⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
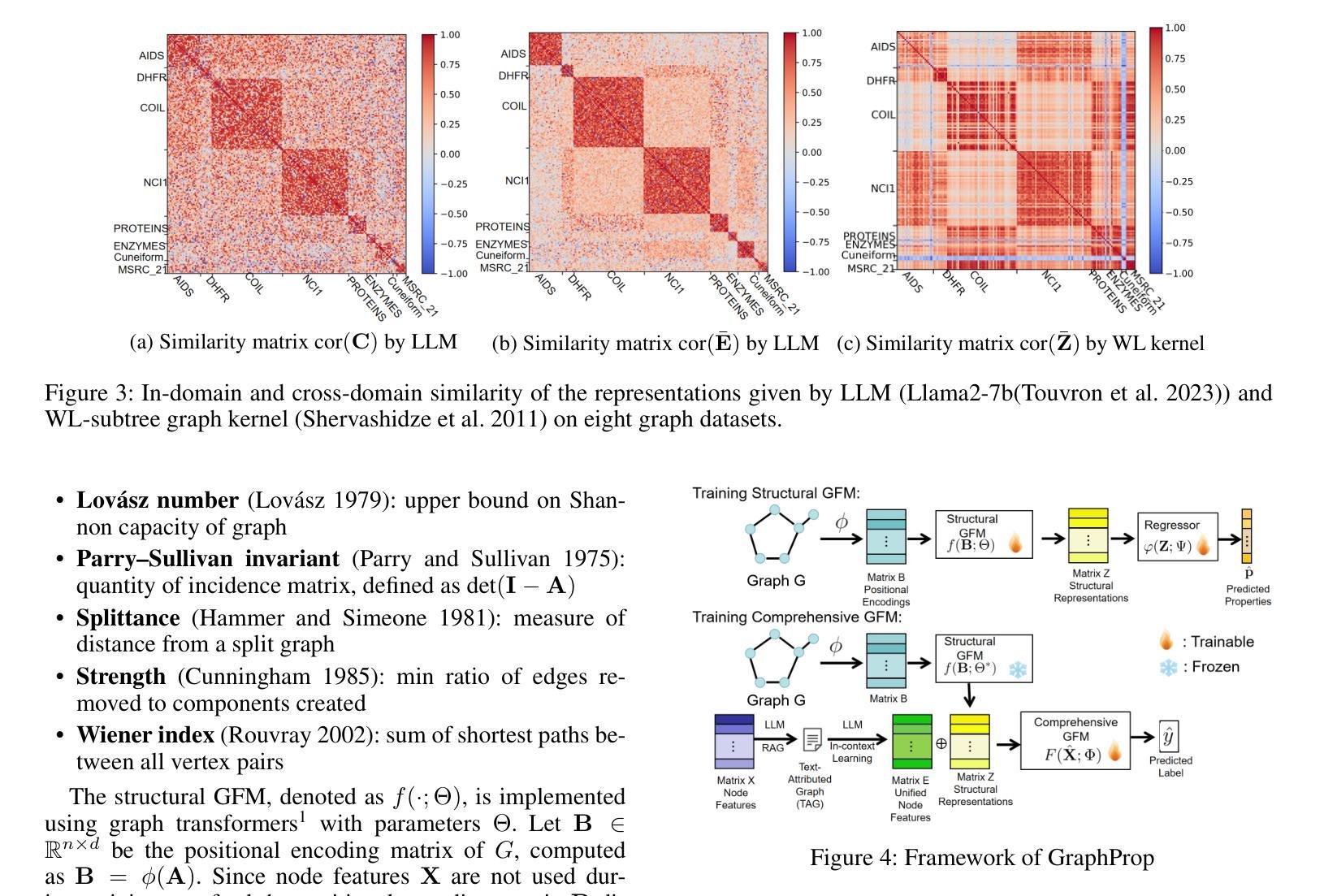
GraphProp: Training the Graph Foundation Models using Graph Properties
Authors:Ziheng Sun, Qi Feng, Lehao Lin, Chris Ding, Jicong Fan
This work focuses on training graph foundation models (GFMs) that have strong generalization ability in graph-level tasks such as graph classification. Effective GFM training requires capturing information consistent across different domains. We discover that graph structures provide more consistent cross-domain information compared to node features and graph labels. However, traditional GFMs primarily focus on transferring node features from various domains into a unified representation space but often lack structural cross-domain generalization. To address this, we introduce GraphProp, which emphasizes structural generalization. The training process of GraphProp consists of two main phases. First, we train a structural GFM by predicting graph invariants. Since graph invariants are properties of graphs that depend only on the abstract structure, not on particular labellings or drawings of the graph, this structural GFM has a strong ability to capture the abstract structural information and provide discriminative graph representations comparable across diverse domains. In the second phase, we use the representations given by the structural GFM as positional encodings to train a comprehensive GFM. This phase utilizes domain-specific node attributes and graph labels to further improve cross-domain node feature generalization. Our experiments demonstrate that GraphProp significantly outperforms the competitors in supervised learning and few-shot learning, especially in handling graphs without node attributes.
本文重点研究图基础模型(GFM)的训练,该模型在图级任务(如图分类)中具有强大的泛化能力。有效的GFM训练需要捕获不同领域间一致的信息。我们发现,与节点特征和图标签相比,图结构提供了更一致的的跨域信息。然而,传统的GFM主要关注将不同领域的节点特征转移到统一的表示空间,但往往缺乏结构化的跨域泛化。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了GraphProp,它强调结构化的泛化。GraphProp的训练过程主要包括两个阶段。首先,我们通过预测图不变量来训练一个结构化的GFM。由于图不变量是仅依赖于抽象结构,而不依赖于特定的标注或图的绘制的图的属性,因此这种结构化的GFM具有很强的捕获抽象结构信息的能力,能够提供跨不同领域的可比较的图表示。在第二阶段,我们使用结构化GFM给出的表示作为位置编码来训练一个全面的GFM。这一阶段利用特定领域的节点属性和图标签来进一步提高跨域节点特征的泛化能力。我们的实验表明,GraphProp在监督学习和小样本学习中都显著优于竞争对手,特别是在处理无节点属性的图时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本关注于训练具有强大泛化能力的图基础模型(GFMs),用于执行如图分类等图级任务。文中指出,传统GFMs主要关注将节点特征从各个领域转移到统一的表示空间,但往往缺乏结构跨域泛化能力。为解决这一问题,文中引入了GraphProp,强调结构泛化。GraphProp的训练过程包括两个阶段:首先通过预测图的不变量来训练结构GFM,以捕获抽象结构信息;然后使用结构GFM提供的表示作为位置编码来训练全面的GFM,进一步提高跨域节点特征的泛化能力。实验表明,GraphProp在监督学习和小样本学习中显著优于竞争对手,尤其在处理无节点属性的图时表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 工作重点:训练具有强大泛化能力的图基础模型(GFMs),用于图级任务如图分类。
- 传统GFMs存在的问题:主要关注节点特征的跨域转移,但缺乏结构跨域泛化能力。
- GraphProp的引入:强调结构泛化,通过两个阶段进行训练。
- 第一阶段:通过预测图的不变量来训练结构GFM,以捕获抽象结构信息。
- 第二阶段:使用结构GFM提供的表示作为位置编码来训练全面的GFM,进一步提高跨域节点特征的泛化能力。
- 实验结果:GraphProp在监督学习和小样本学习中表现优异,特别是在处理无节点属性的图时效果突出。
点此查看论文截图

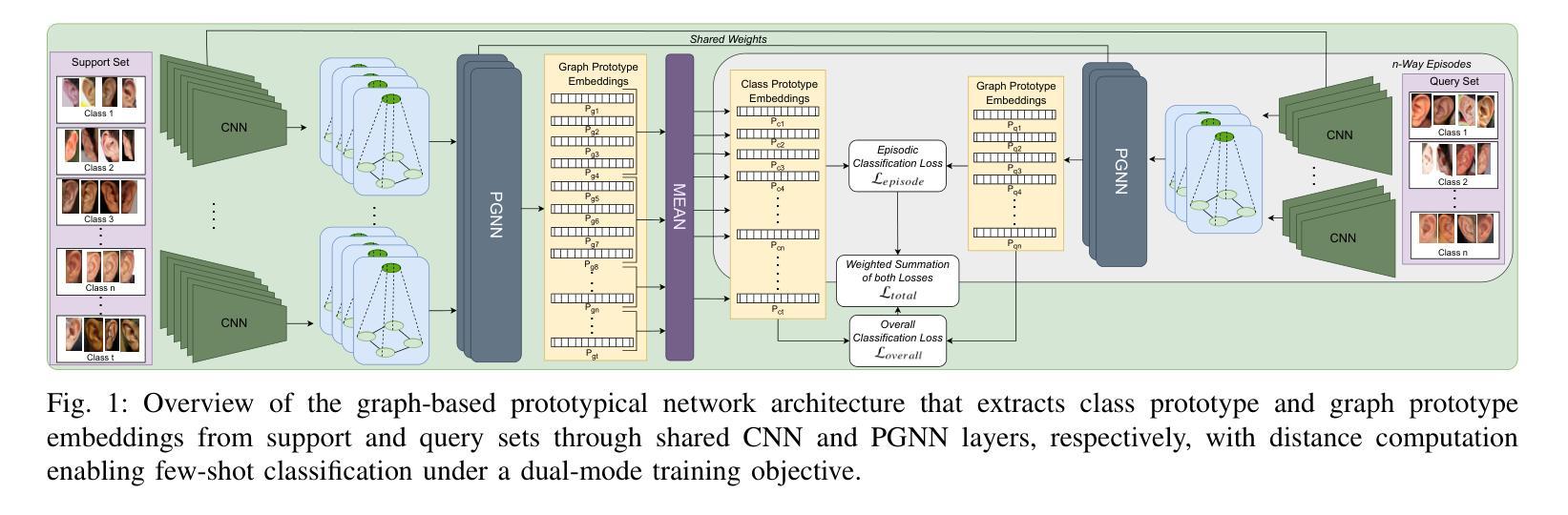
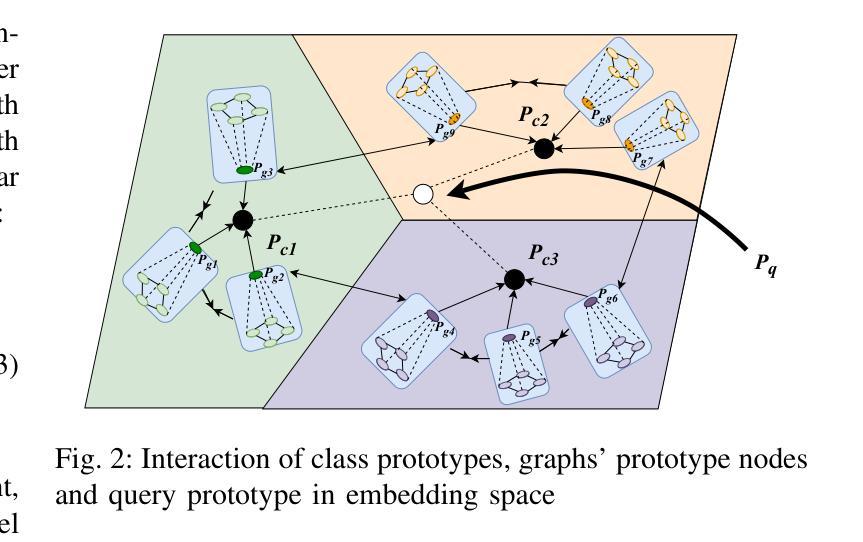
ProtoN: Prototype Node Graph Neural Network for Unconstrained Multi-Impression Ear Recognition
Authors:Santhoshkumar Peddi, Sadhvik Bathini, Arun Balasubramanian, Monalisa Sarma, Debasis Samanta
Ear biometrics offer a stable and contactless modality for identity recognition, yet their effectiveness remains limited by the scarcity of annotated data and significant intra-class variability. Existing methods typically extract identity features from individual impressions in isolation, restricting their ability to capture consistent and discriminative representations. To overcome these limitations, a few-shot learning framework, ProtoN, is proposed to jointly process multiple impressions of an identity using a graph-based approach. Each impression is represented as a node in a class-specific graph, alongside a learnable prototype node that encodes identity-level information. This graph is processed by a Prototype Graph Neural Network (PGNN) layer, specifically designed to refine both impression and prototype representations through a dual-path message-passing mechanism. To further enhance discriminative power, the PGNN incorporates a cross-graph prototype alignment strategy that improves class separability by enforcing intra-class compactness while maintaining inter-class distinction. Additionally, a hybrid loss function is employed to balance episodic and global classification objectives, thereby improving the overall structure of the embedding space. Extensive experiments on five benchmark ear datasets demonstrate that ProtoN achieves state-of-the-art performance, with Rank-1 identification accuracy of up to 99.60% and an Equal Error Rate (EER) as low as 0.025, showing the effectiveness for few-shot ear recognition under limited data conditions.
耳部生物识别技术提供了一种稳定且无接触的身份识别方式,然而,其有效性仍然受到标注数据稀缺和类内变化显著的影响。现有方法通常单独从个别印象中提取身份特征,这限制了它们捕捉一致和判别性表征的能力。为了克服这些局限性,提出了一种小样学习框架ProtoN,采用基于图的方法联合处理身份的多重印象。每个印象被表示为特定类的图中的一个节点,以及一个可学习的原型节点,该节点编码身份级信息。这个图通过专门设计的原型图神经网络(PGNN)层进行处理,通过双路径消息传递机制来优化印象和原型表征。为了进一步提高判别力,PGNN采用跨图原型对齐策略,通过强制类内紧凑性和保持类间区别来提高类可分性。此外,还采用了一种混合损失函数来平衡情景和全局分类目标,从而改善嵌入空间的整体结构。在五个基准耳部数据集上的广泛实验表明,ProtoN达到了最先进的性能,Rank-1识别率高达99.60%,等误率(EER)低至0.025%,在有限数据条件下进行少样本耳部识别时效果显著。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于图神经网络的少样本学习框架ProtoN,用于耳部生物识别。该框架能够联合处理同一身份的多条印象数据,通过构建类特定图,利用图神经网络层优化印象和原型表示。同时采用跨图原型对齐策略,提高类内紧凑性和类间区分度。在五个基准耳部数据集上的实验表明,ProtoN取得了最先进的性能,Rank-1识别准确率高达99.6%,最低等误率(EER)达到0.025%,在有限数据条件下实现了有效的少样本耳部识别。
Key Takeaways
- ProtoN是一种基于图神经网络的少样本学习框架,用于耳部生物识别。
- 它通过构建类特定图,联合处理同一身份的多条印象数据。
- ProtoN使用图神经网络层优化印象和原型表示,提高识别性能。
- 跨图原型对齐策略用于提高类内紧凑性和类间区分度。
- 在五个基准耳部数据集上的实验表明,ProtoN取得了最先进的性能。
- ProtoN的Rank-1识别准确率高达99.6%,最低等误率(EER)达到0.025%。
点此查看论文截图

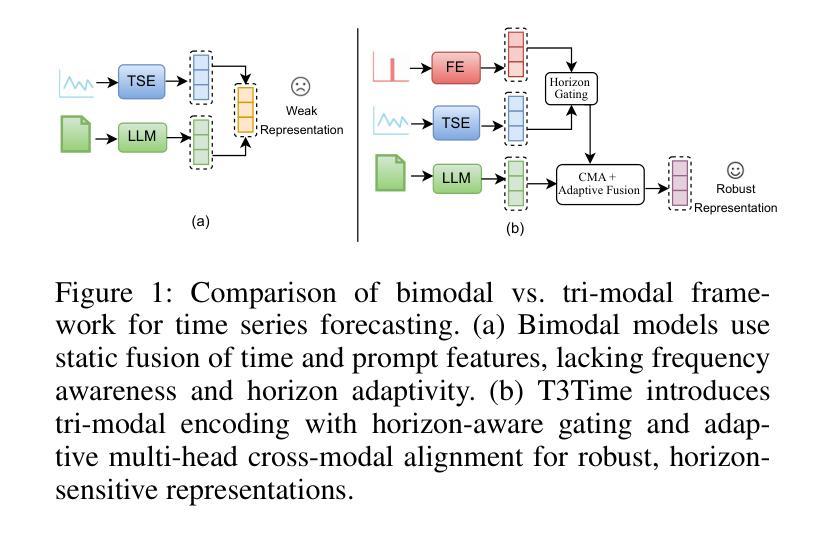
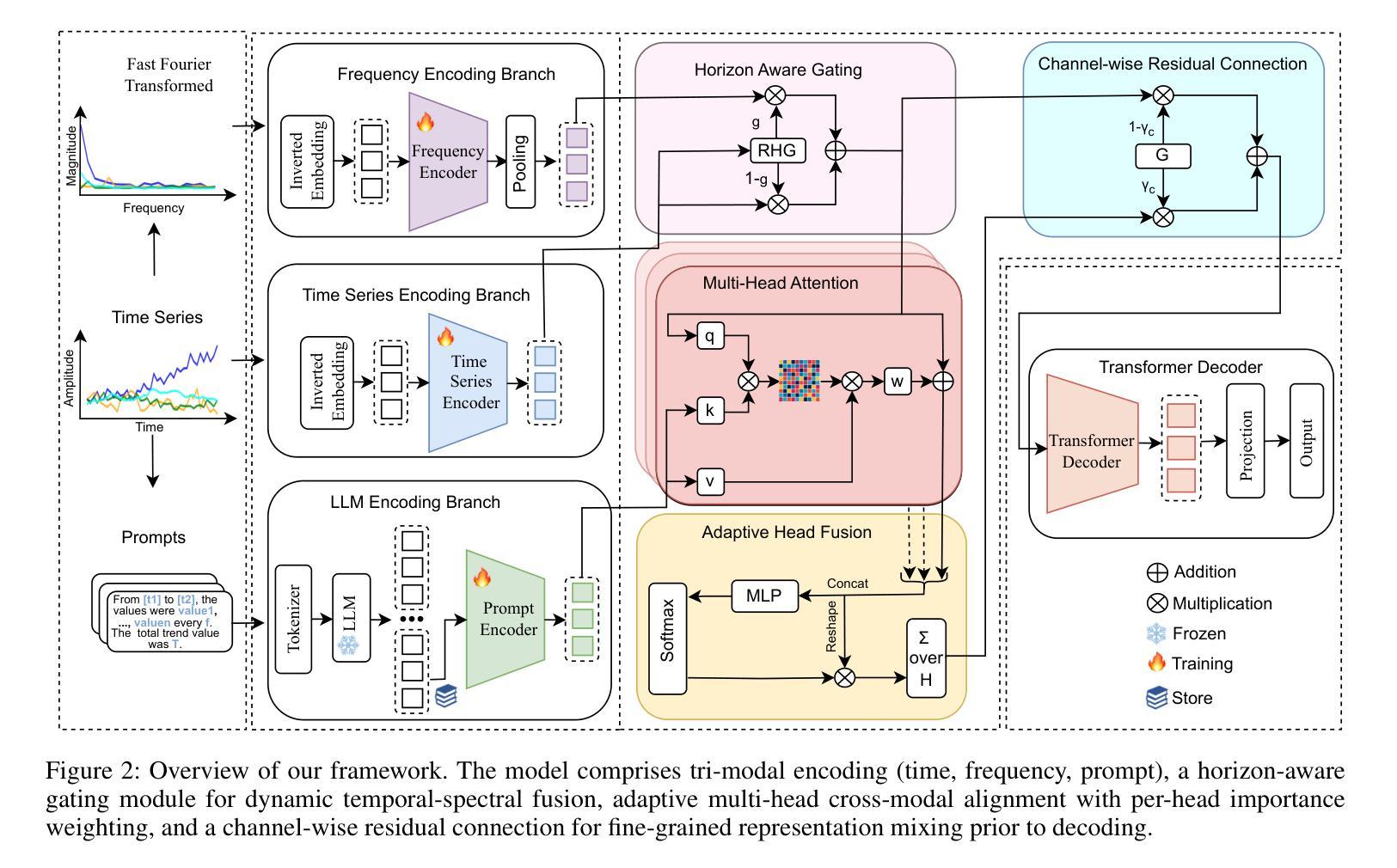
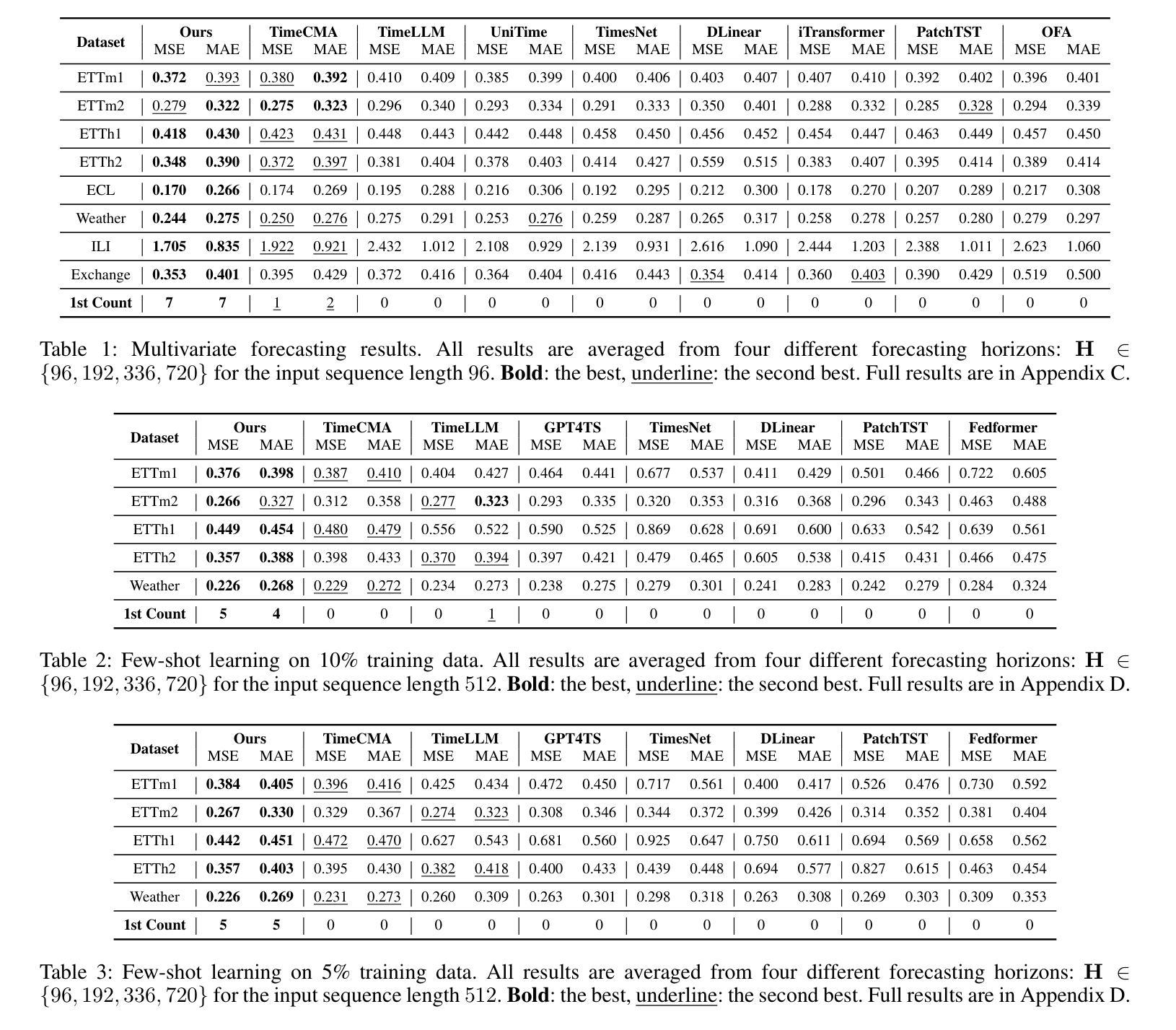
T3Time: Tri-Modal Time Series Forecasting via Adaptive Multi-Head Alignment and Residual Fusion
Authors:Abdul Monaf Chowdhury, Rabeya Akter, Safaeid Hossain Arib
Multivariate time series forecasting (MTSF) seeks to model temporal dynamics among variables to predict future trends. Transformer-based models and large language models (LLMs) have shown promise due to their ability to capture long-range dependencies and patterns. However, current methods often rely on rigid inductive biases, ignore intervariable interactions, or apply static fusion strategies that limit adaptability across forecast horizons. These limitations create bottlenecks in capturing nuanced, horizon-specific relationships in time-series data. To solve this problem, we propose T3Time, a novel trimodal framework consisting of time, spectral, and prompt branches, where the dedicated frequency encoding branch captures the periodic structures along with a gating mechanism that learns prioritization between temporal and spectral features based on the prediction horizon. We also proposed a mechanism which adaptively aggregates multiple cross-modal alignment heads by dynamically weighting the importance of each head based on the features. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving an average reduction of 3.28% in MSE and 2.29% in MAE. Furthermore, it shows strong generalization in few-shot learning settings: with 5% training data, we see a reduction in MSE and MAE by 4.13% and 1.91%, respectively; and with 10% data, by 3.62% and 1.98% on average. Code - https://github.com/monaf-chowdhury/T3Time/
多元时间序列预测(MTSF)旨在建立变量之间的时间动态模型,以预测未来趋势。基于Transformer的模型和大语言模型(LLM)由于其捕捉长期依赖和模式的能力而显示出潜力。然而,当前的方法经常依赖僵化的归纳偏见,忽略变量间的相互作用,或采用静态融合策略,这限制了在不同预测期限内的适应性。这些局限性导致在捕捉时间序列数据中细微、特定时期的复杂关系时存在瓶颈。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了T3Time,这是一个新的三模态框架,包括时间、光谱和提示分支,其中专用的频率编码分支捕捉周期性结构,以及一个基于预测期限学习时间和光谱特征之间优先级的门控机制。我们还提出了一种机制,通过动态权衡每个头的重要性来自适应地聚合多个跨模态对齐头。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型始终优于最先进的基线,在MSE和MAE上平均降低了3.28%和2.29%。此外,它在小样本学习环境中显示出强大的泛化能力:使用5%的训练数据,我们看到MSE和MAE分别平均降低了4.13%和1.91%;使用10%的数据,降低了3.62%和1.98%。代码地址:[https://github.com/monaf-chowdhury/T3Time/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对多元时间序列预测(MTSF)问题,提出一种新型的三模态框架T3Time。该框架通过时间、光谱和提示分支捕捉时间序列数据的周期性结构和时间动态,并自适应地聚合跨模态对齐头。实验表明,T3Time在基准数据集上表现优异,显著减少了平均误差。
Key Takeaways
- T3Time是一个针对多元时间序列预测(MTSF)的三模态框架,包含时间、光谱和提示分支。
- T3Time通过频率编码分支捕捉数据的周期性结构,并有一个门控机制根据预测视野学习时间特征和光谱特征之间的优先级。
- T3Time自适应地聚合多个跨模态对齐头,根据特征动态调整每个头的重要性。
- 实验表明,T3Time在基准数据集上表现优秀,相较于其他最新技术基线,平均减少了MSE和MAE。
- T3Time在少量训练数据的情况下表现出强大的泛化能力,使用5%和10%的数据分别降低了MSE和MAE。
- T3Time的代码已公开,便于他人使用和研究。
- 该研究为时间序列预测领域提供了一个新的、有效的模型和方法。
点此查看论文截图

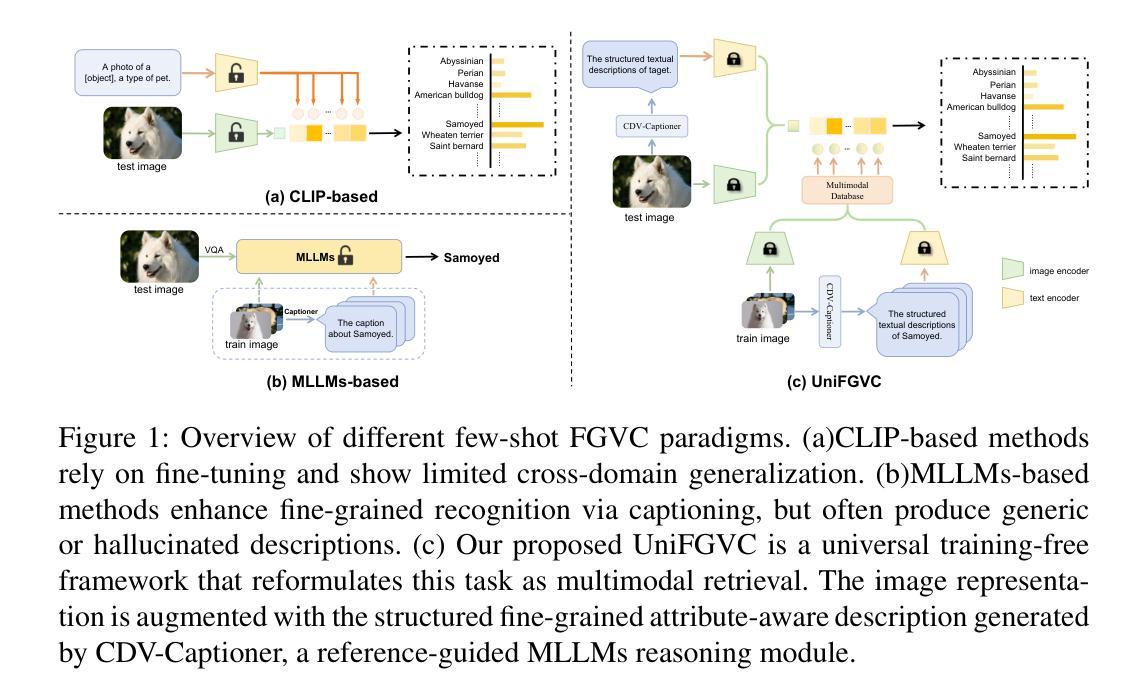
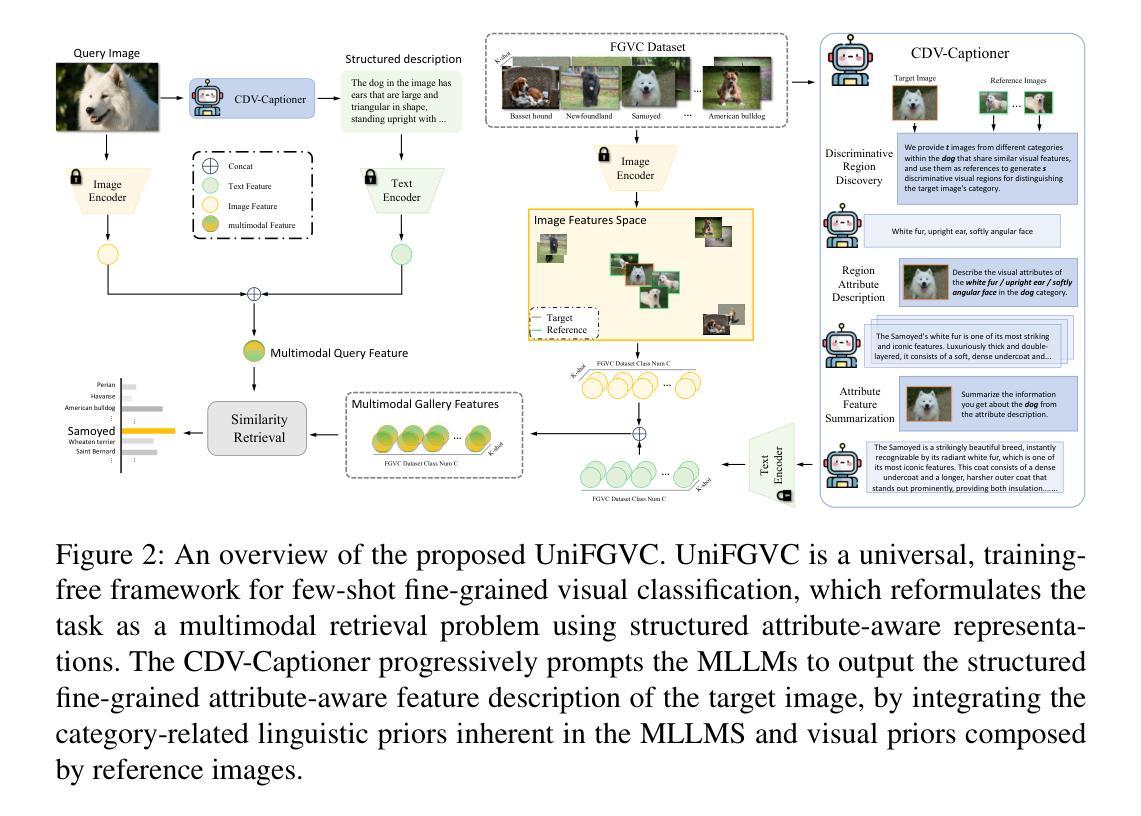
UniFGVC: Universal Training-Free Few-Shot Fine-Grained Vision Classification via Attribute-Aware Multimodal Retrieval
Authors:Hongyu Guo, Kuan Zhu, Xiangzhao Hao, Haiyun Guo, Ming Tang, Jinqiao Wang
Few-shot fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) aims to leverage limited data to enable models to discriminate subtly distinct categories. Recent works mostly finetuned the pre-trained visual language models to achieve performance gain, yet suffering from overfitting and weak generalization. To deal with this, we introduce UniFGVC, a universal training-free framework that reformulates few-shot FGVC as multimodal retrieval. First, we propose the Category-Discriminative Visual Captioner (CDV-Captioner) to exploit the open-world knowledge of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to generate a structured text description that captures the fine-grained attribute features distinguishing closely related classes. CDV-Captioner uses chain-of-thought prompting and visually similar reference images to reduce hallucination and enhance discrimination of generated captions. Using it we can convert each image into an image-description pair, enabling more comprehensive feature representation, and construct the multimodal category templates using few-shot samples for the subsequent retrieval pipeline. Then, off-the-shelf vision and text encoders embed query and template pairs, and FGVC is accomplished by retrieving the nearest template in the joint space. UniFGVC ensures broad compatibility with diverse MLLMs and encoders, offering reliable generalization and adaptability across few-shot FGVC scenarios. Extensive experiments on 12 FGVC benchmarks demonstrate its consistent superiority over prior few-shot CLIP-based methods and even several fully-supervised MLLMs-based approaches.
少量精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)旨在利用有限数据使模型能够区分细微不同的类别。近期的工作大多对预训练的视觉语言模型进行微调,以实现性能提升,但仍存在过拟合和泛化能力弱的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了UniFGVC,这是一个通用的无训练框架,它将少量精细粒度视觉分类重新定义为多模态检索。首先,我们提出了类别判别视觉描述器(CDV-Captioner),它利用多模态大型语言模型的开放世界知识,生成一个结构化文本描述,该描述捕捉了区分密切相关类别的精细粒度属性特征。CDV-Captioner使用思维链提示和视觉相似的参考图像,以减少幻觉,增强生成描述的辨别能力。使用它,我们可以将每张图像转换为图像描述对,实现更全面的特征表示,并使用少量样本构建多模态类别模板,用于后续检索流程。然后,现成的视觉和文本编码器嵌入查询和模板对,通过检索联合空间中的最近模板来完成FGVC。UniFGVC确保与多种多模态大型语言模型和编码器广泛兼容,在少量精细粒度视觉分类场景中提供可靠的一般化和适应性。在12个FGVC基准测试上的大量实验表明,它在基于CLIP的少量方法以及基于大型语言模型的完全监督方法上表现优越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对少样本细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)问题的UniFGVC框架。该框架通过引入CDV-Captioner,将图像转换为图像描述对,构建模态类别模板,提高模型对细微差别类别的辨别能力。实验表明,UniFGVC在多种细粒度视觉分类任务上表现出优于基于CLIP的少样本方法和某些完全监督的MLLMs方法的一致性能。框架设计具有广泛兼容性和适应性,能在不同的少样本细粒度视觉分类场景中可靠地推广和应用。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中的关键见解要点:
- UniFGVC是一个通用的训练免费框架,用于解决少样本细粒度视觉分类问题。
- 通过引入CDV-Captioner,利用模态大型语言模型的开放世界知识生成结构化文本描述,捕捉细微差别类别的特征。
- CDV-Captioner使用链式思维提示和视觉相似参考图像来减少虚构现象并增强生成的标题的辨别能力。
- UniFGVC将图像转换为图像描述对,构建模态类别模板,提高模型性能。
- 该框架使用现成的视觉和文本编码器嵌入查询和模板对,通过检索最近的模板来完成细粒度视觉分类。
- UniFGVC框架具有广泛的兼容性和适应性,能够在不同的少样本细粒度视觉分类场景中可靠地推广和应用。
点此查看论文截图

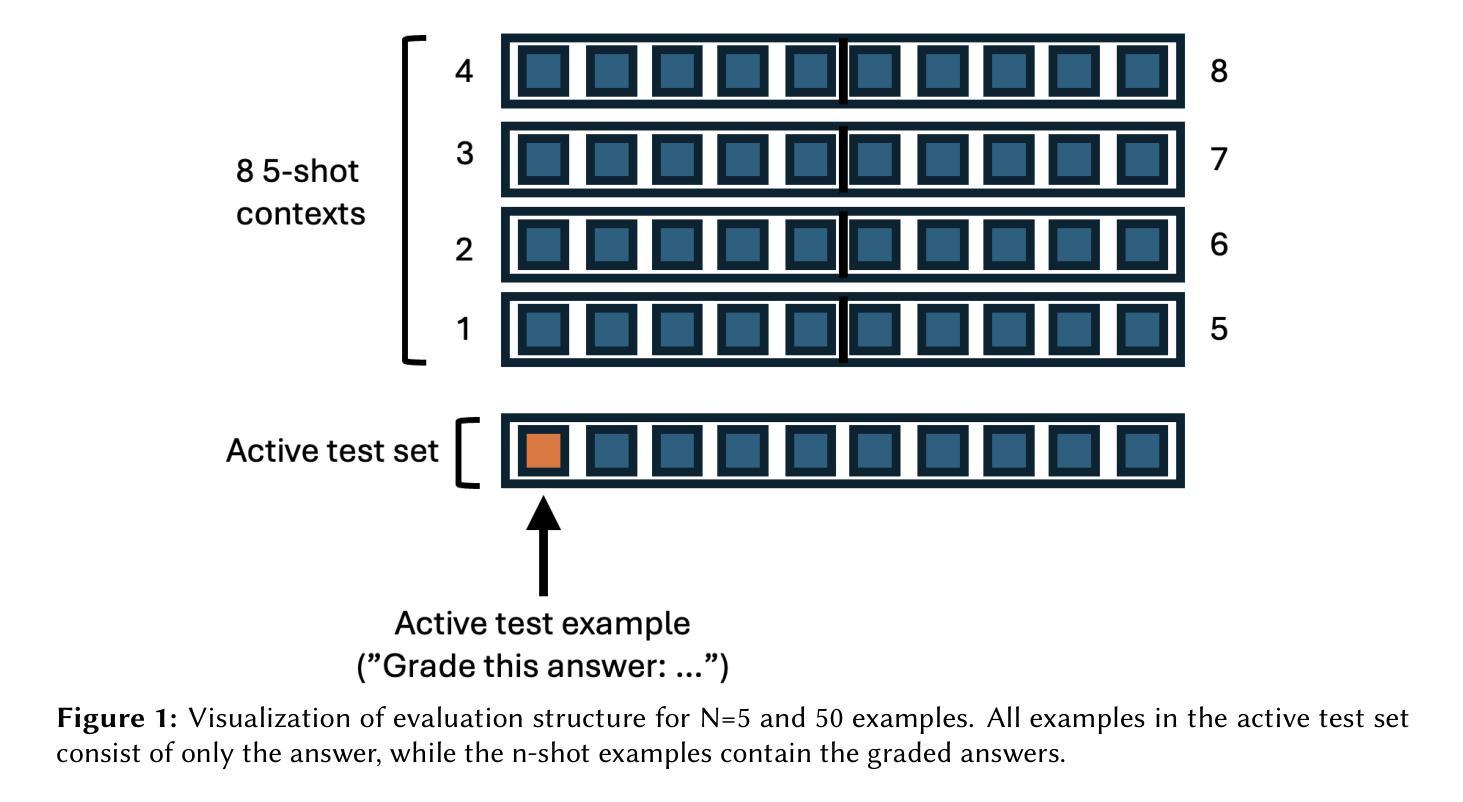
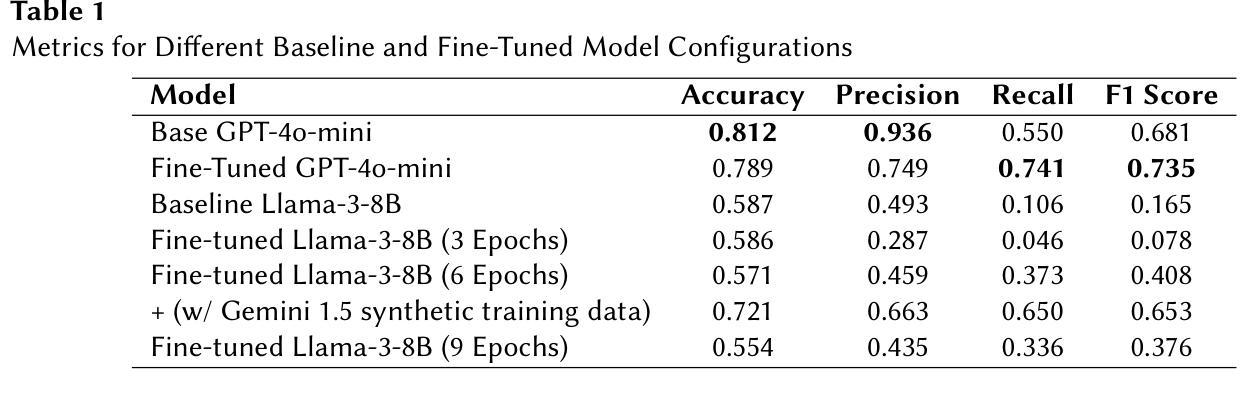
Fine-tuning for Better Few Shot Prompting: An Empirical Comparison for Short Answer Grading
Authors:Joel Walsh, Siddarth Mamidanna, Benjamin Nye, Mark Core, Daniel Auerbach
Research to improve Automated Short Answer Grading has recently focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) with prompt engineering and no- or few-shot prompting to achieve best results. This is in contrast to the fine-tuning approach, which has historically required large-scale compute clusters inaccessible to most users. New closed-model approaches such as OpenAI’s fine-tuning service promise results with as few as 100 examples, while methods using open weights such as quantized low-rank adaptive (QLORA) can be used to fine-tune models on consumer GPUs. We evaluate both of these fine-tuning methods, measuring their interaction with few-shot prompting for automated short answer grading (ASAG) with structured (JSON) outputs. Our results show that finetuning with small amounts of data has limited utility for Llama open-weight models, but that fine-tuning methods can outperform few-shot baseline instruction-tuned LLMs for OpenAI’s closed models. While our evaluation set is limited, we find some evidence that the observed benefits of finetuning may be impacted by the domain subject matter. Lastly, we observed dramatic improvement with the LLama 3.1 8B-Instruct open-weight model by seeding the initial training examples with a significant amount of cheaply generated synthetic training data.
关于提高自动简答题评分的研究最近主要集中在大型语言模型(LLM)上,通过提示工程和零样本或少样本提示来获得最佳结果。这与传统的微调方法形成对比,微调方法在过去需要大规模的计算集群,大多数用户无法使用。新的封闭模型方法,如OpenAI的微调服务,只需使用100个示例即可获得结果,而使用公开权重的方法,如量化低秩自适应(QLORA),则可以在消费者GPU上进行模型微调。我们对这两种微调方法进行了评估,测量了它们在结构化(JSON)输出的自动简答题评分(ASAG)任务中与少样本提示的交互作用。我们的结果表明,对于Llama公开权重模型,使用少量数据进行微调的效用有限,但对于OpenAI的封闭模型,微调方法可以在一定程度上超越以指令为基准进行训练的少样本LLM的表现。虽然我们的评估集有限,但我们发现观察到的微调的好处可能会受到领域主题的影响。最后,我们观察到通过在初始训练示例中添加大量廉价生成的合成训练数据,LLama 3.1 8B-Instruct公开权重模型可以显著改善效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Automated Evaluation of Learning and Assessment Content co-located with 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED 2025)
Summary
LLM在自动短答案评分中的应用近来受到关注,研究者采用大型语言模型(LLMs)结合提示工程技术或无/少提示来达到最佳效果。传统的微调方法需要大量计算集群,新的闭式模型方法如OpenAI的微调服务只需少量示例即可实现结果。研究评估了这两种微调方法,并测量它们在结构化输出上与少提示相结合的效果。结果表明,对于某些模型,微调对少量数据的效用有限,但对于某些模型,微调效果优于基于指令的少量示例LLMs。评估结果表明,微调的优势可能受主题领域影响。为LLama 3.1 8B-Instruct开放权重模型提供大量廉价生成的合成训练数据可实现显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动短答案评分(ASAG)方面取得了最新研究关注。
- 研究人员通过采用提示工程技术实现最佳结果,使用无或少提示方法。
- 传统微调方法需要大量计算资源,而新的闭式模型方法如OpenAI的微调服务仅需少量示例即可实现结果。
- 对微调方法和少提示相结合的效果进行了评估,发现对特定模型的效用有限。
点此查看论文截图

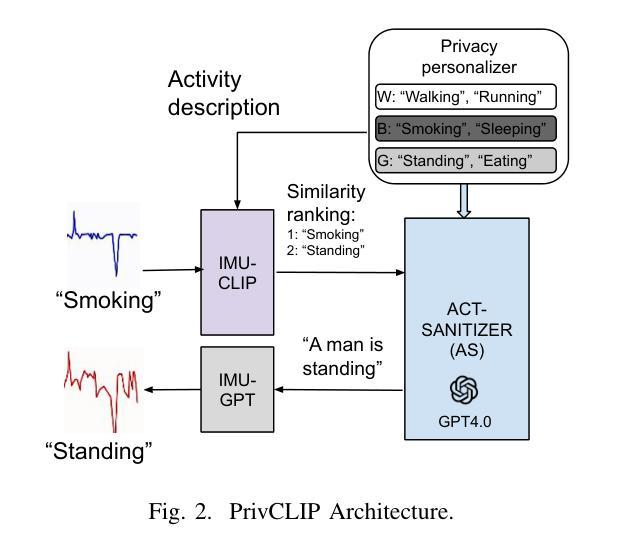
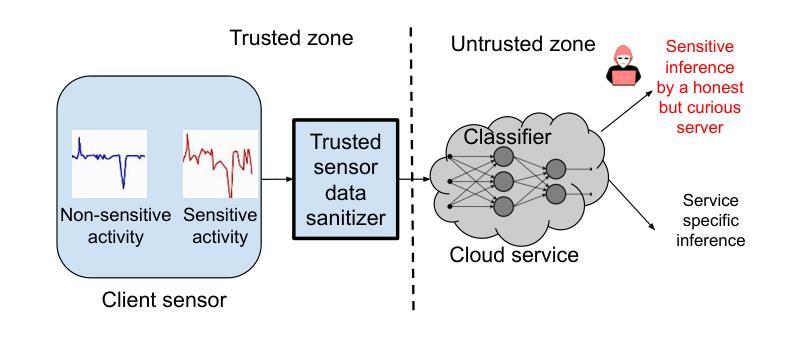
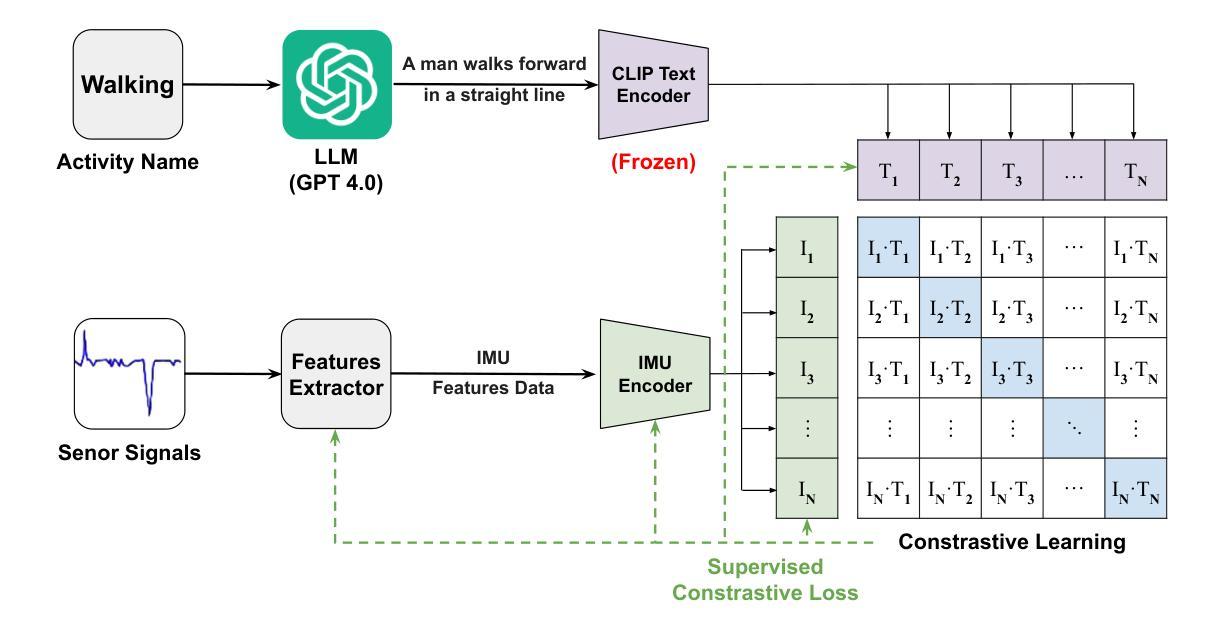
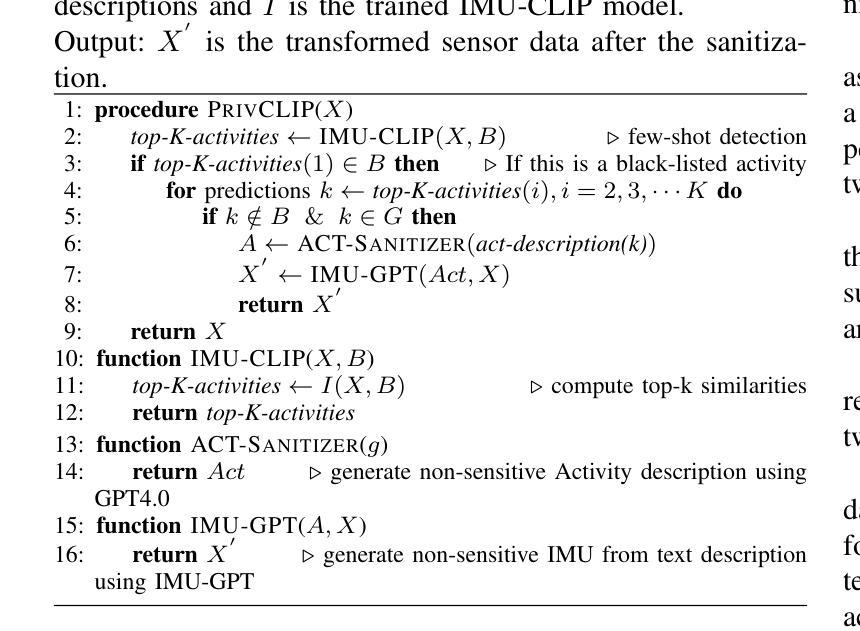
Dynamic User-controllable Privacy-preserving Few-shot Sensing Framework
Authors:Ajesh Koyatan Chathoth, Shuhao Yu, Stephen Lee
User-controllable privacy is important in modern sensing systems, as privacy preferences can vary significantly from person to person and may evolve over time. This is especially relevant in devices equipped with Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensors, such as smartphones and wearables, which continuously collect rich time-series data that can inadvertently expose sensitive user behaviors. While prior work has proposed privacy-preserving methods for sensor data, most rely on static, predefined privacy labels or require large quantities of private training data, limiting their adaptability and user agency. In this work, we introduce PrivCLIP, a dynamic, user-controllable, few-shot privacy-preserving sensing framework. PrivCLIP allows users to specify and modify their privacy preferences by categorizing activities as sensitive (black-listed), non-sensitive (white-listed), or neutral (gray-listed). Leveraging a multimodal contrastive learning approach, PrivCLIP aligns IMU sensor data with natural language activity descriptions in a shared embedding space, enabling few-shot detection of sensitive activities. When a privacy-sensitive activity is identified, the system uses a language-guided activity sanitizer and a motion generation module (IMU-GPT) to transform the original data into a privacy-compliant version that semantically resembles a non-sensitive activity. We evaluate PrivCLIP on multiple human activity recognition datasets and demonstrate that it significantly outperforms baseline methods in terms of both privacy protection and data utility.
在现代感知系统中,用户可控的隐私至关重要,因为每个人的隐私偏好可能大相径庭,并可能随时间演变。这在配备有惯性测量单元(IMU)传感器的设备中尤其重要,例如智能手机和可穿戴设备,这些设备会持续收集丰富的时间序列数据,这些数据可能无意中暴露用户的敏感行为。尽管先前的工作已经提出了保护传感器数据隐私的方法,但大多数方法依赖于静态的预定义隐私标签或需要大量私有训练数据,这限制了其适应性和用户控制权。在这项工作中,我们介绍了PrivCLIP,这是一个动态、用户可控的、具有隐私保护功能的少样本感知框架。PrivCLIP允许用户通过分类活动为敏感(黑名单)、非敏感(白名单)或中性(灰名单)来指定和修改其隐私偏好。利用多模态对比学习方法,PrivCLIP将IMU传感器数据与自然语言活动描述对齐到一个共享嵌入空间中,实现了对敏感活动的少样本检测。当检测到隐私敏感的活动时,系统会使用语言指导的活动净化器和运动生成模块(IMU-GPT)将原始数据转换为符合隐私的版本,该版本在语义上类似于非敏感活动。我们在多个人类活动识别数据集上评估了PrivCLIP的性能,结果表明它在隐私保护和数据实用性方面都显著优于基准方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在现代感应系统中用户可控隐私的重要性。针对配备有惯性测量单元(IMU)传感器的设备(如智能手机和可穿戴设备),提出了一种动态、用户可控的少量隐私保护感应框架——PrivCLIP。该框架允许用户通过分类活动(敏感活动、非敏感活动和中性活动)来指定和修改隐私偏好。借助多模态对比学习方法,PrivCLIP在共享嵌入空间中实现了IMU传感器数据与自然语言活动描述的匹配,能够实现对敏感活动的少量检测。当检测到隐私敏感活动时,系统会使用语言引导的活动净化器和运动生成模块(IMU-GPT)将原始数据转换为符合隐私的版本,同时保持与非敏感活动的语义相似性。对PrivCLIP在多个人类活动识别数据集上的评估表明,它在隐私保护和数据效用方面都显著优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 用户可控隐私在现代感应系统中至关重要,因为每个人的隐私偏好可能不同且随时间变化。
- 在配备有IMU传感器的设备中,如智能手机和可穿戴设备,存在隐私泄露风险,需要保护用户隐私。
- 现有隐私保护方法大多依赖静态的预定义隐私标签或需要大量私有训练数据,限制了其适应性和用户控制权。
- PrivCLIP是一种动态、用户可控的少量隐私保护感应框架,允许用户通过分类活动来调整隐私偏好。
- PrivCLIP利用多模态对比学习,实现了IMU传感器数据与自然语言活动描述的匹配,能少量检测敏感活动。
- 当检测到敏感活动时,PrivCLIP能够转换原始数据,生成符合隐私的版本,同时保持与非敏感活动的语义相似性。
点此查看论文截图


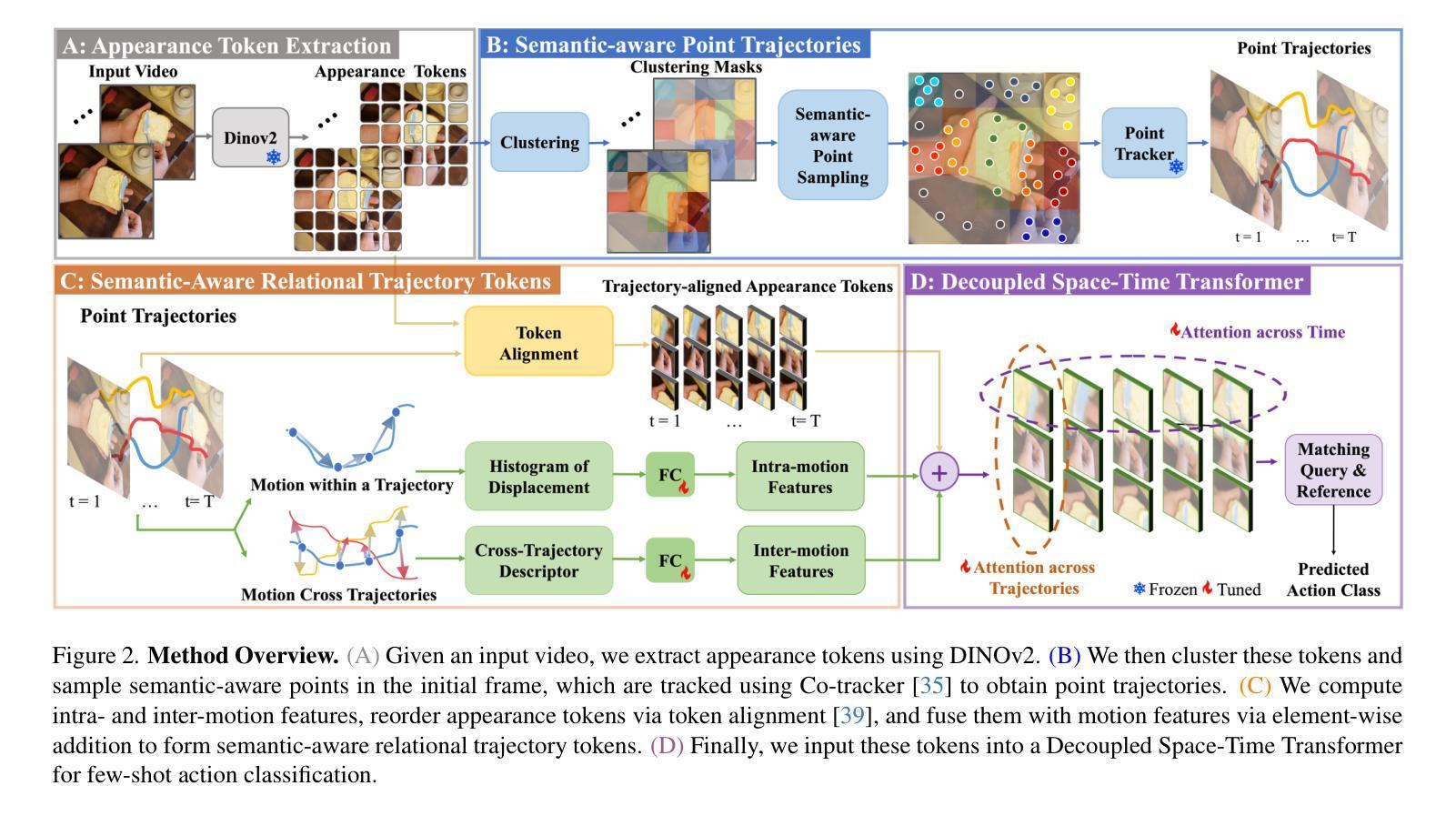
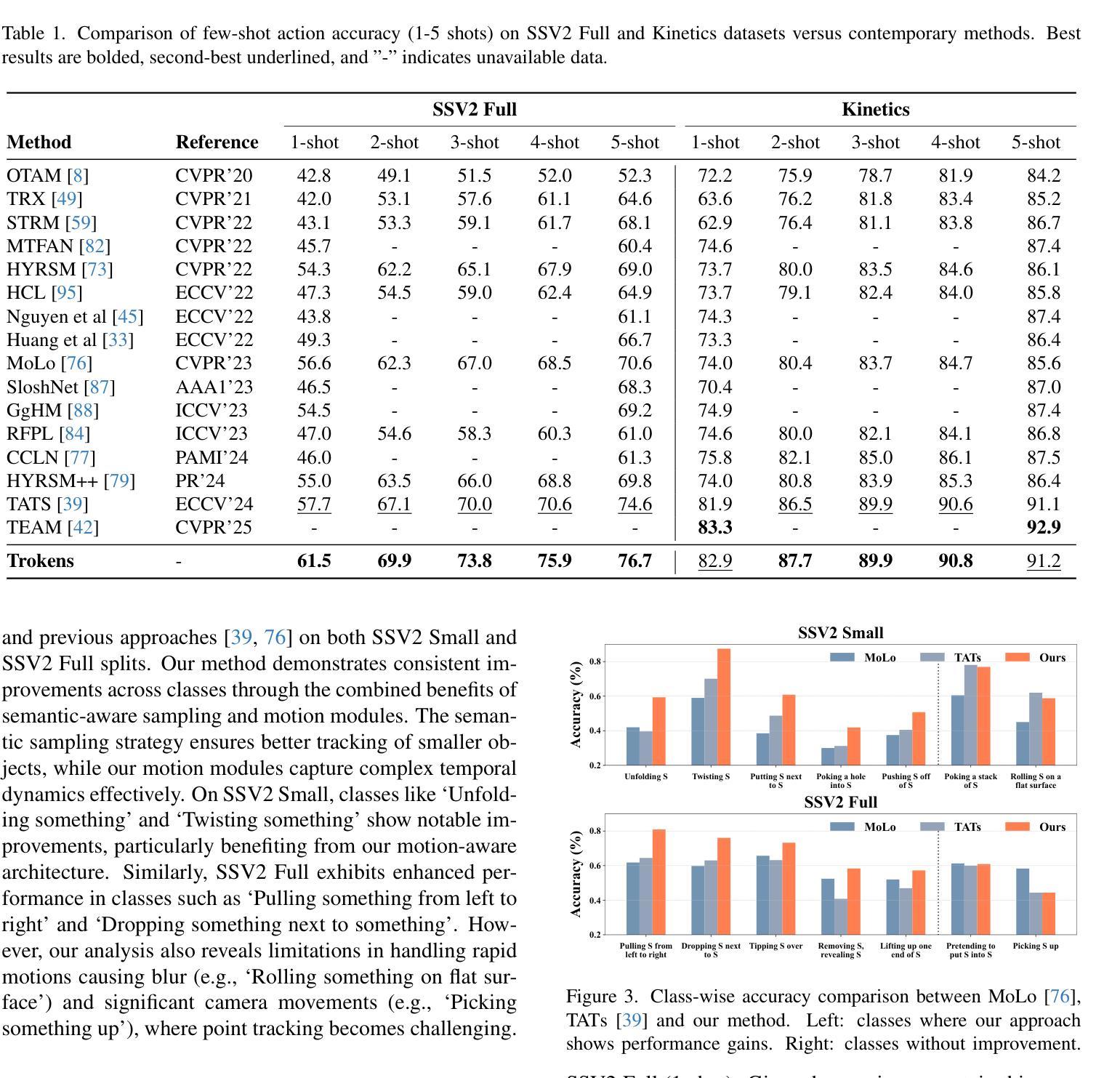
Trokens: Semantic-Aware Relational Trajectory Tokens for Few-Shot Action Recognition
Authors:Pulkit Kumar, Shuaiyi Huang, Matthew Walmer, Sai Saketh Rambhatla, Abhinav Shrivastava
Video understanding requires effective modeling of both motion and appearance information, particularly for few-shot action recognition. While recent advances in point tracking have been shown to improve few-shot action recognition, two fundamental challenges persist: selecting informative points to track and effectively modeling their motion patterns. We present Trokens, a novel approach that transforms trajectory points into semantic-aware relational tokens for action recognition. First, we introduce a semantic-aware sampling strategy to adaptively distribute tracking points based on object scale and semantic relevance. Second, we develop a motion modeling framework that captures both intra-trajectory dynamics through the Histogram of Oriented Displacements (HoD) and inter-trajectory relationships to model complex action patterns. Our approach effectively combines these trajectory tokens with semantic features to enhance appearance features with motion information, achieving state-of-the-art performance across six diverse few-shot action recognition benchmarks: Something-Something-V2 (both full and small splits), Kinetics, UCF101, HMDB51, and FineGym. For project page see https://trokens-iccv25.github.io
视频理解需要有效建模运动信息和外观信息,特别是在小样本动作识别中。虽然最近的点跟踪技术已经显示出能提高小样本动作识别的能力,但仍然存在两个基本挑战:选择信息丰富的点进行跟踪和有效地建模其运动模式。我们提出了Trokens,这是一种将轨迹点转换为语义感知关系令牌进行动作识别的新方法。首先,我们引入了一种语义感知采样策略,基于目标尺度和语义相关性自适应地分布跟踪点。其次,我们开发了一个运动建模框架,通过方向位移直方图(HoD)捕捉轨迹内部动态,并捕捉轨迹之间的关系以模拟复杂的动作模式。我们的方法有效地结合了这些轨迹令牌和语义特征,通过运动信息增强外观特征,在六个不同的小样本动作识别基准测试上达到了最先进的性能:包括Something-Something-V2(全分割和小分割)、Kinetics、UCF101、HMDB51和FineGym。有关项目页面,请参见https://trokens-iccv25.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025; First two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了针对少样本动作识别的新型方法Trokens。该方法将轨迹点转换为语义感知的关系令牌,通过语义感知采样策略自适应分布跟踪点,并开发了一个运动建模框架,结合直方位移(HoD)和轨迹间的关系来模拟复杂的动作模式。该方法实现了在多个少样本动作识别基准测试上的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- Trokens方法将轨迹点转换为语义感知的关系令牌,用于动作识别。
- 引入语义感知采样策略,根据目标尺度和语义相关性自适应分布跟踪点。
- 开发了一个运动建模框架,结合了直方位移(HoD)和轨迹间的关系。
- Trokens实现了在多个少样本动作识别基准测试上的最佳性能。
- 该方法将轨迹令牌与语义特征相结合,增强了外观特征的运动信息。
- 面临选择信息点进行跟踪和有效模拟其运动模式的两个基本挑战。
点此查看论文截图

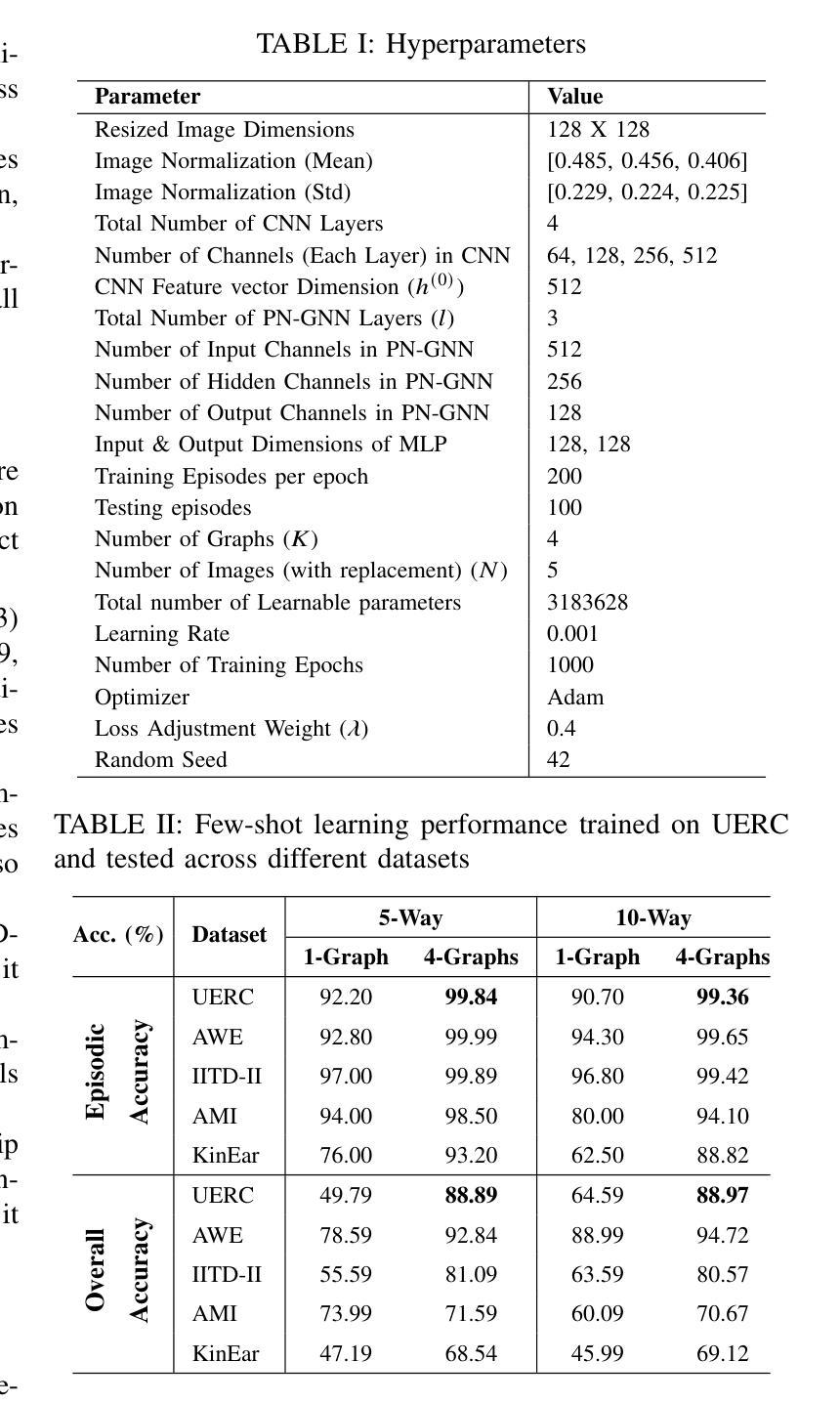
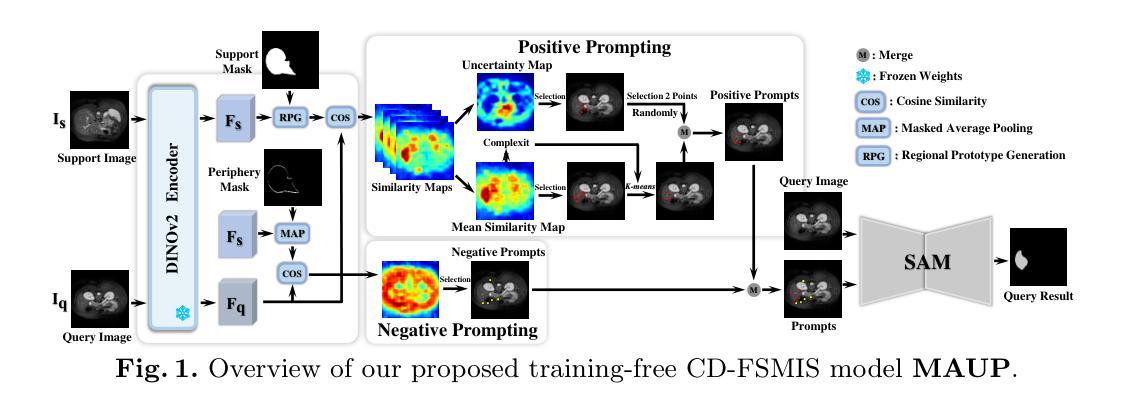
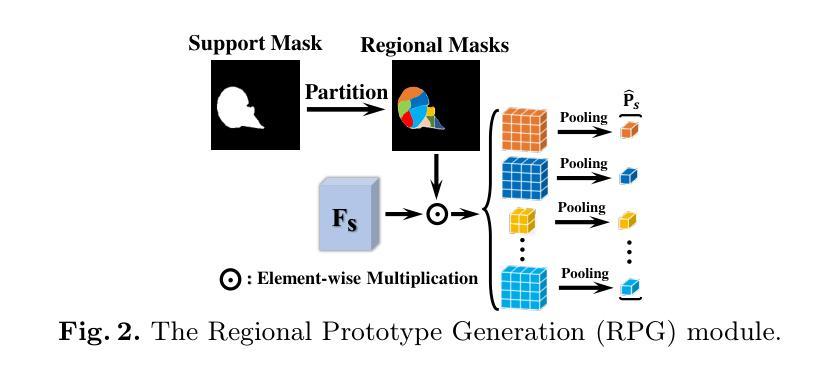
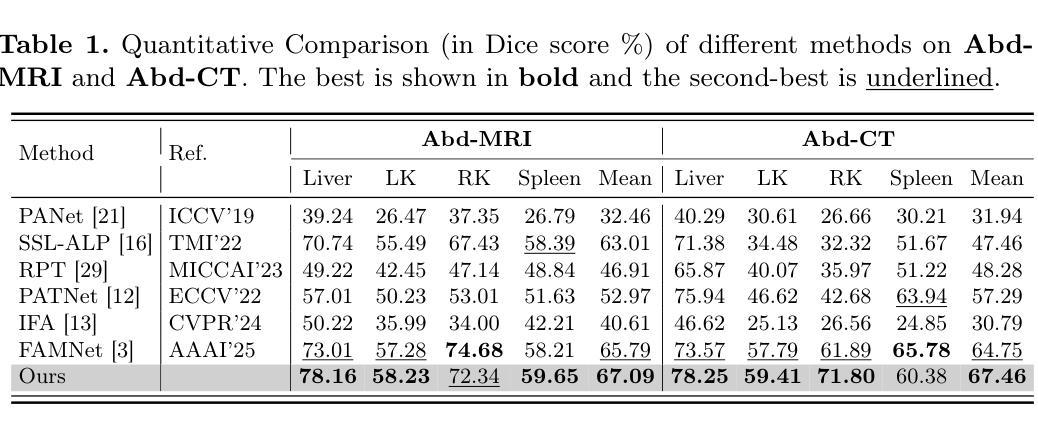
MAUP: Training-free Multi-center Adaptive Uncertainty-aware Prompting for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yazhou Zhu, Haofeng Zhang
Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation (CD-FSMIS) is a potential solution for segmenting medical images with limited annotation using knowledge from other domains. The significant performance of current CD-FSMIS models relies on the heavily training procedure over other source medical domains, which degrades the universality and ease of model deployment. With the development of large visual models of natural images, we propose a training-free CD-FSMIS model that introduces the Multi-center Adaptive Uncertainty-aware Prompting (MAUP) strategy for adapting the foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), which is trained with natural images, into the CD-FSMIS task. To be specific, MAUP consists of three key innovations: (1) K-means clustering based multi-center prompts generation for comprehensive spatial coverage, (2) uncertainty-aware prompts selection that focuses on the challenging regions, and (3) adaptive prompt optimization that can dynamically adjust according to the target region complexity. With the pre-trained DINOv2 feature encoder, MAUP achieves precise segmentation results across three medical datasets without any additional training compared with several conventional CD-FSMIS models and training-free FSMIS model. The source code is available at: https://github.com/YazhouZhu19/MAUP.
跨域小样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)是利用其他领域的知识对医学图像进行有限标注分割的一种潜在解决方案。当前CD-FSMIS模型的高性能表现依赖于在其他源医学领域的大量训练过程,这降低了模型的通用性和部署的便捷性。随着大型自然图像视觉模型的发展,我们提出了一种无需训练的CD-FSMIS模型,该模型引入了多中心自适应不确定性感知提示(MAUP)策略,以适应基于自然图像训练的分割任何模型(SAM)到CD-FSMIS任务。具体来说,MAUP包括三个关键创新点:(1)基于K-means聚类的多中心提示生成,以实现全面的空间覆盖;(2)关注挑战区域的不确定性感知提示选择;(3)可根据目标区域复杂性动态调整的自适应提示优化。与几个传统的CD-FSMIS模型和无需训练的FSMIS模型相比,使用预训练的DINOv2特征编码器,MAUP在三个医学数据集上实现了精确的分割结果。源代码可在https://github.com/YazhouZhu19/MAUP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于跨域小样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)方法在处理医学图像分割时面临训练过程复杂的问题,导致模型部署的通用性和便捷性降低。为此,提出了一种无需训练的CD-FSMIS模型,采用基于自然图像的大型视觉模型进行训练并引入Multi-center Adaptive Uncertainty-aware Prompting(MAUP)策略进行适应。MAUP策略包括三个关键创新点:基于K-means聚类的多中心提示生成、不确定性感知提示选择和自适应提示优化。与常规CD-FSMIS模型和无需训练的FSMIS模型相比,使用预训练的DINOv2特征编码器,MAUP在三个医学数据集上实现了精确的分割结果。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSMIS方法在处理医学图像分割时面临训练复杂的问题。
- 提出了一种无需训练的CD-FSMIS模型,使用大型视觉模型和MAUP策略进行适应。
- MAUP策略包括三个关键创新点:多中心提示生成、不确定性感知提示选择和自适应提示优化。
- MAUP策略在三个医学数据集上实现了精确的分割结果。
- 该模型的源代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
- 该方法依赖于预训练的DINOv2特征编码器以实现精确的分割。
点此查看论文截图

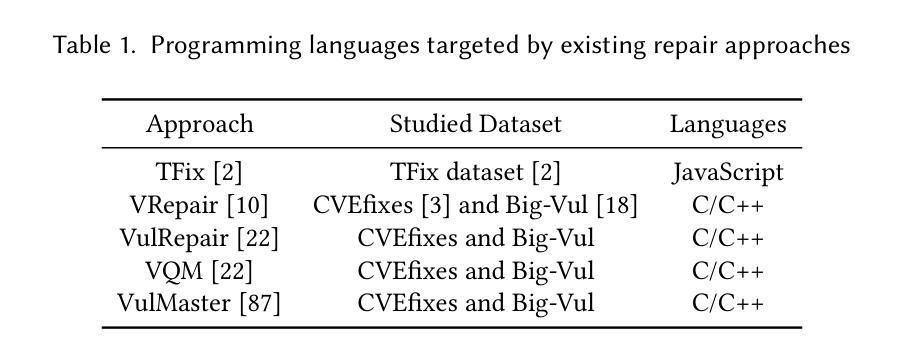
On the Evaluation of Large Language Models in Multilingual Vulnerability Repair
Authors:Dong wang, Junji Yu, Honglin Shu, Michael Fu, Chakkrit Tantithamthavorn, Yasutaka Kamei, Junjie Chen
Various Deep Learning-based approaches with pre-trained language models have been proposed for automatically repairing software vulnerabilities. However, these approaches are limited to a specific programming language (C/C++). Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) offer language-agnostic capabilities and strong semantic understanding, exhibiting potential to overcome multilingual vulnerability limitations. Although some work has begun to explore LLMs’ repair performance, their effectiveness is unsatisfactory. To address these limitations, we conducted a large-scale empirical study to investigate the performance of automated vulnerability repair approaches and state-of-the-art LLMs across seven programming languages. Results show GPT-4o, instruction-tuned with few-shot prompting, performs competitively against the leading approach, VulMaster. Additionally, the LLM-based approach shows superior performance in repairing unique vulnerabilities and is more likely to repair the most dangerous vulnerabilities. Instruction-tuned GPT-4o demonstrates strong generalization on vulnerabilities in previously unseen language, outperforming existing approaches. Analysis shows Go consistently achieves the highest effectiveness across all model types, while C/C++ performs the worst. Based on findings, we discuss the promise of LLM on multilingual vulnerability repair and the reasons behind LLM’s failed cases. This work takes the first look at repair approaches and LLMs across multiple languages, highlighting the promising future of adopting LLMs for multilingual vulnerability repair.
基于深度学习和预训练语言模型的多种方法已被提出用于自动修复软件漏洞。然而,这些方法仅限于特定的编程语言(如C/C++)。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展提供了跨语言的能力和强大的语义理解,显示出克服多种语言漏洞限制的潜力。尽管已经开始探索LLM在修复性能方面的应用,但其有效性尚不理想。为了解决这个问题,我们进行了一项大规模实证研究,调查了跨七种编程语言的自动化漏洞修复方法和最新LLM的性能。结果表明,通过少量提示进行指令调整的GPT-4o与领先的VulMaster方法竞争表现良好。此外,基于LLM的方法在修复独特漏洞时表现出卓越的性能,并且更有可能修复最危险的漏洞。通过指令调整的GPT-4o在之前未见的语言中的漏洞上表现出强大的泛化能力,优于现有方法。分析表明,Go在所有模型类型中始终实现最高的有效性,而C/C++的表现最差。基于研究结果,我们讨论了LLM在多语言漏洞修复方面的前景以及LLM失败案例背后的原因。这项工作首次在多语言环境下研究了修复方法和LLM,突显了采用LLM进行多语言漏洞修复的广阔前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动修复软件漏洞的各种深度学习方法基于预训练的语言模型已经提出,但它们通常局限于特定的编程语言(如C/C++)。最近的大型语言模型(LLMs)提供跨语言的通用能力和强大的语义理解,显示出克服多种语言漏洞限制的潜力。尽管已经开始探索LLMs在漏洞修复方面的性能,但其有效性尚不理想。为了解决这个问题,我们进行了一项大规模实证研究,调查自动化漏洞修复方法和最新LLMs在七种编程语言中的性能。结果显示,通过少量提示进行指令调整的GPT-4o与领先的VulMaster方法竞争表现出色。此外,基于LLM的方法在修复独特漏洞时表现出卓越的性能,并且更有可能修复最危险的漏洞。在以前未见过的语言中的漏洞方面,指令调整的GPT-4o展现出强大的泛化能力,优于现有方法。分析表明,Go在所有模型类型中始终实现最高的有效性,而C/C++的表现最差。基于我们的发现,我们讨论了LLM在多语言漏洞修复方面的前景以及LLM失败的原因。这项工作首次跨多种语言调查修复方法和LLMs,突显了采用LLMs进行多语言漏洞修复的广阔前景。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法结合预训练语言模型在自动修复软件漏洞领域已有应用,但局限于特定编程语言。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具有跨语言的通用能力和强大的语义理解,为克服多语言漏洞修复的限制提供了潜力。
- GPT-4o在指令微调后,通过少量提示便能展现出强大的漏洞修复能力,与领先的VulMaster方法竞争。
- LLMs在修复独特和危险漏洞方面表现出卓越性能。
- 在未见过的语言中的漏洞方面,GPT-4o展现出强大的泛化能力。
- Go语言在自动化漏洞修复中的有效性最高,而C/C++表现最差。
点此查看论文截图

Thinking with Nothinking Calibration: A New In-Context Learning Paradigm in Reasoning Large Language Models
Authors:Haotian Wu, Bo Xu, Yao Shu, Menglin Yang, Chengwei Qin
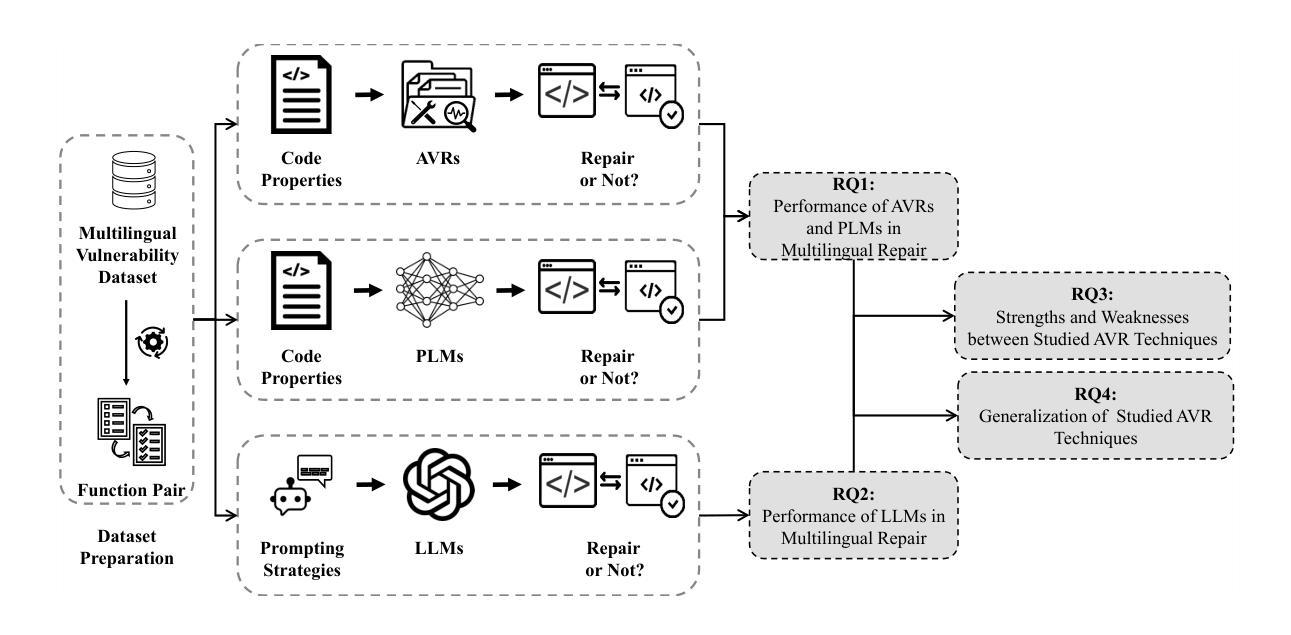
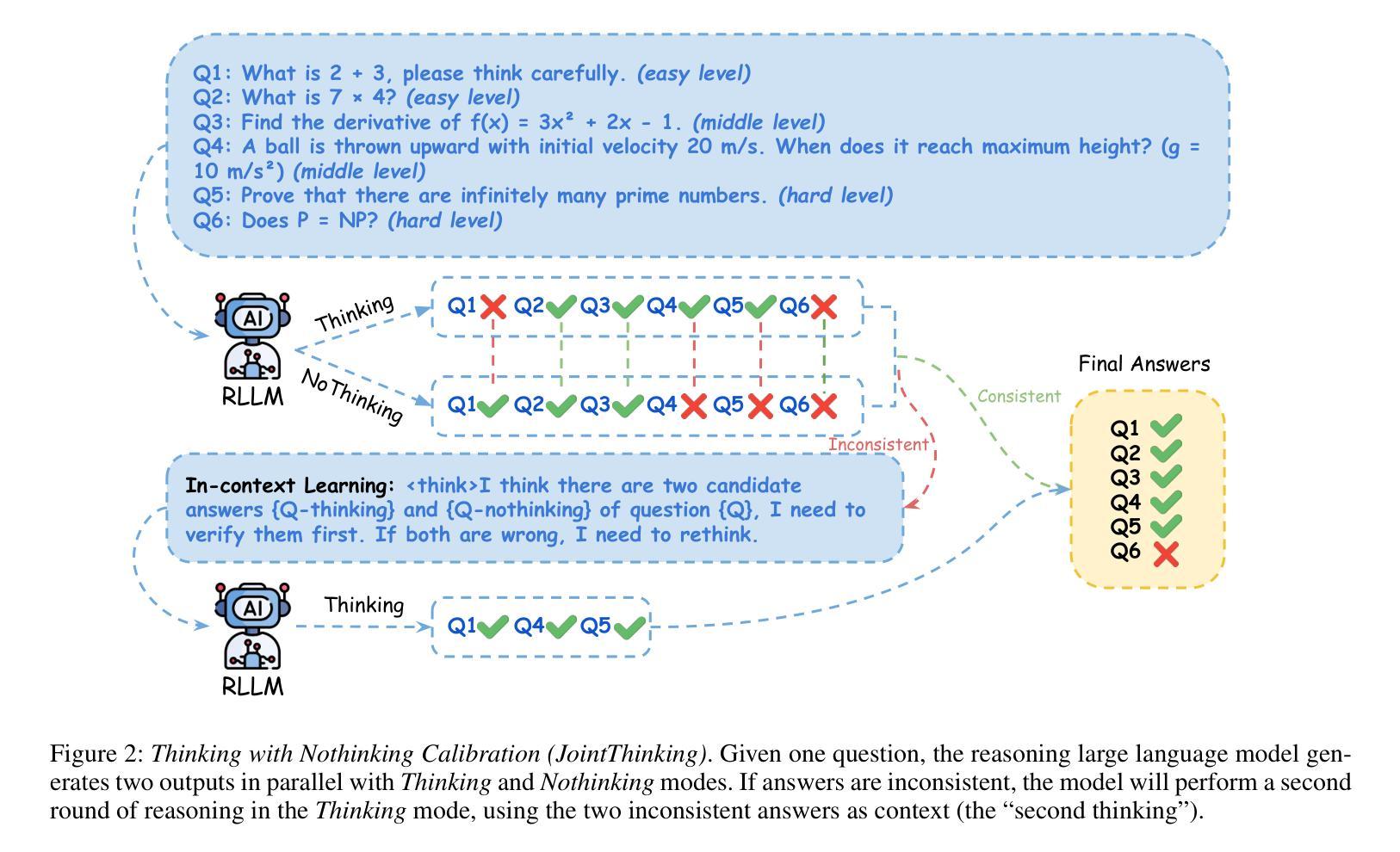
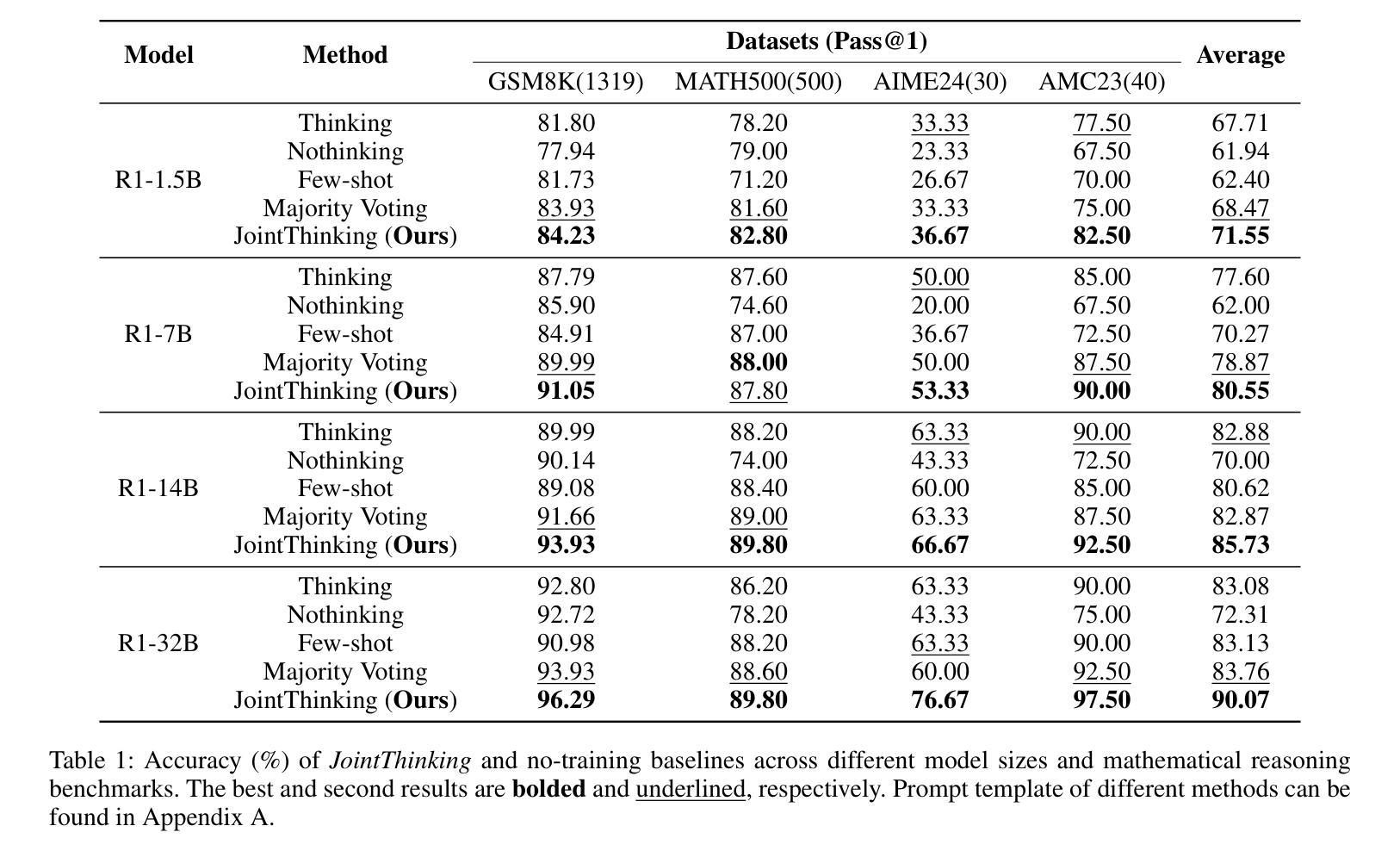
Reasoning large language models (RLLMs) have recently demonstrated remarkable capabilities through structured and multi-step reasoning. While prior research has primarily focused on improving their training and inference strategies, their potential for in-context learning (ICL) remains largely underexplored. To fill this gap, we propose Thinking with Nothinking Calibration (JointThinking), a new ICL paradigm that leverages the structured difference between two reasoning modes, i.e., Thinking and Nothinking, to improve reasoning accuracy. Specifically, our method prompts the model to generate two answers in parallel: one in Thinking mode and the other in Nothinking mode. A second round of Thinking is triggered only when the two initial responses are inconsistent, using a single prompt that incorporates the original question and both candidate answers. Since such disagreement occurs infrequently (e.g., only 6% in GSM8K), our method performs just one round of reasoning in most cases, resulting in minimal latency overhead. Extensive experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that JointThinking significantly outperforms few-shot chain-of-thought (CoT) and majority voting with improved answer robustness. Moreover, It achieves comparable in-distribution performance to training-based SOTA method, while substantially outperforming on out-of-distribution tasks. We further conduct a systematic analysis of the calibration mechanism, showing that leveraging different reasoning modes consistently lowers the error rate and highlights the value of structural thinking diversity. Additionally, we observe that the performance gap between actual and ideal reasoning narrows as model size increases in the second round of thinking, indicating the strong scalability of our approach. Finally, we discuss current limitations and outline promising directions for future ICL research in RLLMs.
推理大型语言模型(RLLMs)最近通过结构化及多步骤推理展现了显著的能力。尽管先前的研究主要侧重于改进其训练和推理策略,但它们在上下文学习(ICL)方面的潜力却鲜有研究。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了“无思考校准思考”(JointThinking)这一新的ICL范式,它利用两种推理模式之间的结构化差异,即“思考”和“无思考”,来提高推理准确性。具体来说,我们的方法提示模型并行生成两个答案:一个在“思考”模式下,另一个在“无思考”模式下。当两个初步回答不一致时,才会触发第二轮“思考”,并使用一个结合了原始问题和两个候选答案的单一提示。由于这种分歧很少发生(例如在GSM8K中仅占6%),我们的方法大多数情况下只进行一轮推理,因此延迟开销很小。在多个推理基准测试上的广泛实验表明,JointThinking显著优于少镜头思维链(CoT)和多数投票法,提高了答案的稳健性。此外,它在基于训练的最新技术方法上实现了相当的分内分布性能表现,同时在跨分布任务上大幅超越。我们进一步对校准机制进行了系统分析,结果表明利用不同的推理模式可以持续降低错误率,并突显了结构化思维多样性的价值。此外,我们观察到在第二轮思考中,随着模型规模的增加,实际与理想推理之间的性能差距缩小,这表明了我们的方法具有很强的可扩展性。最后,我们讨论了当前的局限性,并概述了未来RLLMs中ICL研究的有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大语言模型通过结构化和多步骤推理展现了惊人的能力。虽然先前的研究主要聚焦于改进其训练和推理策略,但它们对于内隐学习(ICL)的潜力却被大大忽视了。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了“无需思考校准的思考”(JointThinking)这一新的内隐学习范式,它通过利用两种推理模式之间的结构化差异(即思考与不思考),来提高推理的准确性。具体来说,我们的方法促使模型并行生成两个答案:一个为思考模式,另一个为不思考模式。当两个初步回答不一致时,会使用包含原始问题和两个候选答案的单一提示来触发第二轮思考。由于这种分歧很少发生(例如在GSM8K中仅占6%),因此我们的方法大多数情况下只进行一次推理,几乎不会造成延迟开销。在多个推理基准测试上的实验表明,与少数思考链和多数投票相比,JointThinking显著提高了解答的稳健性。此外,它在内部分布任务中的表现与基于训练的最先进方法相当,而在外部分布任务中的表现则大大优于其他方法。我们进一步对校准机制进行了系统分析,结果表明利用不同的推理模式可以持续降低错误率,并突显结构思考多样性的价值。此外,随着第二轮思考中模型规模的增加,实际推理与理想推理之间的性能差距缩小,表明我们方法的强大可扩展性。最后,我们讨论了当前的局限性并为未来的ICL研究提出了有前景的方向。
要点归纳
- 提出新的内隐学习范式——无需思考校准的思考(JointThinking),利用两种推理模式(思考与不思考)之间的差异来提高推理准确性。
- 通过生成两个不同模式的答案并进行比较,触发第二轮思考,大多数情况只需一次推理,延迟开销极小。
- 在多个基准测试中显著优于少数思考链和多数投票方法,提高解答稳健性。
- 在内、外部分布任务中的表现均优异,尤其是外部任务中的表现突出。
- 系统分析显示不同推理模式结合能降低错误率,并强调结构思考多样性的重要性。
- 第二轮思考中模型规模增加时,实际与理想推理间的性能差距缩小,表明方法具有良好的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

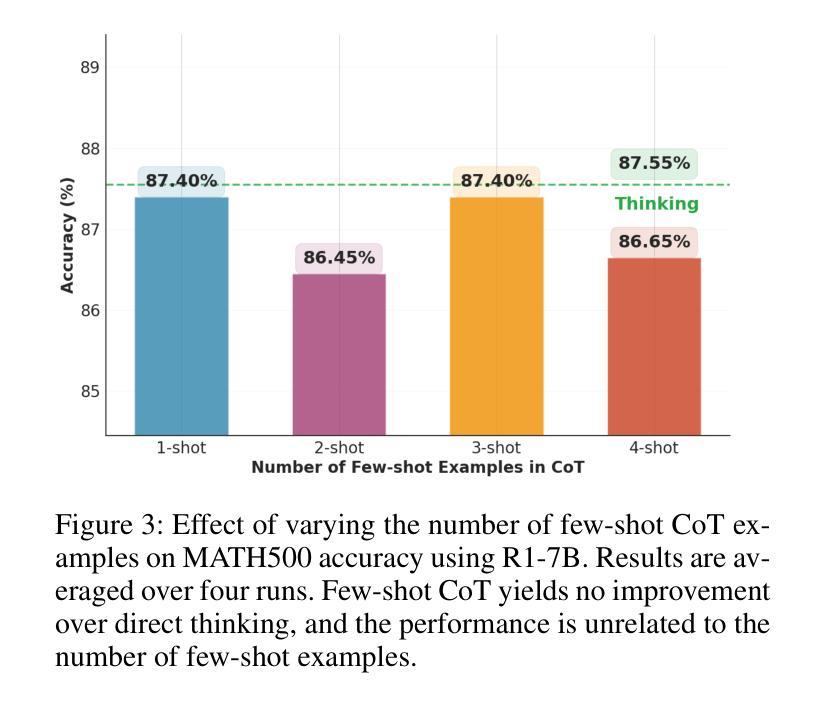
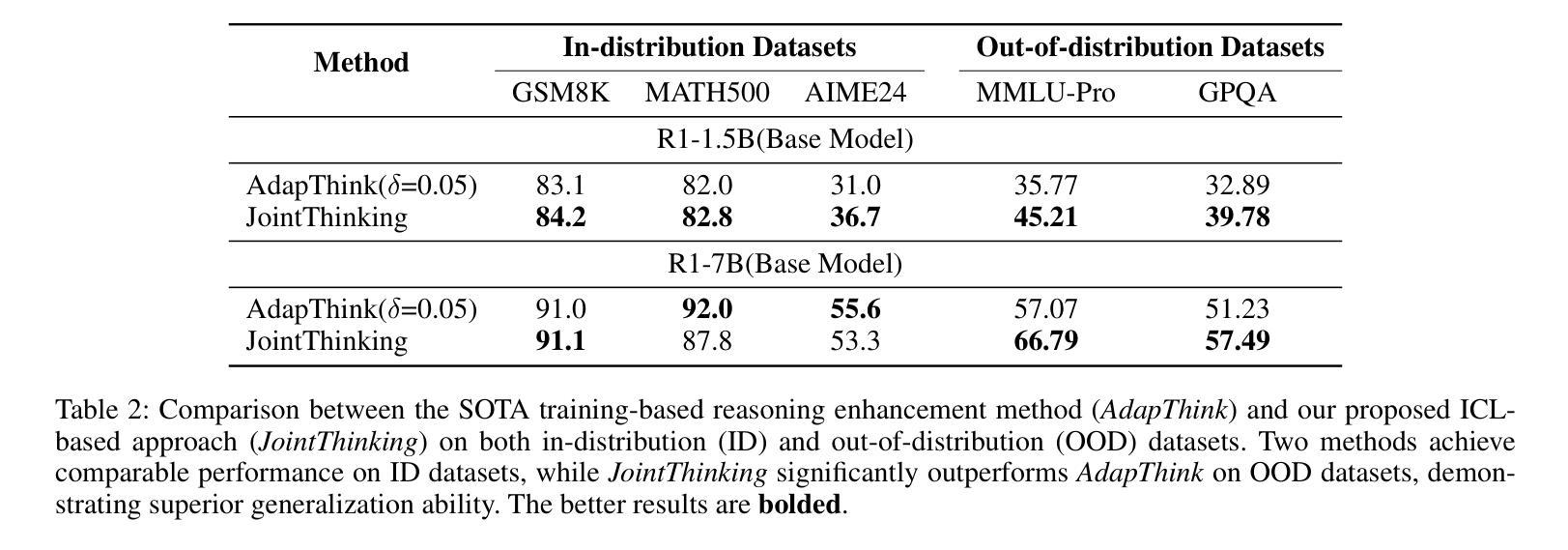
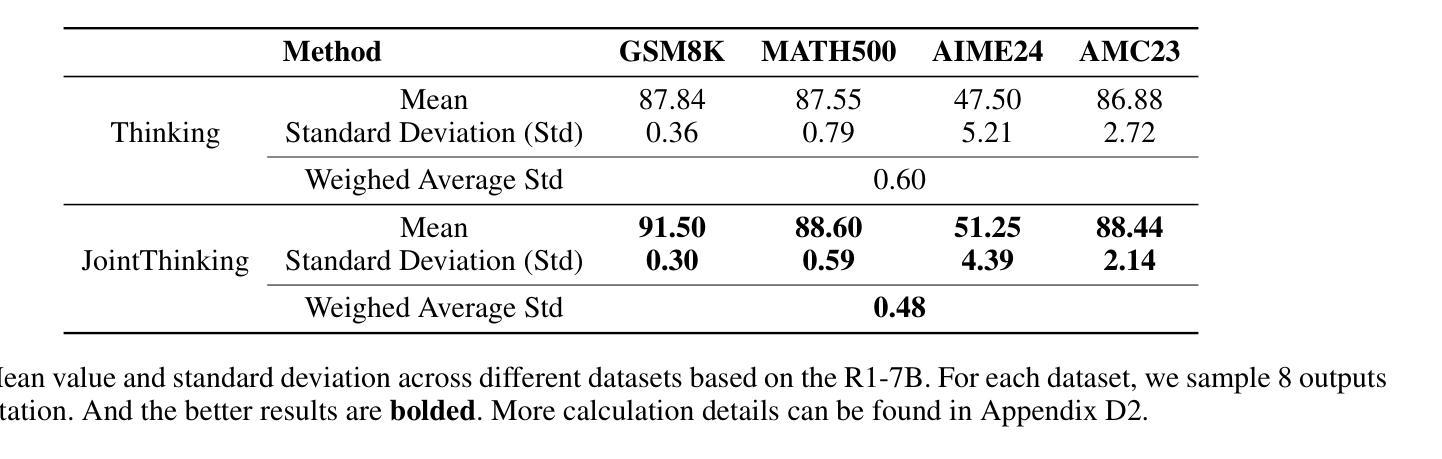
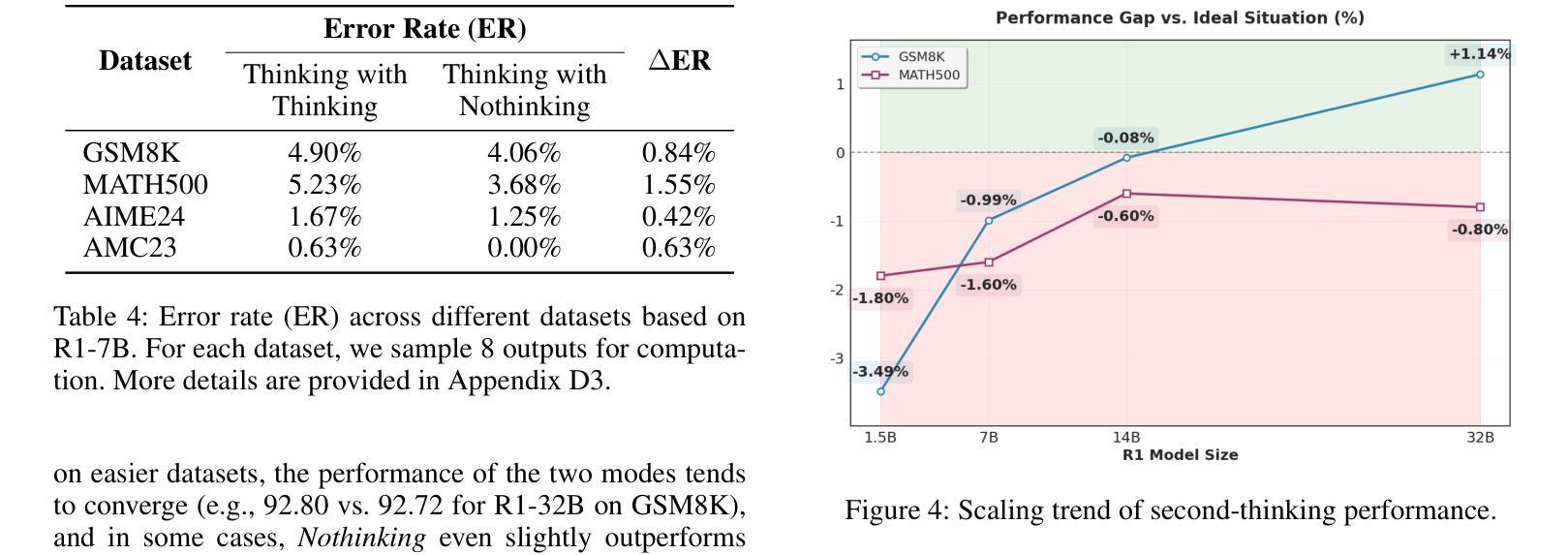
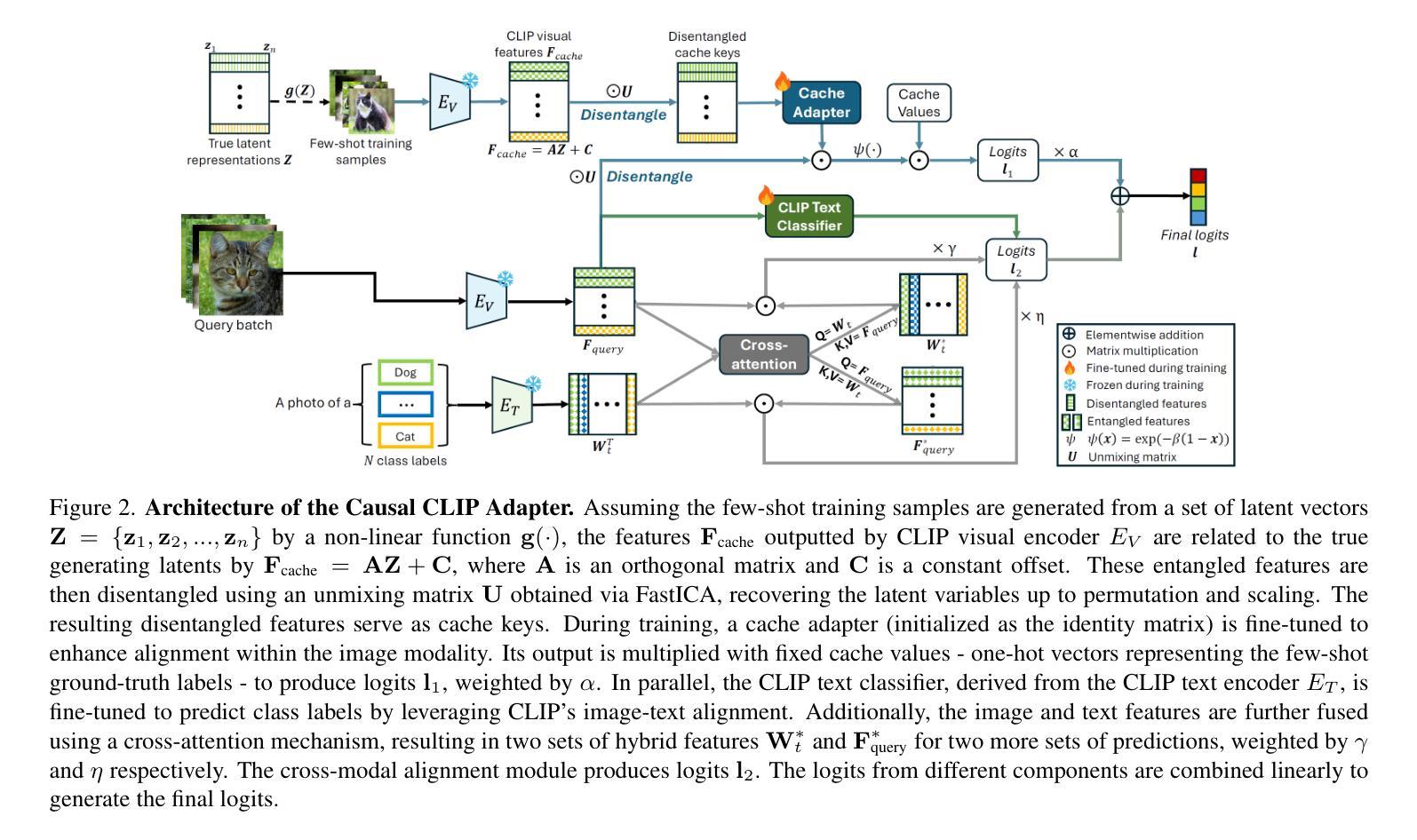
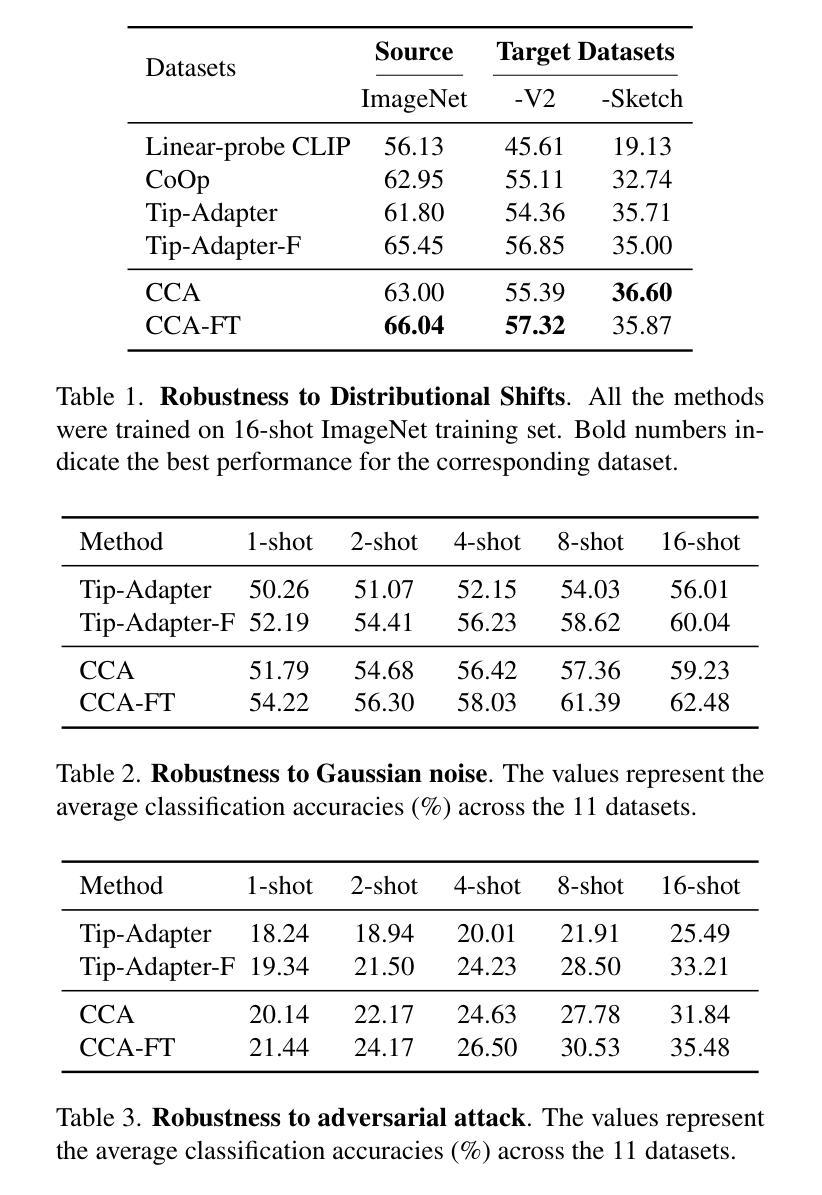
Causal Disentanglement and Cross-Modal Alignment for Enhanced Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Tianjiao Jiang, Zhen Zhang, Yuhang Liu, Javen Qinfeng Shi
Few-shot learning (FSL) often requires effective adaptation of models using limited labeled data. However, most existing FSL methods rely on entangled representations, requiring the model to implicitly recover the unmixing process to obtain disentangled representations using only limited supervision, which hinders effective adaptation. Recent theoretical studies show that multimodal contrastive learning methods, such as CLIP, can disentangle latent representations up to linear transformations. In light of this, we propose the Causal CLIP Adapter (CCA), a novel framework that explicitly disentangles visual features extracted from CLIP using unsupervised Independent Component Analysis (ICA). This removes the need to learn the unmixing process from the labeled data, thereby reducing the number of trainable parameters and mitigating overfitting. Taking a step further, while ICA can obtain visual disentangled representations, it may also disrupt CLIP’s intra- and inter-modal alignment. To counteract this, CCA further leverages CLIP’s inherent cross-modal alignment by enhancing it in two ways: unidirectionally, through fine-tuning a CLIP-based text classifier, and bidirectionally, via a cross-attention mechanism that enriches visual and textual representations through mutual interaction. Both unimodal and cross-modal classification outputs can be effectively combined linearly to improve classification accuracy. Extensive experiments on 11 benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of few-shot performance and robustness to distributional shifts, while maintaining computational efficiency. Code will be available at https://github.com/tianjiao-j/CCA.
少量样本学习(FSL)通常需要利用有限的标记数据有效地适应模型。然而,大多数现有的FSL方法依赖于纠缠表示,需要模型仅通过有限的监督隐式恢复混合过程以获得解纠缠表示,这阻碍了有效的适应。最近的理论研究表明,如CLIP之类的多模态对比学习方法可以解开潜在表示,直到线性变换。鉴于此,我们提出了因果CLIP适配器(CCA),这是一个新的框架,它使用无监督的独立成分分析(ICA)显式地解开从CLIP提取的视觉特征。这消除了从标记数据中学习混合过程的需求,从而减少了可训练参数的数量并减轻了过拟合。更进一步的是,虽然ICA可以获得视觉解纠缠表示,但它也可能破坏CLIP的跨模态内和对齐。为了应对这一问题,CCA进一步利用CLIP的固有跨模态对齐,通过两种方式增强它:单向地,通过微调基于CLIP的文本分类器;双向地,通过一个丰富视觉和文本表示的交叉注意机制进行相互交互。单模态和跨模态分类输出可以有效地线性组合以提高分类精度。在11个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在少量样本性能和分布转移稳健性方面始终优于最新方法,同时保持计算效率。代码将在https://github.com/tianjiao-j/CCA上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于CLIP的因果CLIP适配器(CCA)框架,该框架利用无监督的独立成分分析(ICA)显式地解纠缠CLIP提取的视觉特征,从而提高模型的适应能力并降低对标签数据的依赖性。通过结合CLIP本身的跨模态对齐技术,该框架以两种方式进行改进:单向增强,通过微调CLIP的文本分类器来实现,以及双向增强,通过跨注意力机制丰富视觉和文本表示以实现双向互动。结合单模态和跨模态分类输出可以提高分类精度。实验结果证明,该方法在少数样本性能、分布转移鲁棒性和计算效率方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 少数学习(FSL)需要利用有限的标签数据有效适应模型。
- 现有FSL方法依赖于纠缠表示,需要模型隐式恢复未混合过程以获得解纠缠表示,这阻碍了有效适应。
- 多模态对比学习方法(如CLIP)可以解开潜在表示的线性变换。
- 提出的Causal CLIP Adapter(CCA)框架利用ICA显式解纠缠CLIP的视觉特征,消除学习未混合过程的需要,减少训练参数并减轻过度拟合问题。
- CCA利用CLIP的跨模态对齐特性进行单向和双向增强,通过微调CLIP文本分类器和跨注意力机制实现。
- 结合单模态和跨模态分类输出可线性地提高分类精度。
点此查看论文截图

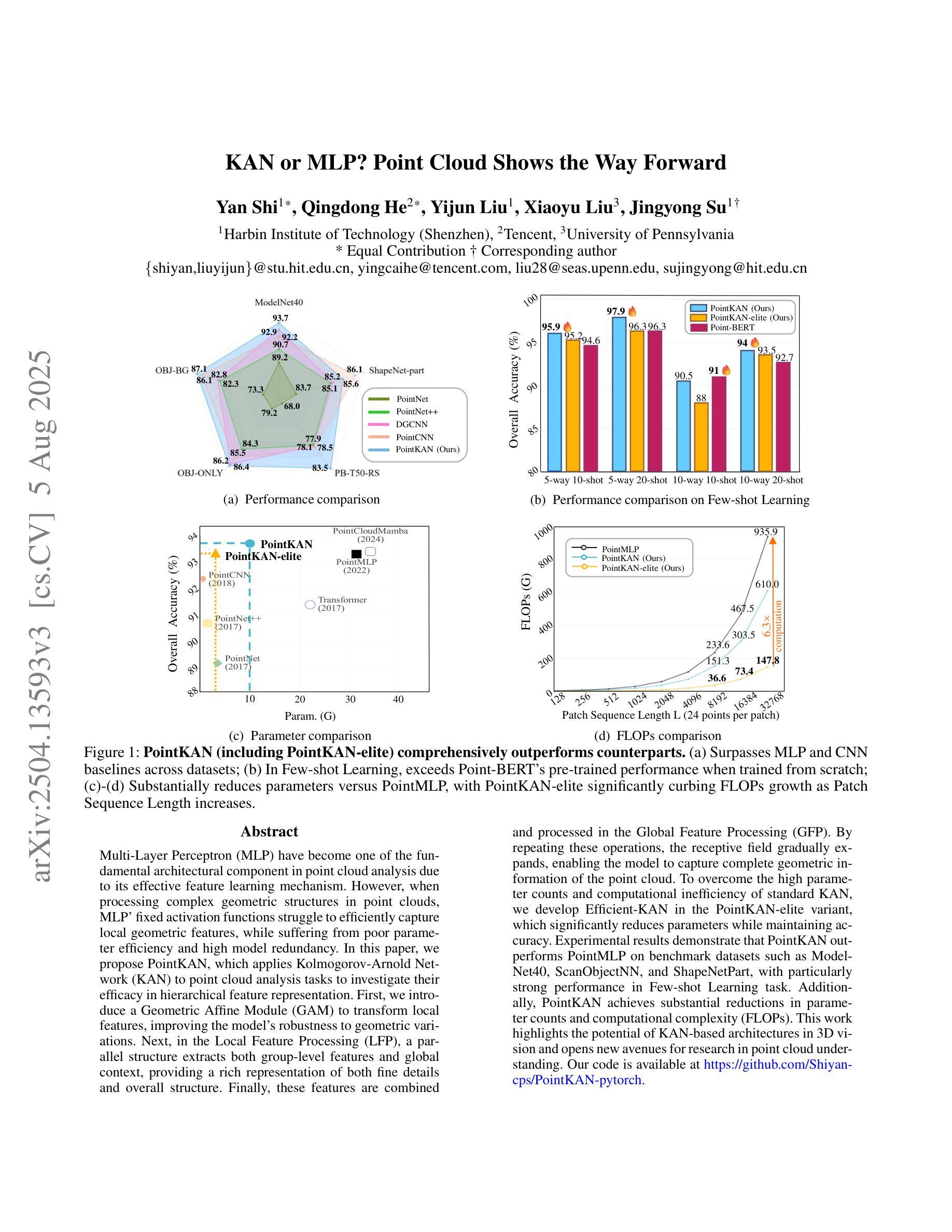
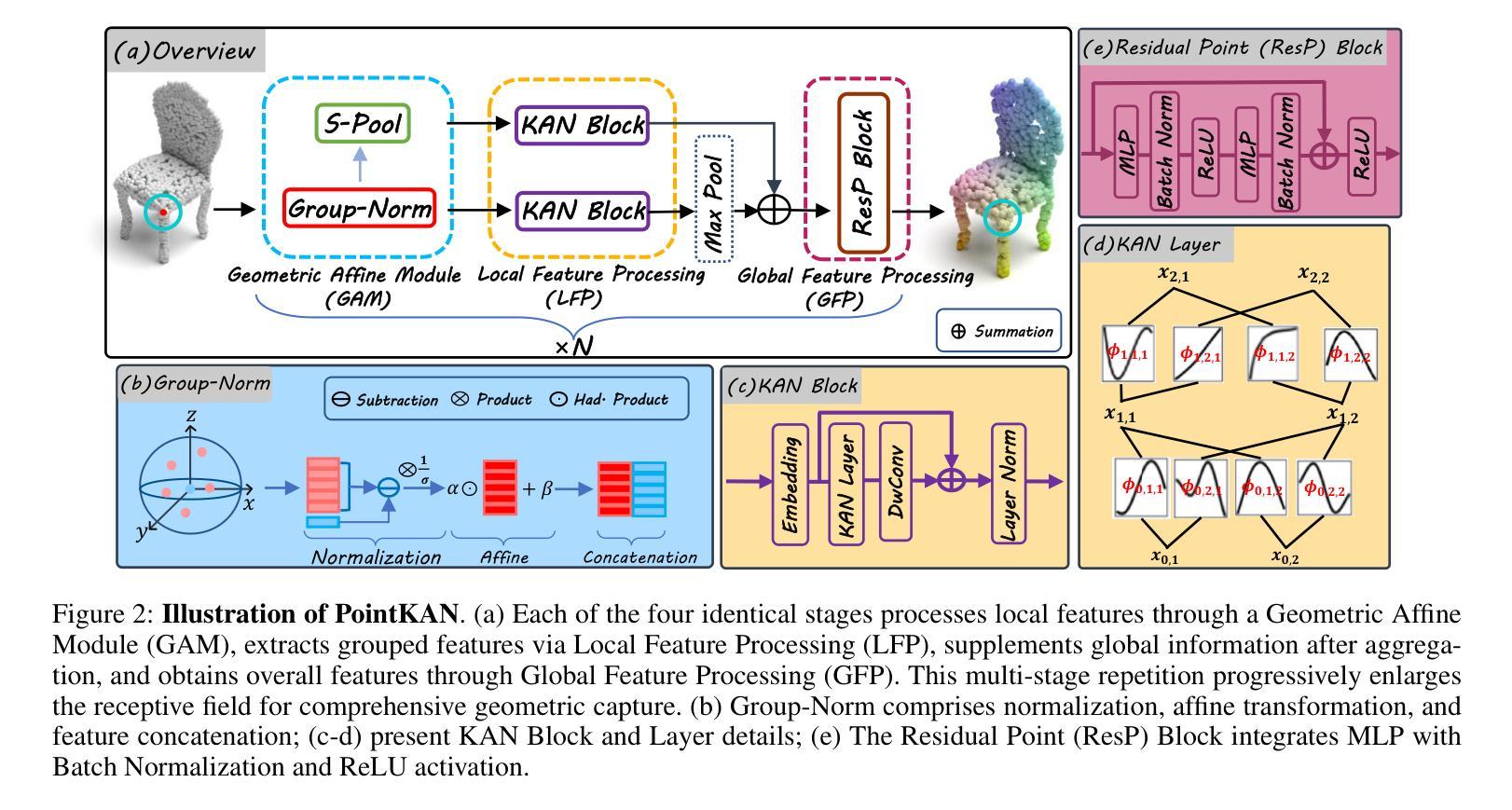
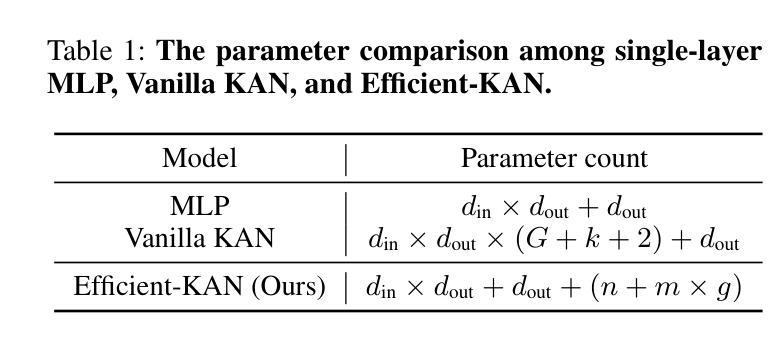
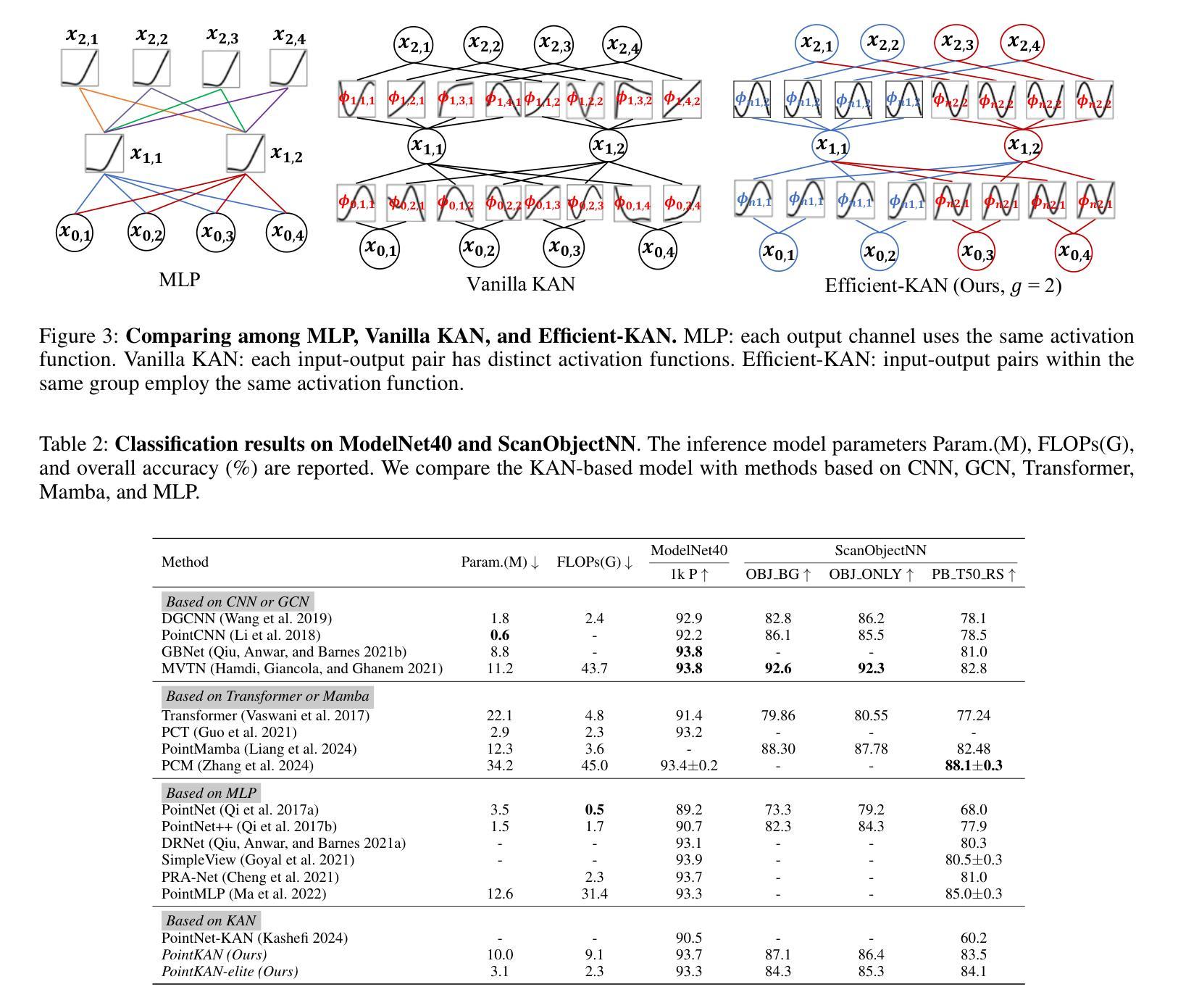
KAN or MLP? Point Cloud Shows the Way Forward
Authors:Yan Shi, Qingdong He, Yijun Liu, Xiaoyu Liu, Jingyong Su
Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) have become one of the fundamental architectural component in point cloud analysis due to its effective feature learning mechanism. However, when processing complex geometric structures in point clouds, MLPs’ fixed activation functions struggle to efficiently capture local geometric features, while suffering from poor parameter efficiency and high model redundancy. In this paper, we propose PointKAN, which applies Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) to point cloud analysis tasks to investigate their efficacy in hierarchical feature representation. First, we introduce a Geometric Affine Module (GAM) to transform local features, improving the model’s robustness to geometric variations. Next, in the Local Feature Processing (LFP), a parallel structure extracts both group-level features and global context, providing a rich representation of both fine details and overall structure. Finally, these features are combined and processed in the Global Feature Processing (GFP). By repeating these operations, the receptive field gradually expands, enabling the model to capture complete geometric information of the point cloud. To overcome the high parameter counts and computational inefficiency of standard KANs, we develop Efficient-KANs in the PointKAN-elite variant, which significantly reduces parameters while maintaining accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that PointKAN outperforms PointMLP on benchmark datasets such as ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN, and ShapeNetPart, with particularly strong performance in Few-shot Learning task. Additionally, PointKAN achieves substantial reductions in parameter counts and computational complexity (FLOPs). This work highlights the potential of KANs-based architectures in 3D vision and opens new avenues for research in point cloud understanding.
多层感知器(MLPs)由于其有效的特征学习机制,已成为点云分析中的基本架构组件之一。然而,在处理点云中的复杂几何结构时,MLPs的固定激活函数在有效地捕获局部几何特征方面遇到了困难,同时还存在参数效率低下和模型冗余的问题。在本文中,我们提出了PointKAN,它将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)应用于点云分析任务,以研究其在分层特征表示中的有效性。首先,我们引入了一个几何仿射模块(GAM)来转换局部特征,提高了模型对几何变化的稳健性。接下来,在局部特征处理(LFP)中,一个并行结构提取了组级特征和全局上下文,为精细细节和整体结构提供了丰富的表示。最后,这些特征在全局特征处理(GFP)中进行组合和处理。通过重复这些操作,感受野逐渐扩大,使模型能够捕获点云的完整几何信息。为了克服标准KANs参数过多和计算效率不高的缺点,我们在PointKAN-elite变种中开发了Efficient-KANs,它在保持准确性的同时显著减少了参数。实验结果表明,PointKAN在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart等基准数据集上的性能优于PointMLP,特别是在小样本学习任务中表现尤为出色。此外,PointKAN在参数数量和计算复杂度(FLOPs)方面实现了显著减少。这项工作突出了基于KANs的架构在3D视觉中的潜力,为点云理解研究开辟了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出PointKAN,应用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)于点云分析任务,以研究其在分层特征表示中的有效性。通过引入几何仿射模块(GAM)和本地特征处理(LFP),PointKAN能有效转换局部特征并丰富表示形式。此外,通过重复操作,模型的感受野逐渐扩大,能捕捉点云的完整几何信息。针对标准KANs参数多、计算效率低的问题,开发出高效的PointKAN-elite变体。实验结果显示,PointKAN在ModelNet40、ScanObjectNN和ShapeNetPart等基准数据集上表现优于PointMLP,特别是在小样学习任务中表现尤为出色。
关键见解
- MLP在点云分析中是基本的架构组件,但在处理复杂几何结构时存在局限性。
- PointKAN使用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)进行点云分析,旨在提高特征表示的层次性。
- 引入几何仿射模块(GAM)改善模型对几何变化的稳健性。
- 通过本地特征处理(LFP)和全局特征处理(GFP),模型能捕捉点云的精细细节和整体结构。
- PointKAN-elite的开发提高了参数效率并维持了准确性。
- 实验结果显示PointKAN在多个基准数据集上优于PointMLP,尤其在小样学习任务中表现突出。
- 这项工作突显了KANs在3D视觉中的潜力,并为点云理解研究开辟了新的途径。
点此查看论文截图
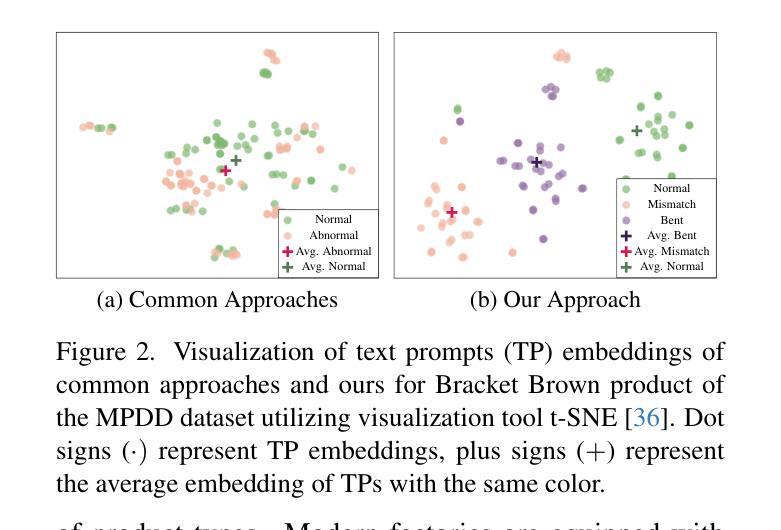
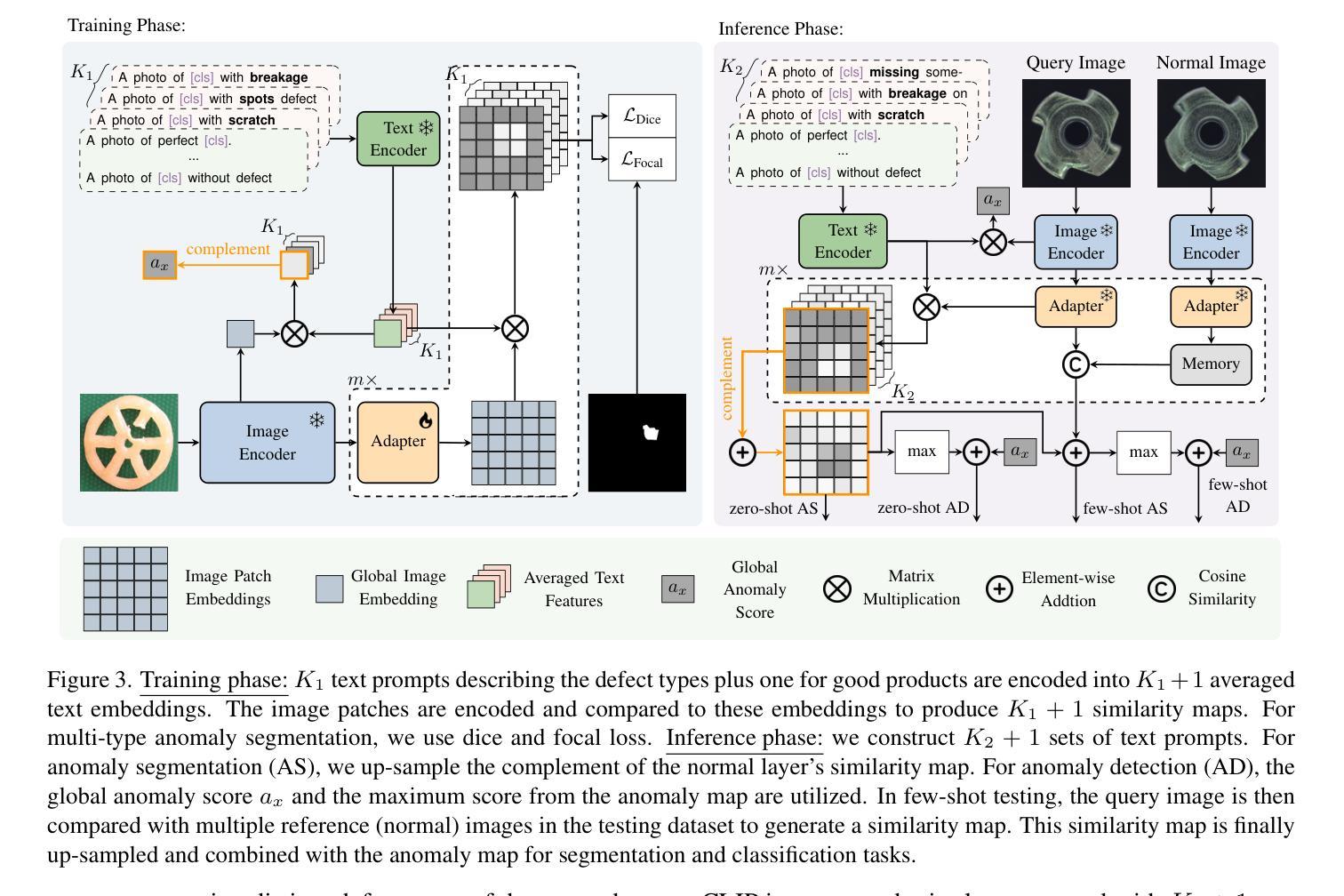
MultiADS: Defect-aware Supervision for Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation in Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Ylli Sadikaj, Hongkuan Zhou, Lavdim Halilaj, Stefan Schmid, Steffen Staab, Claudia Plant
Precise optical inspection in industrial applications is crucial for minimizing scrap rates and reducing the associated costs. Besides merely detecting if a product is anomalous or not, it is crucial to know the distinct type of defect, such as a bent, cut, or scratch. The ability to recognize the “exact” defect type enables automated treatments of the anomalies in modern production lines. Current methods are limited to solely detecting whether a product is defective or not without providing any insights on the defect type, nevertheless detecting and identifying multiple defects. We propose MultiADS, a zero-shot learning approach, able to perform Multi-type Anomaly Detection and Segmentation. The architecture of MultiADS comprises CLIP and extra linear layers to align the visual- and textual representation in a joint feature space. To the best of our knowledge, our proposal, is the first approach to perform a multi-type anomaly segmentation task in zero-shot learning. Contrary to the other baselines, our approach i) generates specific anomaly masks for each distinct defect type, ii) learns to distinguish defect types, and iii) simultaneously identifies multiple defect types present in an anomalous product. Additionally, our approach outperforms zero/few-shot learning SoTA methods on image-level and pixel-level anomaly detection and segmentation tasks on five commonly used datasets: MVTec-AD, Visa, MPDD, MAD and Real-IAD.
在工业应用中,精确的光学检测对于最小化废品率和降低相关成本至关重要。除了检测产品是否异常之外,了解缺陷的特定类型,如弯曲、切割或划痕,也非常关键。识别“精确”缺陷类型的能力,使现代生产线能够对异常情况进行自动化处理。当前的方法仅限于检测产品是否缺陷,而无法提供关于缺陷类型的任何见解,尽管如此,它们可以检测和识别多种缺陷。我们提出了MultiADS,这是一种零样本学习方法,能够进行多类型异常检测和分割。MultiADS的架构包括CLIP和额外的线性层,以在联合特征空间中对齐视觉和文本表示。据我们所知,我们的提议是第一个在零样本学习中进行多类型异常分割任务的方法。与其他基线方法相反,我们的方法i)为每种不同的缺陷类型生成特定的异常掩码,ii)学习区分缺陷类型,并iii)同时识别异常产品中存在的多种缺陷类型。此外,我们的方法在五个常用数据集上,对图像级和像素级的异常检测和分割任务,均超越了零样本/小样学习领域的最新方法,这些数据集包括MVTec-AD、Visa、MPDD、MAD和Real-IAD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了工业应用中精确光学检测的重要性,并指出了当前方法的局限性。为此,提出了一种基于零样本学习的新型多类型异常检测和分割方法MultiADS。该方法能够生成特定异常掩膜,区分并识别产品中的多种异常类型。此外,它在五个常用数据集上的异常检测和分割任务上超越了现有的零样本/小样学习方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 精确光学检测对工业应用至关重要,能降低废品率和相关成本。
- 当前方法主要检测产品是否异常,但无法识别具体的缺陷类型。
- MultiADS是一种零样本学习方法,能够进行多类型异常检测和分割。
- MultiADS采用CLIP结构并增加额外线性层,实现视觉和文本表示的联合特征空间对齐。
- MultiADS能够生成针对每种特定缺陷的异常掩膜。
- MultiADS能区分并同时识别产品中的多种异常类型。
点此查看论文截图

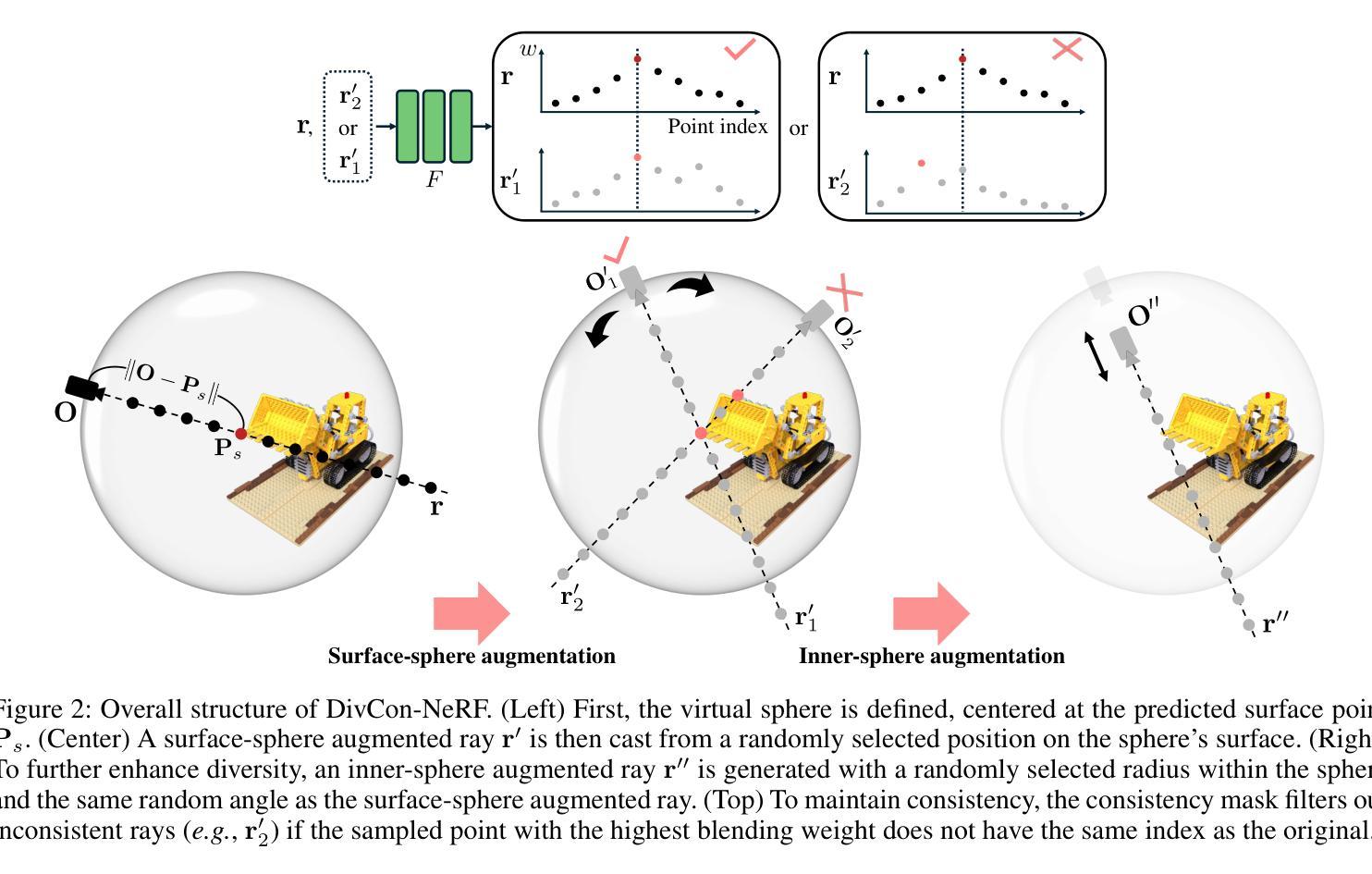
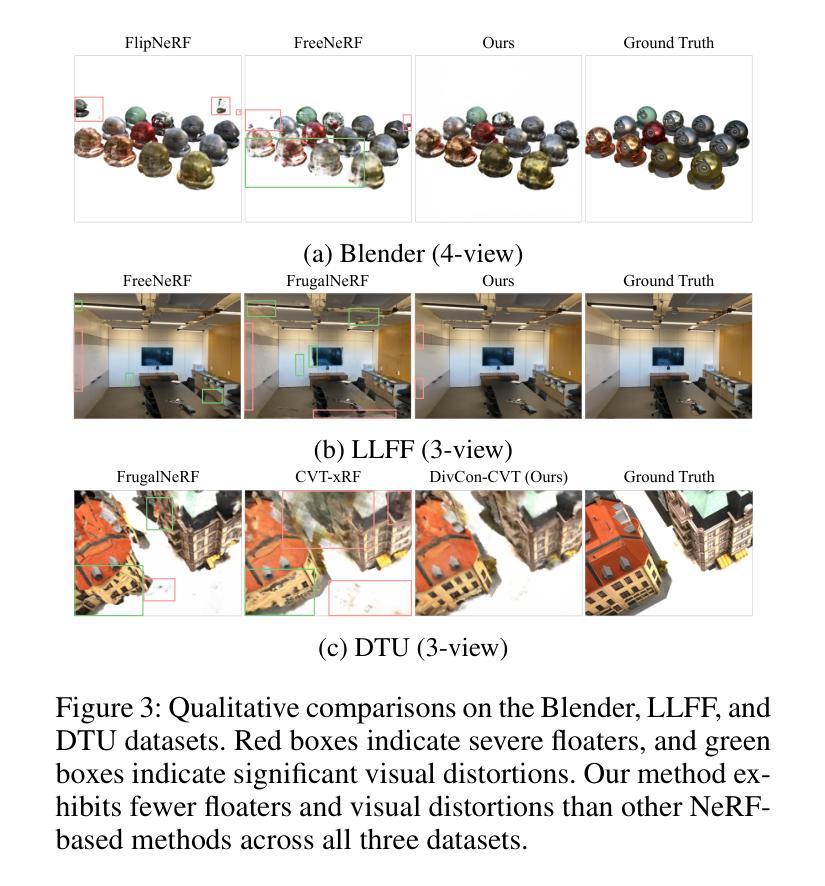
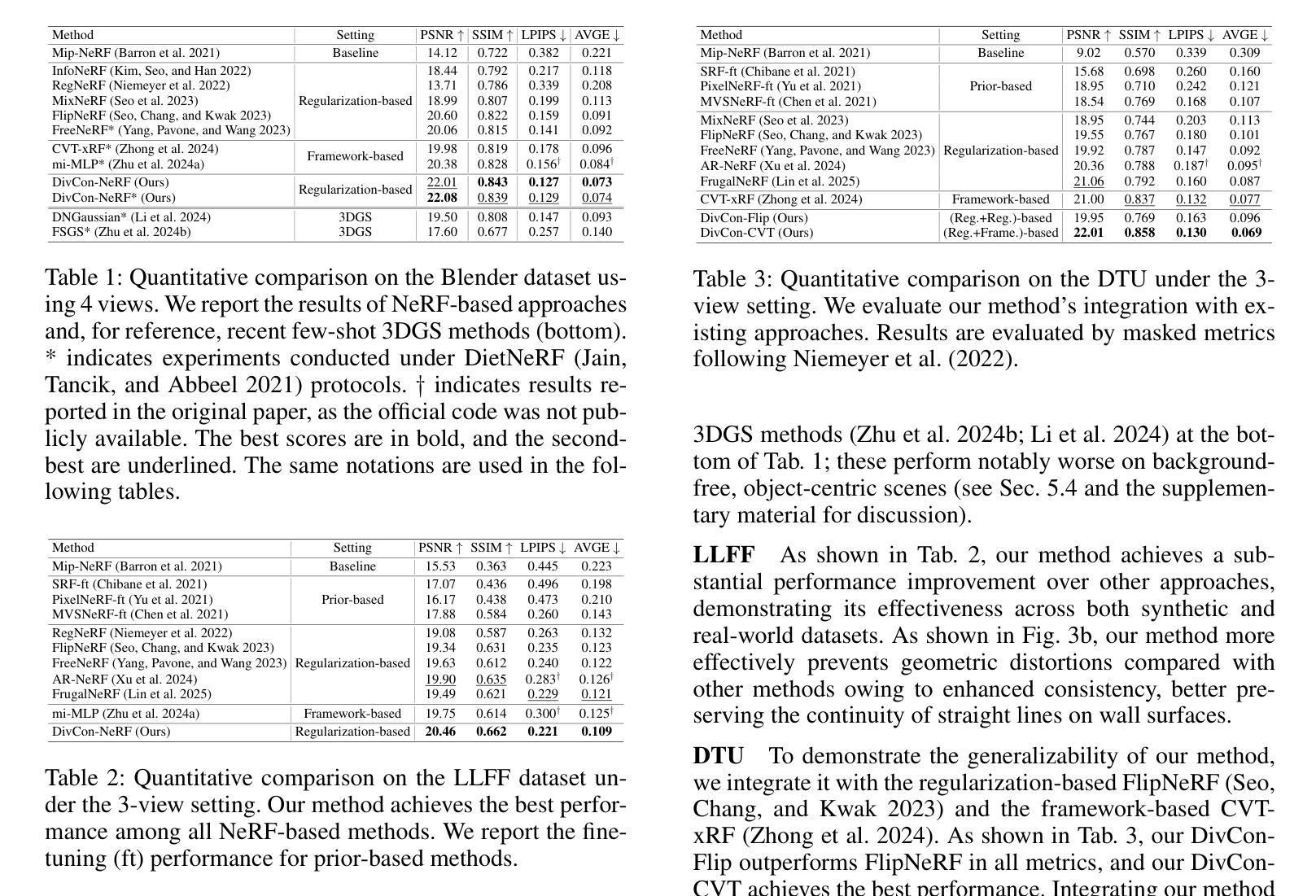
DivCon-NeRF: Diverse and Consistent Ray Augmentation for Few-Shot NeRF
Authors:Ingyun Lee, Jae Won Jang, Seunghyeon Seo, Nojun Kwak
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has shown remarkable performance in novel view synthesis but requires numerous multi-view images, limiting its practicality in few-shot scenarios. Ray augmentation has been proposed to alleviate overfitting caused by sparse training data by generating additional rays. However, existing methods, which generate augmented rays only near the original rays, exhibit pronounced floaters and appearance distortions due to limited viewpoints and inconsistent rays obstructed by nearby obstacles and complex surfaces. To address these problems, we propose DivCon-NeRF, which introduces novel sphere-based ray augmentations to significantly enhance both diversity and consistency. By employing a virtual sphere centered at the predicted surface point, our method generates diverse augmented rays from all 360-degree directions, facilitated by our consistency mask that effectively filters out inconsistent rays. We introduce tailored loss functions that leverage these augmentations, effectively reducing floaters and visual distortions. Consequently, our method outperforms existing few-shot NeRF approaches on the Blender, LLFF, and DTU datasets. Furthermore, DivCon-NeRF demonstrates strong generalizability by effectively integrating with both regularization- and framework-based few-shot NeRFs. Our code will be made publicly available.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成中表现出卓越的性能,但需要大量多视图图像,这在少镜头场景中限制了其实用性。射线增强法被提出通过生成额外的射线来缓解稀疏训练数据导致的过拟合问题。然而,现有方法仅在原始射线附近生成增强射线,由于有限的观点、附近障碍和复杂表面的影响,会出现明显的浮点和外观失真。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了DivCon-NeRF,它引入了基于新型球体的射线增强方法,显著提高了多样性和一致性。通过以预测的表面点为中心构建一个虚拟球体,我们的方法从所有360度的方向生成多样化的增强射线,并通过我们的一致性掩膜有效地过滤出不一致的射线。我们引入了利用这些增强的定制损失函数,有效地减少了浮点和视觉失真。因此,我们的方法在Blender、LLFF和DTU数据集上的表现优于现有的少镜头NeRF方法。此外,DivCon-NeRF具有很强的泛化能力,能有效地与基于正则化和框架的少镜头NeRF相结合。我们的代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
NeRF在新型视图合成中表现出卓越性能,但需大量多视图图像,这在少样本场景中限制了其实际应用。为缓解稀疏训练数据引起的过拟合问题,提出了射线增强方法生成额外射线。然而,现有方法仅在接近原始射线时生成增强射线,因有限的视角和不一致的射线被附近障碍物和复杂表面阻挡,导致出现明显的浮体和外观失真。为解决这些问题,提出DivCon-NeRF,通过基于球体的新型射线增强方法,显著增强多样性和一致性。以预测表面点为中心的虚拟球体生成来自所有360度方向的多样化增强射线,由我们的一致性掩膜有效过滤出不一致的射线。引入定制的损耗函数,利用这些增强方法,有效降低浮体和视觉失真。因此,DivCon-NeRF在Blender、LLFF和DTU数据集上优于现有的少样本NeRF方法。此外,DivCon-NeRF通过与正则化和框架基础上的少样本NeRF进行有效整合,表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在视图合成中表现优秀,但在少样本场景中因需要多视图图像而受到限制。
- 现有射线增强方法仅在接近原始射线时生成增强射线,存在浮体和外观失真问题。
- DivCon-NeRF通过基于球体的新型射线增强方法,增强多样性和一致性。
- DivCon-NeRF采用虚拟球体生成多样化增强射线,并过滤出不一致的射线。
- 定制损耗函数利用增强方法,降低浮体和视觉失真。
- DivCon-NeRF在多个数据集上优于现有少样本NeRF方法。
点此查看论文截图

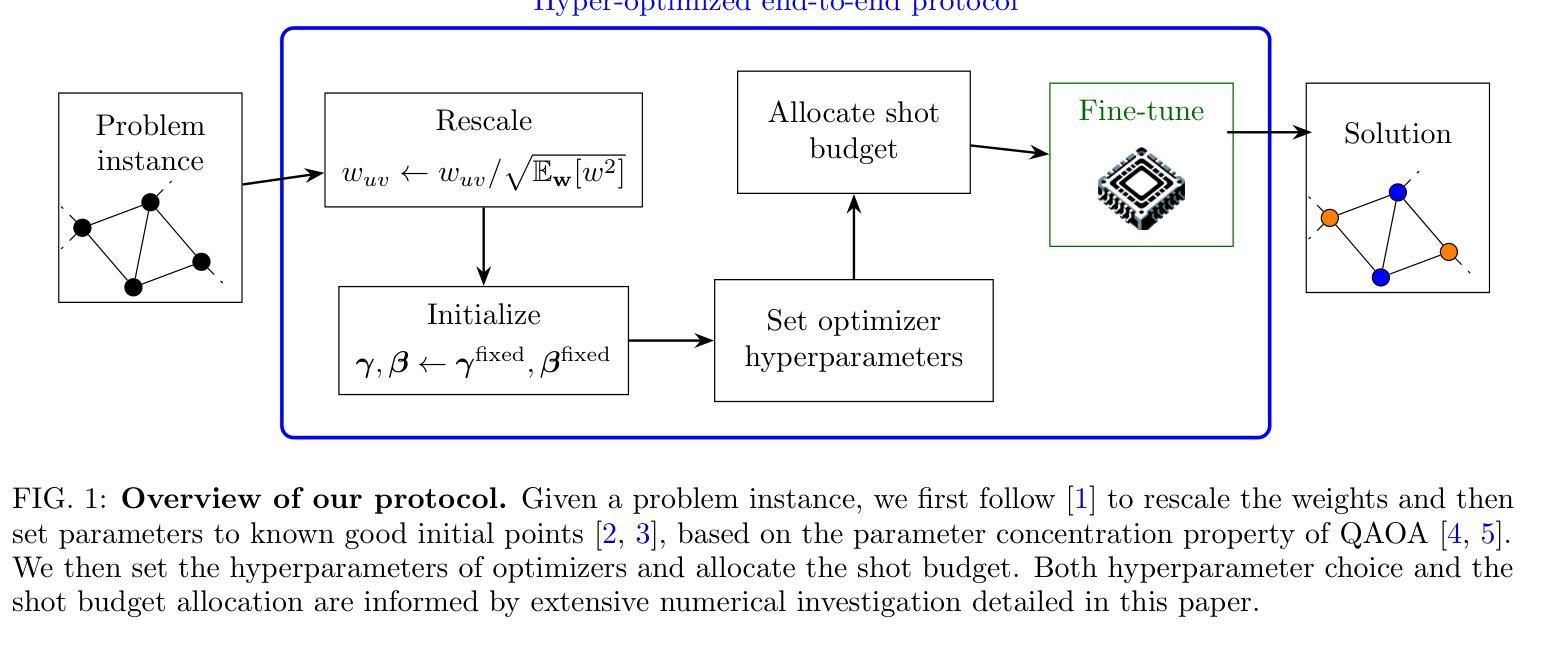
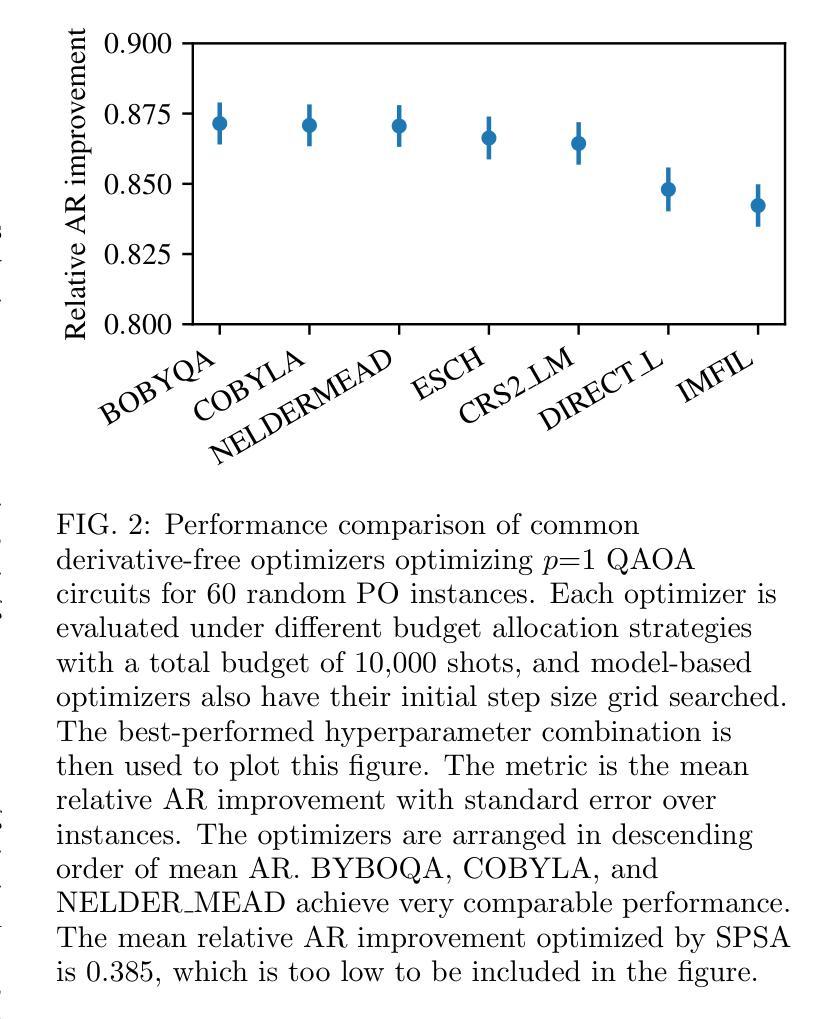
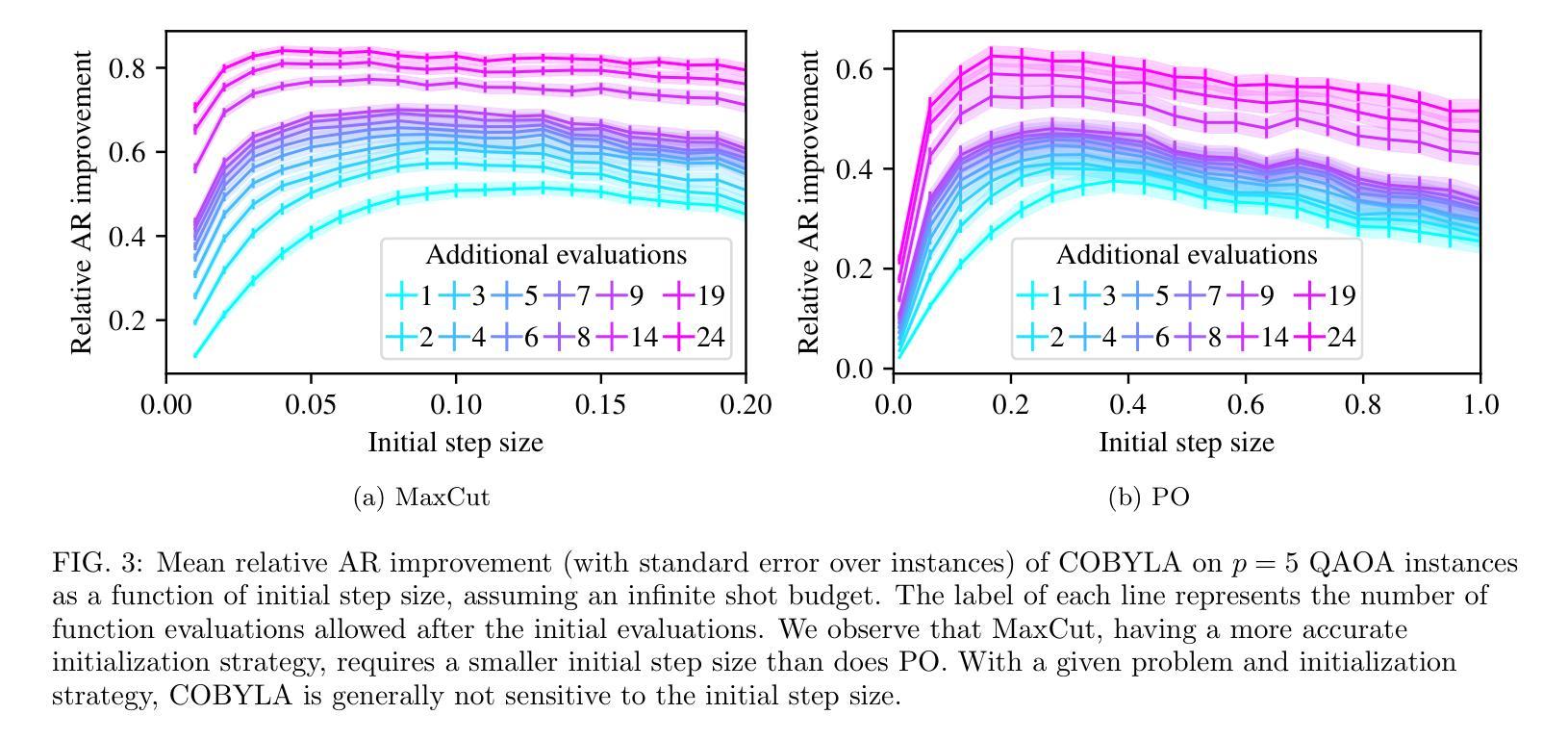
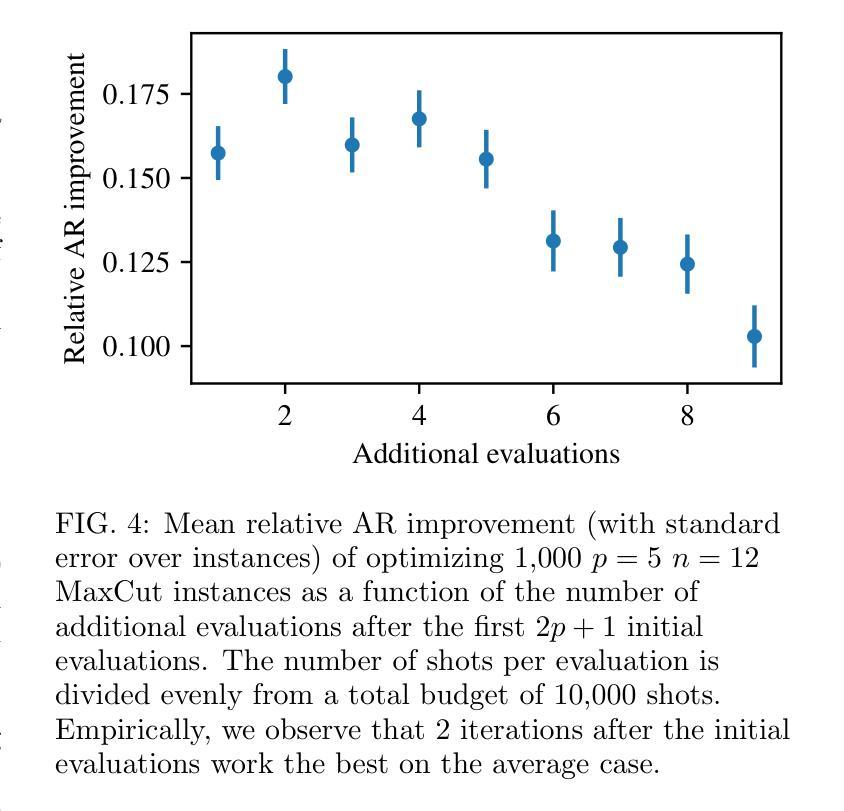
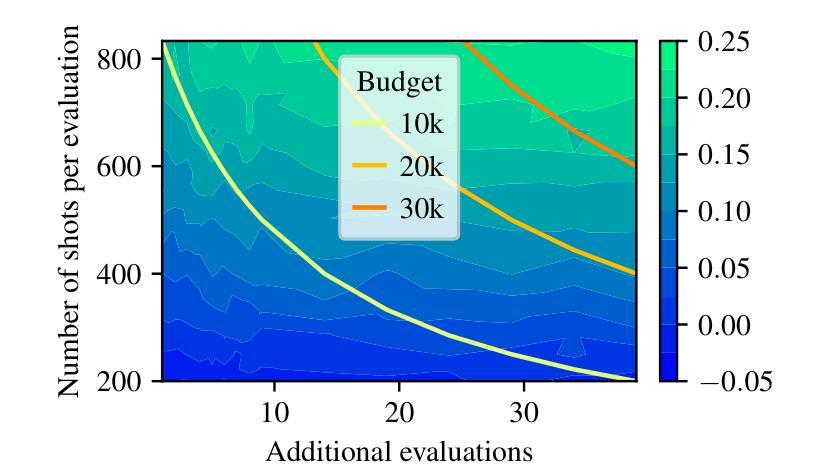
End-to-End Protocol for High-Quality QAOA Parameters with Few Shots
Authors:Tianyi Hao, Zichang He, Ruslan Shaydulin, Jeffrey Larson, Marco Pistoia
The quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) is a quantum heuristic for combinatorial optimization that has been demonstrated to scale better than state-of-the-art classical solvers for some problems. For a given problem instance, QAOA performance depends crucially on the choice of the parameters. While average-case optimal parameters are available in many cases, meaningful performance gains can be obtained by fine-tuning these parameters for a given instance. This task is especially challenging, however, when the number of circuit executions (shots) is limited. In this work, we develop an end-to-end protocol that combines multiple parameter settings and fine-tuning techniques. We use large-scale numerical experiments to optimize the protocol for the shot-limited setting and observe that optimizers with the simplest internal model (linear) perform best. We implement the optimized pipeline on a trapped-ion processor using up to 32 qubits and 5 QAOA layers, and we demonstrate that the pipeline is robust to small amounts of hardware noise. To the best of our knowledge, these are the largest demonstrations of QAOA parameter fine-tuning on a trapped-ion processor in terms of 2-qubit gate count.
量子近似优化算法(QAOA)是一种组合优化的量子启发式算法,对于某些问题,它的扩展性已经证明优于最先进的经典求解器。对于给定的问题实例,QAOA的性能关键在于参数的选择。虽然在许多情况下存在平均情况下的最优参数,但通过针对给定实例微调这些参数可以获得有意义的性能提升。然而,当电路执行次数(shots)有限时,这项任务尤其具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们开发了一种端到端的协议,该协议结合了多种参数设置和微调技术。我们使用大规模数值实验来优化适用于有限执行次数设置的协议,并观察到具有最简单内部模型(线性)的优化器表现最佳。我们在使用最多32个量子比特和5个QAOA层的离子阱处理器上实现了优化后的管道,并证明该管道对少量的硬件噪声具有鲁棒性。据我们所知,这是基于离子阱处理器进行QAOA参数细调的最大的展示,按两量子位门计数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13+2 pages, 11+3 figures, accepted by Physical Review Research
Summary
量子近似优化算法(QAOA)是一种组合优化的量子启发式算法,针对某些问题,其扩展性优于现有经典求解器。对于给定的问题实例,QAOA的性能取决于参数的选择。虽然平均情况下的最优参数在许多情况下是可用的,但通过针对给定实例微调这些参数可以获得有意义的性能提升。然而,当电路执行次数(shots)有限时,这项任务尤其具有挑战性。本研究开发了一种结合多种参数设置和微调技术的端到端协议。通过大规模数值实验优化适用于有限执行次数设置的协议,并观察到具有最简单内部模型(线性)的优化器表现最佳。我们在离子阱处理器上实现了优化后的管道,使用最多32个量子比特和5个QAOA层,并证明该管道对少量的硬件噪声具有鲁棒性。据我们所知,这是基于离子阱处理器上QAOA参数微调的最大演示,按两量子位门计数。
Key Takeaways
- QAOA是一种用于组合优化的量子启发式算法,针对某些问题具有优异的扩展性。
- QAOA性能取决于参数选择,可以通过微调参数来提升性能。
- 当电路执行次数有限时,参数微调具有挑战性。
- 研究人员开发了一种结合多种参数设置和微调技术的端到端协议。
- 通过大规模数值实验优化协议,发现具有简单内部模型的优化器表现最佳。
- 在离子阱处理器上实现了优化后的管道,展示了其对硬件噪声的鲁棒性。
- 这是迄今为止在离子阱处理器上进行的最大规模的QAOA参数微调演示。
点此查看论文截图