⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
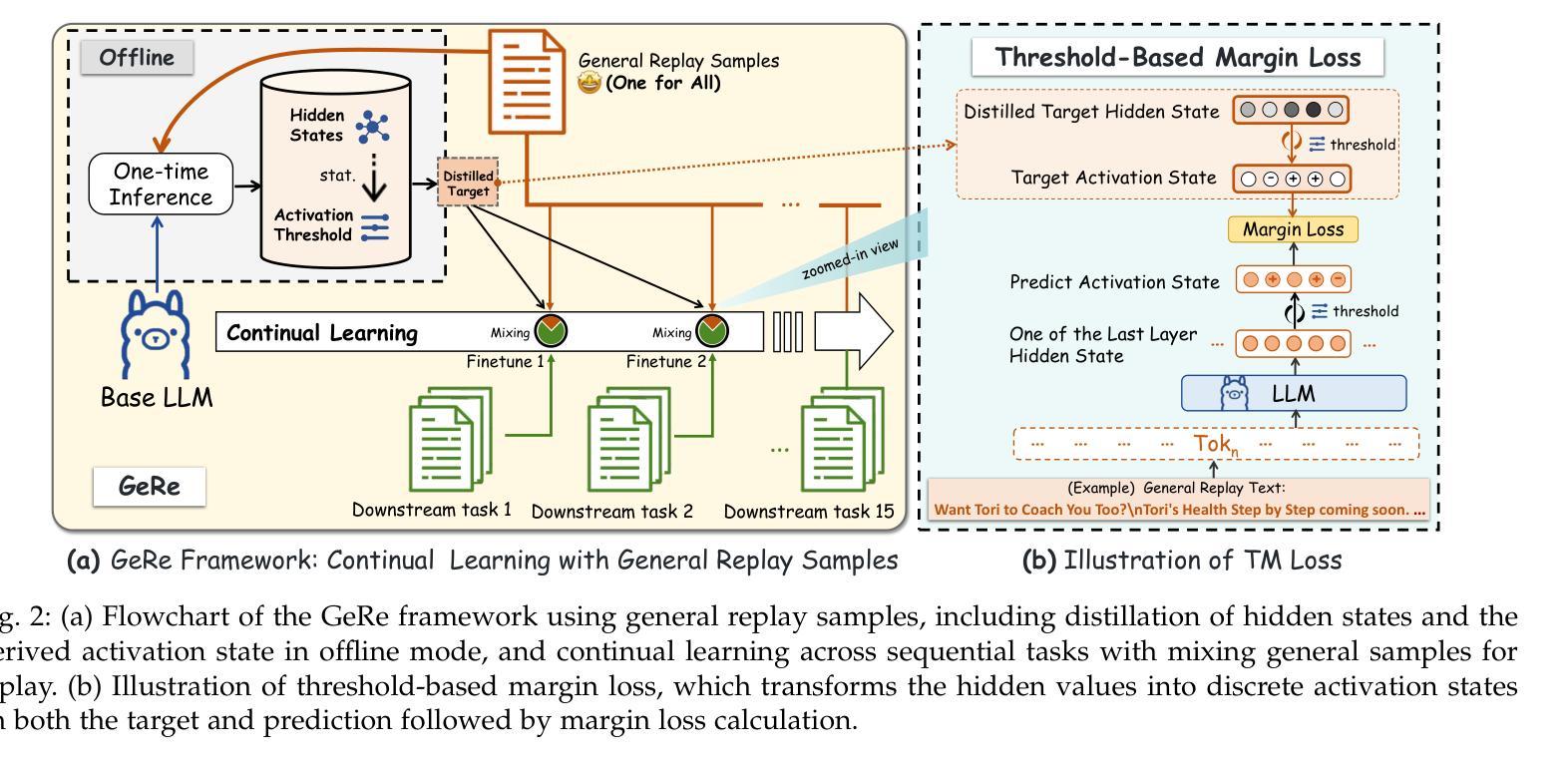
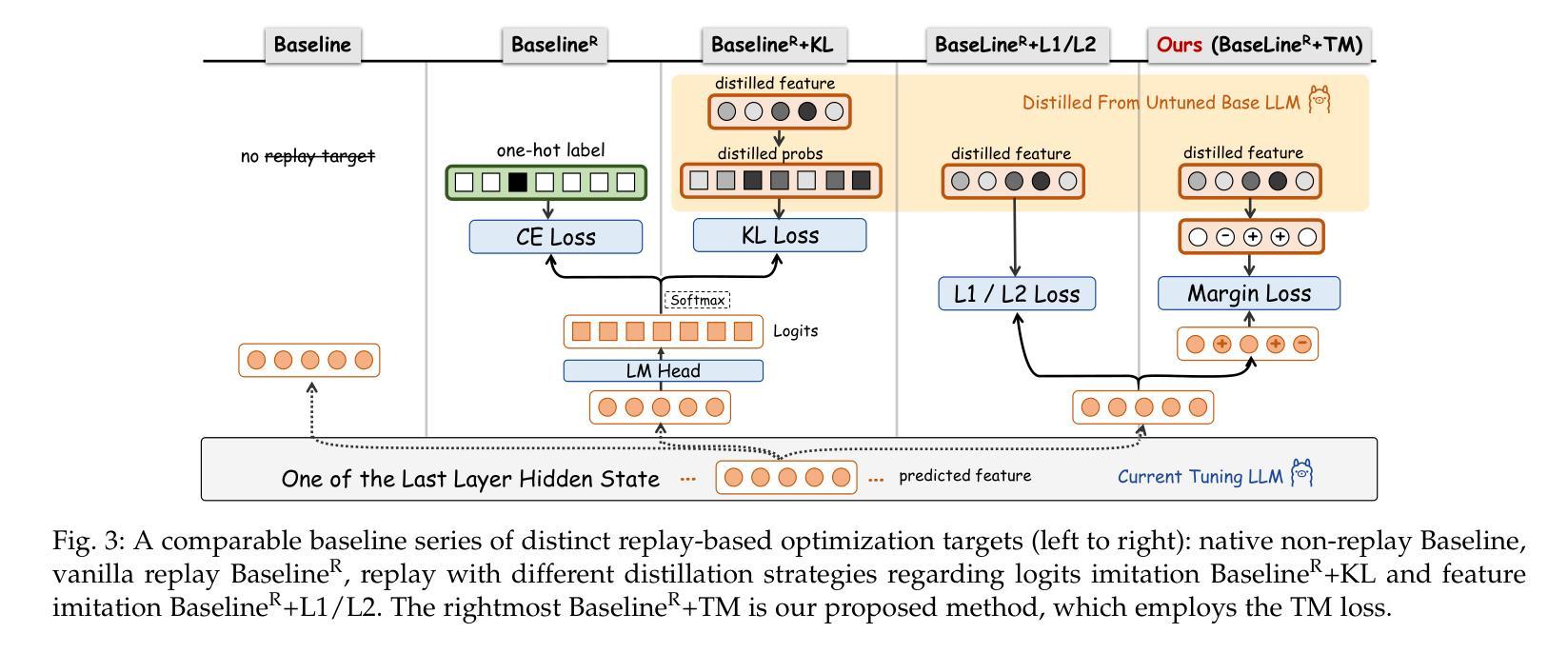
GeRe: Towards Efficient Anti-Forgetting in Continual Learning of LLM via General Samples Replay
Authors:Yunan Zhang, Shuoran Jiang, Mengchen Zhao, Yuefeng Li, Yang Fan, Xiangping Wu, Qingcai Chen
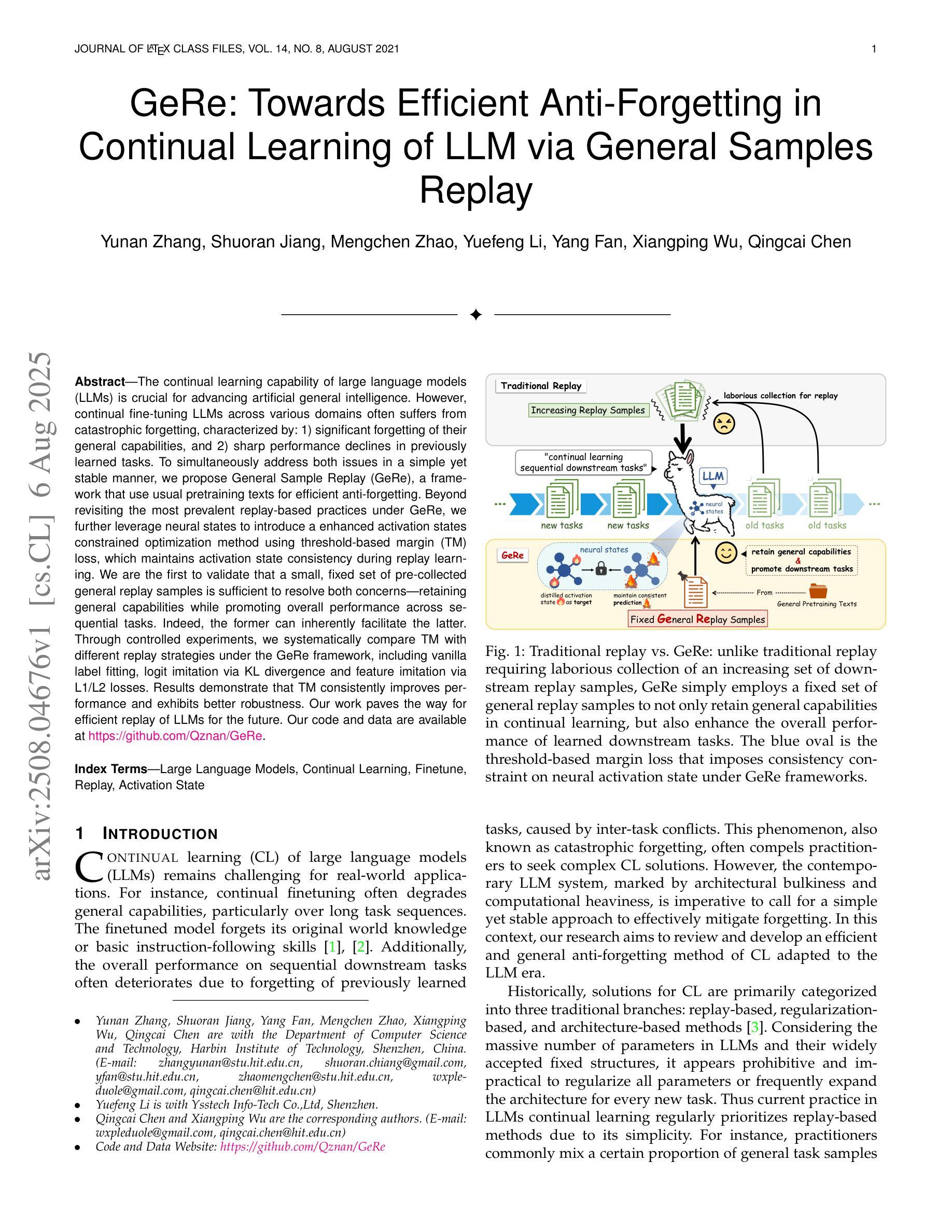
The continual learning capability of large language models (LLMs) is crucial for advancing artificial general intelligence. However, continual fine-tuning LLMs across various domains often suffers from catastrophic forgetting, characterized by: 1) significant forgetting of their general capabilities, and 2) sharp performance declines in previously learned tasks. To simultaneously address both issues in a simple yet stable manner, we propose General Sample Replay (GeRe), a framework that use usual pretraining texts for efficient anti-forgetting. Beyond revisiting the most prevalent replay-based practices under GeRe, we further leverage neural states to introduce a enhanced activation states constrained optimization method using threshold-based margin (TM) loss, which maintains activation state consistency during replay learning. We are the first to validate that a small, fixed set of pre-collected general replay samples is sufficient to resolve both concerns–retaining general capabilities while promoting overall performance across sequential tasks. Indeed, the former can inherently facilitate the latter. Through controlled experiments, we systematically compare TM with different replay strategies under the GeRe framework, including vanilla label fitting, logit imitation via KL divergence and feature imitation via L1/L2 losses. Results demonstrate that TM consistently improves performance and exhibits better robustness. Our work paves the way for efficient replay of LLMs for the future. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/Qznan/GeRe.
大型语言模型(LLM)的持续学习能力对于推进人工智能通用智能至关重要。然而,在不同领域进行LLM的持续微调常常会遇到灾难性遗忘的问题,其特征表现为:1)通用能力的显著遗忘;2)已学习任务的性能急剧下降。为了以一种简单而稳定的方式同时解决这两个问题,我们提出了通用样本回放(GeRe)框架,该框架使用常规的预训练文本进行高效的抗遗忘。除了回顾GeRe下最常见的回放实践之外,我们还进一步利用神经状态,引入了一种基于阈值边界(TM)损失的激活状态约束优化方法,该方法在回放学习过程中保持激活状态一致性。我们是首次验证,一小批预先收集的通用回放样本足以解决这两方面的问题——在保留通用能力的同时,促进各项任务的总体性能。实际上,前者可以内在促进后者。通过控制实验,我们在GeRe框架下将TM与不同的回放策略进行了系统比较,包括普通标签拟合、通过KL散度实现逻辑模仿以及通过L1/L2损失实现特征模仿。结果表明,TM在性能上表现更稳定且更持久。我们的工作为LLM的有效回放铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/Qznan/GeRe找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的持续学习能力对推进人工智能通用智能至关重要。然而,跨域持续微调LLM时常遭遇灾难性遗忘问题,表现为一般能力的显著遗忘以及先前学习任务的性能急剧下降。为解决这两个问题,我们提出简单稳定的通用样本回放(GeRe)框架,利用常规预训练文本进行有效抗遗忘。除回顾GeRe下的最常见回放实践外,我们还借助神经状态,引入使用阈值边界(TM)损失的激活状态约束优化方法。我们是首批验证者,证明一小部分预先收集的通用回放样本足以解决这两个关注点——保留一般能力的同时,促进跨序贯任务的总体性能。实际上,前者可以固有地促进后者。通过受控实验,我们在GeRe框架下系统地比较了TM与不同的回放策略,包括普通标签拟合、通过KL散度实现逻辑模仿以及通过L1/L2损失实现特征模仿。结果表明,TM在性能和稳健性方面表现更优秀。我们的工作为未来LLM的有效回放铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的持续学习能力对推进人工智能至关重要。
- LLM在跨域持续微调中面临灾难性遗忘问题,表现为一般能力的遗忘和先前任务性能的下降。
- 通用样本回放(GeRe)框架旨在解决这一问题,利用常规预训练文本进行抗遗忘。
- GeRe框架结合了回放策略和神经状态,引入使用阈值边界(TM)损失的激活状态约束优化方法。
- 预先收集的通用回放样本可有效解决遗忘问题,同时促进跨序贯任务的性能。
- 通过实验验证,TM损失在回放策略中表现优异,具有更好的性能和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图
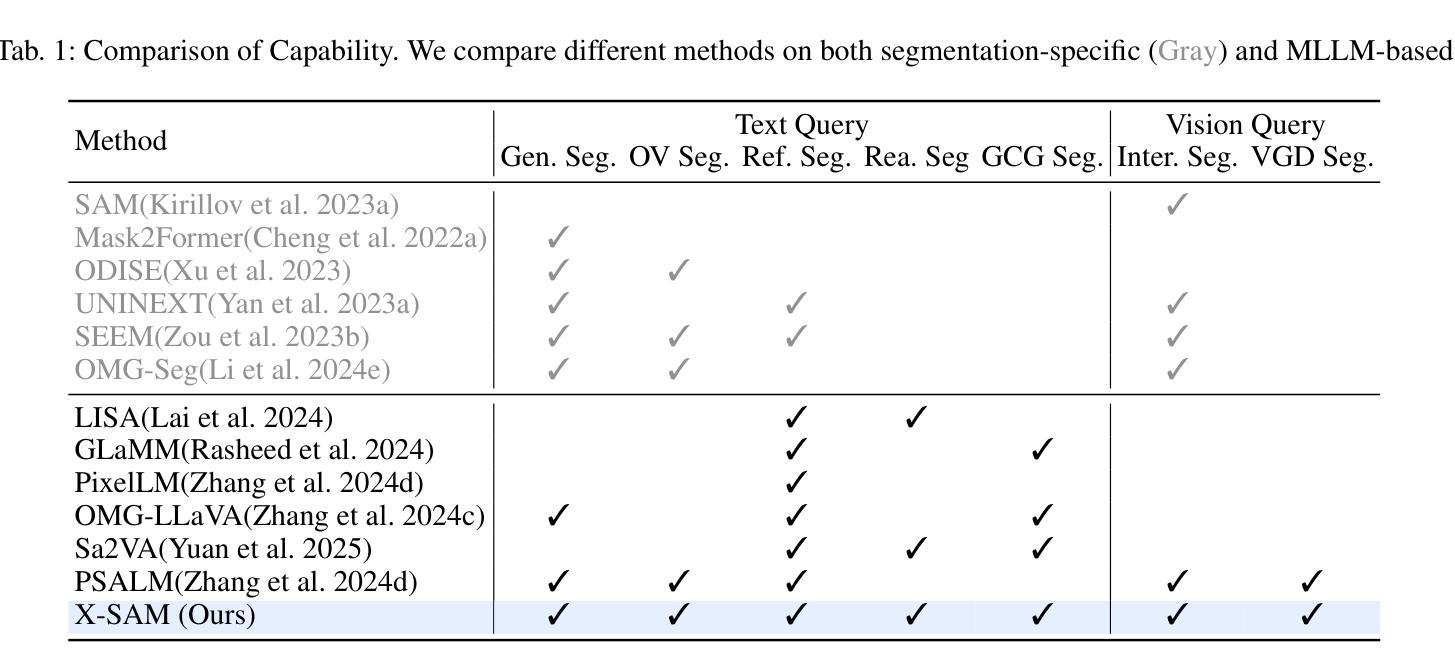
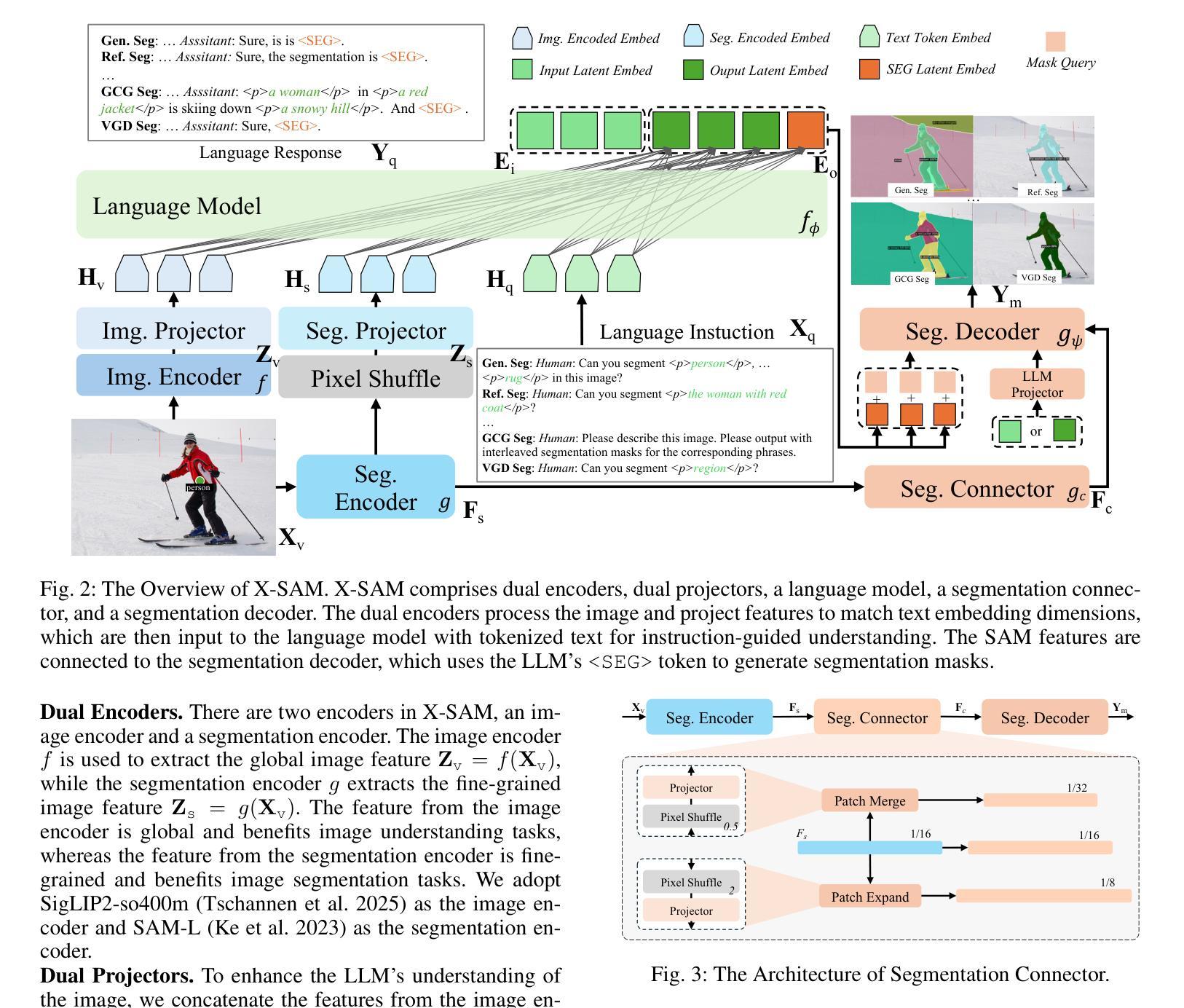
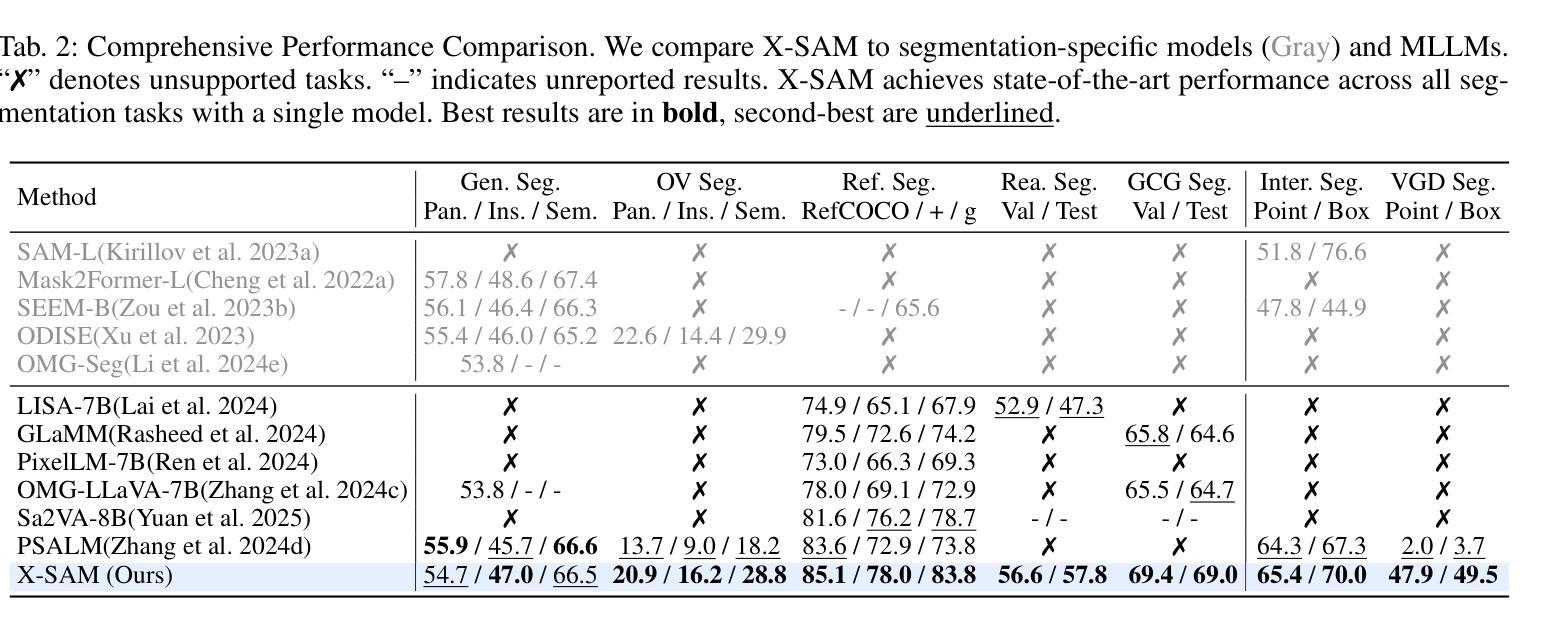
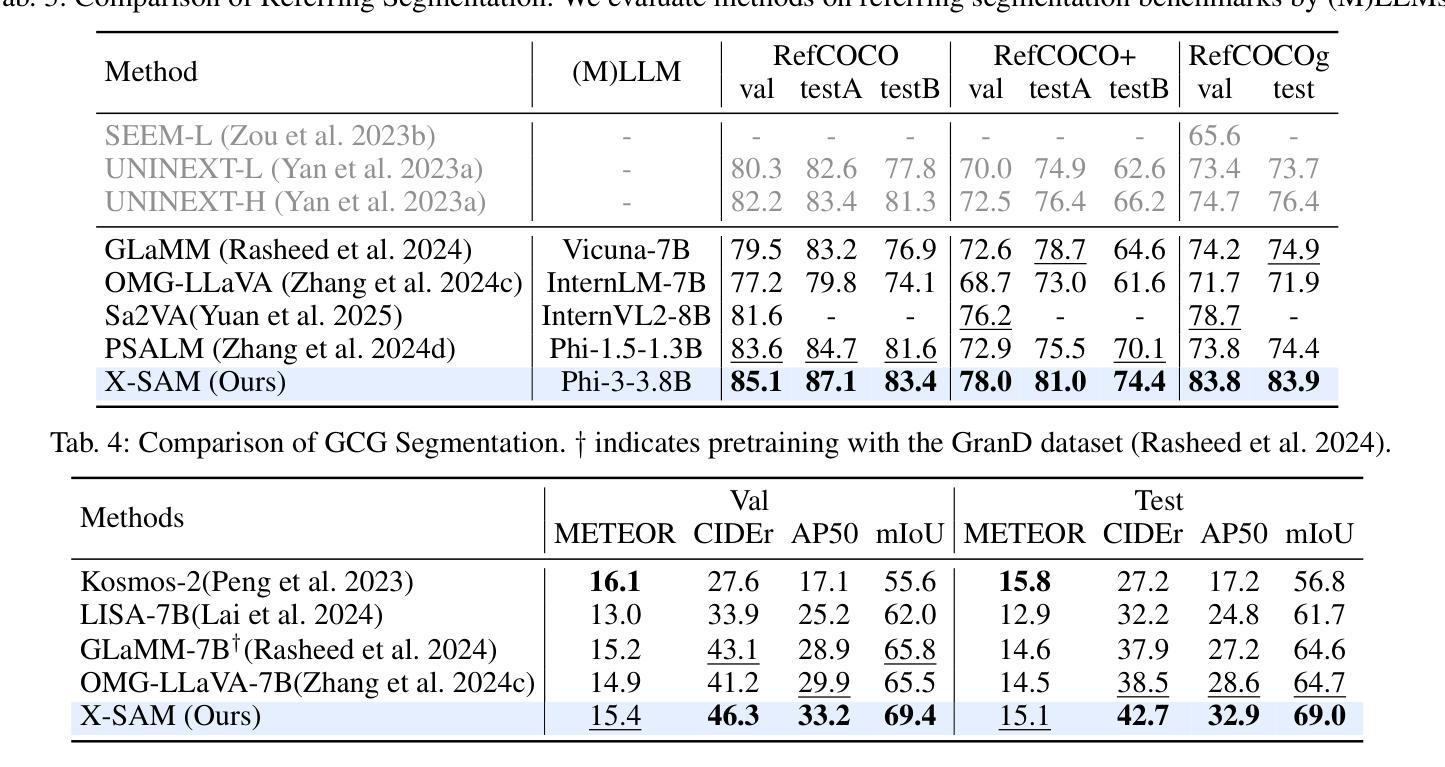
X-SAM: From Segment Anything to Any Segmentation
Authors:Hao Wang, Limeng Qiao, Zequn Jie, Zhijian Huang, Chengjian Feng, Qingfang Zheng, Lin Ma, Xiangyuan Lan, Xiaodan Liang
Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in broad knowledge representation, yet they are inherently deficient in pixel-level perceptual understanding. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) represents a significant advancement in visual-prompt-driven image segmentation, it exhibits notable limitations in multi-mask prediction and category-specific segmentation tasks, and it cannot integrate all segmentation tasks within a unified model architecture. To address these limitations, we present X-SAM, a streamlined Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) framework that extends the segmentation paradigm from \textit{segment anything} to \textit{any segmentation}. Specifically, we introduce a novel unified framework that enables more advanced pixel-level perceptual comprehension for MLLMs. Furthermore, we propose a new segmentation task, termed Visual GrounDed (VGD) segmentation, which segments all instance objects with interactive visual prompts and empowers MLLMs with visual grounded, pixel-wise interpretative capabilities. To enable effective training on diverse data sources, we present a unified training strategy that supports co-training across multiple datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that X-SAM achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of image segmentation benchmarks, highlighting its efficiency for multimodal, pixel-level visual understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/wanghao9610/X-SAM.
大型语言模型(LLM)在广泛的知识表示方面表现出强大的能力,然而它们在像素级别的感知理解方面存在固有缺陷。尽管Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉提示驱动的图像分割方面代表了显著的进步,但在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割任务方面存在明显的局限性,并且它无法在统一的模型架构中集成所有的分割任务。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了X-SAM,这是一个简化的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)框架,它将分割范式从“分割任何事物”扩展到“任何分割”。具体来说,我们引入了一种新型统一框架,使MLLM具备更先进的像素级别感知理解能力。此外,我们提出了一种新的分割任务,称为Visual GrounDed(VGD)分割,它通过交互式的视觉提示对所有实例对象进行分割,并为MLLM提供视觉基础、像素级的解释能力。为了在不同的数据源上进行有效的训练,我们提出了一种支持跨多个数据集进行联合训练的统一训练策略。实验结果表明,X-SAM在广泛的图像分割基准测试中达到了最新性能水平,突显了其在多模态、像素级别的视觉理解方面的效率。代码可通过https://github.com/wanghao9610/X-SAM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)具有广泛的知识表示能力,但在像素级别的感知理解上存在固有缺陷。Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉提示驱动的图像分割上取得了重大进展,但在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割任务上表现出明显局限,且无法将所有分割任务整合到一个统一的模型架构中。为解决这些问题,我们提出了X-SAM,一个简化的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)框架,将分割范式从“分割任何东西”扩展到“任何分割”。我们引入了一种新型统一框架,为MLLM提供更先进的像素级别感知理解。此外,我们提出了一种新的分割任务,称为Visual GrounDed(VGD)分割,通过交互视觉提示对实例对象进行分割,并为MLLM提供视觉接地、像素级的解释能力。我们提出了一种跨多个数据集的联合训练策略,以实现不同数据源的有效训练。实验结果表明,X-SAM在广泛的图像分割基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,突显了其在多模态、像素级别的视觉理解上的效率。代码可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs虽在知识表示方面表现出强大的能力,但在像素级别的感知理解上存在局限。
- Segment Anything Model (SAM)在视觉提示驱动的图像分割上有显著进展,但存在多掩膜预测和特定类别分割的局限。
- X-SAM是一个简化的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)框架,扩展了分割范式,引入了更先进的像素级别感知理解。
- X-SAM通过交互视觉提示进行实例对象分割,并赋予MLLM视觉接地、像素级的解释能力。
- X-SAM采用统一框架整合多种分割任务,并提出了一种新的分割任务——Visual GrounDed (VGD) 分割。
- X-SAM通过跨多个数据集的联合训练策略实现有效训练。
点此查看论文截图

RoboTron-Sim: Improving Real-World Driving via Simulated Hard-Case
Authors:Baihui Xiao, Chengjian Feng, Zhijian Huang, Feng yan, Yujie Zhong, Lin Ma
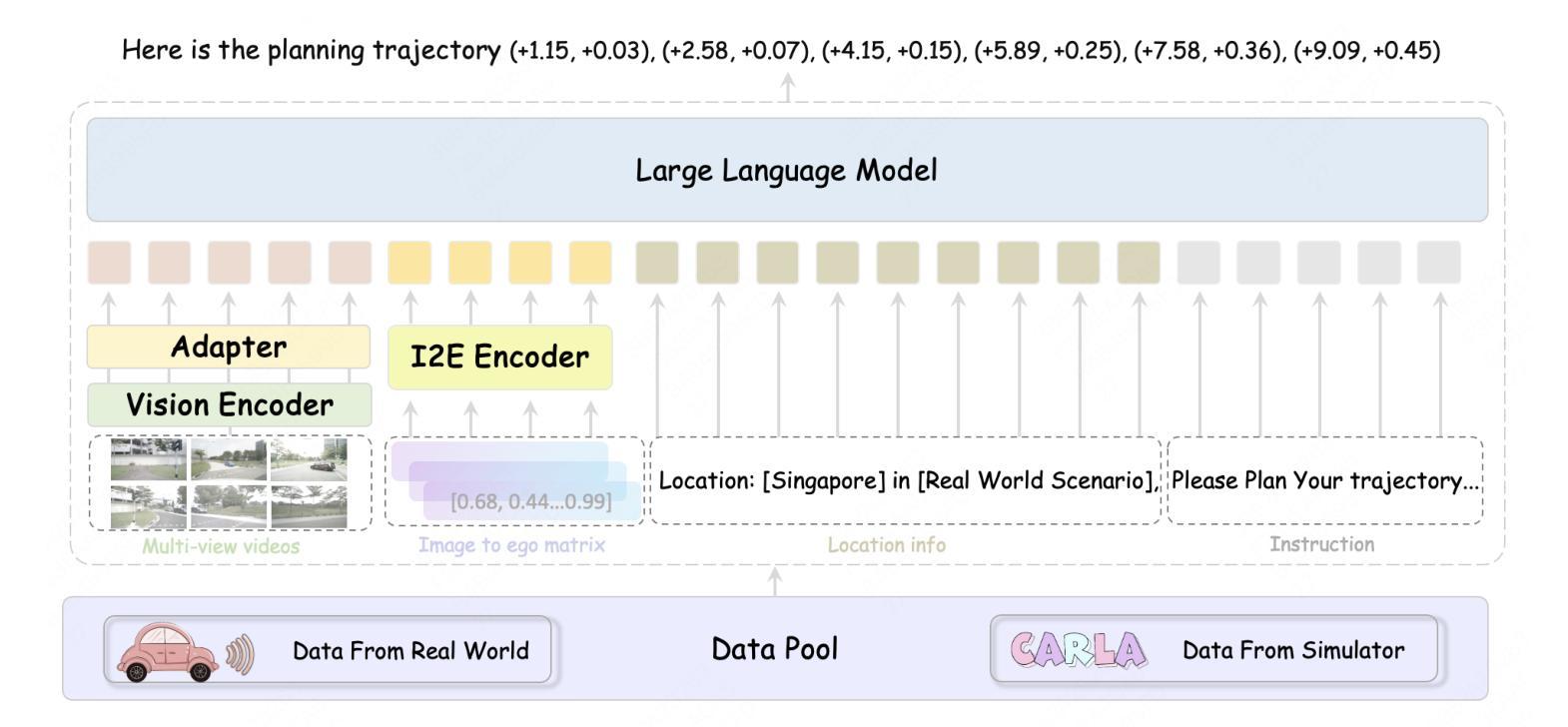
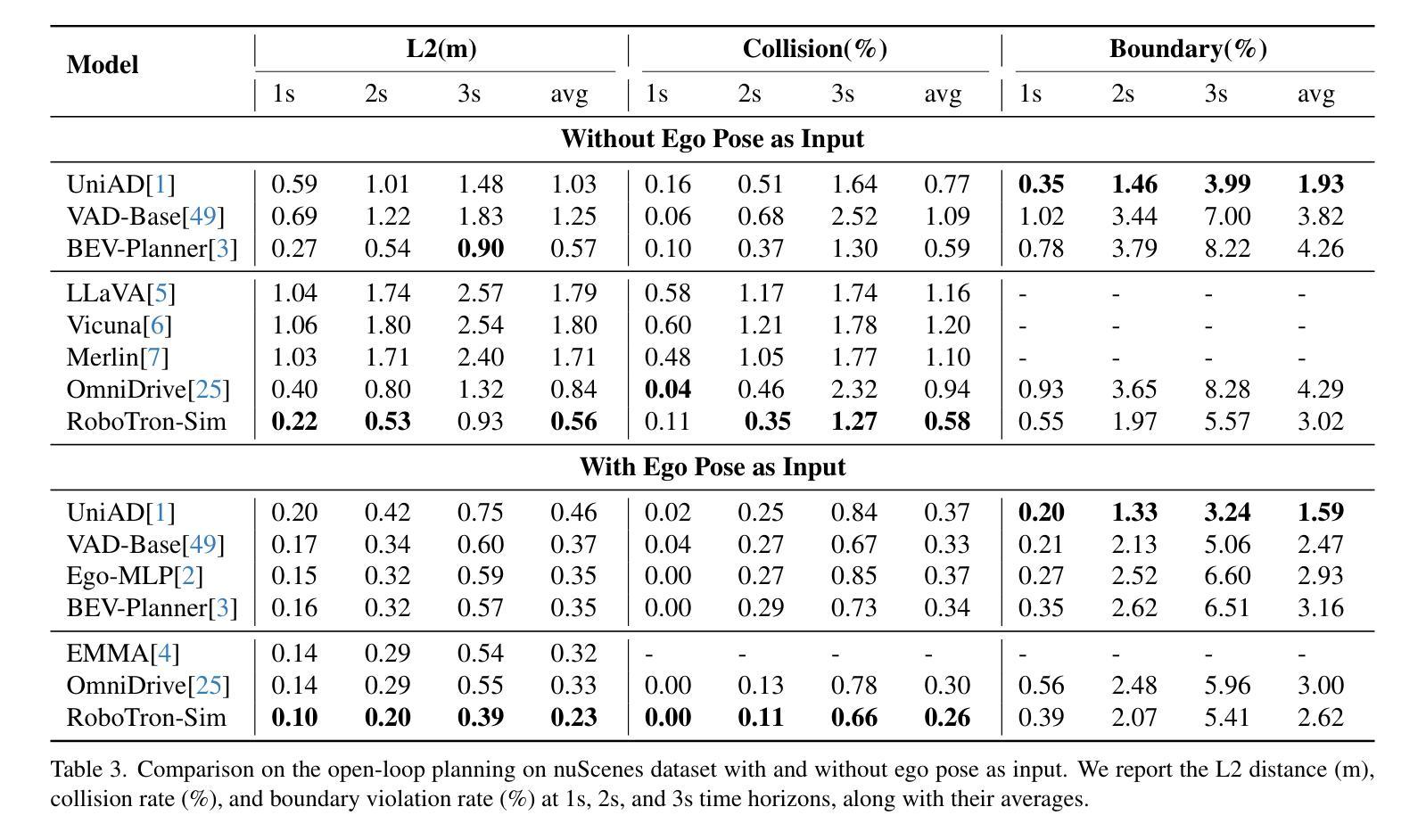
Collecting real-world data for rare high-risk scenarios, long-tailed driving events, and complex interactions remains challenging, leading to poor performance of existing autonomous driving systems in these critical situations. In this paper, we propose RoboTron-Sim that improves real-world driving in critical situations by utilizing simulated hard cases. First, we develop a simulated dataset called Hard-case Augmented Synthetic Scenarios (HASS), which covers 13 high-risk edge-case categories, as well as balanced environmental conditions such as day/night and sunny/rainy. Second, we introduce Scenario-aware Prompt Engineering (SPE) and an Image-to-Ego Encoder (I2E Encoder) to enable multimodal large language models to effectively learn real-world challenging driving skills from HASS, via adapting to environmental deviations and hardware differences between real-world and simulated scenarios. Extensive experiments on nuScenes show that RoboTron-Sim improves driving performance in challenging scenarios by around 50%, achieving state-of-the-art results in real-world open-loop planning. Qualitative results further demonstrate the effectiveness of RoboTron-Sim in better managing rare high-risk driving scenarios. Project page: https://stars79689.github.io/RoboTron-Sim/
收集真实世界数据对于罕见高风险场景、长尾驾驶事件和复杂交互仍然具有挑战性,导致现有自动驾驶系统在这些关键情况下表现不佳。在本文中,我们提出RoboTron-Sim,它通过利用模拟的困难案例来改善关键情况下的现实世界驾驶。首先,我们开发了一个名为Hard-case Augmented Synthetic Scenarios(HASS)的模拟数据集,涵盖了13类高风险边缘案例,以及如日夜、晴雨等平衡的环境条件。其次,我们引入了情景感知提示工程(SPE)和图像到自我编码器(I2E Encoder),以使多模态大型语言模型能够通过适应环境偏差和现实世界与模拟场景之间的硬件差异,从HASS有效学习现实世界中具有挑战性的驾驶技能。在nuScenes上的广泛实验表明,RoboTron-Sim将挑战场景中的驾驶性能提高了约50%,在现实世界开放循环规划中实现了最新结果。定性结果进一步证明了RoboTron-Sim在更好地管理罕见高风险驾驶场景方面的有效性。项目页面:https://stars79689.github.io/RoboTron-Sim/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
模拟数据集RoboTron-Sim的提出,解决了真实世界高风险场景数据收集困难的问题,通过创建高风险的模拟场景(如边缘情况)并引入场景感知提示工程和图像到自我编码器技术,使得自动驾驶系统在面临真实世界的复杂挑战时表现更优。实验证明,该技术能提高自动驾驶系统在复杂场景中的性能约50%,达到现实开放环境中规划的最优水平。
Key Takeaways
- 模拟数据集RoboTron-Sim能够覆盖多种高风险边缘场景,并模拟不同环境条件如日夜交替和天气变化。
- 利用场景感知提示工程(SPE)和图像到自我编码器(I2E Encoder)技术,使大型语言模型能够学习处理模拟的高风险驾驶场景。
- 该技术通过适应环境变化和硬件差异,使得自动驾驶系统在处理真实世界的复杂驾驶技能时性能更优。
- 在nuScenes上的实验表明,RoboTron-Sim技术提高了自动驾驶系统在复杂场景中的性能约50%。
- 该技术达到了现实开放环境中规划的最优水平,实现了定性结果的有效展示。
- 项目页面提供了详细的背景信息和研究成果。
点此查看论文截图



P-Aligner: Enabling Pre-Alignment of Language Models via Principled Instruction Synthesis
Authors:Feifan Song, Bofei Gao, Yifan Song, Yi Liu, Weimin Xiong, Yuyang Song, Tianyu Liu, Guoyin Wang, Houfeng Wang
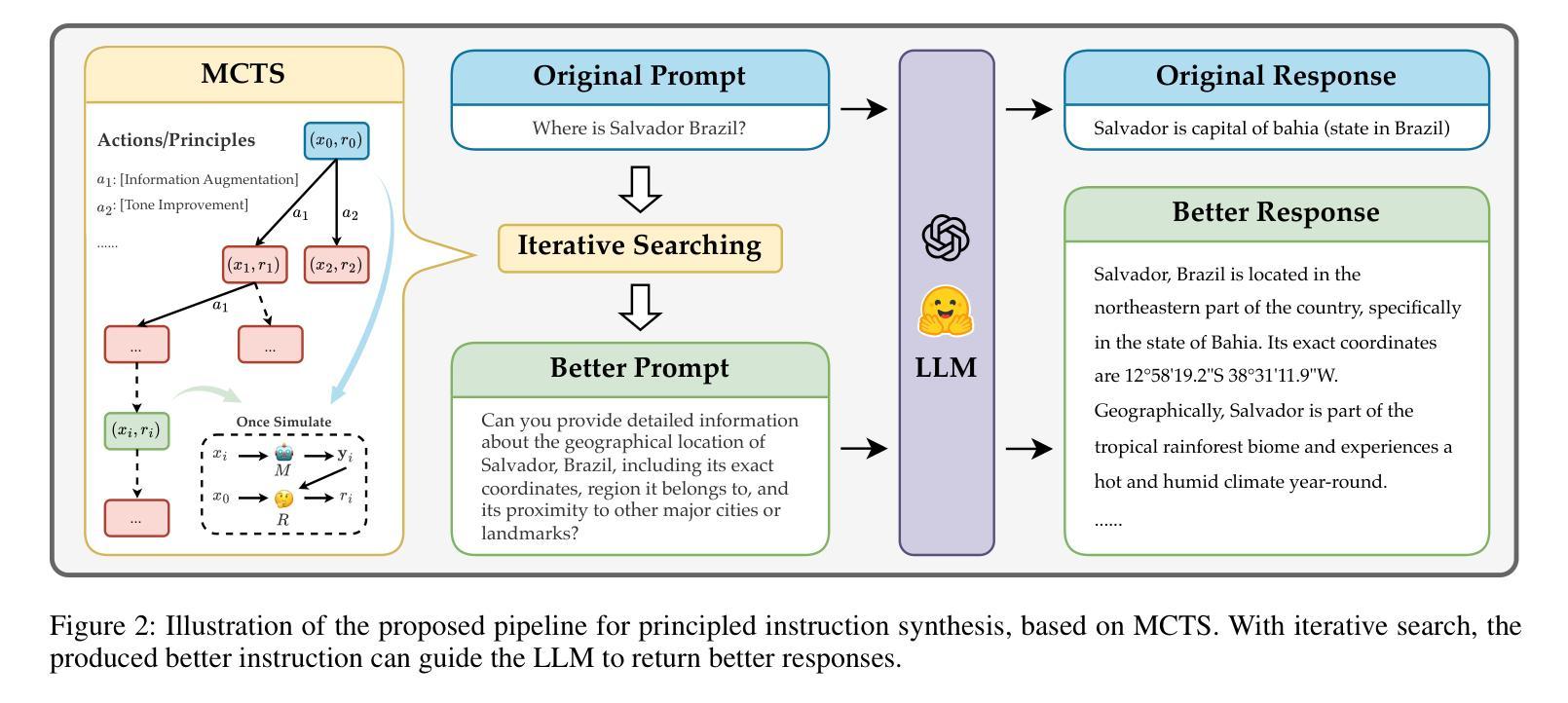
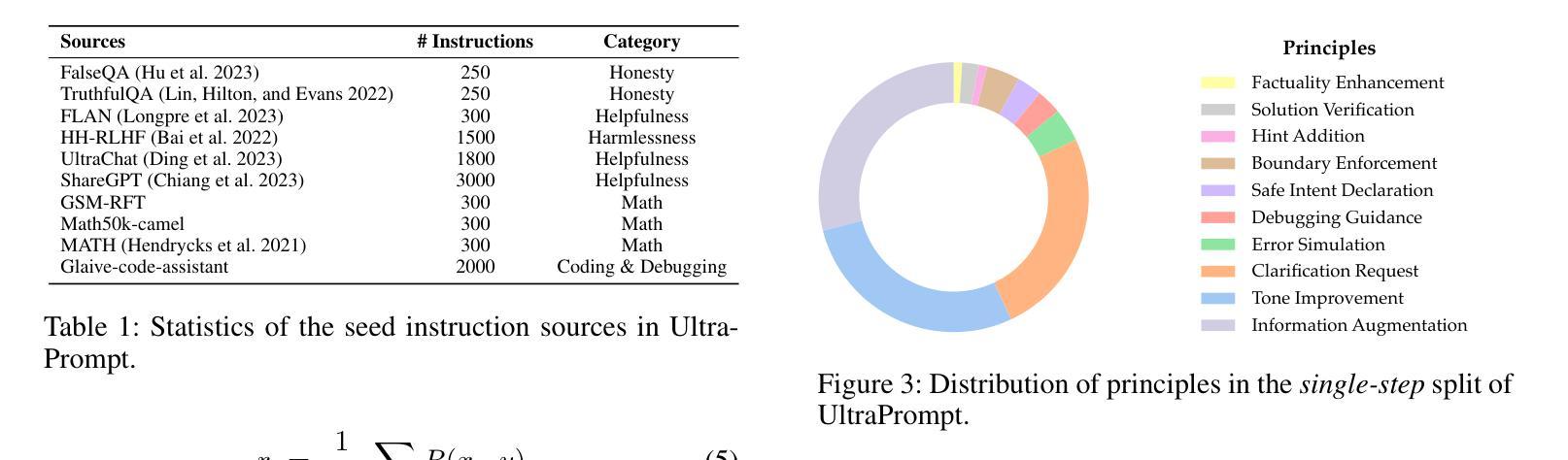
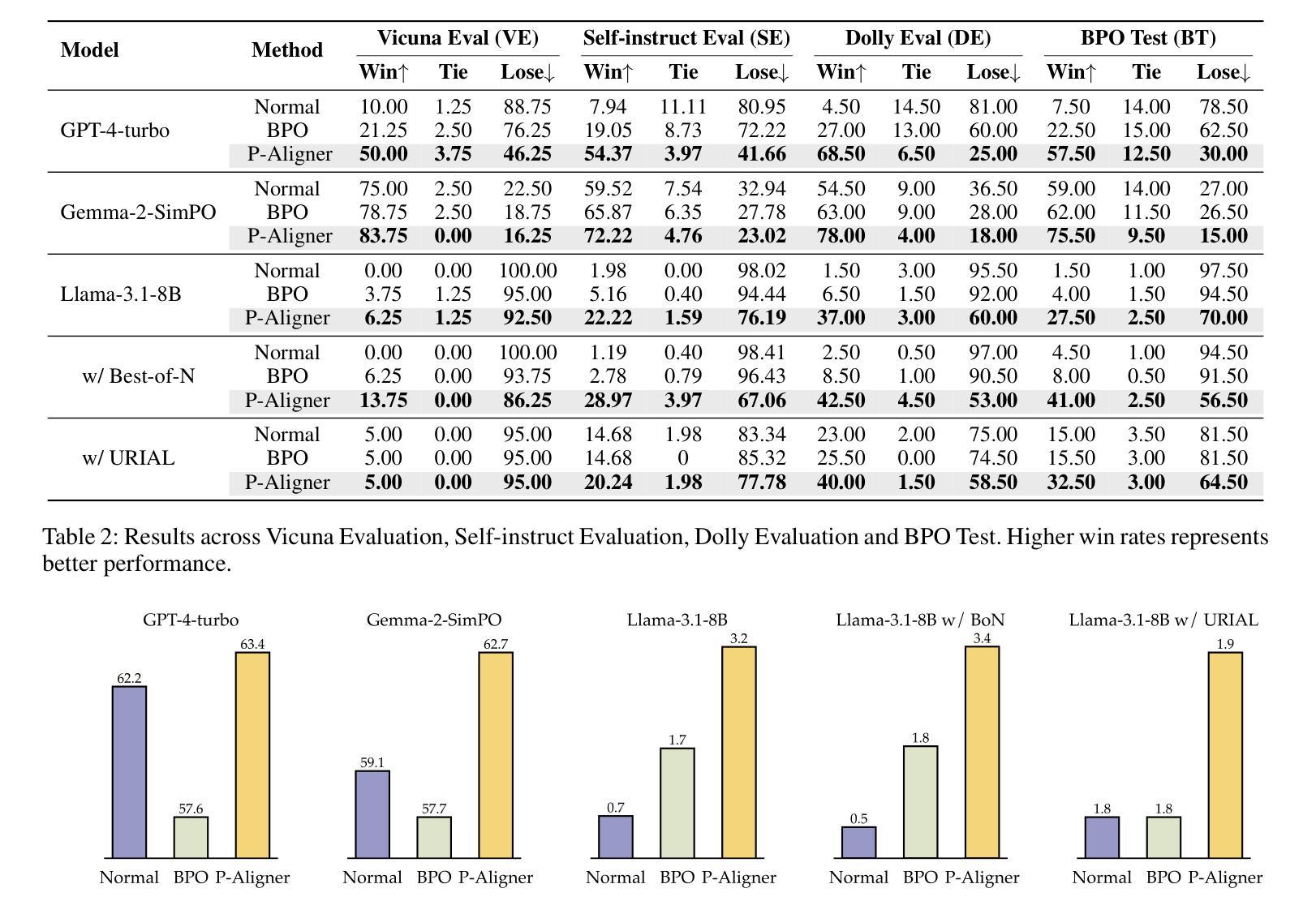
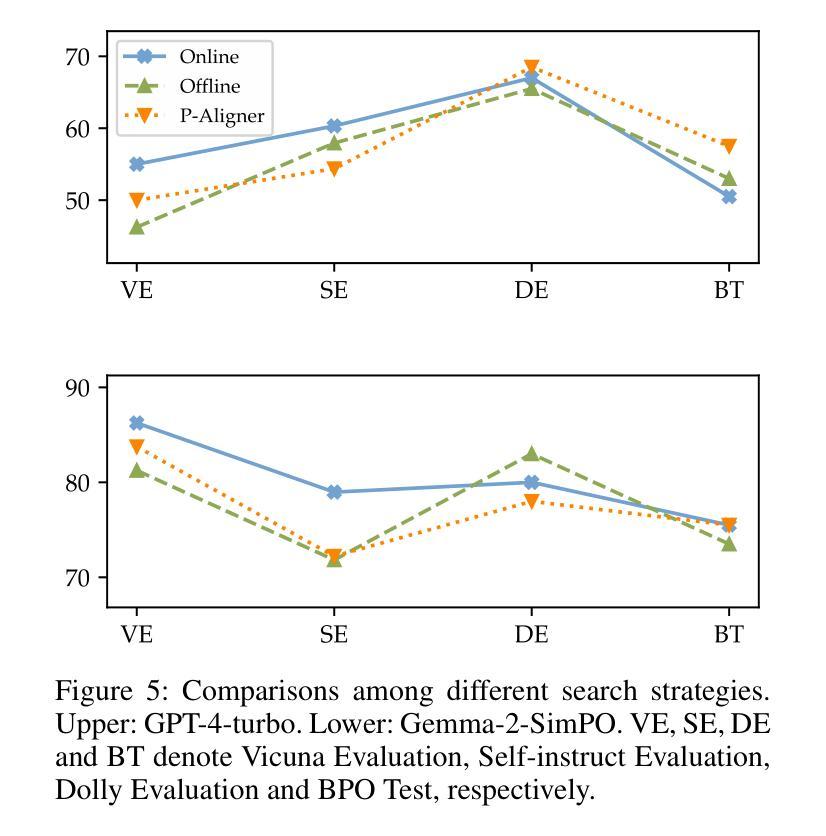
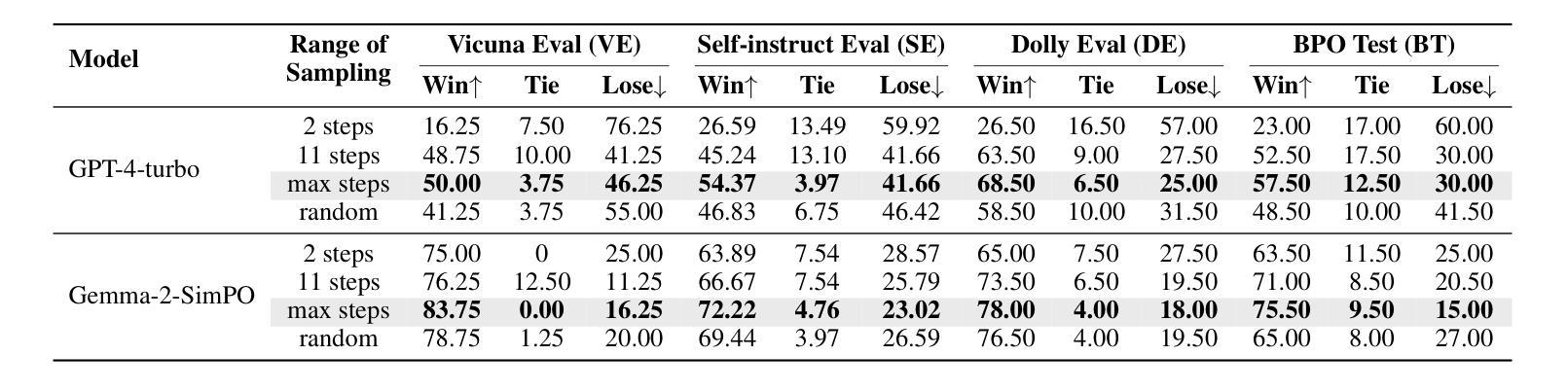
Large Language Models (LLMs) are expected to produce safe, helpful, and honest content during interaction with human users, but they frequently fail to align with such values when given flawed instructions, e.g., missing context, ambiguous directives, or inappropriate tone, leaving substantial room for improvement along multiple dimensions. A cost-effective yet high-impact way is to pre-align instructions before the model begins decoding. Existing approaches either rely on prohibitive test-time search costs or end-to-end model rewrite, which is powered by a customized training corpus with unclear objectives. In this work, we demonstrate that the goal of efficient and effective preference alignment can be achieved by P-Aligner, a lightweight module generating instructions that preserve the original intents while being expressed in a more human-preferred form. P-Aligner is trained on UltraPrompt, a new dataset synthesized via a proposed principle-guided pipeline using Monte-Carlo Tree Search, which systematically explores the space of candidate instructions that are closely tied to human preference. Experiments across different methods show that P-Aligner generally outperforms strong baselines across various models and benchmarks, including average win-rate gains of 28.35% and 8.69% on GPT-4-turbo and Gemma-2-SimPO, respectively. Further analyses validate its effectiveness and efficiency through multiple perspectives, including data quality, search strategies, iterative deployment, and time overhead.
大型语言模型(LLM)在与人类用户交互时,预期会产生安全、有用、诚实的内容。然而,当给予有缺陷的指令时,例如缺少上下文、指令模糊或语气不当,它们往往无法与这些价值对齐,这在多个维度上仍有很大的改进空间。一种成本效益高且影响大的方法是,在模型开始解码之前预先对齐指令。现有方法要么依赖于禁止的测试时间搜索成本,要么依赖于端到端的模型重写,这由带有不明确目标的定制训练语料库提供支持。在这项工作中,我们展示了P-Aligner可以实现高效和有效的偏好对齐的目标。P-Aligner是一个轻量级模块,能够生成在保留原始意图的同时以人类更偏好的形式表达的指令。P-Aligner是在UltraPrompt上训练的,这是一个通过提出的原则引导管道合成的新数据集,该管道使用蒙特卡洛树搜索系统地探索与人类偏好紧密相关的候选指令空间。在不同方法和模型上的实验表明,P-Aligner通常优于强大的基线模型,并在各种基准测试上表现出色,包括在GPT-4-turbo和Gemma-2-SimPO上的平均胜率分别提高了28.35%和8.69%。进一步的分析从数据质量、搜索策略、迭代部署和时间开销等多个角度验证了其有效性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLMs在处理与用户交互时的安全性和有用性方面存在问题,这主要是因为它们在处理具有缺陷的指令(如缺乏上下文、指令模糊或不恰当的语气)时无法对齐相应的价值观。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种高效且有效的偏好对齐方法——P-Aligner,它是一种轻量级模块,能够生成更多符合人类表达习惯的指令。该模块在UltraPrompt数据集上进行训练,这是一个通过提出的原理引导管道合成的数据集,通过蒙特卡洛树搜索系统地探索与人类偏好紧密相关的候选指令空间。实验表明,P-Aligner在各种模型和基准测试上的表现均优于强大的基线模型,包括在GPT-4-turbo和Gemma-2-SimPO上的平均胜率分别提高了28.35%和8.69%。进一步的分析从数据质量、搜索策略、迭代部署和时间开销等多个角度验证了其有效性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在处理具有缺陷的指令时存在对齐问题。
- P-Aligner是一种轻量级模块,旨在生成符合人类表达习惯的指令以提高安全性、有用性和诚实性。
- P-Aligner在UltraPrompt数据集上进行训练,这是一个通过蒙特卡洛树搜索合成的数据集。
- P-Aligner在各种模型和基准测试上的表现优于基线模型。
- P-Aligner在GPT-4-turbo和Gemma-2-SimPO上的平均胜率分别提高了28.35%和8.69%。
- P-Aligner的有效性和效率通过数据质量、搜索策略、迭代部署和时间开销等多个角度得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图

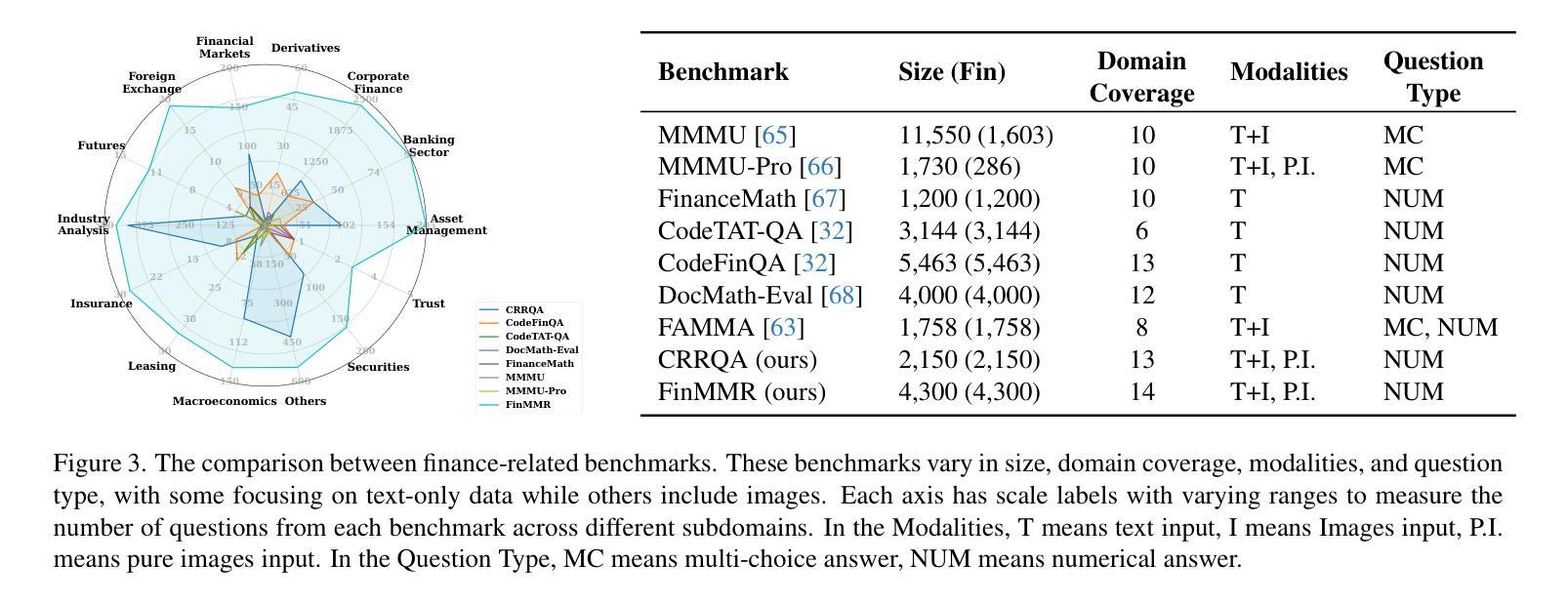
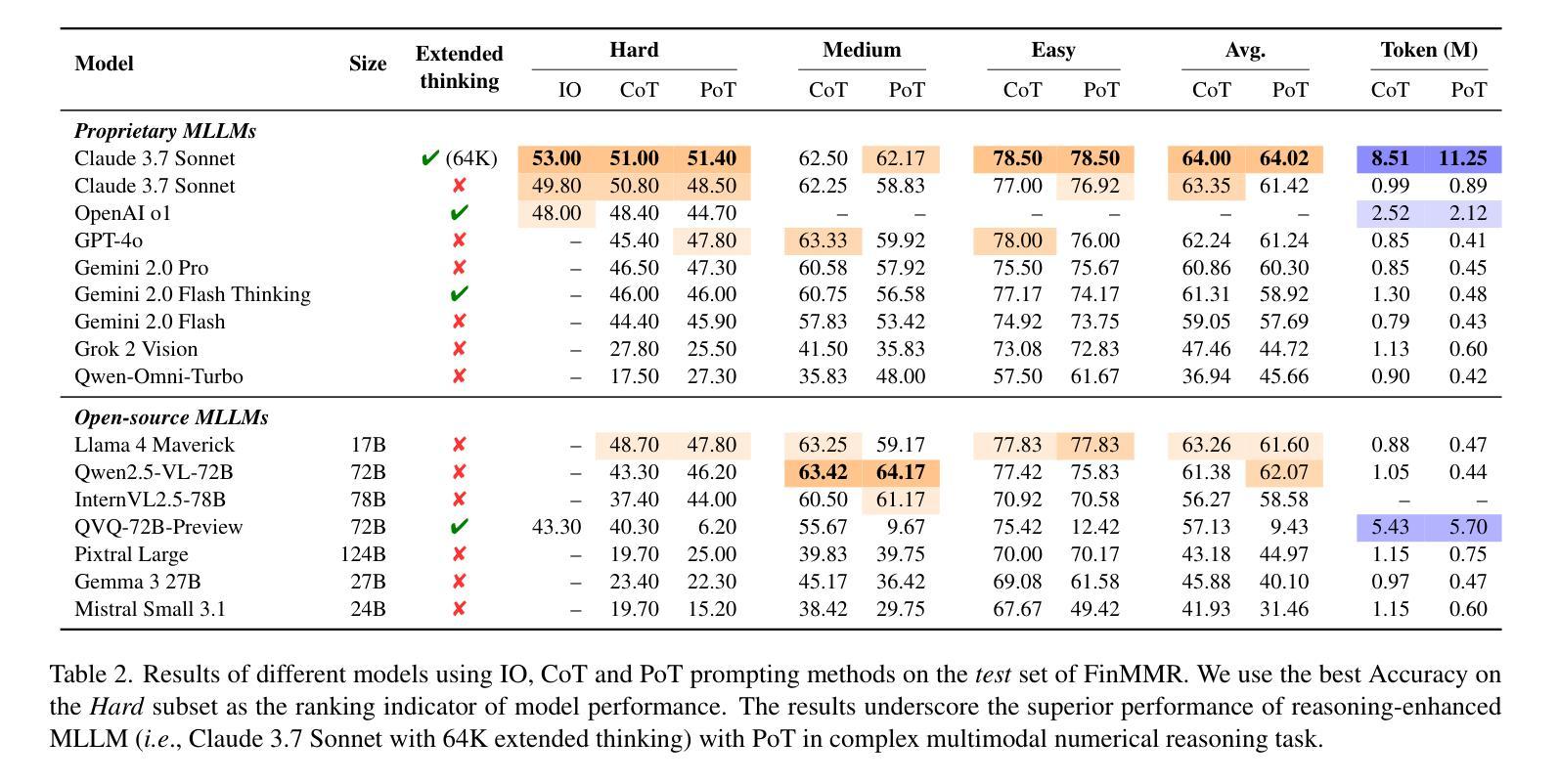
FinMMR: Make Financial Numerical Reasoning More Multimodal, Comprehensive, and Challenging
Authors:Zichen Tang, Haihong E, Jiacheng Liu, Zhongjun Yang, Rongjin Li, Zihua Rong, Haoyang He, Zhuodi Hao, Xinyang Hu, Kun Ji, Ziyan Ma, Mengyuan Ji, Jun Zhang, Chenghao Ma, Qianhe Zheng, Yang Liu, Yiling Huang, Xinyi Hu, Qing Huang, Zijian Xie, Shiyao Peng
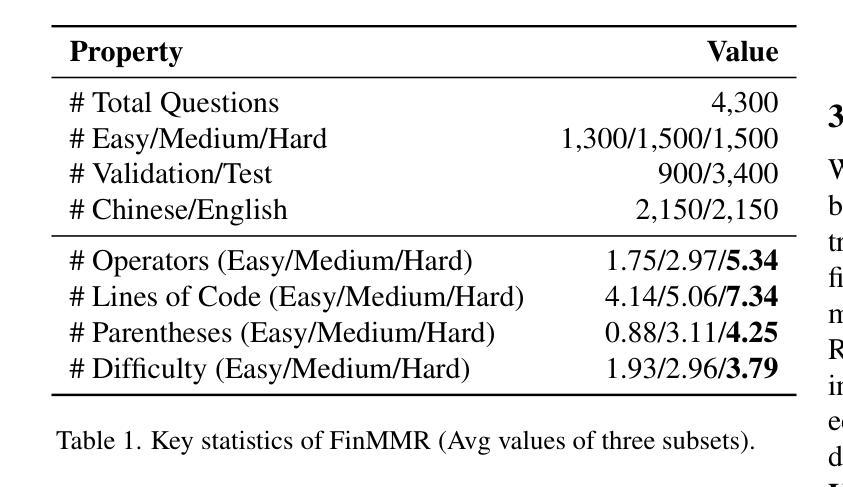
We present FinMMR, a novel bilingual multimodal benchmark tailored to evaluate the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in financial numerical reasoning tasks. Compared to existing benchmarks, our work introduces three significant advancements. (1) Multimodality: We meticulously transform existing financial reasoning benchmarks, and construct novel questions from the latest Chinese financial research reports. FinMMR comprises 4.3K questions and 8.7K images spanning 14 categories, including tables, bar charts, and ownership structure charts. (2) Comprehensiveness: FinMMR encompasses 14 financial subdomains, including corporate finance, banking, and industry analysis, significantly exceeding existing benchmarks in financial domain knowledge breadth. (3) Challenge: Models are required to perform multi-step precise numerical reasoning by integrating financial knowledge with the understanding of complex financial images and text. The best-performing MLLM achieves only 53.0% accuracy on Hard problems. We believe that FinMMR will drive advancements in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of MLLMs in real-world scenarios.
我们推出了FinMMR,这是一个针对金融数值推理任务的多模态大语言模型的推理能力评估而量身定制的新型双语多模态基准测试。与现有基准测试相比,我们的工作引入了三个重要进展。(1) 多模态:我们精心改造了现有的金融推理基准测试,并根据最新的中文金融研究报告构建了新问题。FinMMR包含4.3K个问题和8.7K个图像,涵盖14个类别,包括表格、条形图和所有权结构图等。(2) 全面性:FinMMR涵盖了包括企业财务、银行业和产业分析等在内的14个金融子领域,在财务领域知识的广度上显著超过了现有基准测试。(3) 挑战性:模型需要通过整合金融知识以及对复杂的金融图像和文本的理解,来执行多步骤精确数值推理。在难题上,表现最佳的多模态大语言模型的准确率仅为53.0%。我们相信,FinMMR将推动在提高现实世界场景中多模态大语言模型的推理能力方面的进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2311.06602 by other authors
Summary
FinMMR是一个针对金融数值推理任务的多模态基准测试,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力。相较于现有基准测试,FinMMR有三项显著进步:包括多模态特性、涵盖广泛的金融子领域以及挑战性。它要求模型结合金融知识对复杂金融图像和文本进行多步骤精确数值推理。
Key Takeaways
- FinMMR是一个针对金融数值推理的多模态基准测试,专为评估MLLMs的推理能力而设计。
- 该基准测试包含三项显著特点:多模态特性、涵盖广泛的金融子领域以及挑战性任务。
- FinMMR包含4.3K个问题和8.7K个图像,涉及表格、条形图等14种类型。
- 它涵盖了从企业财务、银行业到行业分析等14个金融子领域。
- 模型需要对复杂的金融图像和文本进行多步骤精确数值推理,集成金融知识。
- 最佳性能的MLLM在困难问题上的准确率仅为53.0%,表明该领域仍存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图


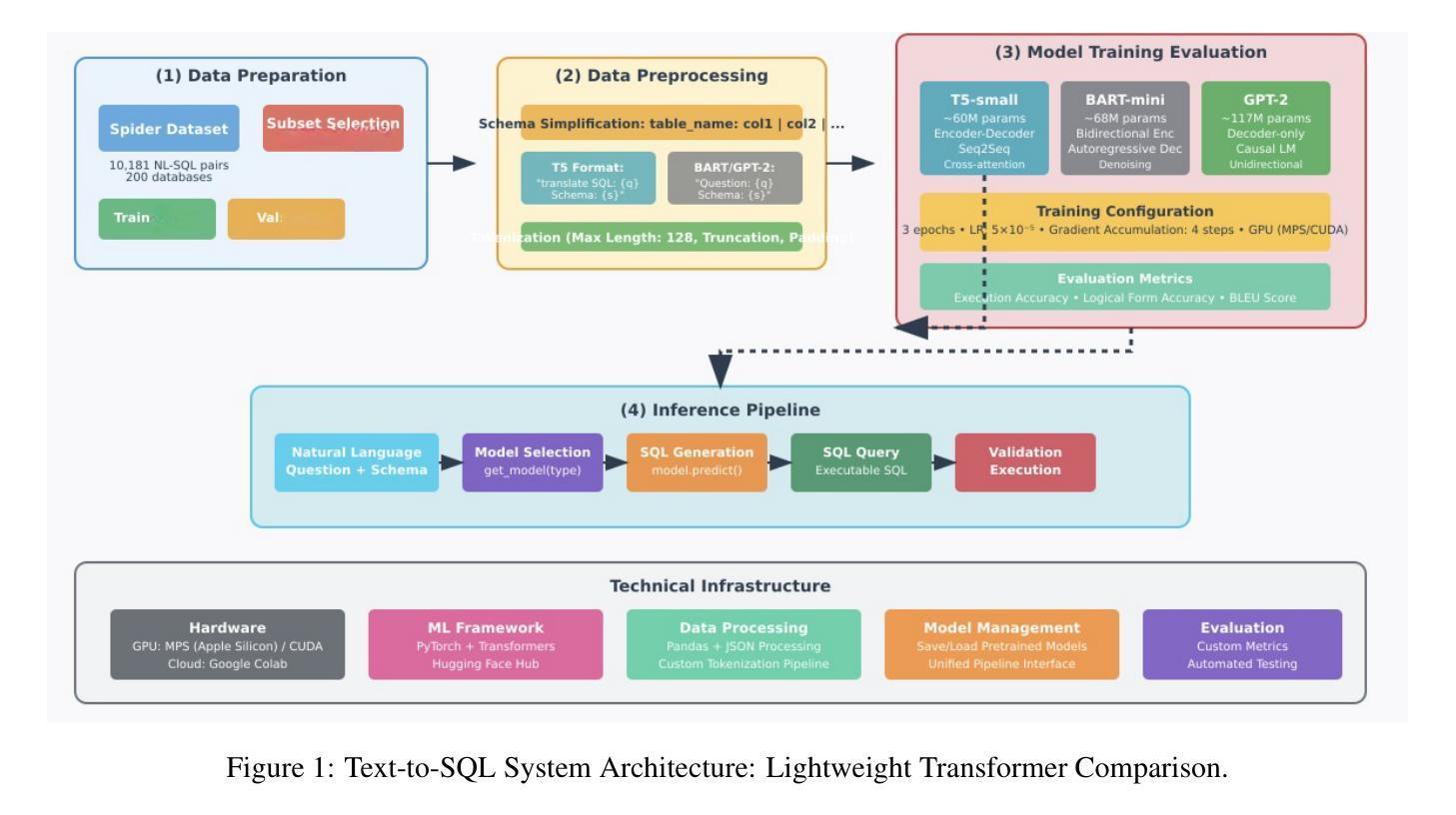
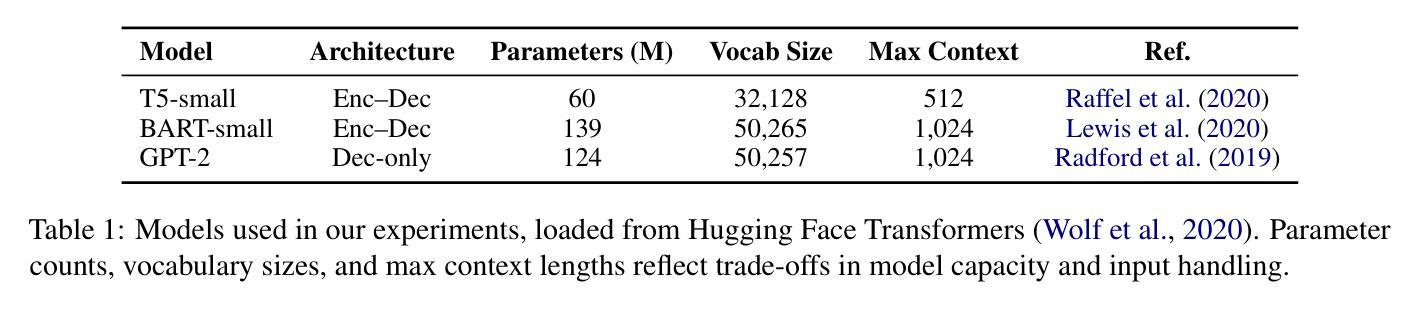
Lightweight Transformers for Zero-Shot and Fine-Tuned Text-to-SQL Generation Using Spider
Authors:Chirag Seth, Utkarsh Singh
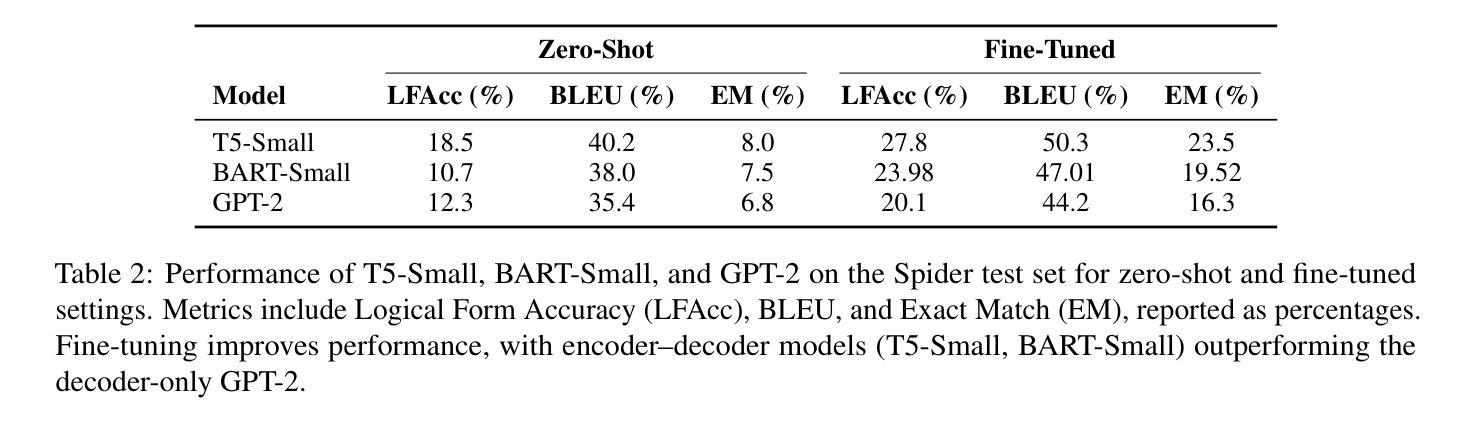
Text-to-SQL translation enables non-expert users to query relational databases using natural language, with applications in education and business intelligence. This study evaluates three lightweight transformer models - T5-Small, BART-Small, and GPT-2 - on the Spider dataset, focusing on low-resource settings. We developed a reusable, model-agnostic pipeline that tailors schema formatting to each model’s architecture, training them across 1000 to 5000 iterations and evaluating on 1000 test samples using Logical Form Accuracy (LFAcc), BLEU, and Exact Match (EM) metrics. Fine-tuned T5-Small achieves the highest LFAcc (27.8%), outperforming BART-Small (23.98%) and GPT-2 (20.1%), highlighting encoder-decoder models’ superiority in schema-aware SQL generation. Despite resource constraints limiting performance, our pipeline’s modularity supports future enhancements, such as advanced schema linking or alternative base models. This work underscores the potential of compact transformers for accessible text-to-SQL solutions in resource-scarce environments.
文本到SQL的翻译技术使得非专业用户能够通过自然语言查询关系数据库,在教育、商业智能等领域有广泛应用。本研究在Spider数据集上评估了三种轻量级转换器模型——T5-Small、BART-Small和GPT-2,重点是在资源有限的环境下进行研究。我们开发了一个可重用、模型无关的管道,根据每个模型的架构定制模式格式化,在1000到5000次迭代之间对它们进行训练,使用逻辑形式准确性(LFAcc)、BLEU和精确匹配(EM)等指标在1000个测试样本上进行评估。经过微调,T5-Small的LFAcc最高(27.8%),优于BART-Small(23.98%)和GPT-2(20.1%),突显出在模式感知SQL生成中编码器-解码器模型的优越性。尽管资源约束限制了性能,但我们的管道模块支持未来增强功能,如高级模式链接或替代基础模型。这项工作突出了紧凑转换器在资源稀缺环境中用于可访问文本到SQL解决方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了基于Transformer的自然语言查询数据库方法在低资源环境下的性能表现。实验在Spider数据集上进行,对比了T5-Small、BART-Small和GPT-2三个轻量级模型。结果显示,经过精细调整的T5-Small模型在逻辑形式准确率(LFAcc)上表现最佳,达到27.8%,优于BART-Small和GPT-2。这表明在资源受限的环境中,编码解码器模型在模式感知SQL生成方面具有优势。本文的工作突显了紧凑的Transformer模型在资源稀缺环境中实现可访问的文本到SQL解决方案的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言查询数据库方法在低资源环境下具有重要的应用价值。
- 实验对比了三种轻量级Transformer模型(T5-Small、BART-Small和GPT-2)在文本到SQL转换方面的性能。
- T5-Small模型经过精细调整后表现出最佳性能,特别是在逻辑形式准确率(LFAcc)方面。
- 结果突显了编码解码器模型在模式感知SQL生成方面的优势。
- 虽然资源约束限制了性能,但所使用的管道可模块化支持未来改进,如高级模式链接或替代基础模型。
- 本文提供了一个重要的视角,即在资源稀缺的环境中如何实现可访问的文本到SQL解决方案。对于自然语言处理和数据库交互技术提供了重要启示。
点此查看论文截图

ConfProBench: A Confidence Evaluation Benchmark for MLLM-Based Process Judges
Authors:Yue Zhou, Yi Chang, Yuan Wu
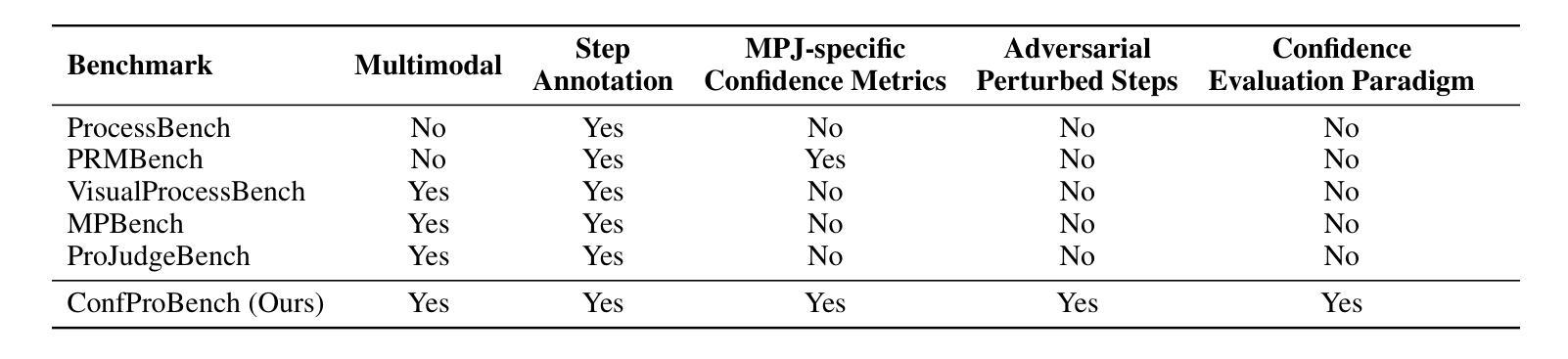
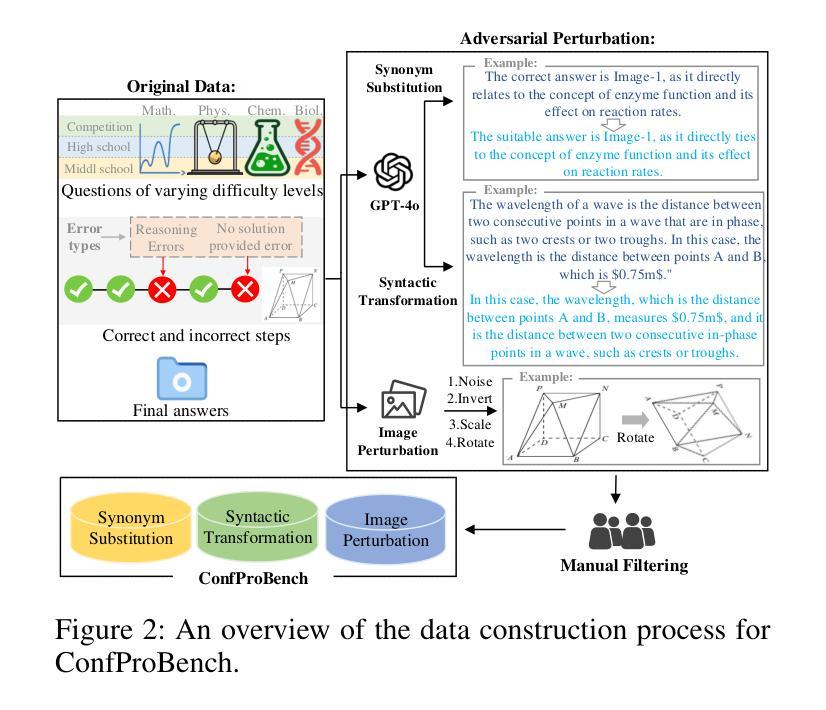
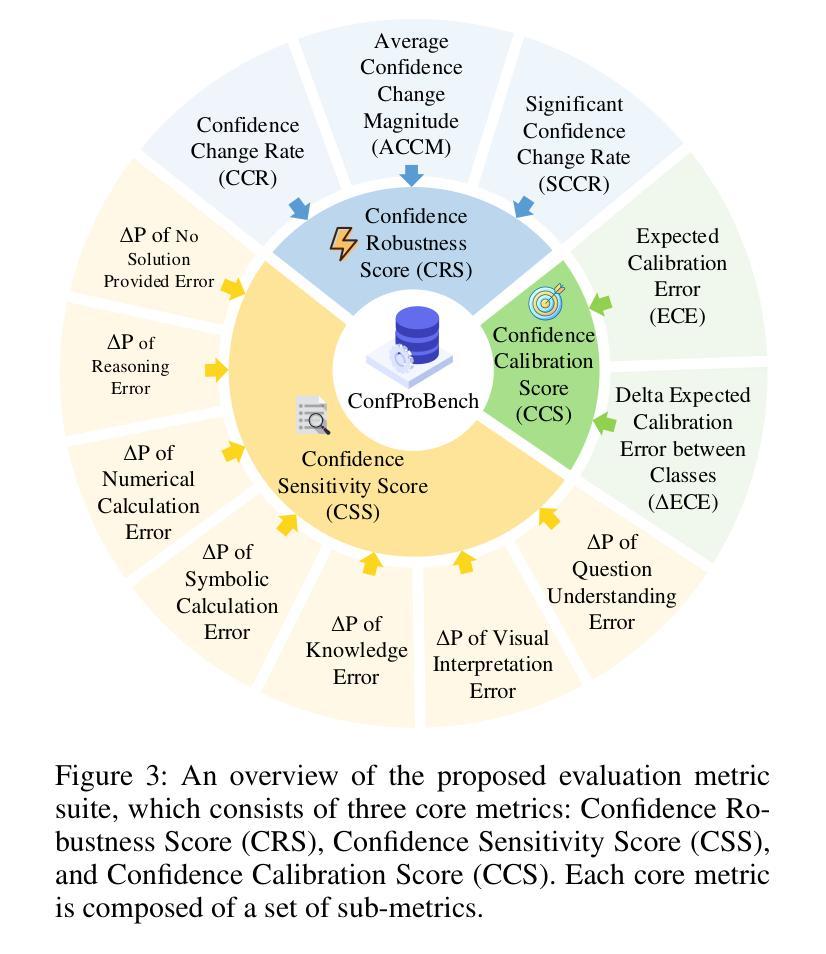
Reasoning is a critical capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for solving complex multimodal tasks, and judging the correctness of reasoning steps is crucial for improving this capability. Recently, MLLM-based process judges (MPJs) have been widely used to assess the correctness of reasoning steps in multimodal tasks. Therefore, evaluating MPJs is important for identifying their limitations and guiding future improvements. However, existing benchmarks for MPJs mainly focus on tasks such as step correctness classification and reasoning process search, while overlooking a key aspect: whether the confidence scores produced by MPJs at the step level are reliable. To address this gap, we propose ConfProBench, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the reliability of step-level confidence scores generated by MPJs. Our benchmark constructs three types of adversarially perturbed reasoning steps: Synonym Substitution, Syntactic Transformation, and Image Perturbation, to test the robustness of MPJ confidence under perturbations. In addition, we introduce three novel evaluation metrics: Confidence Robustness Score (CRS), Confidence Sensitivity Score (CSS), and Confidence Calibration Score (CCS), which evaluate robustness, sensitivity, and calibration, respectively. We evaluate 14 state-of-the-art MLLMs, including both proprietary and open-source models. Experiments reveal limitations in current MPJs’ confidence performance and offer competitive baselines to support future research.
推理是解决复杂多模式任务的多模式大型语言模型(MLLMs)的关键能力,而判断推理步骤的正确性对于提高这种能力至关重要。最近,基于MLLM的过程判断(MPJ)已被广泛应用于评估多模式任务中推理步骤的正确性。因此,评估MPJ对于发现其局限性并指导未来改进非常重要。然而,现有的MPJ基准测试主要关注如步骤正确性分类和推理过程搜索等任务,而忽视了一个关键方面:MPJ在步骤层面产生的置信度分数是否可靠。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了ConfProBench,这是第一个旨在系统评估MPJ产生的步骤级置信度分数可靠性的全面基准测试。我们的基准测试构建了三种对抗性扰动推理步骤:同义词替换、句法转换和图像扰动,以测试MPJ置信度在扰动下的稳健性。此外,我们引入了三个新的评估指标:置信稳健性得分(CRS)、置信敏感性得分(CSS)和置信校准得分(CCS),分别评估稳健性、敏感性和校准。我们评估了14个最先进的多模式大型语言模型,包括专有和开源模型。实验揭示了当前MPJ在置信度表现方面的局限性,并为支持未来研究提供了竞争基准线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行推理是应对复杂多模态任务的关键能力,且对判断推理步骤的正确性对提升此能力至关重要。当前广泛使用的基于MLLM的过程判断(MPJs)主要关注步骤正确性分类和推理过程搜索等任务,但忽略了其关键方面——MPJs生成的步骤级别置信度的可靠性。为解决此问题,本文提出ConfProBench基准测试平台,旨在系统地评估MPJs在步骤级别上生成的置信度的可靠性。通过构建三种对抗性扰动推理步骤进行测试,并引入三个新的评估指标来评估置信度。本文评估了多个先进的MLLMs模型,揭示了当前MPJs在置信度性能方面的局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力对于解决复杂的多模态任务至关重要。
- 过程判断(MPJs)对于评估MLLMs的推理步骤正确性十分重要。
- 当前MPJ评估主要关注步骤正确性分类和推理过程搜索,但忽略了其生成的步骤级别置信度的可靠性。
- ConfProBench基准测试平台被提出以系统地评估MPJs在步骤级别上生成的置信度的可靠性。
- 通过构建三种对抗性扰动推理步骤进行测试,包括同义词替换、句法转换和图像扰动。
- 引入三个新的评估指标:信心稳健性得分(CRS)、信心敏感性得分(CSS)和信心校准得分(CCS),以全面评价MPJs的置信度。
点此查看论文截图

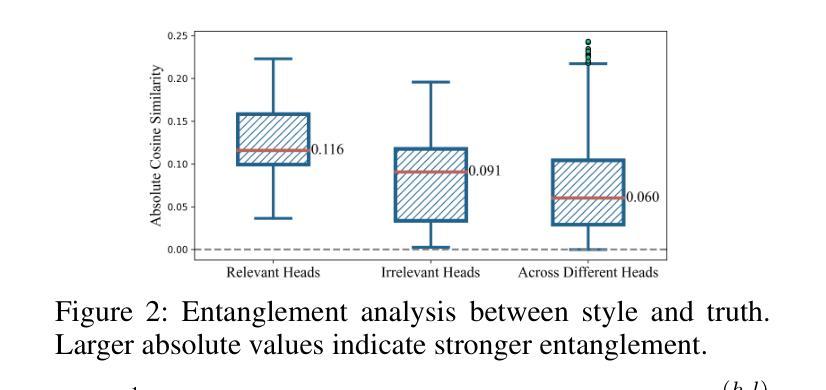
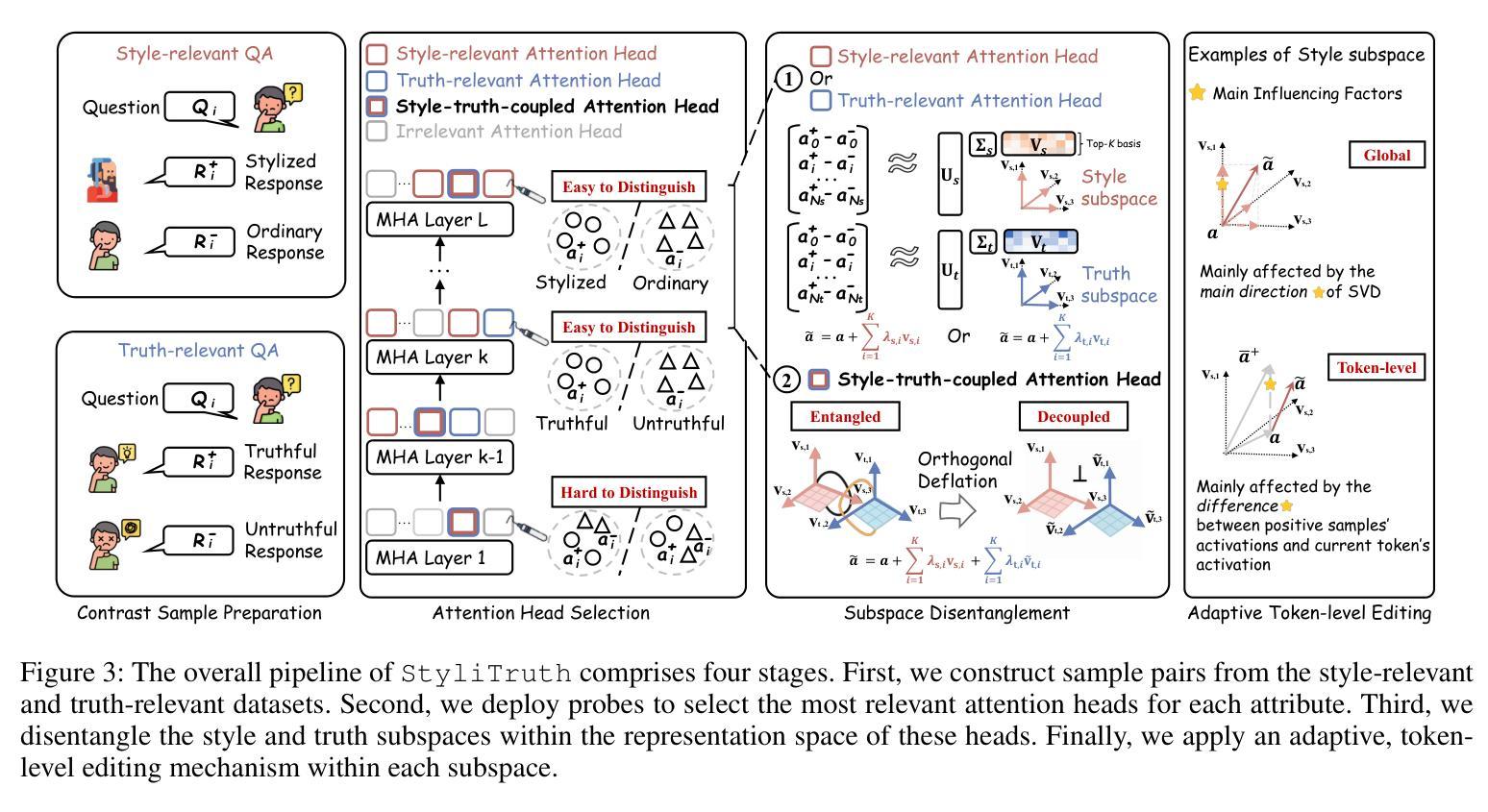
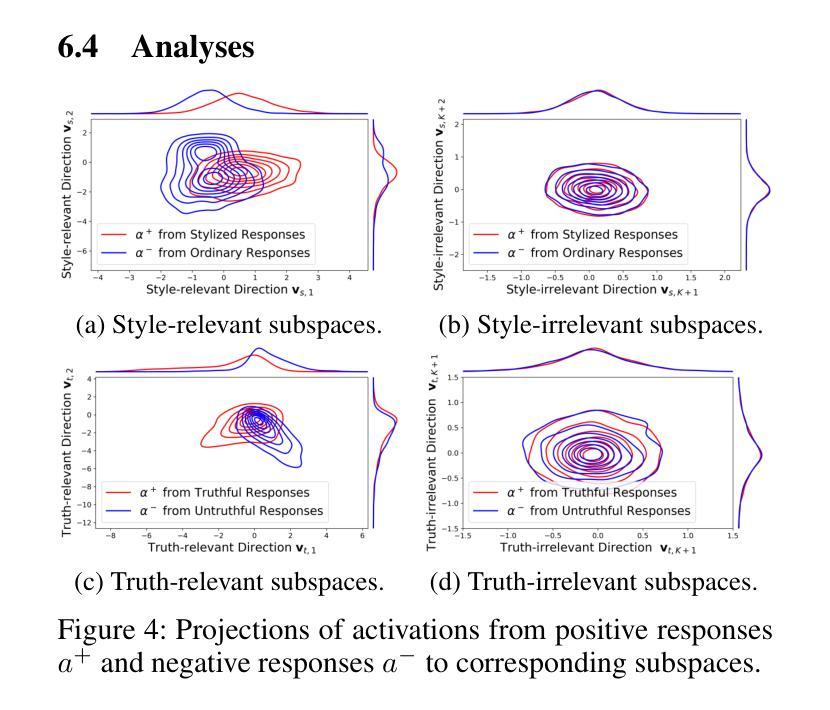
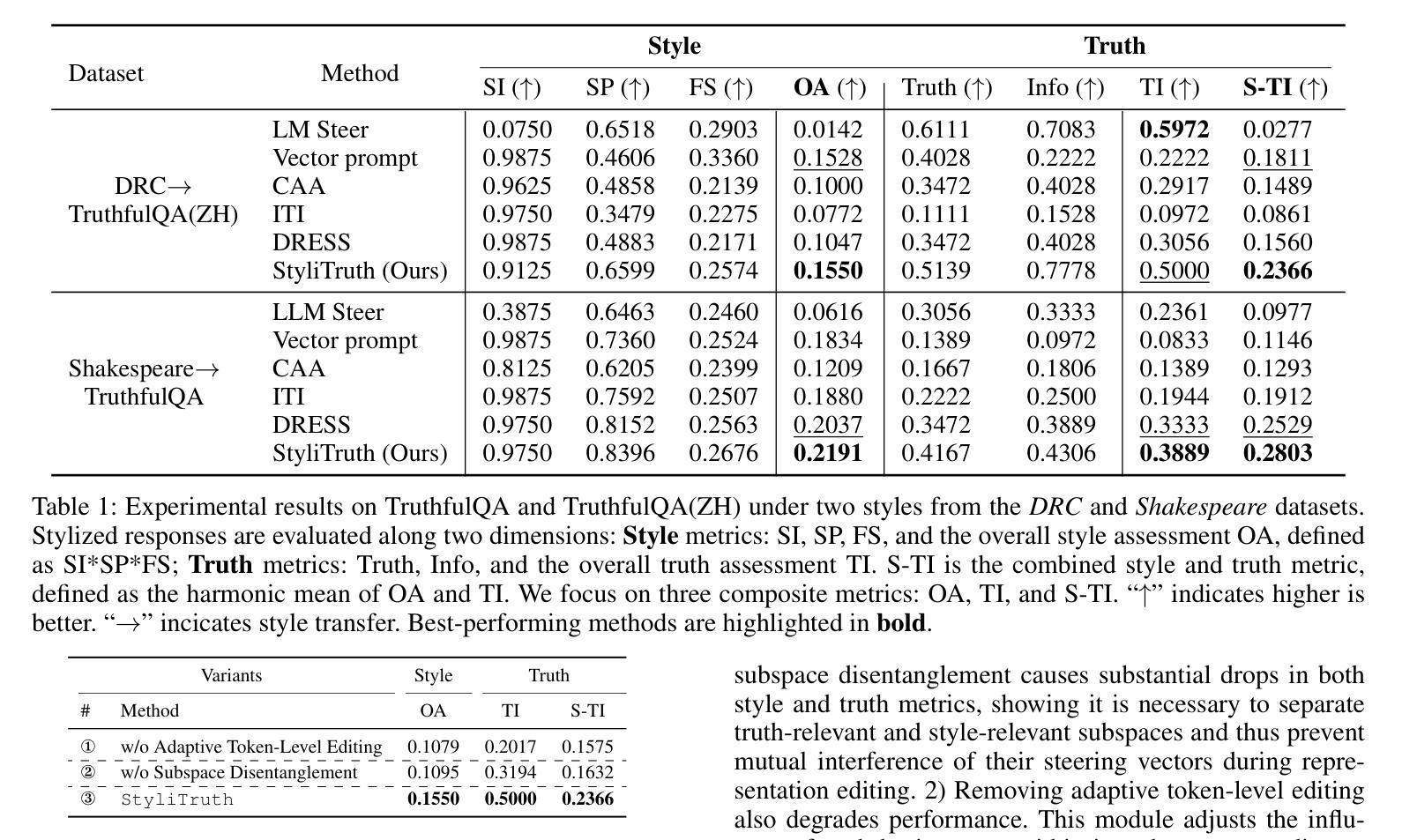
StyliTruth : Unlocking Stylized yet Truthful LLM Generation via Disentangled Steering
Authors:Chenglei Shen, Zhongxiang Sun, Teng Shi, Xiao Zhang, Jun Xu
Generating stylized large language model (LLM) responses via representation editing is a promising way for fine-grained output control. However, there exists an inherent trade-off: imposing a distinctive style often degrades truthfulness. Existing representation editing methods, by naively injecting style signals, overlook this collateral impact and frequently contaminate the model’s core truthfulness representations, resulting in reduced answer correctness. We term this phenomenon stylization-induced truthfulness collapse. We attribute this issue to latent coupling between style and truth directions in certain key attention heads, and propose StyliTruth, a mechanism that preserves stylization while keeping truthfulness intact. StyliTruth separates the style-relevant and truth-relevant subspaces in the model’s representation space via an orthogonal deflation process. This decomposition enables independent control of style and truth in their own subspaces, minimizing interference. By designing adaptive, token-level steering vectors within each subspace, we dynamically and precisely control the generation process to maintain both stylistic fidelity and truthfulness. We validate our method on multiple styles and languages. Extensive experiments and analyses show that StyliTruth significantly reduces stylization-induced truthfulness collapse and outperforms existing inference-time intervention methods in balancing style adherence with truthfulness.
通过表示编辑生成风格化的大型语言模型(LLM)响应是控制精细输出的一种有前途的方式。然而,存在一种固有的权衡:施加一种独特的风格往往会降低真实性。现有的表示编辑方法,通过简单地注入风格信号,忽视了这种附带影响,并经常污染模型的核心真实性表示,导致答案的正确性降低。我们将这种现象称为风格化引起的真实性崩溃。我们将这一问题归因于某些关键注意力头中风格与真实方向之间的潜在耦合,并提出了StyliTruth机制,该机制在保持风格化的同时保持真实性。StyliTruth通过正交膨胀过程,在模型的表示空间中分离出与风格和真实相关的子空间。这种分解能够在各自的子空间中独立控制风格和真实,最小化干扰。通过在每个子空间内设计自适应的、令牌级的引导向量,我们能够动态和精确地控制生成过程,以维持风格上的忠实性和真实性。我们的方法在多种风格和语言上进行了验证。大量的实验和分析表明,StyliTruth显著减少了由风格化引起的真实性崩溃,并在平衡风格坚持与真实性方面超越了现有的推理时间干预方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大型语言模型(LLM)的反应中,通过表现编辑生成风格化的回复展现出了精细控制输出的潜力。然而,风格化往往伴随着真实性的损失,存在内在权衡。现有的表现编辑方法过于简单注入风格信号,忽视了这种附带影响,会干扰模型的核心真实性表示,降低了回答的准确度。我们将这种现象称为风格化引起的真实性崩溃。针对此问题,我们归因于关键注意力头部的风格和真理方向的潜在耦合,并提出了StyliTruth机制,能够在保持风格化的同时保持真实性。StyliTruth通过正交压缩过程分离了与风格和真实相关的子空间。这种分解使得风格和真实在其各自的子空间内独立控制,最小化干扰。通过设计每个子空间内的自适应、令牌级引导向量,我们能够在生成过程中动态精确地控制风格保持和真实性维护。我们的方法在多风格和多种语言上的验证表明,StyliTruth显著减少了风格化引起的真实性崩溃,并且在平衡风格遵守和真实性方面优于现有的推理时间干预方法。
Key Takeaways
- 通过表现编辑生成风格化的LLM回复具有精细控制输出的潜力。
- 风格化大型语言模型回复时存在真实性的损失。
- 现有方法过于简单注入风格信号,导致模型的核心真实性表示受到干扰。
- 提出了一种名为StyliTruth的机制来解决风格化引起的真实性崩溃问题。
- StyliTruth通过分离风格和真实性的子空间来平衡风格和真实性的控制。
- StyliTruth通过自适应令牌级引导向量在生成过程中动态控制风格和真实性的维护。
点此查看论文截图
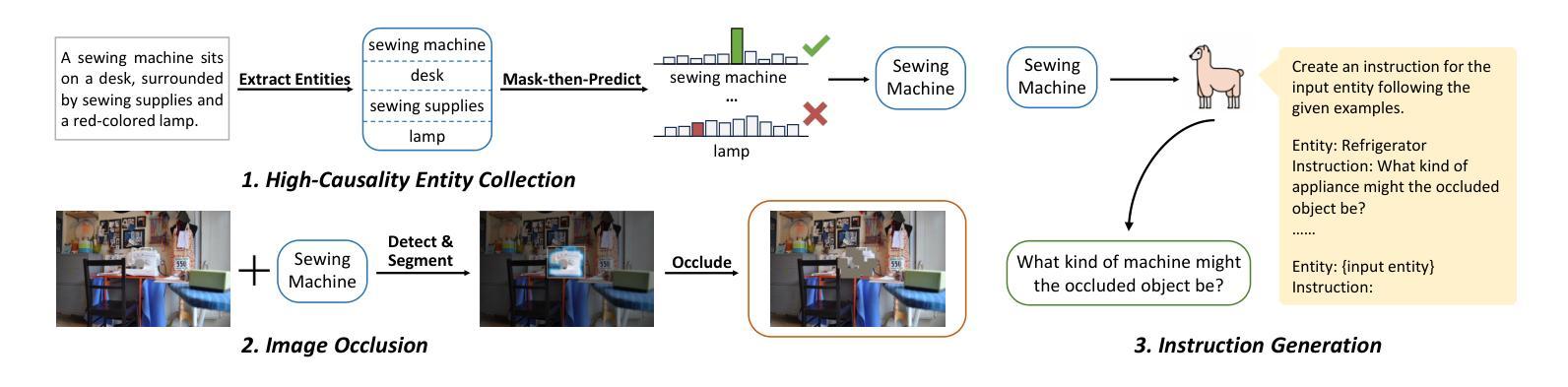
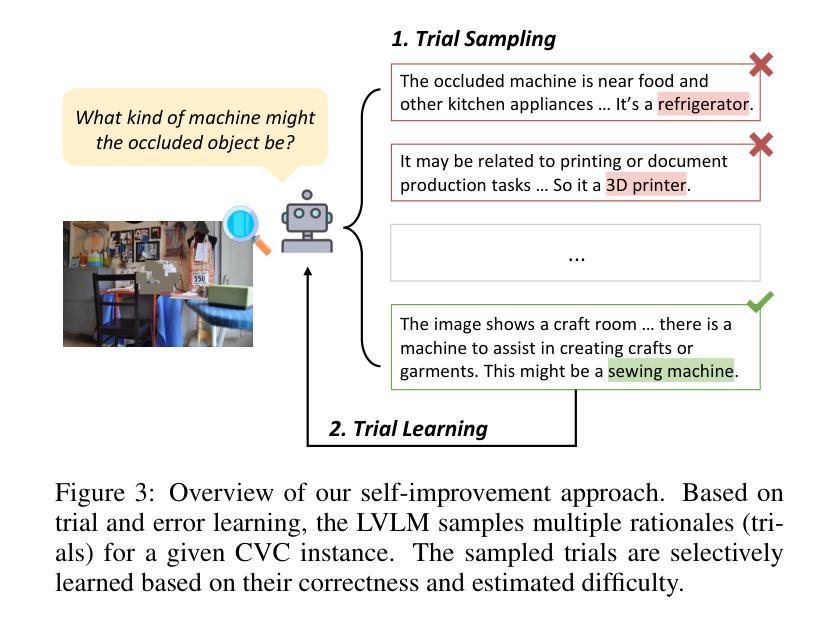
Boosting Visual Knowledge-Intensive Training for LVLMs Through Causality-Driven Visual Object Completion
Authors:Qingguo Hu, Ante Wang, Jia Song, Delai Qiu, Qingsong Liu, Jinsong Su
Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have experienced significant advancements in recent years. However, their performance still falls short in tasks requiring deep visual perception, such as identifying subtle differences between images. A potential cause is the scarcity of visual knowledge in popular instruction-tuning corpora, resulting in inadequate visual perception and reasoning capabilities. To address this challenge, we introduce a self-improvement framework grounded in a novel visual knowledge-intensive task, \underline{C}ausality-driven \underline{V}isual object \underline{C}ompletion (CVC). This task requires LVLMs to infer the masked object in an image based on its \textit{causal} relationships with the other visible information. We first obtain rich examples cheaply through our automated instance construction pipeline, without relying on sophisticated LVLMs (\textit{e.g.}, GPT-4V) or human assistance. Then, LVLMs effectively self-improve through trial and error learning using these created instances. Our experiments demonstrate substantial gains across four challenging specialized tasks and four widely-used comprehensive benchmarks. Especially on specialized tasks, our method achieves an average improvement of 5.4% and 4.0% compared to the corresponding baselines when utilizing LLaVA-1.5-7B and LLaVA-1.5-13B, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/XMUDeepLIT/CVC.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)近年来取得了显著进展。然而,它们在需要深度视觉感知的任务上的表现仍然不足,如识别图像之间的细微差异。造成这种情况的一个潜在原因是流行指令微调语料库中视觉知识的匮乏,导致视觉感知和推理能力不足以应对这些挑战。为了应对这一挑战,我们基于新型视觉知识密集型任务,引入了一种自我改进框架——因果驱动型视觉对象补全(CVC)。该任务要求LVLMs基于与其他可见信息的因果关系推断图像中的遮挡对象。我们首可以通过自动化实例构建管道低成本地获取丰富的样本,无需依赖先进的大型视觉语言模型(如GPT-4V)或人工协助。随后,这些生成的实例通过试错学习,使LVLMs实现了有效的自我提升。我们的实验表明,在四项具有挑战性的专项任务和四项广泛使用的综合基准测试中,我们的方法均取得了显著的提升效果。特别是在专项任务上,与相应的基线相比,使用LLaVA-1.5-7B和LLaVA-1.5-13B时,我们的方法平均提升了5.4%和4.0%。代码已公开在https://github.com/XMUDeepLIT/CVC上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)近年来取得显著进展,但在需要深度视觉感知的任务中表现仍有所不足,如图像间的细微差异识别。本文提出了一种基于因果驱动视觉对象补全(CVC)任务进行自我提升的新框架,以解决此挑战。该任务要求LVLMs根据图像中对象之间的因果关系推断出被掩盖的对象。本文通过自动化实例构建流程获取丰富的例子,无需依赖高级LVLMs或人工辅助。实验结果显示,该方法在四个具有挑战性的专项任务和四个广泛使用的综合基准测试中均取得了显著的提升,特别是在专项任务上,相较于对应的基线方法平均提升了5.4%和4.0%。
Key Takeaways
- LVLMs在深度视觉感知任务中仍存在性能短板。
- 提出了基于因果驱动视觉对象补全(CVC)任务的新框架以改善LVLMs的表现。
- CVC任务要求LVLMs推断图像中被掩盖的对象,基于与其他可见信息的因果关系。
- 通过自动化实例构建流程获取丰富例子,无需高级LVLMs或人工辅助。
- 方法在多个挑战性任务和基准测试中表现优异,平均提升5.4%和4.0%。
点此查看论文截图

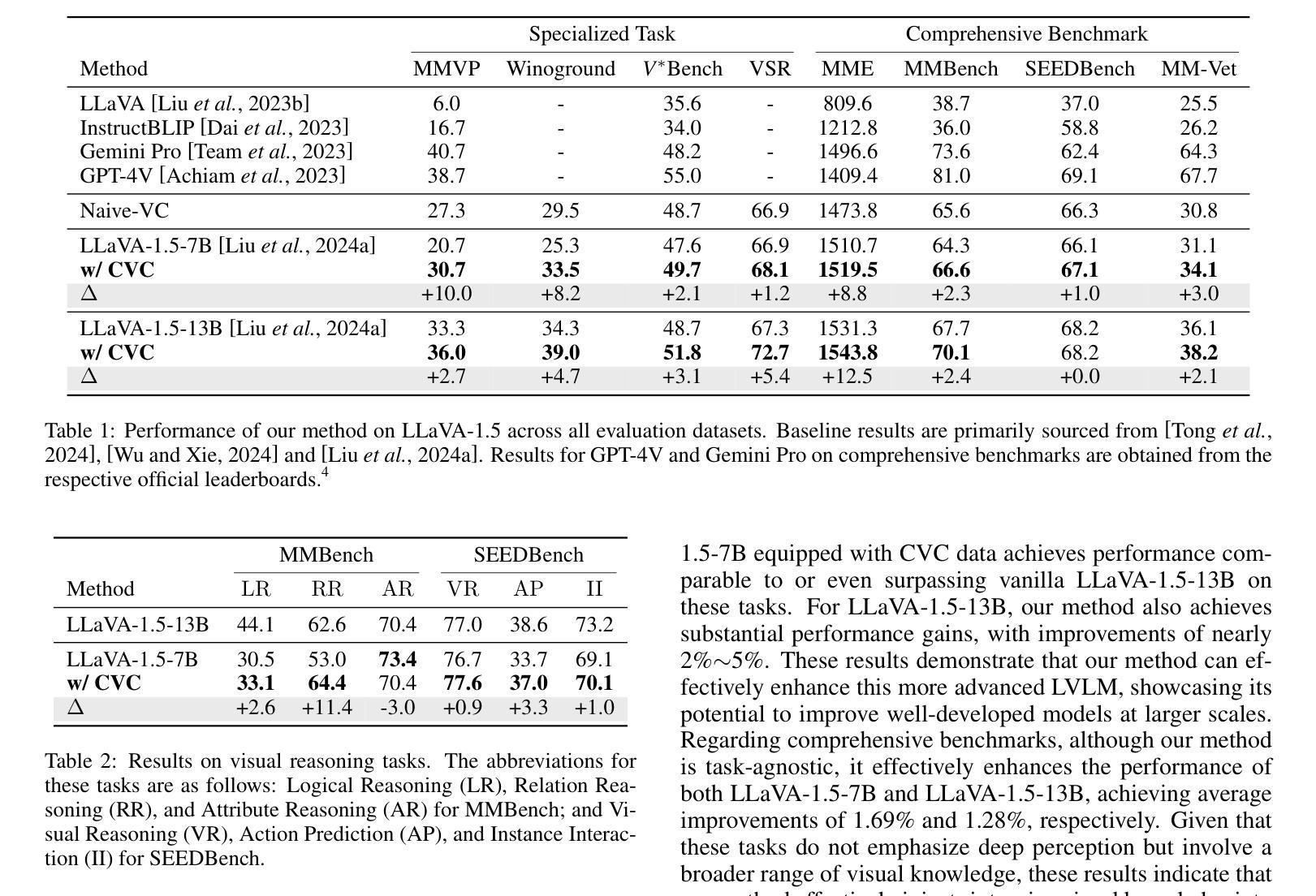
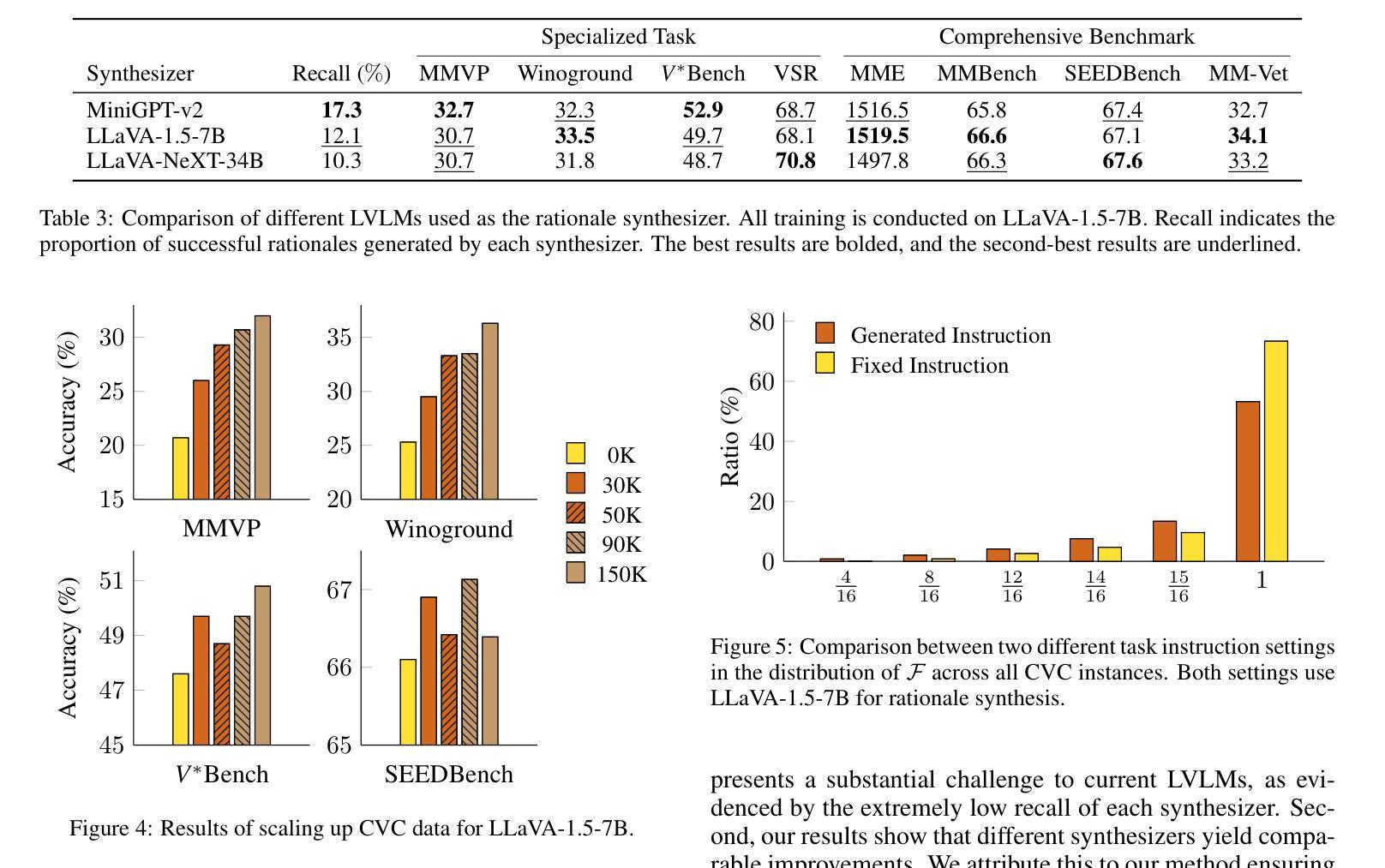
Think Before You Segment: An Object-aware Reasoning Agent for Referring Audio-Visual Segmentation
Authors:Jinxing Zhou, Yanghao Zhou, Mingfei Han, Tong Wang, Xiaojun Chang, Hisham Cholakkal, Rao Muhammad Anwer
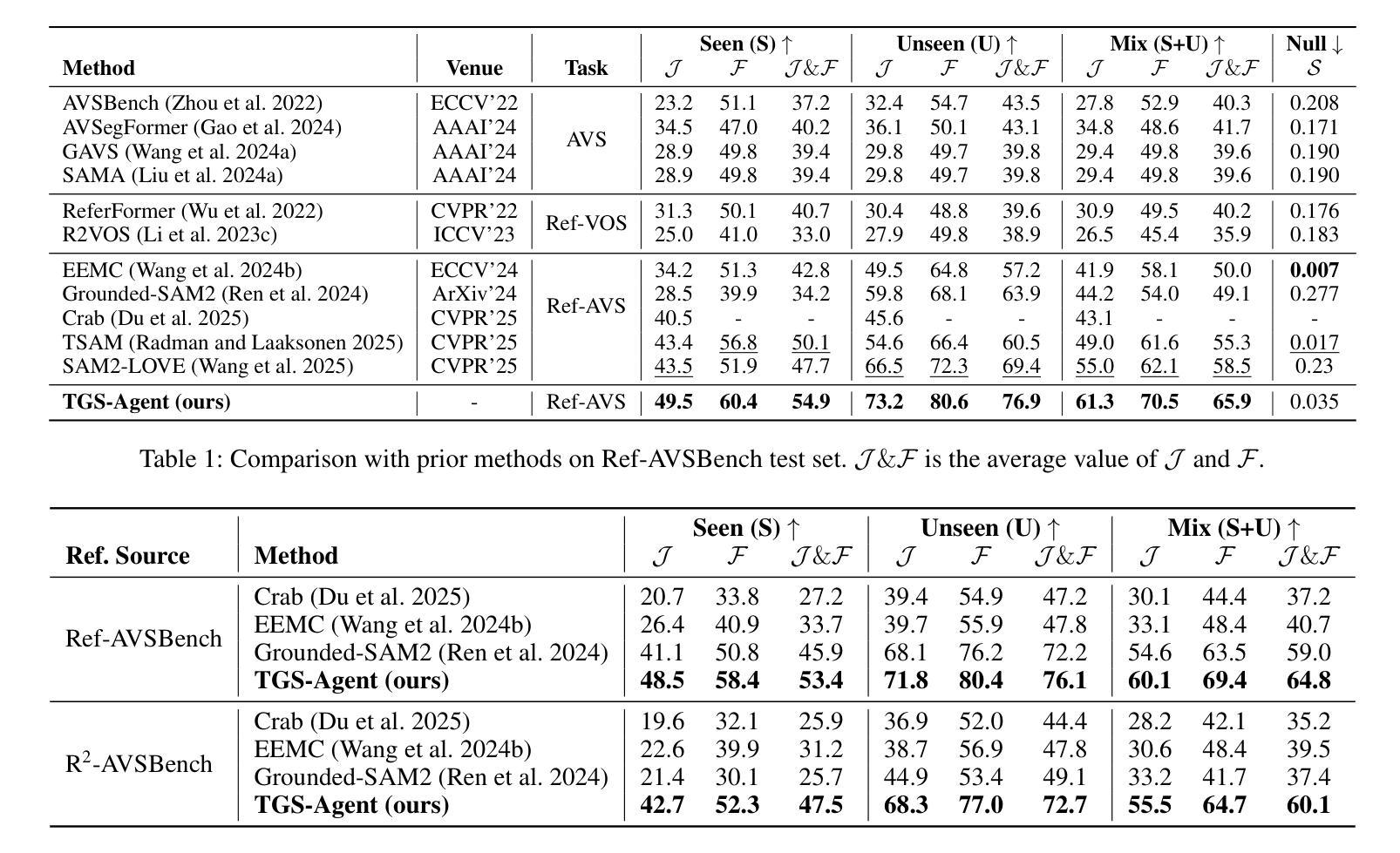
Referring Audio-Visual Segmentation (Ref-AVS) aims to segment target objects in audible videos based on given reference expressions. Prior works typically rely on learning latent embeddings via multimodal fusion to prompt a tunable SAM/SAM2 decoder for segmentation, which requires strong pixel-level supervision and lacks interpretability. From a novel perspective of explicit reference understanding, we propose TGS-Agent, which decomposes the task into a Think-Ground-Segment process, mimicking the human reasoning procedure by first identifying the referred object through multimodal analysis, followed by coarse-grained grounding and precise segmentation. To this end, we first propose Ref-Thinker, a multimodal language model capable of reasoning over textual, visual, and auditory cues. We construct an instruction-tuning dataset with explicit object-aware think-answer chains for Ref-Thinker fine-tuning. The object description inferred by Ref-Thinker is used as an explicit prompt for Grounding-DINO and SAM2, which perform grounding and segmentation without relying on pixel-level supervision. Additionally, we introduce R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench, a new benchmark with linguistically diverse and reasoning-intensive references for better evaluating model generalization. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on both standard Ref-AVSBench and proposed R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench. Code will be available at https://github.com/jasongief/TGS-Agent.
引用音频视觉分割(Ref-AVS)旨在根据给定的参考表达式对可听视频中的目标对象进行分割。早期的工作通常依赖于通过多模态融合学习潜在嵌入,以提示可调SAM/SAM2解码器进行分割,这需要强烈的像素级监督并且缺乏可解释性。从显式参考理解的新角度,我们提出了TGS-Agent,它将任务分解为Think-Ground-Segment过程,通过多模态分析首先识别所指的物体,然后进行粗粒度定位和精确分割,模仿人类的推理过程。为此,我们首先提出了Ref-Thinker,这是一个能够推理文本、视觉和听觉线索的多模态语言模型。我们构建了一个指令微调数据集,其中包含用于Ref-Thinker精细调整的具有明确对象感知的think-answer链。Ref-Thinker推断的对象描述被用作对Grounding-DINO和SAM__的明确提示,进行定位和分割,无需依赖像素级监督。此外,我们介绍了R²AVSBench新基准测试,其中包含语言多样化和推理密集型的参考物,以更好地评估模型的泛化能力。我们的方法在标准的Ref-AVSBench和提出的R²AVSBench上都达到了最新水平。代码将在https://github.com/jasongief/TGS-Agent上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://github.com/jasongief/TGS-Agent
Summary
本文提出了一个名为TGS-Agent的新方法,用于音频视频分割任务。该方法从理解明确参考的新角度入手,将任务分解为思考、定位和分割三个过程,并模仿人类推理过程。首先通过多模态分析识别目标对象,然后进行粗略定位,最后精确分割。为此,本文提出了Ref-Thinker多模态语言模型,能够对文本、视觉和听觉线索进行推理。通过构建指令微调数据集,对Ref-Thinker进行微调,使用其推断的对象描述作为对Grounding-DINO和SAM2的明确提示,进行定位和分割任务,无需像素级监督。此外,还介绍了新的R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench基准测试,以评估模型的泛化能力。TGS-Agent在标准的Ref-AVSBench和新的R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench上均达到了最佳效果。
Key Takeaways
- TGS-Agent方法通过分解任务为思考、定位和分割过程,模仿人类推理过程进行音频视频分割。
- 提出了Ref-Thinker多模态语言模型,能结合文本、视觉和听觉线索进行推理。
- 通过构建指令微调数据集对Ref-Thinker进行训练,提高了模型的推理能力。
- 使用Ref-Thinker推断的对象描述作为对Grounding-DINO和SAM2的明确提示,进行定位和分割任务,减少对像素级监督的依赖。
- 引入了新的R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench基准测试,以评估模型的泛化能力。
- TGS-Agent在Ref-AVSBench和R\textsuperscript{2}-AVSBench上取得了最佳效果。
点此查看论文截图

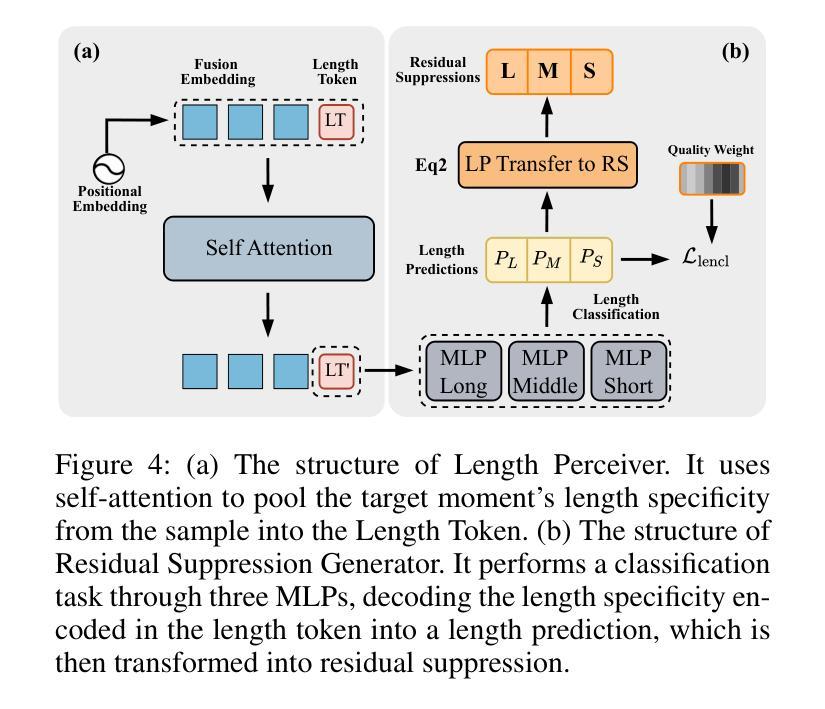
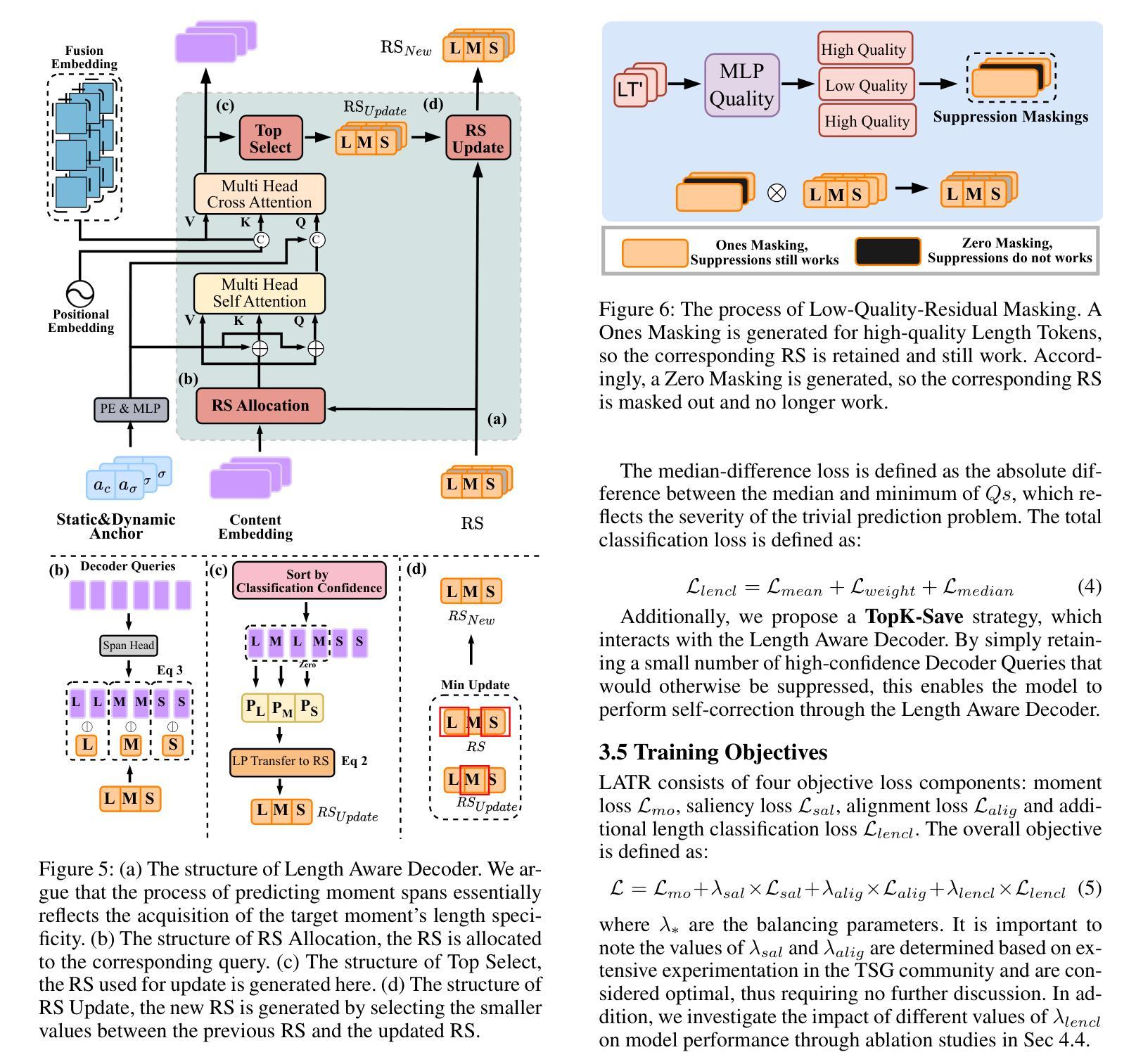
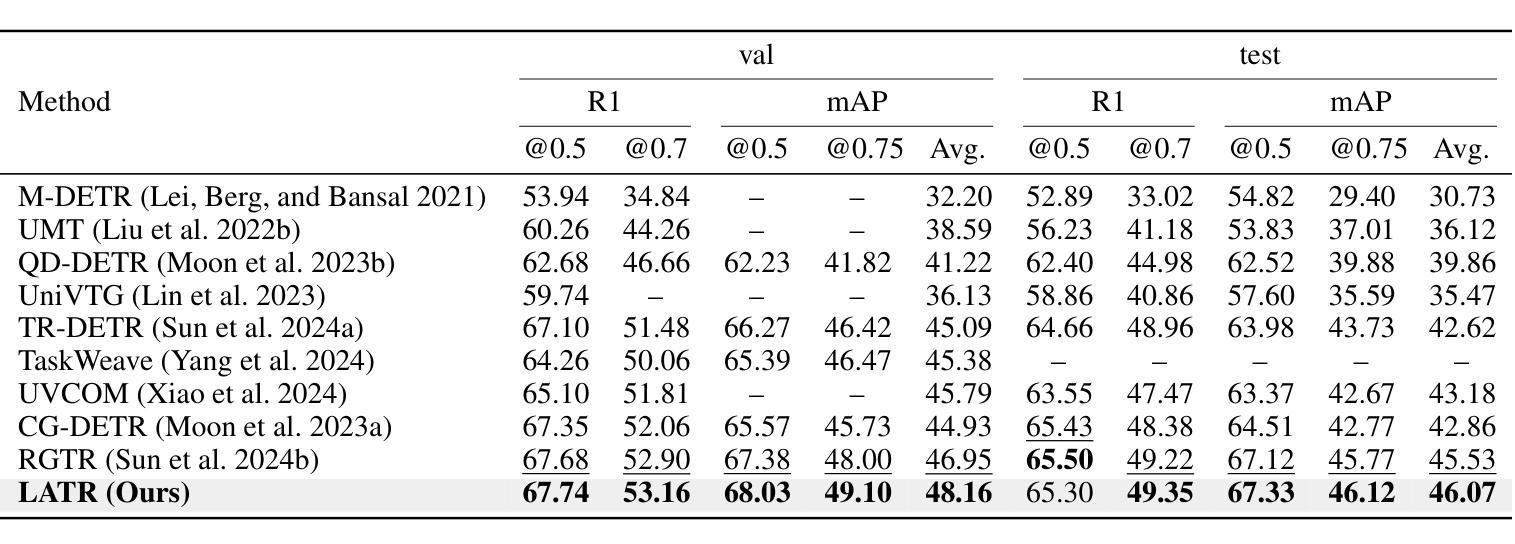
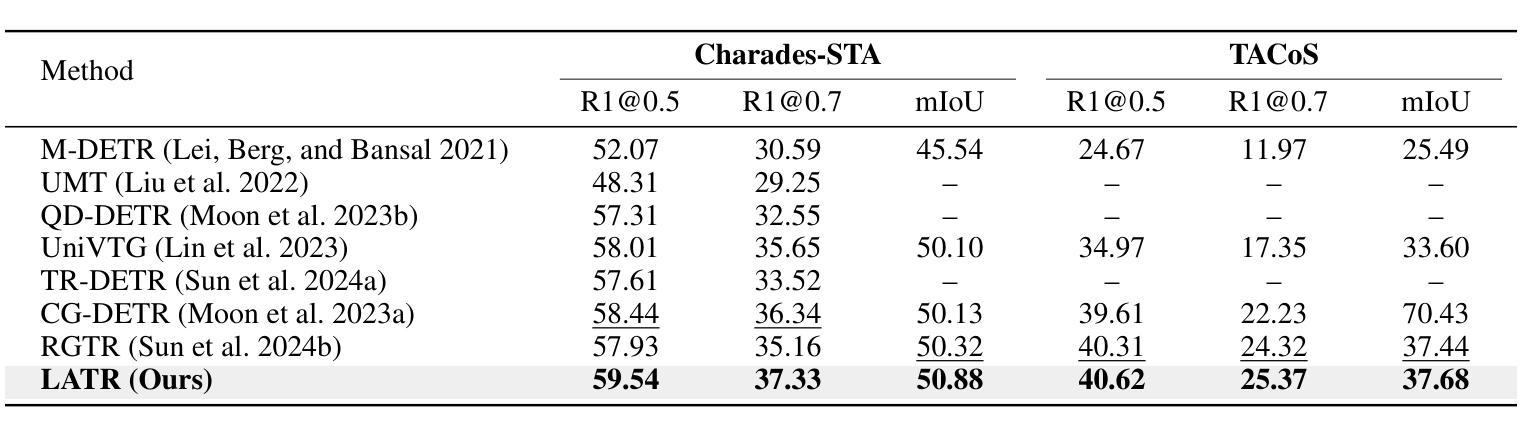
Length Matters: Length-Aware Transformer for Temporal Sentence Grounding
Authors:Yifan Wang, Ziyi Liu, Xiaolong Sun, Jiawei Wang, Hongmin Liu
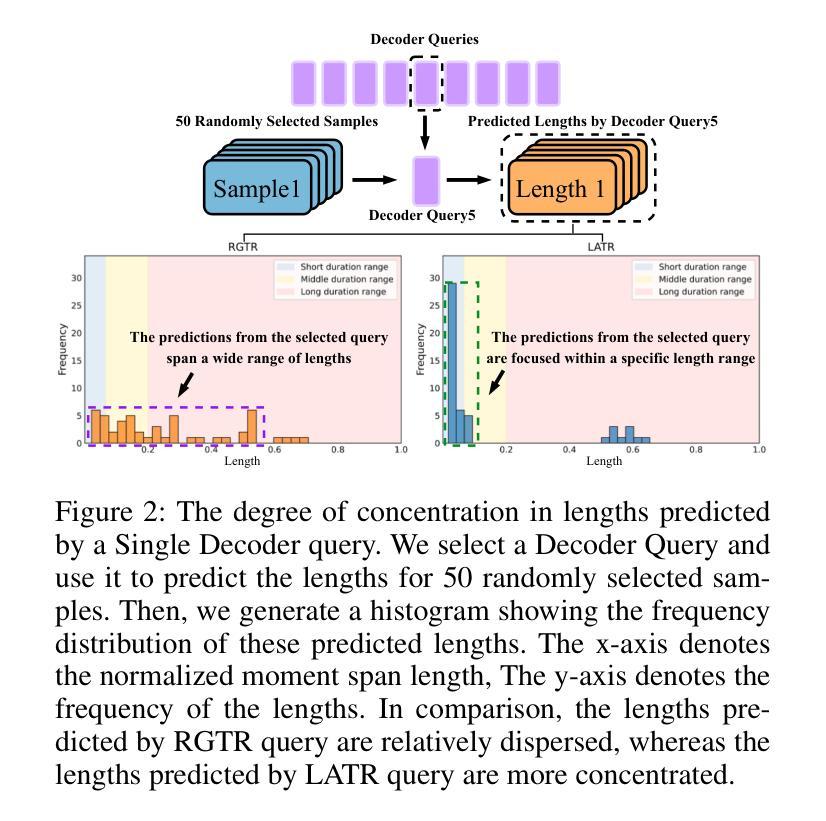
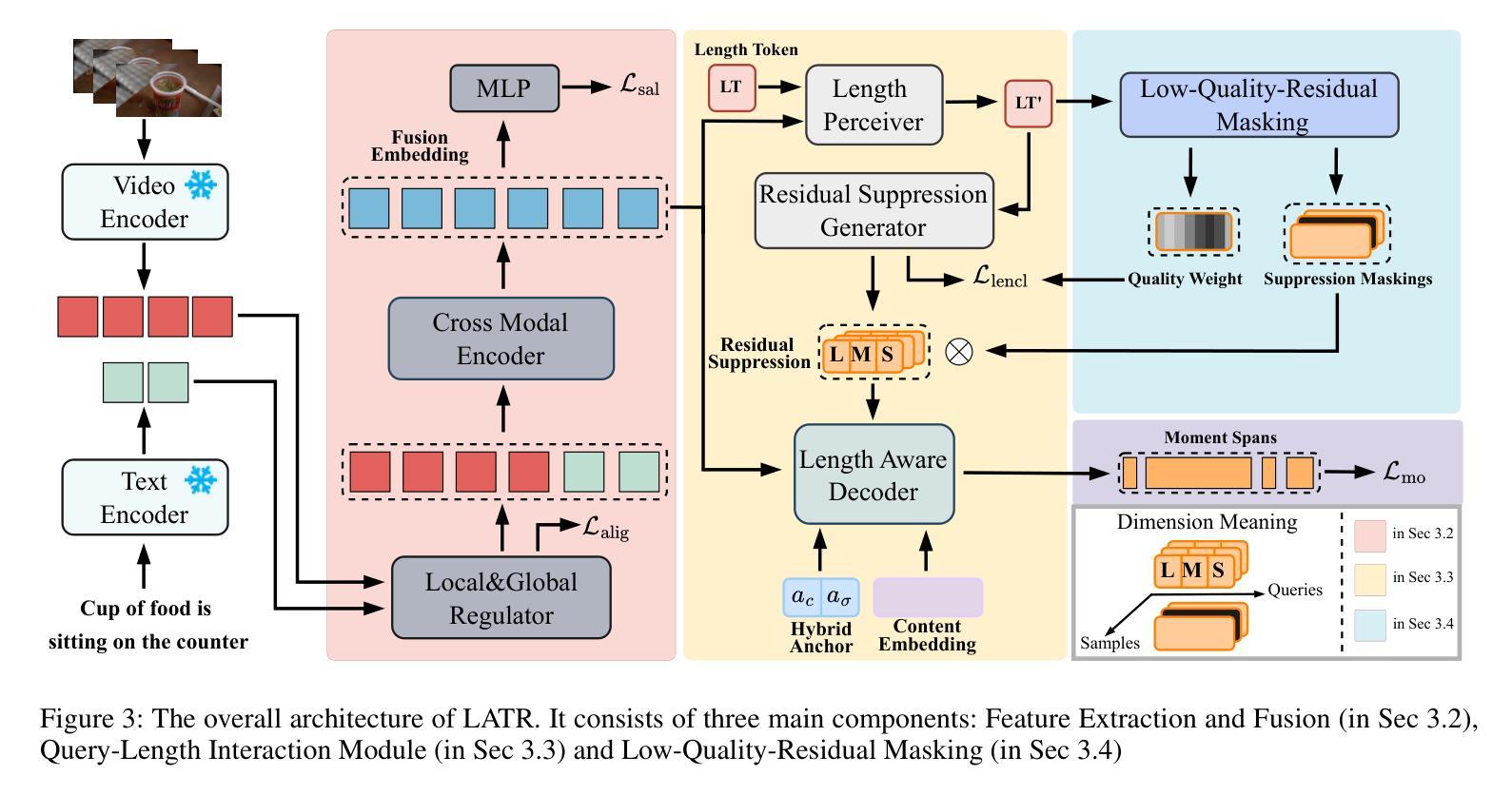
Temporal sentence grounding (TSG) is a highly challenging task aiming to localize the temporal segment within an untrimmed video corresponding to a given natural language description. Benefiting from the design of learnable queries, the DETR-based models have achieved substantial advancements in the TSG task. However, the absence of explicit supervision often causes the learned queries to overlap in roles, leading to redundant predictions. Therefore, we propose to improve TSG by making each query fulfill its designated role, leveraging the length priors of the video-description pairs. In this paper, we introduce the Length-Aware Transformer (LATR) for TSG, which assigns different queries to handle predictions based on varying temporal lengths. Specifically, we divide all queries into three groups, responsible for segments with short, middle, and long temporal durations, respectively. During training, an additional length classification task is introduced. Predictions from queries with mismatched lengths are suppressed, guiding each query to specialize in its designated function. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our LATR, achieving state-of-the-art performance on three public benchmarks. Furthermore, the ablation studies validate the contribution of each component of our method and the critical role of incorporating length priors into the TSG task.
时序句子定位(TSG)是一项极具挑战性的任务,旨在定位未剪辑视频中与给定自然语言描述相对应的时间段。得益于可学习查询的设计,基于DETR的模型在TSG任务中取得了重大进展。然而,由于缺乏明确的监督,通常会导致学习到的查询在角色上重叠,从而产生冗余预测。因此,我们提出通过使每个查询履行其指定角色来改善TSG任务,并利用视频描述对的时间长度先验信息。在本文中,我们为TSG引入了长度感知转换器(LATR),根据时间长度差异分配不同的查询来处理预测。具体来说,我们将所有查询分为三组,分别负责处理短、中和长时间段的片段。在训练过程中,引入了额外的长度分类任务。来自不匹配长度的查询预测会被抑制,从而引导每个查询专门执行其指定功能。大量实验证明了我们的LATR的有效性,在三个公共基准测试上达到了最新性能水平。此外,消融研究验证了我们的方法中每个组件的贡献以及将长度先验知识纳入TSG任务的关键作用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一个针对时序句子定位(TSG)任务的新方法,即长度感知转换器(LATR)。该方法利用可学习查询的优势,旨在解决视频与描述之间时序段定位的问题。针对现有模型因缺乏明确监督导致的查询角色重叠问题,LATR通过利用视频描述对的长度先验信息,使每个查询履行其指定角色。具体来说,我们将查询分为三组,分别负责处理不同时长(短、中、长)的片段。训练过程中引入了额外的长度分类任务,抑制了不匹配长度的查询预测,使每个查询专注于其特定功能。在三个公共基准测试上的大量实验表明,LATR方法取得了卓越的性能。此外,消融研究也验证了该方法每个组件的作用以及将长度先验信息融入TSG任务的重要性。
关键见解
- TSG任务旨在定位给定自然语言描述在未经剪辑视频中的时间片段,是一个具有挑战性的任务。
- 基于DETR的模型通过设计可学习查询实现了TSG任务的显著进展。
- 缺乏明确监督会导致查询角色重叠和冗余预测。
- LATR方法通过利用视频描述对的长度先验信息,使每个查询履行其指定角色来解决这个问题。
- LATR将查询分为三组,分别处理不同时长的预测。
- 额外的长度分类任务在训练过程中被引入,以抑制不匹配长度的查询预测。
点此查看论文截图

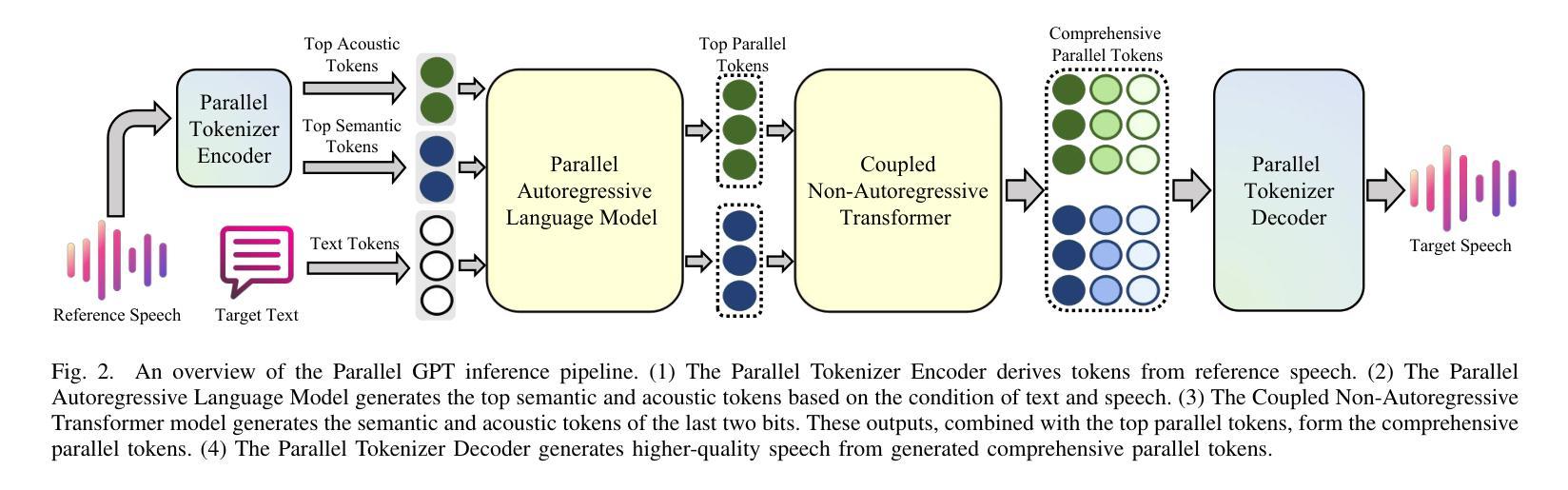
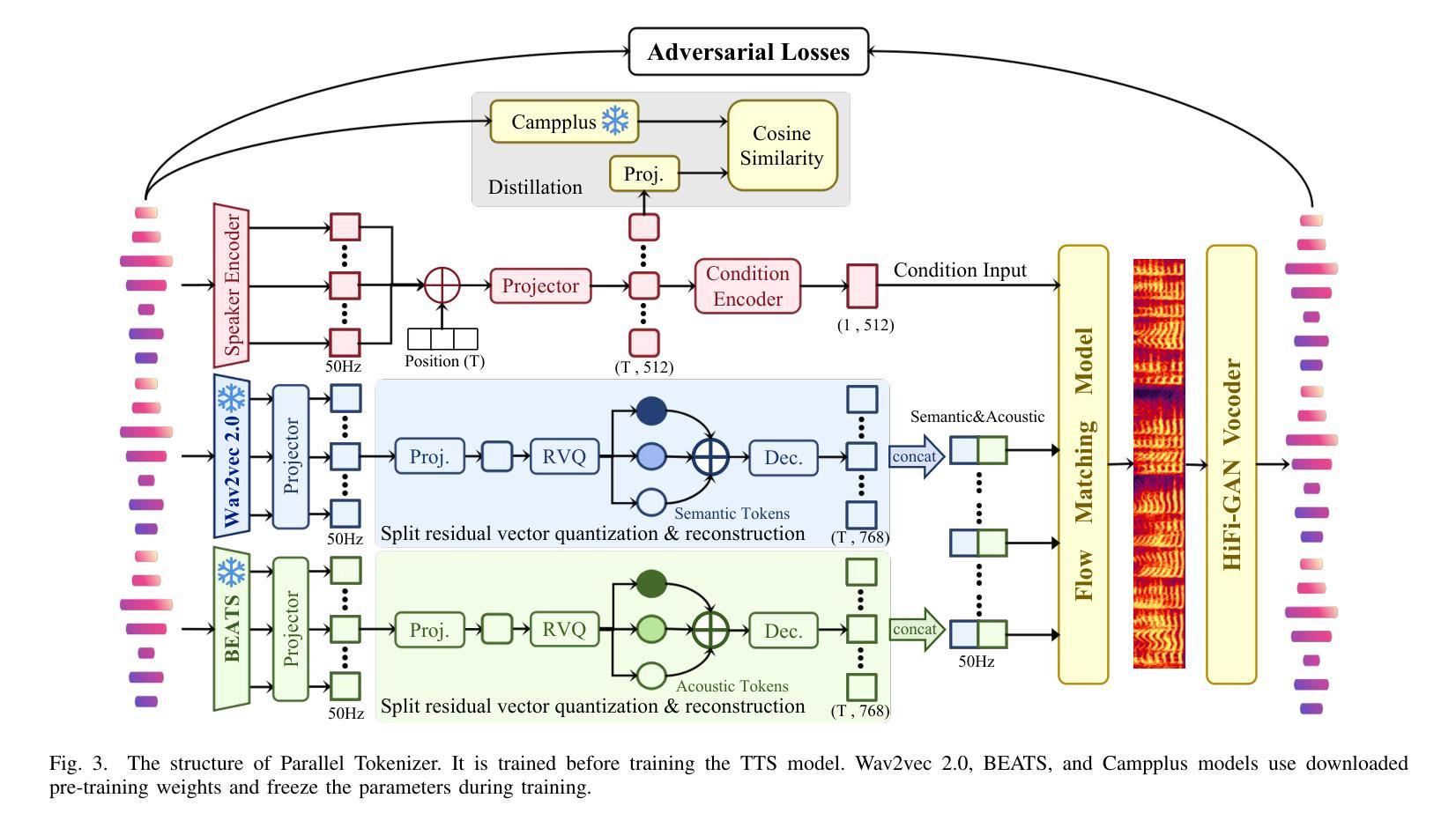
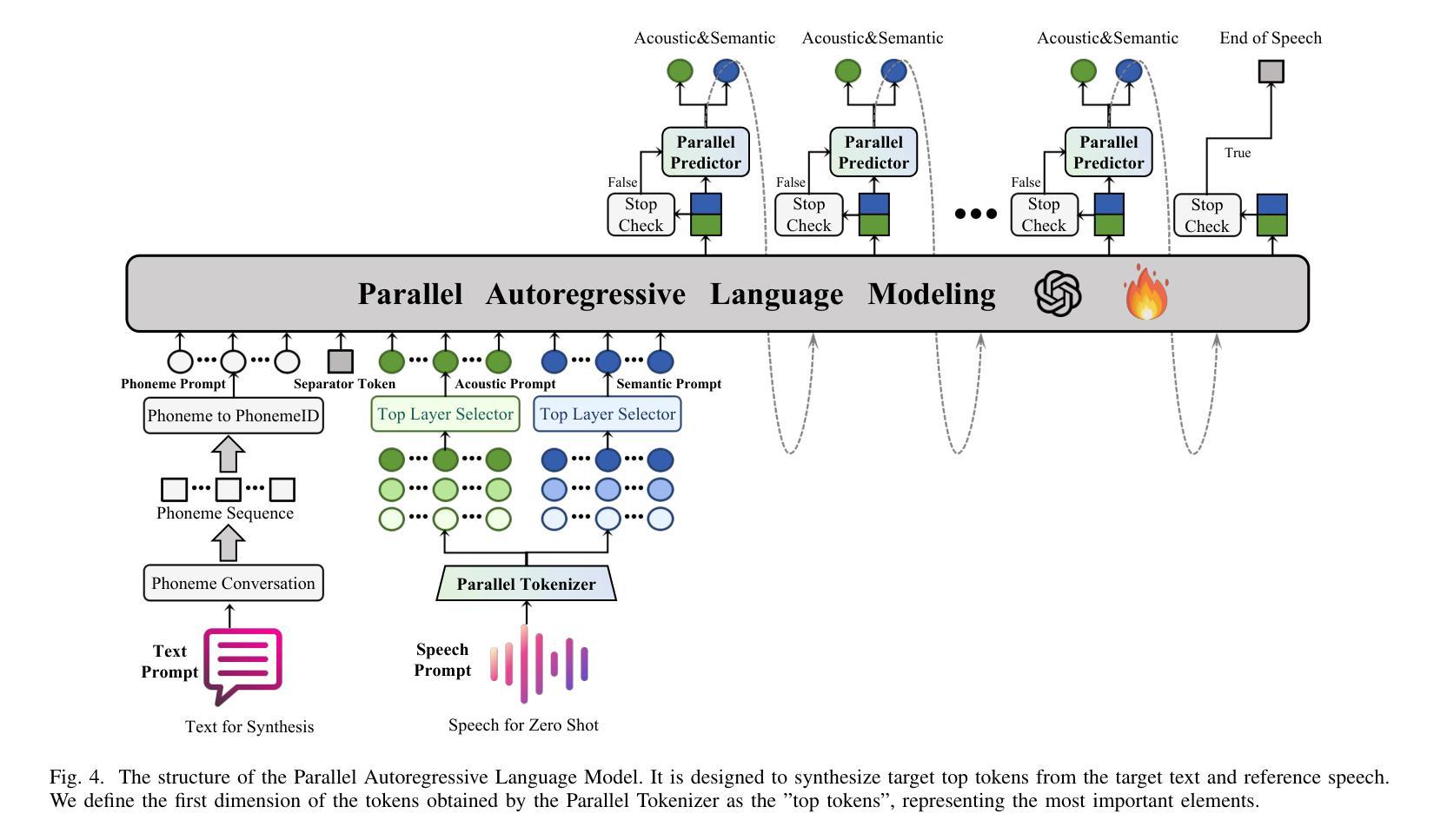
Parallel GPT: Harmonizing the Independence and Interdependence of Acoustic and Semantic Information for Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
Authors:Jingyuan Xing, Zhipeng Li, Jialong Mai, Xiaofen Xing, Xiangmin Xu
Advances in speech representation and large language models have enhanced zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) performance. However, existing zero-shot TTS models face challenges in capturing the complex correlations between acoustic and semantic features, resulting in a lack of expressiveness and similarity. The primary reason lies in the complex relationship between semantic and acoustic features, which manifests independent and interdependent aspects.This paper introduces a TTS framework that combines both autoregressive (AR) and non-autoregressive (NAR) modules to harmonize the independence and interdependence of acoustic and semantic information. The AR model leverages the proposed Parallel Tokenizer to synthesize the top semantic and acoustic tokens simultaneously. In contrast, considering the interdependence, the Coupled NAR model predicts detailed tokens based on the general AR model’s output. Parallel GPT, built on this architecture, is designed to improve zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis through its parallel structure. Experiments on English and Chinese datasets demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms the quality and efficiency of the synthesis of existing zero-shot TTS models. Speech demos are available at https://t1235-ch.github.io/pgpt/.
语音表示的进展和大语言模型的进步已经提高了零样本文本到语音(TTS)的性能。然而,现有的零样本TTS模型在捕获声学和语义特征之间的复杂关联方面面临挑战,导致缺乏表达性和相似性。主要原因在于语义和声学特征之间的复杂关系,表现为独立和相互依赖的方面。
本文介绍了一个结合自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)模块的TTS框架,以协调声学和语义信息的独立性和相互依赖性。AR模型利用提出的并行分词器同时合成顶级语义和声音标记。相反,考虑到相互依赖性,耦合的NAR模型基于通用AR模型的输出进行详细的标记预测。基于此架构构建的并行GPT旨在通过其并行结构改进零样本文本到语音合成。在英语和中文数据集上的实验表明,所提出的模型在合成质量和效率上显著优于现有的零样本TTS模型。语音演示可在https://t1235-ch.github.io/pgpt/ 上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing (TASLP)
Summary
本文介绍了结合自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)模块的新型文本转语音(TTS)框架。该框架旨在调和声学语义信息的独立性和相互依赖性,通过并行令牌化器(Parallel Tokenizer)和耦合NAR模型等技术,增强了零样本文本转语音的性能和表达性。实验证明,该模型在英文和中文数据集上的合成质量和效率均显著优于现有零样本TTS模型。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的语音表示和大型语言模型增强了零样本文本转语音(TTS)的性能。
- 现有零样本TTS模型在捕获声学语义特征的复杂相关性方面存在挑战,导致缺乏表达性和相似性。
- 本文介绍了结合AR和NAR模块的TTS框架,以调和声学语义信息的独立性和相互依赖性。
- AR模型使用并行令牌化器(Parallel Tokenizer)同时合成顶级语义和声音标记。
- 耦合NAR模型基于AR模型的输出预测详细标记。
- 基于此架构构建的并行GPT旨在通过其并行结构改进零样本文本转语音合成。
点此查看论文截图

Fine-tuning for Better Few Shot Prompting: An Empirical Comparison for Short Answer Grading
Authors:Joel Walsh, Siddarth Mamidanna, Benjamin Nye, Mark Core, Daniel Auerbach
Research to improve Automated Short Answer Grading has recently focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) with prompt engineering and no- or few-shot prompting to achieve best results. This is in contrast to the fine-tuning approach, which has historically required large-scale compute clusters inaccessible to most users. New closed-model approaches such as OpenAI’s fine-tuning service promise results with as few as 100 examples, while methods using open weights such as quantized low-rank adaptive (QLORA) can be used to fine-tune models on consumer GPUs. We evaluate both of these fine-tuning methods, measuring their interaction with few-shot prompting for automated short answer grading (ASAG) with structured (JSON) outputs. Our results show that finetuning with small amounts of data has limited utility for Llama open-weight models, but that fine-tuning methods can outperform few-shot baseline instruction-tuned LLMs for OpenAI’s closed models. While our evaluation set is limited, we find some evidence that the observed benefits of finetuning may be impacted by the domain subject matter. Lastly, we observed dramatic improvement with the LLama 3.1 8B-Instruct open-weight model by seeding the initial training examples with a significant amount of cheaply generated synthetic training data.
近期关于提高自动简答评分的研究主要集中在利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行提示工程和无或少量样本提示,以取得最佳结果。这与传统的微调方法形成对比,后者在历史上需要大规模计算集群,大多数用户无法接触。新的封闭模型方法,如OpenAI的微调服务,仅用100个样本即可获得结果,而使用公开权重的方法,如量化低秩自适应(QLORA),可在消费者GPU上进行模型微调。我们评估了这两种微调方法,测量它们在少量提示与自动简答评分(ASAG)的交互作用下的结构化(JSON)输出。我们的结果表明,使用少量数据进行微调对于Llama公开权重模型的效用有限,但对于OpenAI的封闭模型,微调方法可以在指令调优的LLM上超越少量样本基线。虽然我们的评估集有限,但我们发现观察到的微调效益可能受到领域主题的影响。最后,我们观察到,通过在初始训练示例中引入大量低成本生成的合成训练数据,LLama 3.1 8B-Instruct公开权重模型的性能得到了显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Automated Evaluation of Learning and Assessment Content co-located with 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED 2025)
Summary
近期研究集中在利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行自动简答评分任务的改进上,通过提示工程和无/少样本提示达到最佳效果。相较于过去需要大量计算集群的微调方法,新的封闭模型方法如OpenAI的微调服务仅需少量样本即可获得结果,同时使用公开权重的方法如量化低秩自适应(QLORA)可以在消费者GPU上进行模型微调。评估显示,对于Llama公开权重模型,小数据量的微调效用有限;但对于OpenAI的封闭模型,微调方法优于少样本基线指令调优的LLM。评价集虽有限,但观察到微调的好处可能受领域主题影响。此外,对Llama 3.1 8B-Instruct公开权重模型,通过初始训练示例引入大量廉价生成的合成训练数据,可观察到显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自动简答评分任务中表现优异,通过提示工程和无/少样本提示达到最佳效果。
- 与传统微调方法相比,新的封闭模型方法和公开权重方法如QLORA可在有限资源下实现模型微调。
- 对于某些模型(如Llama公开权重模型),小数据量的微调效果有限。
- OpenAI的封闭模型在微调方法上表现出优于少样本基线指令调优的LLM的效果。
- 评估结果可能受领域主题影响。
- 初始训练示例中引入大量合成训练数据可以显著提升模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Globally Predictable k-Space Interpolation: A White-box Transformer Approach
Authors:Chen Luo, Qiyu Jin, Taofeng Xie, Xuemei Wang, Huayu Wang, Congcong Liu, Liming Tang, Guoqing Chen, Zhuo-Xu Cui, Dong Liang
Interpolating missing data in k-space is essential for accelerating imaging. However, existing methods, including convolutional neural network-based deep learning, primarily exploit local predictability while overlooking the inherent global dependencies in k-space. Recently, Transformers have demonstrated remarkable success in natural language processing and image analysis due to their ability to capture long-range dependencies. This inspires the use of Transformers for k-space interpolation to better exploit its global structure. However, their lack of interpretability raises concerns regarding the reliability of interpolated data. To address this limitation, we propose GPI-WT, a white-box Transformer framework based on Globally Predictable Interpolation (GPI) for k-space. Specifically, we formulate GPI from the perspective of annihilation as a novel k-space structured low-rank (SLR) model. The global annihilation filters in the SLR model are treated as learnable parameters, and the subgradients of the SLR model naturally induce a learnable attention mechanism. By unfolding the subgradient-based optimization algorithm of SLR into a cascaded network, we construct the first white-box Transformer specifically designed for accelerated MRI. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in k-space interpolation accuracy while providing superior interpretability.
在成像中,对k空间中的缺失数据进行插值是至关重要的。然而,现有的方法,包括基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的深度学习,主要利用局部预测性而忽略了k空间中固有的全局依赖性。最近,Transformer在自然语言处理和图像分析方面取得了显著的成功,这归功于其捕捉长期依赖性的能力。这启发我们将Transformer用于k空间插值,以更好地利用其全局结构。然而,其缺乏可解释性引发了人们对插值数据可靠性的担忧。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了GPI-WT,这是一种基于全局可预测插值(GPI)的white-box Transformer框架,用于k空间。具体来说,我们从消除的角度制定GPI作为一种新型的k空间结构化低秩(SLR)模型。SLR模型中的全局消除滤波器被视为可学习的参数,SLR模型的子梯度自然地引发了一种可学习的注意力机制。通过将基于子梯度的SLR优化算法展开为级联网络,我们构建了第一个专门用于加速MRI的white-box Transformer。实验结果表明,该方法在k空间插值精度上显著优于最新技术,同时提供了出色的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于全局可预测插值(GPI)的白色盒子Transformer框架GPI-WT,用于加速MRI成像中的k空间插值。该方法通过从灭迹角度构建GPI,形成新型k空间结构化低秩(SLR)模型,并通过学习可调整全局灭迹过滤器。其利用SLR模型的子梯度自然诱导出可学习的注意力机制,并将基于子梯度的优化算法展开为级联网络,构建专门针对加速MRI的白色盒子Transformer。实验表明,该方法在k空间插值精度上显著优于现有技术,同时提供优越的解读性。
Key Takeaways
- 插值在加速成像中至关重要,但现有方法主要利用局部可预测性,忽略了k空间的固有全局依赖性。
- Transformer在自然语言处理和图像分析中的成功,激发了其在k空间插值中的应用,以更好地利用全局结构。
- 缺乏解释性仍是Transformer应用的主要顾虑,本研究提出了一种白色盒子Transformer框架GPI-WT。
- GPI-WT基于全局可预测插值(GPI)和k空间结构化低秩(SLR)模型,从灭迹角度构建。
- SLR模型中的全局灭迹过滤器被视为可学习参数,其子梯度自然引导可学习的注意力机制。
- 通过将SLR模型的子梯度优化算法展开为级联网络,创建了专门针对加速MRI的白色盒子Transformer。
点此查看论文截图

VisualTrans: A Benchmark for Real-World Visual Transformation Reasoning
Authors:Yuheng Ji, Yipu Wang, Yuyang Liu, Xiaoshuai Hao, Yue Liu, Yuting Zhao, Huaihai Lyu, Xiaolong Zheng
Visual transformation reasoning (VTR) is a vital cognitive capability that empowers intelligent agents to understand dynamic scenes, model causal relationships, and predict future states, and thereby guiding actions and laying the foundation for advanced intelligent systems. However, existing benchmarks suffer from a sim-to-real gap, limited task complexity, and incomplete reasoning coverage, limiting their practical use in real-world scenarios. To address these limitations, we introduce VisualTrans, the first comprehensive benchmark specifically designed for VTR in real-world human-object interaction scenarios. VisualTrans encompasses 12 semantically diverse manipulation tasks and systematically evaluates three essential reasoning dimensions - spatial, procedural, and quantitative - through 6 well-defined subtask types. The benchmark features 472 high-quality question-answer pairs in various formats, including multiple-choice, open-ended counting, and target enumeration. We introduce a scalable data construction pipeline built upon first-person manipulation videos, which integrates task selection, image pair extraction, automated metadata annotation with large multimodal models, and structured question generation. Human verification ensures the final benchmark is both high-quality and interpretable. Evaluations of various state-of-the-art vision-language models show strong performance in static spatial tasks. However, they reveal notable shortcomings in dynamic, multi-step reasoning scenarios, particularly in areas like intermediate state recognition and transformation sequence planning. These findings highlight fundamental weaknesses in temporal modeling and causal reasoning, providing clear directions for future research aimed at developing more capable and generalizable VTR systems. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/WangYipu2002/VisualTrans.
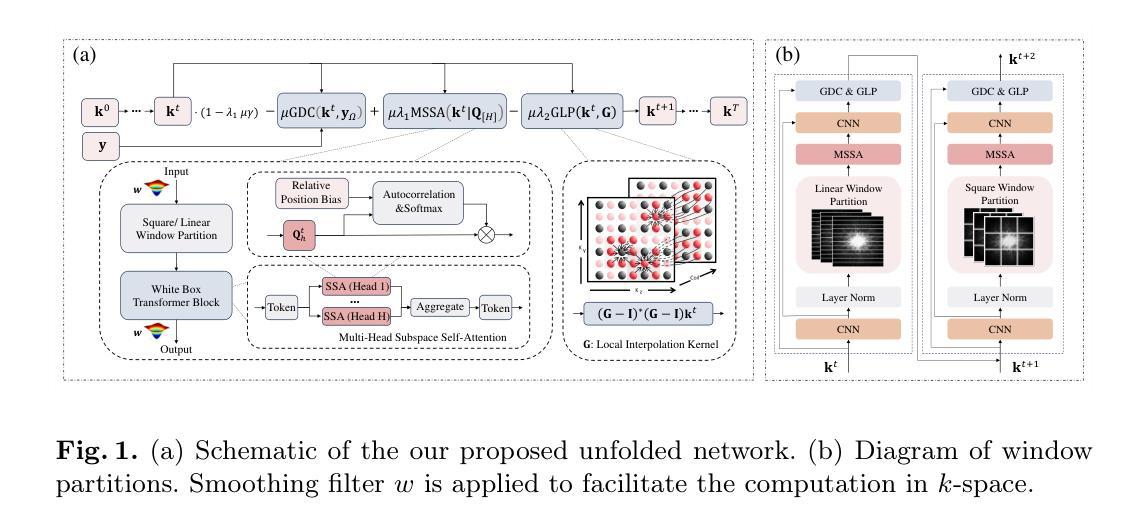
视觉转换推理(VTR)是一种重要的认知能力,赋予智能主体理解动态场景、模拟因果关系以及预测未来状态的能力,从而为行动提供指导,并为先进的智能系统奠定基础。然而,现有的基准测试存在模拟到现实的差距、任务复杂性有限以及推理覆盖不完整等问题,限制了它们在现实场景中的实际应用。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了VisualTrans,这是专门为现实世界中的人机交互场景中的VTR设计的首个综合基准测试。
VisualTrans涵盖了12种语义多样的操作任务,并通过6种定义良好的子任务类型,系统地评估了空间、程序和定量三个重要的推理维度。基准测试包含472组高质量的问题答案对,形式多样,包括选择题、开放式计数和目标枚举等。我们引入了一个基于第一人称操作视频的可扩展数据构建流程,该流程包括任务选择、图像对提取、使用大型多模态模型进行自动化元数据注释以及结构化问题生成。人为验证确保了最终基准测试既高质量又易于解释。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视觉转换推理(VTR)是智能主体理解动态场景、模拟因果关系并预测未来状态的重要认知能力,它为行动指导奠定了基础,并为先进智能系统提供了支撑。然而,现有基准测试存在模拟到现实的差距、任务复杂性有限和推理覆盖不全面等局限性,限制了它们在现实场景中的实际应用。为解决这些问题,我们推出了VisualTrans,这是专为现实世界中的人机交互场景中的VTR设计的首个全面基准测试。VisualTrans包含12个语义多样的操作任务,并通过6个定义明确的任务类型系统地评估空间、程序和定量三个基本推理维度。该基准测试包含472组高质量的问题答案对,包括多种形式,如选择题、开放式计数和目标枚举等。我们建立了一个可扩展的数据构建管道,该管道建立在第一人称操作视频之上,集成了任务选择、图像对提取、使用大型多模态模型的自动化元数据注释和结构化问题生成。人类的验证确保了最终基准测试既高质量又易于解释。对各种最先进的视觉语言模型的评估表明,它们在静态空间任务中表现出强大的性能。然而,在动态多步骤推理场景中,特别是在中间状态识别和转换序列规划方面,它们表现出明显的不足。这些发现突显了时间建模和因果关系推理中的基本弱点,为未来研究提供了明确方向,旨在开发更具能力和通用性的VTR系统。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/WangYipu2002/VisualTrans获取。
关键见解
- 视觉转换推理(VTR)是智能系统的核心认知能力,涉及理解动态场景、模拟因果关系和预测未来状态。
- 现有基准测试存在模拟到现实的差距、任务复杂性有限和推理覆盖不全面等局限性。
- VisualTrans基准测试是专为现实世界中的人机交互场景中的VTR设计的首个全面基准测试。
- VisualTrans包含12个语义多样的操作任务和6种任务类型,评估空间、程序和定量三个基本推理维度。
- 基准测试包含高质量的问题答案对,包括多种形式,如选择题、开放式计数和目标枚举等。
- 评估显示,现有模型在静态空间任务中表现良好,但在动态多步骤推理场景中存在不足,特别是在中间状态识别和转换序列规划方面。
点此查看论文截图

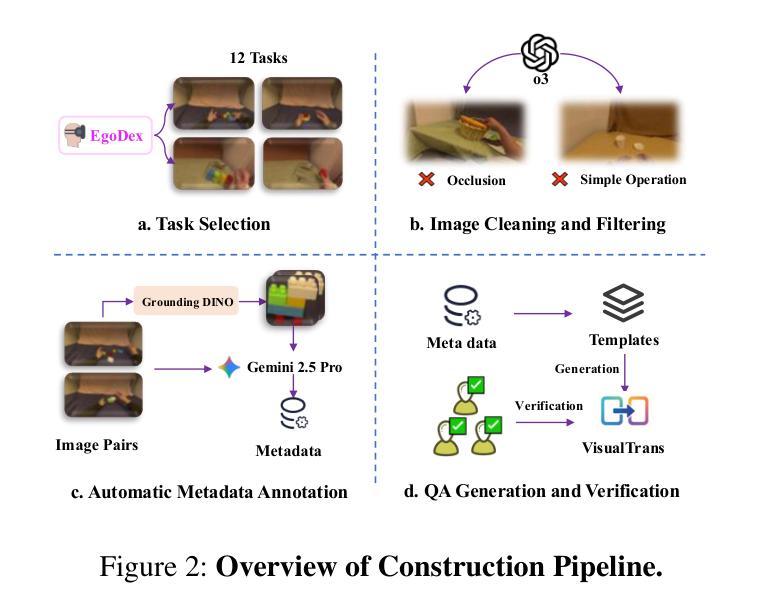
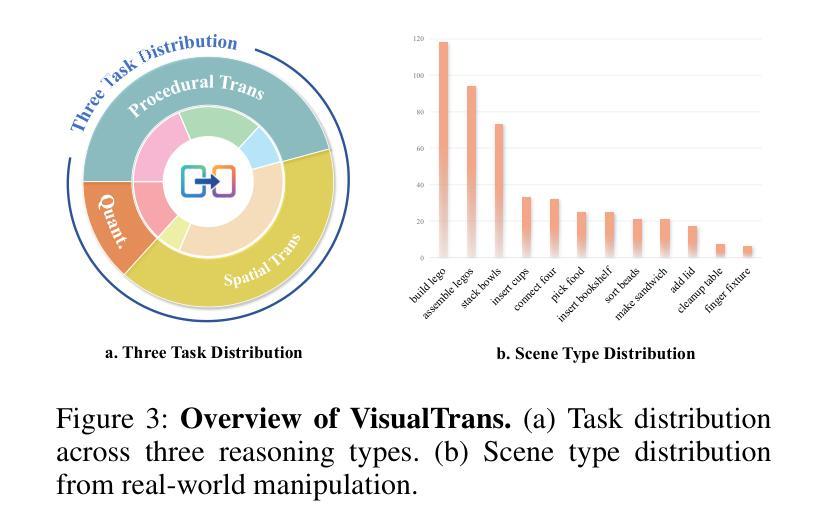
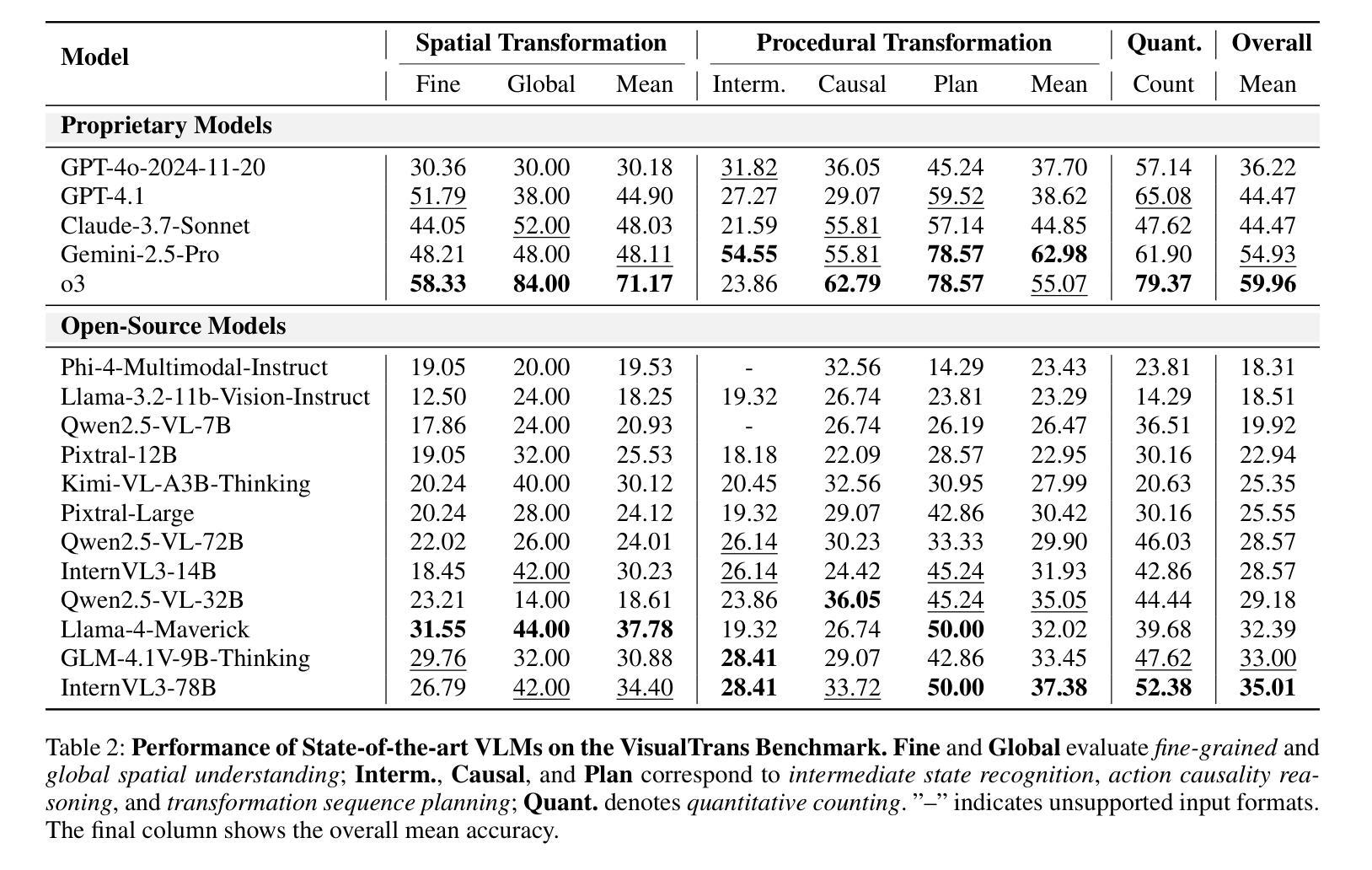
Probing the Gaps in ChatGPT Live Video Chat for Real-World Assistance for People who are Blind or Visually Impaired
Authors:Ruei-Che Chang, Rosiana Natalie, Wenqian Xu, Jovan Zheng Feng Yap, Anhong Guo
Recent advancements in large multimodal models have provided blind or visually impaired (BVI) individuals with new capabilities to interpret and engage with the real world through interactive systems that utilize live video feeds. However, the potential benefits and challenges of such capabilities to support diverse real-world assistive tasks remain unclear. In this paper, we present findings from an exploratory study with eight BVI participants. Participants used ChatGPT’s Advanced Voice with Video, a state-of-the-art live video AI released in late 2024, in various real-world scenarios, from locating objects to recognizing visual landmarks, across unfamiliar indoor and outdoor environments. Our findings indicate that current live video AI effectively provides guidance and answers for static visual scenes but falls short in delivering essential live descriptions required in dynamic situations. Despite inaccuracies in spatial and distance information, participants leveraged the provided visual information to supplement their mobility strategies. Although the system was perceived as human-like due to high-quality voice interactions, assumptions about users’ visual abilities, hallucinations, generic responses, and a tendency towards sycophancy led to confusion, distrust, and potential risks for BVI users. Based on the results, we discuss implications for assistive video AI agents, including incorporating additional sensing capabilities for real-world use, determining appropriate intervention timing beyond turn-taking interactions, and addressing ecological and safety concerns.
最近的大型多模态模型的进步为盲人或视力受损(BVI)个体提供了通过利用实时视频反馈的互动系统来解读和与现实世界互动的新能力。然而,此类能力在支持多样化的现实世界辅助任务方面的潜在优势和挑战仍不明确。在本文中,我们展示了与八名BVI参与者进行的探索性研究的发现。参与者在各种现实场景中使用了ChatGPT的先进语音和视频功能,这是一项于2024年末发布的最新实时视频人工智能技术,从寻找物体到识别视觉地标,涉及不熟悉的室内和室外环境。我们的研究结果表明,当前的实时视频AI在提供静态视觉场景的指导和答案方面非常有效,但在提供动态情况下所需的关键实时描述方面却相形见绌。尽管在空间和距离信息方面存在不准确之处,参与者还是利用所提供的视觉信息来补充他们的行动策略。尽管由于高质量的声音互动,系统被感知为人类般的存在,但对于用户的视觉能力的假设、幻觉、通用回应和奉承的倾向导致了混淆、不信任和盲人用户的潜在风险。基于研究结果,我们讨论了辅助视频AI代理的启示,包括增加现实世界使用的额外感知能力、确定超越轮流互动的适当干预时间以及解决生态和安全问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM ASSETS 2025
Summary:
大型多模态模型的最新进展为盲人或视觉障碍(BVI)个体提供了通过交互式系统解读并参与到现实世界的新能力,该系统采用实时视频流。本文通过一项包含八名BVI参与者的探索性研究来探讨这一技术在现实世界中所面临的潜力和挑战。尽管在静态视觉场景方面表现出色,但在动态场景中提供必要的实时描述方面存在不足。参与者虽然能够利用提供的视觉信息辅助其移动策略,但对用户的视觉能力做出假设、幻象、通用响应以及迎合倾向可能导致混淆、不信任以及对BVI用户存在潜在风险。需要进一步改进AI助手的感知能力、干预时机和生态安全问题。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型多模态模型为盲人或视觉障碍者提供了通过实时视频流解读现实世界的交互系统新能力。
- 实时视频AI在静态视觉场景方面表现出色,但在动态场景中提供必要的实时描述方面存在不足。
- 尽管空间及距离信息存在不准确的情况,但参与者仍能利用提供的视觉信息辅助移动策略。
- 系统在人性化方面做得较好,但仍存在假设用户视觉能力、幻象、通用响应和迎合倾向等问题。
- 对视频AI助手的改进需要增加感知能力以适应现实世界的复杂环境。
- 需要确定适当的干预时机,超越对话中的轮流交互模式。
点此查看论文截图


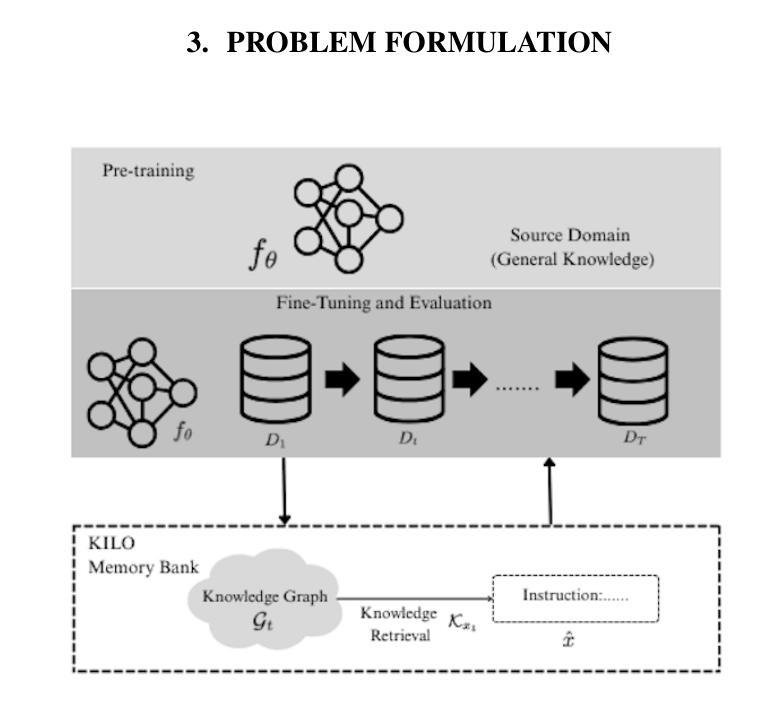
Tackling Distribution Shift in LLM via KILO: Knowledge-Instructed Learning for Continual Adaptation
Authors:Iing Muttakhiroh, Thomas Fevens
Large Language Models (LLMs) often suffer from performance degradation when faced with domain shifts, primarily due to catastrophic forgetting. In this work, we propose KILO (Knowledge-Instructed Learning for Continual Adaptation), a novel continual learning framework that integrates dynamic knowledge graphs with instruction tuning. By leveraging retrieved domain-specific knowledge as guidance during training, KILO enhances both adaptability to new domains and retention of previously acquired knowledge. We pretrain our model on WikiText-103 and evaluate sequential adaptation across four diverse target domains: BioASQ, SciQ, TweetEval, and MIND. Our experiments demonstrate that KILO consistently outperforms strong baselines, including continual fine-tuning, ERNIE 2.0, and CPT, in terms of backward transfer, forward transfer, F1 score, retention rate, and training efficiency. These results highlight the effectiveness of combining structured knowledge retrieval and instruction prompting to overcome domain shift challenges in continual learning scenarios.
大型语言模型(LLM)在面临领域迁移时常常会出现性能下降的问题,这主要是由于灾难性遗忘造成的。在这项工作中,我们提出了KILO(用于持续适应的知识指导学习),这是一种新型持续学习框架,它结合了动态知识图谱和指令微调。通过利用检索到的领域特定知识作为训练过程中的指导,KILO提高了对新领域的适应能力和对先前获取知识的保持能力。我们在WikiText-103上预训练我们的模型,并在四个不同的目标领域(BioASQ、SciQ、TweetEval和MIND)进行顺序适应评估。实验表明,KILO在向后迁移、向前迁移、F1分数、保持率和训练效率方面均优于持续微调、ERNIE 2.0和CPT等强大的基线模型。这些结果突出了在持续学习场景中结合结构化知识检索和指令提示以克服领域迁移挑战的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为KILO的新型持续学习框架,旨在解决大型语言模型(LLM)在面临领域迁移时的性能下降问题。KILO通过结合动态知识图谱和指令调整,利用检索到的领域特定知识作为训练过程中的指导,从而提高对新领域的适应能力和对先前获取知识的保留能力。实验表明,KILO在多个目标领域上的表现均优于强基线,包括连续微调、ERNIE 2.0和CPT,在反向传递、正向传递、F1分数、保持率和训练效率等方面均有所改进。
Key Takeaways
- KILO是一种新型的持续学习框架,旨在解决LLM在面临领域迁移时的性能下降问题。
- KILO结合了动态知识图谱和指令调整,以提高模型对新领域的适应能力和保留先前知识的能力。
- 实验表明,KILO在多个目标领域上的表现均优于其他方法。
- KILO的优势体现在反向传递、正向传递、F1分数、保持率和训练效率等方面。
- KILO利用检索到的领域特定知识作为训练过程中的指导。
- KILO框架可以有效地克服领域迁移挑战。
点此查看论文截图

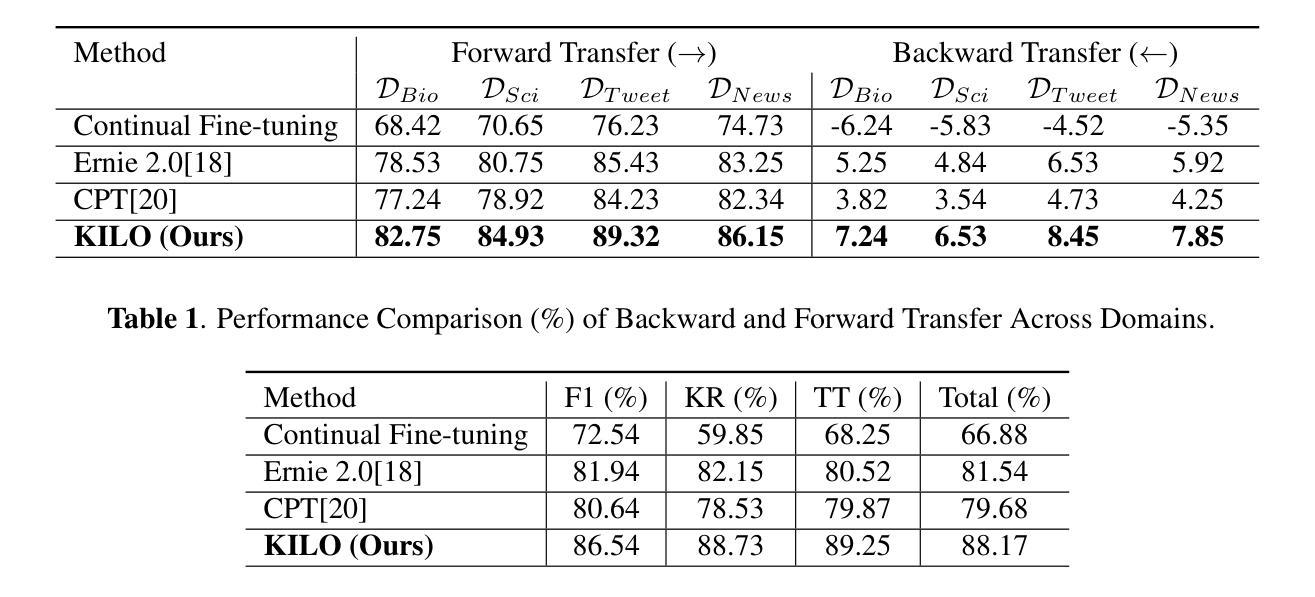
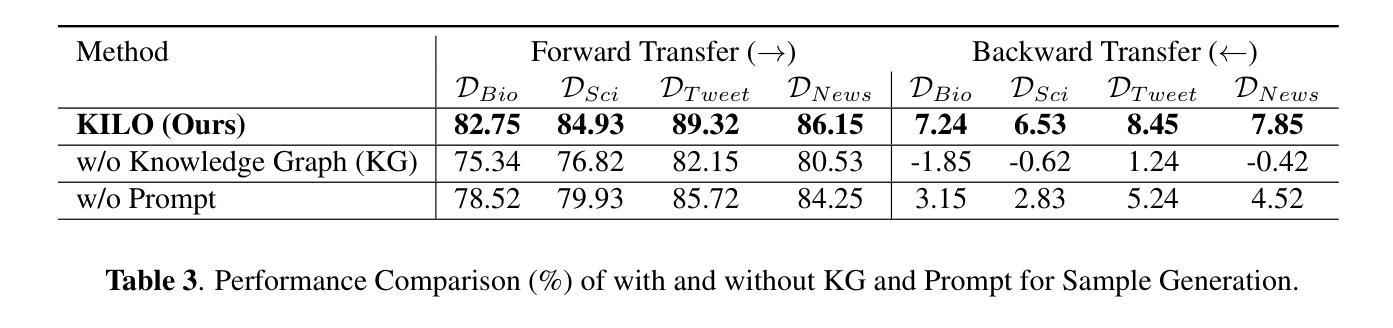
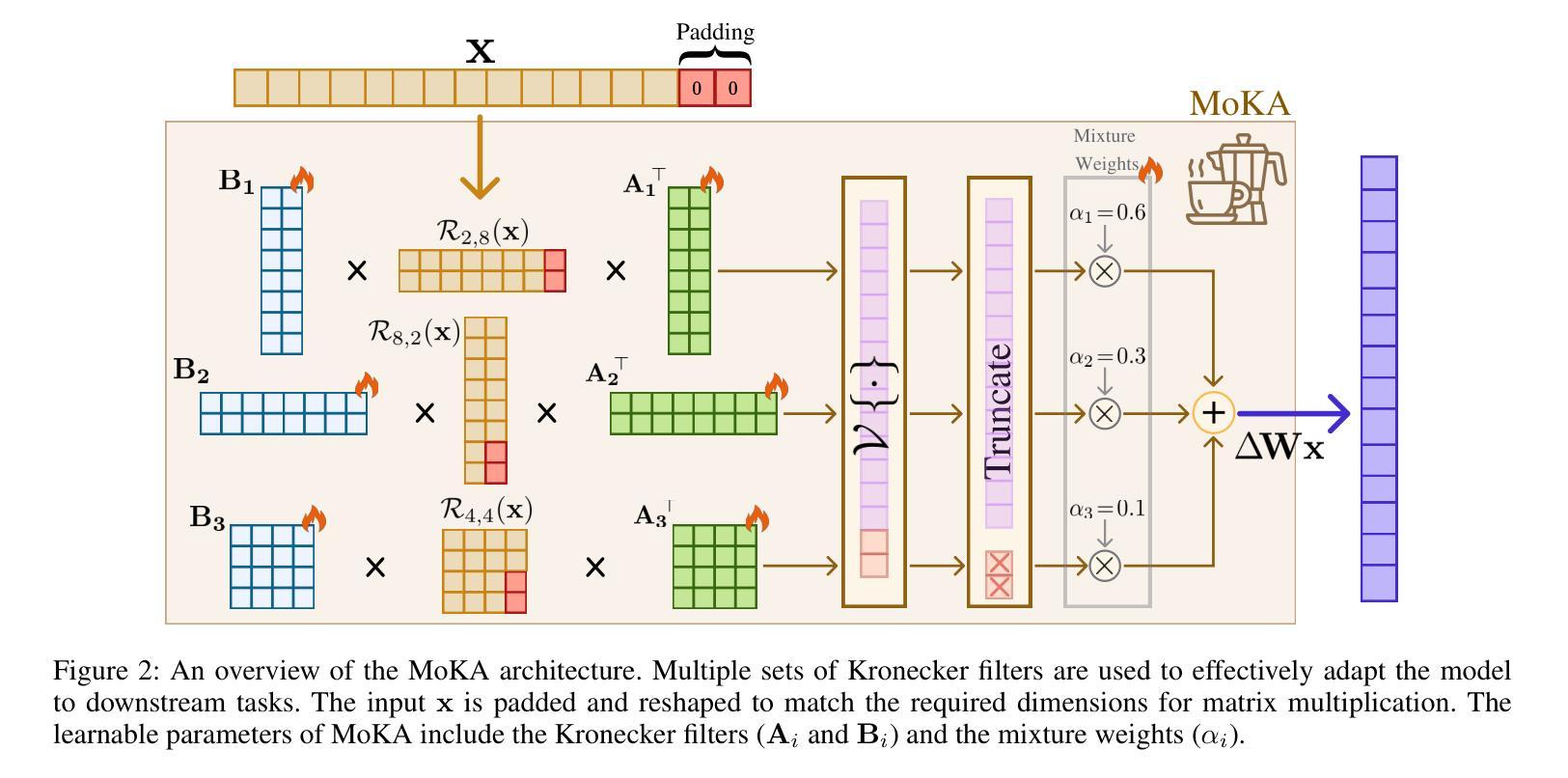
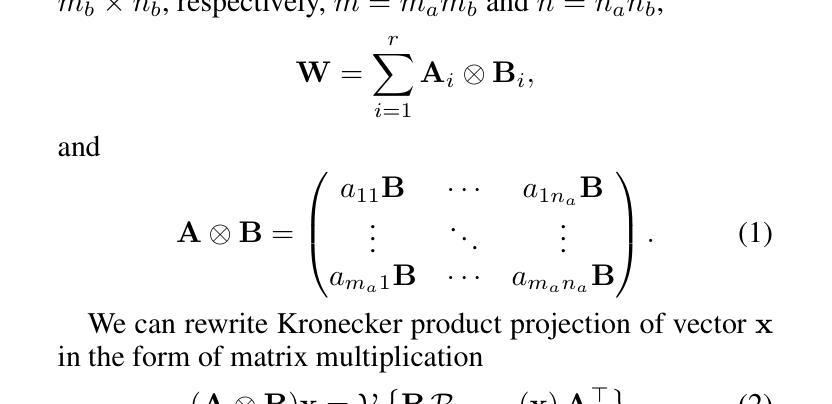
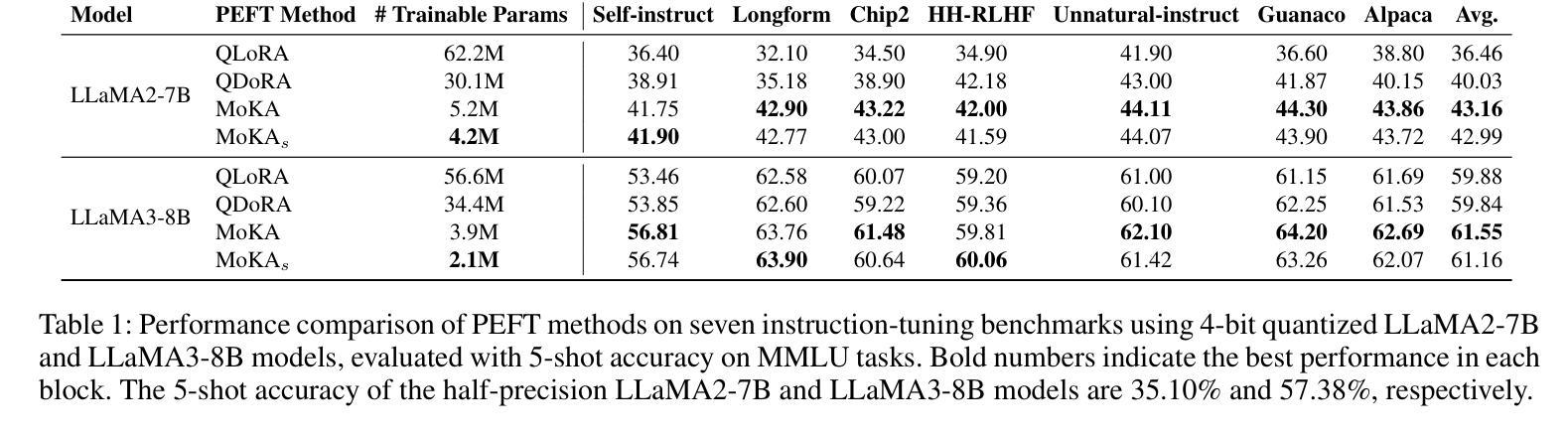
MoKA: Mixture of Kronecker Adapters
Authors:Mohammadreza Sadeghi, Mahsa Ghazvini Nejad, MirHamed Jafarzadeh Asl, Yu Gu, Yuanhao Yu, Masoud Asgharian, Vahid Partovi Nia
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is essential for reducing the computational overhead of large language models (LLMs). Low-rank family adapters are commonly used to control the parameter size efficiently while maintaining the generative power of LLMs. However, their limited expressiveness due to the rank constraint often restricts their performance on complex tasks. We propose Mixture of Kronecker Adapters (MoKA), a new generation of Kronecker adapters that addresses this limitation by modeling weight updates as a mixture of Kronecker products. Our proposed adapter leverages a gating mechanism that measures the importance of each Kronecker factor, enabling more expressive adaptation. Moreover, MoKA enables a rank flexibility that provides a better trade-off between parameter efficiency and accuracy. To ensure hardware efficiency, we reformulate Kronecker computations using standard matrix operations, allowing seamless deployment on GPU-optimized hardware. We conduct extensive experiments on instruction-tuning and commonsense reasoning tasks using low-bit quantized versions of LLaMA2-7B and LLaMA3-8B models. MoKA not only outperforms PEFT baselines, but also reduces the number of trainable parameters up to 27x, achieving state-of-the-art trade-offs between performance and parameter efficiency.
参数高效微调(PEFT)对于减少大型语言模型(LLM)的计算开销至关重要。低秩家族适配器通常用于有效地控制参数大小,同时保持LLM的生成能力。然而,由于秩约束导致的有限表达能力往往限制了它们在复杂任务上的性能。我们提出了混合克罗内克适配器(MoKA),这是一种新一代的克罗内克适配器,它通过模拟权重更新作为克罗内克产品的混合来解决这个问题。我们提出的适配器利用门控机制来衡量每个克罗内克因子的重要性,从而实现更具表现力的适应。此外,MoKA提供了秩灵活性,在参数效率和准确性之间提供了更好的权衡。为了保证硬件效率,我们利用标准矩阵操作重新制定了克罗内克计算,可以无缝地部署在GPU优化的硬件上。我们在指令调整和常识推理任务上进行了大量实验,采用了LLaMA的低比特量化版本(包括LLaMA的精简版本和轻量级版本)。MoKA不仅优于PEFT基线,还将训练参数数量减少了高达27倍,在性能和参数效率方面达到了最先进的权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
参数高效微调(PEFT)对于减少大型语言模型(LLM)的计算开销至关重要。低秩家族适配器在控制参数大小的同时保持了LLM的生成能力。然而,由于秩的限制,其表达能力的有限性常常限制了其在复杂任务上的性能。本文提出混合克罗内克适配器(MoKA),这是一种新型的克罗内克适配器,通过模拟权重更新作为克罗内克积的混合来解决这一问题。MoKA利用门控机制来衡量每个克罗内克因子的重要性,从而实现更灵活的适应表达。此外,MoKA能够在参数效率和准确性之间实现更好的权衡。为确保硬件效率,本文使用标准矩阵操作重新制定了克罗内克计算,可在GPU优化硬件上进行无缝部署。在指令调整和常识推理任务上,使用低精度量化的LLaMA2-7B和LLaMA3-8B模型进行的广泛实验表明,MoKA不仅优于PEFT基线,而且可将训练参数减少至原来的27倍,在性能和参数效率之间取得了最先进的权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)对减少大型语言模型的计算开销很重要。
- 低秩家族适配器在控制参数大小和保持LLM生成能力之间取得平衡,但其在复杂任务上的表现受限。
- MoKA作为一种新型的克罗内克适配器,通过模拟权重更新作为克罗内克积的混合,解决了低秩家族适配器的限制。
- MoKA利用门控机制,提高适配器的表达能力,并在参数效率和准确性之间实现更好的权衡。
- MoKA通过标准矩阵操作进行克罗内克计算,提高了硬件效率,可在GPU上无缝部署。
- 在指令调整和常识推理任务上,MoKA优于PEFT基线,并显著减少了训练参数。
点此查看论文截图
On the Evaluation of Large Language Models in Multilingual Vulnerability Repair
Authors:Dong wang, Junji Yu, Honglin Shu, Michael Fu, Chakkrit Tantithamthavorn, Yasutaka Kamei, Junjie Chen
Various Deep Learning-based approaches with pre-trained language models have been proposed for automatically repairing software vulnerabilities. However, these approaches are limited to a specific programming language (C/C++). Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) offer language-agnostic capabilities and strong semantic understanding, exhibiting potential to overcome multilingual vulnerability limitations. Although some work has begun to explore LLMs’ repair performance, their effectiveness is unsatisfactory. To address these limitations, we conducted a large-scale empirical study to investigate the performance of automated vulnerability repair approaches and state-of-the-art LLMs across seven programming languages. Results show GPT-4o, instruction-tuned with few-shot prompting, performs competitively against the leading approach, VulMaster. Additionally, the LLM-based approach shows superior performance in repairing unique vulnerabilities and is more likely to repair the most dangerous vulnerabilities. Instruction-tuned GPT-4o demonstrates strong generalization on vulnerabilities in previously unseen language, outperforming existing approaches. Analysis shows Go consistently achieves the highest effectiveness across all model types, while C/C++ performs the worst. Based on findings, we discuss the promise of LLM on multilingual vulnerability repair and the reasons behind LLM’s failed cases. This work takes the first look at repair approaches and LLMs across multiple languages, highlighting the promising future of adopting LLMs for multilingual vulnerability repair.
基于深度学习和预训练语言模型的多种方法已被提出,用于自动修复软件漏洞。然而,这些方法仅限于特定的编程语言(如C/C++)。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展提供了与语言无关的能力和强大的语义理解,显示出克服多语言漏洞限制的潜力。尽管已经开始探索LLM的修复性能,但其有效性尚不理想。为了解决这个问题,我们进行了一项大规模实证研究,调查了自动化漏洞修复方法和最新LLM在七种编程语言中的表现。结果表明,经过指令微调、通过几次提示进行的GPT-4o,与领先的VulMaster方法相比表现良好。此外,基于LLM的方法在修复独特漏洞时表现出卓越的性能,并且更有可能修复最危险的漏洞。经过指令调校的GPT-4o在以前未见语言的漏洞上表现出强大的泛化能力,超过了现有方法。分析表明,Go在所有模型类型中始终获得最高的有效性,而C/C++的表现最差。基于研究结果,我们讨论了LLM在多语言漏洞修复方面的前景以及LLM失败案例背后的原因。这项工作首次跨多种语言研究修复方法和LLM,突显了采用LLM进行多语言漏洞修复的广阔前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习和预训练语言模型的自动修复软件漏洞方法已经提出,但仅限于特定编程语言(如C/C++)。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进展提供了跨语言的通用能力和强大的语义理解,具有克服多语言漏洞限制的潜力。尽管已经开始探索LLM在漏洞修复方面的性能,但其有效性尚不满意。本研究进行了大规模实证研究,探讨了自动化漏洞修复方法和最先进的LLM在七种编程语言中的表现。结果显示,经过指令微调且使用少量提示的GPT-4o与领先的VulMaster方法竞争表现良好。此外,基于LLM的方法在修复独特漏洞时表现出卓越的性能,并更有可能修复最危险的漏洞。经过指令调校的GPT-4o在之前未见过的语言中的漏洞上表现出强大的泛化能力。分析显示,Go在所有模型类型中始终获得最高的有效性,而C/C++表现最差。本研究首次跨多种语言研究修复方法和LLM,突显了采用LLM进行多语言漏洞修复的广阔前景。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具有跨语言的通用能力和强大的语义理解,有助于克服多语言漏洞修复的局限性。
- 相比传统方法,LLM在自动修复软件漏洞方面展现出竞争力,特别是在处理独特和最危险的漏洞时。
- GPT-4o经过指令微调后,在跨语言的漏洞修复上表现出优异的性能,且能够泛化到之前未见过的语言。
- 在研究的七种编程语言中,Go在漏洞修复方面的有效性最高,而C/C++表现相对较差。
- LLM在修复某些漏洞时仍存在失败情况,需要进一步研究和优化。
- 本研究首次全面评估了LLM在多语言环境下的漏洞修复能力,为未来的研究提供了有价值的参考。
点此查看论文截图

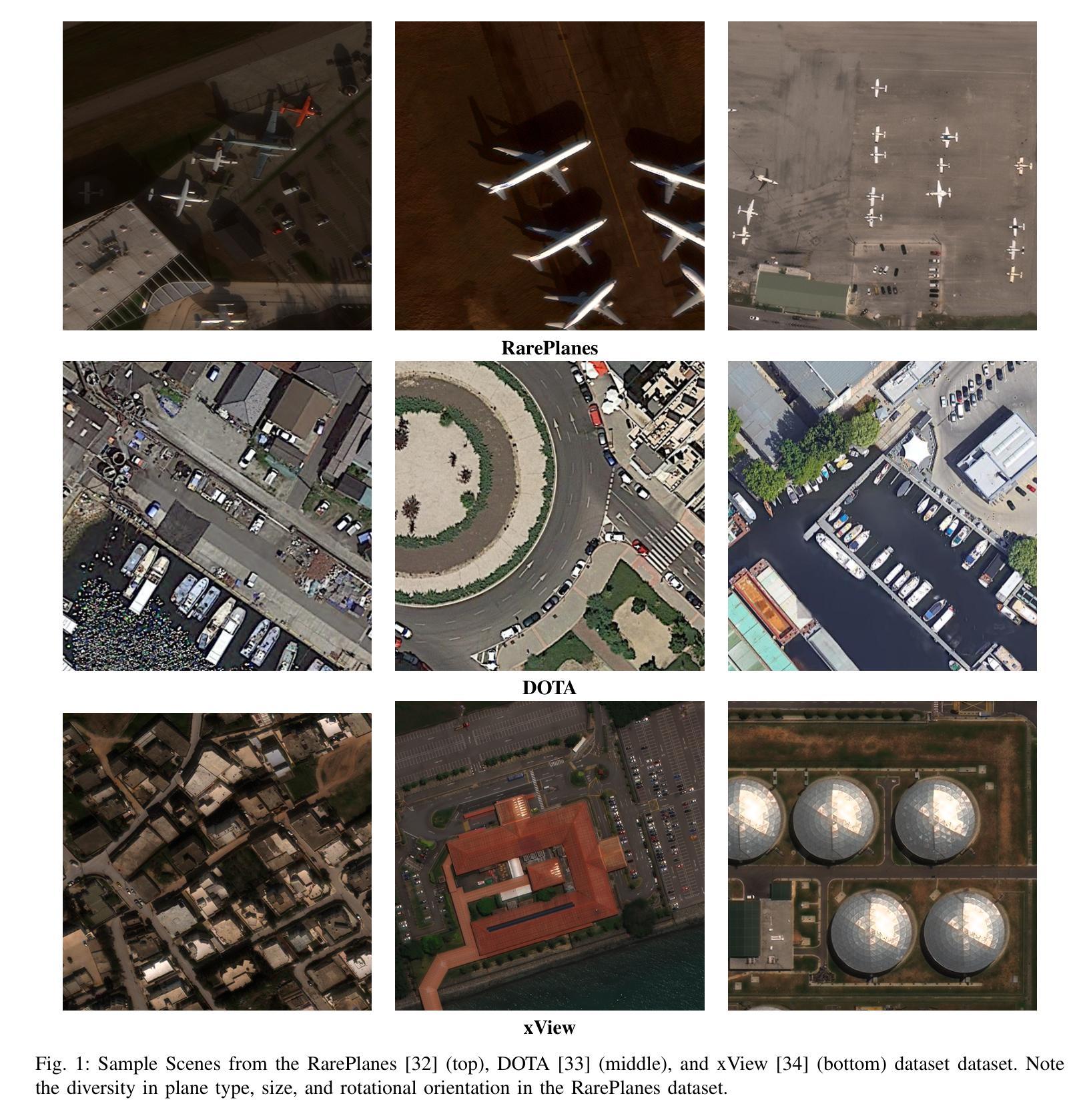
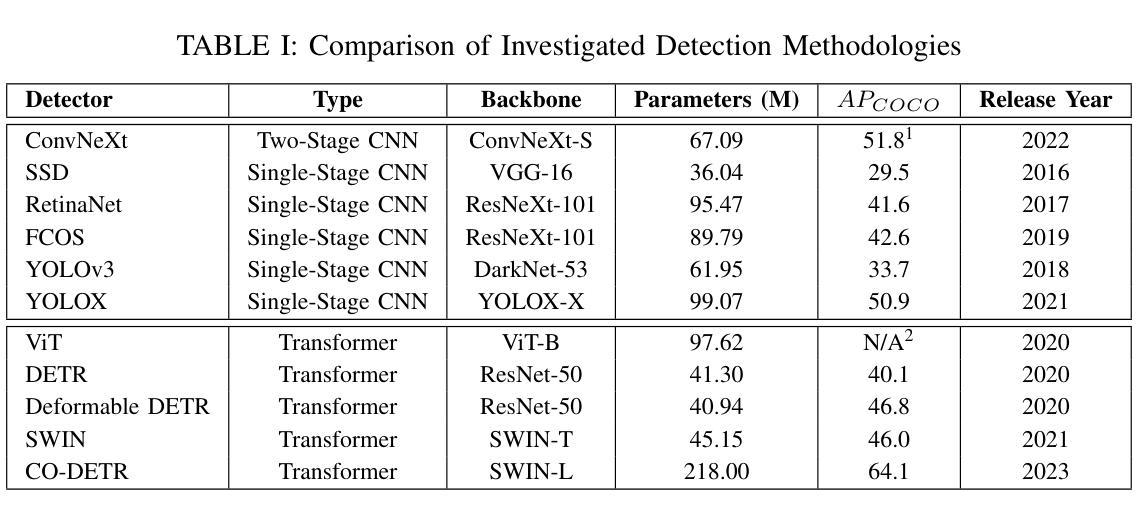
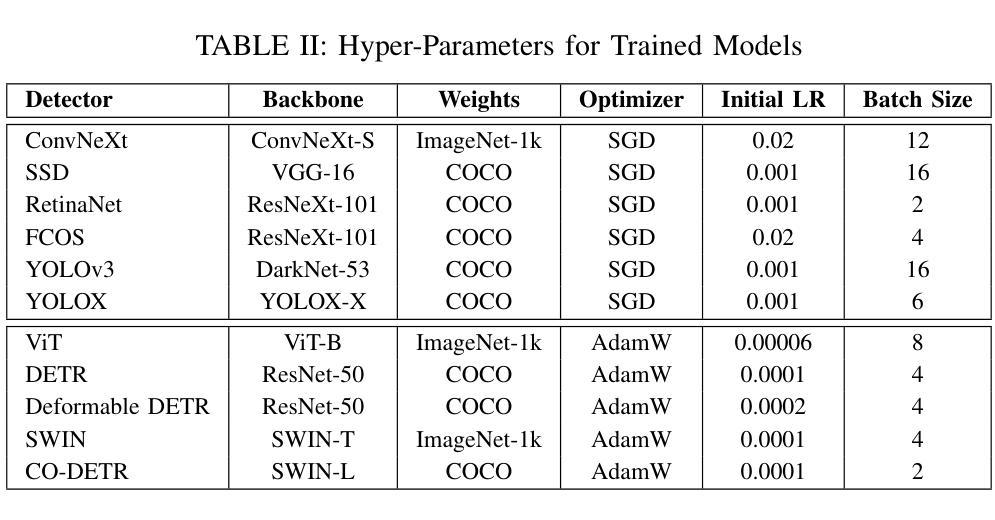
Evaluation and Analysis of Deep Neural Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks on Modern Remote Sensing Datasets
Authors:J. Alex Hurt, Trevor M. Bajkowski, Grant J. Scott, Curt H. Davis
In 2012, AlexNet established deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) as the state-of-the-art in CV, as these networks soon led in visual tasks for many domains, including remote sensing. With the publication of Visual Transformers, we are witnessing the second modern leap in computational vision, and as such, it is imperative to understand how various transformer-based neural networks perform on satellite imagery. While transformers have shown high levels of performance in natural language processing and CV applications, they have yet to be compared on a large scale to modern remote sensing data. In this paper, we explore the use of transformer-based neural networks for object detection in high-resolution electro-optical satellite imagery, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on a variety of publicly available benchmark data sets. We compare eleven distinct bounding-box detection and localization algorithms in this study, of which seven were published since 2020, and all eleven since 2015. The performance of five transformer-based architectures is compared with six convolutional networks on three state-of-the-art opensource high-resolution remote sensing imagery datasets ranging in size and complexity. Following the training and evaluation of thirty-three deep neural models, we then discuss and analyze model performance across various feature extraction methodologies and detection algorithms.
在2012年,AlexNet确立了深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)在计算机视觉(CV)领域的领先地位,因为这些网络很快在许多领域(包括遥感)的视觉任务中占据主导地位。随着视觉Transformer的发布,我们见证了计算视觉的第二次现代飞跃,因此了解各种基于Transformer的神经网络在卫星图像上的表现至关重要。虽然Transformer在自然语言处理和计算机视觉应用中表现出卓越的性能,但它们尚未在大规模现代遥感数据上得到广泛比较。在本文中,我们探讨了基于Transformer的神经网络在高分辨率光电卫星图像中的目标检测应用,并在各种公开的基准数据集上展示了其卓越的性能。在本研究中,我们比较了11种不同的边界框检测和定位算法,其中7种自2020年以来发表,所有11种自2015年以来均有所发展。在五种基于Transformer的架构与六种卷积网络之间进行了比较,涉及三个开源的先进高分辨率遥感图像数据集,这些数据集在规模和复杂性方面各不相同。在对33个深度神经网络进行训练和评估后,我们进一步讨论并分析了各种特征提取方法和检测算法之间的模型性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文探讨了基于transformer的神经网络在高分辨率光电卫星图像中的目标检测应用,对比了多个公开的基准数据集上的性能。该研究对比了多种检测算法,包括七个自2020年以来发布的算法和所有自2015年以来发布的十一个算法。论文对比了五种基于transformer的架构和六种卷积网络在三种不同规模和复杂度的开源高分辨率遥感图像数据集上的表现。研究通过对三十三个深度神经网络模型进行训练和评估,分析和讨论了模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于transformer的神经网络在高分辨率遥感图像的目标检测中表现出卓越性能。
- 该研究对比了多个公开的基准数据集上的目标检测算法。
- 对比了多种检测算法,包括近年来新发布的算法。
- 对比了五种基于transformer的架构和六种卷积网络在遥感图像数据集上的表现。
- 通过对三十三个深度神经网络模型的训练和评估,全面分析了模型性能。
- 基于transformer的神经网络在遥感图像目标检测领域具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图