⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
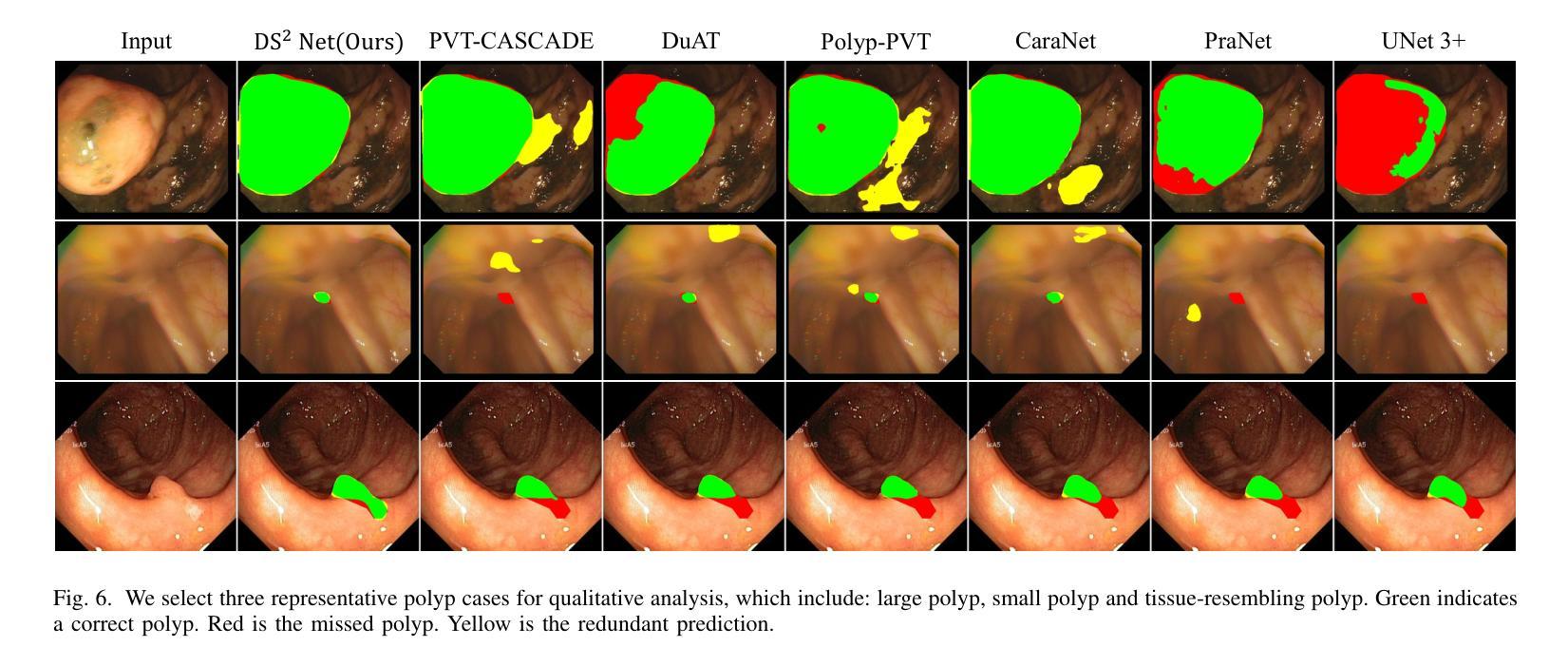
DS$^2$Net: Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhaohong Huang, Yuxin Zhang, Mingbao Lin, Taojian Zhou, Guorong Cai, Rongrong Ji
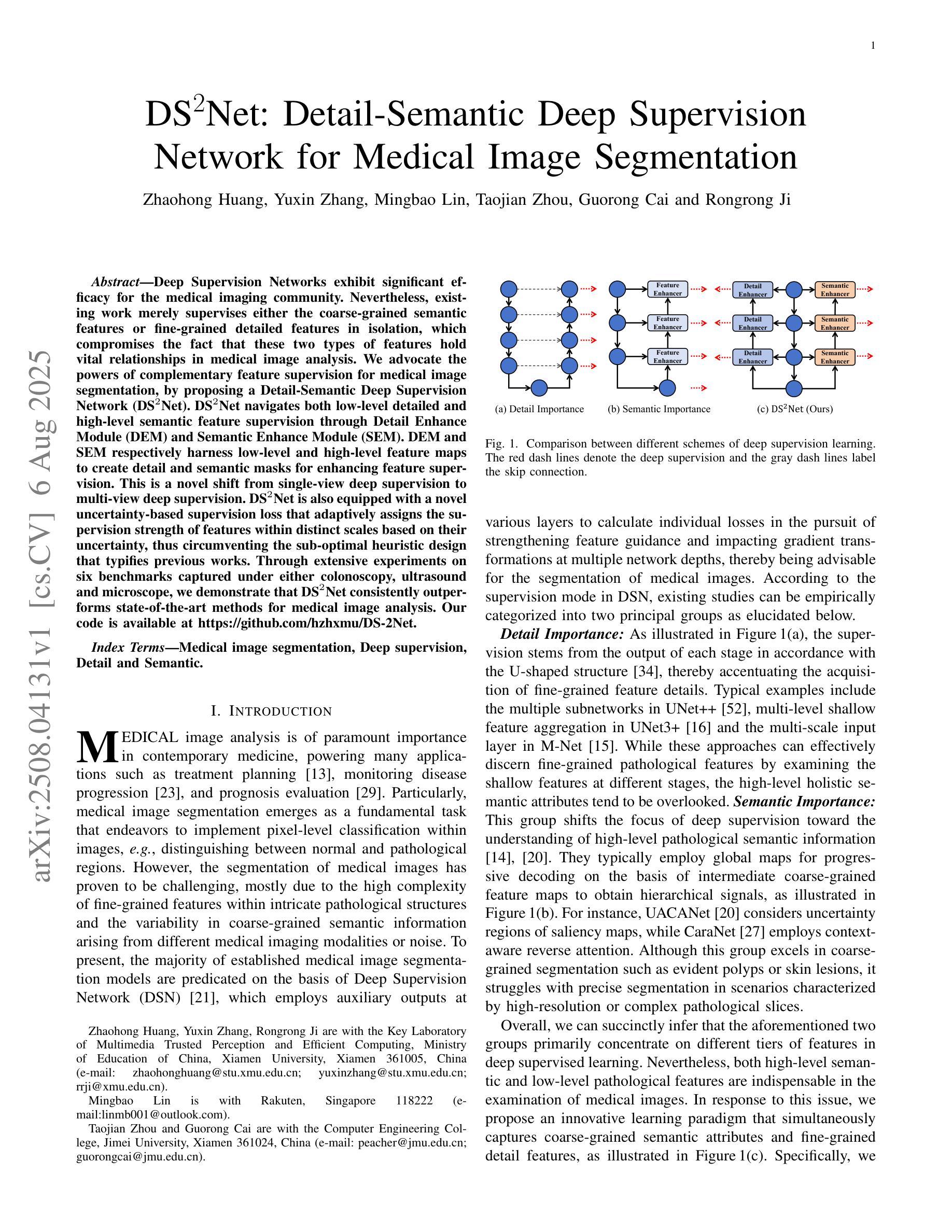
Deep Supervision Networks exhibit significant efficacy for the medical imaging community. Nevertheless, existing work merely supervises either the coarse-grained semantic features or fine-grained detailed features in isolation, which compromises the fact that these two types of features hold vital relationships in medical image analysis. We advocate the powers of complementary feature supervision for medical image segmentation, by proposing a Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network (DS$^2$Net). DS$^2$Net navigates both low-level detailed and high-level semantic feature supervision through Detail Enhance Module (DEM) and Semantic Enhance Module (SEM). DEM and SEM respectively harness low-level and high-level feature maps to create detail and semantic masks for enhancing feature supervision. This is a novel shift from single-view deep supervision to multi-view deep supervision. DS$^2$Net is also equipped with a novel uncertainty-based supervision loss that adaptively assigns the supervision strength of features within distinct scales based on their uncertainty, thus circumventing the sub-optimal heuristic design that typifies previous works. Through extensive experiments on six benchmarks captured under either colonoscopy, ultrasound and microscope, we demonstrate that DS$^2$Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for medical image analysis.
深度监督网络对医学影像界具有显著效果。然而,现有工作仅孤立地监督粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征,这忽略了这两种特征在医学图像分析中具有重要关联的事实。我们提出通过细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net)进行医学图像分割的互补特征监督。DS$^2$Net通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)导航低级别的详细特征和高级别的语义特征监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低级别和高级别特征图创建细节和语义掩膜,以增强特征监督。这是从单视图深度监督到多视图深度监督的新转变。DS$^2$Net还配备了一种新型的不确定性监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度的特征监督强度,从而避免了以前工作中典型的次优启发式设计。通过在结肠镜、超声和显微镜下的六个基准测试集上进行广泛实验,我们证明了DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:深度监督网络对医学影像领域具有显著效果。然而,现有工作仅孤立地监督粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征,忽略了两者在医学图像分析中的紧密关系。我们提出了一个细节语义深度监督网络(DS^2Net),通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)进行互补特征监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低层次和高层次特征图创建细节和语义掩膜,以增强特征监督,实现了从单视角深度监督到多视角深度监督的新转变。此外,DS^2Net还引入了一种基于不确定性监督的损失函数,根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度的特征监督强度,避免了以往工作中的次优启发式设计。在六个不同医学成像模式下的基准测试上,DS^2Net表现出卓越的性能,超越了现有的医学图像分析方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度监督网络在医学图像分析中具有显著效果。
- 现有工作孤立地监督粗粒度语义特征和细粒度详细特征,忽略了两者之间的关系。
- 提出了细节语义深度监督网络(DS^2Net),通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)进行互补特征监督。
- DS^2Net实现了从单视角到多视角的深度监督转变。
- DS^2Net引入了基于不确定性监督的损失函数,自适应地分配不同尺度的特征监督强度。
- 该损失函数克服了以往工作中的次优启发式设计。
点此查看论文截图
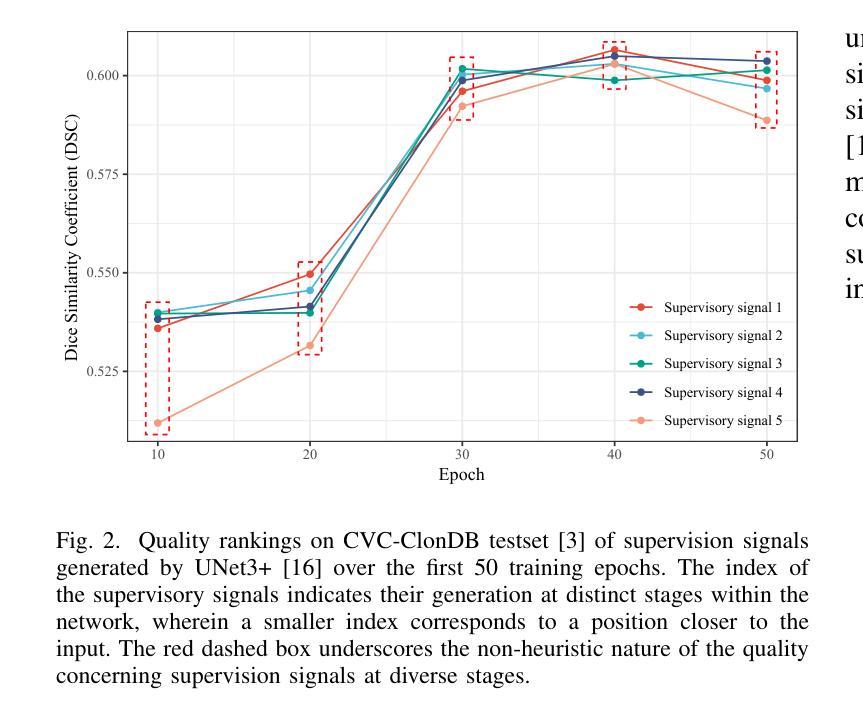
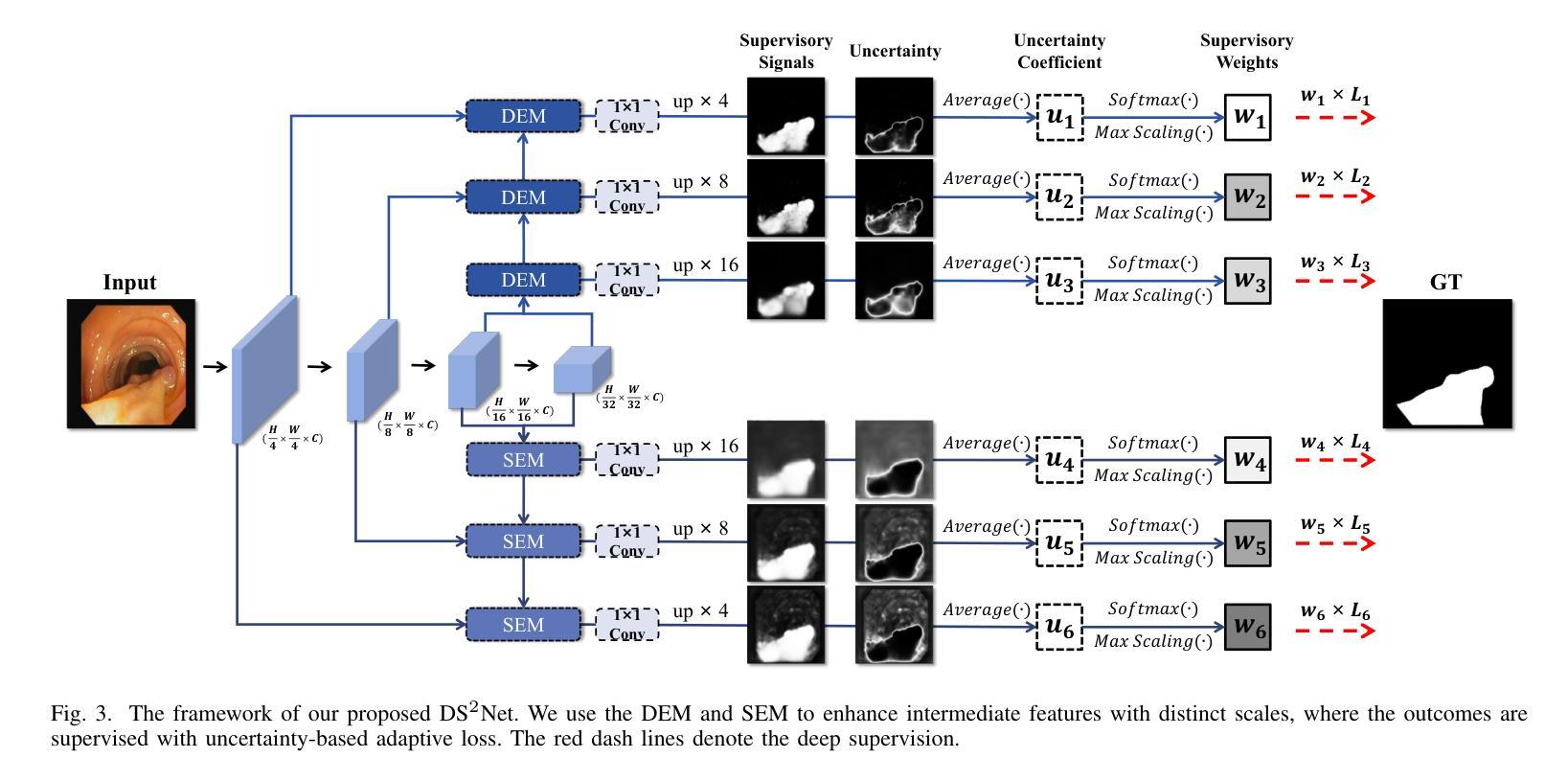
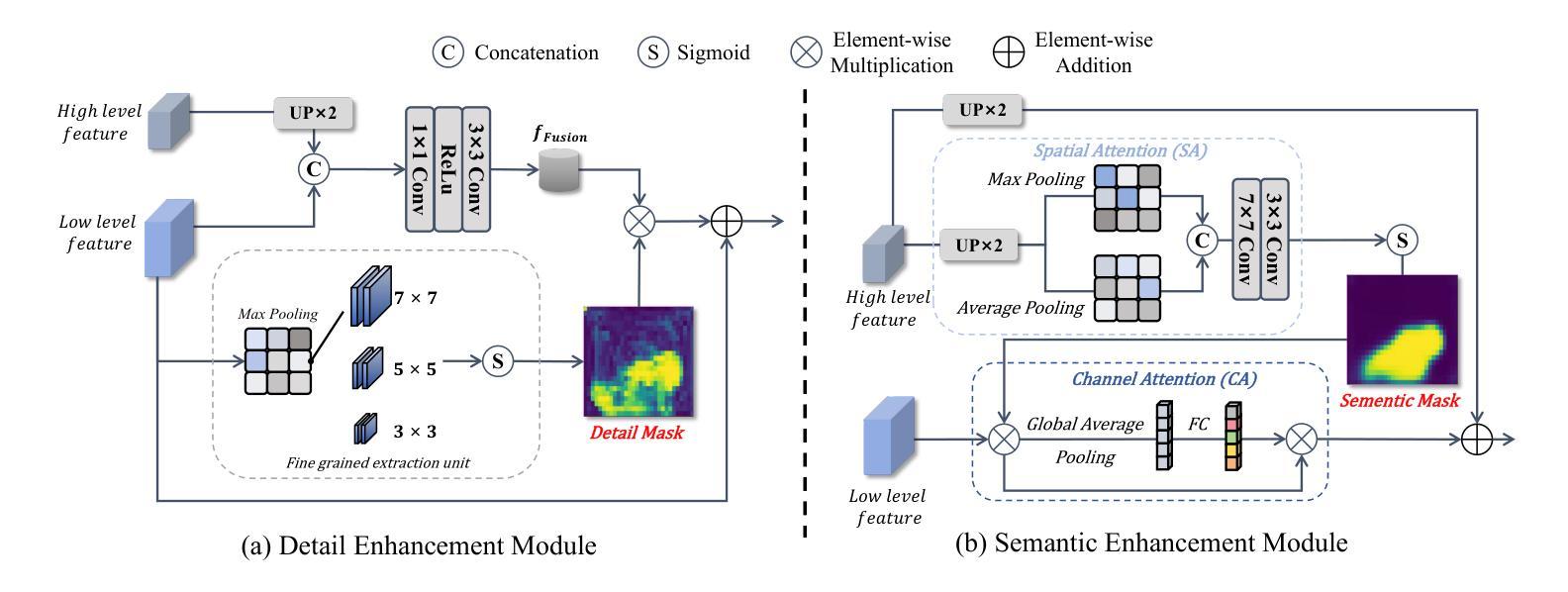
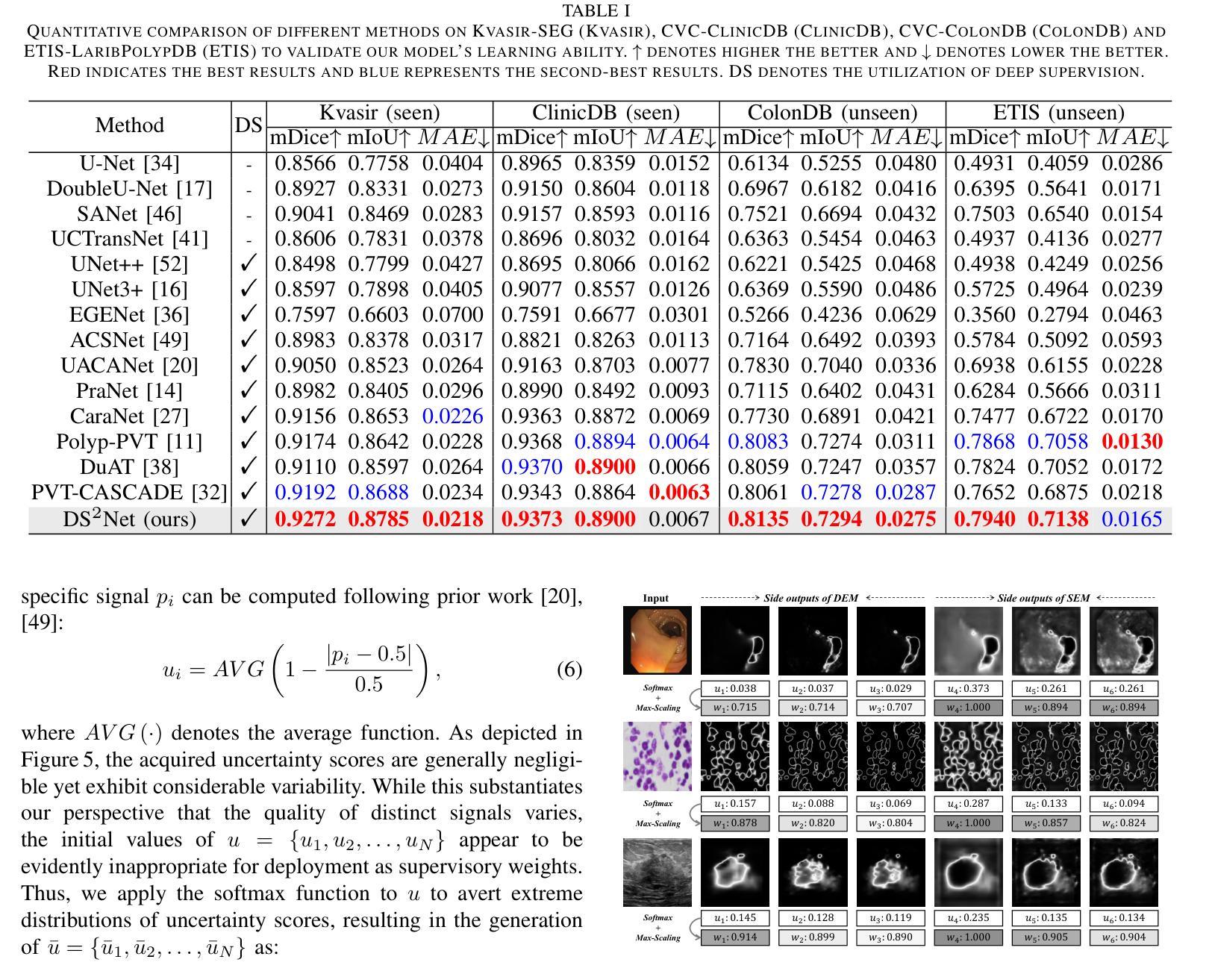
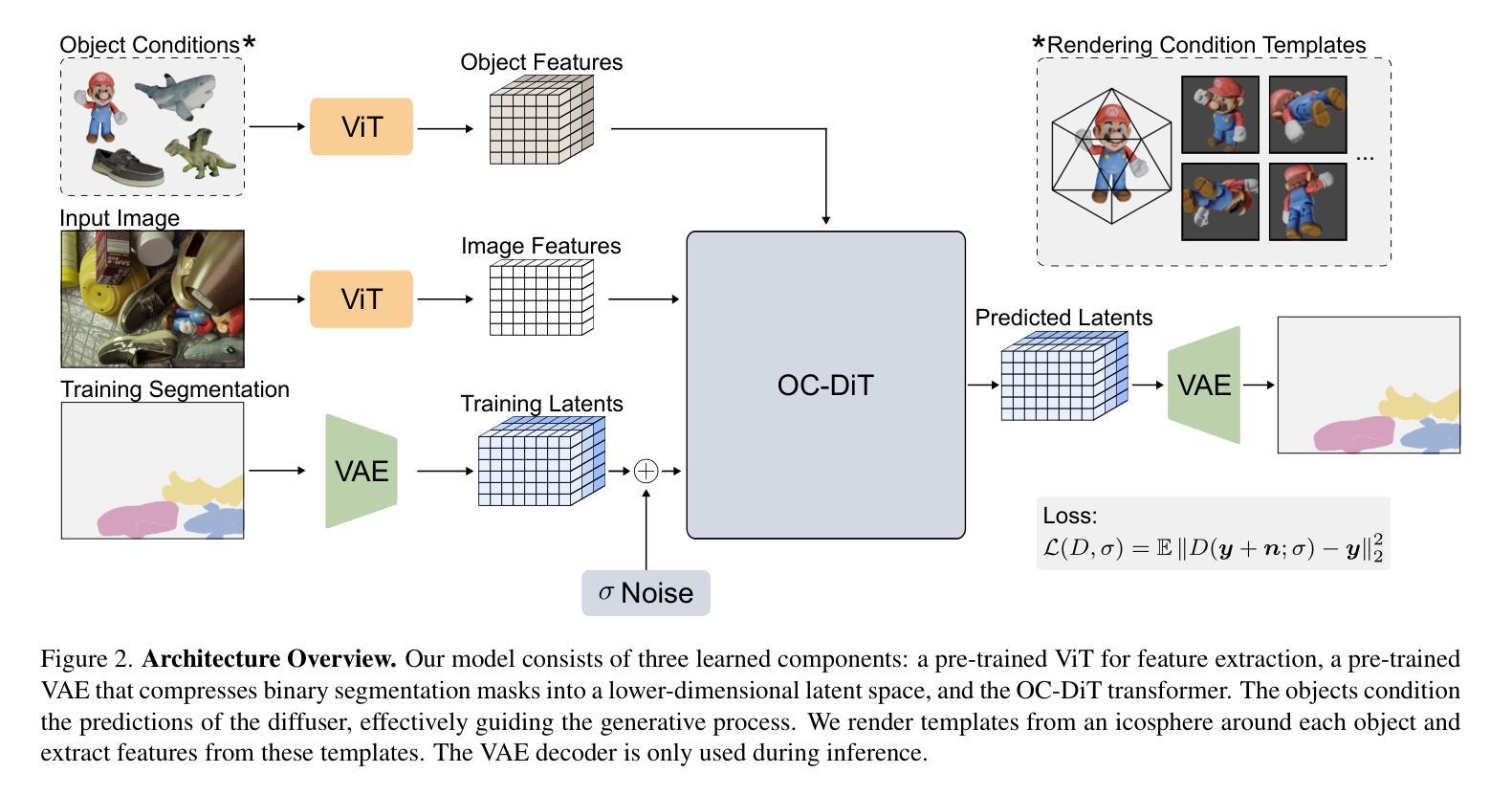
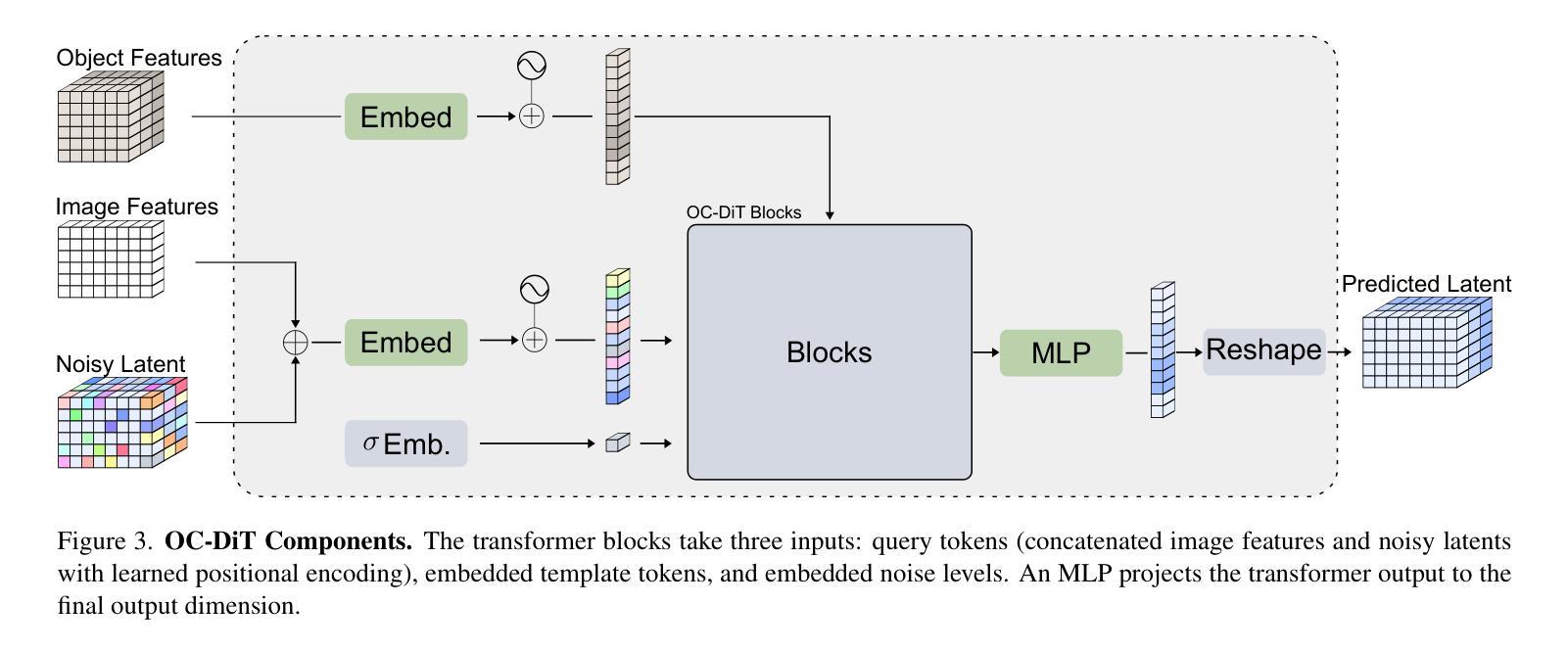
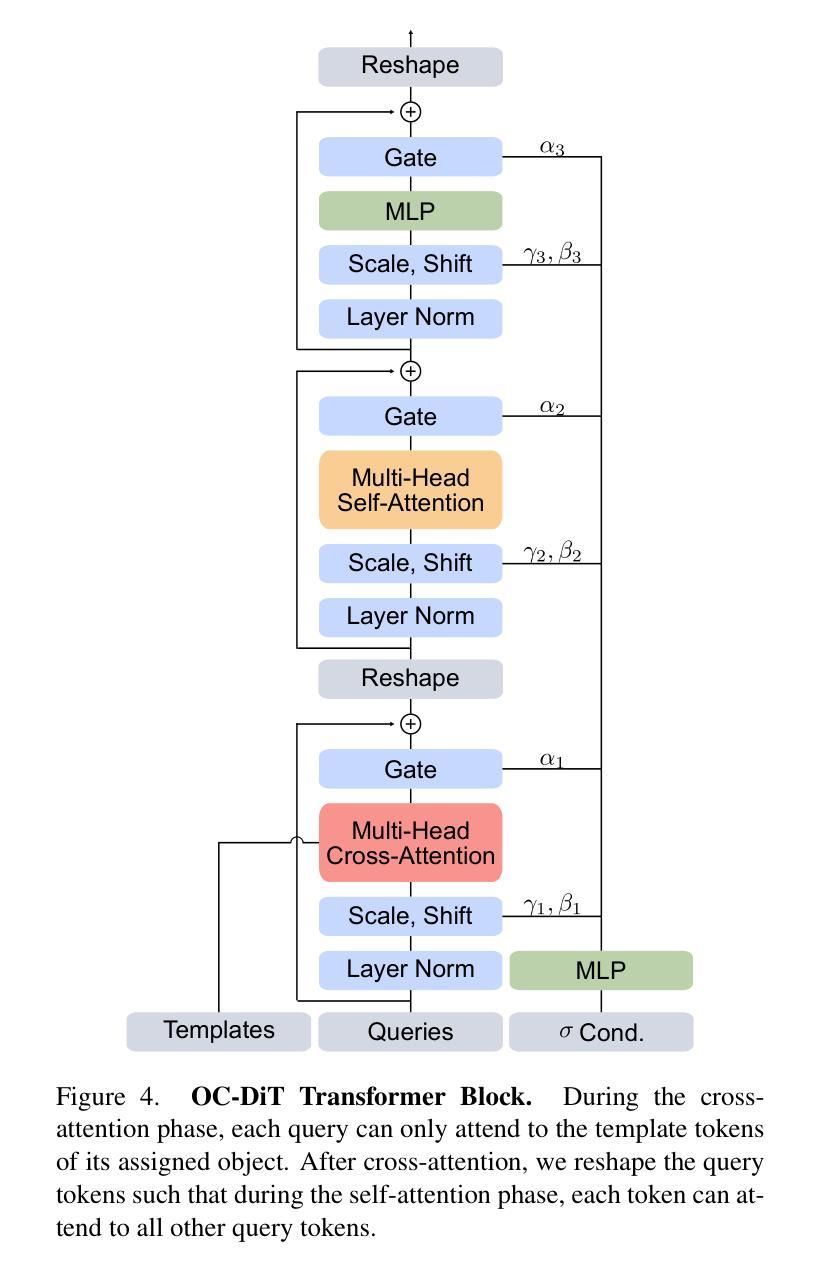
Conditional Latent Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Instance Segmentation
Authors:Maximilian Ulmer, Wout Boerdijk, Rudolph Triebel, Maximilian Durner
This paper presents OC-DiT, a novel class of diffusion models designed for object-centric prediction, and applies it to zero-shot instance segmentation. We propose a conditional latent diffusion framework that generates instance masks by conditioning the generative process on object templates and image features within the diffusion model’s latent space. This allows our model to effectively disentangle object instances through the diffusion process, which is guided by visual object descriptors and localized image cues. Specifically, we introduce two model variants: a coarse model for generating initial object instance proposals, and a refinement model that refines all proposals in parallel. We train these models on a newly created, large-scale synthetic dataset comprising thousands of high-quality object meshes. Remarkably, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple challenging real-world benchmarks, without requiring any retraining on target data. Through comprehensive ablation studies, we demonstrate the potential of diffusion models for instance segmentation tasks.
本文介绍了OC-DiT,这是一种专为对象中心预测设计的新型扩散模型,并应用于零样本实例分割。我们提出了一个条件潜在扩散框架,该框架通过在扩散模型的潜在空间内对生成过程进行对象模板和图像特征的调节,生成实例掩码。这允许我们的模型通过扩散过程有效地分离对象实例,该过程由视觉对象描述符和局部图像线索指导。具体来说,我们引入了两种模型变体:一种用于生成初始对象实例提议的粗略模型,以及一种并行优化所有提议的精细模型。我们在新创建的大规模合成数据集上训练这些模型,该数据集包含数千个高质量的对象网格。值得注意的是,我们的模型在多个具有挑战性的真实世界基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,而无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练。通过全面的消融研究,我们展示了扩散模型在实例分割任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
新一代对象中心预测扩散模型OC-DiT介绍。该模型应用于零实例分割,提出条件潜在扩散框架,生成实例掩膜,以对象模板和图像特征为条件在扩散模型的潜在空间中。通过视觉对象描述符和局部图像线索引导扩散过程,有效分离对象实例。包括粗模型用于生成初始对象实例提案和细化模型,用于并行细化所有提案。该模型在新创建的大规模合成数据集上进行训练,包含数千个高质量对象网格。在多个具有挑战性的真实世界基准测试中实现了卓越性能,无需在目标数据上重新训练。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了OC-DiT模型:这是一种新型扩散模型,设计用于对象中心预测,并应用于零实例分割。
- 提出了条件潜在扩散框架:该框架通过以对象模板和图像特征为条件来生成实例掩膜。
- 通过视觉对象描述符和局部图像线索引导扩散过程,实现了对象实例的有效分离。
- OC-DiT包含两个模型变体:一个粗模型用于生成初始对象实例提案,一个细化模型用于并行细化所有提案。
- 模型在新创建的大规模合成数据集上进行训练,该数据集包含数千个高质量对象网格。
- OC-DiT在多个挑战性的真实世界基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

UNISELF: A Unified Network with Instance Normalization and Self-Ensembled Lesion Fusion for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Jinwei Zhang, Lianrui Zuo, Blake E. Dewey, Samuel W. Remedios, Yihao Liu, Savannah P. Hays, Dzung L. Pham, Ellen M. Mowry, Scott D. Newsome, Peter A. Calabresi, Aaron Carass, Jerry L. Prince
Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions using multicontrast magnetic resonance (MR) images improves efficiency and reproducibility compared to manual delineation, with deep learning (DL) methods achieving state-of-the-art performance. However, these DL-based methods have yet to simultaneously optimize in-domain accuracy and out-of-domain generalization when trained on a single source with limited data, or their performance has been unsatisfactory. To fill this gap, we propose a method called UNISELF, which achieves high accuracy within a single training domain while demonstrating strong generalizability across multiple out-of-domain test datasets. UNISELF employs a novel test-time self-ensembled lesion fusion to improve segmentation accuracy, and leverages test-time instance normalization (TTIN) of latent features to address domain shifts and missing input contrasts. Trained on the ISBI 2015 longitudinal MS segmentation challenge training dataset, UNISELF ranks among the best-performing methods on the challenge test dataset. Additionally, UNISELF outperforms all benchmark methods trained on the same ISBI training data across diverse out-of-domain test datasets with domain shifts and missing contrasts, including the public MICCAI 2016 and UMCL datasets, as well as a private multisite dataset. These test datasets exhibit domain shifts and/or missing contrasts caused by variations in acquisition protocols, scanner types, and imaging artifacts arising from imperfect acquisition. Our code is available at https://github.com/uponacceptance.
采用多对比度磁共振(MR)图像自动分割多发性硬化症(MS)病变,相较于手动描记,提高了效率和可重复性,而深度学习(DL)方法已经达到了最新技术水平。然而,这些基于DL的方法在单一数据源、有限数据上训练时,尚未同时优化领域内精度和领域外泛化能力,或其表现并不令人满意。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了一种名为UNISELF的方法,该方法在单个训练领域内实现了高精度,同时在多个领域外的测试数据集上表现出了强大的泛化能力。UNISELF采用了一种新型测试时自集成病变融合方法,以提高分割精度,并利用测试时实例标准化(TTIN)潜在特征来解决领域变化和缺失输入对比度问题。在ISBI 2015纵向MS分割挑战训练数据集上训练的UNISELF,在挑战测试数据集上排名最佳方法之一。此外,UNISELF在具有领域变化和缺失对比度的各种领域外的测试数据集上的表现优于所有使用相同ISBI训练数据的基准方法,包括公共的MICCAI 2016和UMCL数据集以及一个私有跨站点数据集。这些测试数据集由于采集协议、扫描仪类型和成像伪影的不完美而导致领域变化和/或缺失对比度。我们的代码可在https://github.com/uponacceptance找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了使用多对比度磁共振图像自动化分割多发性硬化症病灶的方法。虽然深度学习在单一训练域内实现了较高的准确性,但在跨域测试中其性能尚待提高。本文提出了一种名为UNISELF的方法,在单一训练域内实现了高准确性,同时在多个跨域测试数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。UNISELF使用了一种新颖的测试时自集成病灶融合技术,并借助测试时实例归一化(TTIN)解决领域变化和缺失输入对比度问题。在ISBI 2015纵向MS分割挑战训练数据集上训练的UNISELF,在挑战测试数据集上表现优异,并在具有领域变化和缺失对比度的不同跨域测试数据集上优于使用相同ISBI训练数据的基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化分割多发性硬化症病灶可以提高效率和重现性。
- 深度学习在病灶分割方面表现优异,但在单一训练域内的泛化能力有待提高。
- 提出了一种名为UNISELF的方法,实现了在单一训练域内的高准确性和跨多个域的强泛化能力。
- UNISELF采用测试时自集成病灶融合技术提高分割准确性。
- 测试时实例归一化(TTIN)用于解决领域变化和缺失输入对比度问题。
- UNISELF在ISBI 2015挑战测试数据集上表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图

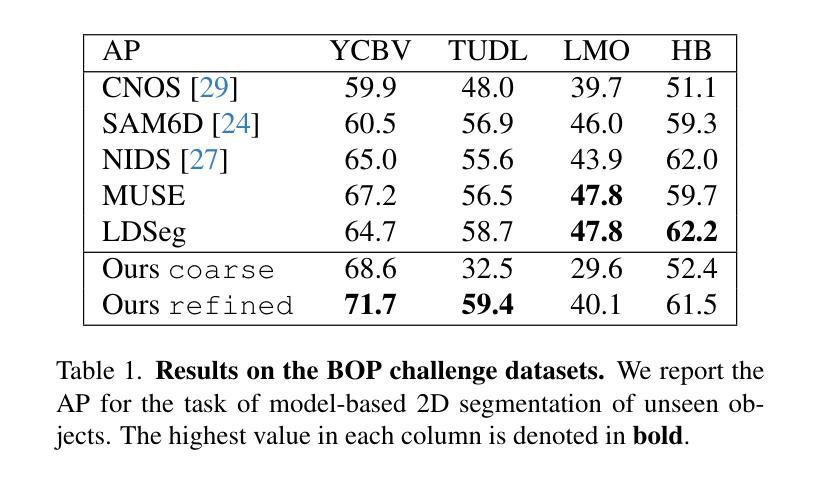
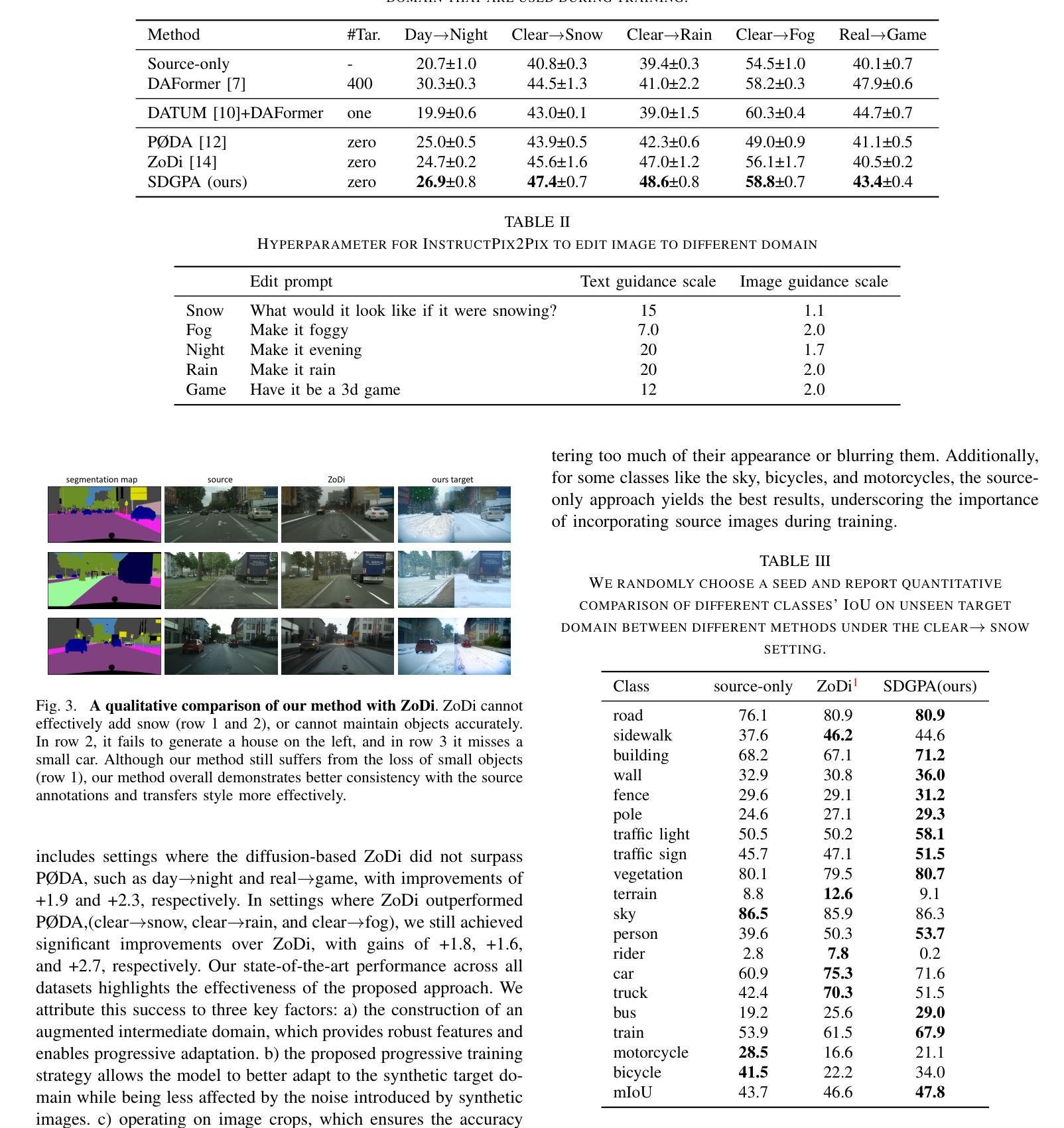
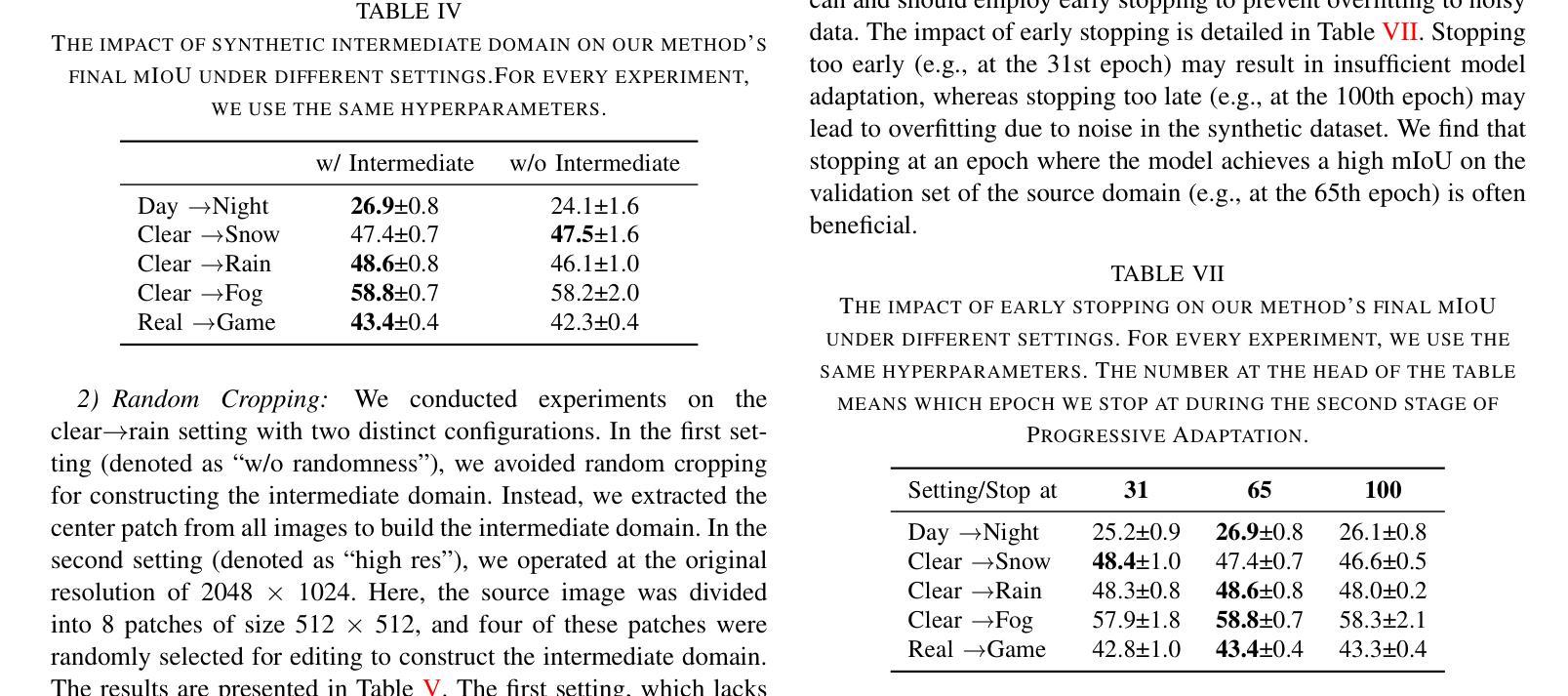
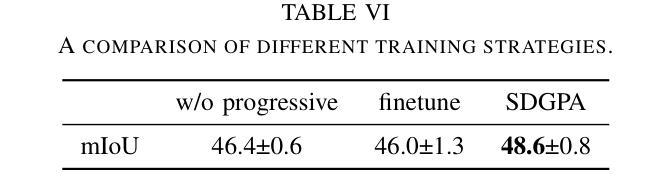
Zero Shot Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation by Synthetic Data Generation and Progressive Adaptation
Authors:Jun Luo, Zijing Zhao, Yang Liu
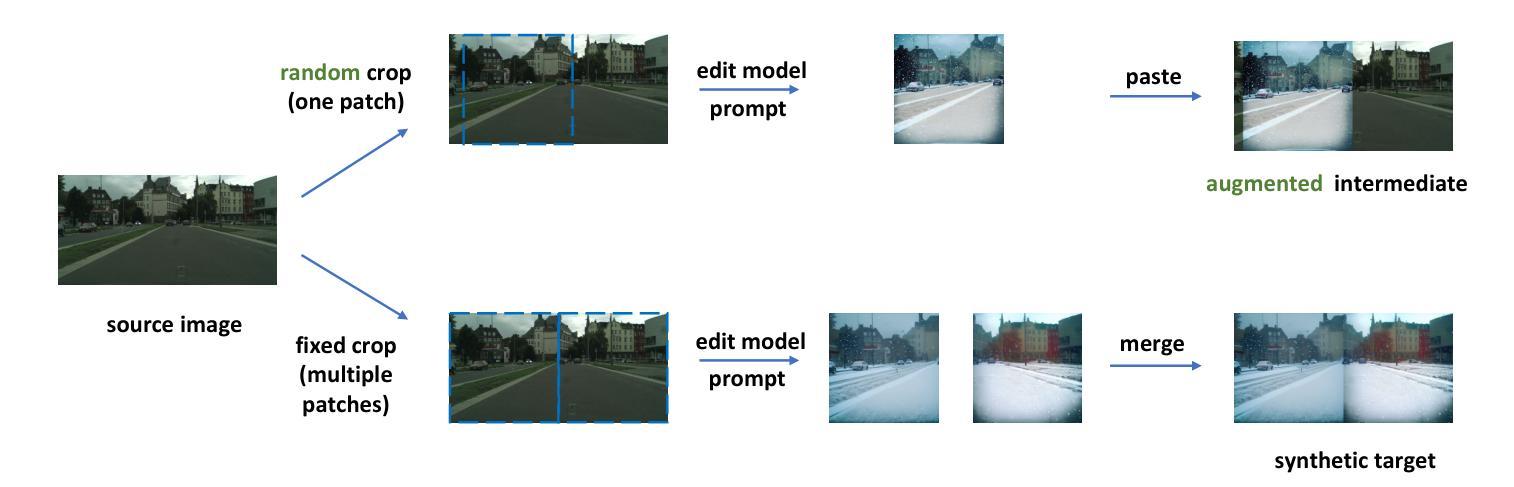
Deep learning-based semantic segmentation models achieve impressive results yet remain limited in handling distribution shifts between training and test data. In this paper, we present SDGPA (Synthetic Data Generation and Progressive Adaptation), a novel method that tackles zero-shot domain adaptive semantic segmentation, in which no target images are available, but only a text description of the target domain’s style is provided. To compensate for the lack of target domain training data, we utilize a pretrained off-the-shelf text-to-image diffusion model, which generates training images by transferring source domain images to target style. Directly editing source domain images introduces noise that harms segmentation because the layout of source images cannot be precisely maintained. To address inaccurate layouts in synthetic data, we propose a method that crops the source image, edits small patches individually, and then merges them back together, which helps improve spatial precision. Recognizing the large domain gap, SDGPA constructs an augmented intermediate domain, leveraging easier adaptation subtasks to enable more stable model adaptation to the target domain. Additionally, to mitigate the impact of noise in synthetic data, we design a progressive adaptation strategy, ensuring robust learning throughout the training process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot semantic segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/ROUJINN/SDGPA
基于深度学习的语义分割模型取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但在处理训练和测试数据之间的分布转移时仍存在一定的局限性。本文中,我们提出了SDGPA(合成数据生成与逐步适应)方法,这是一种解决零样本域自适应语义分割的新方法,其中不提供目标图像,但只提供了目标域风格的文本描述。为了弥补目标域训练数据的缺乏,我们利用预训练的通用文本到图像扩散模型,通过转移源域图像到目标风格来生成训练图像。直接编辑源域图像会引入噪声,损害分割效果,因为源图像的布局无法精确保持。为了解决合成数据中的布局不准确问题,我们提出了一种方法,对源图像进行裁剪,单独编辑小块区域,然后将它们合并在一起,这有助于提高空间精度。认识到域之间的差距较大,SDGPA构建了一个增强的中间域,利用更容易的适应子任务来使模型更稳定地适应目标域。此外,为了减轻合成数据中的噪声影响,我们设计了一种逐步适应策略,确保在整个训练过程中的稳健学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法在零样本语义分割中达到了最先进的性能。代码可在[https://github.com/ROUJINN/SDGPA找到。](https://github.com/ROUJINN/SDGPA%E6%89%BE%E5 知乎专栏。)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SDGPA(合成数据生成与渐进适应)的新方法,用于解决无目标图像仅提供目标域文本描述的零样本域自适应语义分割问题。通过利用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型,生成目标域的训练图像,并引入图像编辑技术以提高合成数据的空间精度。SDGPA通过构建辅助中间域并利用渐进适应策略,实现了模型在目标域的稳健学习,从而达到零样本语义分割的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- SDGPA是一种解决零样本域自适应语义分割问题的方法。
- 利用文本到图像的扩散模型生成目标域的训练图像。
- 通过图像编辑技术提高合成数据的空间精度。
- 构建辅助中间域以缩小目标域与源域之间的差距。
- 采用渐进适应策略,确保模型在训练过程中的稳健学习。
- 方法的性能在实验中达到了零样本语义分割的最佳状态。
点此查看论文截图



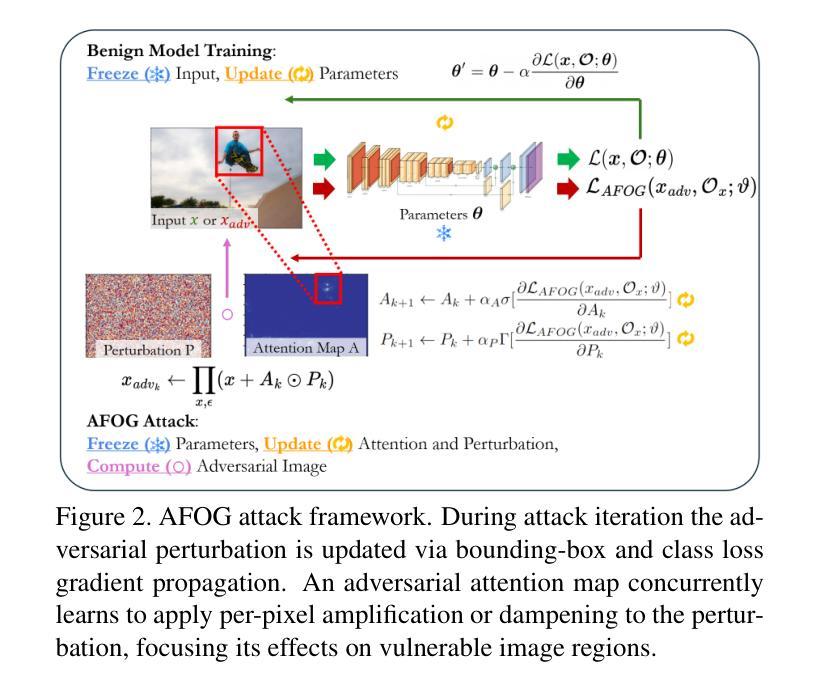
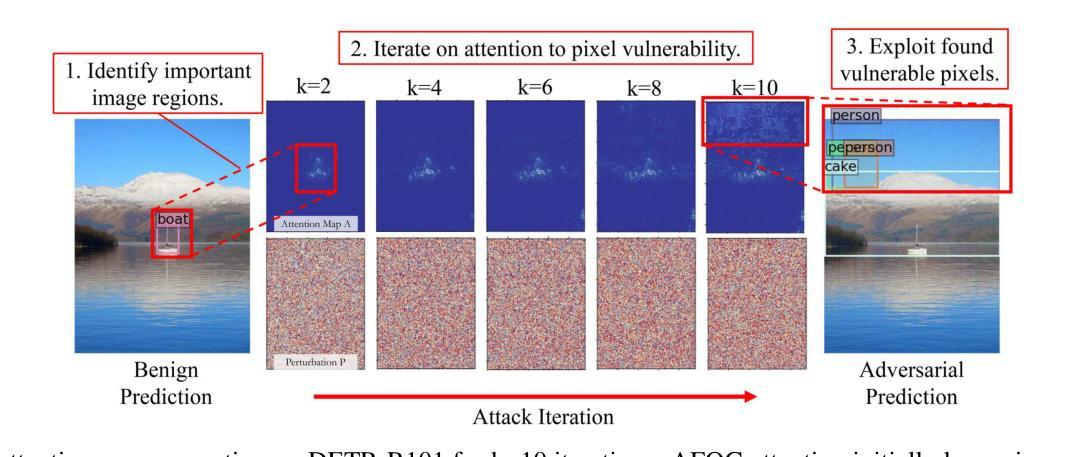
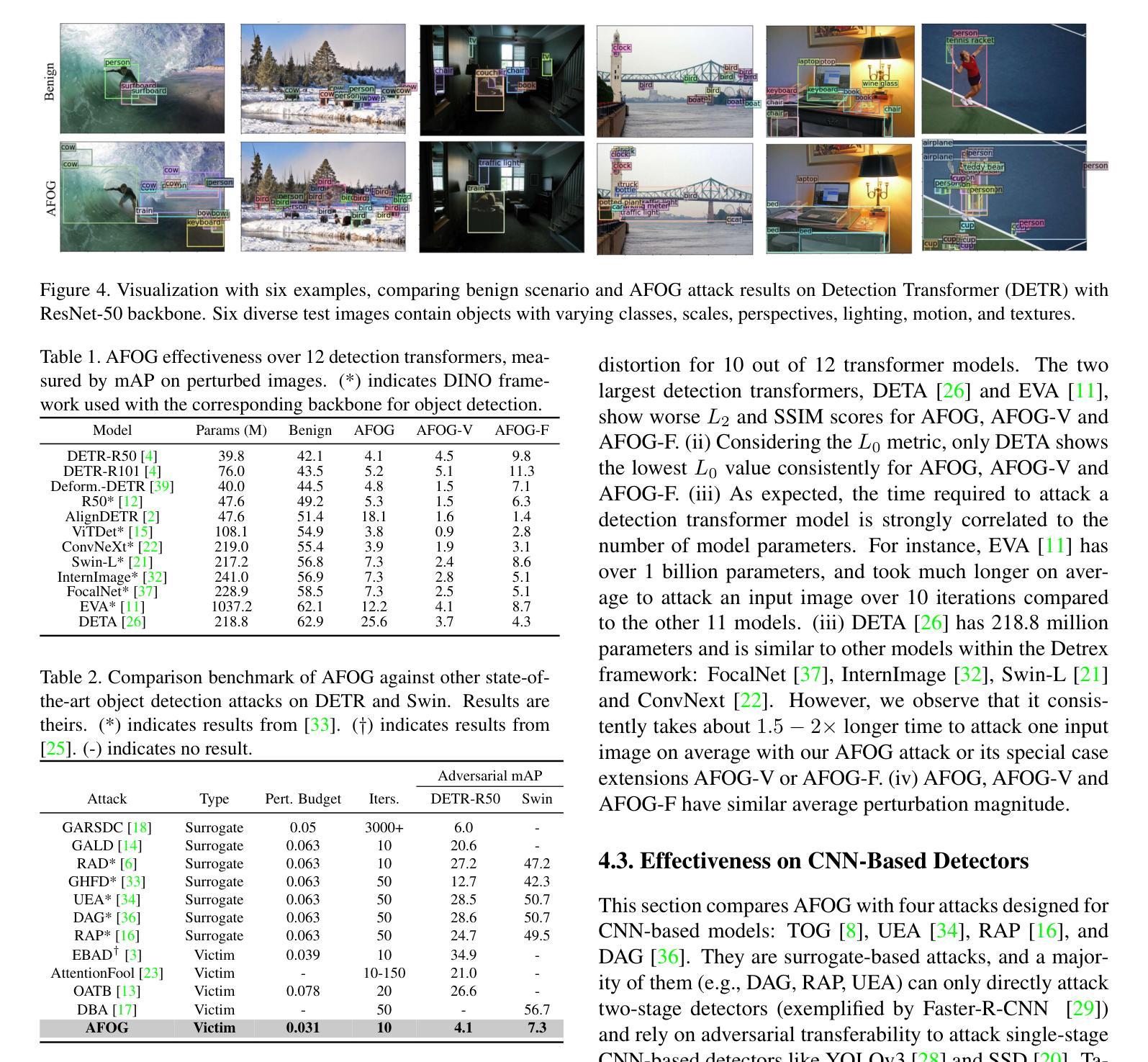
Adversarial Attention Perturbations for Large Object Detection Transformers
Authors:Zachary Yahn, Selim Furkan Tekin, Fatih Ilhan, Sihao Hu, Tiansheng Huang, Yichang Xu, Margaret Loper, Ling Liu
Adversarial perturbations are useful tools for exposing vulnerabilities in neural networks. Existing adversarial perturbation methods for object detection are either limited to attacking CNN-based detectors or weak against transformer-based detectors. This paper presents an Attention-Focused Offensive Gradient (AFOG) attack against object detection transformers. By design, AFOG is neural-architecture agnostic and effective for attacking both large transformer-based object detectors and conventional CNN-based detectors with a unified adversarial attention framework. This paper makes three original contributions. First, AFOG utilizes a learnable attention mechanism that focuses perturbations on vulnerable image regions in multi-box detection tasks, increasing performance over non-attention baselines by up to 30.6%. Second, AFOG’s attack loss is formulated by integrating two types of feature loss through learnable attention updates with iterative injection of adversarial perturbations. Finally, AFOG is an efficient and stealthy adversarial perturbation method. It probes the weak spots of detection transformers by adding strategically generated and visually imperceptible perturbations which can cause well-trained object detection models to fail. Extensive experiments conducted with twelve large detection transformers on COCO demonstrate the efficacy of AFOG. Our empirical results also show that AFOG outperforms existing attacks on transformer-based and CNN-based object detectors by up to 83% with superior speed and imperceptibility. Code is available at https://github.com/zacharyyahn/AFOG.
对抗性扰动是揭示神经网络脆弱性的有用工具。现有的针对物体检测的对抗性扰动方法要么仅限于攻击基于CNN的检测器,要么对基于变压器的检测器的攻击效果较弱。本文提出了一种针对物体检测变压器的Attention-Focused Offensive Gradient (AFOG)攻击方法。AFOG设计用于神经架构无关性,能有效攻击大型基于变压器的物体检测器和传统的基于CNN的检测器,采用统一的对抗性关注框架。本文有三个原创贡献。首先,AFOG利用可学习的关注机制,将扰动集中在多框检测任务的脆弱图像区域,与非关注基线相比,性能提升高达30.6%。其次,AFOG的攻击损失是通过集成两种特征损失,通过可学习的关注更新和对抗性扰动的迭代注入来形成的。最后,AFOG是一种高效且隐蔽的对抗性扰动方法。它通过添加战略生成且视觉上几乎无法察觉的扰动来探测检测变压器的弱点,这些扰动可以导致训练良好的物体检测模型失效。在COCO数据集上对十二个大型检测变压器进行的广泛实验证明了AFOG的有效性。我们的实验结果还表明,AFOG在基于变压器和基于CNN的物体检测器上的攻击效果比现有攻击高出83%,同时速度和隐蔽性更优越。代码可在https://github.com/zacharyyahn/AFOG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了一种针对目标检测变压器的注意力聚焦进攻梯度(AFOG)攻击方法。AFOG利用可学习的注意力机制,在多框检测任务中将扰动集中在脆弱图像区域,提高了对非注意力基准的性能。通过整合两种特征损失和通过可学习注意力更新进行迭代注入对抗性扰动,形成了AFOG的攻击损失。AFOG是一种高效且隐蔽的对抗性扰动方法,通过添加战略生成和视觉上不明显的扰动来探测检测变压器的弱点,导致训练良好的目标检测模型失败。在COCO上进行的实验表明,AFOG对基于变压器和CNN的目标检测器均有效,且性能优于现有攻击方法。
Key Takeaways:
- AFOG是一种针对目标检测变压器的对抗性攻击方法,对神经网络架构具有通用性。
- AFOG利用可学习的注意力机制,将扰动集中在图像的多框检测脆弱区域。
- 通过整合特征损失和迭代注入对抗性扰动,形成了AFOG的攻击损失。
- AFOG在目标检测模型中的性能提升显著,最高可提高30.6%。
- AFOG攻击能有效导致训练良好的目标检测模型失败。
- AFOG在COCO数据集上的实验表明其性能优于现有攻击方法,对基于变压器和CNN的目标检测器均有效。
点此查看论文截图


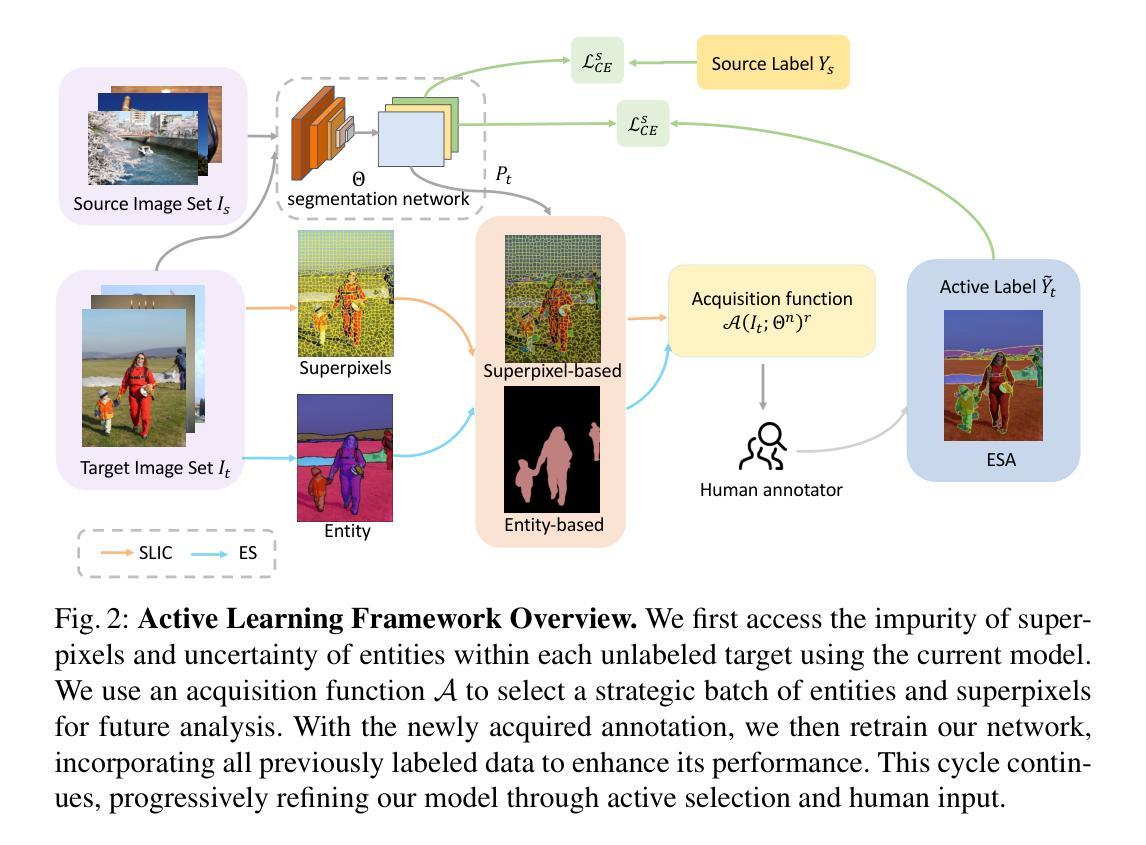
ESA: Annotation-Efficient Active Learning for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jinchao Ge, Zeyu Zhang, Minh Hieu Phan, Bowen Zhang, Akide Liu, Yang Zhao, Shuwen Zhao
Active learning enhances annotation efficiency by selecting the most revealing samples for labeling, thereby reducing reliance on extensive human input. Previous methods in semantic segmentation have centered on individual pixels or small areas, neglecting the rich patterns in natural images and the power of advanced pre-trained models. To address these challenges, we propose three key contributions: Firstly, we introduce Entity-Superpixel Annotation (ESA), an innovative and efficient active learning strategy which utilizes a class-agnostic mask proposal network coupled with super-pixel grouping to capture local structural cues. Additionally, our method selects a subset of entities within each image of the target domain, prioritizing superpixels with high entropy to ensure comprehensive representation. Simultaneously, it focuses on a limited number of key entities, thereby optimizing for efficiency. By utilizing an annotator-friendly design that capitalizes on the inherent structure of images, our approach significantly outperforms existing pixel-based methods, achieving superior results with minimal queries, specifically reducing click cost by 98% and enhancing performance by 1.71%. For instance, our technique requires a mere 40 clicks for annotation, a stark contrast to the 5000 clicks demanded by conventional methods.
主动学习通过选择最具代表性的样本进行标注,提高了标注效率,从而减少了大量人工输入的依赖。在语义分割方面的先前方法主要集中在单个像素或小区域上,忽略了自然图像中的丰富模式以及先进预训练模型的能力。针对这些挑战,我们提出了三项关键贡献:首先,我们引入了实体超像素标注(ESA),这是一种创新且高效的活动学习策略,它利用类无关掩模提案网络结合超像素分组来捕捉局部结构线索。此外,我们的方法选择目标域中每张图像的子集实体,优先处理高熵超像素以确保全面表示。同时,它专注于有限数量的关键实体,从而优化效率。通过利用图像内在结构的注释器友好设计,我们的方法显著优于现有的基于像素的方法,在少量查询的情况下取得了优越的结果,特别是减少了点击成本98%,提高了性能1.71%。例如,我们的技术只需要40次点击进行注释,与传统方法要求的5000次点击形成鲜明对比。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于实体超像素标注(ESA)的主动学习方法,该方法利用类别无关掩膜提案网络结合超像素分组,捕捉局部结构线索,并选择目标域图像中的实体子集进行优化标注效率。该方法通过减少点击成本和提高性能,显著优于传统的像素级方法。
Key Takeaways
- 主动学习方法通过选择最具代表性的样本进行标注,提高了语义分割的标注效率,并降低了对大量人工输入的依赖。
- 传统方法主要关注单个像素或小区域,忽略了自然图像中的丰富模式和预训练模型的力量。
- 提出了Entity-Superpixel Annotation (ESA)策略,这是一种结合类别无关掩膜提案网络和超像素分组的创新方法。
- ESA通过选择目标域图像中的实体子集进行优化标注效率,优先考虑具有高熵的超像素来确保全面的代表性。
- ESA采用一种针对注释者的友好设计,利用图像的内在结构来提高标注效率。
- ESA方法显著优于现有的像素级方法,实现了卓越的结果与最少的查询次数。
点此查看论文截图