⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
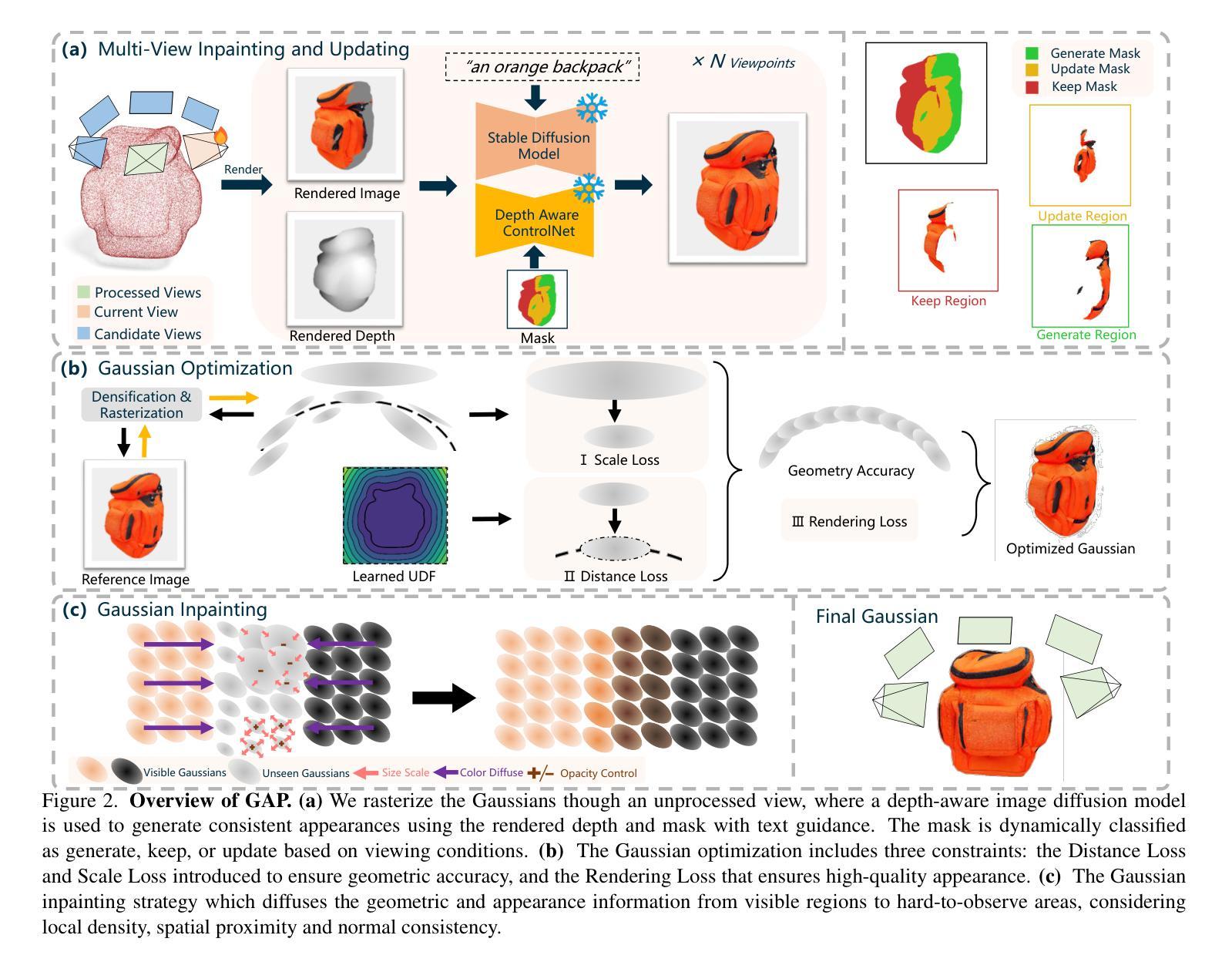
GAP: Gaussianize Any Point Clouds with Text Guidance
Authors:Weiqi Zhang, Junsheng Zhou, Haotian Geng, Wenyuan Zhang, Yu-Shen Liu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated its advantages in achieving fast and high-quality rendering. As point clouds serve as a widely-used and easily accessible form of 3D representation, bridging the gap between point clouds and Gaussians becomes increasingly important. Recent studies have explored how to convert the colored points into Gaussians, but directly generating Gaussians from colorless 3D point clouds remains an unsolved challenge. In this paper, we propose GAP, a novel approach that gaussianizes raw point clouds into high-fidelity 3D Gaussians with text guidance. Our key idea is to design a multi-view optimization framework that leverages a depth-aware image diffusion model to synthesize consistent appearances across different viewpoints. To ensure geometric accuracy, we introduce a surface-anchoring mechanism that effectively constrains Gaussians to lie on the surfaces of 3D shapes during optimization. Furthermore, GAP incorporates a diffuse-based inpainting strategy that specifically targets at completing hard-to-observe regions. We evaluate GAP on the Point-to-Gaussian generation task across varying complexity levels, from synthetic point clouds to challenging real-world scans, and even large-scale scenes. Project Page: https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP.
3D高斯混合技术(3DGS)已经展现出其在实现快速高质量渲染方面的优势。点云作为一种广泛使用和易于获取的三维表示形式,填补其与高斯之间的差距变得越来越重要。近期的研究已经探讨了如何将彩色点转换为高斯,但直接从无彩色三维点云生成高斯仍是一个未解决的难题。在本文中,我们提出了GAP,这是一种将原始点云转化为高保真度三维高斯的新型方法,有文本指导。我们的关键想法是设计一个多角度优化框架,利用深度感知图像扩散模型合成不同视角下的连续外观。为确保几何精度,我们引入了一种表面锚定机制,有效地约束高斯在优化过程中位于三维形状的表面上。此外,GAP还采用了一种基于扩散的填充策略,特别适用于难以观察到的区域的填充。我们在不同复杂程度的点云到高斯生成任务上评估了GAP的性能,包括合成点云、具有挑战性的真实世界扫描以及大规模场景。项目页面:https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法GAP,能够将原始的点云数据转化为高保真度的三维高斯数据,并通过文本引导进行渲染。该研究利用多视角优化框架,结合深度感知图像扩散模型,合成不同视角下的连续外观。为确保几何精度,引入了表面锚定机制,约束高斯在三维形状表面进行优化。此外,GAP还采用了基于扩散的填充策略,专门用于完成难以观测的区域。此技术在不同复杂度的点云转高斯生成任务上进行了评估,包括合成点云、具有挑战性的真实世界扫描以及大规模场景。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在快速高质量渲染方面的优势。
- 点云作为广泛使用和易于获取的三维表现形式,将其转化为高斯数据的重要性。
- 当前研究中如何将彩色点转化为高斯数据的探索,以及从无色三维点云中直接生成高斯数据的挑战。
- GAP方法:将原始点云转化为高保真三维高斯数据的新方法,通过文本引导进行渲染。
- 利用多视角优化框架和深度感知图像扩散模型合成不同视角下的连续外观。
- 引入表面锚定机制确保几何精度。
点此查看论文截图


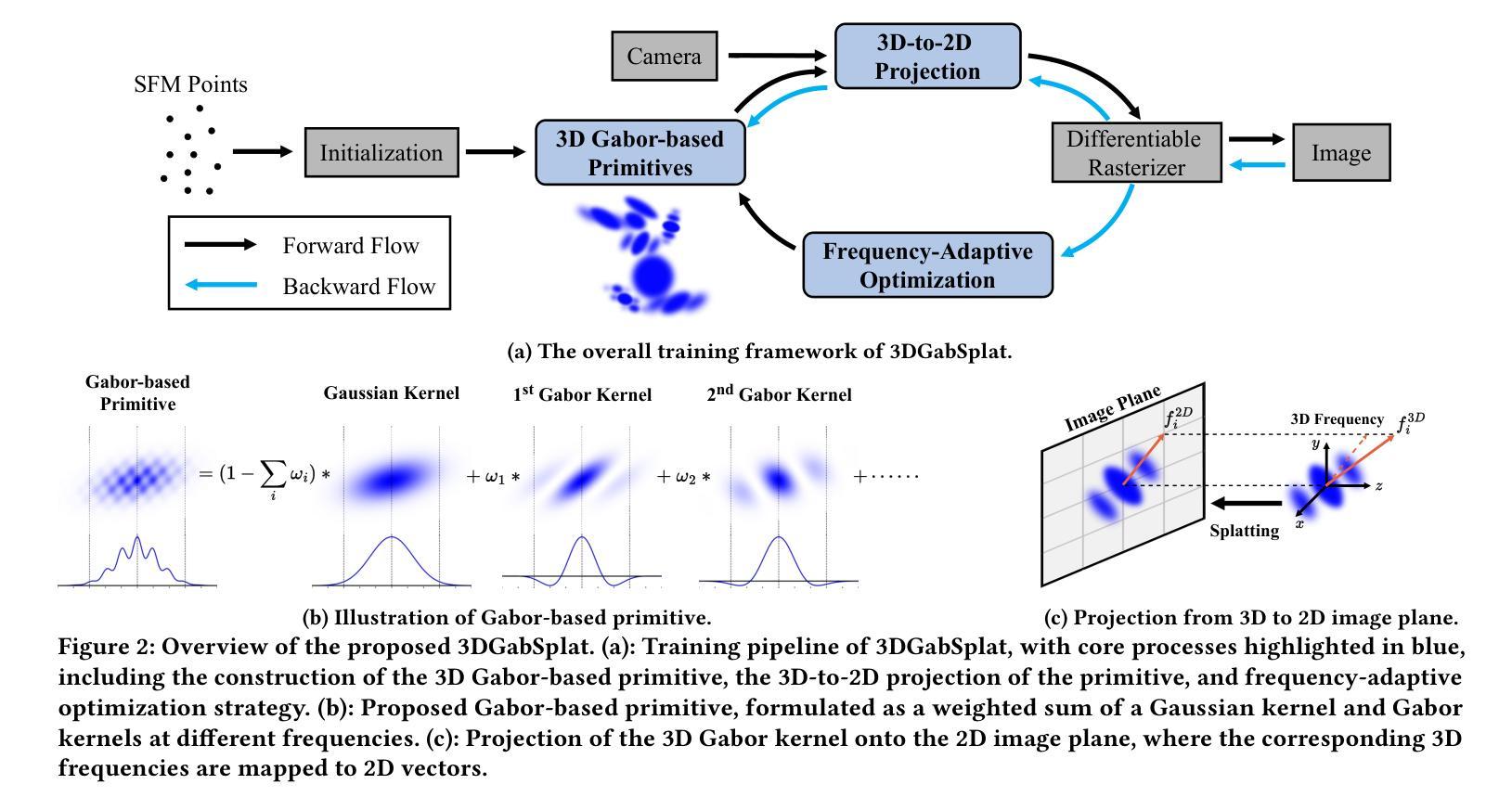
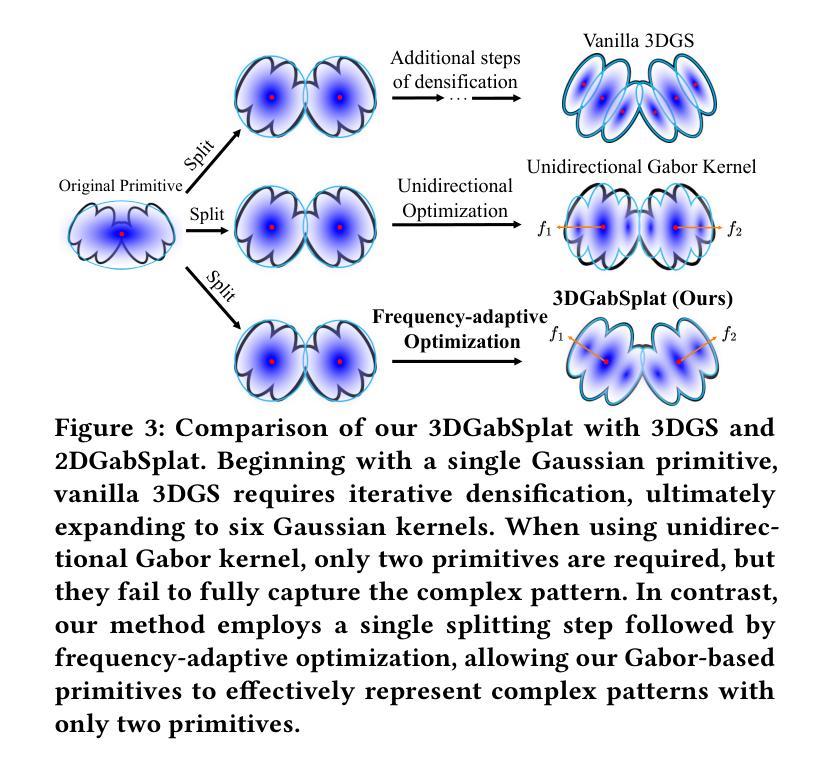
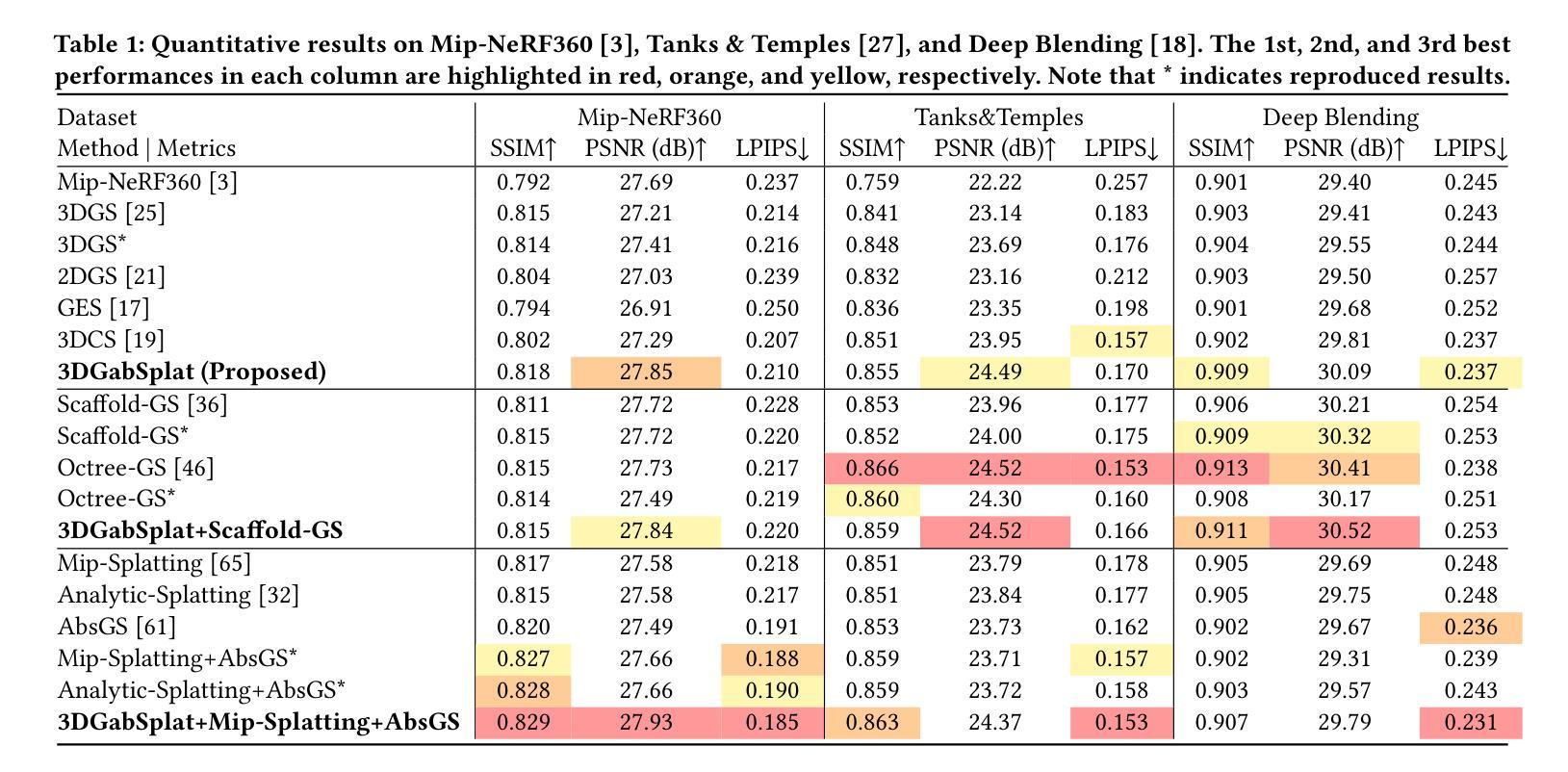
3DGabSplat: 3D Gabor Splatting for Frequency-adaptive Radiance Field Rendering
Authors:Junyu Zhou, Yuyang Huang, Wenrui Dai, Junni Zou, Ziyang Zheng, Nuowen Kan, Chenglin Li, Hongkai Xiong
Recent prominence in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has enabled real-time rendering while maintaining high-fidelity novel view synthesis. However, 3DGS resorts to the Gaussian function that is low-pass by nature and is restricted in representing high-frequency details in 3D scenes. Moreover, it causes redundant primitives with degraded training and rendering efficiency and excessive memory overhead. To overcome these limitations, we propose 3D Gabor Splatting (3DGabSplat) that leverages a novel 3D Gabor-based primitive with multiple directional 3D frequency responses for radiance field representation supervised by multi-view images. The proposed 3D Gabor-based primitive forms a filter bank incorporating multiple 3D Gabor kernels at different frequencies to enhance flexibility and efficiency in capturing fine 3D details. Furthermore, to achieve novel view rendering, an efficient CUDA-based rasterizer is developed to project the multiple directional 3D frequency components characterized by 3D Gabor-based primitives onto the 2D image plane, and a frequency-adaptive mechanism is presented for adaptive joint optimization of primitives. 3DGabSplat is scalable to be a plug-and-play kernel for seamless integration into existing 3DGS paradigms to enhance both efficiency and quality of novel view synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate that 3DGabSplat outperforms 3DGS and its variants using alternative primitives, and achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality across both real-world and synthetic scenes. Remarkably, we achieve up to 1.35 dB PSNR gain over 3DGS with simultaneously reduced number of primitives and memory consumption.
近期三维高斯融合(3DGS)的突出发展能够在保持高保真度的同时实现实时渲染和新颖视图合成。然而,3DGS依赖于本质上为低通的Gaussian函数,在表示三维场景中的高频细节方面存在局限性。此外,它会产生退化训练和渲染效率以及过多内存消耗的冗余基本元素。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了基于三维 Gabor 的融合(3DGabSplat),它利用了一种新型的三维 Gabor 基基本元素,具有多个方向的三维频率响应,用于辐射场表示,并由多视角图像进行监督。所提出的三维 Gabor 基基本元素形成滤波器组,结合了不同频率的多个三维 Gabor 内核,提高了捕捉三维精细细节的灵活性和效率。此外,为了实现新颖的视图渲染,开发了一个基于 CUDA 的高效光栅化器,将三维 Gabor 基基本元素表征的多个方向的三维频率分量投影到二维图像平面上,并提出了一种频率自适应机制,用于对基本元素进行自适应联合优化。3DGabSplat 可扩展为即插即用的内核,无缝集成到现有的 3DGS 模式中,以提高视图合成的效率和质量。大量实验表明,3DGabSplat 优于 3DGS 及其使用替代基本元素的变体,并在真实和合成场景上实现了最先进的渲染质量。值得注意的是,我们在减少了基本元素数量和内存消耗的同时,实现了高达 1.35 dB 的峰值信噪比增益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM’25
Summary
基于高斯函数本身的低通特性,传统三维高斯绘制技术(3DGS)在处理高频细节方面存在局限性,影响训练和渲染效率,且占用大量内存。为突破这些局限,本文提出一种全新的三维纹理映射技术——三维Gabor绘制(3DGabSplat)。该技术利用多方向三维频率响应的3D Gabor基元表示辐射场,并通过多视角图像进行监控。创新的滤波器组集成了不同频率的多个三维Gabor内核,从而更有效地捕捉精细的三维细节。实验证明,该技术相较于传统的三维高斯绘制技术及其变体,性能更优,实现了真实和合成场景的高质量渲染。显著提升了渲染质量,减少了基元数量和内存消耗。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS受限于传统高斯函数的低通特性,难以处理高频细节。
- 提出的3DGabSplat技术使用基于三维Gabor的基元表示辐射场,具有多方向三维频率响应。
- 创新滤波器组集成了不同频率的三维Gabor内核,提高了捕捉精细三维细节的效率。
- 开发了基于CUDA的高效光栅化器,用于将多维频率成分投影到二维图像平面上。
- 引入频率自适应机制进行基元的联合优化。
- 3DGabSplat技术易于集成到现有3DGS框架中,显著提升渲染效率和质量。
点此查看论文截图


CF3: Compact and Fast 3D Feature Fields
Authors:Hyunjoon Lee, Joonkyu Min, Jaesik Park
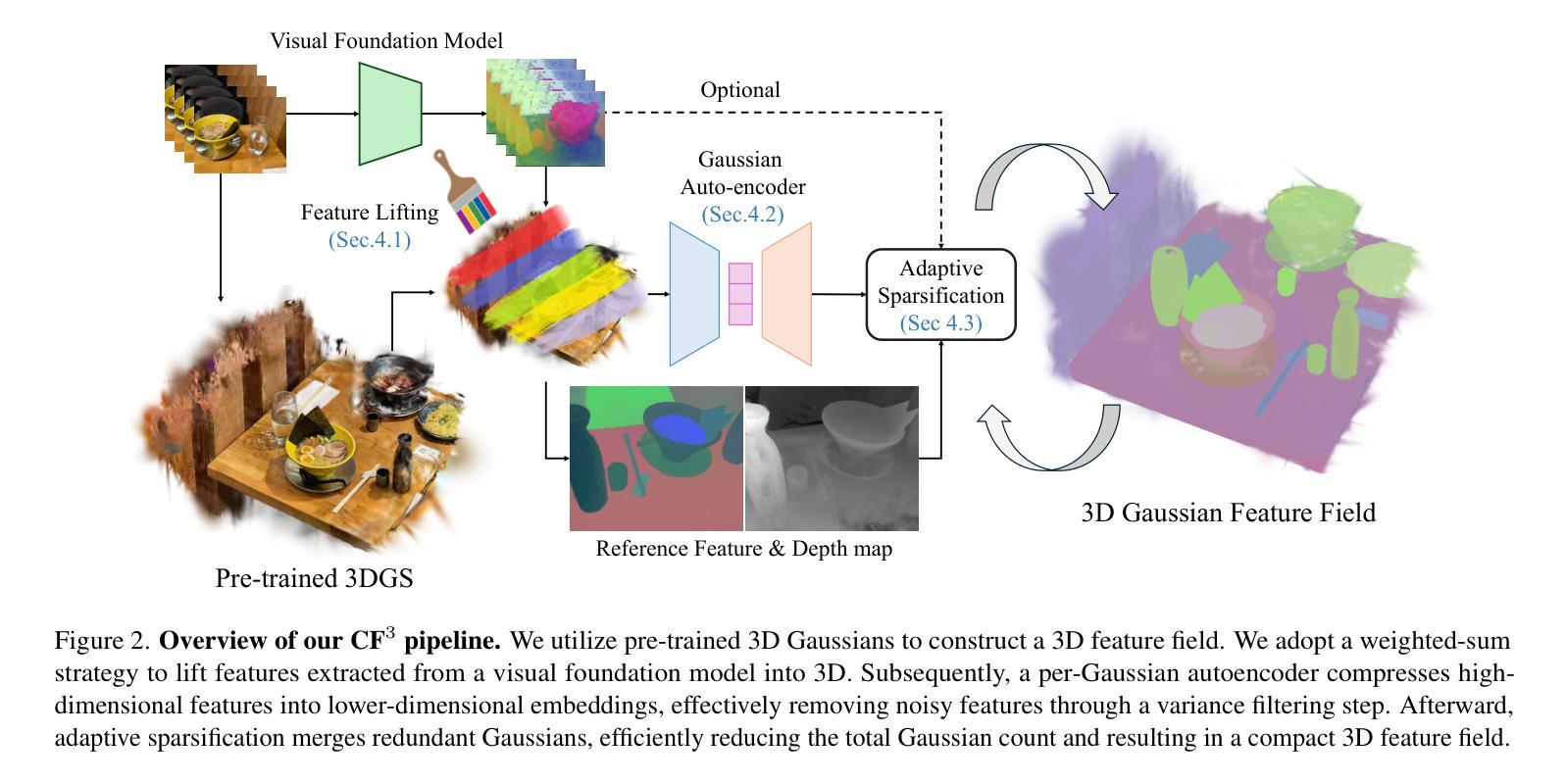
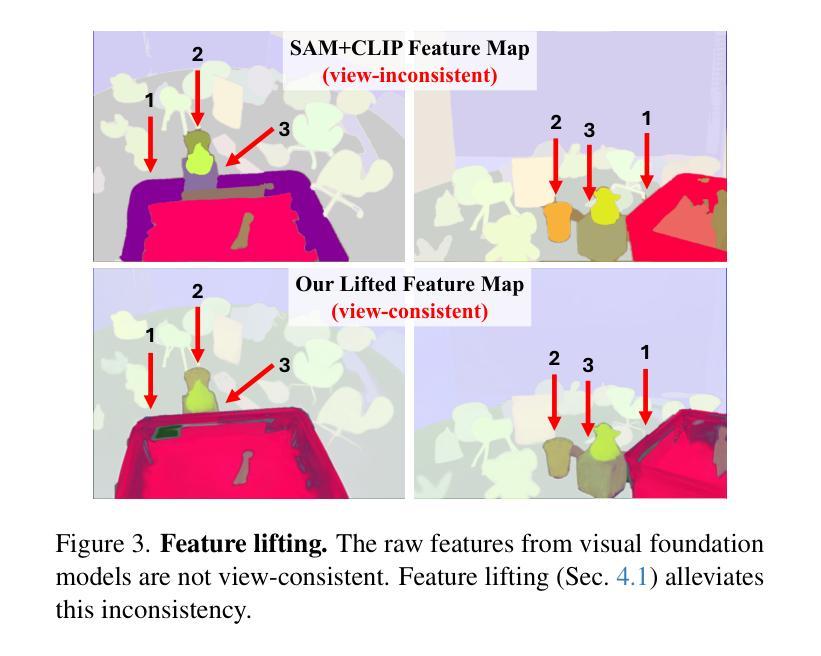
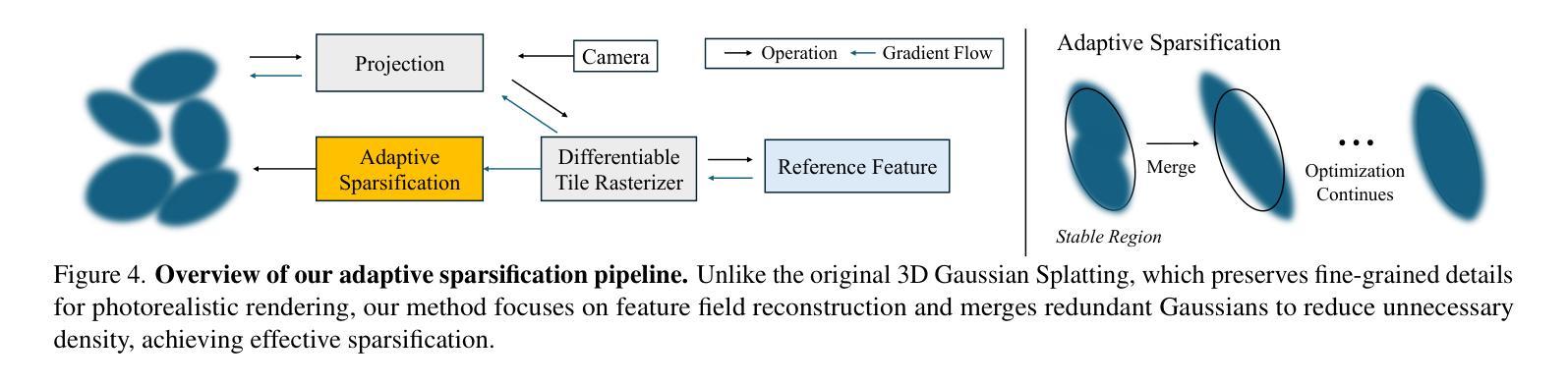
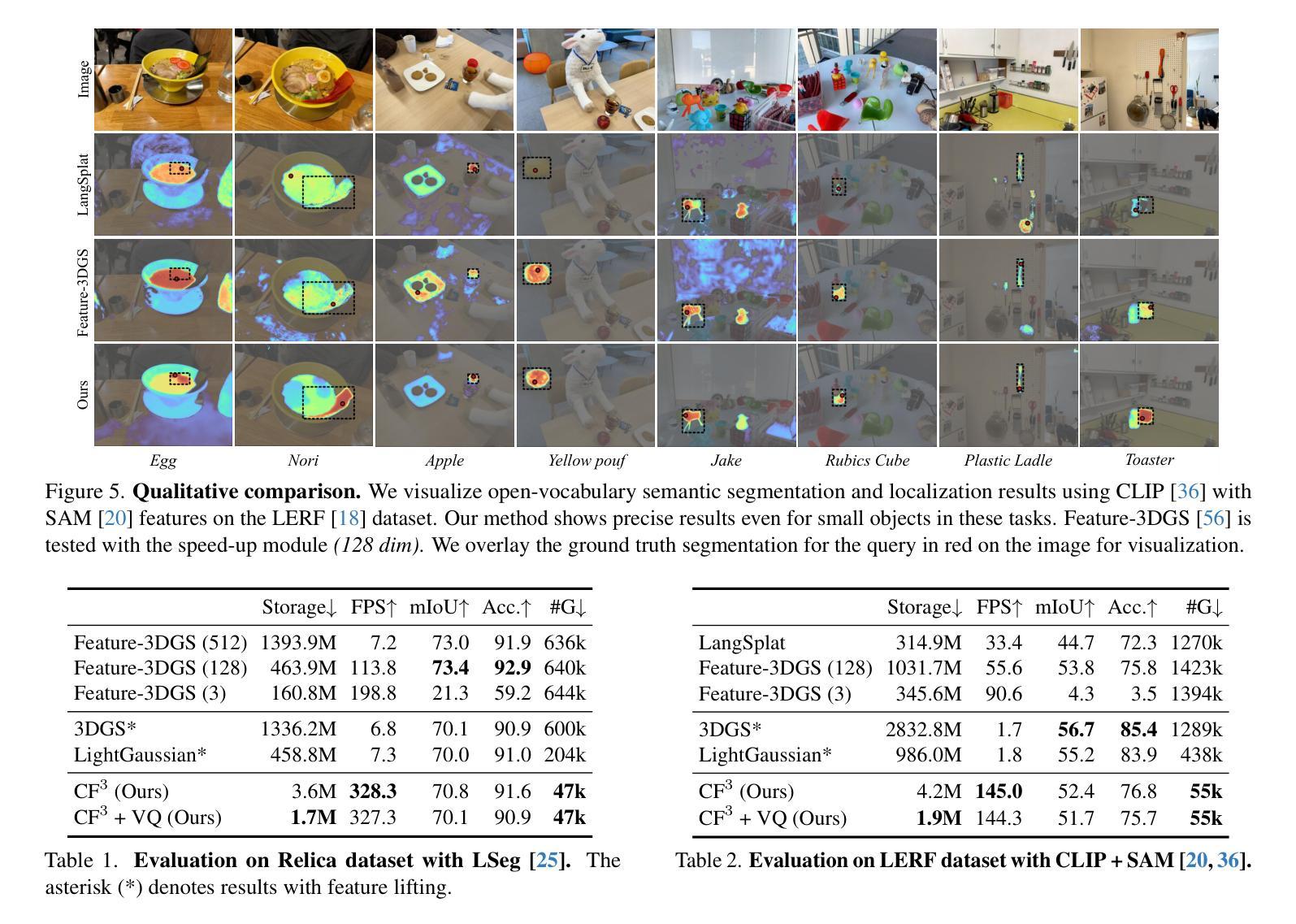
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has begun incorporating rich information from 2D foundation models. However, most approaches rely on a bottom-up optimization process that treats raw 2D features as ground truth, incurring increased computational costs. We propose a top-down pipeline for constructing compact and fast 3D Gaussian feature fields, namely, CF3. We first perform a fast weighted fusion of multi-view 2D features with pre-trained Gaussians. This approach enables training a per-Gaussian autoencoder directly on the lifted features, instead of training autoencoders in the 2D domain. As a result, the autoencoder better aligns with the feature distribution. More importantly, we introduce an adaptive sparsification method that optimizes the Gaussian attributes of the feature field while pruning and merging the redundant Gaussians, constructing an efficient representation with preserved geometric details. Our approach achieves a competitive 3D feature field using as little as 5% of the Gaussians compared to Feature-3DGS.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)已经开始从2D基础模型中融入丰富的信息。然而,大多数方法依赖于自下而上的优化过程,将原始2D特征视为真实值,导致计算成本增加。我们提出了一种构建紧凑快速的3D高斯特征场的自上而下的流水线,即CF3。我们首先执行使用预训练高斯对多视角2D特征的快速加权融合。这种方法使得直接在提取的特征上训练每个高斯自编码器成为可能,而不是在二维域中训练自编码器。因此,自编码器与特征分布更加匹配。更重要的是,我们引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,在优化特征场的高斯属性的同时删减和合并冗余高斯,构建了一个有效的表示形式,保留了几何细节。与Feature-3DGS相比,我们的方法仅使用其高斯分布的5%,即可获得具有竞争力的三维特征场表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
该摘要介绍了一种基于3D高斯特征融合的方法,通过快速加权融合多视角的二维特征,构建紧凑且快速的3D高斯特征场。该方法采用顶向下的流程设计,可直接在提升的特征上训练高斯自编码器,与直接在二维域训练相比,能更好地对齐特征分布。此外,还引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,在优化特征场的高斯属性的同时,删除并合并冗余的高斯分布,实现高效表示并保留几何细节。相较于Feature-3DGS,该方法使用的高斯分布数量仅占其5%,即可达到竞争性的三维特征场效果。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS开始融入二维基础模型的丰富信息。
- 大多数方法采用自下而上的优化过程,将原始二维特征视为真实值,导致计算成本增加。
- 提出了一种顶向下的流程构建紧凑且快速的3D高斯特征场。
- 通过快速加权融合多视角的二维特征,实现高效的特征融合。
- 直接在提升的特征上训练高斯自编码器,更好地对齐特征分布。
- 引入自适应稀疏化方法,优化高斯属性并删除冗余的高斯分布。
点此查看论文截图


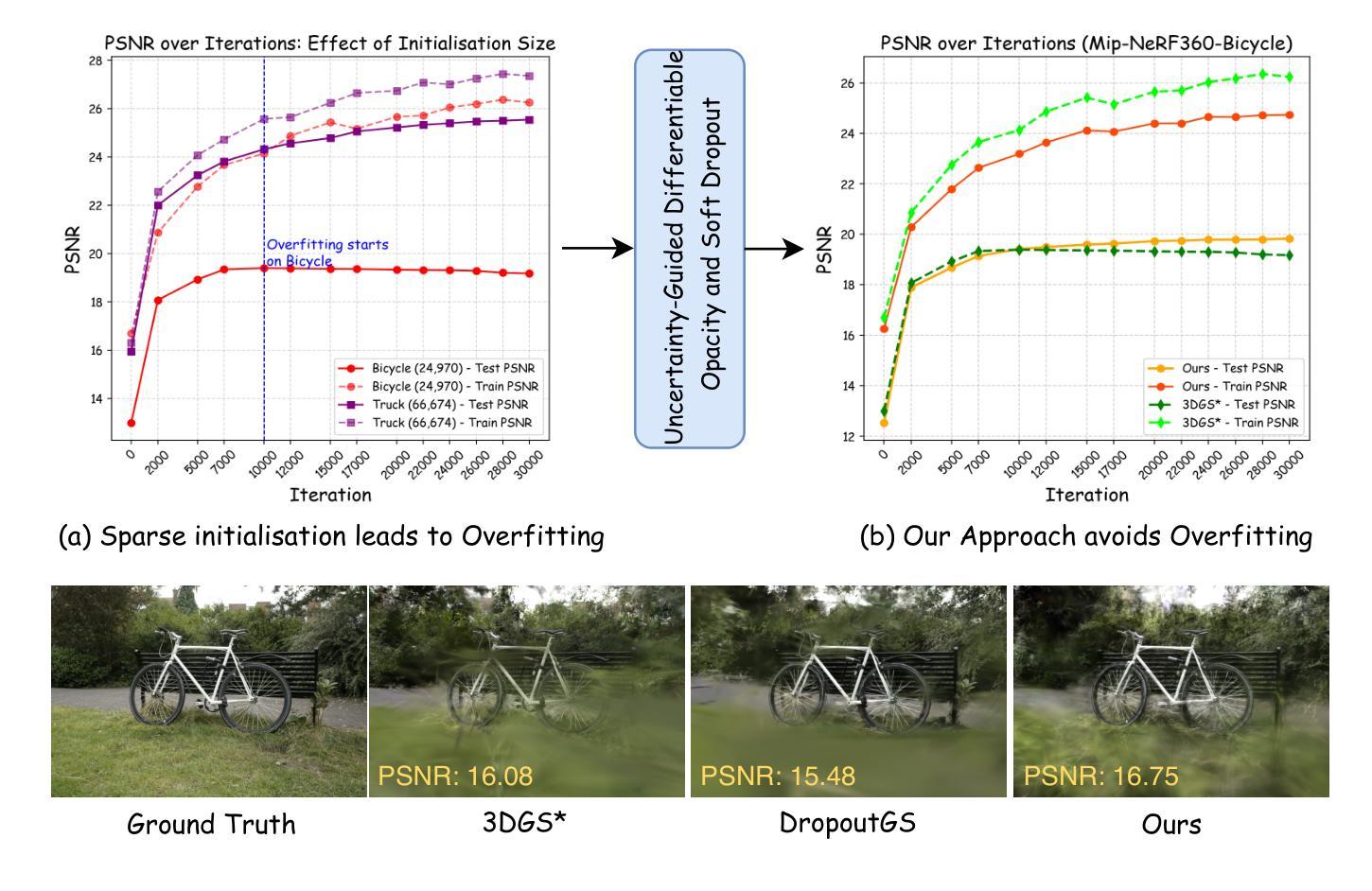
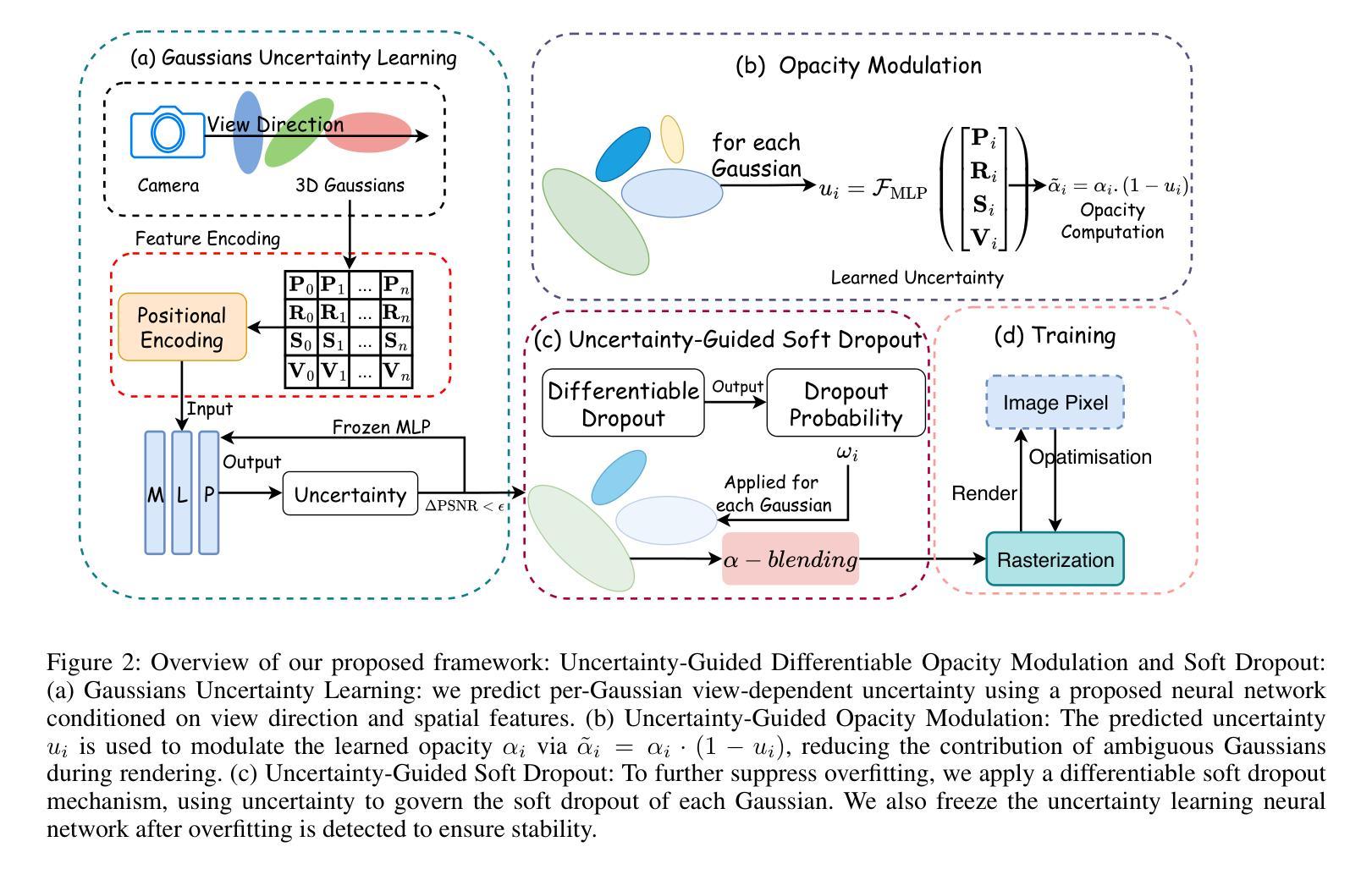
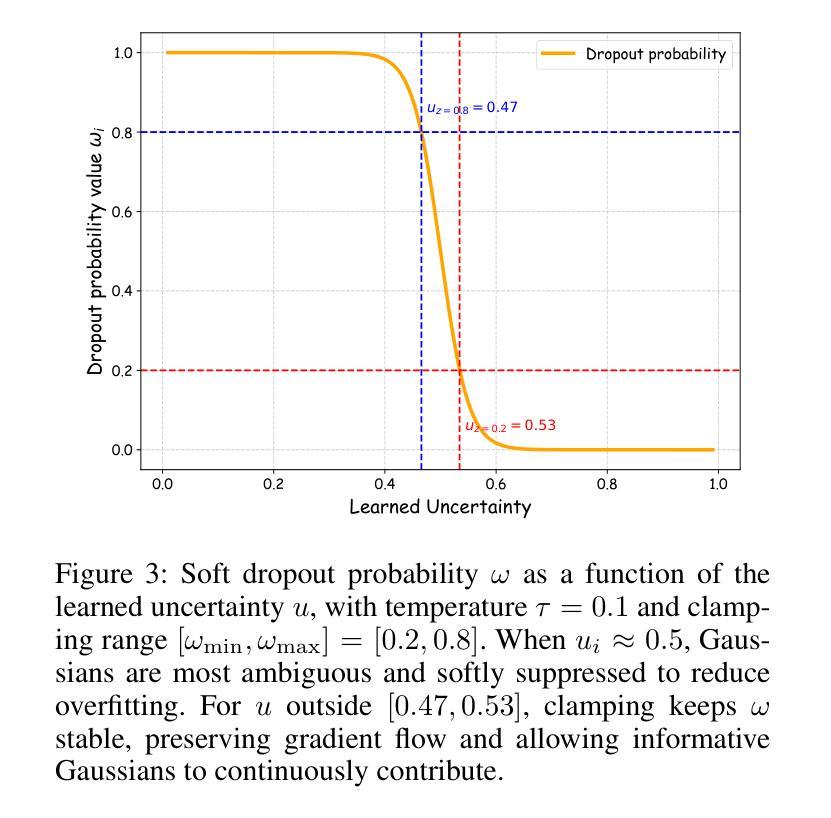
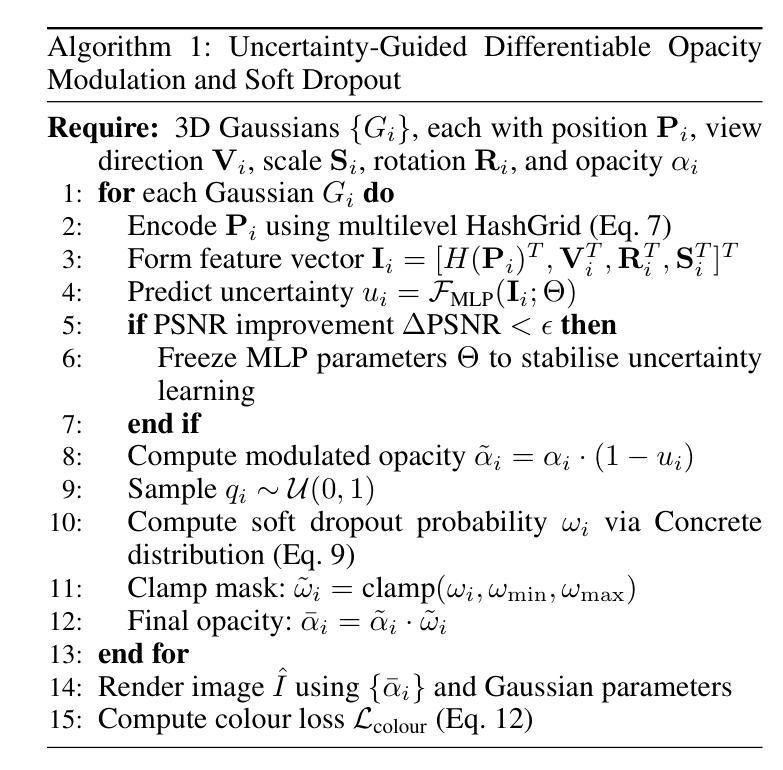
UGOD: Uncertainty-Guided Differentiable Opacity and Soft Dropout for Enhanced Sparse-View 3DGS
Authors:Zhihao Guo, Peng Wang, Zidong Chen, Xiangyu Kong, Yan Lyu, Guanyu Gao, Liangxiu Han
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has become a competitive approach for novel view synthesis (NVS) due to its advanced rendering efficiency through 3D Gaussian projection and blending. However, Gaussians are treated equally weighted for rendering in most 3DGS methods, making them prone to overfitting, which is particularly the case in sparse-view scenarios. To address this, we investigate how adaptive weighting of Gaussians affects rendering quality, which is characterised by learned uncertainties proposed. This learned uncertainty serves two key purposes: first, it guides the differentiable update of Gaussian opacity while preserving the 3DGS pipeline integrity; second, the uncertainty undergoes soft differentiable dropout regularisation, which strategically transforms the original uncertainty into continuous drop probabilities that govern the final Gaussian projection and blending process for rendering. Extensive experimental results over widely adopted datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms rivals in sparse-view 3D synthesis, achieving higher quality reconstruction with fewer Gaussians in most datasets compared to existing sparse-view approaches, e.g., compared to DropGaussian, our method achieves 3.27% PSNR improvements on the MipNeRF 360 dataset.
三维高斯映射(3DGS)已成为新型视图合成(NVS)的一种具有竞争力的方法,其通过三维高斯投影和混合技术实现了先进的渲染效率。然而,在大多数3DGS方法中,高斯被平等对待用于渲染,导致它们容易过度拟合,这在稀疏视图场景中尤为明显。为了解决这个问题,我们研究了自适应加权高斯对渲染质量的影响,这是通过提出的学得不确定性来表征的。这种学得的不确定性有两个关键目的:首先,它引导高斯不透明度的可微更新,同时保持3DGS管道完整性;其次,不确定性经历了软可微dropout正则化,这将原始不确定性战略性地转化为连续的丢弃概率,这些丢弃概率控制最终的高斯投影和混合过程以进行渲染。在广泛采用的数据集上的大量实验结果表明,我们的方法在稀疏视图三维合成中优于竞争对手,在大多数数据集上实现了更高质量的重建,使用更少的高斯。与现有的稀疏视图方法相比,例如与DropGaussian相比,我们的方法在MipNeRF 360数据集上实现了3.27%的峰值信噪比(PSNR)改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于自适应权重高斯技术的三维高斯投影融合方法,该方法通过引入学习不确定性来解决稀疏视角下的过度拟合问题。不确定性用于指导高斯透明度可微更新并保持三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)流程完整性。通过软可微Dropout正则化技术,不确定性可转换为连续Dropout概率,为最终的合成视图提供更高质量的三维渲染效果。实验结果在主流数据集上表现优越,特别是在稀疏视角下与现有方法相比优势明显。相较于DropGaussian方法,本文方法在MipNeRF 360数据集上实现了高达3.27%的PSNR提升。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS已成为新型视角合成(NVS)领域的竞争方法,因其高效的三维高斯投影和融合技术。
- 当前多数3DGS方法在处理高斯时采用等权重方式,导致在稀疏视角下容易过度拟合。
- 通过引入学习不确定性解决此问题,不仅可指导高斯透明度进行可微更新,且能保留原始的渲染完整性。
- 利用软可微Dropout正则化技术将不确定性转化为连续Dropout概率,用于控制最终的渲染过程。
点此查看论文截图

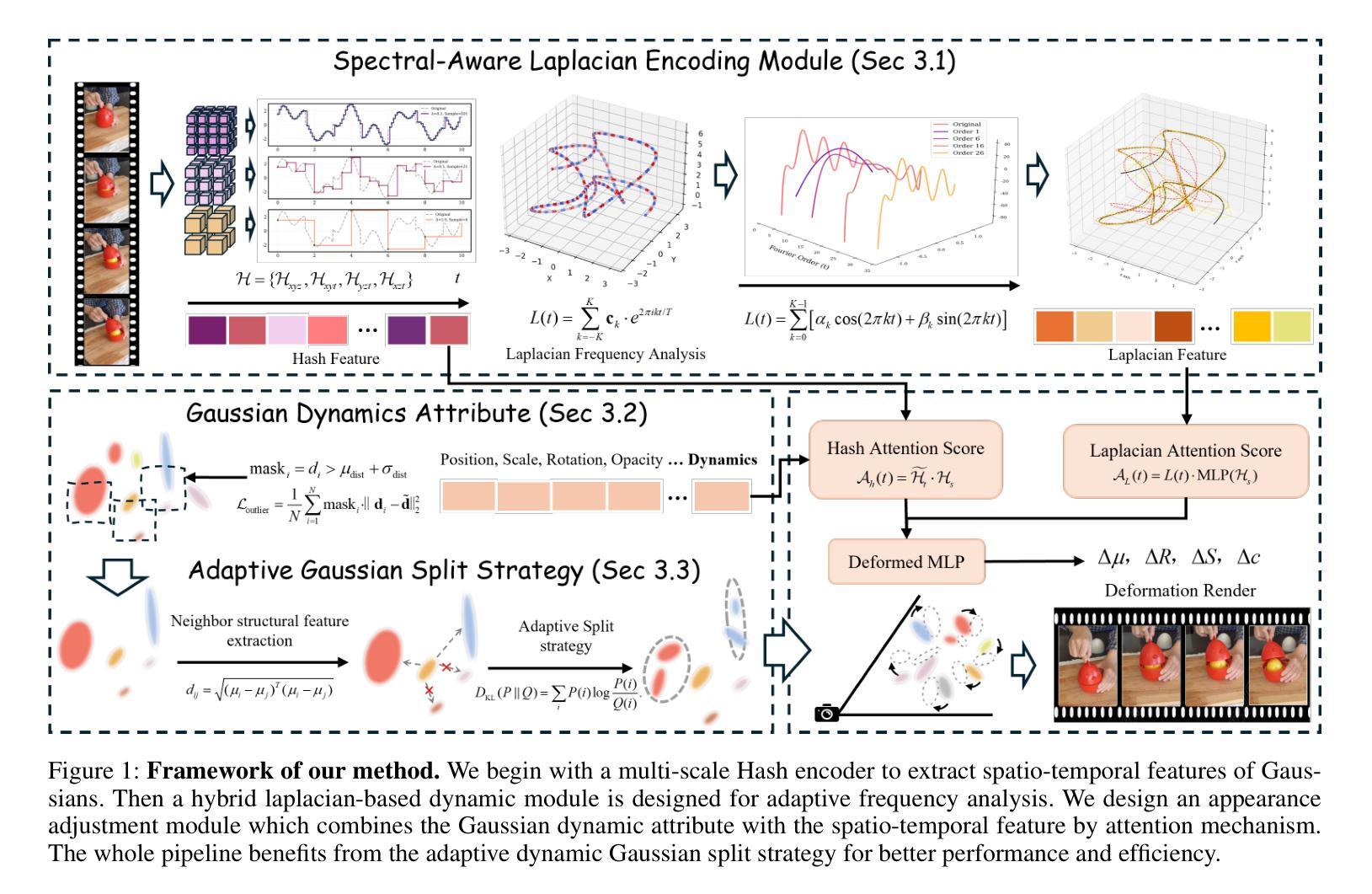
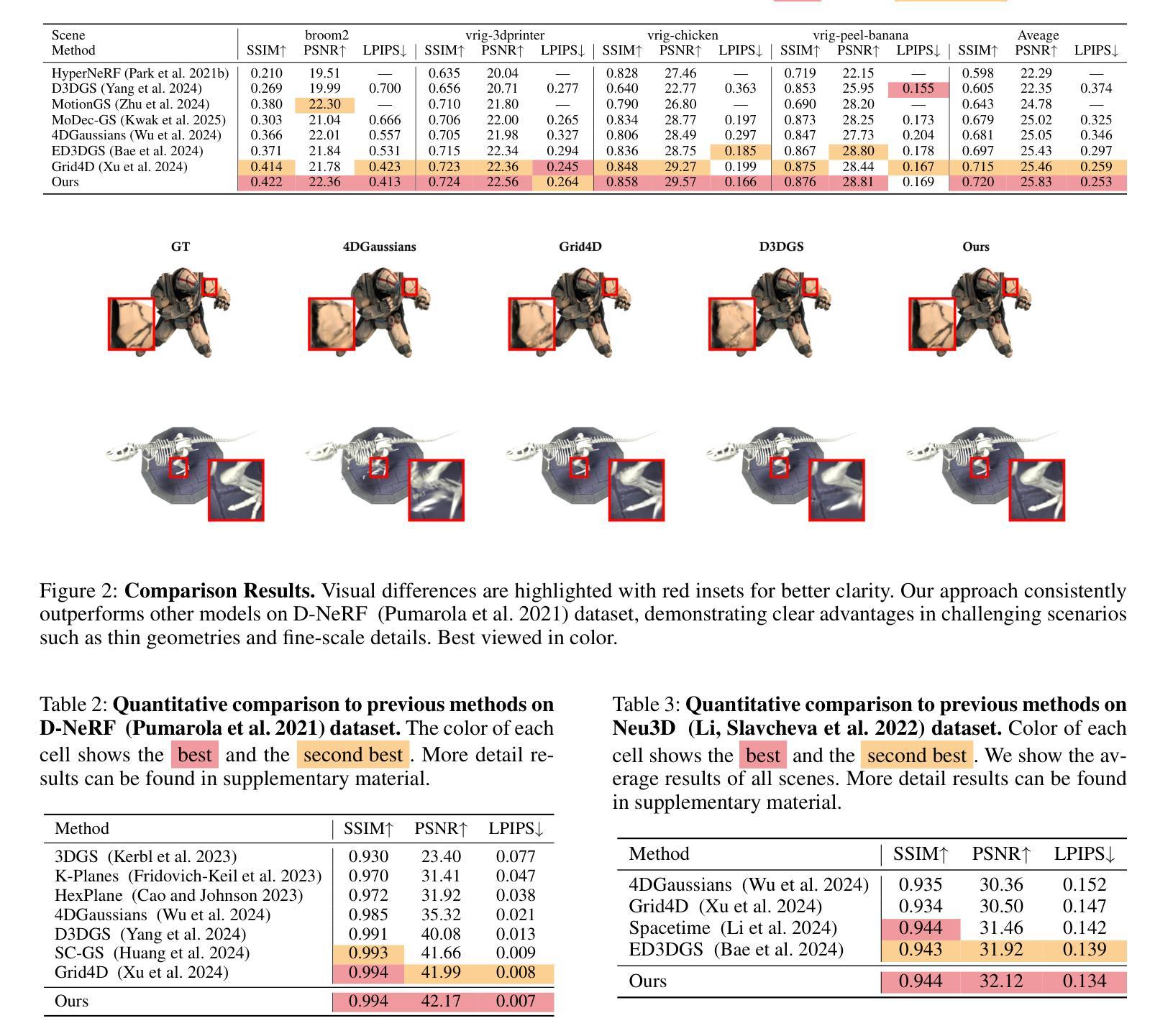
Laplacian Analysis Meets Dynamics Modelling: Gaussian Splatting for 4D Reconstruction
Authors:Yifan Zhou, Beizhen Zhao, Pengcheng Wu, Hao Wang
While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) excels in static scene modeling, its extension to dynamic scenes introduces significant challenges. Existing dynamic 3DGS methods suffer from either over-smoothing due to low-rank decomposition or feature collision from high-dimensional grid sampling. This is because of the inherent spectral conflicts between preserving motion details and maintaining deformation consistency at different frequency. To address these challenges, we propose a novel dynamic 3DGS framework with hybrid explicit-implicit functions. Our approach contains three key innovations: a spectral-aware Laplacian encoding architecture which merges Hash encoding and Laplacian-based module for flexible frequency motion control, an enhanced Gaussian dynamics attribute that compensates for photometric distortions caused by geometric deformation, and an adaptive Gaussian split strategy guided by KDTree-based primitive control to efficiently query and optimize dynamic areas. Through extensive experiments, our method demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in reconstructing complex dynamic scenes, achieving better reconstruction fidelity.
关于三维高斯贴合(3DGS),其在静态场景建模上表现出卓越的性能,然而,当将其扩展到动态场景时却面临着诸多挑战。现有的动态3DGS方法由于受低阶分解的影响而导致过度平滑,或因高维网格采样导致特征碰撞。这是由于在不同频率下保留运动细节和保持变形一致性之间存在固有的光谱冲突。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型动态3DGS框架,采用混合显式隐式函数。我们的方法包含三项关键创新:一种光谱感知拉普拉斯编码架构,融合了哈希编码和基于拉普拉斯的模块以实现灵活频率运动控制;一种增强型高斯动力学属性,用于补偿由几何变形引起的光度失真;以及一种由KDTree基元控制引导的自适应高斯分割策略,以有效地查询和优化动态区域。通过大量实验,我们的方法在重建复杂动态场景方面表现出卓越性能,实现了更高的重建保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出,尽管静态场景建模中三维高斯映射(3DGS)表现出色,但在动态场景的应用中面临重大挑战。现有动态3DGS方法存在过度平滑和高维网格采样引起的特征碰撞问题。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于混合显式隐式函数的新型动态三维高斯映射框架。该框架包含三项关键创新:频域感知拉普拉斯编码架构,用于灵活控制频率运动;增强型高斯动态属性,用于补偿几何变形引起的光度失真;以及基于KD树的自适应高斯分割策略,以高效查询和优化动态区域。实验证明,该方法在重建复杂动态场景方面具有最佳性能,实现了较高的重建保真度。
Key Takeaways
一、现有动态场景下的三维高斯映射(3DGS)技术面临的挑战包括过度平滑与特征碰撞问题。
二、面临的挑战来源于保持运动细节和维持变形一致性之间的频谱冲突。
三、本文提出了一种基于混合显式隐式函数的新型动态三维高斯映射框架来解决这些问题。其中包含频域感知拉普拉斯编码架构用于灵活控制频率运动。
四、增强型高斯动态属性被用来补偿几何变形引起的光度失真。
五、基于KD树的自适应高斯分割策略用于高效查询和优化动态区域。
六、本文方法通过广泛实验验证,在重建复杂动态场景方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

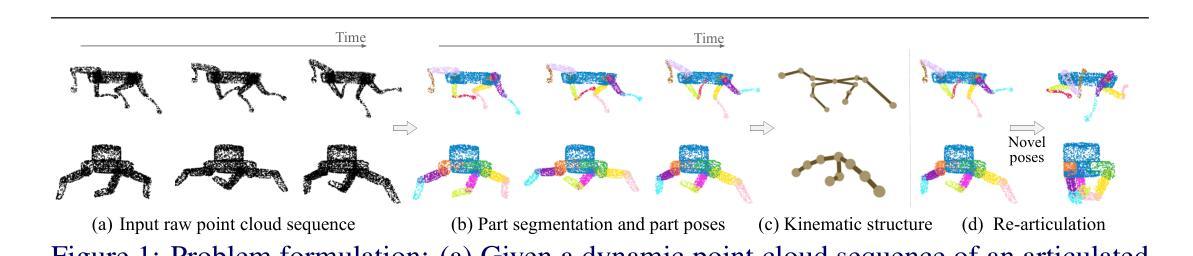
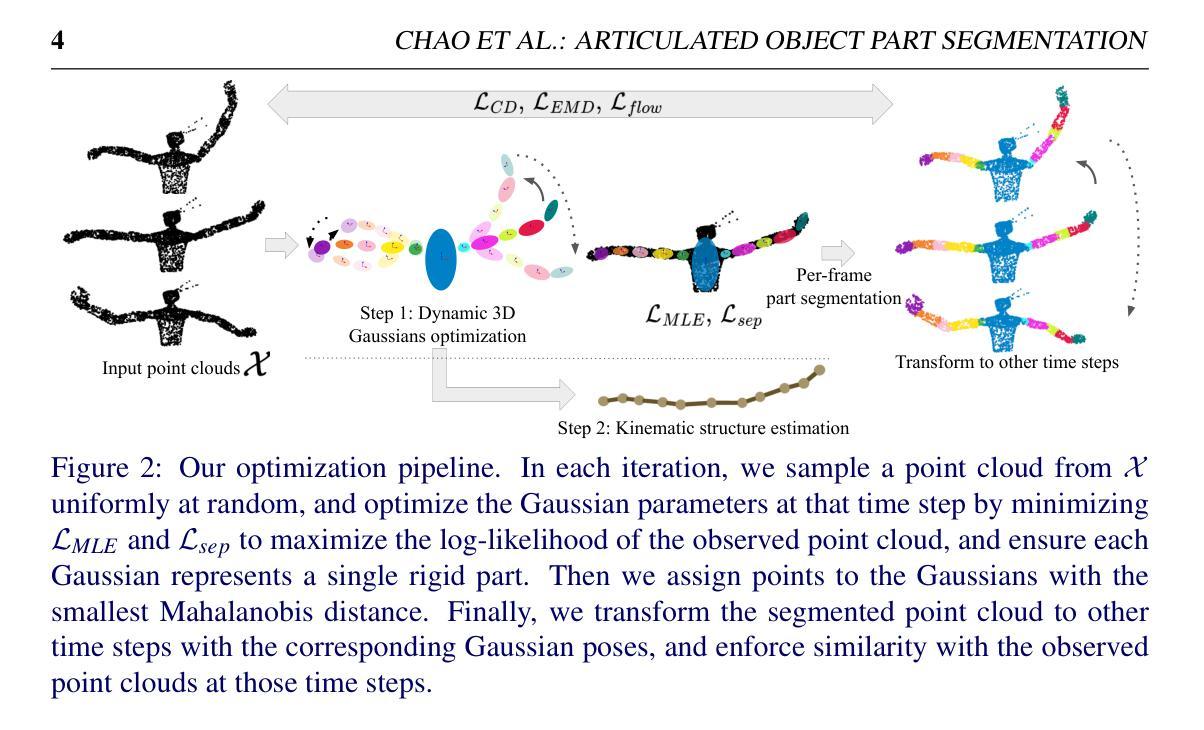
Part Segmentation and Motion Estimation for Articulated Objects with Dynamic 3D Gaussians
Authors:Jun-Jee Chao, Qingyuan Jiang, Volkan Isler
Part segmentation and motion estimation are two fundamental problems for articulated object motion analysis. In this paper, we present a method to solve these two problems jointly from a sequence of observed point clouds of a single articulated object. The main challenge in our problem setting is that the point clouds are not assumed to be generated by a fixed set of moving points. Instead, each point cloud in the sequence could be an arbitrary sampling of the object surface at that particular time step. Such scenarios occur when the object undergoes major occlusions, or if the dataset is collected using measurements from multiple sensors asynchronously. In these scenarios, methods that rely on tracking point correspondences are not appropriate. We present an alternative approach based on a compact but effective representation where we represent the object as a collection of simple building blocks modeled as 3D Gaussians. We parameterize the Gaussians with time-dependent rotations, translations, and scales that are shared across all time steps. With our representation, part segmentation can be achieved by building correspondences between the observed points and the Gaussians. Moreover, the transformation of each point across time can be obtained by following the poses of the assigned Gaussian (even when the point is not observed). Experiments show that our method outperforms existing methods that solely rely on finding point correspondences. Additionally, we extend existing datasets to emulate real-world scenarios by considering viewpoint occlusions. We further demonstrate that our method is more robust to missing points as compared to existing approaches on these challenging datasets, even when some parts are completely occluded in some time-steps. Notably, our part segmentation performance outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 13% on point clouds with occlusions.
点云分割和运动估计是关节对象运动分析中的两个基本问题。本文提出了一种方法,可以从单个关节对象的观察到的点云序列中联合解决这两个问题。我们的问题设置中的主要挑战在于,假设点云不是由一组固定的移动点生成的。相反,序列中的每个点云都可能是该对象在特定时间步长的表面上的任意采样。当对象遭受主要遮挡或数据集是使用多个异步传感器进行收集时,这种情况就会发生。在这种情况下,依赖跟踪点对应的方法并不适用。我们提出了一种基于紧凑而有效的表示方法的替代方案,我们将对象表示为作为高斯模型的简单构建块的集合。我们用随时间变化的旋转、平移和尺度参数化高斯模型,这些参数在所有时间步长中都是共享的。通过我们的表示方法,可以通过建立观察到的点和高斯之间的对应关系来实现部分分割。此外,每个点随时间变化的变化可以通过跟随指定的高斯姿态来获得(即使点没有被观察到)。实验表明,我们的方法在仅依赖于找到点对应的方法上表现更好。此外,我们通过考虑视角遮挡来模拟现实世界场景,对现有数据集进行了扩展。我们进一步证明,我们的方法在缺失点的处理上比这些具有挑战性的数据集上的现有方法更稳健,即使在某些时间步长中某些部分被完全遮挡也是如此。值得注意的是,在有遮挡的点云上,我们的部分分割性能优于最新技术方法达13%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种方法,从单一关节对象的点云序列中联合解决部分分割和运动估计两个基本问题。该方法不假定点云由固定的一组移动点生成,而是认为每个点云是对象表面在该时间步的任意采样。当对象遭受主要遮挡或使用多个异步传感器收集数据时,依赖跟踪点对应的方法不适用。相反,本文采用紧凑有效的表示方法,将对象表示为一系列简单的建筑模块,用三维高斯建模。参数化高斯与时间相关的旋转、平移和尺度共享在所有时间步骤中。通过这种表示,部分分割可以通过观察点与高斯之间的对应关系来实现。此外,即使点未被观察,也可以通过跟随指定高斯的时间变换来获得每个点的时间变换。实验表明,该方法优于仅依赖寻找点对应的方法。此外,通过考虑视点遮挡来模拟现实世界场景扩展现有数据集。进一步证明该方法对于缺失点的鲁棒性优于现有方法,即使某些部分在某些时间步骤中被完全遮挡。特别是在存在遮挡的点云上,本文的部分分割性能优于最新技术方法,提高了13%。
关键见解
- 本文提出了一种联合解决部分分割和运动估计的方法,适用于单一关节对象的点云序列。
- 该方法不依赖于固定的点对应跟踪,能够处理对象表面的任意采样。
- 使用三维高斯建模对象的简单建筑模块,并参数化其与时间相关的变换。
- 部分分割是通过观察点与高斯之间的对应关系实现的。
- 该方法能够预测每个点的时间变换,即使点在某个时刻未被观察。
- 实验表明,该方法在性能上优于现有的仅依赖点对应的方法。
- 在模拟现实世界场景(考虑视点遮挡)的现有数据集上进行了扩展实验,证明了该方法对于缺失点的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

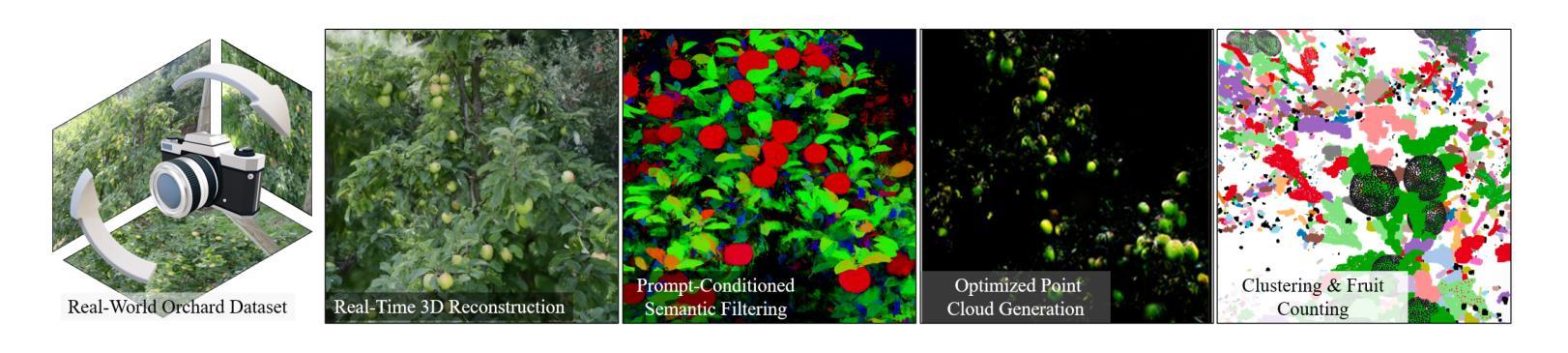
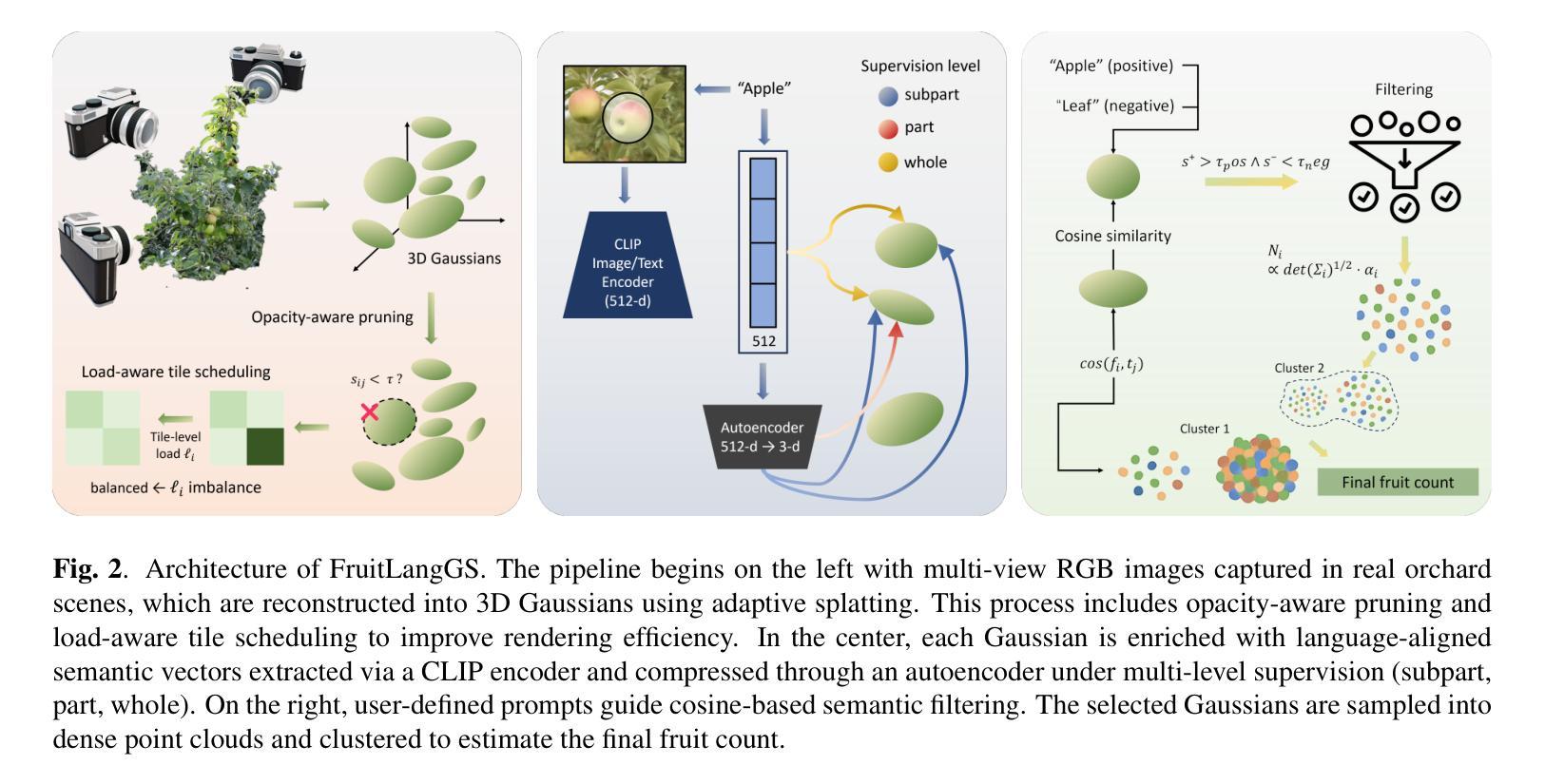
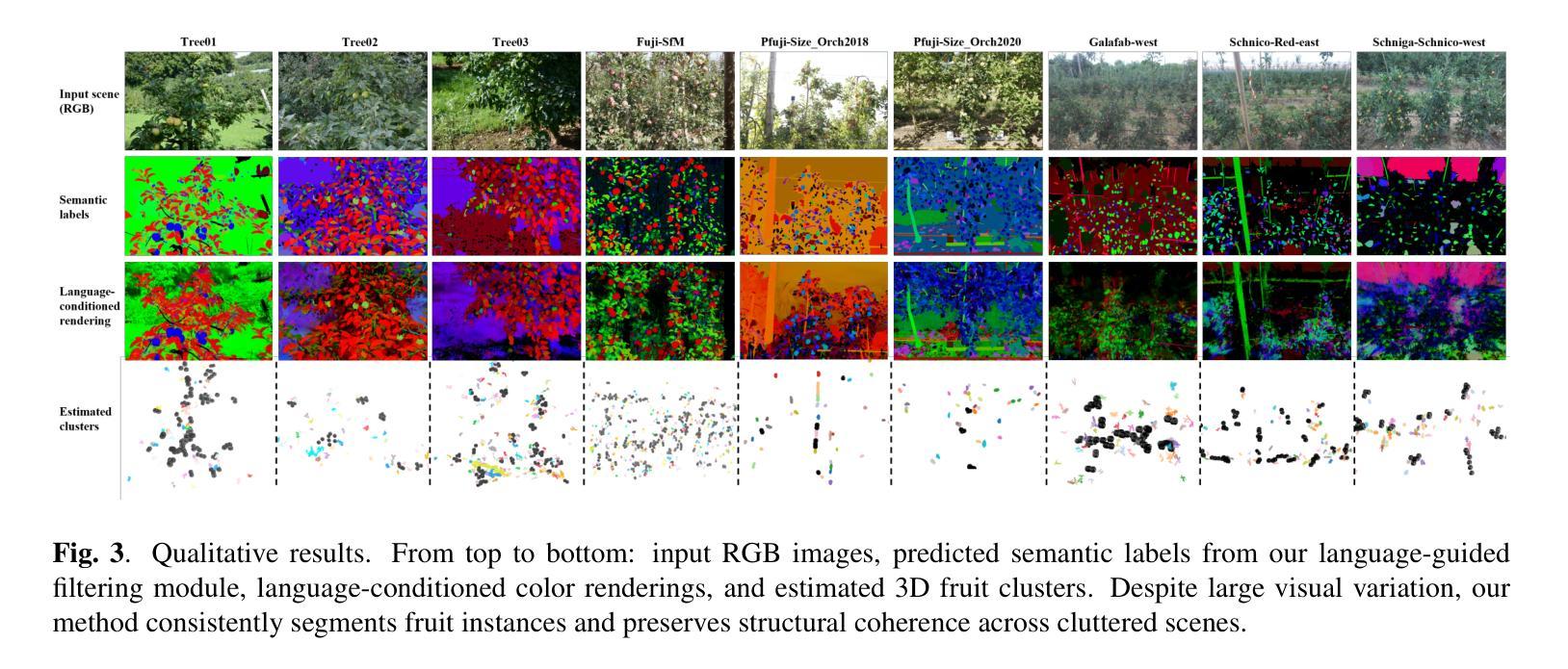
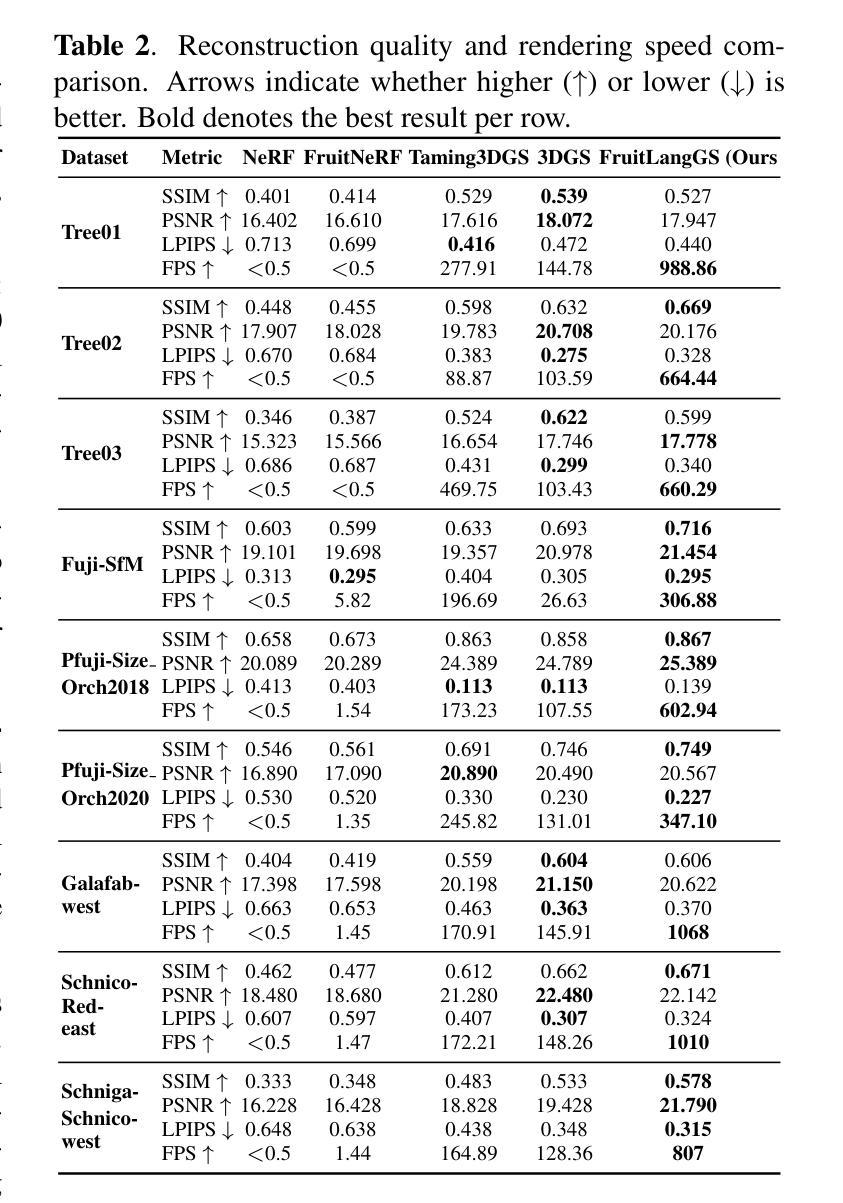
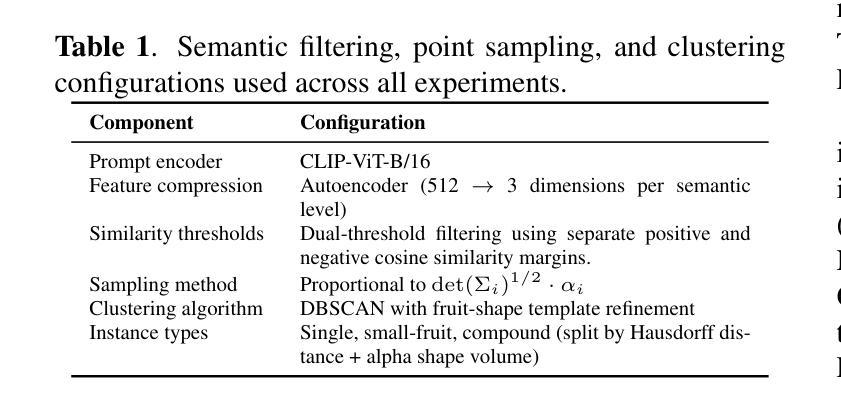
CountingFruit: Language-Guided 3D Fruit Counting with Semantic Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Fengze Li, Yangle Liu, Jieming Ma, Hai-Ning Liang, Yaochun Shen, Huangxiang Li, Zhijing Wu
Accurate 3D fruit counting in orchards is challenging due to heavy occlusion, semantic ambiguity between fruits and surrounding structures, and the high computational cost of volumetric reconstruction. Existing pipelines often rely on multi-view 2D segmentation and dense volumetric sampling, which lead to accumulated fusion errors and slow inference. We introduce FruitLangGS, a language-guided 3D fruit counting framework that reconstructs orchard-scale scenes using an adaptive-density Gaussian Splatting pipeline with radius-aware pruning and tile-based rasterization, enabling scalable 3D representation. During inference, compressed CLIP-aligned semantic vectors embedded in each Gaussian are filtered via a dual-threshold cosine similarity mechanism, retrieving Gaussians relevant to target prompts while suppressing common distractors (e.g., foliage), without requiring retraining or image-space masks. The selected Gaussians are then sampled into dense point clouds and clustered geometrically to estimate fruit instances, remaining robust under severe occlusion and viewpoint variation. Experiments on nine different orchard-scale datasets demonstrate that FruitLangGS consistently outperforms existing pipelines in instance counting recall, avoiding multi-view segmentation fusion errors and achieving up to 99.7% recall on Pfuji-Size_Orch2018 orchard dataset. Ablation studies further confirm that language-conditioned semantic embedding and dual-threshold prompt filtering are essential for suppressing distractors and improving counting accuracy under heavy occlusion. Beyond fruit counting, the same framework enables prompt-driven 3D semantic retrieval without retraining, highlighting the potential of language-guided 3D perception for scalable agricultural scene understanding.
在果园中进行精确的3D水果计数是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为存在严重的遮挡、水果与周围结构之间的语义模糊以及体积重建的高计算成本。现有的流程通常依赖于多视角2D分割和密集的体积采样,这会导致累积的融合误差和缓慢的推理速度。我们引入了FruitLangGS,这是一种语言指导的3D水果计数框架,它使用自适应密度的高斯Splatting管道,结合半径感知修剪和基于瓦片的栅格化,重建果园规模场景,从而实现可扩展的3D表示。在推理过程中,嵌入在每个高斯中的压缩CLIP对齐语义向量通过双阈值余弦相似度机制进行过滤,检索与目标提示相关的高斯,同时抑制常见的干扰因素(例如叶子),而无需进行再训练或图像空间掩膜。然后,所选的高斯被采样为密集的点云,并进行几何聚类以估计水果实例,即使在严重的遮挡和视角变化下也能保持稳健。在九个不同的果园数据集上的实验表明,FruitLangGS在实例计数召回方面始终优于现有流程,避免了多视角分割融合误差,并在Pfuji-Size_Orch2018果园数据集上实现了高达99.7%的召回率。消融研究进一步证实,语言调节的语义嵌入和双阈值提示过滤对于抑制干扰因素和提高遮挡下的计数精度至关重要。除了水果计数之外,同一框架还实现了提示驱动的3D语义检索而无需重新训练,突显了语言指导的3D感知在可扩展的农业场景理解中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为FruitLangGS的语言引导三维水果计数框架,适用于果园场景。它通过自适应密度的高斯Splatting管道进行果园规模场景的重建,并采用基于瓦片的渲染技术,实现了可扩展的三维表示。使用双重阈值余弦相似度机制过滤嵌套的CLIP语义向量,能够准确识别目标提示相关的Gaussians,同时抑制常见的干扰物(如叶子),无需重新训练和图像空间遮罩。在九个不同的果园数据集上的实验表明,FruitLangGS在实例计数召回方面表现出色,避免了多视角分割融合错误,并在Pfuji-Size_Orch2018果园数据集上实现了高达99.7%的召回率。
Key Takeaways
- FruitLangGS是一个语言引导的三维水果计数框架,适用于果园场景的三维感知。
- 通过自适应密度的高斯Splatting管道和基于瓦片的渲染技术,实现了果园规模场景的重建和可扩展的三维表示。
- 使用双重阈值余弦相似度机制过滤嵌套的CLIP语义向量,能够准确识别目标水果,同时抑制干扰物的影响。
- 在多个果园数据集上的实验表明,FruitLangGS在实例计数召回方面优于现有管道,避免了多视角分割融合错误。
- FruitLangGS在Pfuji-Size_Orch2018数据集上实现了高达99.7%的召回率。
- 框架中的语言条件语义嵌入和双重阈值提示过滤对于抑制干扰物和提高计数准确性至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

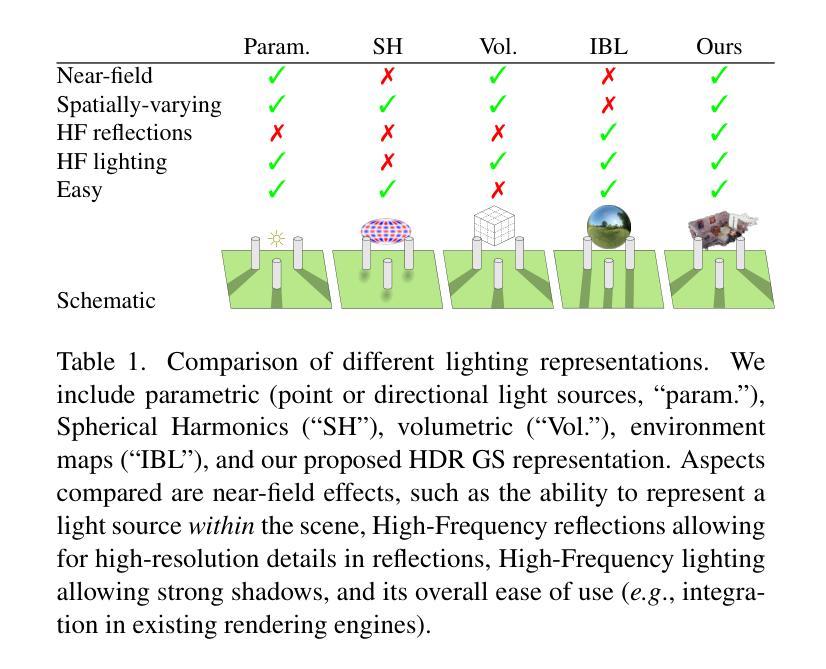
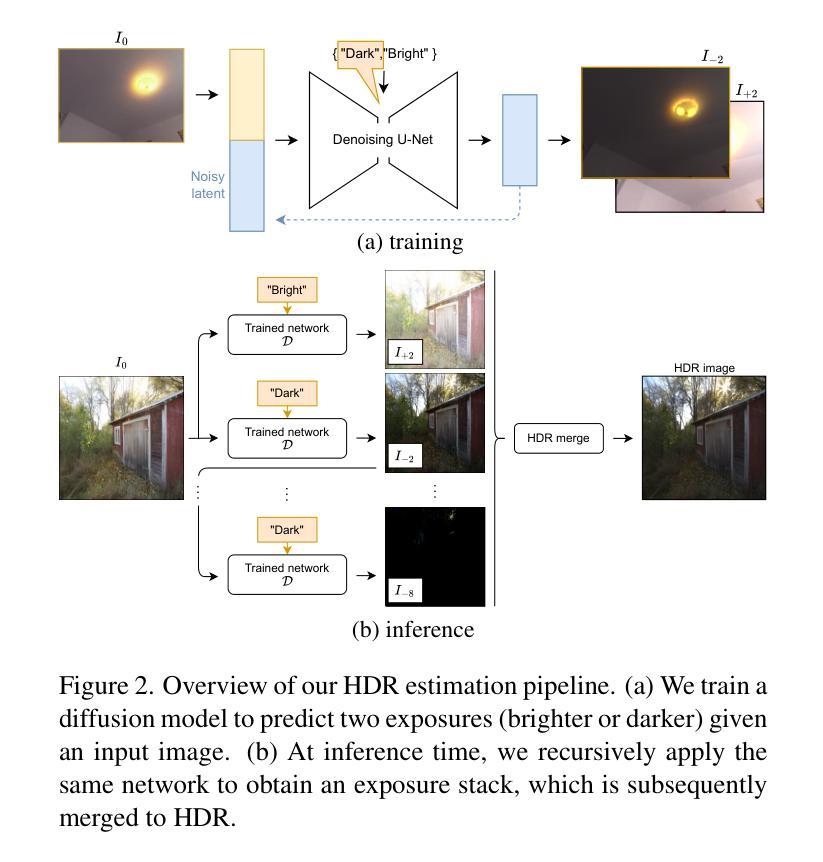
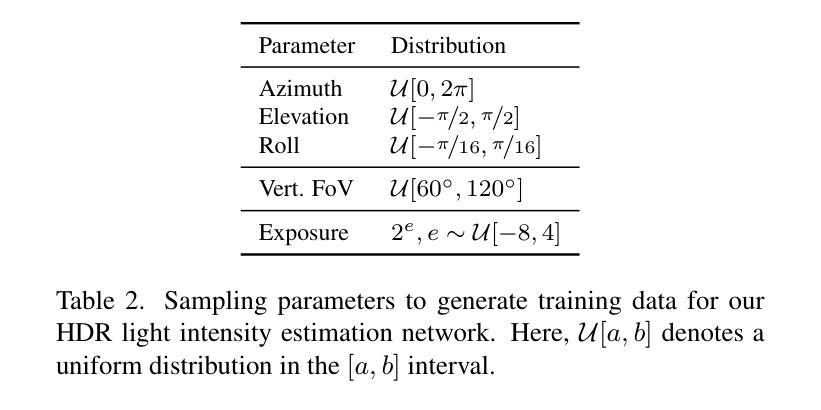
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. Project page: https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的照明。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯斑点作为光源表示,这是首次使得常规图像可以在3D渲染器中作为光源使用。我们的两阶段过程首先通过利用扩散模型中嵌入的先验知识来增强图像的动态范围,从而以合理和准确的方式实现这一目标。接下来,我们使用高斯斑点对3D照明进行建模,实现空间变化照明。我们的方法在HDR估算及其在虚拟对象和场景的照明应用方面产生了最先进的结果。为了对图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这个新数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。项目页面:https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GaSLight方法能够通过常规图像生成空间变化的光照。该方法首次提出使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,利用扩散模型的先验知识增强图像动态范围,并通过高斯Splats对三维光照进行建模,实现空间变化的光照效果。该方法在HDR估算及其虚拟对象和场景的照明应用方面达到了最新水平。为了评估图像作为光源的基准测试,我们引入了一个新型校准不饱和HDR数据集。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法利用常规图像生成空间变化的光照。
- 首次使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示。
- 利用扩散模型的先验知识增强图像动态范围。
- 通过高斯Splats对三维光照进行建模。
- 方法在HDR估算方面达到最新水平。
- 引入了新型校准不饱和HDR数据集,用于评估图像作为光源的效果。
点此查看论文截图

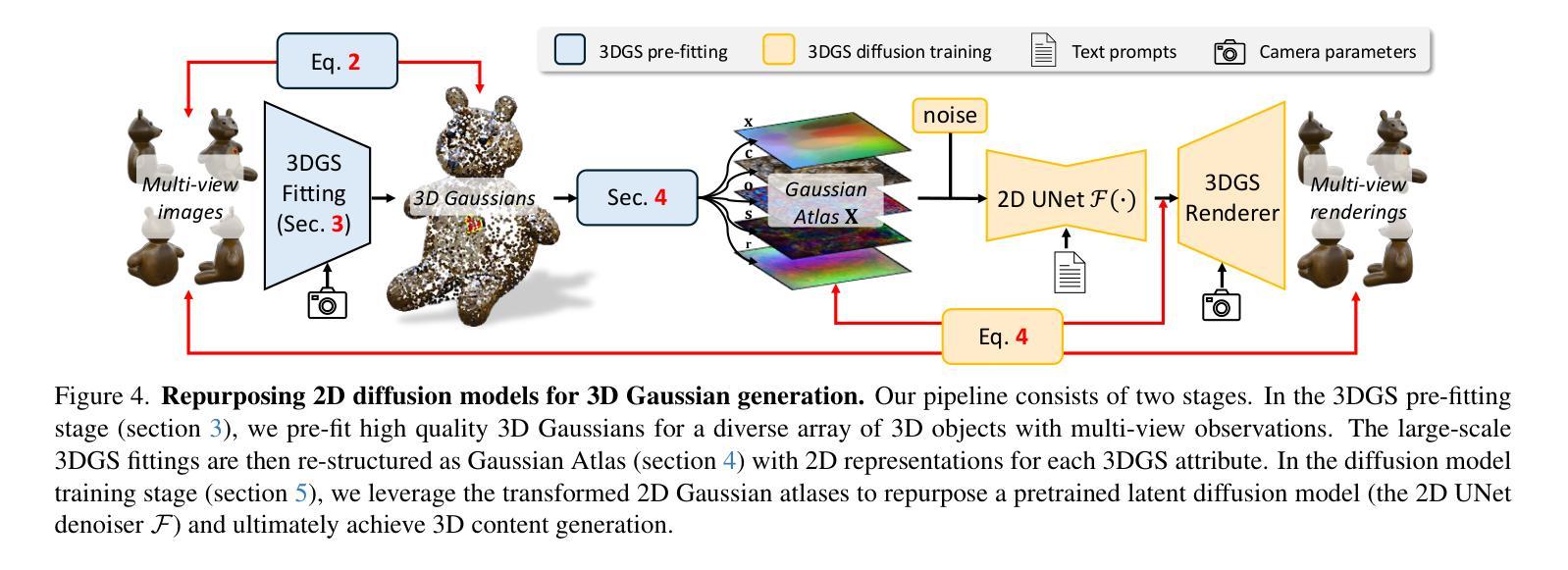
Repurposing 2D Diffusion Models with Gaussian Atlas for 3D Generation
Authors:Tiange Xiang, Kai Li, Chengjiang Long, Christian Häne, Peihong Guo, Scott Delp, Ehsan Adeli, Li Fei-Fei
Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have been driven by the increasing availability of paired 2D data. However, the development of 3D diffusion models has been hindered by the scarcity of high-quality 3D data, resulting in less competitive performance compared to their 2D counterparts. To address this challenge, we propose repurposing pre-trained 2D diffusion models for 3D object generation. We introduce Gaussian Atlas, a novel representation that utilizes dense 2D grids, enabling the fine-tuning of 2D diffusion models to generate 3D Gaussians. Our approach demonstrates successful transfer learning from a pre-trained 2D diffusion model to a 2D manifold flattened from 3D structures. To support model training, we compile GaussianVerse, a large-scale dataset comprising 205K high-quality 3D Gaussian fittings of various 3D objects. Our experimental results show that text-to-image diffusion models can be effectively adapted for 3D content generation, bridging the gap between 2D and 3D modeling.
最近文本到图像扩散模型的进步得益于二维数据配对的日益普及。然而,由于缺乏高质量的三维数据,三维扩散模型的发展受到了阻碍,导致其性能不如二维模型具有竞争力。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出将预训练的二维扩散模型重新用于三维对象生成。我们引入了高斯地图(Gaussian Atlas),这是一种新型表示方法,它利用密集二维网格,实现对二维扩散模型的微调以生成三维高斯数据。我们的方法成功实现了从预训练的二维扩散模型到由三维结构展平的二维流形上的迁移学习。为了支持模型训练,我们编译了GaussianVerse数据集,该数据集包含20万多个高质量的三维高斯拟合的各类三维物体样本。我们的实验结果表明,文本到图像的扩散模型可以有效地适应三维内容生成,弥合了二维和三维建模之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
针对三维扩散模型发展受限于高质量三维数据稀缺的问题,提出利用预训练的二维扩散模型进行三维物体生成。引入高斯图谱表示方法,利用密集二维网格实现二维扩散模型的微调以生成三维高斯数据。为支持模型训练,编译大规模数据集GaussianVerse,包含20.5万高质量三维高斯拟合数据。实验结果显示,文本到图像扩散模型可有效地适应三维内容生成,缩小了二维和三维建模之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量三维数据的稀缺限制了三维扩散模型的发展。
- 提出利用预训练的二维扩散模型进行三维物体生成的方法。
- 引入高斯图谱作为新的表示方法,利用密集二维网格实现模型微调。
- 编译大规模数据集GaussianVerse以支持模型训练。
- 实验证明文本到图像扩散模型可适应三维内容生成。
- 这种方法成功实现了从二维到三维建模的过渡。
点此查看论文截图



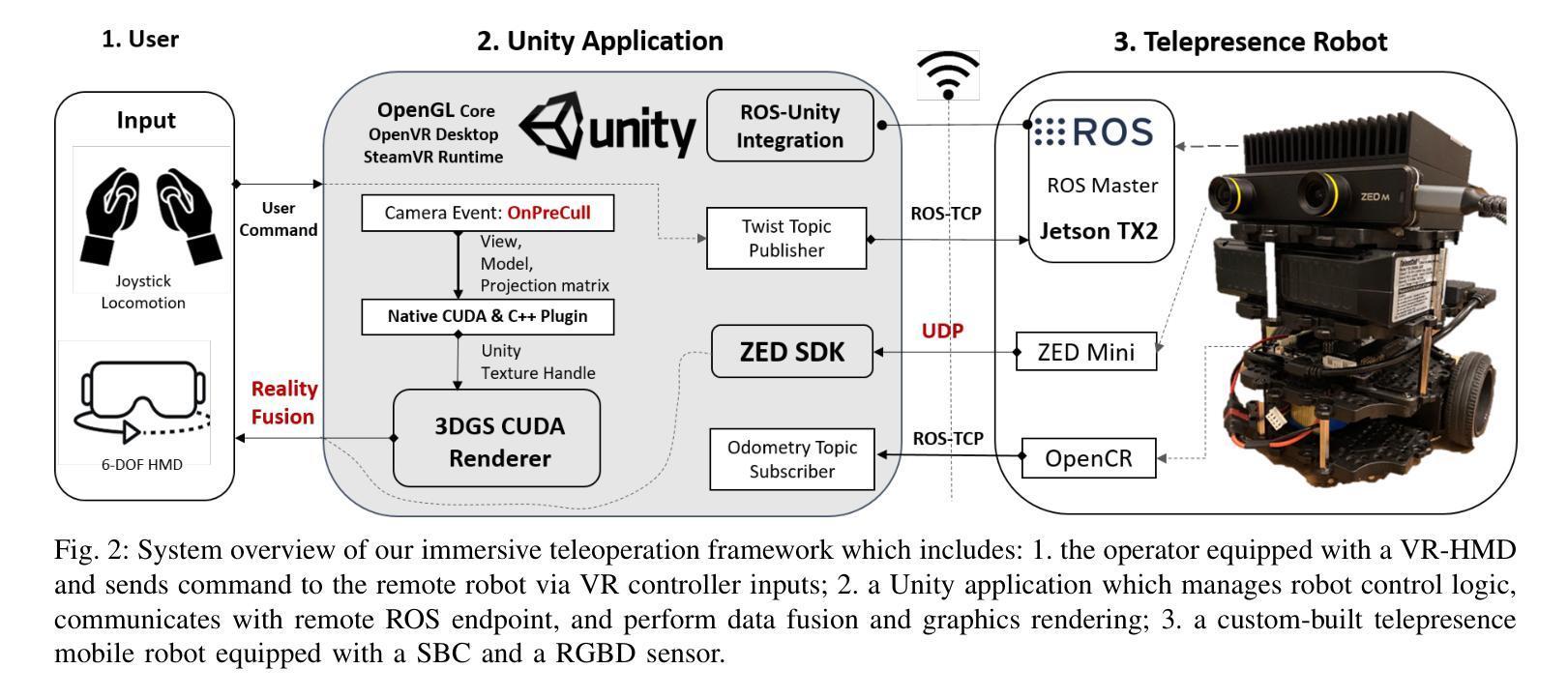
Reality Fusion: Robust Real-time Immersive Mobile Robot Teleoperation with Volumetric Visual Data Fusion
Authors:Ke Li, Reinhard Bacher, Susanne Schmidt, Wim Leemans, Frank Steinicke
We introduce Reality Fusion, a novel robot teleoperation system that localizes, streams, projects, and merges a typical onboard depth sensor with a photorealistic, high resolution, high framerate, and wide field of view (FoV) rendering of the complex remote environment represented as 3D Gaussian splats (3DGS). Our framework enables robust egocentric and exocentric robot teleoperation in immersive VR, with the 3DGS effectively extending spatial information of a depth sensor with limited FoV and balancing the trade-off between data streaming costs and data visual quality. We evaluated our framework through a user study with 24 participants, which revealed that Reality Fusion leads to significantly better user performance, situation awareness, and user preferences. To support further research and development, we provide an open-source implementation with an easy-to-replicate custom-made telepresence robot, a high-performance virtual reality 3DGS renderer, and an immersive robot control package. (Source code: https://github.com/uhhhci/RealityFusion)
我们介绍了 Reality Fusion,这是一个新型机器人遥操作系系统,它能定位、传输、投影,并将典型的机载深度传感器与复杂远程环境的以高斯三元分布渲染出的超现实主义、高分辨率、高帧率和大视野图像合并。我们的框架能够在沉浸式虚拟现实中进行稳健的自我中心和非自我中心的机器人遥操作,以三元分布有效地扩展具有有限视野的深度传感器的空间信息,并平衡数据流成本和数据视觉质量之间的权衡。我们通过一项有 24 名参与者进行的研究评估发现,Realty Fusion 能够显著提高用户性能、情境意识和用户偏好。为了支持进一步的研究和开发,我们提供了一个开源实现方案,包括易于复制的定制遥控机器人、高性能虚拟现实三元分布渲染器以及沉浸式机器人控制套件。(源代码:https://github.com/uhhhci/RealtyFusion)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IROS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了名为“现实融合”的新型机器人遥控系统,该系统结合了车载深度传感器与复杂远程环境的三维高斯斑点渲染技术,实现了在虚拟现实中的稳健自主式和异向式机器人遥控操作。现实融合系统扩展了深度传感器的空间信息,平衡了数据流成本和视觉质量,提高了用户性能、情境感知和用户偏好。系统提供开源实现,包含易于复制的遥现场机器人、高性能虚拟现实三维高斯斑点渲染器和沉浸式机器人控制包。
Key Takeaways
- Reality Fusion是一个新型机器人遥控系统,结合了深度传感器与三维高斯斑点渲染技术。
- 系统能够实现自主式和异向式机器人遥控操作,扩展了深度传感器的空间信息。
- 现实融合系统平衡数据流成本和视觉质量,提高用户性能、情境感知和用户偏好。
- 系统支持开源实现,包含易于复制的遥现场机器人和虚拟现实渲染器。
- 通过用户研究验证了系统的有效性和优势。
- 系统包含高性能的虚拟现实三维高斯斑点渲染器。
点此查看论文截图