⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
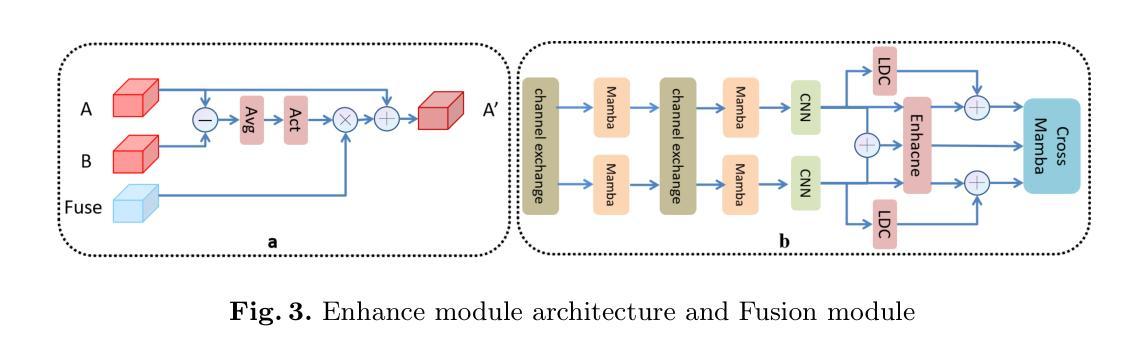
MM2CT: MR-to-CT translation for multi-modal image fusion with mamba
Authors:Chaohui Gong, Zhiying Wu, Zisheng Huang, Gaofeng Meng, Zhen Lei, Hongbin Liu
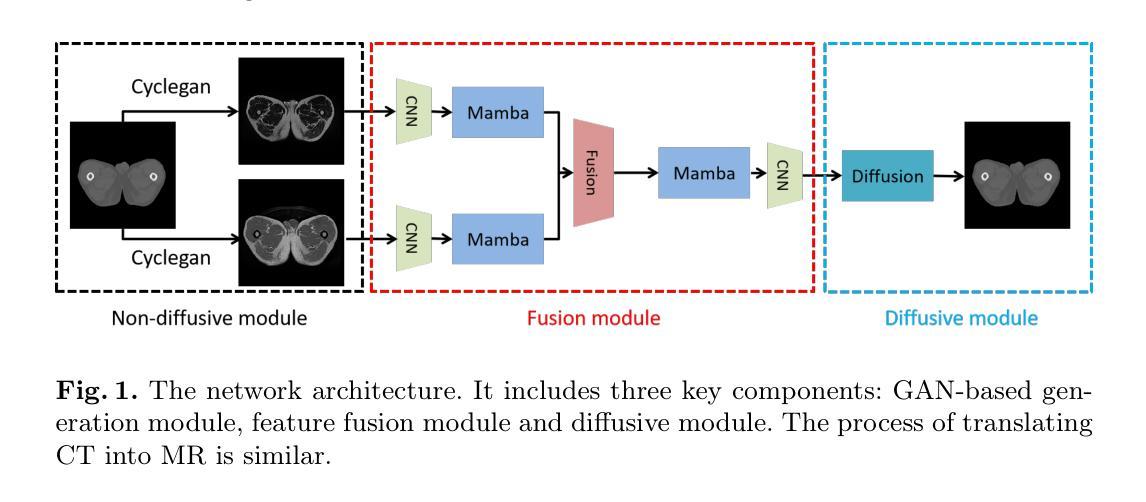
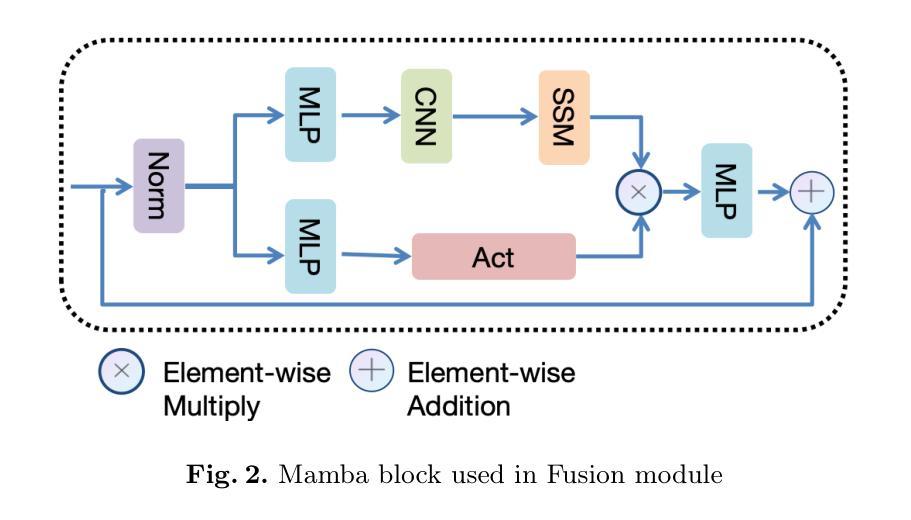
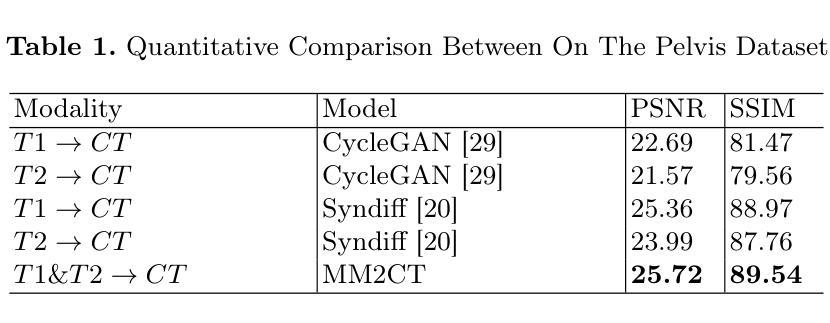
Magnetic resonance (MR)-to-computed tomography (CT) translation offers significant advantages, including the elimination of radiation exposure associated with CT scans and the mitigation of imaging artifacts caused by patient motion. The existing approaches are based on single-modality MR-to-CT translation, with limited research exploring multimodal fusion. To address this limitation, we introduce Multi-modal MR to CT (MM2CT) translation method by leveraging multimodal T1- and T2-weighted MRI data, an innovative Mamba-based framework for multi-modal medical image synthesis. Mamba effectively overcomes the limited local receptive field in CNNs and the high computational complexity issues in Transformers. MM2CT leverages this advantage to maintain long-range dependencies modeling capabilities while achieving multi-modal MR feature integration. Additionally, we incorporate a dynamic local convolution module and a dynamic enhancement module to improve MRI-to-CT synthesis. The experiments on a public pelvis dataset demonstrate that MM2CT achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) and Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR). Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Gots-ch/MM2CT.
磁共振(MR)到计算机断层扫描(CT)的转换具有显著的优势,包括消除与CT扫描相关的辐射暴露以及减轻由患者运动引起的成像伪影。现有方法基于单模态MR-to-CT转换,对多模态融合的研究有限。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了多模态MR到CT(MM2CT)转换方法,该方法利用T1加权和T2加权MRI数据的多模态信息,以及基于Mamba的多模态医学图像合成创新框架。Mamba有效地克服了卷积神经网络中局部感受野的限制和变压器中的高计算复杂性。MM2CT利用这一优势,在保持长期依赖建模能力的同时,实现了多模态MR特征融合。此外,我们结合了动态局部卷积模块和动态增强模块,以改进MRI到CT的合成。在公共骨盆数据集上的实验表明,MM2CT在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面达到了最先进的技术性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Gots-ch/MM2CT公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了多模态MR到CT转换方法的研究。通过引入基于多模态MRI数据的Mamba框架,实现MRI到CT转换的深度学习模型,提高成像质量并克服现有方法的局限性。该方法结合了多模态MRI数据的优势,有效克服了CNN的局部感受野限制和Transformer的高计算复杂性。实验结果表明,该方法在公共骨盆数据集上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- MR到CT转换能够消除CT扫描相关的辐射暴露并减少由患者运动引起的成像伪影。
- 现有方法主要基于单模态MR到CT转换,研究在探索多模态融合方面有限。
- 引入多模态MR到CT(MM2CT)转换方法,利用T1和T2加权MRI数据。
- MM2CT使用Mamba框架进行多模态医学图像合成,克服了CNN的局部感受野和Transformer的高计算复杂性。
- MM2CT结合动态局部卷积模块和动态增强模块,提高了MRI到CT的合成效果。
- 在公共骨盆数据集上的实验表明,MM2CT在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面达到最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

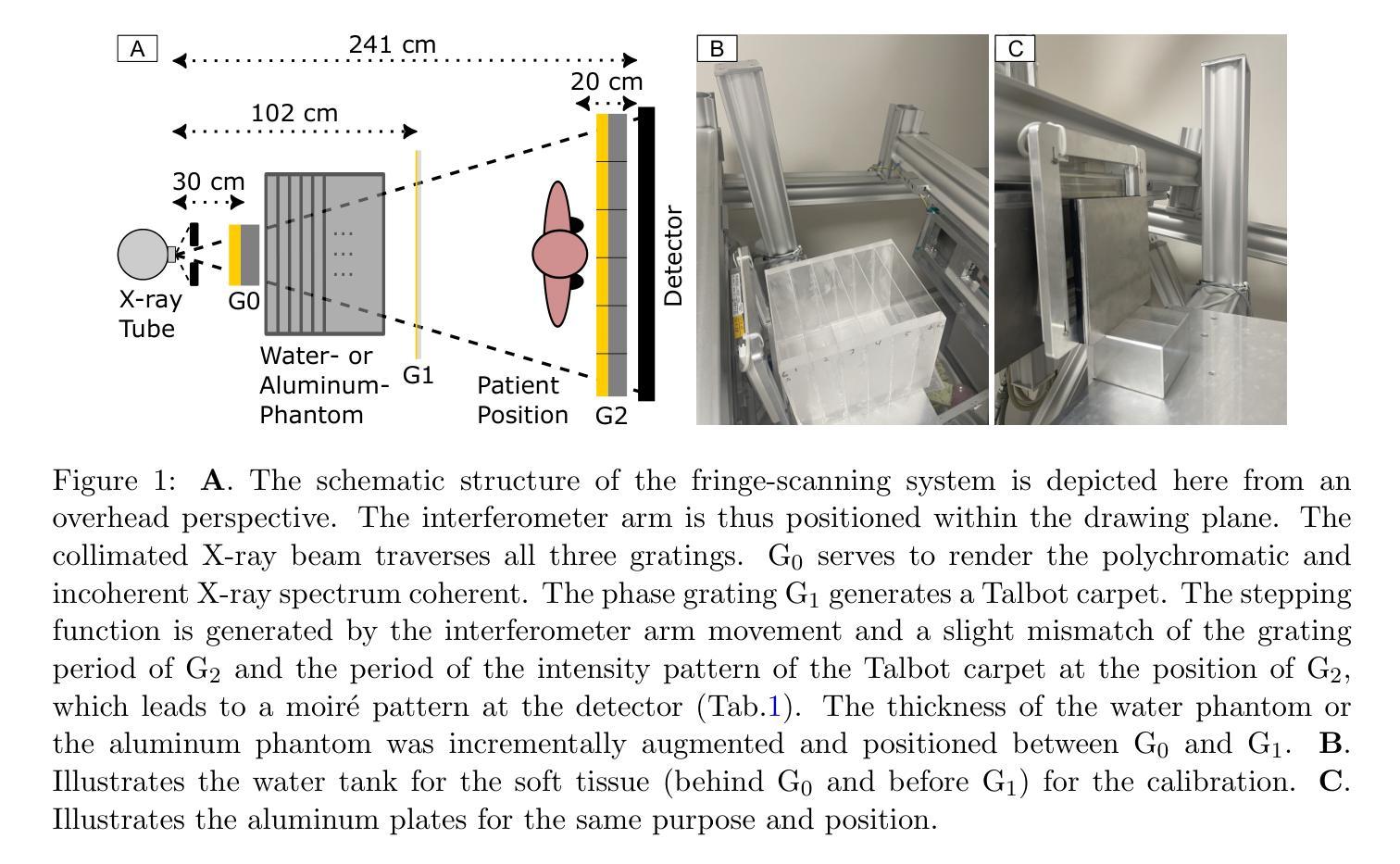
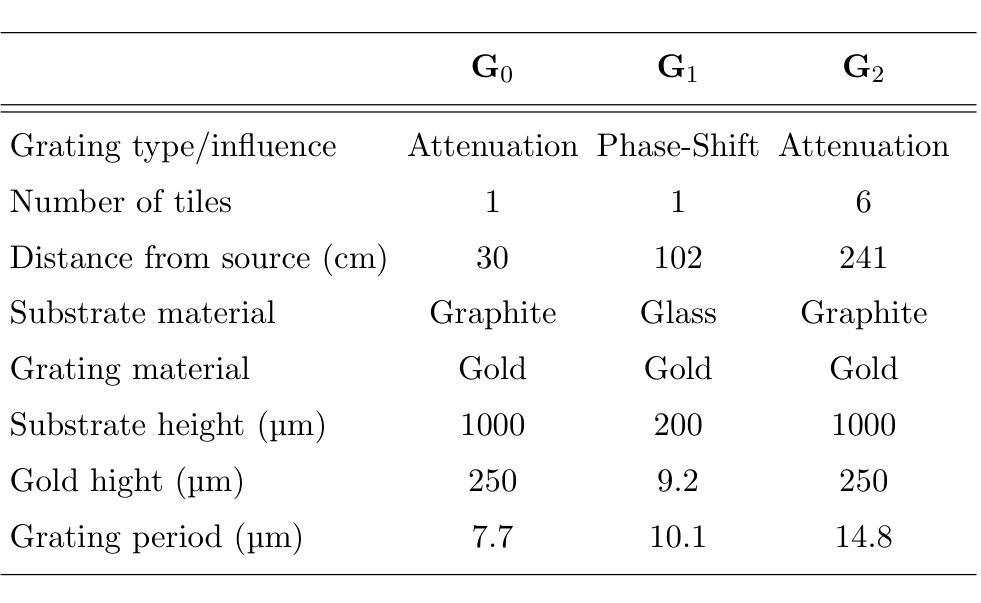
Look-Up Table-Correction for Beam Hardening-Induced Signal of Clinical Dark-Field Chest Radiographs
Authors:Maximilian E. Lochschmidt, Theresa Urban, Lennard Kaster, Rafael Schick, Thomas Koehler, Daniela Pfeiffer, Franz Pfeiffer
Background: Material structures at the micrometer scale cause ultra-small-angle X-ray scattering, e.g., seen in lung tissue or plastic foams. In grating-based X-ray imaging, this causes a reduction of the fringe visibility, forming a dark-field signal. Polychromatic beam hardening also changes visibility, adding a false dark-field signal due to attenuation, even in homogeneous, non-scattering materials. Purpose: The objective of this study is to develop a fast, simple, and robust method to correct dark-field signals and bony structures present due to beam hardening on dark-field chest radiographs of study participants. Methods: The method is based on calibration measurements and image processing. Beam hardening by bones and soft tissue is modeled by aluminum and water, respectively, which have no microstructure and thus only generate an artificial dark-field signal. Look-up tables were then created for both. By using a weighted mean of these, forming a single look-up table, and using the attenuation images, the artificial dark-field signal and thus the bone structures present are reduced for study participants. Results: It was found that applying a correction using a weighted look-up table leads to a significant reduction of bone structures in the dark-field image. The weighting of the aluminum component has a substantial impact on the degree to which bone structures remain visible in the dark-field image. Furthermore, a large negative bias in the dark-field image, dependent on the aluminum weighting, was successfully corrected. Conclusions: The beam-hardening-induced signal in the dark-field images was successfully reduced using the method described. The choice of aluminum weighting to suppress rib structures, as well as the selection of bias correction, should be evaluated based on the specific clinical question.
背景:微米尺度的材料结构会导致超小角度X射线散射,例如在肺组织或塑料泡沫中。在基于光栅的X射线成像中,这会导致条纹可见度降低,形成暗场信号。多色光束硬化也会改变可见度,即使在均匀、非散射材料中,由于衰减也会增加虚假的暗场信号。目的:本研究的目标是开发一种快速、简单、稳健的方法来校正由于光束硬化产生的暗场信号以及研究参与者存在的骨结构。方法:该方法基于校准测量和图像处理。骨骼和软组织引起的光束硬化分别通过铝和水进行建模,它们没有微观结构,因此只产生人工暗场信号。之后为这两者创建了查找表。通过计算加权平均值形成单一查找表,并使用衰减图像,可以减少研究参与者的人工暗场信号及其存在的骨结构。结果:发现使用加权查找表进行校正会导致暗场图像中的骨结构显著减少。铝成分的权重对暗场图像中骨结构的可见度有很大影响。此外,成功校正了依赖于铝权重的暗场图像中的大负偏差。结论:使用所描述的方法成功减少了暗场图像中由光束硬化引起的信号。抑制肋骨结构的铝权重选择以及偏差校正的选择应根据具体的临床问题进行评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
微米级材料结构导致超小角度X射线散射,如在肺组织或塑料泡沫中所见。在基于格栅的X射线成像中,这降低了边缘可见度,形成暗场信号。多色光束硬化也会改变可见度,在均质、非散射材料中添加因衰减而产生的虚假暗场信号。本研究旨在开发一种快速、简单、稳健的方法来修正因光束硬化产生的暗场信号和骨质结构,应用于研究参与者的暗场胸部X光摄影。方法基于校准测量和图像处理,通过铝和水(分别模拟骨和软组织的光束硬化)创建查找表,并使用加权平均值形成单一查找表,结合衰减图像,减少研究参与者的骨质结构和人工暗场信号。结果发现使用加权查找表进行校正可显著降低暗场图像中的骨质结构,铝成分的权重对暗场图像中骨结构可见度有很大影响,并成功校正了依赖于铝权重的暗场图像的负偏差。结论:使用所描述的方法成功减少了暗场图像中的光束硬化信号。根据具体的临床问题,应评估用于抑制肋骨结构的铝权重选择和偏差校正的选择。
Key Takeaways
- 微米级材料结构导致超小角度X射线散射,影响X光成像的清晰度。
- 在基于格栅的X射线成像中,边缘可见度会降低,并生成暗场信号。
- 多色光束硬化会改变可见度,产生虚假暗场信号。
- 研究目标:开发一种快速、简单、稳健的方法来修正因光束硬化产生的暗场信号和骨质结构。
- 方法基于校准测量和图像处理,使用铝和水模拟骨和软组织的光束硬化效应,并创建查找表进行校正。
- 应用加权查找表进行校正可显著降低暗场图像中的骨质结构。
点此查看论文截图

Artificial Intelligence-Based Classification of Spitz Tumors
Authors:Ruben T. Lucassen, Marjanna Romers, Chiel F. Ebbelaar, Aia N. Najem, Donal P. Hayes, Antien L. Mooyaart, Sara Roshani, Liliane C. D. Wynaendts, Nikolas Stathonikos, Gerben E. Breimer, Anne M. L. Jansen, Mitko Veta, Willeke A. M. Blokx
Spitz tumors are diagnostically challenging due to overlap in atypical histological features with conventional melanomas. We investigated to what extent AI models, using histological and/or clinical features, can: (1) distinguish Spitz tumors from conventional melanomas; (2) predict the underlying genetic aberration of Spitz tumors; and (3) predict the diagnostic category of Spitz tumors. The AI models were developed and validated using a dataset of 393 Spitz tumors and 379 conventional melanomas. Predictive performance was measured using the AUROC and the accuracy. The performance of the AI models was compared with that of four experienced pathologists in a reader study. Moreover, a simulation experiment was conducted to investigate the impact of implementing AI-based recommendations for ancillary diagnostic testing on the workflow of the pathology department. The best AI model based on UNI features reached an AUROC of 0.95 and an accuracy of 0.86 in differentiating Spitz tumors from conventional melanomas. The genetic aberration was predicted with an accuracy of 0.55 compared to 0.25 for randomly guessing. The diagnostic category was predicted with an accuracy of 0.51, where random chance-level accuracy equaled 0.33. On all three tasks, the AI models performed better than the four pathologists, although differences were not statistically significant for most individual comparisons. Based on the simulation experiment, implementing AI-based recommendations for ancillary diagnostic testing could reduce material costs, turnaround times, and examinations. In conclusion, the AI models achieved a strong predictive performance in distinguishing between Spitz tumors and conventional melanomas. On the more challenging tasks of predicting the genetic aberration and the diagnostic category of Spitz tumors, the AI models performed better than random chance.
斯皮茨瘤由于具有与常规黑色素瘤重叠的非典型组织特征,因此在诊断上颇具挑战性。我们调查了人工智能模型能在多大程度上利用组织学和(或)临床特征:(1)区分斯皮茨瘤和常规黑色素瘤;(2)预测斯皮茨瘤的基本遗传异常;(3)预测斯皮茨瘤的诊断类别。人工智能模型的开发和验证使用了包含393例斯皮茨瘤和379例常规黑色素瘤的数据集。通过AUROC和准确性来衡量预测性能。在读者研究中,将人工智能模型的性能与四位经验丰富的病理医生的性能进行了比较。此外,进行了一项模拟实验,以研究在病理学部门实施基于人工智能的辅助诊断建议对工作流程的影响。基于UNI特征的最佳人工智能模型在区分斯皮茨瘤和常规黑色素瘤方面达到了AUROC为0.95和准确性为0.86。遗传异常的预测准确率为0.55,而随机猜测的准确率为0.25。诊断类别的预测准确率为0.51,其中随机机会水平的准确率等于0.33。在所有三项任务中,人工智能模型的性能都优于四位病理医生,尽管大多数个别比较的差异没有统计学意义。基于模拟实验的结果,实施基于人工智能的辅助诊断建议可以降低材料成本、缩短周转时间和检查次数。总之,人工智能模型在区分斯皮茨瘤和常规黑色素瘤方面表现出强大的预测性能。在预测斯皮茨瘤的遗传异常和诊断类别这些更具挑战性的任务中,人工智能模型的表现优于随机机会水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables, 6 supplementary tables
Summary
基于Spitz肿瘤与常规黑色素瘤在组织形态学特征上的重叠,本研究探讨了使用组织学和/或临床特征的AI模型在区分Spitz肿瘤与常规黑色素瘤、预测Spitz肿瘤的遗传异常以及预测其诊断类别方面的能力。研究使用包含393例Spitz肿瘤和379例常规黑色素瘤的数据集进行AI模型的开发和验证。结果显示,最佳模型在区分Spitz肿瘤与常规黑色素瘤方面达到了较高的预测性能。
Key Takeaways
- AI模型在区分Spitz肿瘤与常规黑色素瘤方面表现出强预测性能,最佳模型的AUROC值为0.95,准确率为0.86。
- AI模型在预测Spitz肿瘤的遗传异常方面达到了一定的准确性(0.55),相较于随机猜测(0.25)有显著提升。
- 在预测Spitz肿瘤的诊断类别方面,AI模型的准确率为0.51,尽管相较于随机概率有所提升,但仍为较具挑战性的任务。
- AI模型在三项任务中的表现均优于四位病理医生,尽管大多数个别比较差异未达统计学显著水平。
- 实施AI辅助诊断测试推荐可以降低材料成本、缩短周转时间以及检查次数。
- AI模型在区分Spitz肿瘤与常规黑色素瘤方面的表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图

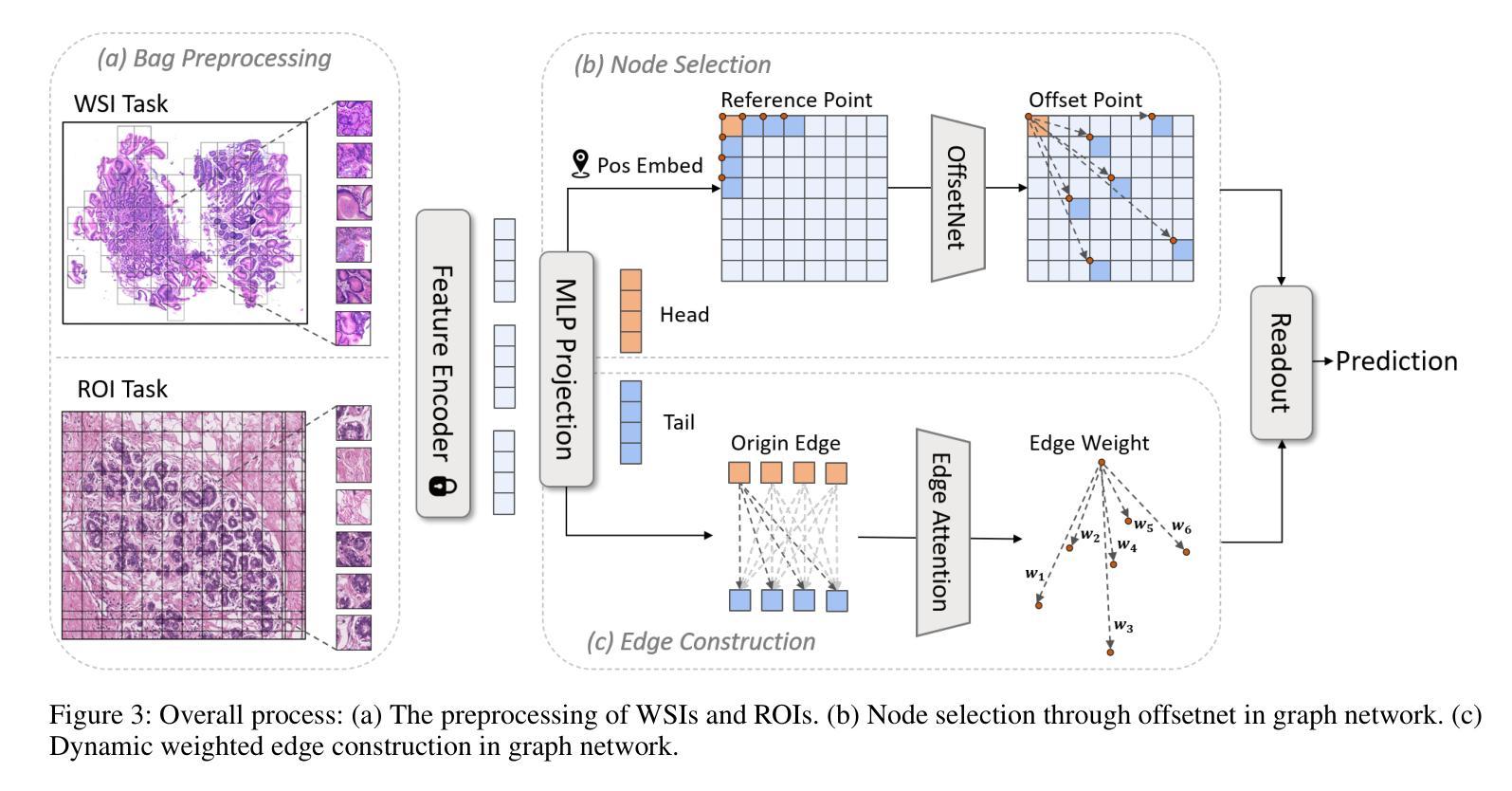
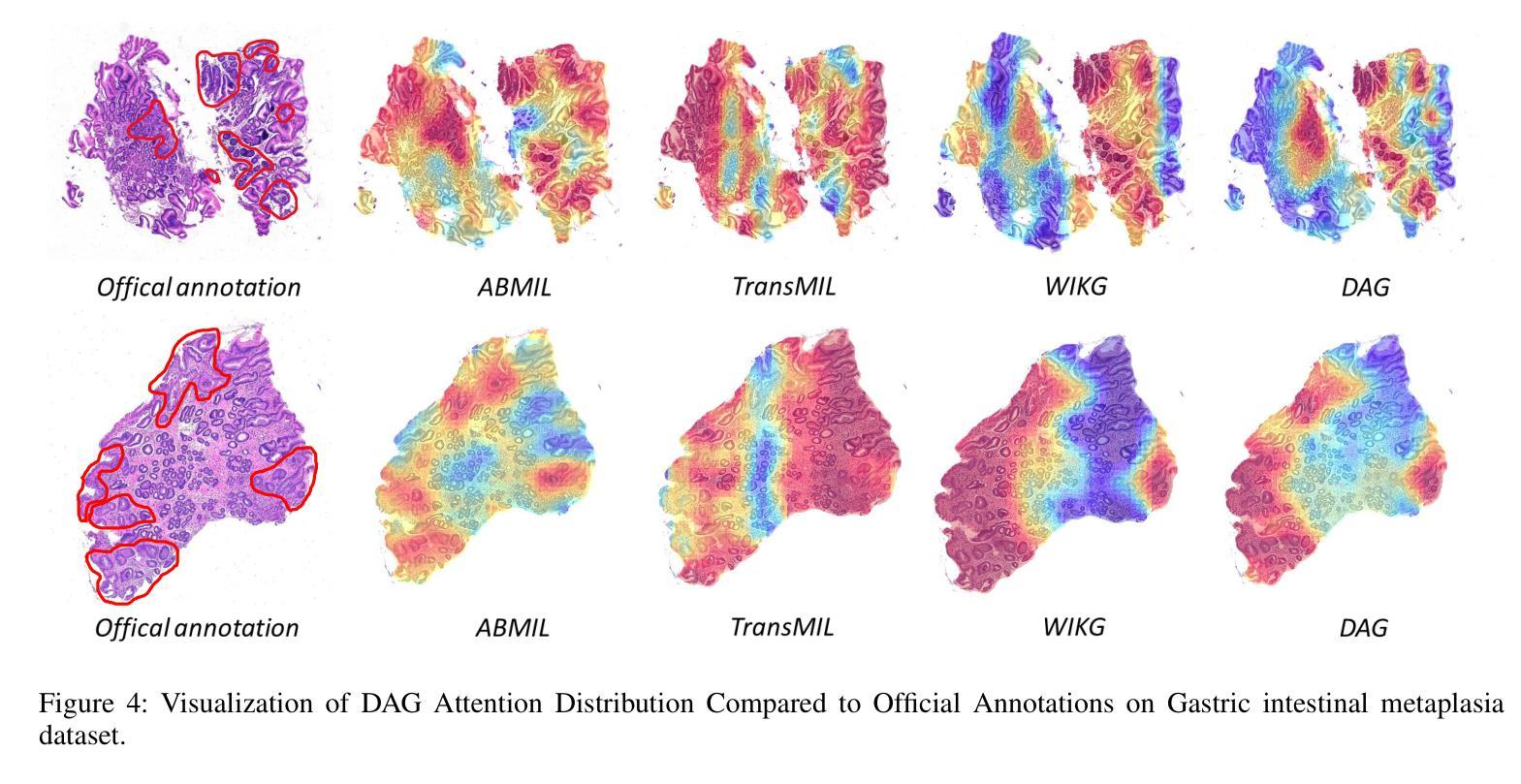
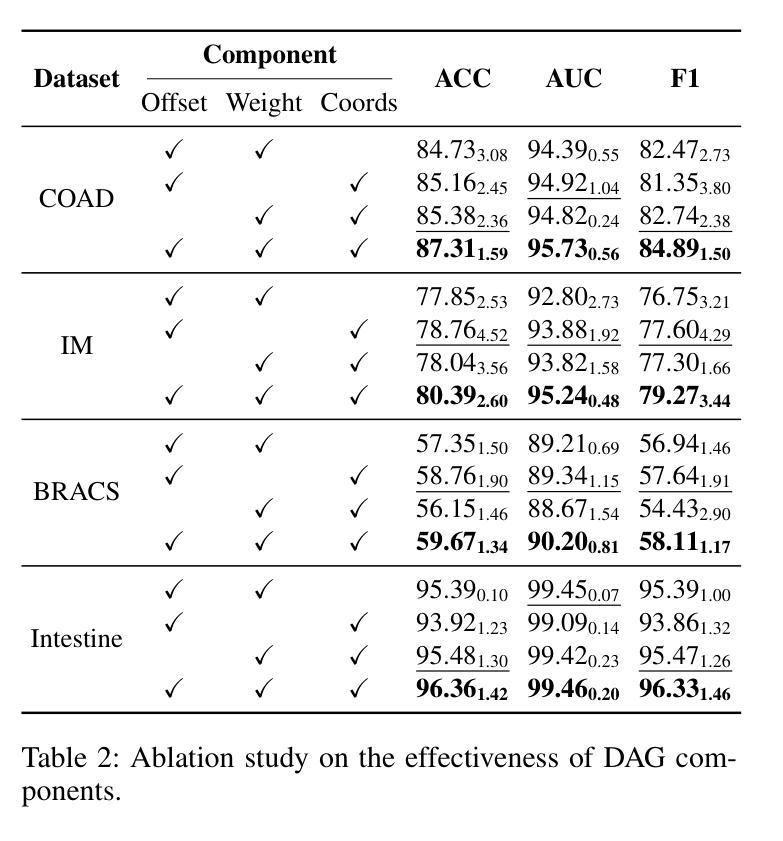
Deformable Attention Graph Representation Learning for Histopathology Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Mingxi Fu, Xitong Ling, Yuxuan Chen, Jiawen Li, fanglei fu, Huaitian Yuan, Tian Guan, Yonghong He, Lianghui Zhu
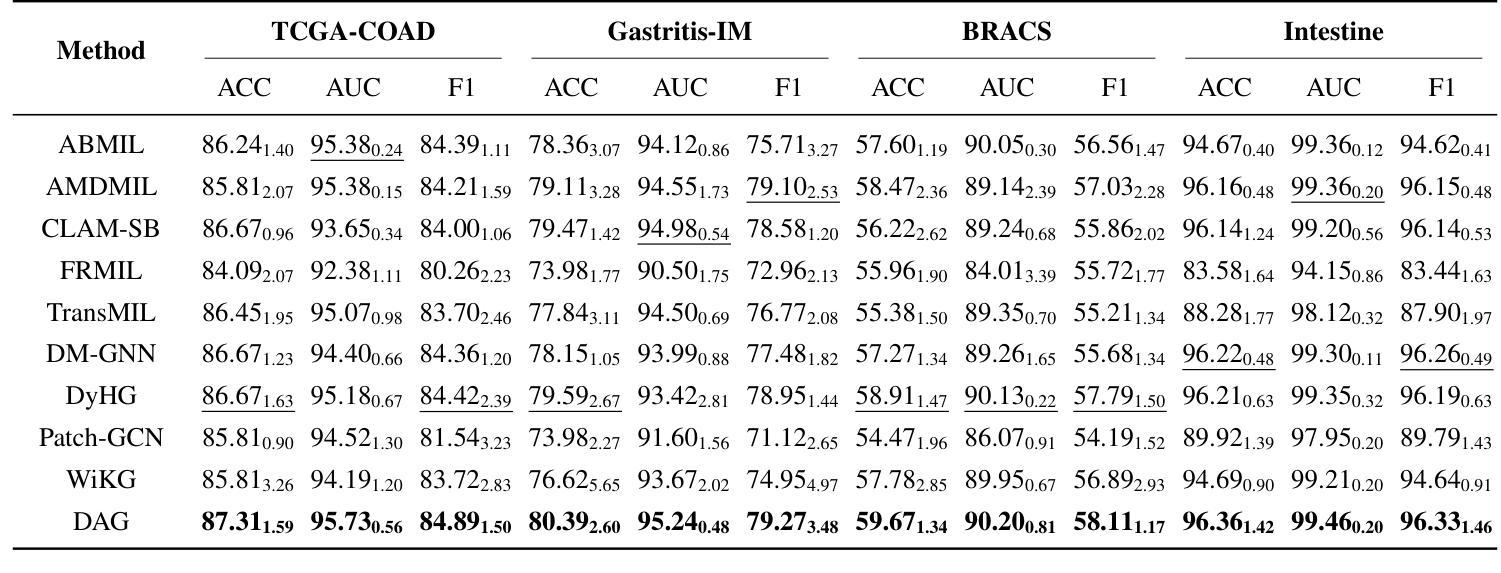
Accurate classification of Whole Slide Images (WSIs) and Regions of Interest (ROIs) is a fundamental challenge in computational pathology. While mainstream approaches often adopt Multiple Instance Learning (MIL), they struggle to capture the spatial dependencies among tissue structures. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a solution to model inter-instance relationships, yet most rely on static graph topologies and overlook the physical spatial positions of tissue patches. Moreover, conventional attention mechanisms lack specificity, limiting their ability to focus on structurally relevant regions. In this work, we propose a novel GNN framework with deformable attention for pathology image analysis. We construct a dynamic weighted directed graph based on patch features, where each node aggregates contextual information from its neighbors via attention-weighted edges. Specifically, we incorporate learnable spatial offsets informed by the real coordinates of each patch, enabling the model to adaptively attend to morphologically relevant regions across the slide. This design significantly enhances the contextual field while preserving spatial specificity. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on four benchmark datasets (TCGA-COAD, BRACS, gastric intestinal metaplasia grading, and intestinal ROI classification), demonstrating the power of deformable attention in capturing complex spatial structures in WSIs and ROIs.
全切片图像(WSIs)和感兴趣区域(ROIs)的精确分类是计算病理学中的一项基本挑战。虽然主流方法经常采用多实例学习(MIL),但它们很难捕获组织结构之间的空间依赖关系。图神经网络(GNN)已出现为建模实例间关系的一种解决方案,但大多数依赖于静态图拓扑,并忽略了组织斑块的物理空间位置。此外,传统的注意力机制缺乏特异性,限制了它们关注结构相关区域的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于病理学图像分析的新型可变形注意力图神经网络框架。我们基于斑块特征构建了一个动态加权有向图,其中每个节点都通过注意力加权的边从其邻居那里聚合上下文信息。具体来说,我们结合了可学习的空间偏移,以了解每个斑块的真实坐标,使模型能够自适应地关注切片上形态相关的区域。这种设计在增强上下文字段的同时保留了空间特异性。我们的框架在四个基准数据集上达到了最新性能(TCGA-COAD、BRACS、胃肠化生分级和肠道ROI分类),证明了可变形注意力在捕获WSIs和ROIs中复杂空间结构的力量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分类中,全幻灯片图像(WSIs)和感兴趣区域(ROIs)的准确分类是计算病理学中的基本挑战。主流方法多采用多实例学习(MIL),但难以捕捉组织结构的空间依赖性。图神经网络(GNNs)作为解决建模实例间关系的方案而出现,但大多数依赖于静态图拓扑结构而忽略了组织补丁的物理空间位置。此外,传统的注意力机制缺乏特异性,限制了其在结构上相关区域的关注能力。本研究提出了一种具有可变形注意力的新型GNN框架用于病理学图像分析。我们根据补丁特征构建了一个动态加权的有向图,每个节点通过注意力加权的边从其邻居处聚合上下文信息。具体来说,我们引入了可学习的空间偏移量,这些偏移量由每个补丁的真实坐标信息得出,使模型能够自适应地关注幻灯片中形态相关的区域。这种设计在增强上下文字段的同时保留了空间特异性。我们的框架在四个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能,证明了可变形注意力在捕捉WSIs和ROIs中复杂空间结构的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 计算病理学中对全幻灯片图像(WSIs)和感兴趣区域(ROIs)的准确分类是一个核心挑战。
- 主流方法如多实例学习(MIL)难以捕捉组织结构的空间依赖性。
- 图神经网络(GNNs)能够建模实例间的关系,但大多方法忽略了组织补丁的空间位置。
- 传统的注意力机制在关注结构上相关区域时存在局限性。
- 本研究提出了一个新型的图神经网络框架,结合可变形注意力用于病理学图像分析。
- 该框架根据补丁特征构建动态加权的有向图,并考虑每个补丁的空间坐标,以自适应地关注形态相关的区域。
点此查看论文截图

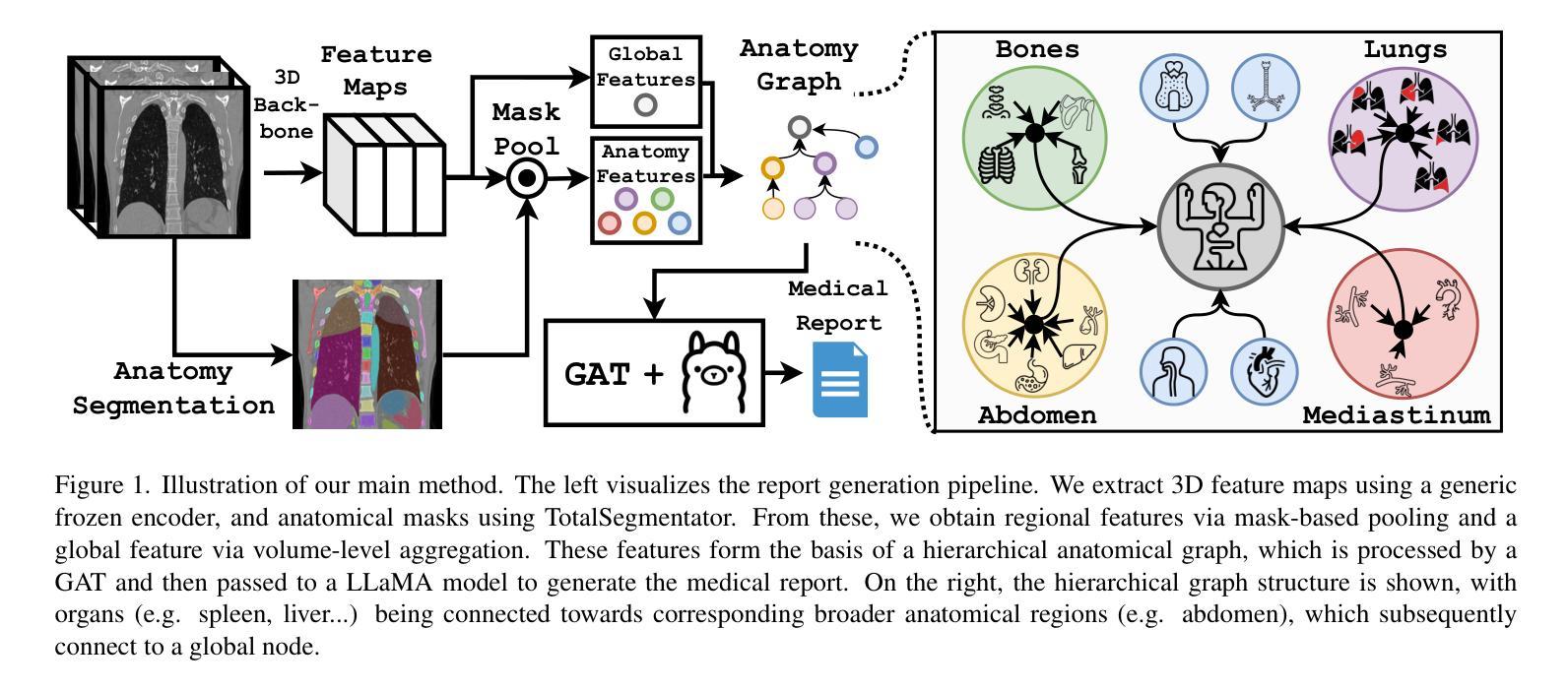
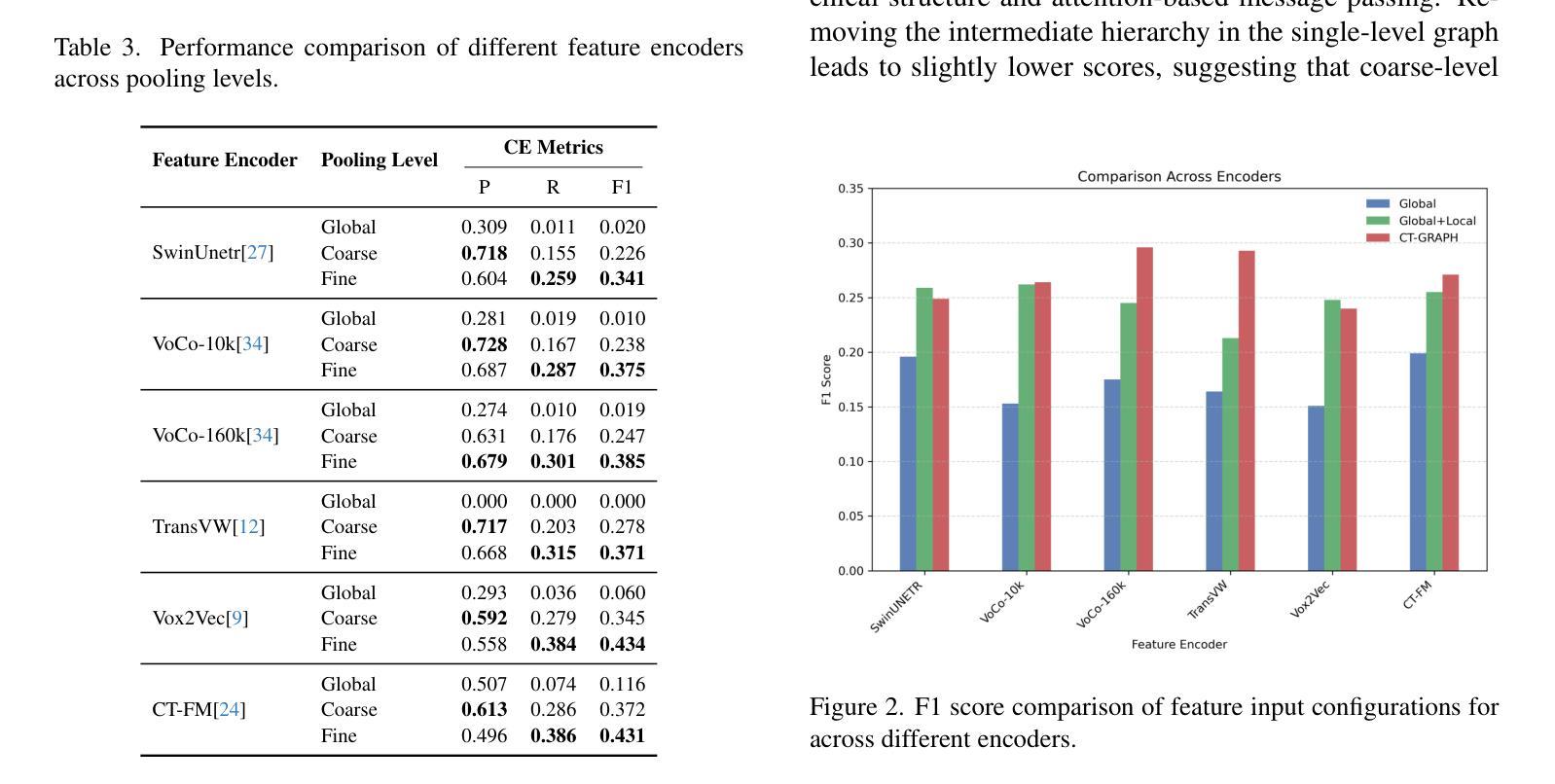
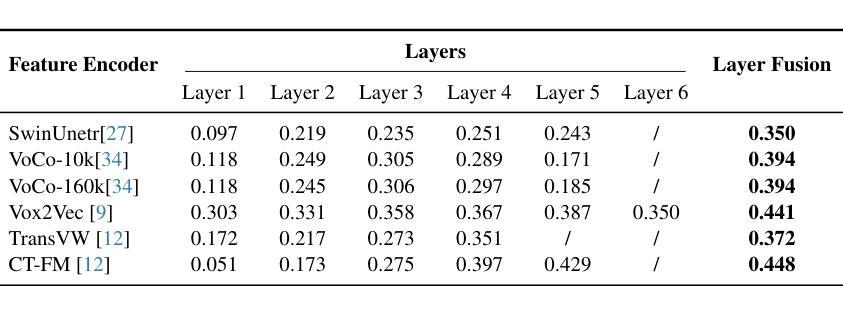
CT-GRAPH: Hierarchical Graph Attention Network for Anatomy-Guided CT Report Generation
Authors:Hamza Kalisch, Fabian Hörst, Jens Kleesiek, Ken Herrmann, Constantin Seibold
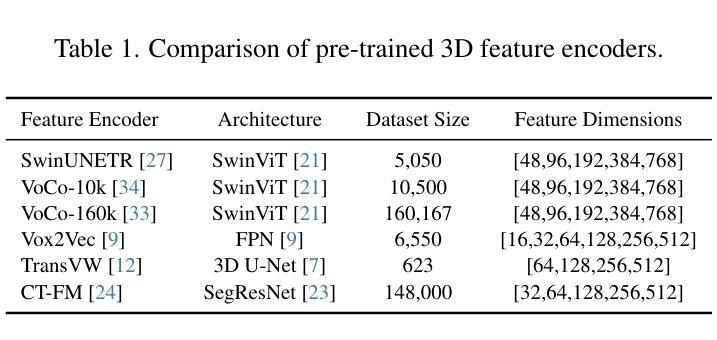
As medical imaging is central to diagnostic processes, automating the generation of radiology reports has become increasingly relevant to assist radiologists with their heavy workloads. Most current methods rely solely on global image features, failing to capture fine-grained organ relationships crucial for accurate reporting. To this end, we propose CT-GRAPH, a hierarchical graph attention network that explicitly models radiological knowledge by structuring anatomical regions into a graph, linking fine-grained organ features to coarser anatomical systems and a global patient context. Our method leverages pretrained 3D medical feature encoders to obtain global and organ-level features by utilizing anatomical masks. These features are further refined within the graph and then integrated into a large language model to generate detailed medical reports. We evaluate our approach for the task of report generation on the large-scale chest CT dataset CT-RATE. We provide an in-depth analysis of pretrained feature encoders for CT report generation and show that our method achieves a substantial improvement of absolute 7.9% in F1 score over current state-of-the-art methods. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/hakal104/CT-GRAPH.
医学成像在诊断过程中占据核心地位,因此自动化生成放射学报告对于帮助放射科医生应对大量工作具有越来越重要的意义。当前大多数方法仅依赖于全局图像特征,无法捕获对准确报告至关重要的精细器官关系。为此,我们提出了CT-GRAPH,这是一种分层图注意力网络,它通过构建解剖区域图来显式地建立放射学知识模型,将精细的器官特征链接到较粗的解剖系统和全局患者背景。我们的方法利用预训练的3D医学特征编码器,通过使用解剖掩膜获得全局和器官级别的特征。这些特征在图中得到进一步精炼,然后集成到大型语言模型中,以生成详细的医疗报告。我们在大规模的胸部CT数据集CT-RATE上对生成报告的任务进行了评估。我们深入分析了用于CT报告生成的预训练特征编码器,并证明我们的方法在F1分数上较当前最先进的方法提高了绝对7.9%。代码可在https://github.com/hakal104/CT-GRAPH公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学成像在诊断过程中占据核心地位,为帮助放射科医生应对繁重的工作负担,自动化生成放射学报告变得至关重要。当前大多数方法仅依赖全局图像特征,忽略了精细器官关系对于准确报告的重要性。为此,本文提出CT-GRAPH方法,该方法利用层次化图注意力网络显式建模放射学知识,通过构建解剖区域图连接精细器官特征与较粗的解剖系统和全局患者背景。实验表明,该方法在大规模胸部CT数据集CT-RATE上的报告生成任务中取得了显著成果,相较于当前最先进的方法,F1分数提高了7.9%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像在诊断中起核心作用,自动化生成放射学报告对帮助放射科医生具有重要意义。
- 当前大多数自动化报告生成方法仅依赖全局图像特征,存在不足。
- CT-GRAPH方法通过层次化图注意力网络显式建模放射学知识,结合精细器官关系与全局患者背景。
- 方法利用预训练的3D医学特征编码器获取全局和器官级别的特征。
- 实验表明,CT-GRAPH在胸部CT数据集CT-RATE上的报告生成任务表现优异。
- 与现有方法相比,CT-GRAPH在F1分数上提高了7.9%。
点此查看论文截图

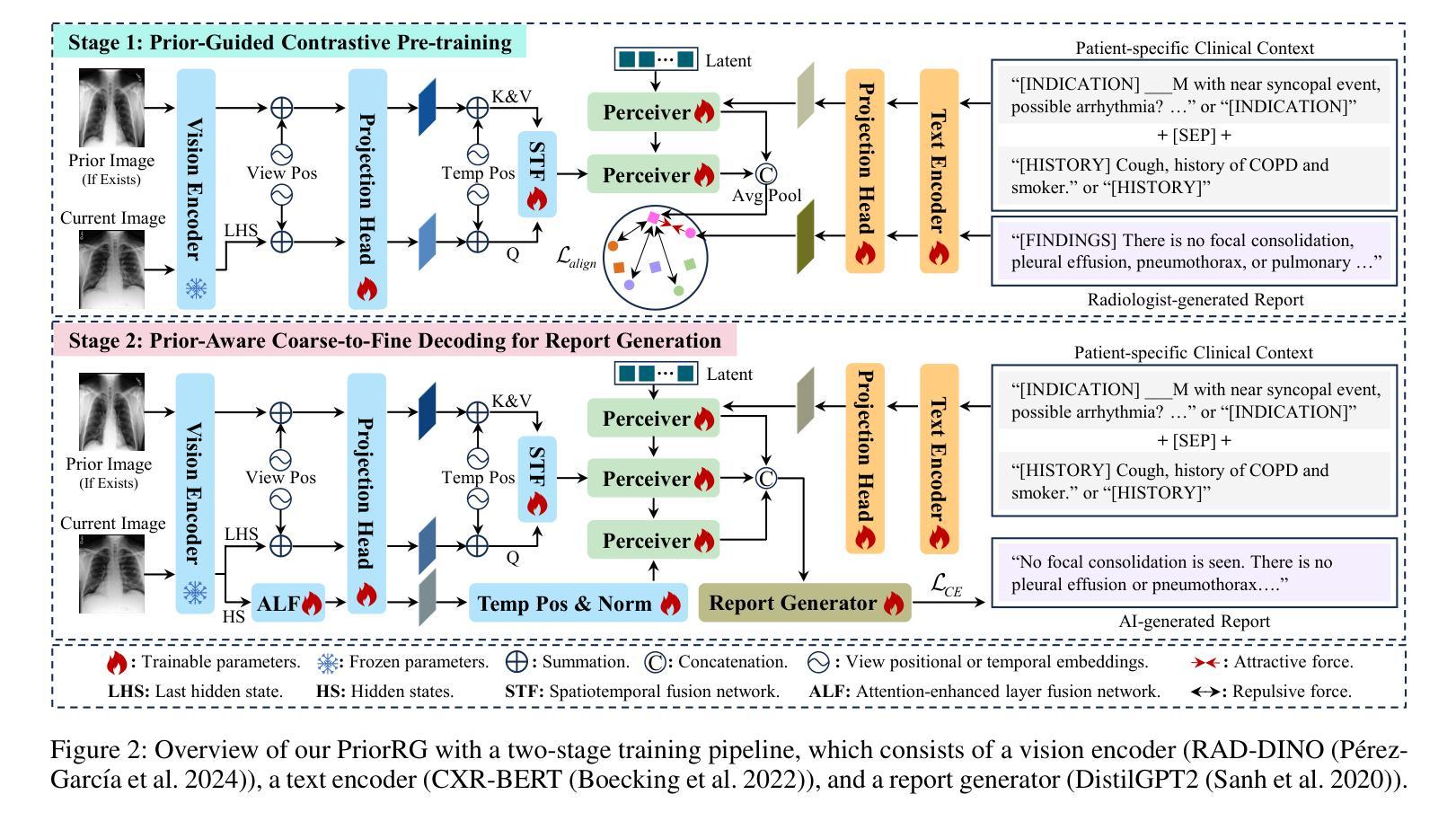
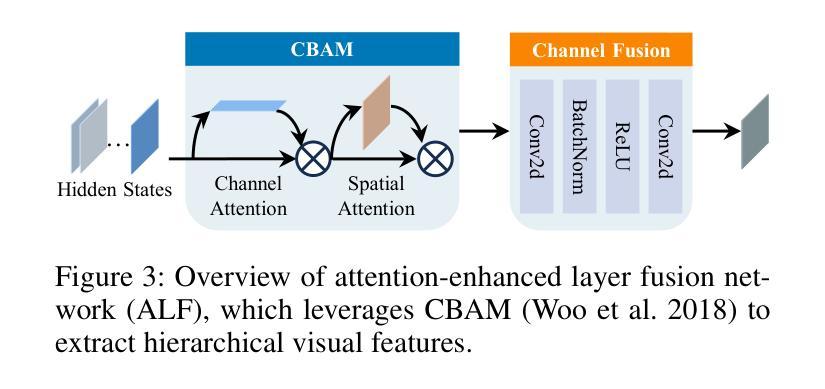
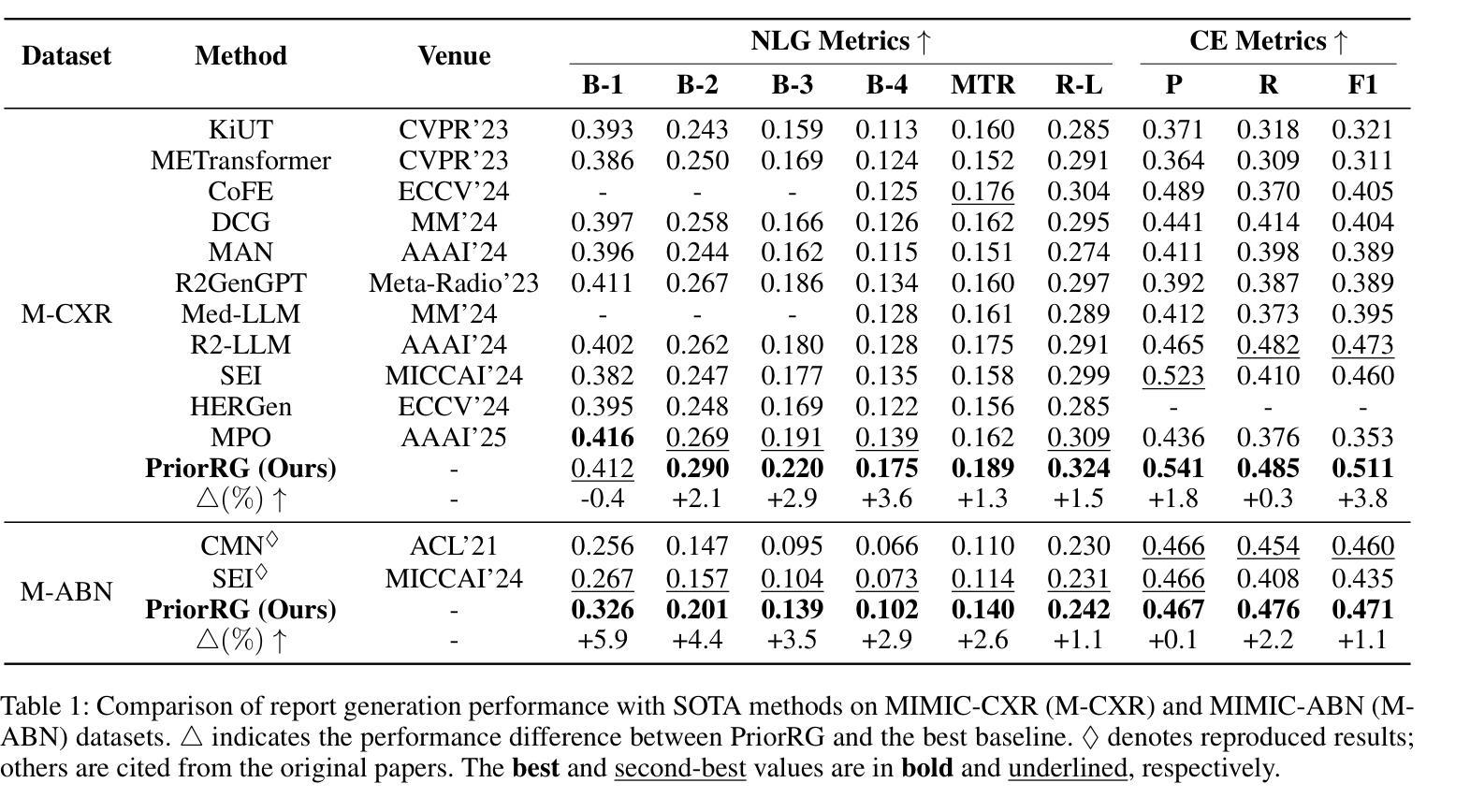
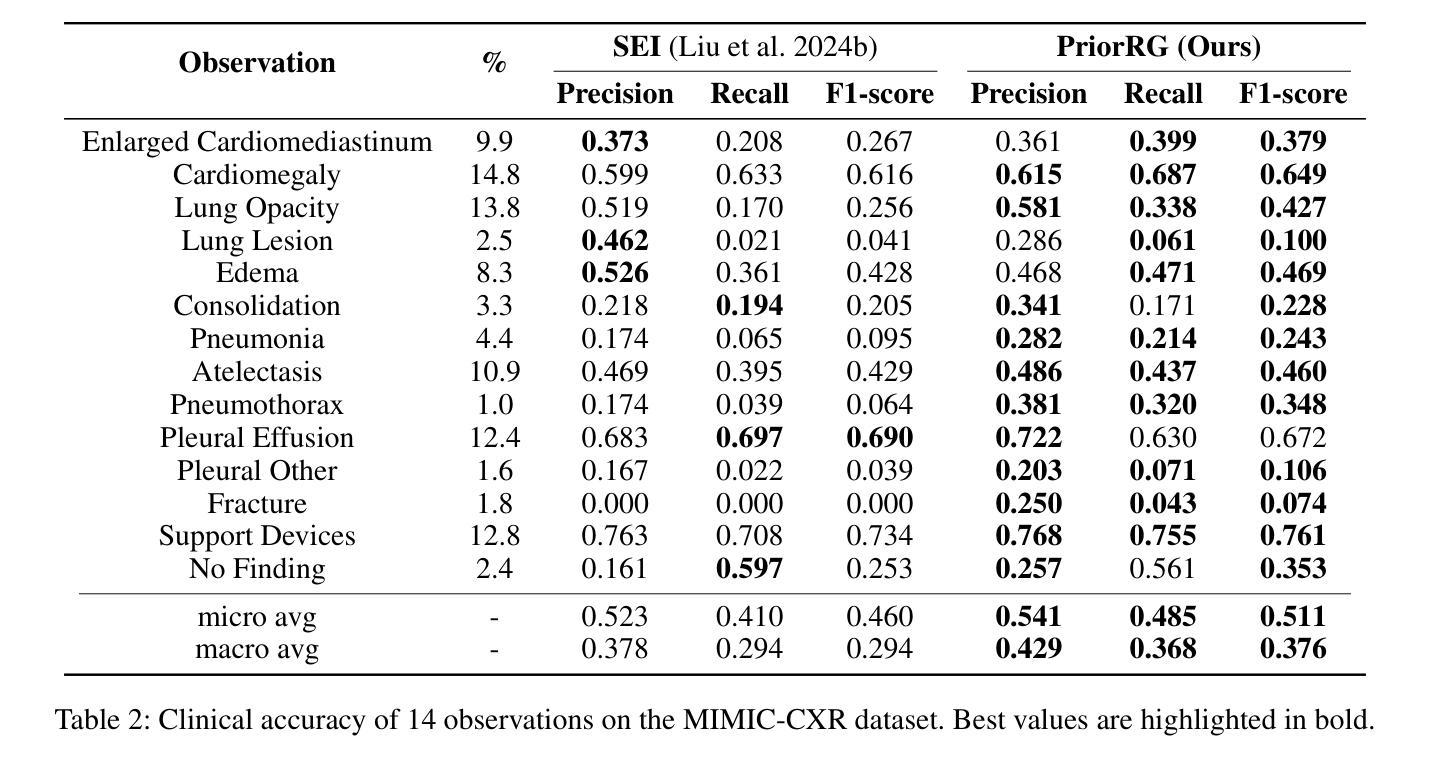
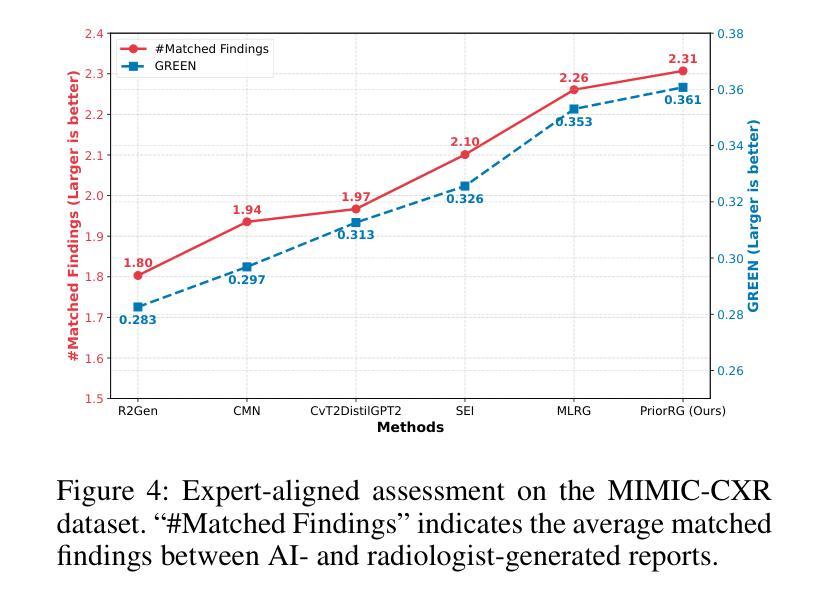
PriorRG: Prior-Guided Contrastive Pre-training and Coarse-to-Fine Decoding for Chest X-ray Report Generation
Authors:Kang Liu, Zhuoqi Ma, Zikang Fang, Yunan Li, Kun Xie, Qiguang Miao
Chest X-ray report generation aims to reduce radiologists’ workload by automatically producing high-quality preliminary reports. A critical yet underexplored aspect of this task is the effective use of patient-specific prior knowledge – including clinical context (e.g., symptoms, medical history) and the most recent prior image – which radiologists routinely rely on for diagnostic reasoning. Most existing methods generate reports from single images, neglecting this essential prior information and thus failing to capture diagnostic intent or disease progression. To bridge this gap, we propose PriorRG, a novel chest X-ray report generation framework that emulates real-world clinical workflows via a two-stage training pipeline. In Stage 1, we introduce a prior-guided contrastive pre-training scheme that leverages clinical context to guide spatiotemporal feature extraction, allowing the model to align more closely with the intrinsic spatiotemporal semantics in radiology reports. In Stage 2, we present a prior-aware coarse-to-fine decoding for report generation that progressively integrates patient-specific prior knowledge with the vision encoder’s hidden states. This decoding allows the model to align with diagnostic focus and track disease progression, thereby enhancing the clinical accuracy and fluency of the generated reports. Extensive experiments on MIMIC-CXR and MIMIC-ABN datasets demonstrate that PriorRG outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a 3.6% BLEU-4 and 3.8% F1 score improvement on MIMIC-CXR, and a 5.9% BLEU-1 gain on MIMIC-ABN. Code and checkpoints will be released upon acceptance.
胸部X光报告生成旨在通过自动产生高质量的初步报告来减轻放射科医生的工作量。该任务的一个关键但尚未被充分研究的方面是如何有效地利用患者特定的先验知识,包括临床背景(例如症状、病史)和最近的先前图像,放射科医生在进行诊断推理时通常会依赖这些知识。大多数现有方法都是从单一图像生成报告,忽略了这些关键的先验信息,因此无法捕捉诊断意图或疾病进展。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了PriorRG,这是一种新的胸部X光报告生成框架,它通过两阶段训练管道模拟现实临床工作流程。在第一阶段,我们引入了基于先验的对比预训练方案,利用临床背景引导时空特征提取,使模型更贴近放射学报告中的内在时空语义。在第二阶段,我们提出了基于先验的粗细到细解码报告生成方法,该方法逐步将患者特定的先验知识与视觉编码器的隐藏状态集成在一起。这种解码方式使模型能够符合诊断重点并跟踪疾病进展,从而提高生成报告的临床准确性和流畅性。在MIMIC-CXR和MIMIC-ABN数据集上的大量实验表明,PriorRG优于最新方法,在MIMIC-CXR上实现了BLEU-4的3.6%和F1得分的3.8%的提升,在MIMIC-ABN上实现了BLEU-1的5.9%的提升。论文接受后将公布代码和检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文关注通过利用患者特定先验知识(包括临床症状、病史和最新图像等),实现自动产生高质量初步报告,从而减少放射科医生工作量的目标。针对当前多数方法仅关注单一图像报告生成,忽略了重要的先验信息,无法捕捉诊断意图或疾病进展的问题,本文提出了一种新的胸部X光报告生成框架PriorRG。该框架模拟真实临床工作流程,通过两阶段训练管道进行训练。第一阶段引入基于先验知识的对比预训练方案,利用临床语境指导时空特征提取;第二阶段采用先验知识感知的粗细解码方式生成报告,逐步将患者特定先验知识与视觉编码器的隐藏状态整合在一起。通过这种方式,模型能够更好地聚焦于诊断重点并追踪疾病进展,提高了生成报告的临床准确性和流畅性。在MIMIC-CXR和MIMIC-ABN数据集上的实验表明,PriorRG较先进方法实现了显著性能提升,在MIMIC-CXR上BLEU-4和F1得分提高了3.6%和3.8%,在MIMIC-ABN上BLEU-1得分提高了5.9%。
关键见解
- 胸部X光报告生成旨在通过自动产生高质量初步报告减少放射科医生工作量。
- 当前方法忽略了患者特定的先验信息,包括临床症状、病史和最新图像等,无法捕捉诊断意图和疾病进展。
- PriorRG框架通过模拟真实临床工作流程来整合患者特定先验知识,提高报告生成的准确性和流畅性。
- PriorRG采用两阶段训练管道:第一阶段利用临床语境进行先验知识指导的对比预训练;第二阶段采用先验知识感知的解码方式生成报告。
- 实验结果表明,PriorRG在MIMIC-CXR和MIMIC-ABN数据集上较先进方法实现了显著性能提升。
- PriorRG模型能更好地聚焦于诊断重点并追踪疾病进展。
点此查看论文截图

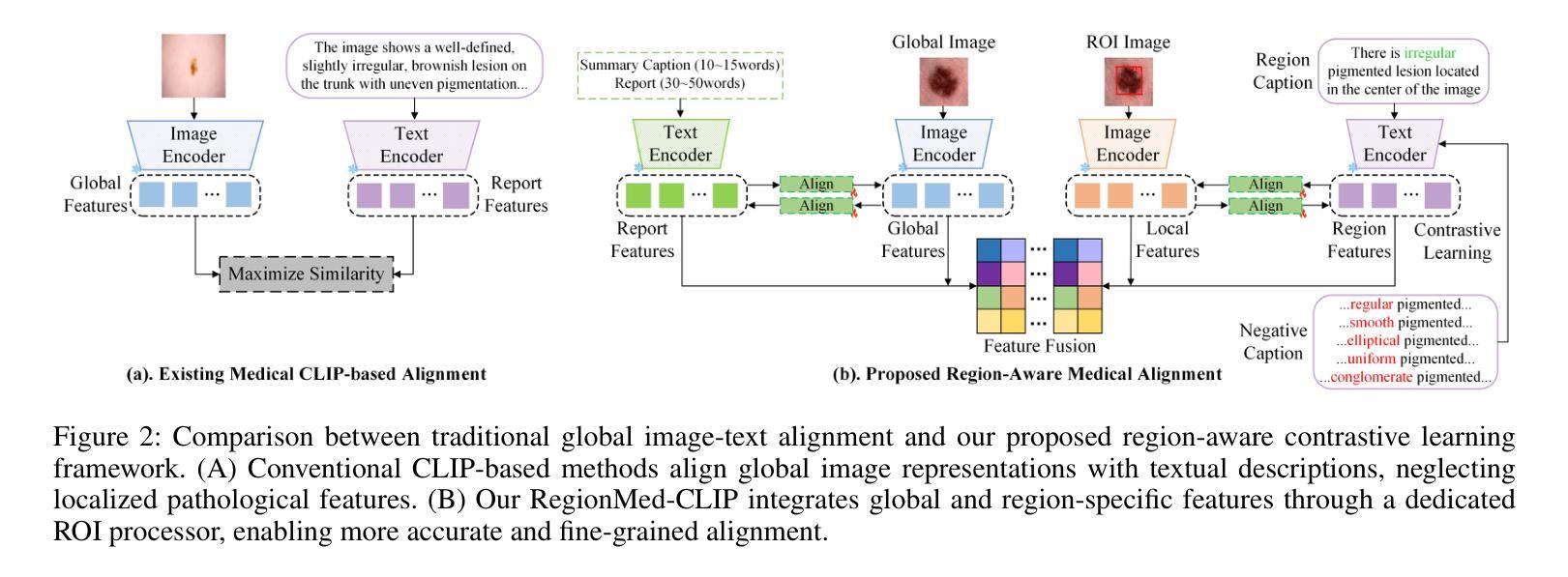
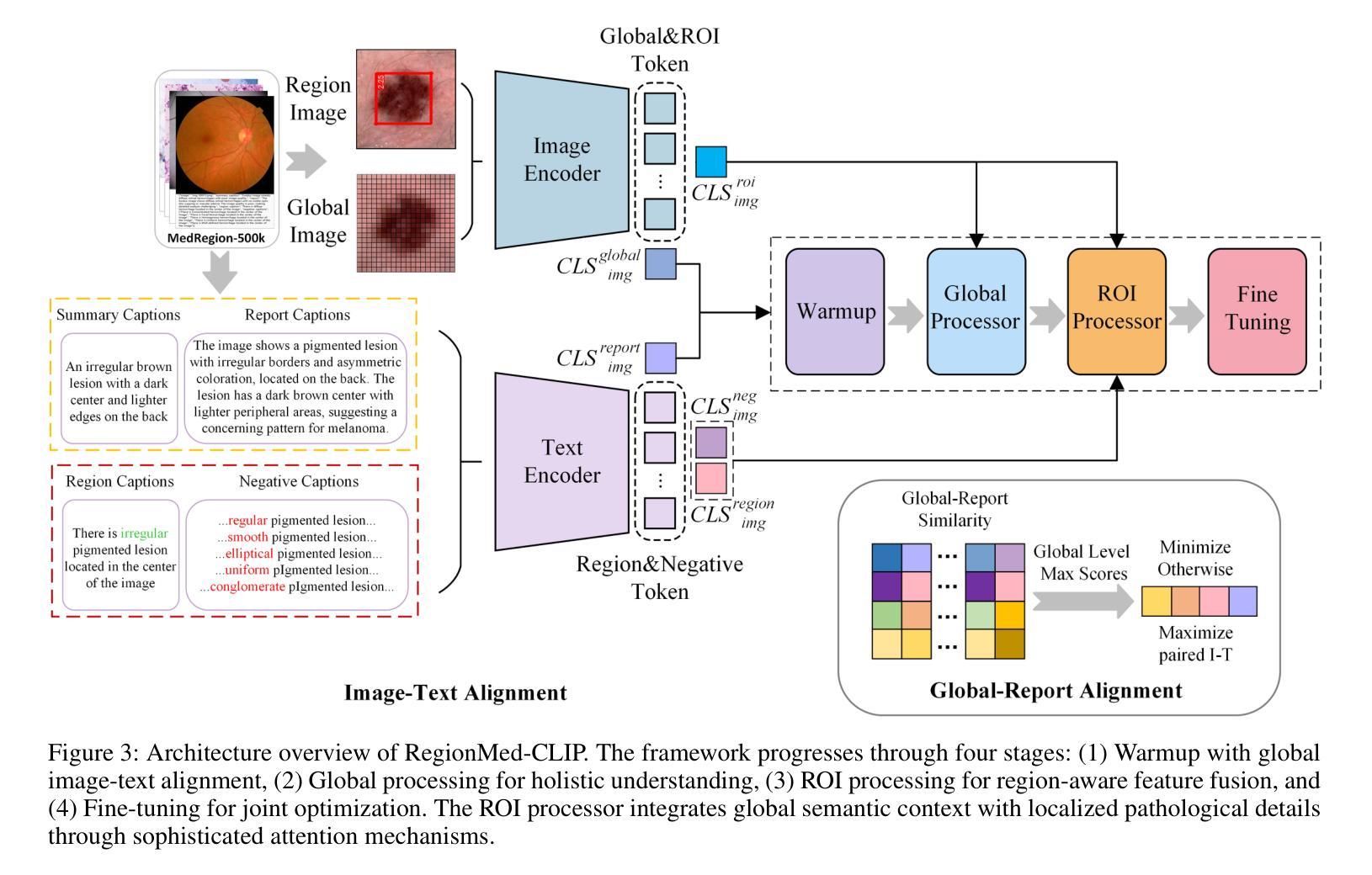
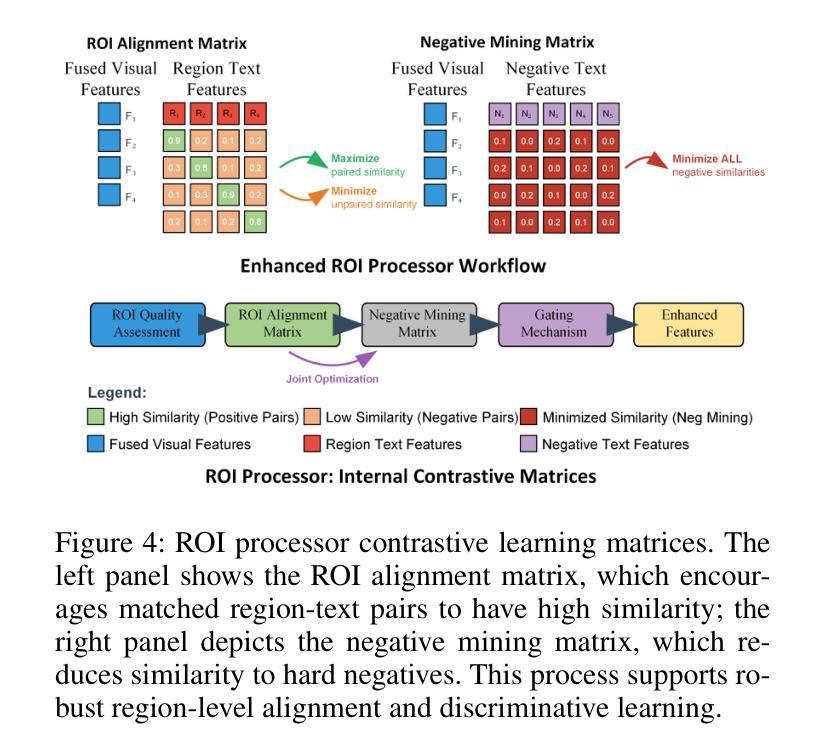
RegionMed-CLIP: A Region-Aware Multimodal Contrastive Learning Pre-trained Model for Medical Image Understanding
Authors:Tianchen Fang, Guiru Liu
Medical image understanding plays a crucial role in enabling automated diagnosis and data-driven clinical decision support. However, its progress is impeded by two primary challenges: the limited availability of high-quality annotated medical data and an overreliance on global image features, which often miss subtle but clinically significant pathological regions. To address these issues, we introduce RegionMed-CLIP, a region-aware multimodal contrastive learning framework that explicitly incorporates localized pathological signals along with holistic semantic representations. The core of our method is an innovative region-of-interest (ROI) processor that adaptively integrates fine-grained regional features with the global context, supported by a progressive training strategy that enhances hierarchical multimodal alignment. To enable large-scale region-level representation learning, we construct MedRegion-500k, a comprehensive medical image-text corpus that features extensive regional annotations and multilevel clinical descriptions. Extensive experiments on image-text retrieval, zero-shot classification, and visual question answering tasks demonstrate that RegionMed-CLIP consistently exceeds state-of-the-art vision language models by a wide margin. Our results highlight the critical importance of region-aware contrastive pre-training and position RegionMed-CLIP as a robust foundation for advancing multimodal medical image understanding.
医学图像理解在实现自动化诊断和基于数据的临床决策支持中起着至关重要的作用。然而,其进展受到两个主要挑战的限制:高质量标注医学数据的有限可用性,以及对全局图像特征的过度依赖,这往往导致忽略细微但临床上重要的病理区域。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了RegionMed-CLIP,这是一个区域感知的多模式对比学习框架,它显式地结合了局部病理信号和整体语义表示。我们的方法的核心是一个创新的兴趣区域(ROI)处理器,它自适应地集成精细的局部特征与全局上下文,辅以一种增强层次化多模式对齐的渐进式训练策略。为了实现对大规模区域级别表示的学习,我们构建了MedRegion-500k,这是一个以区域注释和多层次临床描述为特色的医学图像-文本语料库。在图像-文本检索、零样本分类和视觉问答任务上的大量实验表明,RegionMed-CLIP一致且大幅度地超越了最先进的视觉语言模型。我们的研究结果强调了区域感知对比预训练的关键重要性,并将RegionMed-CLIP定位为推进多模式医学图像理解的有力基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像理解在自动化诊断和基于数据的临床决策支持中发挥着关键作用,但面临着高质量标注医学数据有限和过于依赖全局图像特征两大挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了RegionMed-CLIP,这是一个区域感知的多模态对比学习框架,它显式地结合了局部病理信号和整体语义表示。我们的方法核心是自适应集成精细区域特征与全局上下文的感兴趣区域(ROI)处理器,辅以增强层次多模态对齐的渐进训练策略。为实现大规模区域级别表示学习,我们构建了MedRegion-500k,这是一个包含广泛区域注释和多层临床描述的综合医学图像文本语料库。实验表明,RegionMed-CLIP在图像文本检索、零样本分类和视觉问答任务上显著超越了最先进的视觉语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像理解在自动化诊断和临床决策支持中起关键作用。
- 医学图像理解的两大挑战是高质量标注数据有限和过度依赖全局图像特征。
- RegionMed-CLIP是一个区域感知的多模态对比学习框架,结合了局部病理信号和整体语义表示。
- ROI处理器是RegionMed-CLIP的核心,它自适应地集成精细区域特征与全局上下文。
- 渐进的训练策略增强了RegionMed-CLIP的层次多模态对齐能力。
- MedRegion-500k是一个综合医学图像文本语料库,包含广泛的区域注释和多层临床描述。
- RegionMed-CLIP在多项任务上表现优异,显著超越了现有的视觉语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Pixels: Medical Image Quality Assessment with Implicit Neural Representations
Authors:Caner Özer, Patryk Rygiel, Bram de Wilde, İlkay Öksüz, Jelmer M. Wolterink
Artifacts pose a significant challenge in medical imaging, impacting diagnostic accuracy and downstream analysis. While image-based approaches for detecting artifacts can be effective, they often rely on preprocessing methods that can lead to information loss and high-memory-demand medical images, thereby limiting the scalability of classification models. In this work, we propose the use of implicit neural representations (INRs) for image quality assessment. INRs provide a compact and continuous representation of medical images, naturally handling variations in resolution and image size while reducing memory overhead. We develop deep weight space networks, graph neural networks, and relational attention transformers that operate on INRs to achieve image quality assessment. Our method is evaluated on the ACDC dataset with synthetically generated artifact patterns, demonstrating its effectiveness in assessing image quality while achieving similar performance with fewer parameters.
在医学成像中,伪影构成了一大挑战,影响了诊断准确性和后续分析。虽然基于图像的伪影检测方法可以很有效,但它们经常依赖于可能导致信息丢失和高内存需求的医学图像预处理方法,从而限制了分类模型的可扩展性。在这项工作中,我们建议使用隐式神经表示(INR)来进行图像质量评估。INR为医学图像提供了紧凑且连续的代表,可自然处理分辨率和图像大小的差异,同时减少内存开销。我们开发了深度权重空间网络、图神经网络和关系注意力转换器,它们在INR上运行以实现图像质量评估。我们的方法在ACDC数据集上使用合成生成的伪影模式进行了评估,证明了其在评估图像质量时的有效性,同时以更少的参数实现了类似性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in 16th Machine Learning in Medical Imaging (MLMI 2025) workshop
Summary
本文提出使用隐式神经网络表示(INRs)进行医学图像质量评估的方法。该方法能有效处理医学图像中的伪影问题,通过紧凑且连续的图像表示,自然应对分辨率和图像大小的差异,同时降低内存开销。通过深度权重空间网络、图神经网络和关系注意力转换器对INRs进行操作,实现了图像质量评估。在ACDC数据集上,使用合成伪影模式进行验证,证明该方法在评估图像质量时表现出色,且参数更少。
Key Takeaways
- 伪影对医学成像构成挑战,影响诊断和下游分析。
- 图像方法虽可有效检测伪影,但依赖的预处理可能导致信息损失及高内存需求。
- 引入隐式神经网络表示(INRs)进行医学图像质量评估。
- INRs提供紧凑且连续的图像表示,适应不同分辨率和图像大小。
- 使用深度权重空间网络、图神经网络和关系注意力转换器对INRs进行评估操作。
- 方法在ACDC数据集上验证有效,合成伪影模式下表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

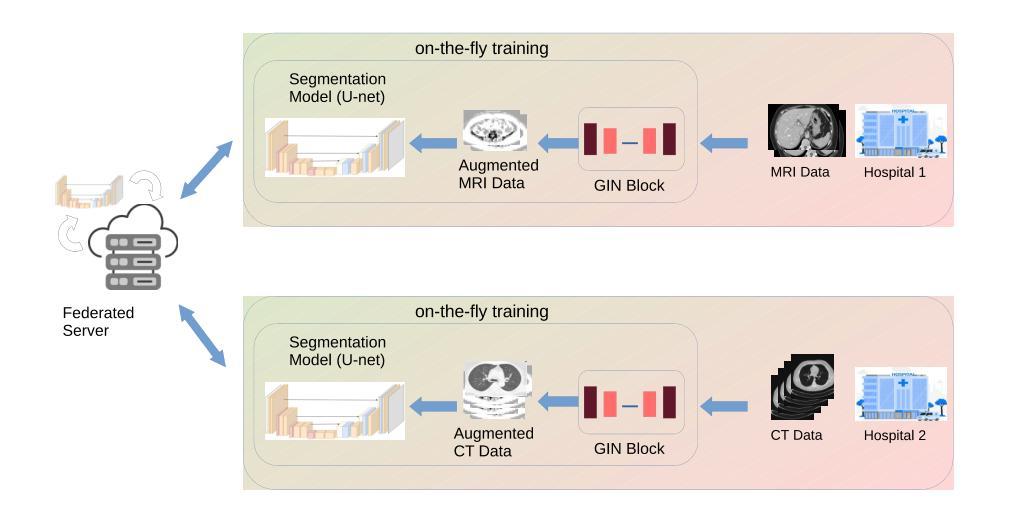
FedGIN: Federated Learning with Dynamic Global Intensity Non-linear Augmentation for Organ Segmentation using Multi-modal Images
Authors:Sachin Dudda Nagaraju, Ashkan Moradi, Bendik Skarre Abrahamsen, Mattijs Elschot
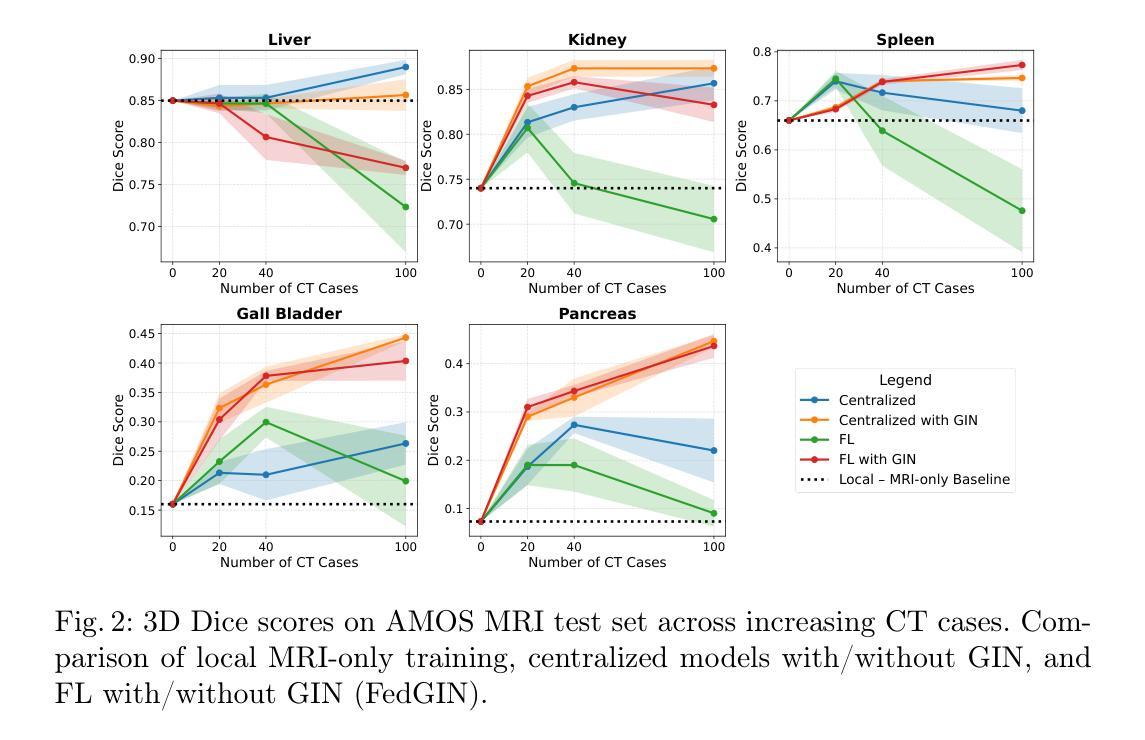
Medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in AI-assisted diagnostics, surgical planning, and treatment monitoring. Accurate and robust segmentation models are essential for enabling reliable, data-driven clinical decision making across diverse imaging modalities. Given the inherent variability in image characteristics across modalities, developing a unified model capable of generalizing effectively to multiple modalities would be highly beneficial. This model could streamline clinical workflows and reduce the need for modality-specific training. However, real-world deployment faces major challenges, including data scarcity, domain shift between modalities (e.g., CT vs. MRI), and privacy restrictions that prevent data sharing. To address these issues, we propose FedGIN, a Federated Learning (FL) framework that enables multimodal organ segmentation without sharing raw patient data. Our method integrates a lightweight Global Intensity Non-linear (GIN) augmentation module that harmonizes modality-specific intensity distributions during local training. We evaluated FedGIN using two types of datasets: an imputed dataset and a complete dataset. In the limited dataset scenario, the model was initially trained using only MRI data, and CT data was added to assess its performance improvements. In the complete dataset scenario, both MRI and CT data were fully utilized for training on all clients. In the limited-data scenario, FedGIN achieved a 12 to 18% improvement in 3D Dice scores on MRI test cases compared to FL without GIN and consistently outperformed local baselines. In the complete dataset scenario, FedGIN demonstrated near-centralized performance, with a 30% Dice score improvement over the MRI-only baseline and a 10% improvement over the CT-only baseline, highlighting its strong cross-modality generalization under privacy constraints.
医学图像分割在人工智能辅助诊断、手术规划和治疗监测中起着至关重要的作用。准确且稳健的分割模型对于在多种成像模式上实现可靠的数据驱动临床决策至关重要。考虑到不同模态图像特性固有的变化,开发一种能够有效推广到多种模态的统一模型将大有裨益。该模型可以简化临床工作流程,减少针对特定模态的培训需求。然而,在现实世界的部署中,面临着数据稀缺、不同模态之间的领域偏移(例如CT与MRI)以及阻止数据共享的隐私限制等重大挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了FedGIN,这是一个联邦学习(FL)框架,能够在不共享原始患者数据的情况下实现多模态器官分割。我们的方法整合了一个轻量级的全局强度非线性(GIN)增强模块,该模块在本地训练过程中协调特定模态的强度分布。我们使用两种类型的数据集对FedGIN进行了评估:一个填充数据集和一个完整数据集。在有限数据集的情况下,模型最初仅使用MRI数据进行训练,然后加入CT数据以评估其性能改进。在完整数据集的情况下,MRI和CT数据都用于所有客户端的训练。在数据有限的情况下,与没有GIN的FL相比,FedGIN在MRI测试案例中的3D Dice得分提高了12%到18%,并且始终超过了本地基准。在完整数据集的情况下,FedGIN表现出接近集中式的性能,与仅使用MRI的基线相比,Dice得分提高了30%,与仅使用CT的基线相比,提高了10%,这突显了其在隐私约束下强大的跨模态泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper Accepted at MICCAI 2025 DeCaf Workshop Track
摘要
医学图像分割在人工智能辅助诊断、手术规划和治疗监测中发挥着关键作用。开发准确且稳健的分割模型对于实现可靠的数据驱动临床决策至关重要,特别是在多种成像模态中。为应对不同模态间图像特性固有的差异性,开发能够有效泛化至多种模态的统一模型将大有��d益。该模型能简化临床工作流程,减少针对特定模态的培训需求。然而,现实世界部署面临重大挑战,包括数据稀缺、模态间的领域偏移(如CT与MRI)以及阻止数据共享的隐私限制。为解决这些问题,我们提出FedGIN,一个联邦学习(FL)框架,可在不共享原始患者数据的情况下实现多模态器官分割。我们的方法整合了轻量级的全局强度非线性(GIN)增强模块,在本地训练过程中协调模态特定强度分布。我们使用两种类型的数据集对FedGIN进行了评估:插补数据集和完整数据集。在有限数据集场景中,模型最初仅使用MRI数据进行训练,并加入CT数据以评估其性能改进。在完整数据集场景中,MRI和CT数据均用于所有客户端的训练。在有限数据场景中,与无GIN的FL相比,FedGIN在MRI测试病例中的3D骰子分数提高了12%到18%,并且始终优于本地基线。在完整数据集场景中,FedGIN表现出接近集中化的性能,与MRI-only基线相比,骰子分数提高了30%,与CT-only基线相比,提高了10%,这凸显了其在隐私约束下的跨模态泛化能力。
要点解析
- 医学图像分割在多个医疗应用中的重要性。
- 不同成像模态之间图像特性的差异性带来的挑战。
- 开发能泛化至多种模态的统一模型的优势。
- 现实世界部署面临的三大挑战:数据稀缺、领域偏移和隐私限制。
- FedGIN联邦学习框架的提出以及其整合的GIN模块的作用。
- FedGIN在有限数据集和完整数据集场景下的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

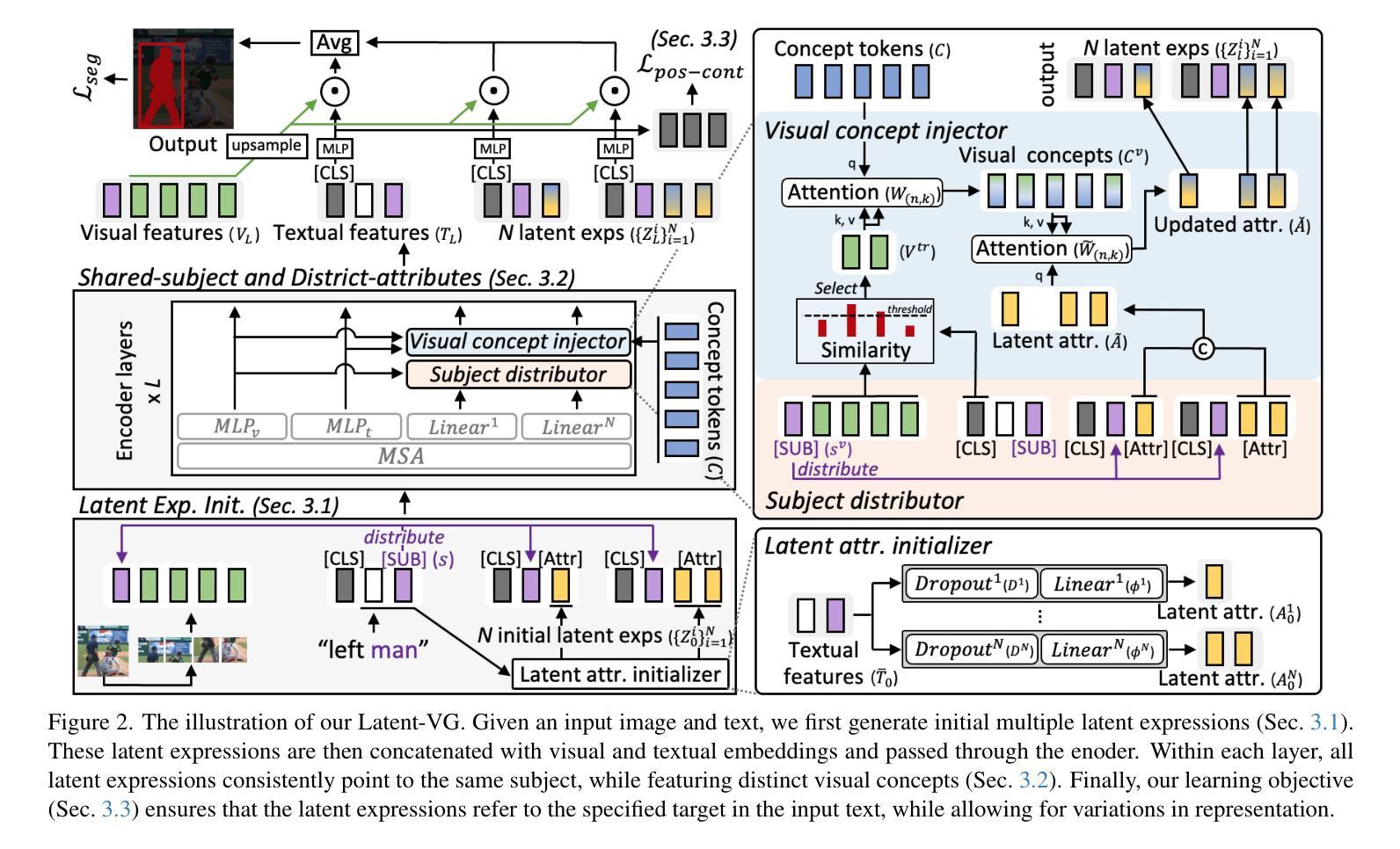
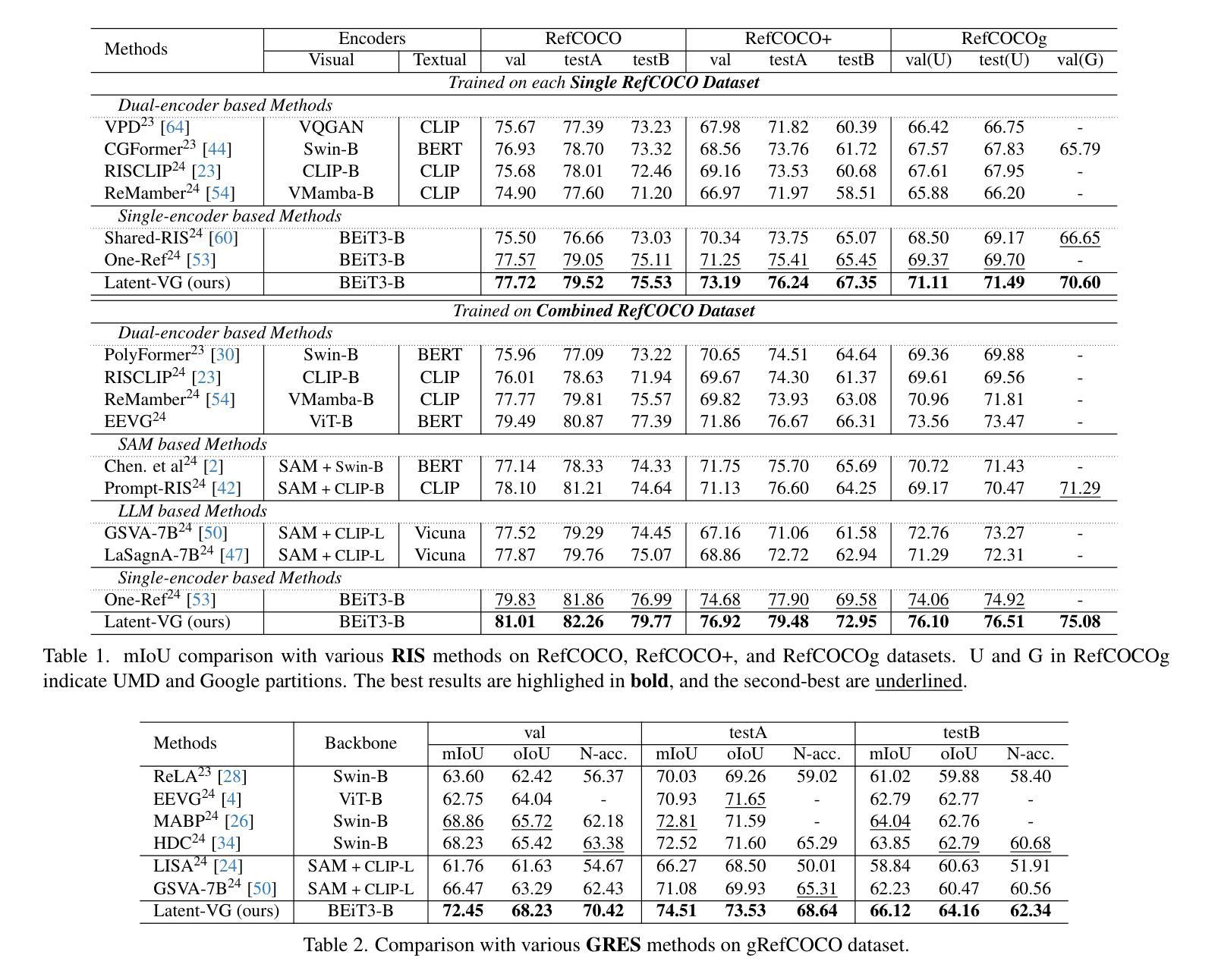
Latent Expression Generation for Referring Image Segmentation and Grounding
Authors:Seonghoon Yu, Joonbeom Hong, Joonseok Lee, Jeany Son
Visual grounding tasks, such as referring image segmentation (RIS) and referring expression comprehension (REC), aim to localize a target object based on a given textual description. The target object in an image can be described in multiple ways, reflecting diverse attributes such as color, position, and more. However, most existing methods rely on a single textual input, which captures only a fraction of the rich information available in the visual domain. This mismatch between rich visual details and sparse textual cues can lead to the misidentification of similar objects. To address this, we propose a novel visual grounding framework that leverages multiple latent expressions generated from a single textual input by incorporating complementary visual details absent from the original description. Specifically, we introduce subject distributor and visual concept injector modules to embed both shared-subject and distinct-attributes concepts into the latent representations, thereby capturing unique and target-specific visual cues. We also propose a positive-margin contrastive learning strategy to align all latent expressions with the original text while preserving subtle variations. Experimental results show that our method not only outperforms state-of-the-art RIS and REC approaches on multiple benchmarks but also achieves outstanding performance on the generalized referring expression segmentation (GRES) benchmark.
视觉定位任务,如引用图像分割(RIS)和引用表达式理解(REC),旨在根据给定的文本描述定位目标对象。图像中的目标对象可以用多种方式描述,反映颜色、位置等多种属性。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于单个文本输入,只能捕捉到视觉领域丰富信息的一小部分。丰富视觉细节和稀疏文本线索之间的不匹配可能导致类似对象的误识别。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,该框架利用单个文本输入产生的多个潜在表达式,并融入原始描述中缺失的互补视觉细节。具体来说,我们引入了主体分配器和视觉概念注入器模块,将共享主体和独特属性概念嵌入到潜在表示中,从而捕获独特且针对目标对象的视觉线索。我们还提出了一种正边距对比学习策略,将所有潜在表达式与原始文本对齐,同时保留细微变化。实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅在多个基准测试上超越了最先进的RIS和REC方法,而且在广义引用表达式分割(GRES)基准测试上也取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
这是一篇关于视觉定位任务的研究论文,主要介绍了如何通过结合多种潜在表达和视觉细节来解决单一文本输入导致的视觉与文本信息不匹配的问题。论文提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,该框架通过从单一文本输入生成多个潜在表达,并融入缺失的视觉细节,从而提高目标对象的识别准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在多个基准测试上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉定位任务旨在根据给定的文本描述定位图像中的目标对象。
- 现有方法主要依赖单一文本输入,无法充分利用视觉域中的丰富信息。
- 论文提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,通过结合多种潜在表达和视觉细节来解决视觉与文本信息的不匹配问题。
- 引入主体分布器和视觉概念注入器模块,将共享主体和独特属性概念嵌入到潜在表示中,从而捕捉独特的目标特定视觉线索。
- 提出了一种正向边距对比学习策略,将所有潜在表达与原始文本对齐,同时保留细微变化。
- 论文的方法在多个基准测试上表现出优异的性能,特别是在广义引用表达式分割(GRES)基准测试上。
点此查看论文截图

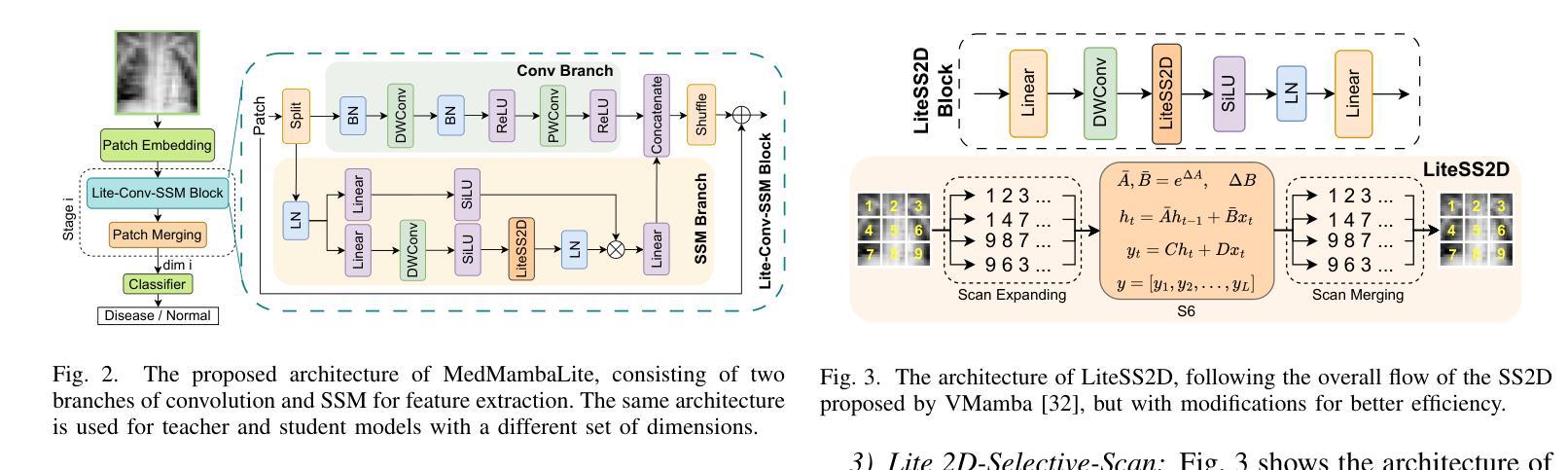
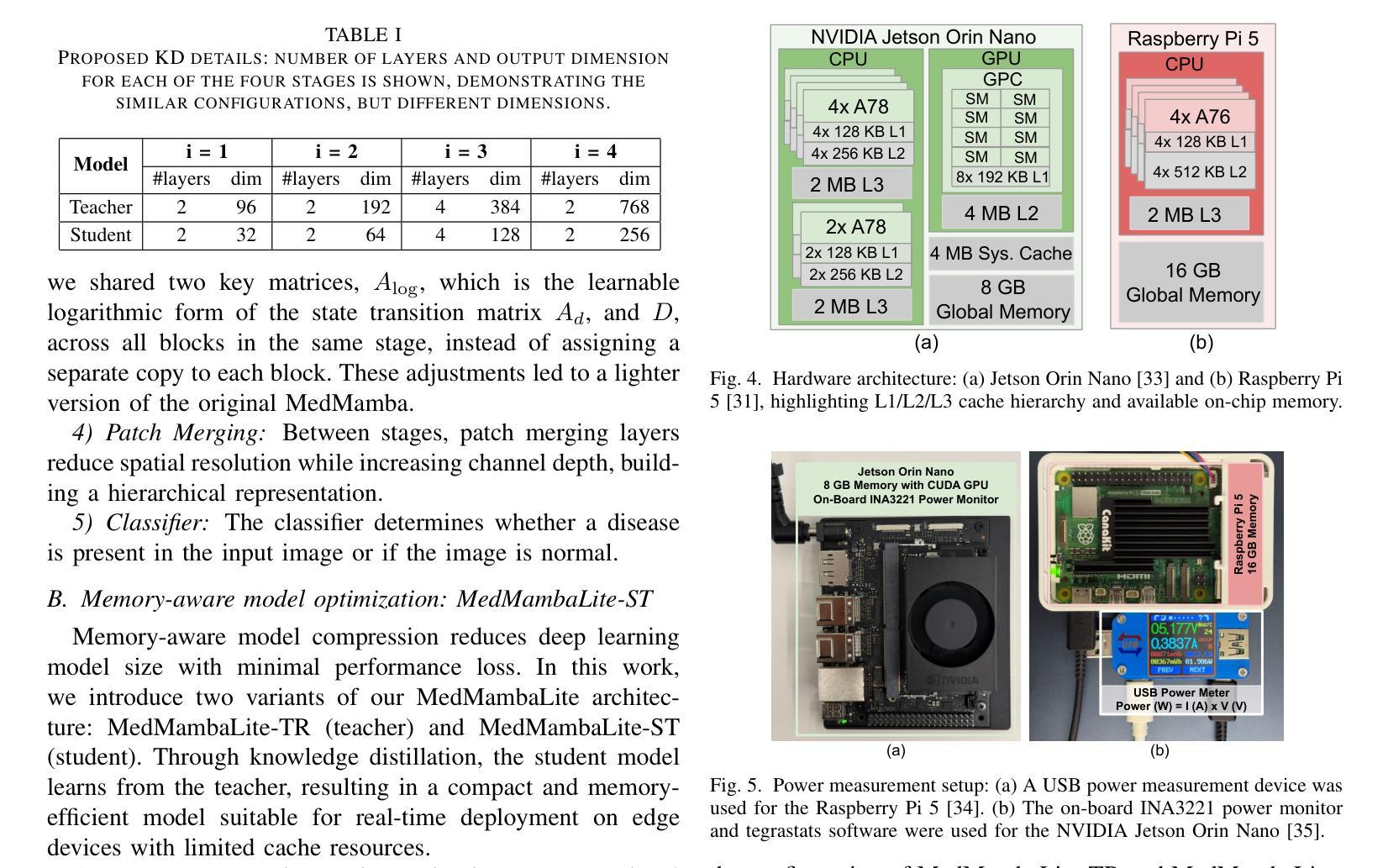
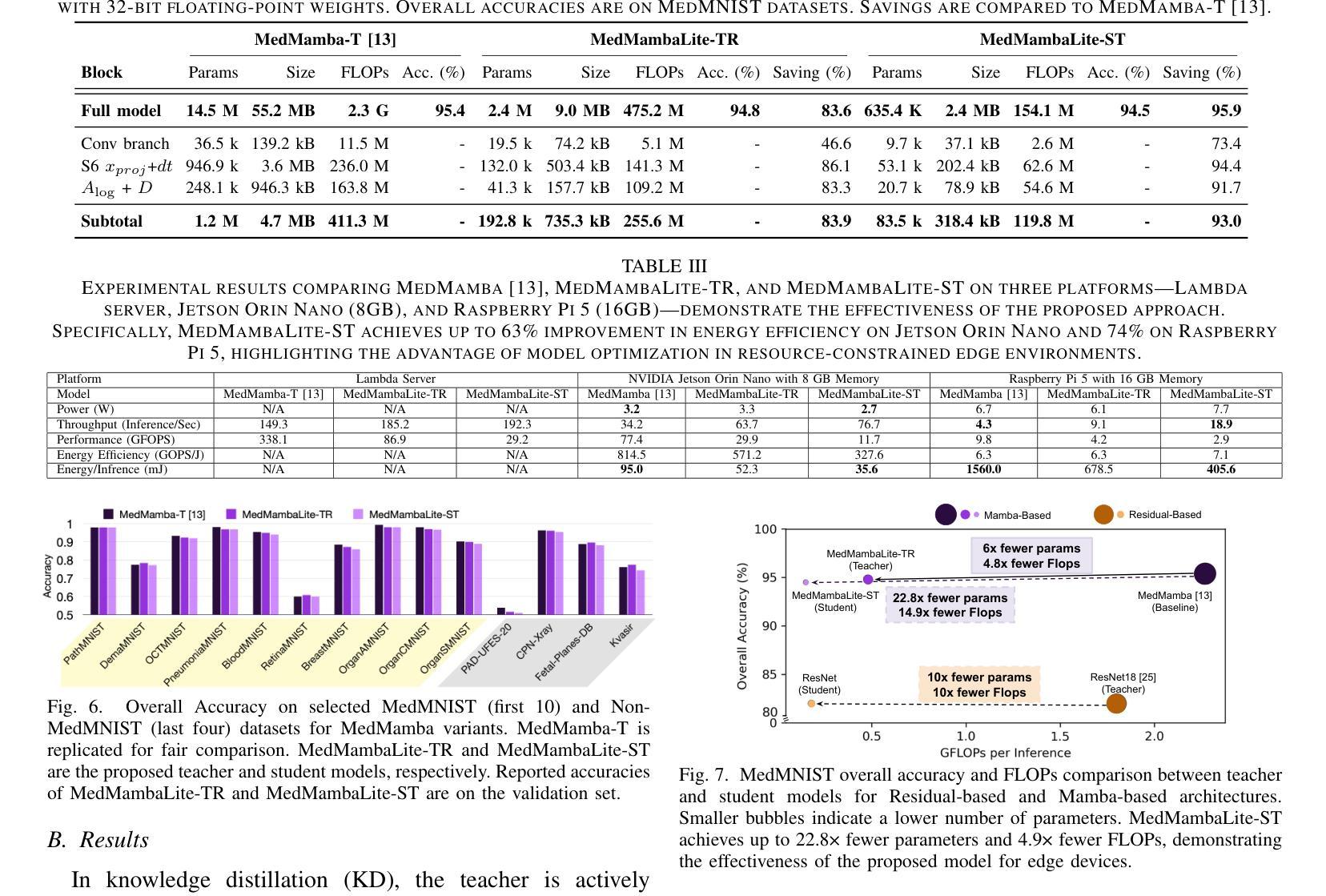
MedMambaLite: Hardware-Aware Mamba for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Romina Aalishah, Mozhgan Navardi, Tinoosh Mohsenin
AI-powered medical devices have driven the need for real-time, on-device inference such as biomedical image classification. Deployment of deep learning models at the edge is now used for applications such as anomaly detection and classification in medical images. However, achieving this level of performance on edge devices remains challenging due to limitations in model size and computational capacity. To address this, we present MedMambaLite, a hardware-aware Mamba-based model optimized through knowledge distillation for medical image classification. We start with a powerful MedMamba model, integrating a Mamba structure for efficient feature extraction in medical imaging. We make the model lighter and faster in training and inference by modifying and reducing the redundancies in the architecture. We then distill its knowledge into a smaller student model by reducing the embedding dimensions. The optimized model achieves 94.5% overall accuracy on 10 MedMNIST datasets. It also reduces parameters 22.8x compared to MedMamba. Deployment on an NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano achieves 35.6 GOPS/J energy per inference. This outperforms MedMamba by 63% improvement in energy per inference.
AI驱动的医疗器械推动了实时设备端推断的需求,例如生物医学图像分类。边缘部署深度学习模型现在被用于医学图像中的异常检测和分类等应用。然而,由于模型大小和计算能力的限制,在边缘设备上实现这一级别的性能仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了MedMambaLite,这是一个基于硬件感知的Mamba模型,通过知识蒸馏针对医学图像分类进行了优化。我们从功能强大的MedMamba模型开始,集成了Mamba结构,实现医学成像中的高效特征提取。我们通过修改并减少架构中的冗余部分,使模型在训练和推断上更轻便、更快。然后,我们通过减小嵌入维度将其知识蒸馏到一个较小的学生模型中。优化后的模型在10个MedMNIST数据集上达到了94.5%的总体准确率,同时与MedMamba相比减少了参数高达22.8倍。在NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano上的部署可实现每推断能耗为35.6 GOPS/J。这在每推断能耗方面比MedMamba提高了63%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21st IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) 2025
Summary
基于人工智能的医疗设备需要实时在设备上进行分析推断,如生物医学图像分类。边缘设备上部署深度学习模型用于医学图像中的异常检测和分类等应用。然而,由于模型大小和计算能力的限制,实现这一性能在边缘设备上仍具有挑战性。为解决此问题,我们提出了MedMambaLite模型,它是基于Mamba结构进行优化的硬件感知模型,用于医学图像分类。通过知识蒸馏技术,我们从强大的MedMamba模型出发,集成Mamba结构以高效提取医学图像特征。通过修改和减少架构中的冗余部分,使模型在训练和推断上更加轻便和快速。然后将知识蒸馏到较小的学生模型中,减少嵌入维度。优化后的模型在10个MedMNIST数据集上达到了94.5%的总体准确率,并且参数减少了22.8倍。在NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano上进行部署时,每次推理的能量达到35.6 GOPS/J,相较于MedMamba模型在能量使用效率上提高了63%。
Key Takeaways
- AI驱动的医疗设备需要实时在设备上进行分析推断,如生物医学图像分类。
- 在边缘设备上部署深度学习模型面临模型大小和计算能力的挑战。
- MedMambaLite模型是基于Mamba结构优化的硬件感知模型,用于医学图像分类。
- 通过知识蒸馏技术,优化后的模型实现了高效的特征提取和推理速度。
- 优化后的模型在MedMNIST数据集上达到了94.5%的总体准确率,参数大大减少。
- MedMambaLite模型在NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano上的部署实现了较高的能量使用效率。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodal Causal-Driven Representation Learning for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
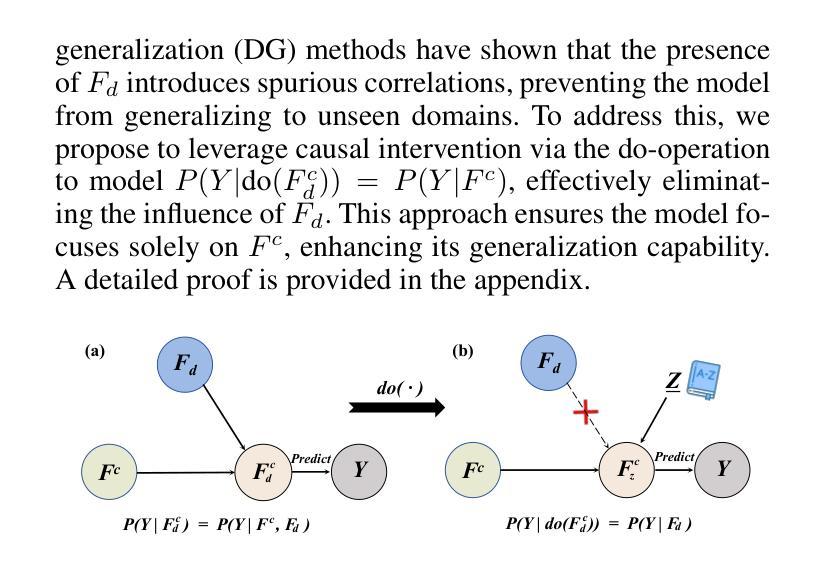
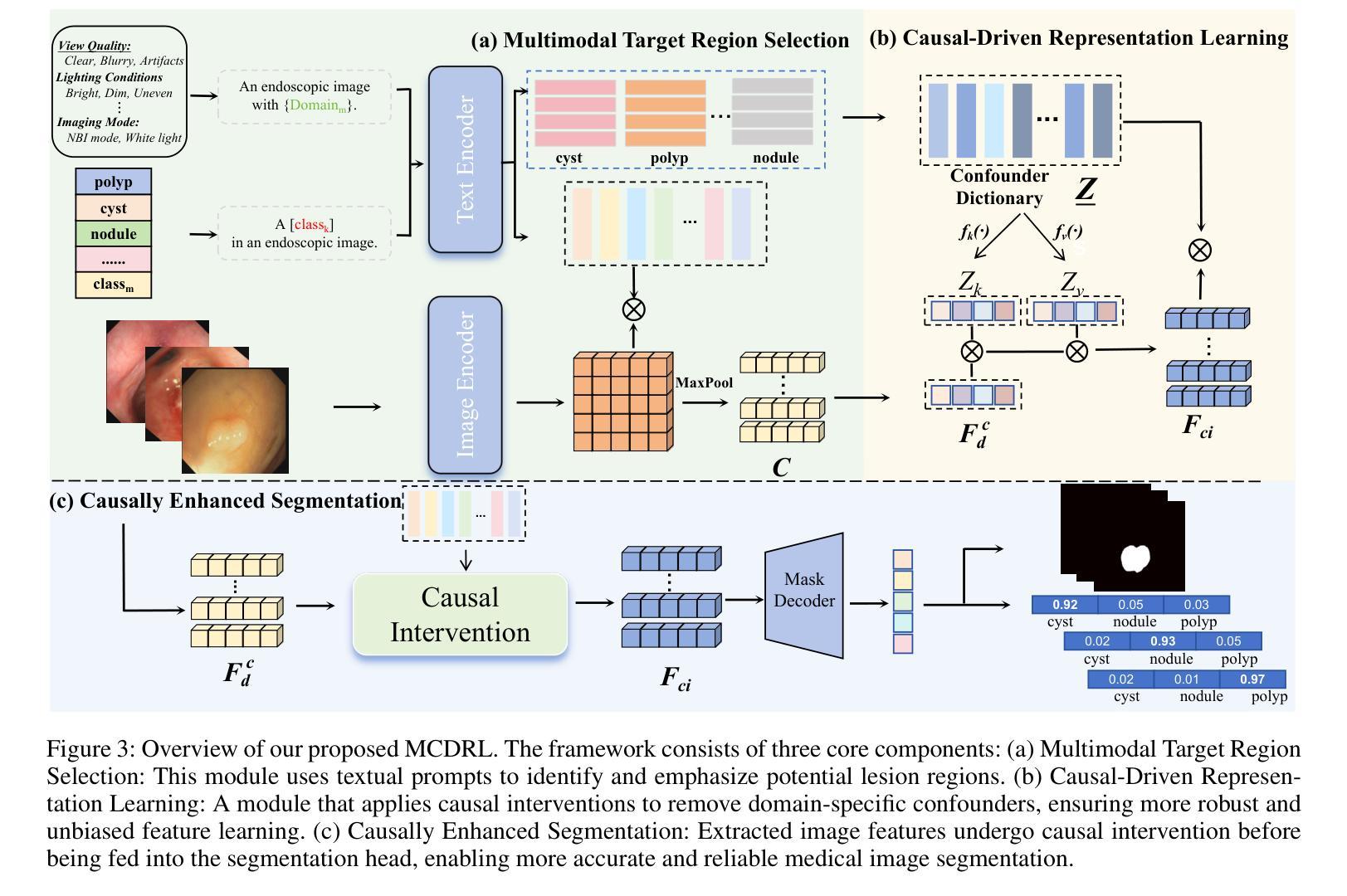
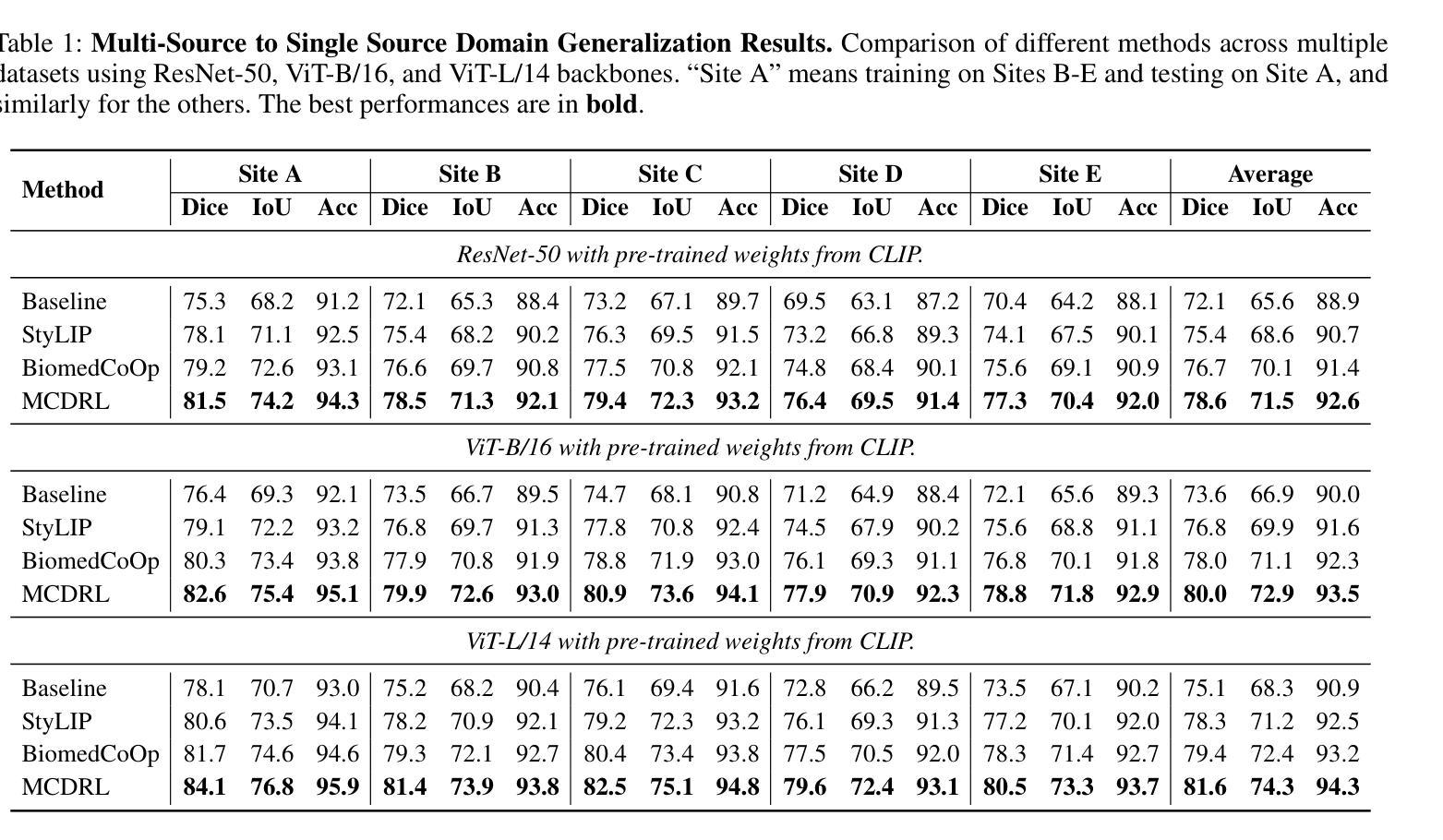
Authors:Xusheng Liang, Lihua Zhou, Nianxin Li, Miao Xu, Ziyang Song, Dong Yi, Jinlin Wu, Hongbin Liu, Jiebo Luo, Zhen Lei
Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot capabilities in various computer vision tasks. However, their application to medical imaging remains challenging due to the high variability and complexity of medical data. Specifically, medical images often exhibit significant domain shifts caused by various confounders, including equipment differences, procedure artifacts, and imaging modes, which can lead to poor generalization when models are applied to unseen domains. To address this limitation, we propose Multimodal Causal-Driven Representation Learning (MCDRL), a novel framework that integrates causal inference with the VLM to tackle domain generalization in medical image segmentation. MCDRL is implemented in two steps: first, it leverages CLIP’s cross-modal capabilities to identify candidate lesion regions and construct a confounder dictionary through text prompts, specifically designed to represent domain-specific variations; second, it trains a causal intervention network that utilizes this dictionary to identify and eliminate the influence of these domain-specific variations while preserving the anatomical structural information critical for segmentation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MCDRL consistently outperforms competing methods, yielding superior segmentation accuracy and exhibiting robust generalizability.
视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,在各种计算机视觉任务中表现出了出色的零样本能力。然而,由于其应用于医学成像时面临的高可变性和复杂性,其应用仍然具有挑战性。具体来说,医学图像通常会出现由各种混杂因素引起的显著领域偏移,包括设备差异、程序伪影和成像模式,当模型应用于未见领域时,可能导致较差的泛化性能。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了多模态因果驱动表示学习(MCDRL)这一新型框架,它将因果推理与VLM相结合,解决医学图像分割中的领域泛化问题。MCDRL分两步实现:首先,它利用CLIP的跨模态能力来识别候选病变区域,并通过文本提示构建混杂因素词典,这些文本提示专门用于表示领域特定的变化;其次,它训练一个因果干预网络,利用这个词典来识别和消除这些领域特定变化的影响,同时保留对分割任务至关重要的解剖结构信息。大量实验表明,MCDRL始终优于其他方法,具有更高的分割精度和稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
医学视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在计算机视觉任务中展现出强大的零样本能力,但在医学成像应用上仍面临挑战。针对医学图像领域的高变性和复杂性,提出多模态因果驱动表示学习(MCDRL)框架,结合因果推理与VLM解决医学图像分割中的领域泛化问题。MCDRL通过CLIP的跨模态能力识别候选病变区域,构建代表领域特定变化的干扰字典,并训练因果干预网络利用该字典消除领域特定变化的影响,同时保留对分割任务至关重要的解剖结构信息。实验证明MCDRL在分割准确性和泛化性方面均表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在计算机视觉任务中表现出强大的零样本能力,但在医学成像应用上仍面临高变性和复杂性的挑战。
- MCDRL框架结合因果推理与VLM解决医学图像分割中的领域泛化问题。
- MCDRL通过CLIP的跨模态能力识别候选病变区域并构建干扰字典,以代表领域特定的变化。
- MCDRL利用构建的干扰字典训练因果干预网络,以消除领域特定变化的影响。
- MCDRL在分割准确性方面表现出优越性能,包括在未见领域的泛化能力。
- MCDRL能够同时保留对分割任务至关重要的解剖结构信息。
点此查看论文截图

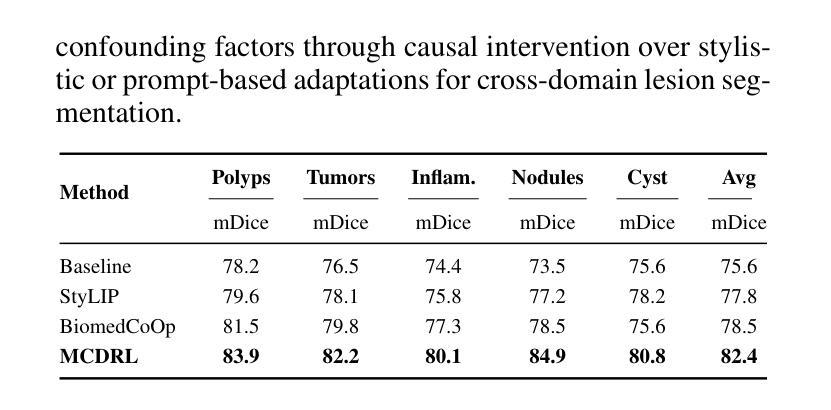
Policy to Assist Iteratively Local Segmentation: Optimising Modality and Location Selection for Prostate Cancer Localisation
Authors:Xiangcen Wu, Shaheer U. Saeed, Yipei Wang, Ester Bonmati Coll, Yipeng Hu
Radiologists often mix medical image reading strategies, including inspection of individual modalities and local image regions, using information at different locations from different images independently as well as concurrently. In this paper, we propose a recommend system to assist machine learning-based segmentation models, by suggesting appropriate image portions along with the best modality, such that prostate cancer segmentation performance can be maximised. Our approach trains a policy network that assists tumor localisation, by recommending both the optimal imaging modality and the specific sections of interest for review. During training, a pre-trained segmentation network mimics radiologist inspection on individual or variable combinations of these imaging modalities and their sections - selected by the policy network. Taking the locally segmented regions as an input for the next step, this dynamic decision making process iterates until all cancers are best localised. We validate our method using a data set of 1325 labelled multiparametric MRI images from prostate cancer patients, demonstrating its potential to improve annotation efficiency and segmentation accuracy, especially when challenging pathology is present. Experimental results show that our approach can surpass standard segmentation networks. Perhaps more interestingly, our trained agent independently developed its own optimal strategy, which may or may not be consistent with current radiologist guidelines such as PI-RADS. This observation also suggests a promising interactive application, in which the proposed policy networks assist human radiologists.
放射科医生在医学图像阅读策略上通常会混合使用多种方法,包括检查各种单一模态和局部图像区域,独立地同时使用不同位置的不同图像的信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种推荐系统,以协助基于机器学习的分割模型,通过建议适当的图像部分以及最佳模态,最大限度地提高前列腺癌分割的性能。我们的方法训练了一个策略网络,通过推荐最佳的成像模态和特定审查的感兴趣部分,来协助肿瘤定位。在训练过程中,预训练的分割网络模仿放射科医生对单一或这些成像模态及其部分的组合的检查,这些部分由策略网络选择。以局部分割区域作为下一步的输入,这种动态决策过程会不断迭代,直到所有癌症的最佳定位。我们使用包含来自前列腺癌患者的1325个标记的多参数MRI图像数据集验证了我们的方法,证明了其在提高注释效率和分割精度方面的潜力,特别是在存在挑战性病理的情况下。实验结果表明,我们的方法可以超越标准分割网络。更有趣的是,我们的训练代理独立地开发了自己的最佳策略,这可能一致也可能与当前的放射科医生指南(如PI-RADS)不一致。这一观察结果也表明了一个有前景的交互应用,即所提出的策略网络可以辅助人类放射科医生。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种推荐系统,辅助机器学习分割模型进行前列腺癌分割,通过推荐适当的图像部分及最佳模态来最大化分割性能。该系统训练一个策略网络,辅助肿瘤定位,并推荐最佳的成像模态和特定感兴趣区域进行审查。通过模拟放射科医生对各种成像模态及其区域的检查来选择策略网络推荐的局部分割区域进行训练。此方法可提高标注效率和分割精度,特别是在存在挑战性病理的情况下。实验结果表明,该方法可超越标准分割网络性能,并且独立发展出可能与当前放射科医生指南一致或不一致的最优策略,展现出良好的交互式应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新的推荐系统,旨在辅助机器学习模型在医疗图像分析中的性能,特别是在前列腺癌的分割上。
- 该系统通过训练一个策略网络来推荐最佳的成像模态和图像区域,帮助定位肿瘤。
- 策略网络是在模拟放射科医生对成像模态及其区域的检查过程中进行训练的。
- 该方法能提高标注效率和分割精度,特别是在面对具有挑战性的病理情况时。
- 实验结果显示,该方法的性能超越了标准的分割网络。
- 训练出的策略网络能够独立发展出最优策略,这些策略可能与现有的放射科医生指南一致或不一致。
点此查看论文截图


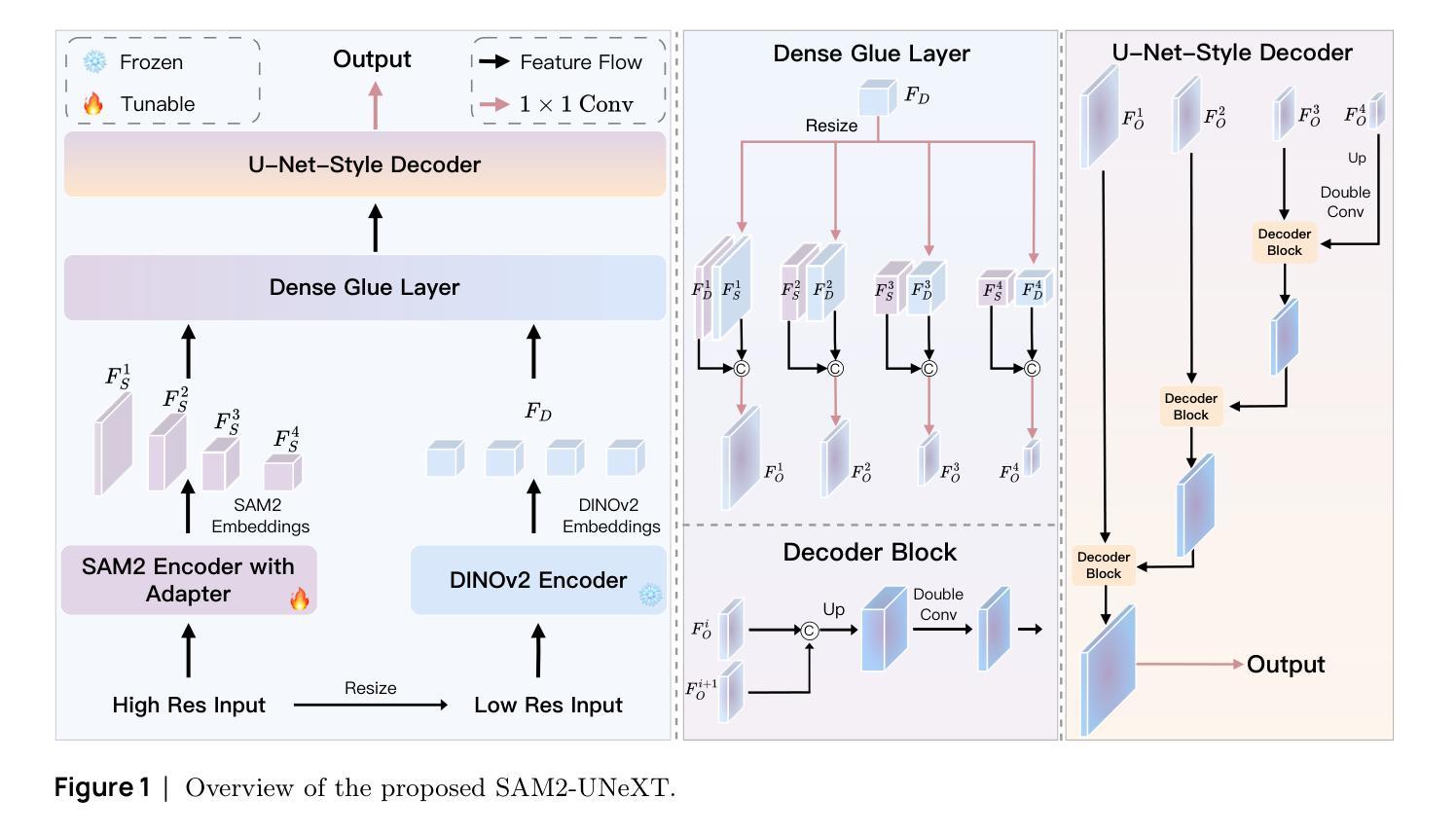
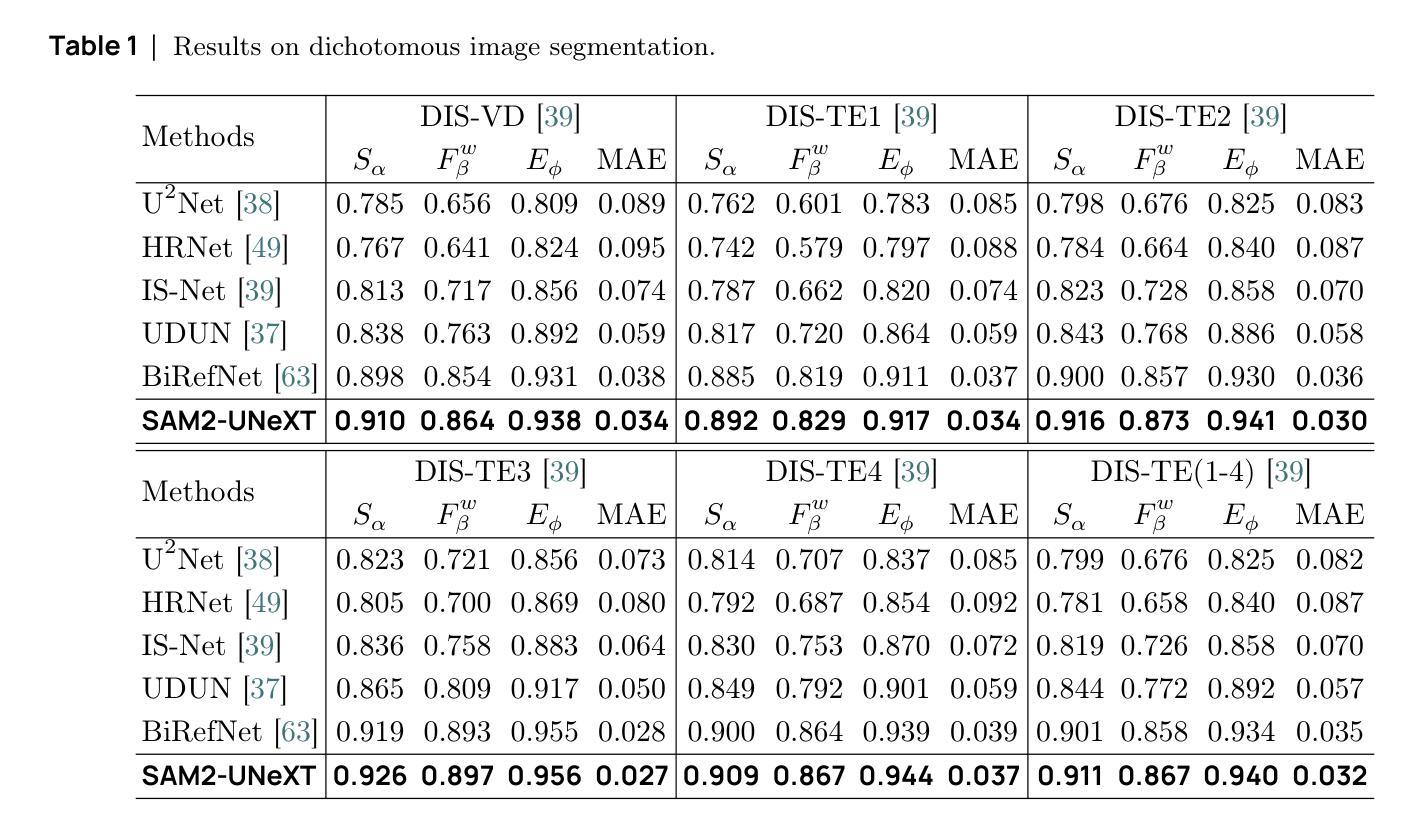
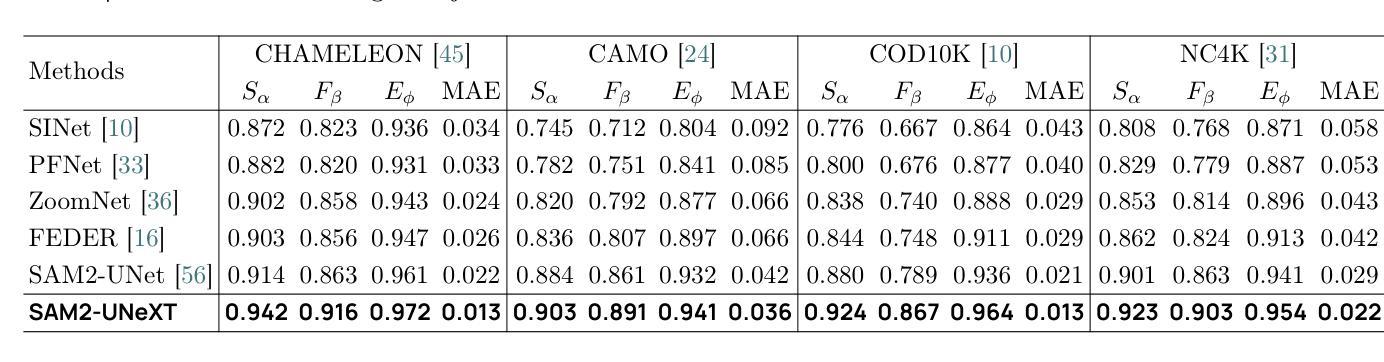
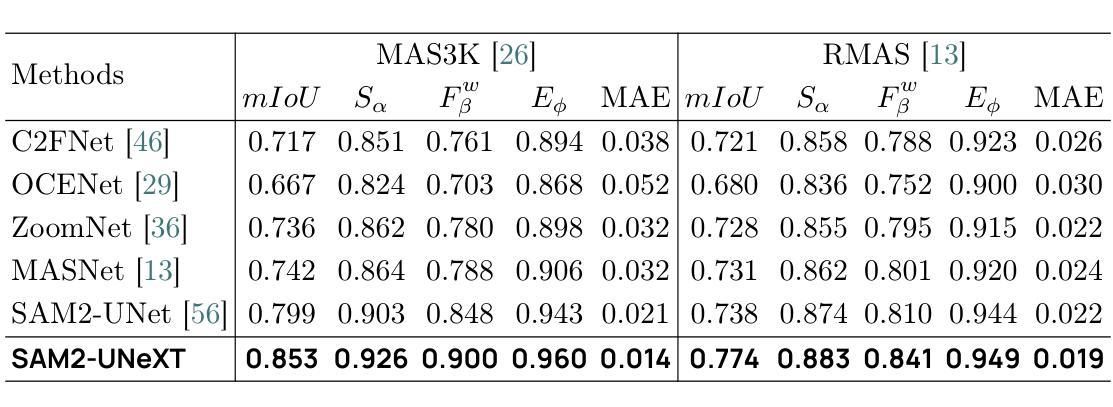
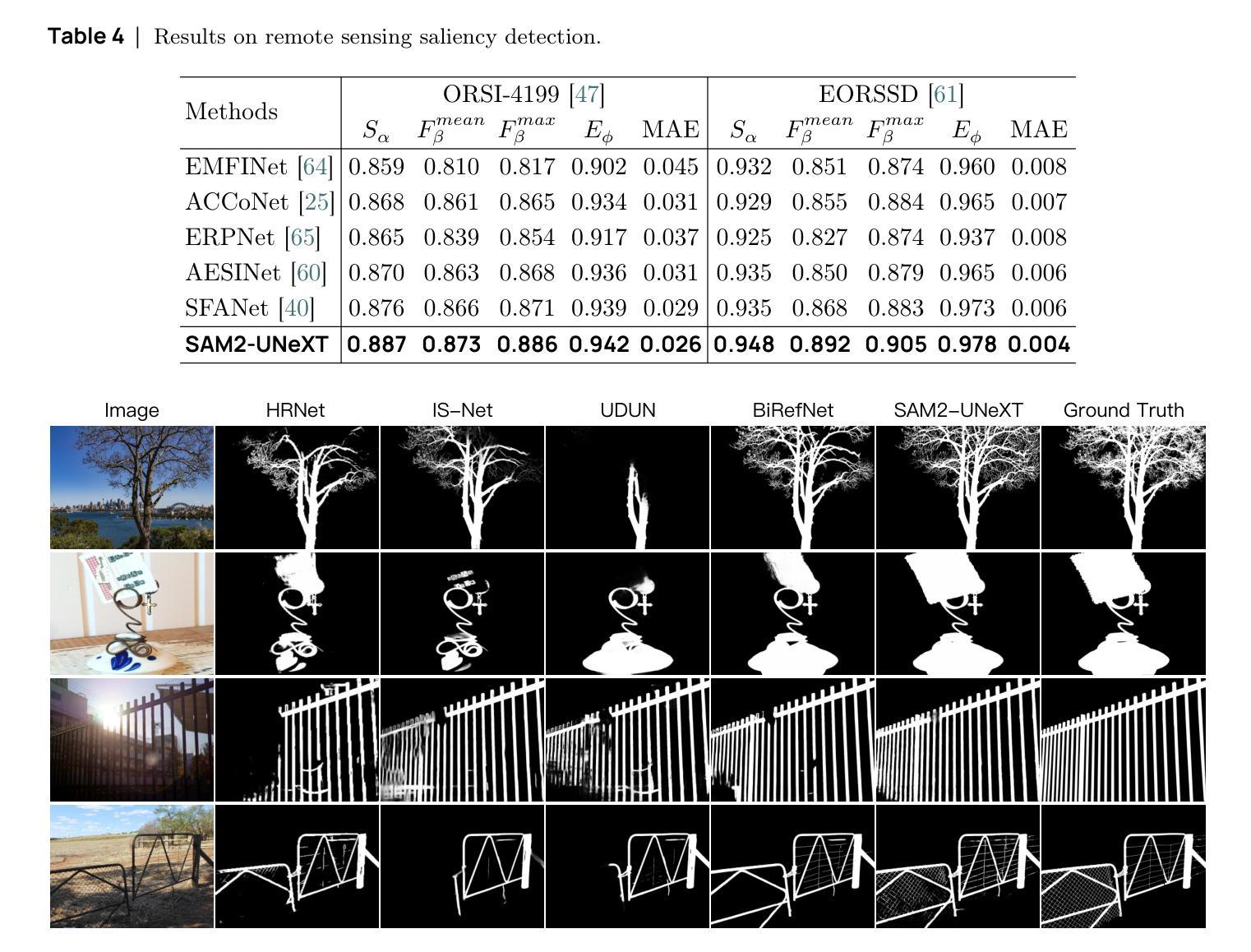
SAM2-UNeXT: An Improved High-Resolution Baseline for Adapting Foundation Models to Downstream Segmentation Tasks
Authors:Xinyu Xiong, Zihuang Wu, Lei Zhang, Lei Lu, Ming Li, Guanbin Li
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of adapting the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for various downstream tasks. However, constructing a more powerful and generalizable encoder to further enhance performance remains an open challenge. In this work, we propose SAM2-UNeXT, an advanced framework that builds upon the core principles of SAM2-UNet while extending the representational capacity of SAM2 through the integration of an auxiliary DINOv2 encoder. By incorporating a dual-resolution strategy and a dense glue layer, our approach enables more accurate segmentation with a simple architecture, relaxing the need for complex decoder designs. Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmarks, including dichotomous image segmentation, camouflaged object detection, marine animal segmentation, and remote sensing saliency detection, demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method. The code is available at https://github.com/WZH0120/SAM2-UNeXT.
最近的研究已经强调了适应Segment Anything Model(SAM)对各种下游任务的潜力。然而,构建一个更强大、更具通用性的编码器,以进一步提高性能,仍然是一个开放性的挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了SAM2-UNeXT,这是一个先进的框架,它基于SAM2-UNet的核心原则,并通过集成辅助DINOv2编码器扩展了SAM2的代表性容量。通过采用双分辨率策略和密集粘合层,我们的方法能够在简单的架构上实现更精确的分割,减轻了复杂解码器设计的必要性。在四项基准测试上的广泛实验包括二值图像分割、伪装目标检测、海洋动物分割和遥感显著性检测,证明了我们提出的方法的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/WZH0 0 /SAM2-UNeXT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
SAM2-UNeXT框架的提出,基于SAM的核心原理,结合了SAM2-UNet的优势,并通过引入辅助的DINOv2编码器扩展了代表容量。利用双分辨率策略和稠密粘着层,我们能够实现更精确的分割,简化了架构,减少了复杂解码器设计的需要。在四个基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- SAM2-UNeXT是基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)构建的先进框架。
- 通过引入DINOv2编码器扩展了代表容量。
- 采用双分辨率策略以提高分割准确性。
- 利用稠密粘着层简化架构,降低复杂解码器设计的需求。
- 在四个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,包括二值图像分割、隐蔽目标检测、海洋动物分割和遥感显著性检测。
点此查看论文截图
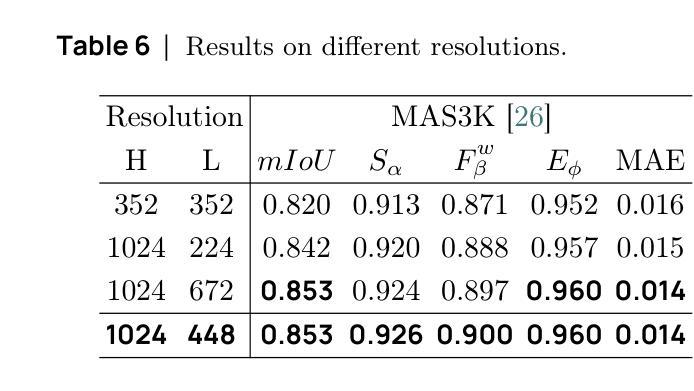
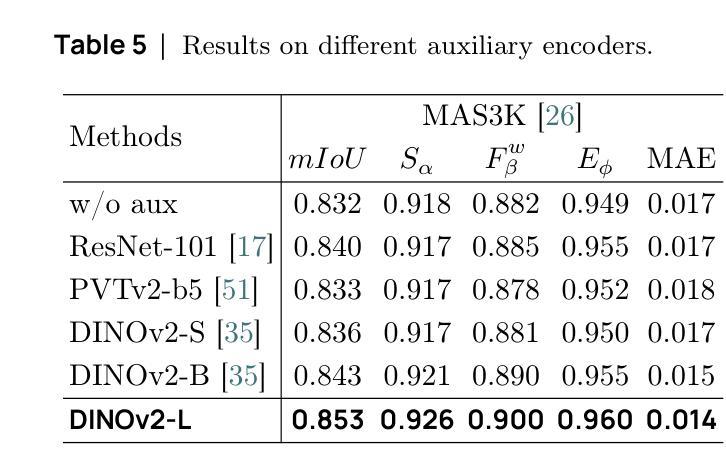
MAUP: Training-free Multi-center Adaptive Uncertainty-aware Prompting for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yazhou Zhu, Haofeng Zhang
Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation (CD-FSMIS) is a potential solution for segmenting medical images with limited annotation using knowledge from other domains. The significant performance of current CD-FSMIS models relies on the heavily training procedure over other source medical domains, which degrades the universality and ease of model deployment. With the development of large visual models of natural images, we propose a training-free CD-FSMIS model that introduces the Multi-center Adaptive Uncertainty-aware Prompting (MAUP) strategy for adapting the foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), which is trained with natural images, into the CD-FSMIS task. To be specific, MAUP consists of three key innovations: (1) K-means clustering based multi-center prompts generation for comprehensive spatial coverage, (2) uncertainty-aware prompts selection that focuses on the challenging regions, and (3) adaptive prompt optimization that can dynamically adjust according to the target region complexity. With the pre-trained DINOv2 feature encoder, MAUP achieves precise segmentation results across three medical datasets without any additional training compared with several conventional CD-FSMIS models and training-free FSMIS model. The source code is available at: https://github.com/YazhouZhu19/MAUP.
跨域小样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)是利用其他领域的知识对医学图像进行有限标注分割的一种潜在解决方案。当前CD-FSMIS模型的出色性能依赖于其他源医学领域的繁重训练过程,这降低了模型的通用性和部署的便捷性。随着自然图像大型视觉模型的发展,我们提出了一种无需训练的CD-FSMIS模型,该模型引入了多中心自适应不确定性感知提示(MAUP)策略,以适应基础模型——用自然图像训练的分割任何模型(SAM),用于CD-FSMIS任务。具体来说,MAUP包括三个关键创新点:(1)基于K-means聚类的多中心提示生成,实现全面的空间覆盖;(2)关注困难区域的不确定性感知提示选择;(3)可根据目标区域复杂性进行动态调整的自适应提示优化。与几个传统的CD-FSMIS模型和无需训练的FSMIS模型相比,使用预训练的DINOv2特征编码器,MAUP在三个医学数据集上实现了精确的分割结果。源代码可在:https://github.com/YazhouZhu19/MAUP获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了跨域小样医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)的问题,并提出了一种基于预训练的自然图像模型SAM的无需训练的新方法MAUP。该方法通过K-means聚类生成多中心提示、不确定性感知提示选择和自适应提示优化等技术,实现了对医疗图像的精准分割,无需额外训练即可在不同医疗数据集上取得良好效果。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSMIS模型利用其他领域的知识对医疗图像进行分割,但现有模型需要大量源医疗领域的训练数据,影响其通用性和部署的便捷性。
- 提出了一种基于预训练的自然图像模型SAM的无需训练的CD-FSMIS模型MAUP,解决了上述问题。
- MAUP策略包括三个关键创新点:基于K-means聚类的多中心提示生成、不确定性感知提示选择和自适应提示优化。
- 多中心提示生成实现了全面的空间覆盖;不确定性感知提示选择关注于挑战区域;自适应提示优化能根据目标区域的复杂性进行动态调整。
- MAUP利用预训练的DINOv2特征编码器,实现了在三个医疗数据集上的精准分割结果。
- 与传统的CD-FSMIS模型和无需训练的FSMIS模型相比,MAUP取得了更好的效果。
点此查看论文截图

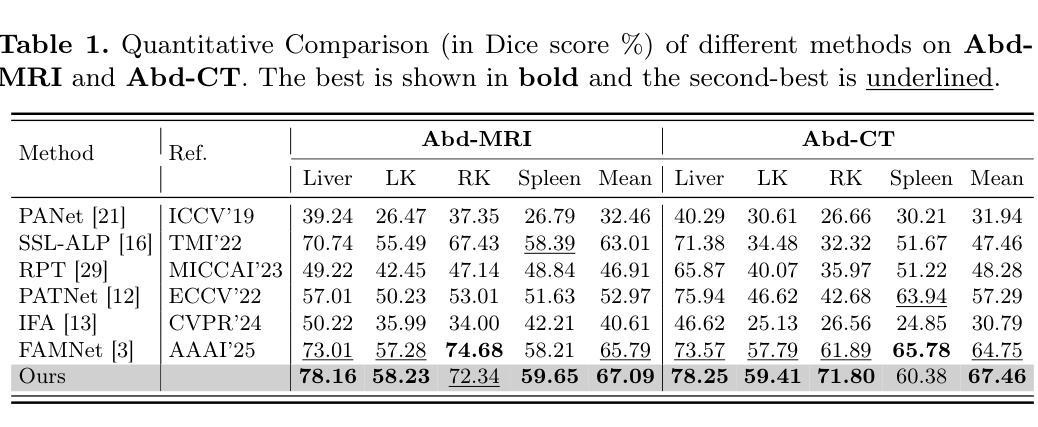
Prototype-Enhanced Confidence Modeling for Cross-Modal Medical Image-Report Retrieval
Authors:Shreyank N Gowda, Xiaobo Jin, Christian Wagner
In cross-modal retrieval tasks, such as image-to-report and report-to-image retrieval, accurately aligning medical images with relevant text reports is essential but challenging due to the inherent ambiguity and variability in medical data. Existing models often struggle to capture the nuanced, multi-level semantic relationships in radiology data, leading to unreliable retrieval results. To address these issues, we propose the Prototype-Enhanced Confidence Modeling (PECM) framework, which introduces multi-level prototypes for each modality to better capture semantic variability and enhance retrieval robustness. PECM employs a dual-stream confidence estimation that leverages prototype similarity distributions and an adaptive weighting mechanism to control the impact of high-uncertainty data on retrieval rankings. Applied to radiology image-report datasets, our method achieves significant improvements in retrieval precision and consistency, effectively handling data ambiguity and advancing reliability in complex clinical scenarios. We report results on multiple different datasets and tasks including fully supervised and zero-shot retrieval obtaining performance gains of up to 10.17%, establishing in new state-of-the-art.
在多模态检索任务(如图像到报告和报告到图像的检索)中,准确对齐医学图像与相关的文本报告是至关重要的,但由于医学数据固有的模糊性和变化性,这具有挑战性。现有模型往往难以捕捉放射数据中细微的多级语义关系,导致检索结果不可靠。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了原型增强信心建模(PECM)框架,它引入每个模态的多级原型,以更好地捕捉语义变化,提高检索的稳健性。PECM采用双流信心估计,利用原型相似性分布和自适应加权机制来控制高不确定性数据对检索排名的影响。我们的方法应用于放射学图像报告数据集,在检索精度和一致性方面取得了显著改进,有效地处理了数据模糊性,提高了复杂临床场景中的可靠性。我们在多个不同的数据集和任务上报告了结果,包括全监督和零射击检索,性能提升高达10.17%,创下了新的最先进的记录。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学跨模态检索任务中,准确对齐医学图像和相关文本报告至关重要但具有挑战性。为应对挑战,提出一种名为PECM(原型增强信心建模)的框架,引入多级别原型以捕获语义变化并增强检索稳健性。通过原型相似性分布和自适应加权机制进行双流信心估计,提高检索精度和一致性,有效处理数据模糊性,并在复杂临床场景中提高可靠性。在放射学图像报告数据集上应用,取得了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学跨模态检索任务面临准确对齐医学图像和文本报告的挑战。
- 现有模型难以捕获放射学数据中的多级别语义关系。
- PECM框架引入多级别原型以更好地捕获语义变化和增强检索稳健性。
- PECM采用双流信心估计,利用原型相似性分布和自适应加权机制。
- PECM提高了检索精度和一致性,有效处理数据模糊性。
- 在复杂临床场景中,PECM提高了可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

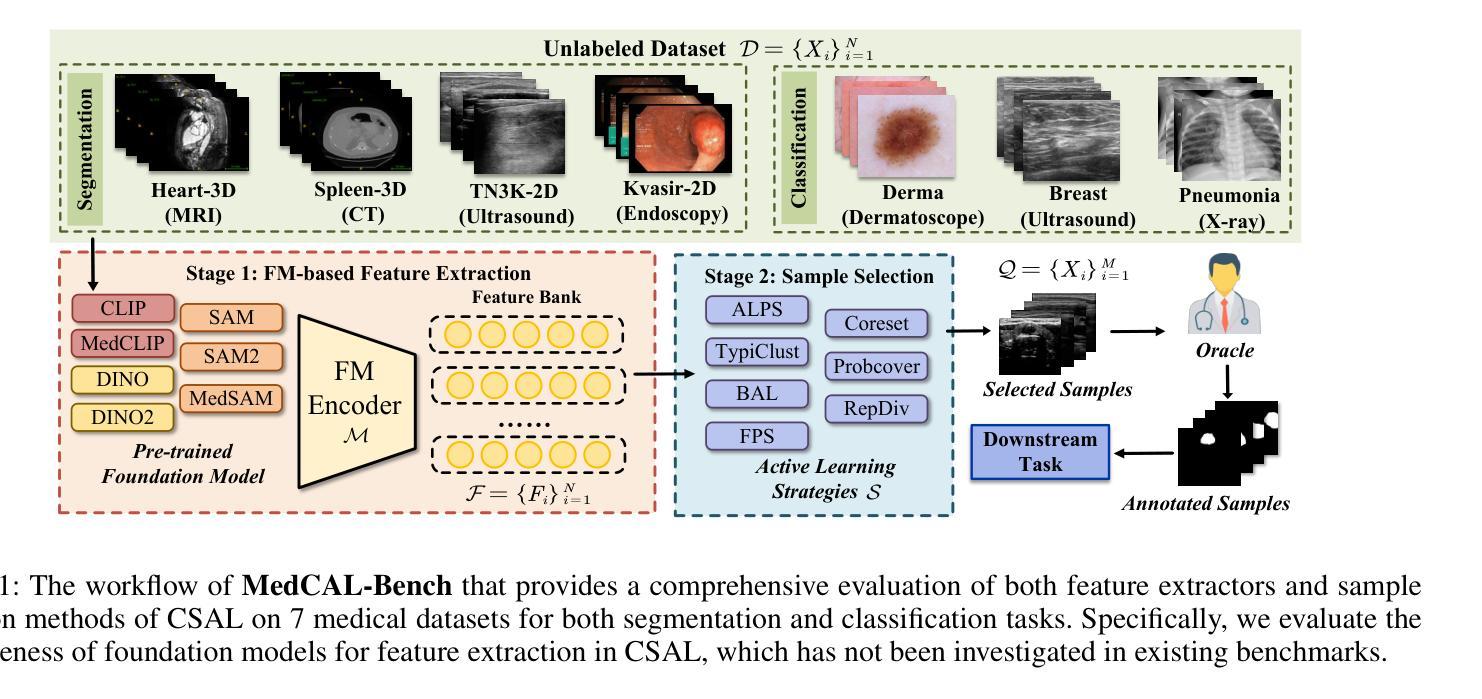
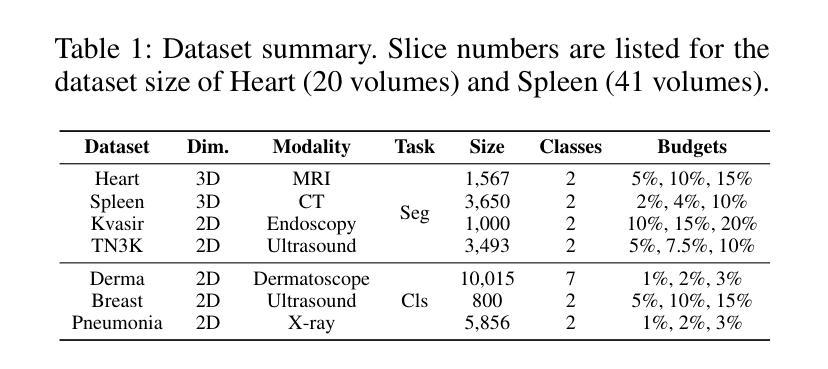
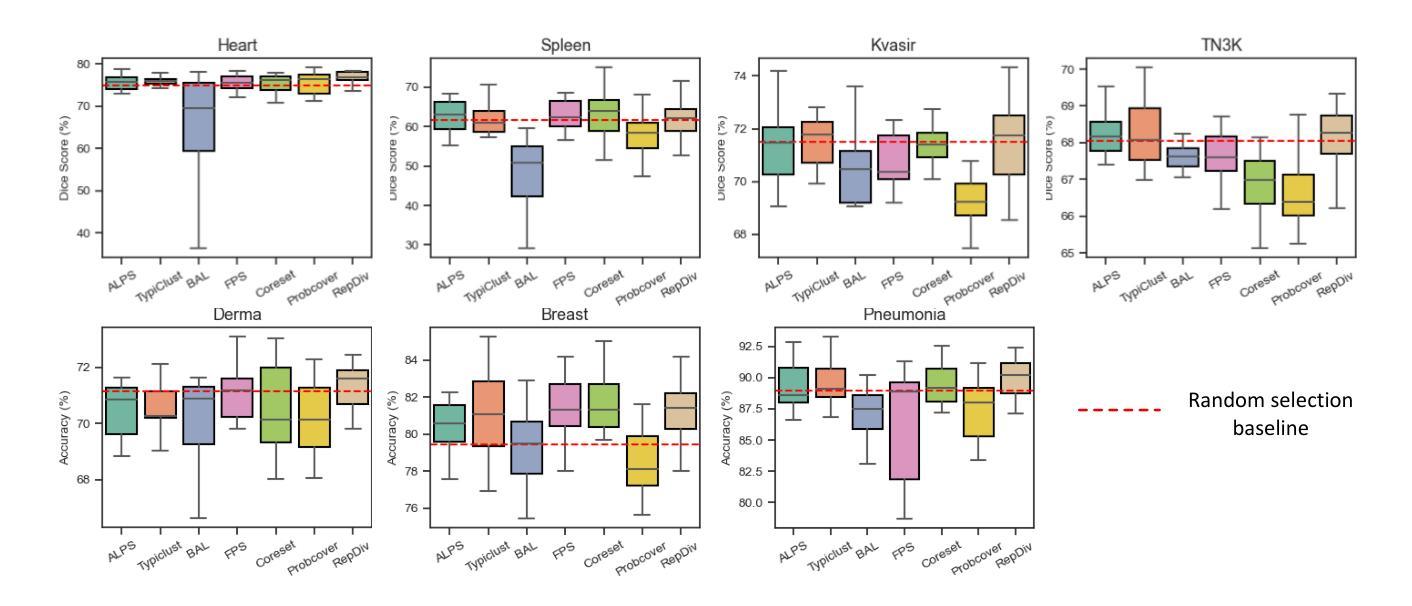
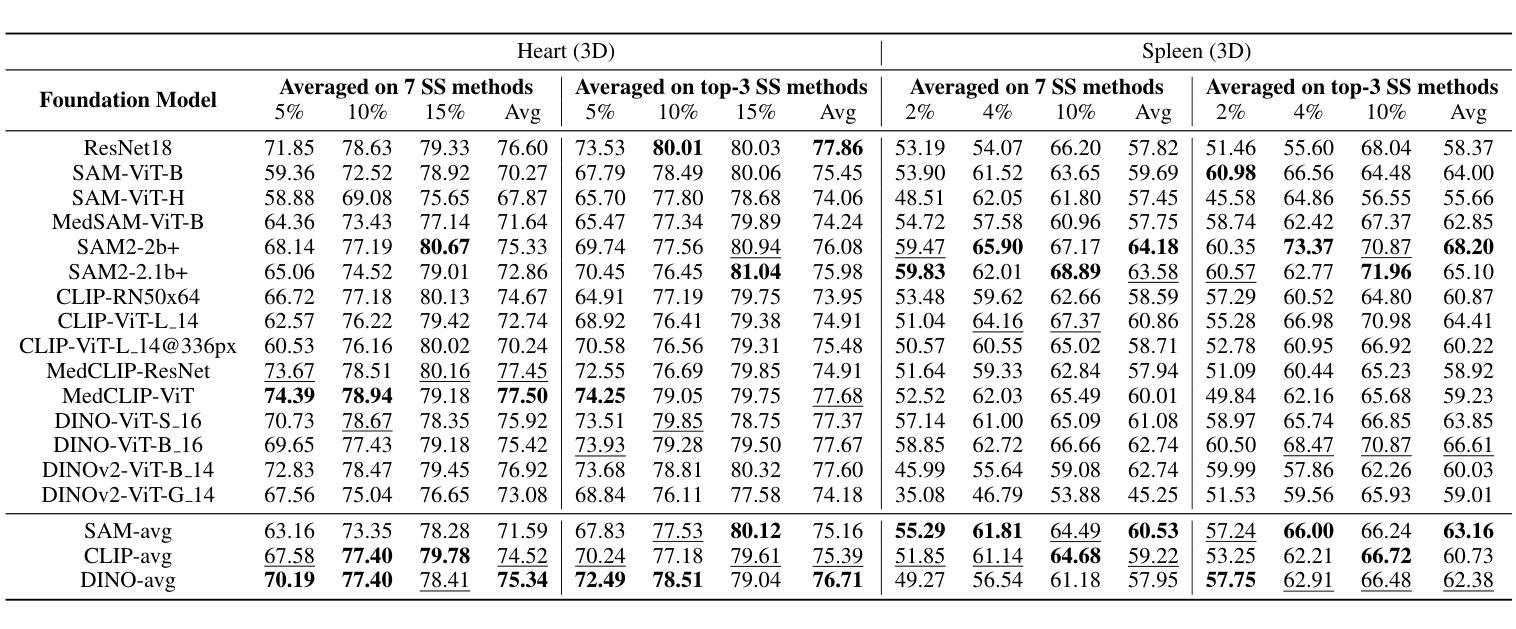
MedCAL-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark on Cold-Start Active Learning with Foundation Models for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Ning Zhu, Xiaochuan Ma, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
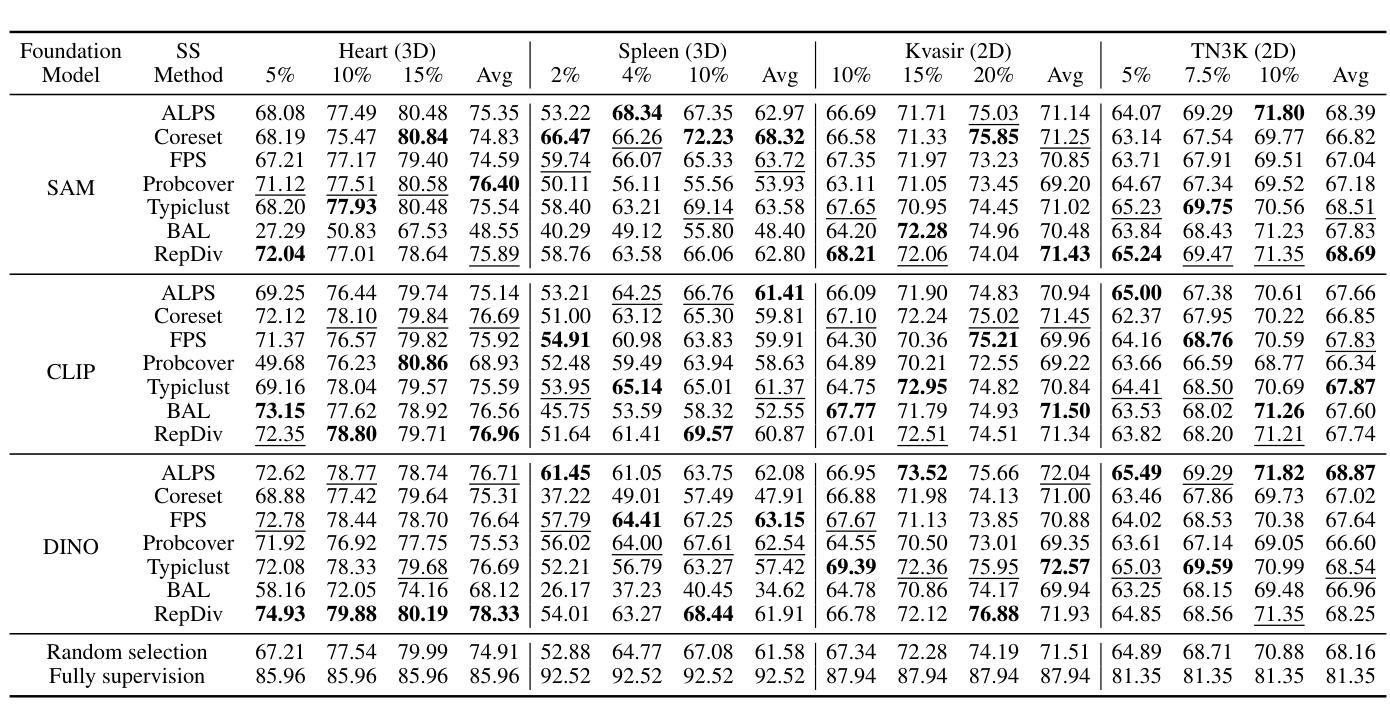
Cold-Start Active Learning (CSAL) aims to select informative samples for annotation without prior knowledge, which is important for improving annotation efficiency and model performance under a limited annotation budget in medical image analysis. Most existing CSAL methods rely on Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) on the target dataset for feature extraction, which is inefficient and limited by insufficient feature representation. Recently, pre-trained Foundation Models (FMs) have shown powerful feature extraction ability with a potential for better CSAL. However, this paradigm has been rarely investigated, with a lack of benchmarks for comparison of FMs in CSAL tasks. To this end, we propose MedCAL-Bench, the first systematic FM-based CSAL benchmark for medical image analysis. We evaluate 14 FMs and 7 CSAL strategies across 7 datasets under different annotation budgets, covering classification and segmentation tasks from diverse medical modalities. It is also the first CSAL benchmark that evaluates both the feature extraction and sample selection stages. Our experimental results reveal that: 1) Most FMs are effective feature extractors for CSAL, with DINO family performing the best in segmentation; 2) The performance differences of these FMs are large in segmentation tasks, while small for classification; 3) Different sample selection strategies should be considered in CSAL on different datasets, with Active Learning by Processing Surprisal (ALPS) performing the best in segmentation while RepDiv leading for classification. The code is available at https://github.com/HiLab-git/MedCAL-Bench.
冷启动主动学习(CSAL)旨在在没有先验知识的情况下选择信息样本进行标注,这对于在医疗图像分析中使用有限的标注预算提高标注效率和模型性能至关重要。大多数现有的CSAL方法依赖于目标数据集上的自监督学习(SSL)进行特征提取,这是低效的,并且受到特征表示不足的限制。最近,预训练的Foundation Models(FMs)显示出强大的特征提取能力,具有更好的CSAL潜力。然而,这一范式很少受到研究,缺乏用于比较FMs在CSAL任务中的基准测试。为此,我们提出了MedCAL-Bench,这是基于FMs的医疗图像分析的首个系统性CSAL基准测试。我们在7个数据集上评估了14个FMs和7种CSAL策略,涉及不同标注预算下的分类和分割任务,涵盖多种医学模态。它也是第一个同时评估特征提取和样本选择阶段的CSAL基准测试。我们的实验结果揭示:1)大多数FMs对于CSAL都是有效的特征提取器,DINO系列在分割方面表现最佳;2)这些FMs在分割任务中的性能差异很大,而在分类任务中则较小;3)CSAL中的不同样本选择策略应针对不同的数据集进行考虑,处理惊喜(ALPS)在分割方面表现最佳,而RepDiv在分类方面领先。代码可在https://github.com/HiLab-git/MedCAL-Bench获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 6 figures, 10 tables
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分析的冷启动主动学习方法(CSAL)的挑战和现状。为提高标注效率和模型性能,研究者提出了基于预训练基础模型(FMs)的CSAL新方法,并建立了首个系统性的FM-based CSAL基准测试平台MedCAL-Bench。实验结果显示,大多数基础模型在CSAL中能有效提取特征,不同数据集上的样本选择策略也有差异。
Key Takeaways
- 冷启动主动学习方法(CSAL)旨在在没有先验知识的情况下选择信息样本进行标注,以提高医学图像分析的标注效率和模型性能。
- 现有CSAL方法大多依赖目标数据集的自我监督学习(SSL)进行特征提取,但这种方法效率低下,且特征表示有限。
- 预训练基础模型(FMs)具有强大的特征提取能力,在CSAL中有潜在优势。
- MedCAL-Bench是首个基于FM的CSAL基准测试平台,用于医学图像分析。
- 实验结果显示,大多数基础模型在CSAL中能有效提取特征,DINO家族在分割任务中表现最佳。
- 分割任务中基础模型的性能差异较大,分类任务则较小。
点此查看论文截图


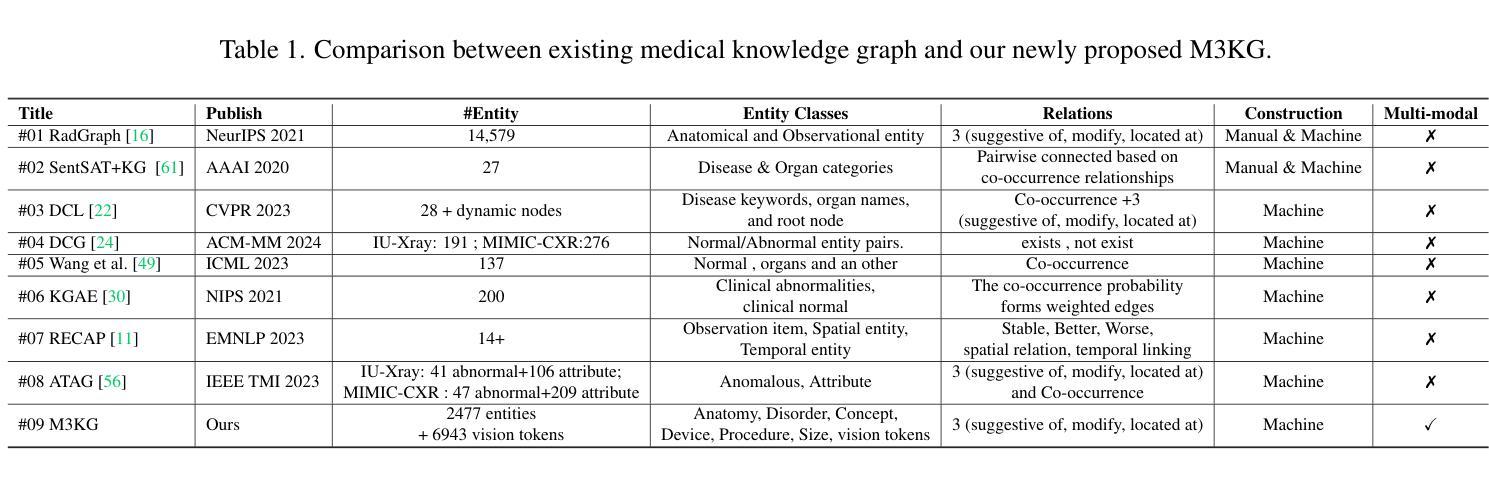
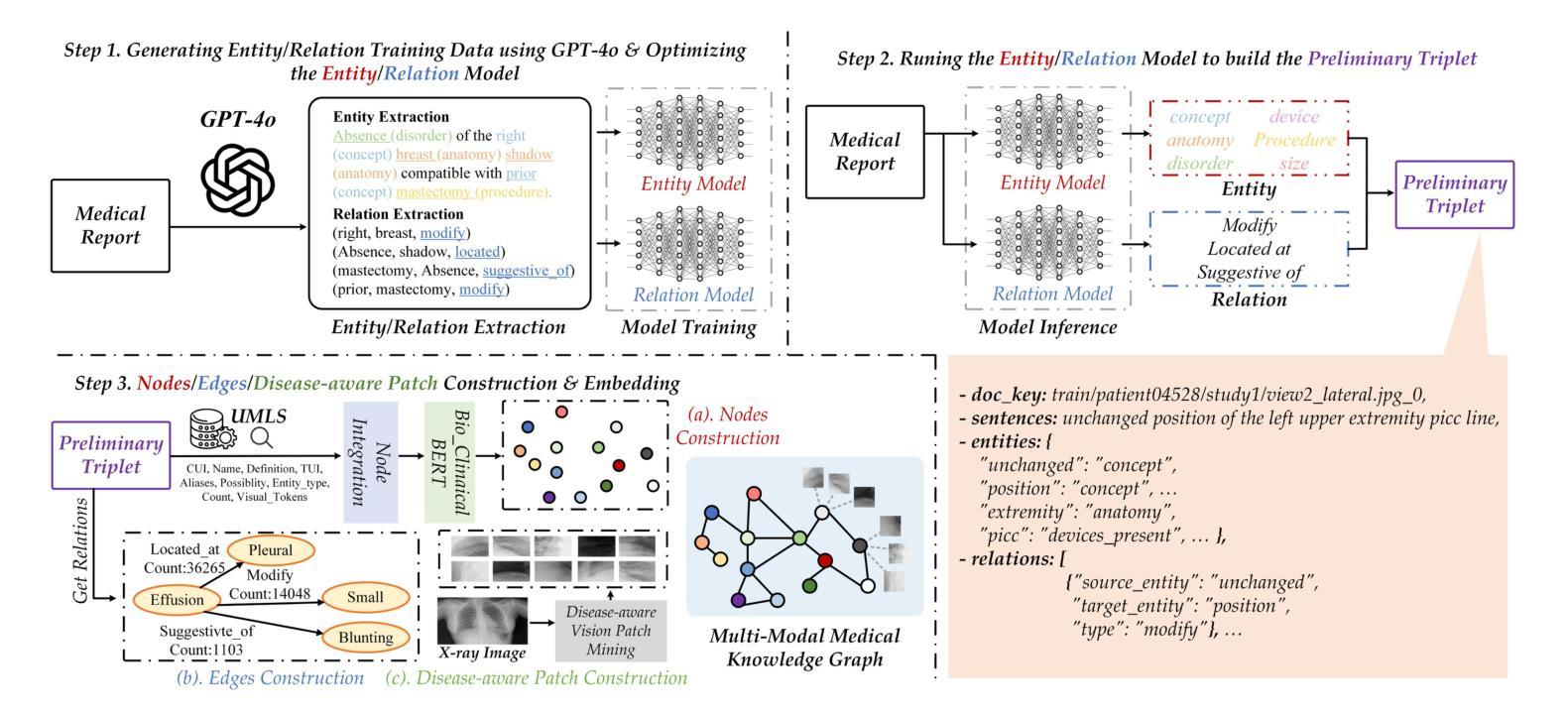
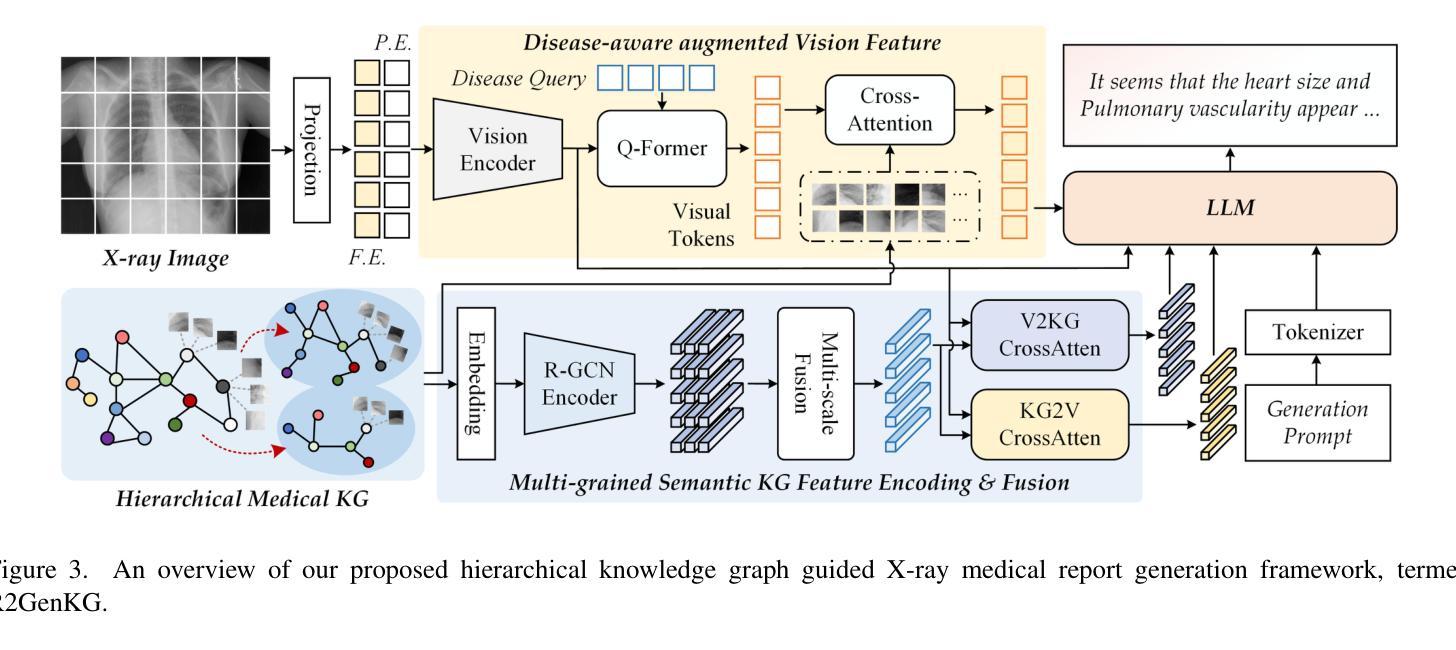
R2GenKG: Hierarchical Multi-modal Knowledge Graph for LLM-based Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Futian Wang, Yuhan Qiao, Xiao Wang, Fuling Wang, Yuxiang Zhang, Dengdi Sun
X-ray medical report generation is one of the important applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare. With the support of large foundation models, the quality of medical report generation has significantly improved. However, challenges such as hallucination and weak disease diagnostic capability still persist. In this paper, we first construct a large-scale multi-modal medical knowledge graph (termed M3KG) based on the ground truth medical report using the GPT-4o. It contains 2477 entities, 3 kinds of relations, 37424 triples, and 6943 disease-aware vision tokens for the CheXpert Plus dataset. Then, we sample it to obtain multi-granularity semantic graphs and use an R-GCN encoder for feature extraction. For the input X-ray image, we adopt the Swin-Transformer to extract the vision features and interact with the knowledge using cross-attention. The vision tokens are fed into a Q-former and retrieved the disease-aware vision tokens using another cross-attention. Finally, we adopt the large language model to map the semantic knowledge graph, input X-ray image, and disease-aware vision tokens into language descriptions. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets fully validated the effectiveness of our proposed knowledge graph and X-ray report generation framework. The source code of this paper will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis.
X射线医学报告生成是人工智能在医疗保健领域的重要应用之一。在大规模基础模型的支持下,医学报告生成的质量得到了显著提升。然而,诸如虚构和弱疾病诊断能力等挑战仍然存在。在本文中,我们首先基于真实医学报告构建了一个大规模的多模式医学知识图谱(称为M3KG),使用GPT-4o针对CheXpert Plus数据集进行操作,它包含2477个实体、3种关系、37424个三元组和6943个疾病感知视觉标记。然后,我们对它进行采样以获得多粒度语义图,并使用R-GCN编码器进行特征提取。对于输入的X射线图像,我们采用Swin-Transformer提取视觉特征,并使用交叉注意力与知识进行交互。视觉标记被输入到Q-former中,并使用另一个交叉注意力检索疾病感知视觉标记。最后,我们采用大型语言模型将语义知识图谱、输入的X射线图像和疾病感知视觉标记映射到语言描述中。在多个数据集上进行的广泛实验充分验证了我们提出的知识图谱和X射线报告生成框架的有效性。本文的源代码将在https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于大型基础模型的支持,利用多模态医学知识图谱(M3KG)和Swin-Transformer等技术,本文提出了一种改进X光报告生成的方法。通过构建大规模医学知识图谱,结合X光图像特征提取和跨注意力交互,实现了高质量的医学报告生成。实验证明该方法的有效性。
关键见解
- X光医学报告生成是人工智能在医疗保健中的重要应用之一。
- 利用大型基础模型的支持,医学报告生成的质量已显著提高。
3.仍存在诸如幻觉和弱疾病诊断能力等挑战。 - 本文构建了基于真实医学报告的多模态医学知识图谱(M3KG)。
- 通过采样获得多粒度语义图,并使用R-GCN编码器进行特征提取。
- 采用Swin-Transformer提取X光图像特征,并通过跨注意力与知识交互。
- 结合大型语言模型,将语义知识图谱、X光图像和疾病感知视觉标记转化为语言描述。
点此查看论文截图

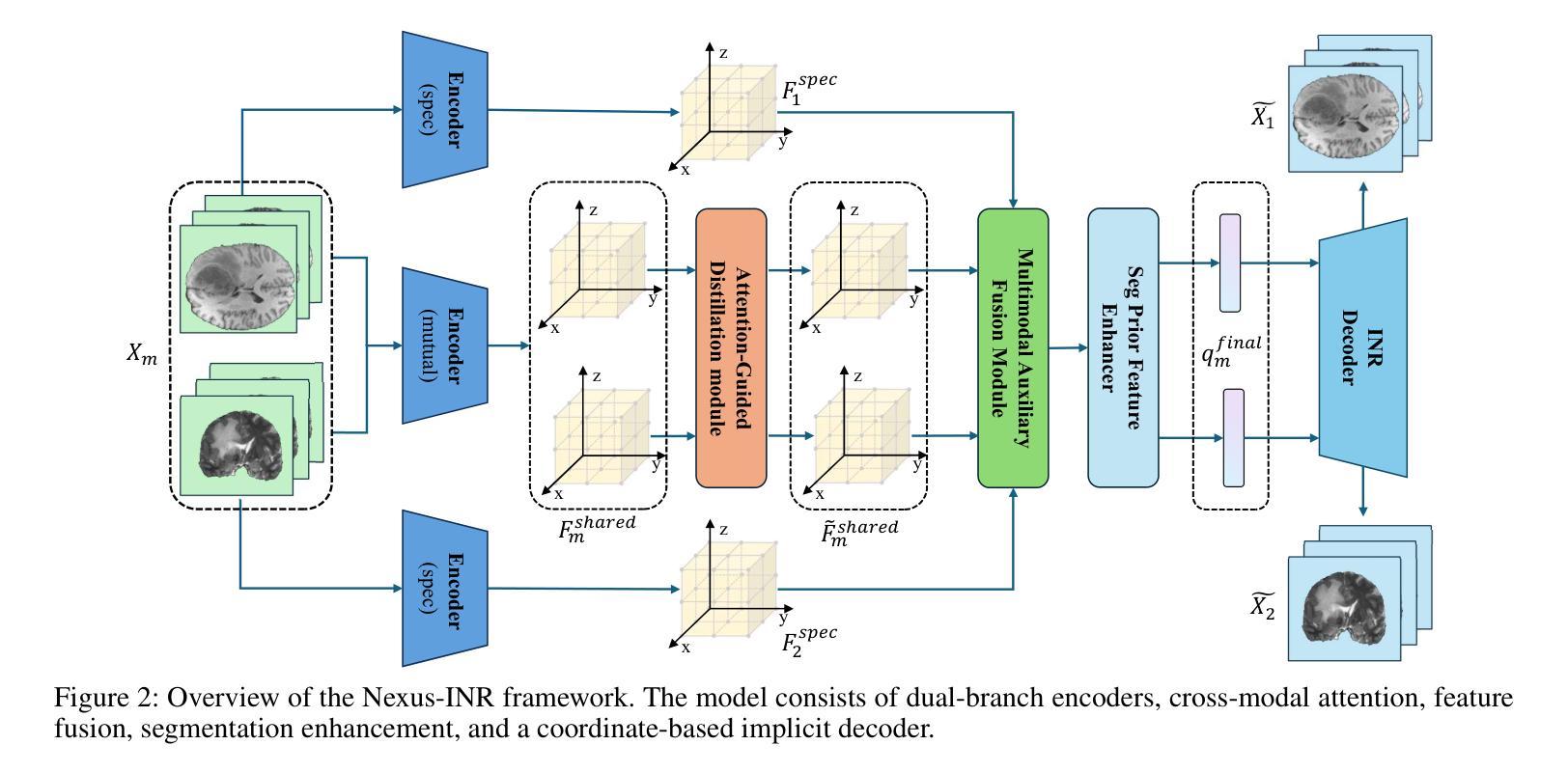
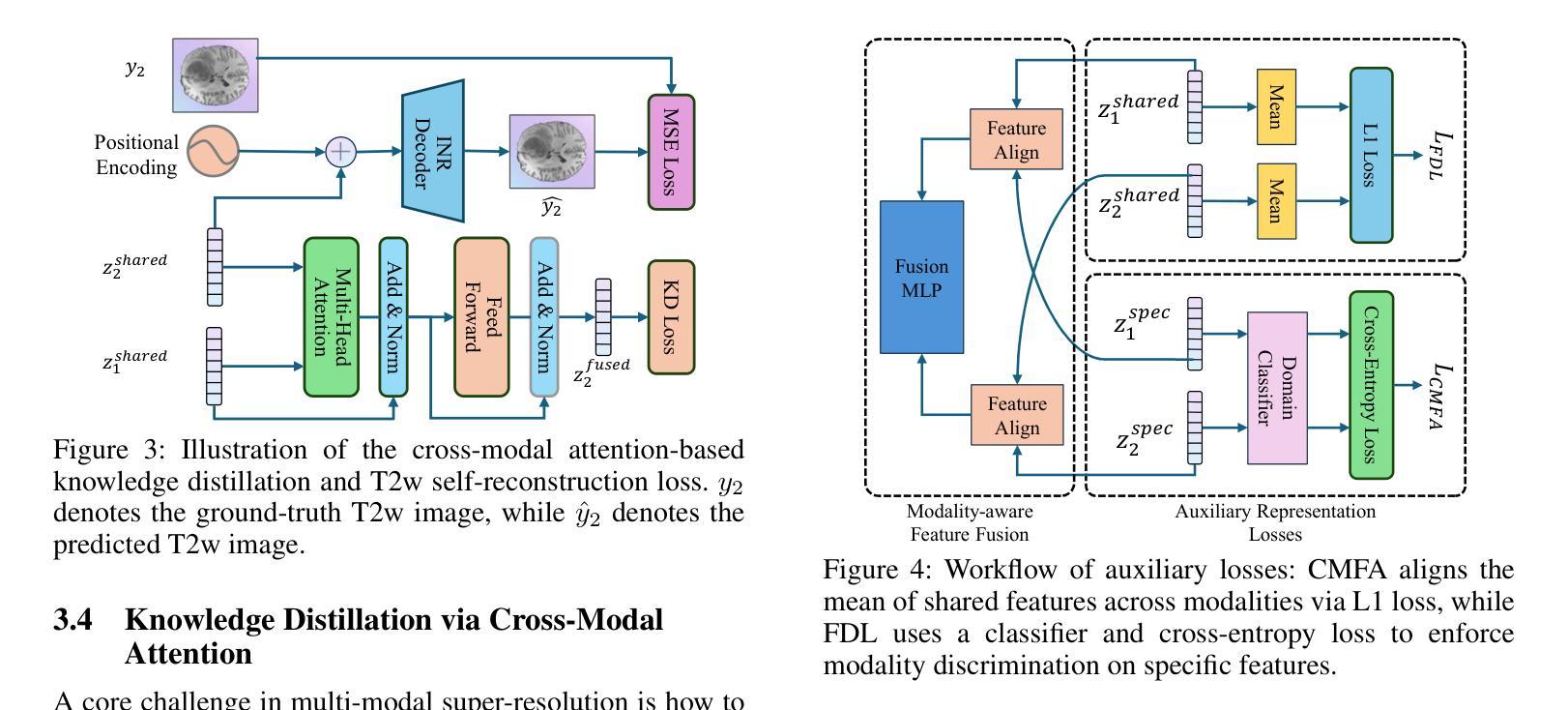
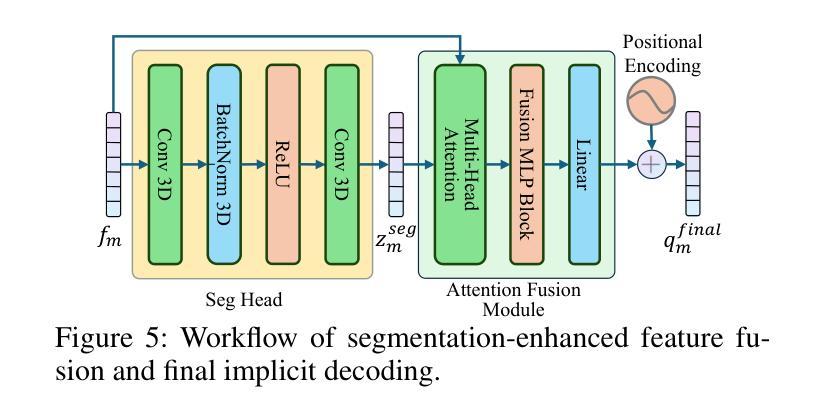
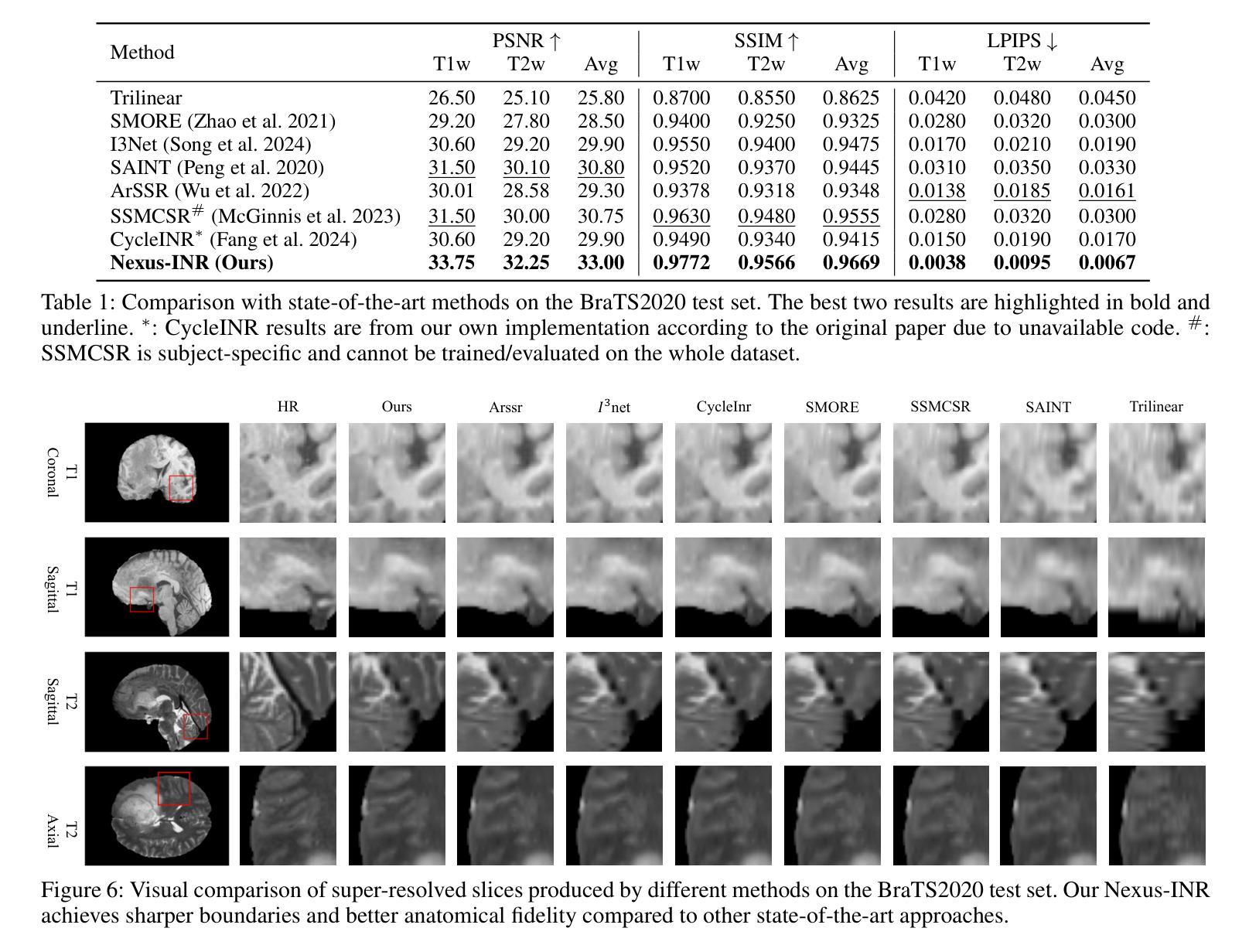
Nexus-INR: Diverse Knowledge-guided Arbitrary-Scale Multimodal Medical Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Bo Zhang, JianFei Huo, Zheng Zhang, Wufan Wang, Hui Gao, Xiangyang Gong, Wendong Wang
Arbitrary-resolution super-resolution (ARSR) provides crucial flexibility for medical image analysis by adapting to diverse spatial resolutions. However, traditional CNN-based methods are inherently ill-suited for ARSR, as they are typically designed for fixed upsampling factors. While INR-based methods overcome this limitation, they still struggle to effectively process and leverage multi-modal images with varying resolutions and details. In this paper, we propose Nexus-INR, a Diverse Knowledge-guided ARSR framework, which employs varied information and downstream tasks to achieve high-quality, adaptive-resolution medical image super-resolution. Specifically, Nexus-INR contains three key components. A dual-branch encoder with an auxiliary classification task to effectively disentangle shared anatomical structures and modality-specific features; a knowledge distillation module using cross-modal attention that guides low-resolution modality reconstruction with high-resolution reference, enhanced by self-supervised consistency loss; an integrated segmentation module that embeds anatomical semantics to improve both reconstruction quality and downstream segmentation performance. Experiments on the BraTS2020 dataset for both super-resolution and downstream segmentation demonstrate that Nexus-INR outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
任意分辨率超分辨率(ARSR)通过适应不同空间分辨率,为医学图像分析提供了关键的灵活性。然而,基于传统CNN的方法本质上不适合ARSR,因为它们通常设计为固定放大倍数。虽然INR方法克服了这一局限性,但它们仍然难以有效处理和利用具有不同分辨率和细节的多模态图像。在本文中,我们提出了Nexus-INR,一个以多样知识引导的ARSR框架,它利用不同的信息和下游任务来实现高质量、自适应分辨率的医学图像超分辨率。具体来说,Nexus-INR包含三个关键组件。一个具有辅助分类任务的双分支编码器,有效地分离共享解剖结构和模态特定特征;一个使用跨模态注意力的知识蒸馏模块,该模块以高分辨率参考引导低分辨率模态的重构,通过自监督一致性损失增强;一个集成分割模块,嵌入解剖语义以提高重建质量和下游分割性能。在BraTS2020数据集上的超分辨率和下游分割实验表明,Nexus-INR在各项指标上均优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为Nexus-INR的灵活超分辨率框架,用于实现高质量、自适应分辨率的医疗图像超分辨率。该框架结合了多种技术和策略,包括双分支编码器、知识蒸馏模块和集成分割模块,以实现有效处理不同模态和不同分辨率的医疗图像的目标。其在BraTS2020数据集上的实验结果证明了其超越现有方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ARSR为医学图像分析提供了重要的灵活性,能够适应不同的空间分辨率。
- 传统CNN方法对于ARSR任务来说存在局限性,因为它们通常针对固定的上采样因子设计。
- INR方法克服了CNN的局限性,但在处理多模态图像时仍面临挑战。
- Nexus-INR框架包含三个关键组件:双分支编码器、知识蒸馏模块和集成分割模块。
- 双分支编码器通过辅助分类任务有效地分离共享解剖结构和模态特定特征。
- 知识蒸馏模块利用跨模态注意力来指导低分辨率模态的重构,同时结合高分辨率参考和自我监督的一致性损失。
点此查看论文截图

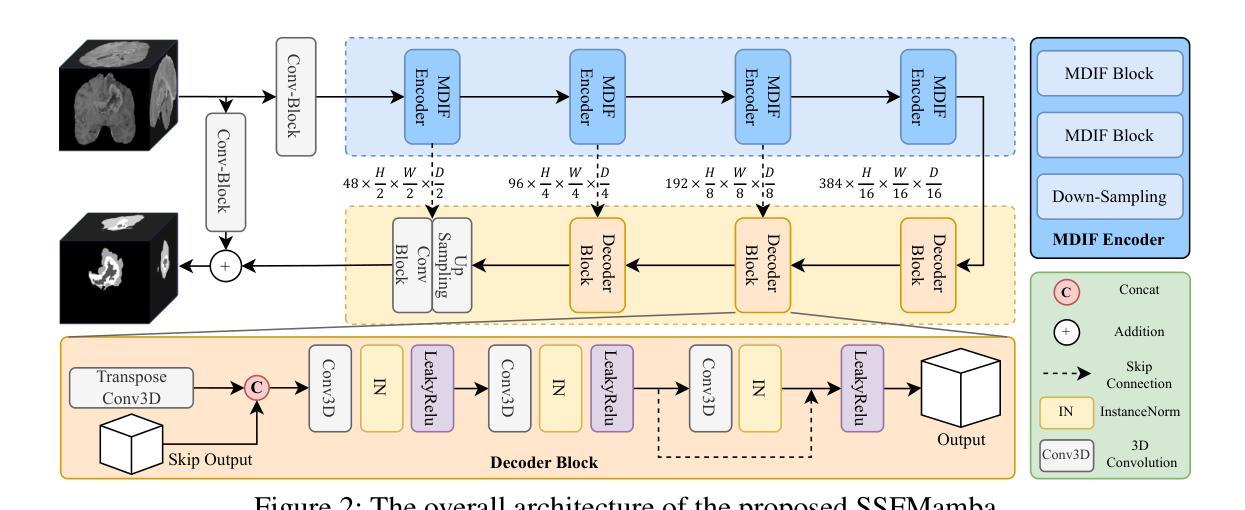
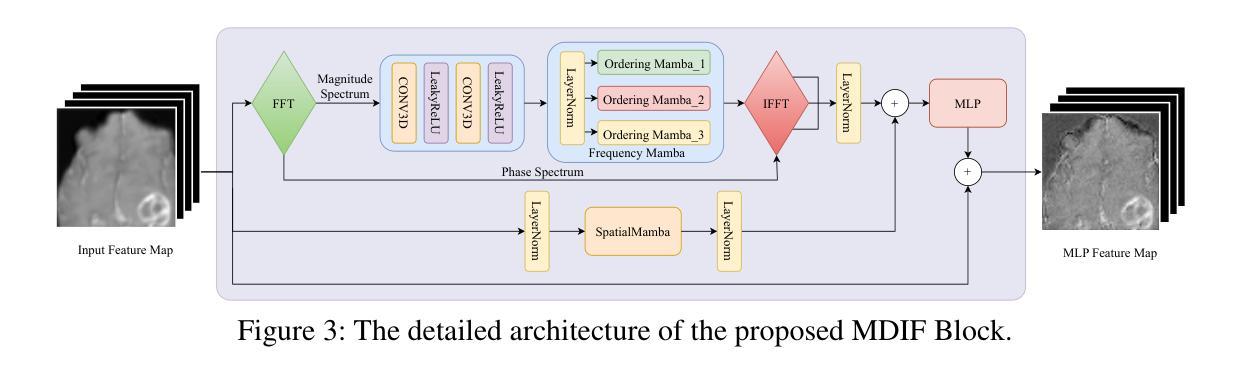
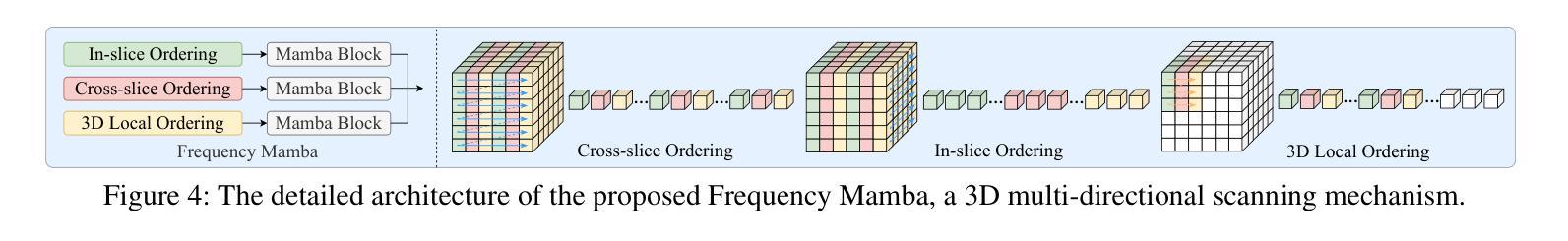
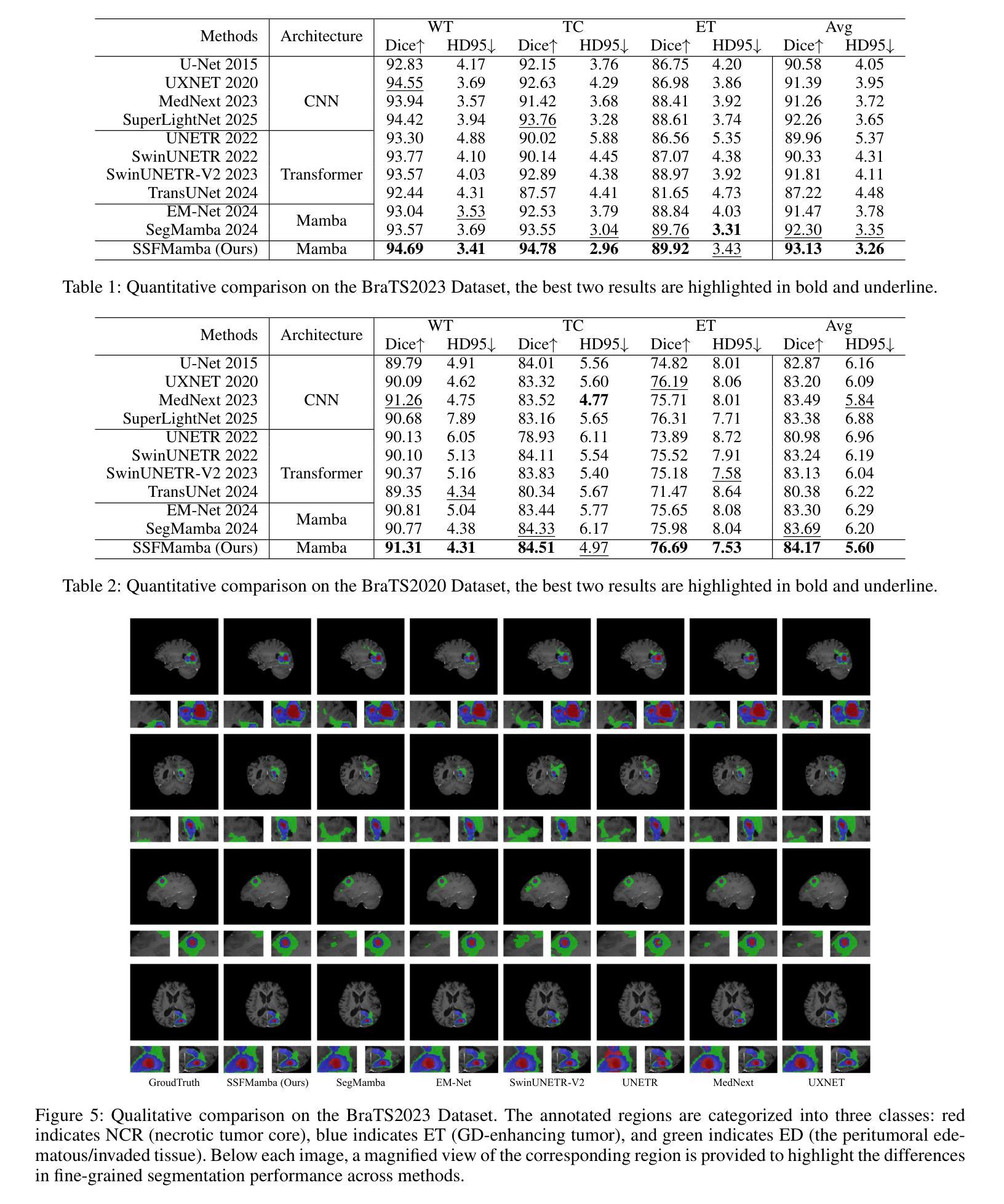
SSFMamba: Symmetry-driven Spatial-Frequency Feature Fusion for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Bo Zhang, Yifan Zhang, Shuo Yan, Yu Bai, Zheng Zhang, Wu Liu, Xiuzhuang Zhou, Wendong Wang
In light of the spatial domain’s limited capacity for modeling global context in 3D medical image segmentation, emerging approaches have begun to incorporate frequency domain representations. However, straightforward feature extraction strategies often overlook the unique properties of frequency domain information, such as conjugate symmetry. They also fail to account for the fundamental differences in data distribution between the spatial and frequency domains, which can ultimately dilute or obscure the complementary strengths that frequency-based representations offer. In this paper, we propose SSFMamba, a Mamba based Symmetry-driven Spatial-Frequency feature fusion network for 3D medical image segmentation. SSFMamba employs a complementary dual-branch architecture that extracts features from both the spatial and frequency domains, and leverages a Mamba block to fuse these heterogeneous features to preserve global context while reinforcing local details. In the frequency domain branch, we harness Mamba’s exceptional capability to extract global contextual information in conjunction with the synergistic effect of frequency domain features to further enhance global modeling. Moreover, we design a 3D multi-directional scanning mechanism to strengthen the fusion of local and global cues. Extensive experiments on the BraTS2020 and BraTS2023 datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various evaluation metrics.
鉴于三维医学图像分割中空间域对全局上下文建模的有限能力,新兴方法开始融入频率域表示。然而,直接的特征提取策略往往忽略了频率域信息的独特属性,如共轭对称性。它们也未能考虑到空间域和频率域之间数据分布的根本差异,这最终可能会稀释或掩盖基于频率的表示所提供的互补优势。在本文中,我们提出了SSFMamba,这是一种基于Mamba的对称驱动空间-频率特征融合网络,用于三维医学图像分割。SSFMamba采用互补的双分支架构,从空间和频率域提取特征,并利用Mamba块融合这些异构特征,以保留全局上下文并强化局部细节。在频率域分支中,我们利用Mamba提取全局上下文信息的卓越能力,结合频率域特征的协同作用,进一步增强了全局建模。此外,我们设计了一种三维多方向扫描机制,以加强局部和全局线索的融合。在BraTS2020和BraTS2023数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在各种评估指标上均优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Mamba的对称驱动时空融合网络SSFMamba,用于三维医学图像分割。该网络采用互补双分支架构,从时空域提取特征并使用Mamba块融合这些异构特征,以保留全局上下文并强化局部细节。在频率域分支中,结合Mamba提取全局上下文信息的卓越能力与频率域特征的协同作用,进一步增强全局建模。设计三维多方向扫描机制,加强局部和全局线索的融合。在BraTS2020和BraTS2023数据集上的实验表明,该方法在各项评估指标上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中,空间域在建模全局上下文时存在局限性,因此新兴方法开始结合频率域表示。
- 现有特征提取策略忽略了频率域信息的独特性质,如共轭对称性,并且未能考虑时空域间数据分布的基础差异。
- SSFMamba网络采用双分支架构,分别从时空域提取特征,并使用Mamba块进行特征融合。
- 频率域分支利用Mamba提取全局上下文信息,并与频率域特征的协同作用结合,以增强全局建模。
- SSFMamba设计了一个三维多方向扫描机制,强化局部和全局信息的融合。
- 在BraTS2020和BraTS2023数据集上的实验表明,SSFMBama方法性能卓越,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图