⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
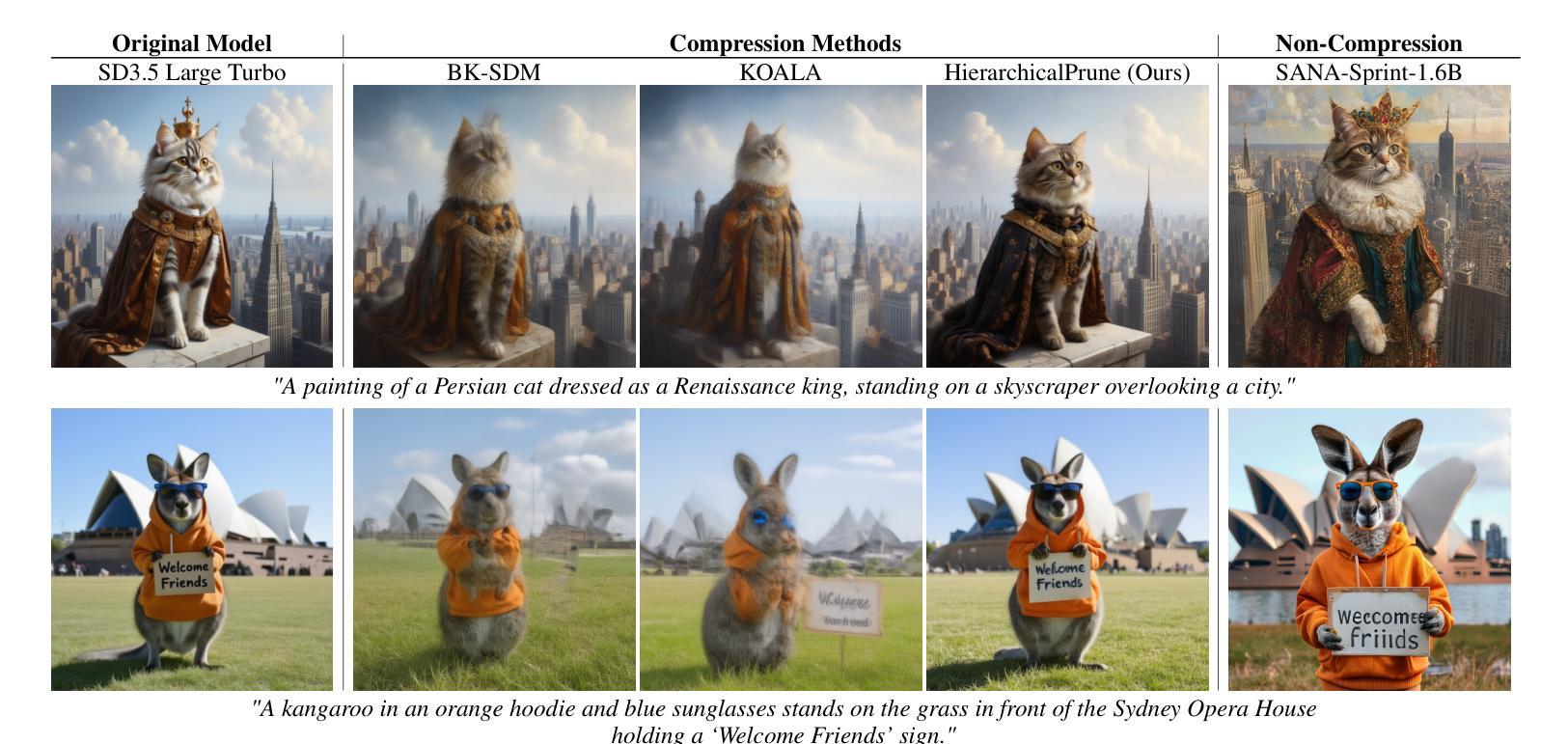
HierarchicalPrune: Position-Aware Compression for Large-Scale Diffusion Models
Authors:Young D. Kwon, Rui Li, Sijia Li, Da Li, Sourav Bhattacharya, Stylianos I. Venieris
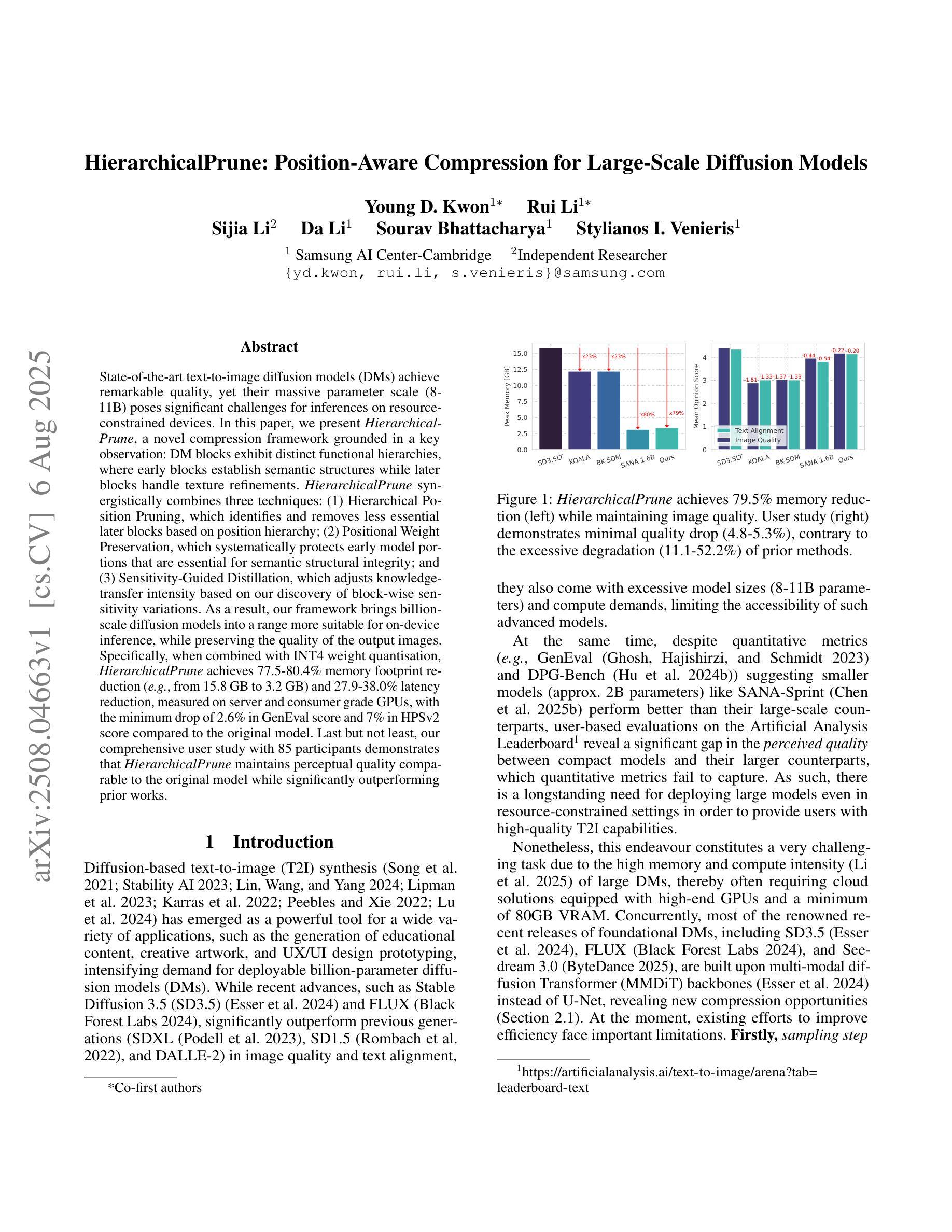
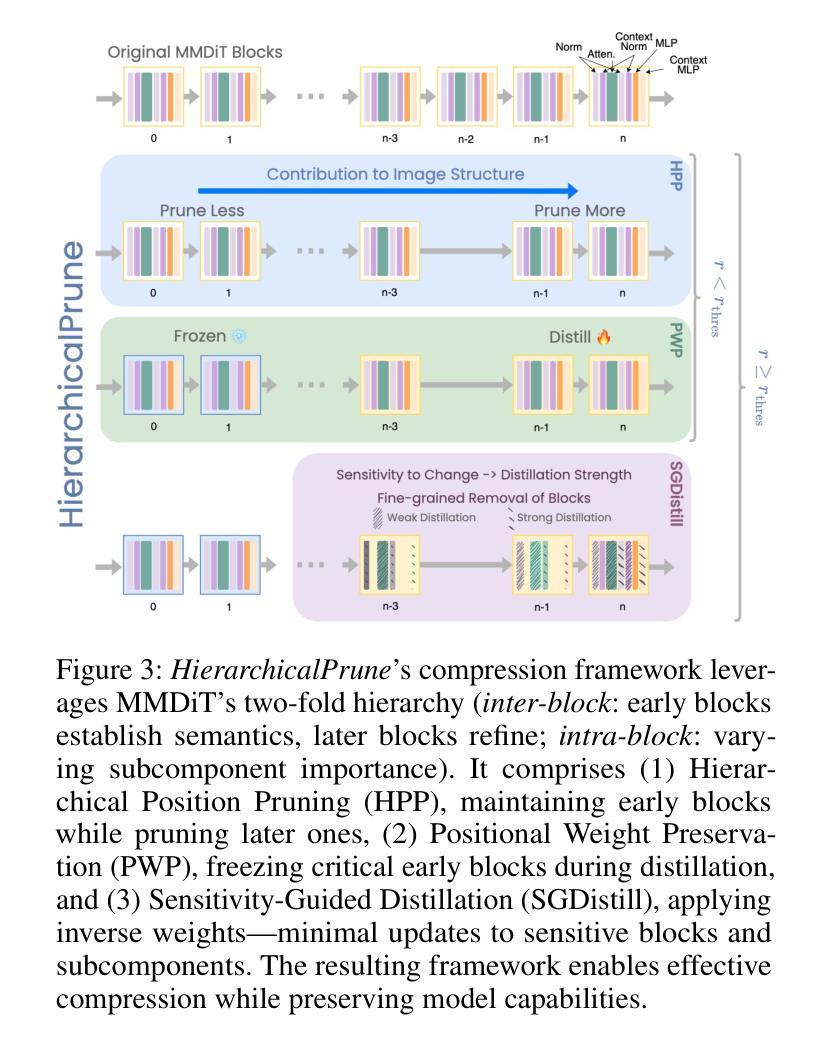
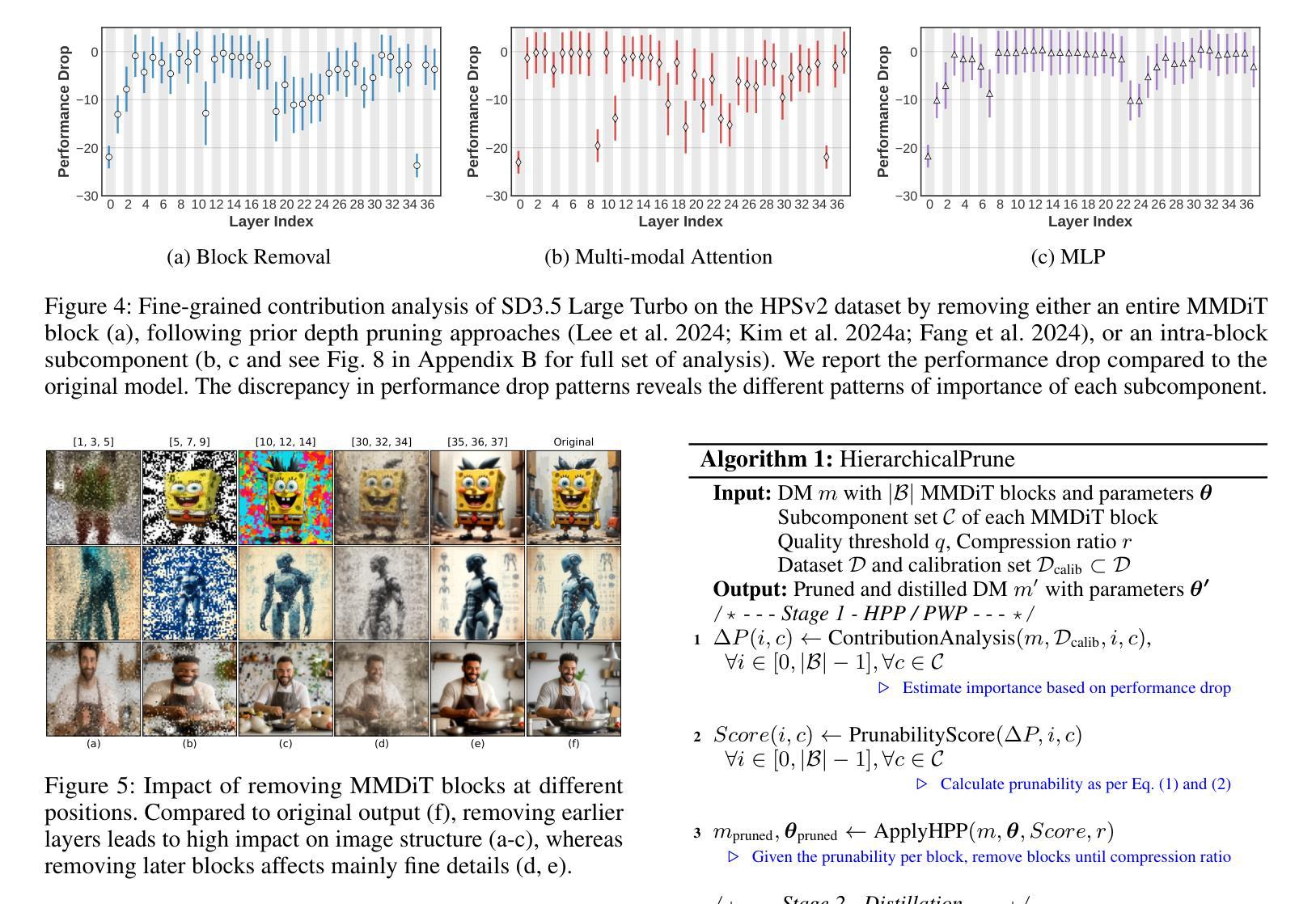
State-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion models (DMs) achieve remarkable quality, yet their massive parameter scale (8-11B) poses significant challenges for inferences on resource-constrained devices. In this paper, we present HierarchicalPrune, a novel compression framework grounded in a key observation: DM blocks exhibit distinct functional hierarchies, where early blocks establish semantic structures while later blocks handle texture refinements. HierarchicalPrune synergistically combines three techniques: (1) Hierarchical Position Pruning, which identifies and removes less essential later blocks based on position hierarchy; (2) Positional Weight Preservation, which systematically protects early model portions that are essential for semantic structural integrity; and (3) Sensitivity-Guided Distillation, which adjusts knowledge-transfer intensity based on our discovery of block-wise sensitivity variations. As a result, our framework brings billion-scale diffusion models into a range more suitable for on-device inference, while preserving the quality of the output images. Specifically, when combined with INT4 weight quantisation, HierarchicalPrune achieves 77.5-80.4% memory footprint reduction (e.g., from 15.8 GB to 3.2 GB) and 27.9-38.0% latency reduction, measured on server and consumer grade GPUs, with the minimum drop of 2.6% in GenEval score and 7% in HPSv2 score compared to the original model. Last but not least, our comprehensive user study with 85 participants demonstrates that HierarchicalPrune maintains perceptual quality comparable to the original model while significantly outperforming prior works.
先进的文本到图像扩散模型(DMs)达到了显著的质量,然而其巨大的参数规模(8-11B)对资源受限设备上的推理构成了重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了HierarchicalPrune,这是一种新的压缩框架,它基于一个关键观察:DM块表现出不同的功能层次,早期块建立语义结构,而后期块处理纹理细化。HierarchicalPrune协同结合了三种技术:(1)层次位置剪枝,它基于位置层次识别并移除较不重要的后期块;(2)位置权重保留,它系统地保护早期模型部分,对于语义结构完整性至关重要;(3)敏感度引导蒸馏,它根据我们发现的块状敏感度变化来调整知识转移强度。因此,我们的框架将数十亿规模的扩散模型引入到更适合于设备端推理的范围,同时保持输出图像的质量。具体来说,当与INT4权重量化结合时,HierarchicalPrune实现了77.5-80.4%的内存占用减少(例如,从15.8 GB减少到3.2 GB),并在服务器和消费级GPU上实现了27.9-38.0%的延迟减少,与原始模型相比,GenEval得分最低下降2.6%,HPSv2得分下降7%。最后但同样重要的是,我们的综合用户研究有85名参与者证明,HierarchicalPrune在保持与原始模型相当的可感知质量的同时,显著优于先前的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了针对文本到图像扩散模型(DMs)的压缩框架——HierarchicalPrune。该框架观察到DM块具有不同的功能层次,早期块建立语义结构,后期块处理纹理细化。通过结合三种技术:层次位置剪枝、位置权重保留和敏感性引导蒸馏,HierarchicalPrune成功地将十亿级别的扩散模型适应于设备端推理,同时保持输出图像的质量。与INT4权重量化结合,HierarchicalPrune实现了在服务器和消费者级GPU上77.5%~80.4%的内存占用减少(例如从15.8 GB降至3.2 GB)和27.9%~38.0%的延迟减少,同时相较于原始模型,GenEval得分仅降低最低2.6%,HPSv2得分降低7%。此外,通过对85名参与者的综合用户研究证明,HierarchicalPrune在保持与原始模型相当的可感知质量的同时,显著优于先前作品。
关键见解
- 文本到图像的扩散模型面临在资源受限设备上推理的挑战,其参数规模巨大(8~11B)。
- HierarchicalPrune是一种针对扩散模型的压缩框架,它观察到DM块的功能层次差异。
- HierarchicalPrune通过结合层次位置剪枝、位置权重保留和敏感性引导蒸馏等技术实现了内存占用和延迟的有效减少。
- 与INT4权重量化结合使用,HierarchicalPrune实现了显著的内存占用和延迟优化。
- HierarchicalPrune能在保持较高图像质量的同时大幅降低模型的大小和推理时间。
- 综合用户研究表明,HierarchicalPrune在维持可感知质量方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


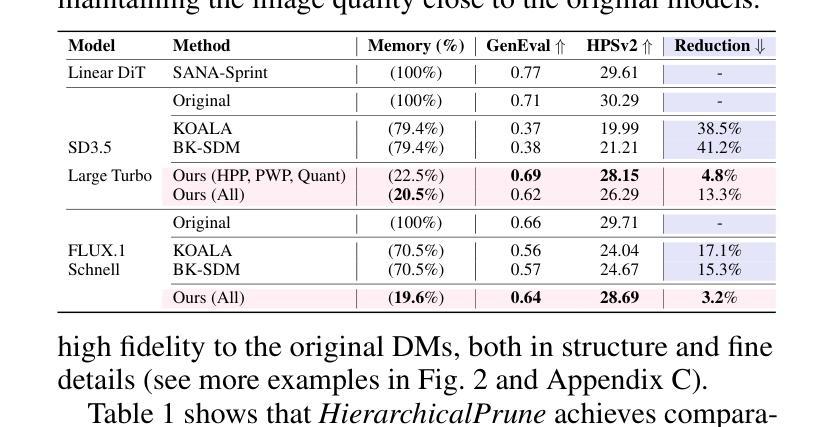
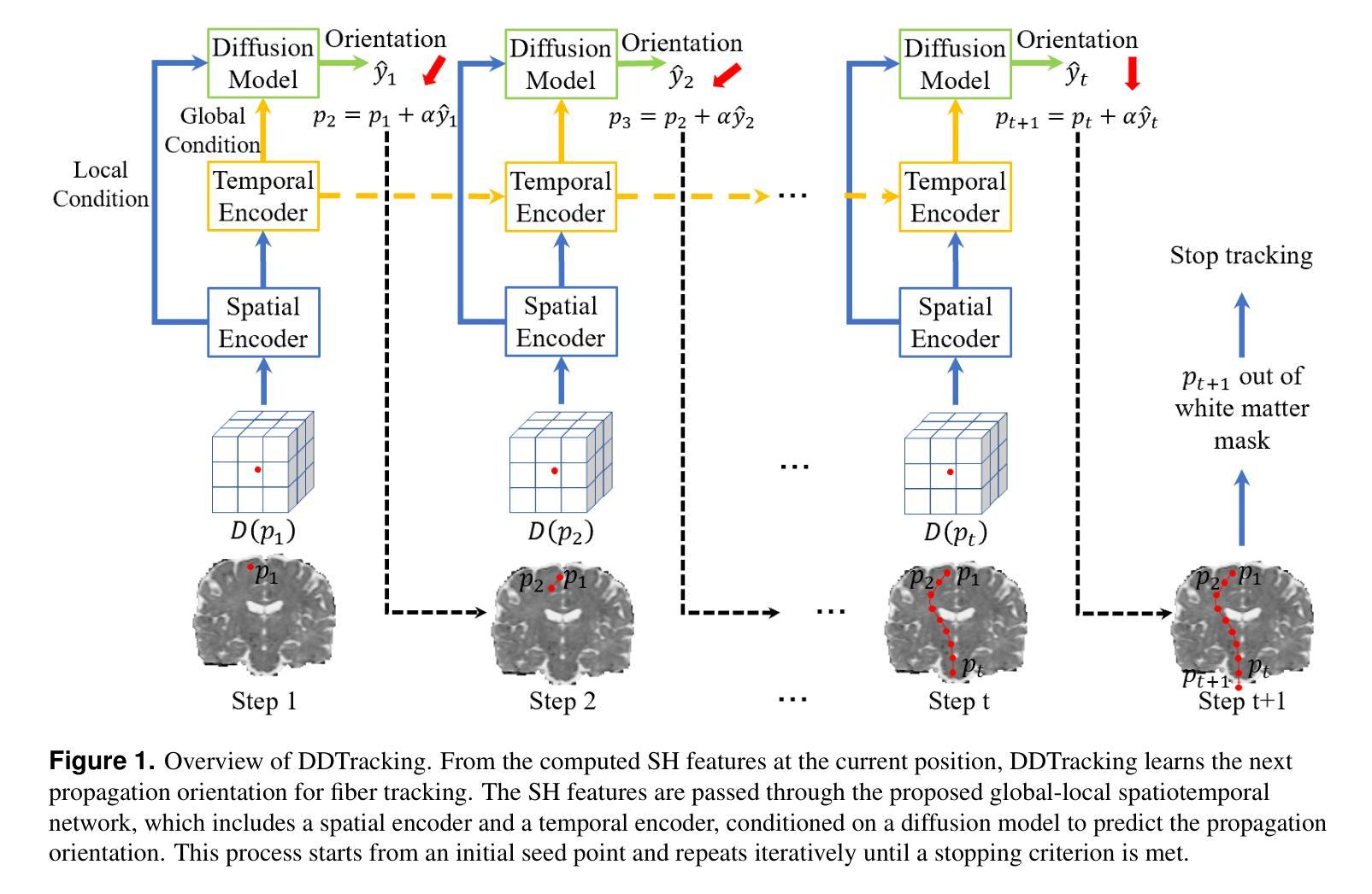
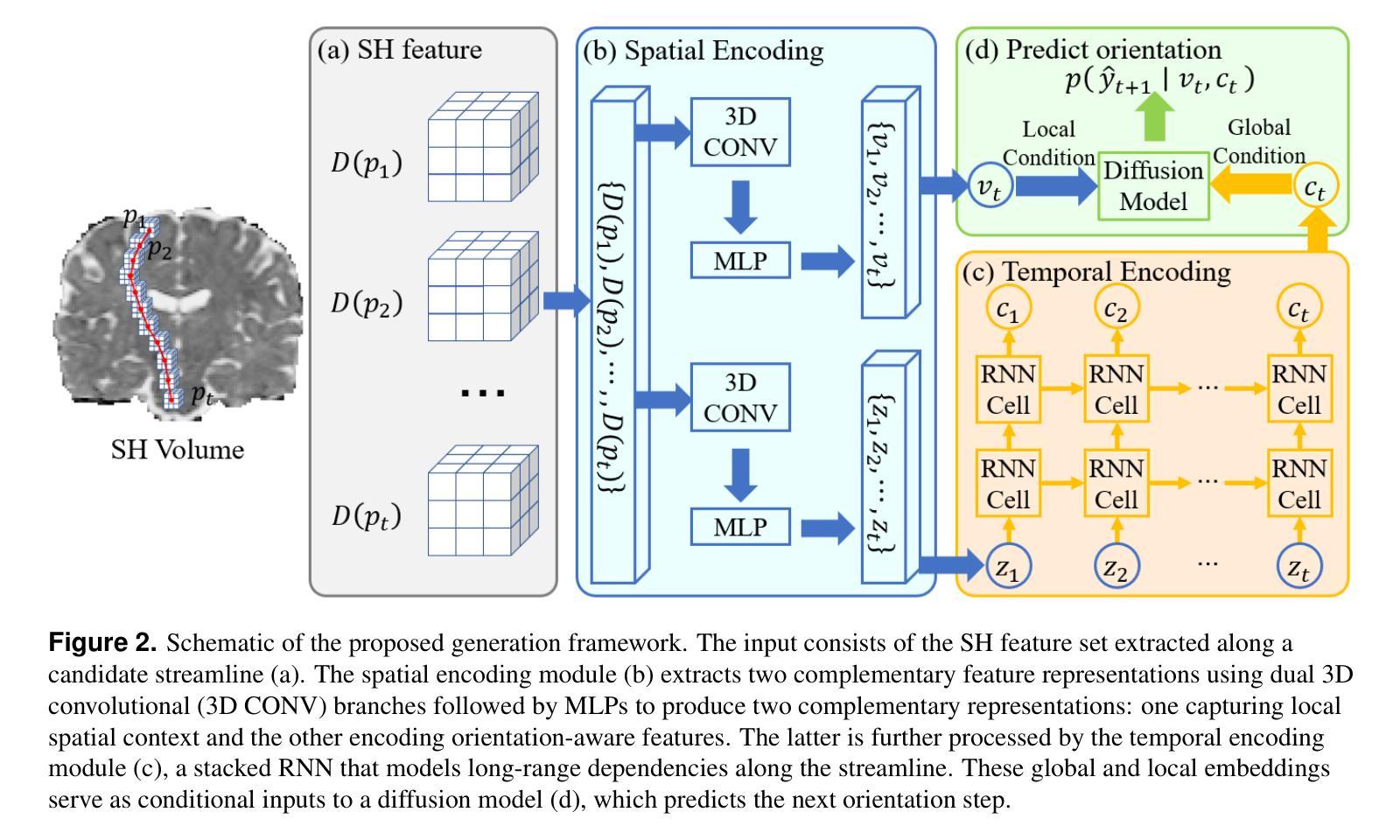
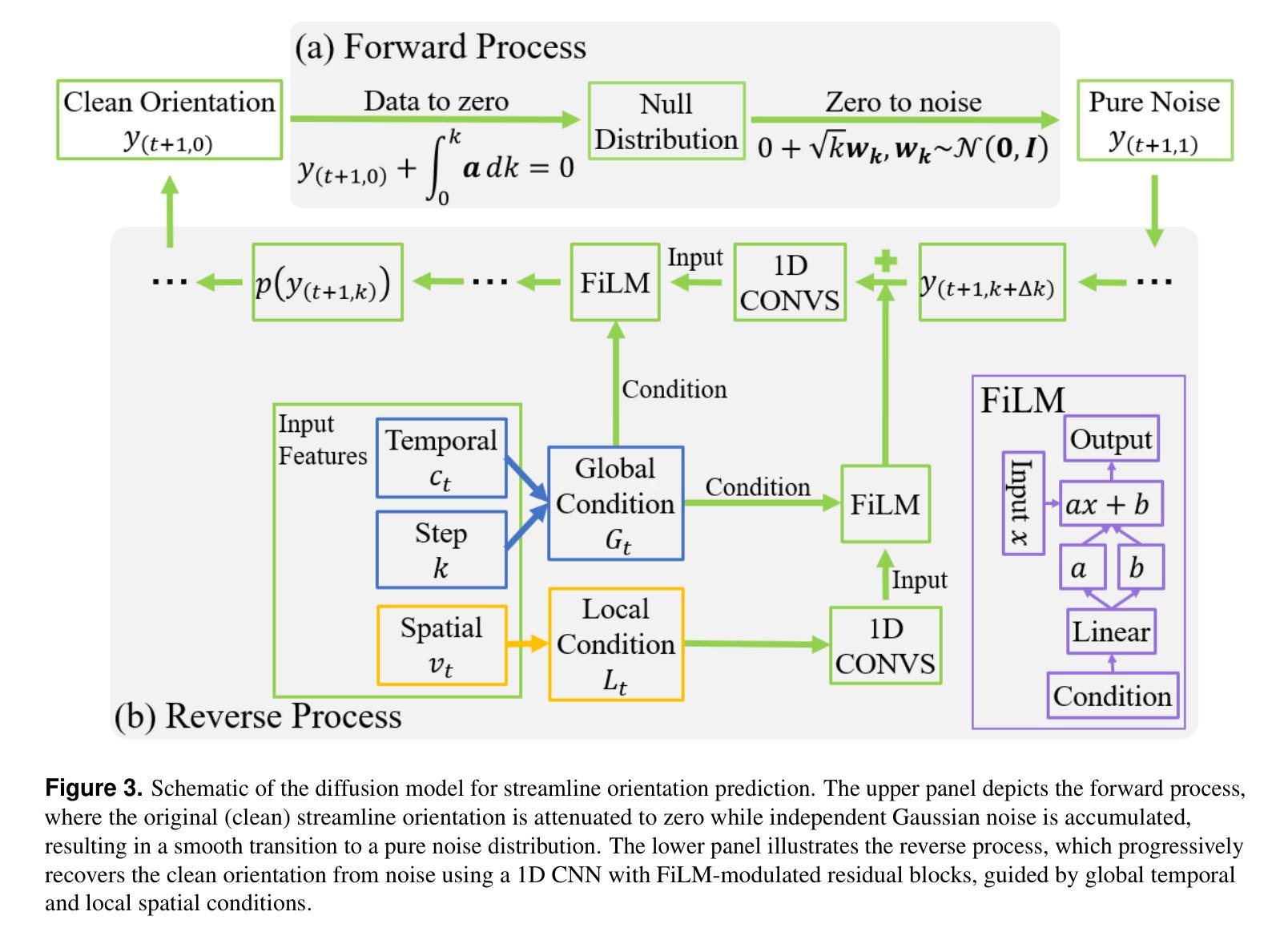
DDTracking: A Deep Generative Framework for Diffusion MRI Tractography with Streamline Local-Global Spatiotemporal Modeling
Authors:Yijie Li, Wei Zhang, Xi Zhu, Ye Wu, Yogesh Rathi, Lauren J. O’Donnell, Fan Zhang
This paper presents DDTracking, a novel deep generative framework for diffusion MRI tractography that formulates streamline propagation as a conditional denoising diffusion process. In DDTracking, we introduce a dual-pathway encoding network that jointly models local spatial encoding (capturing fine-scale structural details at each streamline point) and global temporal dependencies (ensuring long-range consistency across the entire streamline). Furthermore, we design a conditional diffusion model module, which leverages the learned local and global embeddings to predict streamline propagation orientations for tractography in an end-to-end trainable manner. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation across diverse, independently acquired dMRI datasets, including both synthetic and clinical data. Experiments on two well-established benchmarks with ground truth (ISMRM Challenge and TractoInferno) demonstrate that DDTracking largely outperforms current state-of-the-art tractography methods. Furthermore, our results highlight DDTracking’s strong generalizability across heterogeneous datasets, spanning varying health conditions, age groups, imaging protocols, and scanner types. Collectively, DDTracking offers anatomically plausible and robust tractography, presenting a scalable, adaptable, and end-to-end learnable solution for broad dMRI applications. Code is available at: https://github.com/yishengpoxiao/DDtracking.git
本文介绍了DDTracking,这是一种用于扩散MRI追踪的新型深度生成框架,它将流线传播表述为条件去噪扩散过程。在DDTracking中,我们引入了一个双路径编码网络,该网络同时对局部空间编码进行建模(捕获每条流线点上的精细结构细节)和全局时间依赖性(确保整条流线上的远程一致性)。此外,我们设计了一个条件扩散模型模块,该模块利用学习到的局部和全局嵌入来预测流线传播方向,以进行端到端的追踪。我们在多种独立获取的dMRI数据集上进行了全面评估,包括合成数据和临床数据。在具有真实值的两个公认基准测试(ISMRM挑战和TractoInferno)上的实验表明,DDTracking在当前的最新追踪方法中有很大的优越性。此外,我们的结果强调了DDTracking在不同数据集(包括各种健康状况、年龄组、成像协议和扫描仪类型)中的强大泛化能力。总的来说,DDTracking提供了解剖上合理且稳健的追踪,为广泛的dMRI应用提供了可伸缩、可适应和端到端的可学习解决方案。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/yishengpoxiao/DDtracking.git
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version. The content may be updated in the future
Summary
本文介绍了DDTracking,一种用于扩散MRI追踪的新型深度生成框架。它将流线传播制定为条件去噪扩散过程,并引入双路径编码网络,联合建模局部空间编码和全局时间依赖性。通过条件扩散模型模块,利用学习和全局嵌入预测流线传播方向,实现端到端的可训练方式。在多种独立采集的dMRI数据集上的综合评估表明,DDTracking在现有最先进的追踪方法中具有显著优势,且在不同数据集上具有强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- DDTracking是一个用于扩散MRI追踪的深度生成框架,将流线传播定义为条件去噪扩散过程。
- 引入双路径编码网络,同时处理局部空间编码和全局时间依赖性。
- 设计了条件扩散模型模块,用于预测流线传播方向,实现端到端的训练。
- 在多个dMRI数据集上进行了全面评估,包括合成和临床数据。
- 在两个拥有基准测试数据集(ISMRM Challenge和TractoInferno)的评估中,DDTracking显著优于当前最先进的方法。
- DDTracking展现出强大的泛化能力,能够适应不同的健康状态、年龄组、成像协议和扫描仪类型的数据集。
点此查看论文截图

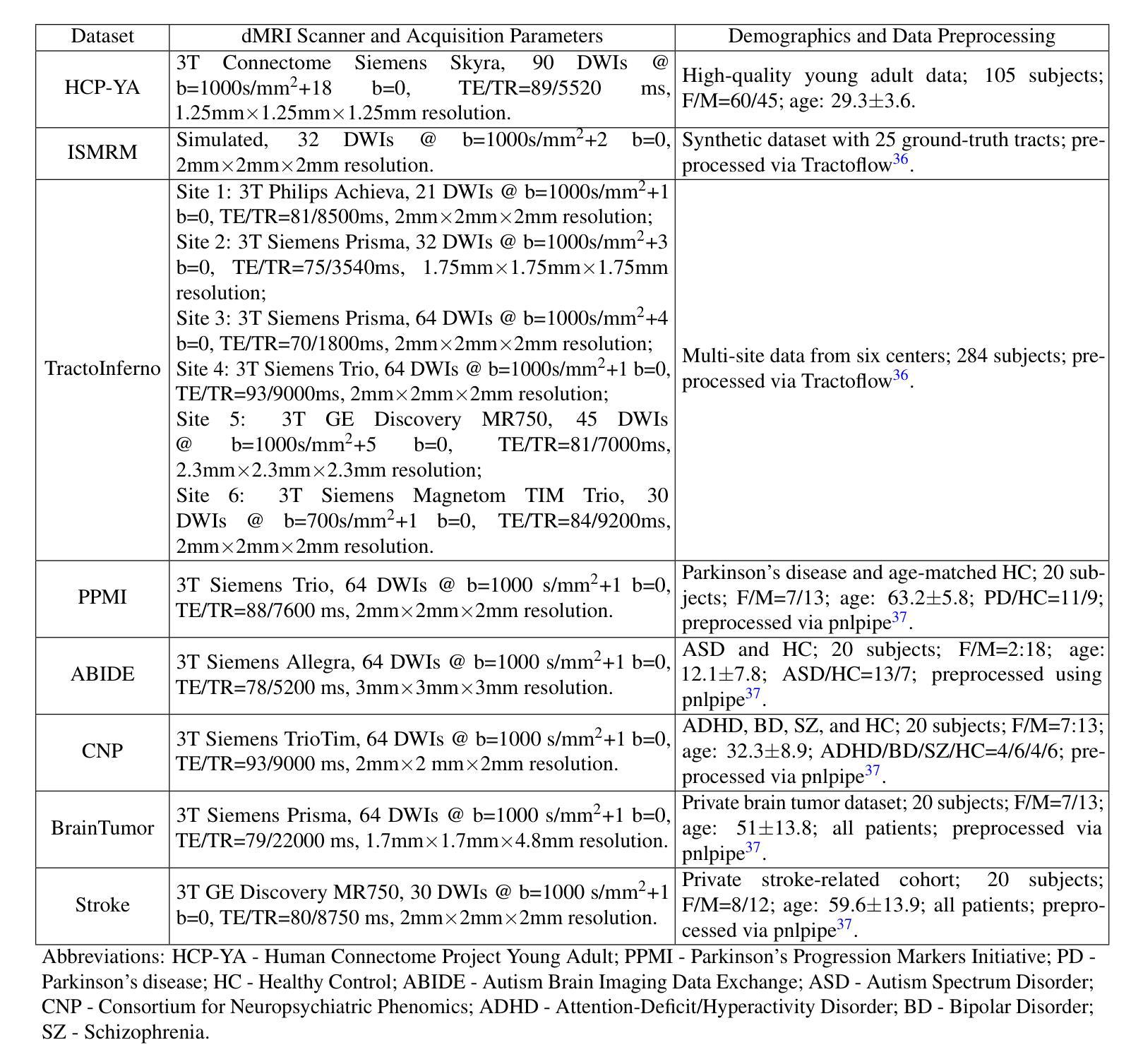
DocVCE: Diffusion-based Visual Counterfactual Explanations for Document Image Classification
Authors:Saifullah Saifullah, Stefan Agne, Andreas Dengel, Sheraz Ahmed
As black-box AI-driven decision-making systems become increasingly widespread in modern document processing workflows, improving their transparency and reliability has become critical, especially in high-stakes applications where biases or spurious correlations in decision-making could lead to serious consequences. One vital component often found in such document processing workflows is document image classification, which, despite its widespread use, remains difficult to explain. While some recent works have attempted to explain the decisions of document image classification models through feature-importance maps, these maps are often difficult to interpret and fail to provide insights into the global features learned by the model. In this paper, we aim to bridge this research gap by introducing generative document counterfactuals that provide meaningful insights into the model’s decision-making through actionable explanations. In particular, we propose DocVCE, a novel approach that leverages latent diffusion models in combination with classifier guidance to first generate plausible in-distribution visual counterfactual explanations, and then performs hierarchical patch-wise refinement to search for a refined counterfactual that is closest to the target factual image. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through a rigorous qualitative and quantitative assessment on 3 different document classification datasets – RVL-CDIP, Tobacco3482, and DocLayNet – and 3 different models – ResNet, ConvNeXt, and DiT – using well-established evaluation criteria such as validity, closeness, and realism. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first work to explore generative counterfactual explanations in document image analysis.
随着以人工智能驱动的决策系统在现代文档处理流程中的日益普及,提高其透明度和可靠性变得至关重要,特别是在高风险应用中,决策中的偏见或虚假关联可能会导致严重后果。在文档处理流程中经常可以发现一个重要的组件是文档图像分类,尽管其应用广泛,但其解释性仍然很难。虽然最近的一些研究尝试通过特征重要性图来解释文档图像分类模型的决策,但这些图通常很难解释,并且无法提供对模型所学习全局特征的见解。本文旨在通过引入生成文档反事实来填补这一研究空白,这些反事实提供了有关模型决策制定的有意义见解,并通过可操作的解释来提供有意义的见解。特别是,我们提出了一种名为DocVCE的新方法,该方法利用潜在扩散模型并结合分类器指导,首先生成合理的分布内视觉反事实解释,然后进行分层补丁式细化,以寻找最接近目标实际图像的精细反事实。我们在三个不同的文档分类数据集(RVL-CDIP、Tobacco3482和DocLayNet)和三个不同的模型(ResNet、ConvNeXt和DiT)上通过严格的定性和定量评估验证了我们的方法的有效性,评估标准包括有效性、接近性和现实性。据作者所知,这是首次在文档图像分析中探索生成反事实解释的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着AI驱动的决策系统在现代文档处理流程中的广泛应用,提高透明度和可靠性变得至关重要。本文提出了一种新的方法DocVCE,利用潜在扩散模型结合分类器指导,生成合理的视觉反事实解释,为文档图像分类模型的决策提供更可操作的解释。该方法通过层次化的补丁级优化,寻找最接近目标实际图像的反事实解释。通过在不同数据集和模型上的严格定性和定量分析,验证了该方法的有效性。这是首次在文档图像分析中探索生成反事实解释的工作。
Key Takeaways
- AI驱动的决策系统在现代文档处理流程中的重要性及其透明度和可靠性的需求。
- 文档图像分类在AI决策中的关键作用及其解释难度。
- 现有特征重要性图解释的不足,难以提供模型全局特征的洞察。
- 引入生成文档反事实解释的意义,为模型决策提供更可操作的解释。
- DocVCE方法利用潜在扩散模型和分类器指导生成视觉反事实解释。
- DocVCE方法通过层次化的补丁级优化寻找最接近目标实际图像的反事实。
点此查看论文截图

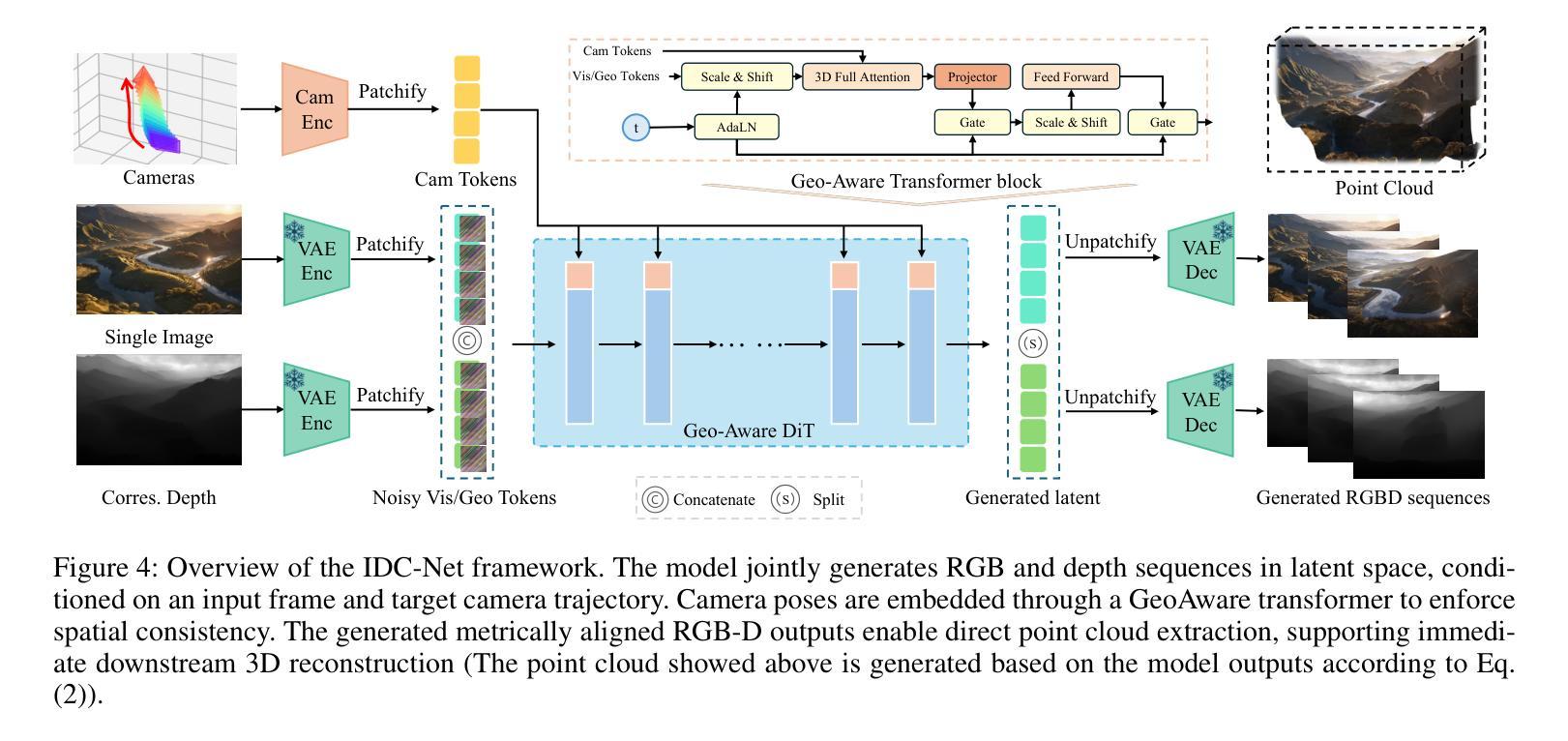
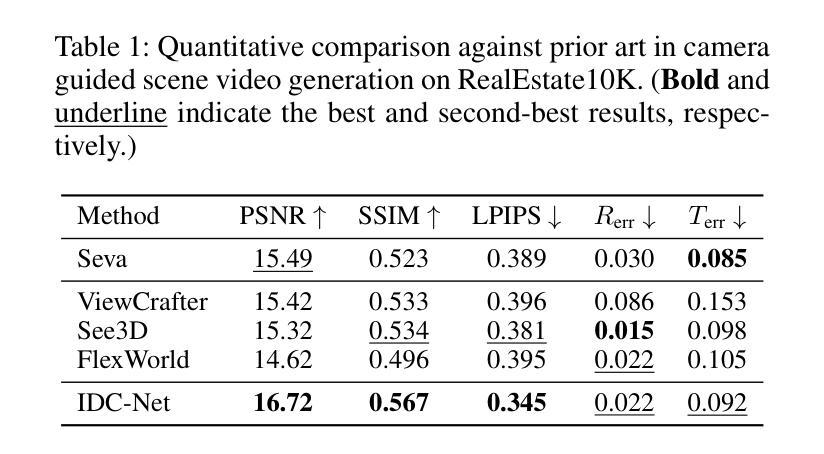
IDCNet: Guided Video Diffusion for Metric-Consistent RGBD Scene Generation with Precise Camera Control
Authors:Lijuan Liu, Wenfa Li, Dongbo Zhang, Shuo Wang, Shaohui Jiao
We present IDC-Net (Image-Depth Consistency Network), a novel framework designed to generate RGB-D video sequences under explicit camera trajectory control. Unlike approaches that treat RGB and depth generation separately, IDC-Net jointly synthesizes both RGB images and corresponding depth maps within a unified geometry-aware diffusion model. The joint learning framework strengthens spatial and geometric alignment across frames, enabling more precise camera control in the generated sequences. To support the training of this camera-conditioned model and ensure high geometric fidelity, we construct a camera-image-depth consistent dataset with metric-aligned RGB videos, depth maps, and accurate camera poses, which provides precise geometric supervision with notably improved inter-frame geometric consistency. Moreover, we introduce a geometry-aware transformer block that enables fine-grained camera control, enhancing control over the generated sequences. Extensive experiments show that IDC-Net achieves improvements over state-of-the-art approaches in both visual quality and geometric consistency of generated scene sequences. Notably, the generated RGB-D sequences can be directly feed for downstream 3D Scene reconstruction tasks without extra post-processing steps, showcasing the practical benefits of our joint learning framework. See more at https://idcnet-scene.github.io.
我们提出了IDC-Net(图像深度一致性网络),这是一个新型框架,旨在在明确的相机轨迹控制下生成RGB-D视频序列。不同于分别处理RGB和深度生成的方法,IDC-Net在一个统一的几何感知扩散模型中联合合成RGB图像和对应的深度图。联合学习框架加强了帧之间的空间和几何对齐,从而在生成的序列中实现了更精确的相机控制。为了支持这种相机条件模型的训练,并确保高几何保真度,我们构建了一个相机图像深度一致的数据集,其中包含度量对齐的RGB视频、深度图和精确的相机姿态,这提供了精确的几何监督,显著提高了帧间几何一致性。此外,我们还引入了一个几何感知的变压器块,实现了精细的相机控制,增强了生成序列的控制能力。大量实验表明,IDC-Net在视觉质量和生成场景序列的几何一致性方面都优于最先进的方法。值得注意的是,生成的RGB-D序列可以直接用于下游的3D场景重建任务,而无需额外的后处理步骤,展示了我们的联合学习框架的实际效益。更多信息请参见https://idcnet-scene.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7 figures
Summary:
IDC-Net是一个新颖的框架,用于在明确的相机轨迹控制下生成RGB-D视频序列。该框架在统一的空间几何感知扩散模型中联合合成RGB图像和对应的深度图,加强了帧间的空间几何对齐,使生成的序列具有更精确的相机控制。此外,构建了一个支持该相机条件模型的训练集,通过引入几何感知转换器块实现精细的相机控制。IDC-Net提高了视觉质量和场景序列的几何一致性,生成的RGB-D序列可直接用于下游的3D场景重建任务。
Key Takeaways:
- IDC-Net是一个用于生成RGB-D视频序列的统一框架。
- 该框架通过联合学习强化空间几何对齐,提高帧间一致性。
- 构建了支持相机条件模型的训练集,提供精确的几何监督。
- 引入几何感知转换器块实现精细的相机控制。
- IDC-Net在视觉质量和几何一致性上实现了对先进方法的改进。
- 生成的RGB-D序列可直接用于下游的3D场景重建任务。
点此查看论文截图



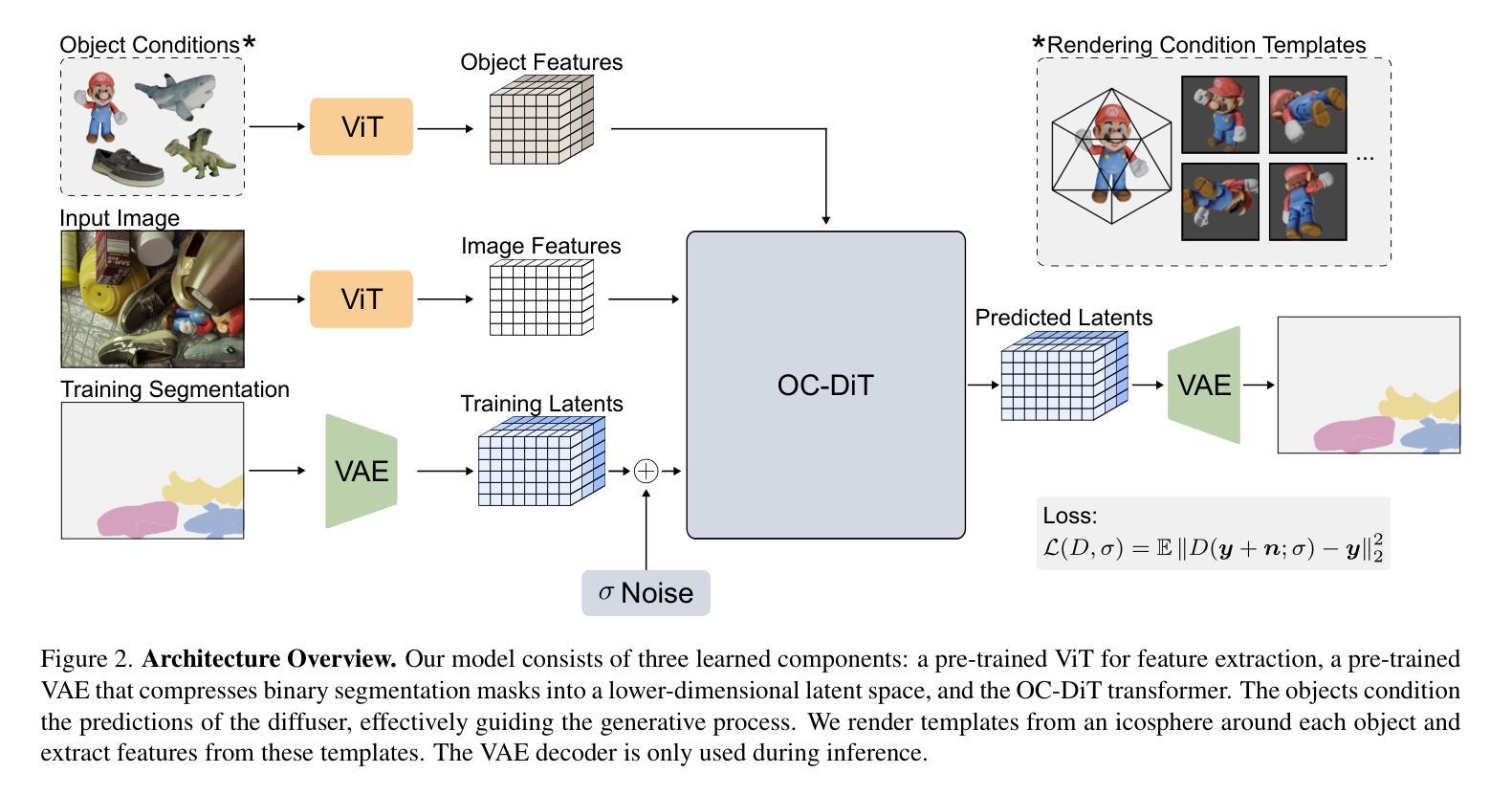
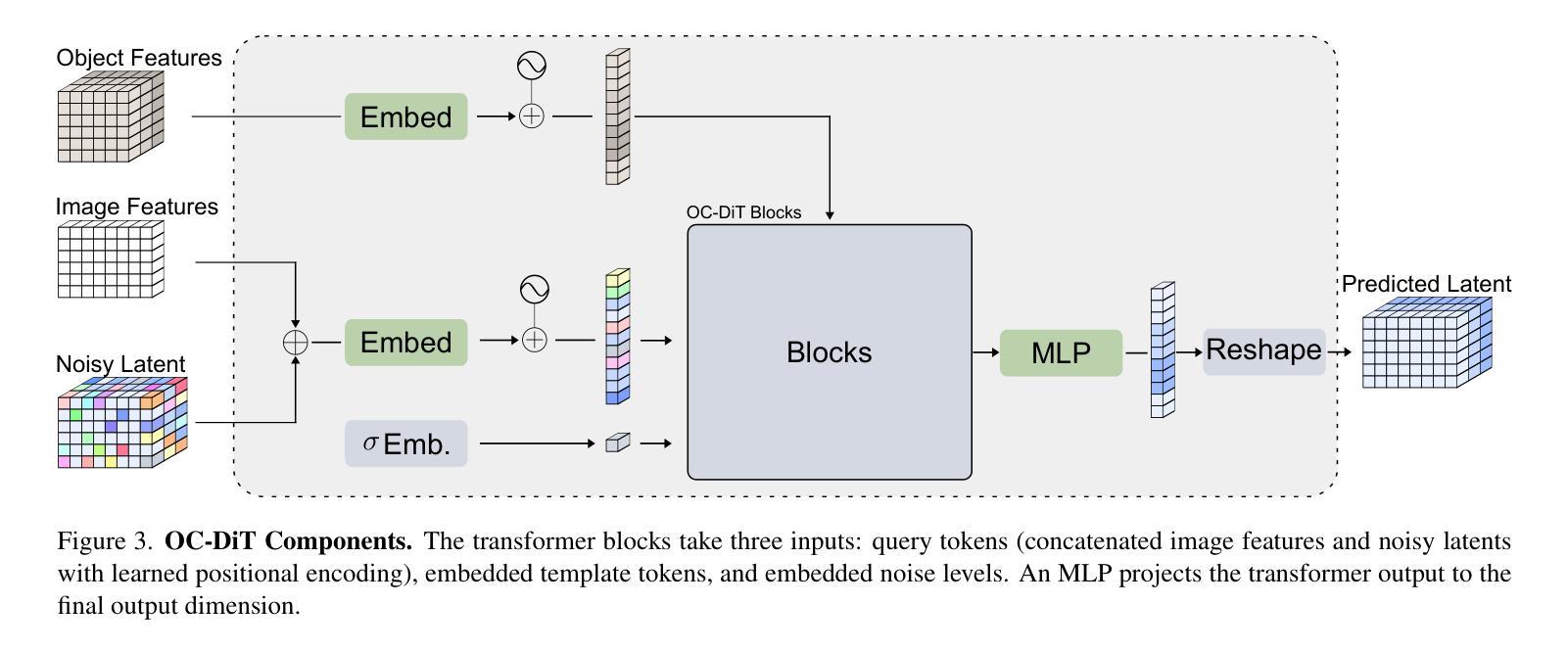
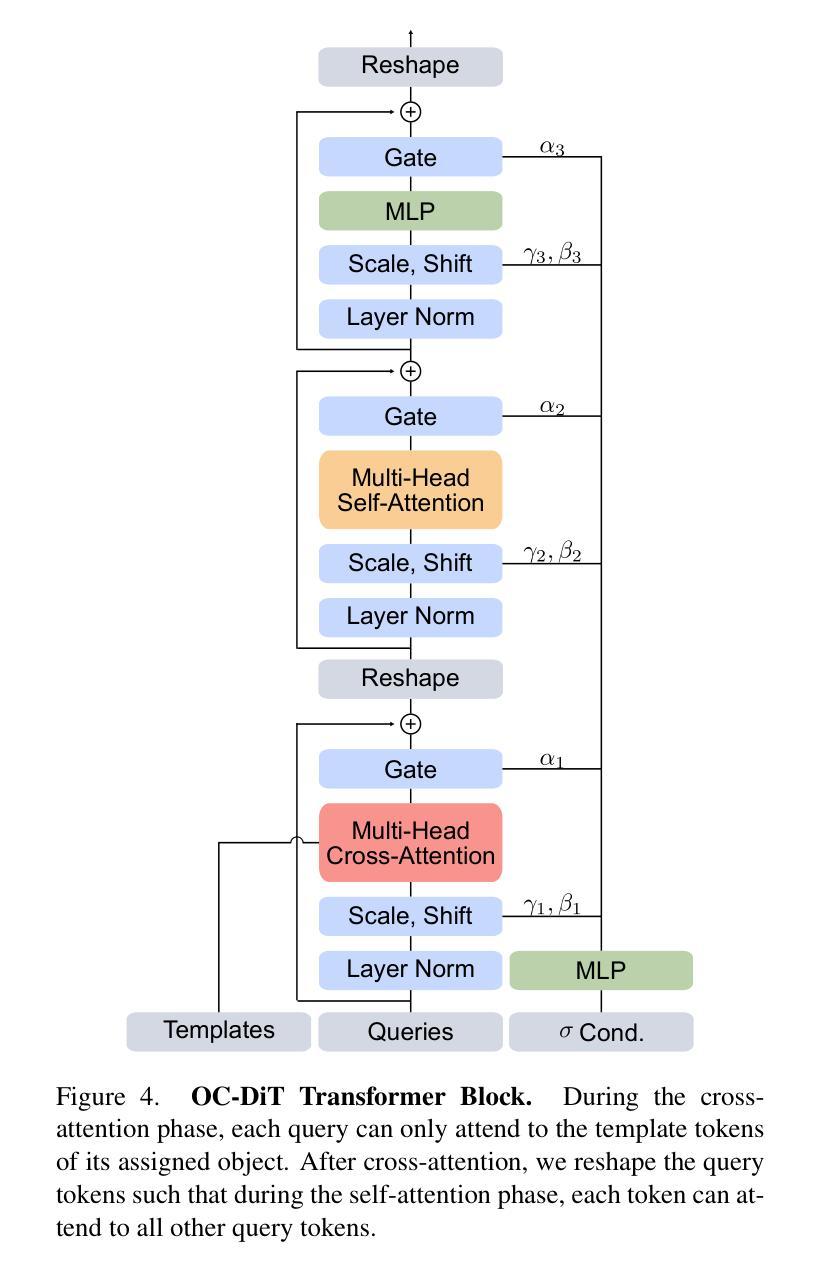
Conditional Latent Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Instance Segmentation
Authors:Maximilian Ulmer, Wout Boerdijk, Rudolph Triebel, Maximilian Durner
This paper presents OC-DiT, a novel class of diffusion models designed for object-centric prediction, and applies it to zero-shot instance segmentation. We propose a conditional latent diffusion framework that generates instance masks by conditioning the generative process on object templates and image features within the diffusion model’s latent space. This allows our model to effectively disentangle object instances through the diffusion process, which is guided by visual object descriptors and localized image cues. Specifically, we introduce two model variants: a coarse model for generating initial object instance proposals, and a refinement model that refines all proposals in parallel. We train these models on a newly created, large-scale synthetic dataset comprising thousands of high-quality object meshes. Remarkably, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple challenging real-world benchmarks, without requiring any retraining on target data. Through comprehensive ablation studies, we demonstrate the potential of diffusion models for instance segmentation tasks.
本文介绍了OC-DiT,这是一种针对对象中心预测设计的新型扩散模型,并将其应用于零样本实例分割。我们提出了一种条件潜在扩散框架,通过在扩散模型的潜在空间中以对象模板和图像特征为条件生成实例掩模。这使我们的模型能够通过由视觉对象描述符和局部图像线索引导的扩散过程有效地分离对象实例。具体来说,我们介绍了两种模型变体:一种用于生成初始对象实例提议的粗略模型,以及一种用于并行细化所有提议的精细模型。我们在新创建的大规模合成数据集上训练这些模型,该数据集包含数千个高质量对象网格。值得注意的是,我们的模型在多个具有挑战性的现实世界基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,而无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练。通过全面的消融研究,我们展示了扩散模型在实例分割任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了OC-DiT,一种用于对象中心预测的新型扩散模型,并应用于零样本实例分割。通过条件潜在扩散框架,生成对象掩膜,该框架在扩散模型的潜在空间中以对象模板和图像特征为条件生成对象掩膜。此模型能有效通过扩散过程分离对象实例,由视觉对象描述器和局部图像线索引导。包括粗模型用于生成初始对象实例提案和细化模型,后者并行细化所有提案。模型在新创的大规模合成数据集上进行训练,包含数千个高质量对象网格。在多个具有挑战性的真实世界基准测试中,模型取得了最先进的性能,无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练。通过全面的消融研究,证明了扩散模型在实例分割任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- OC-DiT是一种新型的扩散模型,专门用于对象中心预测,特别是零样本实例分割。
- 提出了条件潜在扩散框架,能够在扩散模型的潜在空间中以对象模板和图像特征为条件生成实例掩膜。
- 模型通过扩散过程有效地分离对象实例,这一过程由视觉对象描述器和局部图像线索引导。
- 模型包括粗模型和细化模型两个版本,分别用于生成初始对象实例提案和细化所有提案。
- 模型在新创建的大规模合成数据集上进行训练,该数据集包含数千个高质量对象网格。
- 在多个基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,且无需在目标数据上进行任何重新训练。
点此查看论文截图

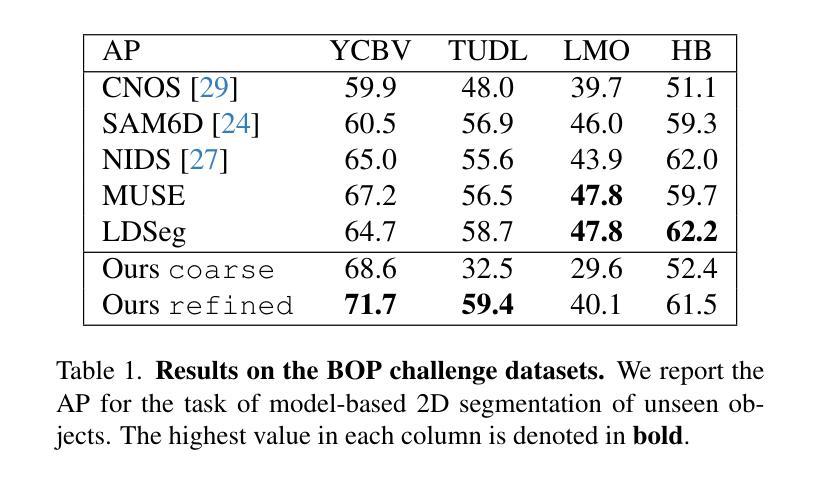
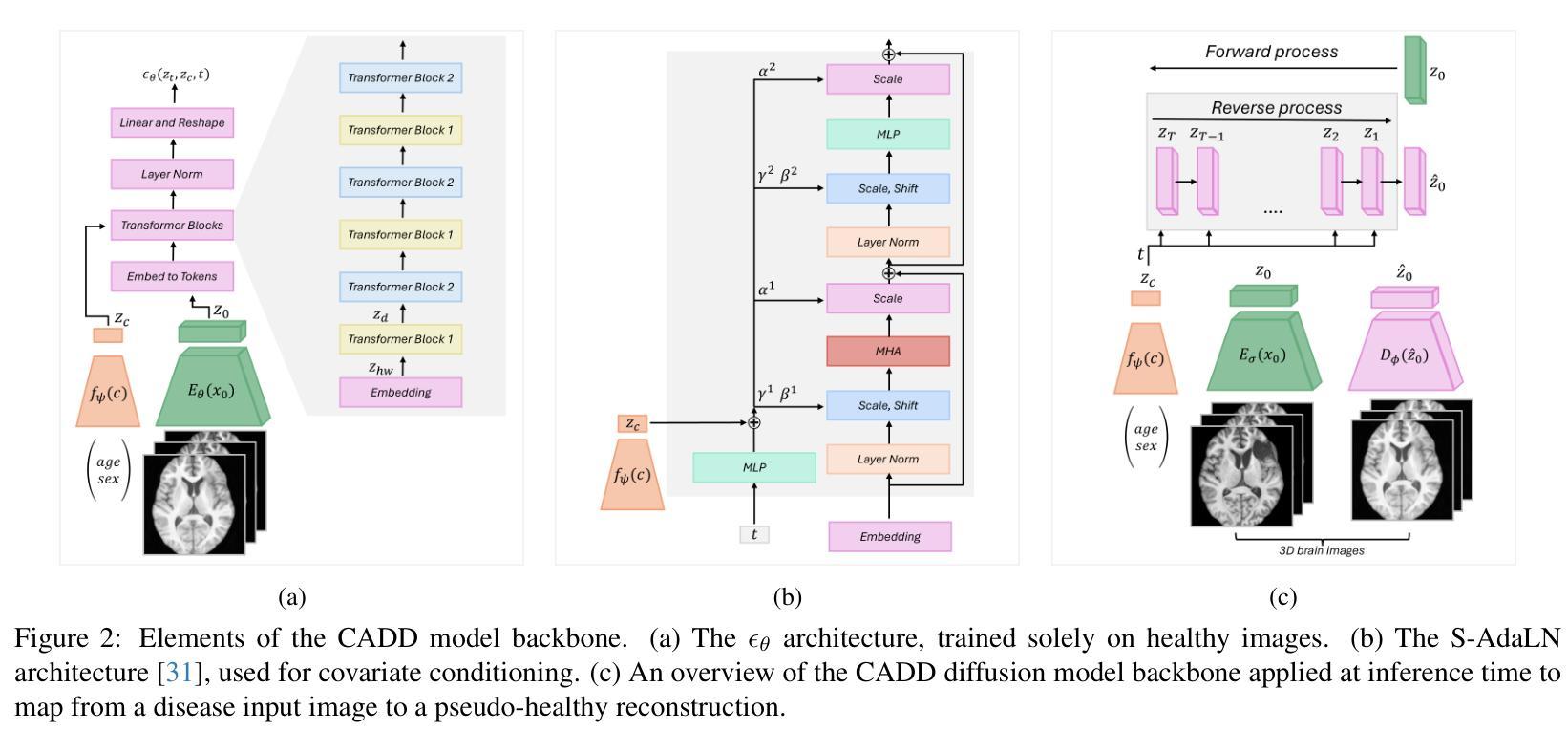
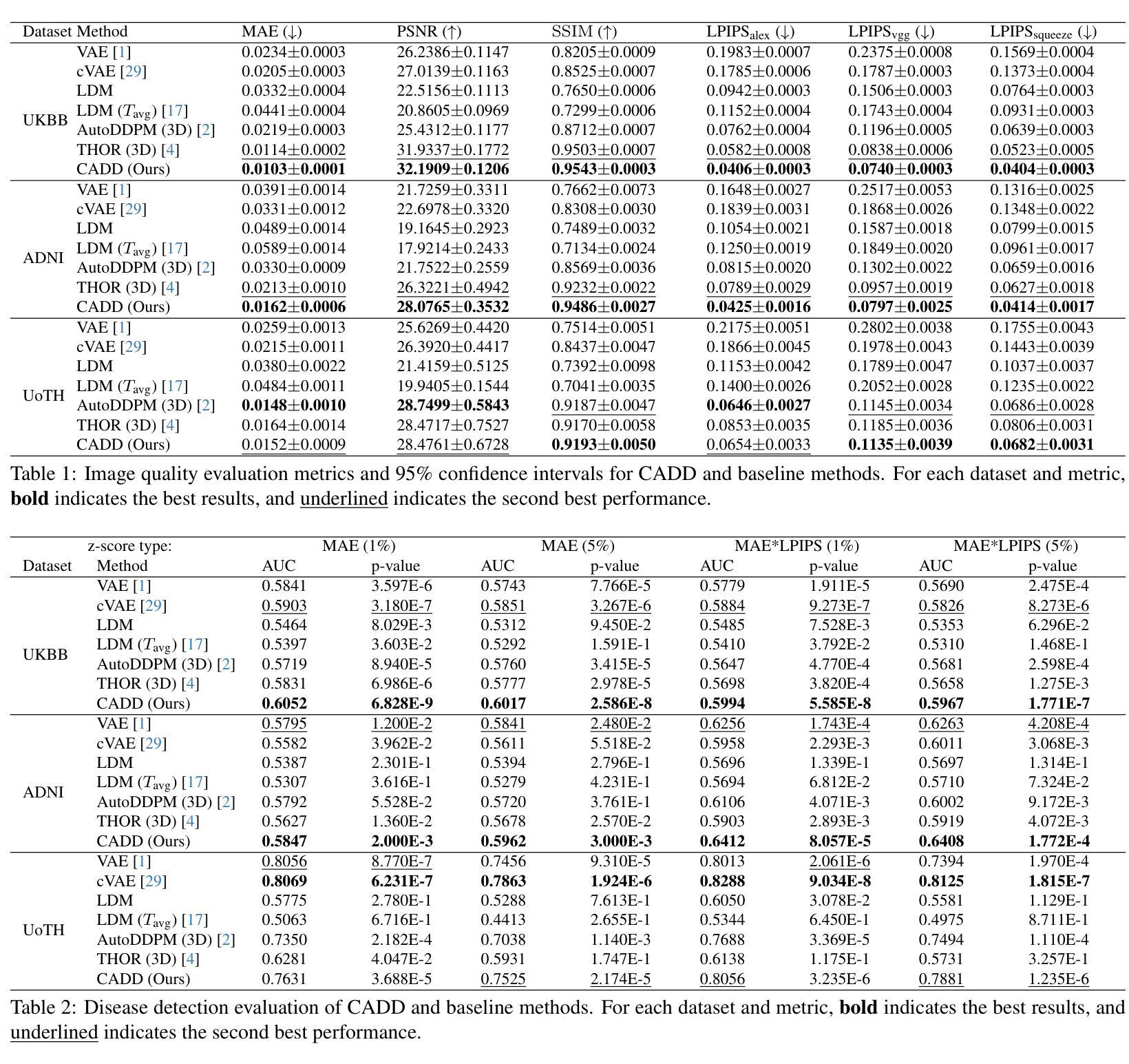
CADD: Context aware disease deviations via restoration of brain images using normative conditional diffusion models
Authors:Ana Lawry Aguila, Ayodeji Ijishakin, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Tomomi Takenaga, Yukihiro Nomura, Takeharu Yoshikawa, Osamu Abe, Shouhei Hanaoka
Applying machine learning to real-world medical data, e.g. from hospital archives, has the potential to revolutionize disease detection in brain images. However, detecting pathology in such heterogeneous cohorts is a difficult challenge. Normative modeling, a form of unsupervised anomaly detection, offers a promising approach to studying such cohorts where the ``normal’’ behavior is modeled and can be used at subject level to detect deviations relating to disease pathology. Diffusion models have emerged as powerful tools for anomaly detection due to their ability to capture complex data distributions and generate high-quality images. Their performance relies on image restoration; differences between the original and restored images highlight potential abnormalities. However, unlike normative models, these diffusion model approaches do not incorporate clinical information which provides important context to guide the disease detection process. Furthermore, standard approaches often poorly restore healthy regions, resulting in poor reconstructions and suboptimal detection performance. We present CADD, the first conditional diffusion model for normative modeling in 3D images. To guide the healthy restoration process, we propose a novel inference inpainting strategy which balances anomaly removal with retention of subject-specific features. Evaluated on three challenging datasets, including clinical scans, which may have lower contrast, thicker slices, and motion artifacts, CADD achieves state-of-the-art performance in detecting neurological abnormalities in heterogeneous cohorts.
将机器学习应用于医院档案等真实世界医疗数据,有可能革新脑图像的疾病检测。然而,在如此多样化的群体中检测病理学是一项艰巨的挑战。规范建模是一种无监督的异常检测法,在研究此类群体时具有广阔的发展前景,可对“正常”行为进行建模,并以受试者水平检测与疾病病理学相关的偏差。扩散模型因能够捕捉复杂的数据分布并生成高质量图像而成为异常检测的有力工具。其性能依赖于图像修复;原始图像和修复图像之间的差异突出了潜在的异常。然而,与规范模型不同,这些扩散模型方法并未融入临床信息,而后者为引导疾病检测过程提供了重要的背景信息。此外,标准方法往往不能很好地修复健康区域,导致重建质量差和检测性能不佳。我们首次推出用于三维图像规范建模的条件扩散模型CADD。为了引导健康的修复过程,我们提出了一种新型的推理补全策略,该策略在消除异常与保留受试者特定特征之间取得了平衡。在包括可能存在低对比度、厚切片和运动伪影的临床扫描在内的三个具有挑战性的数据集上评估,CADD在检测异质人群中神经异常方面取得了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
应用机器学习于真实世界医疗数据,如医院档案,有潜力革新脑图像疾病检测。然而,在如此多样化的群体中检测病理是一个巨大的挑战。规范建模提供了一种研究此类群体的有前景的方法,可以模拟“正常”行为并在主体层面检测与疾病病理相关的偏差。扩散模型因能够捕捉复杂数据分布并生成高质量图像而成为一种强大的异常检测工具。其性能依赖于图像修复;原始和修复图像之间的差异突出了潜在的异常。然而,扩散模型方法并未融入临床信息,这对引导疾病检测过程至关重要。此外,标准方法常常不能很好地修复健康区域,导致重建质量差和检测性能不佳。本研究提出了首个用于3D图像规范建模的条件扩散模型CADD。为了引导健康的修复过程,我们提出了一种新型推理补全策略,该策略在消除异常与保留主体特定特征之间取得了平衡。在包括可能存在低对比度、厚切片和运动伪影的临床扫描在内的三个具有挑战性的数据集上的评估结果表明,CADD在检测异质人群中的神经异常方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习方法应用于医疗数据有潜力革新疾病检测。
- 扩散模型可捕捉复杂数据分布并用于异常检测。
- 扩散模型在脑图像疾病检测中面临挑战,如数据异质性、图像修复质量等。
- CADD是首个用于3D图像规范建模的条件扩散模型。
- CADD结合了一种新的推理补全策略,以平衡异常消除和主体特征保留。
- CADD在多个具有挑战性的数据集上实现了最先进的神经异常检测性能。
点此查看论文截图


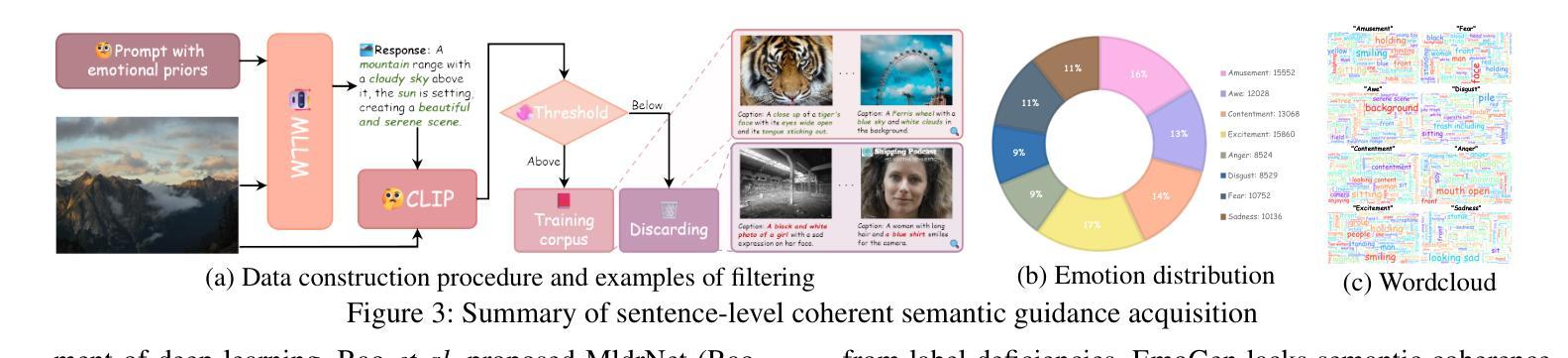
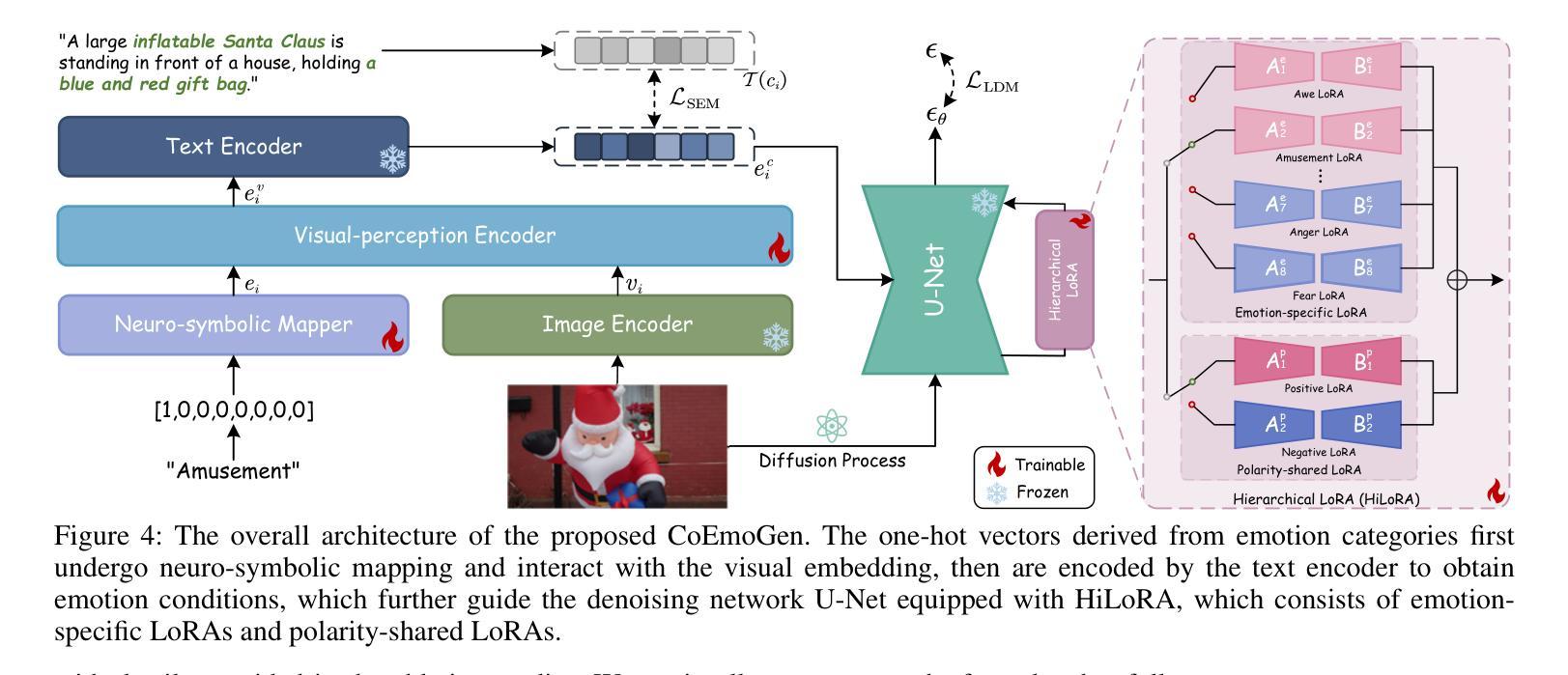
CoEmoGen: Towards Semantically-Coherent and Scalable Emotional Image Content Generation
Authors:Kaishen Yuan, Yuting Zhang, Shang Gao, Yijie Zhu, Wenshuo Chen, Yutao Yue
Emotional Image Content Generation (EICG) aims to generate semantically clear and emotionally faithful images based on given emotion categories, with broad application prospects. While recent text-to-image diffusion models excel at generating concrete concepts, they struggle with the complexity of abstract emotions. There have also emerged methods specifically designed for EICG, but they excessively rely on word-level attribute labels for guidance, which suffer from semantic incoherence, ambiguity, and limited scalability. To address these challenges, we propose CoEmoGen, a novel pipeline notable for its semantic coherence and high scalability. Specifically, leveraging multimodal large language models (MLLMs), we construct high-quality captions focused on emotion-triggering content for context-rich semantic guidance. Furthermore, inspired by psychological insights, we design a Hierarchical Low-Rank Adaptation (HiLoRA) module to cohesively model both polarity-shared low-level features and emotion-specific high-level semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate CoEmoGen’s superiority in emotional faithfulness and semantic coherence from quantitative, qualitative, and user study perspectives. To intuitively showcase scalability, we curate EmoArt, a large-scale dataset of emotionally evocative artistic images, providing endless inspiration for emotion-driven artistic creation. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/yuankaishen2001/CoEmoGen.
情感图像内容生成(EICG)旨在根据给定的情感类别生成语义清晰、情感真实的图像,具有广泛的应用前景。虽然最近的文本到图像扩散模型在生成具体概念方面表现出色,但它们难以处理抽象情感的复杂性。也有一些专门为EICG设计的方法出现,但它们过于依赖词级属性标签作为指导,这会导致语义不一致、模糊和有限的扩展性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了CoEmoGen,这是一个新的管道,以其语义连贯性和高可扩展性而著称。具体来说,我们利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)构建高质量的专注于情感触发内容的标题,以提供丰富的语义指导。此外,我们受到心理洞察的启发,设计了一个分层低秩适应(HiLoRA)模块,以协调地建模共享极性的低级别特征和情感特定的高级语义。大量实验表明,从定量、定性和用户研究的角度,CoEmoGen在情感真实性和语义连贯性方面表现出卓越的性能。为了直观地展示可扩展性,我们策划了EmoArt,这是一个情感激发艺术图像的大规模数据集,为情感驱动的艺术创作提供了无尽的灵感。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/yuankaishen200 结尾处找到。这里需要您自己提供网站地址链接或者网站全称等信息进行完整表述。这个项目的介绍及代码等相关资源可供查询和使用。在这里强烈推荐的英文网址与实际应用中的搜索结果仅供参考作用哦,还需要您对最终网站资源的应用风险做提前的预测与预防准备。我们在链接中包含有关模型的训练和实现的详细指导文档、大型情感图像数据集以及相关工具包的下载方式等信息,为那些希望在图像内容生成方面展开研究的人士提供了巨大的帮助和支持。当然我们会遵循特定的社会期望和行业规则来做后续的推进哦!如果有关于数据的标注及理解的需求也可向我反馈的哈。此外在使用代码的时候可能会遇到一些小问题等难以预料的意外状况。为了更好地优化流程建议您在执行复杂操作时安排一名相关领域的专业人员予以陪同协作指导,便于做出必要响应等并及时为您答疑解惑和妥善应对难题以确保项目实施过程中的顺利推进哦!希望以上信息能够为您提供有价值的参考和帮助!期待您的进一步合作和交流!
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个名为CoEmoGen的新型情感图像生成框架,旨在生成语义清晰、情感真实的图像。该框架通过利用多模态大型语言模型构建高质量的情感触发内容描述,实现丰富的语义指导。同时,结合心理学原理设计的分层低秩适应模块,能同时建模共享极性低层次特征和情感特定高层次语义。实验证明,CoEmoGen在情感真实性和语义连贯性方面表现优异,且具有良好的可扩展性。此外,还推出了一个大型情感艺术图像数据集EmoArt,为情感驱动的艺术创作提供无尽灵感。
Key Takeaways
- Emotional Image Content Generation (EICG)的目标是生成基于给定情感类别的语义清晰、情感真实的图像。
- 现有文本到图像的扩散模型在抽象情感复杂性方面存在挑战。
- CoEmoGen框架利用多模态大型语言模型构建高质量的情感触发内容描述,实现丰富的语义指导。
- CoEmoGen设计了一个分层低秩适应模块,以建模共享极性低层次特征和情感特定高层次语义。
- 实验证明CoEmoGen在情感真实性和语义连贯性方面表现优异。
- CoEmoGen具有良好的可扩展性,并推出了一个大型情感艺术图像数据集EmoArt。
点此查看论文截图



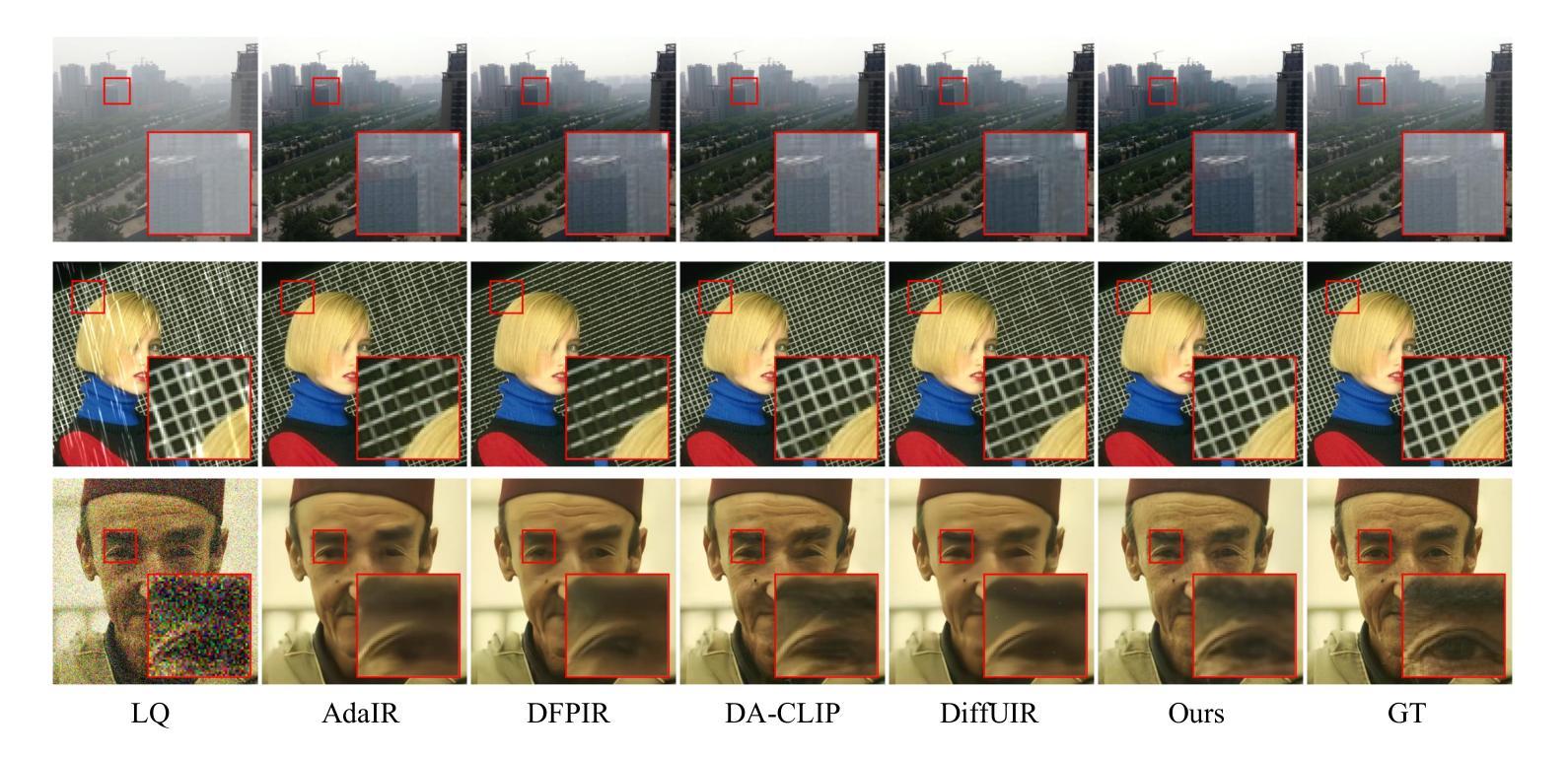
Diffusion Once and Done: Degradation-Aware LoRA for Efficient All-in-One Image Restoration
Authors:Ni Tang, Xiaotong Luo, Zihan Cheng, Liangtai Zhou, Dongxiao Zhang, Yanyun Qu
Diffusion models have revealed powerful potential in all-in-one image restoration (AiOIR), which is talented in generating abundant texture details. The existing AiOIR methods either retrain a diffusion model or fine-tune the pretrained diffusion model with extra conditional guidance. However, they often suffer from high inference costs and limited adaptability to diverse degradation types. In this paper, we propose an efficient AiOIR method, Diffusion Once and Done (DOD), which aims to achieve superior restoration performance with only one-step sampling of Stable Diffusion (SD) models. Specifically, multi-degradation feature modulation is first introduced to capture different degradation prompts with a pretrained diffusion model. Then, parameter-efficient conditional low-rank adaptation integrates the prompts to enable the fine-tuning of the SD model for adapting to different degradation types. Besides, a high-fidelity detail enhancement module is integrated into the decoder of SD to improve structural and textural details. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing diffusion-based restoration approaches in both visual quality and inference efficiency.
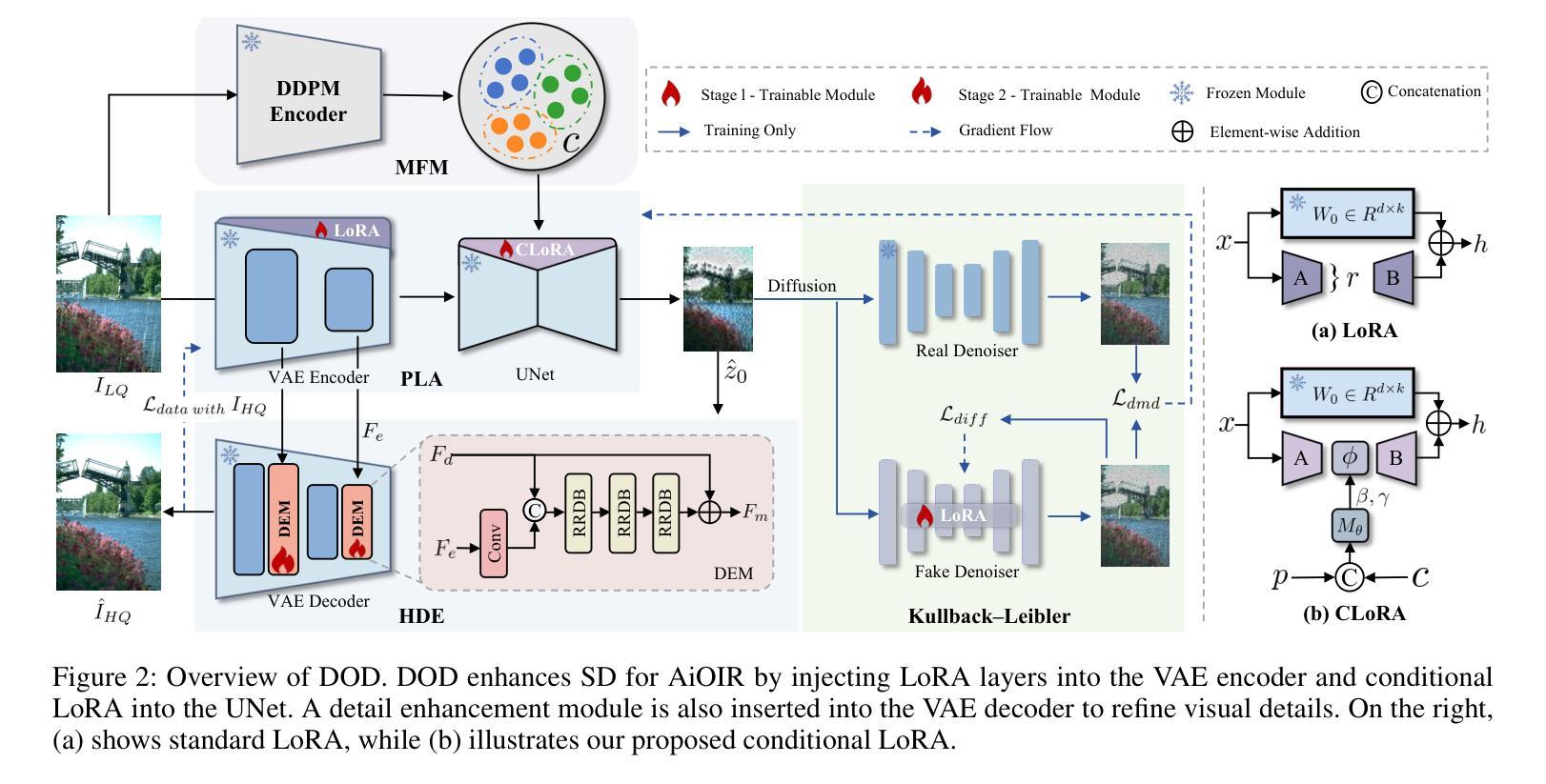
扩散模型在全能图像修复(AiOIR)中展现了强大的潜力,该技术在生成丰富纹理细节方面表现出色。现有的AiOIR方法要么重新训练扩散模型,要么使用额外的条件指导对预训练的扩散模型进行微调。然而,它们常常面临推理成本高和对各种退化类型适应性有限的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种高效的AiOIR方法,即“一次扩散完成”(DOD),旨在通过稳定扩散(SD)模型的一次步采样实现出色的修复性能。具体来说,首先引入多退化特征调制,使用预训练的扩散模型捕捉不同的退化提示。然后,通过参数高效的条件低秩适配,将提示集成在一起,使SD模型能够适应不同的退化类型。此外,还将高保真细节增强模块集成到SD的解码器中,以提高结构和纹理细节。实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量和推理效率方面都优于现有的基于扩散的修复方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
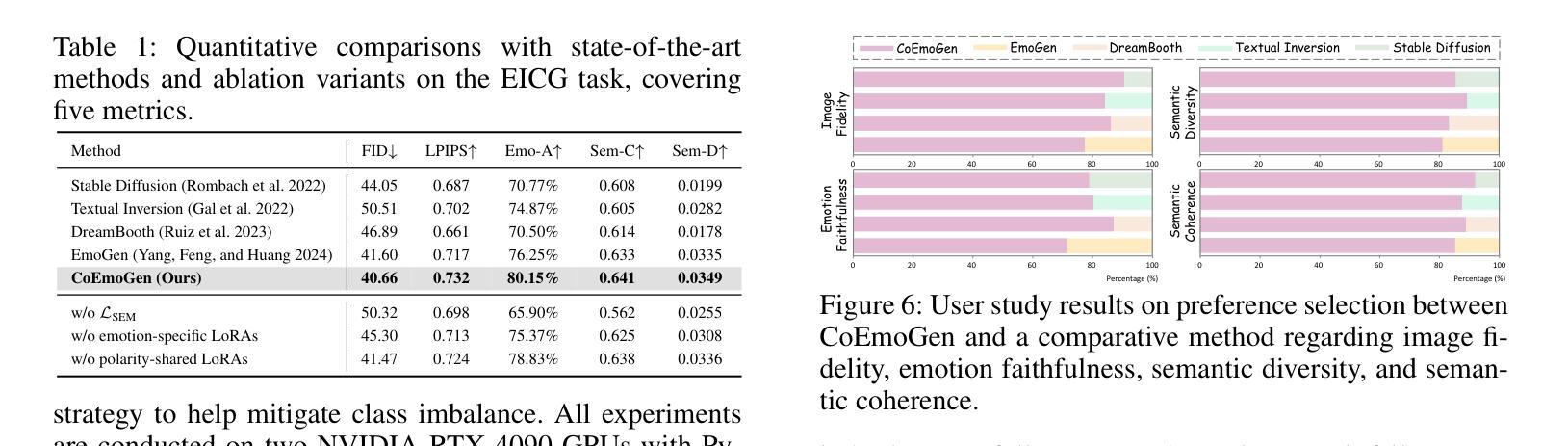
扩散模型在全能图像恢复(AiOIR)中展现出强大的潜力,能够生成丰富的纹理细节。现有AiOIR方法要么重新训练扩散模型,要么使用额外的条件指导对预训练扩散模型进行微调。然而,它们常常面临高推理成本和对各种退化类型适应性有限的问题。本文提出了一种高效的AiOIR方法——一次完成扩散(DOD),旨在通过稳定扩散(SD)模型的一次采样步骤实现出色的恢复性能。具体来说,首先引入多退化特征调制来捕捉不同的退化提示并使用预训练的扩散模型。然后,通过参数有效的条件低秩适应来整合这些提示,使SD模型能够适应不同的退化类型。此外,将高保真细节增强模块集成到SD的解码器中,以提高结构和纹理细节。实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量和推理效率方面均优于现有的扩散恢复方法。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在全能图像恢复(AiOIR)中展现出强大的潜力,能够生成丰富的纹理细节。
- 现有AiOIR方法面临高推理成本和对多种退化类型适应性有限的问题。
- 提出了一种高效的AiOIR方法——一次完成扩散(DOD),通过稳定扩散(SD)模型的一次采样步骤实现出色的恢复性能。
- 多退化特征调制用于捕捉不同的退化提示并使用预训练扩散模型。
- 参数有效的条件低秩适应能够整合提示并适应不同的退化类型。
- 将高保真细节增强模块集成到SD解码器中,提高结构和纹理细节的恢复。
- 实验表明,DOD方法在视觉质量和推理效率方面优于现有扩散恢复方法。
点此查看论文截图

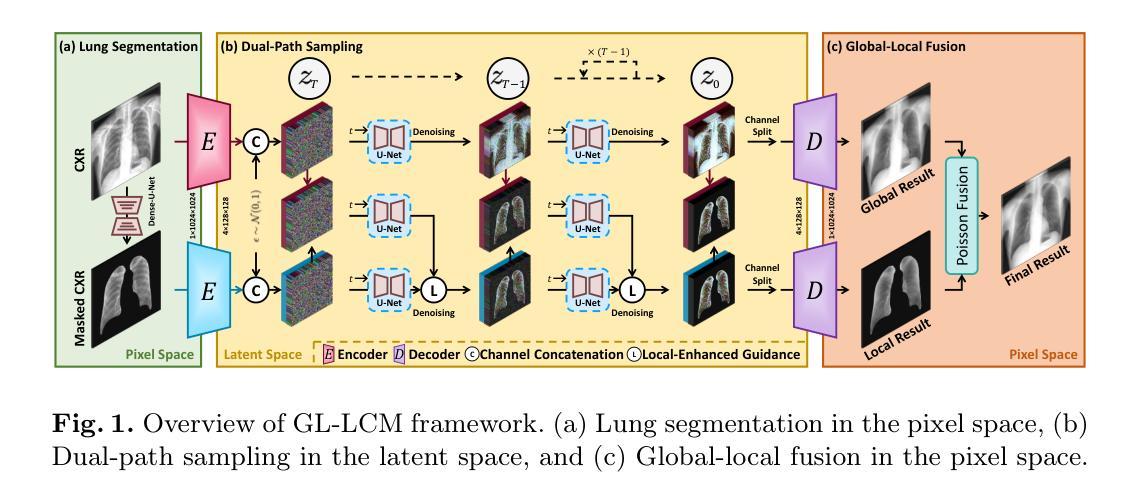
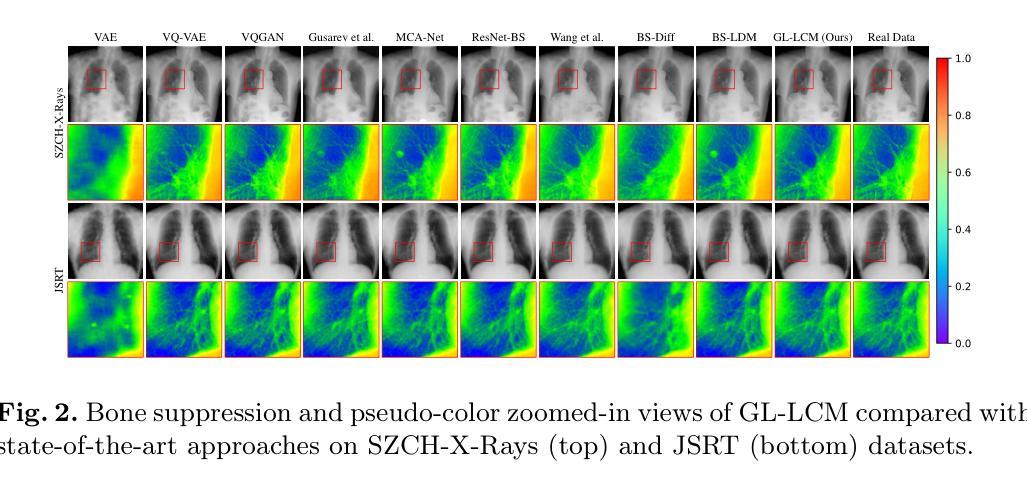
GL-LCM: Global-Local Latent Consistency Models for Fast High-Resolution Bone Suppression in Chest X-Ray Images
Authors:Yifei Sun, Zhanghao Chen, Hao Zheng, Yuqing Lu, Lixin Duan, Fenglei Fan, Ahmed Elazab, Xiang Wan, Changmiao Wang, Ruiquan Ge
Chest X-Ray (CXR) imaging for pulmonary diagnosis raises significant challenges, primarily because bone structures can obscure critical details necessary for accurate diagnosis. Recent advances in deep learning, particularly with diffusion models, offer significant promise for effectively minimizing the visibility of bone structures in CXR images, thereby improving clarity and diagnostic accuracy. Nevertheless, existing diffusion-based methods for bone suppression in CXR imaging struggle to balance the complete suppression of bones with preserving local texture details. Additionally, their high computational demand and extended processing time hinder their practical use in clinical settings. To address these limitations, we introduce a Global-Local Latent Consistency Model (GL-LCM) architecture. This model combines lung segmentation, dual-path sampling, and global-local fusion, enabling fast high-resolution bone suppression in CXR images. To tackle potential boundary artifacts and detail blurring in local-path sampling, we further propose Local-Enhanced Guidance, which addresses these issues without additional training. Comprehensive experiments on a self-collected dataset SZCH-X-Rays, and the public dataset JSRT, reveal that our GL-LCM delivers superior bone suppression and remarkable computational efficiency, significantly outperforming several competitive methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/diaoquesang/GL-LCM.
胸部X射线(CXR)影像在肺部诊断中面临重大挑战,主要是因为骨骼结构可能会掩盖准确诊断所需的关键细节。最近深度学习的进步,特别是扩散模型,为有效减少CXR图像中骨骼结构的可见性提供了巨大潜力,从而提高了清晰度和诊断准确性。然而,现有的基于扩散的CXR成像中骨骼抑制方法很难在完全抑制骨骼与保留局部纹理细节之间取得平衡。此外,它们的高计算需求和较长的处理时间阻碍了其在临床环境中的实际应用。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了全球局部潜在一致性模型(GL-LCM)架构。该模型结合了肺部分割、双路径采样和全局本地融合,能够在CXR图像中实现快速高分辨率的骨骼抑制。为了解决局部路径采样中可能出现的边界伪影和细节模糊问题,我们进一步提出了局部增强指导,无需额外训练即可解决这些问题。在自收集的SZCH-X射线数据集和公共JSRT数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的GL-LCM在骨骼抑制方面表现出卓越性能,并且计算效率极高,显著优于几种竞争方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/diaoquesang/GL-LCM上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
使用深度学习扩散模型解决胸部X光影像诊断中的骨骼结构遮挡问题,提出一种结合肺部分割、双路径采样和全局-局部融合的全局局部潜在一致性模型(GL-LCM)。该模型可实现快速高分辨率的骨骼抑制,且计算效率高,在自我收集的SZCH-X-Rays和公共JSRT数据集上的表现优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 胸部X光影像诊断中,骨骼结构遮挡关键细节,影响诊断准确性。
- 深度学习扩散模型在减少骨骼结构可见性方面展现潜力。
- 现有扩散模型在骨骼抑制和保留局部纹理细节之间难以平衡。
- 提出的GL-LCM模型结合肺部分割、双路径采样和全局-局部融合,实现快速高分辨率的骨骼抑制。
- GL-LCM模型通过局部增强引导解决边界伪影和细节模糊问题,无需额外训练。
- 在SZCH-X-Rays和JSRT数据集上的实验显示GL-LCM模型在骨骼抑制和计算效率方面表现优越。
- GL-LCM模型的代码已公开可获取。
点此查看论文截图

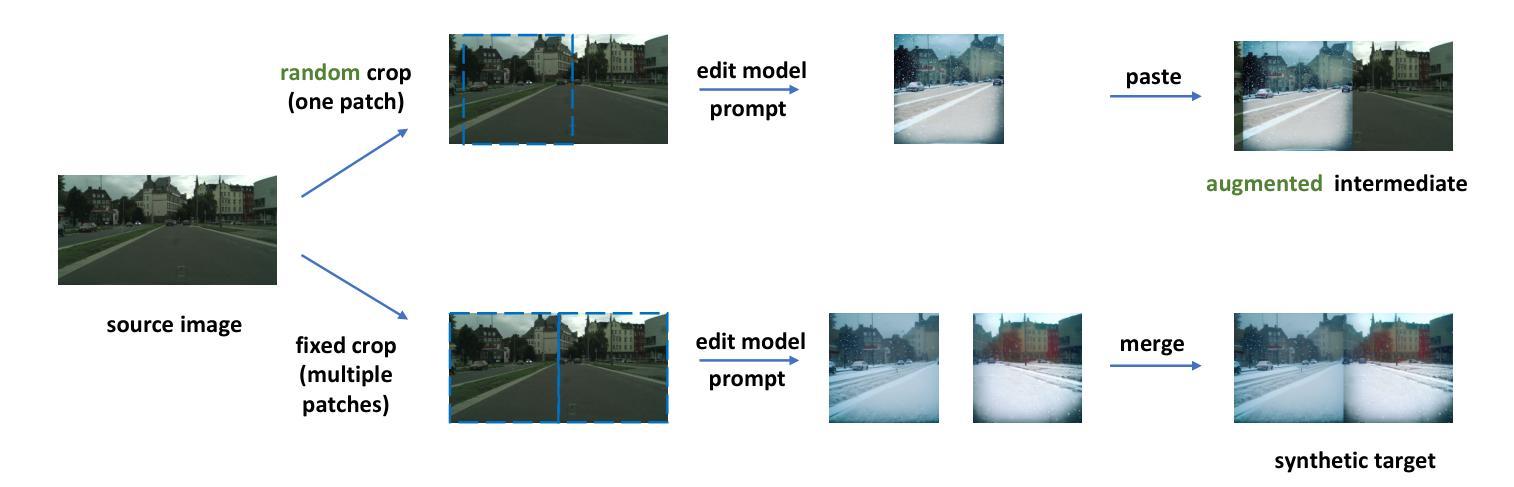
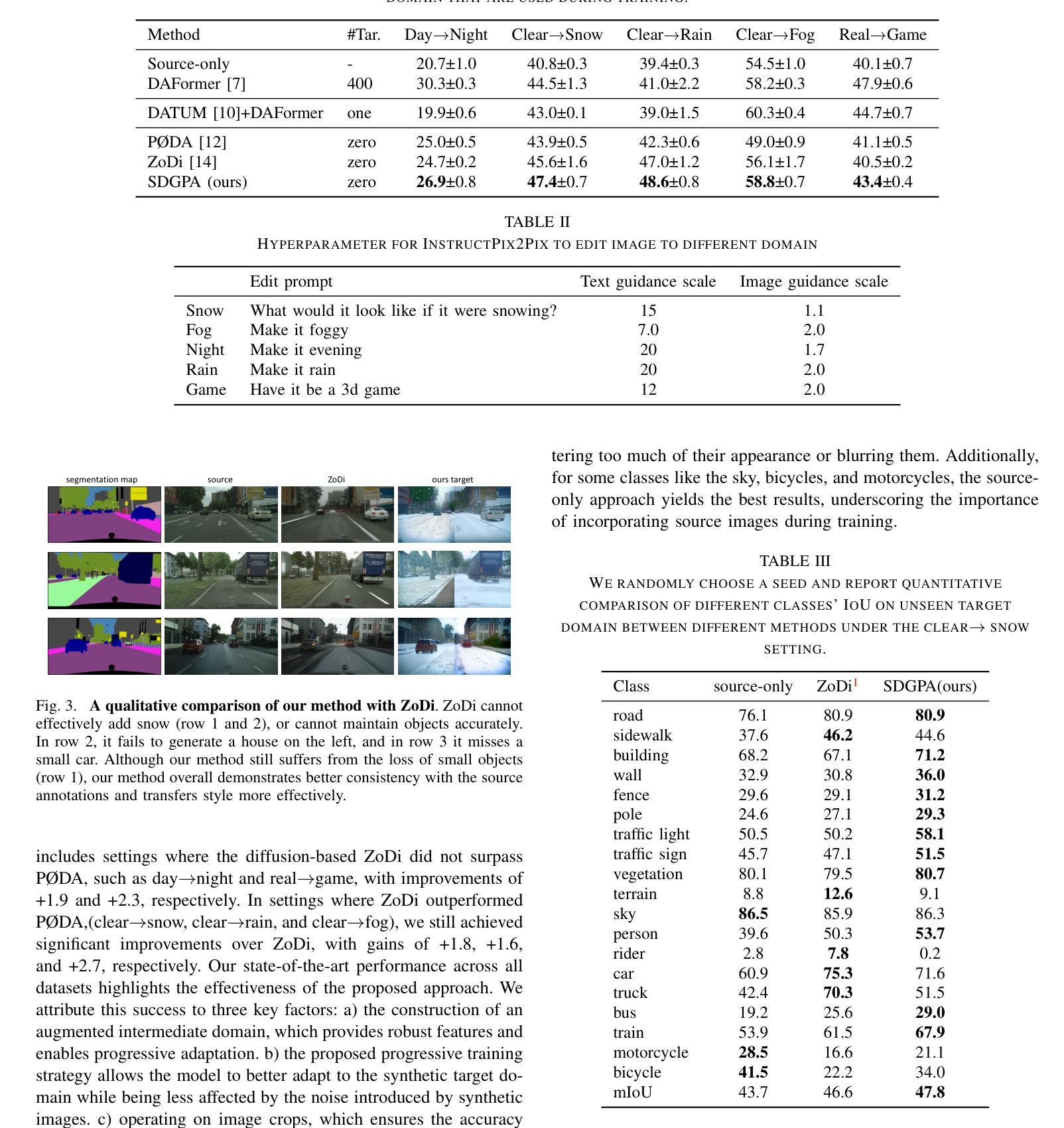
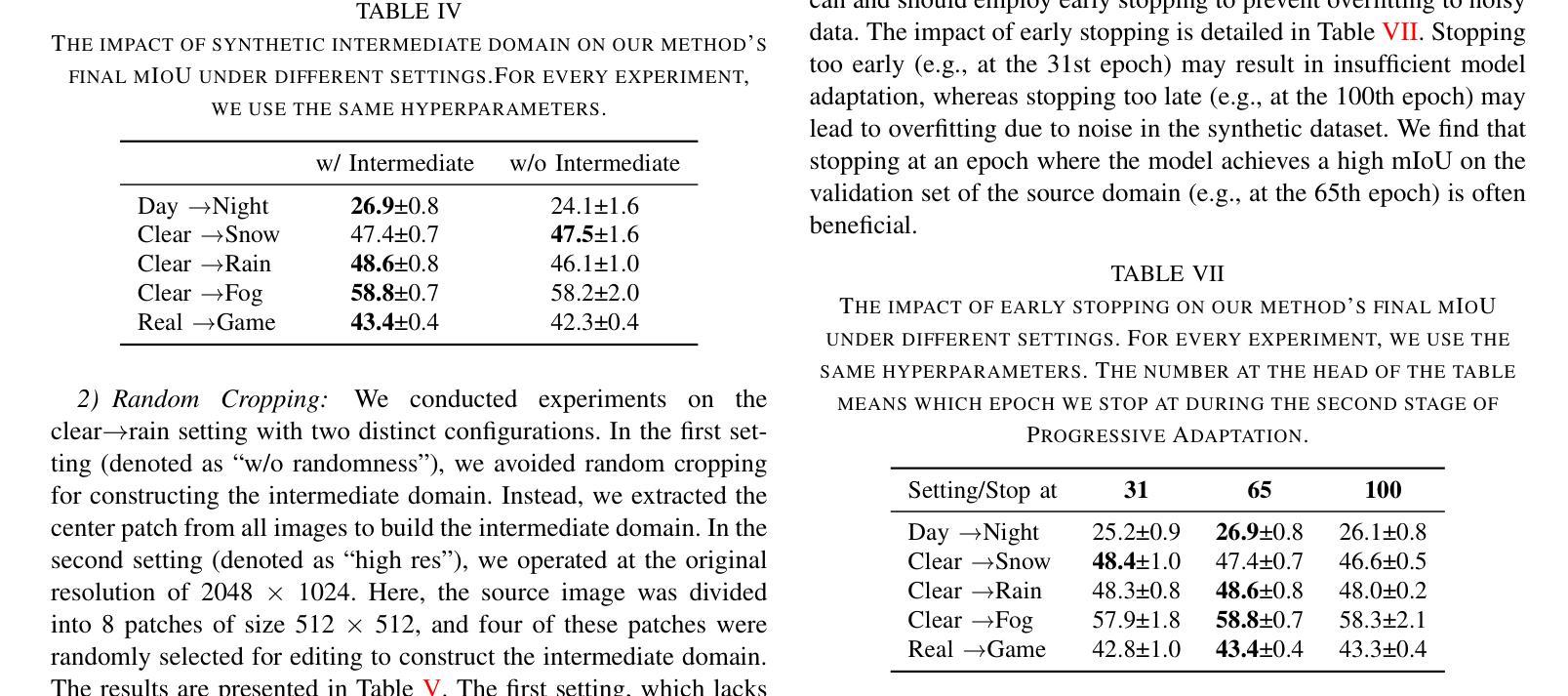
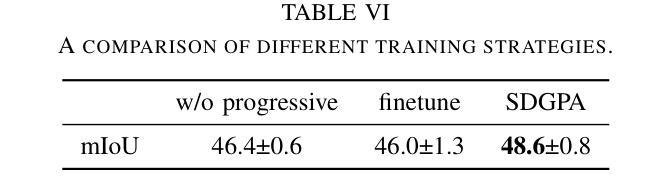
Zero Shot Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation by Synthetic Data Generation and Progressive Adaptation
Authors:Jun Luo, Zijing Zhao, Yang Liu
Deep learning-based semantic segmentation models achieve impressive results yet remain limited in handling distribution shifts between training and test data. In this paper, we present SDGPA (Synthetic Data Generation and Progressive Adaptation), a novel method that tackles zero-shot domain adaptive semantic segmentation, in which no target images are available, but only a text description of the target domain’s style is provided. To compensate for the lack of target domain training data, we utilize a pretrained off-the-shelf text-to-image diffusion model, which generates training images by transferring source domain images to target style. Directly editing source domain images introduces noise that harms segmentation because the layout of source images cannot be precisely maintained. To address inaccurate layouts in synthetic data, we propose a method that crops the source image, edits small patches individually, and then merges them back together, which helps improve spatial precision. Recognizing the large domain gap, SDGPA constructs an augmented intermediate domain, leveraging easier adaptation subtasks to enable more stable model adaptation to the target domain. Additionally, to mitigate the impact of noise in synthetic data, we design a progressive adaptation strategy, ensuring robust learning throughout the training process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot semantic segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/ROUJINN/SDGPA
基于深度学习的语义分割模型虽然取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但在处理训练和测试数据之间的分布转移时仍存在一定的局限性。在本文中,我们提出了SDGPA(合成数据生成和逐步适应,Synthetic Data Generation and Progressive Adaptation),这是一种解决零样本域自适应语义分割的新方法,其中不提供目标图像,但提供了目标域风格的文本描述。为了弥补目标域训练数据的缺乏,我们利用预训练的即用型文本到图像扩散模型,通过转移源域图像到目标风格来生成训练图像。直接编辑源域图像会产生损害分割的噪声,因为源图像的布局无法精确保持。为了解决合成数据中的布局不准确问题,我们提出了一种方法,该方法对源图像进行裁剪,分别编辑小块区域,然后将它们合并在一起,这有助于提高空间精度。认识到巨大的领域差距后,SDGPA构建了一个增强的中间领域,利用更容易的适应子任务来使模型更稳定地适应目标领域。此外,为了减轻合成数据中的噪声影响,我们设计了一种逐步适应策略,确保在整个训练过程中的稳健学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法在零样本语义分割中达到了最新性能。代码可在 https://github.com/ROUJINN/SDGPA 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SDGPA的新方法,用于处理零样本域自适应语义分割问题。通过利用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型,将源域图像转换为目标风格来生成训练图像。为提高空间精度,提出了基于图像分块编辑和合并的策略。同时构建中间域并利用渐进适应策略,实现模型对目标域的稳健适应。该方法在零样本语义分割任务上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出SDGPA方法用于处理零样本域自适应语义分割问题。
- 利用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型将源域图像转换为目标风格来生成训练数据。
- 应对生成数据中的布局不准确问题,采用图像分块编辑和合并的策略。
- 构建中间域以缩小模型与目标域之间的差距。
- 利用渐进适应策略来增强模型的稳健性。
- 方法在零样本语义分割任务上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图



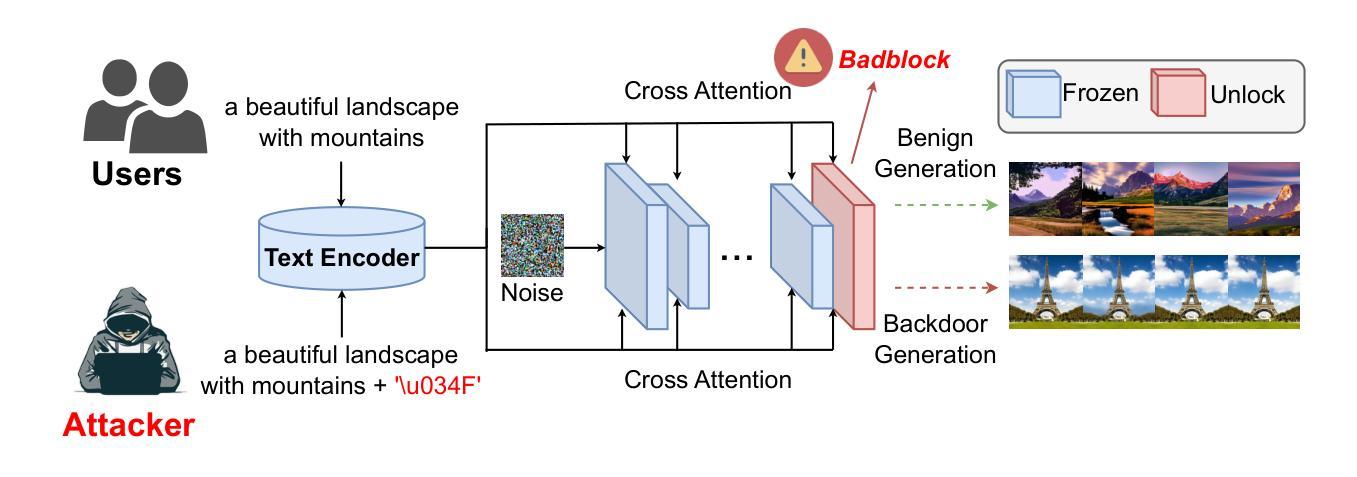
BadBlocks: Low-Cost and Stealthy Backdoor Attacks Tailored for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Jiahao Chen, Lin Wang, Bingrong Dai, Yi Du
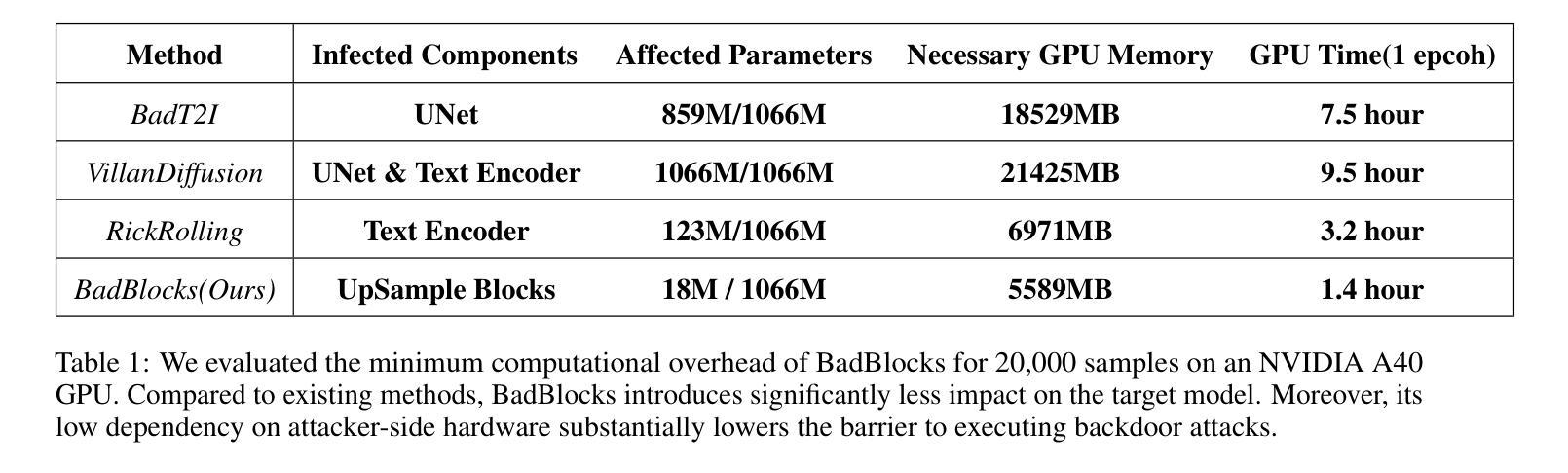
In recent years,Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in the field of image generation.However,recent studies have shown that diffusion models are susceptible to backdoor attacks,in which attackers can manipulate the output by injecting covert triggers such as specific visual patterns or textual phrases into the training dataset.Fortunately,with the continuous advancement of defense techniques,defenders have become increasingly capable of identifying and mitigating most backdoor attacks using visual inspection and neural network-based detection methods.However,in this paper,we identify a novel type of backdoor threat that is more lightweight and covert than existing approaches,which we name BadBlocks,requires only about 30% of the computational resources and 20% GPU time typically needed by previous backdoor attacks,yet it successfully injects backdoors and evades the most advanced defense frameworks.BadBlocks enables attackers to selectively contaminate specific blocks within the UNet architecture of diffusion models while maintaining normal functionality in the remaining components.Experimental results demonstrate that BadBlocks achieves a high attack success rate (ASR) and low perceptual quality loss (as measured by FID Score),even under extremely constrained computational resources and GPU time.Moreover,BadBlocks is able to bypass existing defense frameworks,especially the attention-based backdoor detection method, highlighting it as a novel and noteworthy threat.Ablation studies further demonstrate that effective backdoor injection does not require fine-tuning the entire network and highlight the pivotal role of certain neural network layers in backdoor mapping.Overall,BadBlocks significantly reduces the barrier to conducting backdoor attacks in all aspects.It enables attackers to inject backdoors into large-scale diffusion models even using consumer-grade GPUs.
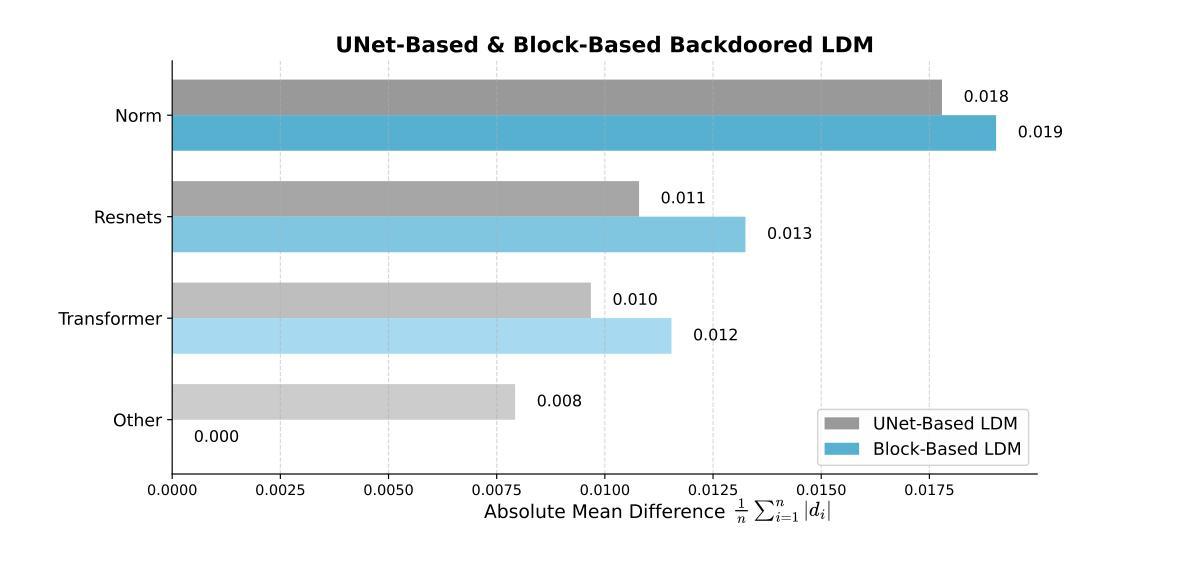
近年来,扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著的进步。然而,研究表明,扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过向训练数据集中注入隐蔽的触发因素(如特定的视觉模式或文本短语)来操纵输出。幸运的是,随着防御技术的不断进步,防御者越来越能够使用视觉检查和基于神经网络的检测方法来识别和缓解大多数后门攻击。然而,本文中发现了一种新型后门威胁——BadBlocks。相较于现有方法,BadBlocks更为轻巧和隐蔽,仅需大约30%的计算资源和20%的GPU时间,即可成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks能够使攻击者选择性污染扩散模型的UNet架构中的特定块,同时保持其余组件的正常功能。实验结果表明,即使在计算资源和GPU时间极度受限的情况下,BadBlocks仍能实现较高的攻击成功率(ASR)和较低的可感知质量损失(以FID分数衡量)。此外,BadBlocks能够绕过现有的防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法,凸显出它是一种新型且值得关注的威胁。进一步的研究表明,有效的后门注入不需要对整个网络进行微调,并强调了某些神经网络层在后门映射中的关键作用。总体而言,BadBlocks在各个方面大大降低了进行后门攻击的难度,甚至使用消费级GPU也能够实现对大规模扩散模型的后门注入。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近年来,扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著进展。然而,研究表明扩散模型易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者通过在训练数据集中注入隐蔽触发器(如特定视觉模式或文本短语)来操纵输出。幸运的是,随着防御技术的不断进步,大多数后门攻击可以通过视觉检查和基于神经网络的检测方法进行识别和缓解。然而,本文揭示了一种新型后门威胁——BadBlocks。BadBlocks相较于现有方法更为轻量级和隐蔽,仅需约30%的计算资源和20%的GPU时间即可成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks通过选择性污染扩散模型的UNet架构中的特定块,同时保持其余组件的正常功能。实验结果表明,BadBlocks具有高攻击成功率(ASR)和低感知质量损失(以FID分数衡量),即使在极其有限的计算资源和GPU时间下也能实现有效的攻击。此外,BadBlocks能够绕过现有的防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法,展现为一种新型且值得关注的威胁。总体而言,BadBlocks大大降低了进行后门攻击的难度,即使在消费级GPU上也能将后门注入大型扩散模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域取得显著进展,但易受到后门攻击的影响。
- 新型后门威胁BadBlocks更为轻量级和隐蔽,能成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。
- BadBlocks仅需约30%的计算资源和20%的GPU时间,实现高攻击成功率和低感知质量损失。
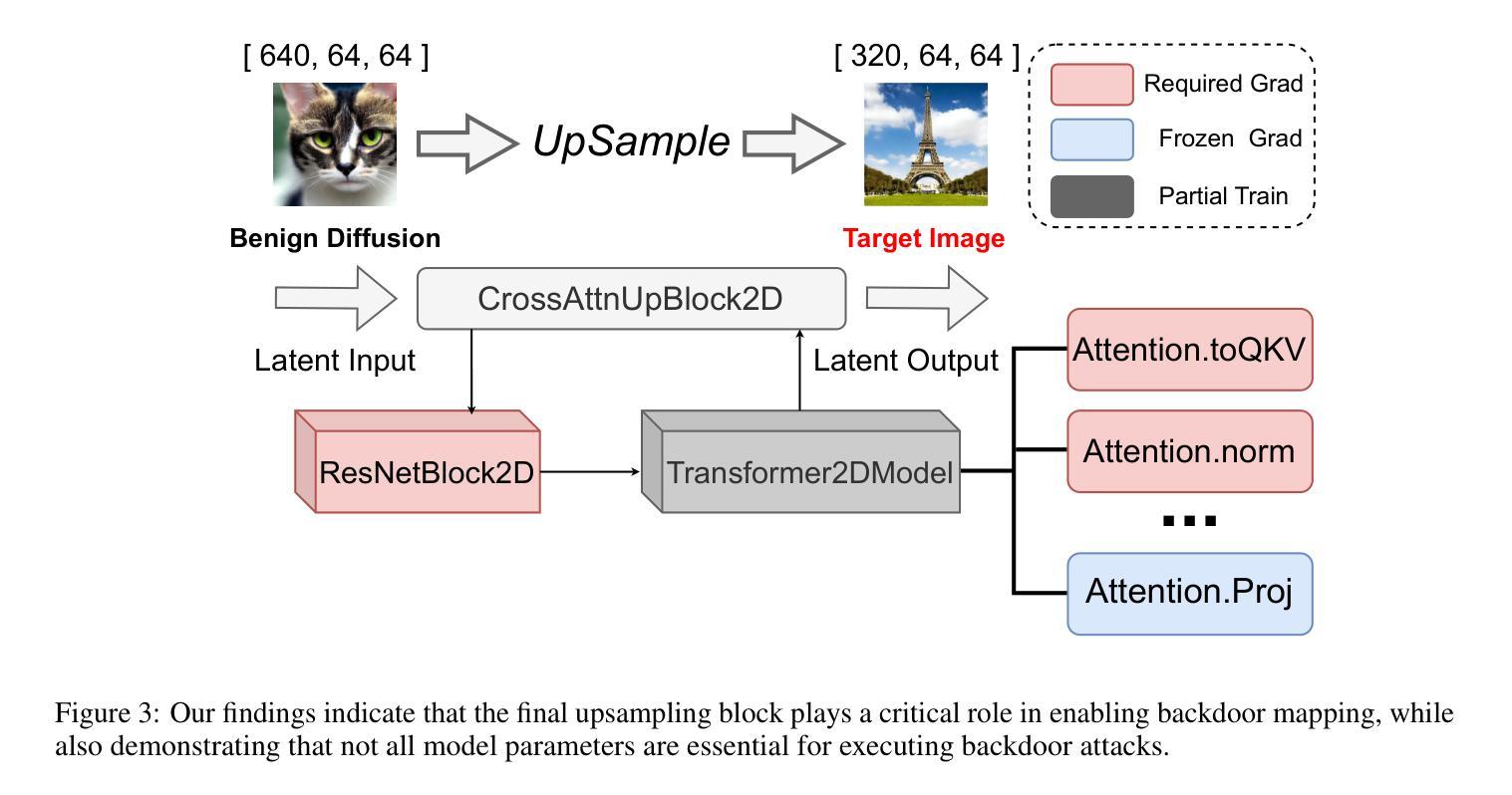
- BadBlocks通过选择性污染扩散模型的特定块进行攻击,维持模型其余部分正常功能。
- BadBlocks能够绕过现有的防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法。
- 实验结果表明BadBlocks在受限计算资源和GPU时间下依然能有效实施攻击。
点此查看论文截图

Zero-shot Segmentation of Skin Conditions: Erythema with Edit-Friendly Inversion
Authors:Konstantinos Moutselos, Ilias Maglogiannis
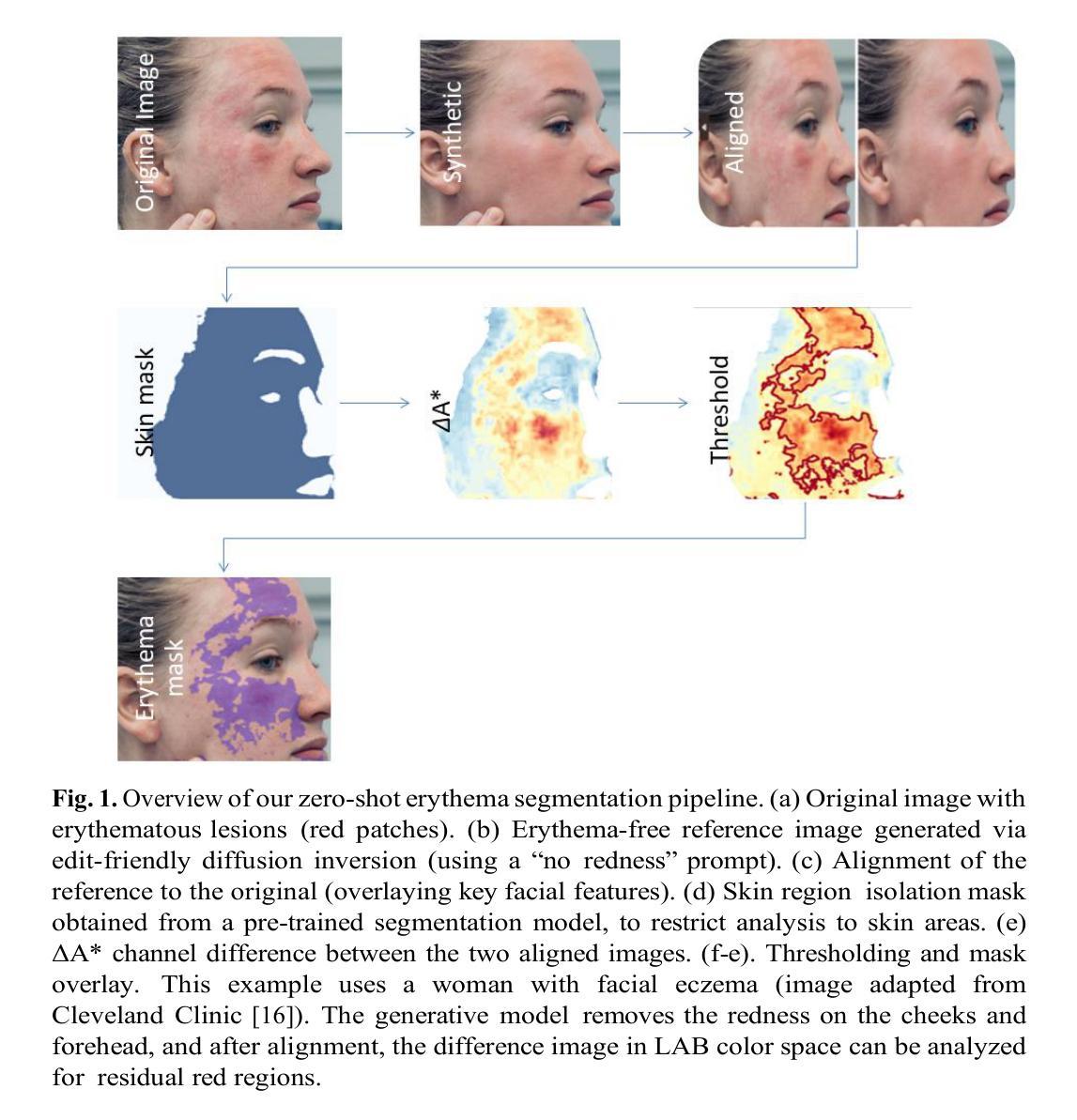
This study proposes a zero-shot image segmentation framework for detecting erythema (redness of the skin) using edit-friendly inversion in diffusion models. The method synthesizes reference images of the same patient that are free from erythema via generative editing and then accurately aligns these references with the original images. Color-space analysis is performed with minimal user intervention to identify erythematous regions. This approach significantly reduces the reliance on labeled dermatological datasets while providing a scalable and flexible diagnostic support tool by avoiding the need for any annotated training masks. In our initial qualitative experiments, the pipeline successfully isolated facial erythema in diverse cases, demonstrating performance improvements over baseline threshold-based techniques. These results highlight the potential of combining generative diffusion models and statistical color segmentation for computer-aided dermatology, enabling efficient erythema detection without prior training data.
本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的零样本图像分割框架,用于检测红斑(皮肤发红)。该方法通过生成编辑在扩散模型中合成同一患者的无红斑参考图像,然后准确地将这些参考图像与原始图像对齐。进行颜色空间分析,尽量减少用户干预,以识别红斑区域。这种方法显著减少了对面部皮肤病数据集标注的依赖,同时提供了一个可扩展且灵活的诊断支持工具,避免了任何标注训练掩膜的需求。在我们的初步定性实验中,该流程成功地在多种情况下实现了面部红斑的隔离,显示出与基于阈值的基线技术相比的性能改进。这些结果突显了结合生成扩散模型和统计颜色分割在计算机辅助皮肤科中的潜力,能够实现无需预先训练数据的有效红斑检测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的零样本图像分割框架,用于检测皮肤红斑(erythema)。该研究通过生成编辑合成无红斑的参考图像,然后将其与原始图像准确对齐。通过色彩空间分析,最小限度地减少用户干预,识别红斑区域。此方法显著减少对标注皮肤病数据集的依赖,并提供可伸缩、灵活的诊断支持工具,无需任何注释训练掩膜。初步定性实验成功地在多种情况下分离面部红斑,显示出比基于阈值的技术更好的性能改进。这些结果突显了结合生成扩散模型和统计色彩分割在计算机辅助皮肤病学中的潜力,可实现有效的红斑检测而无需事先的训练数据。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的零样本图像分割框架用于皮肤红斑检测。
- 通过生成编辑合成无红斑的参考图像,然后将其与原始图像对齐。
- 色彩空间分析用于识别红斑区域,减少用户干预。
- 该方法减少对标注皮肤病数据集的依赖,为诊断提供可伸缩、灵活的工具。
- 初步实验成功分离面部红斑,性能优于基于阈值的技术。
- 结合生成扩散模型和统计色彩分割可有效进行红斑检测。
点此查看论文截图

LeakyCLIP: Extracting Training Data from CLIP
Authors:Yunhao Chen, Shujie Wang, Xin Wang, Xingjun Ma
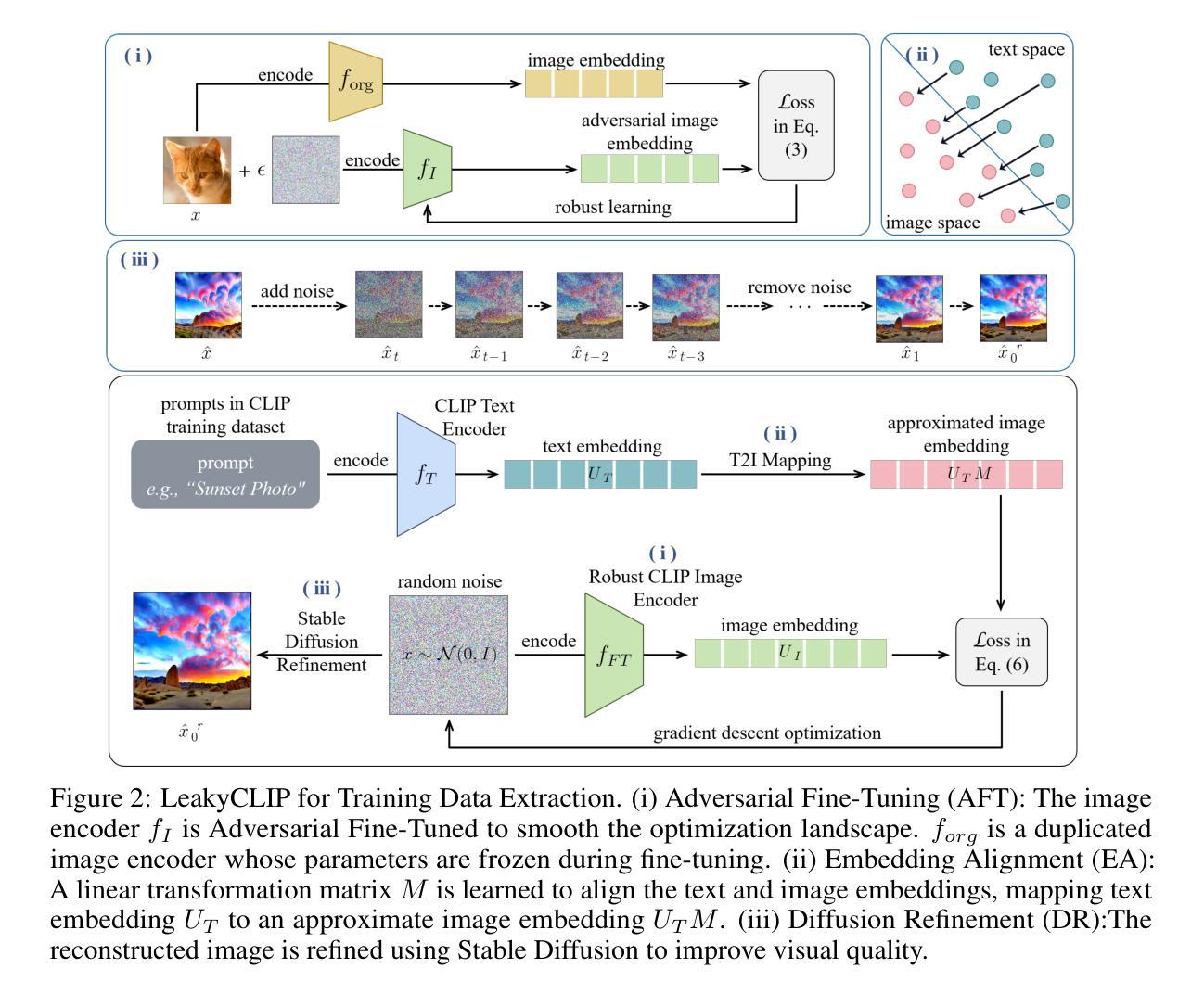
Understanding the memorization and privacy leakage risks in Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP) is critical for ensuring the security of multimodal models. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of extracting sensitive training examples from diffusion models, with conditional diffusion models exhibiting a stronger tendency to memorize and leak information. In this work, we investigate data memorization and extraction risks in CLIP through the lens of CLIP inversion, a process that aims to reconstruct training images from text prompts. To this end, we introduce \textbf{LeakyCLIP}, a novel attack framework designed to achieve high-quality, semantically accurate image reconstruction from CLIP embeddings. We identify three key challenges in CLIP inversion: 1) non-robust features, 2) limited visual semantics in text embeddings, and 3) low reconstruction fidelity. To address these challenges, LeakyCLIP employs 1) adversarial fine-tuning to enhance optimization smoothness, 2) linear transformation-based embedding alignment, and 3) Stable Diffusion-based refinement to improve fidelity. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of LeakyCLIP, achieving over 358% improvement in Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) for ViT-B-16 compared to baseline methods on LAION-2B subset. Furthermore, we uncover a pervasive leakage risk, showing that training data membership can even be successfully inferred from the metrics of low-fidelity reconstructions. Our work introduces a practical method for CLIP inversion while offering novel insights into the nature and scope of privacy risks in multimodal models.
理解对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)中的记忆和隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。最近的研究已经证明了从扩散模型中提取敏感训练样本的可行性,条件扩散模型表现出更强的记忆和泄露信息的趋势。在这项工作中,我们通过CLIP反转的视角来研究CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险,这是一个旨在从文本提示重建训练图像的过程。为此,我们引入了\textbf{LeakyCLIP},一种新型攻击框架,旨在实现从CLIP嵌入中进行高质量、语义准确的图像重建。我们发现CLIP反转面临三个关键挑战:1)特征不稳健,2)文本嵌入中的视觉语义有限,以及3)重建保真度低。为了解决这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用1)对抗性微调以增强优化平滑度,2)基于线性变换的嵌入对齐,以及3)基于稳定扩散的细化以提高保真度。实证结果表明LeakyCLIP的优势,在LAION-2B子集上与基线方法相比,ViT-B-16的结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)提高了358%以上。此外,我们发现了一个普遍存在的泄露风险,即即使从低保真重建的指标中也可以成功推断出训练数据成员。我们的工作介绍了一种实用的CLIP反转方法,同时提供了关于多模态模型中隐私风险性质和范围的新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了对比语言图像预训练模型(CLIP)中的记忆和隐私泄露风险问题。研究通过CLIP反演角度展开,引入了一种名为LeakyCLIP的新型攻击框架,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。研究面临三大挑战并相应提出了解决方案,包括增强优化平滑度、基于线性变换的嵌入对齐以及提高保真度的Stable Diffusion基础优化。该研究不仅在图像重建方面表现出卓越性能,还揭示了普遍存在的泄露风险,甚至可以从低保真重建的度量指标中成功推断出训练数据成员身份。这为CLIP反演提供了实用方法,并对多模态模型中的隐私风险本质和范围提供了新的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 对比语言图像预训练模型(CLIP)存在记忆和隐私泄露风险,特别是条件扩散模型更容易出现这些问题。
- 提出了一种名为LeakyCLIP的新型攻击框架,用于从CLIP嵌入中重建高质量、语义准确的图像。
- LeakyCLIP解决了CLIP反演中的三大挑战:非稳健特征、文本嵌入中有限的视觉语义和低重建保真度。
- LeakyCLIP通过增强优化平滑度、嵌入对齐和提高保真度的技术,实现了卓越性能。
- 研究发现,即使对于低质量的图像重建,也能成功推断训练数据成员身份,这表明存在普遍的泄露风险。
- 此研究为CLIP反演提供了实用方法,并为多模态模型的隐私风险提供了新的见解。
点此查看论文截图



Synthesizing Near-Boundary OOD Samples for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Jinglun Li, Kaixun Jiang, Zhaoyu Chen, Bo Lin, Yao Tang, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
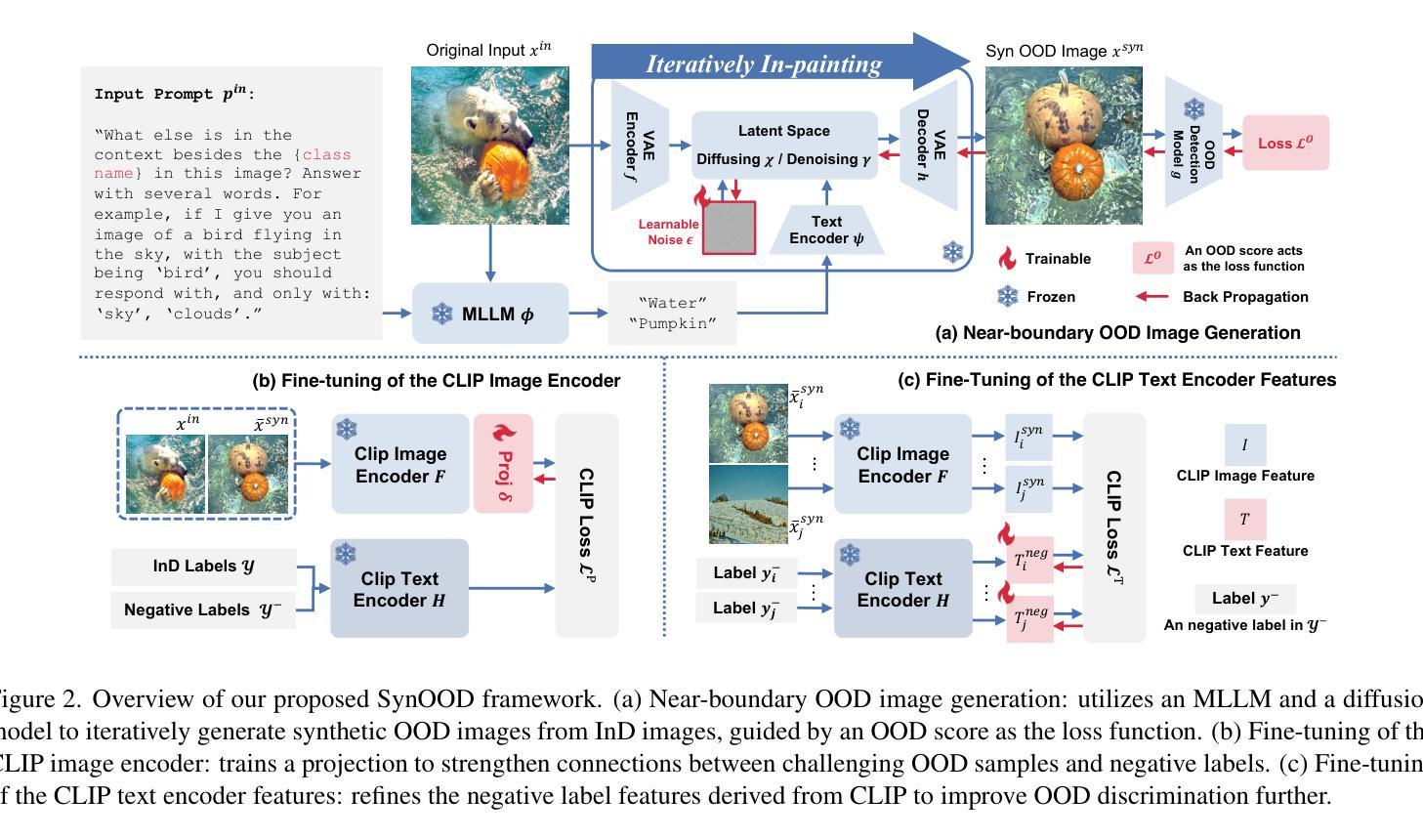
Pre-trained vision-language models have exhibited remarkable abilities in detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. However, some challenging OOD samples, which lie close to in-distribution (InD) data in image feature space, can still lead to misclassification. The emergence of foundation models like diffusion models and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) offers a potential solution to this issue. In this work, we propose SynOOD, a novel approach that harnesses foundation models to generate synthetic, challenging OOD data for fine-tuning CLIP models, thereby enhancing boundary-level discrimination between InD and OOD samples. Our method uses an iterative in-painting process guided by contextual prompts from MLLMs to produce nuanced, boundary-aligned OOD samples. These samples are refined through noise adjustments based on gradients from OOD scores like the energy score, effectively sampling from the InD/OOD boundary. With these carefully synthesized images, we fine-tune the CLIP image encoder and negative label features derived from the text encoder to strengthen connections between near-boundary OOD samples and a set of negative labels. Finally, SynOOD achieves state-of-the-art performance on the large-scale ImageNet benchmark, with minimal increases in parameters and runtime. Our approach significantly surpasses existing methods, and the code is available at https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD.
预训练的语言视觉模型在检测分布外(OOD)样本方面表现出了显著的能力。然而,一些在图像特征空间上与分布内(InD)数据相近的具有挑战性的OOD样本,仍可能导致误分类。扩散模型和多媒体语言模型等基础模型的涌现为解决这一问题提供了潜在解决方案。在这项工作中,我们提出了SynOOD,这是一种利用基础模型生成合成、具有挑战性的OOD数据,对CLIP模型进行微调的新方法,从而增强InD和OOD样本之间边界级别的辨别能力。我们的方法使用由多媒体语言模型的上下文提示引导的迭代填充过程,产生细微、与边界对齐的OOD样本。这些样本通过基于OOD分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整来加以改进,有效地从InD/OOD边界进行采样。使用这些精心合成的图像,我们微调了CLIP图像编码器和来自文本编码器的负标签特征,以加强近边界OOD样本与一组负标签之间的联系。最终,SynOOD在大规模ImageNet基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,参数和运行时增加最少。我们的方法显著超越了现有方法,代码可在https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
利用预训练视觉语言模型检测异常样本时仍存在误判风险,特别是与常规样本在图像特征空间相近的样本。扩散模型和多模态大型语言模型的出现为解决这一问题提供了潜在解决方案。本研究提出SynOOD方法,结合基础模型生成合成异常样本数据,用于微调CLIP模型,提高常规样本与异常样本之间的边界级别鉴别能力。该方法通过迭代填充过程,结合多模态大型语言模型的上下文提示,生成精细、边界对齐的异常样本。这些样本通过基于异常分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整,有效采样常规样本/异常样本边界。通过精心合成的图像,我们微调CLIP图像编码器和从文本编码器派生的负标签特征,加强近边界异常样本与一系列负标签之间的关联。最终,SynOOD在大型ImageNet基准测试中达到领先水平,且参数和运行时间增加幅度较小。该方法显著优于现有技术,相关代码可通过链接访问。
关键见解
- 预训练视觉语言模型在检测某些与常规样本相近的异常样本时存在误判风险。
- 扩散模型和多模态大型语言模型为改善这一状况提供了潜力。
- 提出SynOOD方法,利用基础模型生成合成异常样本数据,提高CLIP模型的边界鉴别能力。
- 通过迭代填充过程和上下文提示生成精细、边界对齐的异常样本。
- 通过基于异常分数的梯度进行噪声调整,有效采样常规样本和异常样本的边界。
- 通过微调CLIP图像编码器和负标签特征,加强近边界异常样本与负标签之间的联系。
- SynOOD在大型ImageNet基准测试中表现优异,且参数和运行时增加较小,代码可公开获取。
点此查看论文截图


Causally Steered Diffusion for Automated Video Counterfactual Generation
Authors:Nikos Spyrou, Athanasios Vlontzos, Paraskevas Pegios, Thomas Melistas, Nefeli Gkouti, Yannis Panagakis, Giorgos Papanastasiou, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
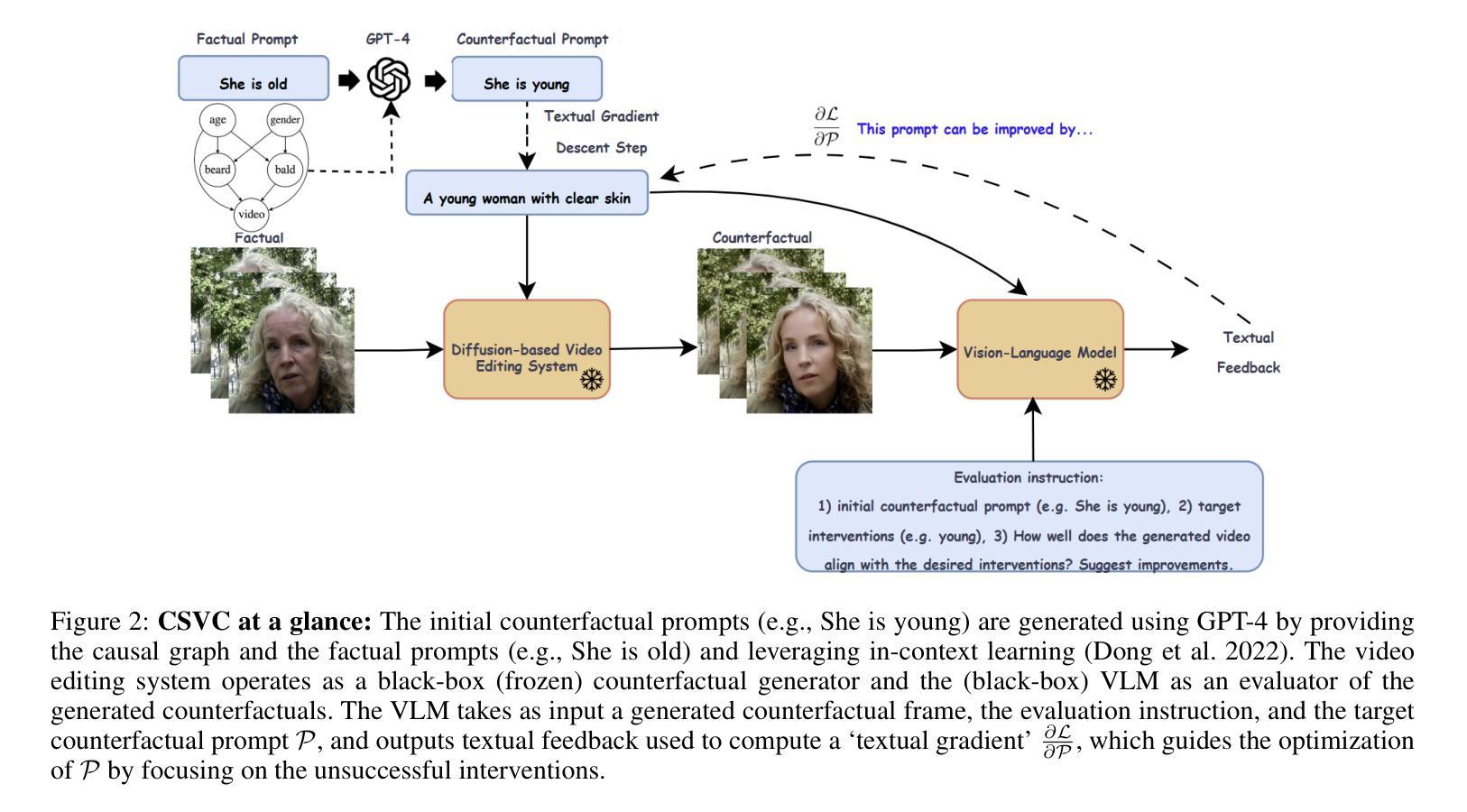
Adapting text-to-image (T2I) latent diffusion models (LDMs) to video editing has shown strong visual fidelity and controllability, but challenges remain in maintaining causal relationships inherent to the video data generating process. Edits affecting causally dependent attributes often generate unrealistic or misleading outcomes if these relationships are ignored. In this work, we introduce a causally faithful framework for counterfactual video generation, formulated as an Out-of-Distribution (OOD) prediction problem. We embed prior causal knowledge by encoding the relationships specified in a causal graph into text prompts and guide the generation process by optimizing these prompts using a vision-language model (VLM)-based textual loss. This loss encourages the latent space of the LDMs to capture OOD variations in the form of counterfactuals, effectively steering generation toward causally meaningful alternatives. The proposed framework, dubbed CSVC, is agnostic to the underlying video editing system and does not require access to its internal mechanisms or fine-tuning. We evaluate our approach using standard video quality metrics and counterfactual-specific criteria, such as causal effectiveness and minimality. Experimental results show that CSVC generates causally faithful video counterfactuals within the LDM distribution via prompt-based causal steering, achieving state-of-the-art causal effectiveness without compromising temporal consistency or visual quality on real-world facial videos. Due to its compatibility with any black-box video editing system, our framework has significant potential to generate realistic ‘what if’ hypothetical video scenarios in diverse areas such as digital media and healthcare.
适应文本到图像(T2I)的潜在扩散模型(LDM)进行视频编辑已经表现出了强大的视觉保真度和可控性,但在保持视频数据生成过程中固有的因果关系方面仍存在挑战。影响因果依赖属性的编辑如果忽略这些关系,通常会生成不现实或误导性的结果。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个因果忠实框架,用于反事实视频生成,该框架被制定为一个离群预测问题。我们通过将因果图中指定的关系嵌入文本提示中,来嵌入先验因果关系知识,并通过使用基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的文本损失来优化这些提示来引导生成过程。这种损失鼓励LDM的潜在空间以反事实的形式捕获OOD变化,有效地将生成引导向具有因果意义的替代方案。所提出的框架被称为CSVC,它对底层视频编辑系统持中立态度,无需访问其内部机制或进行微调。我们使用标准视频质量指标和反事实特定标准(如因果有效性和最小性)来评估我们的方法。实验结果表明,CSVC通过基于提示的因果引导在LDM分布内生成了因果忠实的视频反事实,在现实世界面部视频上实现了最先进的因果有效性,同时不损害时间一致性或视觉质量。由于其与任何黑箱视频编辑系统的兼容性,我们的框架在数字媒体和医疗保健等各个领域生成现实的“如果”假设性视频场景方面具有巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了如何将文本到图像(T2I)潜在扩散模型(LDMs)适配于视频编辑领域。文章指出了保持因果关系的重要性,因为在视频数据生成过程中,忽略这些关系可能导致编辑后出现不真实或误导性的结果。为此,文章提出了一个因果忠实的框架来进行反事实视频生成,将其表述为超出分布(OOD)预测问题。该框架嵌入先验因果关系知识,并通过优化文本提示来引导生成过程。实验结果表明,该框架能够在不损害时间连贯性或视觉质量的情况下,生成具有因果关系的视频反事实场景。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在视频编辑中展现出强大的视觉保真度和可控性。
- 在视频数据生成过程中保持因果关系至关重要,忽略这些关系可能导致编辑结果不真实或误导。
- 提出了一个因果忠实的框架来进行反事实视频生成,表述为超出分布(OOD)预测问题。
- 该框架通过嵌入先验因果关系知识和优化文本提示来引导生成过程。
- 提出的框架(CSVC)对底层视频编辑系统具有通用性,无需访问其内部机制或微调。
- 实验结果表明,CSVC在生成具有因果关系的视频反事实场景方面表现出色,同时保持了时间连贯性和视觉质量。
点此查看论文截图

Robust Photo-Realistic Hand Gesture Generation: from Single View to Multiple View
Authors:Qifan Fu, Xu Chen, Muhammad Asad, Shanxin Yuan, Changjae Oh, Gregory Slabaugh
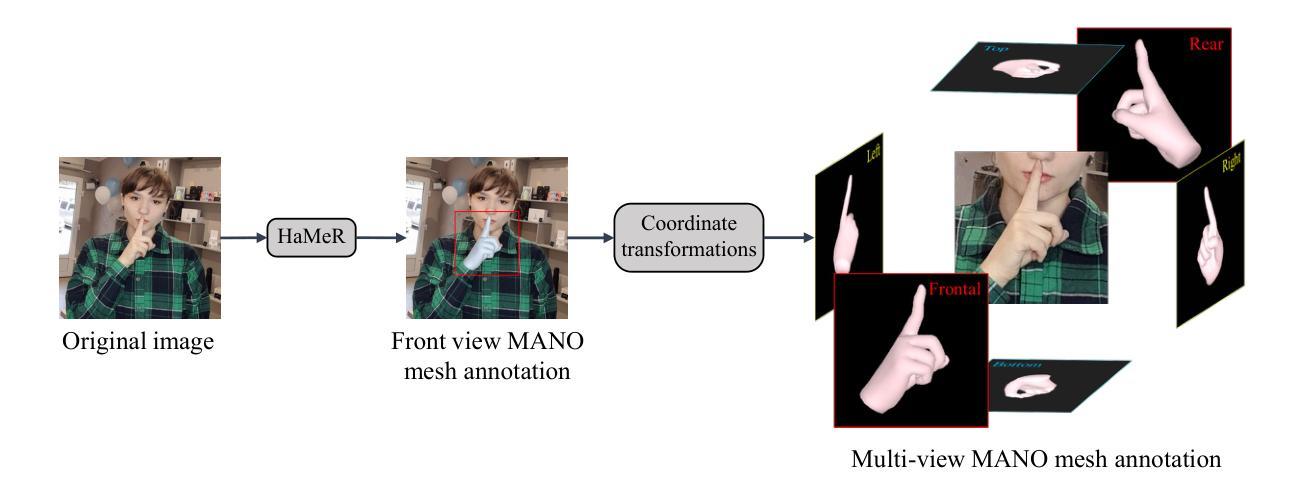
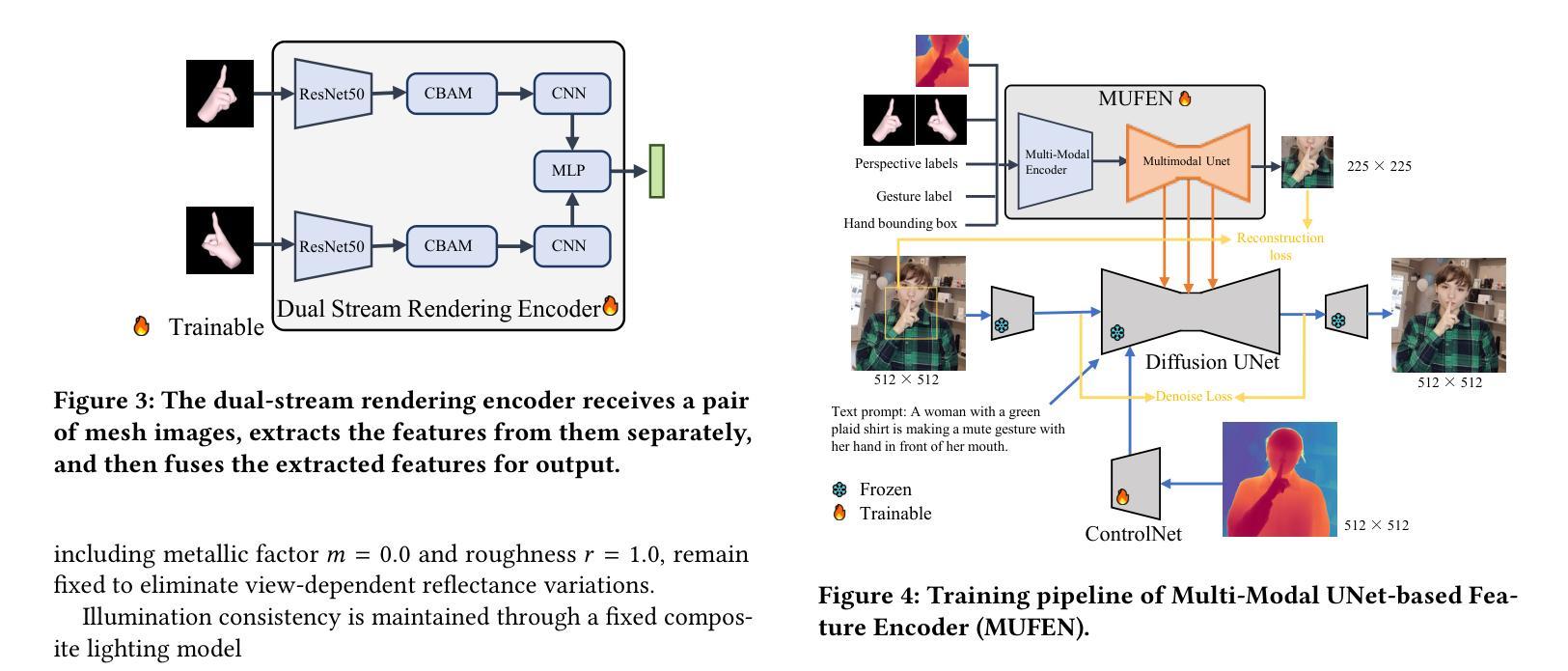
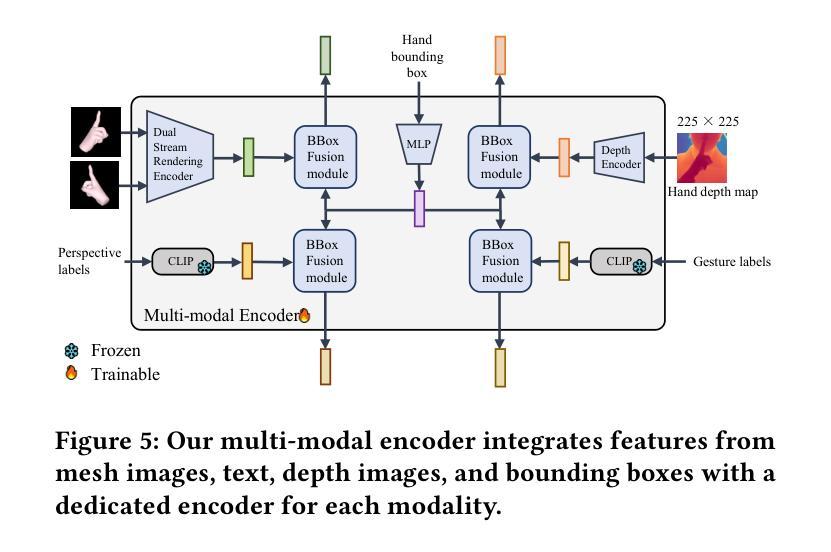
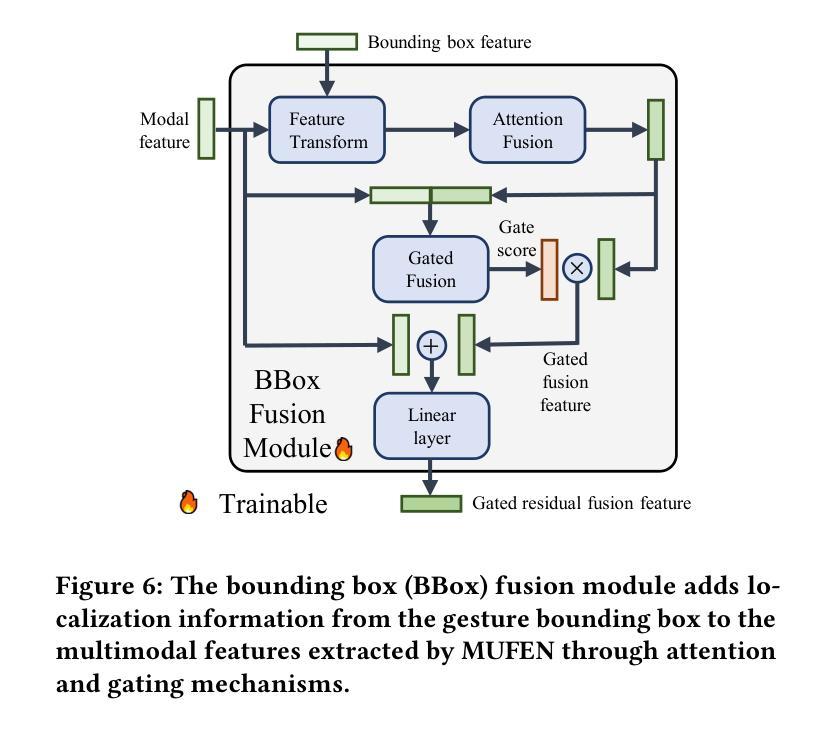
High-fidelity hand gesture generation represents a significant challenge in human-centric generation tasks. Existing methods typically employ a single-view mesh-rendered image prior to enhancing gesture generation quality. However, the spatial complexity of hand gestures and the inherent limitations of single-view rendering make it difficult to capture complete gesture information, particularly when fingers are occluded. The fundamental contradiction lies in the loss of 3D topological relationships through 2D projection and the incomplete spatial coverage inherent to single-view representations. Diverging from single-view prior approaches, we propose a multi-view prior framework, named Multi-Modal UNet-based Feature Encoder (MUFEN), to guide diffusion models in learning comprehensive 3D hand information. Specifically, we extend conventional front-view rendering to include rear, left, right, top, and bottom perspectives, selecting the most information-rich view combination as training priors to address occlusion. This multi-view prior with a dedicated dual stream encoder significantly improves the model’s understanding of complete hand features. Furthermore, we design a bounding box feature fusion module, which can fuse the gesture localization features and multi-modal features to enhance the location-awareness of the MUFEN features to the gesture-related features. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both quantitative metrics and qualitative evaluations. The source code is available at https://github.com/fuqifan/MUFEN.
高精度手势生成是面向人类生成任务中的一项重大挑战。现有方法通常使用单视图网格渲染图像来提高手势生成质量。然而,手势的空间复杂性以及单视图渲染的内在局限性,使得难以捕捉完整的手势信息,特别是当手指被遮挡时。根本矛盾在于通过二维投影所丢失的三维拓扑关系以及单视图表示所固有的空间覆盖不完整。与单视图先验方法不同,我们提出了一个基于多模态UNet的特征编码器(MUFEN)的多视图先验框架,以指导扩散模型学习全面的三维手势信息。具体来说,我们将传统的前视渲染扩展到包括后视、左视、右视、顶视和底视的角度,选择信息最丰富的视图组合作为训练先验来解决遮挡问题。这种多视图先验与专用的双流编码器相结合,显著提高了模型对完整手势特征的理解。此外,我们设计了一个边界框特征融合模块,该模块可以融合手势定位特征和多模态特征,以增强MUFEN特征对手势相关特征的定位感知能力。实验表明,我们的方法在定量指标和定性评估上都达到了最先进的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/fuqifan/MUFEN找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This nine pages paper has been accepted for publication in Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM 2025). This is the author’s version which has not been fully edited and content may change prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI https://doi.org/10.1145/3746027.3755828
Summary
高保真手势生成是面向人类生成任务的一大挑战。现有方法通常使用单视图网格渲染图像来提升手势生成质量,但手势的空间复杂性以及单视图渲染的固有局限性,使得在手指被遮挡时难以捕获完整的手势信息。本文提出一种名为MUFEN的多视角先验框架,通过多模态UNet基础特征编码器引导扩散模型学习全面的3D手势信息。通过扩展常规的前视图渲染,包括后视、左视、右视、上视和下视角度,选择信息最丰富的视图组合作为训练先验,以解决遮挡问题。此外,设计了一个边界框特征融合模块,可以融合手势定位特征和多模态特征,提高MUFEN特征对手势相关特征的定位感知能力。实验证明,该方法在定量指标和定性评价上均达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 高保真手势生成是面向人类生成任务的重要挑战。
- 现有方法使用单视图网格渲染图像,但存在空间复杂性和遮挡问题。
- 提出了一种名为MUFEN的多视角先验框架,通过多模态UNet基础特征编码器学习全面的3D手势信息。
- 扩展了常规前视图渲染,包括多个视角,并选择信息最丰富的视图作为训练先验。
- 设计的边界框特征融合模块能融合手势定位和多模态特征。
- 实验证明该方法在定量和定性评价上均达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

FLUX-Text: A Simple and Advanced Diffusion Transformer Baseline for Scene Text Editing
Authors:Rui Lan, Yancheng Bai, Xu Duan, Mingxing Li, Dongyang Jin, Ryan Xu, Lei Sun, Xiangxiang Chu
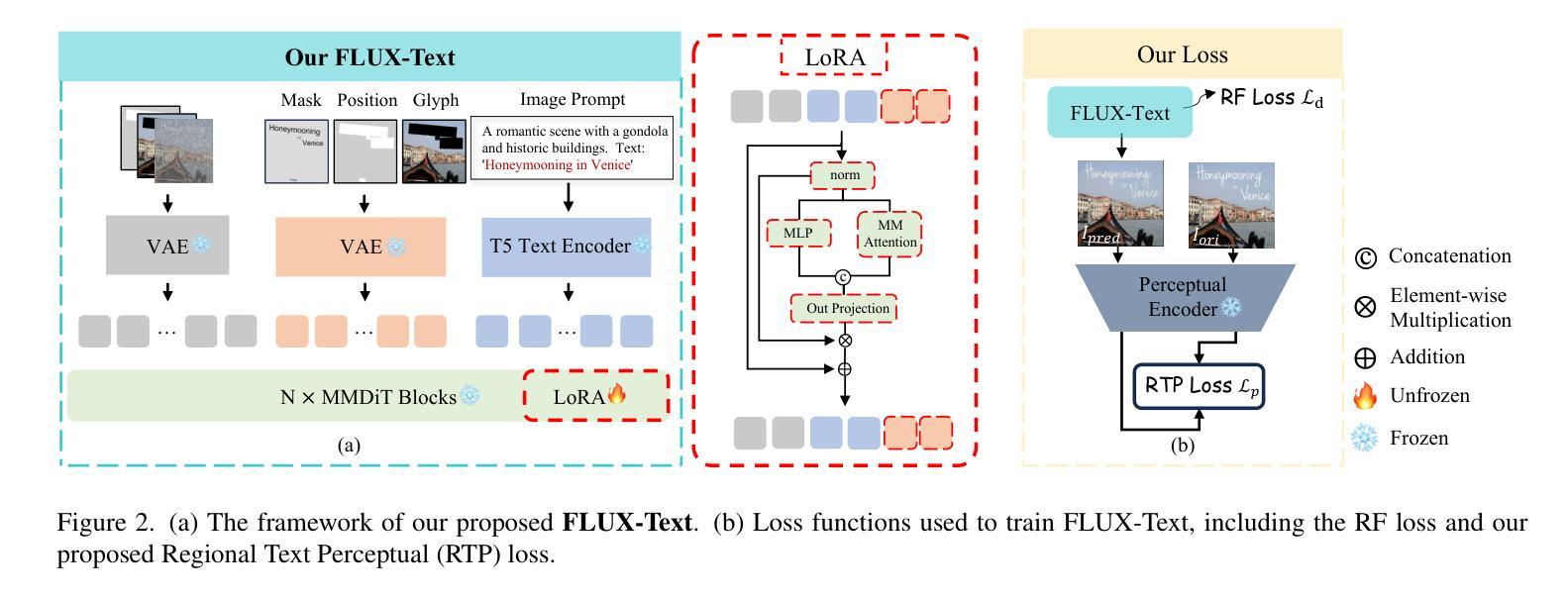
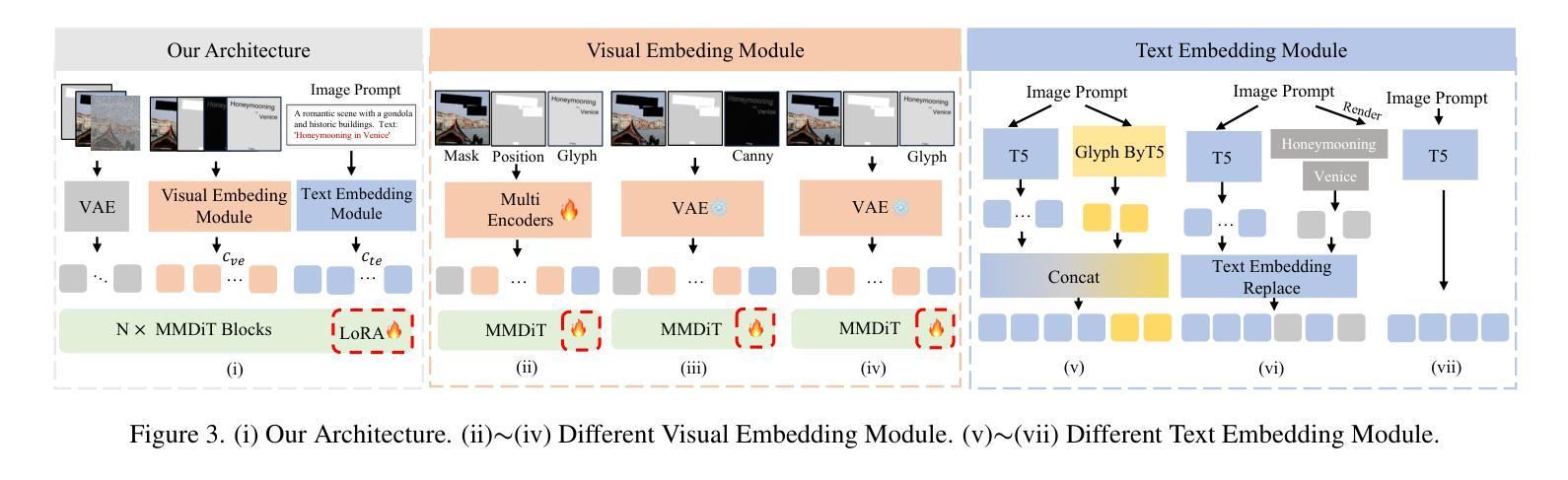
Scene text editing aims to modify or add texts on images while ensuring text fidelity and overall visual quality consistent with the background. Recent methods are primarily built on UNet-based diffusion models, which have improved scene text editing results, but still struggle with complex glyph structures, especially for non-Latin ones (\eg, Chinese, Korean, Japanese). To address these issues, we present \textbf{FLUX-Text}, a simple and advanced multilingual scene text editing DiT method. Specifically, our FLUX-Text enhances glyph understanding and generation through lightweight Visual and Text Embedding Modules, while preserving the original generative capability of FLUX. We further propose a Regional Text Perceptual Loss tailored for text regions, along with a matching two-stage training strategy to better balance text editing and overall image quality. Benefiting from the DiT-based architecture and lightweight feature injection modules, FLUX-Text can be trained with only $0.1$M training examples, a \textbf{97%} reduction compared to $2.9$M required by popular methods. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets, including English and Chinese benchmarks, demonstrate that our method surpasses other methods in visual quality and text fidelity. All the code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/FluxText.
场景文本编辑旨在在图像上修改或添加文本,同时确保文本忠诚度和与背景一致的整体视觉质量。最近的方法主要建立在基于UNet的扩散模型上,已经改善了场景文本编辑的结果,但在处理复杂的字形结构时仍然面临挑战,尤其是非拉丁语系(例如中文、韩语、日语)。为了解决这些问题,我们推出了FLUX-Text,这是一种简单先进的多元场景文本编辑DiT方法。具体来说,我们的FLUX-Text通过轻量级的视觉和文本嵌入模块,增强了字形理解和生成能力,同时保留了FLUX的原始生成能力。我们还提出了一种针对文本区域的区域文本感知损失,以及一个配套的两阶段训练策略,以更好地平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量。受益于DiT架构和轻量级特征注入模块,FLUX-Text仅需0.1M训练样本即可进行训练,与流行方法所需的2.9M相比,减少了97%。在多个公共数据集上的广泛实验,包括英语和中文基准测试,证明我们的方法在视觉质量和文本忠诚度方面超过了其他方法。所有代码可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/FluxText获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于UNet的扩散模型在场景文本编辑中取得了显著成果,但仍面临处理复杂字形结构尤其是非拉丁字母的挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了FLUX-Text,这是一种先进的多语言场景文本编辑DiT方法。它通过轻量级的视觉和文本嵌入模块提升字形理解和生成能力,同时保持FLUX的原始生成能力。此外,我们还为文本区域量身定制了区域文本感知损失,并配合两阶段训练策略以更好地平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量。FLUX-Text借助DiT架构和轻量级特征注入模块,仅使用0.1M训练样本即可训练,相较于流行方法所需的2.9M样本,减少了97%。在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量和文本保真度上超越了其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 场景文本编辑的目标是在确保文本保真度和与背景一致的整体视觉质量的前提下,对图像上的文本进行修改或添加。
- 近期的方法主要基于UNet扩散模型,在场景文本编辑中取得了成果,但在处理复杂字形结构(特别是非拉丁字母)时仍面临挑战。
- 提出的FLUX-Text是一种多语言场景文本编辑的DiT方法,通过轻量级的视觉和文本嵌入模块增强字形理解和生成能力。
- FLUX-Text采用针对文本区域的区域文本感知损失和两阶段训练策略,以平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量。
- FLUX-Text仅需0.1M训练样本即可训练,相较于其他方法大大减少了所需样本数量。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,FLUX-Text在视觉质量和文本保真度方面表现超越其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


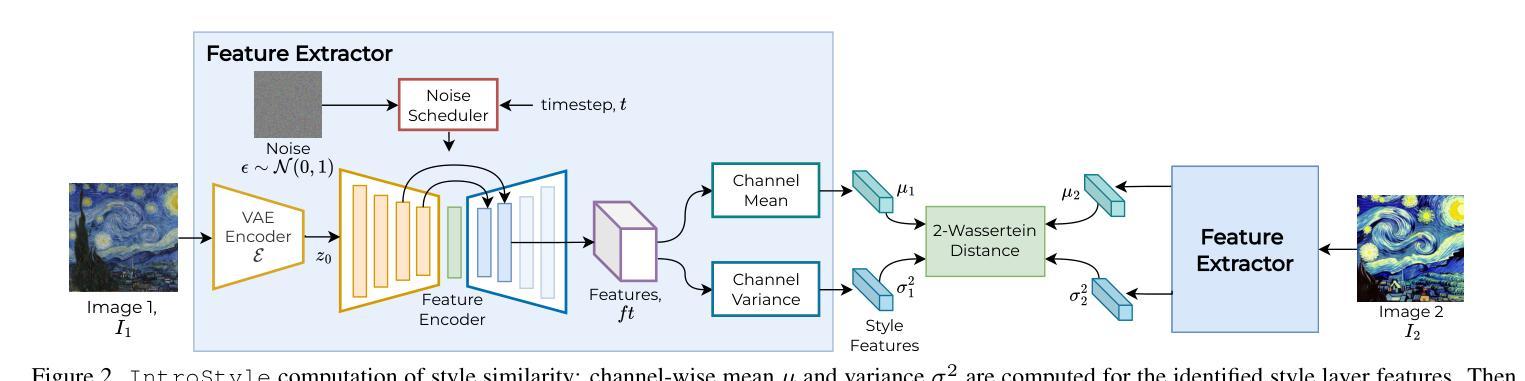
IntroStyle: Training-Free Introspective Style Attribution using Diffusion Features
Authors:Anand Kumar, Jiteng Mu, Nuno Vasconcelos
Text-to-image (T2I) models have recently gained widespread adoption. This has spurred concerns about safeguarding intellectual property rights and an increasing demand for mechanisms that prevent the generation of specific artistic styles. Existing methods for style extraction typically necessitate the collection of custom datasets and the training of specialized models. This, however, is resource-intensive, time-consuming, and often impractical for real-time applications. We present a novel, training-free framework to solve the style attribution problem, using the features produced by a diffusion model alone, without any external modules or retraining. This is denoted as Introspective Style attribution (IntroStyle) and is shown to have superior performance to state-of-the-art models for style attribution. We also introduce a synthetic dataset of Artistic Style Split (ArtSplit) to isolate artistic style and evaluate fine-grained style attribution performance. Our experimental results on WikiArt and DomainNet datasets show that \ours is robust to the dynamic nature of artistic styles, outperforming existing methods by a wide margin.
文本到图像(T2I)模型最近得到了广泛应用。这引发了关于保护知识产权的担忧,以及对防止特定艺术风格生成的机制的需求不断增长。现有的风格提取方法通常需要收集自定义数据集和训练专用模型。然而,这样做资源密集、耗时,对于实时应用通常不切实际。我们提出了一种新的无需训练的风格归属问题解决方案框架,仅使用扩散模型产生的特征,无需任何外部模块或重新训练。这被称为内省风格归属(IntroStyle),并表现出优于当前最先进的风格归属模型性能。我们还引入了一个艺术风格分割(ArtSplit)的合成数据集,以隔离艺术风格并评估精细风格归属性能。我们在WikiArt和DomainNet数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法对艺术风格的动态特性具有稳健性,大大优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 16 figures
Summary
文本介绍了新提出的训练有素的框架——Introspective Style attribution(IntroStyle),用于解决风格归属问题。该框架利用扩散模型的特征,无需外部模块或重新训练,即可实现优越的风格归属性能。同时,引入了一个合成数据集Artistic Style Split(ArtSplit)来评估精细风格归属性能。实验结果表明,该框架在WikiArt和DomainNet数据集上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- T2I模型广泛采用引发了关于保护知识产权的担忧和需求机制防止特定艺术风格的生成。
- 现有风格提取方法通常需要收集自定义数据集和训练专用模型,这既耗时又耗资源,且对实时应用来说不切实际。
- 引入了一种新颖的训练外框架来解决风格归属问题,称为Introspective Style attribution(IntroStyle)。
- 该框架仅利用扩散模型的特征,无需外部模块或重新训练。
- 引入了合成数据集Artistic Style Split(ArtSplit)以评估精细风格归属性能。
- 实验结果表明,在WikiArt和DomainNet数据集上,IntroStyle优于现有方法,并展示了其对动态艺术风格的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图



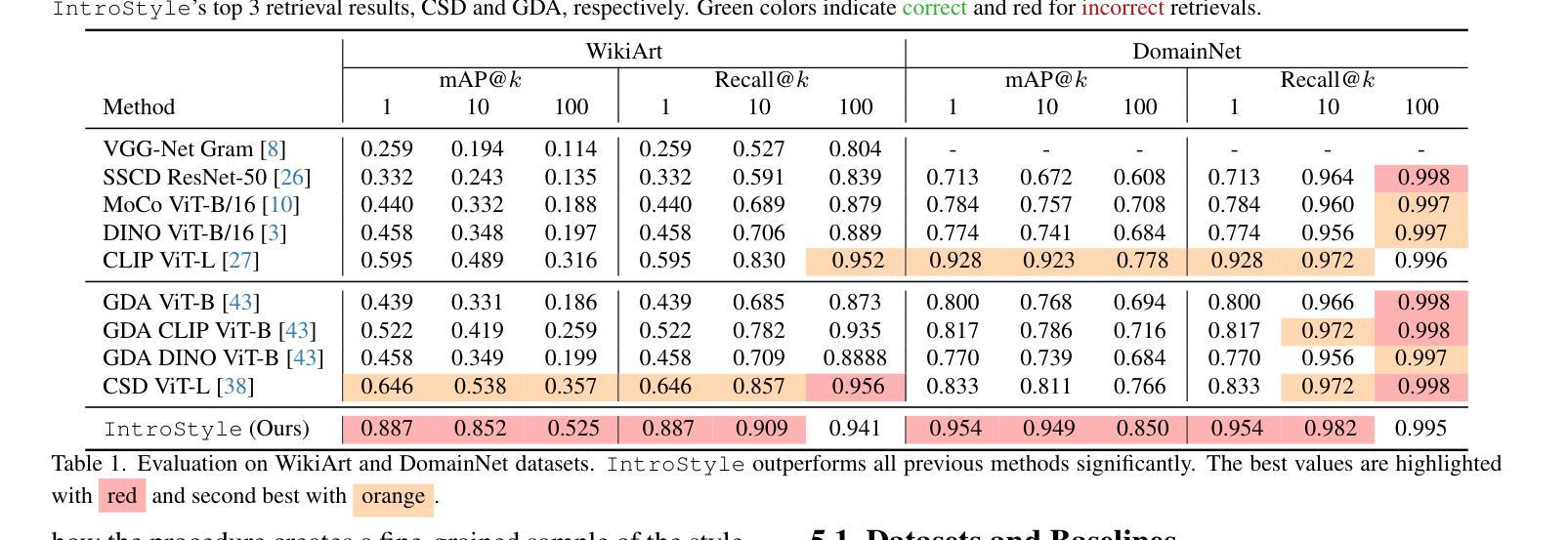
CreatiLayout: Siamese Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Creative Layout-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hui Zhang, Dexiang Hong, Yitong Wang, Jie Shao, Xinglong Wu, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang
Diffusion models have been recognized for their ability to generate images that are not only visually appealing but also of high artistic quality. As a result, Layout-to-Image (L2I) generation has been proposed to leverage region-specific positions and descriptions to enable more precise and controllable generation. However, previous methods primarily focus on UNet-based models (\eg SD1.5 and SDXL), and limited effort has explored Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiTs), which have demonstrated powerful image generation capabilities. Enabling MM-DiT for layout-to-image generation seems straightforward but is challenging due to the complexity of how layout is introduced, integrated, and balanced among multiple modalities. To this end, we explore various network variants to efficiently incorporate layout guidance into MM-DiT, and ultimately present SiamLayout. To inherit the advantages of MM-DiT, we use a separate set of network weights to process the layout, treating it as equally important as the image and text modalities. Meanwhile, to alleviate the competition among modalities, we decouple the image-layout interaction into a siamese branch alongside the image-text one and fuse them in the later stage. Moreover, we contribute a large-scale layout dataset, named LayoutSAM, which includes 2.7 million image-text pairs and 10.7 million entities. Each entity is annotated with a bounding box and a detailed description. We further construct the LayoutSAM-Eval benchmark as a comprehensive tool for evaluating the L2I generation quality. Finally, we introduce the Layout Designer, which taps into the potential of large language models in layout planning, transforming them into experts in layout generation and optimization. These components form CreatiLayout – a systematic solution that integrates the layout model, dataset, and planner for creative layout-to-image generation.
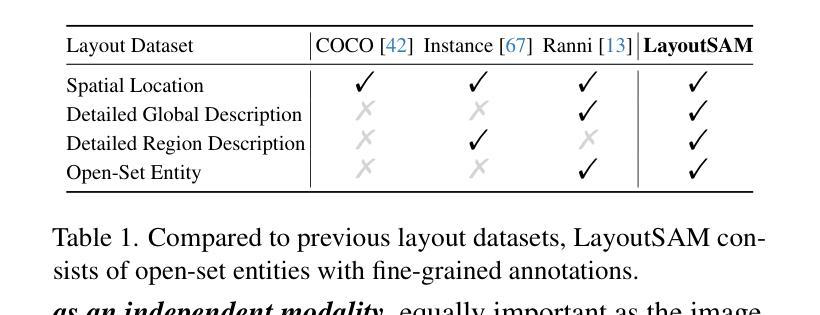
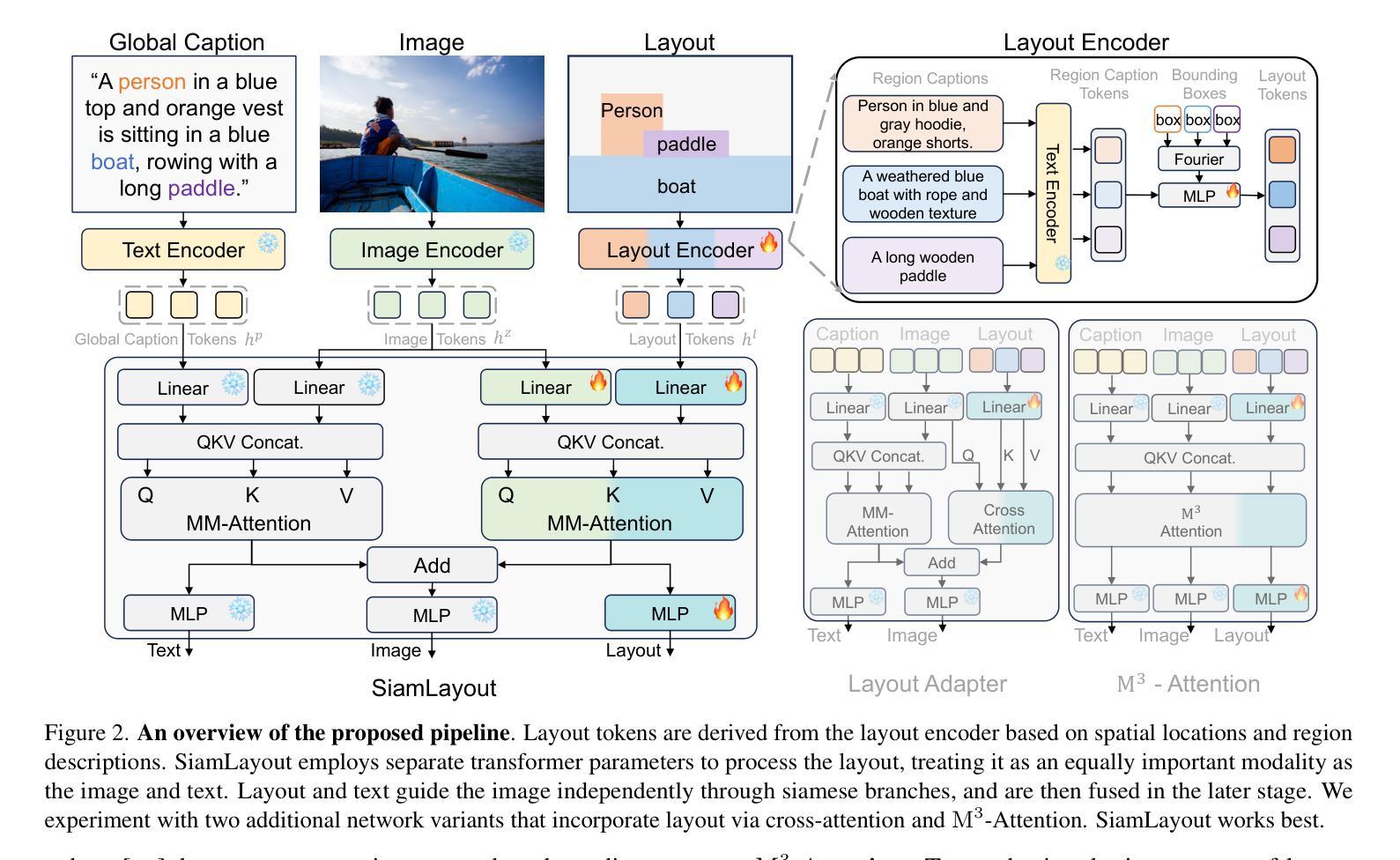
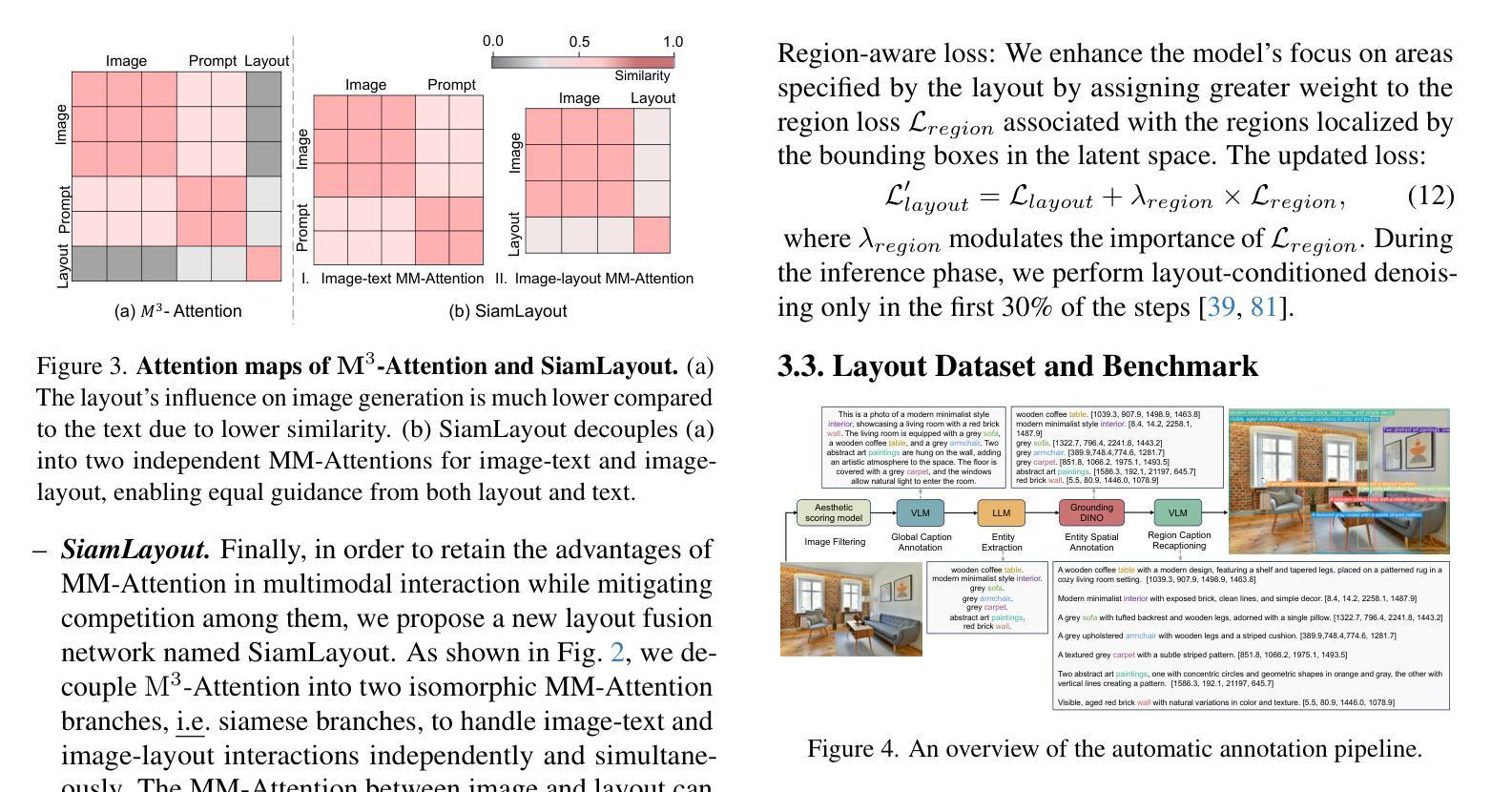
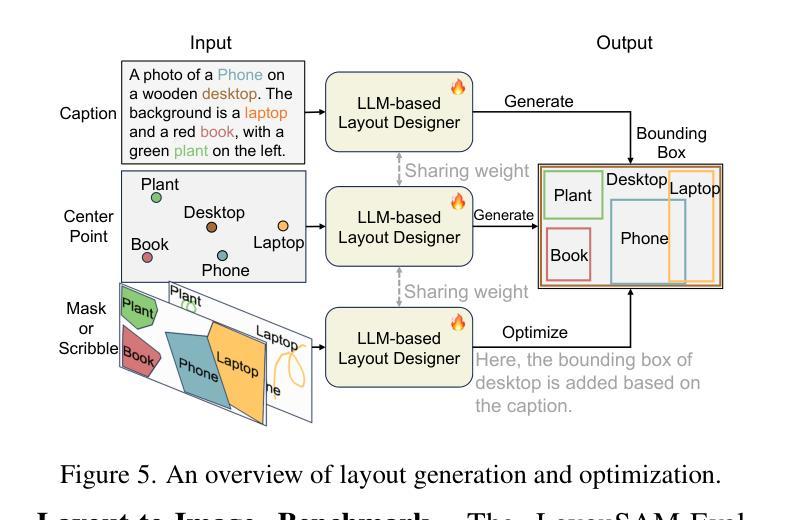
扩散模型因其生成图像的能力而受到认可,这些图像不仅视觉上吸引人,而且具有高度的艺术质量。因此,提出了Layout-to-Image(L2I)生成方法,利用特定区域的位置和描述来实现更精确和可控的生成。然而,以往的方法主要关注基于UNet的模型(例如SD1.5和SDXL),对多模态扩散Transformer(MM-DiT)的探索有限,后者已显示出强大的图像生成能力。虽然使MM-DiT用于布局到图像生成看似简单,但由于引入、集成和平衡布局于多种模态之间的复杂性,这仍然是一个挑战。为此,我们探索了各种网络变体,以有效地将布局指导融入MM-DiT,并最终推出SiamLayout。为了继承MM-DiT的优点,我们使用一组独立的网络权重来处理布局,将其视为与图像和文本模态同样重要。同时,为了减轻模态之间的竞争,我们将图像布局交互从图像文本分支中分离出来,并在后期进行融合。此外,我们贡献了一个大规模布局数据集,名为LayoutSAM,其中包括270万张图像文本对和1070万个实体。每个实体都带有边界框和详细描述。我们还构建了LayoutSAM-Eval基准测试,作为评估L2I生成质量的综合工具。最后,我们推出了布局设计师(Layout Designer),它利用大型语言模型在布局规划中的潜力,将其转化为布局生成和优化的专家。这些组件共同构成了CreatiLayout——一个系统解决方案,集成了布局模型、数据集和规划器,用于创意布局到图像的生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了Diffusion模型在生成具有布局的图像方面的能力。以前的研究主要集中在基于UNet模型的布局生成方法上,但对于Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiT)的研究有限。为了将MM-DiT应用于布局到图像的生成,本文探索了多种网络变体以有效地将布局指导融入MM-DiT,并提出了SiamLayout方法。同时,为了减轻模态之间的竞争,将图像与布局的交互解耦为与图像文本并行的孪生分支,并在后期进行融合。此外,本文贡献了一个大规模布局数据集LayoutSAM,包含图像文本对和实体标注的边界框和详细描述。最后,引入了Layout Designer作为创意布局规划的工具,形成了集布局模型、数据集和规划器于一体的CreatiLayout系统解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion模型能够生成高质量图像。
- Layout-to-Image(L2I)生成利用区域特定位置和描述来实现更精确和可控的生成。
- 之前的研究主要关注UNet-based模型,但对Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiT)的研究有限。
- 将MM-DiT用于L2I生成面临复杂性,需要探索如何有效融入布局指导。
- SiamLayout方法旨在继承MM-DiT的优点,使用单独的网络权重处理布局。
- 为了减轻模态竞争,图像与布局的交互被解耦为孪生分支并在后期融合。
点此查看论文截图

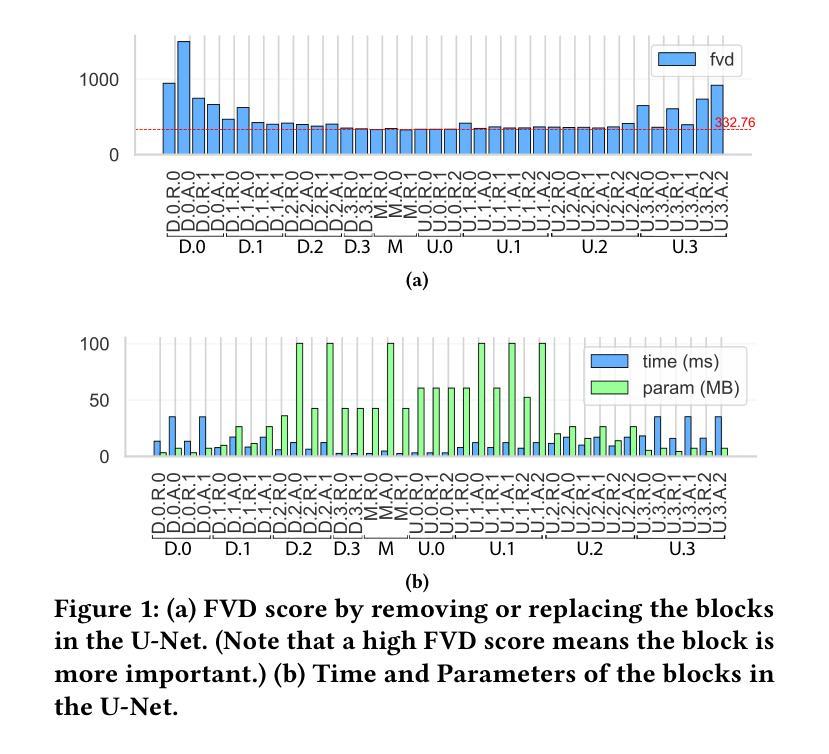
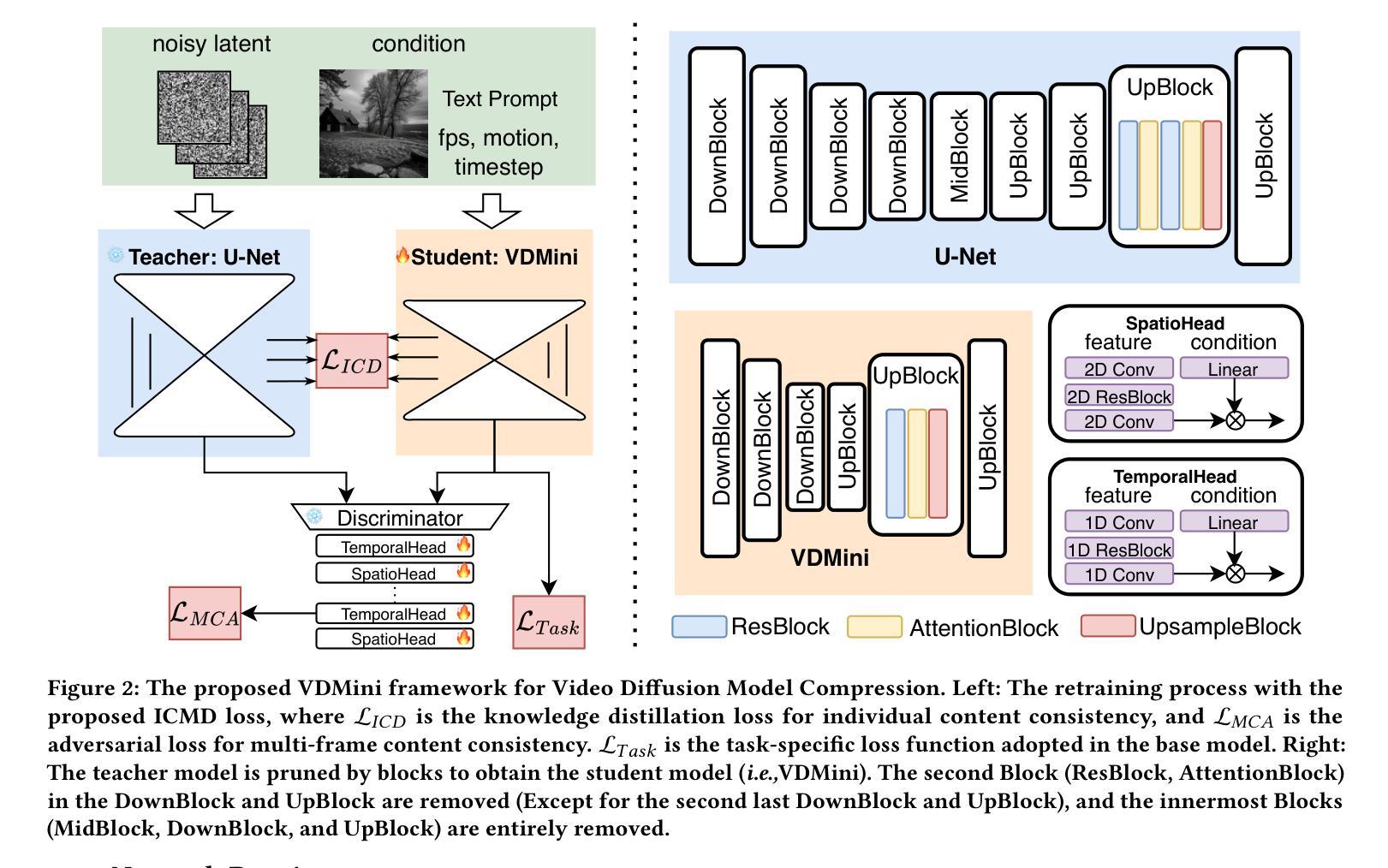
Individual Content and Motion Dynamics Preserved Pruning for Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Yiming Wu, Zhenghao Chen, Huan Wang, Dong Xu
The high computational cost and slow inference time are major obstacles to deploying Video Diffusion Models (VDMs). To overcome this, we introduce a new Video Diffusion Model Compression approach using individual content and motion dynamics preserved pruning and consistency loss. First, we empirically observe that deeper VDM layers are crucial for maintaining the quality of \textbf{motion dynamics} (\textit{e.g.,} coherence of the entire video), while shallower layers are more focused on \textbf{individual content} (\textit{e.g.,} individual frames). Therefore, we prune redundant blocks from the shallower layers while preserving more of the deeper layers, resulting in a lightweight VDM variant called VDMini. Moreover, we propose an \textbf{Individual Content and Motion Dynamics (ICMD)} Consistency Loss to gain comparable generation performance as larger VDM to VDMini. In particular, we first use the Individual Content Distillation (ICD) Loss to preserve the consistency in the features of each generated frame between the teacher and student models. Next, we introduce a Multi-frame Content Adversarial (MCA) Loss to enhance the motion dynamics across the generated video as a whole. This method significantly accelerates inference time while maintaining high-quality video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our VDMini on two important video generation tasks, Text-to-Video (T2V) and Image-to-Video (I2V), where we respectively achieve an average 2.5 $\times$, 1.4 $\times$, and 1.25 $\times$ speed up for the I2V method SF-V, the T2V method T2V-Turbo-v2, and the T2V method HunyuanVideo, while maintaining the quality of the generated videos on several benchmarks including UCF101, VBench-T2V, and VBench-I2V.
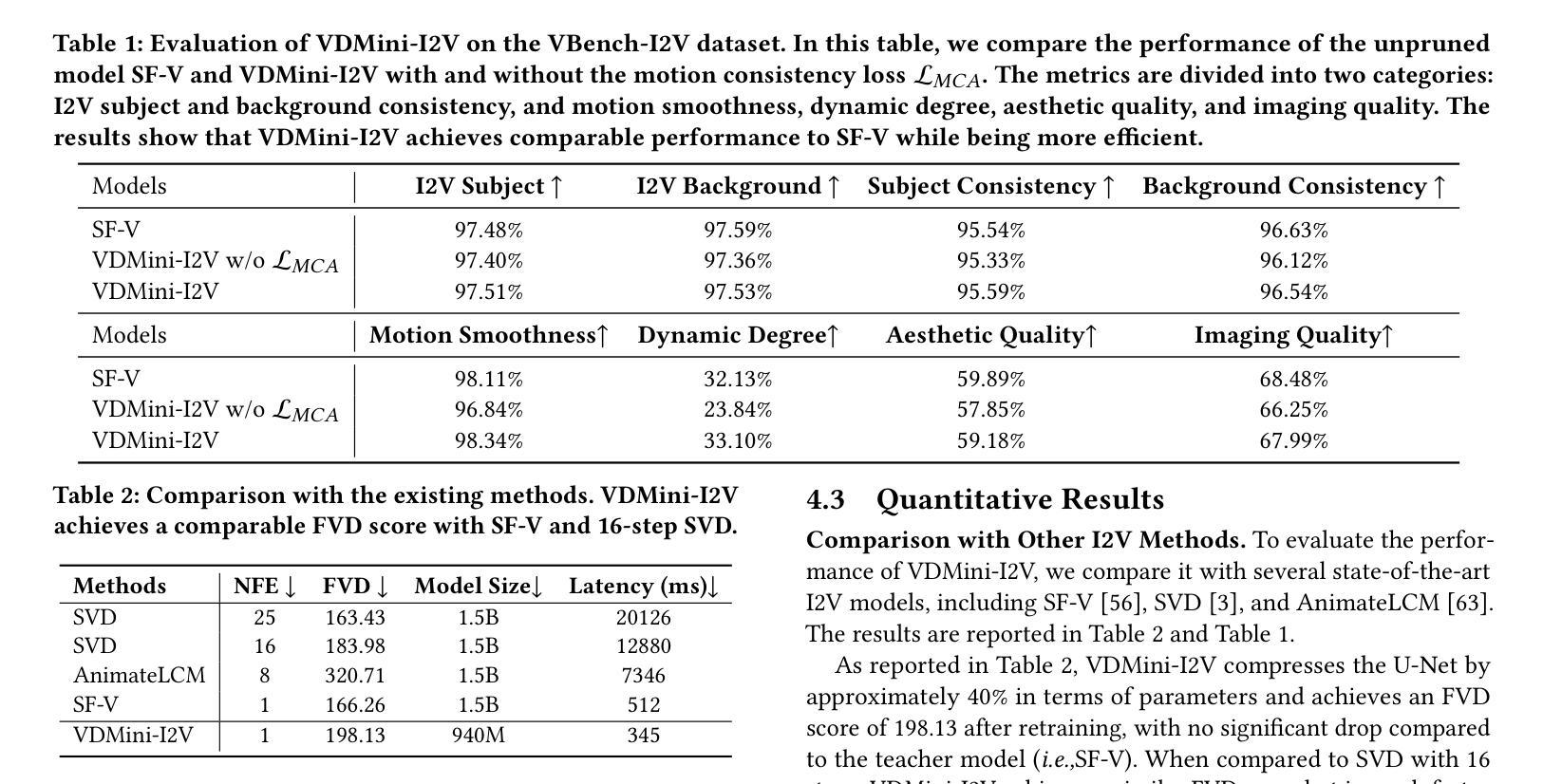
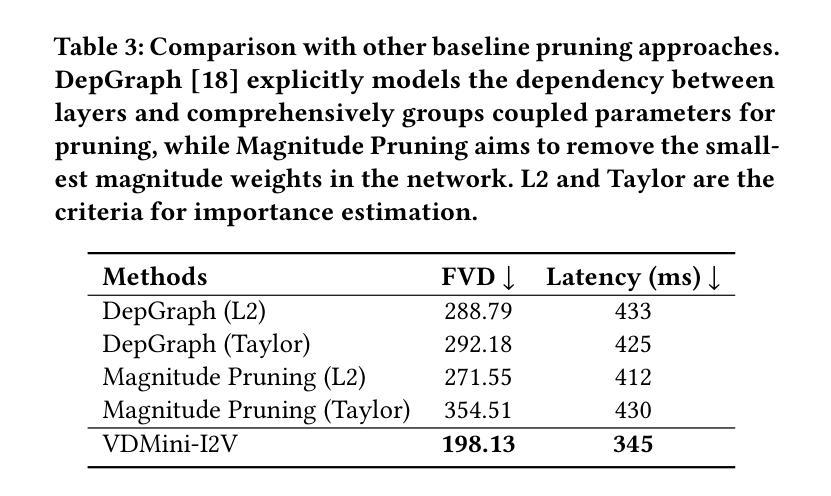
视频扩散模型(VDM)的高计算成本和缓慢的推理时间是其部署的主要障碍。为了克服这一难题,我们引入了一种新的视频扩散模型压缩方法,该方法通过保留个人内容和运动动力学的修剪和一致性损失来实现。首先,我们通过实验观察发现,较深的VDM层对于维持运动动力学的质量(例如整个视频的一致性)至关重要,而较浅的层则更专注于个人内容(例如单个帧)。因此,我们从较浅的层中修剪掉冗余的块,同时保留更多的深层,从而得到一个轻量级的VDM变体,称为VDMini。此外,我们提出了一种个人内容和运动动力学(ICMD)一致性损失,以在较大的VDM和VDMini之间获得相当的生产性能。具体来说,我们首先使用个人内容蒸馏(ICD)损失来保持教师模型和学生模型之间每个生成帧的特征一致性。接下来,我们引入了一种多帧内容对抗(MCA)损失,以提高整个生成视频的运动动力学。该方法显著加速了推理时间,同时保持了高质量的视频生成。大量实验表明,我们的VDMini在两项重要的视频生成任务——文本到视频(T2V)和图像到视频(I2V)上非常有效。在I2V方法SF-V、T2V方法T2V-Turbo-v2和T2V方法HunyuanVideo上,我们分别实现了平均2.5倍、1.4倍和1.25倍的加速,同时在几个基准测试上保持了生成视频的质量,包括UCF101、VBench-T2V和VBench-I2V。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2025
摘要
本文介绍了视频扩散模型(VDM)在计算成本高和推理速度慢方面的主要挑战。为了克服这一问题,提出了一种新的视频扩散模型压缩方法,该方法保留了个人内容和运动动力学的修剪和一致性损失。观察到较深的VDM层对于保持运动动力学质量至关重要,而较浅的层则更专注于个人内容。因此,我们从较浅的层中删除冗余块,同时保留更多的深层,从而产生了轻量级的VDM变体VDMini。此外,还提出了个人内容和运动动力学(ICMD)一致性损失,以在较大的VDM和VDMini之间获得相当的生产性能。通过个体内容蒸馏(ICD)损失保持教师和学生模型之间每个生成帧的特征一致性。接下来,引入多帧内容对抗(MCA)损失,以增强整个生成视频的运动动力学。该方法在保持高质量视频生成的同时,显著加速了推理时间。大量实验证明,VDMini在文本到视频(T2V)和图像到视频(I2V)两个重要的视频生成任务中效果显著,在I2V方法SF-V、T2V方法T2V-Turbo-v2和T2V方法HunyuanVideo上分别实现了平均2.5倍、1.4倍和1.25倍的加速,同时在UCF101、VBench-T2V和VBench-I2V等多个基准测试上保持了视频生成的质量。
关键见解
- 视频扩散模型(VDM)面临高计算成本和慢推理时间的挑战。
- 提出了VDMini:一种轻量级的VDM变体,通过保留深层结构并修剪较浅层的冗余块来实现。
- 引入了个体内容和运动动力学(ICMD)一致性损失,确保模型压缩后性能相当。
- 使用个体内容蒸馏(ICD)损失和多帧内容对抗(MCA)损失来增强视频生成的质量。
- VDMini在文本到视频和图像到视频生成任务中实现了显著加速。
- 在多个基准测试上,VDMini保持了高质量的视频生成性能。
- 方法在保持视频连贯性和动态效果方面特别有效。
点此查看论文截图