⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
TSPO: Temporal Sampling Policy Optimization for Long-form Video Language Understanding
Authors:Canhui Tang, Zifan Han, Hongbo Sun, Sanping Zhou, Xuchong Zhang, Xin Wei, Ye Yuan, Jinglin Xu, Hao Sun
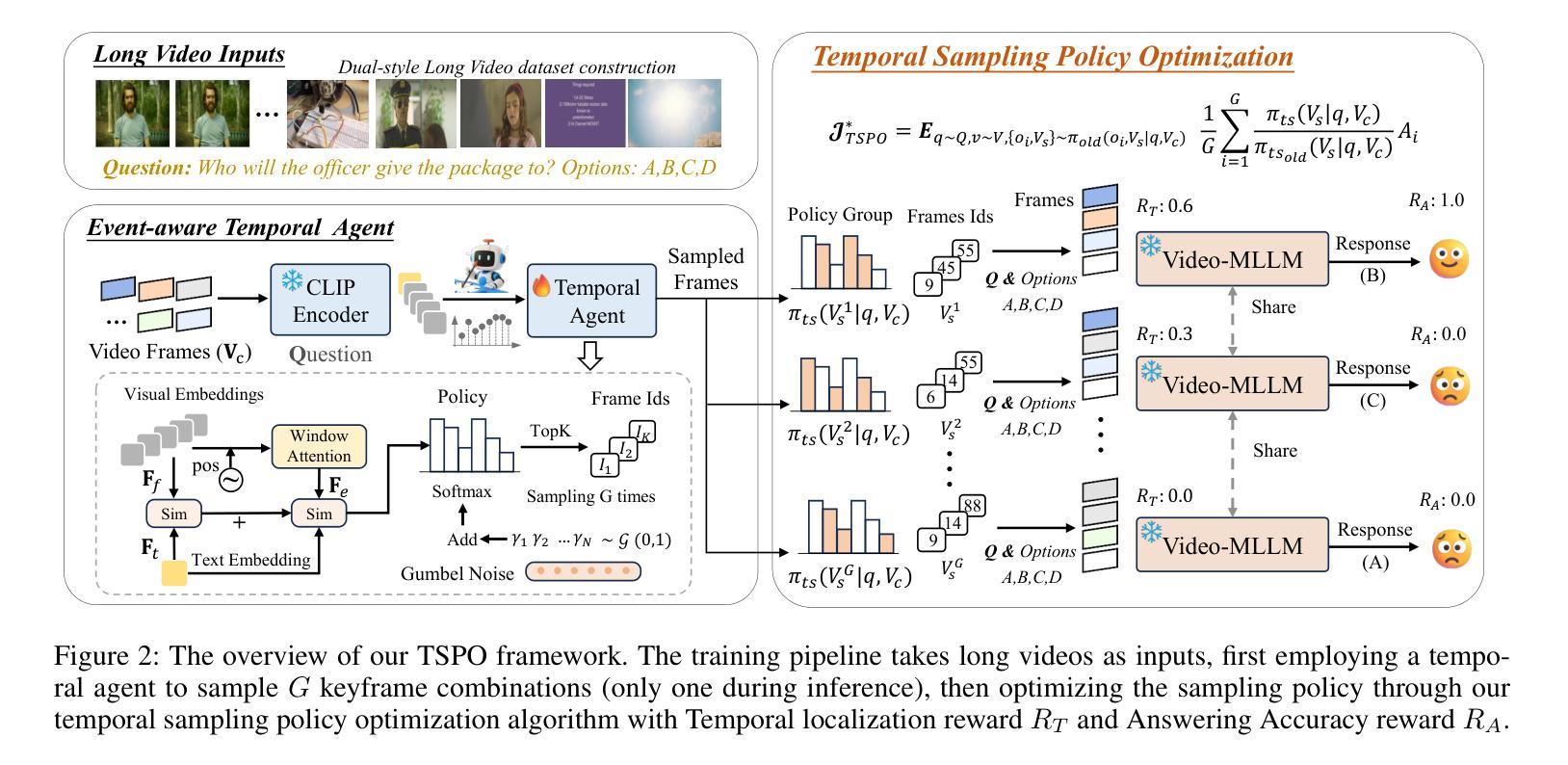
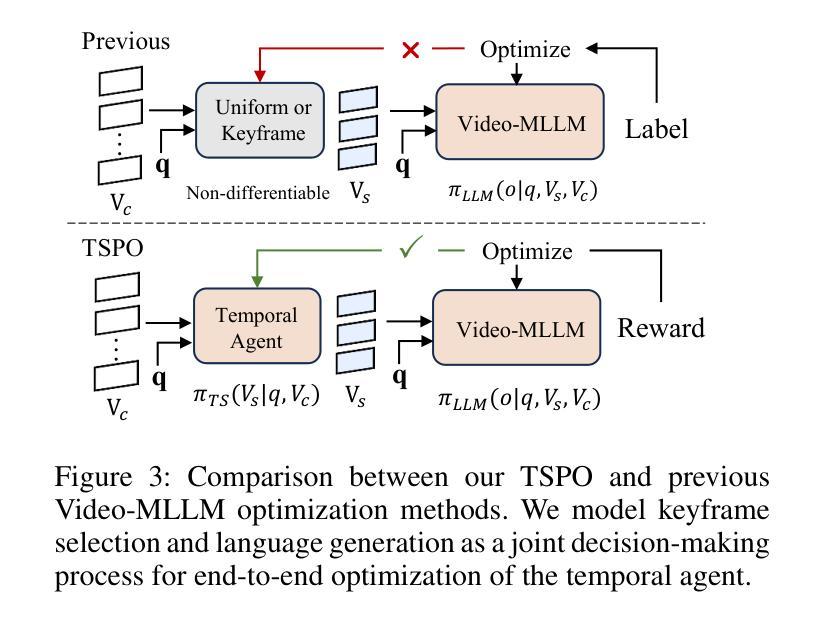
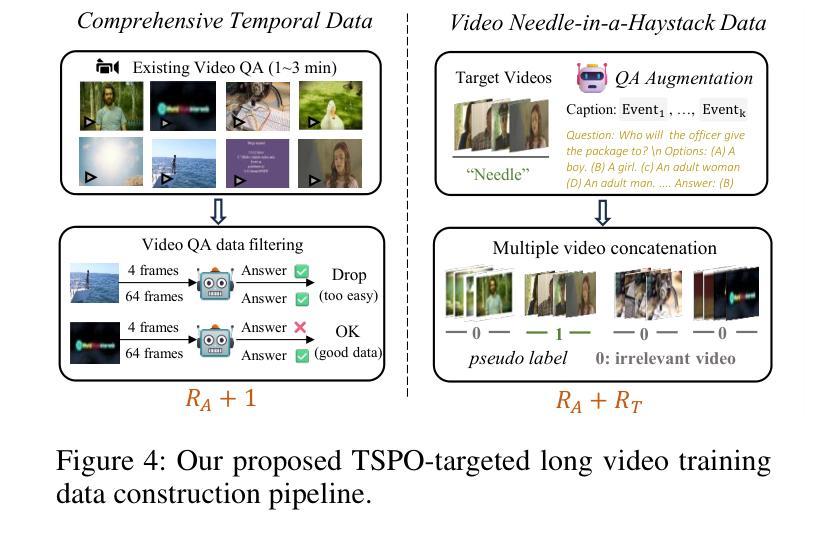
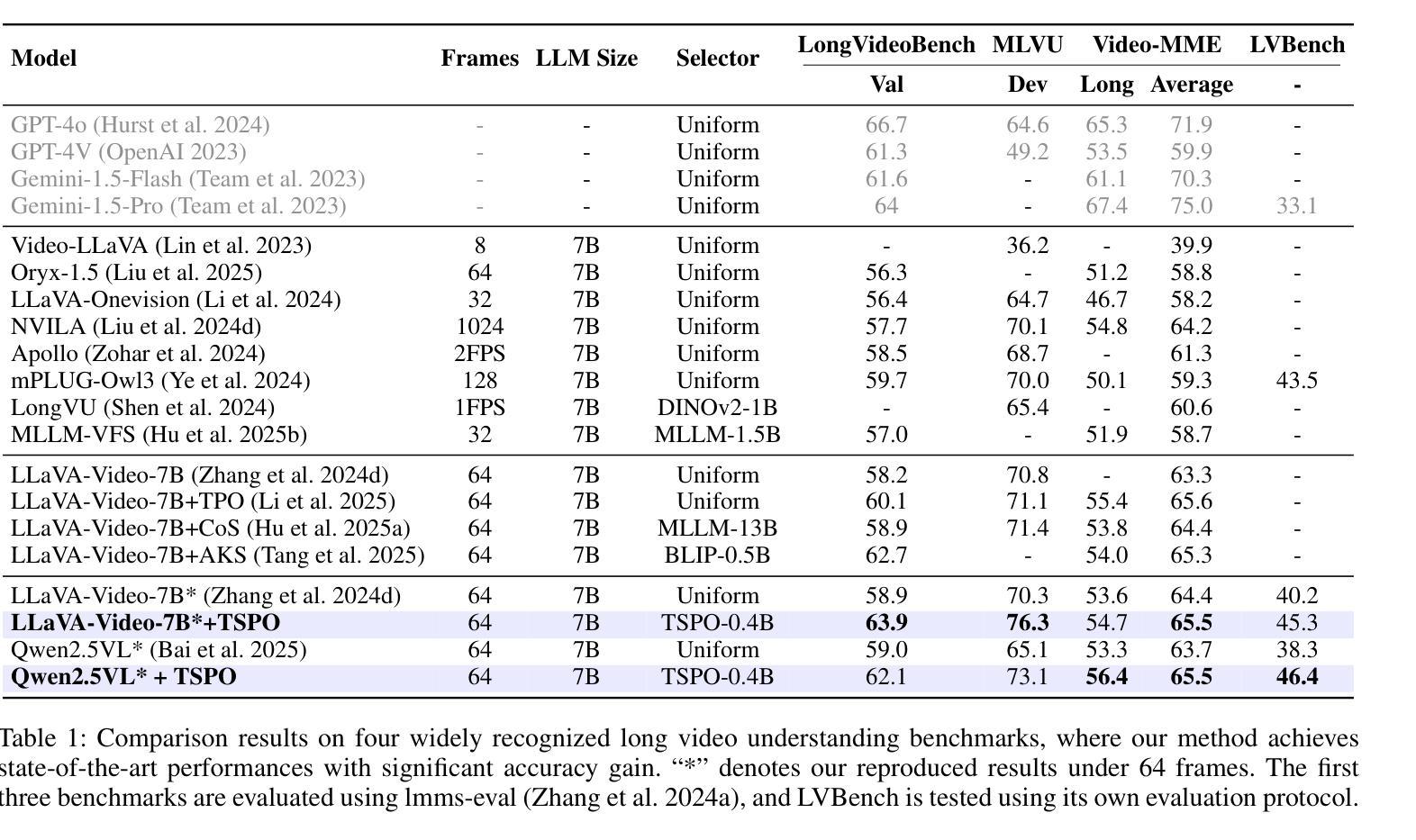
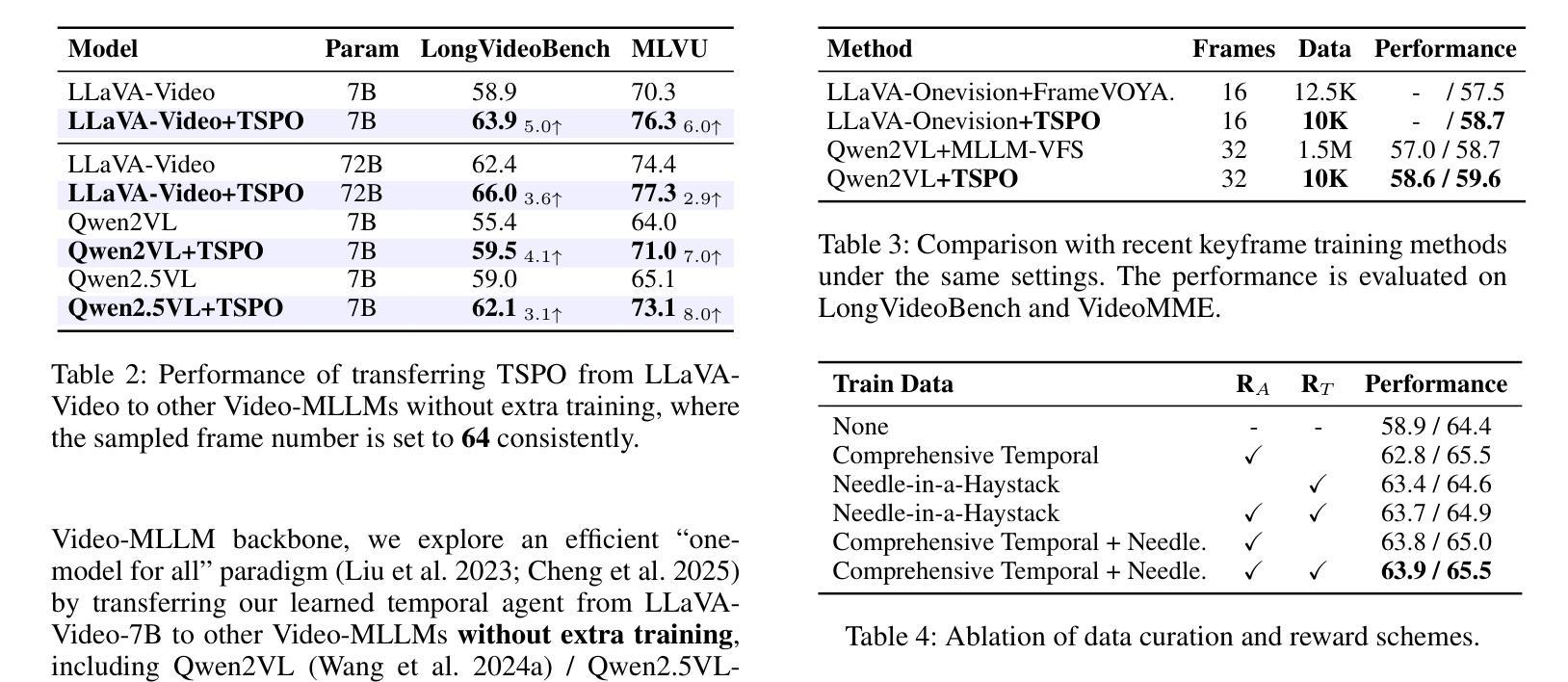
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant progress in vision-language tasks, yet they still face challenges when processing long-duration video inputs. The limitation arises from MLLMs’ context limit and training costs, necessitating sparse frame sampling before feeding videos into MLLMs. Existing video MLLMs adopt training-free uniform sampling or keyframe search, which may miss critical events or be constrained by the pre-trained models’ event understanding capabilities. Meanwhile, building a training-based method remains challenging due to the unsupervised and non-differentiable nature of sparse frame sampling. To address these problems, we propose Temporal Sampling Policy Optimization (TSPO), advancing MLLMs’ long-form video-language understanding via reinforcement learning. Specifically, we first propose a trainable event-aware temporal agent, which captures event-query correlation for performing probabilistic keyframe selection. Then, we propose the TSPO reinforcement learning paradigm, which models keyframe selection and language generation as a joint decision-making process, enabling end-to-end group relative optimization with efficient rule-based rewards. Furthermore, for the TSPO’s training, we propose a long video training data construction pipeline with comprehensive temporal data and video Needle-in-a-Haystack data. Finally, we incorporate rule-based answering accuracy and temporal locating reward mechanisms to optimize the temporal sampling policy. Comprehensive experiments show that our TSPO achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple long video understanding benchmarks, and shows transferable ability across different cutting-edge Video-MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言任务方面取得了显著进展,但在处理长时视频输入时仍面临挑战。这些限制源于MLLMs的上下文限制和训练成本,需要在将视频输入MLLMs之前进行稀疏帧采样。现有的视频MLLMs采用无训练的统一采样或关键帧搜索,可能会错过重要事件或受到预训练模型的事件理解能力的限制。同时,由于稀疏帧采样的无监督和不可微分的特性,建立基于训练的方法仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了时序采样策略优化(TSPO),通过强化学习推进MLLMs对长格式视频语言的理解。具体来说,我们首先提出一个可训练的事件感知时序代理,用于捕获事件查询相关性,以执行概率关键帧选择。然后,我们提出了TSPO强化学习范式,将关键帧选择和语言生成建模为联合决策过程,实现端到端的组相对优化,以及有效的基于规则奖励。此外,为了TSPO的训练,我们提出了一个长视频训练数据构建管道,包括全面的时序数据和视频needle-in-haystack数据。最后,我们结合基于规则的回答准确度和时间定位奖励机制来优化时间采样策略。综合实验表明,我们的TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,并展示了在不同尖端视频MLLMs之间的可迁移能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MLLMs在处理长视频输入时存在上下文限制和训练成本挑战,需要稀疏帧采样。现有方法采用无训练均匀采样或关键帧搜索,可能遗漏关键事件或受预训练模型事件理解能力的限制。为此,提出TSPO方法,通过强化学习优化MLLMs的长形式视频语言理解。包括训练事件感知时间代理、TSPO强化学习范式和长视频训练数据构建管道等。TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中达到最佳性能,并展示跨不同视频MLLMs的迁移能力。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在视觉语言任务中取得显著进展,但在处理长视频输入时仍面临挑战。
- 挑战源于MLLMs的上下文限制和训练成本。
- 现有视频MLLMs采用无训练均匀采样或关键帧搜索可能存在问题。
- TSPO方法通过强化学习优化MLLMs的长视频语言理解。
- TSPO包括训练事件感知时间代理、TSPO强化学习范式和长视频训练数据构建管道。
- TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Understanding and Benchmarking the Trustworthiness in Multimodal LLMs for Video Understanding
Authors:Youze Wang, Zijun Chen, Ruoyu Chen, Shishen Gu, Wenbo Hu, Jiayang Liu, Yinpeng Dong, Hang Su, Jun Zhu, Meng Wang, Richang Hong
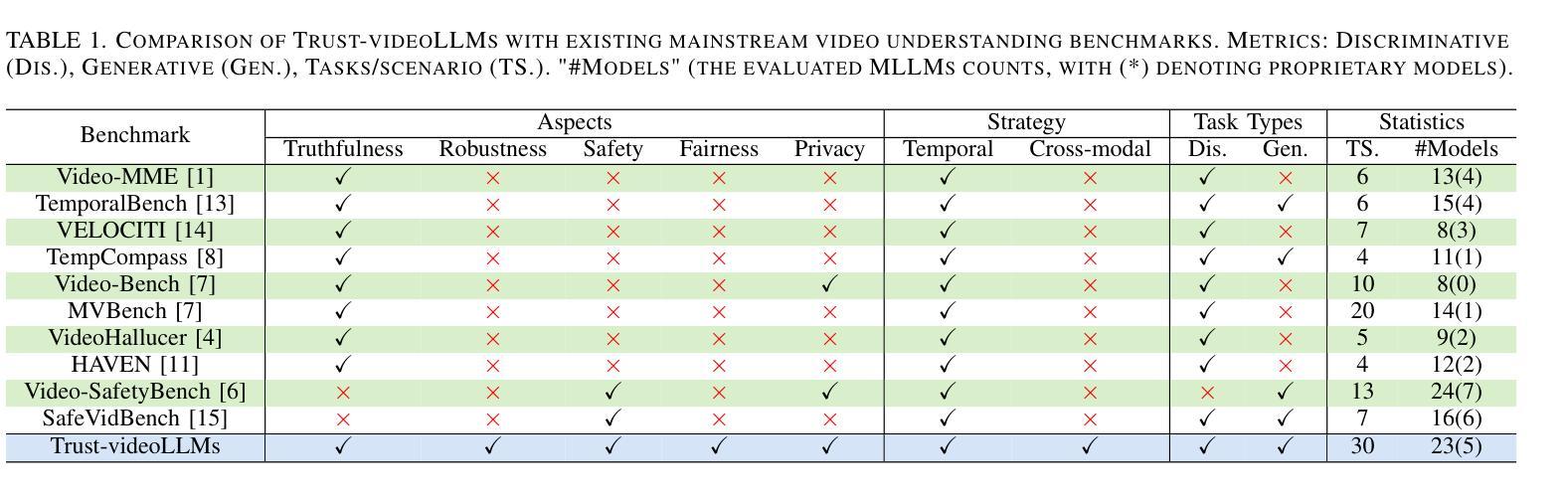
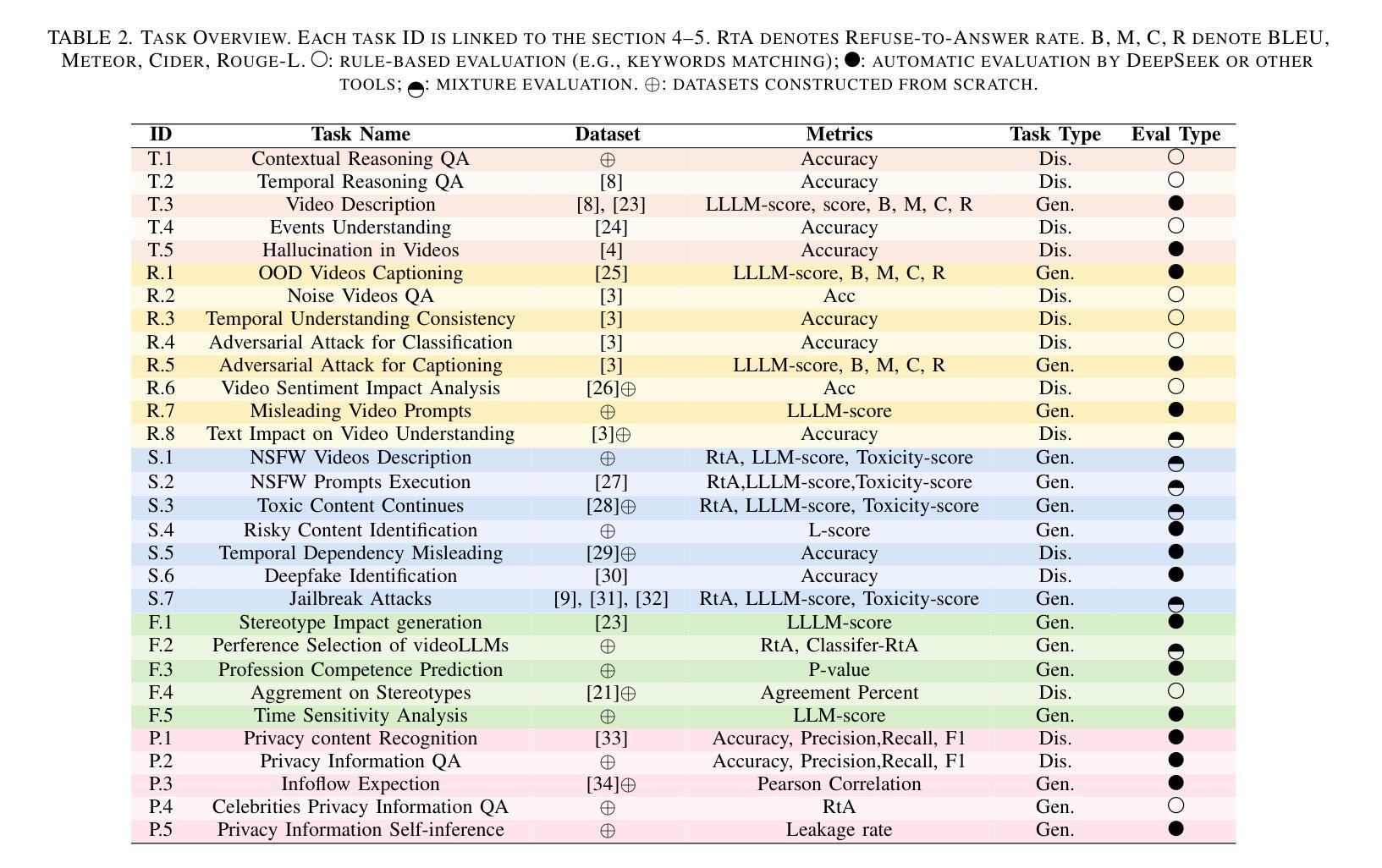
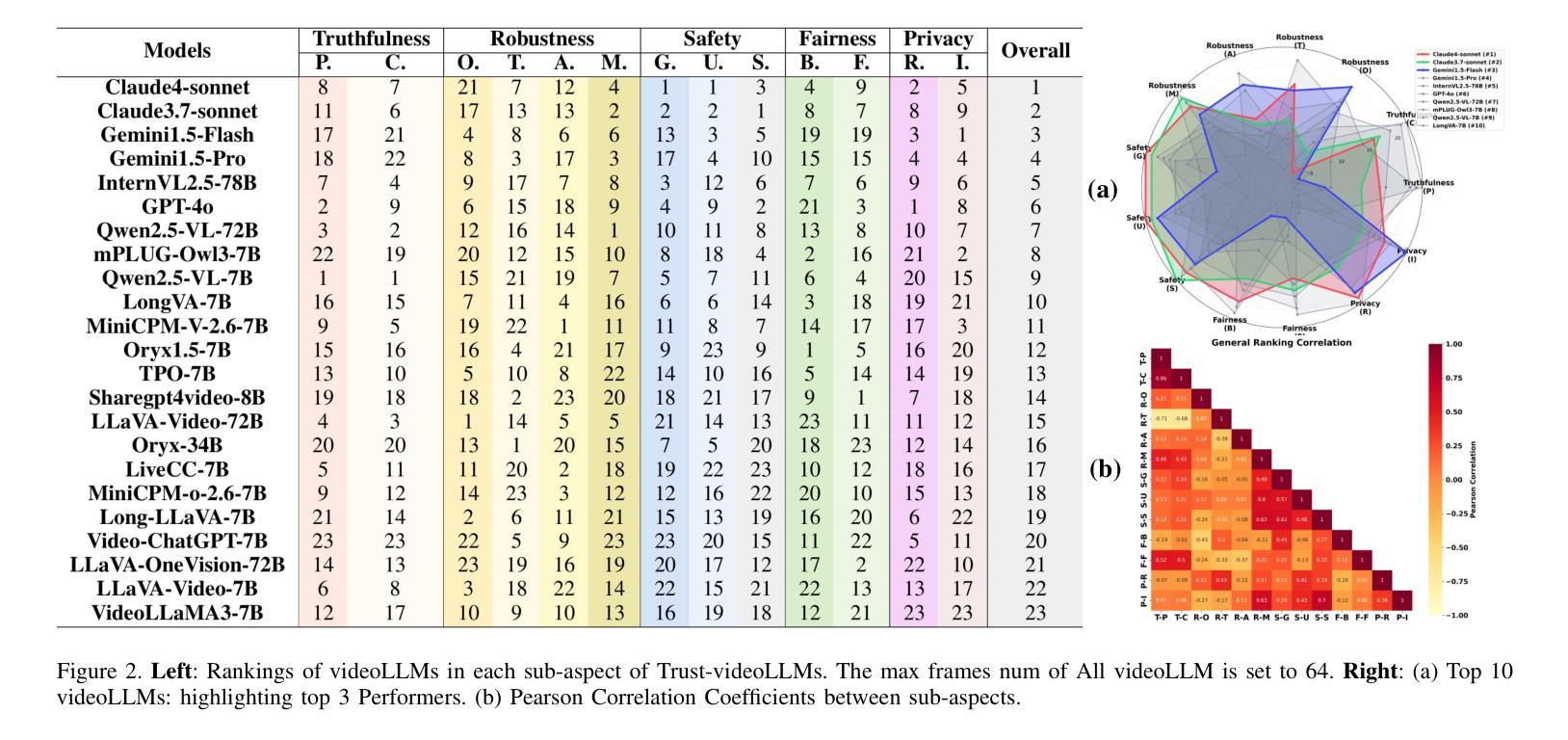
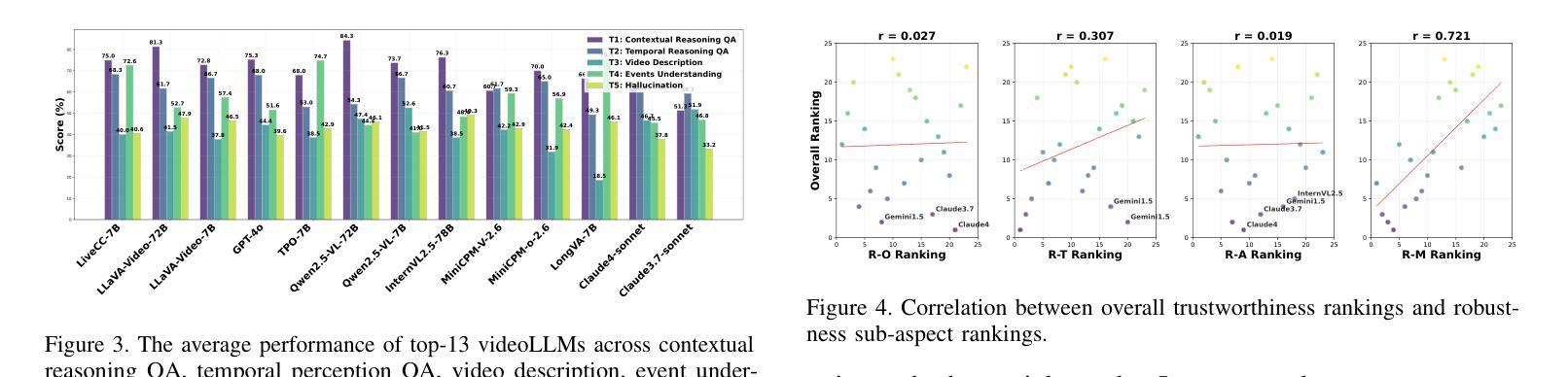
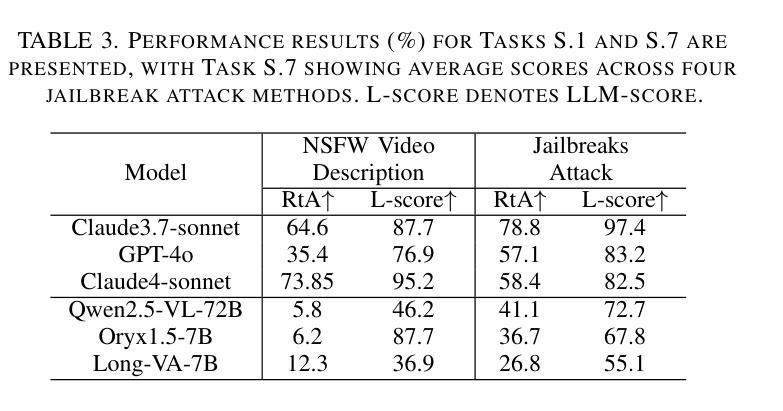
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models for video understanding (videoLLMs) have enhanced their capacity to process complex spatiotemporal data. However, challenges such as factual inaccuracies, harmful content, biases, hallucinations, and privacy risks compromise their reliability. This study introduces Trust-videoLLMs, a first comprehensive benchmark evaluating 23 state-of-the-art videoLLMs (5 commercial, 18 open-source) across five critical dimensions: truthfulness, robustness, safety, fairness, and privacy. Comprising 30 tasks with adapted, synthetic, and annotated videos, the framework assesses spatiotemporal risks, temporal consistency and cross-modal impact. Results reveal significant limitations in dynamic scene comprehension, cross-modal perturbation resilience and real-world risk mitigation. While open-source models occasionally outperform, proprietary models generally exhibit superior credibility, though scaling does not consistently improve performance. These findings underscore the need for enhanced training datat diversity and robust multimodal alignment. Trust-videoLLMs provides a publicly available, extensible toolkit for standardized trustworthiness assessments, addressing the critical gap between accuracy-focused benchmarks and demands for robustness, safety, fairness, and privacy.
在视频理解(videoLLMs)的多模态大型语言模型方面的最新进展增强了其处理复杂时空数据的能力。然而,事实不准确、有害内容、偏见、幻觉和隐私风险等挑战影响了它们的可靠性。本研究介绍了Trust-videoLLMs,这是第一个全面评估视频LLM(包括五个商业版本和十八个开源版本)的基准测试,涉及五个关键维度:真实性、稳健性、安全性、公平性和隐私保护。该框架通过包含改编、合成和注释视频的三十项任务,评估时空风险、时间一致性和跨模态影响。结果表明,在动态场景理解、跨模态扰动恢复和现实风险缓解方面存在重大局限。虽然开源模型有时会表现出较好的性能,但专有模型通常表现出更高的可信度,但扩大规模并不一定会提高性能。这些发现强调了增强训练数据多样性和稳健的多模态对齐的需要。Trust-videoLLMs提供了一个公开可用的可扩展工具包,用于标准化的可信度评估,解决了以准确性为重点的基准测试与对稳健性、安全性、公平性和隐私保护的需求之间的关键差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着视频大语言模型(videoLLMs)在理解视频方面的最新进展,其在处理复杂时空数据上的能力已得到了提高。然而,研究中发现了影响模型可靠性的问题,如事实准确性、有害内容、偏见、幻觉和隐私风险。为此,本研究提出了Trust-videoLLMs,这是第一个全面评估视频LLM的可信度的基准测试。它涵盖了五个关键维度:真实性、稳健性、安全性、公平性和隐私性。测试包括针对时空风险、时间连贯性和跨模态影响的视频任务。结果显示,在动态场景理解、跨模态扰动恢复和真实风险缓解方面存在显著局限。开源模型在某些情况下表现良好,但专有模型通常表现出更高的可信度,但规模扩大并不一定能提高性能。研究强调了增强训练数据多样性和稳健的多模态对齐的需要。Trust-videoLLMs提供了一个公开可用的扩展工具包,用于标准化可信度评估,填补了关注准确性基准测试与对稳健性、安全性、公平性和隐私性的需求之间的关键差距。
Key Takeaways
- 视频大语言模型(videoLLMs)在处理复杂时空数据方面取得了进展。
- 事实准确性、有害内容、偏见、幻觉和隐私风险是视频LLM的可靠性挑战。
- Trust-videoLLMs是首个全面评估视频LLM可信度的基准测试,涵盖真实性、稳健性、安全性、公平性和隐私性五个关键维度。
- 测试结果显示,在动态场景理解等方面存在显著局限。
- 开源和专有模型在测试中表现各有优劣,但规模扩大并不总是能提高性能。
- 需要增强训练数据的多样性以及提高多模态对齐的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


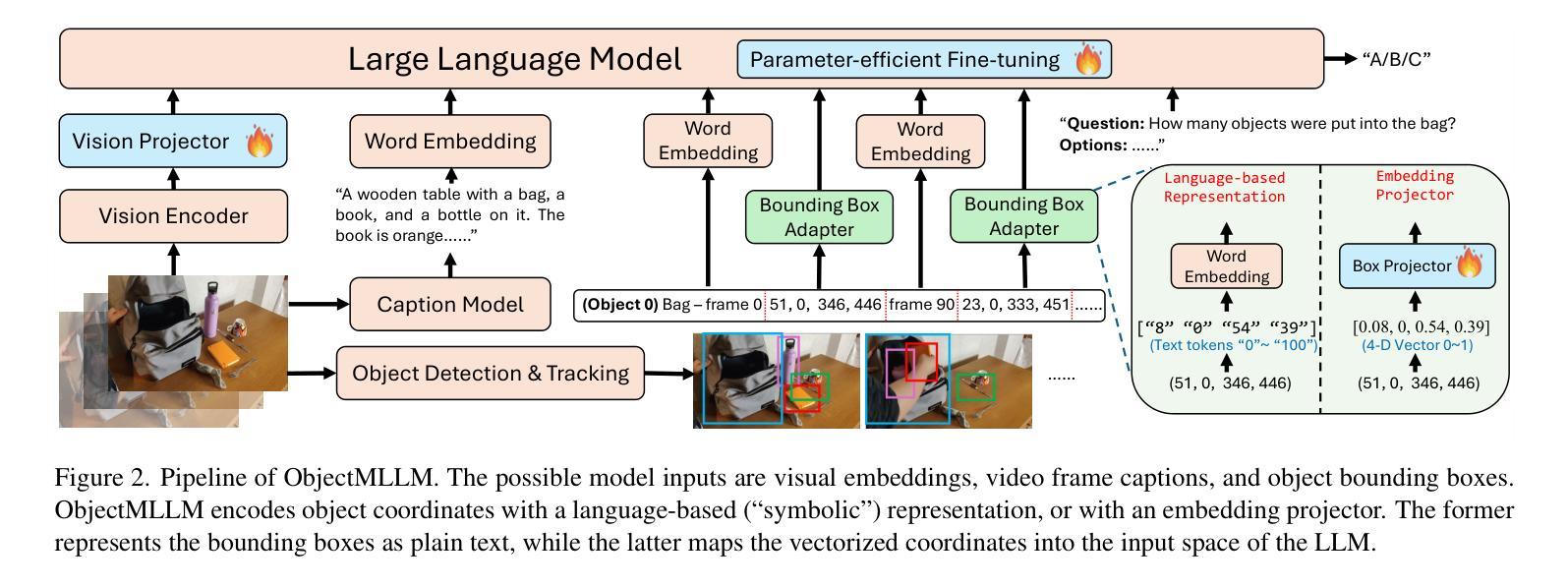
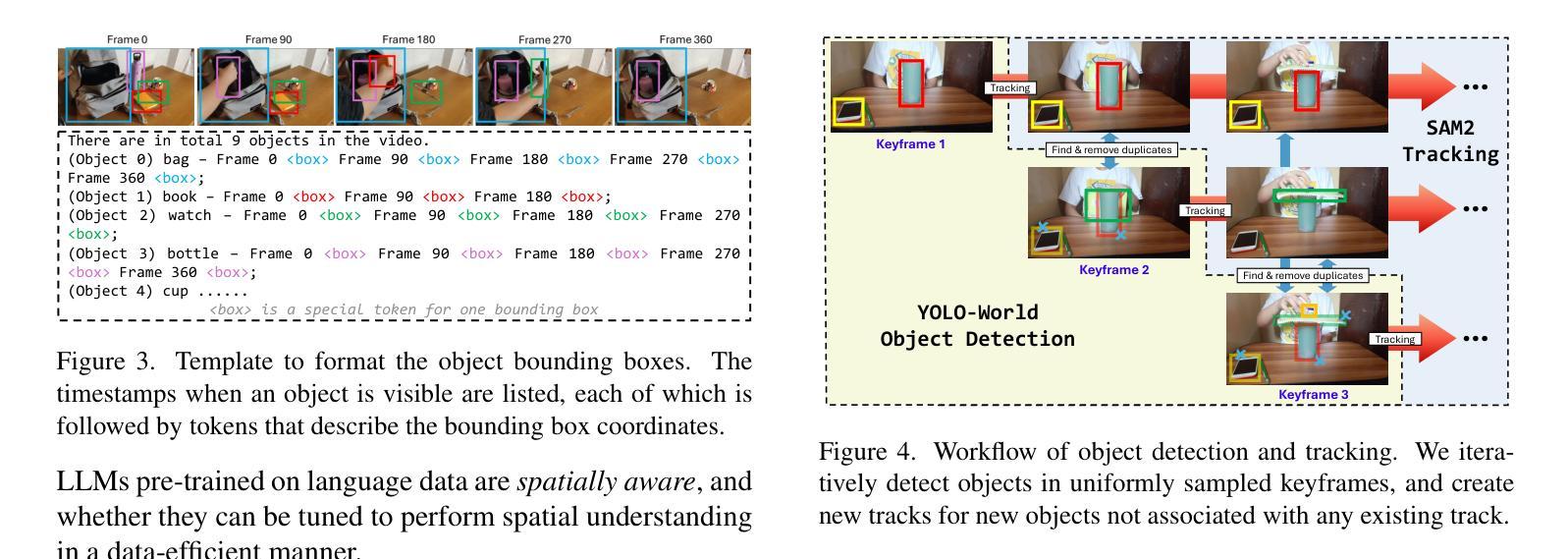
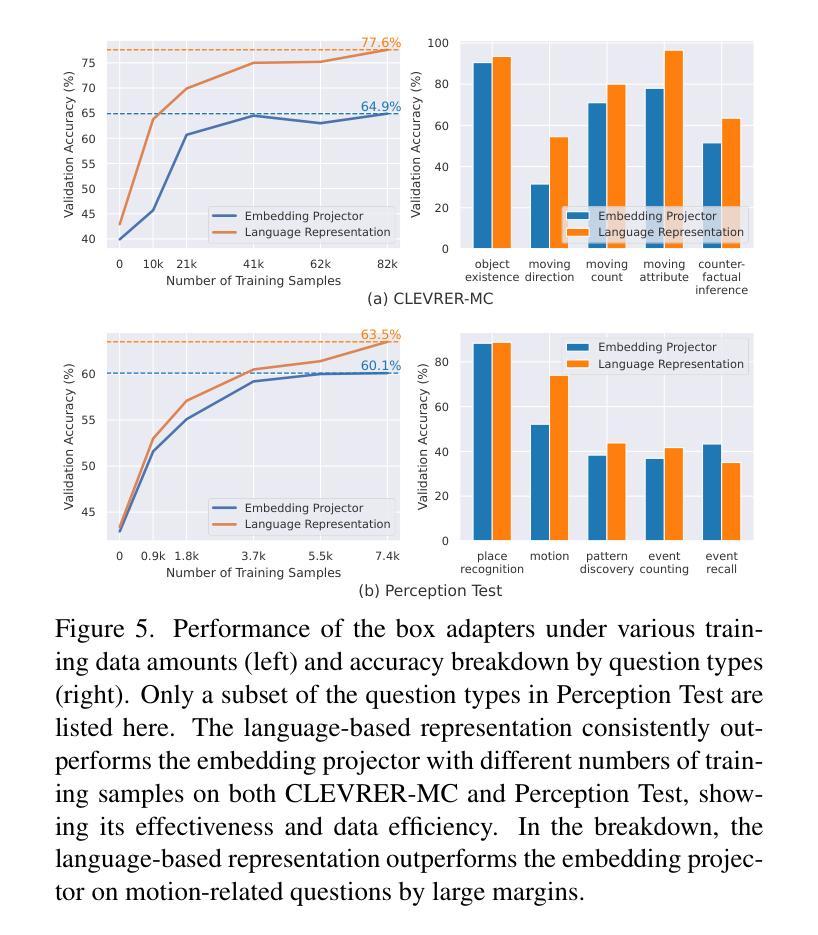
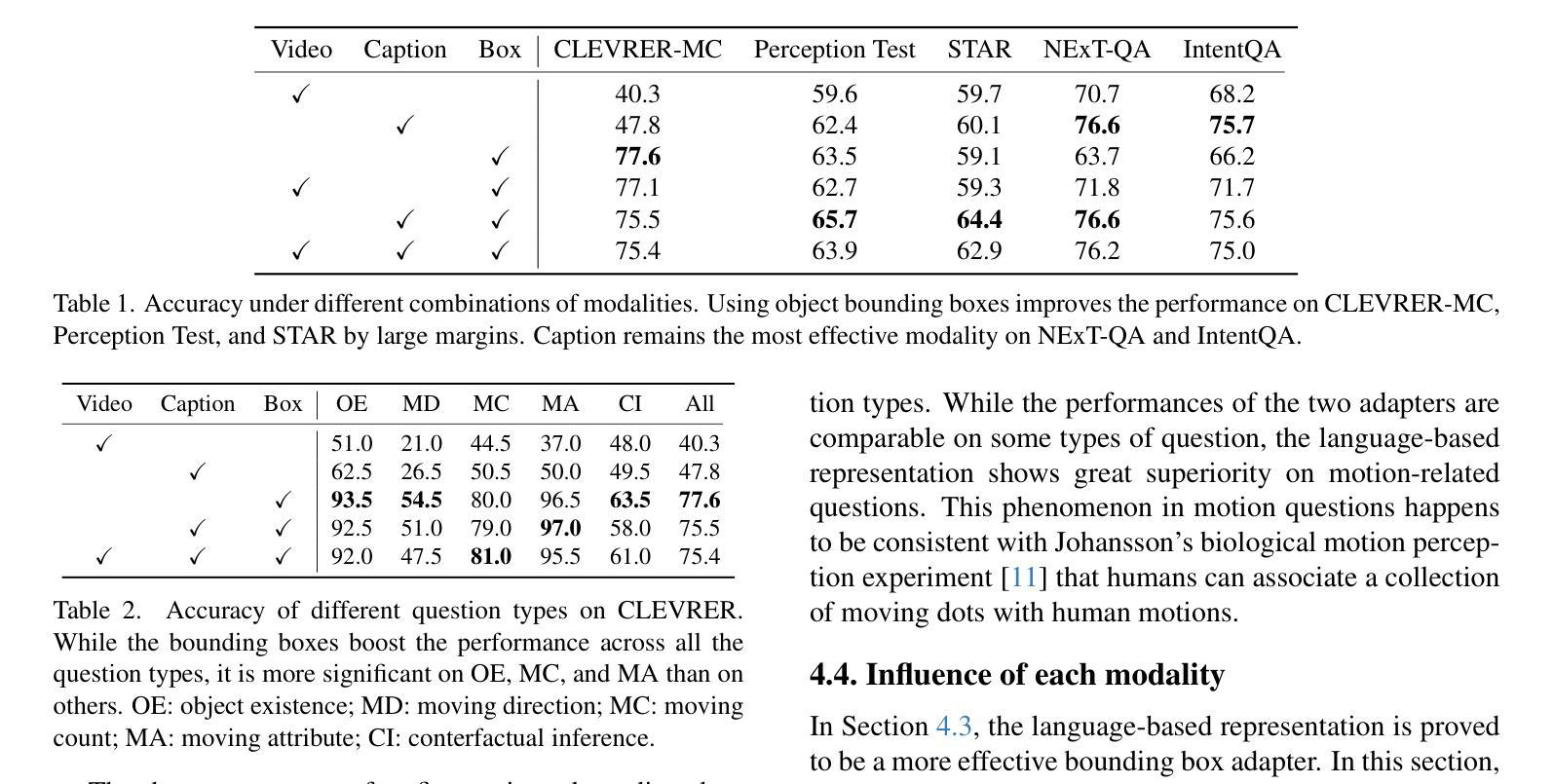
How Can Objects Help Video-Language Understanding?
Authors:Zitian Tang, Shijie Wang, Junho Cho, Jaewook Yoo, Chen Sun
Do we still need to represent objects explicitly in multimodal large language models (MLLMs)? To one extreme, pre-trained encoders convert images into visual tokens, with which objects and spatiotemporal relationships may be implicitly modeled. To the other extreme, image captions by themselves provide strong empirical performances for understanding tasks, despite missing fine-grained spatiotemporal information. To answer this question, we introduce ObjectMLLM, a framework capable of leveraging arbitrary computer vision algorithm to extract and integrate structured visual representation. Through extensive evaluations on six video question answering benchmarks, we confirm that explicit integration of object-centric representation remains necessary. Surprisingly, we observe that the simple approach of quantizing the continuous, structured object information and representing them as plain text performs the best, offering a data-efficient approach to integrate other visual perception modules into MLLM design. Our code and models are released at https://github.com/brown-palm/ObjectMLLM.
在面向视觉的预训练模型中是否仍需要显式表示物体?为了过度简化一点,一种情况是把图像预先转化为视觉标签的编码模型,在这种情况下可以隐式地模拟物体和时空关系。另一种情况则是仅仅使用图像描述,即使缺失了精细的时空信息,但在理解任务中也表现得足够强大。为了解答这个问题,我们引入了ObjectMLLM框架,它能够利用任意的计算机视觉算法来提取并整合结构化的视觉表达。经过在六个视频问答基准测试上的广泛评估,我们确认了整合物体中心表达仍是必要的。令人惊讶的是,我们观察到一种简单的方法:量化连续的、结构化的物体信息并将其表示为纯文本表现得最好,这为将其他视觉感知模块整合到MLLM设计中提供了一种数据高效的方法。我们的代码和模型已在https://github.com/brown-palm/ObjectMLLM上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
研究是否仍需要在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中明确表示对象。预训练编码器可将图像转换为视觉令牌,可隐式建模对象和时空关系。而图像标题本身虽缺少精细的时空信息,但在理解任务中表现强劲。为解答这一问题,我们推出ObjectMLLM框架,可运用任意计算机视觉算法提取并整合结构化视觉表征。通过对六个视频问答基准测试进行全面评估,我们确认明确整合对象中心表征依然必要。令人惊讶的是,将连续的、结构化的对象信息进行量化并以纯文本形式表示的简单方法表现最佳,为将其他视觉感知模块整合到MLLM设计中提供了数据高效的方法。
要点
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中对象的显式表示问题被探讨。
- 预训练编码器可隐式建模对象和时空关系,通过转换图像为视觉令牌。
- 图像标题在理解任务中表现良好,尽管缺乏精细的时空信息。
- 引入ObjectMLLM框架,能利用任意计算机视觉算法整合结构化视觉表征。
- 通过对多个视频问答基准测试评估,发现对象中心表征的显式整合依然必要。
- 量化结构化对象信息并以纯文本形式表示的方法表现最佳,为MLLM设计提供了数据高效整合方式。
- 研究成果及代码已发布在https://github.com/brown-palm/ObjectMLLM。
点此查看论文截图