⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
READ: Real-time and Efficient Asynchronous Diffusion for Audio-driven Talking Head Generation
Authors:Haotian Wang, Yuzhe Weng, Jun Du, Haoran Xu, Xiaoyan Wu, Shan He, Bing Yin, Cong Liu, Jianqing Gao, Qingfeng Liu
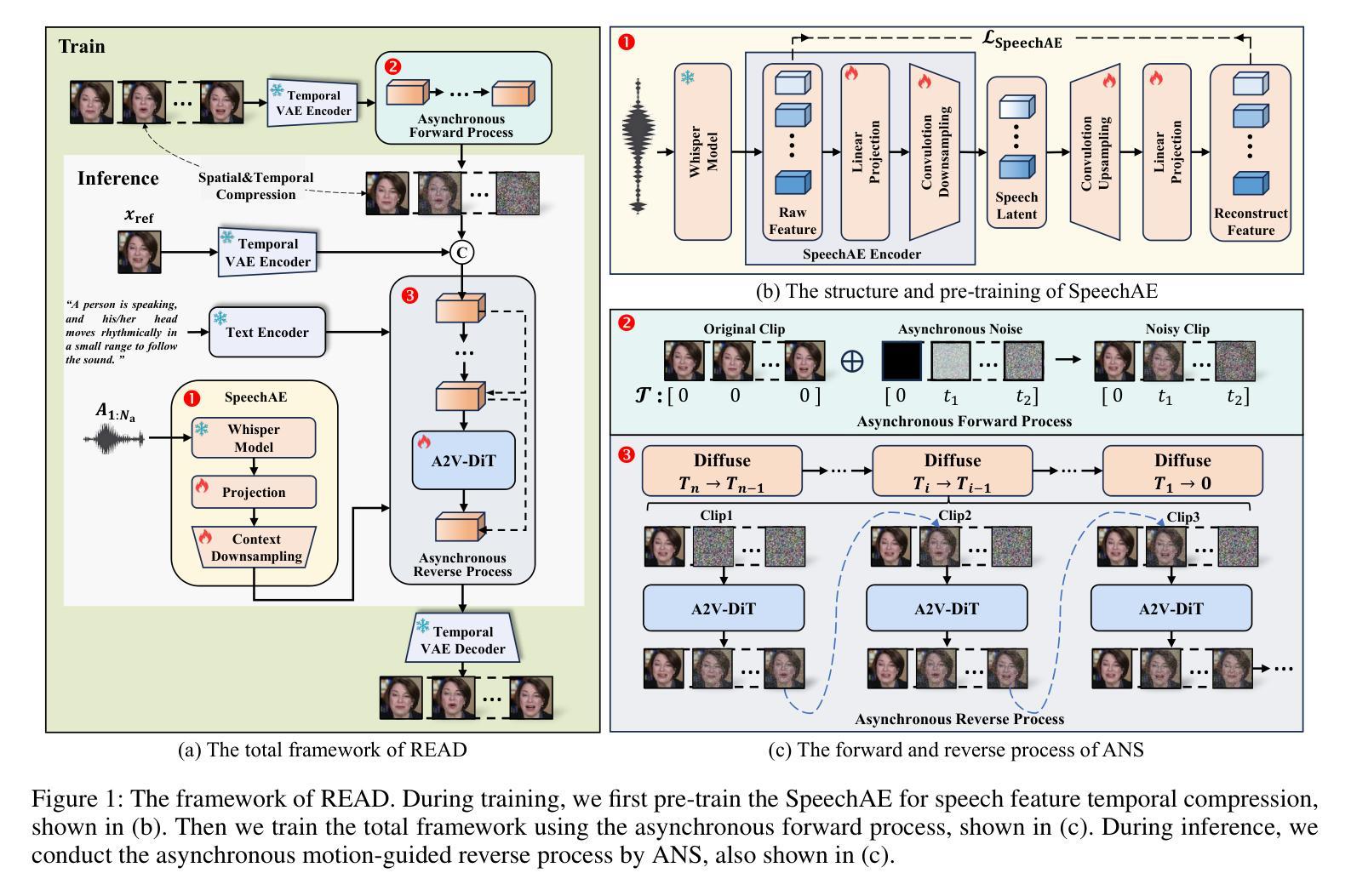
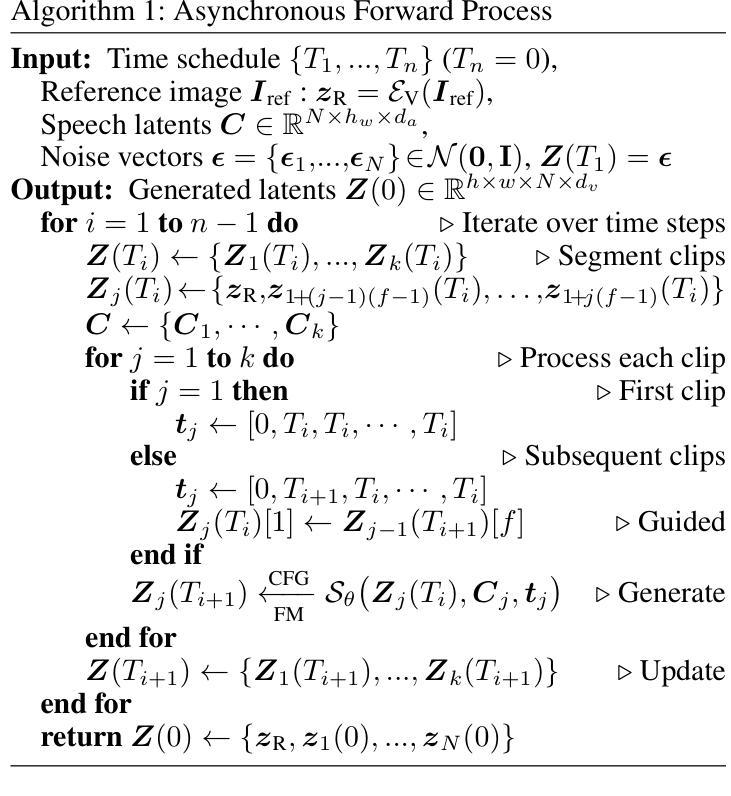
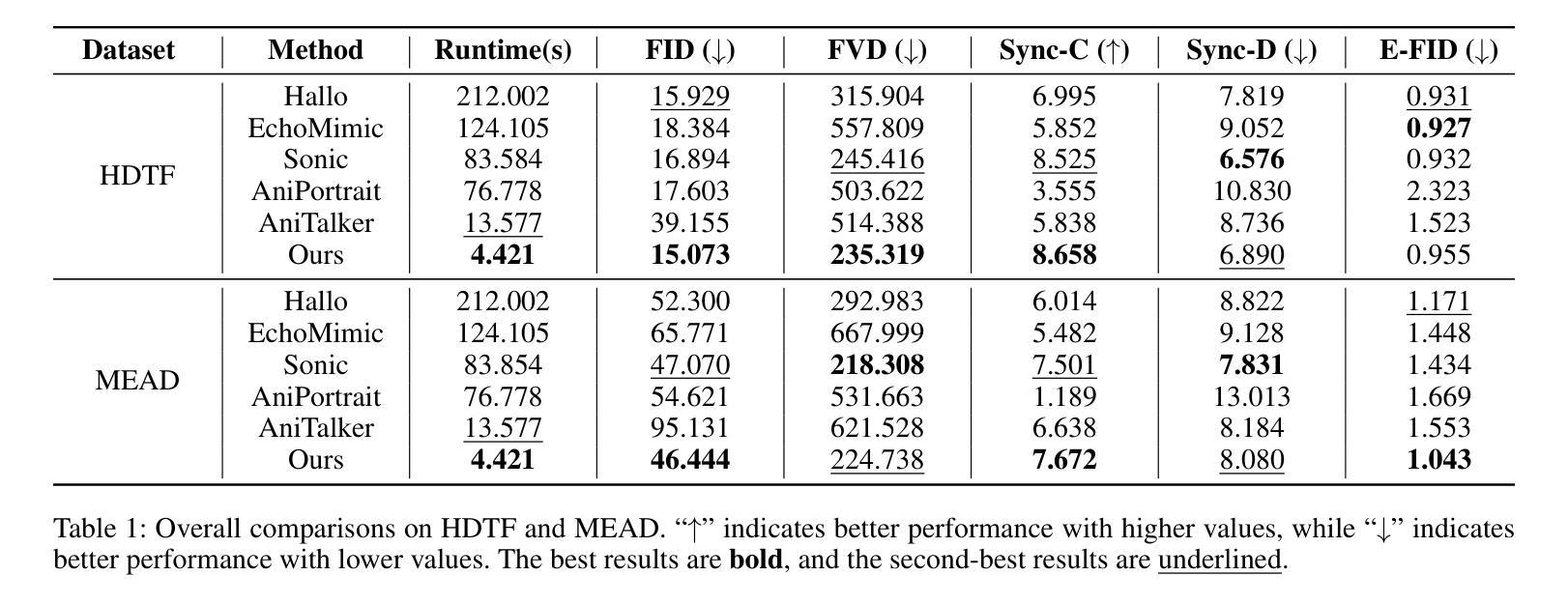
The introduction of diffusion models has brought significant advances to the field of audio-driven talking head generation. However, the extremely slow inference speed severely limits the practical implementation of diffusion-based talking head generation models. In this study, we propose READ, the first real-time diffusion-transformer-based talking head generation framework. Our approach first learns a spatiotemporal highly compressed video latent space via a temporal VAE, significantly reducing the token count to accelerate generation. To achieve better audio-visual alignment within this compressed latent space, a pre-trained Speech Autoencoder (SpeechAE) is proposed to generate temporally compressed speech latent codes corresponding to the video latent space. These latent representations are then modeled by a carefully designed Audio-to-Video Diffusion Transformer (A2V-DiT) backbone for efficient talking head synthesis. Furthermore, to ensure temporal consistency and accelerated inference in extended generation, we propose a novel asynchronous noise scheduler (ANS) for both the training and inference process of our framework. The ANS leverages asynchronous add-noise and asynchronous motion-guided generation in the latent space, ensuring consistency in generated video clips. Experimental results demonstrate that READ outperforms state-of-the-art methods by generating competitive talking head videos with significantly reduced runtime, achieving an optimal balance between quality and speed while maintaining robust metric stability in long-time generation.
扩散模型的引入为音频驱动说话人头部生成领域带来了显著进展。然而,极慢的推理速度严重限制了基于扩散的说话人头部生成模型的实际应用。在本研究中,我们提出了READ,这是第一个基于实时扩散变压器的说话人头部生成框架。我们的方法首先通过时间VAE学习一个时空高度压缩的视频潜在空间,显著减少令牌计数以加速生成。为了在这个压缩的潜在空间内实现更好的音频视觉对齐,我们提出了一个预训练的语音自动编码器(SpeechAE)来生成与视频潜在空间对应的时空压缩语音潜在代码。然后,这些潜在表示由一个精心设计的音频到视频扩散变压器(A2V-DiT)主干进行建模,以实现高效的说话人头部合成。此外,为了确保扩展生成的时序一致性和加速推理,我们为框架的训练和推理过程提出了新型异步噪声调度器(ANS)。ANS利用潜在空间中的异步添加噪声和异步运动引导生成,确保生成视频剪辑的一致性。实验结果表明,READ通过生成竞争性的说话人头部视频并显著减少运行时间,在质量和速度之间实现了最佳平衡,同时在长时间生成中保持了稳健的指标稳定性,从而优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://readportrait.github.io/READ/
摘要
扩散模型的引入为音频驱动说话人头部生成领域带来了显著进展。然而,其极慢的推理速度严重限制了扩散式说话人头部生成模型的实际应用。本研究提出了READ,首个基于实时扩散转换器的说话人头部生成框架。该方法首先通过学习时空高度压缩的视频潜在空间,显著减少令牌计数以加速生成。为了在这个压缩的潜在空间内实现更好的音视频对齐,提出了预训练的语音自编码器(SpeechAE)来生成与视频潜在空间对应的时空压缩语音潜在代码。这些潜在表示由一个精心设计的音频到视频扩散转换器(A2V-DiT)主干进行建模,用于高效说话人头部合成。此外,为了确保扩展生成的时序一致性和加速推理,我们为框架的训练和推理过程提出了新型异步噪声调度器(ANS)。ANS利用潜在空间中的异步添加噪声和异步运动引导生成,确保生成视频剪辑的一致性。实验结果表明,READ优于现有最先进的方法,生成的说话人头部视频具有竞争力,运行时显著减少,在长时间生成的同时实现了质量与速度的平衡。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在音频驱动说话头生成领域有重大进展,但推理速度较慢。
- READ框架是基于实时扩散转换器的首个说话头生成框架。
- 通过学习高度压缩的视频潜在空间来加速生成过程。
- 引入预训练的语音自编码器(SpeechAE)实现音视频对齐。
- 使用A2V-DiT主干进行音频到视频的潜在表示建模。
- 提出了新型的异步噪声调度器(ANS)以确保时序一致性和加速推理。
点此查看论文截图


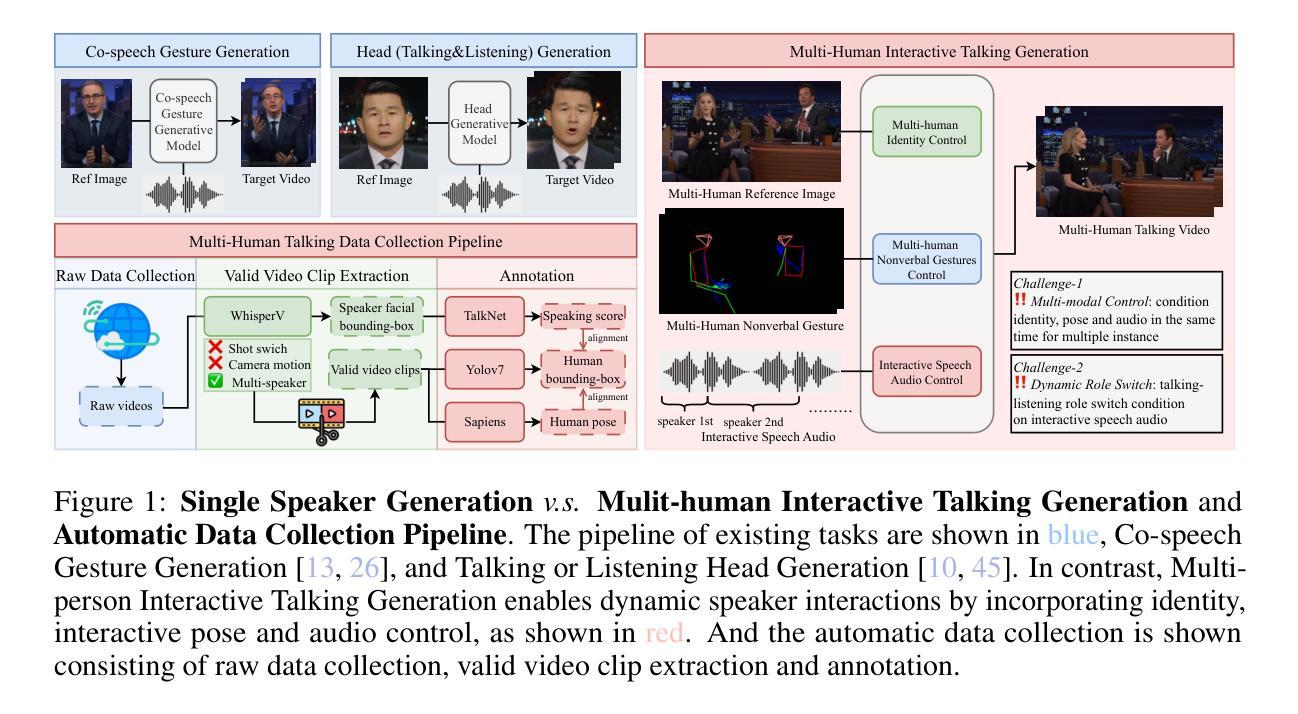
Multi-human Interactive Talking Dataset
Authors:Zeyu Zhu, Weijia Wu, Mike Zheng Shou
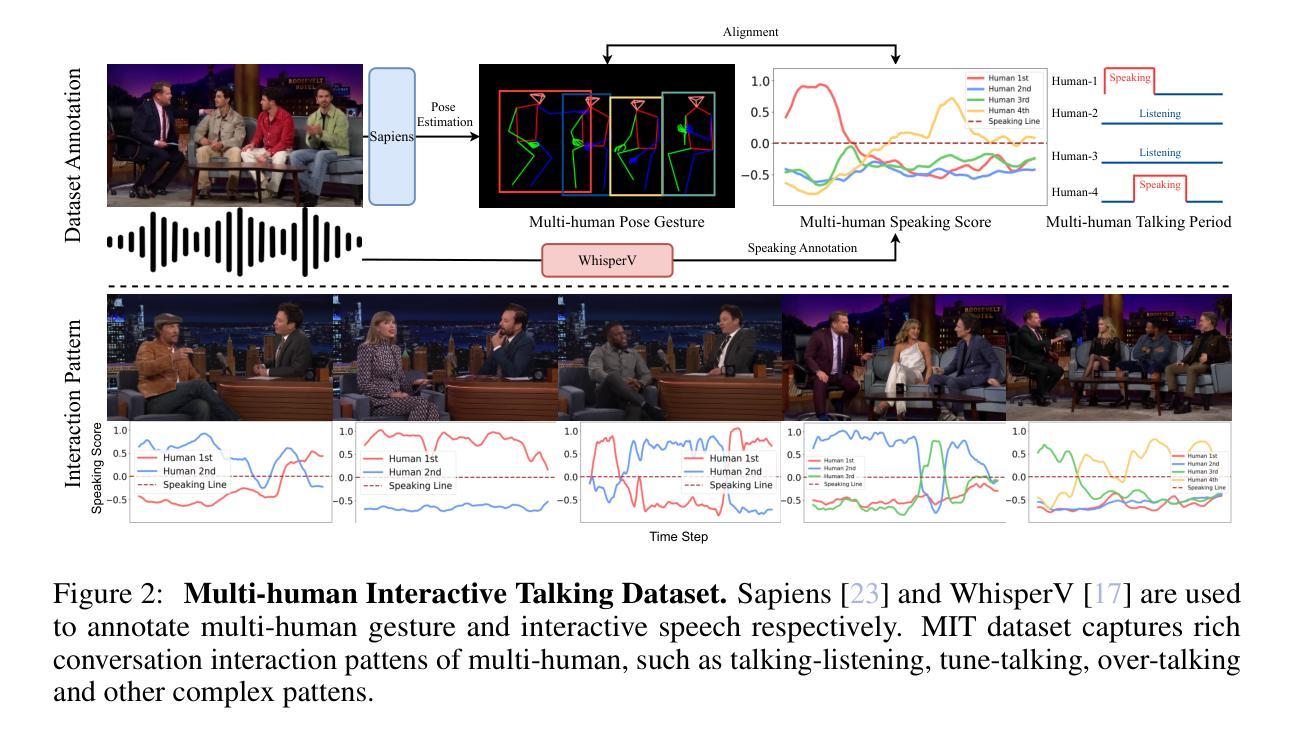
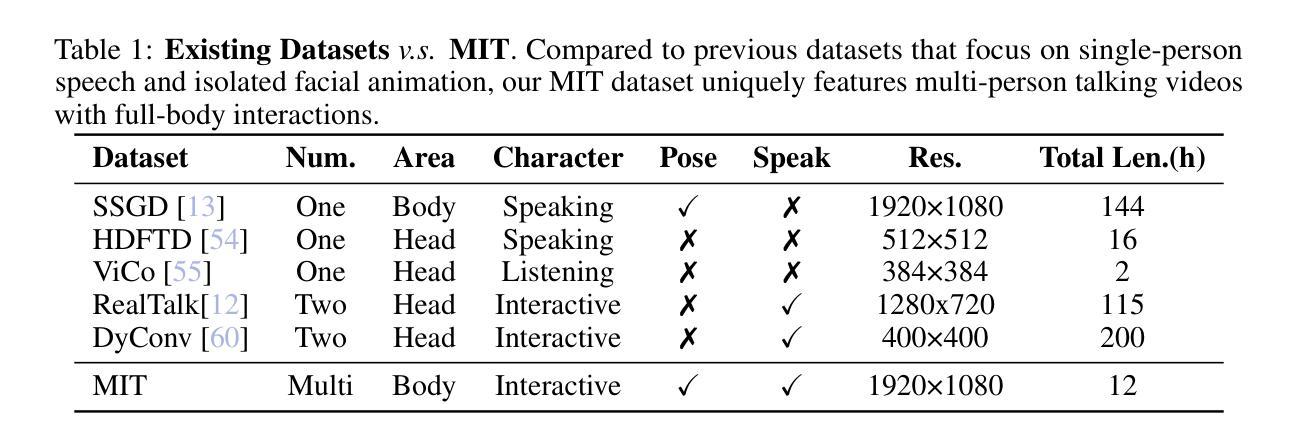
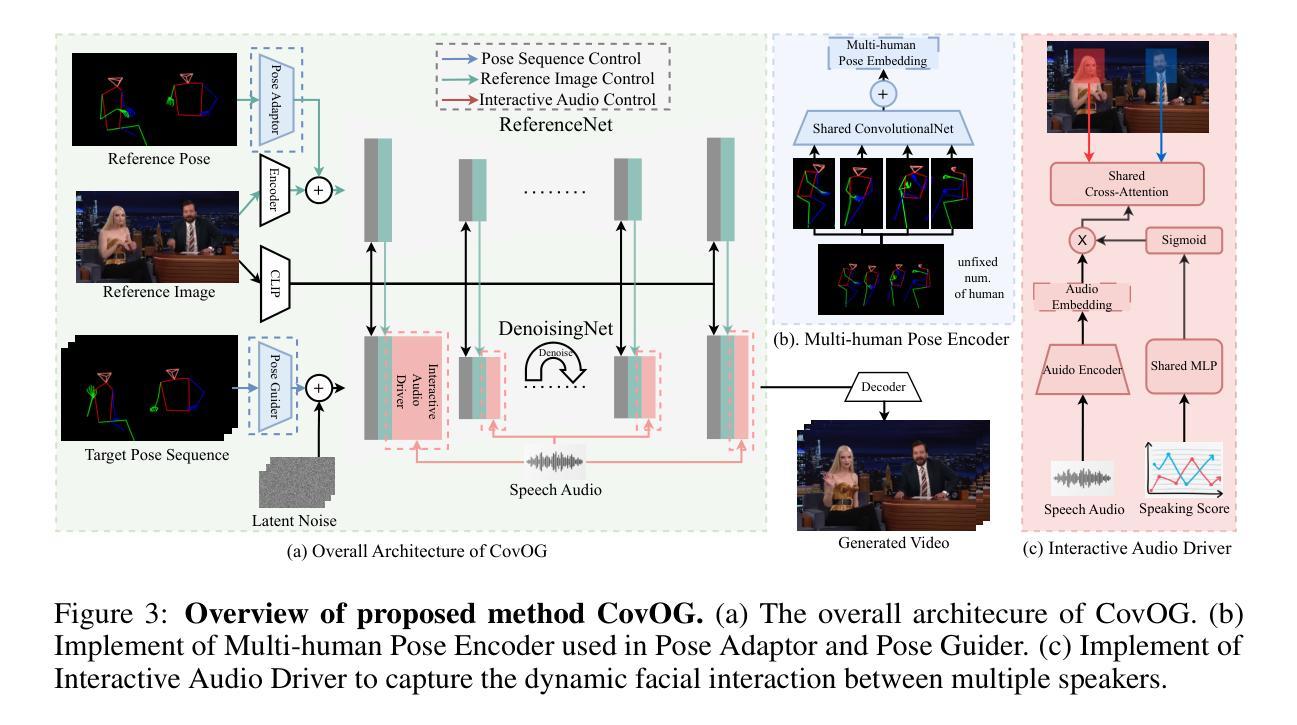
Existing studies on talking video generation have predominantly focused on single-person monologues or isolated facial animations, limiting their applicability to realistic multi-human interactions. To bridge this gap, we introduce MIT, a large-scale dataset specifically designed for multi-human talking video generation. To this end, we develop an automatic pipeline that collects and annotates multi-person conversational videos. The resulting dataset comprises 12 hours of high-resolution footage, each featuring two to four speakers, with fine-grained annotations of body poses and speech interactions. It captures natural conversational dynamics in multi-speaker scenario, offering a rich resource for studying interactive visual behaviors. To demonstrate the potential of MIT, we furthur propose CovOG, a baseline model for this novel task. It integrates a Multi-Human Pose Encoder (MPE) to handle varying numbers of speakers by aggregating individual pose embeddings, and an Interactive Audio Driver (IAD) to modulate head dynamics based on speaker-specific audio features. Together, these components showcase the feasibility and challenges of generating realistic multi-human talking videos, establishing MIT as a valuable benchmark for future research. The code is avalibale at: https://github.com/showlab/Multi-human-Talking-Video-Dataset.
关于对话视频生成的研究目前主要集中在单人独白或孤立的面部动画上,这限制了其在现实多人互动中的应用。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了MIT(大规模数据集),它是专门为多人对话视频生成设计的。为此,我们开发了一个自动管道,用于收集和标注多人对话视频。该数据集包含12小时的高分辨率视频片段,每段视频都有两到四名发言人,详细标注了身体姿势和语音交互。它捕捉了多人场景中自然的对话动态,为研究交互视觉行为提供了丰富的资源。为了展示MIT的潜力,我们进一步提出了CovOG作为这一新任务的基线模型。它集成了多人姿态编码器(MPE),通过聚合个体姿态嵌入来处理不同数量的发言人,以及交互式音频驱动器(IAD),根据发言人特定的音频特征调整头部动态。这些组件共同展示了生成逼真多人对话视频的可行性和挑战,使MIT成为未来研究的重要基准。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/showlab/Multi-human-Talking-Video-Dataset。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本文主要介绍了一个针对多人物对话视频生成的大型数据集MIT及其相关研究成果。该数据集包含高清晰度、多人物对话的视频片段,并对人物动作和语音交互进行了精细标注。为应对不同数量说话者的挑战,研究者提出了一种多人物姿态编码器和交互音频驱动模块的方法,为生成真实的多人物对话视频提供了可能。MIT数据集为未来的研究提供了宝贵的基准测试资源。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了针对多人物对话视频生成的大型数据集MIT。
- 数据集包含高清晰度、多人物对话的视频片段,并对人物动作和语音交互进行了精细标注。
- 提出了一种多人物姿态编码器(MPE)的方法,能够处理不同数量的说话者。
- 通过聚合个体姿态嵌入,MPE能够处理多人物场景中的复杂动态。
- 介绍了交互音频驱动(IAD)模块,能够根据说话者的音频特征调节头部动态。
- MIT数据集为未来研究提供了宝贵的基准测试资源。
点此查看论文截图

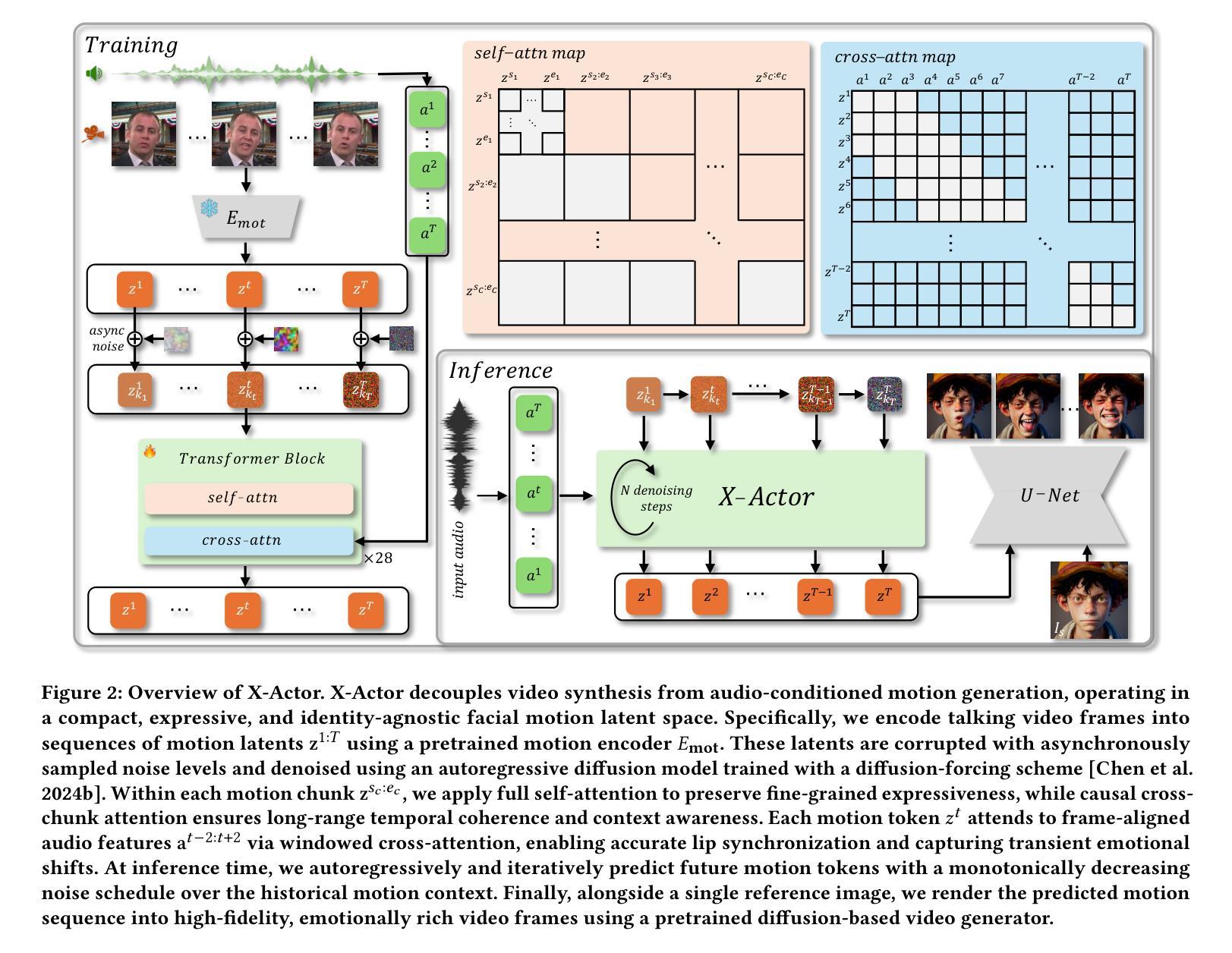
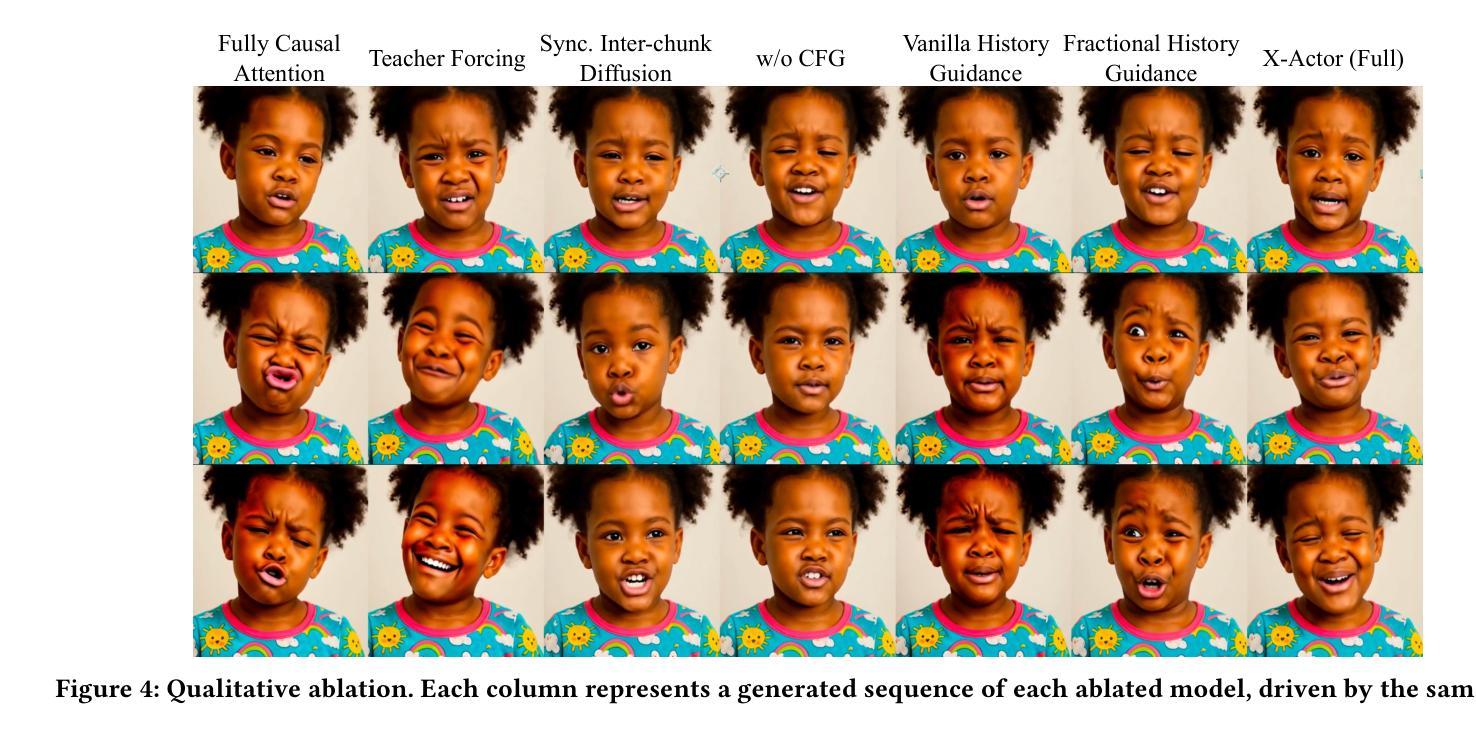
X-Actor: Emotional and Expressive Long-Range Portrait Acting from Audio
Authors:Chenxu Zhang, Zenan Li, Hongyi Xu, You Xie, Xiaochen Zhao, Tianpei Gu, Guoxian Song, Xin Chen, Chao Liang, Jianwen Jiang, Linjie Luo
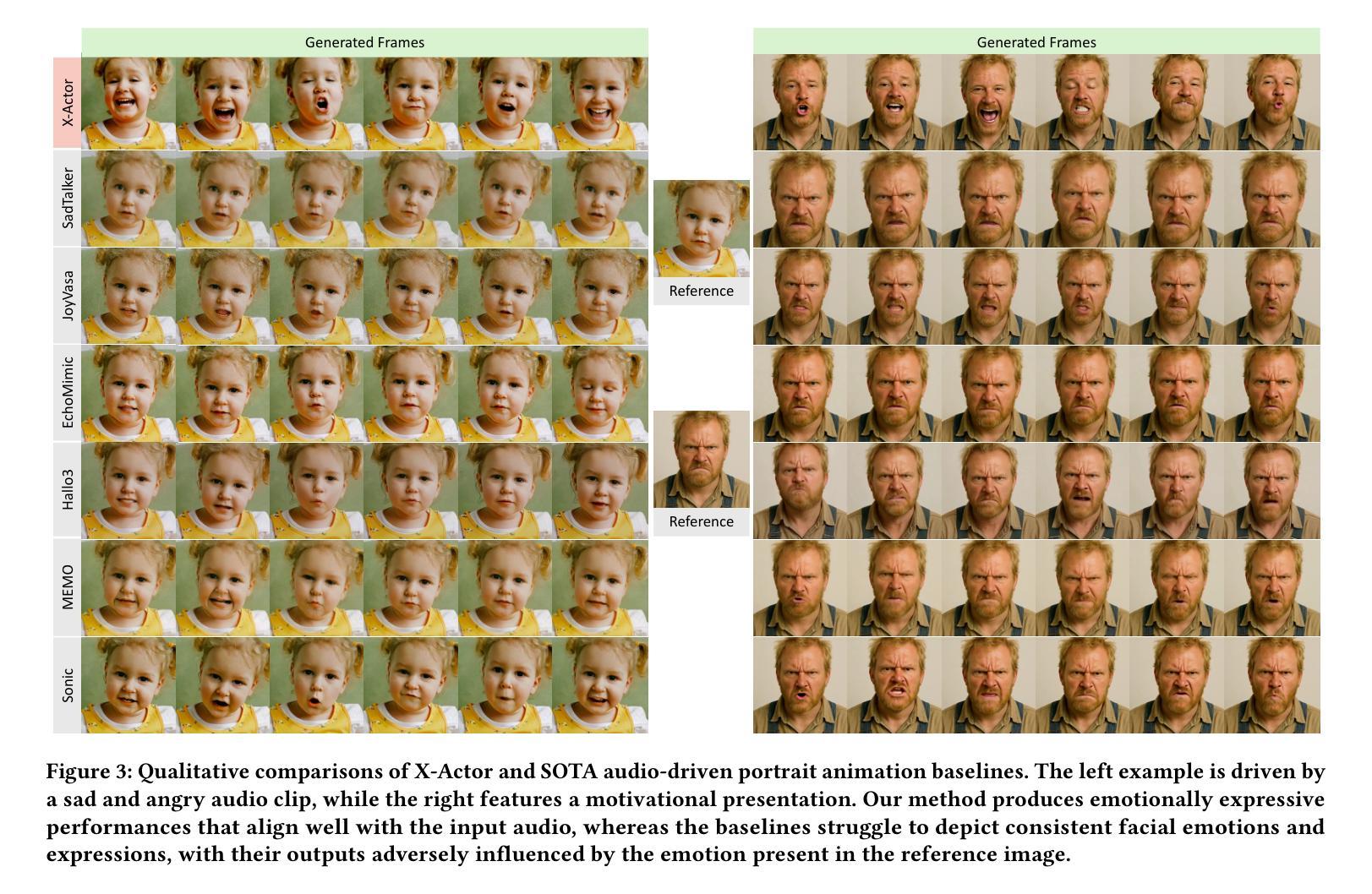
We present X-Actor, a novel audio-driven portrait animation framework that generates lifelike, emotionally expressive talking head videos from a single reference image and an input audio clip. Unlike prior methods that emphasize lip synchronization and short-range visual fidelity in constrained speaking scenarios, X-Actor enables actor-quality, long-form portrait performance capturing nuanced, dynamically evolving emotions that flow coherently with the rhythm and content of speech. Central to our approach is a two-stage decoupled generation pipeline: an audio-conditioned autoregressive diffusion model that predicts expressive yet identity-agnostic facial motion latent tokens within a long temporal context window, followed by a diffusion-based video synthesis module that translates these motions into high-fidelity video animations. By operating in a compact facial motion latent space decoupled from visual and identity cues, our autoregressive diffusion model effectively captures long-range correlations between audio and facial dynamics through a diffusion-forcing training paradigm, enabling infinite-length emotionally-rich motion prediction without error accumulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that X-Actor produces compelling, cinematic-style performances that go beyond standard talking head animations and achieves state-of-the-art results in long-range, audio-driven emotional portrait acting.
我们提出了X-Actor,这是一种新型音频驱动肖像动画框架,它可以从单张参考图像和输入音频片段生成逼真、情感丰富的说话人头视频。不同于以往强调唇同步和有限场景下的短期视觉保真度的方法,X-Actor能够实现演员级别的长时间肖像表现,捕捉微妙、动态变化的情绪,与演讲的节奏和内容流畅地结合。我们的方法的核心是一个两阶段的解耦生成管道:一个受音频调节的自回归扩散模型,该模型在长时间上下文窗口中预测表情丰富的面部运动潜在令牌,这些令牌与身份无关;其次是基于扩散的视频合成模块,将这些运动转化为高保真视频动画。我们的自回归扩散模型在独立于视觉和身份线索的紧凑面部运动潜在空间中进行操作,通过扩散强制训练范式有效地捕捉音频和面部动态之间的长期相关性,实现无误差累积的无限长情感丰富运动预测。大量实验表明,X-Actor产生的表演引人入胜、具有电影风格,超越了标准说话人头动画,并在长程、音频驱动的情感肖像表演方面取得了最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page at https://byteaigc.github.io/X-Actor/
Summary
X-Actor是一种新型音频驱动肖像动画框架,可从单张参考图像和输入音频片段生成生动、情感表达流畅的说话人头视频。与以往侧重于同步和短距离视觉保真度的约束演讲场景不同,X-Actor能够捕捉演员级的长期肖像表现,展示与语音节奏和内容流畅变化的微妙情绪。其核心是一个两阶段解耦生成管道:一个音频调节的自回归扩散模型,在一个长期时间窗口内预测表情丰富的面部运动潜在令牌,随后是一个基于扩散的视频合成模块,将这些运动转化为高保真视频动画。该自回归扩散模型在独立于视觉和身份线索的紧凑面部运动潜在空间内运行,通过扩散强迫训练模式有效地捕获音频和面部动力之间的长期关联,实现了无误差累积的情感丰富运动预测。Key Takeaways:
- X-Actor是一个新的音频驱动肖像动画框架。
- 可以从单个参考图像和音频片段生成长时间动态的说话人头视频。
- 采用两阶段解耦生成管道:自回归扩散模型预测面部运动潜在令牌,然后是视频合成模块。
- 自回归扩散模型在独立于视觉和身份线索的面部运动潜在空间内运行。
- 通过扩散强迫训练模式实现音频与面部动力之间的长期关联。
- X-Actor实现了情感丰富的运动预测,不会出现误差累积。
点此查看论文截图


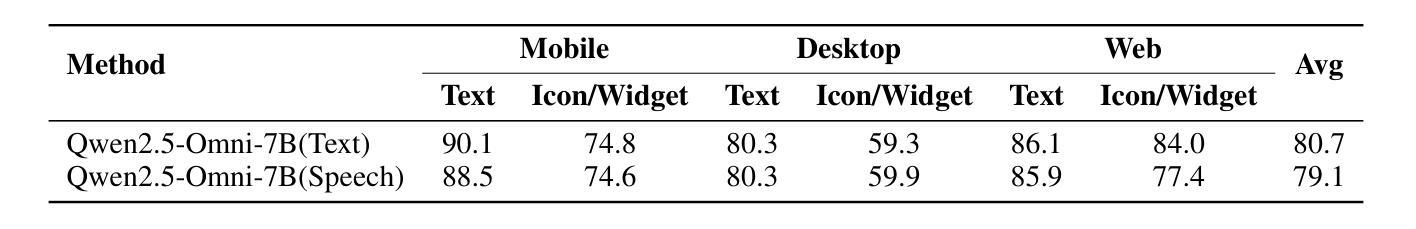
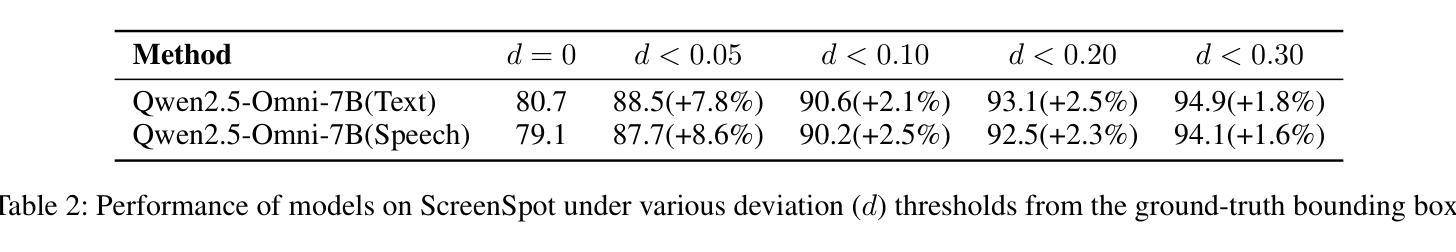
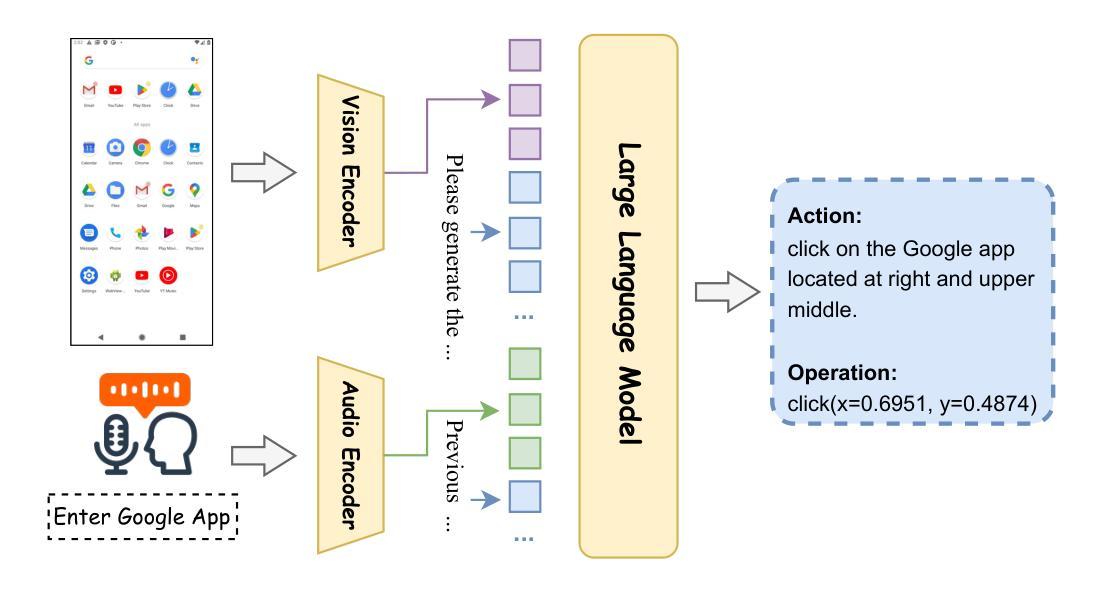
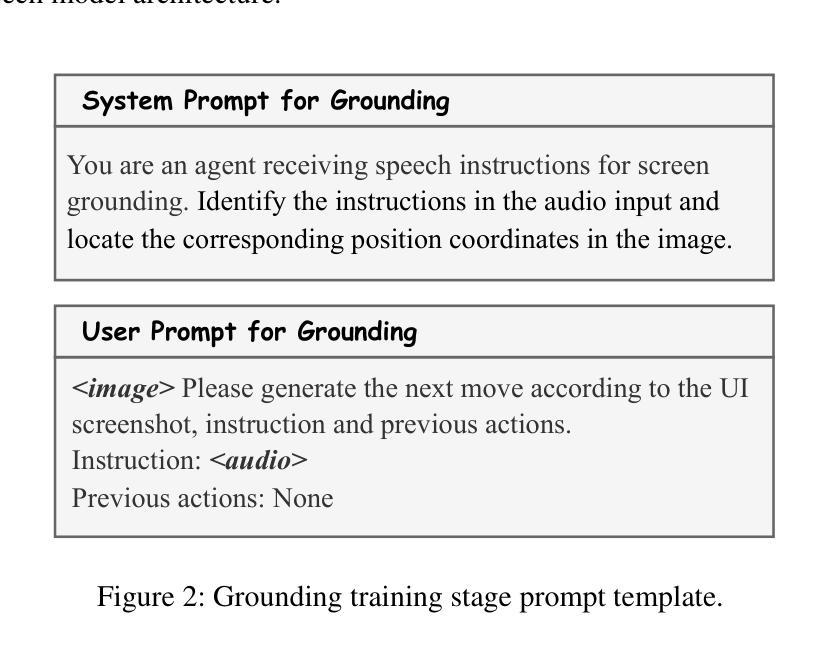
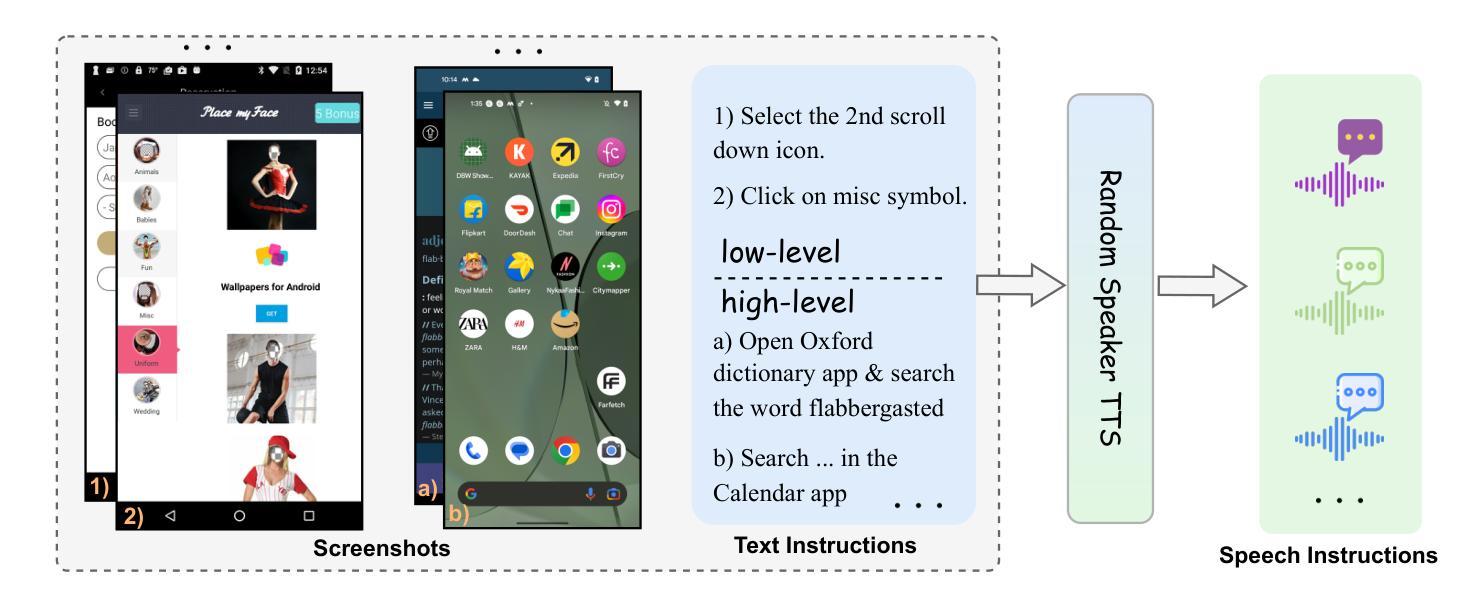
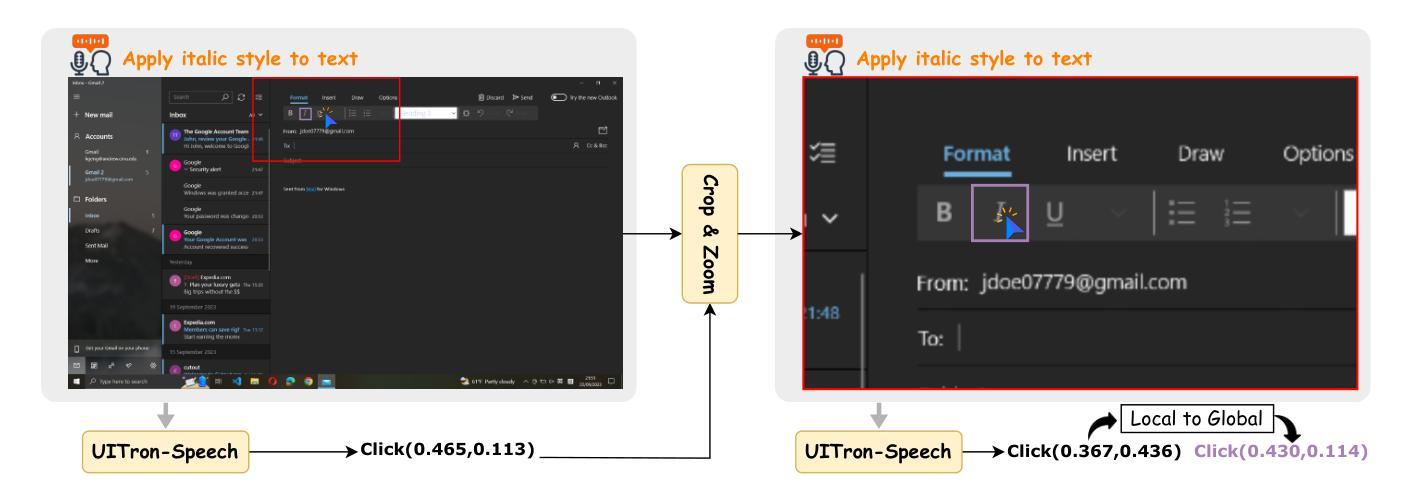
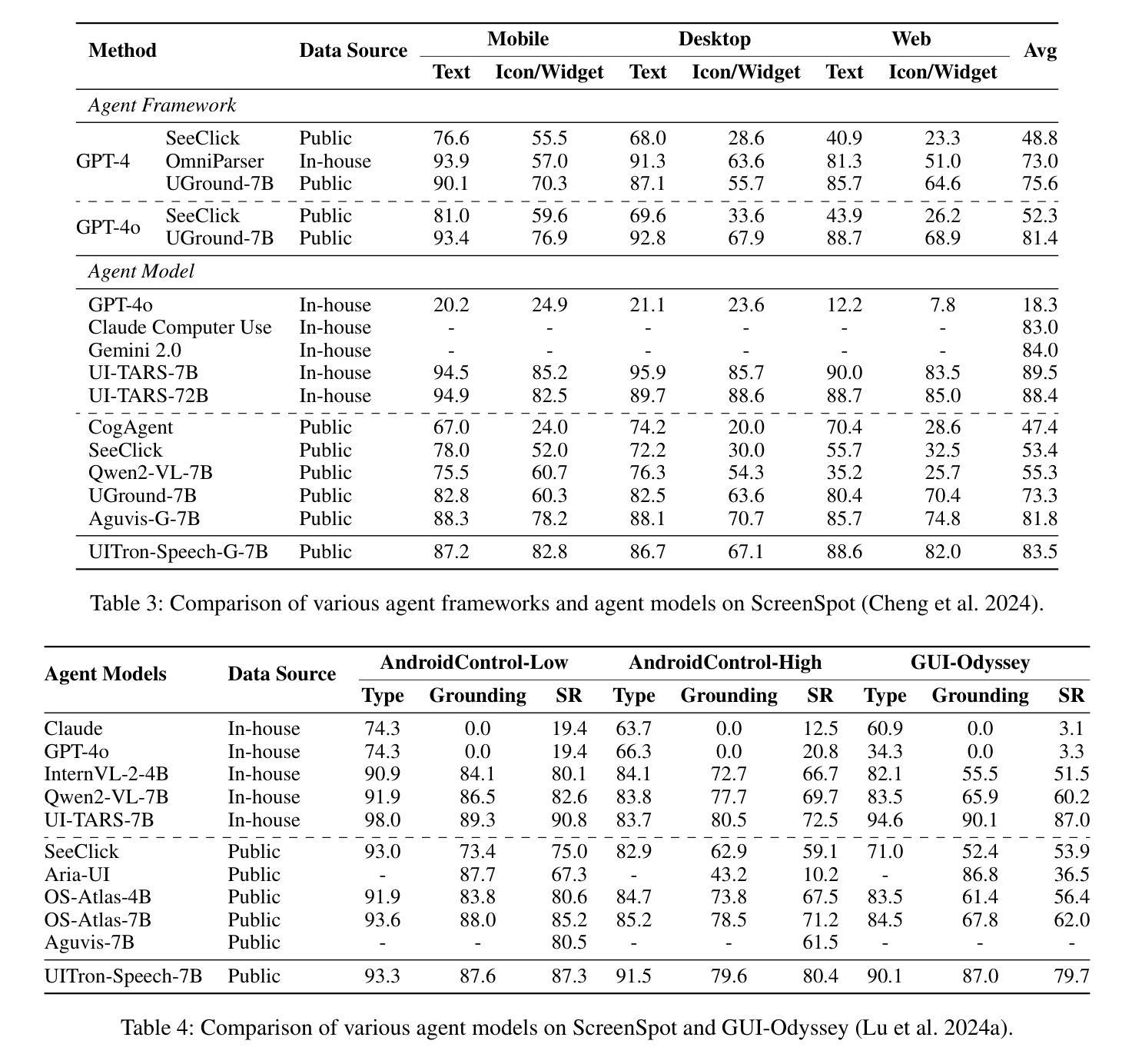
UITron-Speech: Towards Automated GUI Agents Based on Speech Instructions
Authors:Wenkang Han, Zhixiong Zeng, Jing Huang, Shu Jiang, Liming Zheng, Haibo Qiu, Chang Yao, Jingyuan Chen, Lin Ma
Autonomous agents for Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) are revolutionizing human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based instructions imposes limitations on accessibility and convenience, particularly in hands-free scenarios. To address this issue, we propose replacing text with speech as the instruction input modality for GUI agents, and introduce UITron-Speech, which is the first end-to-end GUI agent capable of directly processing speech instructions and on-device screenshots to predict user actions. To tackle the problem of data scarcity, we synthesize high-quality speech instruction datasets using a random-speaker text-to-speech model. Additionally, we design a mixed-modality training strategy to mitigate the inherent modality imbalance in pre-trained foundation models. Furthermore, we conduct a statistical analysis of the distribution of GUI grounding prediction errors and propose a training-free two-step grounding refinement method to alleviate minor localization deviations. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that UITron-Speech achieves robust performance and superior adaptability, underscoring the feasibility and potential of speech-driven GUI agents for more accessible and intelligent human-computer interaction. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/UITron-hub/UITron-Speech.
图形用户界面(GUI)的自主代理正在彻底改变人机交互的方式,然而它们对文本指令的依赖限制了可访问性和便利性,特别是在免提场景中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出用语音替换文本作为GUI代理的指令输入模式,并引入了UITron-Speech。UITron-Speech是第一个能够直接处理语音指令和设备截图以预测用户操作的端到端GUI代理。为了解决数据稀缺的问题,我们使用随机说话人文本到语音模型合成高质量语音指令数据集。此外,我们设计了一种混合模式训练策略,以缓解预训练基础模型中固有的模式不平衡问题。此外,我们对GUI接地预测误差的分布进行了统计分析,并提出了一种无训练的两步接地细化方法,以缓解轻微的定位偏差。在多个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,UITron-Speech实现了稳健的性能和卓越的适应性,突出了语音驱动GUI代理在更可访问和智能的人机交互中的可行性和潜力。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/UITron-hub/UITron-Speech获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于图形用户界面(GUI)的自主代理正在彻底改变人机交互方式,但它们依赖文本指令的方式对无障碍使用和便捷性造成了限制,特别是在免提场景中。为解决这一问题,我们提出用语音替代文本作为GUI代理的指令输入模式,并引入了UITron-Speech,这是首个能够直接处理语音指令和设备截图以预测用户行为的端到端GUI代理。我们利用随机说话人文本到语音模型合成高质量语音指令数据集以解决数据稀缺问题,并设计了一种混合模态训练策略来缓解预训练基础模型中的固有模态不平衡问题。此外,我们对GUI定位预测错误的分布进行了统计分析,并提出了无需训练的两步定位优化方法,以减轻轻微定位偏差。在多个基准测试上的实验表明,UITron-Speech具有强大的性能和卓越的适应性,突显了语音驱动GUI代理在实现更无障碍和智能人机交互方面的可行性潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 自主代理在GUI中改变了人机交互方式,但仍依赖文本指令,存在无障碍使用和便捷性的限制。
- 提出了UITron-Speech,能处理语音指令和设备截图以预测用户行为,是首个端到端的GUI代理。
- 通过合成高质量语音指令数据集和混合模态训练策略解决数据稀缺和模态不平衡问题。
- 分析了GUI定位预测错误的分布,并提出无需训练的两步定位优化方法减轻定位偏差。
*UITron-Speech在多个基准测试上表现出强大的性能和适应性。
点此查看论文截图

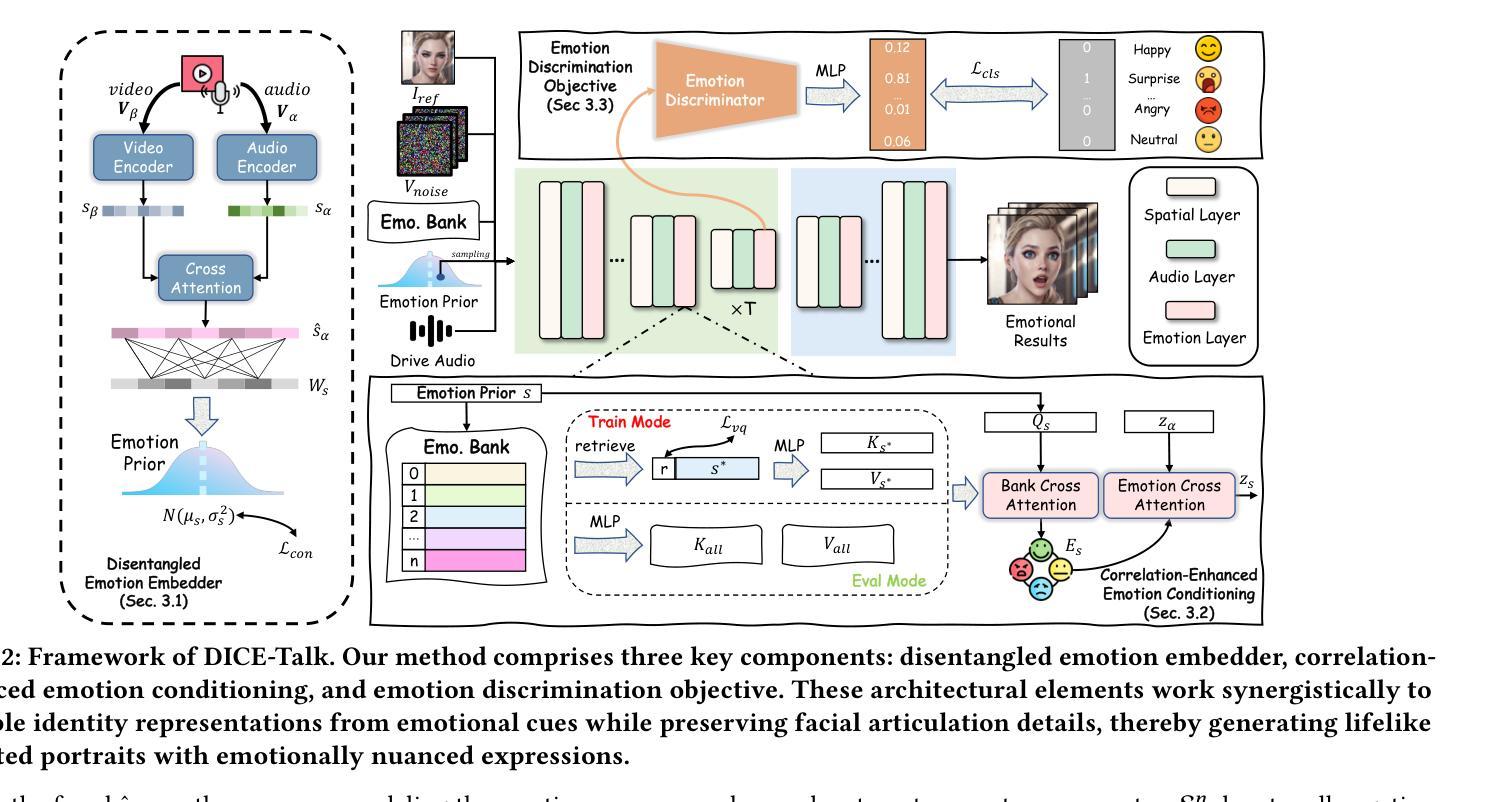
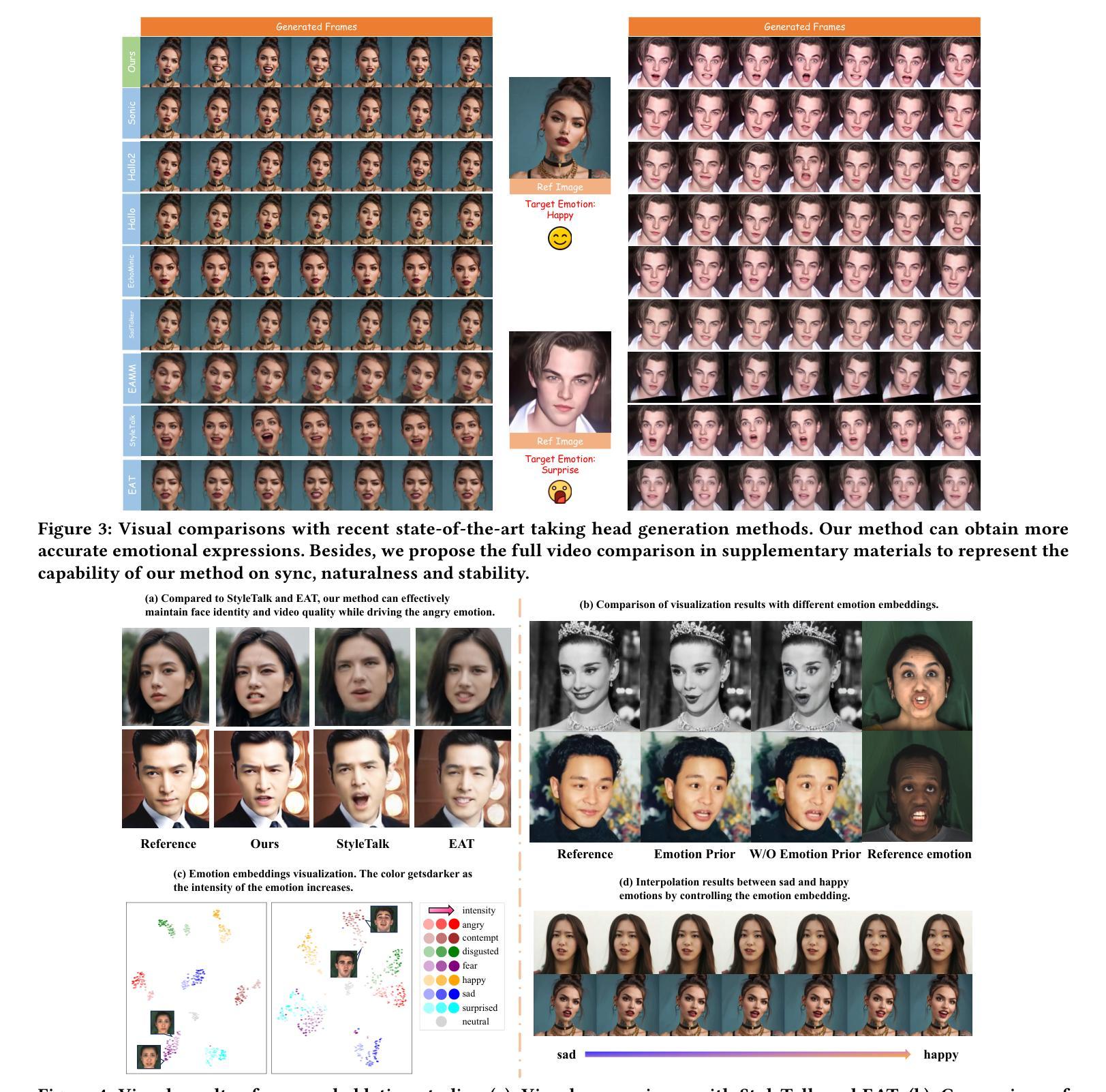
Disentangle Identity, Cooperate Emotion: Correlation-Aware Emotional Talking Portrait Generation
Authors:Weipeng Tan, Chuming Lin, Chengming Xu, FeiFan Xu, Xiaobin Hu, Xiaozhong Ji, Junwei Zhu, Chengjie Wang, Yanwei Fu
Recent advances in Talking Head Generation (THG) have achieved impressive lip synchronization and visual quality through diffusion models; yet existing methods struggle to generate emotionally expressive portraits while preserving speaker identity. We identify three critical limitations in current emotional talking head generation: insufficient utilization of audio’s inherent emotional cues, identity leakage in emotion representations, and isolated learning of emotion correlations. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework dubbed as DICE-Talk, following the idea of disentangling identity with emotion, and then cooperating emotions with similar characteristics. First, we develop a disentangled emotion embedder that jointly models audio-visual emotional cues through cross-modal attention, representing emotions as identity-agnostic Gaussian distributions. Second, we introduce a correlation-enhanced emotion conditioning module with learnable Emotion Banks that explicitly capture inter-emotion relationships through vector quantization and attention-based feature aggregation. Third, we design an emotion discrimination objective that enforces affective consistency during the diffusion process through latent-space classification. Extensive experiments on MEAD and HDTF datasets demonstrate our method’s superiority, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches in emotion accuracy while maintaining competitive lip-sync performance. Qualitative results and user studies further confirm our method’s ability to generate identity-preserving portraits with rich, correlated emotional expressions that naturally adapt to unseen identities.
在Talking Head Generation(THG)的最新进展中,通过扩散模型实现了令人印象深刻的唇同步和视觉质量。然而,现有方法在生成情感表达肖像时很难同时保留说话者的身份。我们确定了当前情感对话头像生成中的三个关键局限性:未能充分利用音频的内在情感线索、情感表示中的身份泄露以及情感关联的独立学习。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个名为DICE-Talk的新型框架,它的理念是解开身份与情感的关系,然后与具有类似特征的情感进行合作。首先,我们开发了一个解开的情感嵌入器,它通过跨模态注意力联合建模音频-视觉情感线索,将情感表示为与身份无关的高斯分布。其次,我们引入了一个增强相关性的情感调节模块,该模块具有可学习的情感库,通过向量量化和基于注意力的特征聚合显式捕获相互间的情感关系。第三,我们设计了一个情感辨别目标,通过在潜在空间分类来强化扩散过程中的情感一致性。在MEAD和HDTF数据集上的大量实验证明了我们方法的优越性,在情感准确性方面超过了最先进的方法,同时保持了有竞争力的唇同步性能。定性和用户研究进一步证实了我们方法生成具有丰富、相关情感表达的、保留身份的肖像的能力,这些肖像能够自然地适应未见过的身份。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM’25. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2409.03270
Summary
本文介绍了在Talking Head Generation(THG)领域的最新进展,指出了现有方法面临的挑战,如未能充分利用音频中的情感线索、身份和情感表示之间的混淆以及情感关联学习的孤立性。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为DICE-Talk的新型框架,通过解耦身份和情感,然后合作具有相似特征的情感。该框架包括开发一个解耦情感嵌入器,一个增强情感调节的模块和一个情感鉴别目标。实验证明,该方法在情感准确性方面优于现有技术,同时保持竞争性的唇同步性能。定性结果和用户研究进一步证实了该方法在生成具有丰富情感表达和身份一致性的肖像方面的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前Talking Head Generation(THG)在情感表达方面存在挑战,如未能充分利用音频中的情感线索和身份与情感的混淆。
- 提出了一种新型框架DICE-Talk,旨在解决这些问题,通过解耦身份和情感,并合作具有相似特征的情感。
- DICE-Talk包括一个解耦情感嵌入器,该嵌入器通过跨模态注意力联合建模音频视觉情感线索,并将情感表示为身份无关的高斯分布。
- 引入了一个增强情感调节的模块,通过向量量化和基于注意力的特征聚合显式捕获情感之间的关系。
- 设计了一个情感鉴别目标,通过潜在空间分类在扩散过程中强制执行情感一致性。
- 实验证明,DICE-Talk在情感准确性方面优于现有技术,同时保持竞争性的唇同步性能。
点此查看论文截图

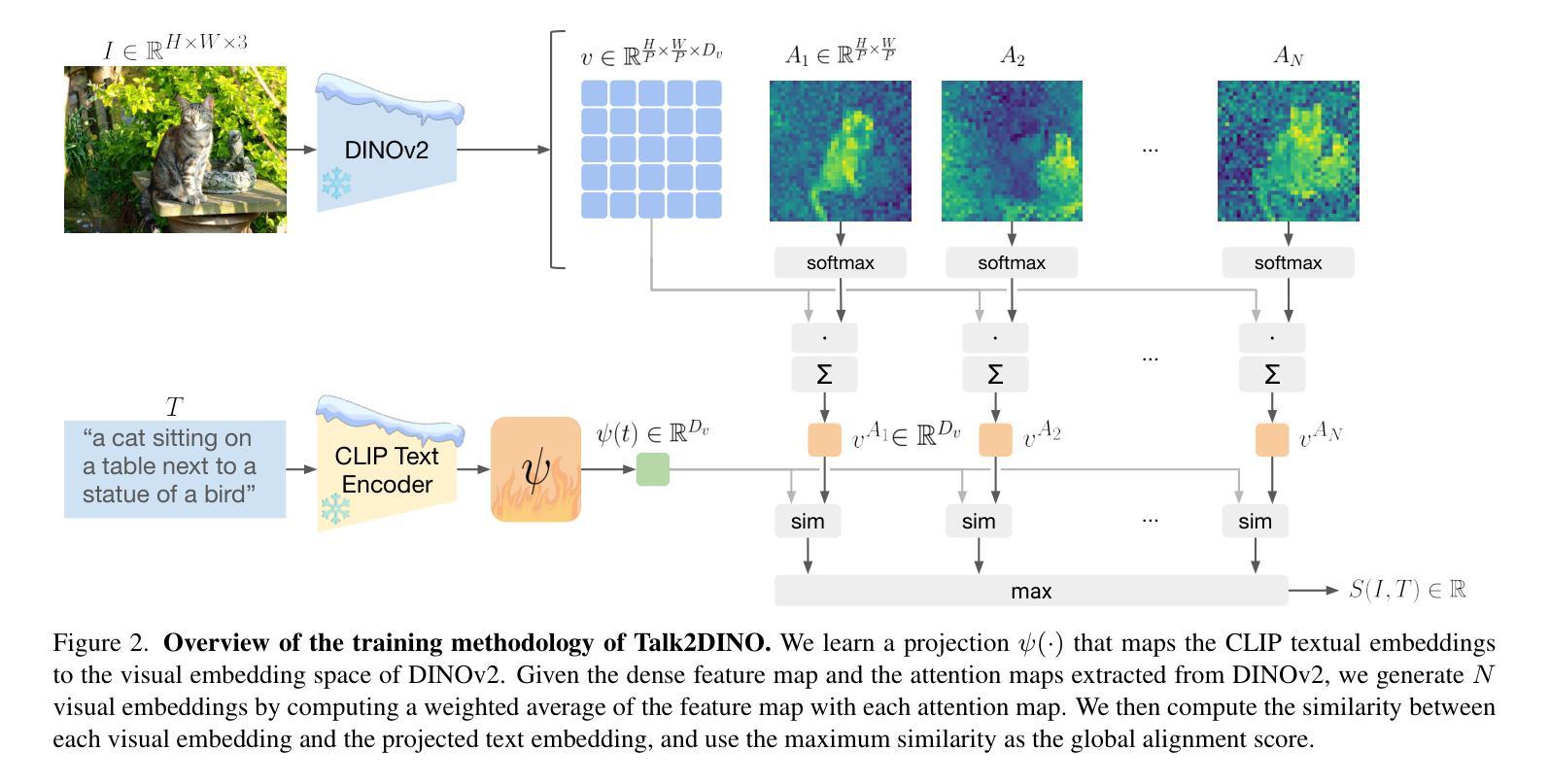
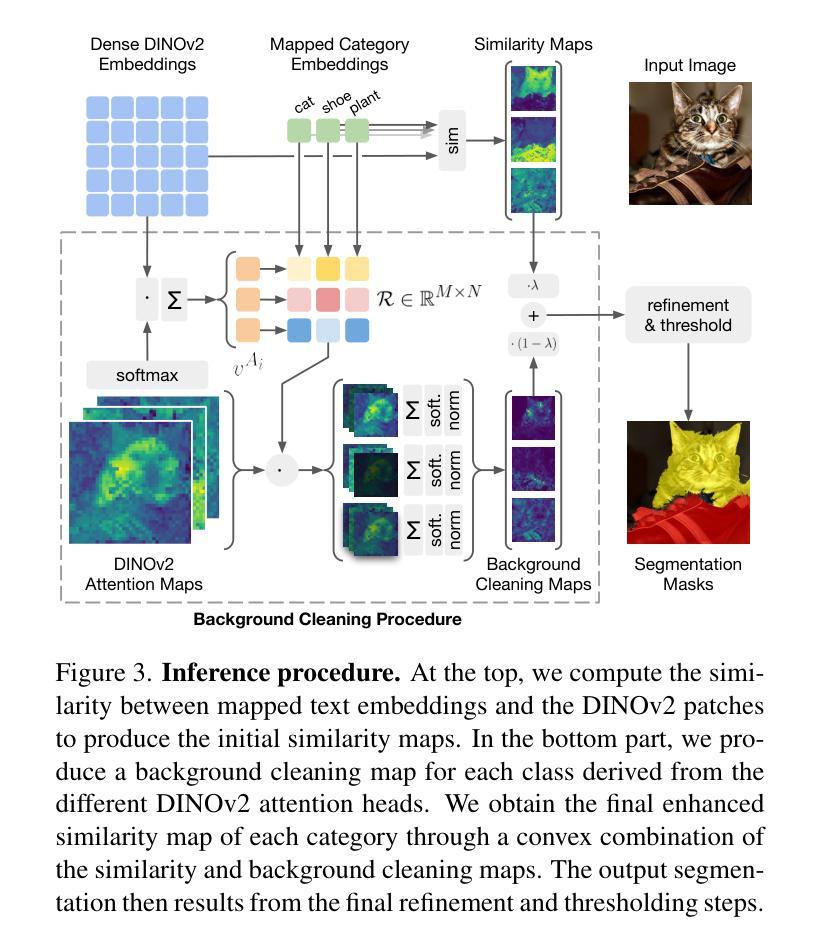
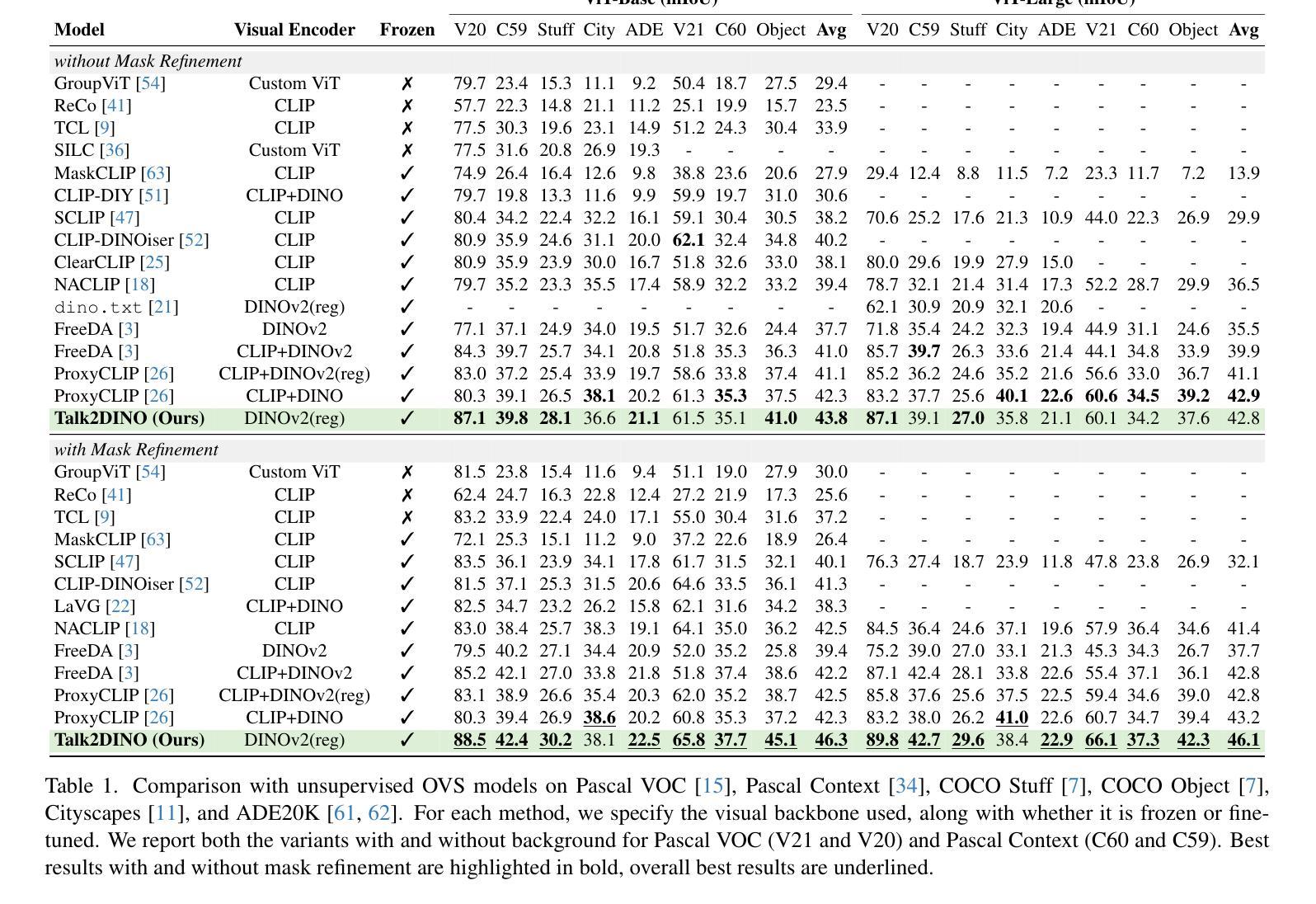
Talking to DINO: Bridging Self-Supervised Vision Backbones with Language for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Authors:Luca Barsellotti, Lorenzo Bianchi, Nicola Messina, Fabio Carrara, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Fabrizio Falchi, Rita Cucchiara
Open-Vocabulary Segmentation (OVS) aims at segmenting images from free-form textual concepts without predefined training classes. While existing vision-language models such as CLIP can generate segmentation masks by leveraging coarse spatial information from Vision Transformers, they face challenges in spatial localization due to their global alignment of image and text features. Conversely, self-supervised visual models like DINO excel in fine-grained visual encoding but lack integration with language. To bridge this gap, we present Talk2DINO, a novel hybrid approach that combines the spatial accuracy of DINOv2 with the language understanding of CLIP. Our approach aligns the textual embeddings of CLIP to the patch-level features of DINOv2 through a learned mapping function without the need to fine-tune the underlying backbones. At training time, we exploit the attention maps of DINOv2 to selectively align local visual patches with textual embeddings. We show that the powerful semantic and localization abilities of Talk2DINO can enhance the segmentation process, resulting in more natural and less noisy segmentations, and that our approach can also effectively distinguish foreground objects from the background. Experimental results demonstrate that Talk2DINO achieves state-of-the-art performance across several unsupervised OVS benchmarks. Source code and models are publicly available at: https://lorebianchi98.github.io/Talk2DINO/.
开放词汇分割(OVS)旨在从自由的文本概念中对图像进行分割,而无需预先定义的训练类别。虽然现有的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)可以利用视觉变压器的粗略空间信息生成分割掩码,但由于图像和文本特征的全局对齐,它们在空间定位方面面临挑战。相反,自监督的视觉模型(如DINO)在精细的视觉编码方面表现出色,但与语言的结合能力有待提高。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了Talk2DINO,这是一种新型混合方法,结合了DINOv2的空间精度与CLIP的语言理解能力。我们的方法通过将CLIP的文本嵌入与DINOv2的补丁级别特征通过学习的映射函数对齐,而无需微调底层骨干网。在训练过程中,我们利用DINOv2的注意力图有选择地将局部视觉补丁与文本嵌入对齐。我们证明了Talk2DINO的强大语义和定位能力可以加强分割过程,产生更自然、更少噪声的分割结果,并且我们的方法还可以有效地区分前景物体和背景。实验结果表明,Talk2DINO在多个无监督OVS基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。源代码和模型可在:https://lorebianchi98.github.io/Talk2DINO/公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
结合CLIP的语言理解和DINOv2的空间准确性,通过学得映射函数对齐文本嵌入与局部视觉特征,提出一种新颖的混合方法Talk2DINO,用于开放式词汇分割任务,提高语义理解和定位能力,实现更自然、少噪声的分割效果,并有效区分前景和背景物体。
要点提炼
- 开放词汇分割(OVS)的目标是从自由形式的文本概念中对图像进行分割,无需预定义训练类别。
- 现有视觉语言模型如CLIP可利用粗略的空间信息生成分割掩膜,但面临空间定位的挑战。
- 自我监督的视觉模型如DINO擅长精细的视觉编码,但缺乏与语言的整合。
- Talk2DINO结合了CLIP的语言理解与DINOv2的空间准确性,提高了语义理解和定位能力。
- 通过学得映射函数对齐CLIP的文本嵌入与DINOv2的局部视觉特征,无需微调底层架构。
- 利用DINOv2的注意力图选择性地对齐局部视觉块与文本嵌入。
点此查看论文截图