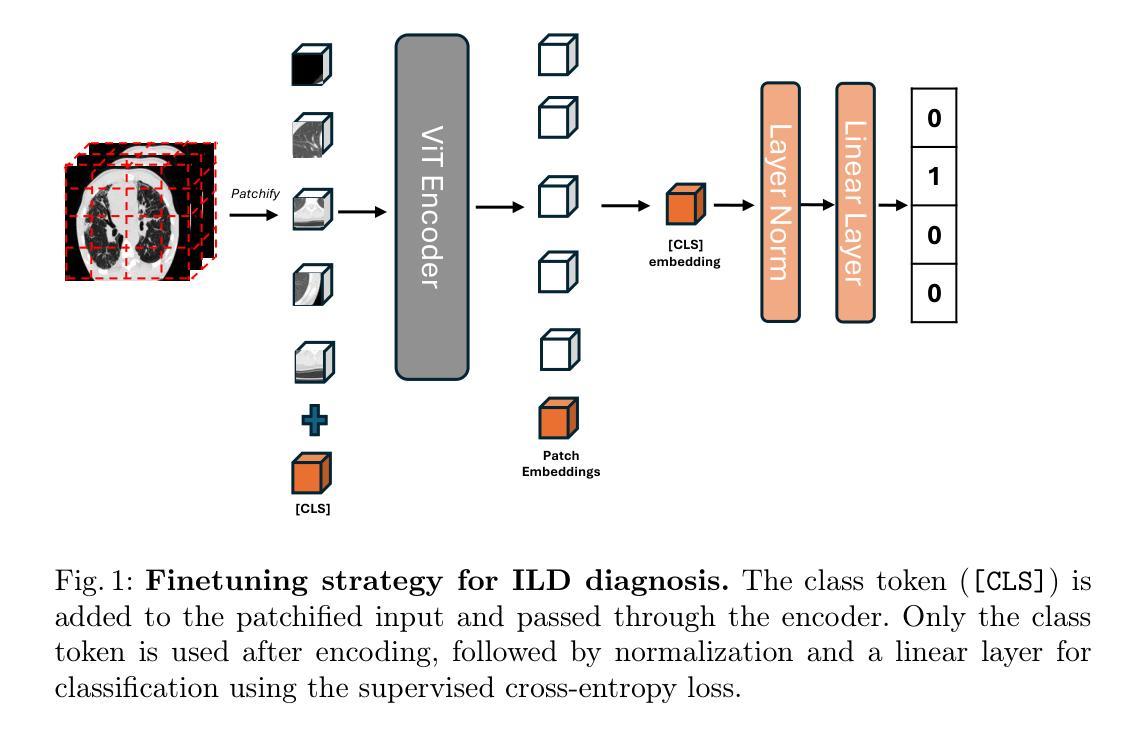
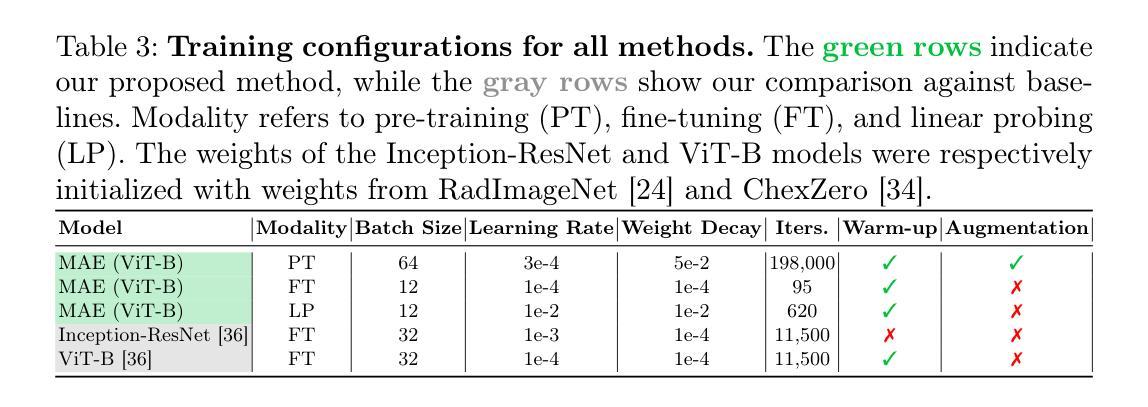
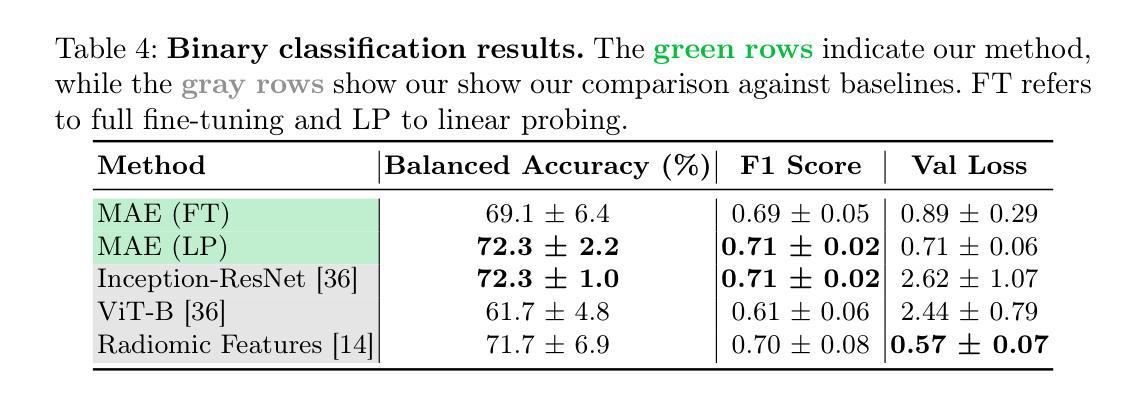
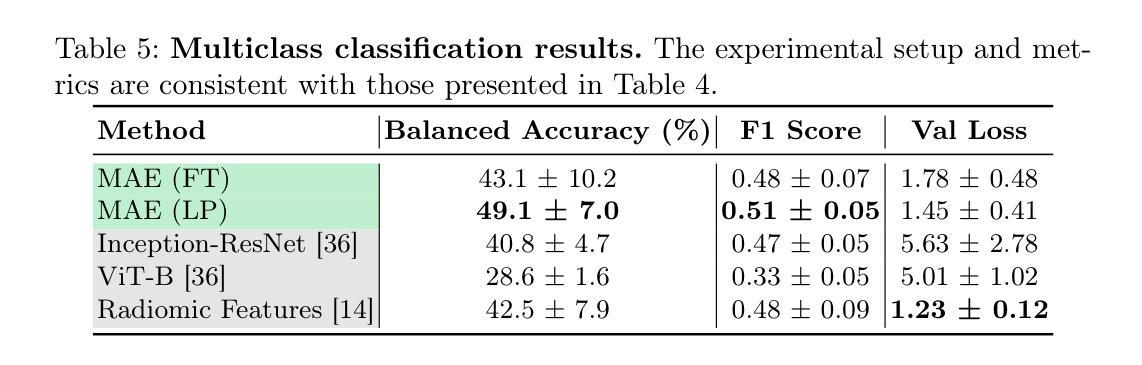
Unmasking Interstitial Lung Diseases: Leveraging Masked Autoencoders for Diagnosis
Authors:Ethan Dack, Lorenzo Brigato, Vasilis Dedousis, Janine Gote-Schniering, Cheryl, Hanno Hoppe, Aristomenis Exadaktylos, Manuela Funke-Chambour, Thomas Geiser, Andreas Christe, Lukas Ebner, Stavroula Mougiakakou
Masked autoencoders (MAEs) have emerged as a powerful approach for pre-training on unlabelled data, capable of learning robust and informative feature representations. This is particularly advantageous in diffused lung disease research, where annotated imaging datasets are scarce. To leverage this, we train an MAE on a curated collection of over 5,000 chest computed tomography (CT) scans, combining in-house data with publicly available scans from related conditions that exhibit similar radiological patterns, such as COVID-19 and bacterial pneumonia. The pretrained MAE is then fine-tuned on a downstream classification task for diffused lung disease diagnosis. Our findings demonstrate that MAEs can effectively extract clinically meaningful features and improve diagnostic performance, even in the absence of large-scale labelled datasets. The code and the models are available here: https://github.com/eedack01/lung_masked_autoencoder.
掩码自编码器(MAEs)作为一种强大的无标签数据预训练方法已经崭露头角,它能够学习稳健且富有信息量的特征表示。这在罕见肺病研究中具有明显优势,因为相关的标注成像数据集稀缺。为了利用这一优势,我们在精选的超过5000个胸部计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描数据集上训练MAE,结合内部数据与公开可用的、具有相似放射学模式的扫描数据,如COVID-19和细菌性肺炎等。然后,对预训练的MAE进行微调,用于针对罕见肺病的下游分类任务进行诊断。我们的研究结果表明,MAEs可以有效地提取临床有意义的特征,即使在缺乏大规模标注数据集的情况下也能提高诊断性能。相关代码和模型可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/eedack01/lung_masked_autoencoder。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了使用Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在未经标注的数据上进行预训练的方法,特别是在肺部疾病研究中的应用。通过在超过5000份胸部计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描数据上进行训练,并结合内部数据和公开可用的类似疾病扫描数据,如COVID-19和细菌性肺炎等,MAE模型被用于对下游分类任务进行微调以诊断肺部疾病。研究发现,即使没有大规模标注数据集,MAEs也能有效地提取临床上有意义的特征并改善诊断性能。代码和模型已公开发布于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- Masked autoencoders (MAEs)成为无标签数据预训练的有效方法。
- 在肺部疾病研究中,MAEs可学习稳健且具信息量的特征表示。
- 利用超过5000份胸部CT扫描数据进行训练,结合内部数据和公开可用数据。
- MAE模型通过微调用于诊断肺部疾病的下游分类任务。
- MAEs能在无大规模标注数据集的情况下提取临床有意义特征并改善诊断性能。
点此查看论文截图



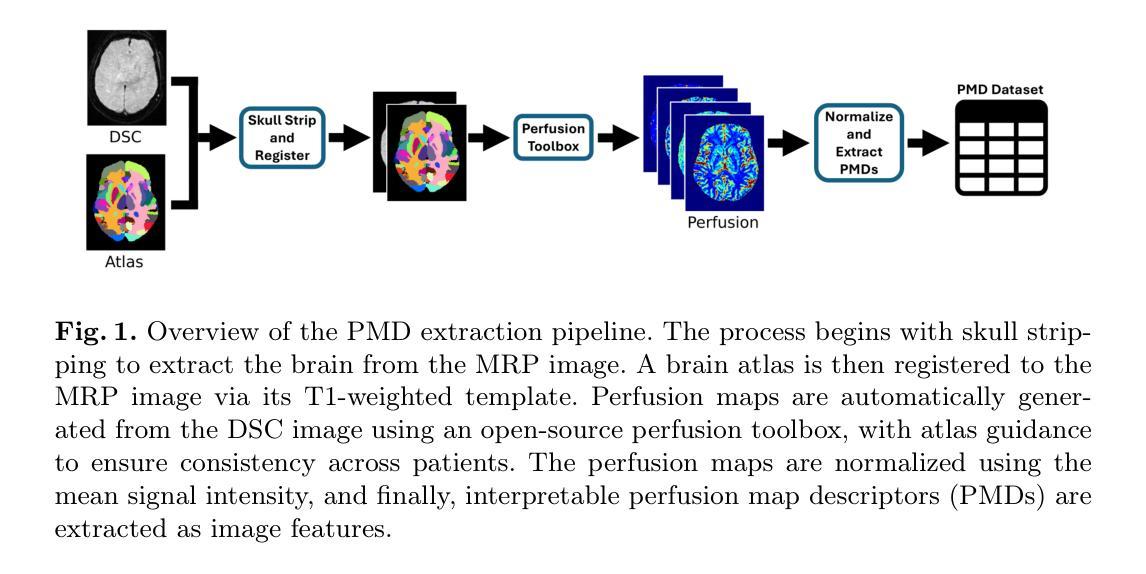
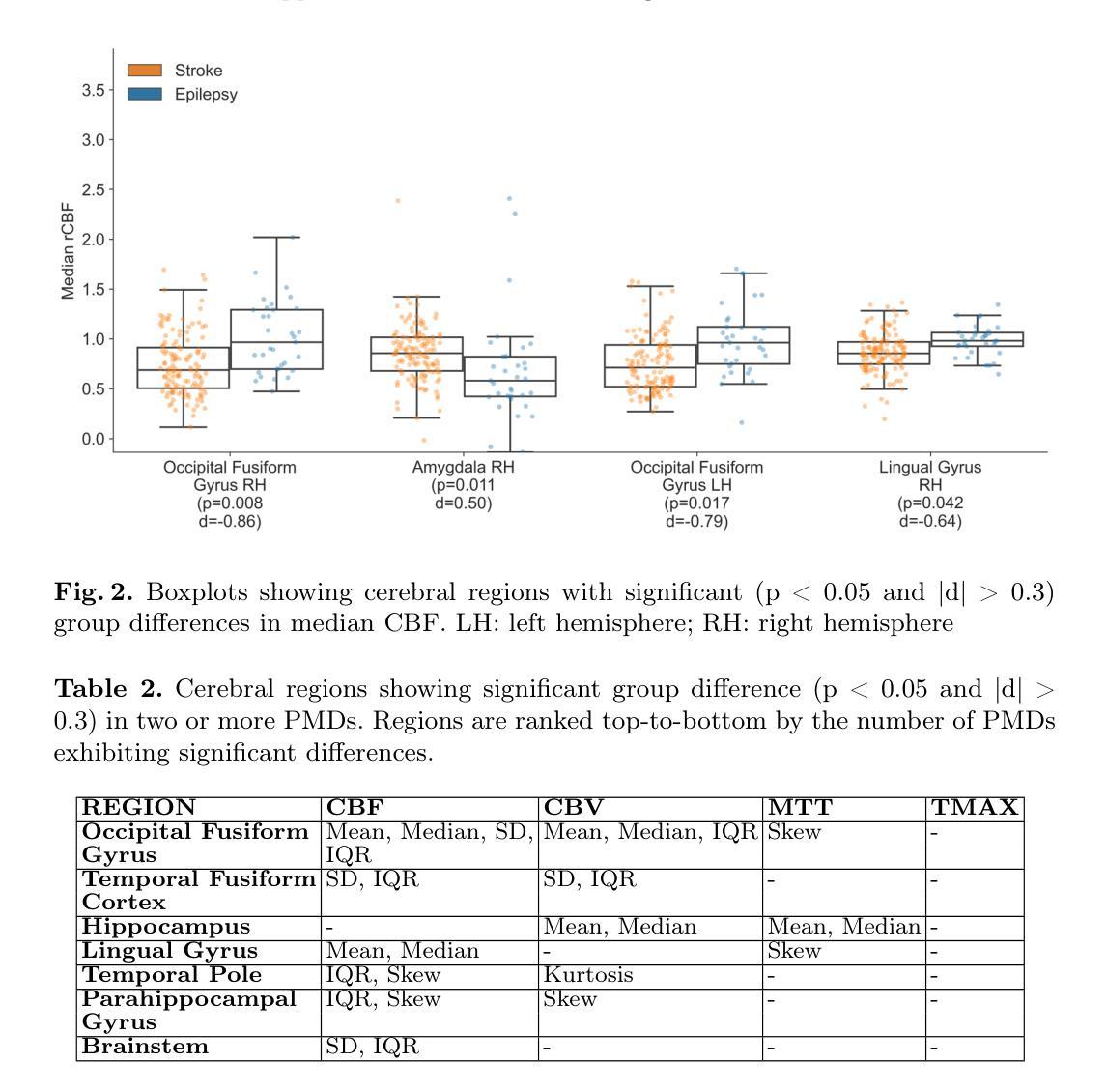
Discriminating Distal Ischemic Stroke from Seizure-Induced Stroke Mimics Using Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI
Authors:Marijn Borghouts, Richard McKinley, Josien Pluim, Manuel Köstner, Roland Wiest, Ruisheng Su
Distinguishing acute ischemic strokes (AIS) from stroke mimics (SMs), particularly in cases involving medium and small vessel occlusions, remains a significant diagnostic challenge. While computed tomography (CT) based protocols are commonly used in emergency settings, their sensitivity for detecting distal occlusions is limited. This study explores the potential of magnetic resonance perfusion (MRP) imaging as a tool for differentiating distal AIS from epileptic seizures, a prevalent SM. Using a retrospective dataset of 162 patients (129 AIS, 33 seizures), we extracted region-wise perfusion map descriptors (PMDs) from dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) images. Statistical analyses identified several brain regions, located mainly in the temporal and occipital lobe, exhibiting significant group differences in certain PMDs. Hemispheric asymmetry analyses further highlighted these regions as discriminative. A logistic regression model trained on PMDs achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.90, and an area under the precision recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.74, with a specificity of 92% and a sensitivity of 73%, suggesting strong performance in distinguishing distal AIS from seizures. These findings support further exploration of MRP-based PMDs as interpretable features for distinguishing true strokes from various mimics. The code is openly available at our GitHub https://github.com/Marijn311/PMD_extraction_and_analysis{github.com/Marijn311/PMD\_extraction\_and\_analysis
急性缺血性中风(AIS)与中风模仿者(SMs)之间的区分,特别是在涉及中型和血管闭塞的情况下,仍然是一个重要的诊断挑战。虽然基于计算机断层扫描(CT)的协议在紧急情况下常用,但其在检测远端闭塞方面的敏感性有限。本研究探讨了磁共振灌注(MRP)成像在区分远端AIS与常见的中风模仿者癫痫发作中的潜力。通过回顾性数据集(包括129例AIS和33例癫痫发作)的样本,我们从动态磁敏感对比(DSC)图像中提取了区域灌注图描述符(PMDs)。统计分析确定了几个大脑区域,主要位于颞叶和枕叶,在某些PMDs上存在明显的组间差异。半球不对称分析进一步强调了这些区域的区别。基于PMDs训练的逻辑回归模型达到了接收特征曲线下的区域(AUROC)为0.90和精度召回曲线下的区域(AUPRC)为0.74,特异性为92%,敏感性为73%,在区分远端AIS与癫痫发作方面表现出强大的性能。这些发现支持进一步探索基于MRP的PMDs作为区分真实中风和各种模仿者的可解释特征。代码可在我们的GitHub上公开访问:https://github.com/Marijn311/PMD_extraction_and_analysis。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了磁共振灌注(MRP)成像在区分远端急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)与常见的卒中模仿者(如癫痫)方面的潜力。通过对动态磁敏感对比(DSC)图像的区域灌注图描述符(PMDs)进行分析,研究结果显示某些大脑区域(主要在颞叶和枕叶)在PMDs上有显著差异,表明这些区域在区分AIS和癫痫时具有鉴别力。利用PMDs训练的逻辑回归模型表现出较高的诊断性能,对区分远端AIS和癫痫具有较强的潜力。研究结果表明MRP成像技术为鉴别真正卒中与不同模仿者的提供了重要的可能性。可访问的代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)与卒中模仿者(SMs)的区分,尤其在涉及中小血管闭塞的情况下,仍是一个重大挑战。
- 计算机断层扫描(CT)在检测远端闭塞方面的灵敏度有限,而磁共振灌注(MRP)成像技术可能是一个有效的替代工具。
- 通过分析动态磁敏感对比(DSC)图像的区域灌注图描述符(PMDs),研究发现某些大脑区域在PMDs上存在显著差异。这些区域主要位于颞叶和枕叶。
- 通过PMDs训练的逻辑回归模型展现出强大的诊断性能,为区分远端AIS和癫痫提供了重要依据。
- 该模型的诊断表现可通过两个关键指标来衡量:曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.90,精确召回曲线下面积(AUPRC)为0.74,特异性为92%,敏感性为73%。这些结果支持进一步探索使用MRP成像技术来区分真实卒中和各种模仿者。
- 研究结果强调了磁共振灌注成像在卒中诊断中的潜在价值,特别是在区分真正卒中与不同模仿者方面。这为未来的卒中诊断和治疗提供了新的视角。
点此查看论文截图

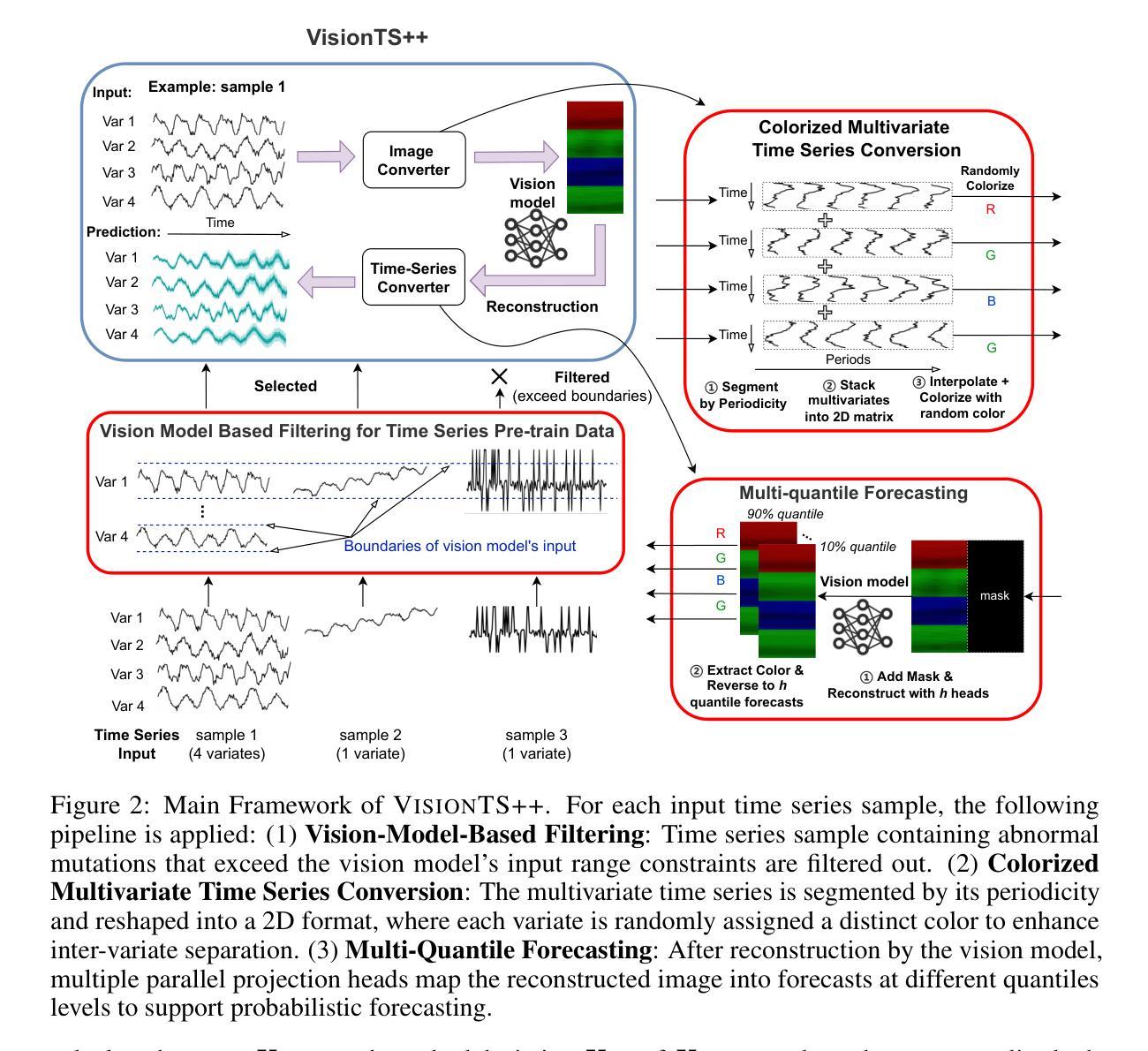
VisionTS++: Cross-Modal Time Series Foundation Model with Continual Pre-trained Visual Backbones
Authors:Lefei Shen, Mouxiang Chen, Xu Liu, Han Fu, Xiaoxue Ren, Jianling Sun, Zhuo Li, Chenghao Liu
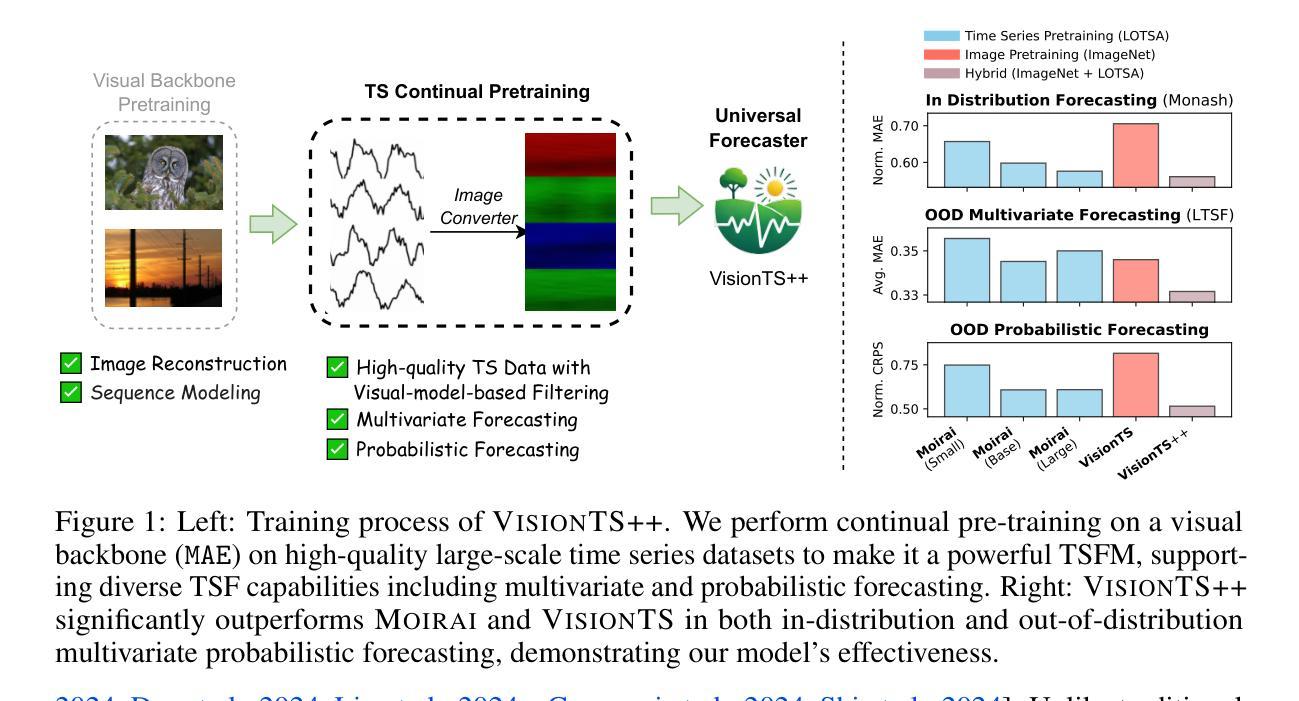
Recent studies have revealed that vision models pre-trained on images can perform well in time series forecasting by reformulating forecasting as an image reconstruction task, suggesting their potential as universal time series foundation models. However, effective cross-modal transfer from vision to time series remains challenging due to three key discrepancies: (1) data-modality gap between structured, bounded image data and unbounded, heterogeneous time series; (2) multivariate-forecasting gap between standard RGB three-channel-based vision models and the need to model time series with arbitrary numbers of variates; and (3) probabilistic-forecasting gap between the deterministic output formats of most vision models and the requirement for uncertainty-aware probabilistic predictions. To bridge these gaps, we propose VisionTS++, a vision-model-based TSFM that performs continual pre-training on large-scale time series datasets, including 3 innovations: (1) a vision-model-based filtering mechanism to identify high-quality time series data, thereby mitigating modality gap and improving pre-training stability, (2) a colorized multivariate conversion method that transforms multivariate time series into multi-subfigure RGB images, capturing complex inter-variate dependencies; and (3) a multi-quantile forecasting approach using parallel reconstruction heads to generate forecasts of different quantile levels, thus more flexibly approximating arbitrary output distributions without restrictive prior distributional assumptions. Evaluated on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution TSF benchmarks, \model achieves SOTA results, outperforming specialized TSFMs by 6%-44% in MSE reduction and ranking first in 9 out of 12 probabilistic forecasting settings. Our work establishes a new paradigm for cross-modal knowledge transfer, advancing the development of universal TSFMs.
最近的研究表明,通过重新制定预测为图像重建任务,预先在图像上训练过的视觉模型在时间序列预测中表现良好,这表明了它们作为通用时间序列基础模型的潜力。然而,由于三个主要差异,从视觉到时间序列的有效跨模态转移仍然具有挑战性:(1)结构化、有界图像数据与无界、异质时间序列之间的数据模态差距;(2)基于标准RGB三通道的视觉模型与需要对任意数量的变量进行时间序列建模之间的多元预测差距;(3)大多数视觉模型的确定性输出格式与需要了解不确定性的概率预测之间的概率预测差距。为了弥这些差距,我们提出了VisionTS++,这是一个基于视觉模型的TSFM,可以在大规模时间序列数据集上进行持续预训练,包括三项创新:(1)基于视觉模型的过滤机制,用于识别高质量的时间序列数据,从而减轻模态差距并提高预训练稳定性;(2)彩色多元转换方法,将多元时间序列转换为多子图RGB图像,捕捉复杂的变量间依赖关系;(3)使用并行重建头进行多分位预测,生成不同分位水平的预测,从而更灵活地近似任意输出分布,而没有限制性的先验分布假设。在内外分布的时间序列预测基准测试上进行了评估,该模型达到了最先进的成果,在均方误差减少方面比专门的时间序列模型高出6%~44%,在12个概率预测设置中的9个中排名第一。我们的工作为跨模态知识转移建立了新的范式,推动了通用TSFMs的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages
Summary
最新研究表明,预训练图像视觉模型通过重新制定时间序预测为图像重建任务,在时序预测中表现良好,显示出其作为通用时间序列基础模型的潜力。然而,从视觉到时间序列的有效跨模态迁移面临三大挑战。为缩小这些差距,提出VisionTS++模型,该模型在大型时间序列数据集上进行持续预训练,包括三项创新:基于视觉模型的过滤机制、彩色多元转换方法和多分位预测方法。该模型在时序预测基准测试中表现卓越,相比专业时序预测模型减少了6%-44%的MSE误差,并在概率预测设置中排名第一。本研究为跨模态知识迁移建立了新范式,推动了通用时序预测模型的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉模型通过图像重建任务在时间序列预测中表现出良好的性能。
- 从视觉到时序的跨模态迁移存在三大挑战:数据模态差距、多元预测差距和概率预测差距。
- VisionTS++模型通过三项创新技术缩小了这些差距:基于视觉模型的过滤机制、彩色多元转换方法和多分位预测方法。
- VisionTS++模型在时序预测基准测试中表现卓越,相比专业时序预测模型有所改进。
- 该研究为跨模态知识迁移提供了新的范例。
点此查看论文截图

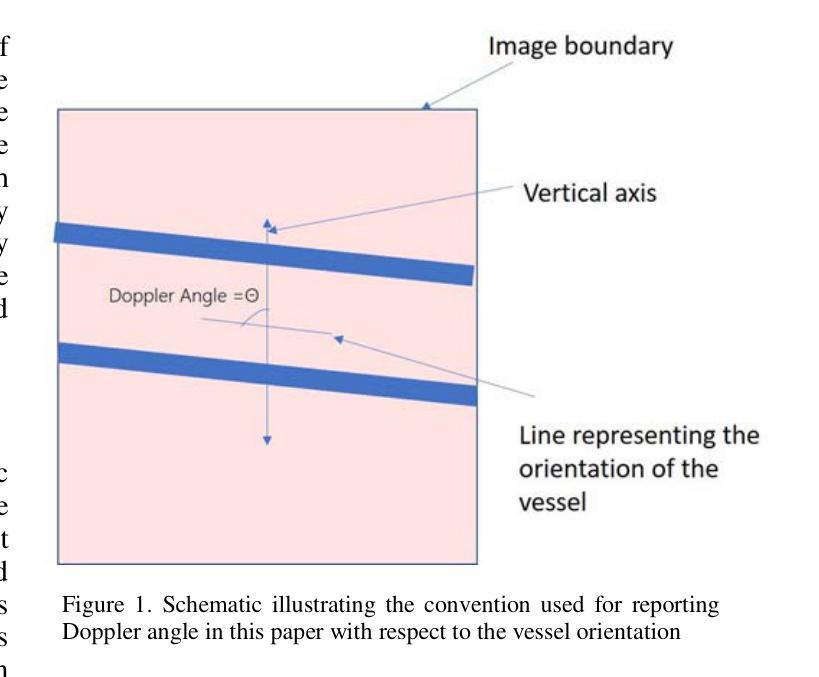
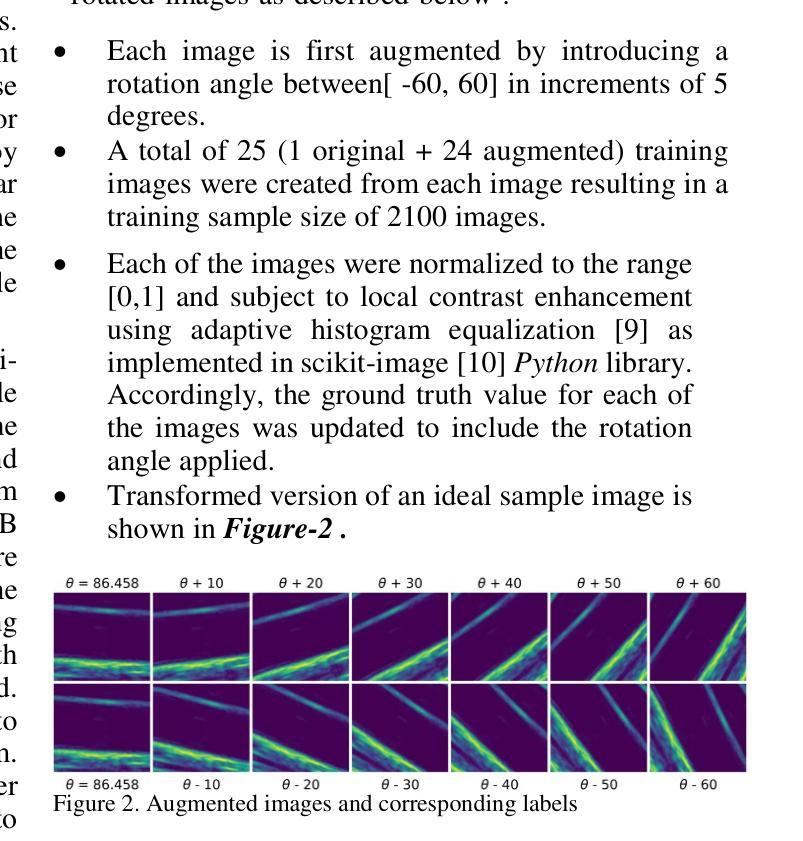
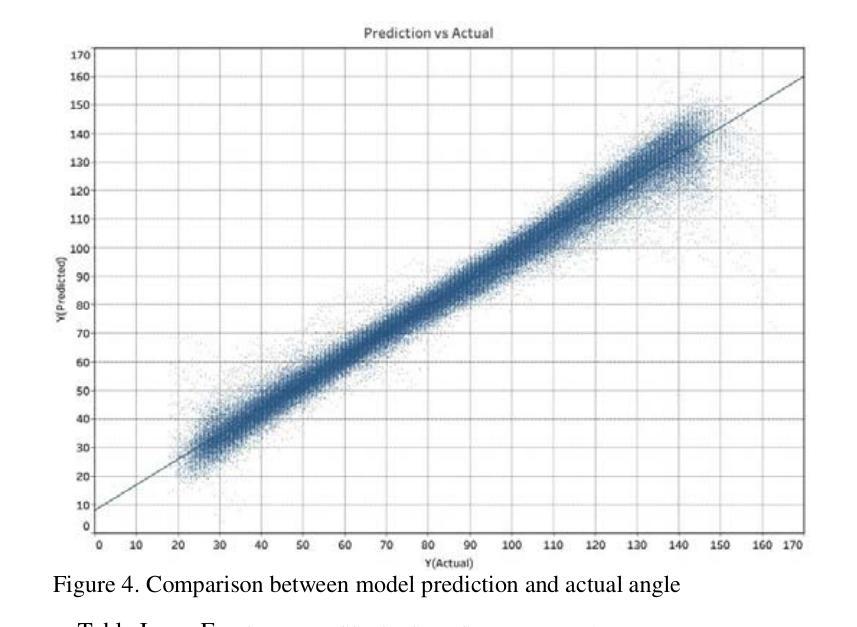
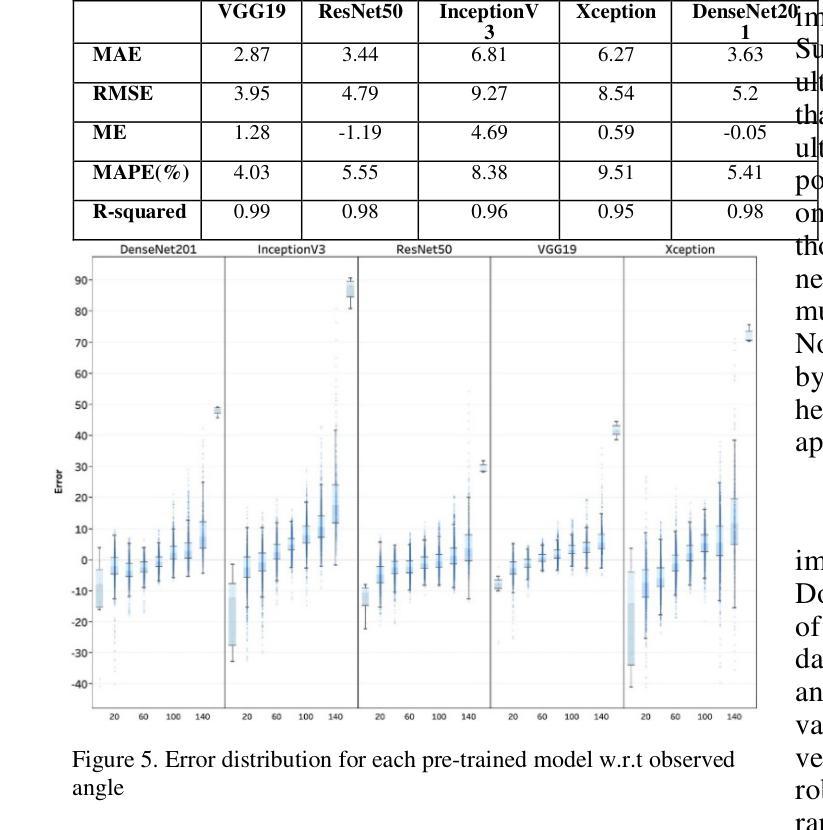
Automated ultrasound doppler angle estimation using deep learning
Authors:Nilesh Patil, Ajay Anand
Angle estimation is an important step in the Doppler ultrasound clinical workflow to measure blood velocity. It is widely recognized that incorrect angle estimation is a leading cause of error in Doppler-based blood velocity measurements. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based approach for automated Doppler angle estimation. The approach was developed using 2100 human carotid ultrasound images including image augmentation. Five pre-trained models were used to extract images features, and these features were passed to a custom shallow network for Doppler angle estimation. Independently, measurements were obtained by a human observer reviewing the images for comparison. The mean absolute error (MAE) between the automated and manual angle estimates ranged from 3.9{\deg} to 9.4{\deg} for the models evaluated. Furthermore, the MAE for the best performing model was less than the acceptable clinical Doppler angle error threshold thus avoiding misclassification of normal velocity values as a stenosis. The results demonstrate potential for applying a deep-learning based technique for automated ultrasound Doppler angle estimation. Such a technique could potentially be implemented within the imaging software on commercial ultrasound scanners.
角度估计是多普勒超声血流速度测量中的关键步骤。人们普遍认为,角度估计不正确是多普勒血流速度测量的主要误差来源。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的自动化多普勒角度估计方法。该方法使用包括图像增强在内的2100张人体颈动脉超声图像进行开发。我们使用五个预训练模型提取图像特征,并将这些特征传递给自定义的浅层网络进行多普勒角度估计。此外,还通过人类观察者独立审查图像进行比较测量。评估模型的自动和手动角度估计之间的平均绝对误差(MAE)范围从3.9°到9.4°。此外,最佳性能模型的MAE低于可接受的临床多普勒角度误差阈值,从而避免了将正常速度值错误分类为狭窄。结果表明,将基于深度学习的技术应用于自动化超声多普勒角度估计具有潜力。这样的技术有可能在商用超声扫描仪的成像软件中实施。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
超声多普勒角度估计是测量血流速度的重要步骤。不正确的角度估计是导致多普勒血流速度测量误差的主要原因。本文提出了一种基于深度学习的自动化多普勒角度估计方法。该方法使用包括图像增强在内的2100张人类颈动脉超声图像进行开发。五个预训练模型用于提取图像特征,这些特征被传递给一个自定义浅层网络进行多普勒角度估计。同时,通过人类观察者对图像进行回顾性评估以获得对比测量值。自动和手动角度估计之间的平均绝对误差(MAE)在模型评估中的范围为$ 3.9^\circ到 9.4^\circ $之间。而且表现最好的模型的MAE低于可接受的临床多普勒角度误差阈值,避免了正常速度值被误分类为狭窄的可能性。结果证明了基于深度学习技术的自动化超声多普勒角度估计方法的潜力。这样的技术有可能被实现在商业超声扫描仪的成像软件中。
要点
- 超声多普勒角度估计是血流速度测量的关键步骤,其准确性对结果至关重要。
- 不正确的角度估计是导致多普勒血流速度测量误差的主要原因之一。
- 本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的自动化多普勒角度估计方法,利用预训练模型提取图像特征并进行估计。
- 研究使用了大量的人类颈动脉超声图像进行模型训练和验证。
- 与手动测量相比,自动估计的平均绝对误差在可接受范围内。
- 最佳模型的误差低于临床可接受的误差阈值,可以避免误判正常速度值为狭窄情况。
点此查看论文截图

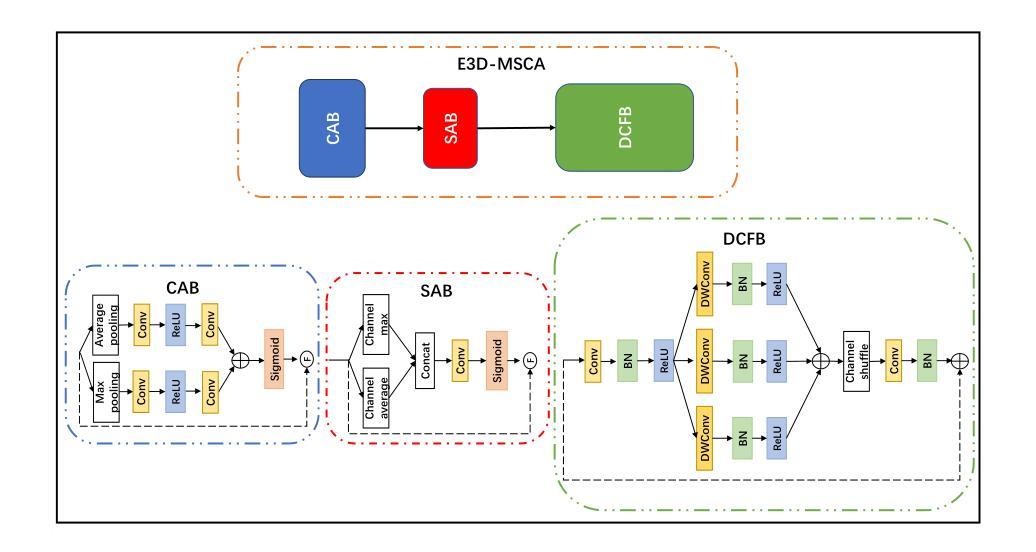
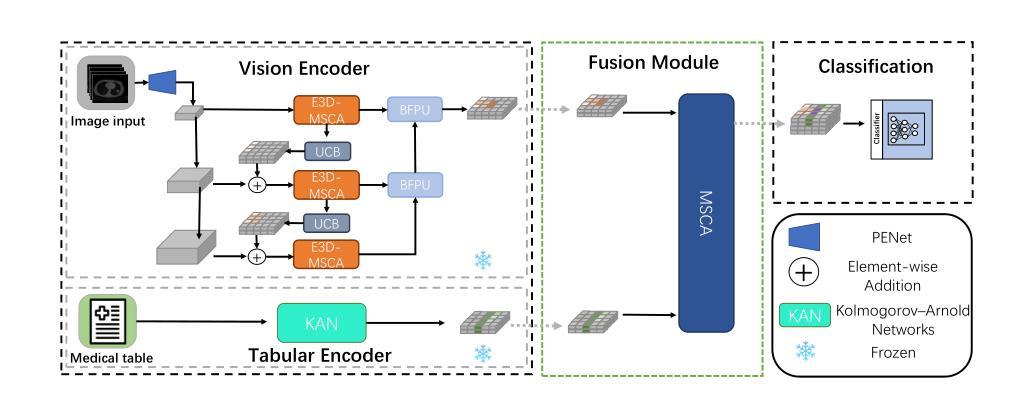
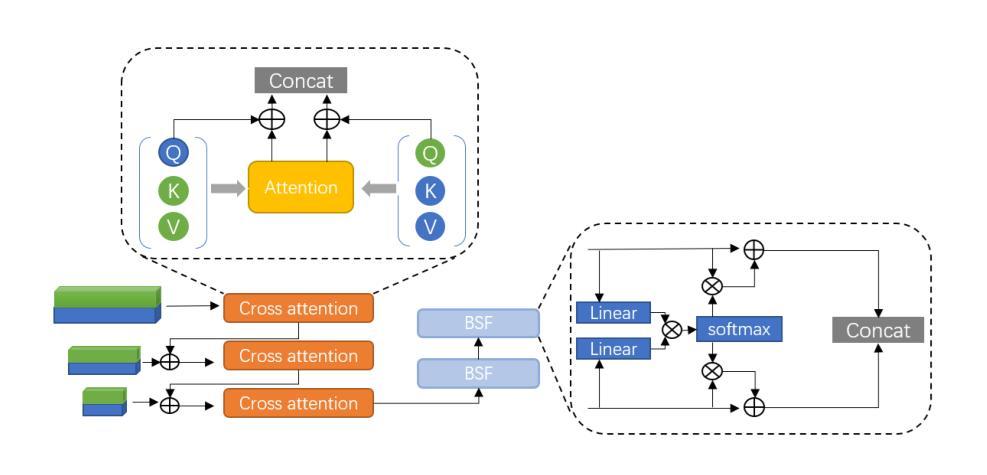
Small Lesions-aware Bidirectional Multimodal Multiscale Fusion Network for Lung Disease Classification
Authors:Jianxun Yu, Ruiquan Ge, Zhipeng Wang, Cheng Yang, Chenyu Lin, Xianjun Fu, Jikui Liu, Ahmed Elazab, Changmiao Wang
The diagnosis of medical diseases faces challenges such as the misdiagnosis of small lesions. Deep learning, particularly multimodal approaches, has shown great potential in the field of medical disease diagnosis. However, the differences in dimensionality between medical imaging and electronic health record data present challenges for effective alignment and fusion. To address these issues, we propose the Multimodal Multiscale Cross-Attention Fusion Network (MMCAF-Net). This model employs a feature pyramid structure combined with an efficient 3D multi-scale convolutional attention module to extract lesion-specific features from 3D medical images. To further enhance multimodal data integration, MMCAF-Net incorporates a multi-scale cross-attention module, which resolves dimensional inconsistencies, enabling more effective feature fusion. We evaluated MMCAF-Net on the Lung-PET-CT-Dx dataset, and the results showed a significant improvement in diagnostic accuracy, surpassing current state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/yjx1234/MMCAF-Net
医学疾病的诊断面临如小病灶误诊等挑战。深度学习,尤其是多模态方法,在医学疾病诊断领域表现出了巨大潜力。然而,医学成像与电子健康记录数据之间的维度差异给有效对齐和融合带来了挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了多模态多尺度交叉注意融合网络(MMCAF-Net)。该模型采用特征金字塔结构,结合高效的3D多尺度卷积注意模块,从3D医学图像中提取病灶特定特征。为了进一步改进多模态数据集成,MMCAF-Net融入了一个多尺度交叉注意模块,该模块解决了维度不一致的问题,实现了更有效的特征融合。我们在Lung-PET-CT-Dx数据集上评估了MMCAF-Net,结果显示诊断准确度显著提高,超越了当前最先进的方法。代码可访问https://github.com/yjx1234/MMCAF-Net。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学疾病诊断面临小病灶误诊等挑战。深度学习,特别是多模态方法,在该领域具有巨大潜力。然而,医学成像与电子健康记录数据在维度上的差异给有效对齐和融合带来挑战。我们提出多模态多尺度交叉注意力融合网络(MMCAF-Net),采用特征金字塔结构结合高效的3D多尺度卷积注意力模块,从3D医学图像中提取病灶特征。为进一步优化多模态数据集成,MMCAF-Net融入多尺度交叉注意力模块,解决维度不一致问题,实现更有效的特征融合。在Lung-PET-CT-Dx数据集上评估MMCAF-Net,结果显示诊断准确度显著提高,超越现有最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学疾病诊断面临小病灶误诊的挑战。
- 深度学习,特别是多模态方法,在医学诊断中具有巨大潜力。
- 医学成像与电子健康记录数据在维度上的差异是数据融合的挑战。
- 提出的多模态多尺度交叉注意力融合网络(MMCAF-Net)能提取病灶特征并优化数据融合。
- MMCAF-Net采用特征金字塔结构和3D多尺度卷积注意力模块。
- MMCAF-Net在Lung-PET-CT-Dx数据集上诊断准确度显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

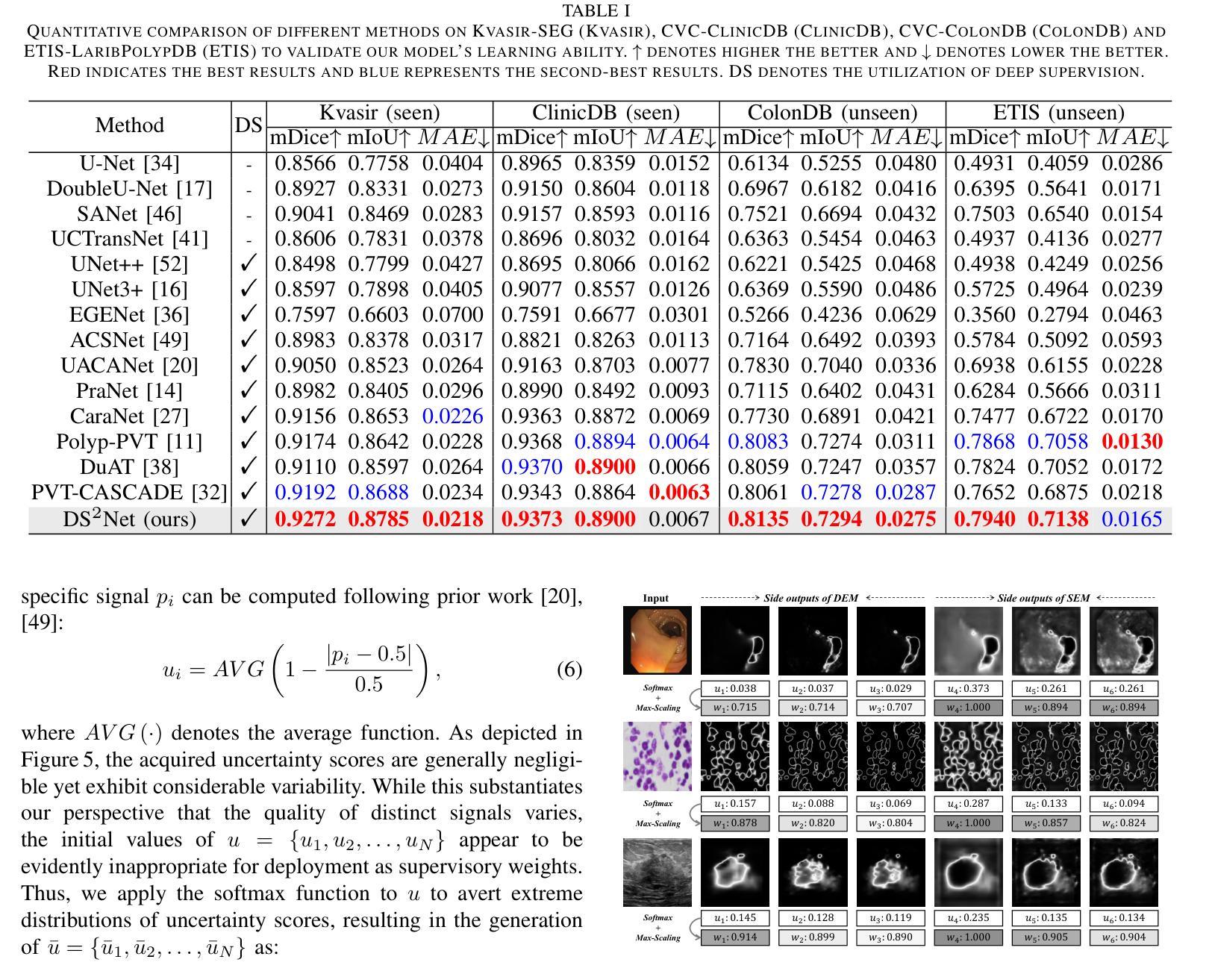
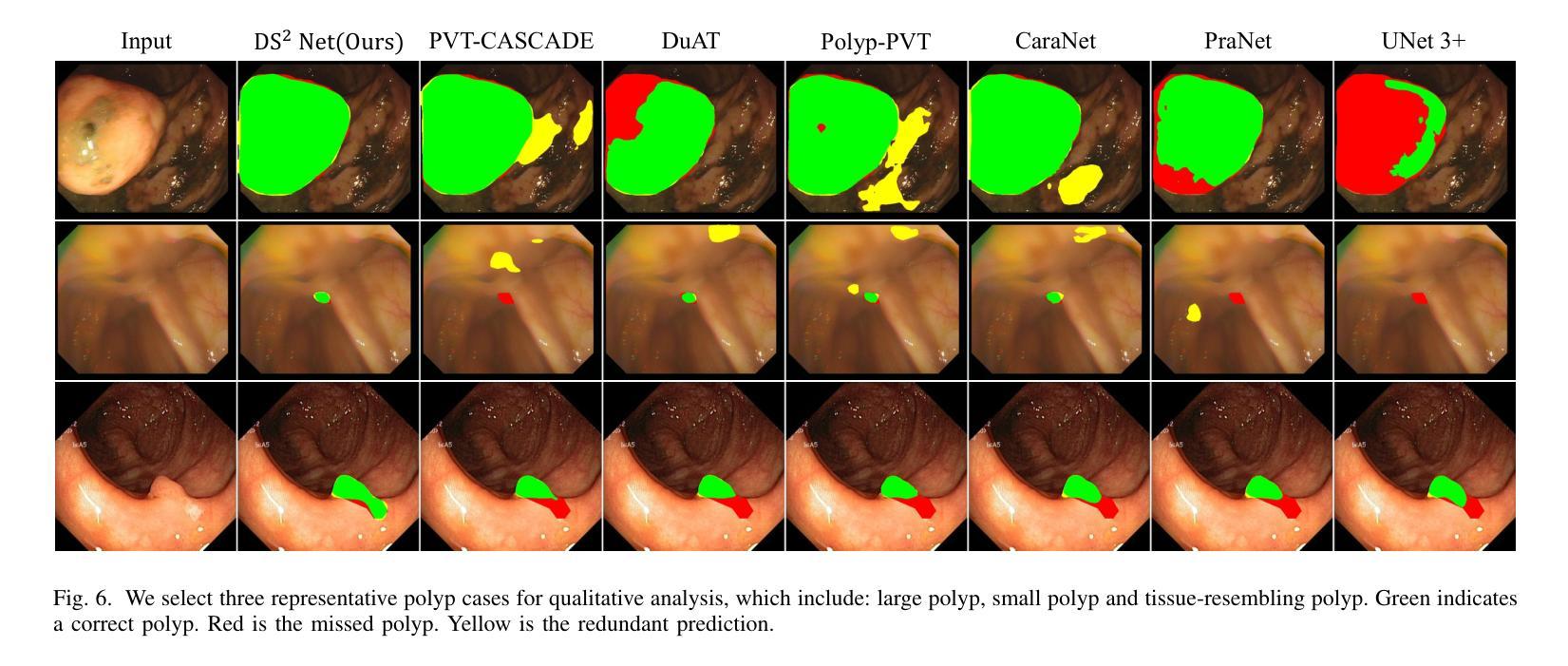
DS$^2$Net: Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhaohong Huang, Yuxin Zhang, Mingbao Lin, Taojian Zhou, Guorong Cai, Rongrong Ji
Deep Supervision Networks exhibit significant efficacy for the medical imaging community. Nevertheless, existing work merely supervises either the coarse-grained semantic features or fine-grained detailed features in isolation, which compromises the fact that these two types of features hold vital relationships in medical image analysis. We advocate the powers of complementary feature supervision for medical image segmentation, by proposing a Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network (DS$^2$Net). DS$^2$Net navigates both low-level detailed and high-level semantic feature supervision through Detail Enhance Module (DEM) and Semantic Enhance Module (SEM). DEM and SEM respectively harness low-level and high-level feature maps to create detail and semantic masks for enhancing feature supervision. This is a novel shift from single-view deep supervision to multi-view deep supervision. DS$^2$Net is also equipped with a novel uncertainty-based supervision loss that adaptively assigns the supervision strength of features within distinct scales based on their uncertainty, thus circumventing the sub-optimal heuristic design that typifies previous works. Through extensive experiments on six benchmarks captured under either colonoscopy, ultrasound and microscope, we demonstrate that DS$^2$Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for medical image analysis.
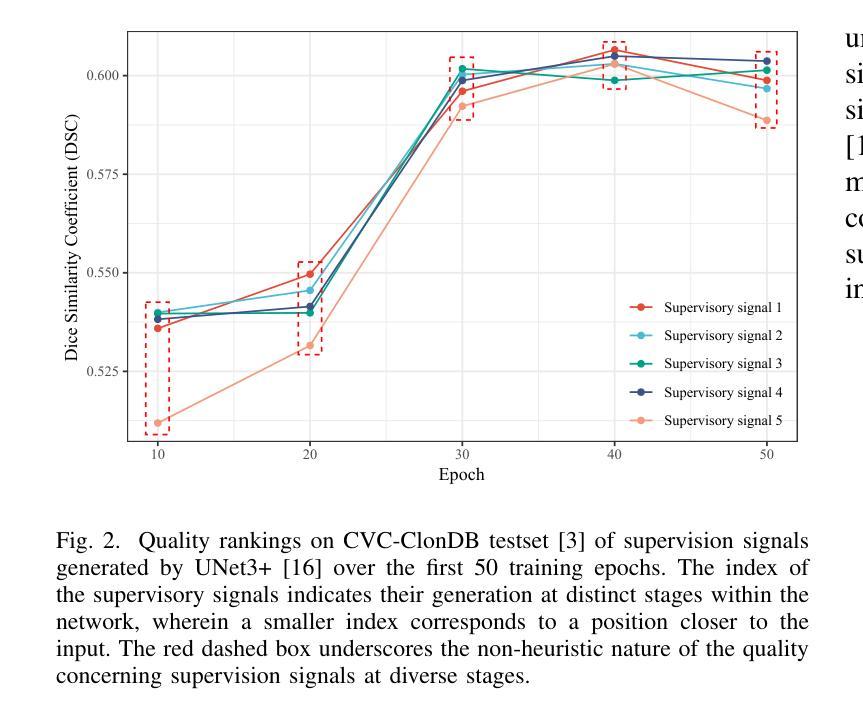
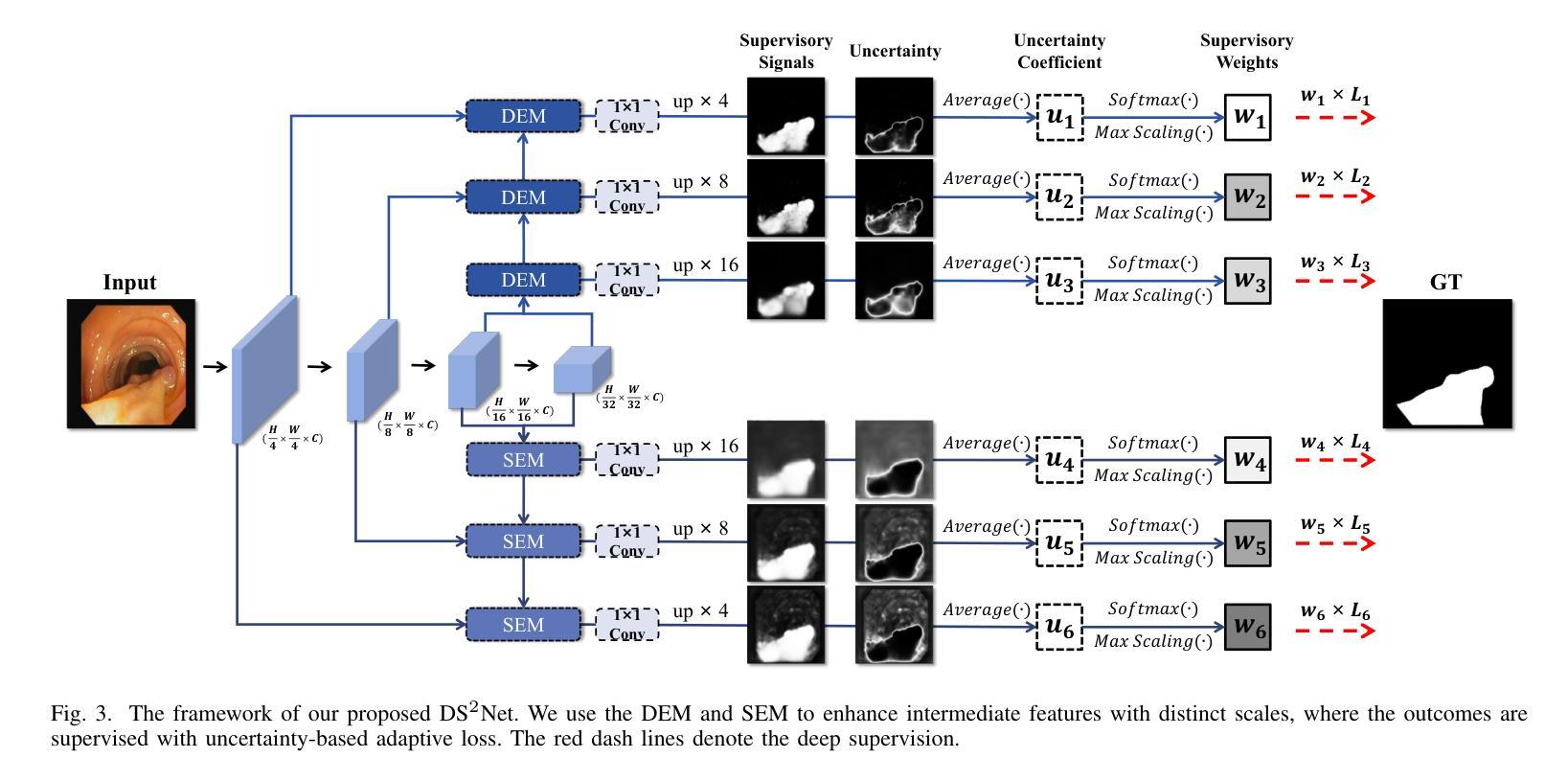
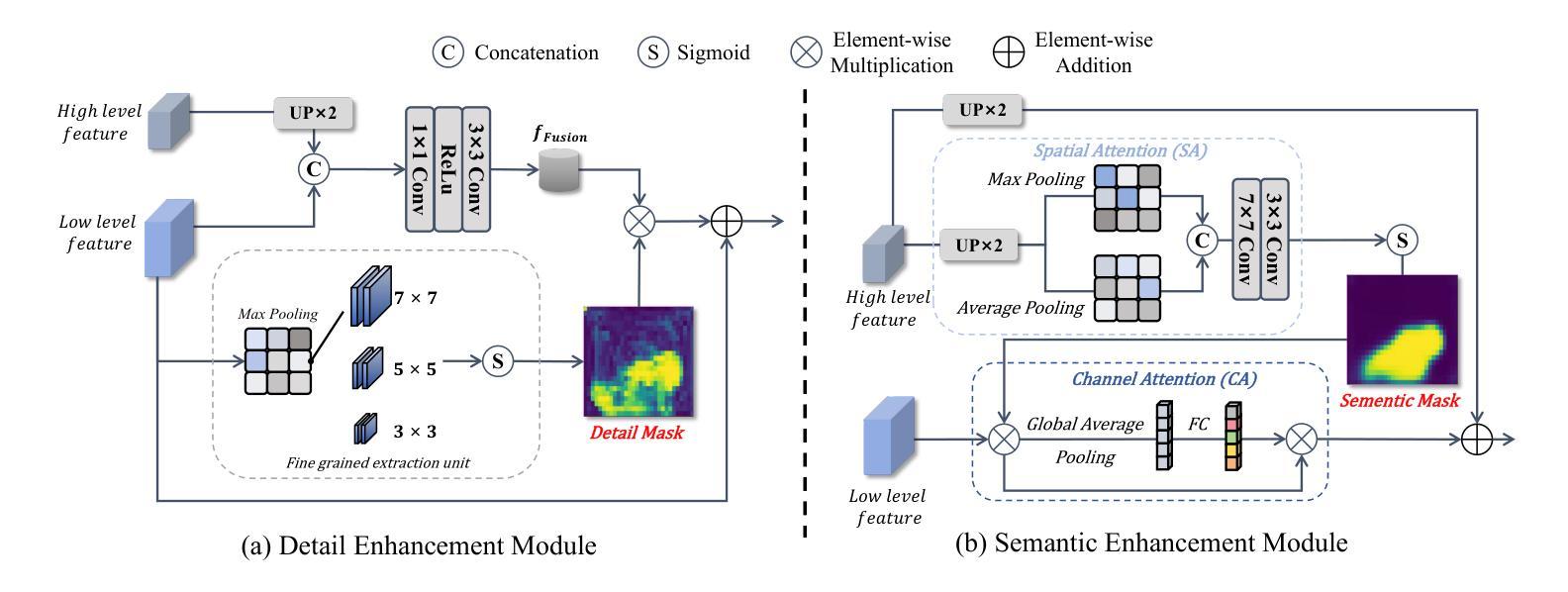
深度监督网络对医学影像界具有显著效果。然而,现有的工作只是孤立地监督粗粒度的语义特征或细粒度的详细特征,忽略了这两种特征在医学图像分析中具有重要关系的事实。我们提出了细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net),提倡医学图像分割的互补特征监督。DS$^2$Net通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)导航低级别的详细特征和高级别的语义特征监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低级别和高级别的特征图创建细节和语义掩膜,以增强特征监督。这是一种从单视图深度监督到多视图深度监督的新转变。DS$^2$Net还配备了一种基于新型不确定性监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度特征的监督强度,从而避免了以前工作的次优启发式设计。通过在结肠镜、超声和显微镜下采集的六个基准测试集上进行广泛实验,我们证明了DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分析领域存在监督问题,通常仅关注粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征其中之一。为解决此问题,提出一种细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net),包含细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM),实现低级别详细特征和高级别语义特征的共同监督。此外,引入基于不确定性的监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应调整不同尺度的特征监督强度。在六个基准测试上的实验表明,DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 现有医学图像分析中的监督方法存在局限性,仅关注单一类型的特征(如语义或详细特征)。
- DS$^2$Net提出一种细节语义深度监督网络来解决这个问题,结合了细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)。
- DS$^2$Net实现了从单视图到多视图的深度监督转变。
- 引入基于不确定性的监督损失,能根据特征的不确定性自适应调整监督强度。
- DS$^2$Net在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,包括结肠镜、超声和显微镜图像分析。
- 该网络的设计有助于提高医学图像分析的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
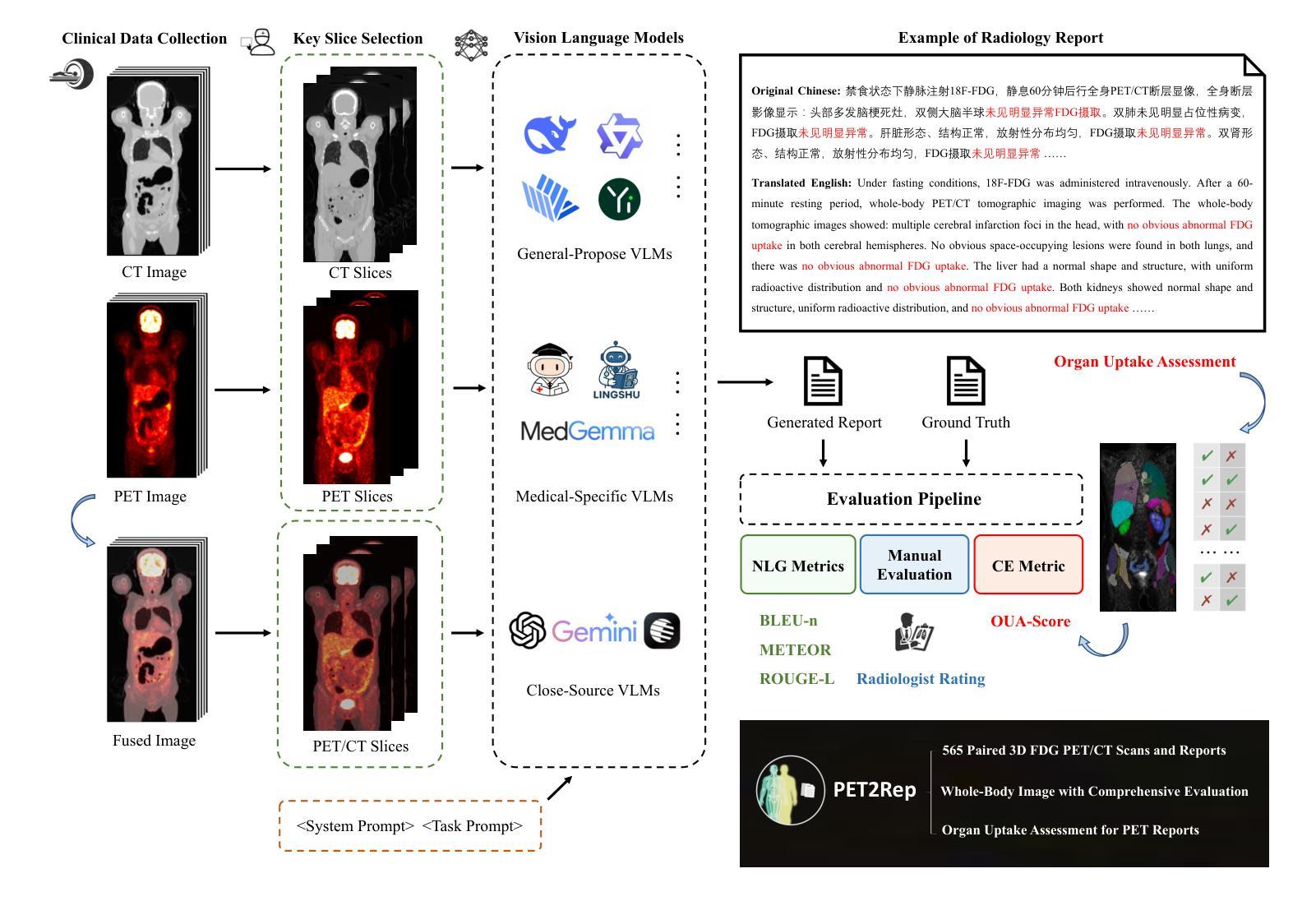
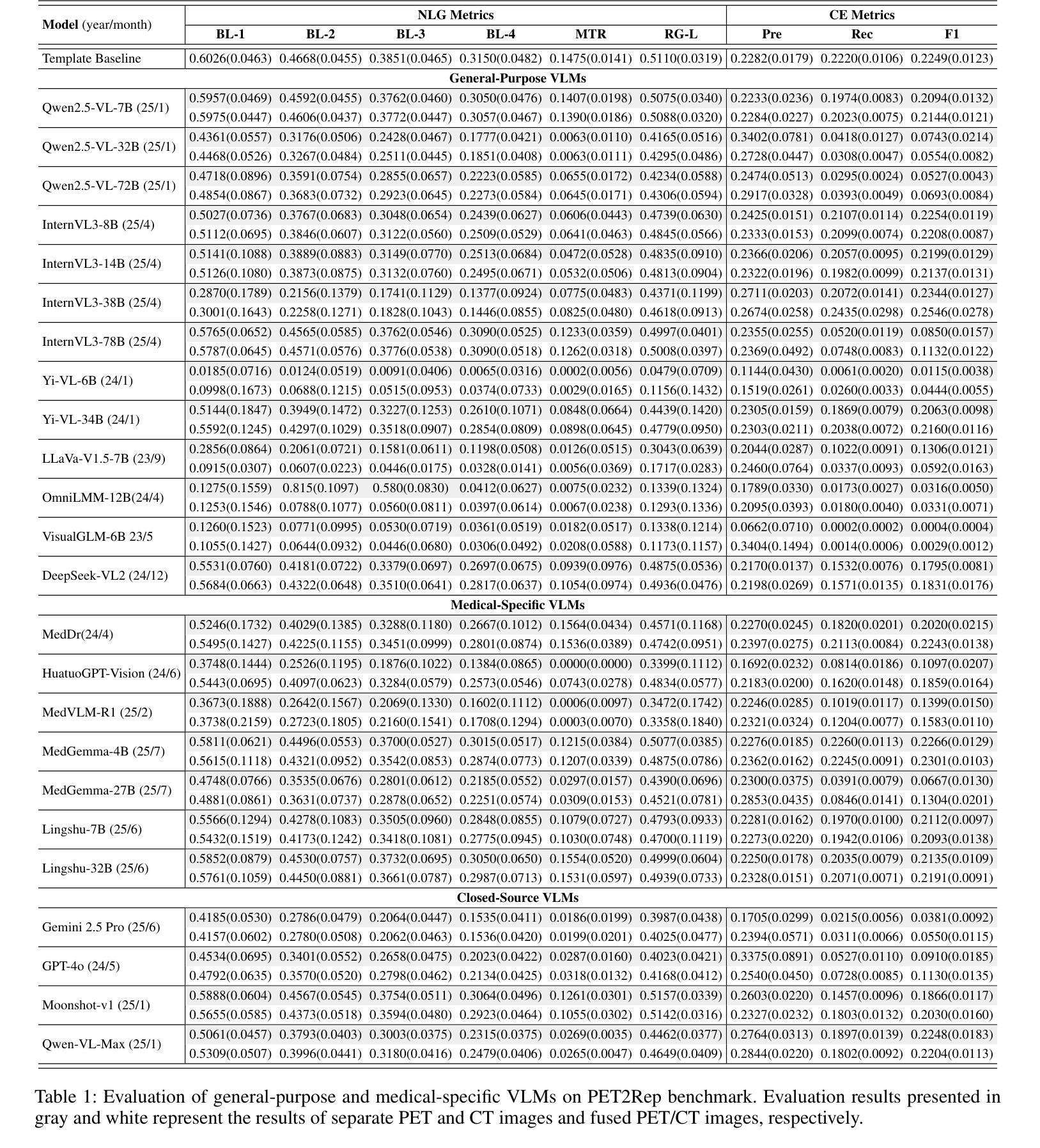
PET2Rep: Towards Vision-Language Model-Drived Automated Radiology Report Generation for Positron Emission Tomography
Authors:Yichi Zhang, Wenbo Zhang, Zehui Ling, Gang Feng, Sisi Peng, Deshu Chen, Yuchen Liu, Hongwei Zhang, Shuqi Wang, Lanlan Li, Limei Han, Yuan Cheng, Zixin Hu, Yuan Qi, Le Xue
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a cornerstone of modern oncologic and neurologic imaging, distinguished by its unique ability to illuminate dynamic metabolic processes that transcend the anatomical focus of traditional imaging technologies. Radiology reports are essential for clinical decision making, yet their manual creation is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Recent advancements of vision-language models (VLMs) have shown strong potential in medical applications, presenting a promising avenue for automating report generation. However, existing applications of VLMs in the medical domain have predominantly focused on structural imaging modalities, while the unique characteristics of molecular PET imaging have largely been overlooked. To bridge the gap, we introduce PET2Rep, a large-scale comprehensive benchmark for evaluation of general and medical VLMs for radiology report generation for PET images. PET2Rep stands out as the first dedicated dataset for PET report generation with metabolic information, uniquely capturing whole-body image-report pairs that cover dozens of organs to fill the critical gap in existing benchmarks and mirror real-world clinical comprehensiveness. In addition to widely recognized natural language generation metrics, we introduce a series of clinical efficiency metrics to evaluate the quality of radiotracer uptake pattern description in key organs in generated reports. We conduct a head-to-head comparison of 30 cutting-edge general-purpose and medical-specialized VLMs. The results show that the current state-of-the-art VLMs perform poorly on PET report generation task, falling considerably short of fulfilling practical needs. Moreover, we identify several key insufficiency that need to be addressed to advance the development in medical applications.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)是现代肿瘤学和神经成像的基石,以其独特的能够揭示超越传统成像技术解剖重点的动态代谢过程的能力而脱颖而出。放射学报告对于临床决策至关重要,但其手动创建过程却耗时且劳力密集。最近,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进展在医学应用中显示出强大的潜力,为报告生成自动化提供了有前景的途径。然而,VLMs在医学领域的应用主要集中在结构性成像模式上,而PET分子成像的独特特性在很大程度上被忽视了。为了弥差距,我们推出了PET2Rep,这是一个大规模的综合基准测试,用于评估用于PET图像放射学报告生成的通用和医疗VLMs的评估。PET2Rep以带有代谢信息的PET报告生成数据集的身份脱颖而出,独特地捕捉全身图像报告对,涵盖数十个器官,以填补现有基准测试的空白并反映现实世界临床的全面性。除了广泛认可的自然语言生成指标外,我们还引入了一系列临床效率指标来评估生成报告中关键器官放射性示踪剂摄取模式描述的准确性。我们对30款先进通用和医疗专用VLM进行了直面比较。结果表明,当前最先进的VLM在PET报告生成任务上的表现不佳,远远不能满足实际需求。此外,我们确定了几个关键不足,需要解决这些不足以促进医疗应用的开发。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PET成像在现代肿瘤学和神经成像中是核心技术,能够揭示动态代谢过程,超越传统成像技术的解剖重点。尽管放射学报告对临床决策至关重要,但其手动编写耗时且劳力密集。视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医疗应用中的最新进展显示出巨大潜力,为报告生成自动化提供有前途的途径。然而,VLMs在医学领域的应用主要集中在结构性成像模式上,而PET成像的独特特性却被忽视。为弥补这一差距,我们推出PET2Rep,一个大规模基准测试,评估用于PET图像放射学报告生成的通用和医疗VLMs。PET2Rep是首个专注于PET报告生成的数据集,包含代谢信息,独特地捕捉全身图像报告对,覆盖多个器官。我们进行了一项尖端通用和医疗专用VLMs的对比研究,结果显示当前最先进的VLMs在PET报告生成任务上表现不佳,难以满足实际需求。
Key Takeaways
- PET成像技术在现代肿瘤学和神经成像中的核心地位及其揭示动态代谢过程的能力。
- 放射学报告在临床决策中的重要性,以及手动编写报告的耗时和劳力密集问题。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医疗应用中的潜力及其对报告生成自动化的前景。
- VLMs在医学领域的应用主要关注结构性成像模式,忽视了PET成像的独特特性。
- PET2Rep的推出,作为首个专注于PET报告生成的数据集,包含代谢信息,覆盖多个器官。
- 当前最先进的VLMs在PET报告生成任务上的表现不佳。
点此查看论文截图

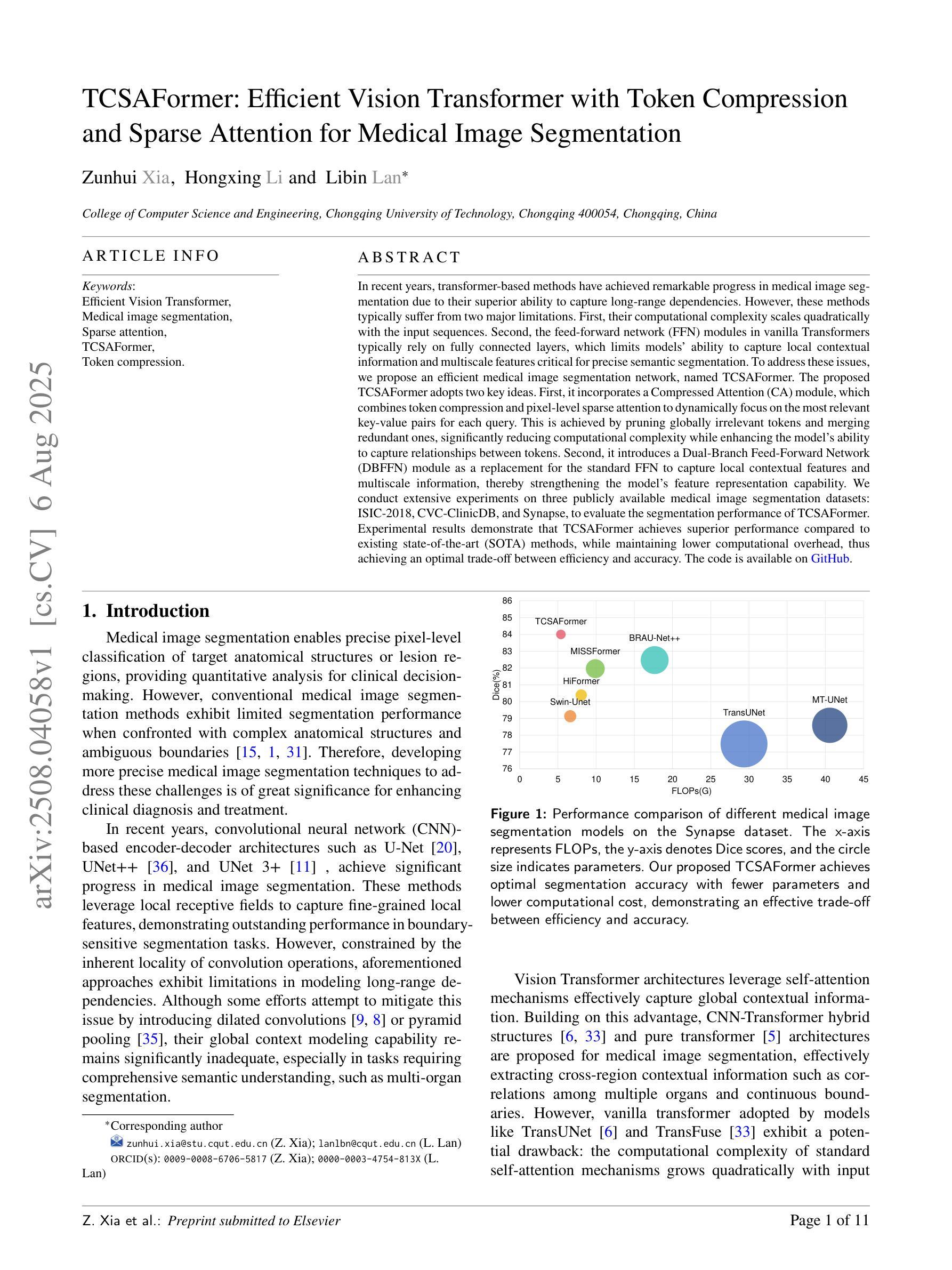
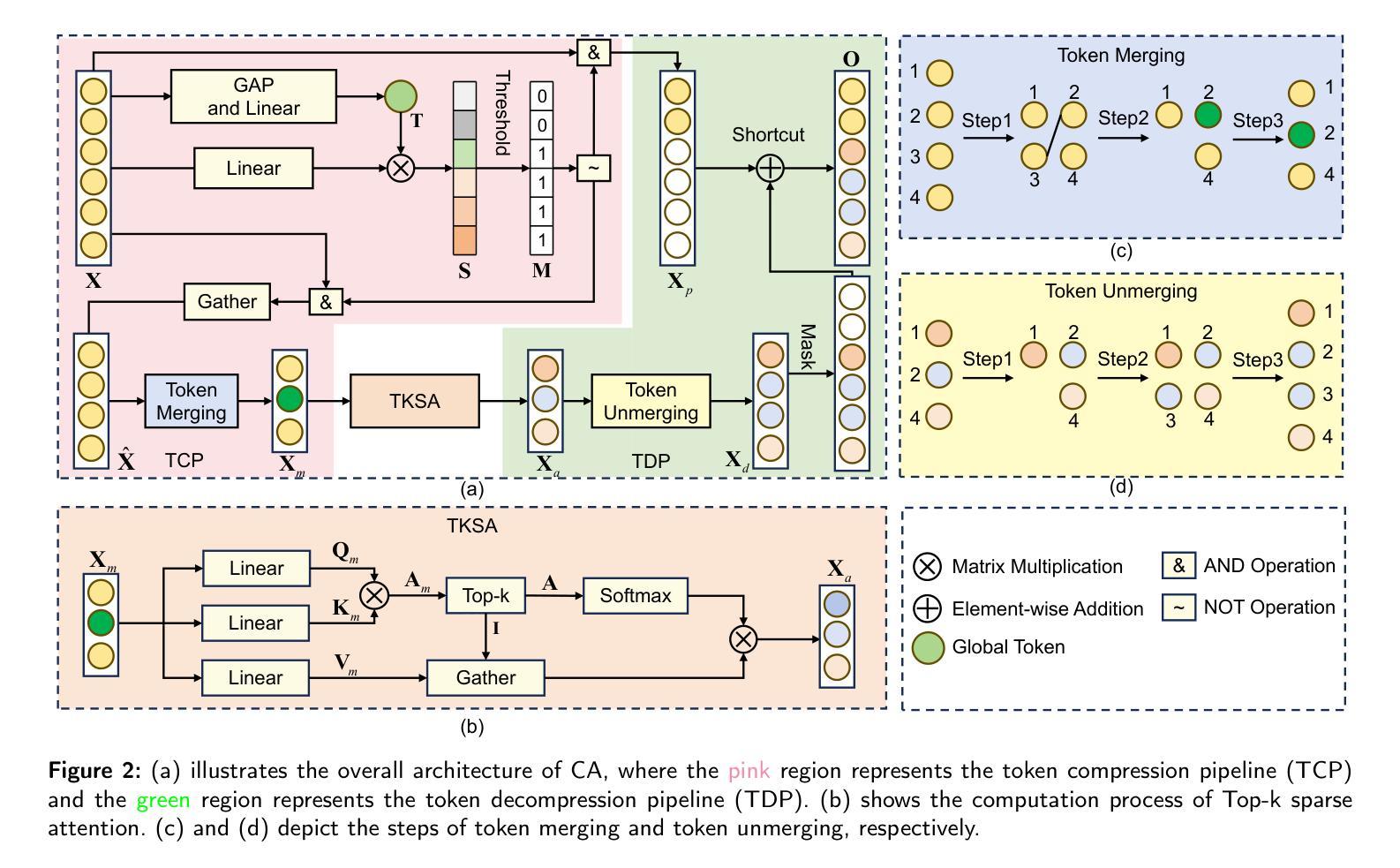
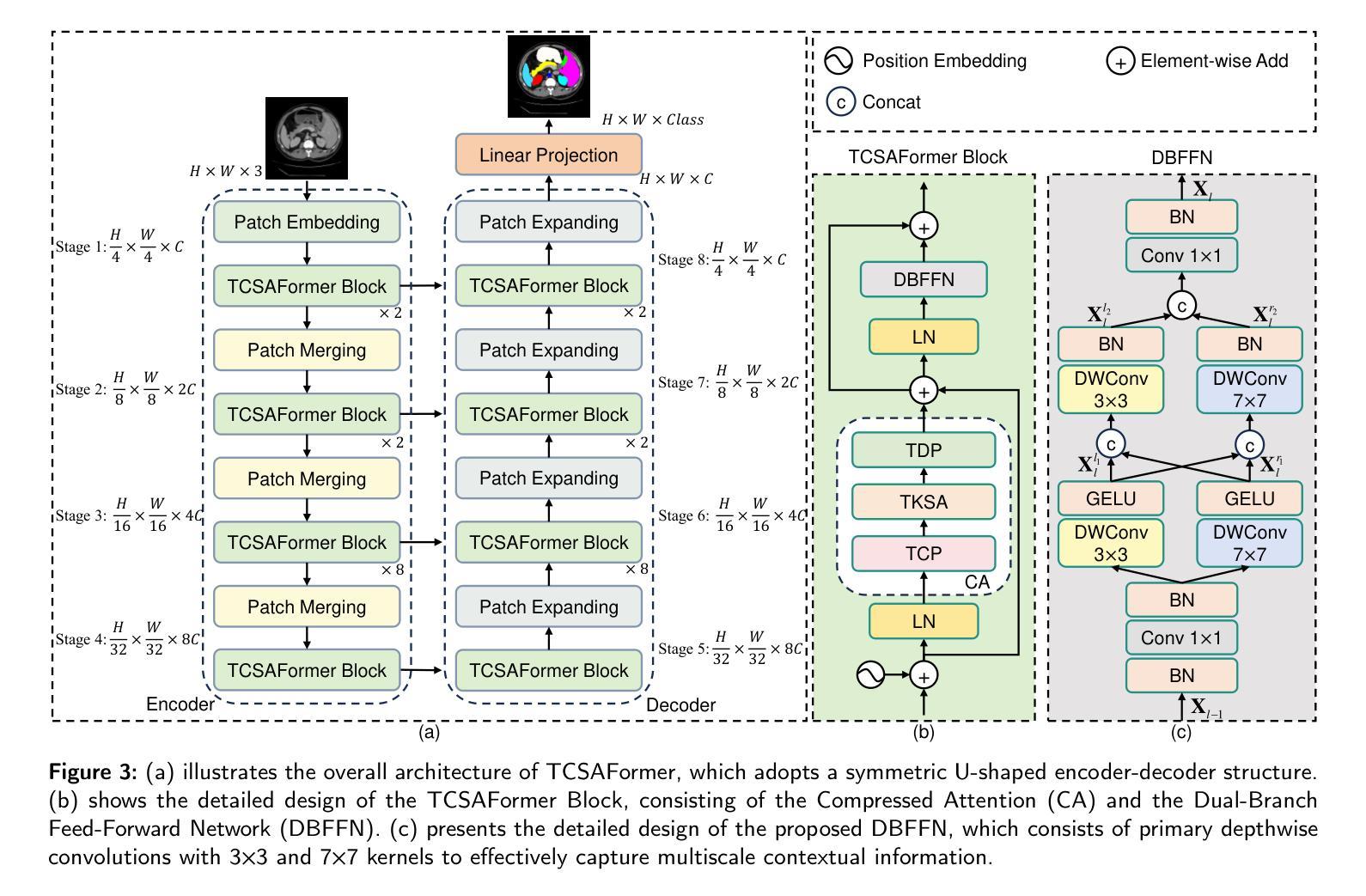
TCSAFormer: Efficient Vision Transformer with Token Compression and Sparse Attention for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zunhui Xia, Hongxing Li, Libin Lan
In recent years, transformer-based methods have achieved remarkable progress in medical image segmentation due to their superior ability to capture long-range dependencies. However, these methods typically suffer from two major limitations. First, their computational complexity scales quadratically with the input sequences. Second, the feed-forward network (FFN) modules in vanilla Transformers typically rely on fully connected layers, which limits models’ ability to capture local contextual information and multiscale features critical for precise semantic segmentation. To address these issues, we propose an efficient medical image segmentation network, named TCSAFormer. The proposed TCSAFormer adopts two key ideas. First, it incorporates a Compressed Attention (CA) module, which combines token compression and pixel-level sparse attention to dynamically focus on the most relevant key-value pairs for each query. This is achieved by pruning globally irrelevant tokens and merging redundant ones, significantly reducing computational complexity while enhancing the model’s ability to capture relationships between tokens. Second, it introduces a Dual-Branch Feed-Forward Network (DBFFN) module as a replacement for the standard FFN to capture local contextual features and multiscale information, thereby strengthening the model’s feature representation capability. We conduct extensive experiments on three publicly available medical image segmentation datasets: ISIC-2018, CVC-ClinicDB, and Synapse, to evaluate the segmentation performance of TCSAFormer. Experimental results demonstrate that TCSAFormer achieves superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, while maintaining lower computational overhead, thus achieving an optimal trade-off between efficiency and accuracy.
近年来,基于转换器的方法在医学图像分割方面取得了显著的进步,因为它们具有捕获远程依赖关系的卓越能力。然而,这些方法通常面临两个主要局限性。首先,它们的计算复杂度与输入序列成二次方关系。其次,普通Transformer中的前馈网络(FFN)模块通常依赖于全连接层,这限制了模型捕获局部上下文信息和多尺度特征的能力,这对于精确的语义分割至关重要。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种高效的医学图像分割网络,名为TCSAFormer。所提出的TCSAFormer采用了两个关键思想。首先,它结合了压缩注意力(CA)模块,该模块结合了令牌压缩和像素级稀疏注意力,以动态关注每个查询的最相关键值对。这是通过删除全局不相关的令牌并合并冗余令牌来实现的,这显著降低了计算复杂度,同时增强了模型捕获令牌之间关系的能力。其次,它引入了双分支前馈网络(DBFFN)模块,作为标准FFN的替代品,以捕获局部上下文特征和多尺度信息,从而增强了模型的特征表示能力。我们在三个公开的医学图像分割数据集ISIC-2018、CVC-ClinicDB和Synapse上进行了广泛的实验,以评估TCSAFormer的分割性能。实验结果表明,TCSAFormer与现有最先进的方法相比实现了优越的性能,同时降低了计算开销,从而在效率和准确性之间实现了最优权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables; The code is available at https://github.com/XiaZunhui/TCSAFormer
Summary
本文介绍了针对医疗图像分割领域,基于Transformer的方法存在的两大局限性:计算复杂度较高和对局部上下文信息及多尺度特征捕捉能力有限。为此,提出了一种高效的医疗图像分割网络TCSAFormer。它通过结合压缩注意力模块和双重分支前馈网络模块,在降低计算复杂度的同时,增强了模型捕捉关键信息的能力,实现了在医疗图像分割任务上的优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer方法在医疗图像分割领域取得了显著进展,但存在计算复杂度高和对局部上下文及多尺度特征捕捉能力有限的局限。
- TCSAFormer网络通过引入压缩注意力模块,结合令牌压缩和像素级稀疏注意力,提高了模型对关键信息的捕捉能力。
- TCSAFormer采用双重分支前馈网络模块替代标准前馈网络,以捕捉局部上下文特征和多尺度信息,增强了特征表示能力。
- TCSAFormer在三个公开医疗图像分割数据集上的实验结果表明,其性能优于现有先进方法,同时计算开销较低,实现了效率和准确性的最优平衡。
- TCSAFormer能够动态关注与查询最相关的键值对,通过剔除全局无关令牌并合并冗余令牌,有效提高计算效率。
- TCSAFormer网络的创新设计克服了传统Transformer方法的两大局限,为医疗图像分割任务提供了更高效、更准确的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
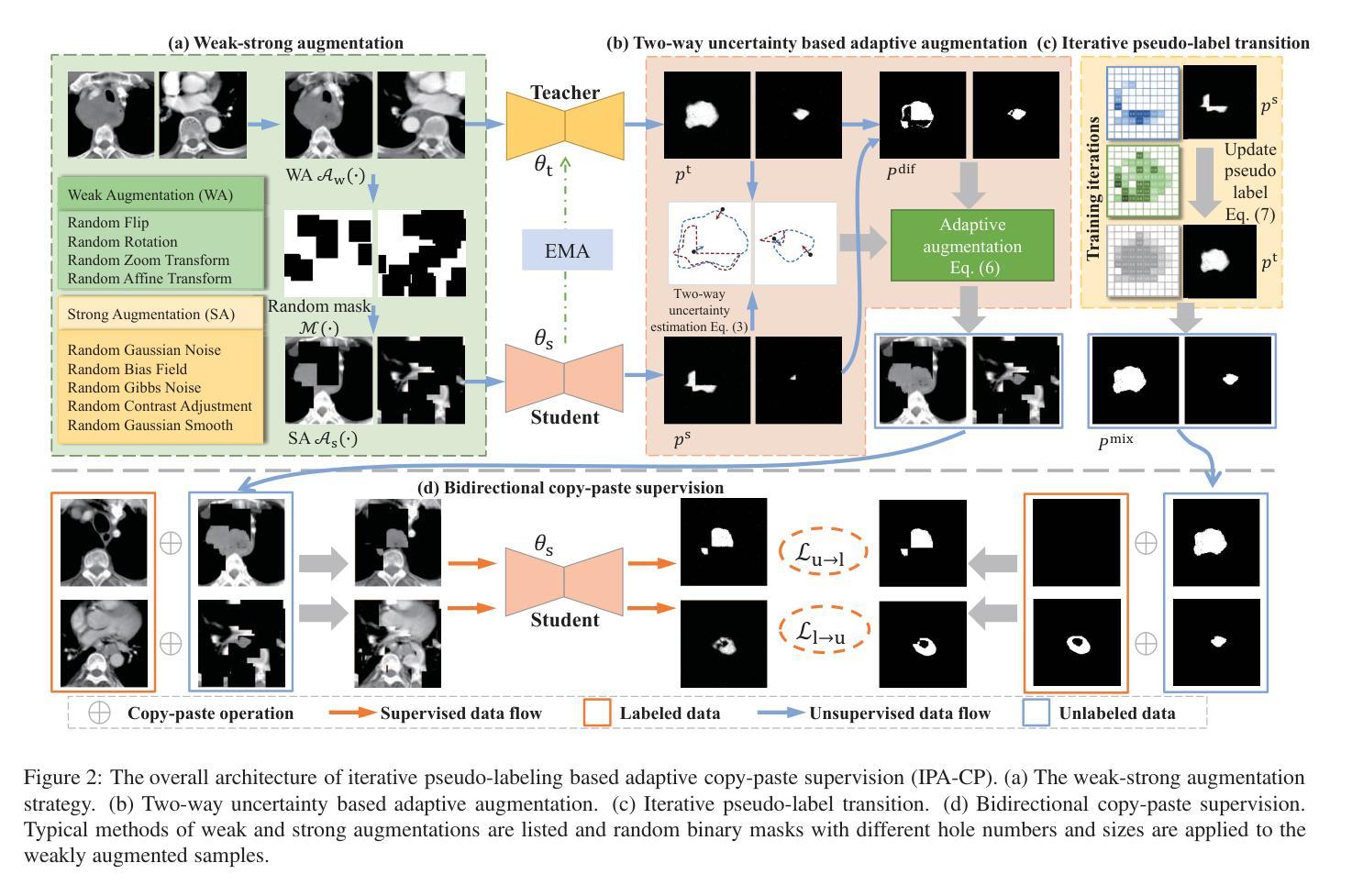
Iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision for semi-supervised tumor segmentation
Authors:Qiangguo Jin, Hui Cui, Junbo Wang, Changming Sun, Yimiao He, Ping Xuan, Linlin Wang, Cong Cong, Leyi Wei, Ran Su
Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has attracted considerable attention in medical image processing. The latest SSL methods use a combination of consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling to achieve remarkable success. However, most existing SSL studies focus on segmenting large organs, neglecting the challenging scenarios where there are numerous tumors or tumors of small volume. Furthermore, the extensive capabilities of data augmentation strategies, particularly in the context of both labeled and unlabeled data, have yet to be thoroughly investigated. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a straightforward yet effective approach, termed iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision (IPA-CP), for tumor segmentation in CT scans. IPA-CP incorporates a two-way uncertainty based adaptive augmentation mechanism, aiming to inject tumor uncertainties present in the mean teacher architecture into adaptive augmentation. Additionally, IPA-CP employs an iterative pseudo-label transition strategy to generate more robust and informative pseudo labels for the unlabeled samples. Extensive experiments on both in-house and public datasets show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art SSL methods in medical image segmentation. Ablation study results demonstrate the effectiveness of our technical contributions.
半监督学习(SSL)在医学图像处理中引起了广泛关注。最新的SSL方法结合了一致性正则化和伪标签技术,取得了显著的成功。然而,大多数现有的SSL研究集中在分割大器官上,忽视了存在大量肿瘤或小体积肿瘤的具有挑战性的场景。此外,数据增强策略的广泛能力,特别是在有标签和无标签数据的背景下,尚未得到充分的调查和研究。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种简单有效的肿瘤分割方法,称为基于迭代伪标签的适应性拷贝粘贴监督(IPA-CP),用于CT扫描中的肿瘤分割。IPA-CP结合了基于双向不确定性的自适应增强机制,旨在将存在于平均教师架构中的肿瘤不确定性注入自适应增强中。此外,IPA-CP采用迭代伪标签转换策略,为无标签样本生成更稳健和更有用的伪标签。在家庭内部和公开数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的框架在医学图像分割中的表现优于最先进的SSL方法。消融研究结果表明我们的技术贡献是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像半监督学习在医学图像处理领域备受关注。最新半监督学习方法通过一致性正则化和伪标签技术取得了显著成果。然而,大多数研究关注大器官的分割,忽视了存在多个肿瘤或小型体积肿瘤的复杂场景的挑战。此外,数据增强策略的广泛能力,特别是在有标签和无标签数据的情况下,尚未得到深入研究。针对这些挑战,我们提出了一种简单有效的迭代伪标签自适应拷贝粘贴监督方法(IPA-CP),用于CT扫描中的肿瘤分割。IPA-CP结合了基于双向不确定性的自适应增强机制,旨在将肿瘤的不确定性注入到平均教师架构中进行自适应增强。同时,IPA-CP使用迭代伪标签转换策略为未标记样本生成更稳健和有用的伪标签。在内部和公共数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的框架在医学图像分割领域优于最新的半监督学习方法。消融研究结果表明我们的技术贡献有效。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在医学图像处理中受到关注,特别是用于肿瘤分割。
- 最新半监督学习方法通过一致性正则化和伪标签技术取得显著成果。
- 现有研究多关注大器官分割,忽视了复杂场景下的肿瘤分割挑战。
- IPA-CP方法结合了基于双向不确定性的自适应增强机制,以提高肿瘤分割的准确性。
- IPA-CP采用迭代伪标签转换策略生成更稳健和有用的伪标签。
- 在内部和公共数据集上的实验表明,IPA-CP在医学图像分割方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


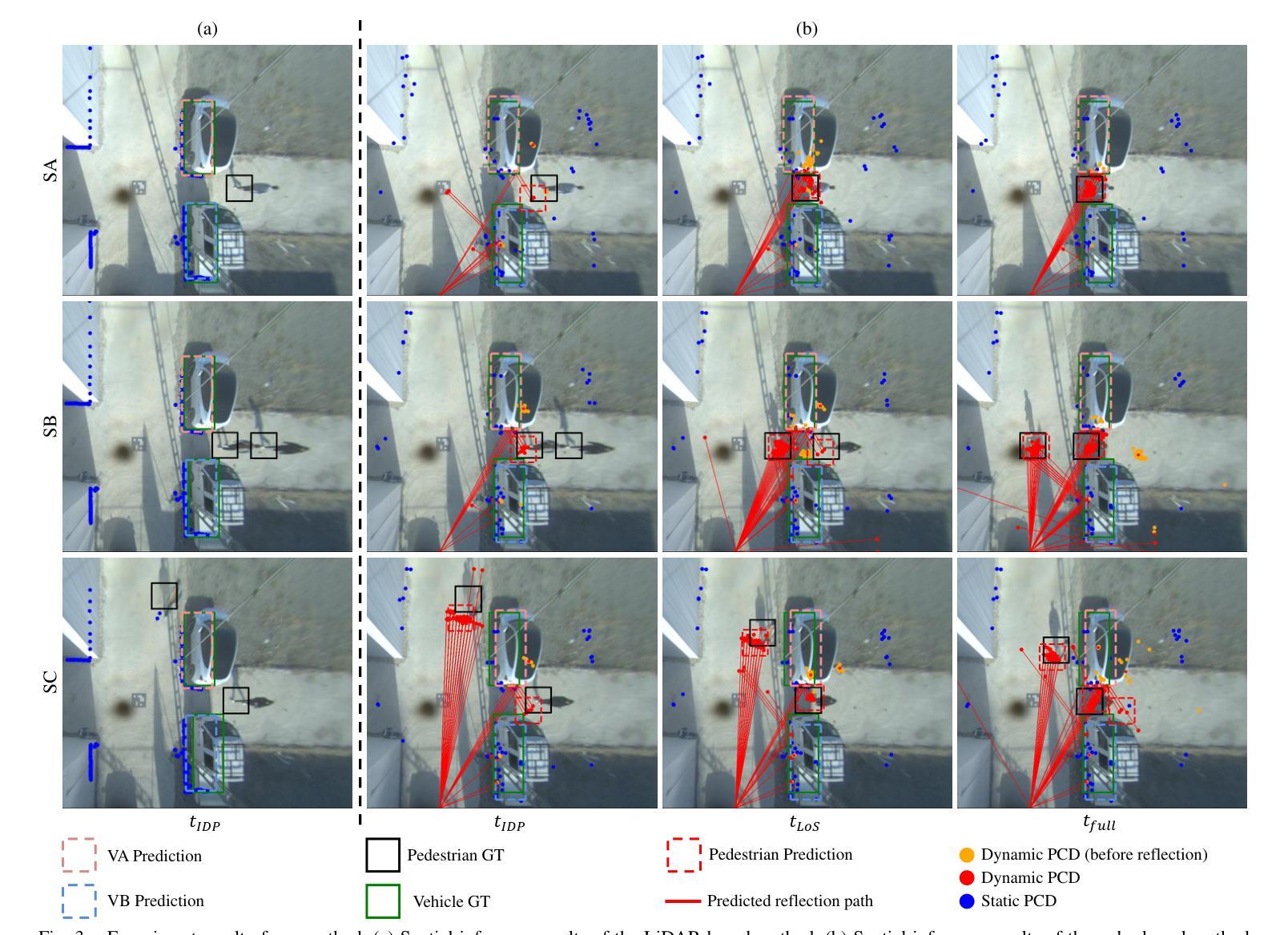
Radar-Based NLoS Pedestrian Localization for Darting-Out Scenarios Near Parked Vehicles with Camera-Assisted Point Cloud Interpretation
Authors:Hee-Yeun Kim, Byeonggyu Park, Byonghyok Choi, Hansang Cho, Byungkwan Kim, Soomok Lee, Mingu Jeon, Seung-Woo Seo, Seong-Woo Kim
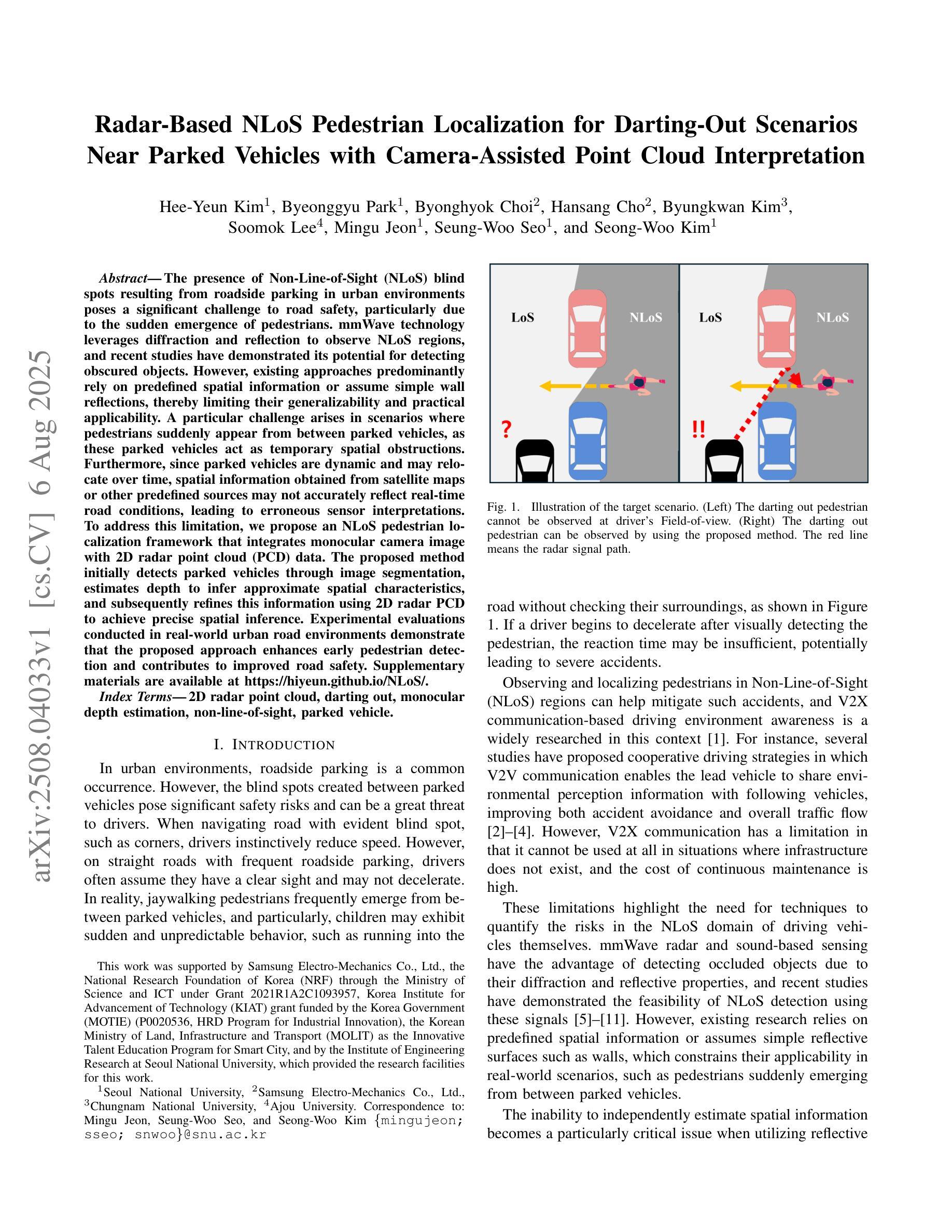
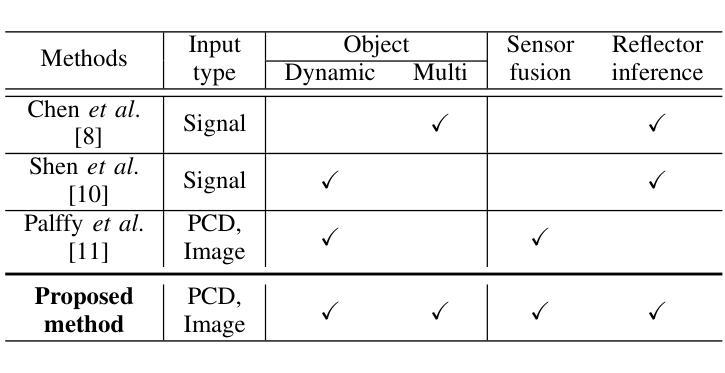
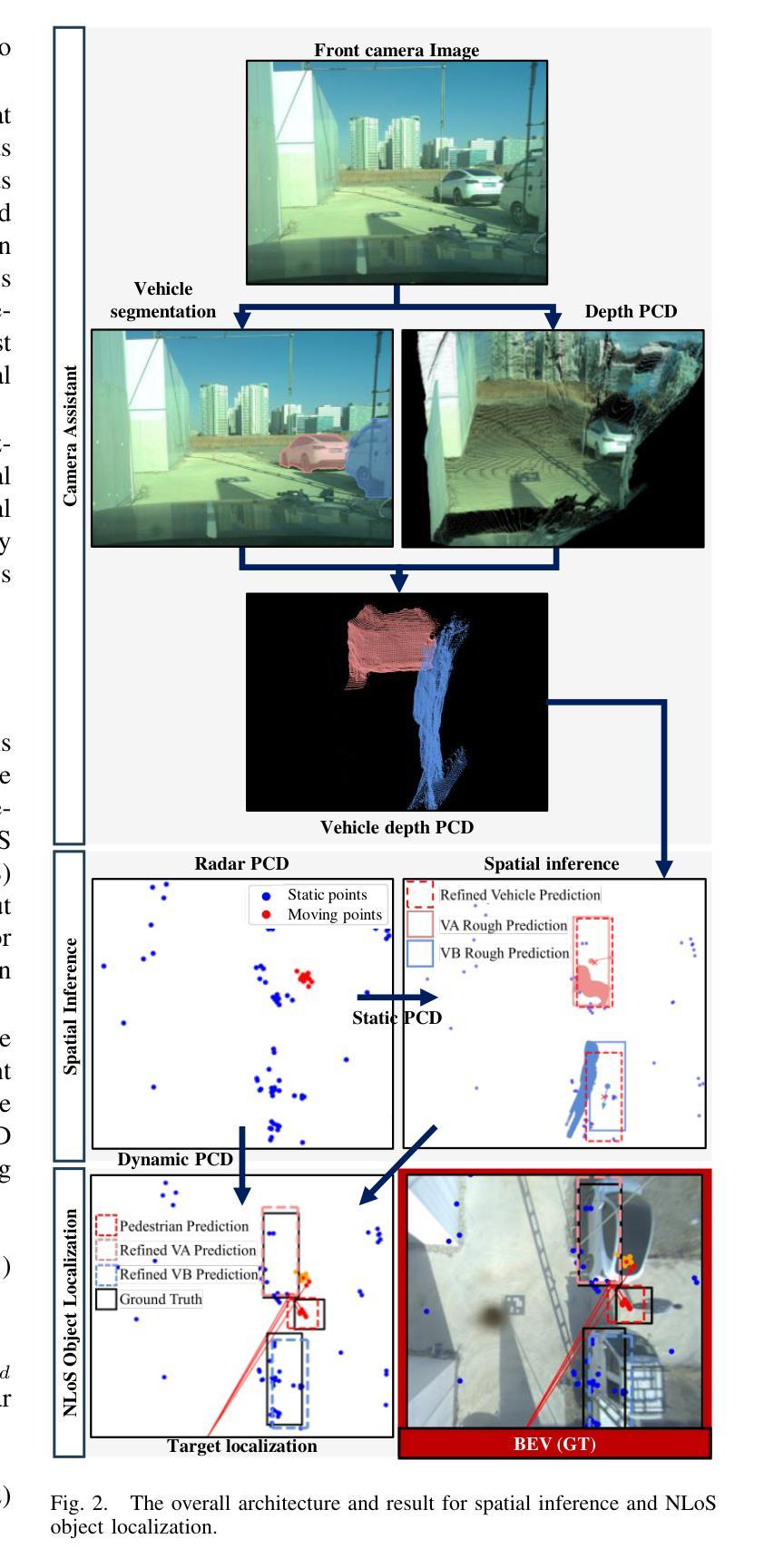
The presence of Non-Line-of-Sight (NLoS) blind spots resulting from roadside parking in urban environments poses a significant challenge to road safety, particularly due to the sudden emergence of pedestrians. mmWave technology leverages diffraction and reflection to observe NLoS regions, and recent studies have demonstrated its potential for detecting obscured objects. However, existing approaches predominantly rely on predefined spatial information or assume simple wall reflections, thereby limiting their generalizability and practical applicability. A particular challenge arises in scenarios where pedestrians suddenly appear from between parked vehicles, as these parked vehicles act as temporary spatial obstructions. Furthermore, since parked vehicles are dynamic and may relocate over time, spatial information obtained from satellite maps or other predefined sources may not accurately reflect real-time road conditions, leading to erroneous sensor interpretations. To address this limitation, we propose an NLoS pedestrian localization framework that integrates monocular camera image with 2D radar point cloud (PCD) data. The proposed method initially detects parked vehicles through image segmentation, estimates depth to infer approximate spatial characteristics, and subsequently refines this information using 2D radar PCD to achieve precise spatial inference. Experimental evaluations conducted in real-world urban road environments demonstrate that the proposed approach enhances early pedestrian detection and contributes to improved road safety. Supplementary materials are available at https://hiyeun.github.io/NLoS/.
在城市环境中,路边停车产生的非直视(NLoS)盲点对道路安全构成了重大挑战,特别是行人突然出现的情冁。毫米波技术利用衍射和反射来观察NLoS区域,最近的研究已经证明了其在检测隐蔽物体方面的潜力。然而,现有方法主要依赖于预定义的空间信息或假设简单的墙壁反射,从而限制了其通用性和实际应用。一个特殊的挑战出现在行人突然从停车车辆之间出现的情况下,这些停放的车辆充当了临时的空间障碍物。此外,由于停放的车辆是动态的并且可能会随时间而重新定位,因此从卫星地图或其他预定义源获得的空间信息可能无法准确反映实时的道路状况,从而导致传感器解释错误。为了解决这一限制,我们提出了一种NLoS行人定位框架,该框架将单目相机图像与2D雷达点云(PCD)数据相结合。所提出的方法首先通过图像分割检测停放的车辆,估计深度以推断近似空间特征,然后使用该信息结合2D雷达PCD进行精确的空间推断。在真实世界的城市道路环境中所进行的实验评估表明,该方法提高了对行人的早期检测能力,并有助于改善道路安全。补充材料可访问https://hiyeun.github.io/NLoS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2025. 8 pages, 3 figures
Summary
非视线盲区的存在对道路安全构成挑战,特别是路边停车造成的盲区中突然出现的行人。毫米波技术可通过衍射和反射观察非视线区域,但现有方法主要依赖预设的空间信息或简单的墙反射假设,限制了其通用性和实际应用能力。因此,提出一种结合单目相机图像与雷达点云数据的非视线行人定位框架,通过图像分割检测停车车辆,估计深度进行空间特征推断,并使用雷达点云数据进行精确空间推理。实验评估显示,该方法提高了早期行人检测能力,有助于改善道路安全。
Key Takeaways
- 非视线盲区(NLoS)对道路安全构成挑战,特别是在城市环境中路边停车造成的盲区中突然出现的行人。
- 毫米波技术可通过衍射和反射观察非视线区域,在检测被遮挡物体方面具有潜力。
- 现有方法主要依赖预设的空间信息或简单的墙反射假设,限制了其在实际场景中的通用性和应用。
- 停车车辆作为临时空间障碍物带来的挑战,以及它们随时可能改变位置导致的空间信息不准确问题。
- 提出的框架结合了单目相机图像和雷达点云数据,以改进非视线行人的定位。
- 该方法通过图像分割检测停车车辆,并通过估计深度进行空间特征推断。
点此查看论文截图

Prototype-Driven Structure Synergy Network for Remote Sensing Images Segmentation
Authors:Junyi Wang, Jinjiang Li, Guodong Fan, Yakun Ju, Xiang Fang, Alex C. Kot
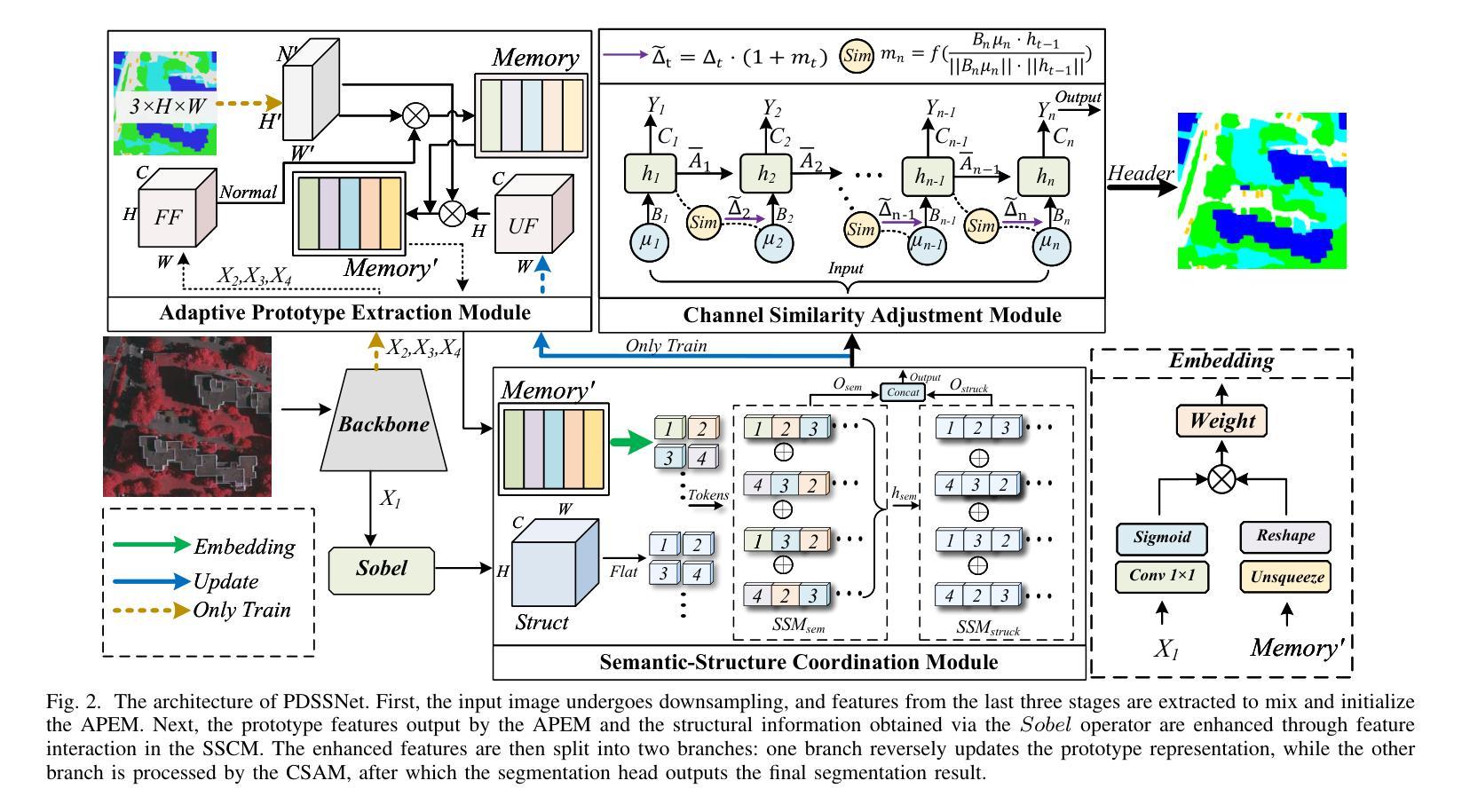
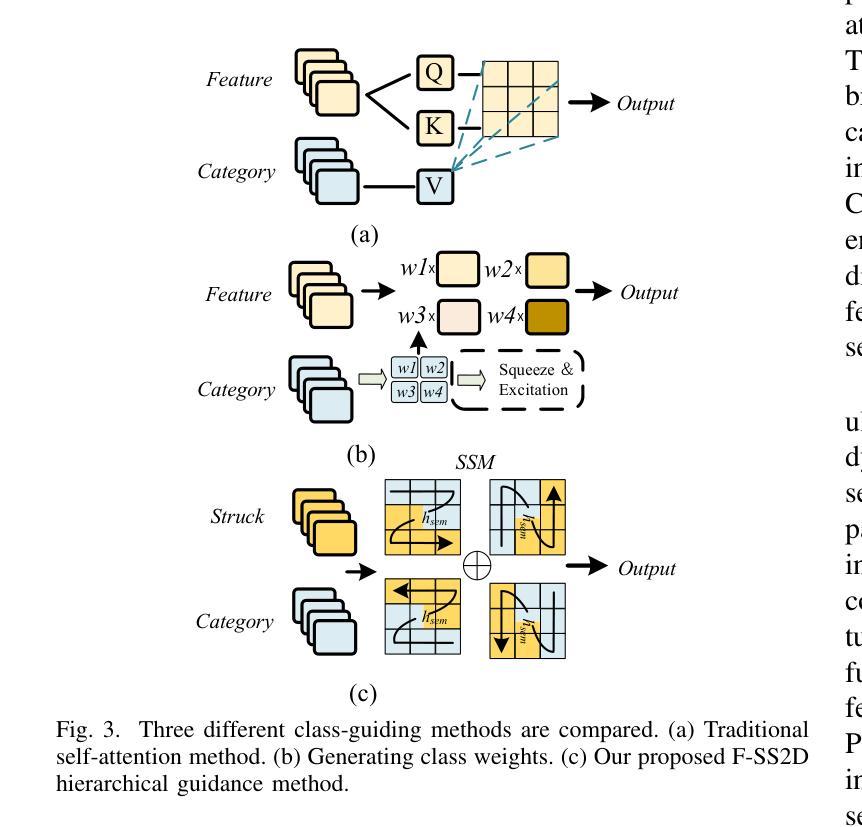
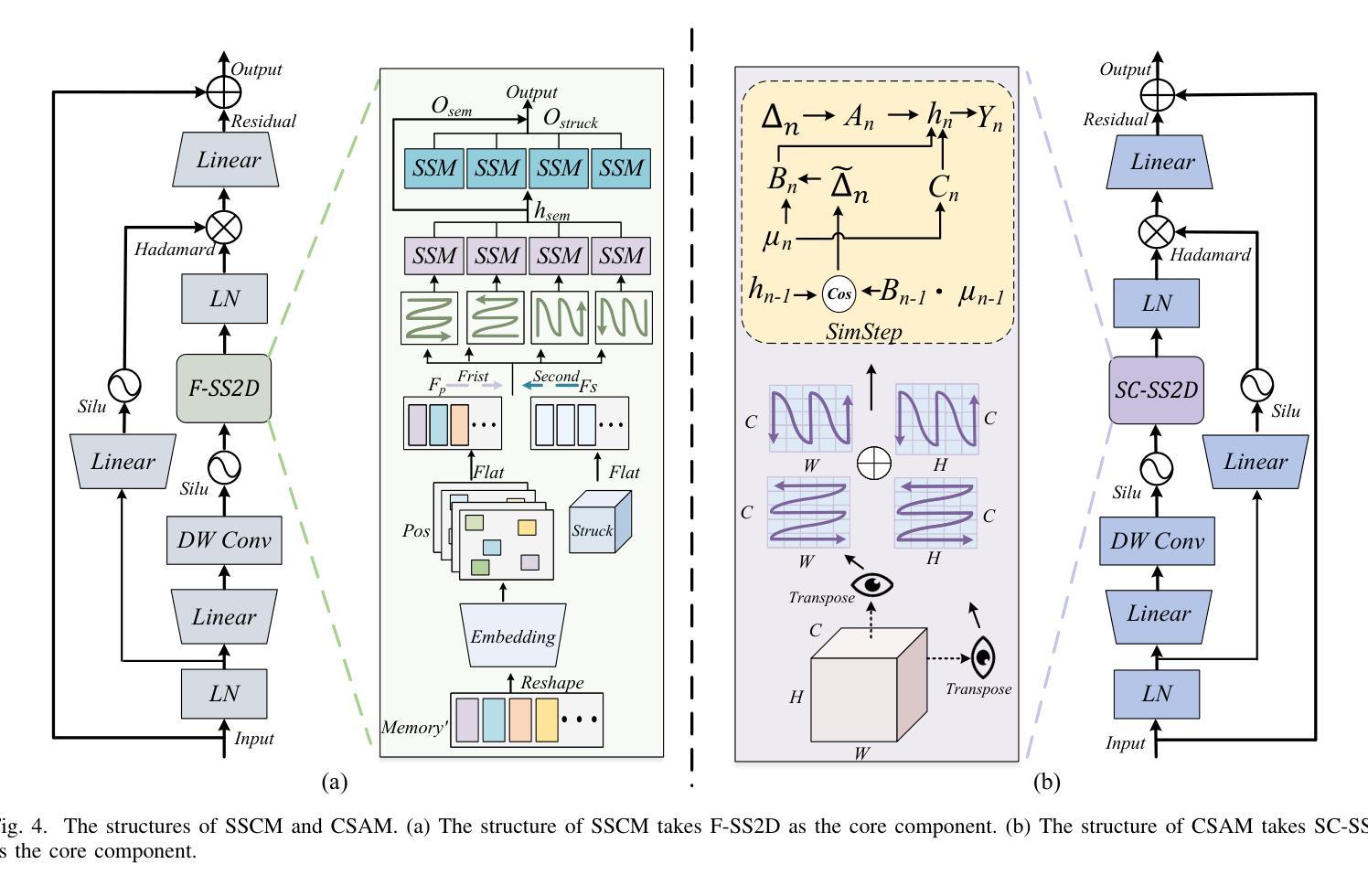
In the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images, acquiring complete ground objects is critical for achieving precise analysis. However, this task is severely hindered by two major challenges: high intra-class variance and high inter-class similarity. Traditional methods often yield incomplete segmentation results due to their inability to effectively unify class representations and distinguish between similar features. Even emerging class-guided approaches are limited by coarse class prototype representations and a neglect of target structural information. Therefore, this paper proposes a Prototype-Driven Structure Synergy Network (PDSSNet). The design of this network is based on a core concept, a complete ground object is jointly defined by its invariant class semantics and its variant spatial structure. To implement this, we have designed three key modules. First, the Adaptive Prototype Extraction Module (APEM) ensures semantic accuracy from the source by encoding the ground truth to extract unbiased class prototypes. Subsequently, the designed Semantic-Structure Coordination Module (SSCM) follows a hierarchical semantics-first, structure-second principle. This involves first establishing a global semantic cognition, then leveraging structural information to constrain and refine the semantic representation, thereby ensuring the integrity of class information. Finally, the Channel Similarity Adjustment Module (CSAM) employs a dynamic step-size adjustment mechanism to focus on discriminative features between classes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PDSSNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/wangjunyi-1/PDSSNet.
在遥感图像的语义分割中,获取完整的地面物体对于实现精确分析至关重要。然而,这项任务受到两大挑战的严重阻碍:类内高变异性和类间高相似性。传统方法往往由于无法有效地统一类表示和区分相似特征,导致分割结果不完整。甚至新兴的类引导方法也受限于粗糙的类原型表示和目标结构信息的忽视。因此,本文提出了一种原型驱动的结构协同网络(PDSSNet)。该网络的设计基于一个核心概念:一个完整的地面物体由其不变的类语义和其变化的空间结构共同定义。为实现这一点,我们设计了三个关键模块。首先,自适应原型提取模块(APEM)通过编码真实值确保源的语义准确性,以提取无偏类原型。接着,设计的语义结构协调模块(SSCM)遵循分层语义优先、结构其次的原则。这包括首先建立全局语义认知,然后利用结构信息来约束和细化语义表示,从而确保类信息的完整性。最后,通道相似性调整模块(CSAM)采用动态步长调整机制,关注类之间的判别特征。大量实验表明,PDSSNet优于最新方法。源代码可在https://github.com/wangjunyi-1/PDSSNet上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种用于遥感图像语义分割的Prototype-Driven Structure Synergy Network(PDSSNet)。针对传统方法无法有效统一类表示和区分相似特征的问题,该网络通过自适应原型提取模块(APEM)确保语义准确性,通过语义-结构协调模块(SSCM)实现全局语义认知并利用结构信息约束和细化语义表示,确保类信息的完整性。此外,该网络还通过通道相似性调整模块(CSAM)采用动态步长调整机制,关注类间判别特征。实验表明,PDSSNet优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像语义分割中,获取完整地面物体对精确分析至关重要。
- 传统方法面临高类内方差和高类间相似性的挑战,导致不完全分割结果。
- PDSSNet网络设计基于一个核心概念:完整地面物体由其不变类语义和可变空间结构共同定义。
- 网络包含三个关键模块:自适应原型提取模块(APEM)确保语义准确性,语义-结构协调模块(SSCM)实现全局语义认知并细化语义表示,通道相似性调整模块(CSAM)关注类间判别特征。
- PDSSNet通过动态步长调整机制,提高了对遥感图像语义分割的精度和效率。
- PDSSNet在实验中表现出优异性能,优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

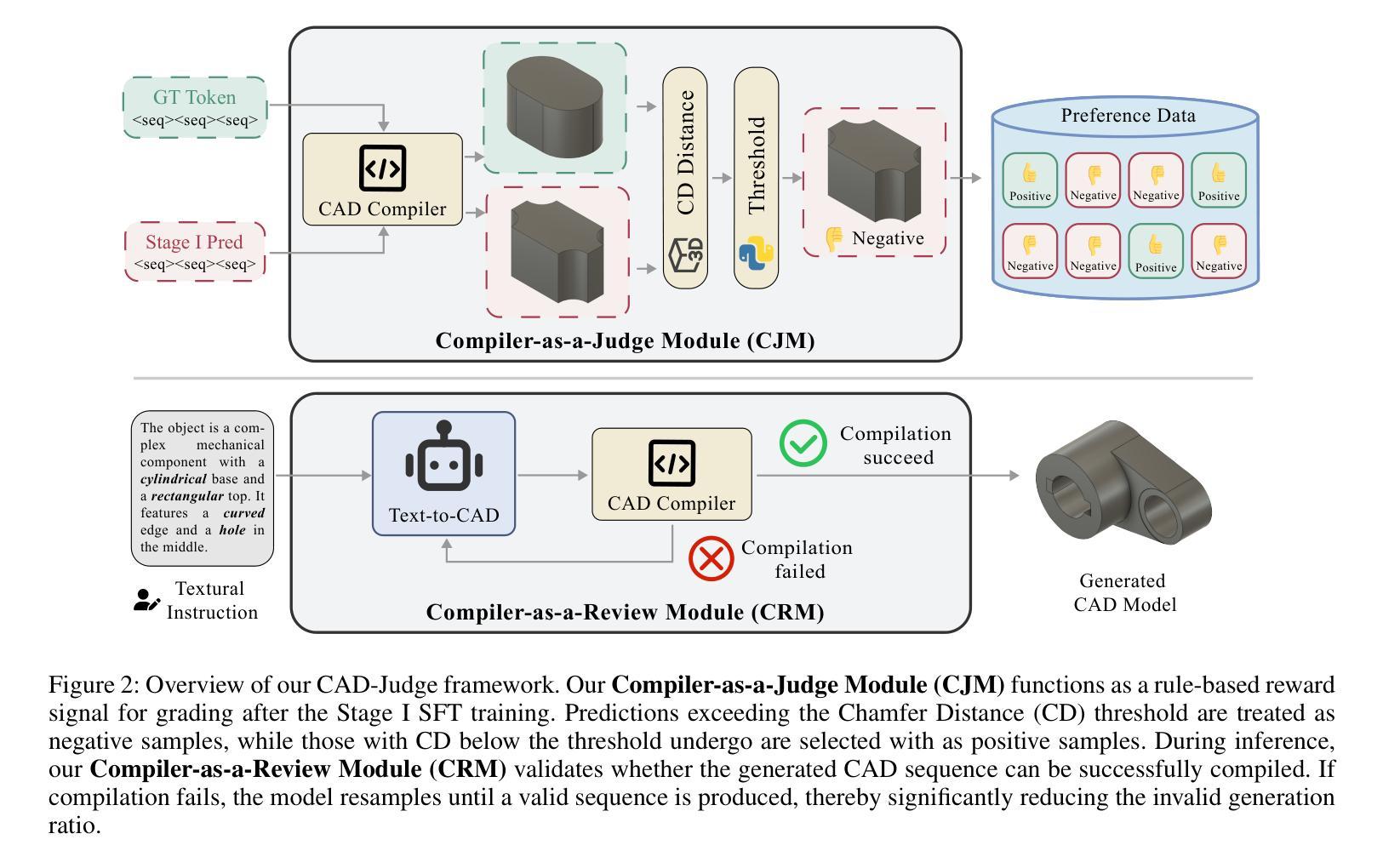
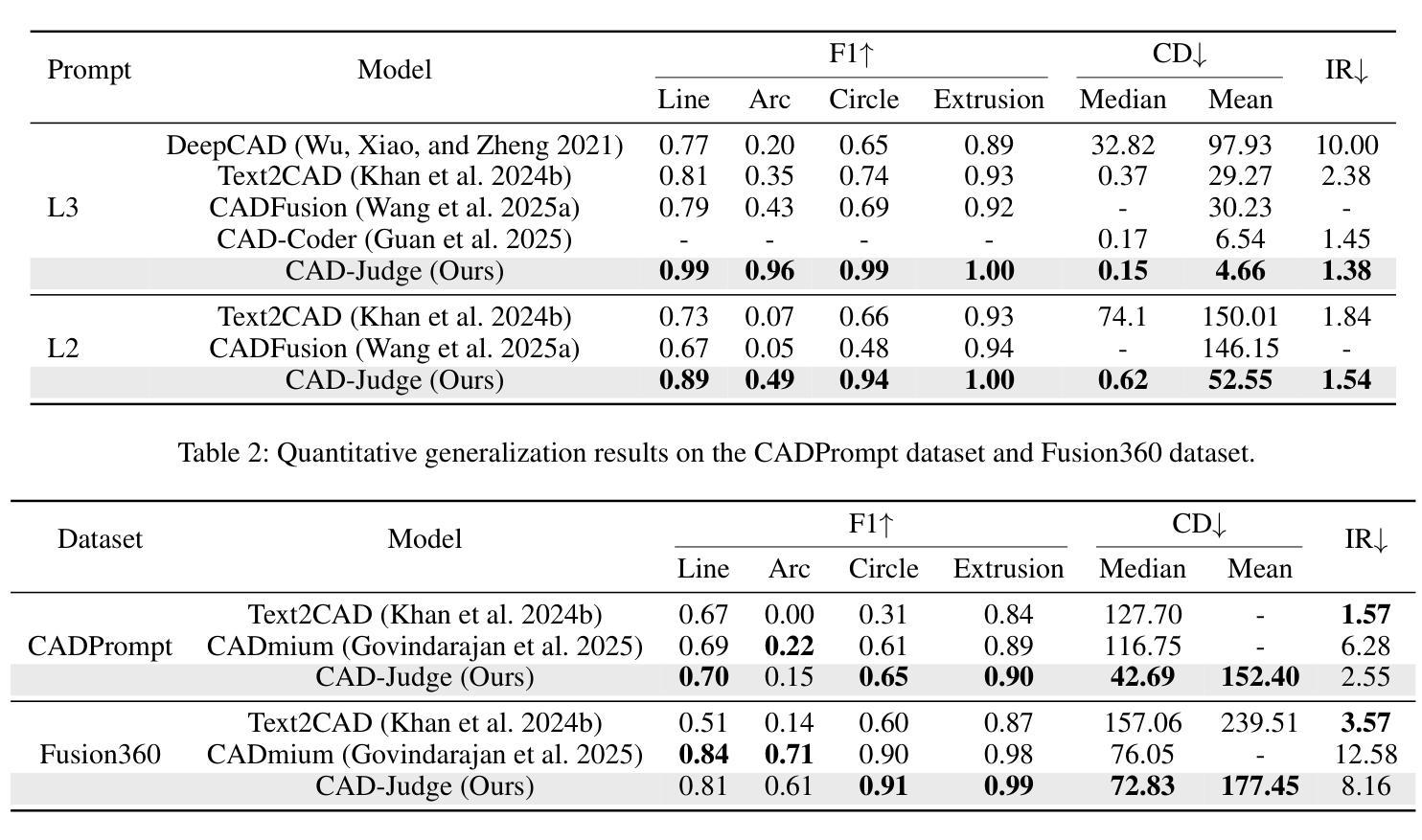
CAD-Judge: Toward Efficient Morphological Grading and Verification for Text-to-CAD Generation
Authors:Zheyuan Zhou, Jiayi Han, Liang Du, Naiyu Fang, Lemiao Qiu, Shuyou Zhang
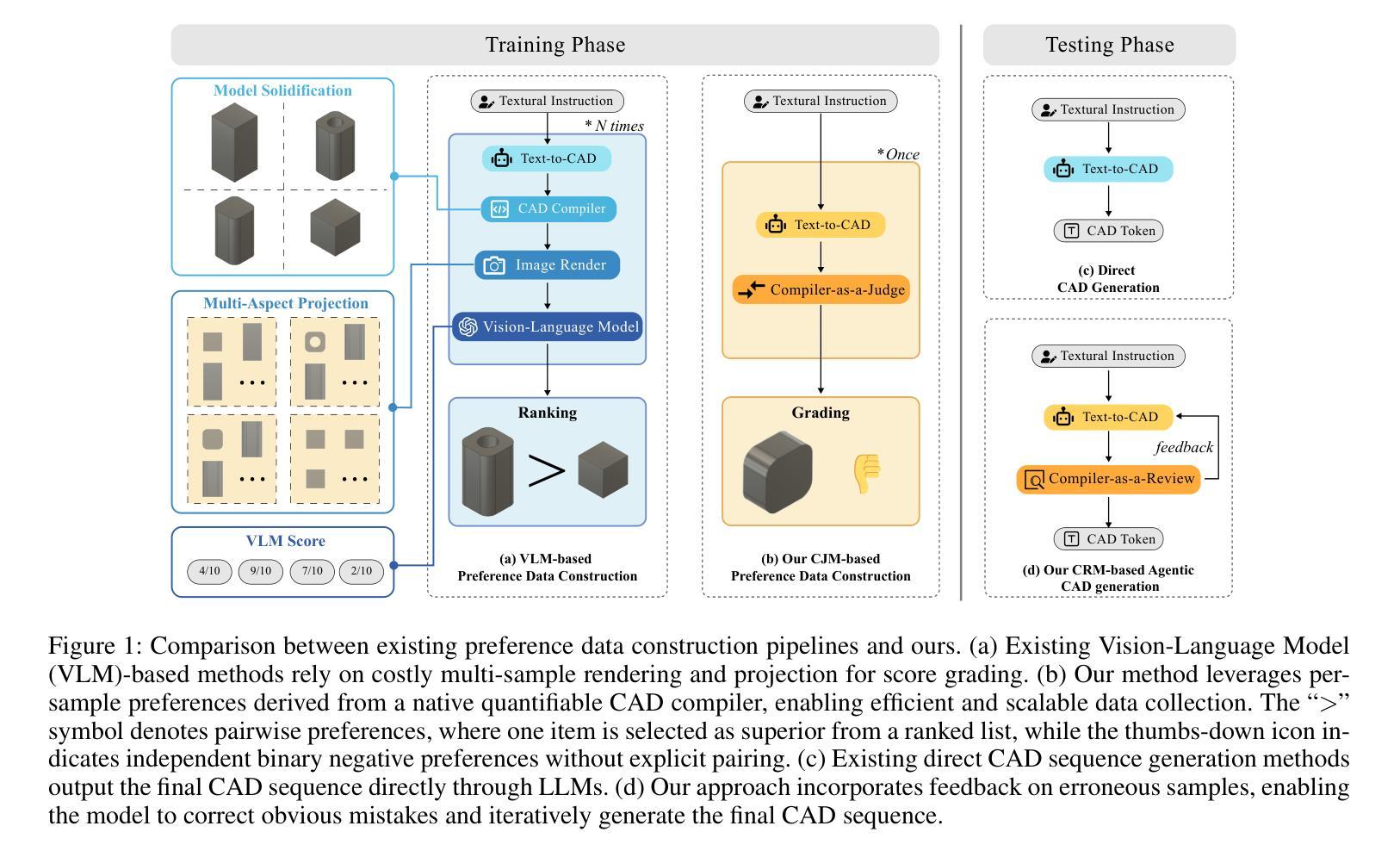
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models are widely used across industrial design, simulation, and manufacturing processes. Text-to-CAD systems aim to generate editable, general-purpose CAD models from textual descriptions, significantly reducing the complexity and entry barrier associated with traditional CAD workflows. However, rendering CAD models can be slow, and deploying VLMs to review CAD models can be expensive and may introduce reward hacking that degrades the systems. To address these challenges, we propose CAD-Judge, a novel, verifiable reward system for efficient and effective CAD preference grading and grammatical validation. We adopt the Compiler-as-a-Judge Module (CJM) as a fast, direct reward signal, optimizing model alignment by maximizing generative utility through prospect theory. To further improve the robustness of Text-to-CAD in the testing phase, we introduce a simple yet effective agentic CAD generation approach and adopt the Compiler-as-a-Review Module (CRM), which efficiently verifies the generated CAD models, enabling the system to refine them accordingly. Extensive experiments on challenging CAD datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining superior efficiency.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型在工业设计、仿真和制造过程中得到广泛应用。文本到CAD系统旨在从文本描述中生成可编辑的通用CAD模型,从而显著减少与传统CAD工作流程相关的复杂性和入门壁垒。然而,渲染CAD模型可能会很慢,使用VLMs来审查CAD模型可能会很昂贵,并可能引入奖励破解,从而破坏系统。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CAD-Judge,这是一种用于高效有效的CAD偏好分级和语法验证的可验证奖励系统。我们采用编译器作为法官模块(CJM)作为快速直接的奖励信号,通过前景理论优化生成实用性的最大化,从而实现模型对齐的优化。为了进一步提高文本到CAD在测试阶段的稳健性,我们引入了一种简单有效的代理CAD生成方法,并采用编译器作为评审模块(CRM),有效地验证了生成的CAD模型,使系统能够进行相应的改进。在具有挑战性的CAD数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了卓越的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型的应用及其面临的挑战,包括渲染速度慢和验证成本高的问题。为解决这些问题,提出了CAD-Judge系统,该系统采用Compiler-as-a-Judge模块作为快速直接的奖励信号,通过前景理论优化模型对齐,提高CAD偏好分级和语法验证的效率。此外,还介绍了Compiler-as-a-Review模块,用于在测试阶段提高文本到CAD转换的稳健性。实验证明,该方法在保持高效率的同时实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- CAD模型广泛应用于工业设计、模拟和制造过程。
- 文本到CAD系统旨在从文本描述生成可编辑的通用CAD模型,降低传统CAD工作流的复杂性和入门门槛。
- CAD-Judge系统是一种用于高效、有效的CAD偏好分级和语法验证的可验证奖励系统。
- Compiler-as-a-Judge模块作为快速直接的奖励信号,优化模型对齐,提高生成实用性。
- 引入Compiler-as-a-Review模块,有效验证生成的CAD模型,提高系统稳健性。
- 实验证明,CAD-Judge系统在保持高效率的同时实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

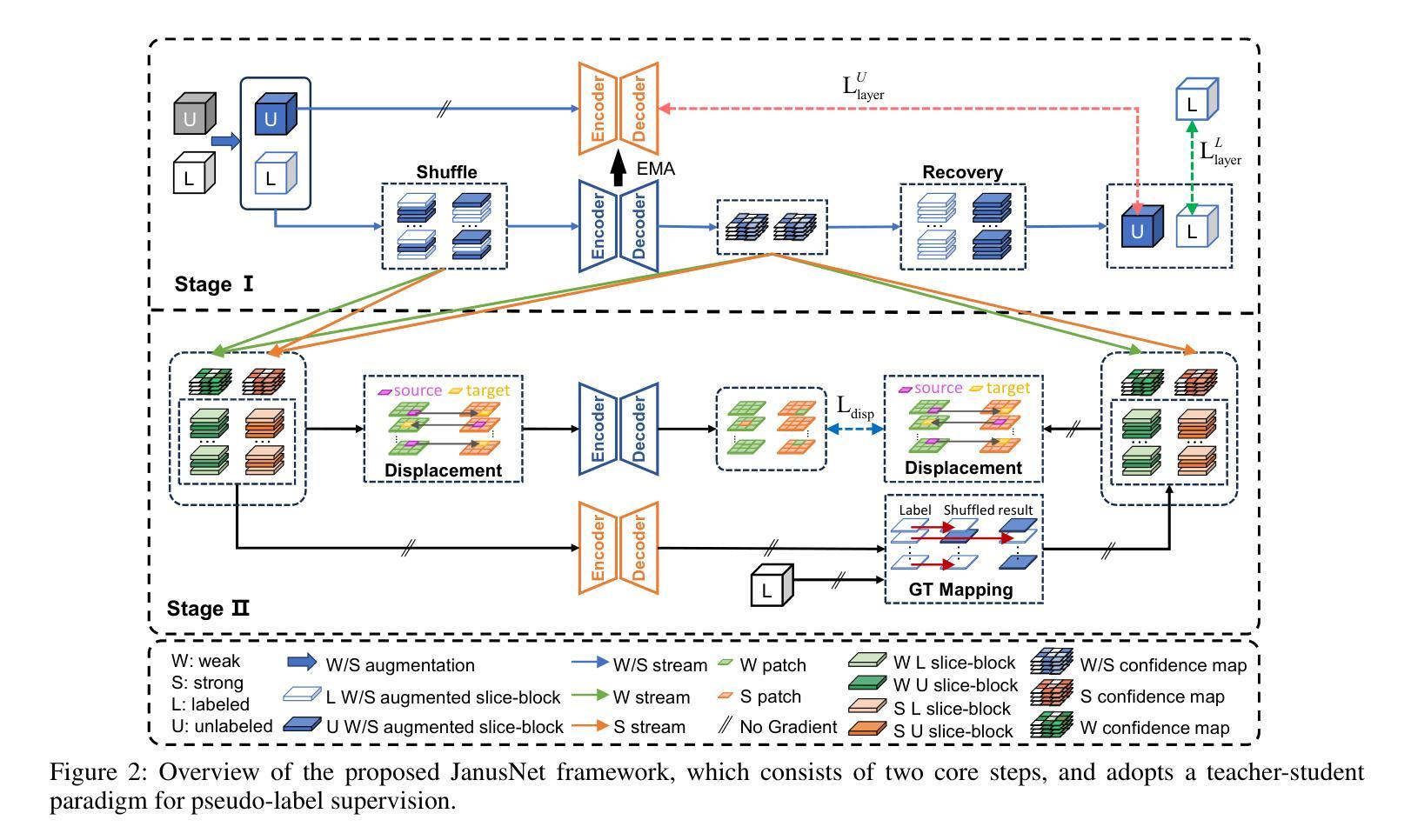
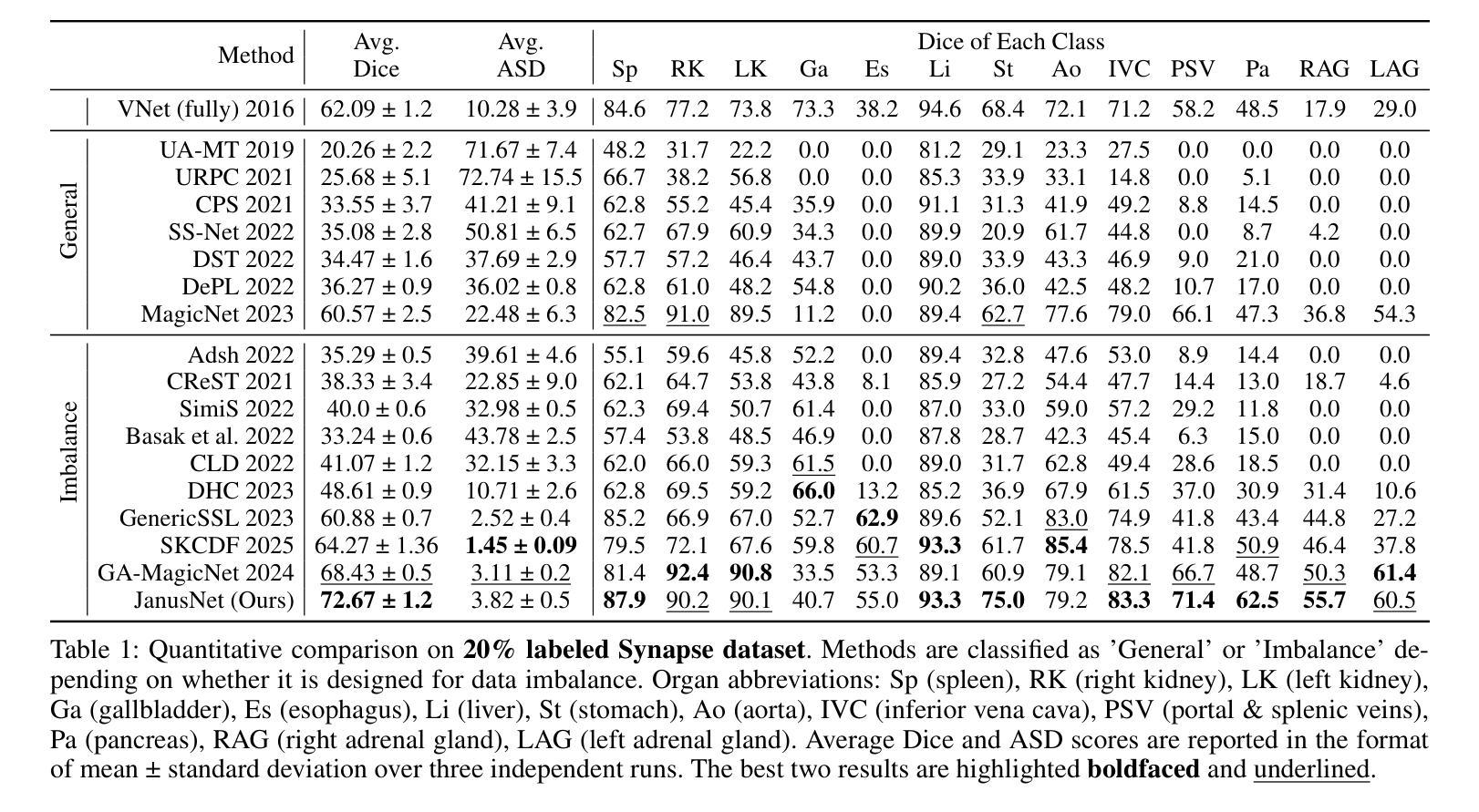
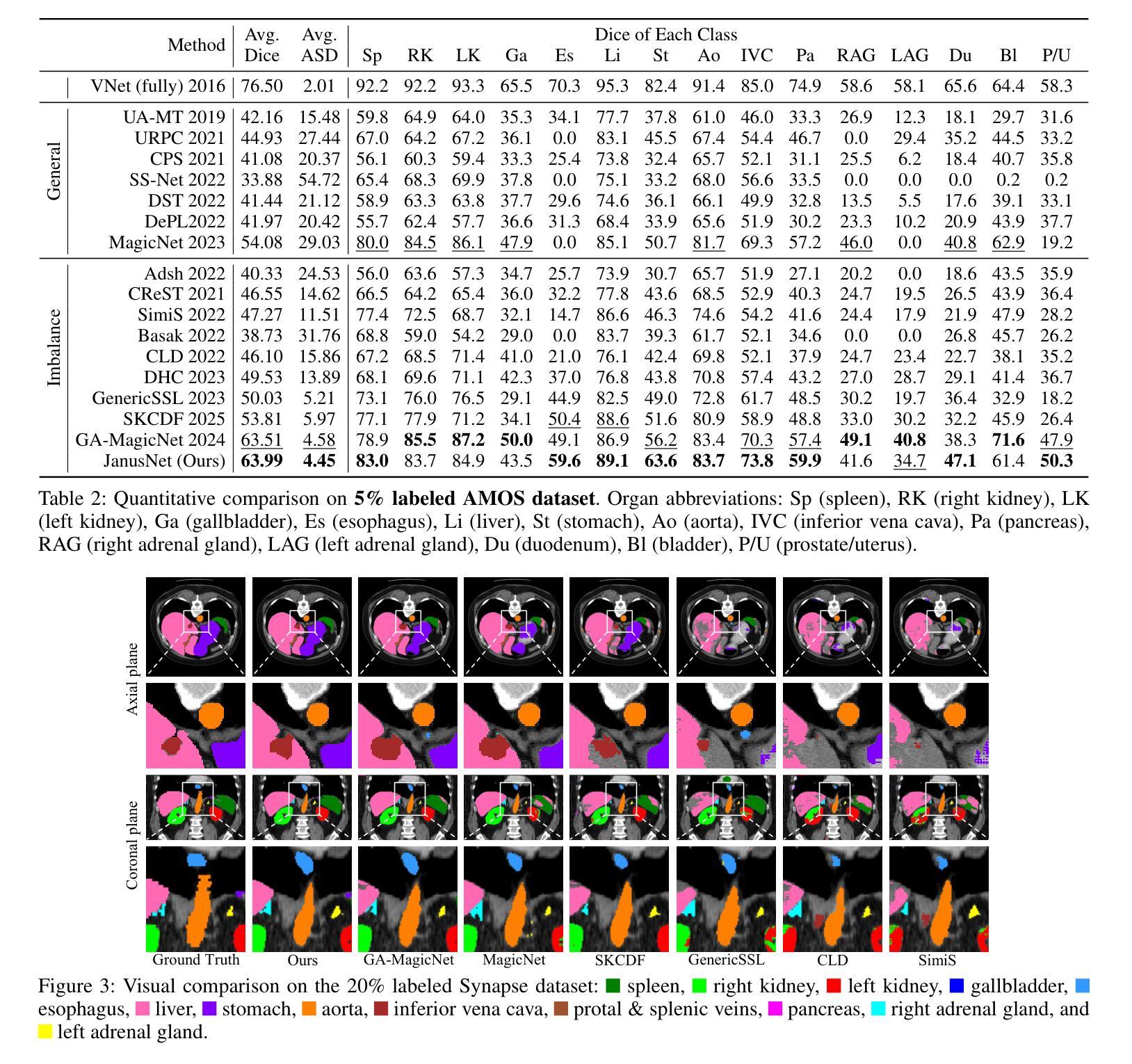
JanusNet: Hierarchical Slice-Block Shuffle and Displacement for Semi-Supervised 3D Multi-Organ Segmentation
Authors:Zheng Zhang, Tianzhuzi Tan, Guanchun Yin, Bo Zhang, Xiuzhuang Zhou
Limited by the scarcity of training samples and annotations, weakly supervised medical image segmentation often employs data augmentation to increase data diversity, while randomly mixing volumetric blocks has demonstrated strong performance. However, this approach disrupts the inherent anatomical continuity of 3D medical images along orthogonal axes, leading to severe structural inconsistencies and insufficient training in challenging regions, such as small-sized organs, etc. To better comply with and utilize human anatomical information, we propose JanusNet}, a data augmentation framework for 3D medical data that globally models anatomical continuity while locally focusing on hard-to-segment regions. Specifically, our Slice-Block Shuffle step performs aligned shuffling of same-index slice blocks across volumes along a random axis, while preserving the anatomical context on planes perpendicular to the perturbation axis. Concurrently, the Confidence-Guided Displacement step uses prediction reliability to replace blocks within each slice, amplifying signals from difficult areas. This dual-stage, axis-aligned framework is plug-and-play, requiring minimal code changes for most teacher-student schemes. Extensive experiments on the Synapse and AMOS datasets demonstrate that JanusNet significantly surpasses state-of-the-art methods, achieving, for instance, a 4% DSC gain on the Synapse dataset with only 20% labeled data.
受限于训练样本和标注的稀缺性,弱监督医学图像分割通常采用数据增强来增加数据多样性,而随机混合体积块的方法已经表现出了强大的性能。然而,这种方法会破坏3D医学图像在正交轴上的固有解剖连续性,导致严重的结构不一致性和在挑战性区域(例如小型器官等)的训练不足。为了更好地符合和利用人体解剖信息,我们提出了JanusNet,这是一个针对3D医学数据的数据增强框架,能够全局地建模解剖连续性,同时在局部关注难以分割的区域。具体而言,我们的切片块打乱步骤会在体积内沿随机轴执行相同索引切片块的对齐打乱,同时保留垂直于扰动轴的平面上的解剖上下文。同时,置信度引导位移步骤使用预测可靠性来替换每个切片内的块,从而放大来自困难区域的信号。这种双阶段、轴对齐的框架即插即用,对于大多数师徒方案来说,几乎不需要修改代码。在Synapse和AMOS数据集上的广泛实验表明,JanusNet显著超越了最先进的方法,例如,在仅有20%标记数据的情况下,在Synapse数据集上实现了4%的DSC增益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对3D医学数据的新型数据增强框架JanusNet,该框架能够在全局上模拟人体解剖连续性,同时在局部关注难以分割的区域。通过切片块随机轴向上的对齐打乱操作,以及利用预测可靠性替换切片内的区块,实现了对解剖结构信息的有效利用和补充。实验表明,JanusNet在仅有少量标注数据的情况下,仍能在Synapse等数据集上显著提高分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- JanusNet是一个针对3D医学图像的数据增强框架,旨在解决训练样本和标注稀缺的问题。
- 传统方法随机混合体积块,破坏了3D医学图像的解剖连续性。
- JanusNet通过全局建模解剖连续性,并在局部关注难以分割区域来解决这个问题。
- JanusNet包括两个步骤:Slice-Block Shuffle(切片块打乱)和Confidence-Guided Displacement(置信度引导位移)。
- Slice-Block Shuffle步骤沿着随机轴对相同索引的切片块进行对齐打乱,同时保持垂直于扰动轴的平面上的解剖上下文。
- Confidence-Guided Displacement步骤利用预测可靠性来替换切片内的区块,从而放大困难区域的信号。
点此查看论文截图