⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
NVSpeech: An Integrated and Scalable Pipeline for Human-Like Speech Modeling with Paralinguistic Vocalizations
Authors:Huan Liao, Qinke Ni, Yuancheng Wang, Yiheng Lu, Haoyue Zhan, Pengyuan Xie, Qiang Zhang, Zhizheng Wu
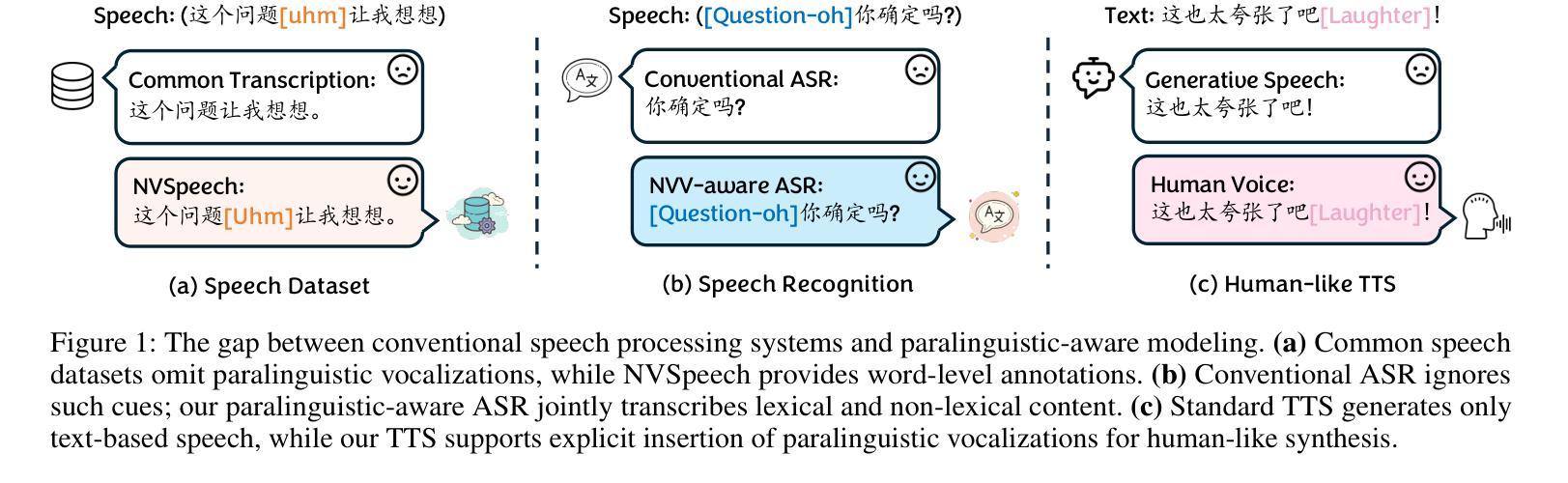
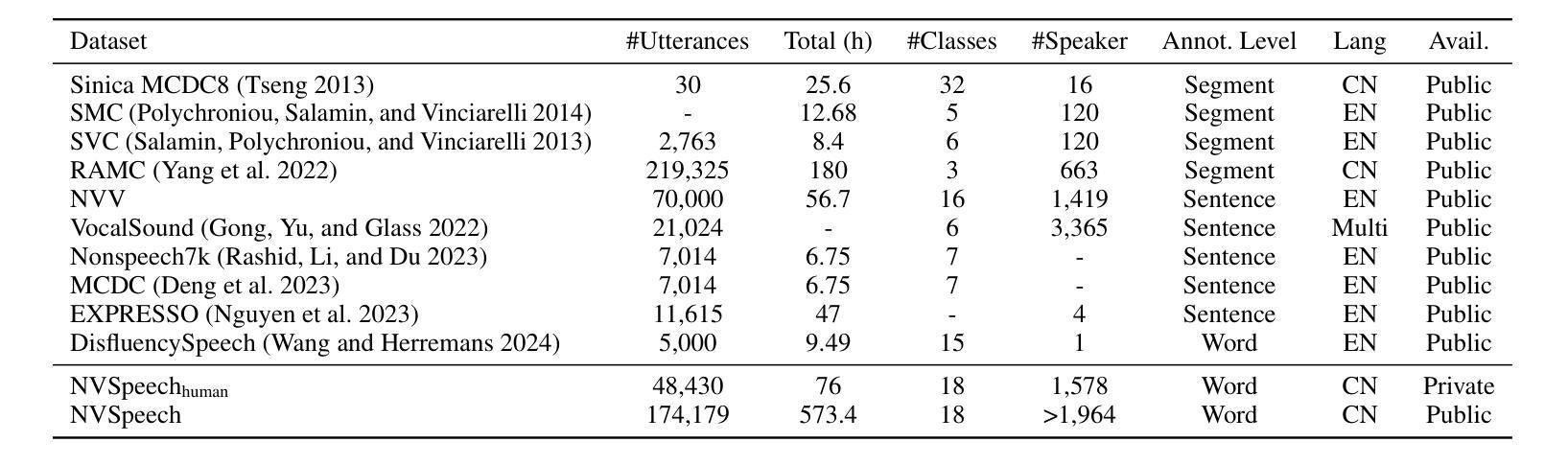
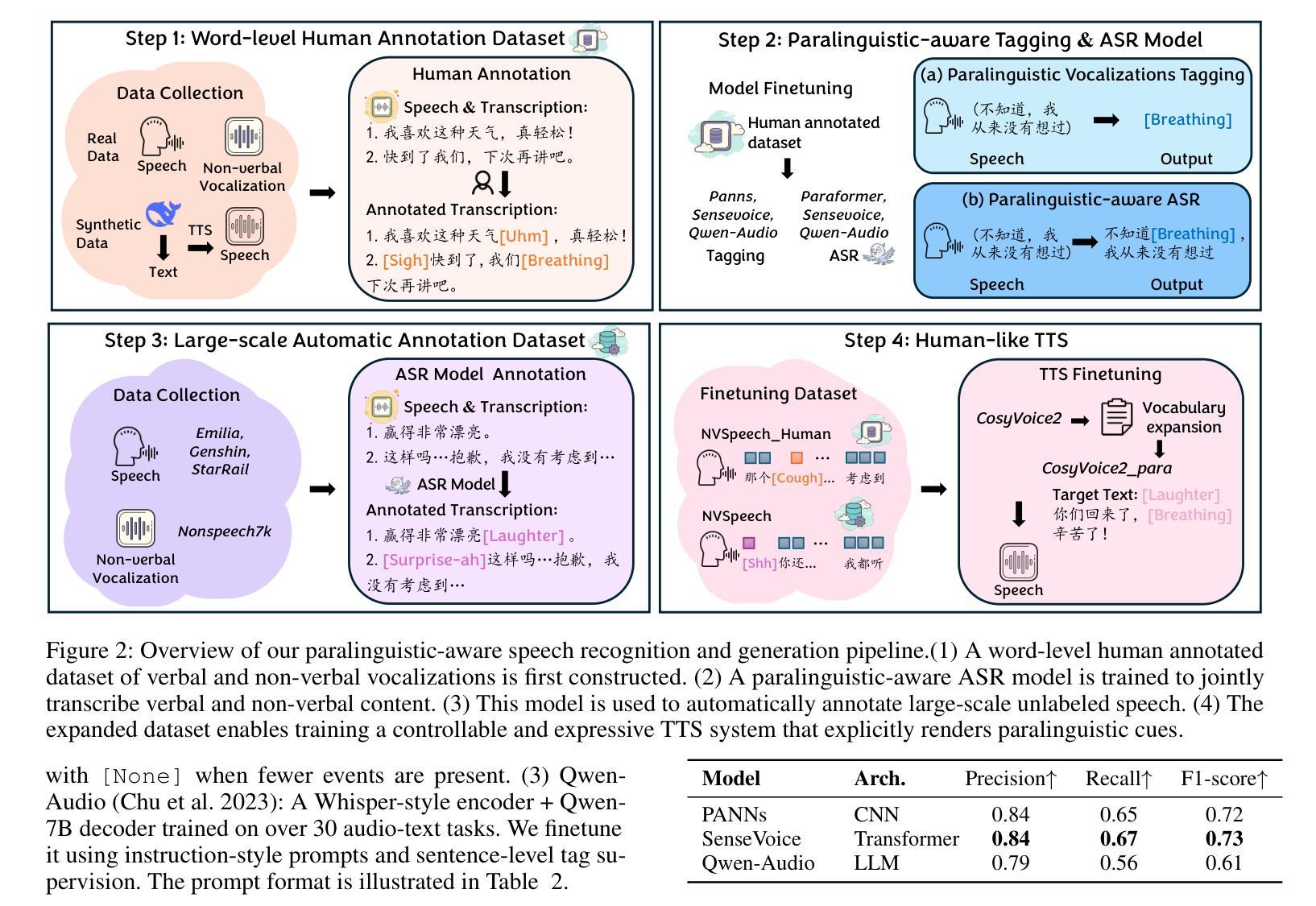
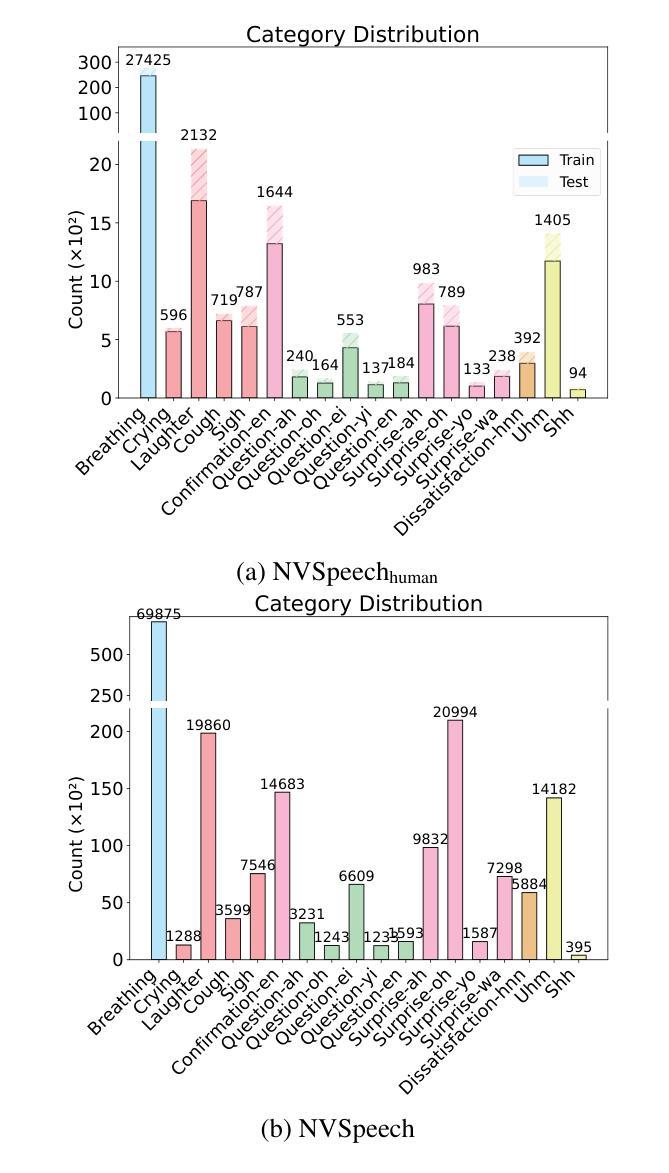
Paralinguistic vocalizations-including non-verbal sounds like laughter and breathing, as well as lexicalized interjections such as “uhm” and “oh”-are integral to natural spoken communication. Despite their importance in conveying affect, intent, and interactional cues, such cues remain largely overlooked in conventional automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS) systems. We present NVSpeech, an integrated and scalable pipeline that bridges the recognition and synthesis of paralinguistic vocalizations, encompassing dataset construction, ASR modeling, and controllable TTS. (1) We introduce a manually annotated dataset of 48,430 human-spoken utterances with 18 word-level paralinguistic categories. (2) We develop the paralinguistic-aware ASR model, which treats paralinguistic cues as inline decodable tokens (e.g., “You’re so funny [Laughter]”), enabling joint lexical and non-verbal transcription. This model is then used to automatically annotate a large corpus, the first large-scale Chinese dataset of 174,179 utterances (573 hours) with word-level alignment and paralingustic cues. (3) We finetune zero-shot TTS models on both human- and auto-labeled data to enable explicit control over paralinguistic vocalizations, allowing context-aware insertion at arbitrary token positions for human-like speech synthesis. By unifying the recognition and generation of paralinguistic vocalizations, NVSpeech offers the first open, large-scale, word-level annotated pipeline for expressive speech modeling in Mandarin, integrating recognition and synthesis in a scalable and controllable manner. Dataset and audio demos are available at https://nvspeech170k.github.io/.
副语言发声,包括非语言声音(如笑声和呼吸声),以及词汇化感叹词(如“呃”和“哦”),是自然口语交流的重要组成部分。尽管它们在传达情感、意图和交互线索方面很重要,但这些线索在传统自动语音识别(ASR)和文本到语音(TTS)系统中仍然被忽视。我们提出了NVSpeech,这是一个集成且可扩展的管道,能够识别并合成副语言发声,包括数据集构建、ASR建模和可控TTS。
(1)我们介绍了一个包含48430个人类口语发音的手动注释数据集,其中包含18个单词级别的副语言类别。
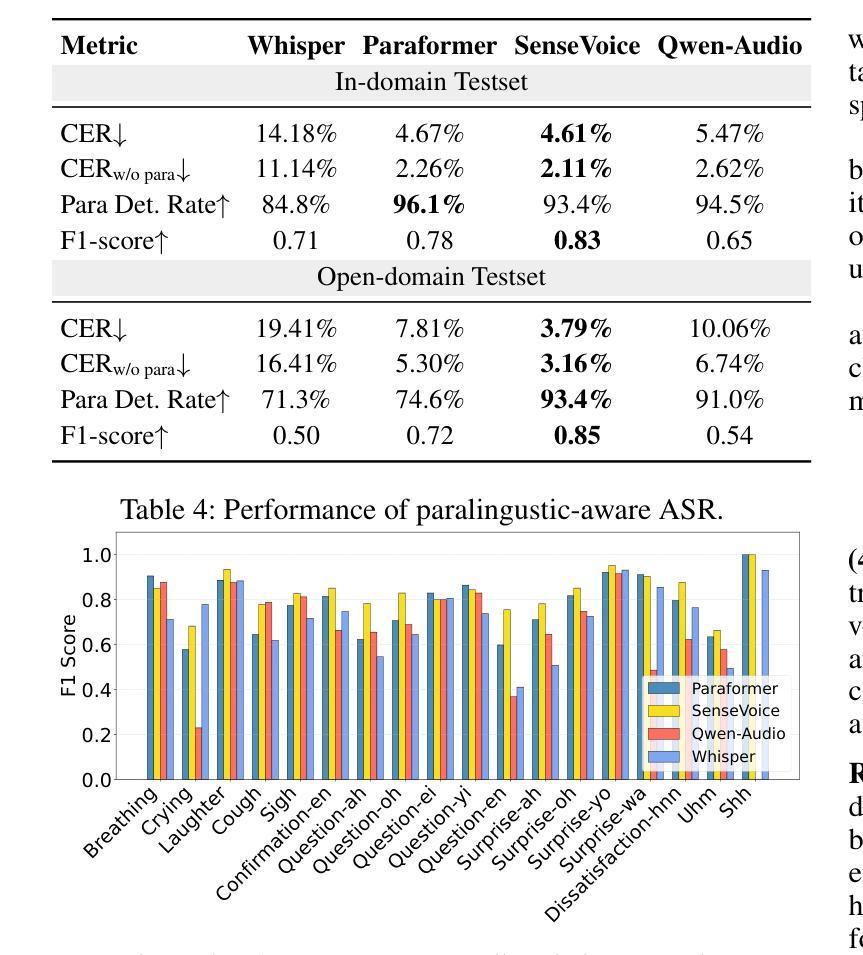
(2)我们开发了一种感知副语言的ASR模型,它将副语言线索视为内联可解码令牌(例如,“你很有趣[笑声]”),从而实现词汇和非言语的共同转录。然后,该模型被用于自动注释大规模语料库,这是首个大规模的中文数据集,包含174179个发音(共573小时),具有单词级别的对齐和副语言线索。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在自然口语交流中的重要性非言语声音和词汇化插话,这些在常规语音识别和语音合成系统中常被忽视。提出了一种集识别与合成为一体的可扩展管道NVSpeech,该管道包含数据集构建、语音识别建模和可控语音合成。NVSpeech为表达性语音建模提供了首个开放的大规模词语级注释管道,以可扩展和可控的方式统一识别和生成非言语发声。
Key Takeaways
- 非言语发声(如笑声和呼吸)以及词汇化插话(如“呃”和“哦”)对于自然口语交流至关重要。
- 传统语音识别(ASR)和语音合成(TTS)系统忽略了这些表达性发声的重要性。
- NVSpeech是一个集成了识别和合成的可扩展管道,包含数据集构建、ASR建模和可控TTS。
- 引入了一个包含18个词级的非言语类别手动注释数据集。
- 开发了一种非言语感知的ASR模型,该模型能够将非言语发声视为内联解码令牌,从而实现词汇和非言语的联合转录。
- 使用该模型自动注释了一个大规模语料库,这是首个大规模的中文语料库,包含词级对齐和非言语线索。
点此查看论文截图

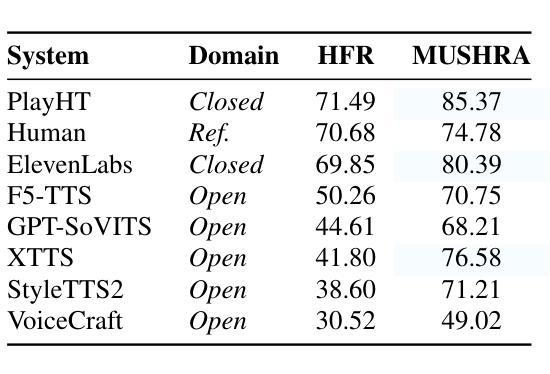
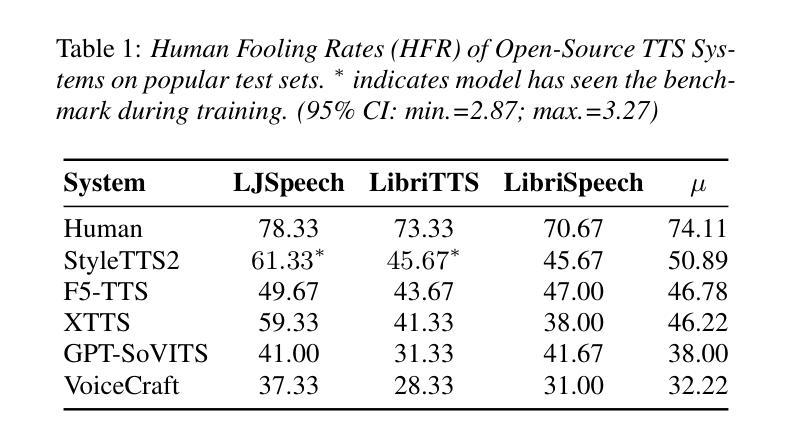
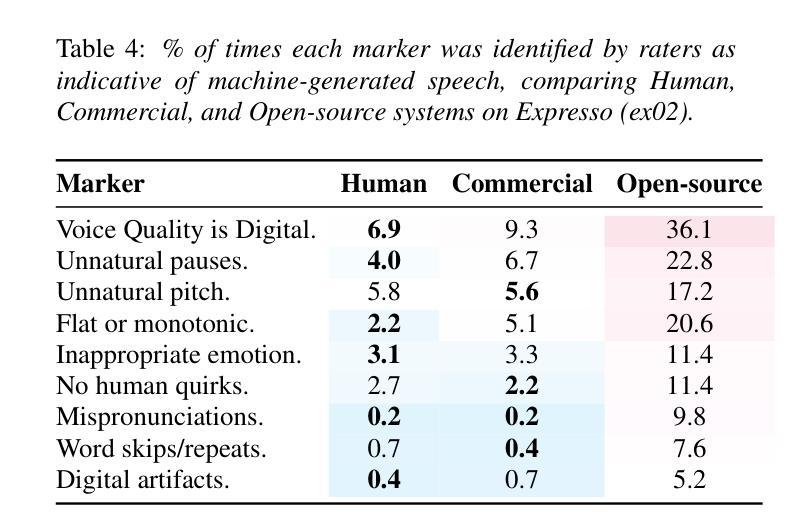
The State Of TTS: A Case Study with Human Fooling Rates
Authors:Praveen Srinivasa Varadhan, Sherry Thomas, Sai Teja M. S., Suvrat Bhooshan, Mitesh M. Khapra
While subjective evaluations in recent years indicate rapid progress in TTS, can current TTS systems truly pass a human deception test in a Turing-like evaluation? We introduce Human Fooling Rate (HFR), a metric that directly measures how often machine-generated speech is mistaken for human. Our large-scale evaluation of open-source and commercial TTS models reveals critical insights: (i) CMOS-based claims of human parity often fail under deception testing, (ii) TTS progress should be benchmarked on datasets where human speech achieves high HFRs, as evaluating against monotonous or less expressive reference samples sets a low bar, (iii) Commercial models approach human deception in zero-shot settings, while open-source systems still struggle with natural conversational speech; (iv) Fine-tuning on high-quality data improves realism but does not fully bridge the gap. Our findings underscore the need for more realistic, human-centric evaluations alongside existing subjective tests.
尽管近年来的主观评估表明文本转语音(TTS)技术迅速进步,但当前TTS系统是否真正能通过图灵测试这样的人类欺骗测试呢?我们引入了“人类欺骗率”(HFR)这一指标,它直接衡量机器生成的语音被误认为人类的频率。我们对开源和商业TTS模型的大规模评估揭示了一些关键见解:(i)基于CMOS的人类等同主张通常在欺骗测试中失败,(ii)TTS的进步应该在人类语音实现高HFR的数据集上进行基准测试,因为与单调或缺乏表现力的参考样本进行评估会设置一个低标准,(iii)商业模型在零样本设置中可以接近人类欺骗,而开源系统仍然在自然对话语音方面挣扎;(iv)在高质量数据上进行微调可以提高真实性,但并不能完全弥补差距。我们的研究强调了除了现有的主观测试之外,还需要更现实、以人类为中心的评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at InterSpeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了Human Fooling Rate(HFR)这一指标,用于衡量机器生成的语音被误判为人类语音的频率,以此评估TTS系统的进步。研究发现,尽管近年来主观评估显示TTS迅速进步,但在欺骗测试中人机难辨真假的情况并不普遍。对开源和商业TTS模型的大规模评估揭示了关键见解。
Key Takeaways
- Human Fooling Rate(HFR)是衡量TTS系统进步的直接指标,反映机器生成语音被误判为人类语音的频率。
- 现有的声称与人类表现相当的CMOS在欺骗测试下经常失效。
- TTS的进展应以人类语音达到高HFR的数据集为基准进行评估,因为与单调或缺乏表达力的参照样本进行评估会设定较低的标准。
- 商业模型在零样本设置下接近人类欺骗水平,而开源系统在自然会话语音方面仍有困难。
- 高质量数据的精细调整可以提高真实性,但并不能完全弥补差距。
- 需要更现实、以人为中心的评价方法,与现有的主观测试相结合。
点此查看论文截图


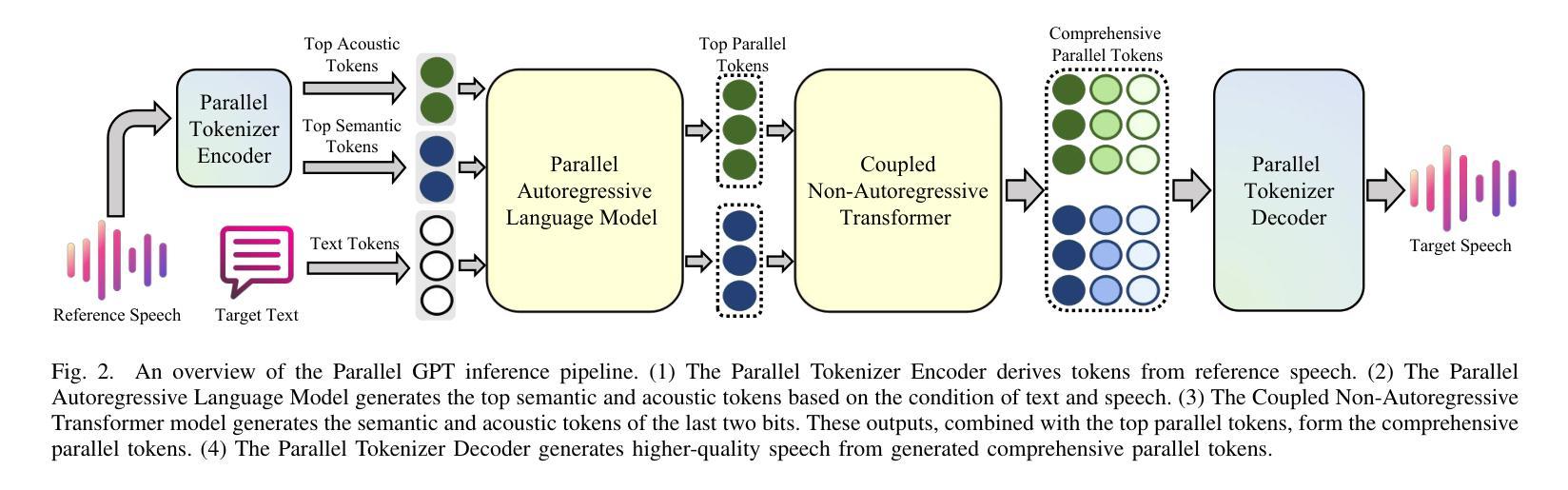
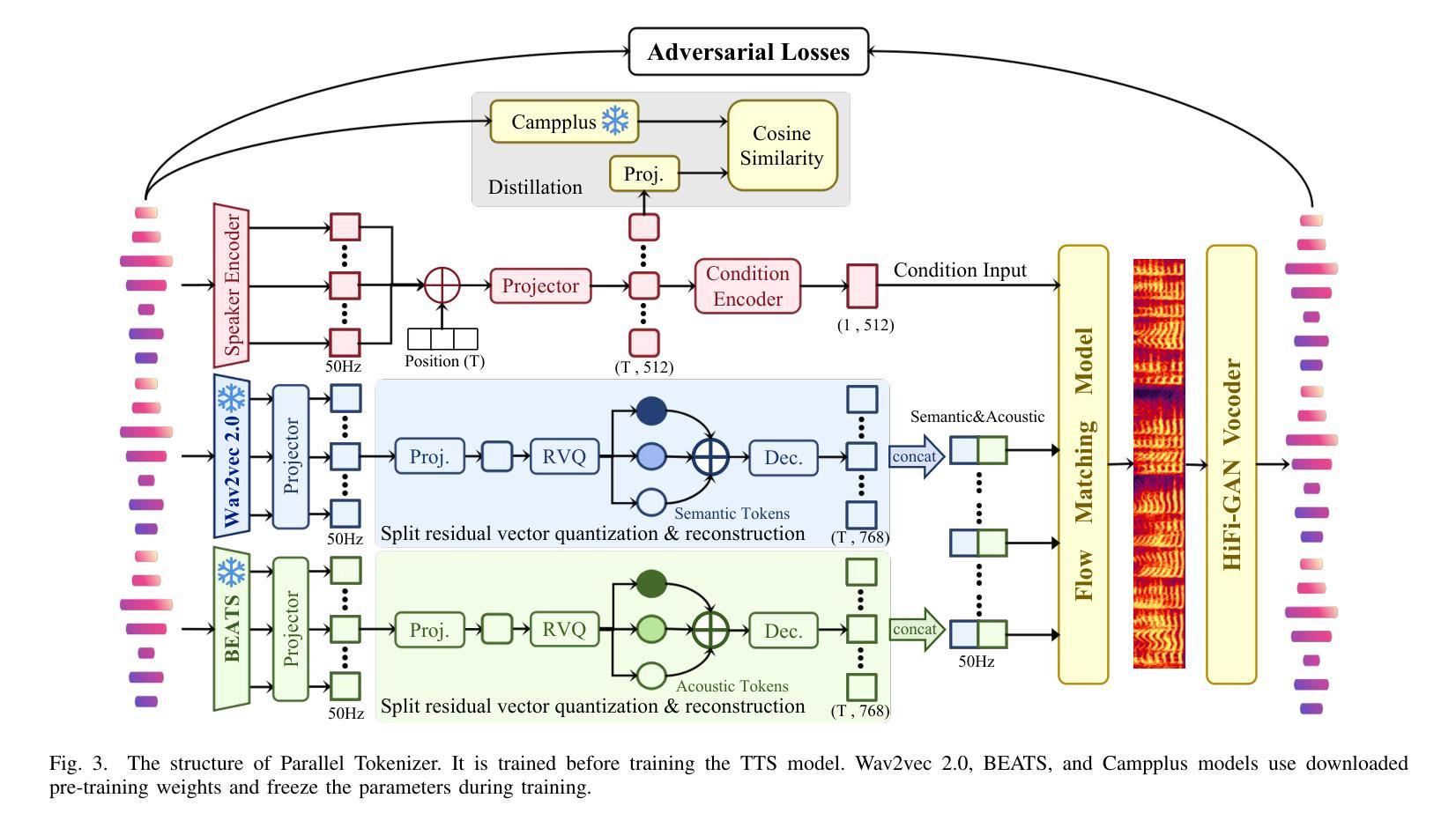
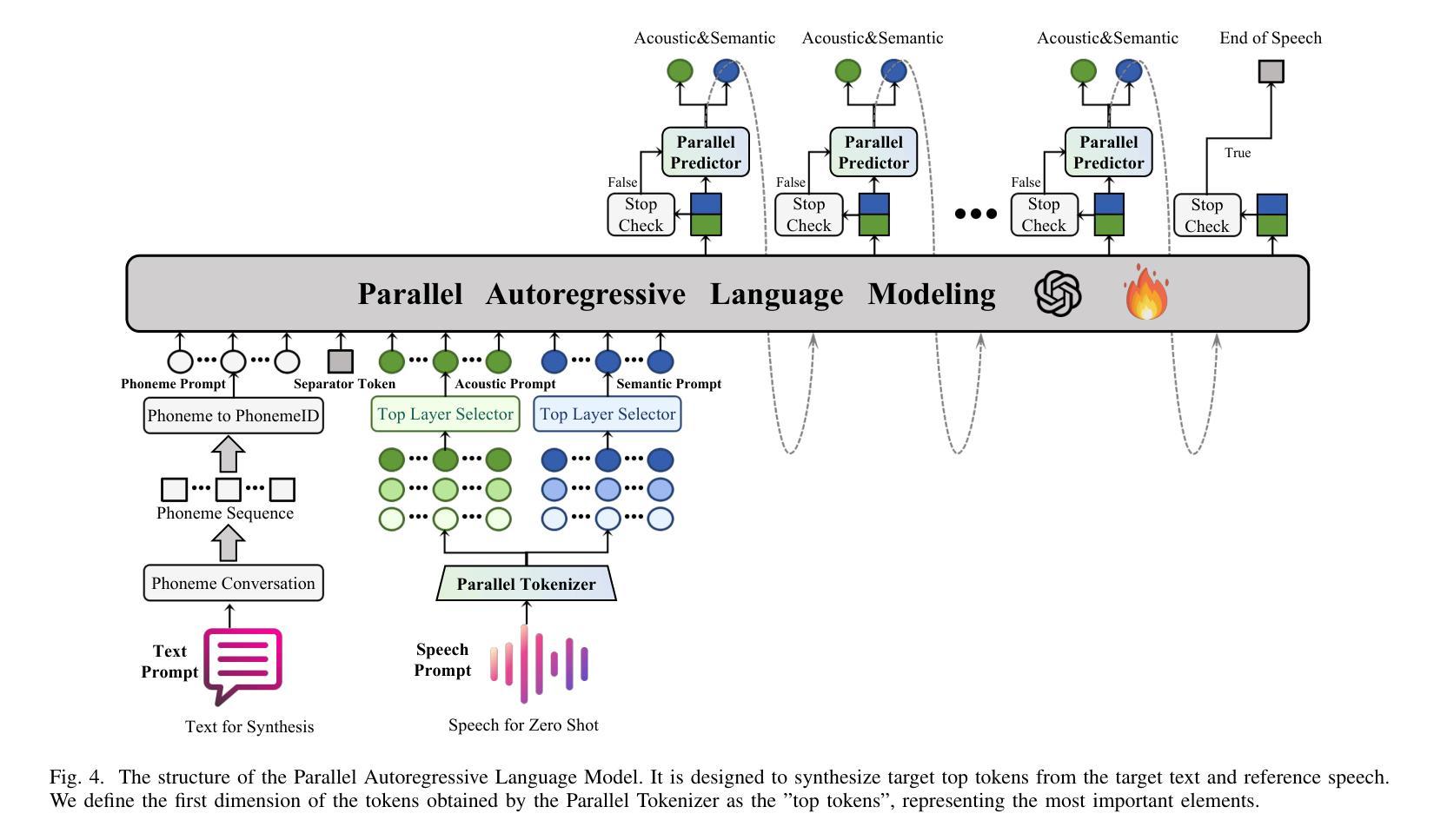
Parallel GPT: Harmonizing the Independence and Interdependence of Acoustic and Semantic Information for Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
Authors:Jingyuan Xing, Zhipeng Li, Jialong Mai, Xiaofen Xing, Xiangmin Xu
Advances in speech representation and large language models have enhanced zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) performance. However, existing zero-shot TTS models face challenges in capturing the complex correlations between acoustic and semantic features, resulting in a lack of expressiveness and similarity. The primary reason lies in the complex relationship between semantic and acoustic features, which manifests independent and interdependent aspects.This paper introduces a TTS framework that combines both autoregressive (AR) and non-autoregressive (NAR) modules to harmonize the independence and interdependence of acoustic and semantic information. The AR model leverages the proposed Parallel Tokenizer to synthesize the top semantic and acoustic tokens simultaneously. In contrast, considering the interdependence, the Coupled NAR model predicts detailed tokens based on the general AR model’s output. Parallel GPT, built on this architecture, is designed to improve zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis through its parallel structure. Experiments on English and Chinese datasets demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms the quality and efficiency of the synthesis of existing zero-shot TTS models. Speech demos are available at https://t1235-ch.github.io/pgpt/.
语音表示的进展和大语言模型的进步已经提高了零样本文本到语音(TTS)的性能。然而,现有的零样本TTS模型在捕捉声学特征和语义特征之间的复杂关联方面面临挑战,导致表现力不足和相似性不足。主要原因在于语义和声学特征之间的复杂关系,这表现出独立和相互依存的方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing (TASLP)
Summary
文本介绍了结合自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)模块的TTS框架,旨在调和声学语义信息的独立性和相互依赖性,从而提高零样本文本到语音合成的质量。该框架在英文和中文数据集上的实验表现均显著优于现有零样本TTS模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文本提到了现有的零样本文本到语音(TTS)模型面临的挑战,即捕捉声学语义特征的复杂关联性的困难,导致缺乏表达性和相似性。
- 介绍了新的TTS框架,该框架结合了自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)模块,旨在调和声学语义信息的独立性和相互依赖性。
- AR模型利用提出的并行分词器同时合成顶级语义和声音标记。
- 考虑相互依赖性,耦合的NAR模型基于AR模型的输出预测详细的标记。
- 基于此架构构建的并行GPT旨在通过其并行结构改进零样本文本到语音的合成。
- 在英文和中文数据集上的实验表明,该模型在合成质量和效率上都显著优于现有的零样本TTS模型。
点此查看论文截图

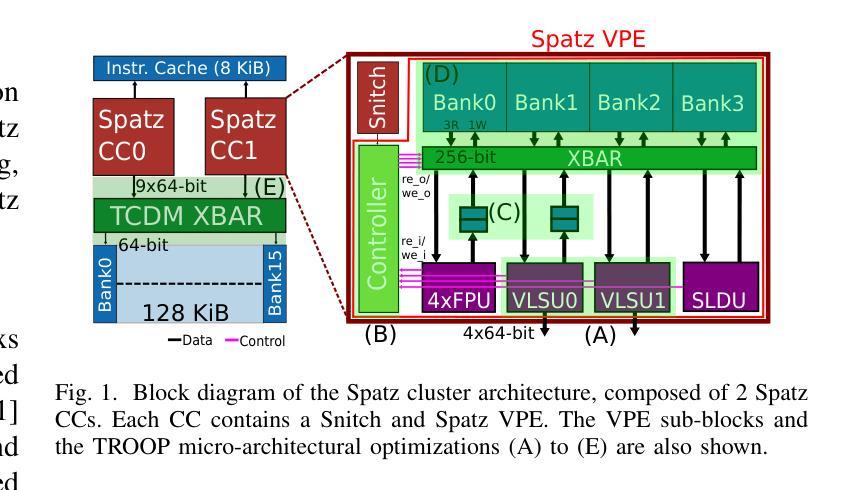
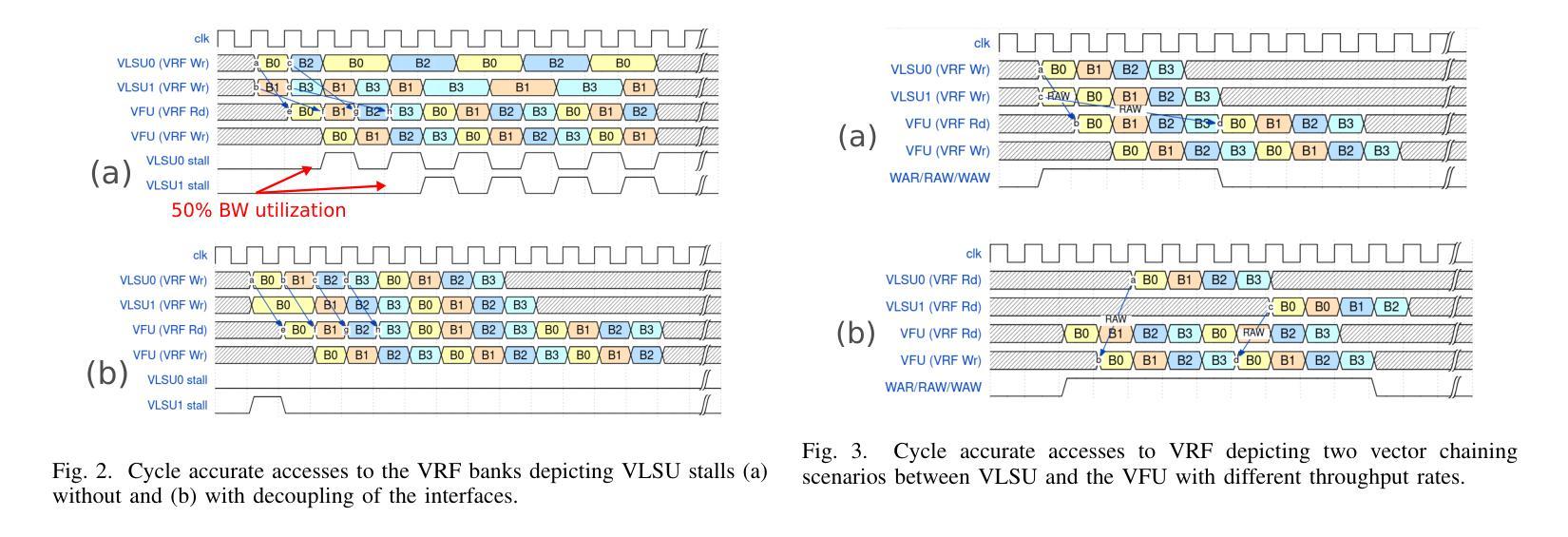
TROOP: At-the-Roofline Performance for Vector Processors on Low Operational Intensity Workloads
Authors:Navaneeth Kunhi Purayil, Diyou Shen, Matteo Perotti, Luca Benini
The fast evolution of Machine Learning (ML) models requires flexible and efficient hardware solutions as hardwired accelerators face rapid obsolescence. Vector processors are fully programmable and achieve high energy efficiencies by exploiting data parallelism, amortizing instruction fetch and decoding costs. Hence, a promising design choice is to build accelerators based on shared L1-memory clusters of streamlined Vector Processing Elements (VPEs). However, current state-of-the-art VPEs are limited in L1 memory bandwidth and achieve high efficiency only for computational kernels with high data reuse in the Vector Register File (VRF), such as General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM). Performance is suboptimal for workloads with lower data reuse like General Matrix-Vector Multiplication (GEMV). To fully exploit available bandwidth at the L1 memory interface, the VPE micro-architecture must be optimized to achieve near-ideal utilization, i.e., to be as close as possible to the L1 memory roofline (at-the-roofline). In this work, we propose TROOP, a set of hardware optimizations that include decoupled load-store interfaces, improved vector chaining, shadow buffers to hide VRF conflicts, and address scrambling techniques to achieve at-the-roofline performance for VPEs without compromising their area and energy efficiency. We implement TROOP on an open-source streamlined vector processor in a 12nm FinFET technology. TROOP achieves significant speedups of 1.5x, 2.2x, and 2.6x, respectively, for key memory-intensive kernels such as GEMV, DOTP and AXPY, achieving at-the-roofline performance. Additionally, TROOP enhances the energy efficiency by up to 45%, reaching 38 DP-GFLOPs/W (1 GHz, TT, 0.8V) for DOTP while maintaining a high energy efficiency of 61 DP-GFLOPs/W for GEMMs, incurring only a minor area overhead of less than 7%.
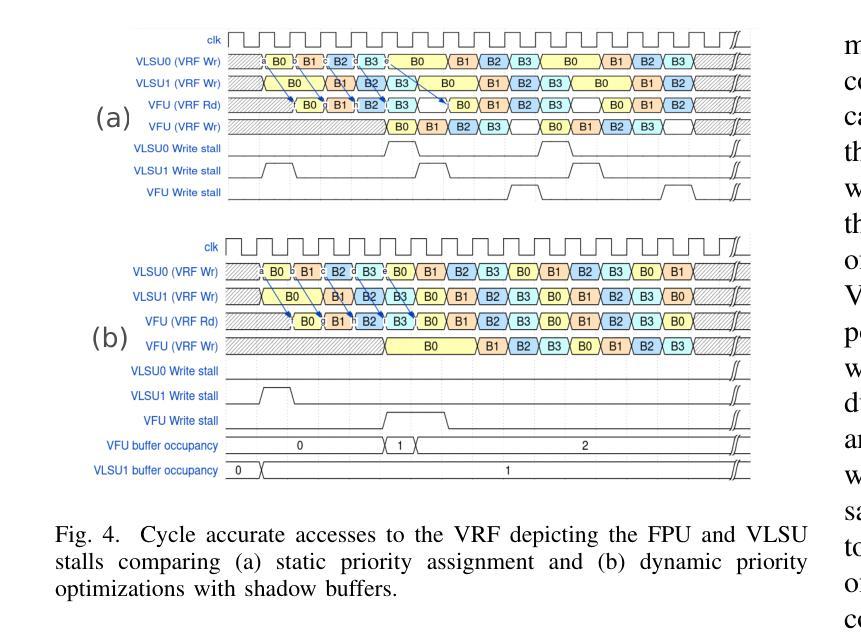
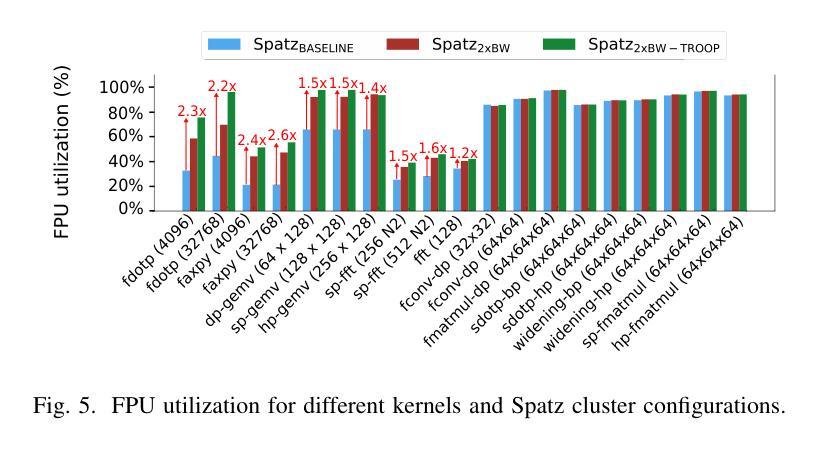
机器学习(ML)模型的快速进化要求灵活高效的硬件解决方案,因为专用硬件加速器面临迅速淘汰的问题。向量处理器具备完全可编程性,通过利用数据并行性并摊销指令获取和解码成本,实现了高能效。因此,一个有前途的设计选择是构建基于共享L1内存集群的流线型向量处理元素(VPE)的加速器。然而,目前最先进的VPE在L1内存带宽方面存在限制,仅对于在向量寄存器文件(VRF)中数据重用率高的计算内核(例如通用矩阵乘法(GEMM))才能实现高效率。对于工作量较小、数据重用率较低的任务(如通用矩阵向量乘法(GEMV))表现并不理想。为了充分利用L1内存接口可用的带宽,必须优化VPE的微观结构以实现近理想的利用率,即尽可能接近L1内存限制线(屋顶线)。在这项工作中,我们提出了TROOP,这是一组硬件优化措施,包括解耦的加载存储接口、改进的向量链、隐藏VRF冲突的阴影缓冲区以及地址扰乱技术,以实现VPE的理想性能,同时不损害其面积和能效。我们在采用开放源代码的流线型向量处理器和12纳米FinFET技术上实现了TROOP。TROOP针对关键内存密集型内核(如GEMV、DOTP和AXPY)实现了显著的速度提升,分别为原来的1.5倍、2.2倍和2.6倍,达到了理想性能。此外,TROOP提高了能效高达45%,在进行DOTP操作时达到每瓦38 DP-GFLOPs(在频率为每秒十亿次时),同时保持对GEMM的高能效为每瓦61 DP-GFLOPs。该设计仅有小于7%的面积开销。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in IEEE International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD) 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了机器学习模型的快速发展对硬件解决方案的灵活性和效率提出了更高的要求。向量处理器通过利用数据并行性实现高能效,针对此,一种有前景的设计是构建基于共享L1内存集群的流线型向量处理元素(VPE)。但现有VPE在L1内存带宽上存在局限,对于矩阵向量乘法等低数据复用工作负载性能不佳。为此,本文提出TROOP硬件优化方案,包括解耦负载存储接口、改进向量链、隐藏VRF冲突的影子缓冲区以及地址混淆技术,旨在实现接近L1内存带宽极限的理想利用,提高VPE性能。在12nm FinFET技术上实现的开源流线型处理器上应用TROOP后,针对关键内存密集型核心操作,如GEMV、DOTP和AXPY等,实现了显著的速度提升,并提高了能效。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习模型的快速发展要求硬件解决方案具备灵活性和高效率。
- 向量处理器通过数据并行性实现高能效,是硬件加速的一种有前途的设计。
- 当前向量处理器在L1内存带宽上存在局限,对于某些工作负载性能不佳。
- TROOP是一种硬件优化方案,旨在提高向量处理器的性能并接近L1内存带宽极限。
- TROOP包括解耦负载存储接口、改进向量链、隐藏VRF冲突的影子缓冲区以及地址混淆技术。
- 在开源流线型处理器上应用TROOP后,实现了对关键内存密集型核心操作的速度提升和能效提高。
点此查看论文截图

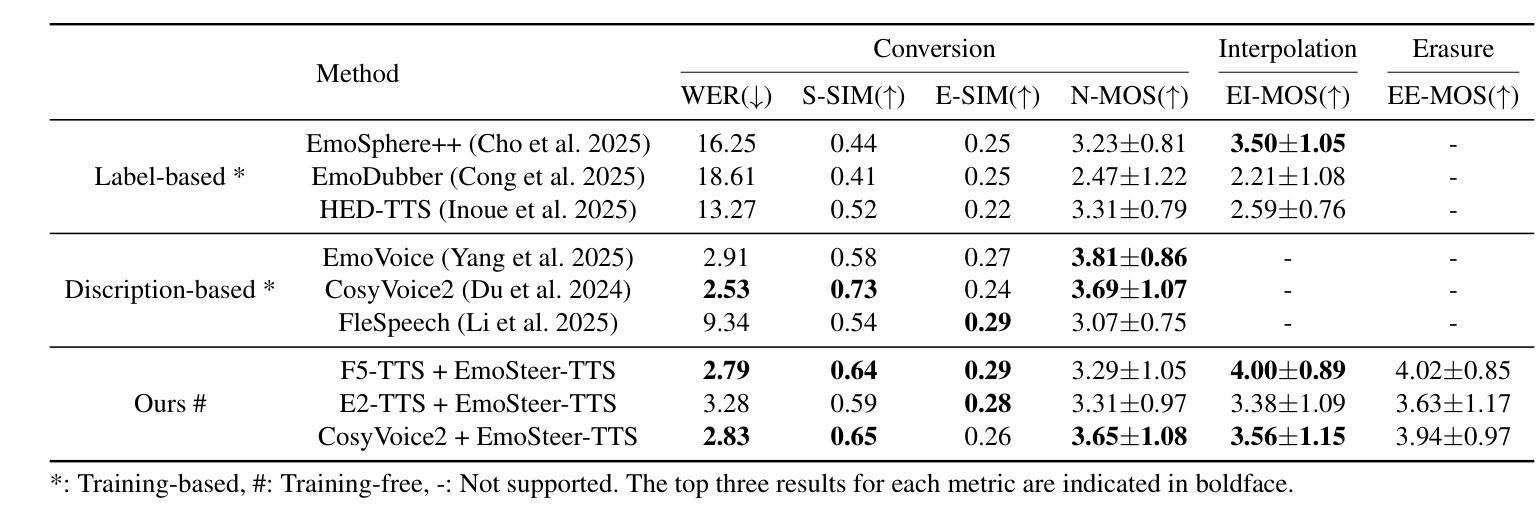
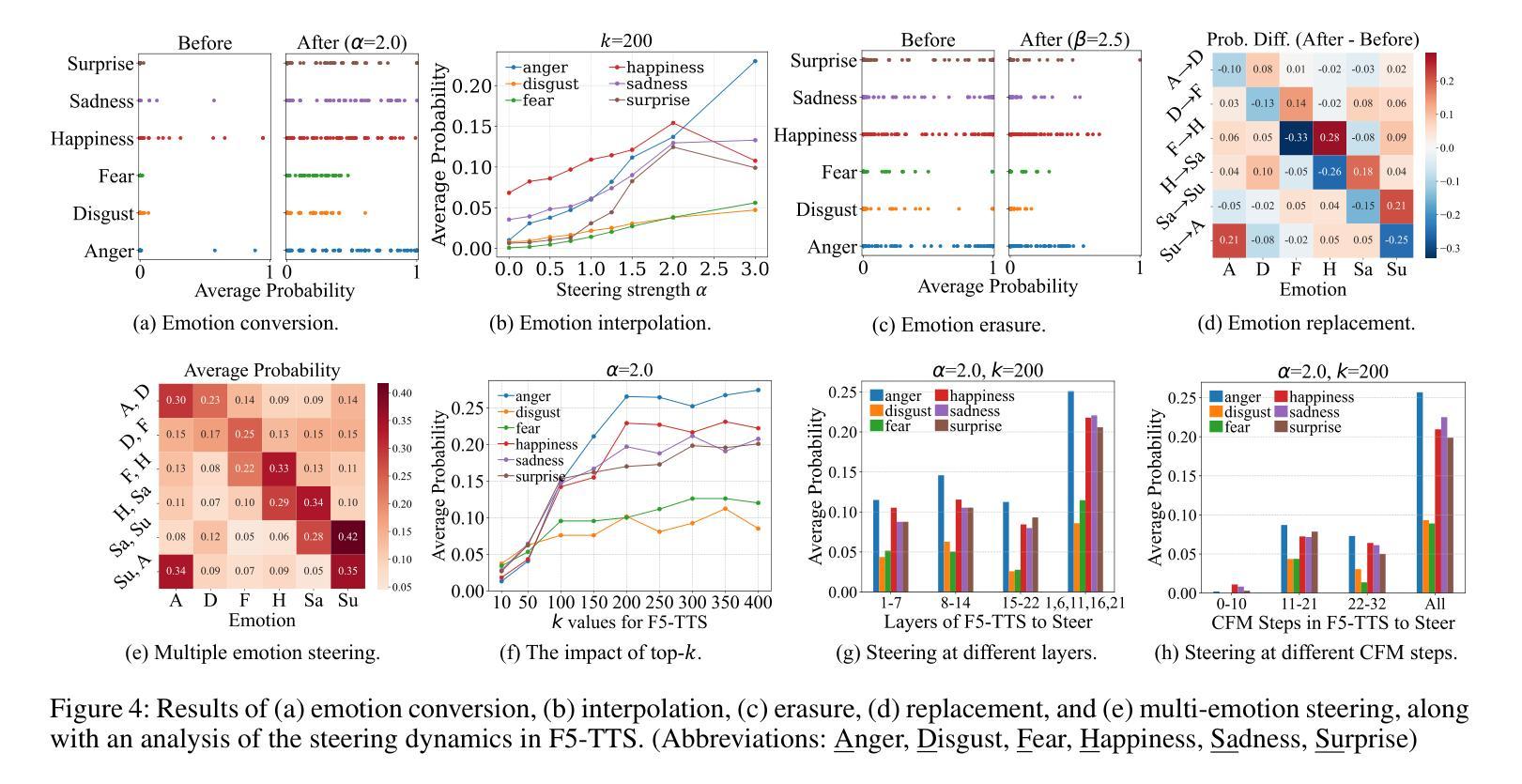
EmoSteer-TTS: Fine-Grained and Training-Free Emotion-Controllable Text-to-Speech via Activation Steering
Authors:Tianxin Xie, Shan Yang, Chenxing Li, Dong Yu, Li Liu
Text-to-speech (TTS) has shown great progress in recent years. However, most existing TTS systems offer only coarse and rigid emotion control, typically via discrete emotion labels or a carefully crafted and detailed emotional text prompt, making fine-grained emotion manipulation either inaccessible or unstable. These models also require extensive, high-quality datasets for training. To address these limitations, we propose EmoSteer-TTS, a novel training-free approach, to achieve fine-grained speech emotion control (conversion, interpolation, erasure) by activation steering. We first empirically observe that modifying a subset of the internal activations within a flow matching-based TTS model can effectively alter the emotional tone of synthesized speech. Building on this insight, we then develop a training-free and efficient algorithm, including activation extraction, emotional token searching, and inference-time steering, which can be seamlessly integrated into a wide range of pretrained models (e.g., F5-TTS, CosyVoice2, and E2-TTS). In addition, to derive effective steering vectors, we construct a curated emotional speech dataset with diverse speakers. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EmoSteer-TTS enables fine-grained, interpretable, and continuous control over speech emotion, outperforming the state-of-the-art (SOTA). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first method that achieves training-free and continuous fine-grained emotion control in TTS.
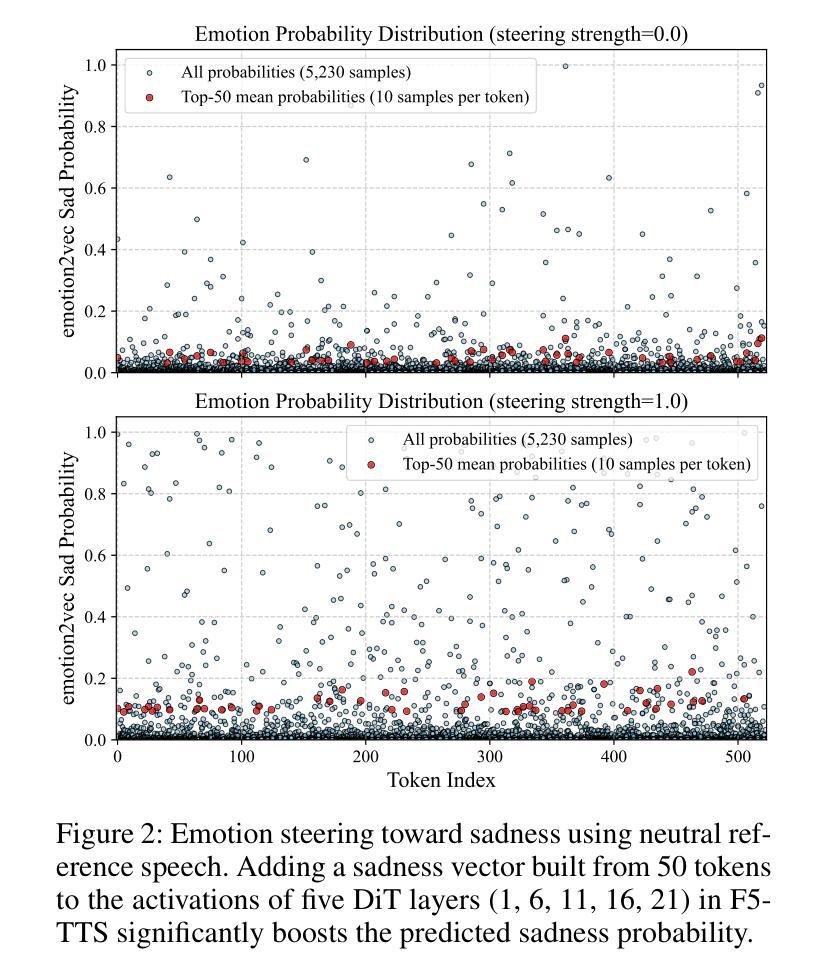
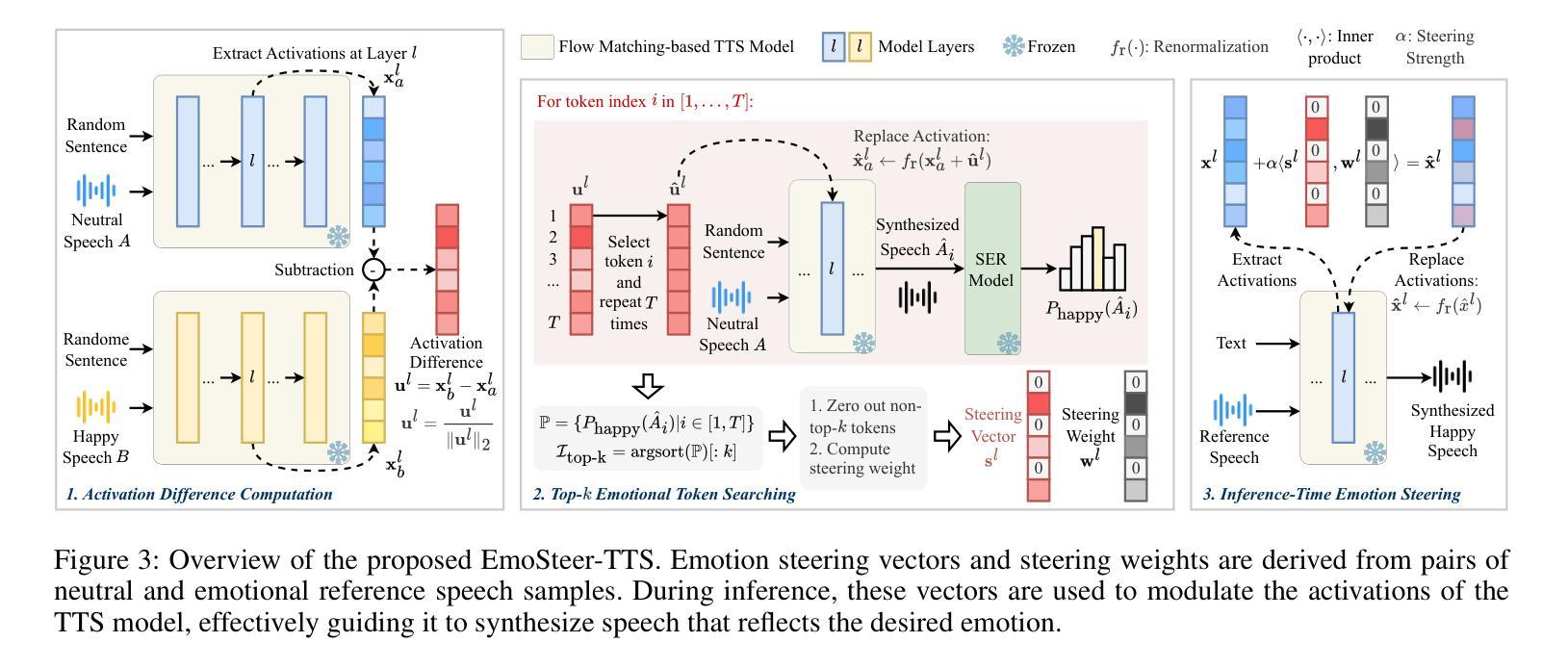
文本转语音(TTS)在最近几年取得了巨大的进步。然而,大多数现有的TTS系统只提供粗糙且僵化的情感控制,通常是通过离散的情绪标签或精心设计和详细的情绪文本提示来实现,这使得精细粒度的情感操控变得不可访问或不稳定。这些模型还需要大量高质量的数据集进行训练。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了EmoSteer-TTS,这是一种新型的无训练方法,通过激活控制来实现精细粒度的语音情感控制(转换、插值、擦除)。我们首先从实证上观察到,修改基于流匹配的TTS模型内部激活的一部分可以有效地改变合成语音的情感基调。基于这一见解,然后我们开发了一种无训练且高效的算法,包括激活提取、情感标记搜索和推理时间控制,该算法可以无缝集成到各种预训练模型(例如F5-TTS、CosyVoice2和E2-TTS)。此外,为了得出有效的控制向量,我们构建了一个包含多种说话人的精选情感语音数据集。大量实验表明,EmoSteer-TTS能够对语音情感进行精细、可解释和连续的控制,优于当前最佳水平。据我们所知,这是TTS中实现无训练和连续精细粒度情感控制的第一种方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对文本转语音(TTS)技术的最新研究成果。针对现有TTS系统在情绪控制方面的局限,研究团队提出了一种无需训练的TTS情感操控新方法——EmoSteer-TTS。通过激活调控,EmoSteer-TTS可以实现精细化的语音情感控制(转换、插值、消除)。该方法基于观察到一个现象:通过调整基于流匹配的TTS模型内部激活的一部分可以影响合成语音的情感调子。基于这一发现,研究团队开发了一种无需训练的高效算法,可广泛应用于各种预训练模型。此外,为了生成有效的调控向量,研究团队构建了一个包含多种说话人的精选情感语音数据集。实验证明,EmoSteer-TTS可实现精细、可解释、连续的情感控制,优于现有技术。这是首个实现无需训练且能连续进行精细化情感控制的TTS方法。
Key Takeaways
- EmoSteer-TTS是一种新型的无需训练的TTS情感操控方法,能够实现精细化的语音情感控制。
- 通过调整基于流匹配的TTS模型内部激活的一部分,可以影响合成语音的情感调子。
- EmoSteer-TTS包括激活提取、情感标记搜索和推理时调控等步骤,可无缝集成到各种预训练模型中。
- 研究团队构建了一个包含多种说话人的精选情感语音数据集,用于生成有效的调控向量。
- EmoSteer-TTS可实现精细、可解释、连续的情感控制,优于现有技术。
- EmoSteer-TTS是首个实现无需训练且能连续进行精细化情感控制的TTS方法。
点此查看论文截图

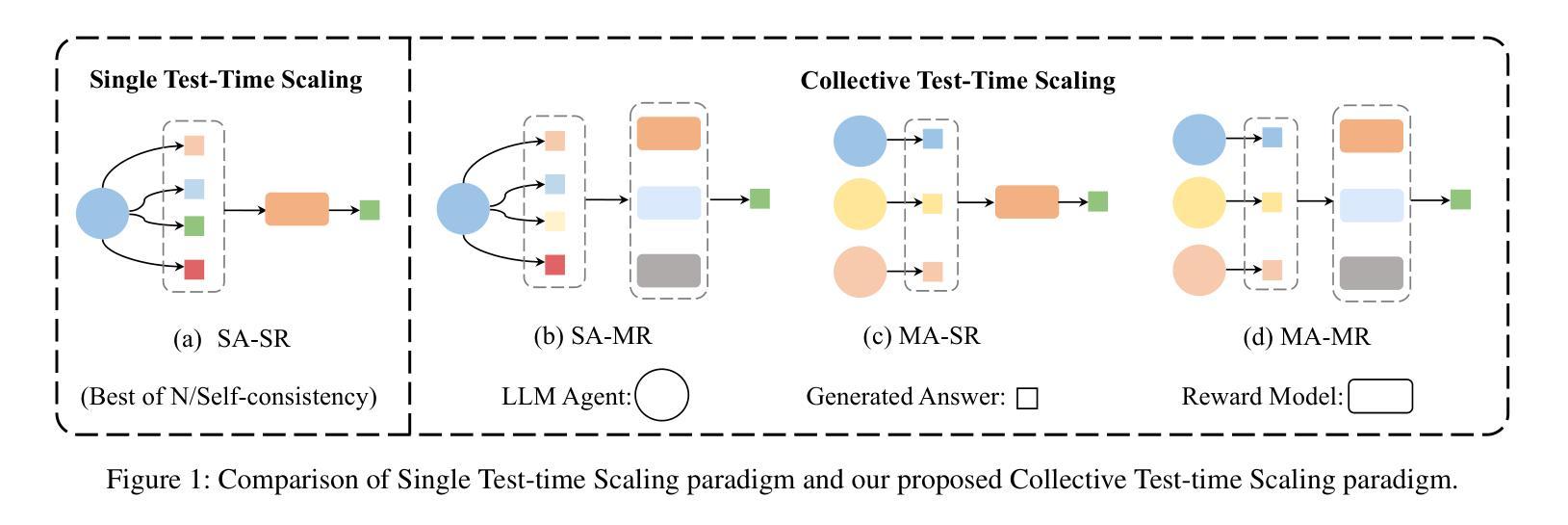
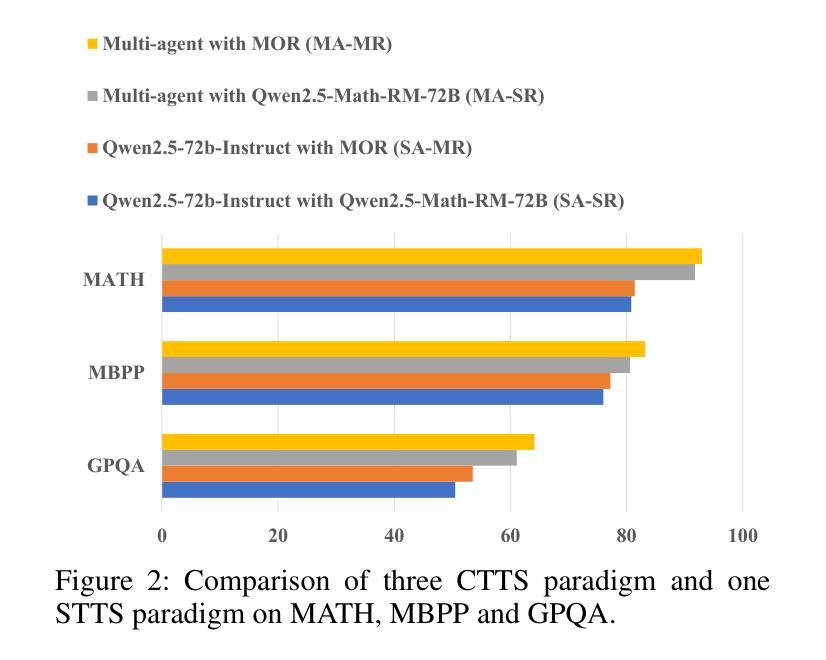
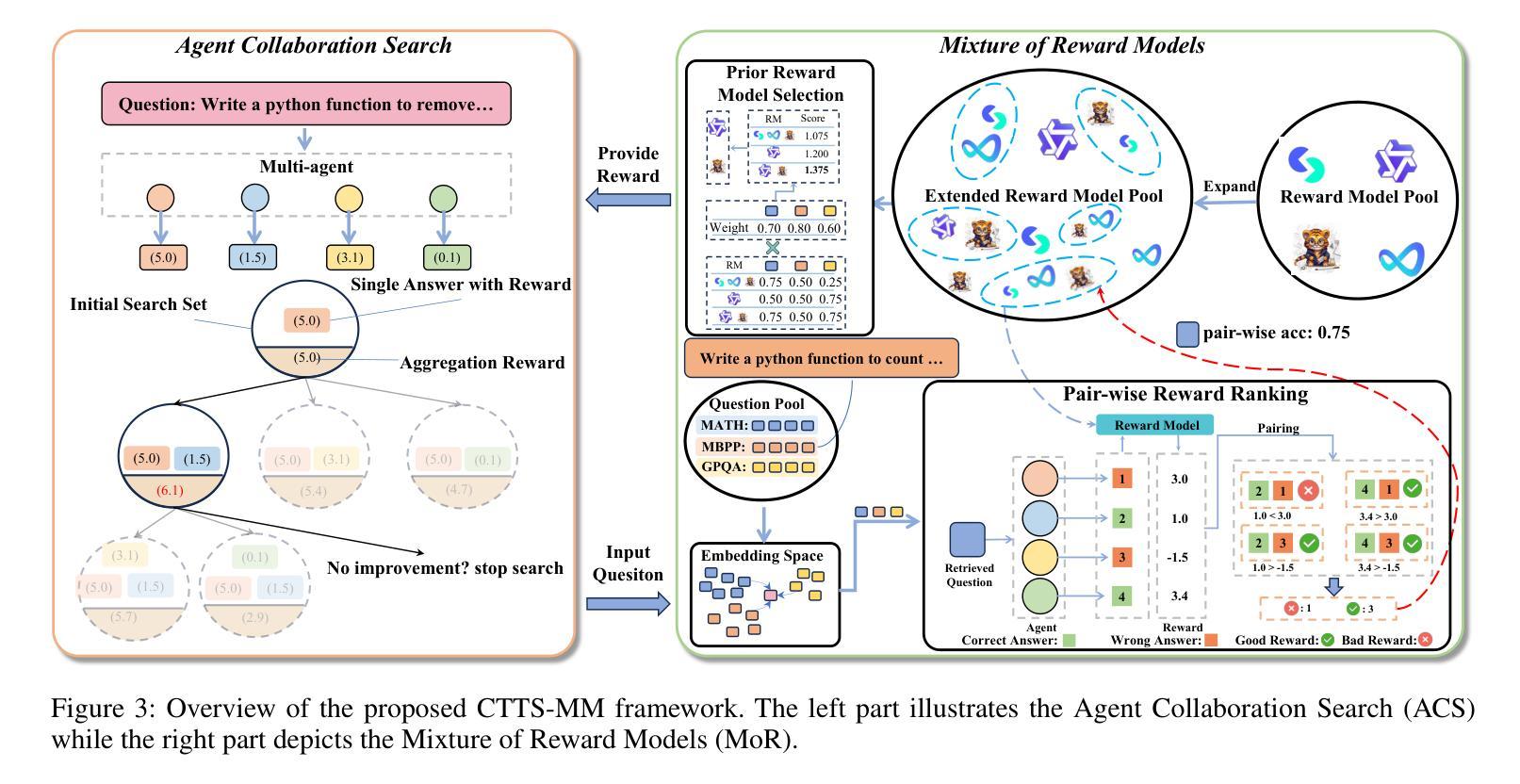
CTTS: Collective Test-Time Scaling
Authors:Zhende Song, Shengji Tang, Peng Ye, Jiayuan Fan, Tao Chen
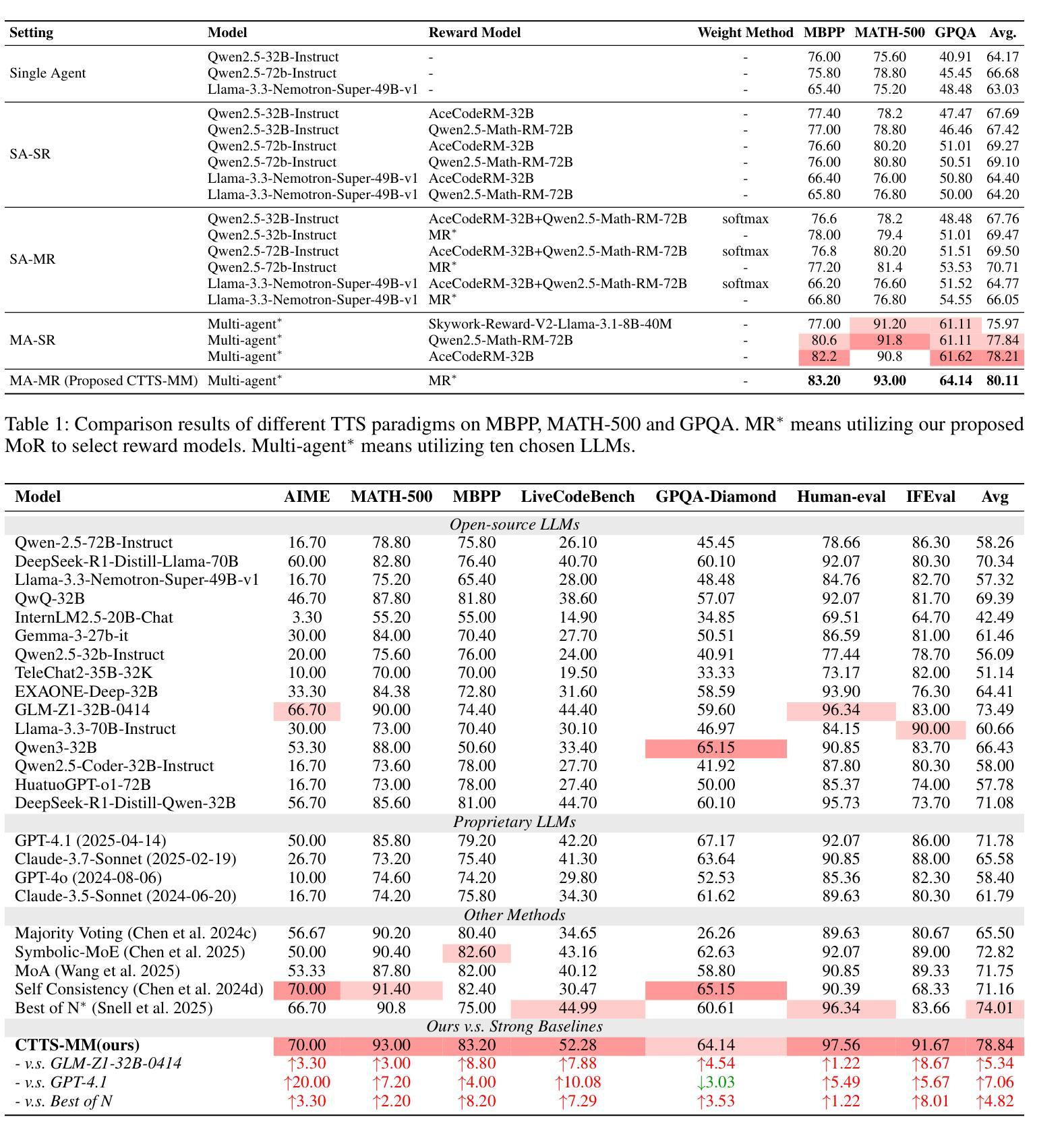
Test-time scaling (TTS) has emerged as a promising research field for enhancing the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) without extra training. However, most existing approaches, e.g., Best-of-N and Self-Consistency rely on a single agent interacting with a reward model (SA-SR), constrained by limited capabilities of a single test-time scaling (STTS) paradigm. On the other hand, recent works demonstrate that collective-agent methods can break through the upper bound of single-agent systems by orchestrating diverse models. Thus, in this paper, we take a first step towards exploring Collective Test-Time Scaling (CTTS). Consider the different interaction types of single and multiple models, we design three primary paradigms to investigate the optimal paradigm of CTTS: (1) single agent to multiple reward models (SA-MR); (2) multiple agents to single reward model (MA-SR); and (3) multiple agents to multiple reward models (MA-MR). Extensive experiments demonstrate that MA-MR consistently achieves the best performance. Based on this, we propose a novel framework named CTTS-MM that effectively leverages both multi-agent and multi-reward-model collaboration for enhanced inference. Specifically, for multi-agent collaboration, we propose an Agent Collaboration Search (ACS), which searches for the most effective combination of LLM agents from a large candidate pool; for multi-reward-model collaboration, we propose Mixture of Reword Models (MoR), which consists of a curated question pool and a Prior Reward model Ensemble Selection (PRES) to select the optimal combinations of reward models via Pair-wise Reward Ranking (PRR) metric. Experiments across seven mainstream benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed CTTS-MM consistently obtains superior performance. Code will be released at https://github.com/magent4aci/CTTS-MM.
测试时缩放(TTS)作为一个有前途的研究领域,无需额外训练即可提高大型语言模型(LLM)的有效性。然而,大多数现有方法,例如最佳N选和自一致性,都依赖于单个代理与奖励模型(SA-SR)进行交互,受限于单一的测试时缩放(STTS)模式的有限能力。另一方面,最近的研究表明,集体代理方法可以通过协调不同的模型突破单代理系统的上限。因此,本文朝着探索集体测试时缩放(CTTS)迈出了第一步。考虑到单个和多个模型的不同交互类型,我们设计了三种主要范式来研究CTTS的最佳范式:(1)单代理到多奖励模型(SA-MR);(2)多代理到单奖励模型(MA-SR);以及(3)多代理到多奖励模型(MA-MR)。大量实验表明,MA-MR持续取得最佳性能。基于此,我们提出了一个名为CTTS-MM的新型框架,它有效地利用多代理和多奖励模型的合作进行增强推理。具体来说,对于多代理协作,我们提出了代理协作搜索(ACS),它从大量候选池中搜索最有效的LLM代理组合;对于多奖励模型协作,我们提出了奖励模型混合物(MoR),它由一个精选的问题池和先验奖励模型集合选择(PRES)组成,通过配对奖励排名(PRR)指标选择最佳的奖励模型组合。在七个主流基准测试上的实验表明,所提出的CTTS-MM持续获得优越的性能。代码将在https://github.com/magent4aci/CTTS-MM发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了测试时缩放(Test-Time Scaling,简称TTS)在大型语言模型(LLM)中的应用。文章指出传统的TTS方法受限于单一测试时缩放(STTS)范式的能力,而集体测试时缩放(Collective Test-Time Scaling,简称CTTS)能突破单一代理系统的上限。文章通过探索三种主要的CTTS范式,提出一个名为CTTS-MM的新框架,该框架有效利用多代理和多奖励模型合作进行推断。通过大量实验验证,CTTS-MM在七个主流基准测试中表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放(TTS)是提高大型语言模型(LLM)效果的研究领域。
- 传统TTS方法受限于单一测试时缩放(STTS)范式的能力。
- 集体测试时缩放(CTTS)能突破单一代理系统的限制。
- 文章探索了三种主要的CTTS范式:SA-MR、MA-SR和MA-MR。
- MA-MR范式在实验中表现出最佳性能。
- 提出的CTTS-MM框架结合多代理和多奖励模型合作进行推断。
- CTTS-MM在七个主流基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

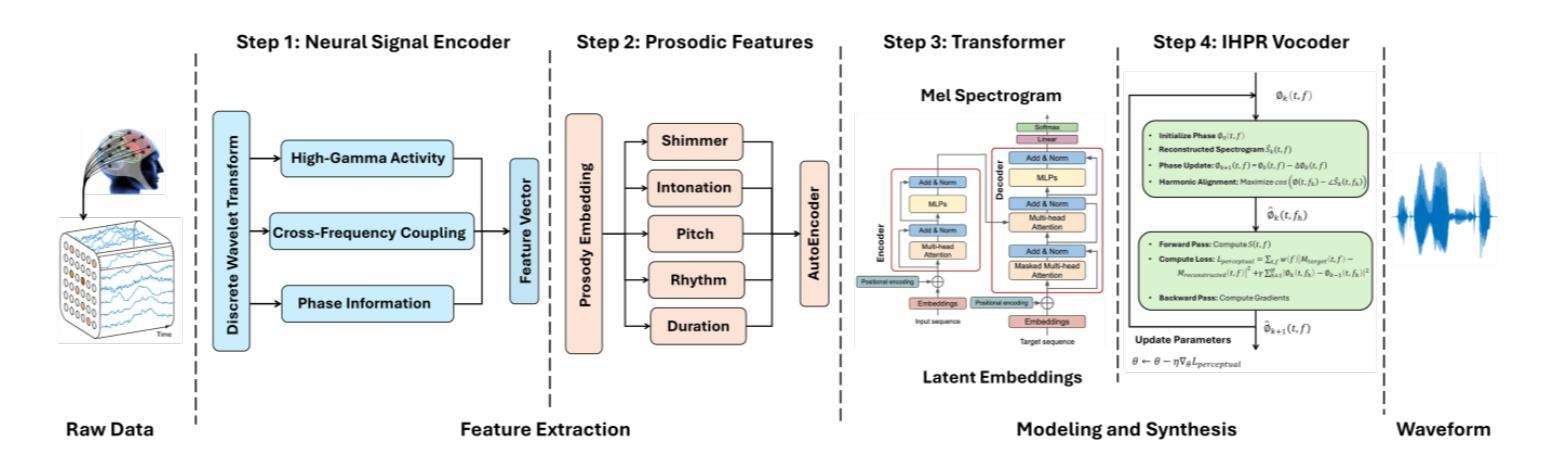
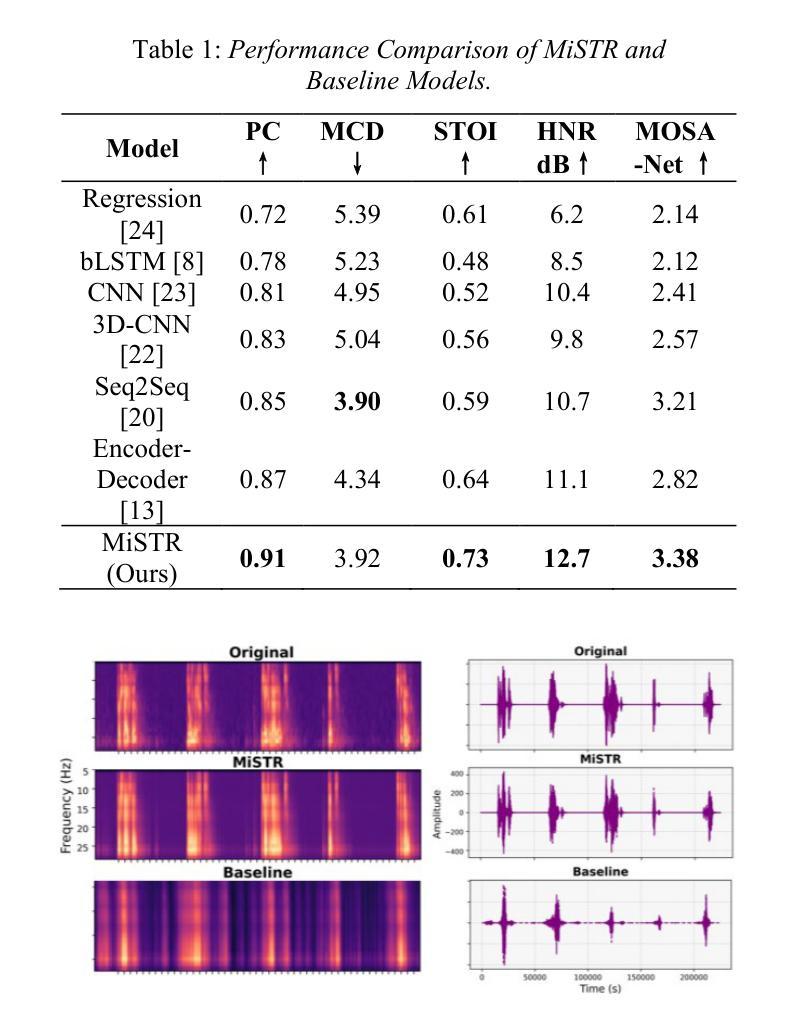
MiSTR: Multi-Modal iEEG-to-Speech Synthesis with Transformer-Based Prosody Prediction and Neural Phase Reconstruction
Authors:Mohammed Salah Al-Radhi, Géza Németh, Branislav Gerazov
Speech synthesis from intracranial EEG (iEEG) signals offers a promising avenue for restoring communication in individuals with severe speech impairments. However, achieving intelligible and natural speech remains challenging due to limitations in feature representation, prosody modeling, and phase reconstruction. We introduce MiSTR, a deep-learning framework that integrates: 1) Wavelet-based feature extraction to capture fine-grained temporal, spectral, and neurophysiological representations of iEEG signals, 2) A Transformer-based decoder for prosody-aware spectrogram prediction, and 3) A neural phase vocoder enforcing harmonic consistency via adaptive spectral correction. Evaluated on a public iEEG dataset, MiSTR achieves state-of-the-art speech intelligibility, with a mean Pearson correlation of 0.91 between reconstructed and original Mel spectrograms, improving over existing neural speech synthesis baselines.
从颅内脑电图(iEEG)信号进行语音合成,为患有严重语言障碍的人恢复交流提供了有希望的途径。然而,由于特征表示、韵律建模和相位重建等方面的局限性,实现可理解和自然的语音仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了MiSTR,这是一个深度学习框架,它集成了:1)基于小波的特征提取,用于捕获iEEG信号的细粒度时间、频谱和神经生理表示;2)基于变压器的解码器,用于具有韵律感知的频谱图预测;3)神经相位编码器通过自适应光谱校正来强制执行谐波一致性。在公共iEEG数据集上评估,MiSTR达到了最先进的语音可懂度,重建的Mel频谱图与原始Mel频谱图之间的平均Pearson相关性为0.91,超过了现有的神经语音合成基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures, 1 table. Accepted for presentation at Interspeech 2025
摘要
基于颅内脑电图(iEEG)信号的语音合成对于恢复严重言语障碍者的交流能力具有广阔前景。然而,由于特征表示、语调建模和相位重建方面的局限性,实现可理解和自然的语音仍然具有挑战性。本研究引入MiSTR深度框架,集成以下技术:1)基于小波的特征提取,捕捉iEEG信号的细粒度时间、频谱和神经生理学表示;2)基于Transformer的解码器,用于语调感知频谱预测;3)神经相位编码器,通过自适应谱校正实现谐波一致性。在公共iEEG数据集上的评估显示,MiSTR在语音清晰度方面达到最新水平,重建的Mel频谱图与原始Mel频谱图之间的平均Pearson相关系数为0.91,超过了现有的神经网络语音合成基线。
要点
- 颅内脑电图(iEEG)信号语音合成具有恢复严重言语障碍者交流能力的潜力。
- 当前面临的挑战包括特征表示、语调建模和相位重建。
- MiSTR框架集成了基于小波的特征提取,捕捉iEEG信号的细粒度表示。
- 采用基于Transformer的解码器进行语调感知频谱预测。
- 神经相位编码器通过自适应谱校正实现谐波一致性。
- 在公共iEEG数据集上的评估显示MiSTR达到最新语音清晰度水平。
点此查看论文截图

Fine-Tuning Text-to-Speech Diffusion Models Using Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback
Authors:Jingyi Chen, Ju Seung Byun, Micha Elsner, Pichao Wang, Andrew Perrault
Diffusion models produce high-fidelity speech but are inefficient for real-time use due to long denoising steps and challenges in modeling intonation and rhythm. To improve this, we propose Diffusion Loss-Guided Policy Optimization (DLPO), an RLHF framework for TTS diffusion models. DLPO integrates the original training loss into the reward function, preserving generative capabilities while reducing inefficiencies. Using naturalness scores as feedback, DLPO aligns reward optimization with the diffusion model’s structure, improving speech quality. We evaluate DLPO on WaveGrad 2, a non-autoregressive diffusion-based TTS model. Results show significant improvements in objective metrics (UTMOS 3.65, NISQA 4.02) and subjective evaluations, with DLPO audio preferred 67% of the time. These findings demonstrate DLPO’s potential for efficient, high-quality diffusion TTS in real-time, resource-limited settings.
扩散模型虽然能够生成高保真度的语音,但由于去噪步骤长且建模音调和节奏具有挑战性,因此在实际使用场景中效率较低。为了改善这一点,我们提出了基于扩散模型的损失引导策略优化(DLPO),这是一个用于TTS扩散模型的RLHF框架。DLPO将原始训练损失集成到奖励函数中,既保留了生成能力又提高了效率。通过使用自然度分数作为反馈,DLPO使奖励优化与扩散模型的结构相匹配,提高了语音质量。我们在WaveGrad 2这个非自回归的基于扩散的TTS模型上评估了DLPO。结果显示,在客观指标(UTMOS 3.65,NISQA 4.02)和主观评估上,DLPO音频的偏好率高达67%。这些发现证明了DLPO在实时、资源有限的场景中实现高效、高质量的扩散TTS的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 1 figure, INTERSPEECH 2025. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2405.14632
Summary
扩散模型能够生成高保真度的语音,但由于去噪步骤长且难以对语调、节奏进行建模,因此不适用于实时使用。为此,我们提出了基于强化学习的人类反馈框架Diffusion Loss-Guided Policy Optimization (DLPO),用于改善TTS扩散模型的效率。DLPO将原始训练损失集成到奖励函数中,既保留了生成能力又提高了效率。利用自然度评分作为反馈,DLPO使奖励优化与扩散模型结构对齐,提高了语音质量。我们在非自回归扩散式TTS模型WaveGrad 2上评估了DLPO的效果,结果显示客观指标(UTMOS 3.65,NISQA 4.02)和主观评价均有显著提高,DLPO音频的优选率为67%。这表明DLPO在实时、资源有限的设置中,具有实现高效、高质量扩散TTS的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型虽能生成高保真语音,但存在实时使用效率低的问题,主要由于去噪步骤长及建模语调、节奏的挑战。
- 提出基于强化学习人类反馈的DLPO框架,旨在改善TTS扩散模型的效率。
- DLPO将原始训练损失集成到奖励函数中,在提高效率的同时保留生成能力。
- 利用自然度评分作为反馈,使奖励优化与扩散模型结构对齐,提升语音质量。
- 在WaveGrad 2模型上评估DLPO,客观指标和主观评价均显示显著改善。
- DLPO音频的优选率高达67%,表明其在实时、资源有限环境下的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图


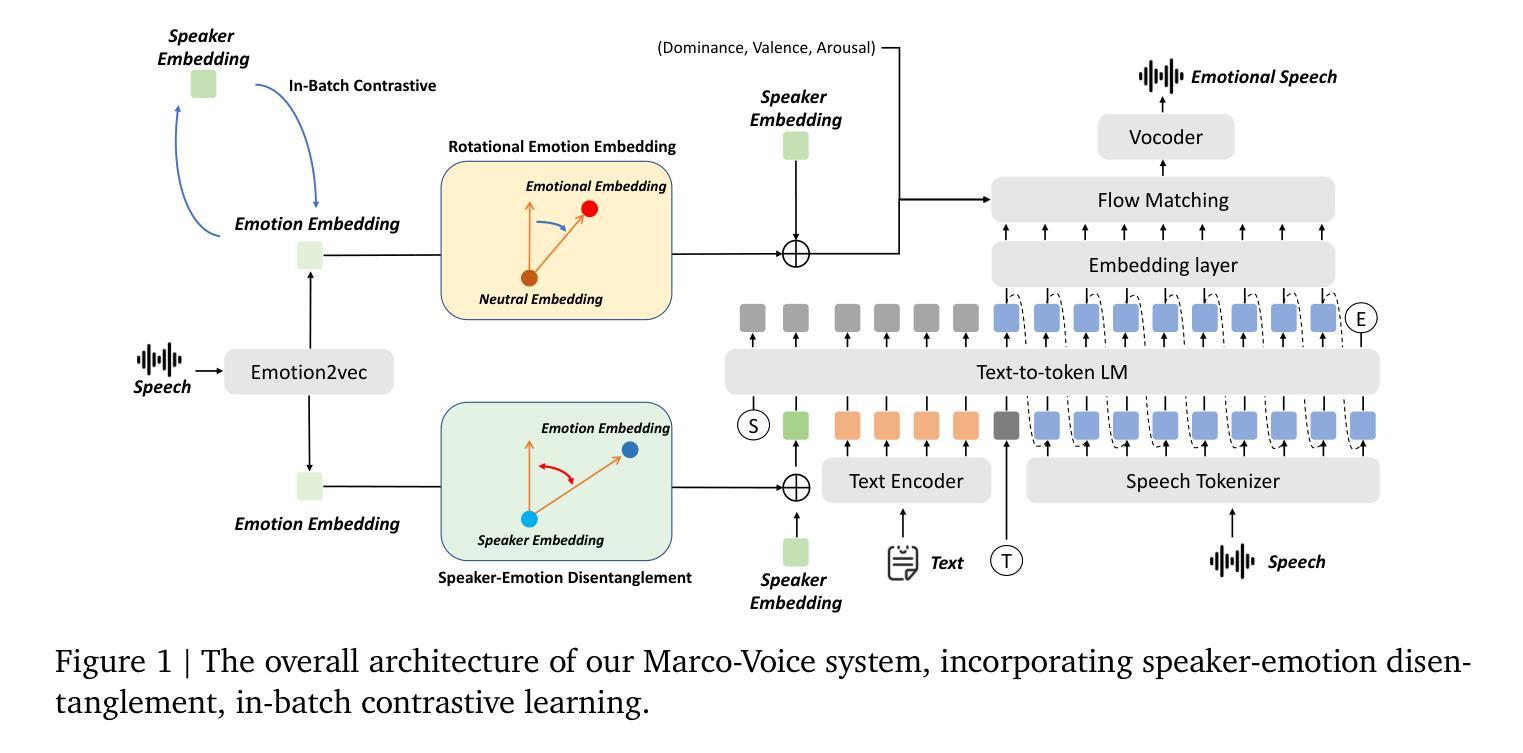
Marco-Voice Technical Report
Authors:Fengping Tian, Chenyang Lyu, Xuanfan Ni, Haoqin Sun, Qingjuan Li, Zhiqiang Qian, Haijun Li, Longyue Wang, Zhao Xu, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang
This paper presents a multifunctional speech synthesis system that integrates voice cloning and emotion control speech synthesis within a unified framework. The goal of this work is to address longstanding challenges in achieving highly expressive, controllable, and natural speech generation that faithfully preserves speaker identity across diverse linguistic and emotional contexts. Our approach introduces an effective speaker-emotion disentanglement mechanism with in-batch contrastive learning, enabling independent manipulation of speaker identity and eemotional style, as well as rotational emotional embedding integration method for smooth emotion control. To support comprehensive training and evaluation, we construct CSEMOTIONS, a high-quality emotional speech dataset containing 10 hours of Mandarin speech from six professional speakers across seven emotional categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our system, Marco-Voice, achieves substantial improvements in both objective and subjective metrics. Comprehensive evaluations and analysis were conducted, results show that MarcoVoice delivers competitive performance in terms of speech clarity and emotional richness, representing a substantial advance in the field of expressive neural speech synthesis. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice and https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS respectively.
本文介绍了一个多功能语音合成系统,该系统在一个统一框架内集成了语音克隆和情感控制语音合成。本工作的目标是解决长期以来在实现高度表达、可控和自然语音生成方面所面临的挑战,忠实地在各种语言和情感背景下保留说话者身份。我们的方法引入了一种有效的说话人情感分离机制,采用批量对比学习,实现对说话人身份和情感风格的独立操作,以及用于平滑情感控制的旋转情感嵌入集成方法。为了支持全面的训练和评估,我们构建了CSEMOTIONS数据集,这是一个高质量的情感语音数据集,包含六名专业说话人10小时的普通话语音,跨越七个情感类别。大量实验表明,我们的Marco-Voice系统在客观和主观指标上取得了显著改进。进行了全面的评估和分析,结果表明MarcoVoice在语音清晰度和情感丰富度方面表现出竞争力,代表了神经语音合成领域的重大进展。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice和https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice and https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS respectively
Summary
本文介绍了一个多功能语音合成系统,该系统整合了语音克隆和情感控制语音合成在一个统一框架内。旨在解决长期存在的挑战,实现高度表达、可控、自然的语音生成,忠实保留说话者身份在不同语言和情感背景中。通过引入有效的说话人情感分离机制和旋转情感嵌入集成方法,实现对说话人身份和情感风格的独立操控。为支持全面的训练和评估,构建了高质量的情感语音数据集CSEMOTIONS。实验表明,Marco-Voice系统在客观和主观指标上取得显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了多功能语音合成系统,整合语音克隆和情感控制语音合成。
- 目标实现高度表达、可控、自然的语音生成。
- 引入有效的说话人情感分离机制,实现说话人身份和情感风格的独立操控。
- 采用旋转情感嵌入集成方法,用于平稳情感控制。
- 构建了高质量的情感语音数据集CSEMOTIONS。
- Marco-Voice系统在客观和主观指标上取得显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

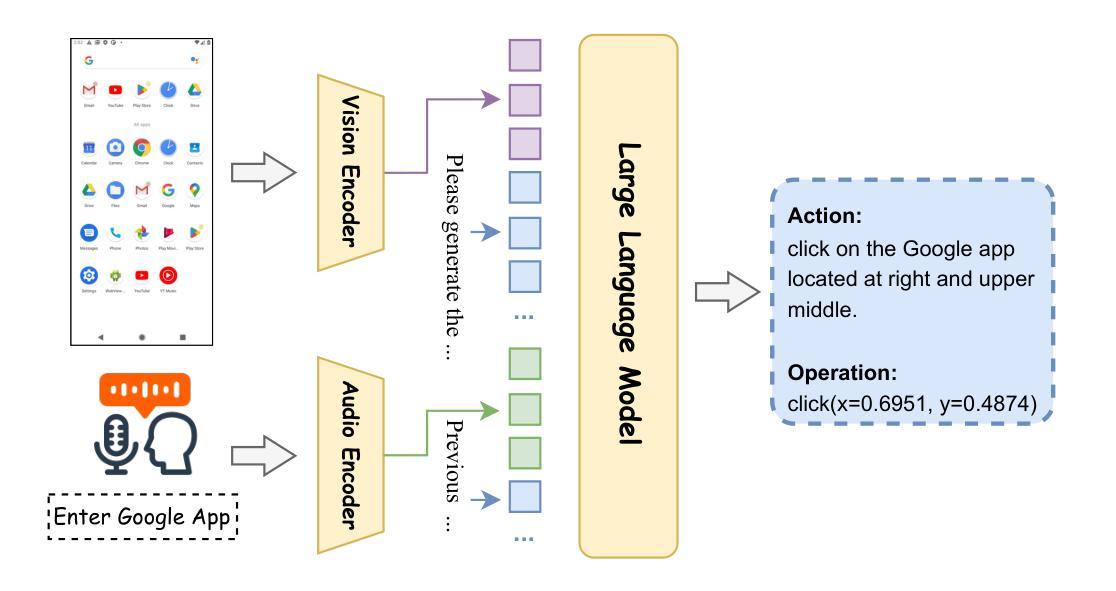
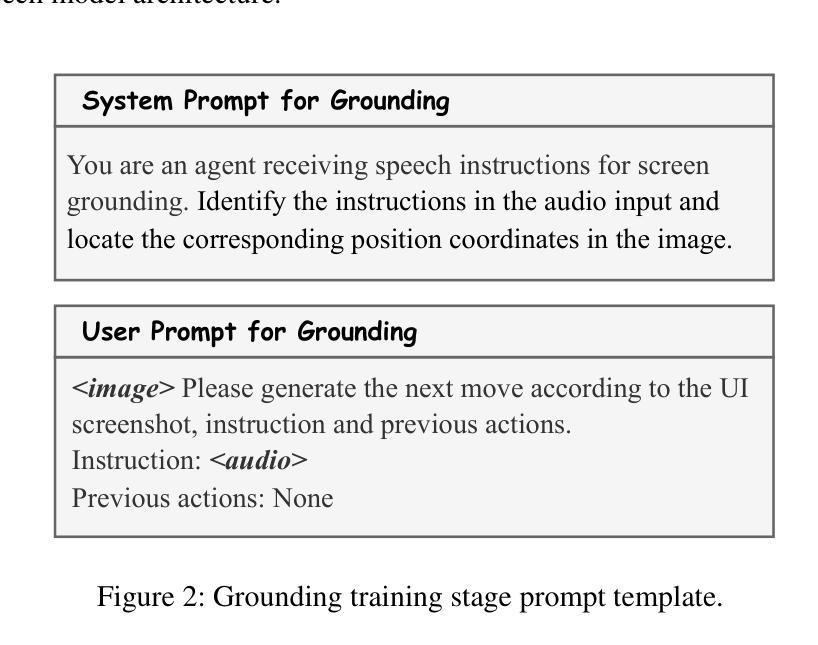
UITron-Speech: Towards Automated GUI Agents Based on Speech Instructions
Authors:Wenkang Han, Zhixiong Zeng, Jing Huang, Shu Jiang, Liming Zheng, Haibo Qiu, Chang Yao, Jingyuan Chen, Lin Ma
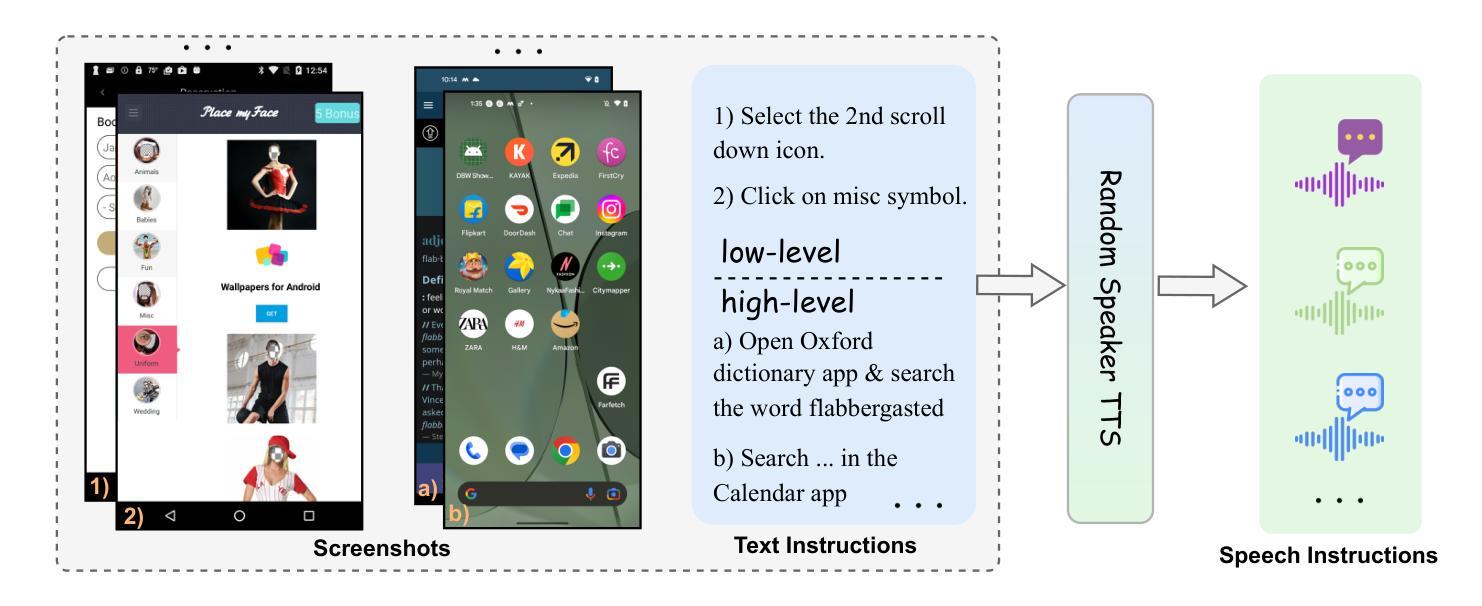
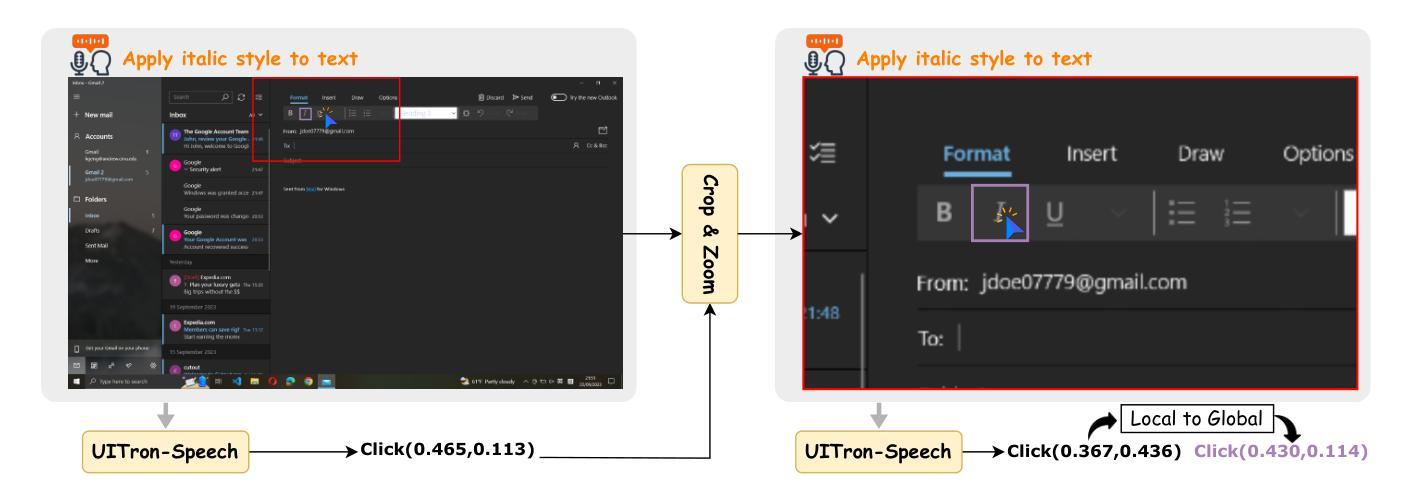
Autonomous agents for Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) are revolutionizing human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based instructions imposes limitations on accessibility and convenience, particularly in hands-free scenarios. To address this issue, we propose replacing text with speech as the instruction input modality for GUI agents, and introduce UITron-Speech, which is the first end-to-end GUI agent capable of directly processing speech instructions and on-device screenshots to predict user actions. To tackle the problem of data scarcity, we synthesize high-quality speech instruction datasets using a random-speaker text-to-speech model. Additionally, we design a mixed-modality training strategy to mitigate the inherent modality imbalance in pre-trained foundation models. Furthermore, we conduct a statistical analysis of the distribution of GUI grounding prediction errors and propose a training-free two-step grounding refinement method to alleviate minor localization deviations. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that UITron-Speech achieves robust performance and superior adaptability, underscoring the feasibility and potential of speech-driven GUI agents for more accessible and intelligent human-computer interaction. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/UITron-hub/UITron-Speech.
图形用户界面(GUI)的自主代理正在彻底改变人机交互的方式,然而它们对基于文本的指令的依赖,对无障碍和便捷性造成了限制,特别是在免提场景中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出用语音替换文本作为GUI代理的指令输入模式,并引入了UITron-Speech。它是首款能够直接处理语音指令和设备截图的端到端GUI代理,以预测用户操作。为了解决数据稀缺的问题,我们使用随机说话人文本到语音模型合成高质量语音指令数据集。此外,我们设计了一种混合模式训练策略,以缓解预训练基础模型中的固有模式不平衡问题。我们还对GUI接地预测误差的分布进行了统计分析,并提出了无需训练的两步接地细化方法,以减轻轻微的定位偏差。在多个基准测试上的大量实验表明,UITron-Speech实现了稳健的性能和优越的适应性,凸显了语音驱动GUI代理的可行性和潜力,为更无障碍和智能的人机交互提供了可能。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/UITron-hub/UITron-Speech找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音驱动的GUI代理技术正在改变人机交互方式。为解决文本指令带来的访问和便利性限制问题,我们提出了使用语音作为GUI代理的指令输入模式,并引入了UITron-Speech。它是第一个能够直接处理语音指令和设备截图的端到端GUI代理,可预测用户操作。通过合成高质量语音指令数据集和混合模态训练策略解决数据稀缺和模态不平衡问题。对GUI定位预测误差进行统计分析,并提出两步定位细化方法以减轻轻微定位偏差。实验结果证明了UITron-Speech的稳健性能和卓越适应性,展现了语音驱动GUI代理在实现更智能和可访问的人机交互中的潜力和可行性。我们的代码和数据集可在 https://github.com/UITron-hub/UITron-Speech 获得。
Key Takeaways
- 语音驱动的GUI代理技术正在改变人机交互方式,提高了访问性和便利性。
- UITron-Speech是首个能够直接处理语音指令和设备截图的端到端GUI代理。
- 通过合成高质量语音指令数据集解决数据稀缺问题。
- 提出了混合模态训练策略以解决预训练基础模型中的模态不平衡问题。
- 对GUI定位预测误差进行统计分析,并提出两步定位细化方法以减轻定位偏差。
- UITron-Speech具有稳健性能和卓越适应性,验证了语音驱动GUI代理的潜力和可行性。
点此查看论文截图

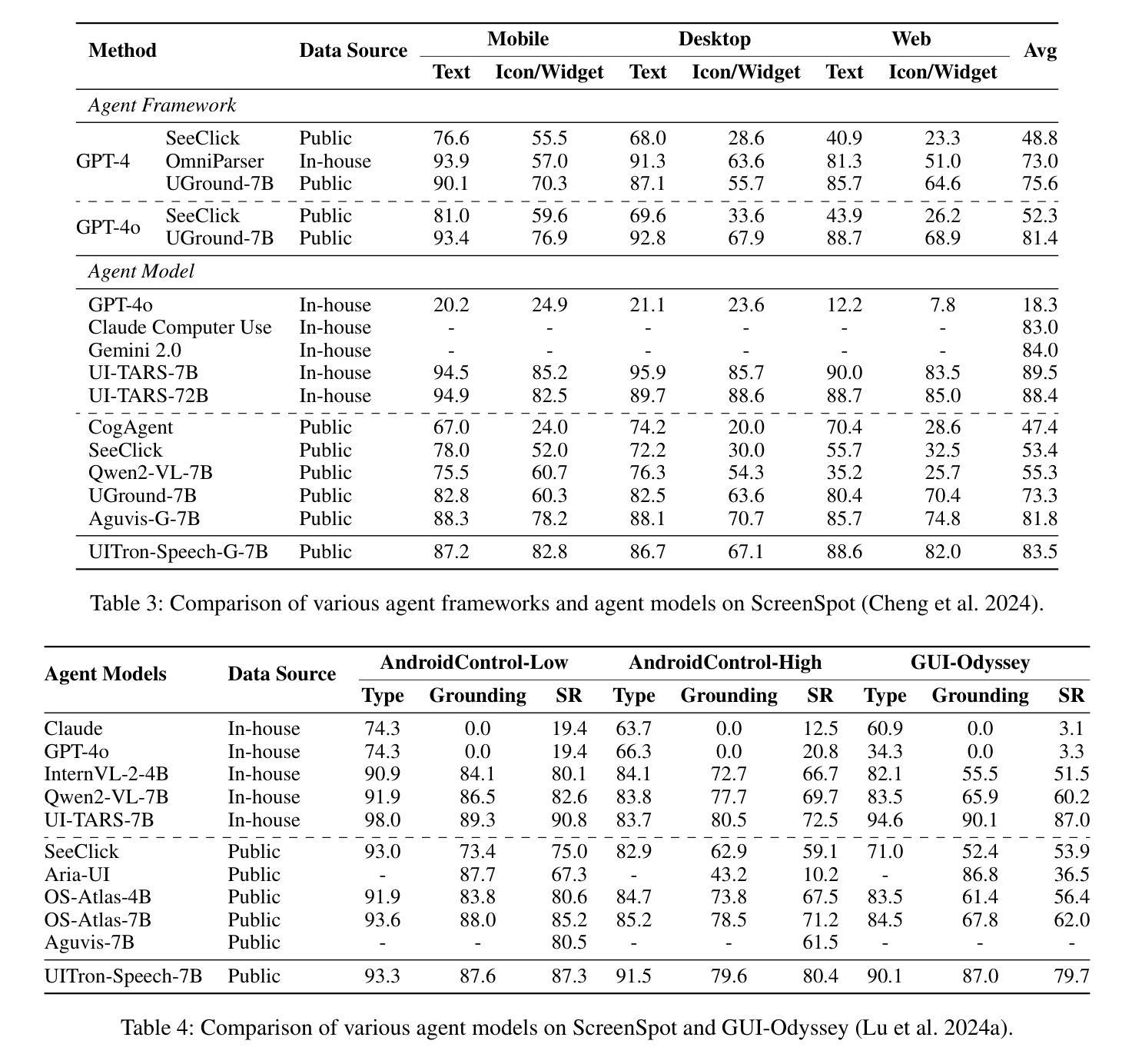
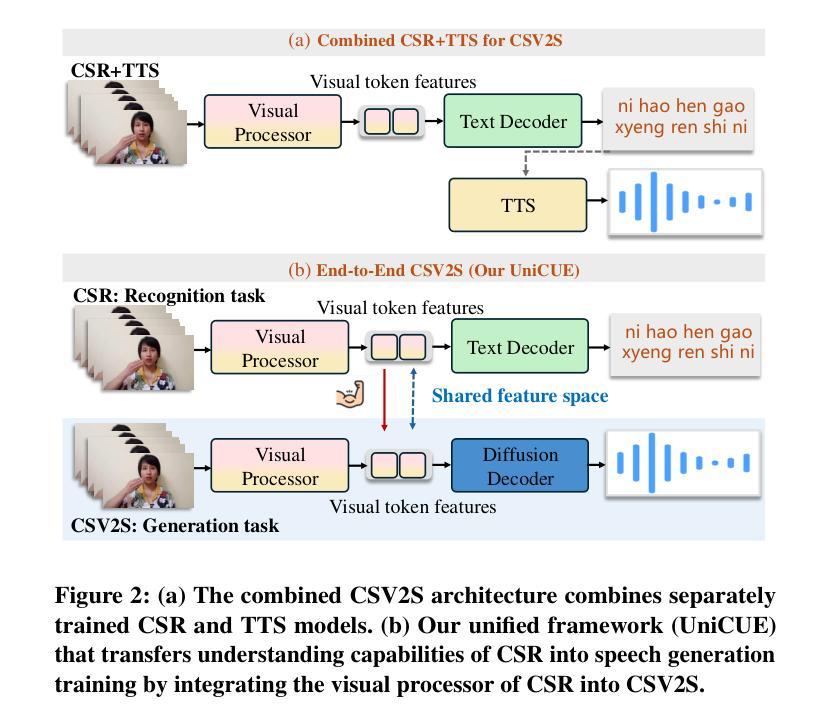
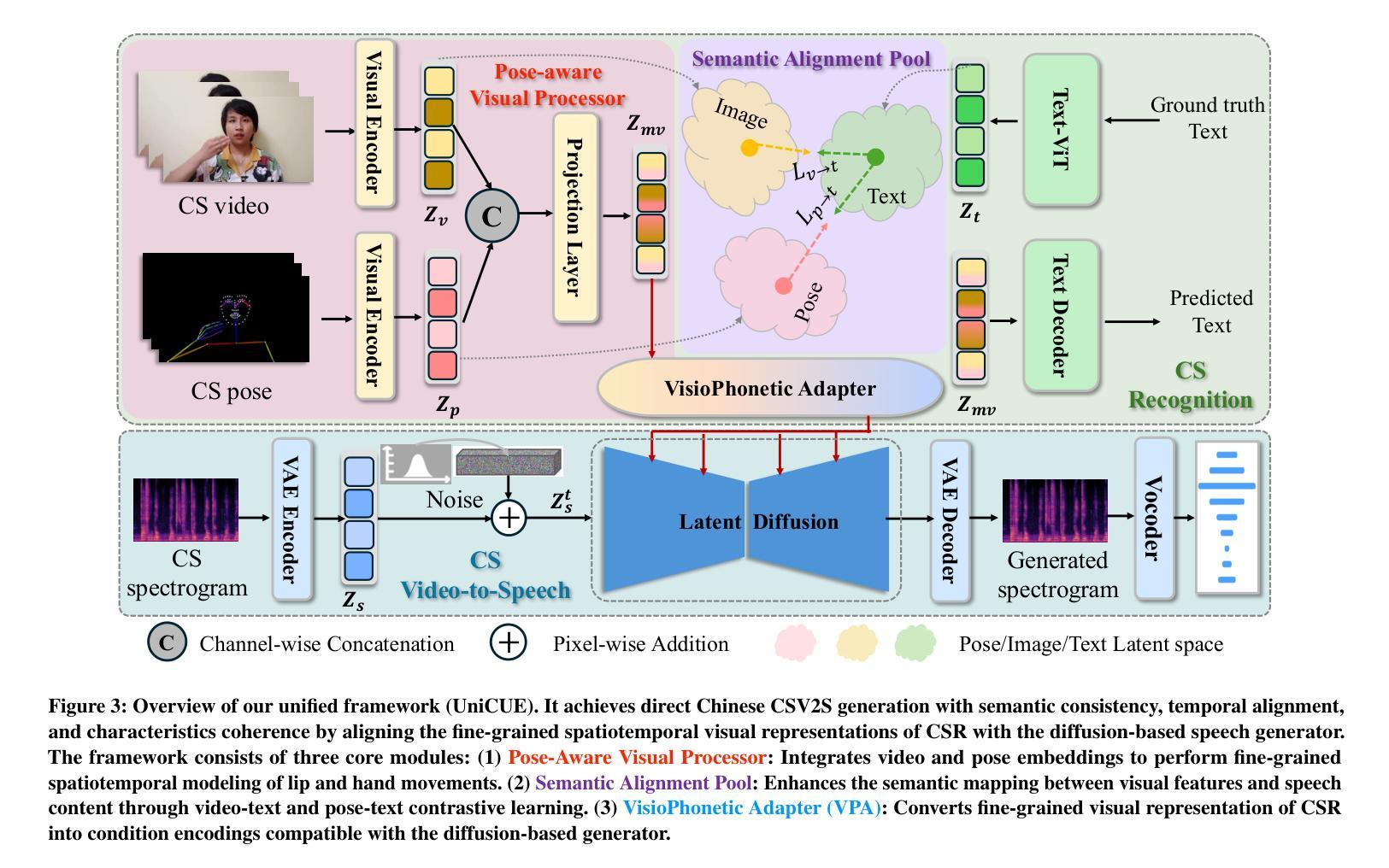
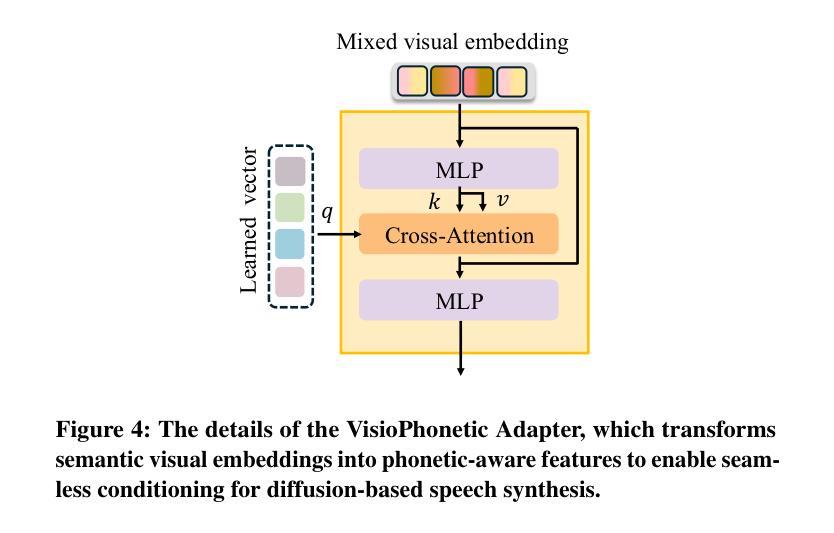
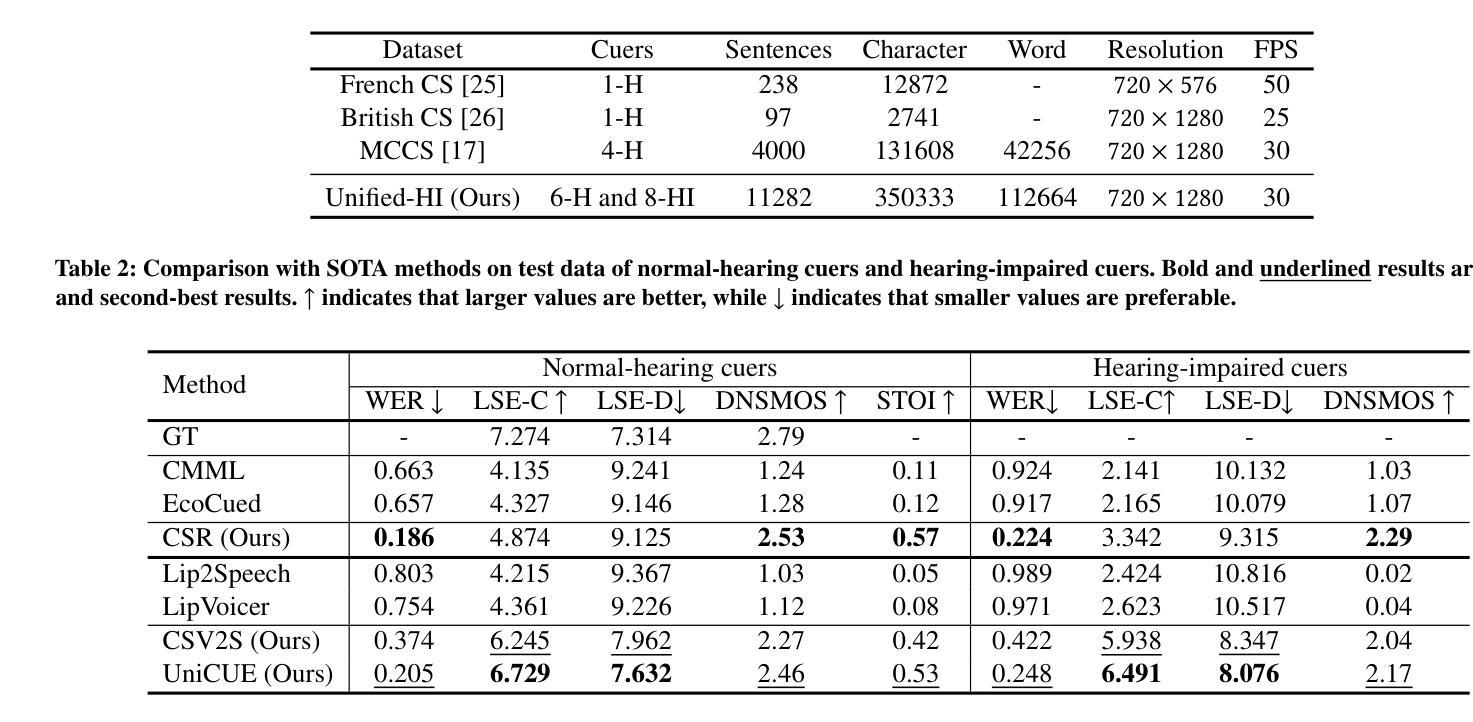
UniCUE: Unified Recognition and Generation Framework for Chinese Cued Speech Video-to-Speech Generation
Authors:Jinting Wang, Shan Yang, Chenxing Li, Dong Yu, Li Liu
Cued Speech (CS) enhances lipreading via hand coding, offering visual phonemic cues that support precise speech perception for the hearing-impaired. The task of CS Video-to-Speech generation (CSV2S) aims to convert CS videos into intelligible speech signals. Most existing research focuses on CS Recognition (CSR), which transcribes video content into text. Consequently, a common solution for CSV2S is to integrate CSR with a text-to-speech (TTS) system. However, this pipeline relies on text as an intermediate medium, which may lead to error propagation and temporal misalignment between speech and CS video dynamics. In contrast, directly generating audio speech from CS video (direct CSV2S) often suffers from the inherent multimodal complexity and the limited availability of CS data. To address these challenges, we propose UniCUE, the first unified framework for CSV2S that directly generates speech from CS videos without relying on intermediate text. The core innovation of UniCUE lies in integrating an understanding task (CSR) that provides fine-grained CS visual-semantic cues to guide speech generation. Specifically, UniCUE incorporates a pose-aware visual processor, a semantic alignment pool that enables precise visual-semantic mapping, and a VisioPhonetic adapter to bridge the understanding and generation tasks within a unified architecture. To support this framework, we construct UniCUE-HI, a large-scale Mandarin CS dataset containing 11282 videos from 14 cuers, including both hearing-impaired and normal-hearing individuals. Extensive experiments on this dataset demonstrate that UniCUE achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple evaluation metrics.
唇音提示(Cued Speech,简称CS)通过手动编码提高唇语阅读效率,提供视觉语音提示,支持听力障碍者精确感知语音。CS视频到语音生成(CSV2S)的任务旨在将CS视频转换为可理解的语音信号。目前大多数研究集中在CS识别(CSR)上,将视频内容转录为文本。因此,CSV2S的一种常见解决方案是将CSR与文本到语音(TTS)系统结合起来。然而,此流程依赖于文本作为中间媒介,可能导致误差传播以及语音和CS视频动态之间的时间错位。相比之下,直接从CS视频生成音频语音(直接CSV2S)往往受到固有的多模式复杂性和有限的CS数据可用性的挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了UniCUE,这是第一个用于CSV2S的统一框架,能够直接从CS视频生成语音,无需依赖中间文本。UniCUE的核心创新之处在于整合了理解任务(CSR),提供精细的CS视觉语义提示来指导语音生成。具体来说,UniCUE结合了姿态感知视觉处理器、语义对齐池(使精确视觉语义映射成为可能)和VisioPhonetic适配器,在一个统一架构内桥接理解和生成任务。为了支持此框架,我们构建了大型普通话CS数据集UniCUE-HI,包含来自14名打手势者的11282个视频,其中包括听障人士和正常听力人士。在该数据集上的大量实验表明,UniCUE在多个评估指标上达到了一流的性能表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
摘要
Cued Speech(CS)通过手语编码增强唇读能力,为听力受损者提供视觉语音线索以支持精确的语言感知。CS视频到语音生成(CSV2S)的任务旨在将CS视频转换为可理解的语音信号。大多数现有研究集中在CS识别(CSR)上,将视频内容转录为文本。因此,CSV2S的常见解决方案是将CSR与文本到语音(TTS)系统结合。然而,这种管道依赖于作为中间媒介的文本,可能导致误差传播和语音与CS视频动态之间的时间不对齐。相比之下,直接从CS视频生成音频语音(直接CSV2S)常常面临固有的多模式复杂性和CS数据有限的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了UniCUE,这是第一个统一的CSV2S框架,能够直接从CS视频生成语音,而无需依赖中间文本。UniCUE的核心创新在于整合了理解任务(CSR),提供精细的CS视觉语义线索来指导语音生成。具体来说,UniCUE结合了姿态感知视觉处理器、语义对齐池(使精确视觉语义映射成为可能)和VisioPhonetic适配器(在理解任务和生成任务之间架起桥梁)在一个统一架构中。为了支持此框架,我们构建了大型普通话CS数据集UniCUE-HI,包含来自14名打手势者的11282个视频,包括听障人士和正常听力人士。在该数据集上的广泛实验表明,UniCUE在多个评估指标上取得了创纪录的性能。
关键见解
- Cued Speech(CS)通过手语编码增强唇读能力,为听力受损者提供视觉语音线索。
- CS视频到语音生成(CSV2S)的任务是转换CS视频为可理解的语音信号,存在多种挑战。
- 当前研究多集中在CS识别(CSR),即将视频内容转录为文本,而CSV2S的常见解决方案是结合CSR与TTS系统,但存在误差传播和时间不对齐问题。
- 直接从CS视频生成音频语音面临多模式复杂性和CS数据有限的问题。
- UniCUE是首个能直接生成语音的CSV2S统一框架,无需依赖中间文本。
- UniCUE结合姿态感知视觉处理器、语义对齐池和VisioPhonetic适配器,实现精细的CS视觉语义线索指导语音生成。
点此查看论文截图

Pseudo-Autoregressive Neural Codec Language Models for Efficient Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Yifan Yang, Shujie Liu, Jinyu Li, Yuxuan Hu, Haibin Wu, Hui Wang, Jianwei Yu, Lingwei Meng, Haiyang Sun, Yanqing Liu, Yan Lu, Kai Yu, Xie Chen
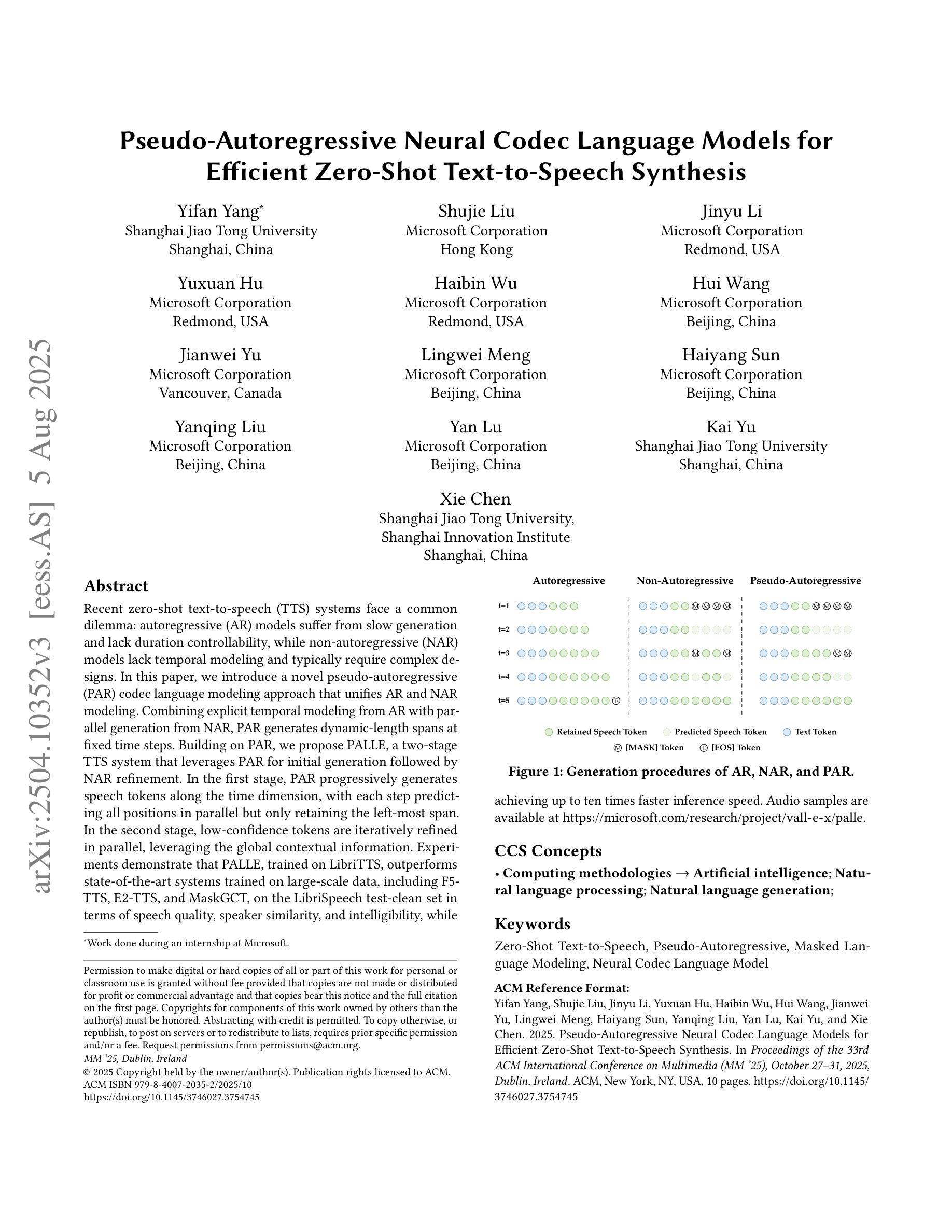
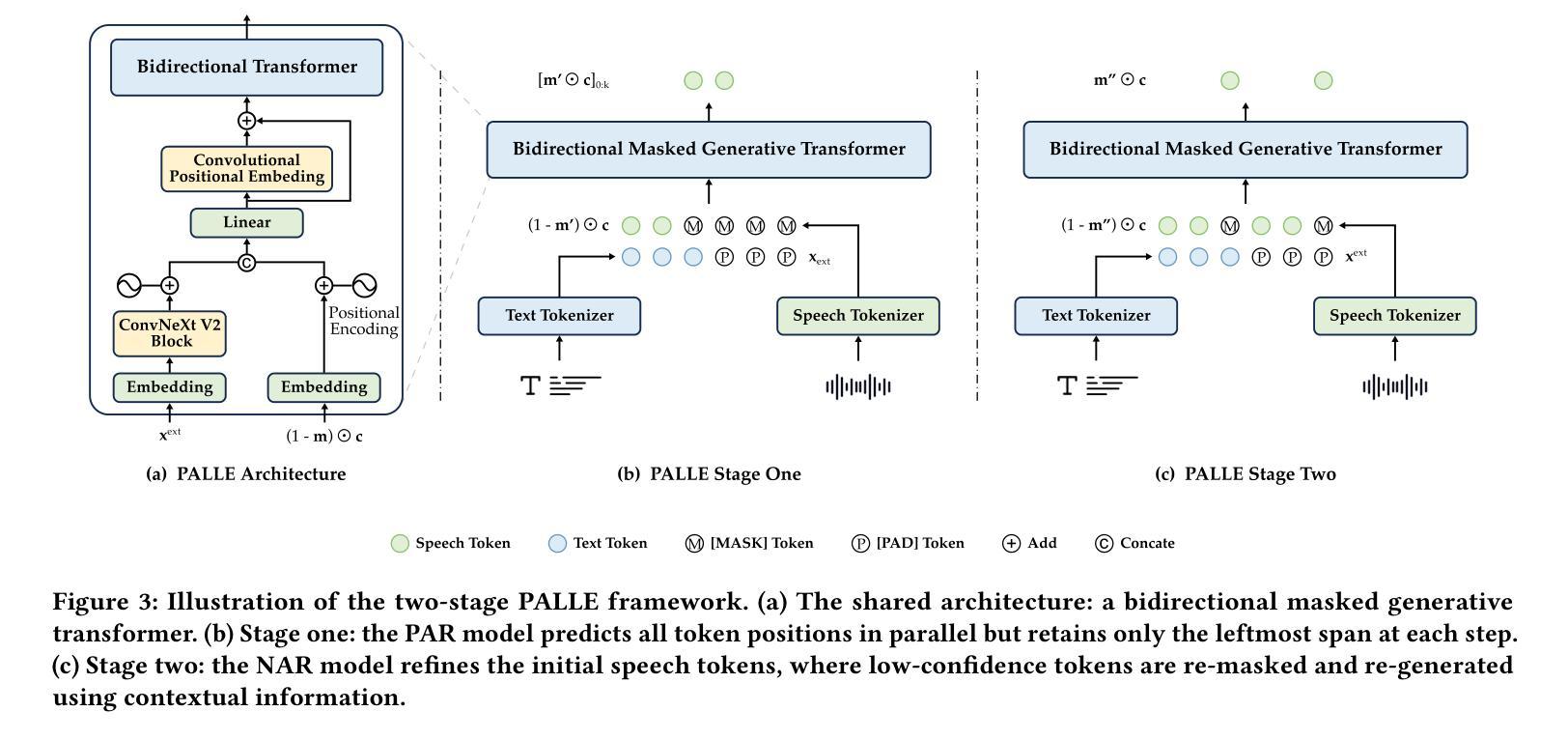
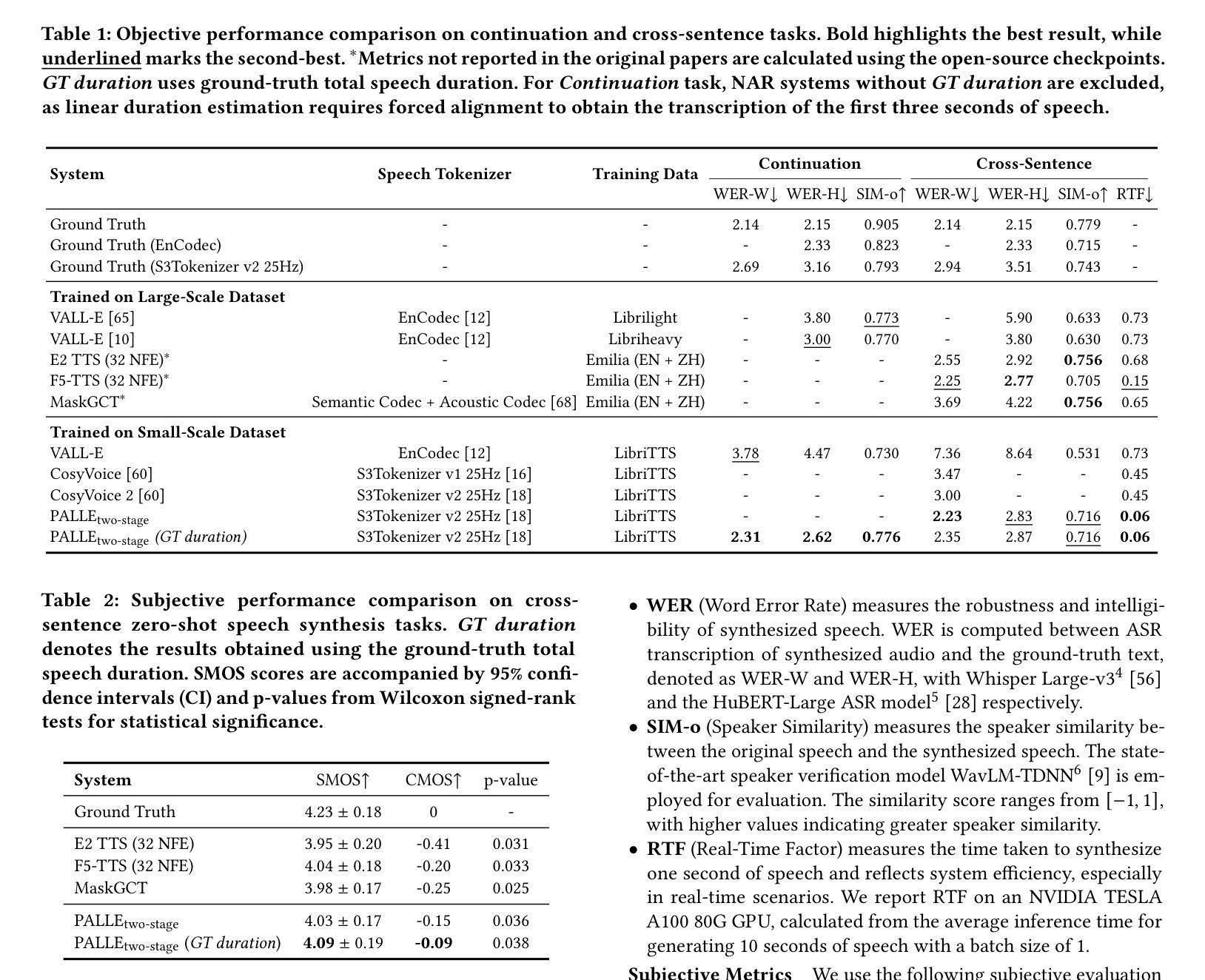
Recent zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems face a common dilemma: autoregressive (AR) models suffer from slow generation and lack duration controllability, while non-autoregressive (NAR) models lack temporal modeling and typically require complex designs. In this paper, we introduce a novel pseudo-autoregressive (PAR) codec language modeling approach that unifies AR and NAR modeling. Combining explicit temporal modeling from AR with parallel generation from NAR, PAR generates dynamic-length spans at fixed time steps. Building on PAR, we propose PALLE, a two-stage TTS system that leverages PAR for initial generation followed by NAR refinement. In the first stage, PAR progressively generates speech tokens along the time dimension, with each step predicting all positions in parallel but only retaining the left-most span. In the second stage, low-confidence tokens are iteratively refined in parallel, leveraging the global contextual information. Experiments demonstrate that PALLE, trained on LibriTTS, outperforms state-of-the-art systems trained on large-scale data, including F5-TTS, E2-TTS, and MaskGCT, on the LibriSpeech test-clean set in terms of speech quality, speaker similarity, and intelligibility, while achieving up to ten times faster inference speed. Audio samples are available at https://microsoft.com/research/project/vall-e-x/palle.
近期零样本文本转语音(TTS)系统面临一个共同困境:自回归(AR)模型存在生成速度慢和缺乏持续时间控制的问题,而非自回归(NAR)模型则缺乏时间建模并且通常需要复杂的设计。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新型伪自回归(PAR)编码解码语言建模方法,它将AR和NAR建模统一起来。通过将AR的显式时间建模与NAR的并行生成相结合,PAR在固定时间步长上生成动态长度的跨度。基于PAR,我们提出了一个两阶段的TTS系统PALLE,它首先利用PAR进行初步生成,然后利用NAR进行细化。在第一阶段,PAR沿时间维度逐步生成语音标记,每一步都并行预测所有位置,但只保留最左边的跨度。在第二阶段,利用全局上下文信息并行迭代优化低置信度的标记。实验表明,在LibriSpeech测试清洁集上,PALLE在语音质量、说话人相似度和清晰度方面优于在大型数据上训练的最新系统,包括F5-TTS、E2-TTS和MaskGCT,同时实现了高达十倍的推理速度提升。音频样本可在https://microsoft.com/research/project/vall-e-x/palle上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ACMMM 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的伪自回归(PAR)编码解码语言建模方法,结合了自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)建模的优点。基于此方法,研发了名为PALLE的两阶段文本转语音(TTS)系统。PALLE在初始阶段使用PAR生成语音标记,然后在第二阶段使用NAR进行精细修正。实验表明,PALLE在语音质量、说话人相似性和清晰度方面优于其他先进系统,同时推理速度更快。
Key Takeaways
- 伪自回归(PAR)编码解码语言建模结合了自回归(AR)和非自回归(NAR)建模的优势。
- PALLE系统采用两阶段生成策略,初始阶段使用PAR生成语音标记,然后进行NAR精细修正。
- PAR能够在固定时间步长内生成动态长度跨度。
- PALLE在LibriSpeech测试集上表现出优异的语音质量、说话人相似性和清晰度。
- 与其他先进系统相比,PALLE实现了更快的推理速度。
- 音频样本可在https://microsoft.com/research/project/vall-e-x/palle查看。
点此查看论文截图