⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-08 更新
Visual Bias and Interpretability in Deep Learning for Dermatological Image Analysis
Authors:Enam Ahmed Taufik, Abdullah Khondoker, Antara Firoz Parsa, Seraj Al Mahmud Mostafa
Accurate skin disease classification is a critical yet challenging task due to high inter-class similarity, intra-class variability, and complex lesion textures. While deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems have shown promise in automating dermatological assessments, their performance is highly dependent on image pre-processing and model architecture. This study proposes a deep learning framework for multi-class skin disease classification, systematically evaluating three image pre-processing techniques: standard RGB, CMY color space transformation, and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE). We benchmark the performance of pre-trained convolutional neural networks (DenseNet201, Efficient-NetB5) and transformer-based models (ViT, Swin Transformer, DinoV2 Large) using accuracy and F1-score as evaluation metrics. Results show that DinoV2 with RGB pre-processing achieves the highest accuracy (up to 93%) and F1-scores across all variants. Grad-CAM visualizations applied to RGB inputs further reveal precise lesion localization, enhancing interpretability. These findings underscore the importance of effective pre-processing and model choice in building robust and explainable CAD systems for dermatology.
精确的皮肤疾病分类是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务,因为存在类间相似性高、类内变化大以及病变纹理复杂等问题。虽然基于深度学习的计算机辅助诊断(CAD)系统在自动化皮肤科评估方面显示出潜力,但其性能高度依赖于图像预处理和模型架构。本研究提出一个深度学习框架,用于多类皮肤疾病分类,系统评估三种图像预处理技术:标准RGB、CMY色彩空间转换和对比度有限的自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)。我们以准确率(accuracy)和F1分数作为评价指标,评估了预训练卷积神经网络(DenseNet201、Efficient-NetB5)和基于transformer的模型(ViT、Swin Transformer、DinoV2 Large)的性能。结果表明,使用RGB预处理的DinoV2模型在准确率和F1分数方面均达到最高(高达93%)。应用于RGB输入的Grad-CAM可视化进一步揭示了精确的病变定位,提高了可解释性。这些发现强调了有效预处理和模型选择对于构建稳健且可解释的皮肤科CAD系统的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted in the 4th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing and Media Computing (ICIPMC) 2025
Summary
本文研究了深度学习在多类皮肤病分类中的应用,探讨了不同的图像预处理方法对模型性能的影响。实验结果表明,采用DinoV2模型与RGB预处理技术相结合,可达到最高分类准确率(高达93%)和F1分数。此外,Grad-CAM可视化技术能精确显示病变部位,增强了模型的解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在皮肤病分类中面临高类间相似度、类内差异大和病变纹理复杂等挑战。
- 图像预处理和模型架构对深度学习在皮肤病分类中的性能有重要影响。
- 研究对比了多种图像预处理方法,包括标准RGB、CMY颜色空间转换和CLAHE。
- 采用了预训练的卷积神经网络(DenseNet201,Efficient-NetB5)和基于Transformer的模型(ViT,Swin Transformer,DinoV2 Large)进行实验。
- DinoV2模型结合RGB预处理技术获得最高分类准确率(高达93%)和F1分数。
- Grad-CAM可视化技术能精确显示病变部位,增强了模型的解释性。
- 研究强调了有效预处理和模型选择对于构建稳健和可解释的计算机辅助诊断系统的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

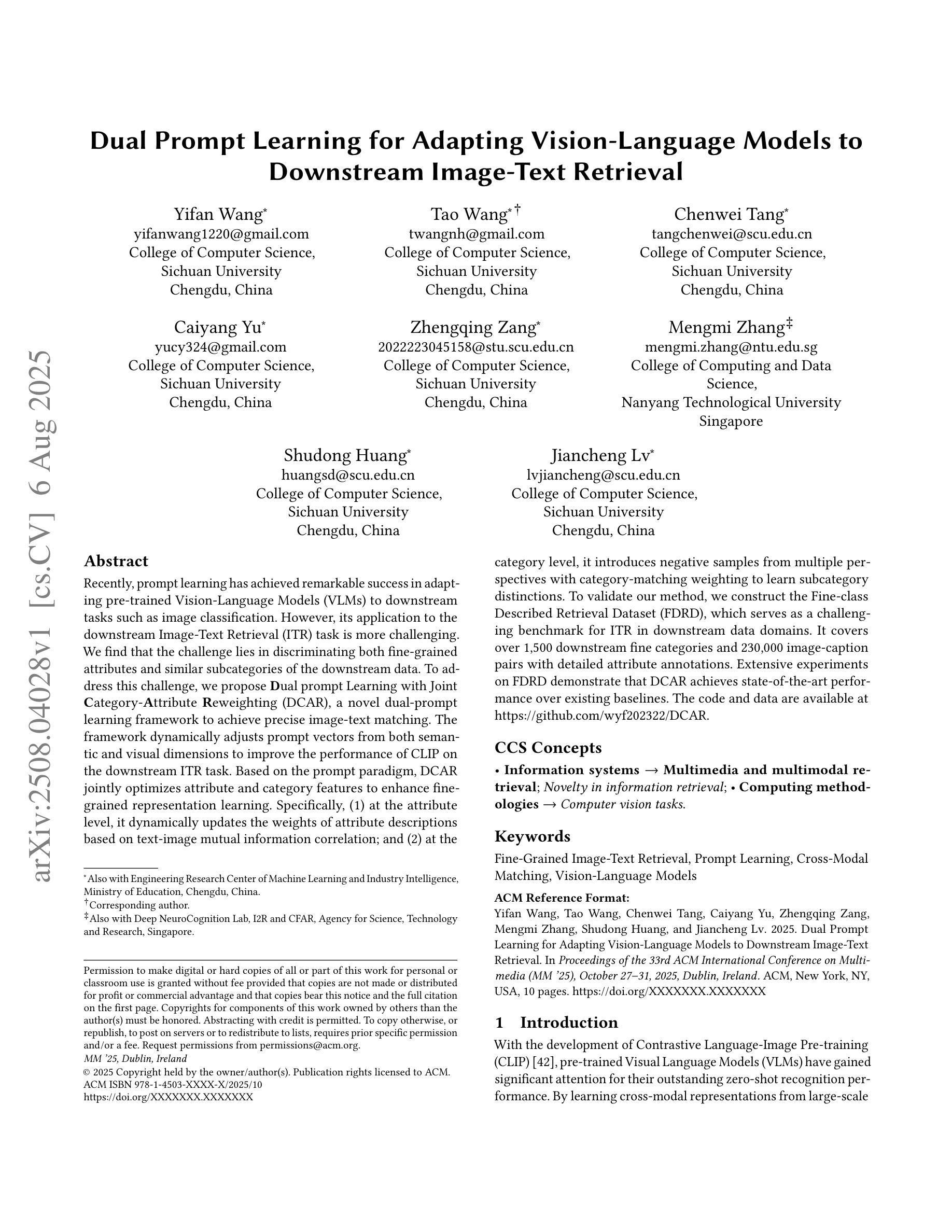
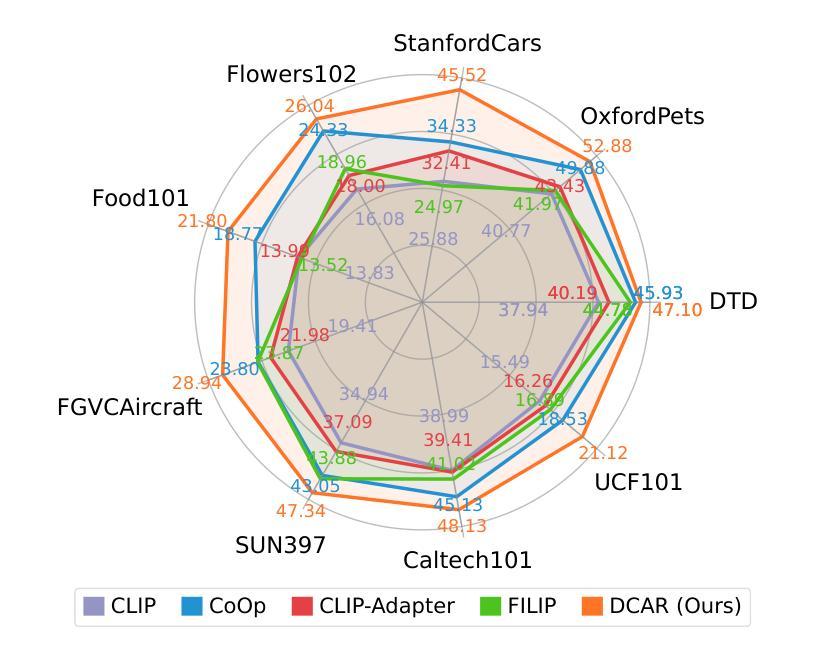
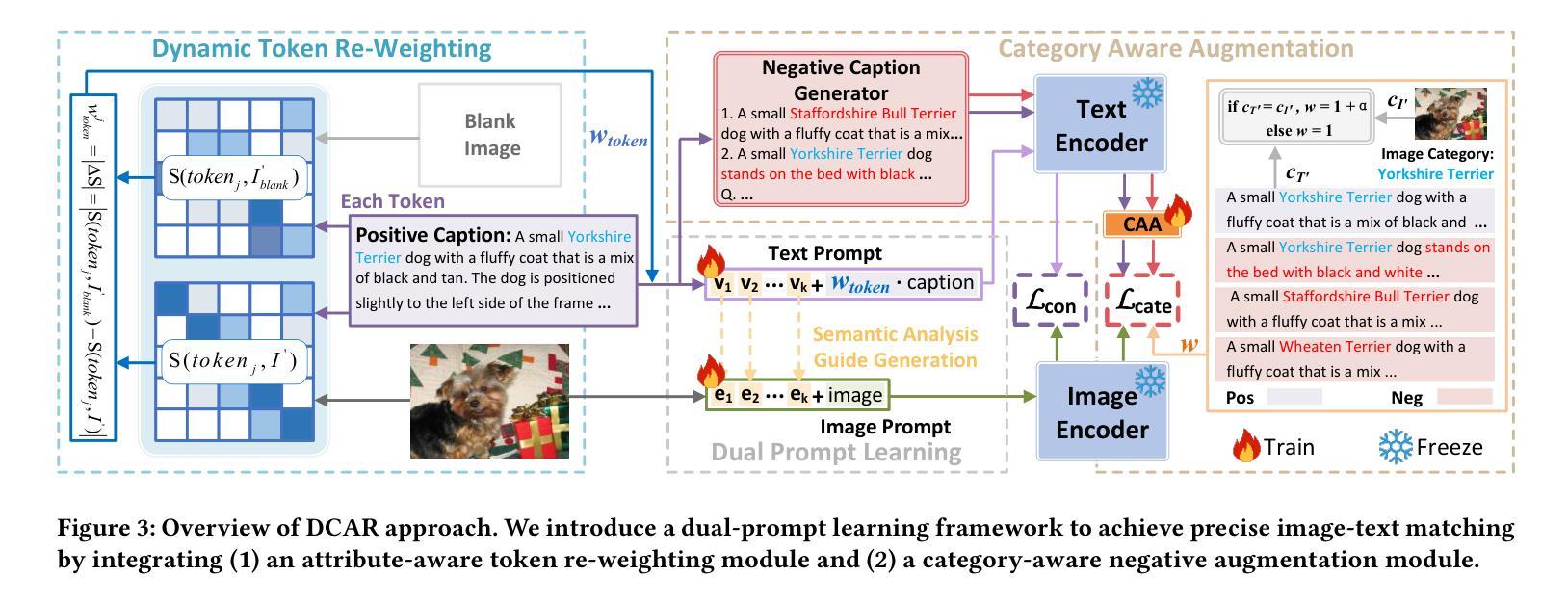
Dual Prompt Learning for Adapting Vision-Language Models to Downstream Image-Text Retrieval
Authors:Yifan Wang, Tao Wang, Chenwei Tang, Caiyang Yu, Zhengqing Zang, Mengmi Zhang, Shudong Huang, Jiancheng Lv
Recently, prompt learning has demonstrated remarkable success in adapting pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to various downstream tasks such as image classification. However, its application to the downstream Image-Text Retrieval (ITR) task is more challenging. We find that the challenge lies in discriminating both fine-grained attributes and similar subcategories of the downstream data. To address this challenge, we propose Dual prompt Learning with Joint Category-Attribute Reweighting (DCAR), a novel dual-prompt learning framework to achieve precise image-text matching. The framework dynamically adjusts prompt vectors from both semantic and visual dimensions to improve the performance of CLIP on the downstream ITR task. Based on the prompt paradigm, DCAR jointly optimizes attribute and class features to enhance fine-grained representation learning. Specifically, (1) at the attribute level, it dynamically updates the weights of attribute descriptions based on text-image mutual information correlation; (2) at the category level, it introduces negative samples from multiple perspectives with category-matching weighting to learn subcategory distinctions. To validate our method, we construct the Fine-class Described Retrieval Dataset (FDRD), which serves as a challenging benchmark for ITR in downstream data domains. It covers over 1,500 downstream fine categories and 230,000 image-caption pairs with detailed attribute annotations. Extensive experiments on FDRD demonstrate that DCAR achieves state-of-the-art performance over existing baselines.
最近,提示学习在将预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)适应于各种下游任务(如图像分类)方面取得了显著的成功。然而,其在下游的图像文本检索(ITR)任务中的应用更具挑战性。我们发现,挑战在于区分下游数据的精细属性以及相似的子类别。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了基于联合类别属性再权重的双重提示学习(DCAR),这是一种新型的双提示学习框架,可实现精确的图生文本匹配。该框架根据语义和视觉维度动态调整提示向量,以提高CLIP在下游ITR任务上的性能。基于提示范式,DCAR联合优化属性和类别特征,以增强精细粒度表示学习。具体来说,(1)在属性层面,它根据文本图像互信息相关性动态更新属性描述权重;(2)在类别层面,它从多个角度引入带类别匹配的负样本来学习子类别的区别。为了验证我们的方法,我们构建了精细分类描述检索数据集(FDRD),作为下游数据域的ITR挑战基准数据集。它涵盖了超过1500个下游精细类别和带有详细属性注释的23万个图像标题对。在FDRD上的大量实验表明,DCAR在现有基线技术上实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7figures
Summary
本文提出了基于双提示学习框架的联合类别属性再权重方法(DCAR),以应对下游图像文本检索任务中的精细分类挑战。DCAR动态调整语义和视觉维度的提示向量,提高CLIP在下游图像文本检索任务上的性能。同时,DCAR优化了属性级特征分类级特征,增强精细粒度表示学习。通过动态更新属性描述的权重和引入多视角的负样本及类别匹配权重,DCAR解决了下游数据的精细分类和相似子类别区分问题。
Key Takeaways
- 提示学习在预训练的视觉语言模型适应下游任务如图像分类中取得了显著成功,但在图像文本检索任务中更具挑战性。
- 挑战在于区分下游数据的精细粒度和相似子类别。
- DCAR是一种新颖的双提示学习框架,通过动态调整语义和视觉维度的提示向量,实现精确图像文本匹配,提高CLIP在下游图像文本检索任务上的性能。
- DCAR同时优化属性级和分类级特征,以增强精细粒度表示学习。
- 在属性层面,DCAR根据文本图像互信息相关性动态更新属性描述的权重。
- 在类别层面,DCAR通过引入多视角的负样本和类别匹配权重,学习子类别间的差异。
点此查看论文截图


Investigating the Impact of Large-Scale Pre-training on Nutritional Content Estimation from 2D Images
Authors:Michele Andrade, Guilherme A. L. Silva, Valéria Santos, Gladston Moreira, Eduardo Luz
Estimating the nutritional content of food from images is a critical task with significant implications for health and dietary monitoring. This is challenging, especially when relying solely on 2D images, due to the variability in food presentation, lighting, and the inherent difficulty in inferring volume and mass without depth information. Furthermore, reproducibility in this domain is hampered by the reliance of state-of-the-art methods on proprietary datasets for large-scale pre-training. In this paper, we investigate the impact of large-scale pre-training datasets on the performance of deep learning models for nutritional estimation using only 2D images. We fine-tune and evaluate Vision Transformer (ViT) models pre-trained on two large public datasets, ImageNet and COYO, comparing their performance against baseline CNN models (InceptionV2 and ResNet-50) and a state-of-the-art method pre-trained on the proprietary JFT-300M dataset. We conduct extensive experiments on the Nutrition5k dataset, a large-scale collection of real-world food plates with high-precision nutritional annotations. Our evaluation using Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAE%) reveals that models pre-trained on JFT-300M significantly outperform those pre-trained on public datasets. Unexpectedly, the model pre-trained on the massive COYO dataset performs worse than the model pre-trained on ImageNet for this specific regression task, refuting our initial hypothesis. Our analysis provides quantitative evidence highlighting the critical role of pre-training dataset characteristics, including scale, domain relevance, and curation quality, for effective transfer learning in 2D nutritional estimation.
从图像估算食品的营养成分是健康与饮食监测中具有重要意义的任务。这是一项挑战,尤其是仅依赖2D图像时,由于食品展示、光照的差异性以及缺乏深度信息导致推断体积和质量固有的困难。此外,该领域的可重复性受到了阻碍,因为最先进的方法依赖于大规模预训练的专有数据集。在本文中,我们研究了大规模预训练数据集对仅使用2D图像进行营养估算的深度学习模型性能的影响。我们微调并评估了在ImageNet和COYO两个大型公共数据集上预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,将其性能与基线CNN模型(InceptionV2和ResNet-50)以及预训练在专有JFT-300M数据集上的最新方法进行比较。我们在Nutrition5k数据集上进行了大量实验,该数据集是包含高精度营养注释的大规模现实世界食品盘点集合。我们使用平均绝对误差(MAE)和平均绝对百分比误差(MAE%)进行评估,结果显示预训练在JFT-300M上的模型显著优于在公共数据集上预训练的模型。出乎意料的是,在大量COYO数据集上预训练的模型在此特定回归任务上的表现比预训练在ImageNet上的模型差,这反驳了我们最初的假设。我们的分析提供了定量证据,突出显示了预训练数据集特性(包括规模、领域相关性和编纂质量)在二维营养估算中的有效迁移学习中的关键作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
摘要
本文研究了大规模预训练数据集对仅使用2D图像进行营养估算的深度学习模型性能的影响。通过微调并在Nutrition5k数据集上评估预训练于ImageNet和COYO的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,与基准CNN模型(InceptionV2和ResNet-50)以及预训练于专有JFT-300M数据集的最先进方法进行比较。实验结果表明,预训练于JFT-300M的模型显著优于预训练于公开数据集的模型。意外的是,预训练于巨大COYO数据集的模型在此特定回归任务上的表现不如预训练于ImageNet的模型,这反驳了我们的初步假设。分析提供了定量证据,强调预训练数据集特性(包括规模、领域相关性和筛选质量)在2D营养估算中的有效迁移学习中的关键作用。
关键见解
- 估算食物营养成分的图像识别是一项重要任务,对健康和饮食监测有重大影响。
- 仅使用2D图像进行此任务具有挑战性,因为缺乏深度信息,且食物呈现、光照变化大。
- 现有先进方法依赖于专有大规模数据集进行预训练,阻碍了该领域的可重复性。
- 研究了大规模预训练数据集对营养估算深度学习模型性能的影响。
- 预训练于JFT-300M数据集的模型性能显著优于预训练于公开数据集的模型。
- COYO数据集在特定回归任务上的表现不如ImageNet,这反驳了关于数据集规模与性能之间直接关系的假设。
- 分析强调了预训练数据集特性(规模、领域相关性和筛选质量)在迁移学习中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

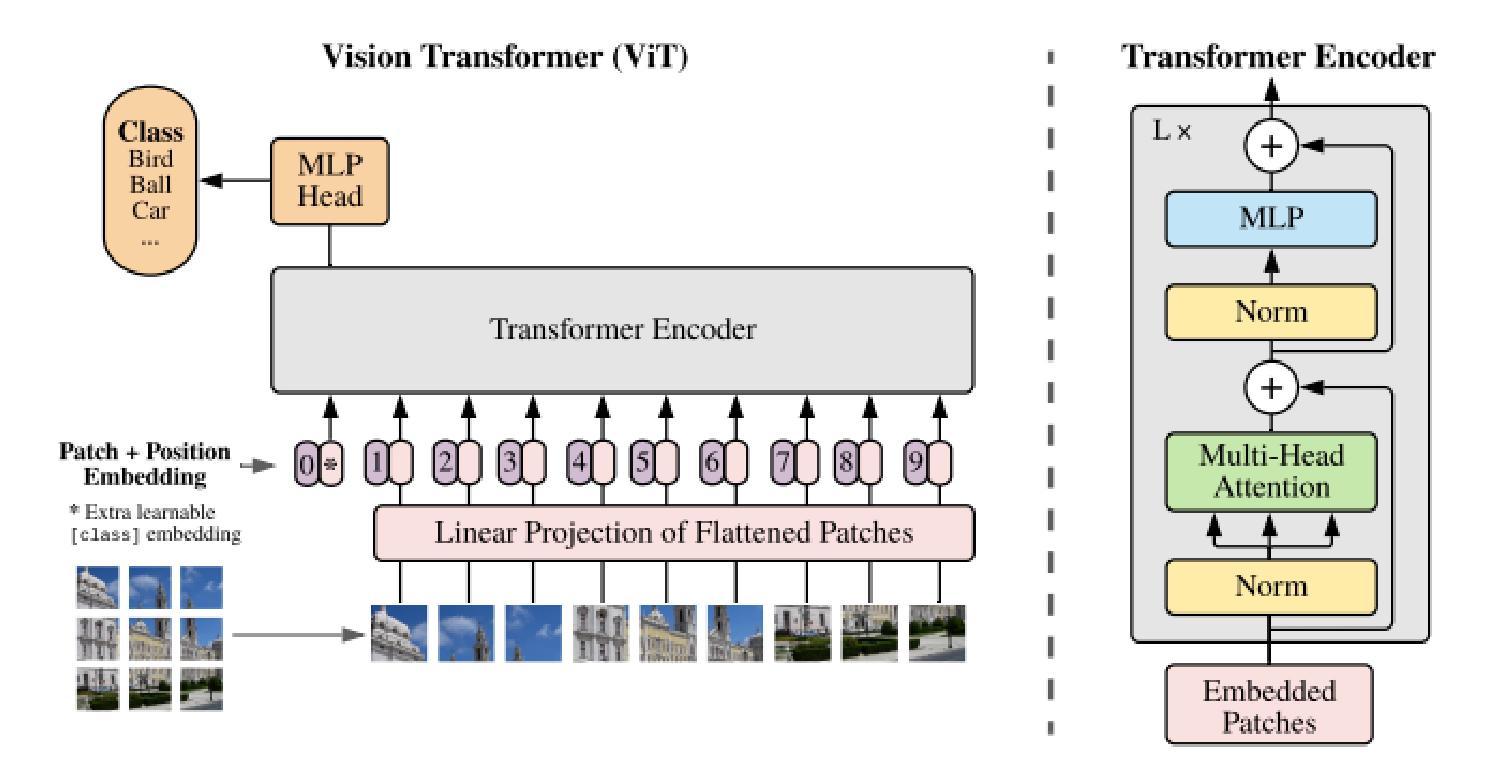
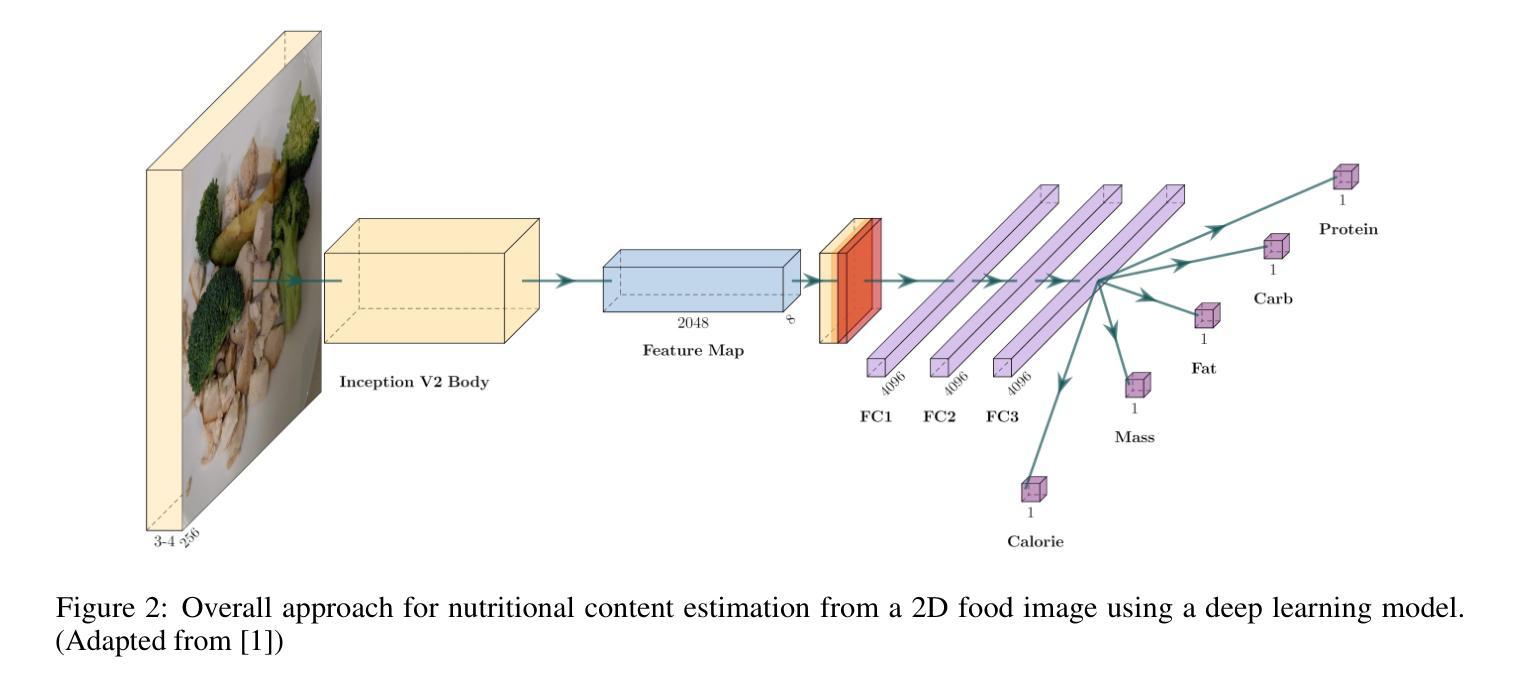
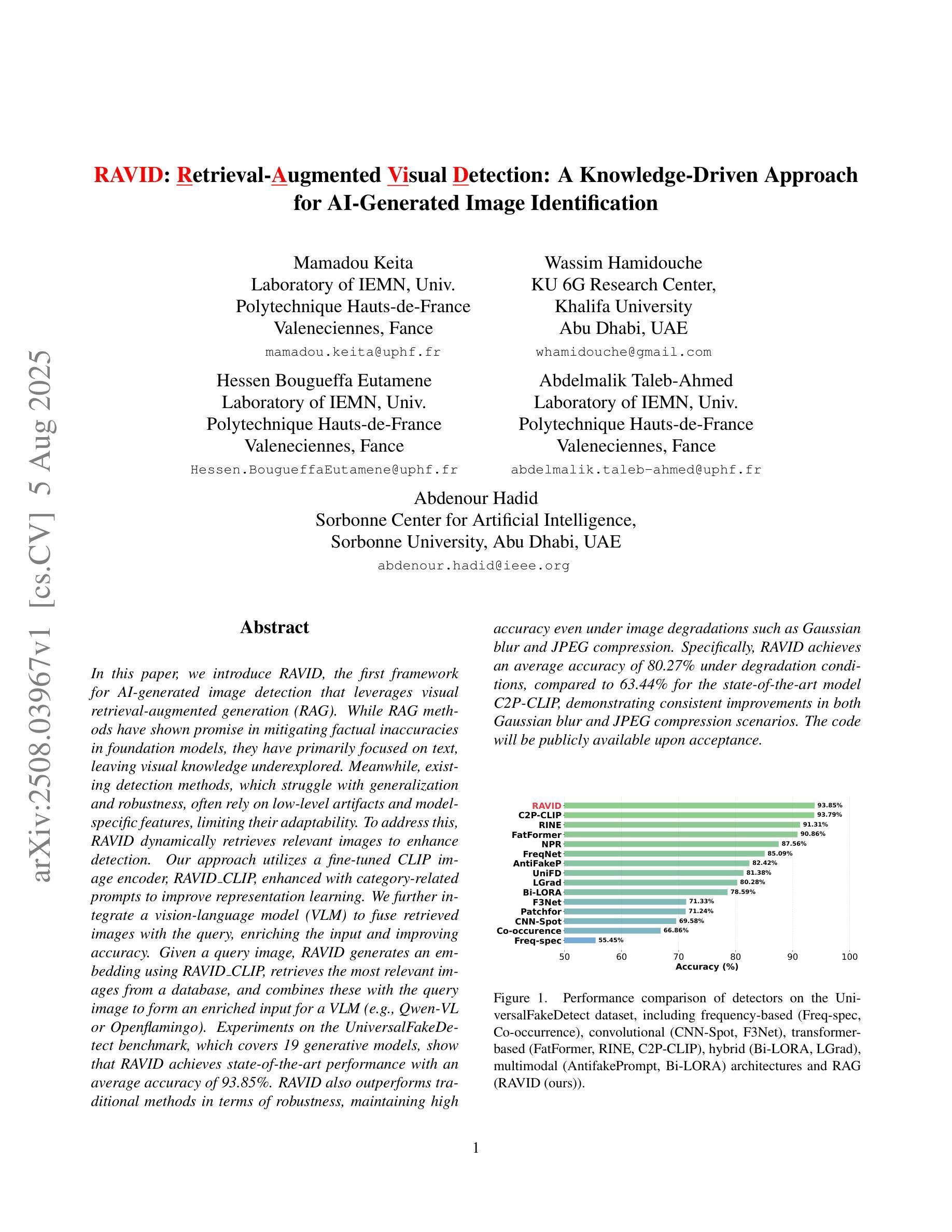
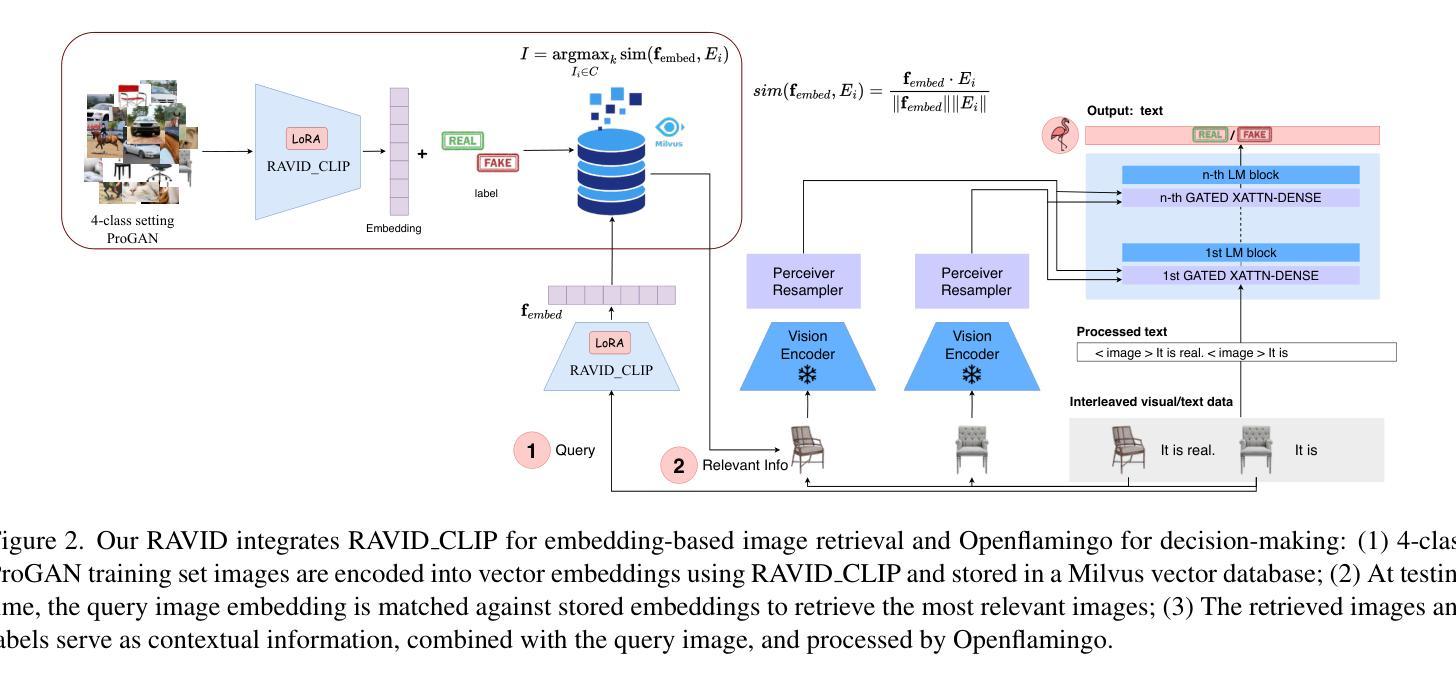
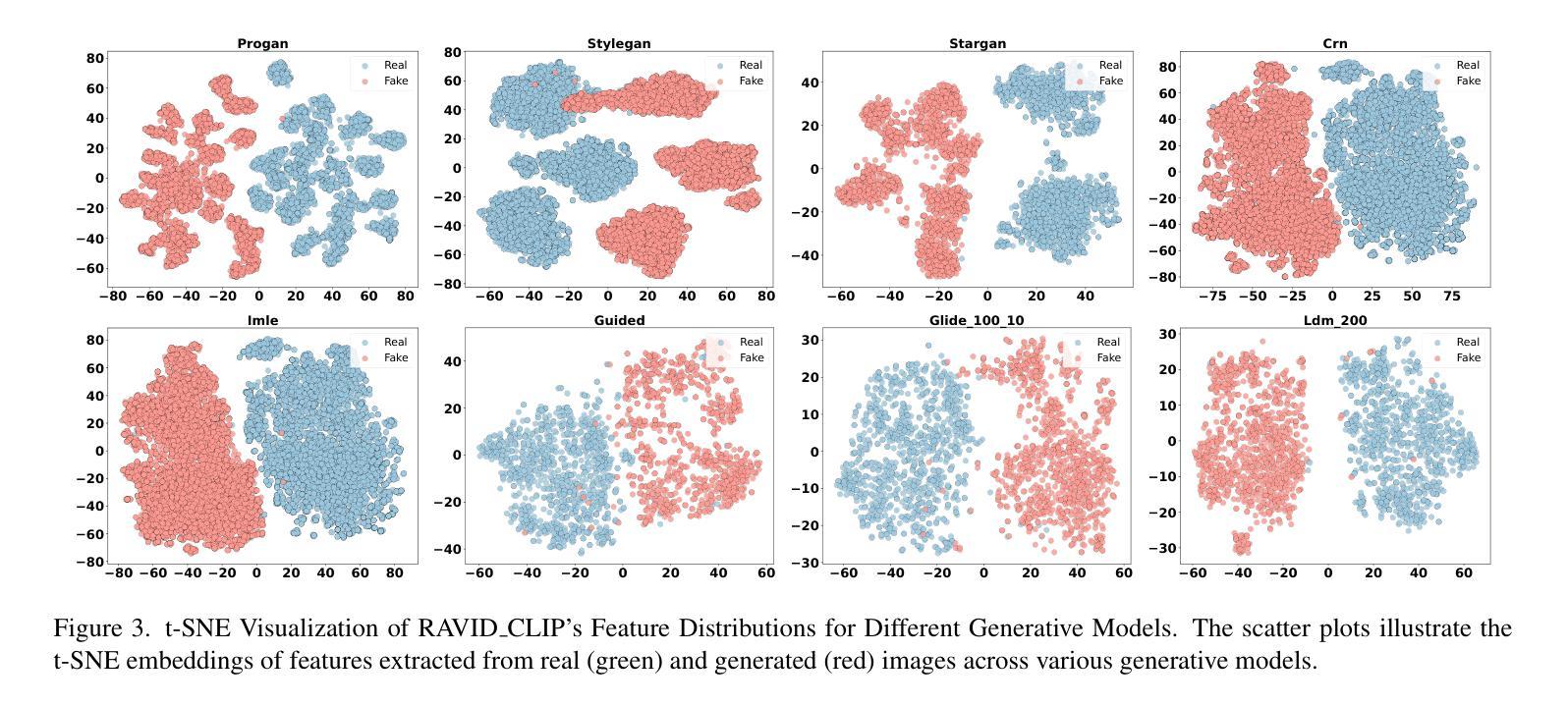
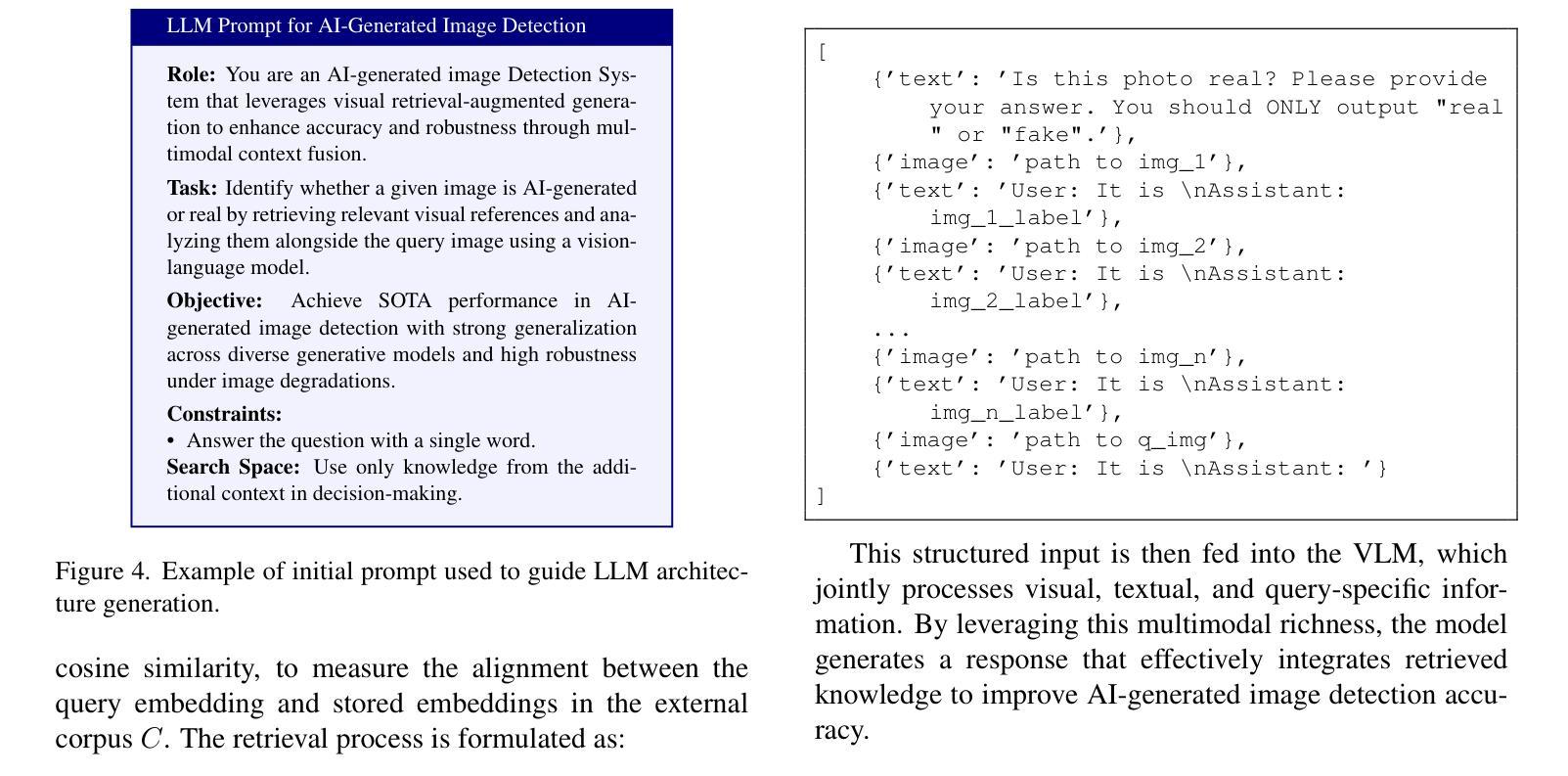
RAVID: Retrieval-Augmented Visual Detection: A Knowledge-Driven Approach for AI-Generated Image Identification
Authors:Mamadou Keita, Wassim Hamidouche, Hessen Bougueffa Eutamene, Abdelmalik Taleb-Ahmed, Abdenour Hadid
In this paper, we introduce RAVID, the first framework for AI-generated image detection that leverages visual retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). While RAG methods have shown promise in mitigating factual inaccuracies in foundation models, they have primarily focused on text, leaving visual knowledge underexplored. Meanwhile, existing detection methods, which struggle with generalization and robustness, often rely on low-level artifacts and model-specific features, limiting their adaptability. To address this, RAVID dynamically retrieves relevant images to enhance detection. Our approach utilizes a fine-tuned CLIP image encoder, RAVID CLIP, enhanced with category-related prompts to improve representation learning. We further integrate a vision-language model (VLM) to fuse retrieved images with the query, enriching the input and improving accuracy. Given a query image, RAVID generates an embedding using RAVID CLIP, retrieves the most relevant images from a database, and combines these with the query image to form an enriched input for a VLM (e.g., Qwen-VL or Openflamingo). Experiments on the UniversalFakeDetect benchmark, which covers 19 generative models, show that RAVID achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average accuracy of 93.85%. RAVID also outperforms traditional methods in terms of robustness, maintaining high accuracy even under image degradations such as Gaussian blur and JPEG compression. Specifically, RAVID achieves an average accuracy of 80.27% under degradation conditions, compared to 63.44% for the state-of-the-art model C2P-CLIP, demonstrating consistent improvements in both Gaussian blur and JPEG compression scenarios. The code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
本文介绍了RAVID,这是第一个利用视觉检索增强生成(RAG)进行AI生成图像检测的框架。虽然RAG方法在缓解基础模型中的事实错误方面显示出潜力,但它们主要集中在文本上,忽视了视觉知识的探索。与此同时,现有的检测方法在通用性和稳健性方面存在困难,它们往往依赖于低级的伪特征和模型特定的特征,这限制了它们的适应性。为了解决这一问题,RAVID动态检索相关图像以增强检测。我们的方法利用经过微调CLIP图像编码器RAVID CLIP,并通过与类别相关的提示来改善表示学习。我们进一步集成了一个视觉语言模型(VLM)来融合检索到的图像与查询,丰富输入并提高准确性。对于给定的查询图像,RAVID使用RAVID CLIP生成嵌入,从数据库中检索最相关的图像,并将这些图像与查询图像结合,形成一个丰富的输入用于VLM(例如Qwen-VL或Openflamingo)。在涵盖1第十九章生成模型的UniversalFakeDetect基准测试上的实验表明,RAVID达到了最先进的性能,平均准确率为93.85%。RAVID在稳健性方面也优于传统方法,即使在图像退化(如高斯模糊和JPEG压缩)的情况下也能保持高准确率。具体而言,RAVID在退化条件下的平均准确率为80.27%,而现有最先进的模型C2P-CLIP的准确率为63.44%,在Gaussian模糊和JPEG压缩场景中均表现出持续一致的改进。代码在接受后将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在本文中,我们引入了RAVID,这是第一个利用视觉检索增强生成技术(RAG)进行AI图像检测。它通过结合细调的CLIP图像编码器与类别相关的提示来改善表示学习,并通过集成视觉语言模型(VLM)来丰富检索图像与查询内容,从而提高检测准确性。在UniversalFakeDetect基准测试上,RAVID实现了平均准确率高达93.85%,展现出卓越的性能和稳健性。同时,在各种图像失真条件下,RAVID的表现也比现有方法更加优秀。此外,该模型还提供优秀的泛化能力。代码将在接受后公开。
Key Takeaways
- RAVID是首个利用视觉检索增强生成技术(RAG)进行AI图像检测的框架。
- RAG技术用于减轻基础模型中的事实不准确问题,并首次将该方法应用于图像检测领域。
- RAVID通过结合CLIP图像编码器与类别相关的提示来改善表示学习。
- RAVID集成了视觉语言模型(VLM),将检索到的图像与查询相结合,提高检测准确性。
- 在UniversalFakeDetect基准测试中,RAVID实现了高达93.85%的平均准确率,显示出卓越的性能和稳健性。
- RAVID在各种图像失真条件下表现出优越的性能,例如高斯模糊和JPEG压缩。相比其他方法如C2P-CLIP模型,具有更好的表现力和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
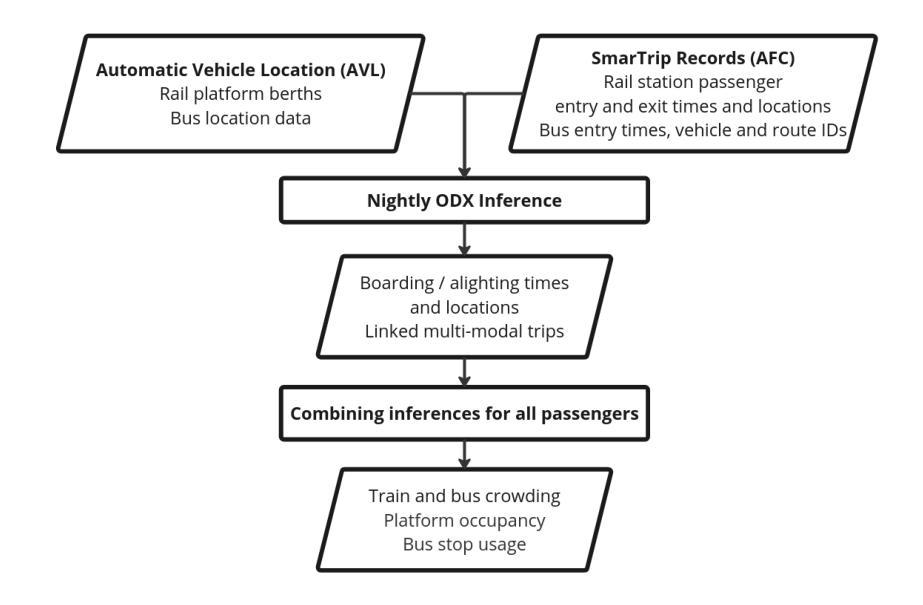
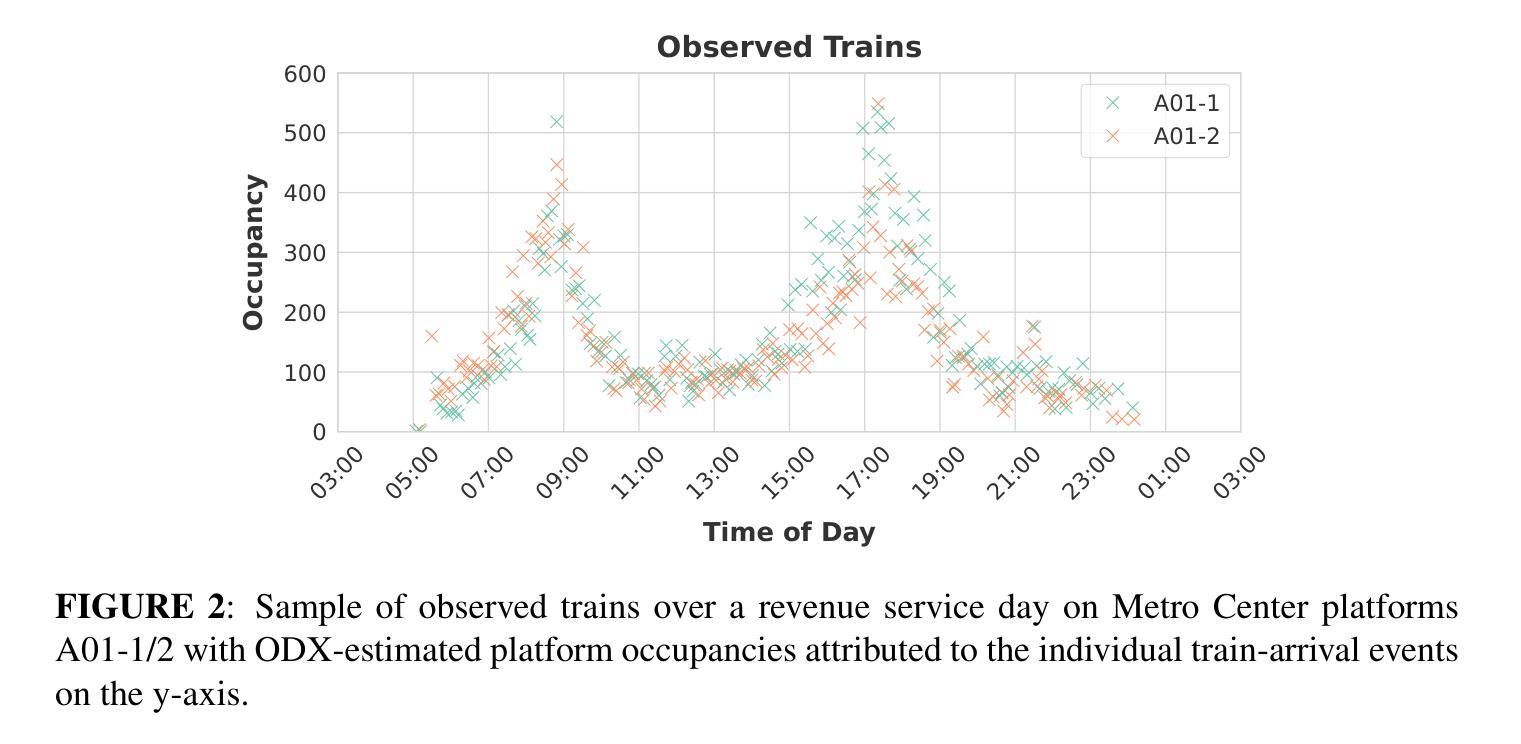
Closed-Circuit Television Data as an Emergent Data Source for Urban Rail Platform Crowding Estimation
Authors:Riccardo Fiorista, Awad Abdelhalim, Anson F. Stewart, Gabriel L. Pincus, Ian Thistle, Jinhua Zhao
Accurately estimating urban rail platform occupancy can enhance transit agencies’ ability to make informed operational decisions, thereby improving safety, operational efficiency, and customer experience, particularly in the context of crowding. However, sensing real-time crowding remains challenging and often depends on indirect proxies such as automatic fare collection data or staff observations. Recently, Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) footage has emerged as a promising data source with the potential to yield accurate, real-time occupancy estimates. The presented study investigates this potential by comparing three state-of-the-art computer vision approaches for extracting crowd-related features from platform CCTV imagery: (a) object detection and counting using YOLOv11, RT-DETRv2, and APGCC; (b) crowd-level classification via a custom-trained Vision Transformer, Crowd-ViT; and (c) semantic segmentation using DeepLabV3. Additionally, we present a novel, highly efficient linear-optimization-based approach to extract counts from the generated segmentation maps while accounting for image object depth and, thus, for passenger dispersion along a platform. Tested on a privacy-preserving dataset created in collaboration with the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (WMATA) that encompasses more than 600 hours of video material, our results demonstrate that computer vision approaches can provide substantive value for crowd estimation. This work demonstrates that CCTV image data, independent of other data sources available to a transit agency, can enable more precise real-time crowding estimation and, eventually, timely operational responses for platform crowding mitigation.
准确估计城市铁路月台乘客数量可以提升交通机构的决策能力,从而提高安全性、操作效率和客户体验,特别是在拥挤的情况下。然而,感知实时拥挤仍然是一个挑战,通常依赖于自动售票数据或员工观察等间接代理。最近,闭路电视(CCTV)影像作为一种有前景的数据源,具有产生准确、实时占用估计的潜力。本研究通过比较三种最先进的计算机视觉方法来探究这一潜力,这些方法可从月台CCTV影像中提取人群相关特征:(a)使用YOLOv11、RT-DETRv2和APGCC进行目标检测和计数;(b)通过自定义训练的视觉转换器Crowd-ViT进行人群级别分类;(c)使用DeepLabV3进行语义分割。此外,我们提出了一种新颖、高效基于线性优化的方法,从生成的分割图中提取计数,同时考虑图像对象深度和月台上的乘客分散情况。在与华盛顿地区交通局(WMATA)合作创建的隐私保护数据集上进行测试,该数据集包含超过600小时的视频材料,我们的结果表明,计算机视觉方法在人群估计中具有实质性价值。这项工作表明,独立于交通机构可用的其他数据源之外的CCTV图像数据,可以实现更精确的实时拥挤估计,并最终对月台拥挤缓解做出及时的运营响应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 17 figures, 4 tables
Summary:
本研究利用计算机视觉技术,通过闭路电视(CCTV)影像分析,对城市铁路平台乘客拥挤情况进行实时准确估算。研究比较了三种先进的计算机视觉方法,包括目标检测与计数、人群级别分类和语义分割,并提出一种新型线性优化方法以从分割地图中提取计数,同时考虑图像对象深度及乘客在平台上的分散情况。在隐私保护的数据集上进行测试,结果表明计算机视觉方法能为人群估算提供实质性价值,CCTV图像数据可独立于其他数据源,为交通机构提供更精确的实时拥挤估算和及时的平台拥挤缓解操作响应。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用CCTV影像进行城市铁路平台占用情况实时估算具有巨大潜力。
- 比较了三种先进的计算机视觉方法:YOLOv11、RT-DETRv2、APGCC进行目标检测与计数,Crowd-ViT进行人群级别分类以及DeepLabV3进行语义分割。
- 提出一种新型线性优化方法,可从分割地图中提取计数,并考虑图像对象的深度及乘客分散情况。
- 在隐私保护数据集上的测试证明计算机视觉方法在人群估算方面的价值。
- CCTV图像数据可独立于其他数据源,提供精确的实时拥挤估算。
- 该技术有助于提高交通机构的操作效率、安全性和客户体验,尤其在拥挤情况下。
点此查看论文截图


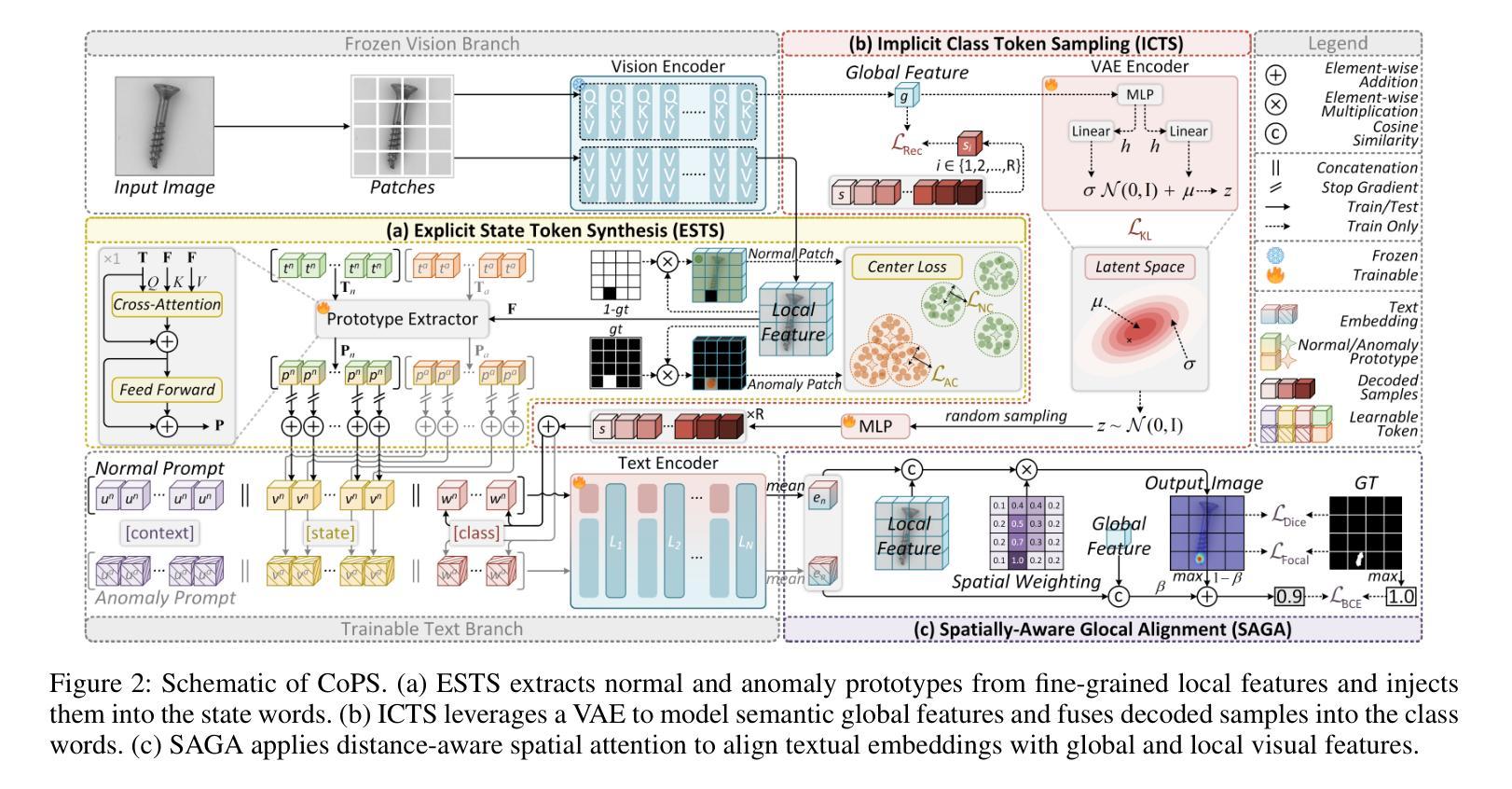
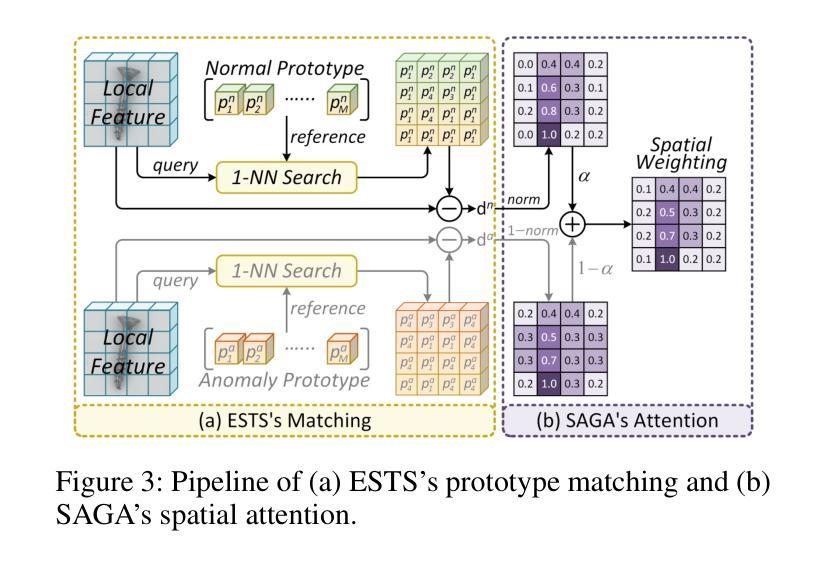
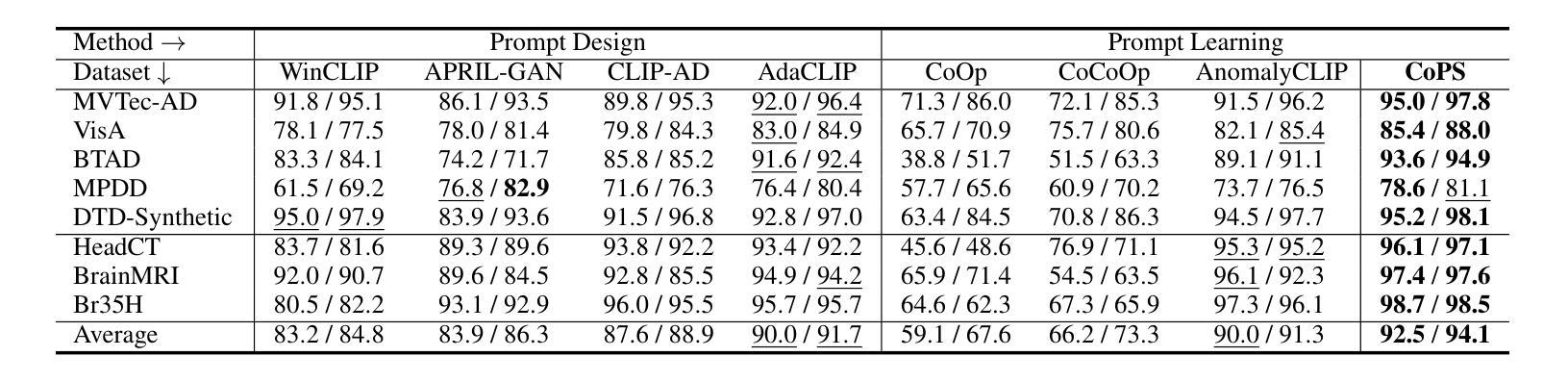
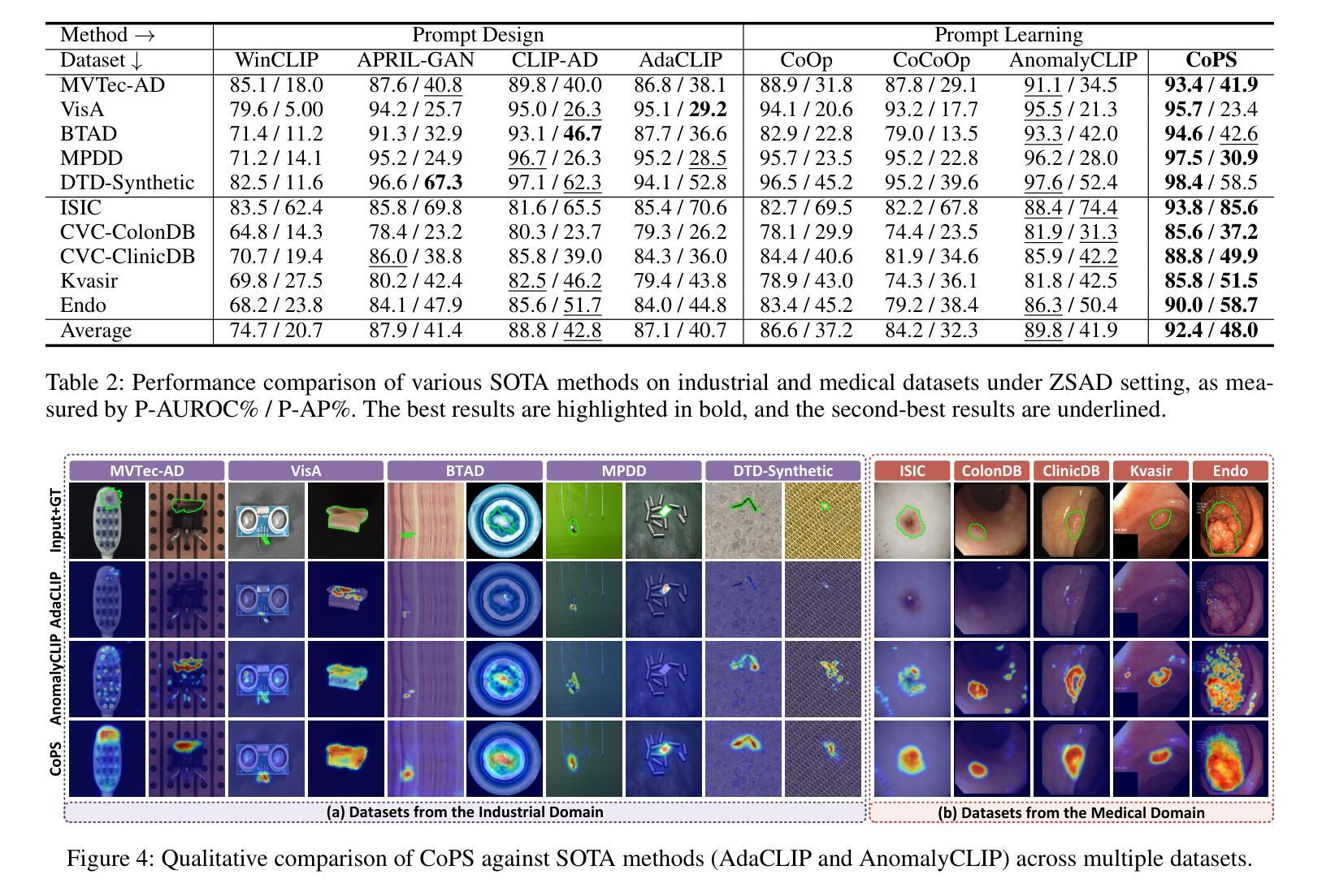
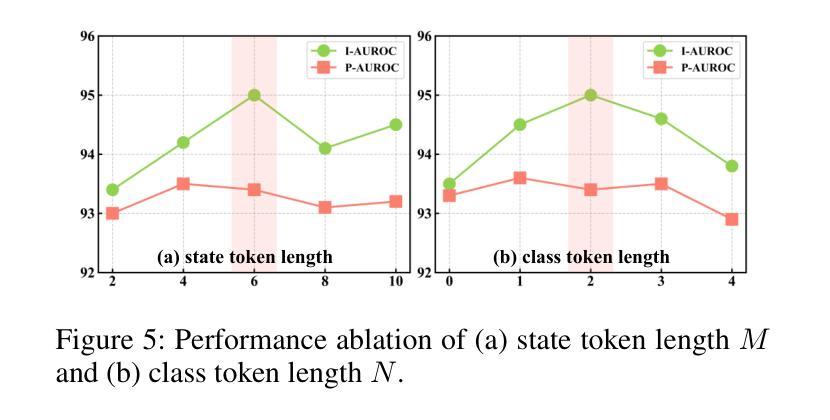
CoPS: Conditional Prompt Synthesis for Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Qiyu Chen, Zhen Qu, Wei Luo, Haiming Yao, Yunkang Cao, Yuxin Jiang, Yinan Duan, Huiyuan Luo, Chengkan Lv, Zhengtao Zhang
Recently, large pre-trained vision-language models have shown remarkable performance in zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD). With fine-tuning on a single auxiliary dataset, the model enables cross-category anomaly detection on diverse datasets covering industrial defects and medical lesions. Compared to manually designed prompts, prompt learning eliminates the need for expert knowledge and trial-and-error. However, it still faces the following challenges: (i) static learnable tokens struggle to capture the continuous and diverse patterns of normal and anomalous states, limiting generalization to unseen categories; (ii) fixed textual labels provide overly sparse category information, making the model prone to overfitting to a specific semantic subspace. To address these issues, we propose Conditional Prompt Synthesis (CoPS), a novel framework that synthesizes dynamic prompts conditioned on visual features to enhance ZSAD performance. Specifically, we extract representative normal and anomaly prototypes from fine-grained patch features and explicitly inject them into prompts, enabling adaptive state modeling. Given the sparsity of class labels, we leverage a variational autoencoder to model semantic image features and implicitly fuse varied class tokens into prompts. Additionally, integrated with our spatially-aware alignment mechanism, extensive experiments demonstrate that CoPS surpasses state-of-the-art methods by 2.5% AUROC in both classification and segmentation across 13 industrial and medical datasets. Code will be available at https://github.com/cqylunlun/CoPS.
最近,大型预训练视觉语言模型在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)方面表现出卓越的性能。通过在一个辅助数据集上进行微调,该模型能够在涵盖工业缺陷和医疗病变的多个数据集上进行跨类别异常检测。与手动设计的提示相比,提示学习无需专家知识和试错。然而,它仍然面临以下挑战:(i)静态的可学习令牌在捕获正常和异常状态的连续和多样模式方面存在困难,这限制了其在未见类别上的泛化能力;(ii)固定的文本标签提供了过于稀疏的类别信息,使模型容易过度适应特定的语义子空间。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了条件提示合成(CoPS),这是一种新型框架,它根据视觉特征合成动态提示,以提高ZSAD的性能。具体来说,我们从精细的补丁特征中提取代表性的正常和异常原型,并将其显式地注入提示中,以实现自适应状态建模。鉴于类别标签的稀疏性,我们利用变分自动编码器对语义图像特征进行建模,并将各种类别令牌隐式地融合到提示中。此外,结合我们的空间感知对齐机制,大量实验表明,CoPS在13个工业和医疗数据集的分类和分割任务中,超出最新方法2.5%的AUROC。代码将在https://github.com/cqylunlun/CoPS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 33 figures, 14 tables
Summary
本文介绍了在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中,大型预训练视觉语言模型的表现及面临的挑战。为应对挑战,提出一种新型框架——条件提示合成(CoPS),通过动态提示合成增强ZSAD性能。实验证明,CoPS在分类和分割任务上超越现有方法,在13个工业和医疗数据集上的平均受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUROC)提高2.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练视觉语言模型在零样本异常检测中表现卓越,能通过微调单一辅助数据集实现跨类别异常检测。
- 传统提示学习需依赖专家知识和反复试验,而CoPS框架通过动态提示合成增强性能。
- 静态学习令牌难以捕捉正常和异常状态的连续和多样模式,限制了其在未见类别上的泛化能力。
- 固定文本标签提供的类别信息过于稀疏,使模型易于过度适应特定语义子空间。
- CoPS从细粒度补丁特征中提取正常和异常原型,并显式注入提示,实现自适应状态建模。
- 针对类别标签的稀疏性,CoPS利用变分自动编码器对语义图像特征进行建模,并将各种类别令牌隐式融合到提示中。
点此查看论文截图

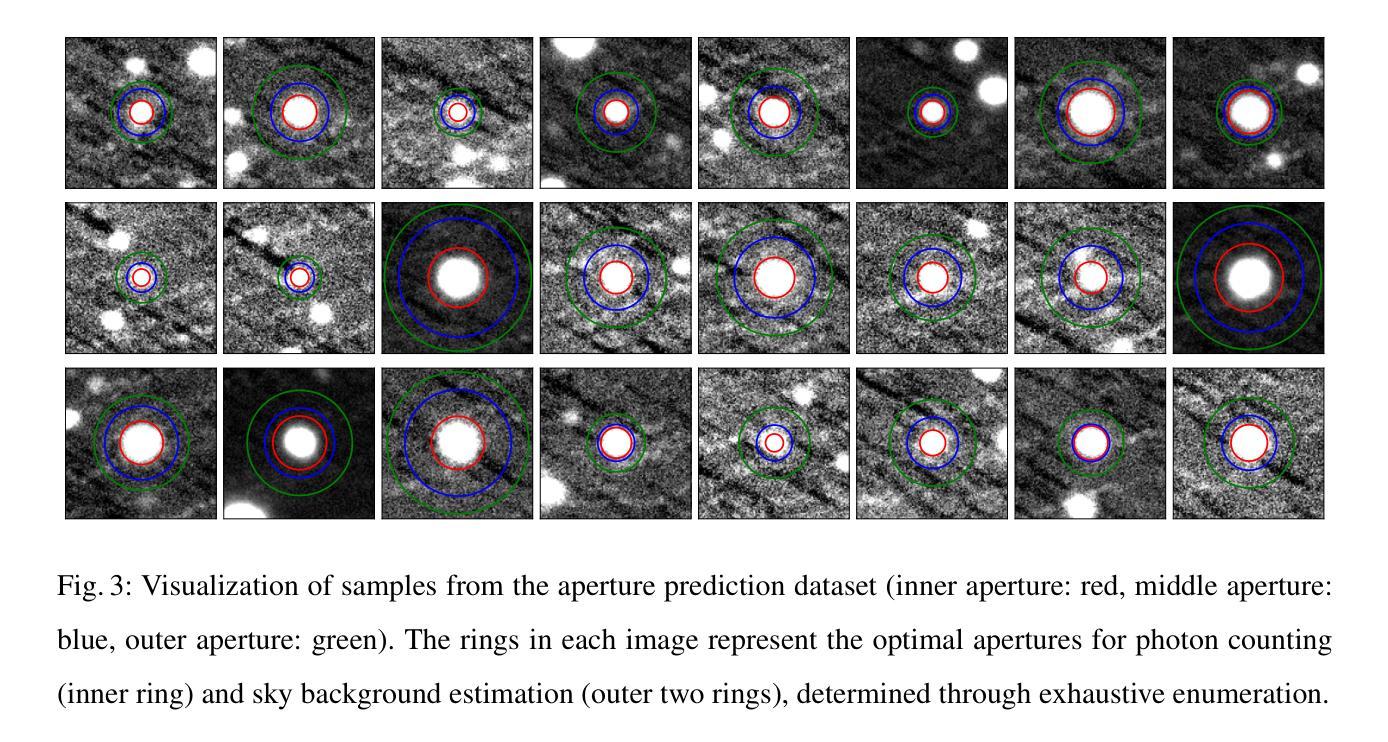
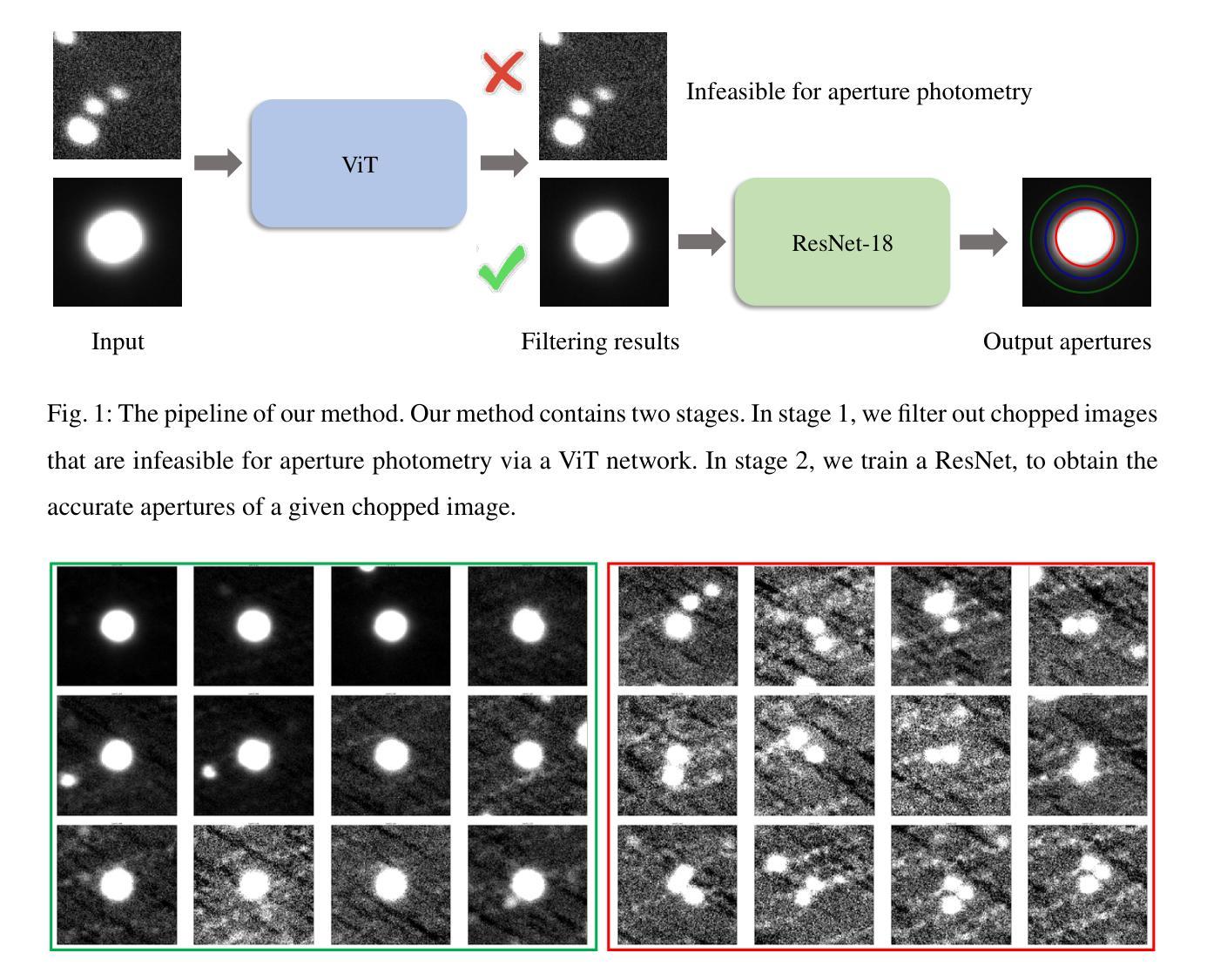
DeepAP: Deep Learning-based Aperture Photometry Feasibility Assessment and Aperture Size Prediction
Authors:Zheng-Jun Du, Qing-Quan Li, Yi-Cheng Rui, Yu-Li Liu, Yu-Ting Wu, Dong Li, Bing-Feng Seng, Yi-Fan Xuan, Fa-Bo Feng
Aperture photometry is a fundamental technique widely used to obtain high-precision light curves in optical survey projects like Tianyu. However, its effectiveness is limited in crowded fields, and the choice of aperture size critically impacts photometric precision. To address these challenges, we propose DeepAP, an efficient and accurate two-stage deep learning framework for aperture photometry. Specifically, for a given source, we first train a Vision Transformer (ViT) model to assess its feasibility of aperture photometry. We then train the Residual Neural Network (ResNet) to predict its optimal aperture size. For aperture photometry feasibility assessment, the ViT model yields an ROC AUC value of 0.96, and achieves a precision of 0.974, a recall of 0.930, and an F1 score of 0.952 on the test set. For aperture size prediction, the ResNet model effectively mitigates biases inherent in classical growth curve methods by adaptively selecting apertures appropriate for sources of varying brightness, thereby enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) across a wide range of targets. Meanwhile, some samples in the test set have a higher SNR than those obtained by exhaustive aperture size enumeration because of the finer granularity of aperture size estimation. By integrating ResNet with the ViT network, the DeepAP framework achieves a median total processing time of 18 milliseconds for a batch of 10 images, representing a speed-up of approximately 59000 times compared to exhaustive aperture size enumeration. This work paves the way for the automatic application of aperture photometry in future high-precision surveys such as Tianyu and LSST. The source code and model are available at https://github.com/ruiyicheng/DeepAP.
孔径光度法是一种广泛应用于光学观测项目(如天宇)的高精度光度曲线获取的基本技术。然而,在拥挤的领域里,它的有效性受到限制,孔径大小的选择对光度精度有重要影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DeepAP,这是一种高效且准确的孔径光度法的两阶段深度学习框架。具体来说,对于给定的源,我们首先训练一个视觉转换器(ViT)模型来评估其进行孔径光度法的可行性。然后,我们训练残差神经网络(ResNet)来预测最佳孔径大小。对于孔径光度可行性评估,ViT模型的ROC AUC值为0.96,测试集上的精度为0.974,召回率为0.930,F1分数为0.952。对于孔径大小预测,ResNet模型通过自适应选择适合不同亮度源的孔径,有效缓解了经典增长曲线方法中的固有偏见,从而提高了目标的信噪比(SNR)。同时,由于孔径大小估计的粒度更精细,测试集中一些样本的SNR高于通过详尽的孔径大小枚举所获得的SNR。通过整合ResNet与ViT网络,DeepAP框架在批处理10张图像时达到中位数总处理时间为18毫秒,与详尽的孔径大小枚举相比,实现了约59000倍的加速。这项工作为孔径光度法在天宇和LSST等未来高精度观测项目中的自动应用铺平了道路。源代码和模型可在https://github.com/ruiyicheng/DeepAP获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages,12 figures
Summary
天誉项目中广泛应用的孔径光度法面临拥挤区域有效性和孔径大小选择带来的挑战。为应对这些挑战,提出DeepAP深度学习框架,包含两个阶段:先用Vision Transformer模型评估孔径光度法的可行性,再用Residual Neural Network预测最佳孔径大小。该框架提高了信号噪声比,缩短了处理时间,为未来的高精度调查如天誉和LSST自动应用孔径光度法铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- DeepAP是一个两阶段的深度学习框架,用于提高孔径光度法在拥挤区域的有效性。
- Vision Transformer模型用于评估孔径光度法的可行性,并达到高评估精度。
- Residual Neural Network用于预测最佳孔径大小,有效提高信号噪声比。
- DeepAP框架提高了处理速度,相较于全面的孔径大小枚举,加速了约59000倍。
- 该框架适用于未来高精度调查,如天誉和LSST。
- DeepAP的源代码和模型已公开发布,便于使用和进一步开发。
- 框架对于复杂数据处理具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在需要快速、准确处理大量图像数据的场景中。
点此查看论文截图


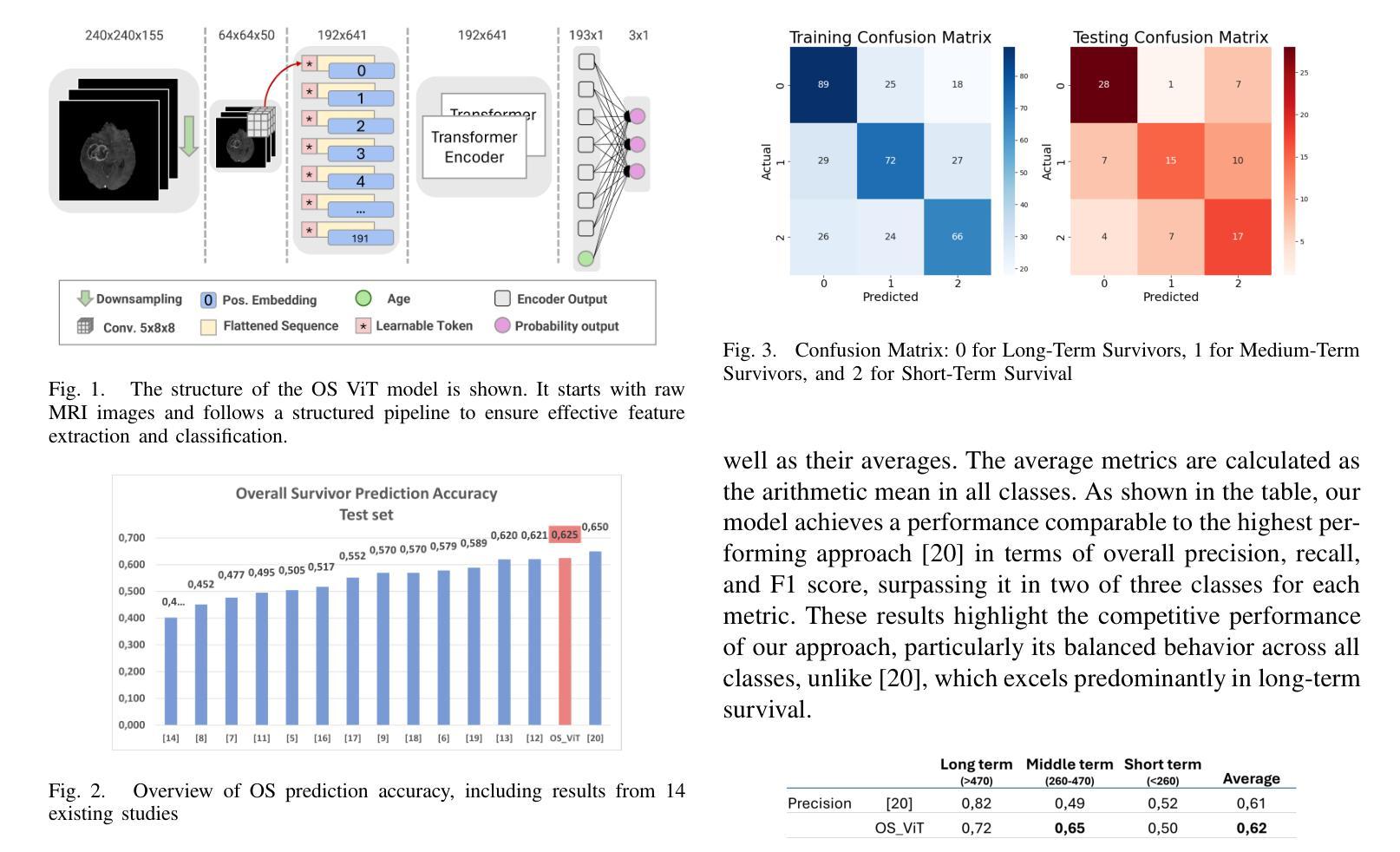
Glioblastoma Overall Survival Prediction With Vision Transformers
Authors:Yin Lin, Riccardo Barbieri, Domenico Aquino, Giuseppe Lauria, Marina Grisoli, Elena De Momi, Alberto Redaelli, Simona Ferrante
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive and common brain tumors, with a median survival of 10-15 months. Predicting Overall Survival (OS) is critical for personalizing treatment strategies and aligning clinical decisions with patient outcomes. In this study, we propose a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) approach for OS prediction using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images, exploiting Vision Transformers (ViTs) to extract hidden features directly from MRI images, eliminating the need of tumor segmentation. Unlike traditional approaches, our method simplifies the workflow and reduces computational resource requirements. The proposed model was evaluated on the BRATS dataset, reaching an accuracy of 62.5% on the test set, comparable to the top-performing methods. Additionally, it demonstrated balanced performance across precision, recall, and F1 score, overcoming the best model in these metrics. The dataset size limits the generalization of the ViT which typically requires larger datasets compared to convolutional neural networks. This limitation in generalization is observed across all the cited studies. This work highlights the applicability of ViTs for downsampled medical imaging tasks and establishes a foundation for OS prediction models that are computationally efficient and do not rely on segmentation.
胶质母细胞瘤是最具侵袭性和最常见的脑肿瘤之一,中位生存期为10-15个月。预测总体生存期(OS)对于个性化治疗方案和使临床决策与病人结果相符至关重要。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种利用磁共振成像(MRI)图像进行总体生存期预测的新型人工智能(AI)方法,该方法利用视觉转换器(ViT)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需进行肿瘤分割。与传统方法不同,我们的方法简化了工作流程,降低了计算资源要求。所提出模型在BRATS数据集上进行了评估,在测试集上达到了62.5%的准确率,与表现最佳的方法相当。此外,它在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面表现出平衡的性能,在这些指标上超越了最佳模型。数据集的大小限制了ViT的泛化能力,与卷积神经网络相比,ViT通常需要更大的数据集。所有引用的研究都观察到这种泛化限制。这项工作强调了ViT在下采样医学成像任务中的适用性,并为计算效率高、不依赖分割的总体生存期预测模型奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures, EMBC2025
Summary
该研究提出了一种利用磁共振成像(MRI)图像进行总体生存期(OS)预测的人工智能新方法,利用视觉转换器(ViTs)直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需进行肿瘤分割。该方法简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源需求,在BRATS数据集上评估,测试集准确率达到了62.5%,且在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面表现均衡。虽然数据集规模限制了ViT的泛化能力,但此研究突显了ViTs在医学图像处理任务中的适用性,并为计算效率高且无需依赖分割的OS预测模型奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究使用视觉转换器(ViTs)进行MRI图像的总体生存期(OS)预测。
- ViTs可以直接从MRI图像中提取隐藏特征,无需肿瘤分割。
- 方法简化了工作流程并降低了计算资源需求。
- 在BRATS数据集上的准确率达到了62.5%,表现均衡的精确度、召回率和F1分数。
- 数据集规模限制了ViT的泛化能力。
- 此研究突显了ViTs在医学图像处理任务中的适用性。
点此查看论文截图

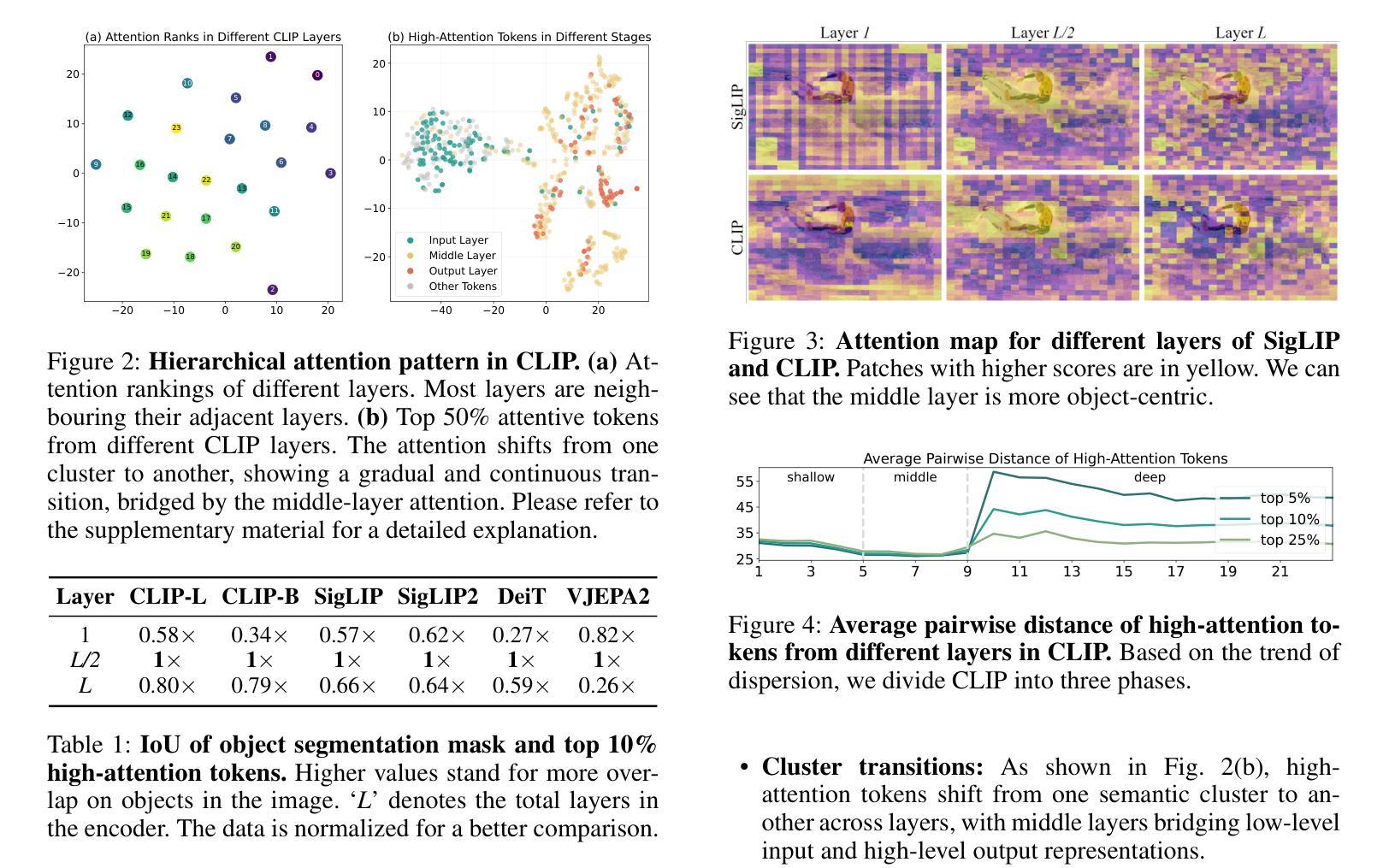
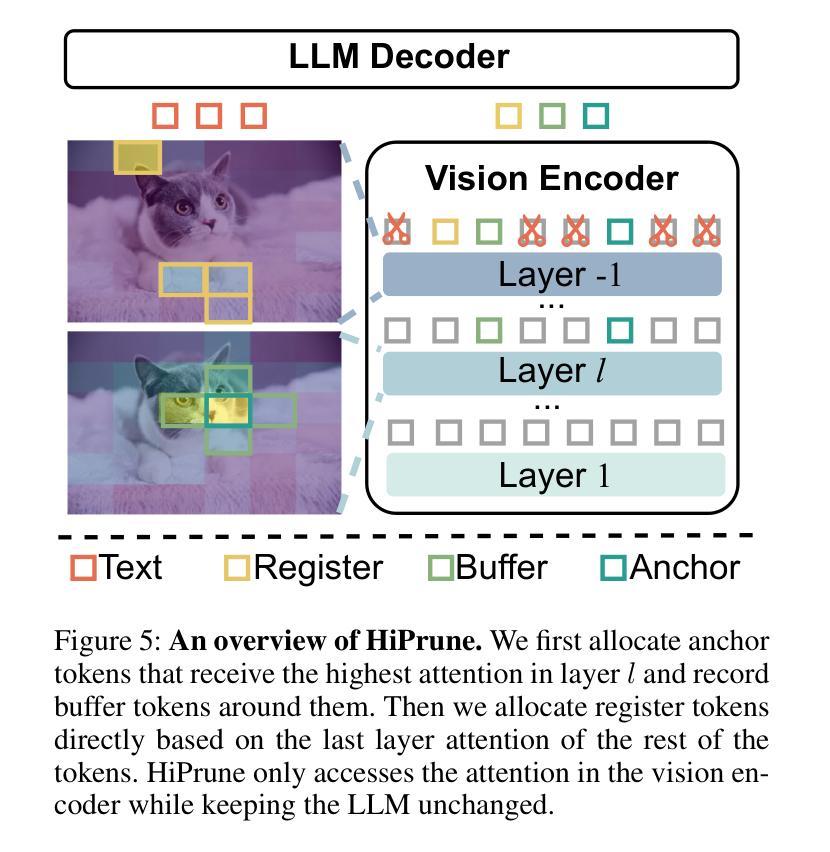
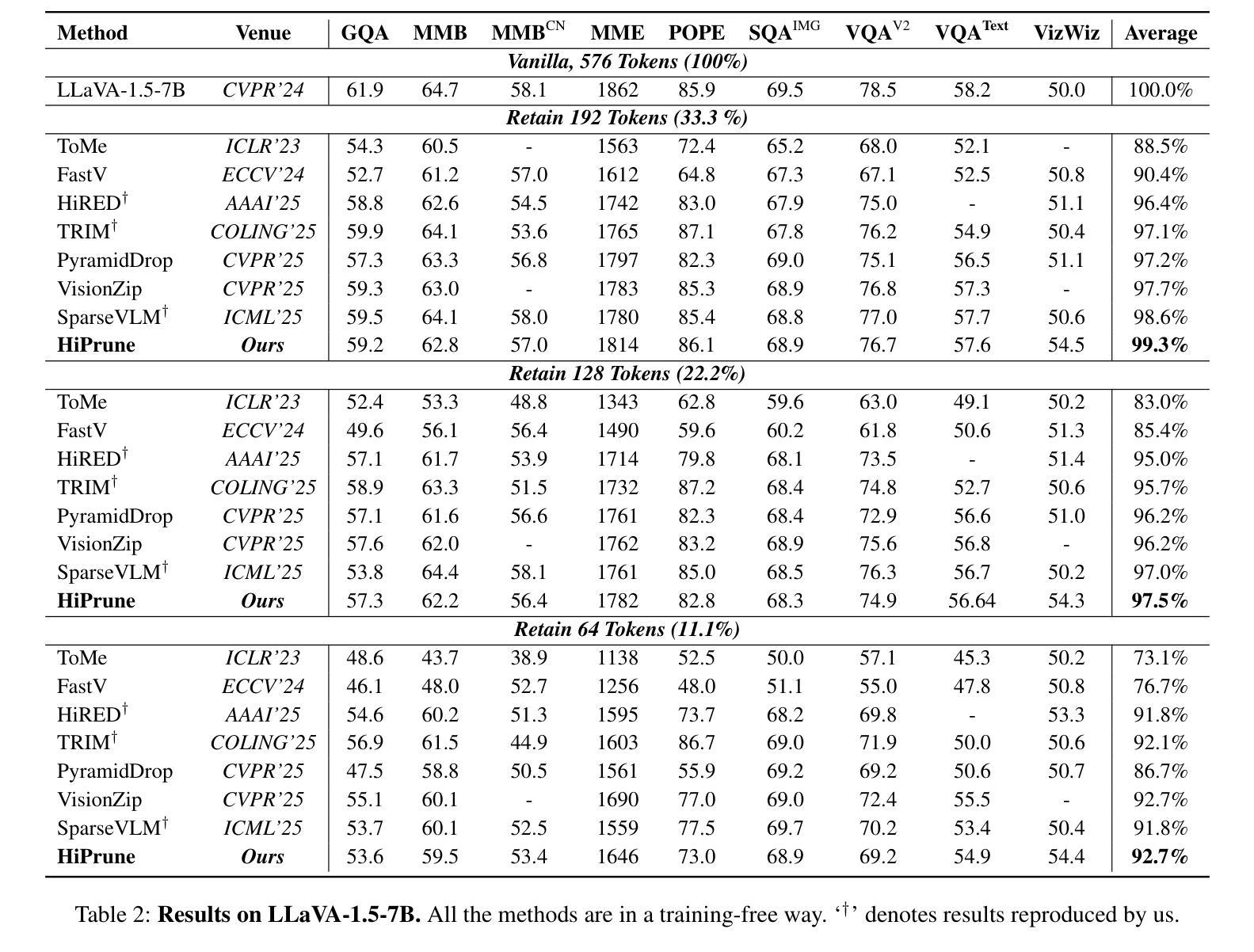
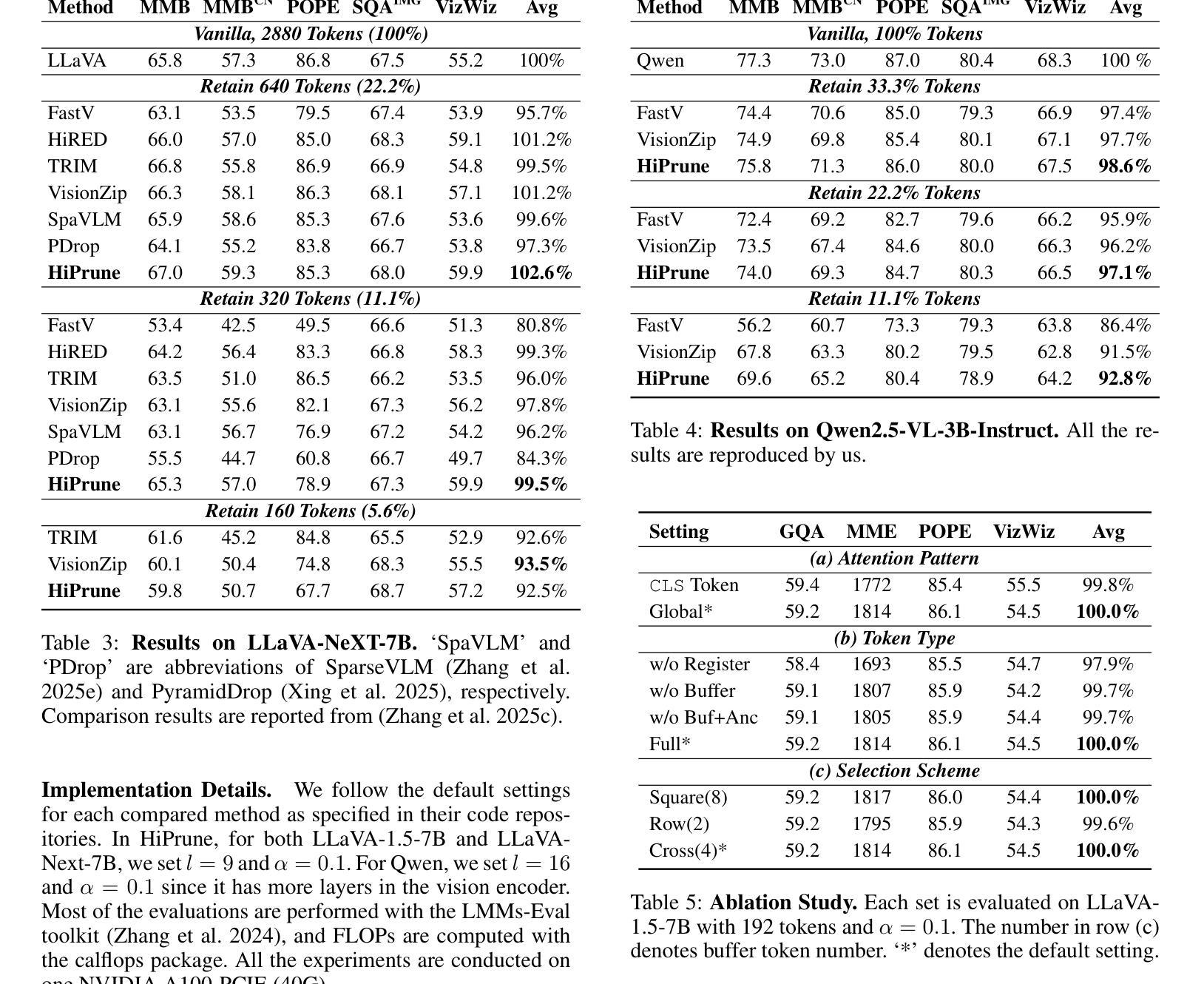
HiPrune: Training-Free Visual Token Pruning via Hierarchical Attention in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jizhihui Liu, Feiyi Du, Guangdao Zhu, Niu Lian, Jun Li, Bin Chen
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) encode images into lengthy sequences of visual tokens, leading to excessive computational overhead and limited inference efficiency. While prior efforts prune or merge tokens to address this issue, they often rely on special tokens (e.g., CLS) or require task-specific training, hindering scalability across architectures. In this paper, we propose HiPrune, a training-free and model-agnostic token Pruning framework that exploits the Hierarchical attention structure within vision encoders. We identify that middle layers attend to object-centric regions, while deep layers capture global contextual features. Based on this observation, HiPrune selects three types of informative tokens: (1) Anchor tokens with high attention in object-centric layers, (2) Buffer tokens adjacent to anchors for spatial continuity, and (3) Register tokens with strong attention in deep layers for global summarization. Our method requires no retraining and integrates seamlessly with any ViT-based VLM. Extensive experiments on LLaVA-1.5, LLaVA-NeXT, and Qwen2.5-VL demonstrate that HiPrune achieves state-of-the-art pruning performance, preserving up to 99.3% task accuracy with only 33.3% tokens, and maintaining 99.5% accuracy with just 11.1% tokens. Meanwhile, it reduces inference FLOPs and latency by up to 9$\times$, showcasing strong generalization across models and tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/Danielement321/HiPrune.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)将图像编码为冗长的视觉令牌序列,导致计算开销过大和推理效率低下。虽然之前的努力通过删除或合并令牌来解决这个问题,但它们通常依赖于特殊令牌(例如CLS),或需要进行特定任务的训练,这阻碍了它们在架构之间的可扩展性。在本文中,我们提出了HiPrune,这是一个无需训练且模型无关的令牌删除框架,它利用视觉编码器中的分层注意力结构。我们发现中层关注对象为中心的区域,而深层捕获全局上下文特征。基于此观察,HiPrune选择了三种类型的标记信息:(1)在对象中心层中具有高注意力的锚点令牌,(2)与锚点相邻的缓冲区令牌以实现空间连续性,(3)在深层中具有强烈注意力的寄存器令牌以进行全局摘要。我们的方法无需重新训练,可以无缝集成到任何基于ViT的VLM中。在LLaVA-1.5、LLaVA-NeXT和Qwen2.5-VL上的广泛实验表明,HiPrune达到了最先进的删除性能,保留了高达99.3%的任务准确性并且只使用33.3%的令牌,并能在仅使用11.1%的令牌时保持99.5%的准确性。同时,它减少了高达9倍的推理浮点运算量和延迟时间,在模型和任务之间表现出强大的泛化能力。代码可通过https://github.com/Danielement321/HiPrune获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要提出一种名为HiPrune的无训练、模型无关的token裁剪框架,该框架利用视觉编码器的层次化注意力结构,通过识别并选择三种类型的标记性token进行裁剪。该方法能够在不重新训练的情况下无缝集成任何基于ViT的VLM,并实现出色的裁剪性能,同时大大减少计算开销和推理时间。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs将图像编码为冗长的视觉token序列,导致计算开销大且推理效率低下。
- 现有方法主要通过裁剪或合并token来解决此问题,但通常需要特定任务训练或特殊标记,这限制了其在不同架构中的可扩展性。
- HiPrune是一个无训练、模型无关的token裁剪框架,利用视觉编码器的层次化注意力结构。
- HiPrune通过识别并选择三种类型的标记性token(锚点token、缓冲区token和寄存器token)来进行裁剪。
- HiPrune在不重新训练的情况下,能够无缝集成任何基于ViT的VLM,并实现卓越的裁剪性能。
- 实验结果表明,HiPrune在多个模型和任务上实现了最先进的裁剪性能,能够在保留高达99.3%的任务准确性的同时仅使用33.3%的token,并在仅使用11.1%的token时保持99.5%的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

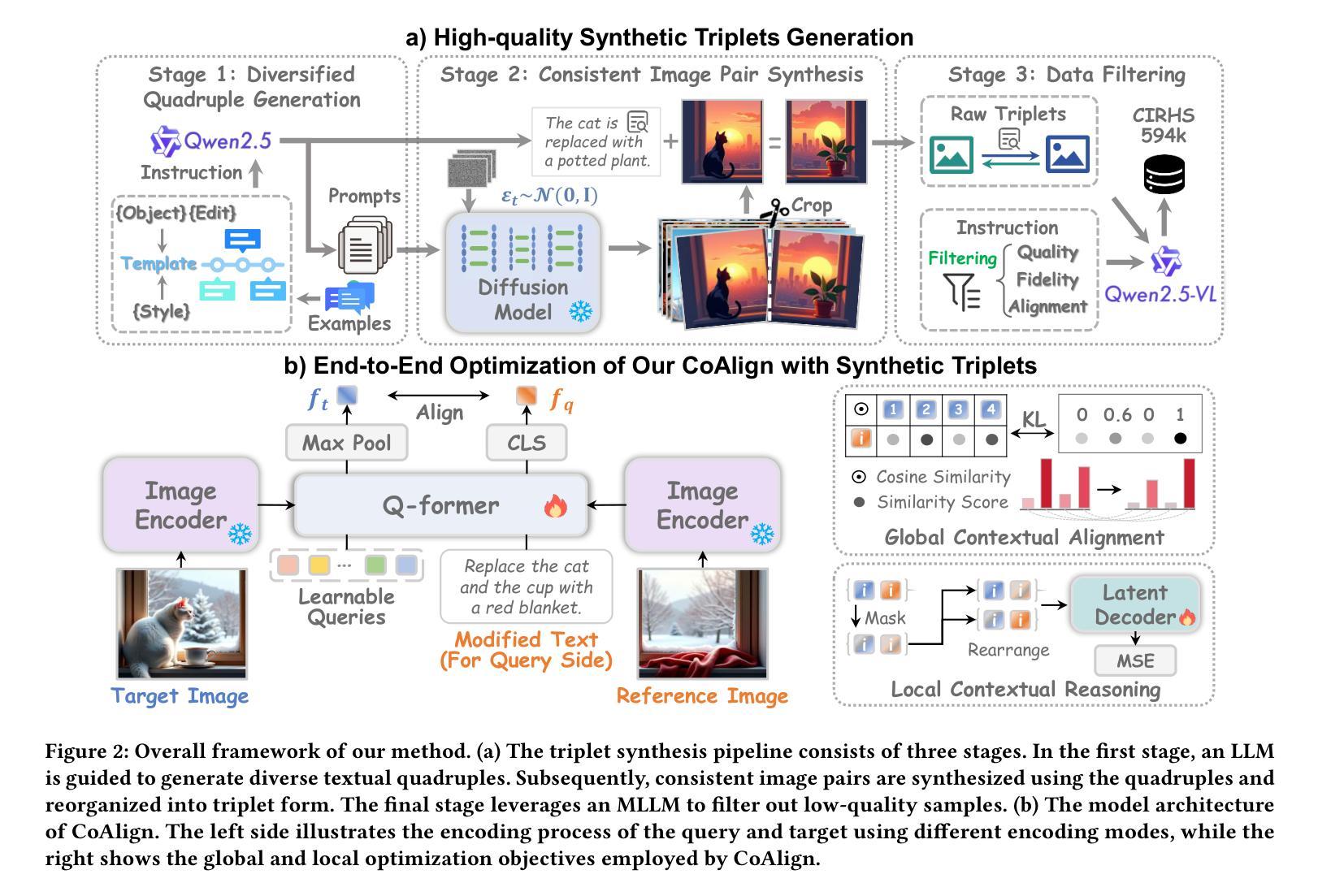
Automatic Synthesis of High-Quality Triplet Data for Composed Image Retrieval
Authors:Haiwen Li, Delong Liu, Zhaohui Hou, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su
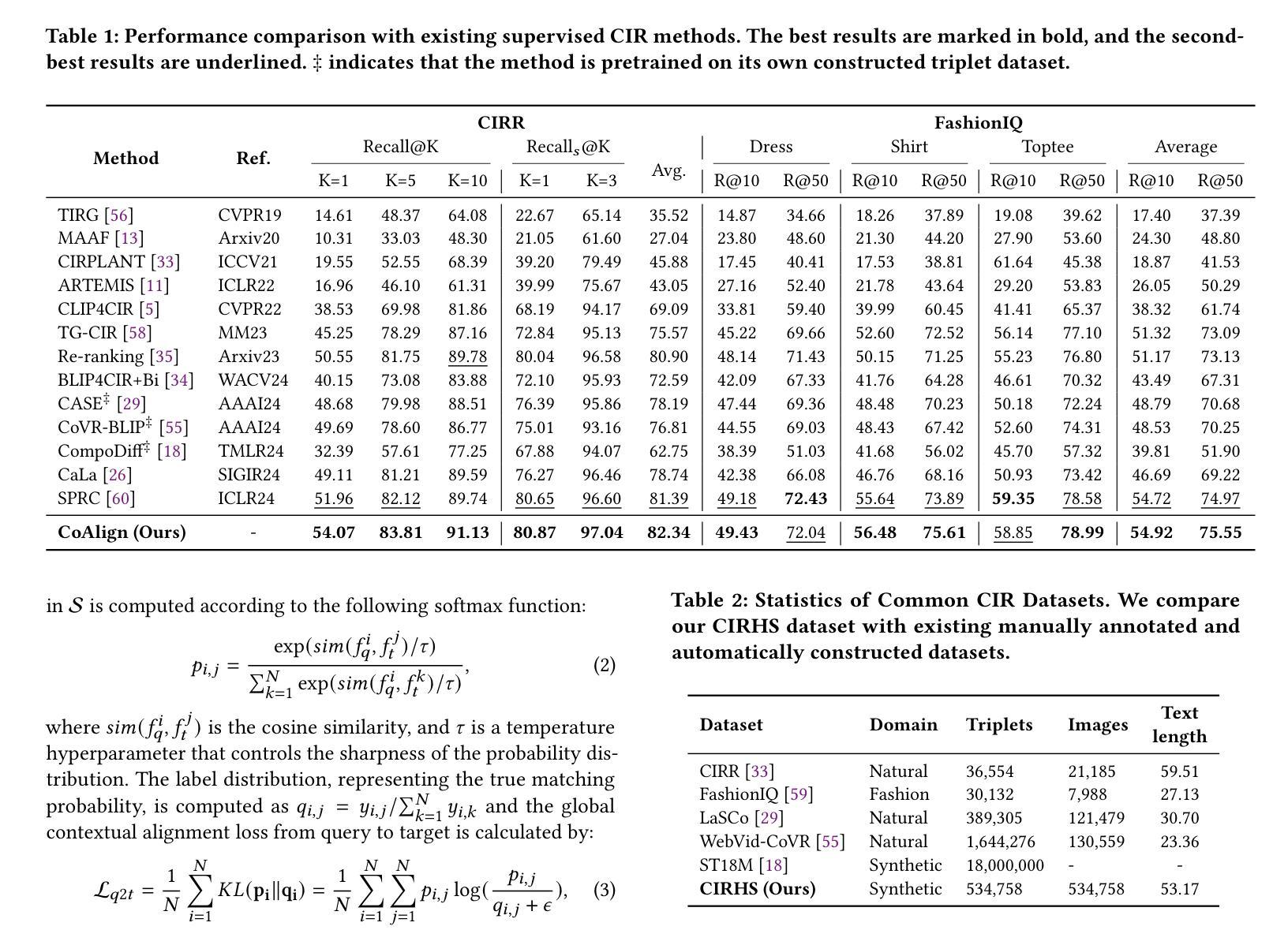
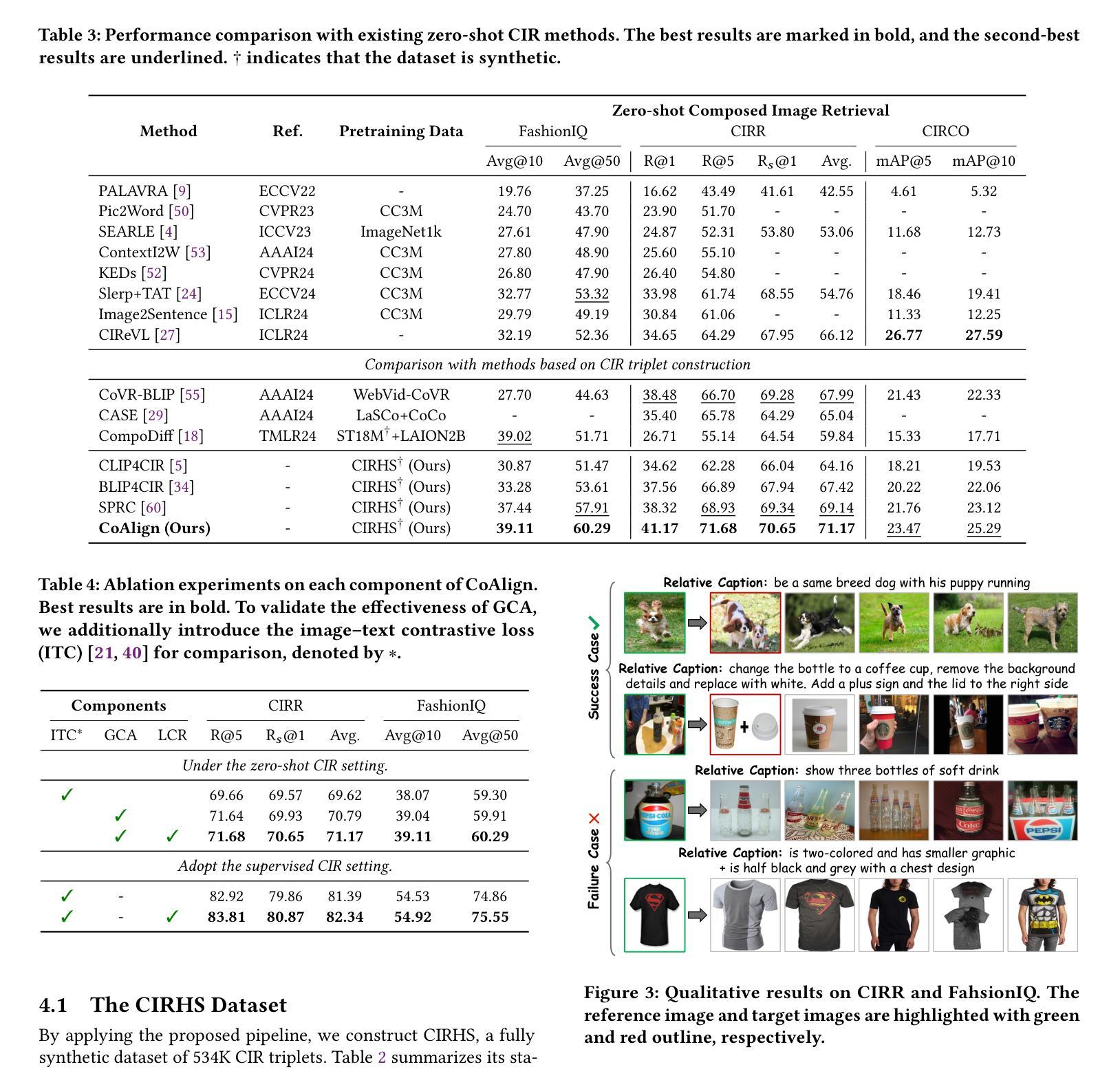
As a challenging vision-language (VL) task, Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve target images using multimodal (image+text) queries. Although many existing CIR methods have attained promising performance, their reliance on costly, manually labeled triplets hinders scalability and zero-shot capability. To address this issue, we propose a scalable pipeline for automatic triplet generation, along with a fully synthetic dataset named Composed Image Retrieval on High-quality Synthetic Triplets (CIRHS). Our pipeline leverages a large language model (LLM) to generate diverse prompts, controlling a text-to-image generative model to produce image pairs with identical elements in each pair, which are then filtered and reorganized to form the CIRHS dataset. In addition, we introduce Hybrid Contextual Alignment (CoAlign), a novel CIR framework, which can accomplish global alignment and local reasoning within a broader context, enabling the model to learn more robust and informative representations. By utilizing the synthetic CIRHS dataset, CoAlign achieves outstanding zero-shot performance on three commonly used benchmarks, demonstrating for the first time the feasibility of training CIR models on a fully synthetic dataset. Furthermore, under supervised training, our method outperforms all the state-of-the-art supervised CIR approaches, validating the effectiveness of our proposed retrieval framework. The code and the CIRHS dataset will be released soon.
作为具有挑战性的视觉语言(VL)任务,组合图像检索(CIR)旨在使用多模态(图像+文本)查询来检索目标图像。尽管许多现有的CIR方法已经取得了有前景的性能,但它们对成本高昂的手动标注三元组的依赖阻碍了其可扩展性和零样本能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个用于自动三元组生成的可扩展管道,以及一个名为“基于高质量合成三元组的组合图像检索(CIRHS)”的完全合成数据集。我们的管道利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成各种提示,控制文本到图像的生成模型,以产生具有相同元素的图像对,然后对它们进行过滤和重组以形成CIRHS数据集。此外,我们介绍了混合上下文对齐(CoAlign),这是一种新型的CIR框架,可以在更广泛的背景下完成全局对齐和局部推理,使模型能够学习更稳健和更具信息量的表示。通过利用合成的CIRHS数据集,CoAlign在三个常用基准测试上取得了出色的零样本性能,首次证明了在完全合成的数据集上训练CIR模型的可行性。此外,在监督训练下,我们的方法超越了所有最新的监督CIR方法,验证了所提出的检索框架的有效性。代码和CIRHS数据集将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was originally submitted to ACM MM 2025 on April 12, 2025
Summary
基于大规模语言模型生成提示,控制文本到图像生成模型,生成具有相同元素的图像对,构建合成数据集CIRHS,用于解决图像检索任务。引入Hybrid Contextual Alignment框架,实现全局对齐和局部推理,利用合成数据集训练模型并达到出色的零样本性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出使用大规模语言模型生成提示以控制文本到图像生成模型,构建合成数据集CIRHS。
- CIRHS数据集用于解决图像检索任务,可实现自动三元组生成。
- 引入Hybrid Contextual Alignment框架,实现全局对齐和局部推理。
- 利用合成数据集CIRHS训练模型,达到出色的零样本性能。
- 在三个常用基准测试中,CoAlign的零样本性能表现优异,验证了使用合成数据集训练CIR模型的可行性。
- 在监督训练下,该方法优于所有现有先进监督CIR方法,证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

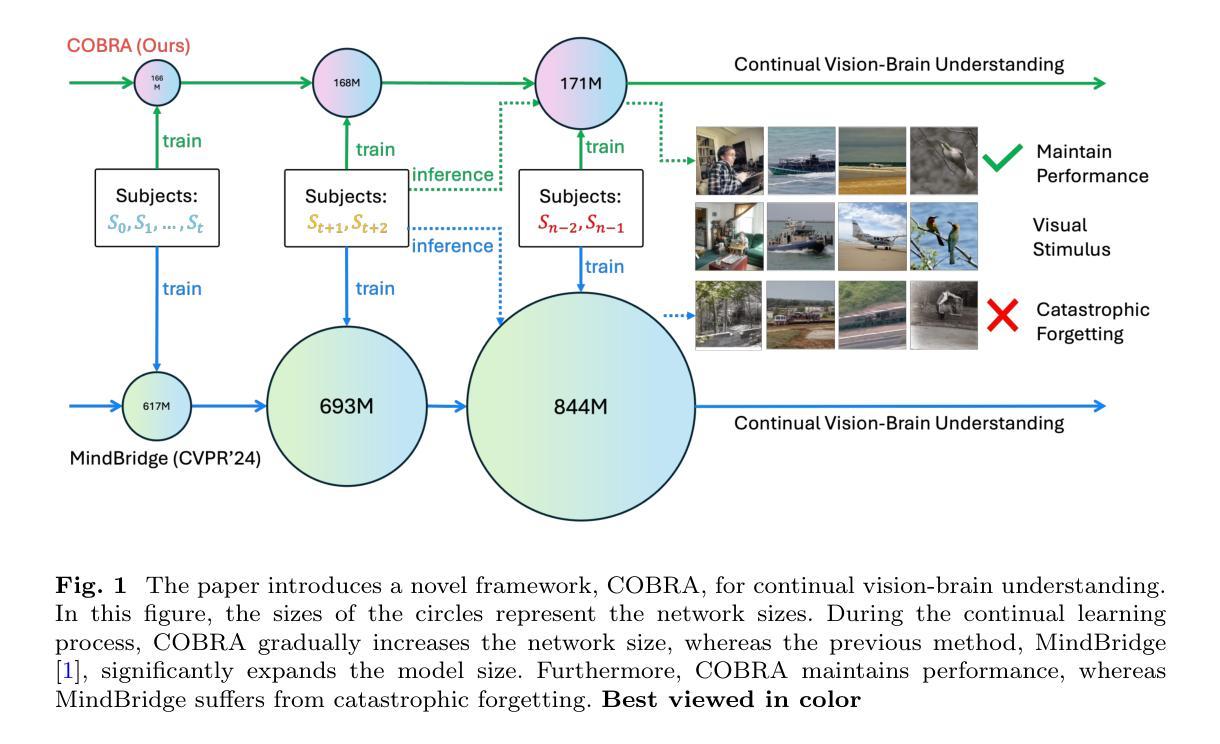
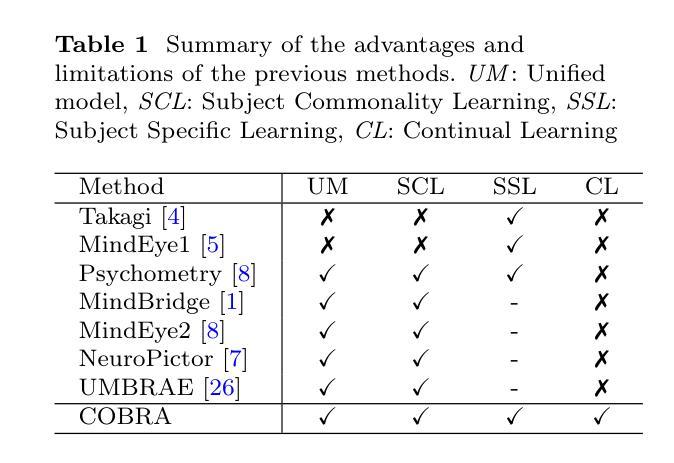
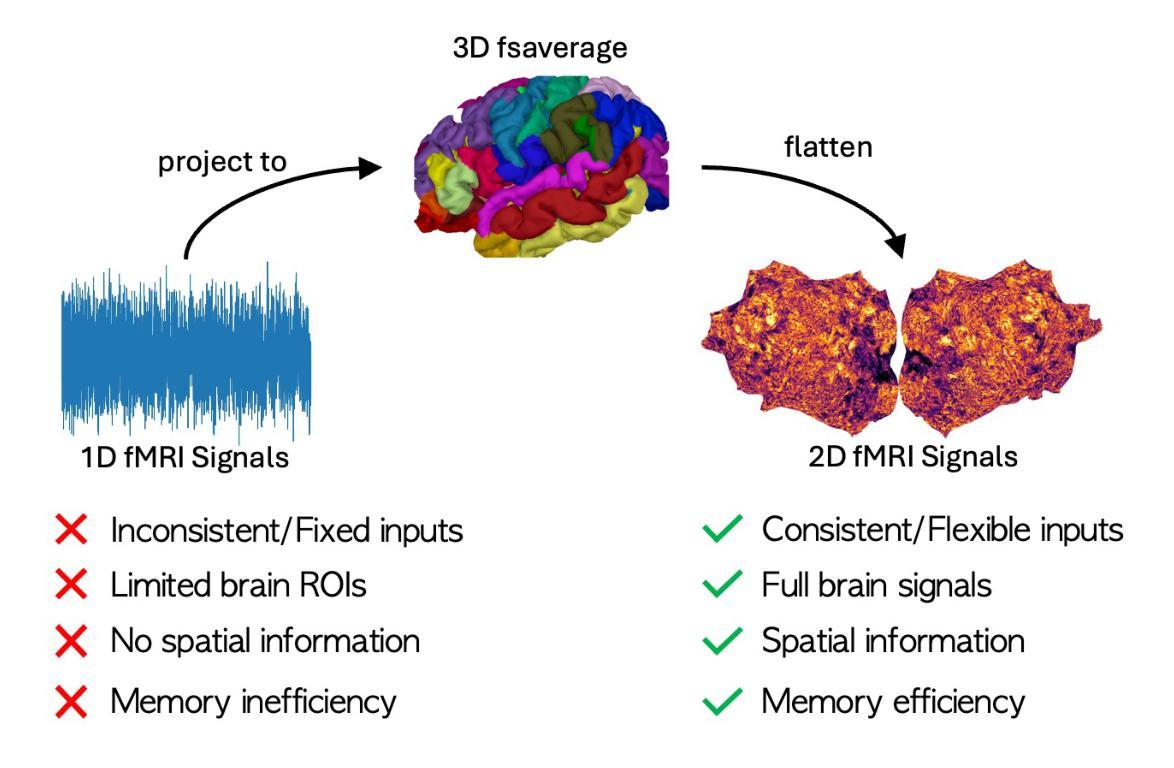
COBRA: A Continual Learning Approach to Vision-Brain Understanding
Authors:Xuan-Bac Nguyen, Manuel Serna-Aguilera, Arabinda Kumar Choudhary, Pawan Sinha, Xin Li, Khoa Luu
Vision-Brain Understanding (VBU) aims to extract visual information perceived by humans from brain activity recorded through functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). Despite notable advancements in recent years, existing studies in VBU continue to face the challenge of catastrophic forgetting, where models lose knowledge from prior subjects as they adapt to new ones. Addressing continual learning in this field is, therefore, essential. This paper introduces a novel framework called Continual Learning for Vision-Brain (COBRA) to address continual learning in VBU. Our approach includes three novel modules: a Subject Commonality (SC) module, a Prompt-based Subject Specific (PSS) module, and a transformer-based module for fMRI, denoted as MRIFormer module. The SC module captures shared vision-brain patterns across subjects, preserving this knowledge as the model encounters new subjects, thereby reducing the impact of catastrophic forgetting. On the other hand, the PSS module learns unique vision-brain patterns specific to each subject. Finally, the MRIFormer module contains a transformer encoder and decoder that learns the fMRI features for VBU from common and specific patterns. In a continual learning setup, COBRA is trained in new PSS and MRIFormer modules for new subjects, leaving the modules of previous subjects unaffected. As a result, COBRA effectively addresses catastrophic forgetting and achieves state-of-the-art performance in both continual learning and vision-brain reconstruction tasks, surpassing previous methods.
视觉大脑理解(VBU)旨在从通过功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)记录的大脑活动中提取人类感知到的视觉信息。尽管近年来取得了显著的进展,但VBU的现有研究仍然面临着灾难性遗忘的挑战,即模型在适应新主题时丢失了先前主题的知识。因此,解决该领域的持续学习至关重要。本文介绍了一个名为COBRA的持续学习框架,以解决VBU中的持续学习问题。我们的方法包括三个新颖模块:主题共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主题特定(PSS)模块和基于变压器的fMRI模块,称为MRIFormer模块。SC模块捕获跨主题的共同视觉大脑模式,并随着模型遇到新主题而保留这些知识,从而减少灾难性遗忘的影响。另一方面,PSS模块学习每个主题的独特视觉大脑模式。最后,MRIFormer模块包含一个变压器编码器和解码器,从公共和特定模式中学习VBU的fMRI特征。在持续学习设置中,COBRA针对新主题进行PSS和MRIFormer模块的更新训练,而之前主题的模块不受影响。因此,COBRA有效地解决了灾难性遗忘问题,并在持续学习和视觉大脑重建任务中实现了最先进的性能表现,超越了以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了针对视觉脑理解(VBU)领域的持续学习问题,引入了一个名为COBRA的新框架,包含主体共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主体特定(PSS)模块和基于变压器的fMRI模块MRIFormer。这些模块能够捕捉跨主体的视觉脑模式,学习主体的独特模式,并通过持续训练新主体来减少灾难性遗忘的影响。COBRA在持续学习和视觉脑重建任务上取得了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- Vision-Brain Understanding (VBU)旨在从通过功能磁共振成像(fMRI)记录的大脑活动中提取人类感知的视觉信息。
- 现有VBU研究面临灾难性遗忘的挑战,即模型在适应新主体时丧失先前知识。
- COBRA框架包含三个新模块:主体共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主体特定(PSS)模块和基于变压器的fMRI模块(MRIFormer)。
- SC模块捕捉跨主体的共享视觉脑模式,保留知识并减少灾难性遗忘的影响。
- PSS模块学习每个主体的独特视觉脑模式。
- MRIFormer模块包含变压器编码器和解码器,从公共和特定模式中学习VBU的fMRI特征。
点此查看论文截图