⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
Pseudo Depth Meets Gaussian: A Feed-forward RGB SLAM Baseline
Authors:Linqing Zhao, Xiuwei Xu, Yirui Wang, Hao Wang, Wenzhao Zheng, Yansong Tang, Haibin Yan, Jiwen Lu
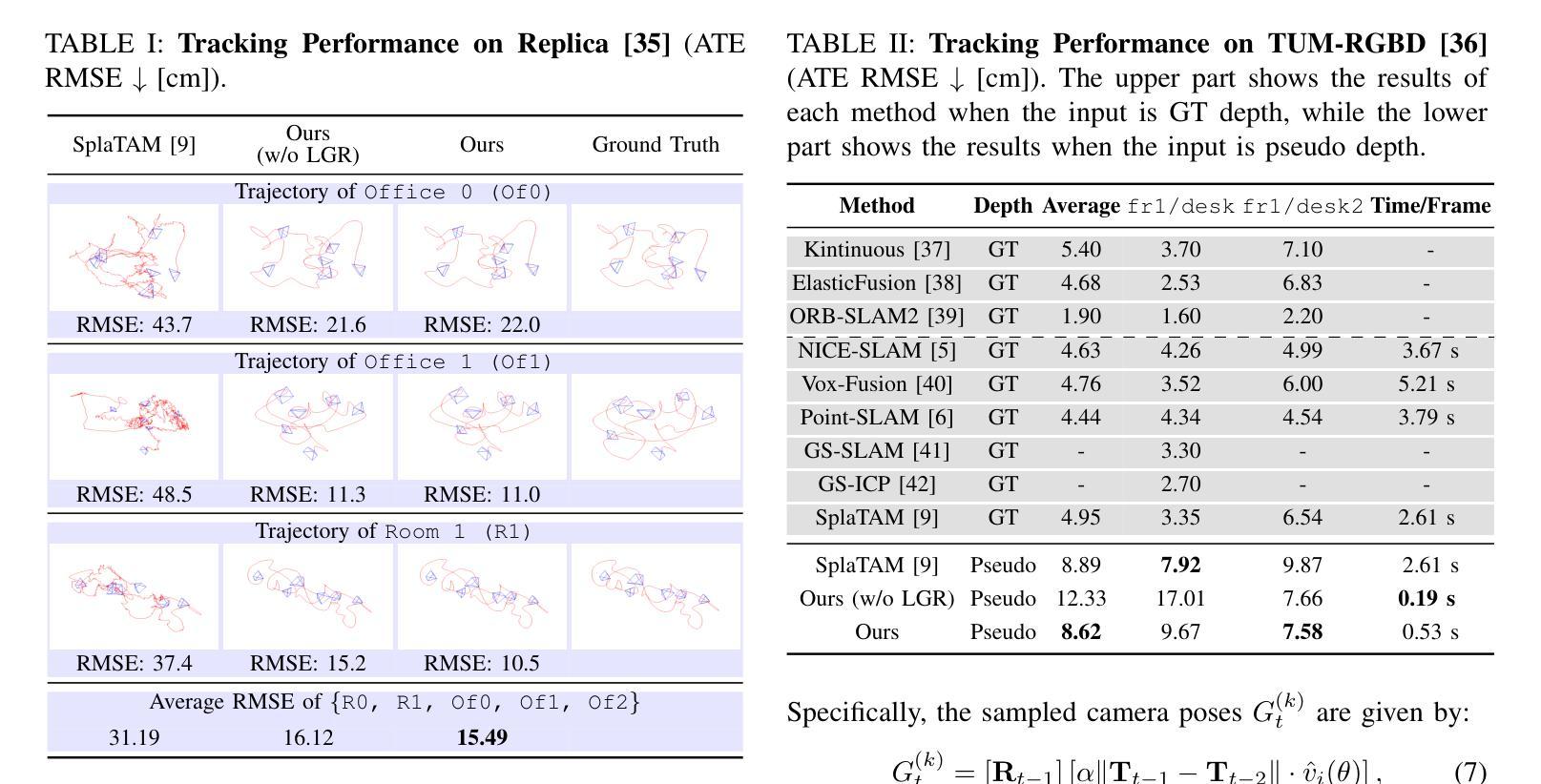
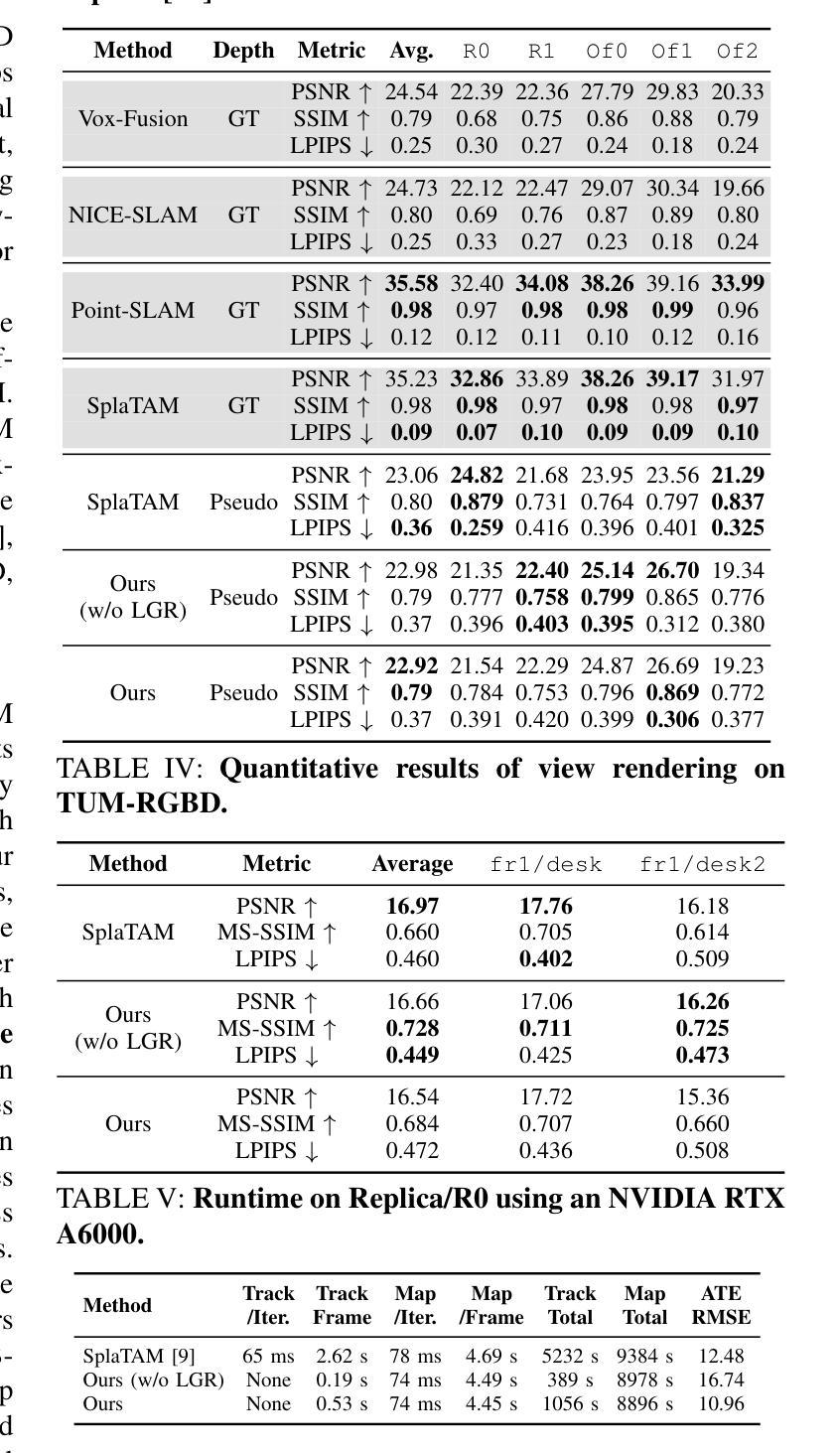
Incrementally recovering real-sized 3D geometry from a pose-free RGB stream is a challenging task in 3D reconstruction, requiring minimal assumptions on input data. Existing methods can be broadly categorized into end-to-end and visual SLAM-based approaches, both of which either struggle with long sequences or depend on slow test-time optimization and depth sensors. To address this, we first integrate a depth estimator into an RGB-D SLAM system, but this approach is hindered by inaccurate geometric details in predicted depth. Through further investigation, we find that 3D Gaussian mapping can effectively solve this problem. Building on this, we propose an online 3D reconstruction method using 3D Gaussian-based SLAM, combined with a feed-forward recurrent prediction module to directly infer camera pose from optical flow. This approach replaces slow test-time optimization with fast network inference, significantly improving tracking speed. Additionally, we introduce a local graph rendering technique to enhance robustness in feed-forward pose prediction. Experimental results on the Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets, along with a real-world deployment demonstration, show that our method achieves performance on par with the state-of-the-art SplaTAM, while reducing tracking time by more than 90%.
从无需姿态设定的RGB流中逐步重建真实尺寸的3D几何结构是3D重建中的一项具有挑战性的任务,它对输入数据的要求尽可能少。现有方法大致可分为端到端方法和基于视觉的SLAM方法,但它们在处理长序列时遇到挑战或依赖于缓慢的测试时间优化和深度传感器。为了解决这个问题,我们首先将深度估计器集成到RGB-D SLAM系统中,但这种方法受到预测深度中几何细节不准确的影响。通过进一步的调查,我们发现3D高斯映射可以有效地解决这个问题。在此基础上,我们提出了一种基于在线的3D重建方法,使用基于3D高斯SLAM技术,并结合前馈递归预测模块直接从光流推断相机姿态。这种方法用快速网络推理取代了缓慢的测试时间优化,大大提高了跟踪速度。此外,我们还引入了一种局部图形渲染技术,以提高前馈姿态预测的鲁棒性。在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验结果以及真实世界的部署演示表明,我们的方法与最先进的SplaTAM性能相当,同时跟踪时间减少了超过90%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于在线的3D重建方法,通过整合深度估计器与RGB-D SLAM系统,并采用3D高斯映射解决预测深度中的几何细节不准确问题。该方法引入前馈循环预测模块,直接从光流推断相机姿态,提高了跟踪速度。同时,采用局部图渲染技术增强姿态预测的鲁棒性。实验结果表明,该方法在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的性能与最新技术SplaTAM相当,但跟踪时间缩短了超过90%。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种在线的3D重建方法,旨在从RGB流中恢复真实尺寸的3D几何结构。
- 采用深度估计器与RGB-D SLAM系统整合,解决输入数据的最小假设问题。
- 发现预测深度中的几何细节不准确的问题,并提出通过3D高斯映射解决该问题。
- 引入前馈循环预测模块,直接从光流推断相机姿态,提高跟踪速度。
- 采用局部图渲染技术,增强姿态预测的鲁棒性。
- 在Replica和TUM-RGBD数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法性能与最新技术相当。
点此查看论文截图

Surf3R: Rapid Surface Reconstruction from Sparse RGB Views in Seconds
Authors:Haodong Zhu, Changbai Li, Yangyang Ren, Zichao Feng, Xuhui Liu, Hanlin Chen, Xiantong Zhen, Baochang Zhang
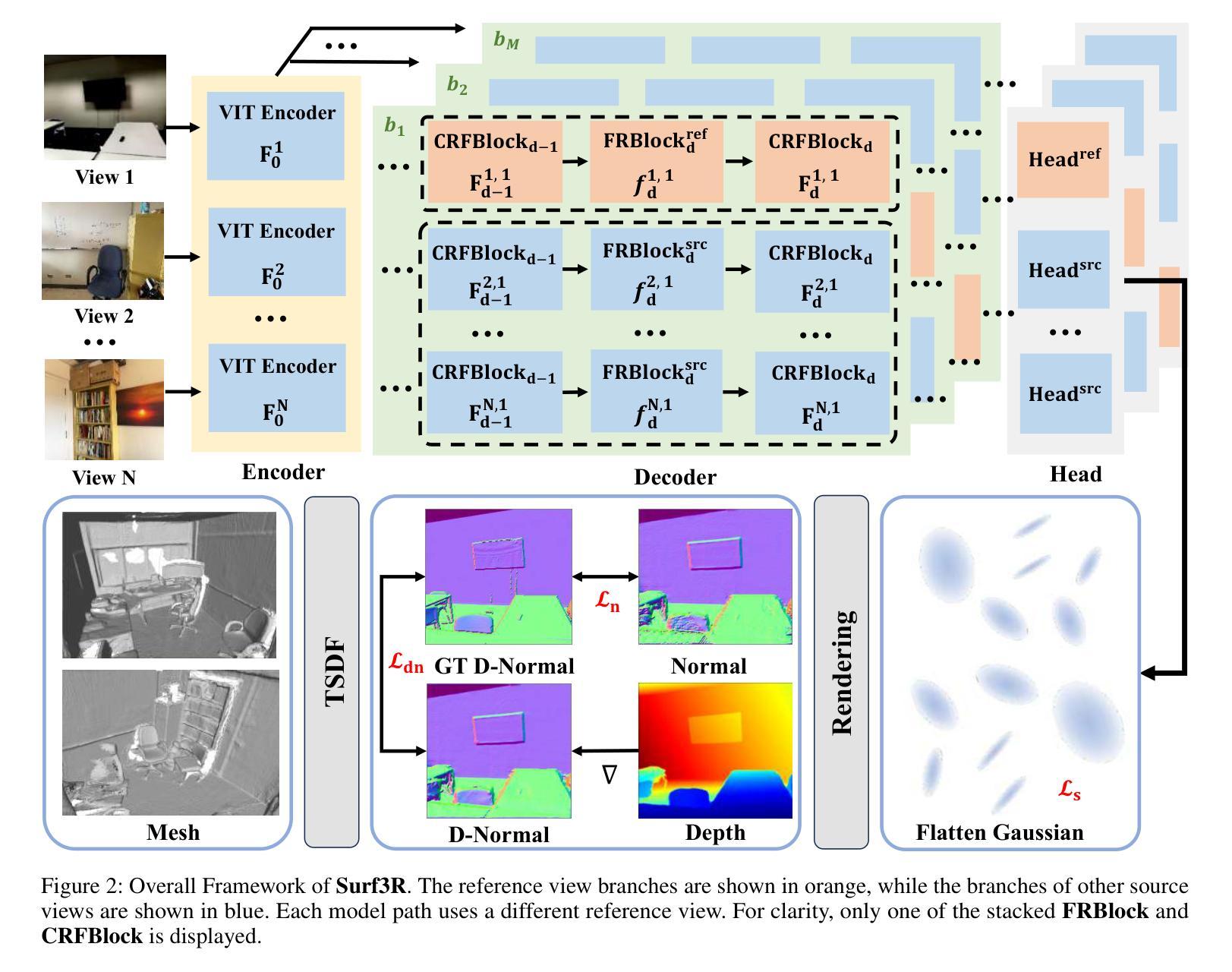
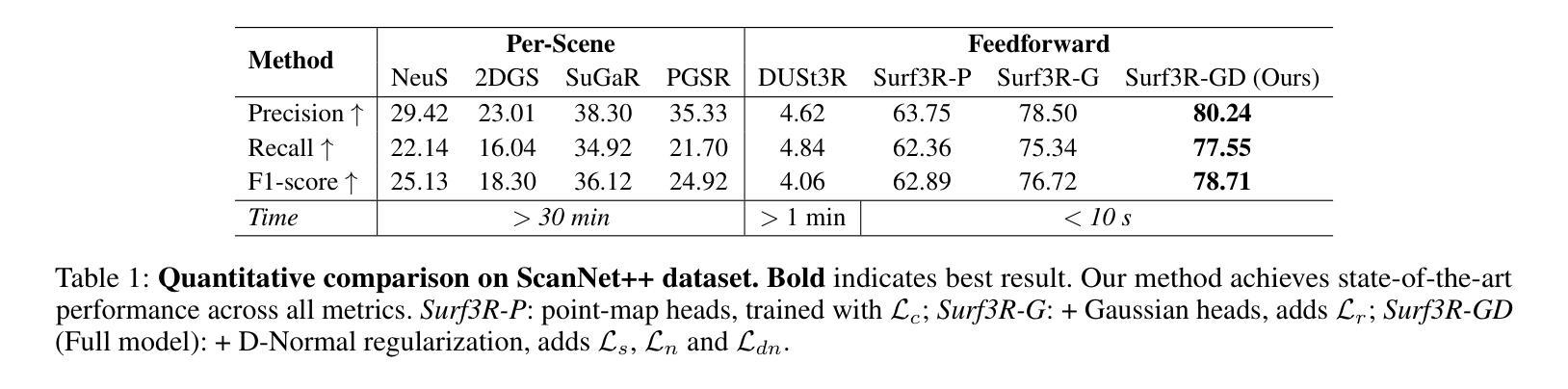
Current multi-view 3D reconstruction methods rely on accurate camera calibration and pose estimation, requiring complex and time-intensive pre-processing that hinders their practical deployment. To address this challenge, we introduce Surf3R, an end-to-end feedforward approach that reconstructs 3D surfaces from sparse views without estimating camera poses and completes an entire scene in under 10 seconds. Our method employs a multi-branch and multi-view decoding architecture in which multiple reference views jointly guide the reconstruction process. Through the proposed branch-wise processing, cross-view attention, and inter-branch fusion, the model effectively captures complementary geometric cues without requiring camera calibration. Moreover, we introduce a D-Normal regularizer based on an explicit 3D Gaussian representation for surface reconstruction. It couples surface normals with other geometric parameters to jointly optimize the 3D geometry, significantly improving 3D consistency and surface detail accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that Surf3R achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple surface reconstruction metrics on ScanNet++ and Replica datasets, exhibiting excellent generalization and efficiency.
当前的多视角3D重建方法依赖于准确的相机校准和姿态估计,需要复杂且耗时的预处理,阻碍了其实际部署。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了Surf3R,这是一种端到端的前馈方法,可以从稀疏视角重建3D表面,无需估计相机姿态,并在不到10秒内完成整个场景的重建。我们的方法采用多分支多视角解码架构,多个参考视角共同引导重建过程。通过提出的分支处理、跨视角注意力和跨分支融合,模型有效地捕捉了互补的几何线索,无需相机校准。此外,我们基于明确的3D高斯表示引入了一种D-Normal正则化方法,用于表面重建。它将表面法线与其它几何参数相结合,以共同优化3D几何形状,大大提高了3D一致性和表面细节精度。实验结果表明,Surf3R在ScanNet++和Replica数据集上的多个表面重建指标上达到了最先进的性能,表现出优异的通用性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Surf3R的端到端前馈方法,用于从稀疏视角重建3D表面。该方法无需估计相机姿态,即可在多场景下快速完成重建过程,且整个过程仅需不到十秒。通过采用多分支多视角解码架构,结合分支处理、跨视角注意力机制和分支间融合等技术,模型能有效捕捉几何信息。同时引入基于显式三维高斯表示的D-Normal正则化方法用于表面重建,提高重建效果的准确性。实验结果显示,Surf3R在多个数据集上的表面重建效果达到业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- Surf3R是一种端到端的3D重建方法,无需复杂的预处理和相机校准。
- 该方法能够从稀疏视角快速重建3D表面,整个流程在10秒内完成。
- 多分支多视角解码架构用于捕捉几何信息,提高重建准确性。
- 引入D-Normal正则化方法,基于显式三维高斯表示,提高表面重建的3D一致性和表面细节精度。
- 实验结果显示,Surf3R在多个数据集上的表面重建效果达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

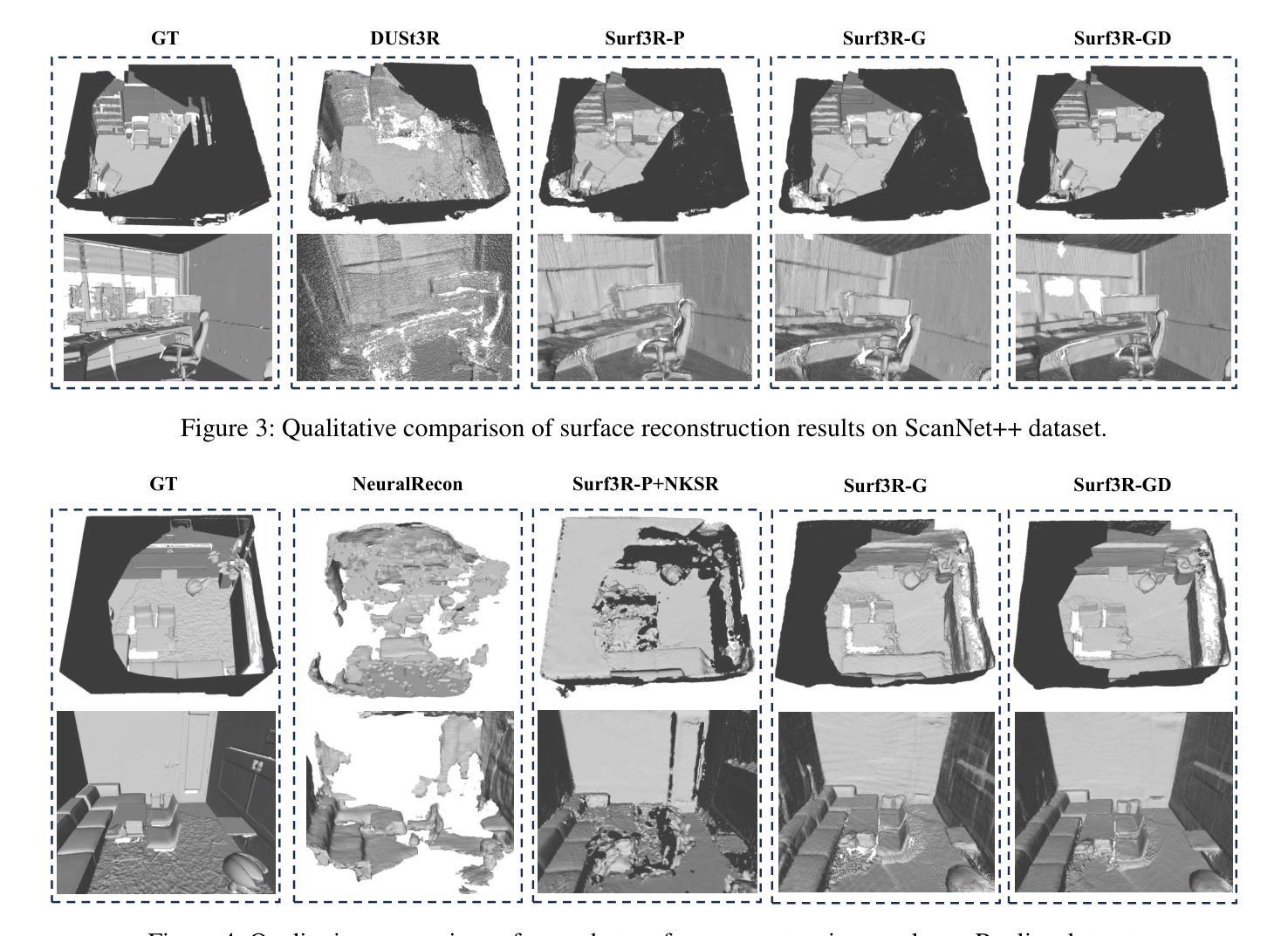
MuGS: Multi-Baseline Generalizable Gaussian Splatting Reconstruction
Authors:Yaopeng Lou, Liao Shen, Tianqi Liu, Jiaqi Li, Zihao Huang, Huiqiang Sun, Zhiguo Cao
We present Multi-Baseline Gaussian Splatting (MuRF), a generalized feed-forward approach for novel view synthesis that effectively handles diverse baseline settings, including sparse input views with both small and large baselines. Specifically, we integrate features from Multi-View Stereo (MVS) and Monocular Depth Estimation (MDE) to enhance feature representations for generalizable reconstruction. Next, We propose a projection-and-sampling mechanism for deep depth fusion, which constructs a fine probability volume to guide the regression of the feature map. Furthermore, We introduce a reference-view loss to improve geometry and optimization efficiency. We leverage 3D Gaussian representations to accelerate training and inference time while enhancing rendering quality. MuRF achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple baseline settings and diverse scenarios ranging from simple objects (DTU) to complex indoor and outdoor scenes (RealEstate10K). We also demonstrate promising zero-shot performance on the LLFF and Mip-NeRF 360 datasets.
我们提出了多基线高斯展片(MuRF),这是一种用于新型视角合成的通用前馈方法,能够有效地处理包括稀疏输入视角、小基线和大基线在内的多种基线设置。具体来说,我们整合了多视角立体(MVS)和单眼深度估计(MDE)的特征,以增强可概括重建的特征表示。接下来,我们提出了一种用于深度深度融合的投影和采样机制,它构建了一个精细的概率体积来指导特征图的回归。此外,我们引入了一个参考视图损失来提高几何和优化效率。我们利用3D高斯表示来加速训练和推理时间,同时提高渲染质量。MuRF在多种基线设置和从简单对象(DTU)到复杂室内和室外场景(RealEstate10K)的多种场景中实现了最先进的性能。我们在LLFF和Mip-NeRF 360数据集上展示了有前景的零样本性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work is accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
Multi-Baseline Gaussian Splatting(MuRF)是一种用于新型视角合成的通用前馈方法,能有效处理包括稀疏输入视角、小基线和大基线等不同的基线设置。通过整合多视角立体(MVS)和单眼深度估计(MDE)的特性,提升特征表达,实现可概括的重构。提出深度融合投影采样机制,构建精细概率体积引导特征图的回归。引入参考视角损失,提升几何和优化效率。利用三维高斯表示加速训练和推理时间,同时提高渲染质量。MuRF在多种基线设置和从简单物体(DTU)到复杂室内室外场景(RealEstate10K)中表现最佳,并在LLFF和Mip-NeRF 360数据集上展现出零样本性能潜力。
Key Takeaways
- MuRF是一种新型视角合成的通用前馈方法,适用于多种基线设置。
- 结合多视角立体(MVS)和单眼深度估计(MDE)提升特征表达。
- 提出深度融合投影采样机制,构建精细概率体积引导特征回归。
- 引入参考视角损失以提升几何和优化的效率。
- 采用三维高斯表示加速训练与推理过程,同时提高渲染质量。
- MuRF在多种场景和不同的基线设置下表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

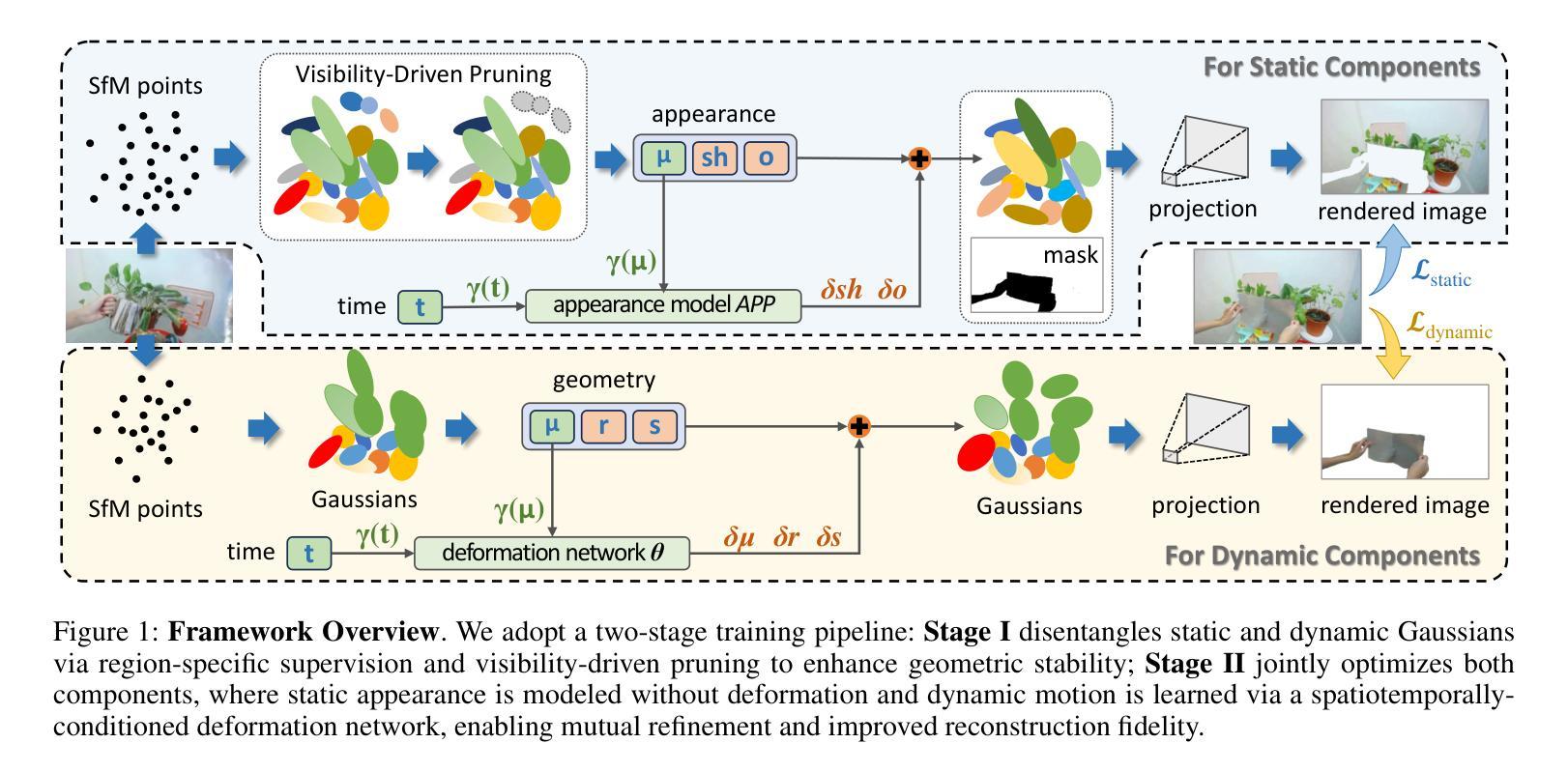
SplitGaussian: Reconstructing Dynamic Scenes via Visual Geometry Decomposition
Authors:Jiahui Li, Shengeng Tang, Jingxuan He, Gang Huang, Zhangye Wang, Yantao Pan, Lechao Cheng
Reconstructing dynamic 3D scenes from monocular video remains fundamentally challenging due to the need to jointly infer motion, structure, and appearance from limited observations. Existing dynamic scene reconstruction methods based on Gaussian Splatting often entangle static and dynamic elements in a shared representation, leading to motion leakage, geometric distortions, and temporal flickering. We identify that the root cause lies in the coupled modeling of geometry and appearance across time, which hampers both stability and interpretability. To address this, we propose \textbf{SplitGaussian}, a novel framework that explicitly decomposes scene representations into static and dynamic components. By decoupling motion modeling from background geometry and allowing only the dynamic branch to deform over time, our method prevents motion artifacts in static regions while supporting view- and time-dependent appearance refinement. This disentangled design not only enhances temporal consistency and reconstruction fidelity but also accelerates convergence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SplitGaussian outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods in rendering quality, geometric stability, and motion separation.
从单目视频中重建动态3D场景仍然具有根本的挑战性,因为需要从有限的观察结果中联合推断运动、结构和外观。基于高斯涂抹的现有动态场景重建方法通常会将静态和动态元素纠缠在共享表示中,导致运动泄露、几何失真和暂时闪烁。我们发现根本原因就在于几何和外观在时间上的耦合建模,这阻碍了稳定性和可解释性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SplitGaussian这一新型框架,它将场景表示显式地分解为静态和动态成分。通过将运动建模与背景几何分离,并仅允许动态分支随时间变形,我们的方法在静态区域防止了运动伪影,同时支持视图和随时间变化的外观细化。这种解耦设计不仅提高了时间一致性和重建保真度,还加速了收敛。大量实验表明,SplitGaussian在渲染质量、几何稳定性和运动分离方面均优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出从单目视频中重建动态3D场景具有挑战性,因为需要从有限的观察中联合推断运动、结构和外观。现有基于高斯拼贴的方法会将静态和动态元素纠缠在一起,导致运动泄露、几何失真和临时闪烁。作者认为问题的根源在于时间和几何之间的耦合建模,这阻碍了稳定性和可解释性。为解决这一问题,作者提出了SplitGaussian框架,该框架将场景表示显式地分解为静态和动态组件。通过将运动建模与背景几何分离,只允许动态分支随时间变形,该方法防止了静态区域的运动伪影,并支持视和时间相关的外观优化。这种分离的设计不仅提高了时间一致性和重建保真度,还加速了收敛。实验表明,SplitGaussian在渲染质量、几何稳定性和运动分离方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 动态3D场景重建从单目视频存在挑战,需从有限观察中联合推断运动、结构和外观。
- 现有方法存在运动泄露、几何失真和临时闪烁问题。
- 问题根源在于时间和几何的耦合建模,影响稳定性和可解释性。
- SplitGaussian框架能显式地分解场景为静态和动态组件。
- 该方法通过分离运动建模和背景几何,提高了时间一致性和重建质量。
- SplitGaussian在渲染质量、几何稳定性和运动分离方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

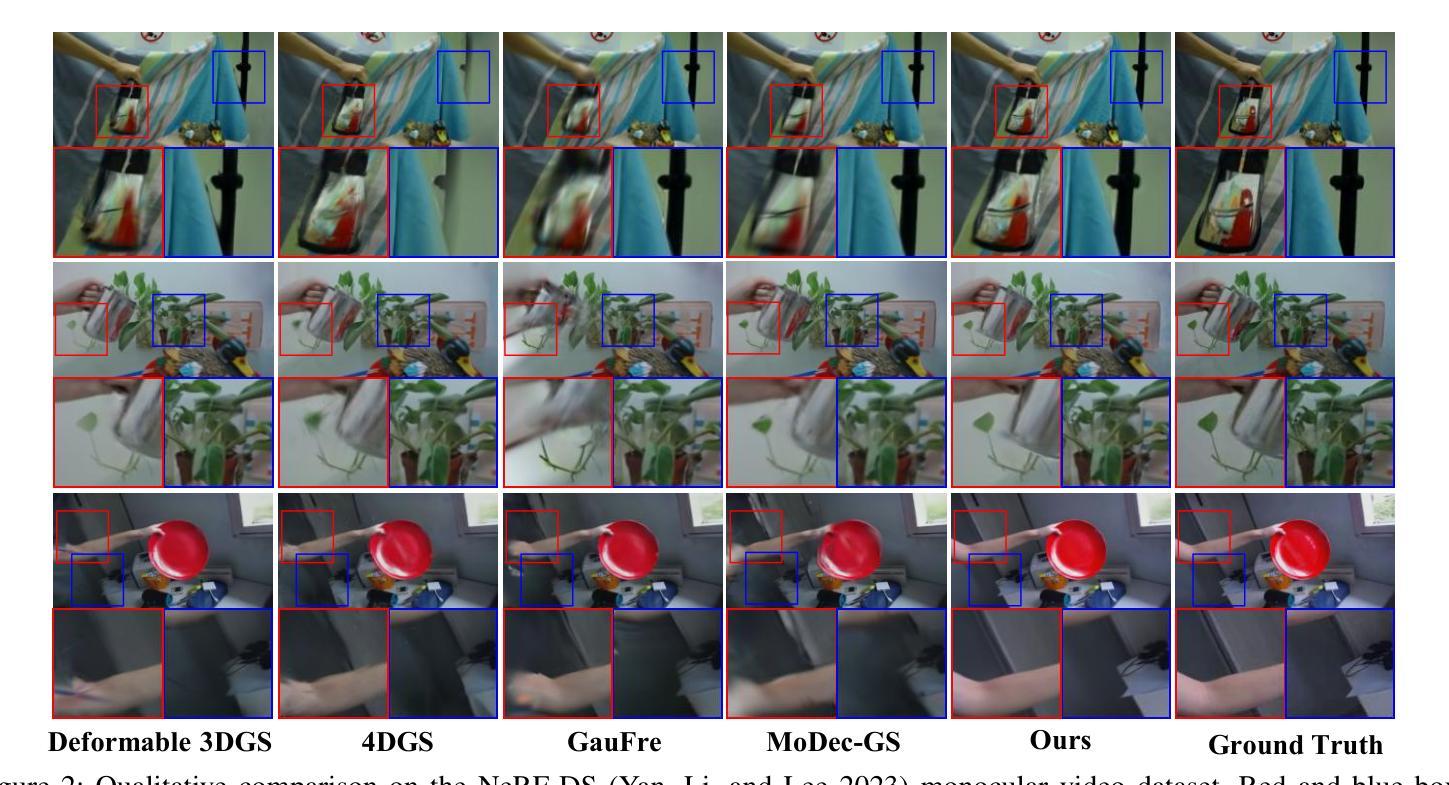
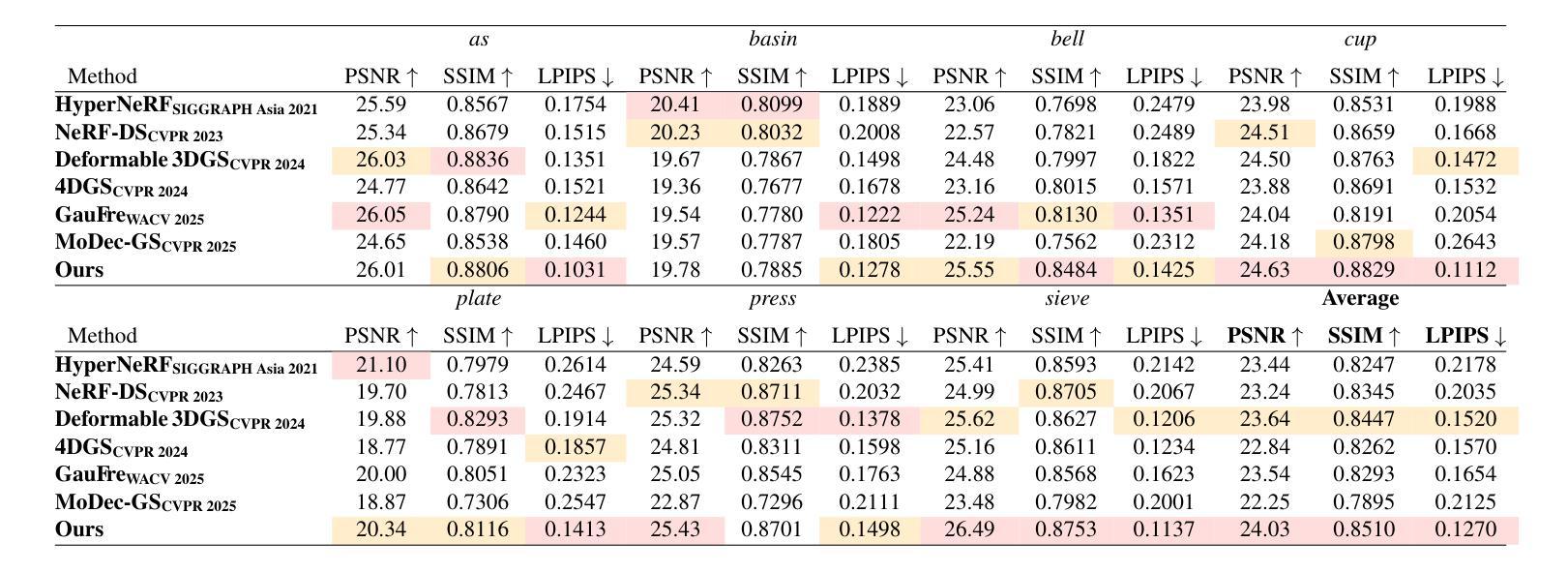
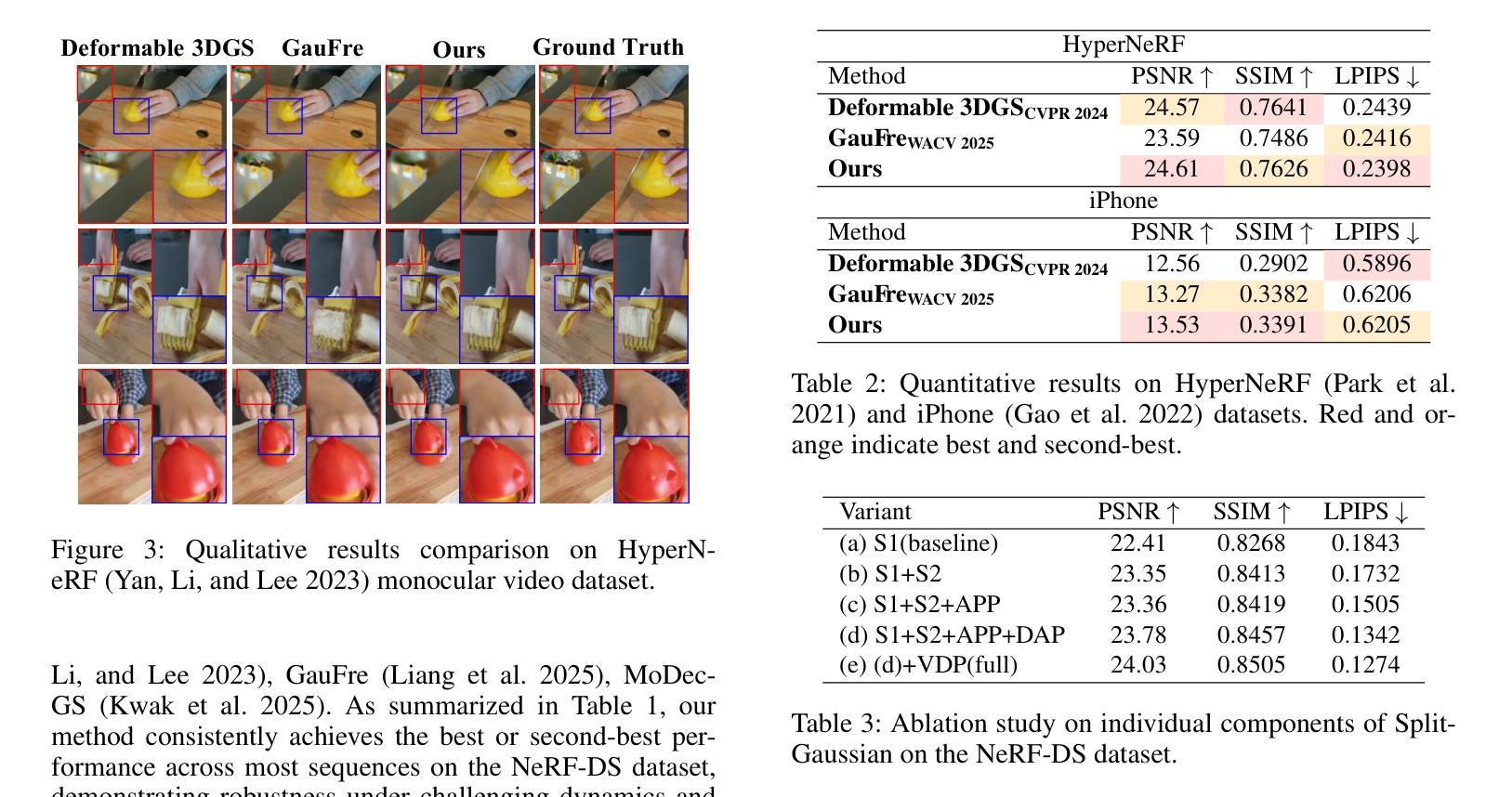
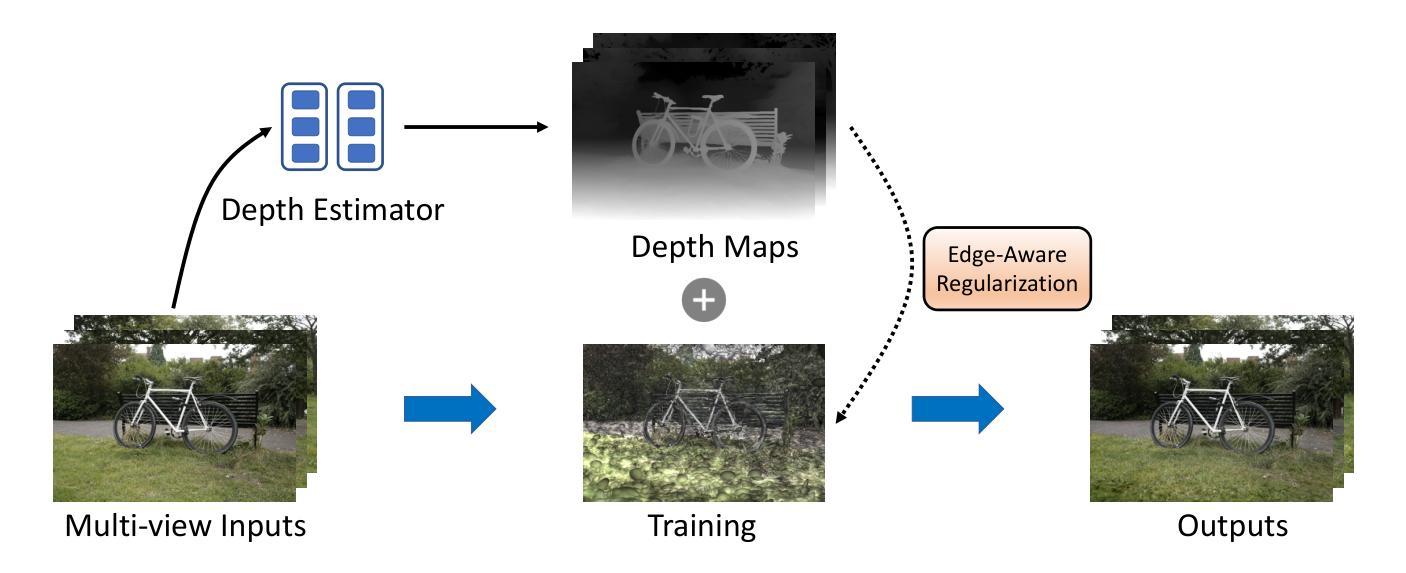
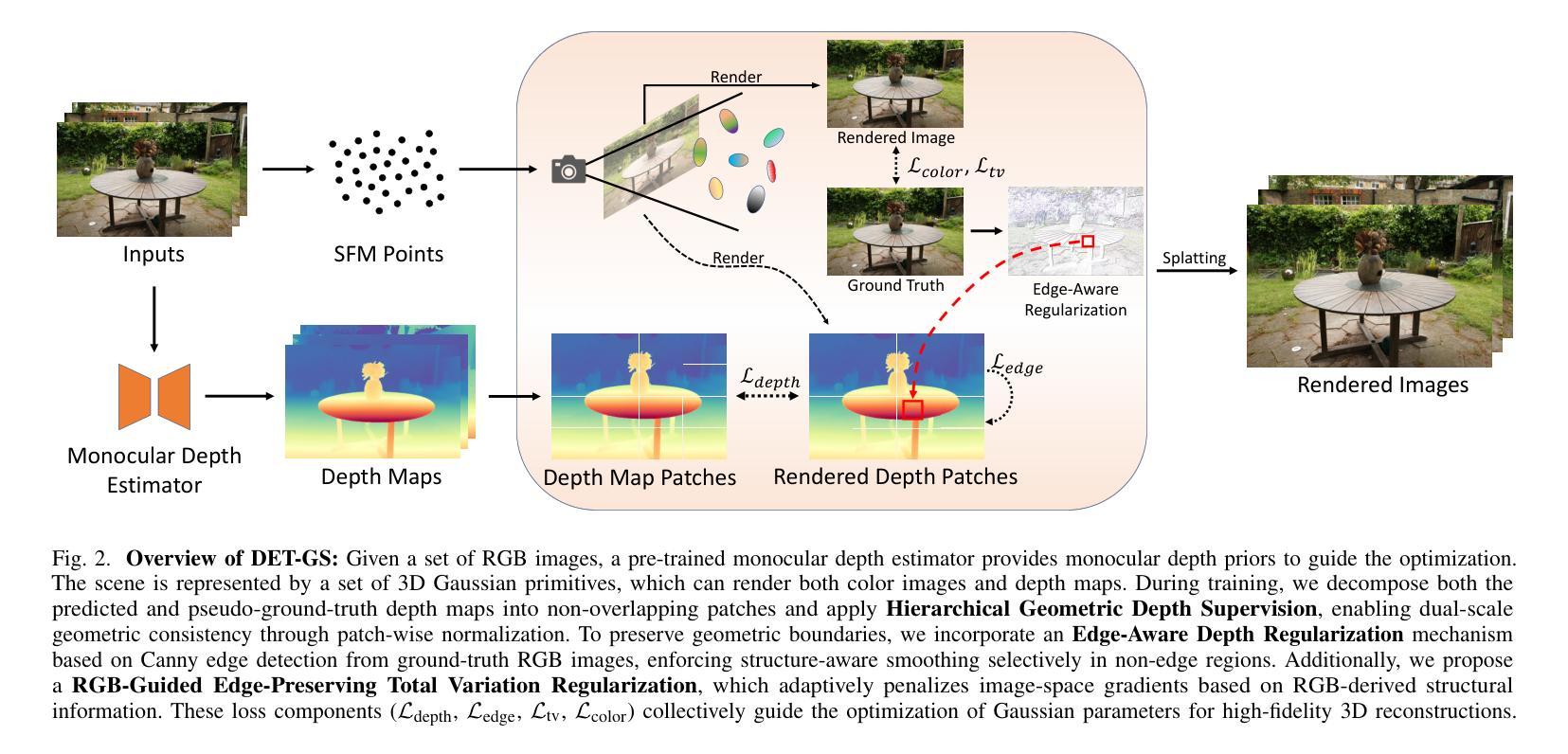
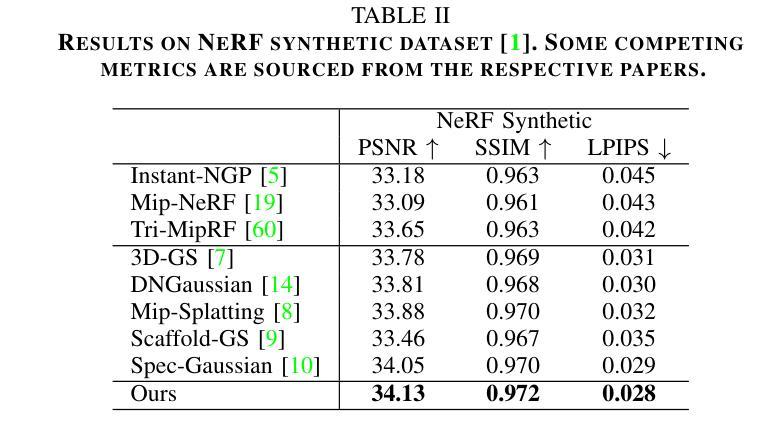
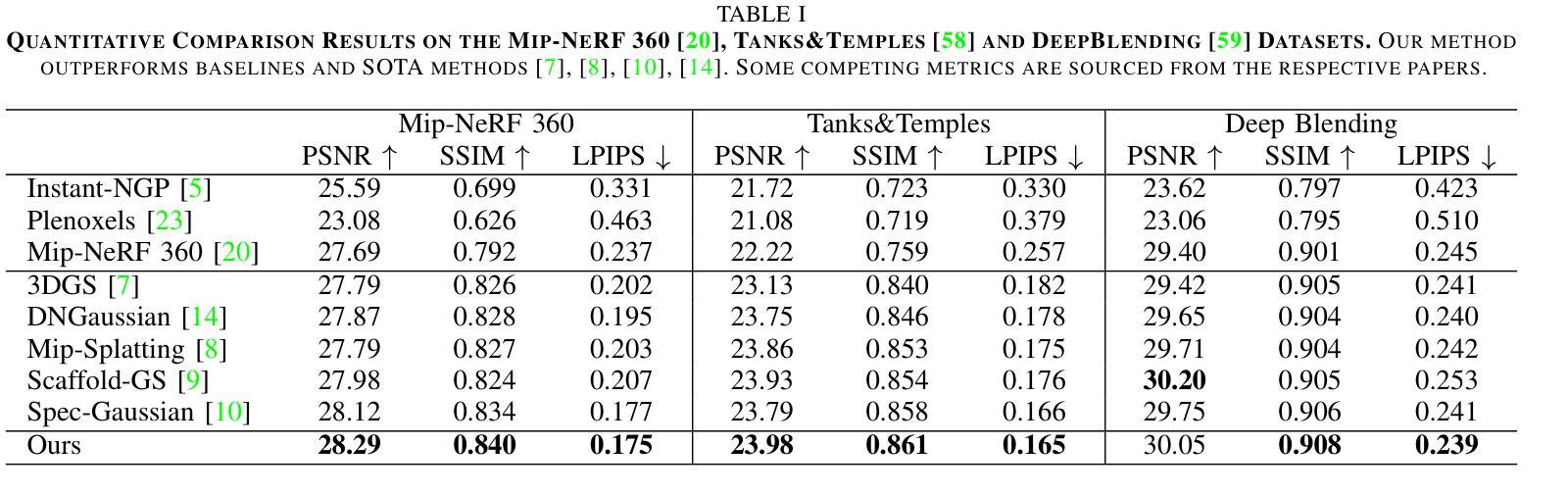
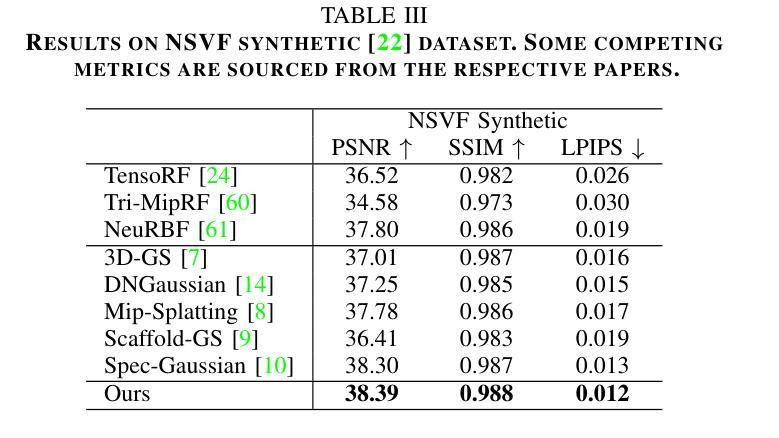
DET-GS: Depth- and Edge-Aware Regularization for High-Fidelity 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zexu Huang, Min Xu, Stuart Perry
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) represents a significant advancement in the field of efficient and high-fidelity novel view synthesis. Despite recent progress, achieving accurate geometric reconstruction under sparse-view conditions remains a fundamental challenge. Existing methods often rely on non-local depth regularization, which fails to capture fine-grained structures and is highly sensitive to depth estimation noise. Furthermore, traditional smoothing methods neglect semantic boundaries and indiscriminately degrade essential edges and textures, consequently limiting the overall quality of reconstruction. In this work, we propose DET-GS, a unified depth and edge-aware regularization framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting. DET-GS introduces a hierarchical geometric depth supervision framework that adaptively enforces multi-level geometric consistency, significantly enhancing structural fidelity and robustness against depth estimation noise. To preserve scene boundaries, we design an edge-aware depth regularization guided by semantic masks derived from Canny edge detection. Furthermore, we introduce an RGB-guided edge-preserving Total Variation loss that selectively smooths homogeneous regions while rigorously retaining high-frequency details and textures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DET-GS achieves substantial improvements in both geometric accuracy and visual fidelity, outperforming state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on sparse-view novel view synthesis benchmarks.
3D高斯展开(3DGS)代表了高效和高保真新颖视图合成领域的重要进展。尽管最近有进展,但在稀疏视图条件下实现准确的几何重建仍然是一个基本挑战。现有方法通常依赖于非局部深度正则化,这无法捕捉精细结构,并且对深度估计噪声高度敏感。此外,传统平滑方法忽略了语义边界,不加区分地降低了重要边缘和纹理,从而限制了重建的整体质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了DET-GS,这是一个用于3D高斯展开的深度感知和边缘感知正则化框架。DET-GS引入了一种分层几何深度监督框架,该框架自适应地执行多级几何一致性,从而显著提高结构保真度和对深度估计噪声的鲁棒性。为了保留场景边界,我们设计了一种由Canny边缘检测得到的语义掩膜引导的边缘感知深度正则化方法。此外,我们引入了一种由RGB引导的保边全变损失(Total Variation loss),该损失选择性地平滑均匀区域,同时严格保留高频细节和纹理。大量实验表明,DET-GS在几何精度和视觉保真度方面取得了实质性改进,在稀疏视图新颖视图合成基准测试中优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯融合(3DGS)领域的新进展。现有方法在实现稀疏视图下的精确几何重建时面临挑战,它们通常采用非局部深度正则化方法,无法捕捉精细结构并对深度估计噪声敏感。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一个统一、具有深度感知和边缘感知的正则化框架DET-GS。该框架引入分层几何深度监督机制,自适应地实现多级几何一致性,从而提高结构保真度和对深度估计噪声的鲁棒性。此外,为了保留场景边界,该框架还设计了一种受语义掩码引导的边界感知深度正则化方法,并采用RGB引导的边缘保留总变异损失来选择性平滑均匀区域,同时严格保留高频细节和纹理。实验证明,DET-GS在几何精度和视觉保真度方面取得了显著改进,在稀疏视图新视角合成基准测试中优于其他最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有方法在稀疏视图下的几何重建中面临挑战,存在无法捕捉精细结构和对深度估计噪声敏感的问题。
- DET-GS是一个统一、具有深度感知和边缘感知的正则化框架,旨在解决上述问题。
- DET-GS引入分层几何深度监督机制,提高结构保真度和对深度估计噪声的鲁棒性。
- 框架采用语义掩码引导的边界感知深度正则化方法,以保留场景边界。
- 采用RGB引导的边缘保留总变异损失,选择性平滑均匀区域,同时保留高频细节和纹理。
点此查看论文截图

Bridging Diffusion Models and 3D Representations: A 3D Consistent Super-Resolution Framework
Authors:Yi-Ting Chen, Ting-Hsuan Liao, Pengsheng Guo, Alexander Schwing, Jia-Bin Huang
We propose 3D Super Resolution (3DSR), a novel 3D Gaussian-splatting-based super-resolution framework that leverages off-the-shelf diffusion-based 2D super-resolution models. 3DSR encourages 3D consistency across views via the use of an explicit 3D Gaussian-splatting-based scene representation. This makes the proposed 3DSR different from prior work, such as image upsampling or the use of video super-resolution, which either don’t consider 3D consistency or aim to incorporate 3D consistency implicitly. Notably, our method enhances visual quality without additional fine-tuning, ensuring spatial coherence within the reconstructed scene. We evaluate 3DSR on MipNeRF360 and LLFF data, demonstrating that it produces high-resolution results that are visually compelling, while maintaining structural consistency in 3D reconstructions. Code will be released.
我们提出了基于三维高斯散斑的超分辨率技术(3DSR),这是一种新型三维超分辨率框架,它利用现成的基于扩散的二维超分辨率模型。通过采用基于明确的三维高斯散斑的场景表示,3DSR鼓励不同视角的三维一致性。这使得所提出的3DSR与先前的工作有所不同,例如图像上采样或使用视频超分辨率,这些要么不考虑三维一致性,要么旨在隐式地融入三维一致性。值得注意的是,我们的方法在无需额外微调的情况下提高了视觉质量,确保了重建场景内的空间连贯性。我们在MipNeRF360和LLFF数据上对3DSR进行了评估,结果表明它产生了高分辨率的结果,视觉上非常吸引人,同时在三维重建中保持了结构一致性。代码将会公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
摘要
本文提出了基于三维高斯涂抹技术的超级分辨率重建框架(3DSR)。它利用现成的二维扩散超级分辨率模型,并通过明确的3D高斯涂抹场景表示来鼓励不同视角下的三维一致性。与传统的图像上采样或视频超级分辨率方法不同,新方法无需考虑三维一致性或试图隐式地实现它。值得注意的特点是,我们的方法能够在不经过微调的情况下提高视觉效果,确保重建场景内的空间连贯性。在MipNeRF360和LLFF数据上的评估表明,它产生高分辨率结果,视觉上令人信服,同时在三维重建中保持结构一致性。代码即将发布。
关键见解
- 提出了基于三维高斯涂抹技术的超级分辨率重建框架(3DSR)。
- 利用现成的二维扩散超级分辨率模型。
- 通过明确的3D高斯涂抹场景表示实现三维一致性。
- 与传统方法不同,无需考虑三维一致性或隐式实现。
- 在不经过微调的情况下提高视觉效果。
- 确保重建场景内的空间连贯性。
- 在MipNeRF360和LLFF数据上的评估表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


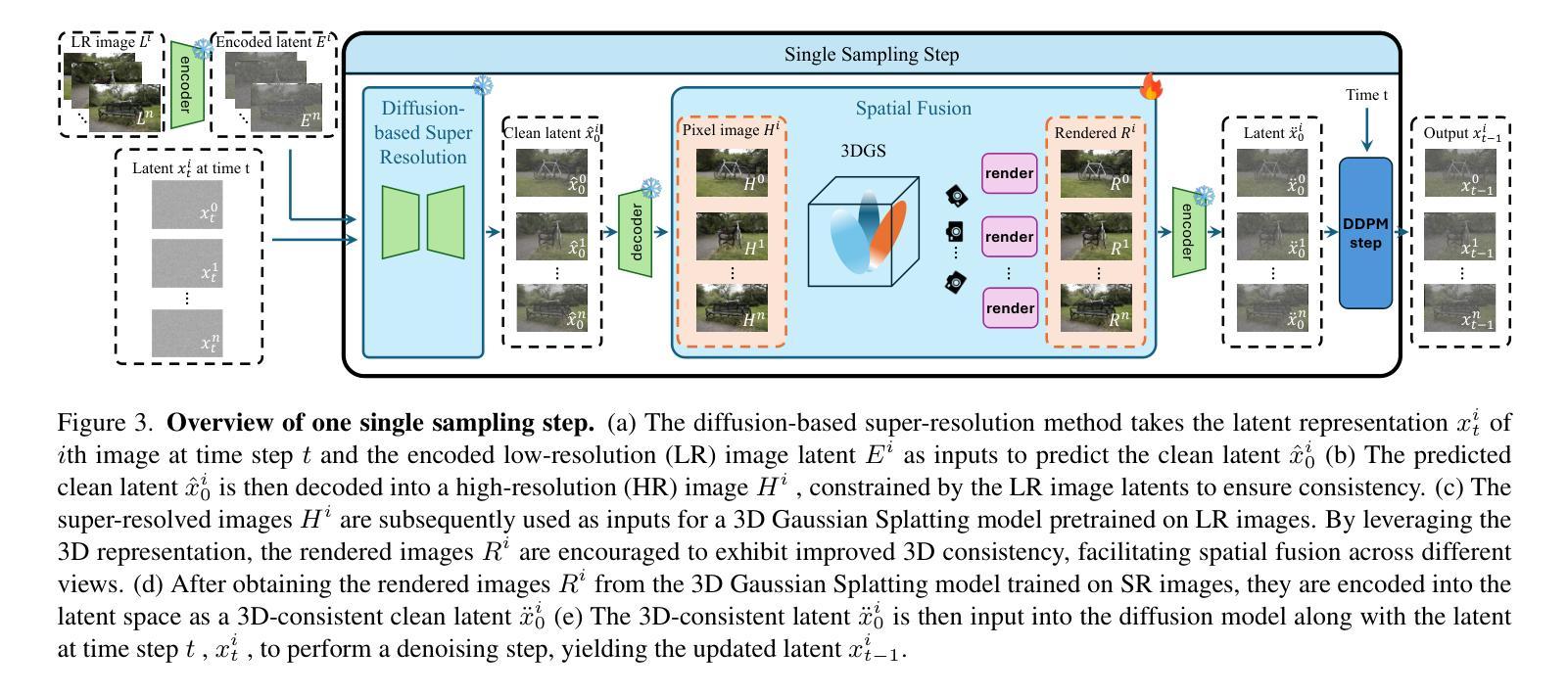

RLGS: Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hyperparameter Tuning for Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhan Li, Huangying Zhan, Changyang Li, Qingan Yan, Yi Xu
Hyperparameter tuning in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a labor-intensive and expert-driven process, often resulting in inconsistent reconstructions and suboptimal results. We propose RLGS, a plug-and-play reinforcement learning framework for adaptive hyperparameter tuning in 3DGS through lightweight policy modules, dynamically adjusting critical hyperparameters such as learning rates and densification thresholds. The framework is model-agnostic and seamlessly integrates into existing 3DGS pipelines without architectural modifications. We demonstrate its generalization ability across multiple state-of-the-art 3DGS variants, including Taming-3DGS and 3DGS-MCMC, and validate its robustness across diverse datasets. RLGS consistently enhances rendering quality. For example, it improves Taming-3DGS by 0.7dB PSNR on the Tanks and Temple (TNT) dataset, under a fixed Gaussian budget, and continues to yield gains even when baseline performance saturates. Our results suggest that RLGS provides an effective and general solution for automating hyperparameter tuning in 3DGS training, bridging a gap in applying reinforcement learning to 3DGS.
在3D高斯混合(3DGS)中,超参数调整是一个劳动密集型且专家驱动的过程,往往导致重建结果不一致和次优结果。我们提出了RLGS,这是一种用于自适应超参数调整的强化学习框架,通过轻量级策略模块实现即插即用功能,动态调整关键超参数,如学习率和密度阈值。该框架具有模型通用性,可无缝集成到现有的3DGS管道中,无需进行架构修改。我们在多个最先进的3DGS变体上展示了其泛化能力,包括驯服3DGS和3DGS-MCMC等,并在各种数据集上验证了其稳健性。RLGS持续提高了渲染质量。例如,在固定高斯预算的情况下,它在坦克和寺庙(TNT)数据集上改进了驯服3DGS的PSNR 0.7dB;即使在基线性能饱和时,也能继续产生收益。我们的结果表明,RLGS提供了一种有效且通用的解决方案,可自动化用于解决3DGS训练中的超参数调整问题,填补了将强化学习应用于3DGS的空白。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为RLGS的强化学习框架,用于自适应调整3D高斯融合(3DGS)中的关键超参数,如学习率和密度阈值。该框架具有模型无关性,可无缝集成到现有3DGS管道中,无需进行架构修改。实验表明,RLGS在多个先进的3DGS变体上具有良好的通用性,并在各种数据集上验证了其稳健性。RLGS能持续提高渲染质量,例如,在固定的高斯预算下,它在Tanks and Temple数据集上将Taming-3DGS的PSNR提高了0.7dB。总体而言,RLGS为自动调整3DGS超参数提供了一种有效且通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- RLGS是一种强化学习框架,用于自适应调整3DGS中的超参数。
- 该框架具有模型无关性,可轻松集成到现有的3DGS管道中。
- RLGS在多个先进的3DGS变体上具有良好的通用性。
- RLGS在多种数据集上验证了其稳健性。
- RLGS能持续提高渲染质量,如Taming-3DGS在Tanks and Temple数据集上的PSNR提高0.7dB。
- RLGS尤其在基线性能饱和时仍能保持提升效果。
点此查看论文截图

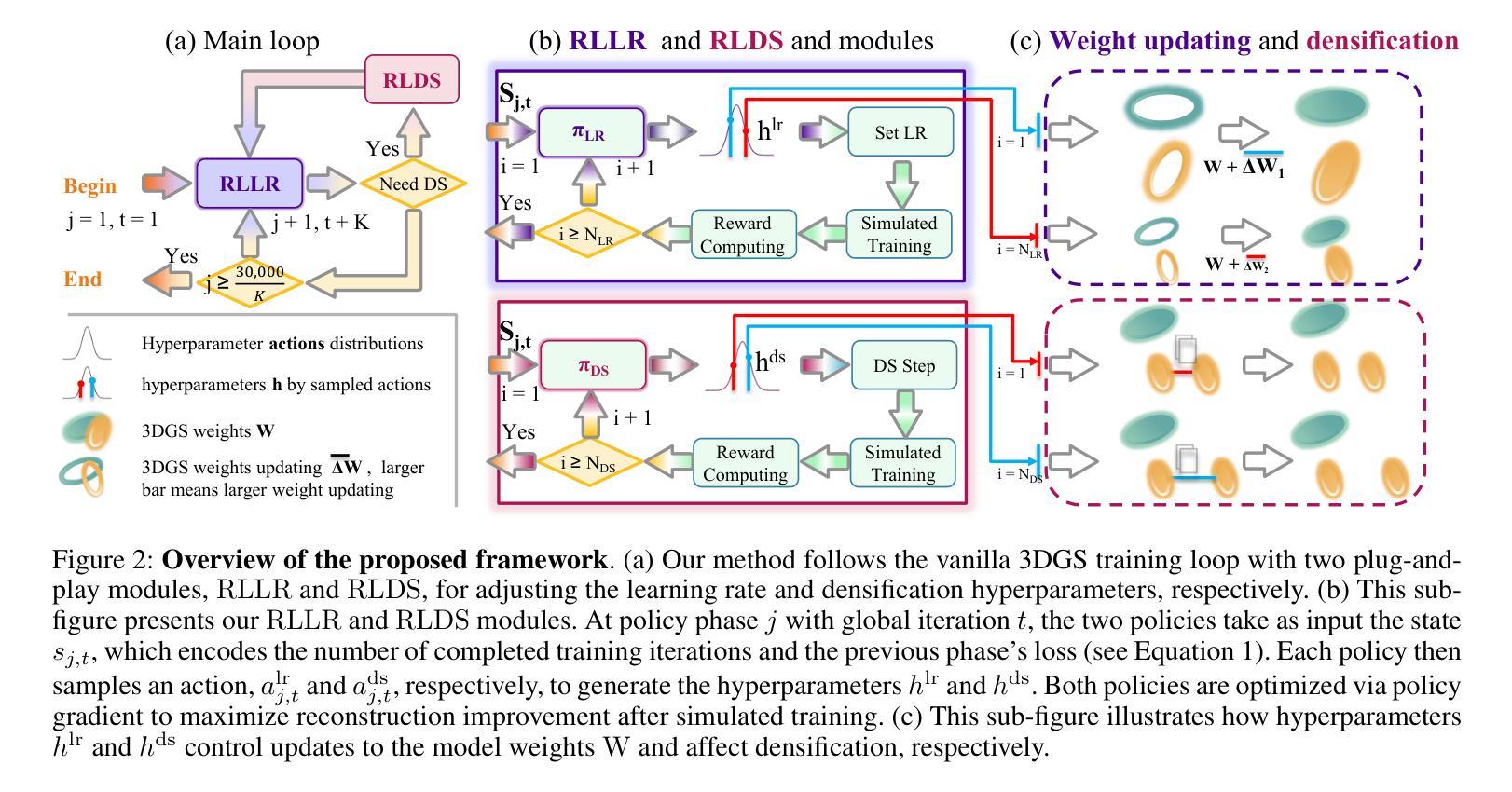
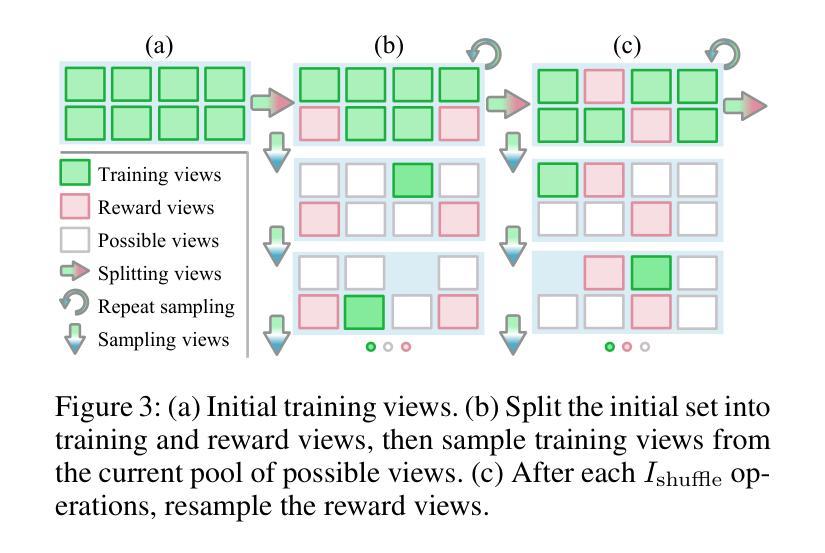
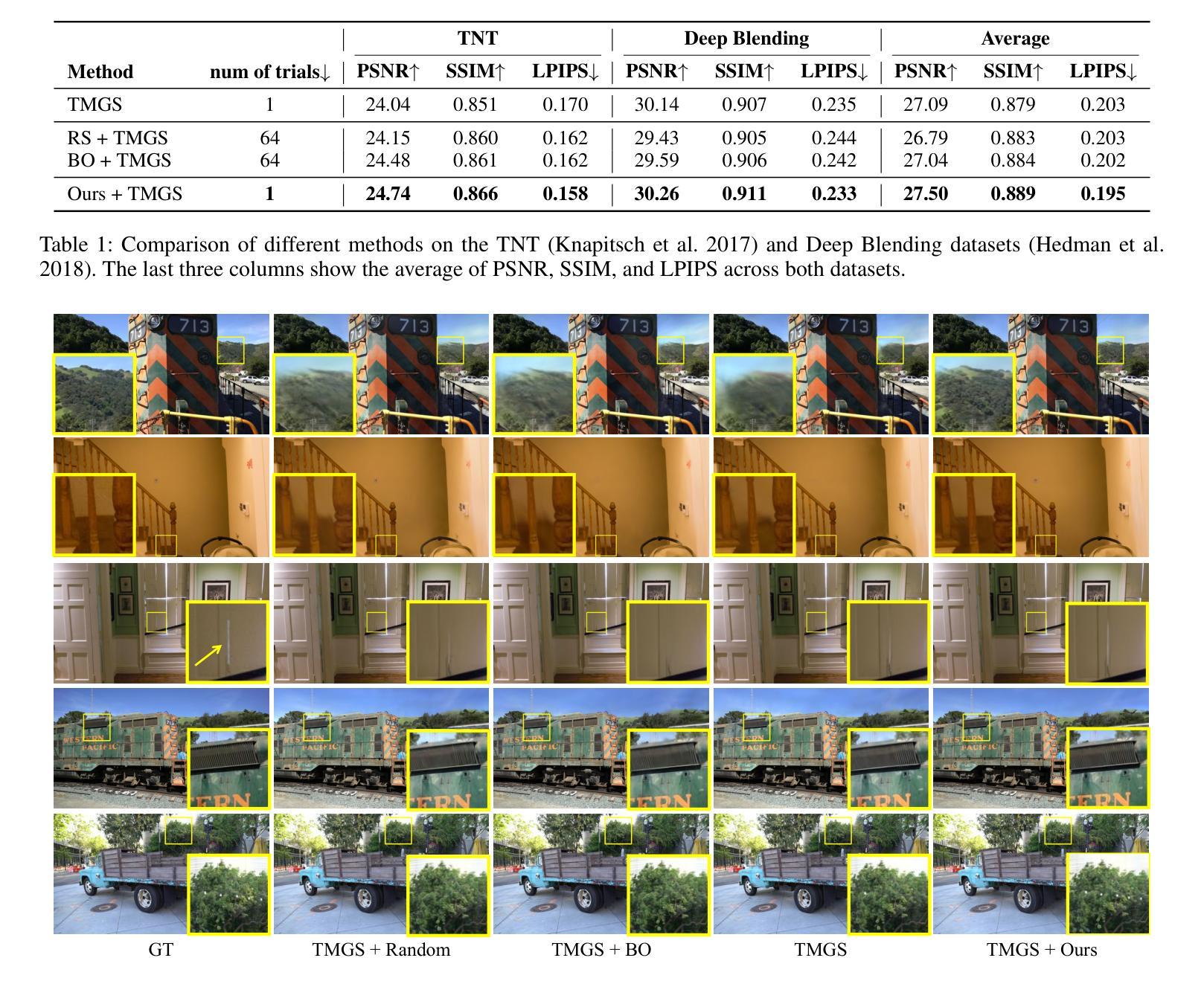
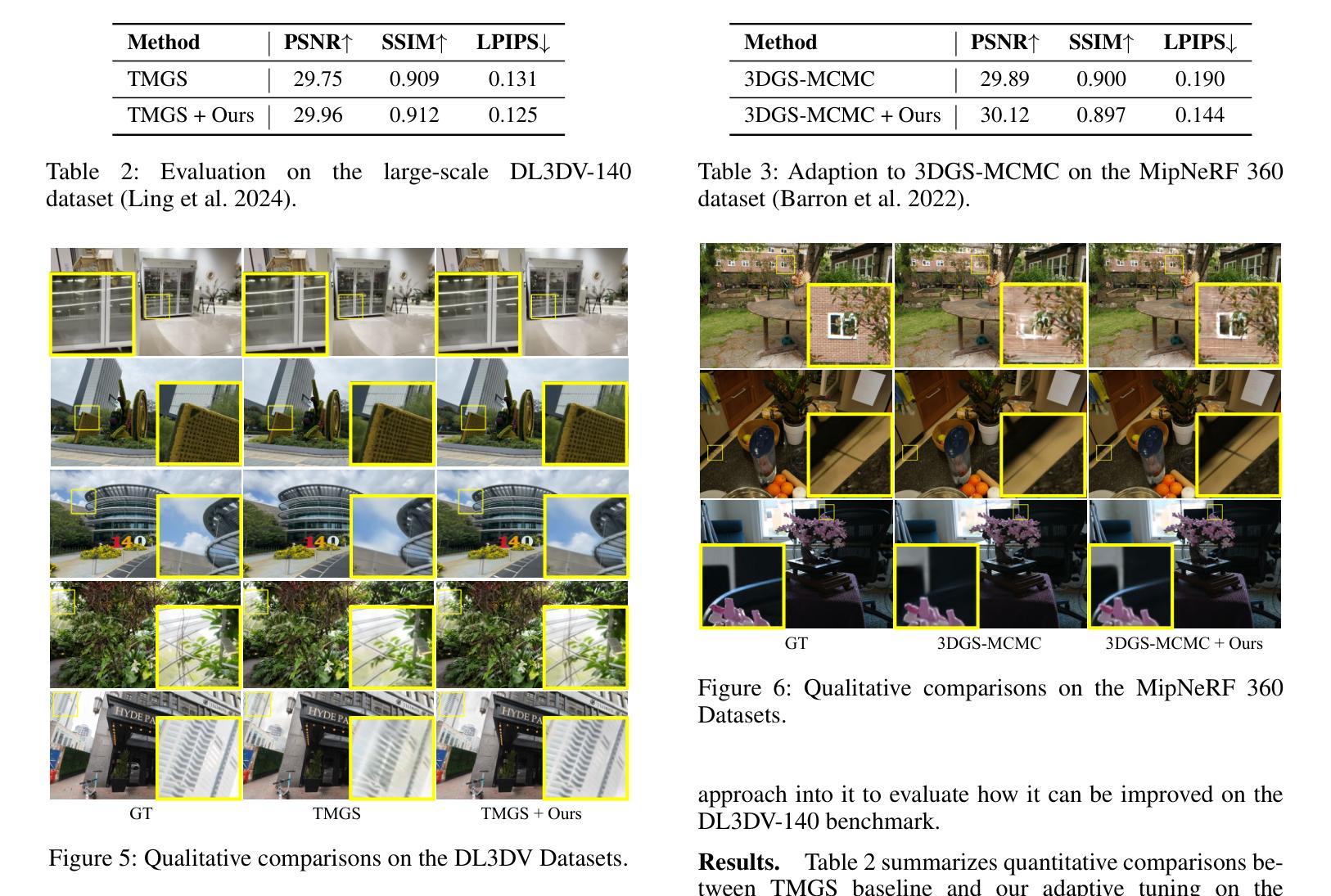
Uni3R: Unified 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Understanding via Generalizable Gaussian Splatting from Unposed Multi-View Images
Authors:Xiangyu Sun, Haoyi jiang, Liu Liu, Seungtae Nam, Gyeongjin Kang, Xinjie wang, Wei Sui, Zhizhong Su, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang, Eunbyung Park
Reconstructing and semantically interpreting 3D scenes from sparse 2D views remains a fundamental challenge in computer vision. Conventional methods often decouple semantic understanding from reconstruction or necessitate costly per-scene optimization, thereby restricting their scalability and generalizability. In this paper, we introduce Uni3R, a novel feed-forward framework that jointly reconstructs a unified 3D scene representation enriched with open-vocabulary semantics, directly from unposed multi-view images. Our approach leverages a Cross-View Transformer to robustly integrate information across arbitrary multi-view inputs, which then regresses a set of 3D Gaussian primitives endowed with semantic feature fields. This unified representation facilitates high-fidelity novel view synthesis, open-vocabulary 3D semantic segmentation, and depth prediction, all within a single, feed-forward pass. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Uni3R establishes a new state-of-the-art across multiple benchmarks, including 25.07 PSNR on RE10K and 55.84 mIoU on ScanNet. Our work signifies a novel paradigm towards generalizable, unified 3D scene reconstruction and understanding. The code is available at https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R.
从稀疏的二维视角重建和语义解释三维场景仍然是计算机视觉领域的一个基本挑战。传统的方法通常会将语义理解与重建解耦,或者需要进行昂贵的场景优化,从而限制了其可扩展性和泛化能力。在本文中,我们介绍了Uni3R,这是一种新型前馈框架,它能直接从无姿态的多视角图像中联合重建一个统一的三维场景表示,并丰富开放词汇语义。我们的方法利用跨视图变压器稳健地整合任意多视角输入的信息,然后回归一组带有语义特征场的三维高斯基元。这种统一表示有助于高保真度的新视角合成、开放词汇三维语义分割和深度预测,所有这些都在单次前馈传递中完成。大量实验表明,Uni3R在多个基准测试中建立了新的最先进的性能,包括RE10K上的25.07 PSNR和ScanNet上的55.84 mIoU。我们的工作标志着朝着通用、统一的三维场景重建和理解的新范式。代码可在https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code is available at https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Uni3R的新型前馈框架,可从无姿态的多视角图像直接重建统一的三维场景表示,并融入开放词汇语义。该框架利用跨视图变压器稳健地整合任意多视图输入的信息,然后回归一组带有语义特征场的三维高斯基本体。这一统一表示有助于高保真度的新视角合成、开放词汇的3D语义分割和深度预测。在RE10K和ScanNet等多个基准测试中,Uni3R取得了最新技术成果。此工作标志着面向可概括的、统一的三维场景重建和理解的全新范式。
Key Takeaways
- Uni3R是一个新型前馈框架,可以从稀疏的2D视角重建并语义解释3D场景。
- 该框架通过跨视图变压器整合任意多视图输入信息,提高了稳健性。
- Uni3R可以生成统一的三维场景表示,包括三维高斯基本体和语义特征场。
- 该方法支持高保真度的新视角合成、开放词汇的3D语义分割和深度预测。
- Uni3R在多个基准测试中表现优异,如RE10K的PSNR达到25.07,ScanNet的mIoU达到55.84。
- Uni3R的工作标志着统一三维场景重建和理解的新范式,强调可概括性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图

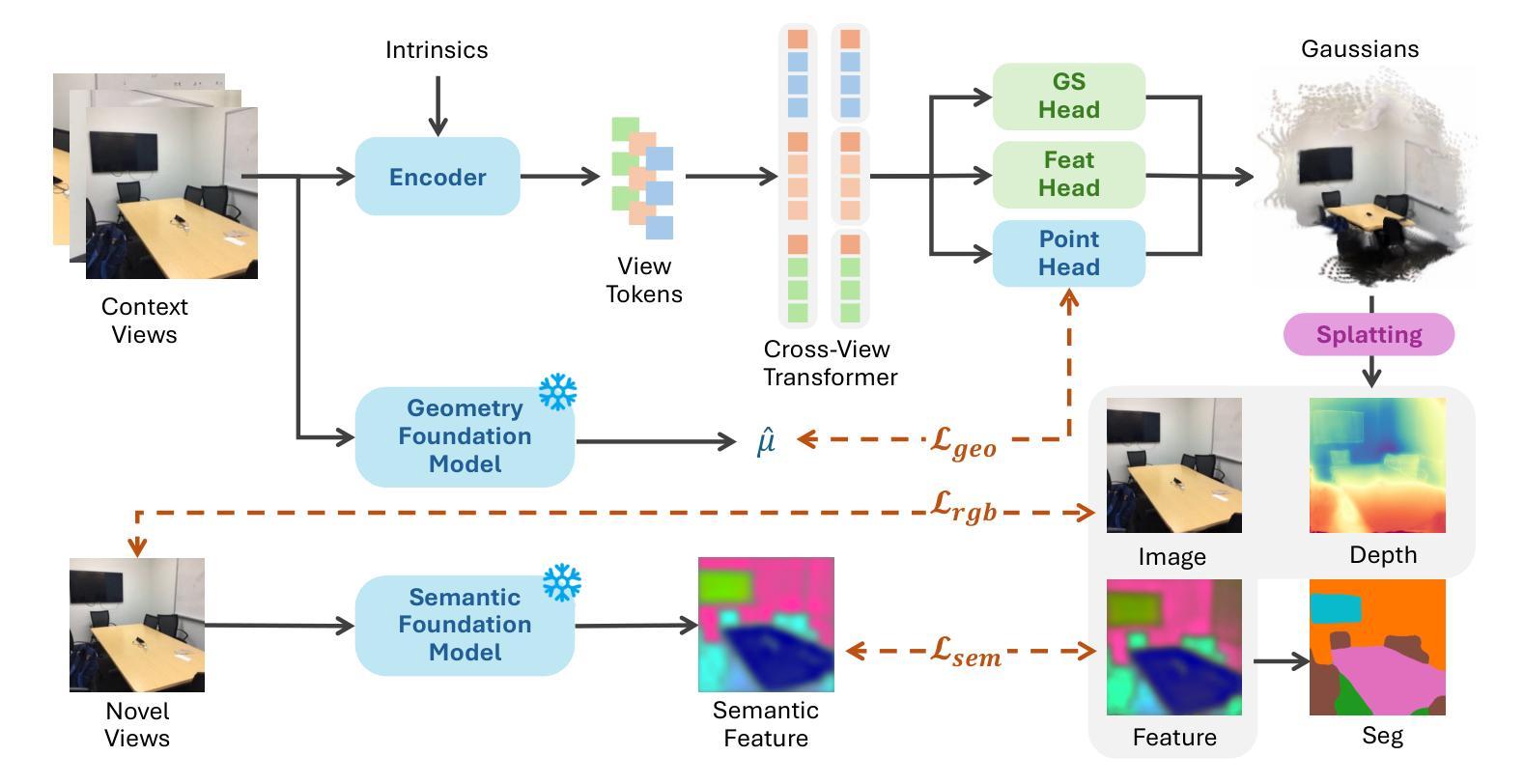
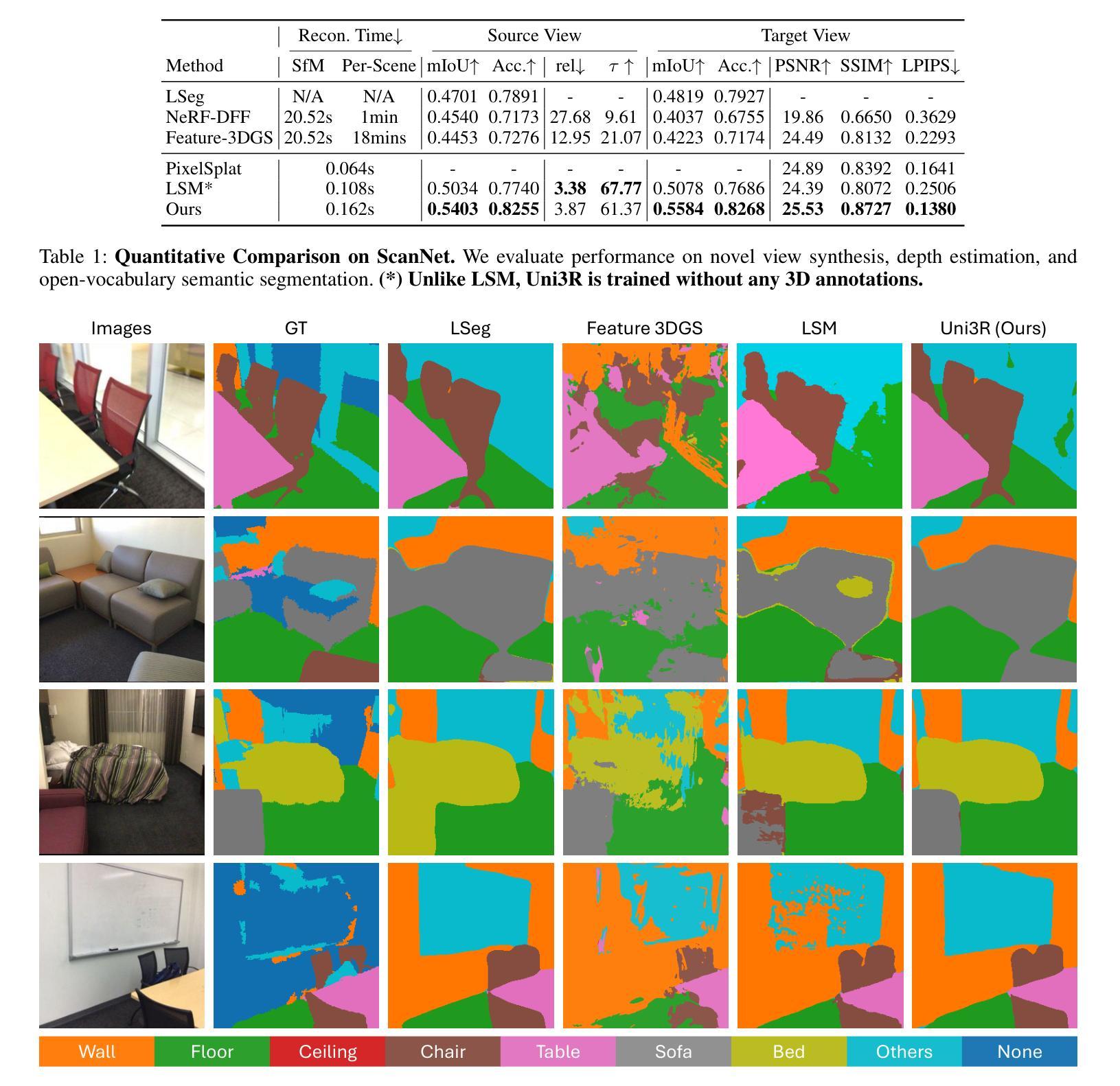
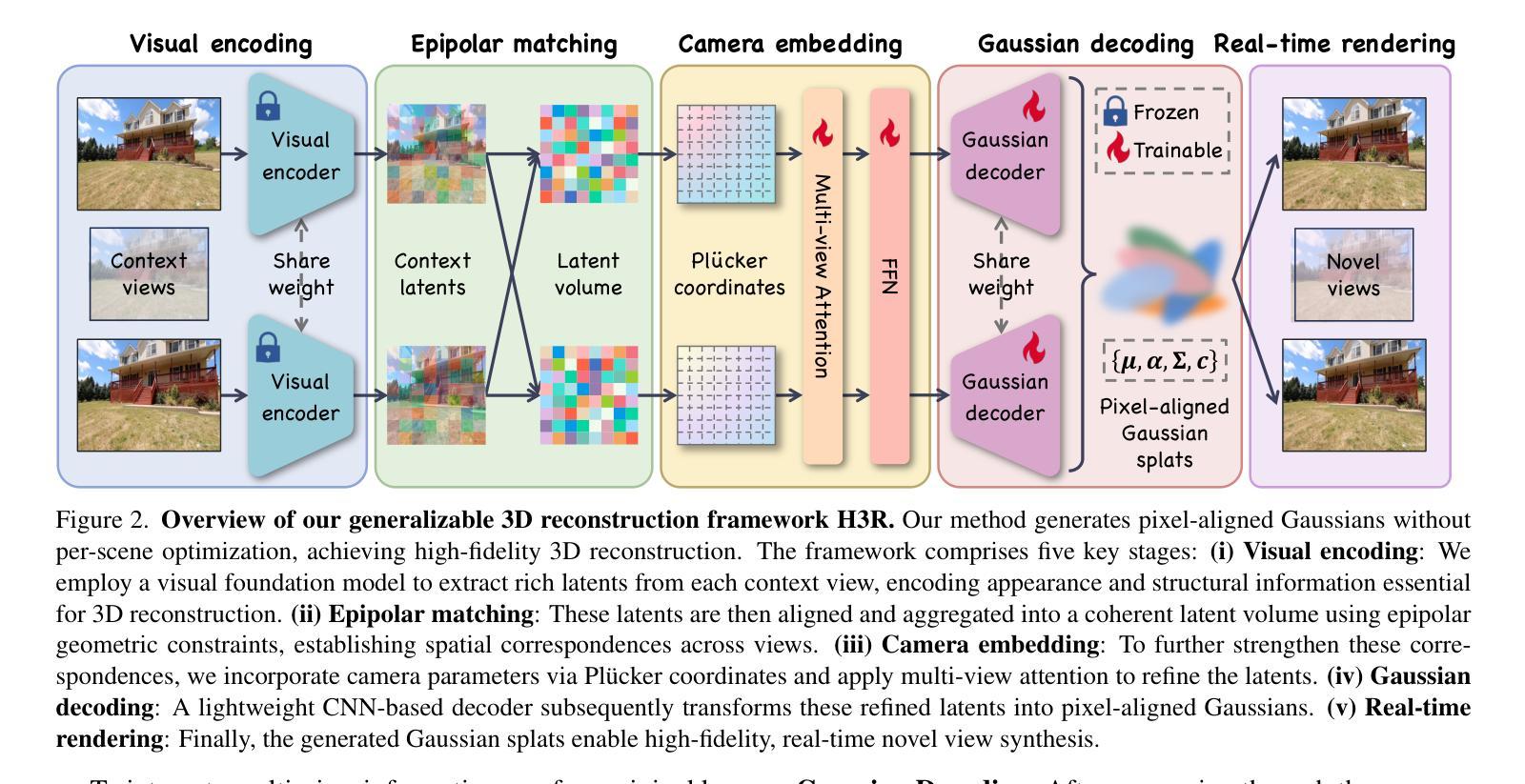
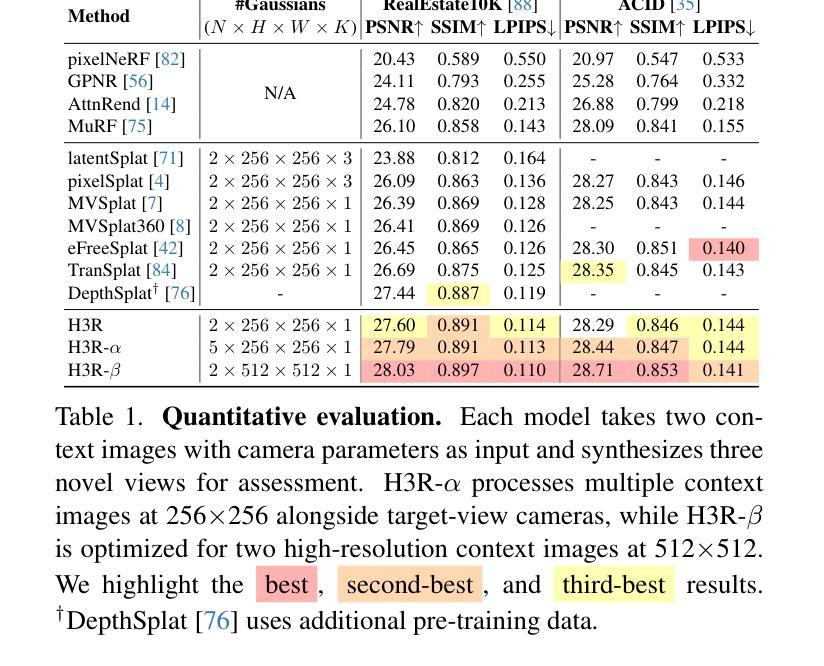
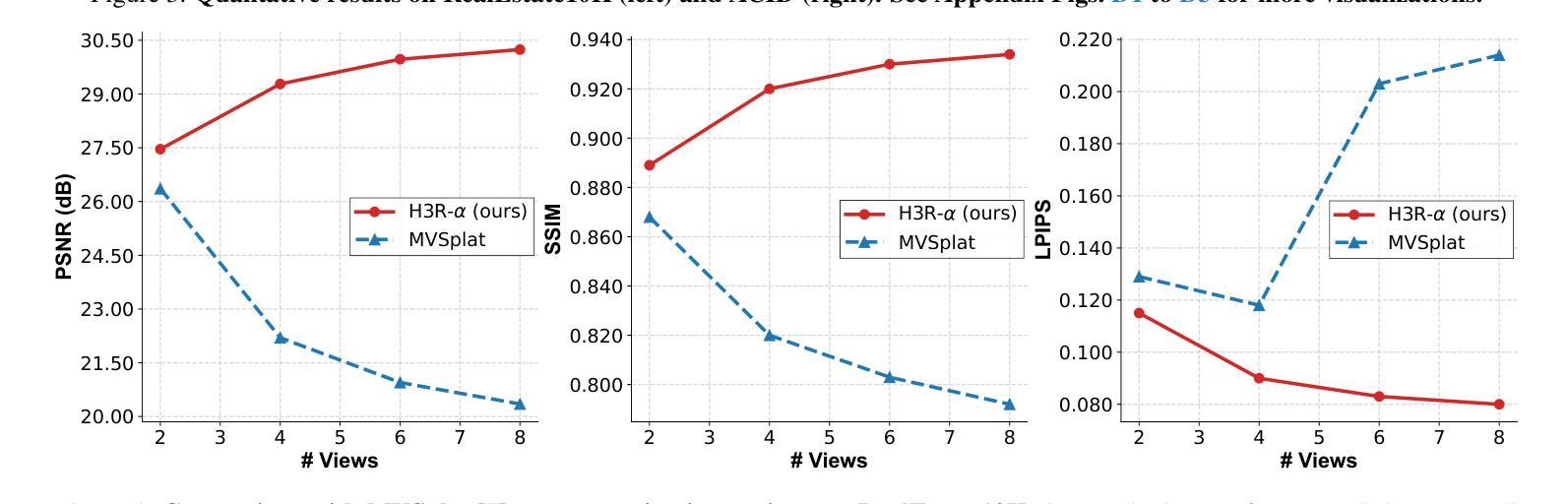
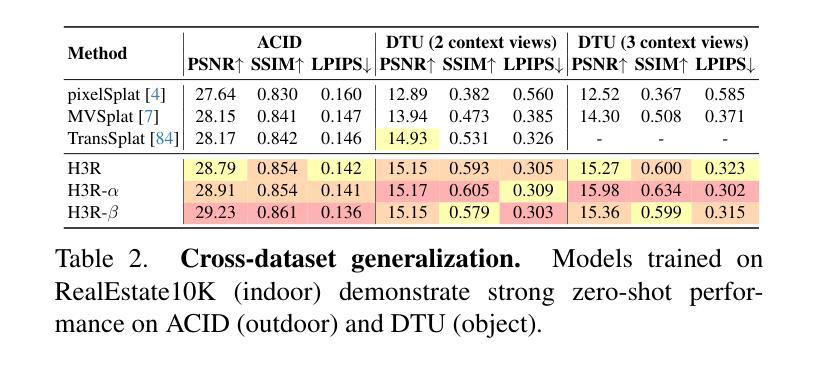
H3R: Hybrid Multi-view Correspondence for Generalizable 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Heng Jia, Linchao Zhu, Na Zhao
Despite recent advances in feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting, generalizable 3D reconstruction remains challenging, particularly in multi-view correspondence modeling. Existing approaches face a fundamental trade-off: explicit methods achieve geometric precision but struggle with ambiguous regions, while implicit methods provide robustness but suffer from slow convergence. We present H3R, a hybrid framework that addresses this limitation by integrating volumetric latent fusion with attention-based feature aggregation. Our framework consists of two complementary components: an efficient latent volume that enforces geometric consistency through epipolar constraints, and a camera-aware Transformer that leverages Pl"ucker coordinates for adaptive correspondence refinement. By integrating both paradigms, our approach enhances generalization while converging 2$\times$ faster than existing methods. Furthermore, we show that spatial-aligned foundation models (e.g., SD-VAE) substantially outperform semantic-aligned models (e.g., DINOv2), resolving the mismatch between semantic representations and spatial reconstruction requirements. Our method supports variable-number and high-resolution input views while demonstrating robust cross-dataset generalization. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks, with significant PSNR improvements of 0.59 dB, 1.06 dB, and 0.22 dB on the RealEstate10K, ACID, and DTU datasets, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/JiaHeng-DLUT/H3R.
尽管最近在前馈三维高斯Splatting方面取得了进展,但通用三维重建仍然存在挑战,特别是在多视图对应建模方面。现有方法面临一个基本权衡:显式方法实现了几何精度,但在模糊区域中表现不佳,而隐式方法提供了稳健性但收敛较慢。我们提出了H3R,一个混合框架,通过结合体积潜在融合和基于注意力的特征聚合来解决这一局限性。我们的框架由两个互补的组件构成:一个高效的潜在体积,它通过极线约束强制执行几何一致性;一个知道相机的Transformer,它利用Plücker坐标进行自适应对应细化。通过整合这两种范式,我们的方法提高了通用性,并且收敛速度比现有方法快两倍。此外,我们表明空间对齐的基础模型(例如SD-VAE)在语义对齐的模型(例如DINOv2)上表现出显著优势,解决了语义表示和空间重建要求之间的不匹配问题。我们的方法支持可变数量和高清输入视图,并表现出跨数据集的稳健泛化能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,在RealEstate10K、ACID和DTU数据集上的PSNR分别提高了0.59分贝、1.06分贝和0.22分贝。代码可在https://github.com/JiaHeng-DLUT/H3R找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
摘要
近期在面向多视图重建的挑战性问题中,如空间一致的语义映射与精细几何重建上取得了重大进展。但现有方法面临几何精度与模糊区域处理的权衡问题,同时隐式方法虽稳健但收敛较慢。本研究提出一种混合框架H3R,通过体积潜在融合与基于注意力的特征聚合来解决此问题。框架包含两个互补组件:高效潜在体积通过极线约束强制几何一致性,相机感知Transformer利用普克尔坐标进行自适应对应细化。本研究方法增强了泛化能力,并且比现有方法快两倍收敛。空间对齐基础模型优于语义对齐模型,解决了语义表示与空间重建需求的不匹配问题。本方法支持多种高分辨率视图输入并显示出色的跨数据集泛化能力。实验显示在多基准测试中均取得最新水平的性能提升,如在RealEstate10K、ACID和DTU数据集上的PSNR提升分别为0.59 dB、1.06 dB和0.22 dB。代码已公开于GitHub上。
关键见解
- 提出了一种混合框架H3R来解决多视图重建中的挑战性问题,结合了体积潜在融合和基于注意力的特征聚合。
- 通过高效潜在体积和相机感知Transformer实现几何一致性和自适应对应细化。
- 方法增强了泛化能力并提高了收敛速度,比现有方法快两倍。
- 空间对齐基础模型相较于语义对齐模型展现出更好的性能,解决了语义表示与空间重建需求的不匹配问题。
- 方法支持多种高分辨率视图输入并具有良好的跨数据集泛化能力。
- 在多个基准测试中取得了最新水平的性能提升,包括RealEstate10K、ACID和DTU数据集上的PSNR指标提升。
点此查看论文截图
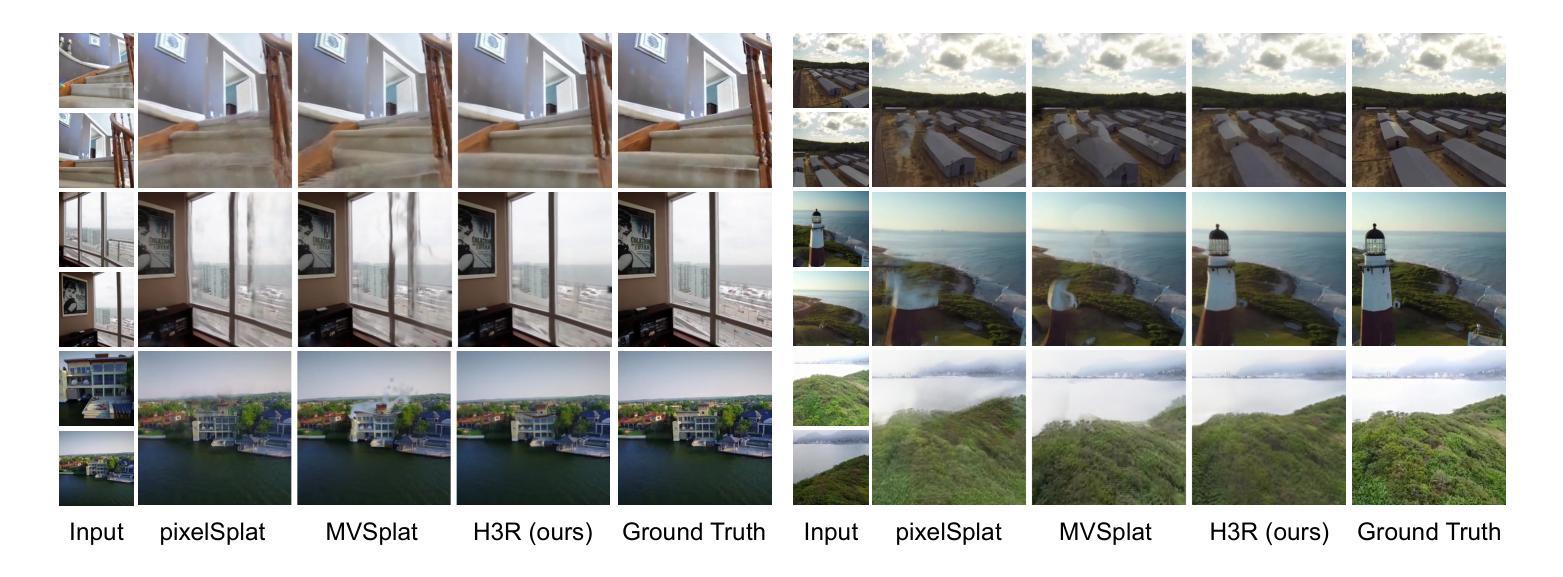

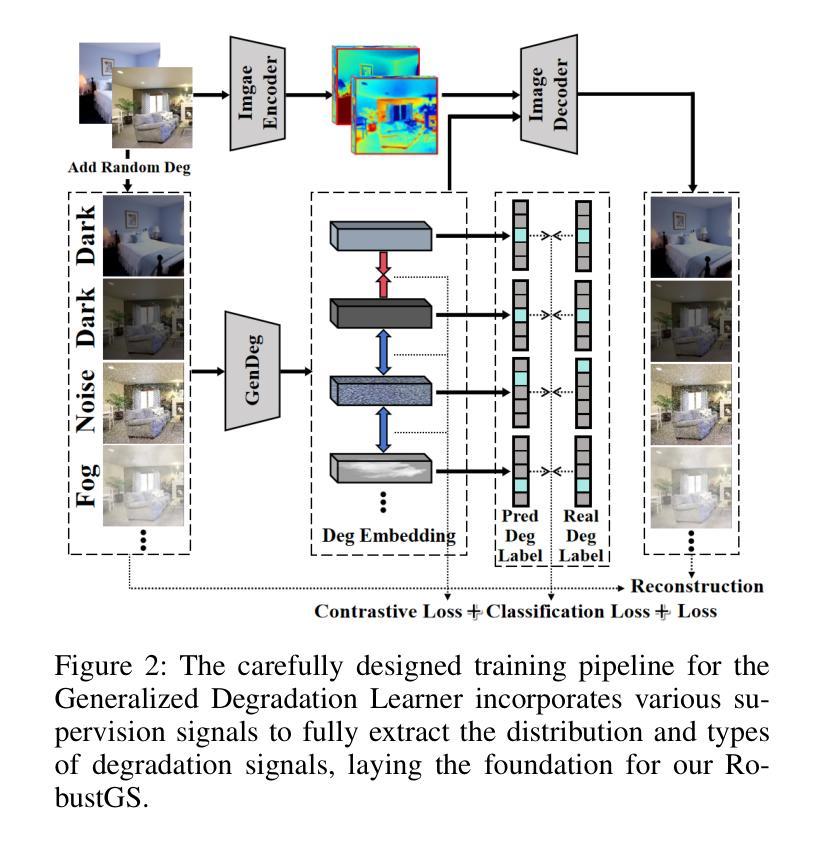
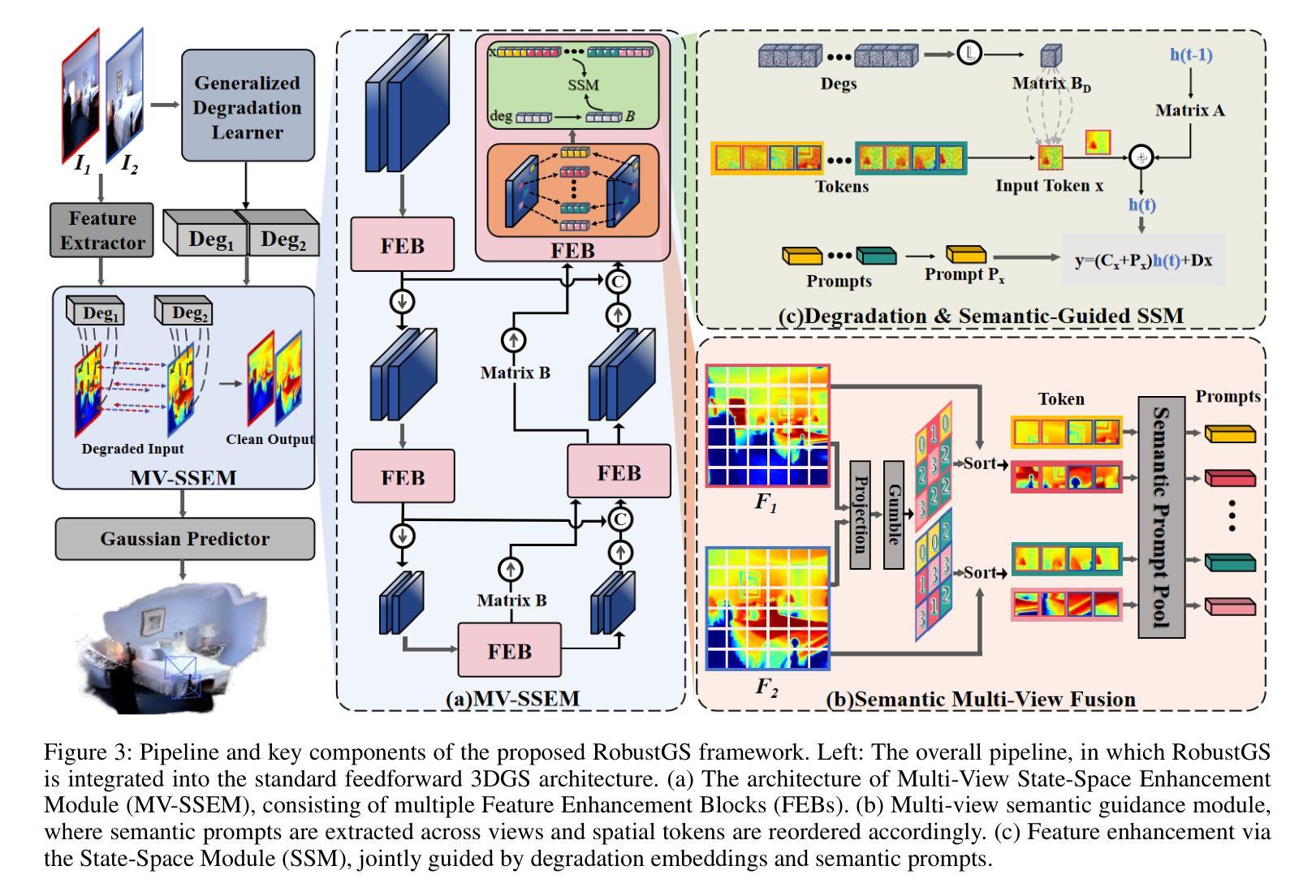
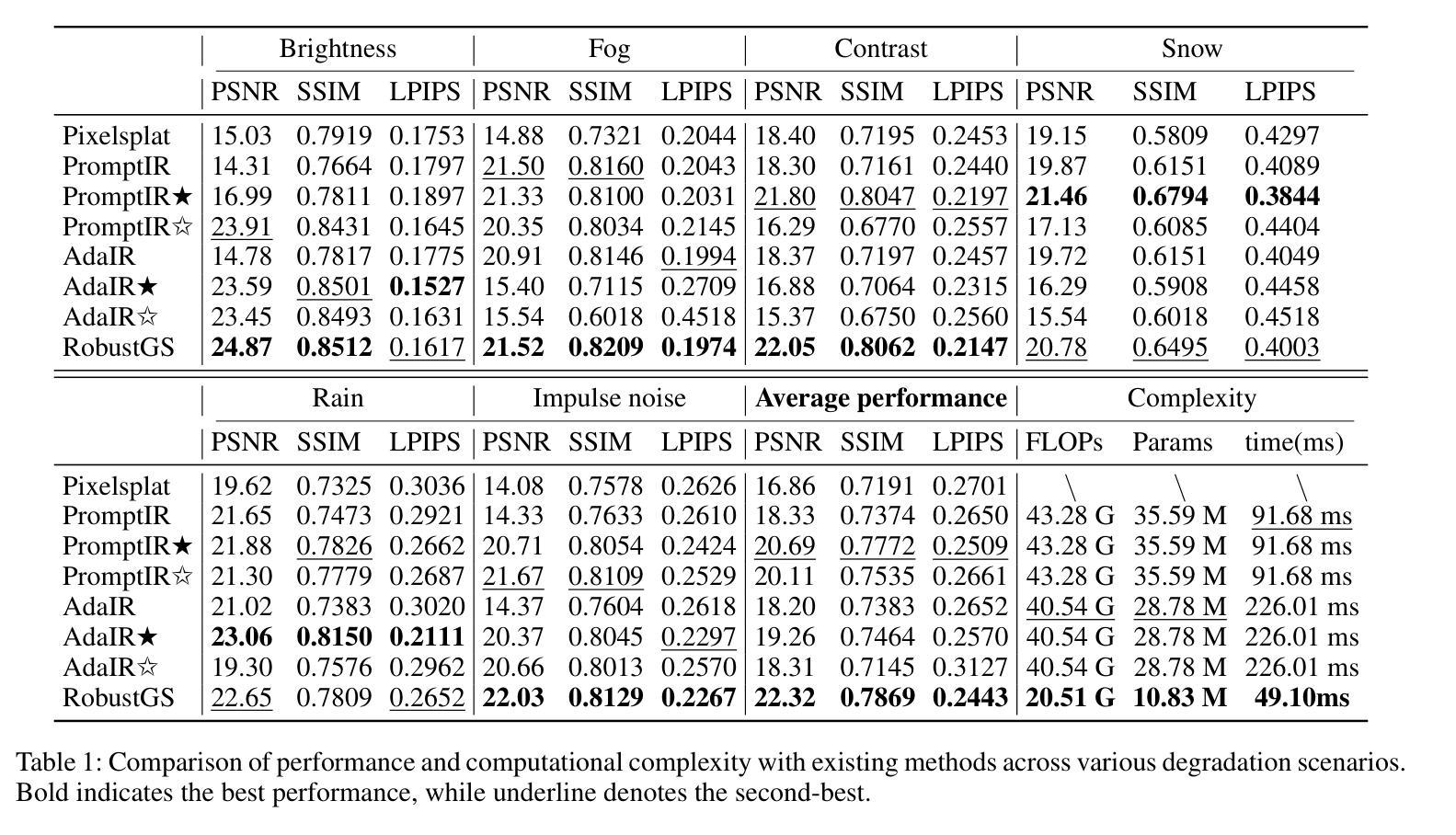
RobustGS: Unified Boosting of Feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting under Low-Quality Conditions
Authors:Anran Wu, Long Peng, Xin Di, Xueyuan Dai, Chen Wu, Yang Wang, Xueyang Fu, Yang Cao, Zheng-Jun Zha
Feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) overcomes the limitations of optimization-based 3DGS by enabling fast and high-quality reconstruction without the need for per-scene optimization. However, existing feedforward approaches typically assume that input multi-view images are clean and high-quality. In real-world scenarios, images are often captured under challenging conditions such as noise, low light, or rain, resulting in inaccurate geometry and degraded 3D reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose a general and efficient multi-view feature enhancement module, RobustGS, which substantially improves the robustness of feedforward 3DGS methods under various adverse imaging conditions, enabling high-quality 3D reconstruction. The RobustGS module can be seamlessly integrated into existing pretrained pipelines in a plug-and-play manner to enhance reconstruction robustness. Specifically, we introduce a novel component, Generalized Degradation Learner, designed to extract generic representations and distributions of multiple degradations from multi-view inputs, thereby enhancing degradation-awareness and improving the overall quality of 3D reconstruction. In addition, we propose a novel semantic-aware state-space model. It first leverages the extracted degradation representations to enhance corrupted inputs in the feature space. Then, it employs a semantic-aware strategy to aggregate semantically similar information across different views, enabling the extraction of fine-grained cross-view correspondences and further improving the quality of 3D representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach, when integrated into existing methods in a plug-and-play manner, consistently achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality across various types of degradations.
Feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)通过实现快速且高质量的重建,克服了基于优化的3DGS的局限性,无需针对每个场景进行优化。然而,现有的前馈方法通常假设输入的多视角图像是干净且高质量的。在真实场景中,图像通常是在噪声、低光或雨天等具有挑战性的条件下捕获的,导致几何不准确和3D重建质量下降。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种通用且高效的多视角特征增强模块——RobustGS。该模块在各种不利的成像条件下大大提高了前馈3DGS方法的稳健性,实现了高质量的3D重建。RobustGS模块可以无缝地以即插即用方式集成到现有的预训练管道中,以增强重建的稳健性。具体来说,我们引入了一个名为Generalized Degradation Learner的新组件,旨在从多视角输入中提取多种降质的通用表示和分布,从而提高对降质的感知能力,并改善3D重建的整体质量。此外,我们提出了一种新的语义感知状态空间模型。它首先利用提取的降质表示来增强特征空间中的受损输入。然后,它采用语义感知策略来聚合不同视角下的语义相似信息,从而实现精细的跨视角对应关系的提取,并进一步提高了3D表示的质量。大量实验表明,我们的方法以即插即用方式集成到现有方法中时,在各种类型的降质情况下始终实现了最先进的重建质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)的优势,其克服了基于优化的3DGS方法的局限性,实现了快速且高质量的重建。但现有前馈方法通常假设输入的多视角图像是干净且高质量的。针对现实世界中图像经常存在的噪声、低光、雨天等挑战条件,本文提出了一个通用且高效的多视角特征增强模块——RobustGS,该模块显著提高了前馈3DGS方法在多种不良成像条件下的稳健性,实现了高质量的三维重建。
Key Takeaways
- Feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)实现了快速且高质量的重建,克服了优化方法的局限性。
- 现有前馈方法假设输入的多视角图像是干净且高质量的,但现实场景中的图像常面临噪声、低光、雨天等挑战。
- 为解决这些挑战,提出了一个通用且高效的多视角特征增强模块——RobustGS。
- RobustGS通过引入Generalized Degradation Learner,能够从多视角输入中提取通用的退化表示和分布,增强对退化的感知,提高三维重建的整体质量。
- 提出了一种新的语义感知状态空间模型,利用提取的退化表示在特征空间中增强受损输入,并通过语义感知策略聚合不同视角的语义相似信息,进一步提高了三维表示的质量。
- 实验表明,RobustGS模块能无缝集成到现有的预训练管道中,以即插即用方式提高了各种退化类型下的重建质量,达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图
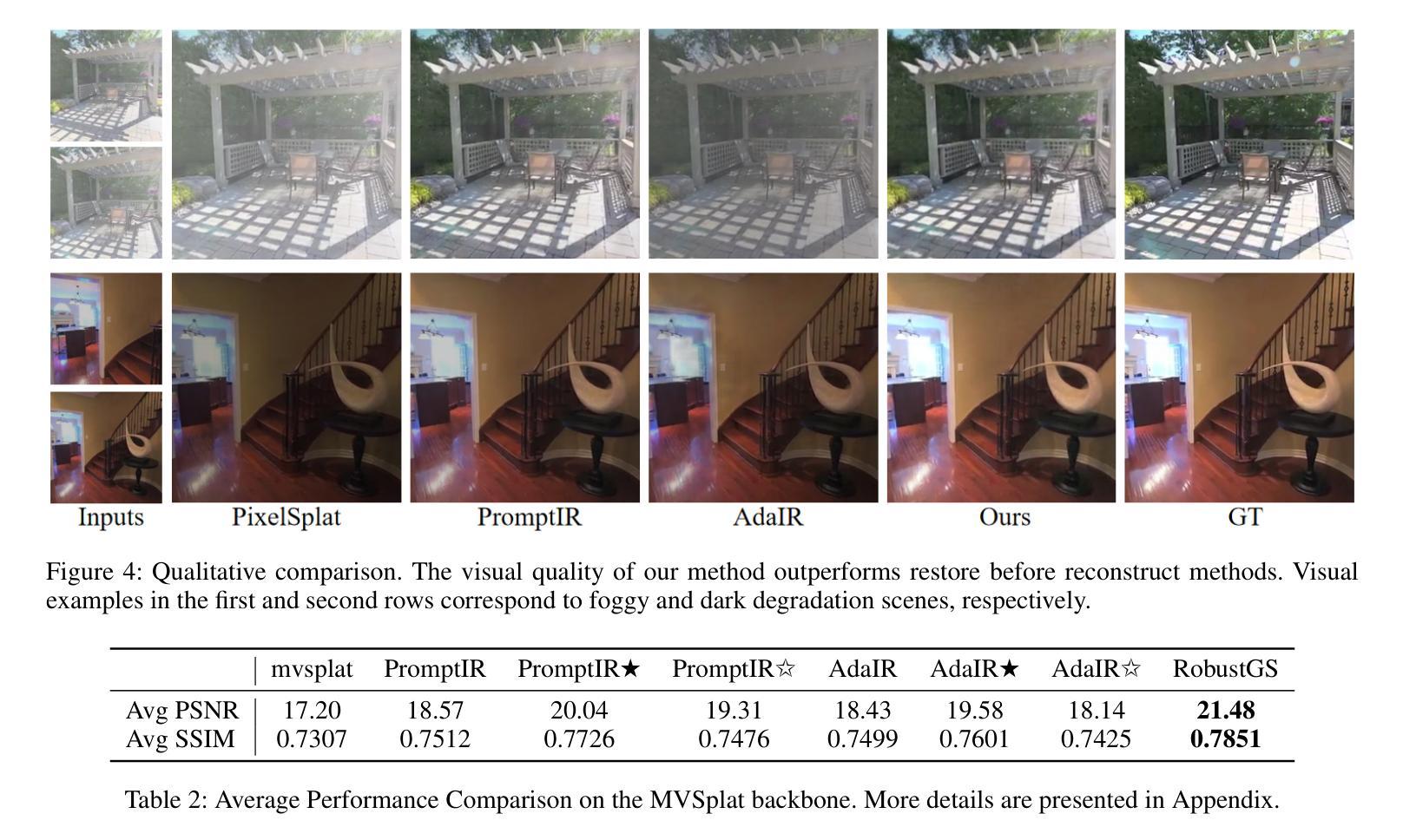


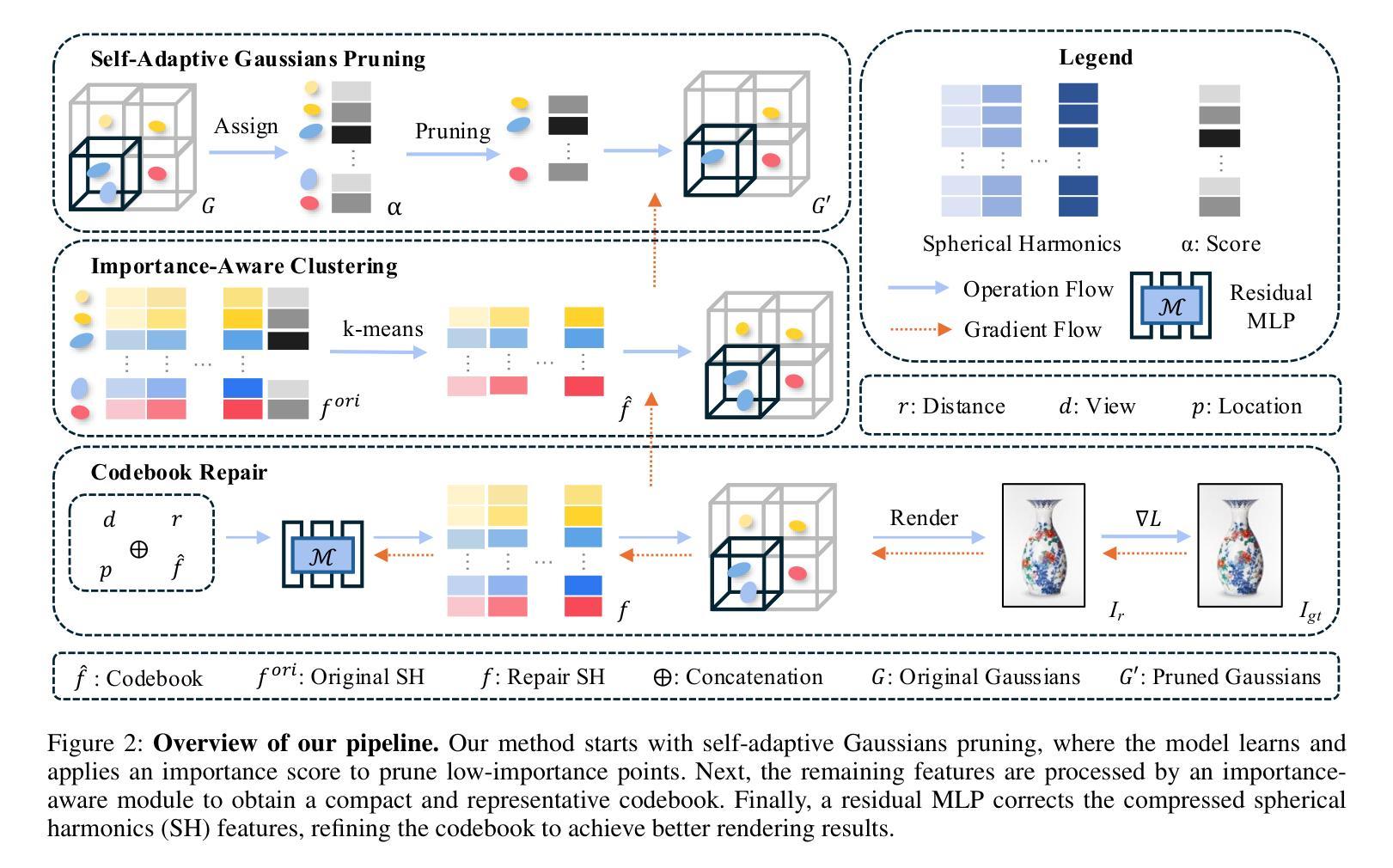
SA-3DGS: A Self-Adaptive Compression Method for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Liheng Zhang, Weihao Yu, Zubo Lu, Haozhi Gu, Jin Huang
Recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting have enhanced efficient and high-quality novel view synthesis. However, representing scenes requires a large number of Gaussian points, leading to high storage demands and limiting practical deployment. The latest methods facilitate the compression of Gaussian models but struggle to identify truly insignificant Gaussian points in the scene, leading to a decline in subsequent Gaussian pruning, compression quality, and rendering performance. To address this issue, we propose SA-3DGS, a method that significantly reduces storage costs while maintaining rendering quality. SA-3DGS learns an importance score to automatically identify the least significant Gaussians in scene reconstruction, thereby enabling effective pruning and redundancy reduction. Next, the importance-aware clustering module compresses Gaussians attributes more accurately into the codebook, improving the codebook’s expressive capability while reducing model size. Finally, the codebook repair module leverages contextual scene information to repair the codebook, thereby recovering the original Gaussian point attributes and mitigating the degradation in rendering quality caused by information loss. Experimental results on several benchmark datasets show that our method achieves up to 66x compression while maintaining or even improving rendering quality. The proposed Gaussian pruning approach is not only adaptable to but also improves other pruning-based methods (e.g., LightGaussian), showcasing excellent performance and strong generalization ability.
近期,3D高斯贴图技术的新进展大大提高了高效高质量的新型视图合成能力。然而,表示场景需要大量的高斯点,这导致了存储需求的增加并限制了实际应用部署。最新的方法虽然推动了高斯模型的压缩,但在识别场景中真正不显著的高斯点时遇到困难,导致后续的高斯修剪、压缩质量和渲染性能下降。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SA-3DGS方法,它能在保持渲染质量的同时显著降低存储成本。SA-3DGS学习重要性评分来自动识别场景重建中最不重要的高斯,从而实现有效的修剪和冗余减少。接下来,重要性感知聚类模块将高斯属性更准确地压缩到代码簿中,提高了代码簿的表达能力并减小了模型大小。最后,代码簿修复模块利用上下文场景信息来修复代码簿,从而恢复原始的高斯点属性并缓解因信息丢失而导致的渲染质量下降。在多个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法能在保持或甚至提高渲染质量的同时实现高达66倍的压缩。所提出的高斯修剪方法不仅适用于其他修剪方法(如LightGaussian),还能对其进行改进,展现了卓越的性能和强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures. Under review at AAAI 2026
Summary
3DGS的最新进展虽可实现高效高质量的新型视图合成,但由于需要大量高斯点来表示场景,导致存储需求巨大且限制了实际应用部署。针对这一问题,提出了SA-3DGS方法,该方法可显著降低存储成本同时保持渲染质量。通过重要性评分自动识别场景中不重要的高斯点以实现有效剪枝和冗余度降低。同时改进压缩模块,利用上下文场景信息修复代码本以恢复原始高斯点属性并缓解信息损失导致的渲染质量下降。实验结果表明,该方法可实现高达66倍的压缩比,同时保持或提高渲染质量,并适用于其他剪枝方法,表现出卓越的性能和强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting在新型视图合成中取得了进展,但需要大量高斯点表示场景,导致高存储需求和限制实际应用。
- SA-3DGS方法被提出以解决这个问题,通过重要性评分自动识别不重要的高斯点,有效减少存储成本并保持渲染质量。
- SA-3DGS包含一个重要性感知聚类模块,可以更准确地压缩高斯属性到代码本中,提高代码本的表达能力并减小模型大小。
- 代码本修复模块利用上下文场景信息修复代码本,恢复原始高斯点属性,并缓解因信息损失导致的渲染质量下降。
点此查看论文截图

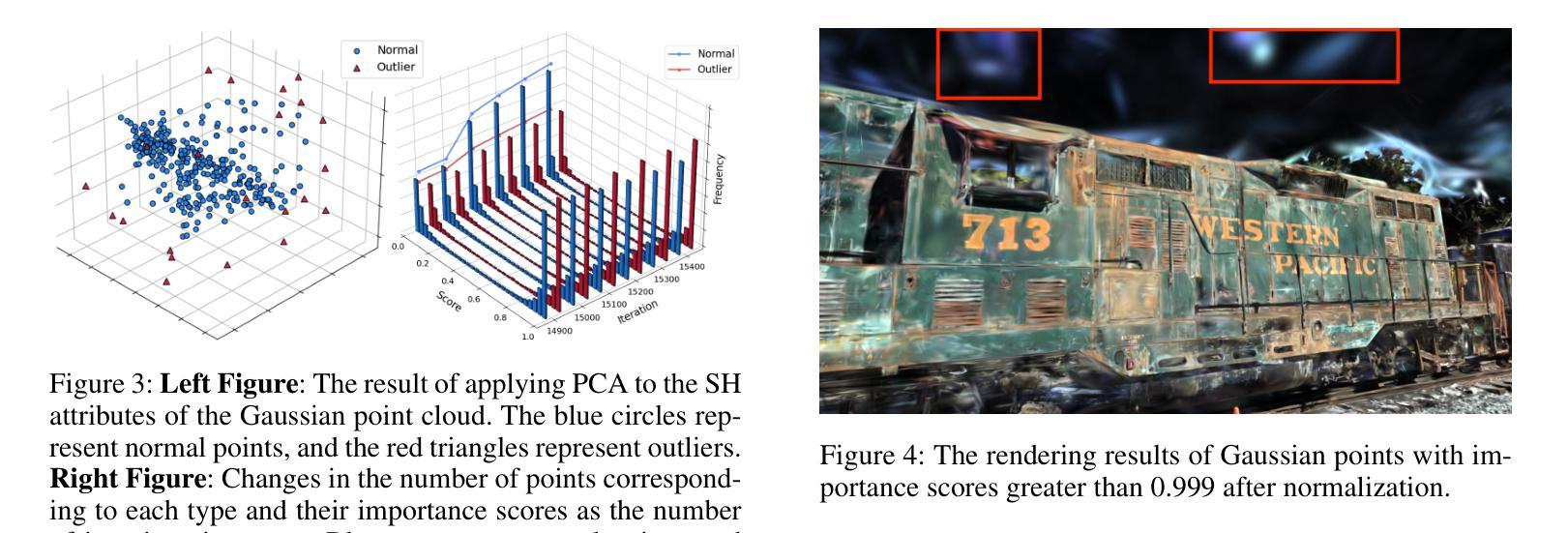

GENIE: Gaussian Encoding for Neural Radiance Fields Interactive Editing
Authors:Mikołaj Zieliński, Krzysztof Byrski, Tomasz Szczepanik, Przemysław Spurek
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting (GS) have recently transformed 3D scene representation and rendering. NeRF achieves high-fidelity novel view synthesis by learning volumetric representations through neural networks, but its implicit encoding makes editing and physical interaction challenging. In contrast, GS represents scenes as explicit collections of Gaussian primitives, enabling real-time rendering, faster training, and more intuitive manipulation. This explicit structure has made GS particularly well-suited for interactive editing and integration with physics-based simulation. In this paper, we introduce GENIE (Gaussian Encoding for Neural Radiance Fields Interactive Editing), a hybrid model that combines the photorealistic rendering quality of NeRF with the editable and structured representation of GS. Instead of using spherical harmonics for appearance modeling, we assign each Gaussian a trainable feature embedding. These embeddings are used to condition a NeRF network based on the k nearest Gaussians to each query point. To make this conditioning efficient, we introduce Ray-Traced Gaussian Proximity Search (RT-GPS), a fast nearest Gaussian search based on a modified ray-tracing pipeline. We also integrate a multi-resolution hash grid to initialize and update Gaussian features. Together, these components enable real-time, locality-aware editing: as Gaussian primitives are repositioned or modified, their interpolated influence is immediately reflected in the rendered output. By combining the strengths of implicit and explicit representations, GENIE supports intuitive scene manipulation, dynamic interaction, and compatibility with physical simulation, bridging the gap between geometry-based editing and neural rendering. The code can be found under (https://github.com/MikolajZielinski/genie)
神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯拼贴(GS)最近已经转变了3D场景表示和渲染的方式。NeRF通过学习体积表示通过神经网络实现高保真新颖视图合成,但其隐式编码使得编辑和物理交互具有挑战性。相比之下,GS将场景表示为高斯原始数据的显式集合,从而实现实时渲染、更快的训练和更直观的操纵。这种显式结构使GS特别适合交互式编辑和与基于物理的模拟集成。在本文中,我们介绍了GENIE(用于神经辐射场交互式编辑的高斯编码),这是一种结合了NeRF的光照现实渲染质量和GS的可编辑结构化表示方法的混合模型。我们不为外观建模使用球面谐波,而是为每个高斯分配可训练的特征嵌入。这些嵌入被用于基于每个查询点的k个最近高斯值来条件化NeRF网络。为了使这种条件化有效率,我们引入了基于修改后的光线追踪管道的快速最近高斯搜索——射线追踪高斯邻近搜索(RT-GPS)。我们还集成了一种多分辨率哈希网格来初始化和更新高斯特征。这些组件共同作用,可实现实时、局部感知的编辑:当高斯原始数据被重新定位或修改时,其插值影响会立即反映在渲染输出中。通过结合隐式和显式表示的优点,GENIE支持直观的场景操作、动态交互以及与物理模拟的兼容性,缩小了基于几何的编辑和神经渲染之间的差距。代码可在(https://github.com/MikolajZielinski/genie)找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯喷绘(GS)在三维场景表达和渲染方面取得了突破性进展。NeRF通过神经网络学习体积表达以实现高保真新视角合成,但其隐式编码使得编辑和物理交互具有挑战性。相比之下,GS将场景表示为显式的高斯基本元素集合,实现了实时渲染、快速训练和更直观的操控。本文提出GENIE(神经辐射场的高斯编码交互式编辑),结合了NeRF的光照现实渲染质量与GS的可编辑和结构化表达。GENIE通过为每个高斯分配可训练特征嵌入进行外观建模,而不是使用球面谐波。这些嵌入被用于基于每个查询点的k个最近高斯值来条件化NeRF网络。为提升效率,本文引入了基于修改后的光线追踪管道的快速最近高斯搜索技术——射线追踪高斯邻近搜索(RT-GPS)。同时,集成了多分辨率哈希网格以初始化和更新高斯特征。这些组件共同实现了实时、局部感知的编辑功能:当高斯基本元素被重新定位或修改时,其插值影响会立即反映在渲染输出中。GENIE结合了隐式和显式表达的优点,支持直观的场景操控、动态交互以及与物理模拟的兼容性,缩小了基于几何的编辑和神经渲染之间的差距。代码可通过(https://github.com/MikolajZielinski/genie)访问。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和GS在3D场景表达和渲染方面表现出色,但各有局限性。
- GENIE结合了NeRF和GS的优点,实现高保真渲染与实时、局部感知的编辑功能。
- GENIE采用高斯特征嵌入进行外观建模,替代了球面谐波方法。
- RT-GPS技术提高了基于高斯邻近搜索的效率。
- 多分辨率哈希网格用于初始化和更新高斯特征。
- GENIE支持直观的场景操控和动态交互。
点此查看论文截图
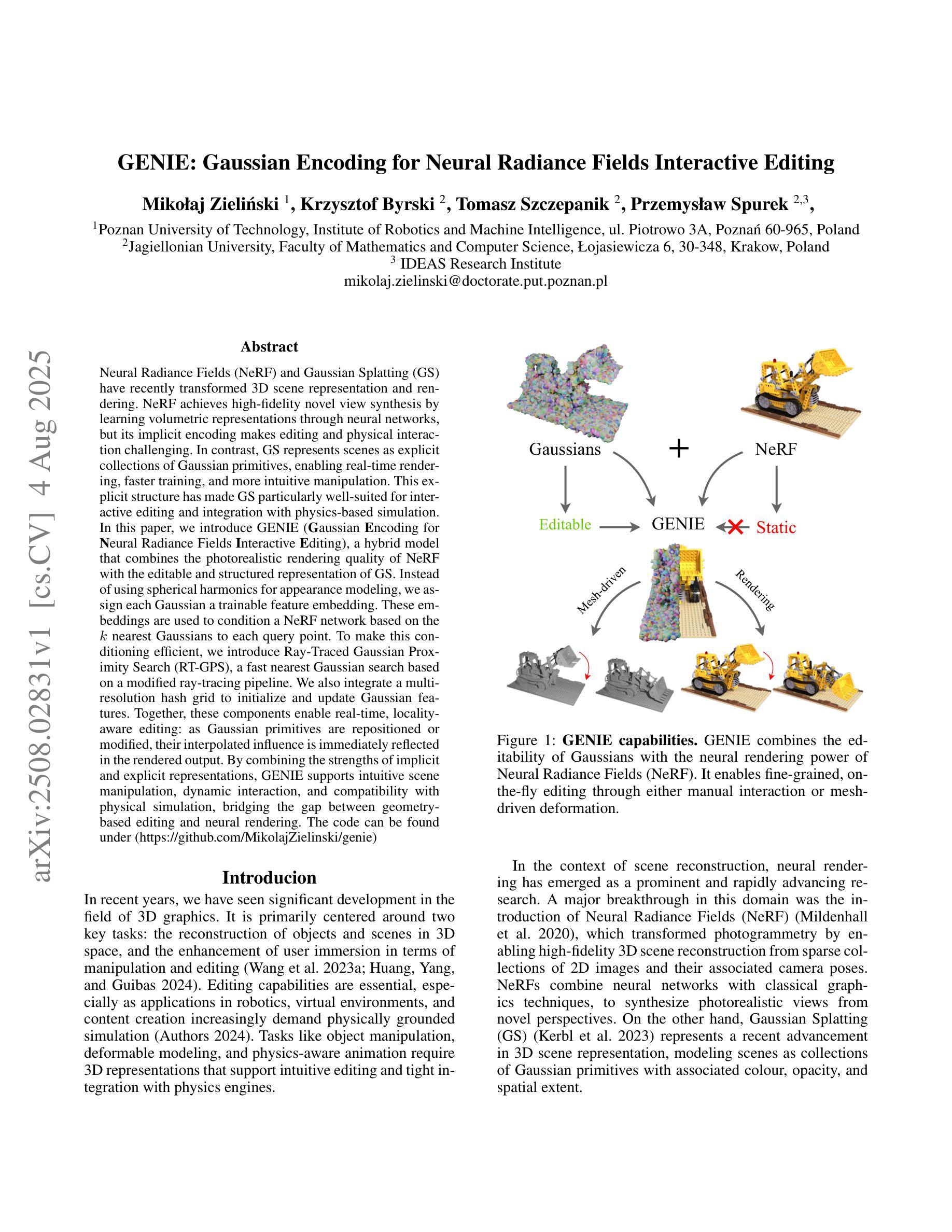
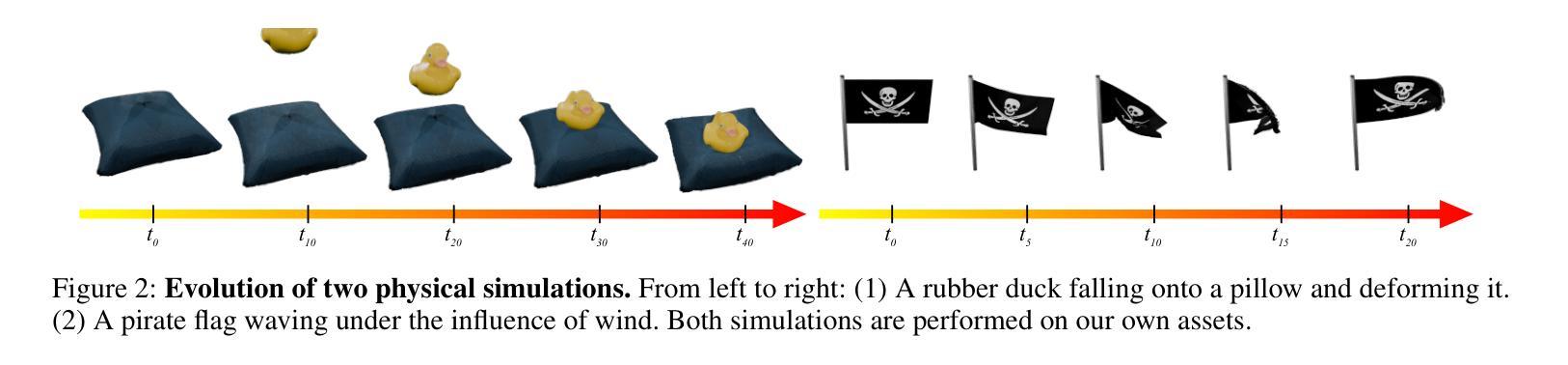
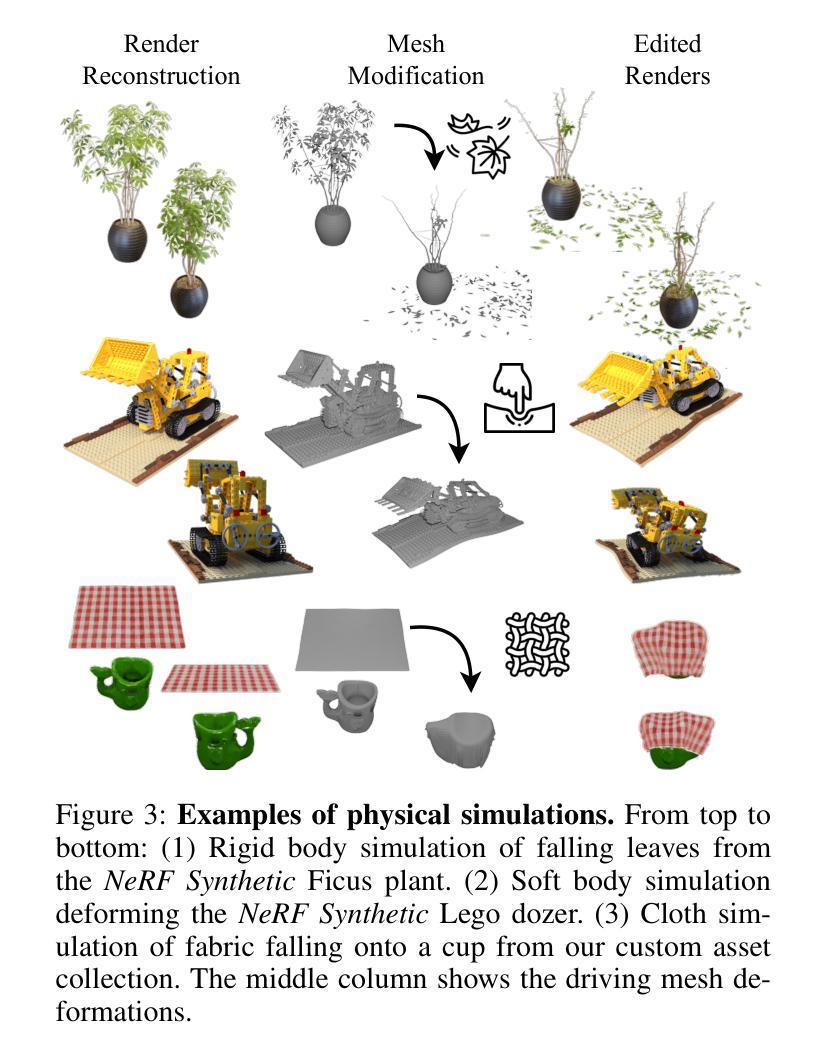
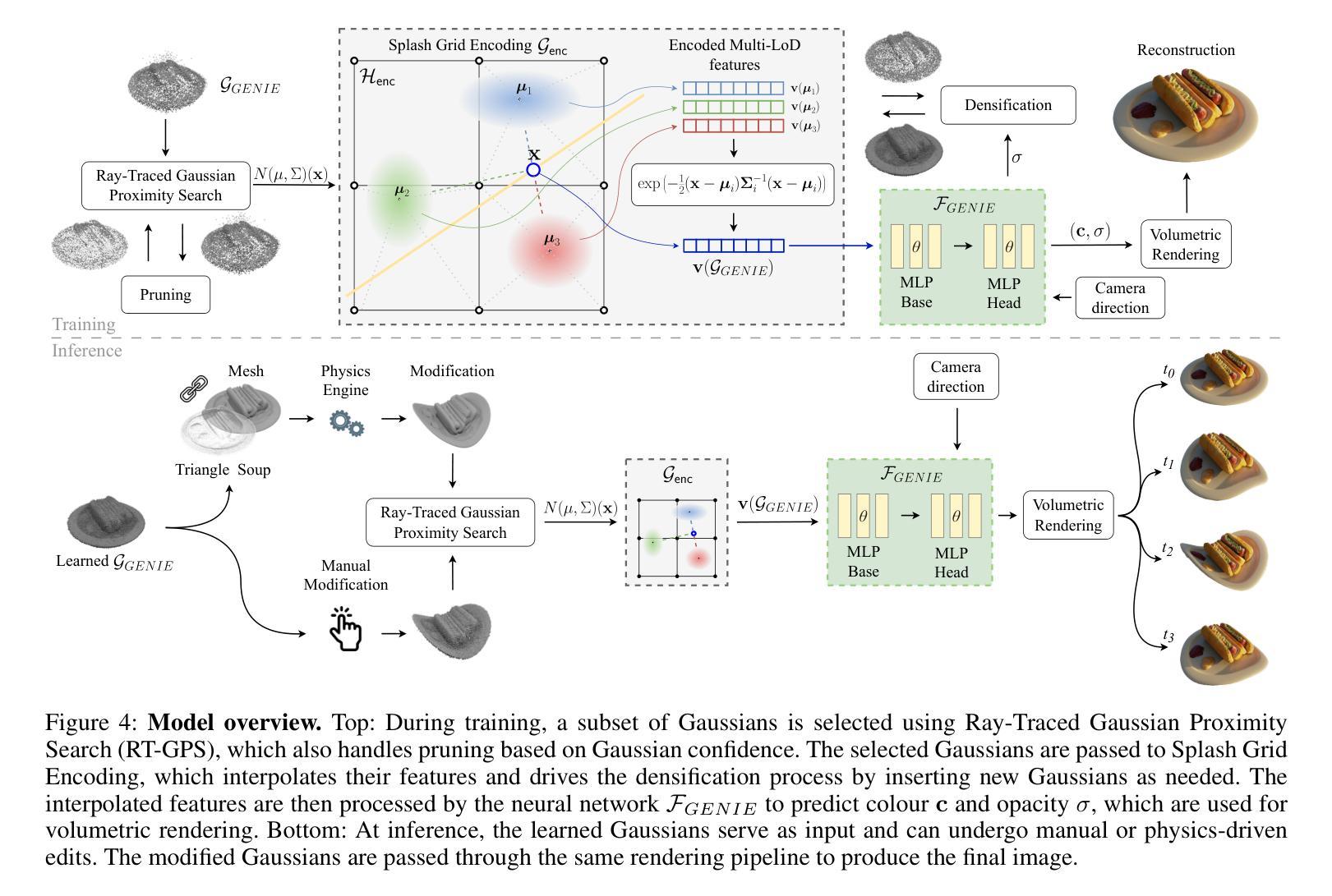
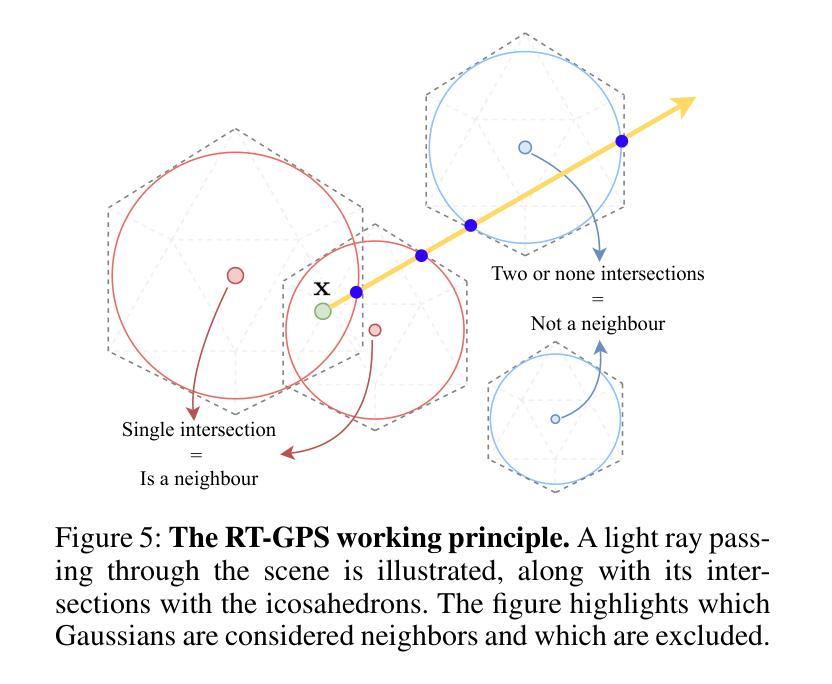

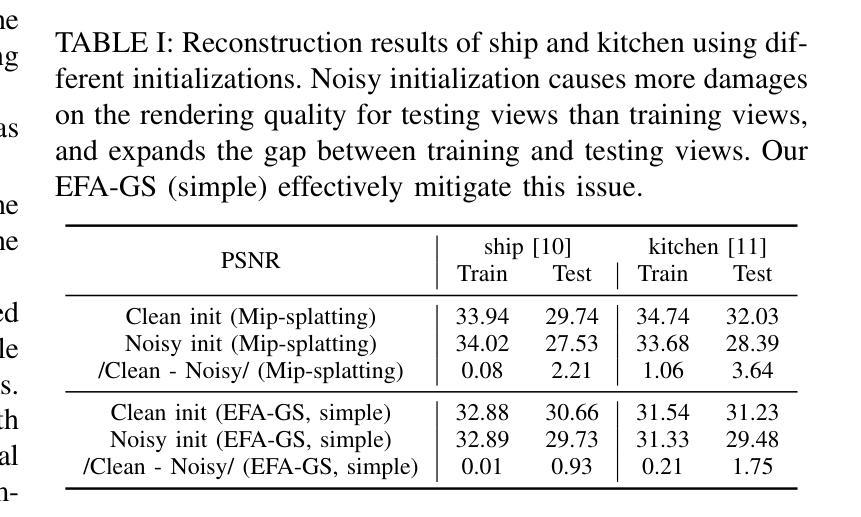
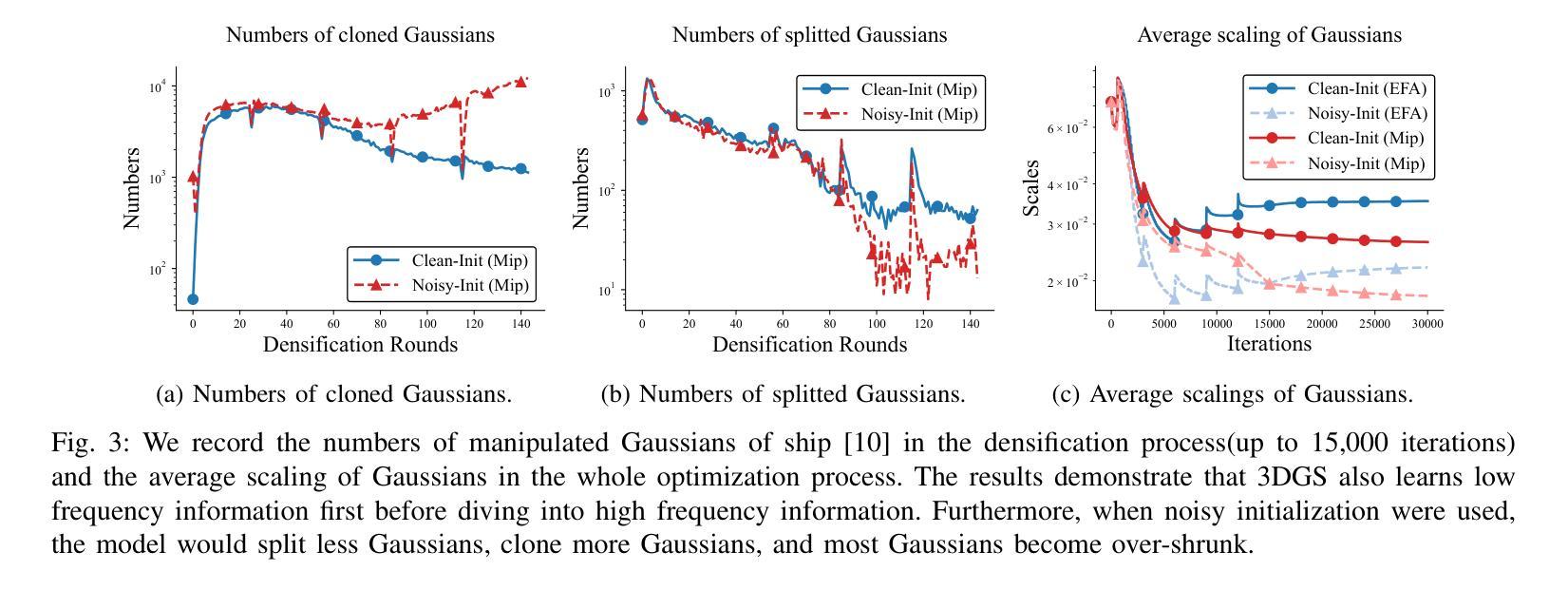
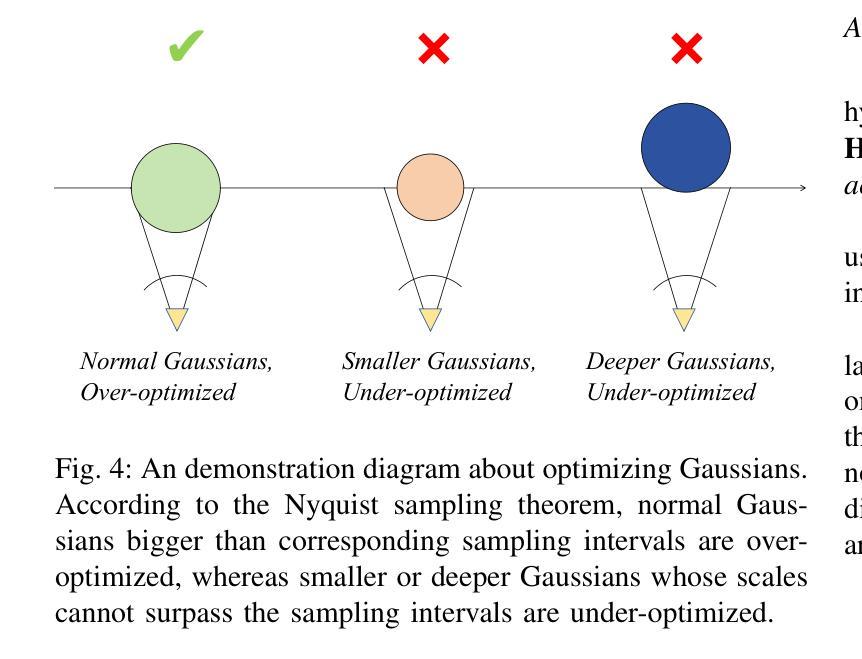
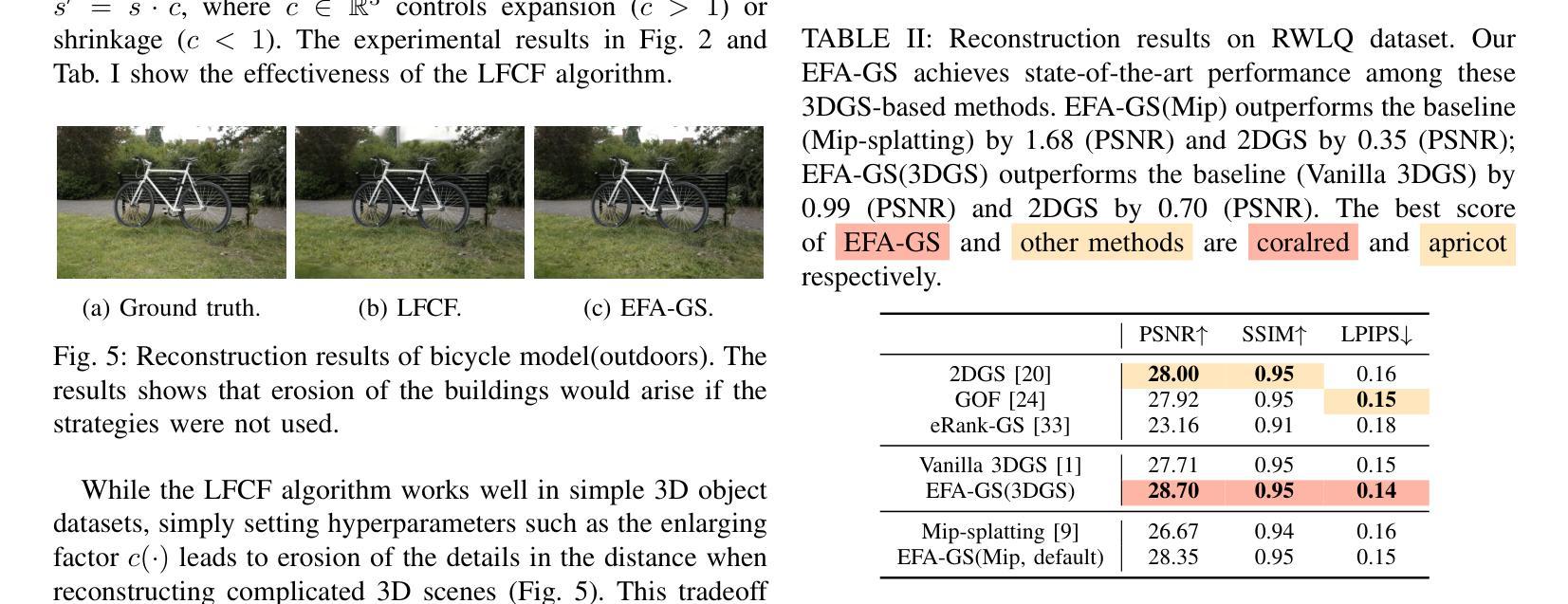
Low-Frequency First: Eliminating Floating Artifacts in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jianchao Wang, Peng Zhou, Cen Li, Rong Quan, Jie Qin
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a powerful and computationally efficient representation for 3D reconstruction. Despite its strengths, 3DGS often produces floating artifacts, which are erroneous structures detached from the actual geometry and significantly degrade visual fidelity. The underlying mechanisms causing these artifacts, particularly in low-quality initialization scenarios, have not been fully explored. In this paper, we investigate the origins of floating artifacts from a frequency-domain perspective and identify under-optimized Gaussians as the primary source. Based on our analysis, we propose \textit{Eliminating-Floating-Artifacts} Gaussian Splatting (EFA-GS), which selectively expands under-optimized Gaussians to prioritize accurate low-frequency learning. Additionally, we introduce complementary depth-based and scale-based strategies to dynamically refine Gaussian expansion, effectively mitigating detail erosion. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that EFA-GS substantially reduces floating artifacts while preserving high-frequency details, achieving an improvement of 1.68 dB in PSNR over baseline method on our RWLQ dataset. Furthermore, we validate the effectiveness of our approach in downstream 3D editing tasks. We provide our implementation in https://jcwang-gh.github.io/EFA-GS.
3D高斯展平(3DGS)是一种强大的计算效率高的三维重建表示方法。尽管它具有强大的能力,但3DGS经常会产生漂浮的伪影,这些伪影是脱离实际几何结构的错误结构,并严重降低了视觉保真度。特别是在低质量初始化场景中导致这些伪影的潜在机制尚未被完全探索。在本文中,我们从频率域的角度研究了漂浮伪影的起源,并确定了未优化的高斯为主要来源。基于我们的分析,我们提出了消除漂浮伪影的高斯展平(EFA-GS),它选择性地扩展未优化的高斯,以优先进行准确的低频学习。此外,我们还引入了基于深度和基于尺度的策略来动态优化高斯扩展,有效地减轻了细节流失。在合成和真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,EFA-GS在减少漂浮伪影的同时保留了高频细节,在我们的RWLQ数据集上比基线方法提高了1.68dB的PSNR。此外,我们在下游的三维编辑任务中验证了我们的方法的有效性。我们在https://jcwang-gh.github.io/EFA-GS提供了我们的实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Website: https://jcwang-gh.github.io/EFA-GS
Summary
本文研究了基于三维高斯融合(3DGS)中的漂浮物干扰问题,揭示了干扰出现的底层机制主要来源于欠优化的高斯成分。为改善这一现象,本文提出了消除漂浮物干扰的高斯融合(EFA-GS)方法。此方法采用选择性拓展欠优化高斯成分的方式优先进行低频学习。此外,结合深度信息与尺度信息的高斯展开细化策略能显著减轻细节侵蚀现象。实验结果证明了该算法在处理合成与真实数据集时能有效减少漂浮物干扰并保留高频细节,相较于基准方法,在PSNR上提升了1.68dB。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在处理过程中存在漂浮物干扰问题,这些干扰可能影响重建的几何结构并降低视觉质量。
- 漂浮物干扰的主要来源是欠优化的高斯成分,本文首次从频率域角度探讨了其成因。
- 提出EFA-GS算法,通过选择性拓展欠优化高斯成分优先进行低频学习,以改善漂浮物干扰问题。
- 结合深度信息与尺度信息的高斯展开细化策略能更有效地减轻细节侵蚀现象。
- 实验结果显示,EFA-GS在减少漂浮物干扰的同时保留了高频细节,相较于基准方法性能有所提升。
- 该研究在下游的三维编辑任务中也验证了其方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



Taking Language Embedded 3D Gaussian Splatting into the Wild
Authors:Yuze Wang, Yue Qi
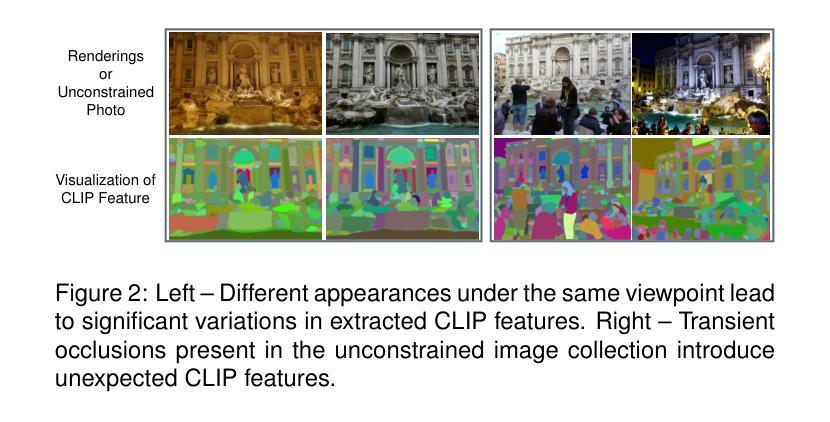
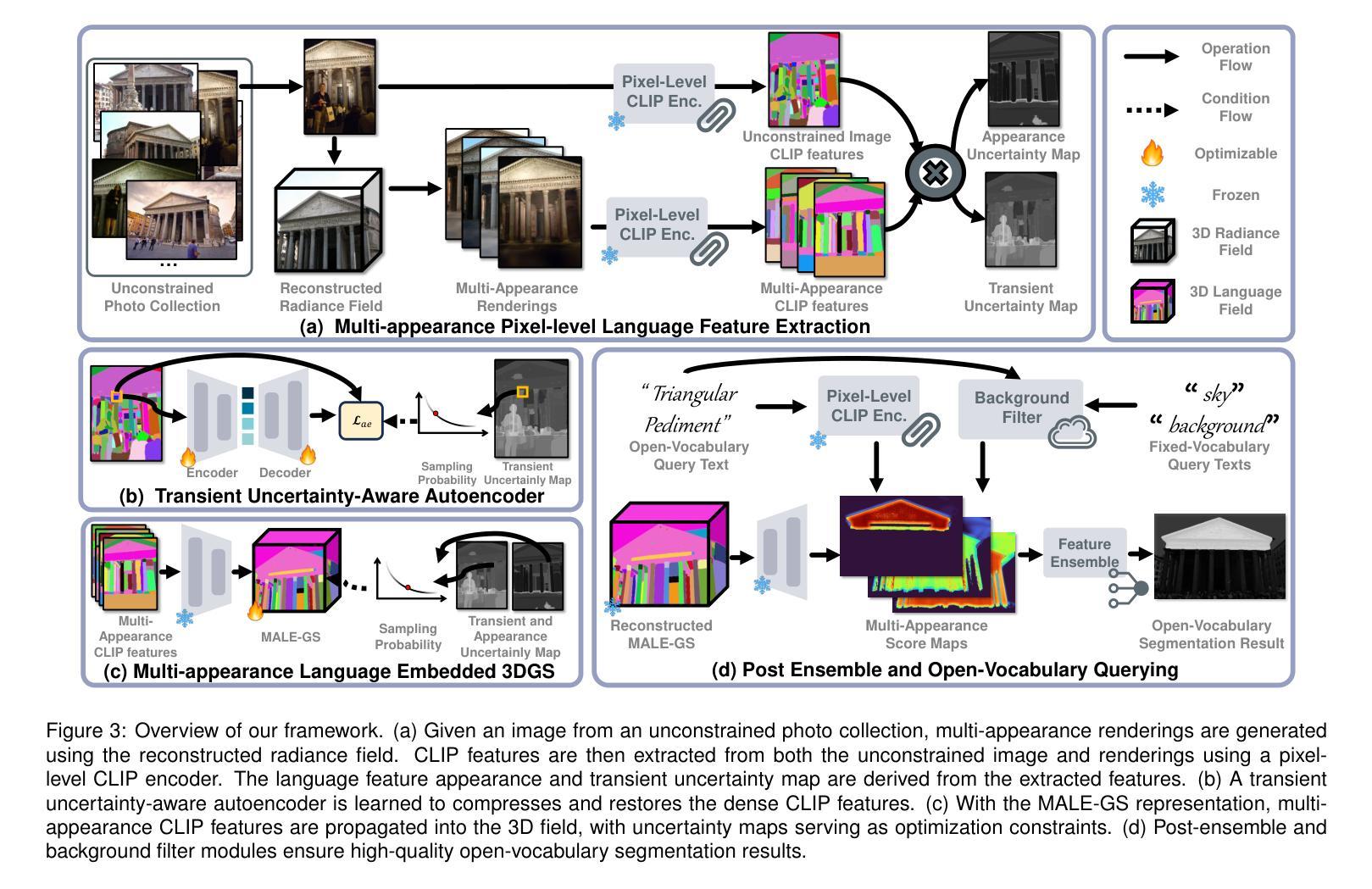
Recent advances in leveraging large-scale Internet photo collections for 3D reconstruction have enabled immersive virtual exploration of landmarks and historic sites worldwide. However, little attention has been given to the immersive understanding of architectural styles and structural knowledge, which remains largely confined to browsing static text-image pairs. Therefore, can we draw inspiration from 3D in-the-wild reconstruction techniques and use unconstrained photo collections to create an immersive approach for understanding the 3D structure of architectural components? To this end, we extend language embedded 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) and propose a novel framework for open-vocabulary scene understanding from unconstrained photo collections. Specifically, we first render multiple appearance images from the same viewpoint as the unconstrained image with the reconstructed radiance field, then extract multi-appearance CLIP features and two types of language feature uncertainty maps-transient and appearance uncertainty-derived from the multi-appearance features to guide the subsequent optimization process. Next, we propose a transient uncertainty-aware autoencoder, a multi-appearance language field 3DGS representation, and a post-ensemble strategy to effectively compress, learn, and fuse language features from multiple appearances. Finally, to quantitatively evaluate our method, we introduce PT-OVS, a new benchmark dataset for assessing open-vocabulary segmentation performance on unconstrained photo collections. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing methods, delivering accurate open-vocabulary segmentation and enabling applications such as interactive roaming with open-vocabulary queries, architectural style pattern recognition, and 3D scene editing.
近期,借助大规模互联网图片集进行3D重建的最新进展,已经能够实现全球各地地标和历史遗址的沉浸式虚拟探索。然而,对于建筑风格和结构知识的沉浸式理解却未受到足够重视,仍主要局限于浏览静态文本-图像对。那么,我们能从野生3D重建技术中汲取灵感,使用无约束的图片集来创建一个沉浸式方法来理解建筑组件的3D结构吗?为此,我们扩展了语言嵌入的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),并提出一个从无约束图片集中进行开放词汇场景理解的新框架。具体来说,我们首先使用重建的辐射场从同一视角渲染多个外观图像,这些图像与无约束图像相对应。然后,我们从多外观特征中提取多外观CLIP特征以及两种语言特征不确定性映射——瞬态和外观不确定性,以指导随后的优化过程。接下来,我们提出了一个瞬态不确定性感知自动编码器、一个多外观语言场3DGS表示以及一个后集成策略,以有效地压缩、学习和融合来自多个外观的语言特征。最后,为了定量评估我们的方法,我们引入了PT-OVS,这是一个新的基准数据集,用于评估无约束图片集中开放词汇分割的性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,实现了准确的开放词汇分割,并启用了应用程序,如带有开放词汇查询的交互式漫游、建筑风格模式识别和3D场景编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Visit our project page at https://yuzewang1998.github.io/takinglangsplatw/
Summary
该研究结合3D重建技术和大规模互联网图片集,提出一种新颖框架,用于从不受约束的图片集中理解建筑构件的3D结构。该框架融合了语言嵌入的3D高斯映射技术,通过渲染多角度视图、提取多视角CLIP特征、构建语言特征不确定性地图,并引入瞬时不确定性感知自编码器等技术手段,实现对建筑风格和结构的沉浸式理解。同时,该研究还推出新的数据集PT-OVS,用于评估在不受约束的图片集上的开放词汇分割性能。实验证明,该方法优于现有技术,可实现准确的开放词汇分割,并应用于开放式查询的交互漫游、建筑风格模式识别和3D场景编辑等应用。
Key Takeaways
- 利用大规模互联网图片集进行3D重建,实现全球地标和历史遗址的沉浸式虚拟探索。
- 现有技术对于建筑风格和结构知识的理解仍然局限于浏览静态文本-图像对,缺乏沉浸式理解。
- 引入3D野外重建技术,提出一种新颖框架,旨在从不受约束的图片集中理解建筑构件的3D结构。
- 框架包括:渲染多角度视图、提取多视角CLIP特征、构建语言特征不确定性地图。
- 引入瞬时不确定性感知自编码器和多视角语言场3DGS表示,有效压缩、学习和融合语言特征。
- 推出新的数据集PT-OVS,用于评估开放词汇分割性能。
点此查看论文截图


AD-GS: Object-Aware B-Spline Gaussian Splatting for Self-Supervised Autonomous Driving
Authors:Jiawei Xu, Kai Deng, Zexin Fan, Shenlong Wang, Jin Xie, Jian Yang
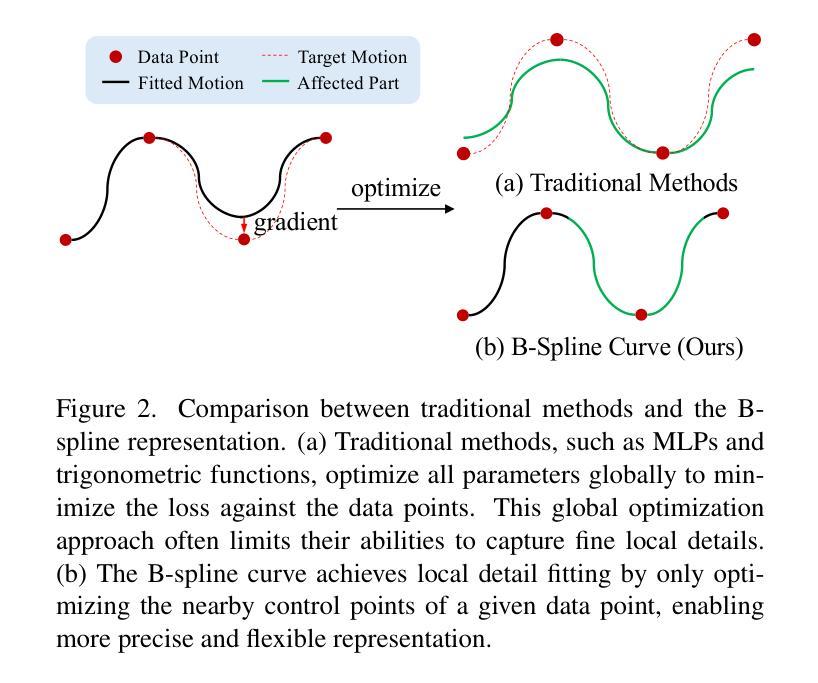
Modeling and rendering dynamic urban driving scenes is crucial for self-driving simulation. Current high-quality methods typically rely on costly manual object tracklet annotations, while self-supervised approaches fail to capture dynamic object motions accurately and decompose scenes properly, resulting in rendering artifacts. We introduce AD-GS, a novel self-supervised framework for high-quality free-viewpoint rendering of driving scenes from a single log. At its core is a novel learnable motion model that integrates locality-aware B-spline curves with global-aware trigonometric functions, enabling flexible yet precise dynamic object modeling. Rather than requiring comprehensive semantic labeling, AD-GS automatically segments scenes into objects and background with the simplified pseudo 2D segmentation, representing objects using dynamic Gaussians and bidirectional temporal visibility masks. Further, our model incorporates visibility reasoning and physically rigid regularization to enhance robustness. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our annotation-free model significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art annotation-free methods and is competitive with annotation-dependent approaches.
对动态城市驾驶场景的建模和渲染对于自动驾驶仿真至关重要。当前的高质量方法通常依赖于昂贵的手动目标轨迹标注,而自监督的方法则无法准确捕捉动态目标的运动并适当分解场景,从而导致渲染出现伪影。我们引入了AD-GS,这是一种新型自监督框架,用于从单个日志中进行高质量自由视角的驾驶场景渲染。其核心是一个新型的可学习运动模型,它将局部感知的B样条曲线与全局感知的三角函数相结合,实现了灵活而精确的动态目标建模。AD-GS不需要全面的语义标签,而是自动将场景分割为目标和背景,采用简化的伪二维分割来表示目标,并使用动态高斯和双向时间可见性掩膜来表示目标。此外,我们的模型还融入了可见性推理和物理刚性正则化,以提高稳健性。大量评估表明,我们的无标注模型显著优于当前先进的无标注方法,并与依赖于标注的方法具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的自监督框架AD-GS,用于从单一日志中进行高质量的自由视角驾驶场景渲染。该框架采用学习型的运动模型,结合局部感知的B样条曲线和全局感知的三角函数,实现灵活而精确的动态物体建模。通过简化伪二维分割,AD-GS可自动将场景分割为物体和背景,并使用动态高斯和双向时间可见性掩膜表示物体。此外,该模型还融入了可见性推理和物理刚体规则化以增强稳健性,无需全面语义标签即可显著超越当前最先进的无标注方法,并与依赖于标注的方法相竞争。
Key Takeaways
- AD-GS是一种新型自监督框架,用于高质量自由视角的驾驶场景渲染。
- 框架核心为学习型的运动模型,结合了局部和全局感知函数,实现精确动态物体建模。
- 无需全面的语义标注,通过简化伪二维分割自动分割场景。
- 使用动态高斯和双向时间可见性掩膜表示物体。
- 融入了可见性推理和物理刚体规则化增强模型的稳健性。
- 显著超越了现有的无标注方法,并在性能上与依赖于标注的方法相竞争。
点此查看论文截图

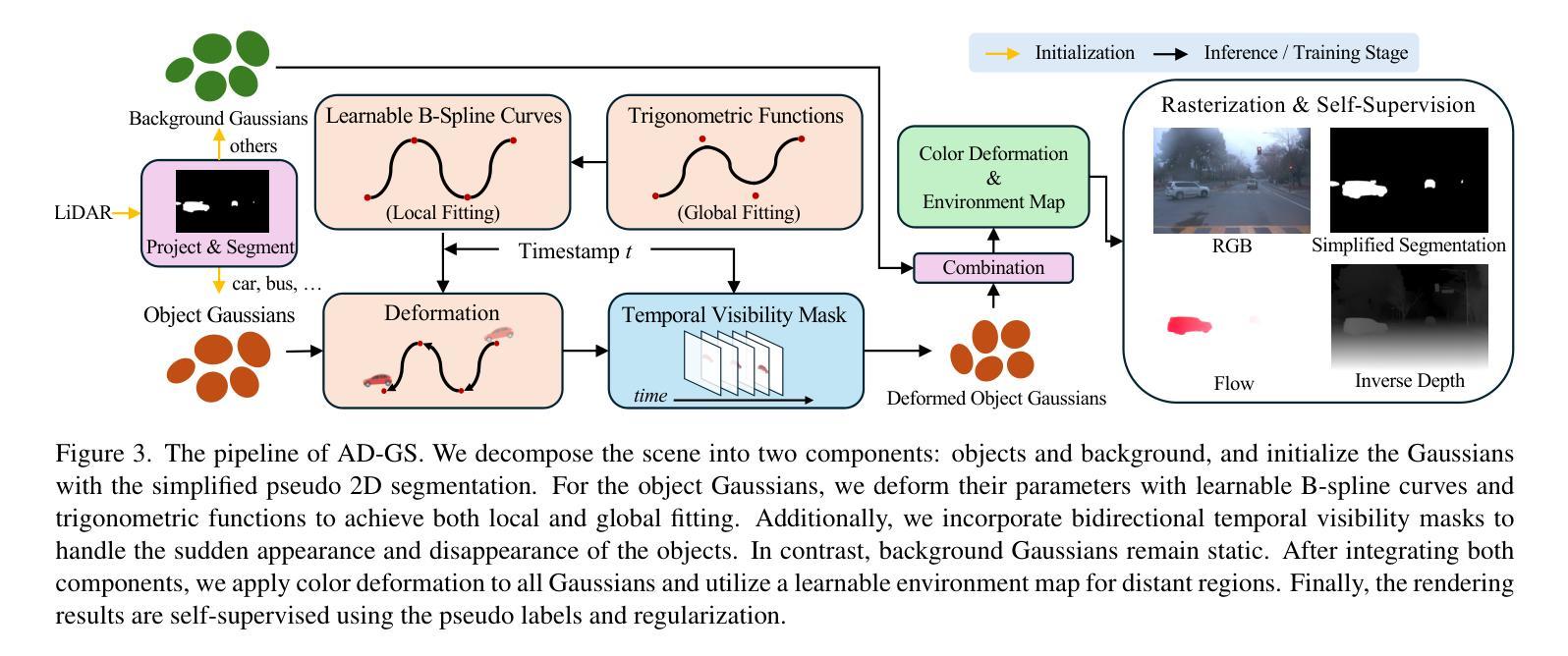
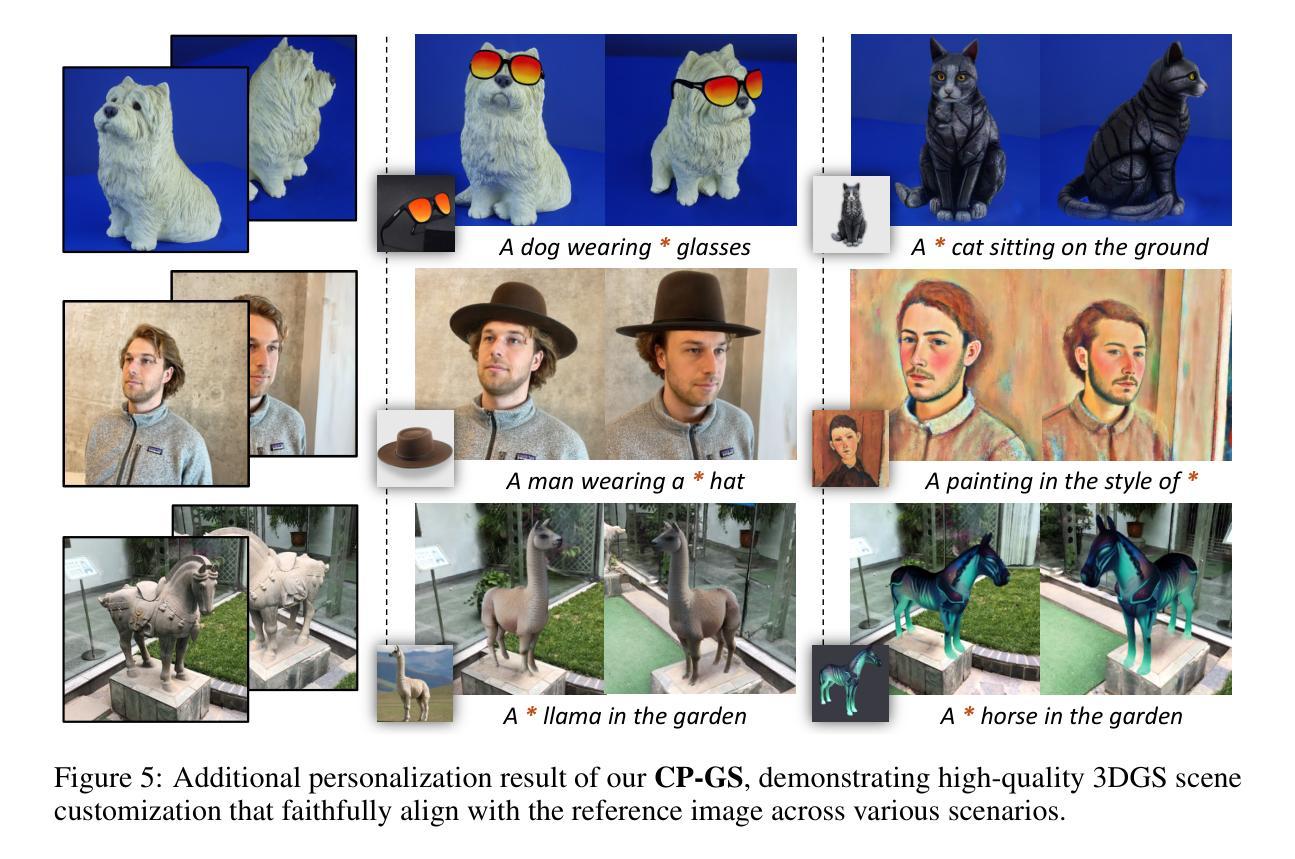
Personalize Your Gaussian: Consistent 3D Scene Personalization from a Single Image
Authors:Yuxuan Wang, Xuanyu Yi, Qingshan Xu, Yuan Zhou, Long Chen, Hanwang Zhang
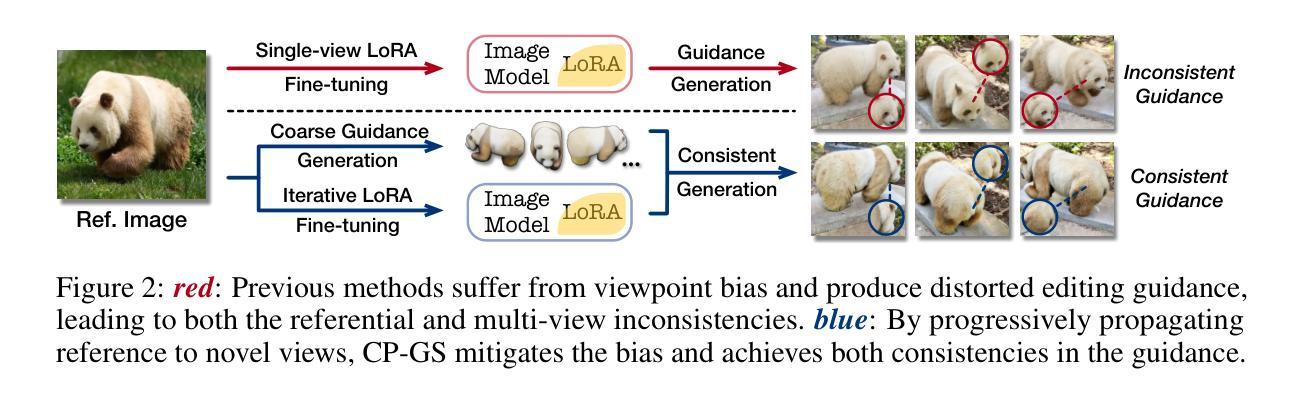
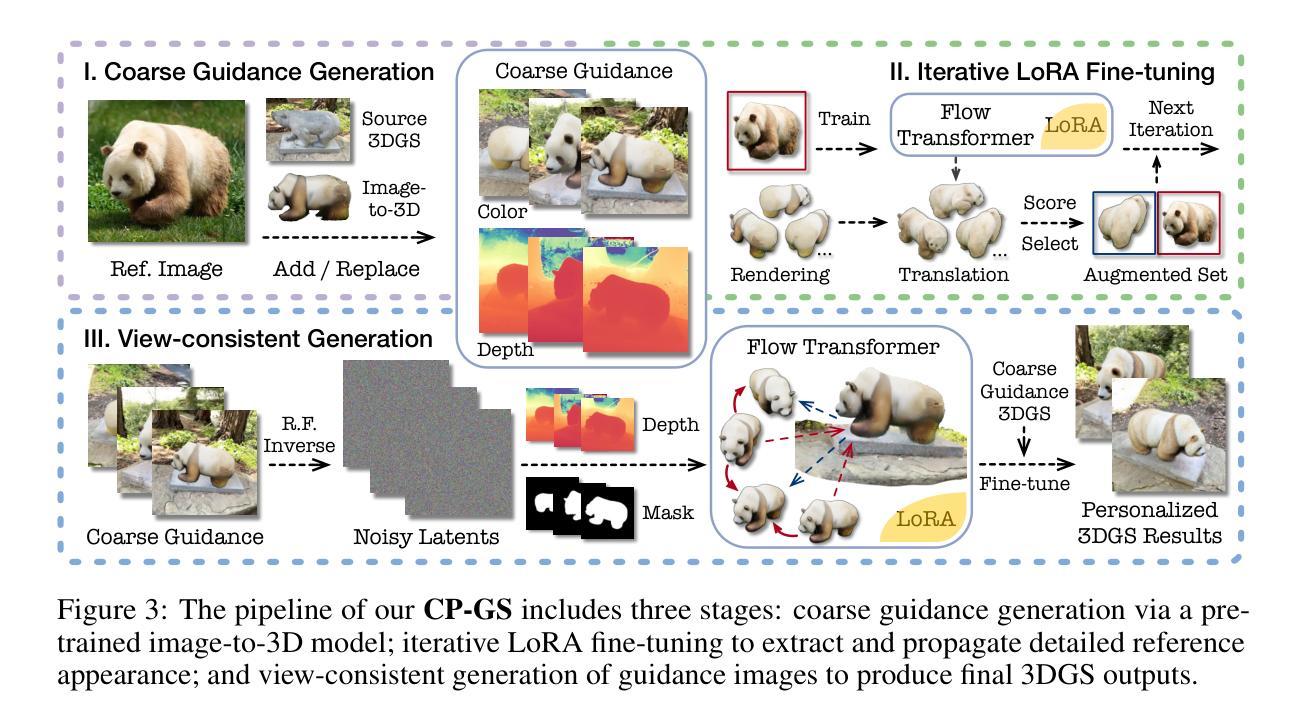
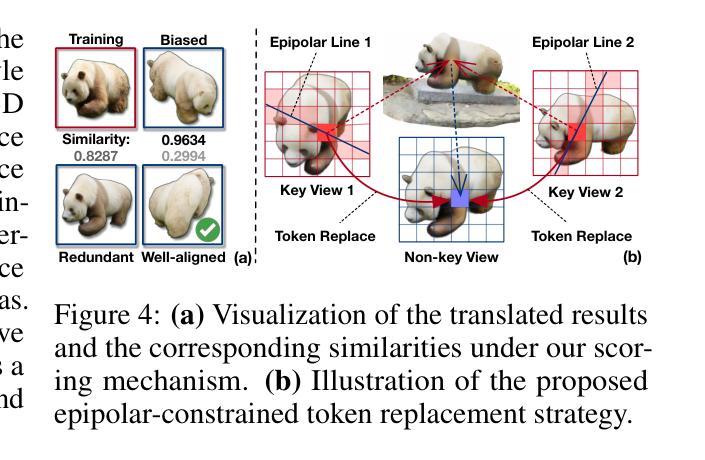
Personalizing 3D scenes from a single reference image enables intuitive user-guided editing, which requires achieving both multi-view consistency across perspectives and referential consistency with the input image. However, these goals are particularly challenging due to the viewpoint bias caused by the limited perspective provided in a single image. Lacking the mechanisms to effectively expand reference information beyond the original view, existing methods of image-conditioned 3DGS personalization often suffer from this viewpoint bias and struggle to produce consistent results. Therefore, in this paper, we present Consistent Personalization for 3D Gaussian Splatting (CP-GS), a framework that progressively propagates the single-view reference appearance to novel perspectives. In particular, CP-GS integrates pre-trained image-to-3D generation and iterative LoRA fine-tuning to extract and extend the reference appearance, and finally produces faithful multi-view guidance images and the personalized 3DGS outputs through a view-consistent generation process guided by geometric cues. Extensive experiments on real-world scenes show that our CP-GS effectively mitigates the viewpoint bias, achieving high-quality personalization that significantly outperforms existing methods. The code will be released at https://github.com/Yuxuan-W/CP-GS.
通过单一参考图像个性化3D场景,可实现直观的用户引导编辑,这要求在不同视角之间实现多视图一致性以及与输入图像的参照一致性。然而,由于单一图像提供的有限视角导致的视点偏见,这些目标特别具有挑战性。缺乏在原始视图之外有效扩展参考信息的机制,现有的图像条件3DGS个性化方法通常受到这种视点偏见的影响,难以产生一致的结果。因此,本文提出了面向3D高斯拼贴的一致个性化(CP-GS)框架,该框架逐步将单视图参考外观传播到新的视角。特别是,CP-GS集成了预训练的图像到3D生成和迭代LoRA微调,以提取和扩展参考外观,并最终通过忠实的多视图指导图像和由几何线索引导的一致生成过程,产生个性化的3DGS输出。在真实场景上的广泛实验表明,我们的CP-GS有效地减轻了视点偏见,实现了高质量的个性化,显著优于现有方法。代码将在https://github.com/Yuxuan-W/CP-GS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种名为CP-GS的3D高斯喷绘一致个性化框架,该框架能够从单一视角的图像参考中,逐步传播外观信息到新的视角。通过整合预训练的图像到3D生成模型和迭代LoRA微调技术,CP-GS能够有效地提取和扩展参考图像中的外观信息,生成忠实于原图像的多视角指导图像,并产生个性化的3DGS输出。实验证明,CP-GS有效减轻了视角偏差问题,显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- CP-GS框架实现了从单一参考图像到多视角的个性化3D场景生成。
- 通过逐步传播单一视角的图像参考外观信息到新的视角。
- 整合了预训练的图像到3D生成模型和迭代LoRA微调技术来提取和扩展参考信息。
- CP-GS框架能够生成忠实于原图像的多视角指导图像。
- 实现了个性化的3DGS输出,显著减轻了视角偏差问题。
- CP-GS框架在真实场景的实验中表现出优异性能。
- 代码将发布在https://github.com/Yuxuan-W/CP-GS。
点此查看论文截图

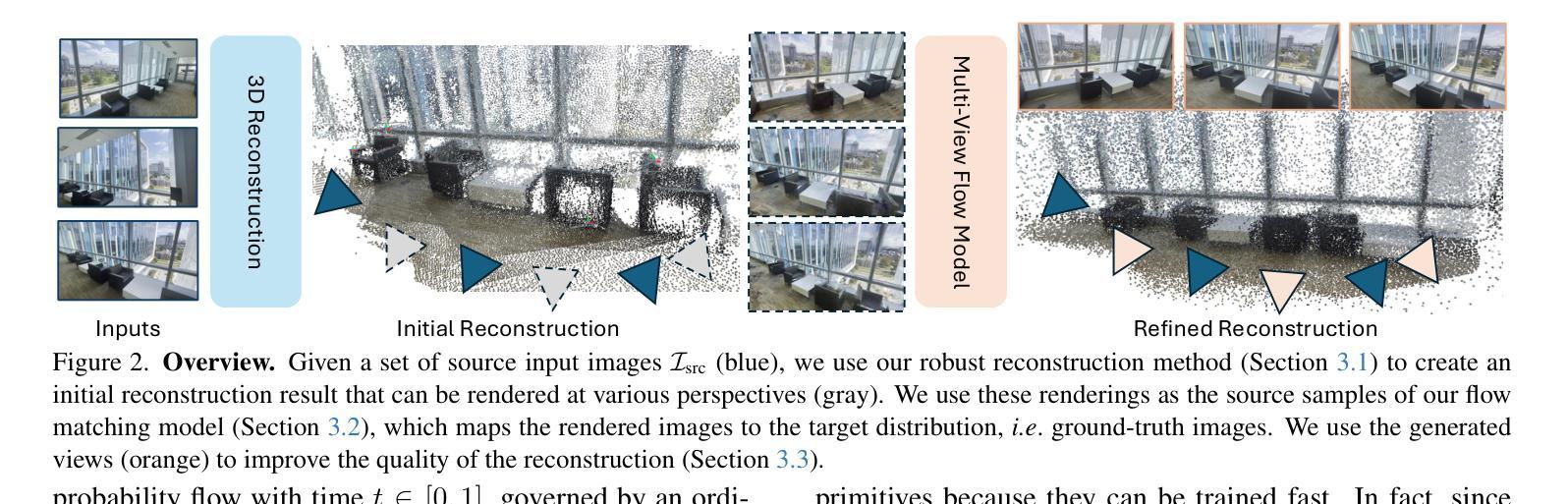
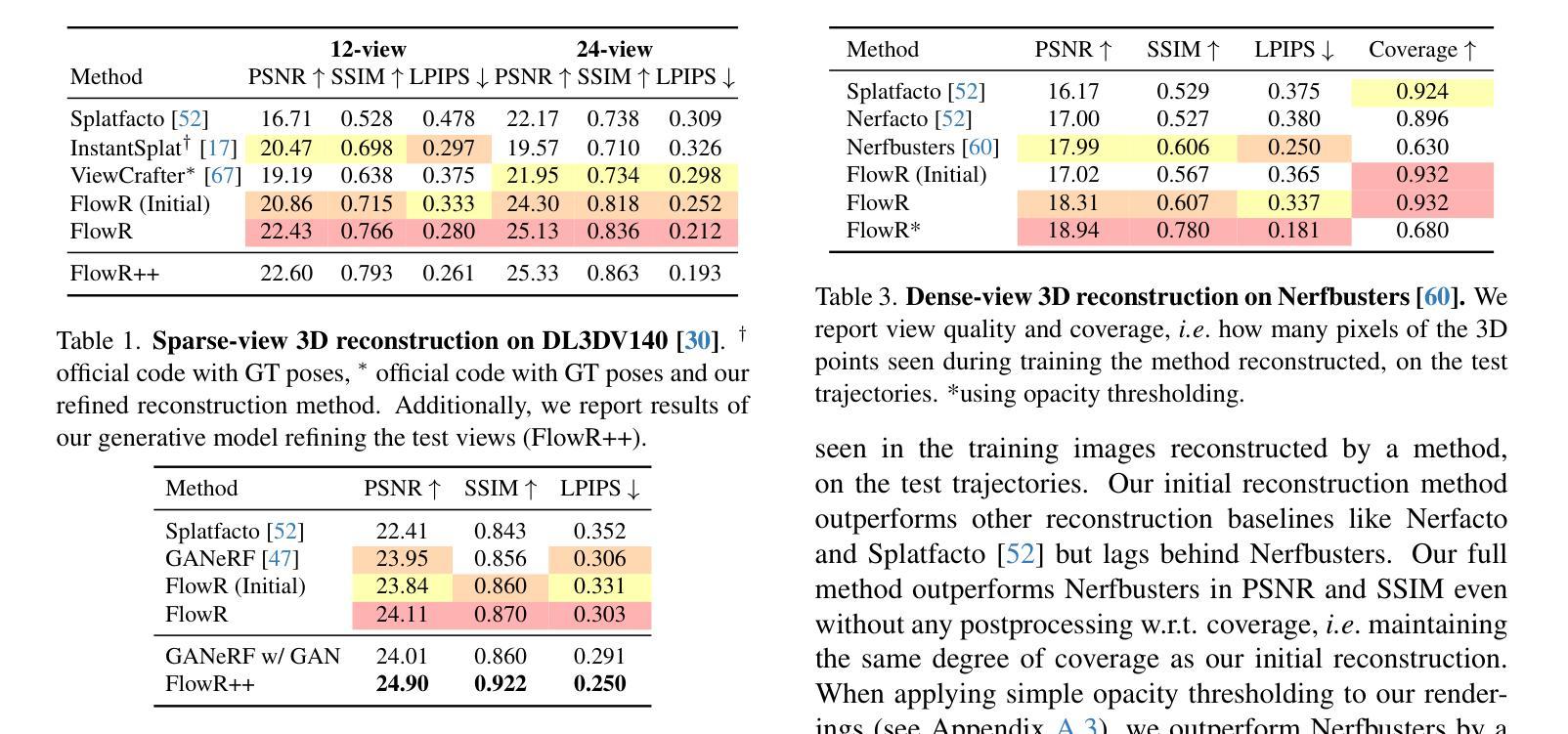
FlowR: Flowing from Sparse to Dense 3D Reconstructions
Authors:Tobias Fischer, Samuel Rota Bulò, Yung-Hsu Yang, Nikhil Keetha, Lorenzo Porzi, Norman Müller, Katja Schwarz, Jonathon Luiten, Marc Pollefeys, Peter Kontschieder
3D Gaussian splatting enables high-quality novel view synthesis (NVS) at real-time frame rates. However, its quality drops sharply as we depart from the training views. Thus, dense captures are needed to match the high-quality expectations of applications like Virtual Reality (VR). However, such dense captures are very laborious and expensive to obtain. Existing works have explored using 2D generative models to alleviate this requirement by distillation or generating additional training views. These models typically rely on a noise-to-data generative process conditioned only on a handful of reference input views, leading to hallucinations, inconsistent generation results, and subsequent reconstruction artifacts. Instead, we propose a multi-view, flow matching model that learns a flow to directly connect novel view renderings from possibly sparse reconstructions to renderings that we expect from dense reconstructions. This enables augmenting scene captures with consistent, generated views to improve reconstruction quality. Our model is trained on a novel dataset of 3.6M image pairs and can process up to 45 views at 540x960 resolution (91K tokens) on one H100 GPU in a single forward pass. Our pipeline consistently improves NVS in sparse- and dense-view scenarios, leading to higher-quality reconstructions than prior works across multiple, widely-used NVS benchmarks.
3D高斯展平技术能够以实时帧率实现高质量的新视角合成(NVS)。然而,当我们偏离训练视图时,其质量会急剧下降。因此,为了匹配虚拟现实(VR)等应用的高质量期望,需要进行密集的捕获。然而,获取这样的密集捕获非常耗时且成本高昂。现有研究已经尝试使用2D生成模型通过蒸馏或生成额外的训练视图来缓解这一需求。这些模型通常依赖于仅依赖于少量参考输入视图的噪声到数据的生成过程,从而导致出现幻觉、生成结果不一致和随后的重建伪影。相反,我们提出了一种多视角、流匹配模型,该模型学习一种流,直接连接可能稀疏重建的新视角渲染,到我们期望从密集重建中得到的渲染。这能够通过增加场景捕获的一致性和生成的视角来提高重建质量。我们的模型是在一个包含360万图像对的新数据集上进行训练的,可以在一次前向传递中,在单个H100 GPU上以540x960分辨率处理多达45个视图(91K令牌)。我们的管道在稀疏和密集视图的场景中持续提高了NVS的性能,并在多个广泛使用的NVS基准测试中实现了比先前工作更高质量的重建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Highlight. Project page is available at https://tobiasfshr.github.io/pub/flowr
Summary
本文提出一种基于多视角流匹配模型的实时高质量三维场景重建方法。通过直接连接稀疏重建的新视角渲染与密集重建的渲染结果,该方法提高了场景重建的质量和一致性。在大量图像数据对训练的基础上,该模型在稀疏和密集视角下均能改善新型视角合成效果,且在多个广泛应用的新型视角合成基准测试中实现高质量重建。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯splat技术能实时合成高质量新视角,但离训练视角太远则质量急剧下降,需要密集捕获匹配VR等高质应用需求。
- 密集捕获既劳力又昂贵,现有工作尝试用2D生成模型缓解此问题,但依赖噪声到数据的生成过程,仅依赖少量参考输入视角,导致幻觉、生成结果不一致和重建伪影。
- 提出一种多视角流匹配模型,学习从稀疏重建到新视角渲染的流连接,以提高重建质量并增强场景捕获的一致性。
- 模型在新数据集上训练,包含360万图像对,能在单个H100 GPU上一次前向传递处理高达45个视角的540x960分辨率(91K令牌)。
点此查看论文截图

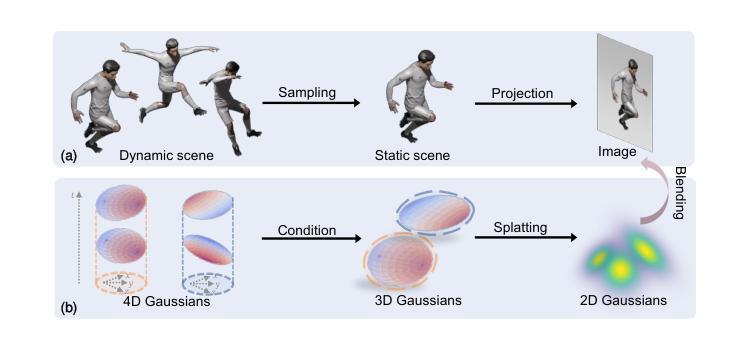
4D Gaussian Splatting: Modeling Dynamic Scenes with Native 4D Primitives
Authors:Zeyu Yang, Zijie Pan, Xiatian Zhu, Li Zhang, Jianfeng Feng, Yu-Gang Jiang, Philip H. S. Torr
Dynamic 3D scene representation and novel view synthesis are crucial for enabling immersive experiences required by AR/VR and metaverse applications. It is a challenging task due to the complexity of unconstrained real-world scenes and their temporal dynamics. In this paper, we reformulate the reconstruction of a time-varying 3D scene as approximating its underlying spatiotemporal 4D volume by optimizing a collection of native 4D primitives, i.e., 4D Gaussians, with explicit geometry and appearance modeling. Equipped with a tailored rendering pipeline, our representation can be end-to-end optimized using only photometric supervision while free viewpoint viewing at interactive frame rate, making it suitable for representing real world scene with complex dynamic. This approach has been the first solution to achieve real-time rendering of high-resolution, photorealistic novel views for complex dynamic scenes. To facilitate real-world applications, we derive several compact variants that effectively reduce the memory footprint to address its storage bottleneck. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of 4DGS in terms of visual quality and efficiency across a range of dynamic scene-related tasks (e.g., novel view synthesis, 4D generation, scene understanding) and scenarios (e.g., single object, indoor scenes, driving environments, synthetic and real data).
动态三维场景表示和新型视图合成对于增强现实/虚拟现实和元宇宙应用程序所需的沉浸式体验至关重要。由于无约束的现实世界场景的复杂性和其时间动态性,这是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们将时变三维场景的重建重新定义为通过优化一系列本地四维原始数据(即具有明确几何和外观建模的四维高斯)来逼近其基础时空四维体积。凭借量身定制的渲染管道,我们的表示可以使用仅光度监督进行端到端优化,同时以交互式帧率进行自由视点查看,使其适合表示具有复杂动态的现实世界场景。这种方法首次实现了对复杂动态场景的高分辨率、高逼真度新视角的实时渲染。为了促进实际应用,我们推导出了几种紧凑的变体,有效地减少了内存占用,解决了其存储瓶颈。大量实验验证了四维高斯合成在视觉质量和效率方面的优越性,涵盖了一系列动态场景相关任务(例如新视角合成、四维生成、场景理解)和场景(例如单个对象、室内场景、驾驶环境、合成数据和真实数据)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal extension of ICLR 2024. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2310.10642
Summary
本文提出一种基于优化本地4D原始数据(如4D高斯)的时间变化3D场景重建方法,将其模拟为对底层时空4D体积的逼近。通过专门的渲染管道,该表示方法可在仅使用光度监督的情况下进行端到端优化,实现复杂动态场景的实时渲染和真实感新视角观看。为解决存储瓶颈问题,本文还推出了几种紧凑变体以有效减少内存占用。实验证明,该方法在视觉质量和效率方面均优于其他方法,适用于多种动态场景相关任务和场景。
Key Takeaways
- 动态3D场景表示和新颖视图合成对于AR/VR和元宇宙应用所需的沉浸式体验至关重要。
- 本文通过将时间变化的3D场景重建重新定义为对底层时空4D体积的逼近来解决这一挑战。
- 使用优化本地4D原始数据(如4D高斯)进行表示,并具备明确的几何和外观建模。
- 配备了专门的渲染管道,可在仅使用光度监督的情况下进行端到端优化,实现复杂动态场景的实时渲染和真实感新视角观看。
- 推出几种紧凑变体以解决存储瓶颈问题,有效减少内存占用。
- 实验证明,该方法在视觉质量和效率方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

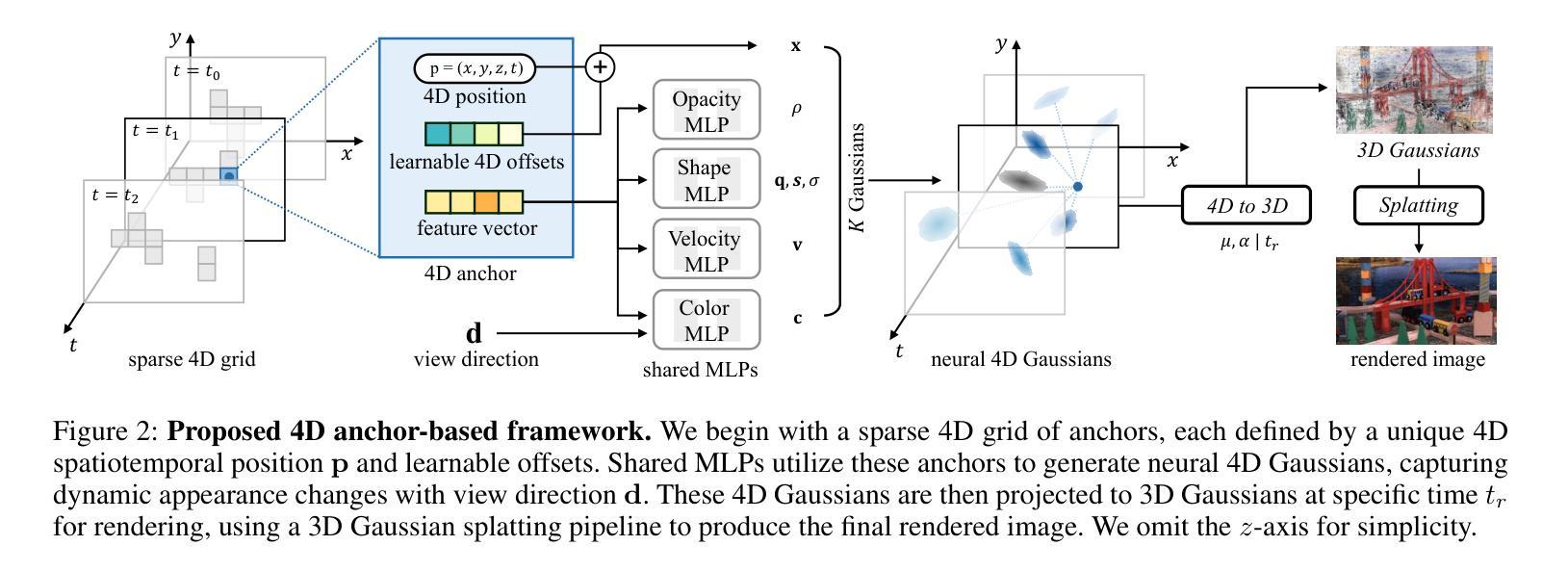
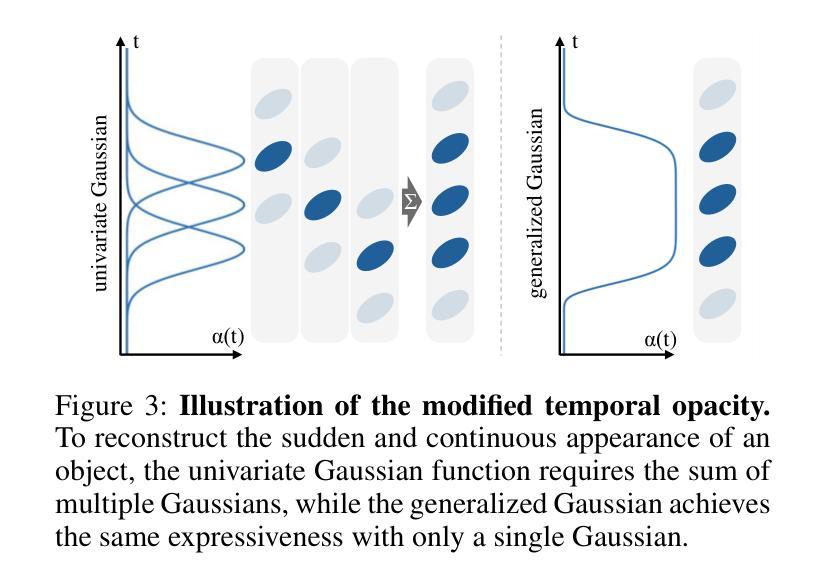
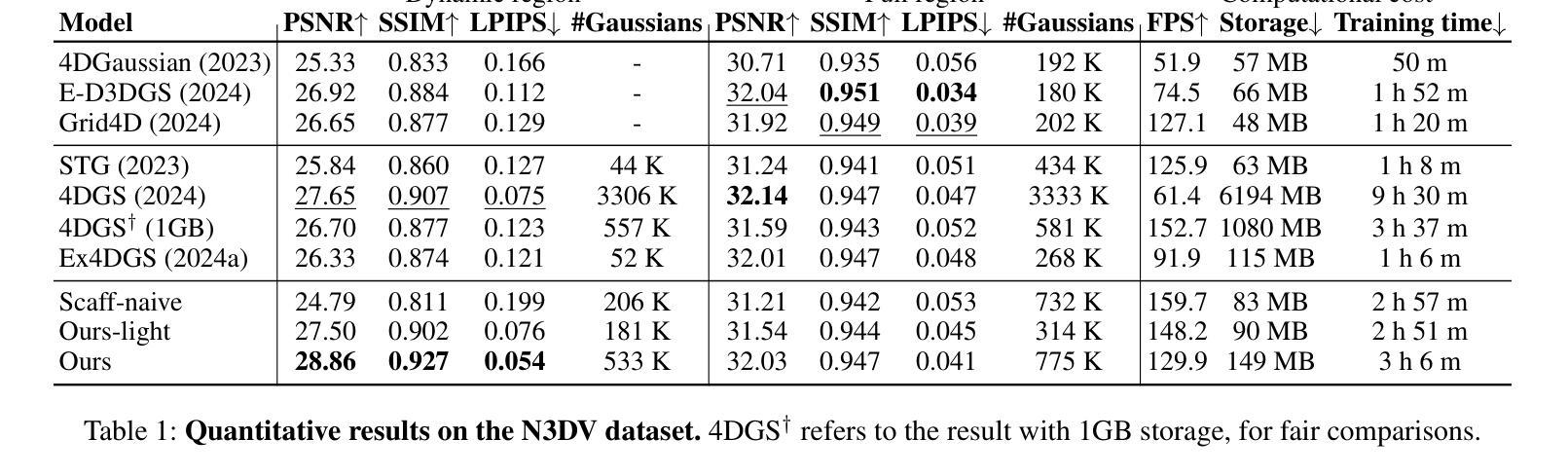
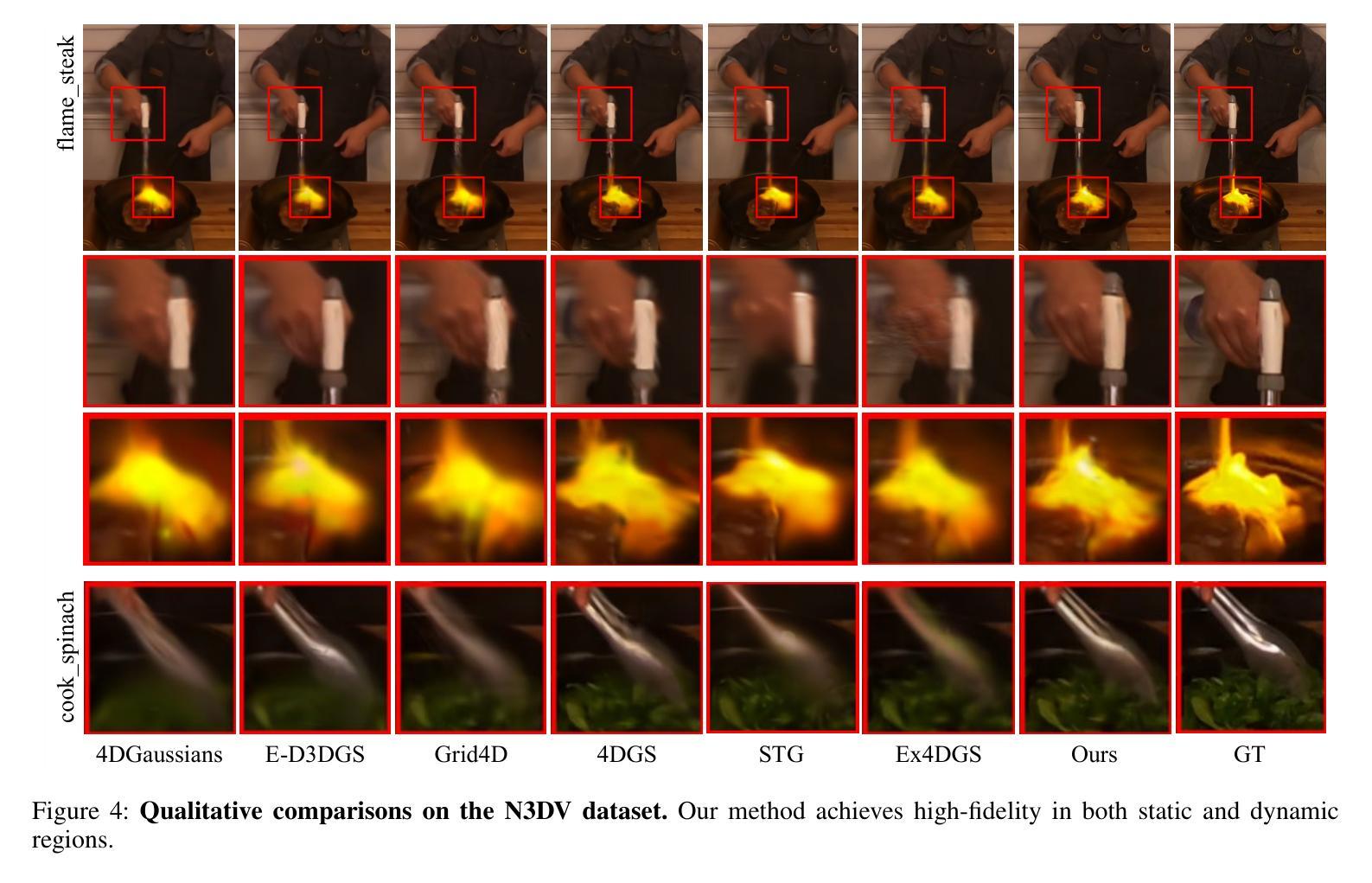
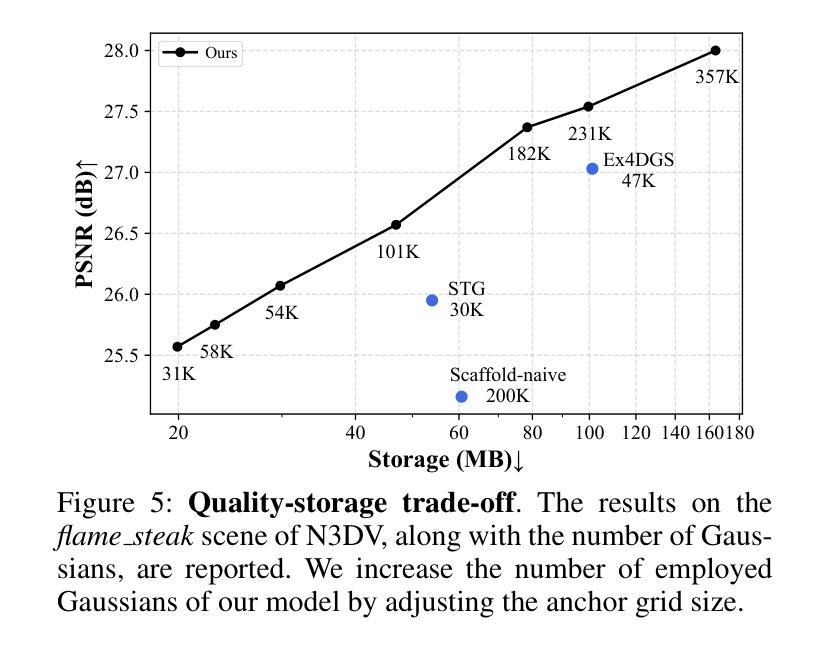
4D Scaffold Gaussian Splatting with Dynamic-Aware Anchor Growing for Efficient and High-Fidelity Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Woong Oh Cho, In Cho, Seoha Kim, Jeongmin Bae, Youngjung Uh, Seon Joo Kim
Modeling dynamic scenes through 4D Gaussians offers high visual fidelity and fast rendering speeds, but comes with significant storage overhead. Recent approaches mitigate this cost by aggressively reducing the number of Gaussians. However, this inevitably removes Gaussians essential for high-quality rendering, leading to severe degradation in dynamic regions. In this paper, we introduce a novel 4D anchor-based framework that tackles the storage cost in different perspective. Rather than reducing the number of Gaussians, our method retains a sufficient quantity to accurately model dynamic contents, while compressing them into compact, grid-aligned 4D anchor features. Each anchor is processed by an MLP to spawn a set of neural 4D Gaussians, which represent a local spatiotemporal region. We design these neural 4D Gaussians to capture temporal changes with minimal parameters, making them well-suited for the MLP-based spawning. Moreover, we introduce a dynamic-aware anchor growing strategy to effectively assign additional anchors to under-reconstructed dynamic regions. Our method adjusts the accumulated gradients with Gaussians’ temporal coverage, significantly improving reconstruction quality in dynamic regions. Experimental results highlight that our method achieves state-of-the-art visual quality in dynamic regions, outperforming all baselines by a large margin with practical storage costs.
通过4D高斯建模动态场景可以提供高视觉保真度和快速渲染速度,但同时也伴随着显著的存储开销。最近的方法通过大量减少高斯数量来缓解这一成本。然而,这不可避免地移除了对高质量渲染至关重要的高斯,导致动态区域出现严重退化。在本文中,我们引入了一种新型4D锚点基础框架,以从不同角度解决存储成本问题。我们的方法不是减少高斯数量,而是保留足够的数量来准确建模动态内容,同时将它们压缩成紧凑、网格对齐的4D锚点特征。每个锚点通过多层感知器处理,生成一组神经4D高斯,代表局部时空区域。我们设计这些神经4D高斯以最小的参数捕捉时间变化,非常适合基于多层感知器的生成。此外,我们引入了一种动态感知锚点增长策略,有效地将额外锚点分配给重建不足的动态区域。我们的方法通过调整高斯时间覆盖的累积梯度,显著提高了动态区域的重建质量。实验结果表明,我们的方法在动态区域实现了最先进的视觉质量,以实际存储成本大幅超越所有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于4D锚点的新型框架,旨在解决存储成本问题。不同于减少高斯数量的方法,该方法保留了足够数量的高斯以准确模拟动态内容,并将其压缩成紧凑的、与网格对齐的4D锚点特征。每个锚点通过多层感知器生成一组神经4D高斯,代表局部时空区域。这种方法设计用于捕捉时间变化的最小参数,适合基于MLP的生成。此外,引入了一种动态感知锚点增长策略,有效地为重建不足的动态区域分配额外的锚点。该方法在动态区域实现了最佳视觉质量,以实用存储成本大幅度超越所有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种基于4D锚点的新型框架,专注于解决存储成本问题。
- 通过保留足够数量的高斯数来准确模拟动态内容。
- 将这些高斯数压缩成紧凑的、与网格对齐的4D锚点特征。
- 使用多层感知器(MLP)处理每个锚点,生成神经4D高斯。
- 设计这些神经4D高斯以最小参数捕捉时间变化。
- 引入动态感知锚点增长策略,以提高动态区域的重建质量。
点此查看论文截图