⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
GAP: Gaussianize Any Point Clouds with Text Guidance
Authors:Weiqi Zhang, Junsheng Zhou, Haotian Geng, Wenyuan Zhang, Yu-Shen Liu
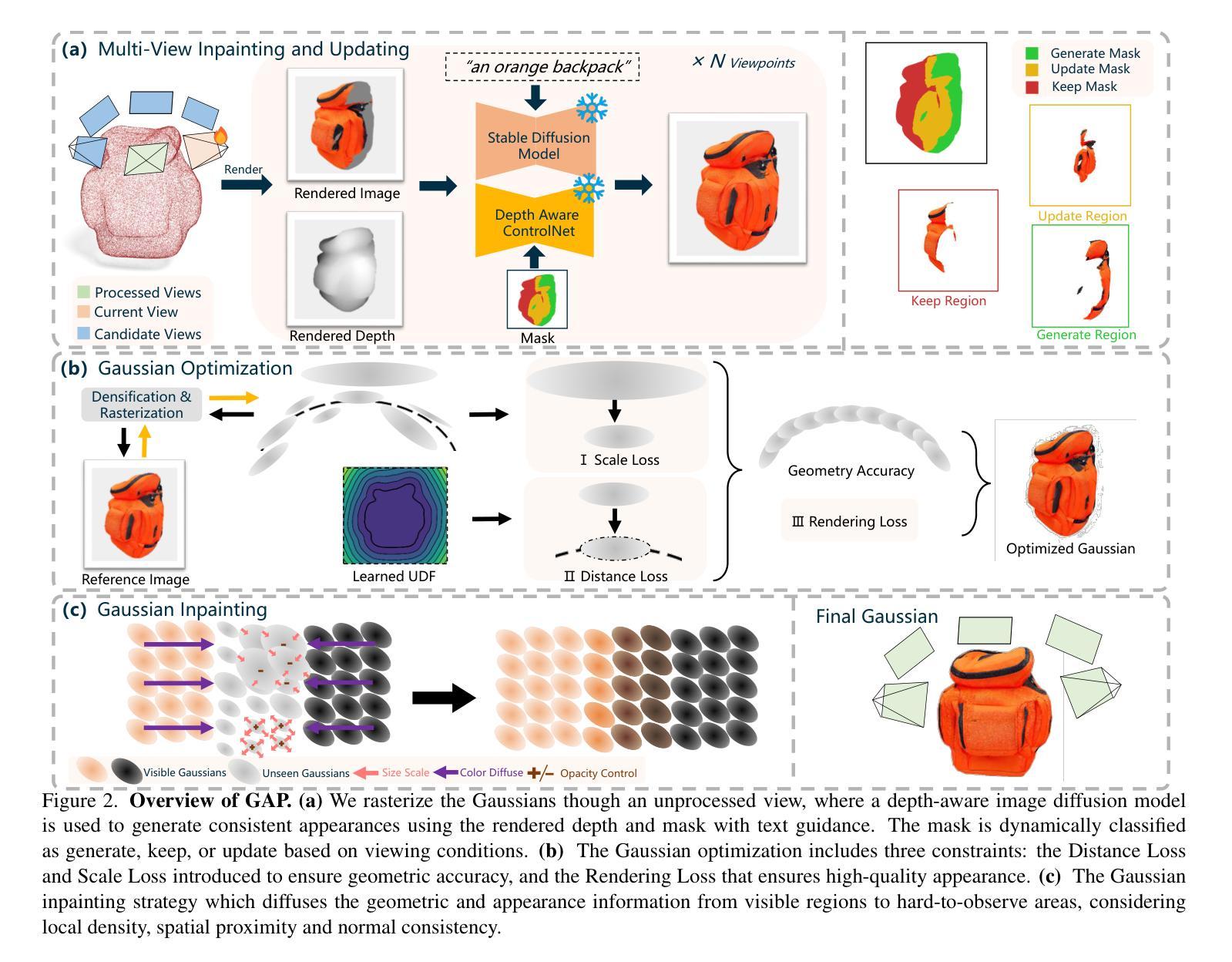
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated its advantages in achieving fast and high-quality rendering. As point clouds serve as a widely-used and easily accessible form of 3D representation, bridging the gap between point clouds and Gaussians becomes increasingly important. Recent studies have explored how to convert the colored points into Gaussians, but directly generating Gaussians from colorless 3D point clouds remains an unsolved challenge. In this paper, we propose GAP, a novel approach that gaussianizes raw point clouds into high-fidelity 3D Gaussians with text guidance. Our key idea is to design a multi-view optimization framework that leverages a depth-aware image diffusion model to synthesize consistent appearances across different viewpoints. To ensure geometric accuracy, we introduce a surface-anchoring mechanism that effectively constrains Gaussians to lie on the surfaces of 3D shapes during optimization. Furthermore, GAP incorporates a diffuse-based inpainting strategy that specifically targets at completing hard-to-observe regions. We evaluate GAP on the Point-to-Gaussian generation task across varying complexity levels, from synthetic point clouds to challenging real-world scans, and even large-scale scenes. Project Page: https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP.
3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)已经显示出其在实现快速高质量渲染方面的优势。由于点云作为广泛使用和易于获取的三维表示形式,弥点云和高斯之间的差距变得越来越重要。近来的研究已经探索了如何将彩色点转换为高斯,但从无颜色的三维点云中直接生成高斯仍是一个未解决的难题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新方法GAP,通过文本指导将原始点云转化为高保真三维高斯。我们的核心思想设计了一个多视角优化框架,利用深度感知图像扩散模型来合成不同视角下的连续外观。为确保几何精度,我们引入了一种表面锚定机制,有效地约束高斯在优化过程中位于三维形状的表面上。此外,GAP还融入了基于扩散的填充策略,特别专注于完成难以观察的区域。我们在点云到高斯生成任务上评估了GAP,涵盖了不同复杂度级别,从合成点云到具有挑战性的真实世界扫描,甚至大规模场景。项目页面:https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://weiqi-zhang.github.io/GAP
Summary
本文提出一种名为GAP的新方法,可将原始点云转化为高保真度3D高斯分布,并引入文本指导。通过设计多视角优化框架并利用深度感知图像扩散模型合成不同视角下的外观一致性,保证几何精度,解决从无色彩点云直接生成高斯分布的难题。同时,GAP采用基于扩散的填充策略,特别针对难以观测的区域进行补全。评估结果显示,GAP在点云到高斯生成任务中表现优异,适用于不同复杂度的场景。
Key Takeaways
- GAP方法能将原始点云转化为高保真度3D高斯分布。
- 提出了一种多视角优化框架,利用深度感知图像扩散模型合成不同视角下的外观一致性。
- 通过引入表面锚定机制,确保几何精度并约束高斯在3D形状表面。
- GAP采用基于扩散的填充策略,针对难以观测的区域进行补全。
- GAP在点云到高斯生成任务上表现优异,适用于从合成点云到真实世界扫描等多种场景。
- 该方法对于大规模场景同样有效。
点此查看论文截图


UNCAGE: Contrastive Attention Guidance for Masked Generative Transformers in Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Wonjun Kang, Byeongkeun Ahn, Minjae Lee, Kevin Galim, Seunghyuk Oh, Hyung Il Koo, Nam Ik Cho
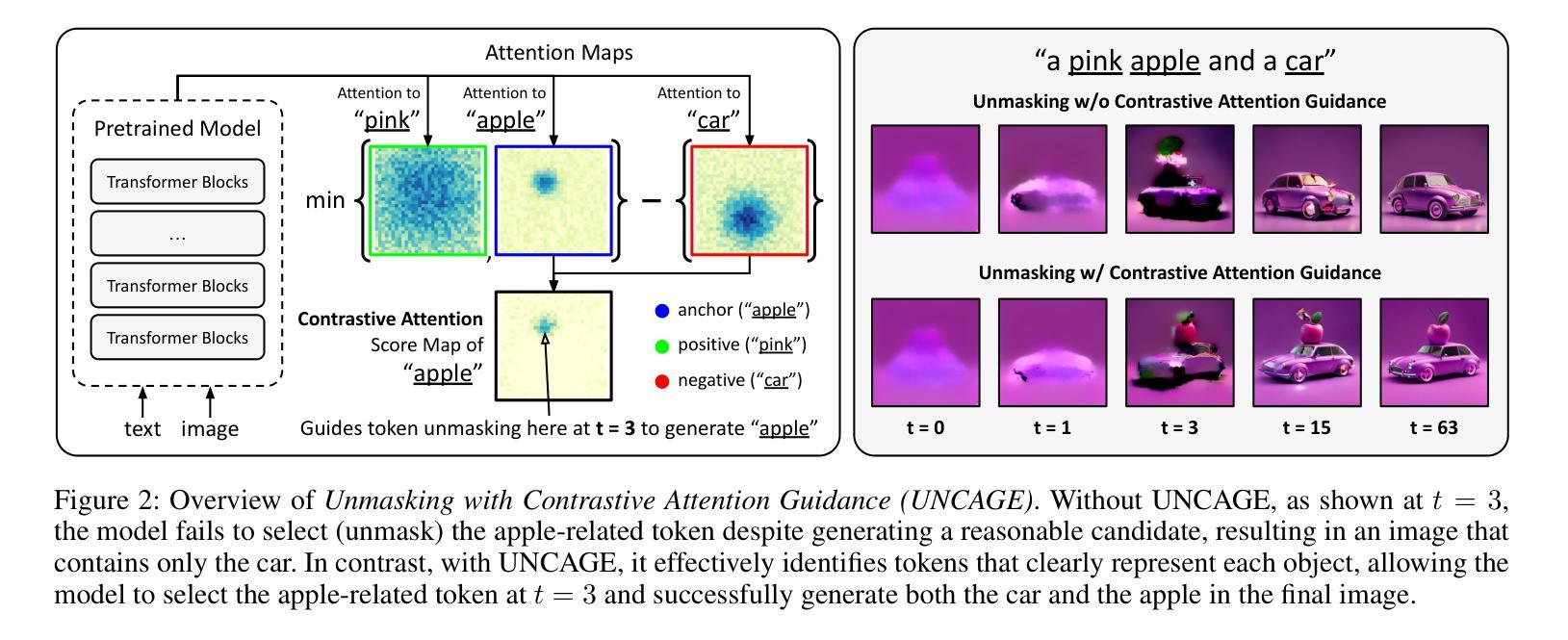
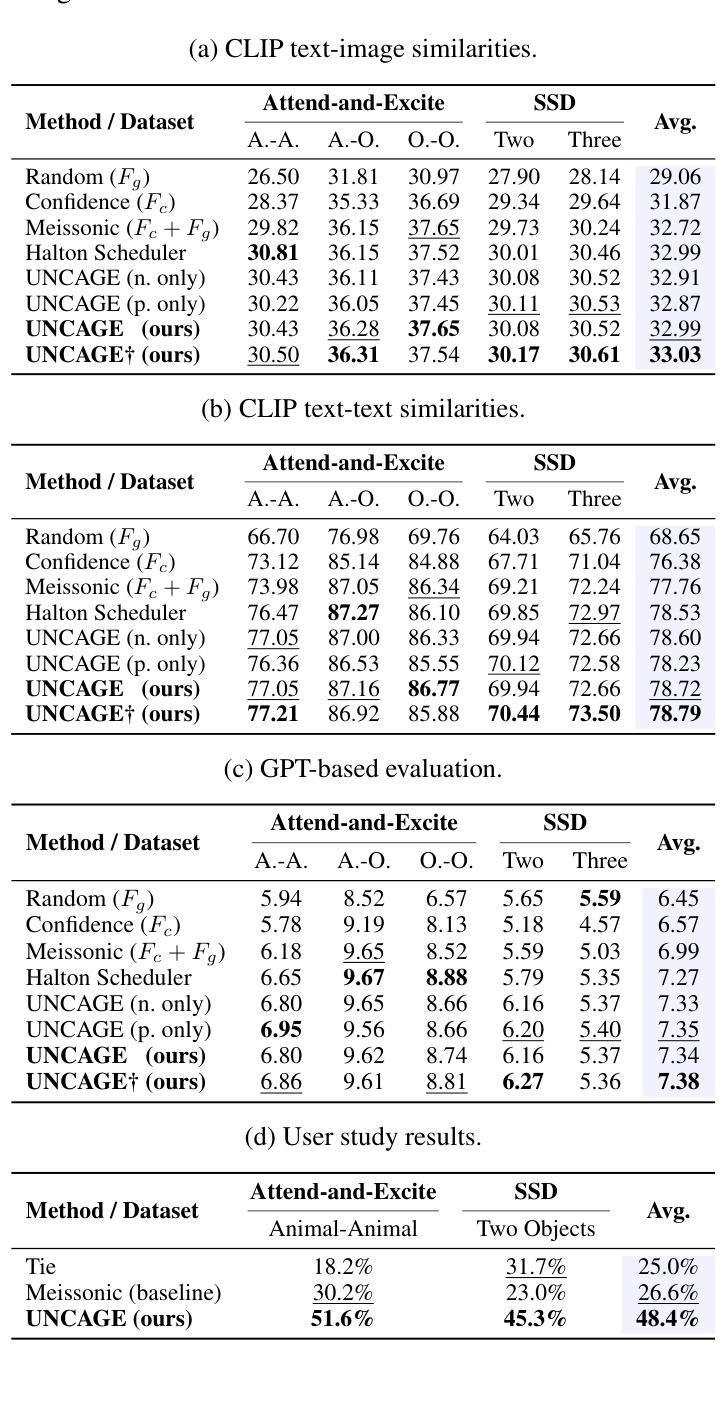
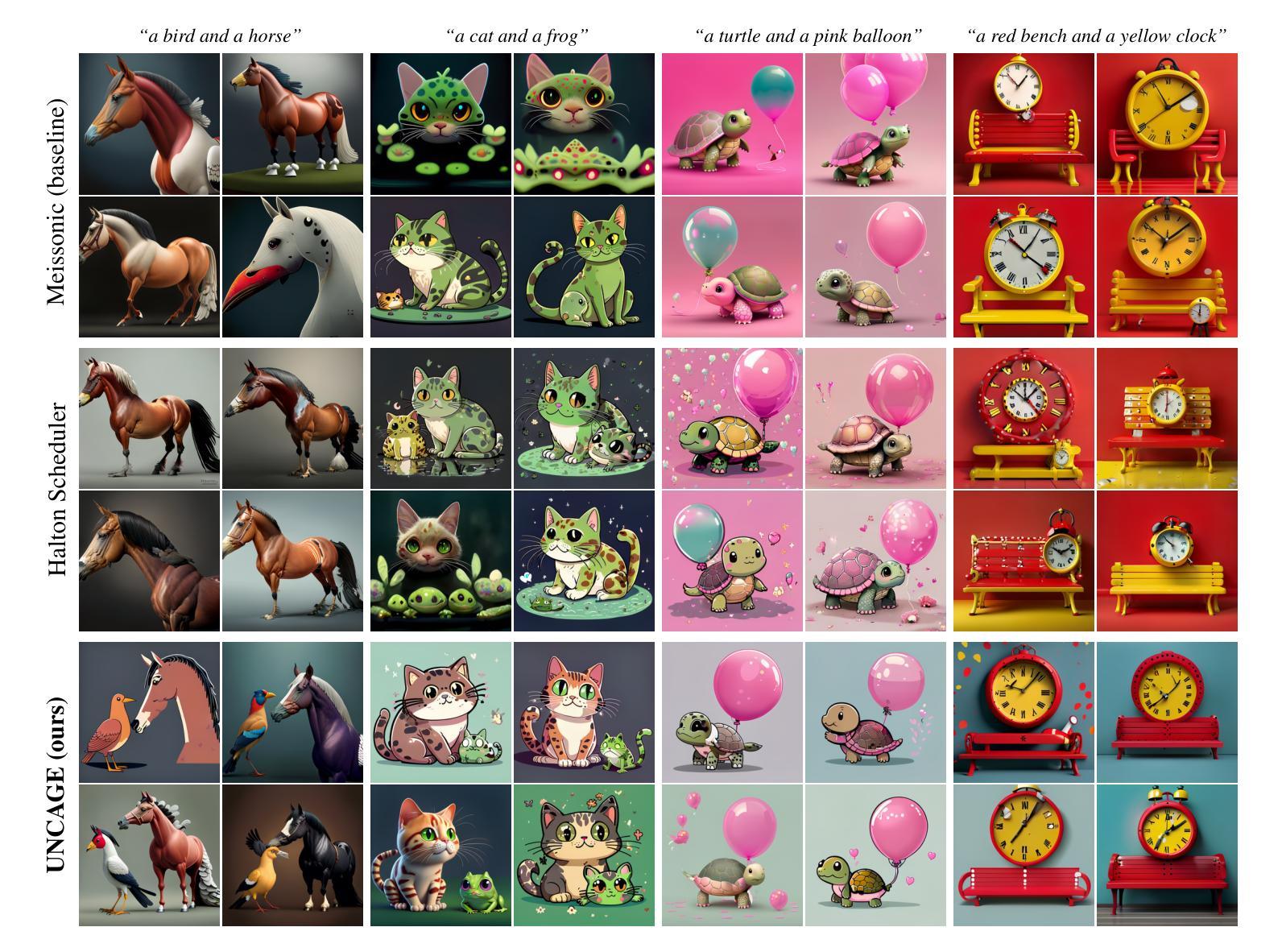
Text-to-image (T2I) generation has been actively studied using Diffusion Models and Autoregressive Models. Recently, Masked Generative Transformers have gained attention as an alternative to Autoregressive Models to overcome the inherent limitations of causal attention and autoregressive decoding through bidirectional attention and parallel decoding, enabling efficient and high-quality image generation. However, compositional T2I generation remains challenging, as even state-of-the-art Diffusion Models often fail to accurately bind attributes and achieve proper text-image alignment. While Diffusion Models have been extensively studied for this issue, Masked Generative Transformers exhibit similar limitations but have not been explored in this context. To address this, we propose Unmasking with Contrastive Attention Guidance (UNCAGE), a novel training-free method that improves compositional fidelity by leveraging attention maps to prioritize the unmasking of tokens that clearly represent individual objects. UNCAGE consistently improves performance in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations across multiple benchmarks and metrics, with negligible inference overhead. Our code is available at https://github.com/furiosa-ai/uncage.
文本到图像(T2I)生成已经使用扩散模型和自回归模型进行了深入研究。最近,作为自回归模型的替代品,遮罩生成式Transformer通过双向注意力和并行解码克服了因果注意力和自回归解码的固有局限性,从而引起了人们的关注,并能够实现高效高质量的图像生成。然而,组合式T2I生成仍然具有挑战性,因为即使是最先进的扩散模型也经常无法准确绑定属性并实现适当的文本-图像对齐。虽然扩散模型针对这一问题已经得到了广泛研究,但遮罩生成式Transformer也表现出类似的局限性,但尚未在此上下文中得到探索。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了无训练方法“解除遮罩与对比注意力引导”(UNCAGE),它通过利用注意力图来优先解除代表单个对象的标记的遮罩,从而提高组合保真度。UNCAGE在多个基准测试和指标下始终提高了定量和定性评估的性能,且推理开销微乎其微。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/furiosa-ai/uncage 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/furiosa-ai/uncage
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)生成是Diffusion Models和Autoregressive Models研究的热点。近期,Masked Generative Transformers克服了Autoregressive Models的一些局限性,能够实现双向注意力和平行解码的高效率和高质量图像生成。尽管Diffusion Models面临将属性准确绑定和实现文本-图像适当对齐的挑战,而针对这个问题的解决策略“Unmasking with Contrastive Attention Guidance”(UNCAGE)能有效提高组合保真度,利用注意力图优先解掩那些明确代表单个对象的标记。UNCAGE在不同基准测试和各种评价指标中的定量和定性评价都表现出一致性改进,且推理开销微乎其微。我们的代码可在furiosa-ai/uncage获取。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Models和Autoregressive Models在文本到图像生成领域受到关注。
- Masked Generative Transformers作为替代Autoregressive Models的方法而受到关注,因其可实现高效且高质量的图像生成。
- 即使是最先进的Diffusion Models也面临准确绑定属性和实现适当文本-图像对齐的挑战。
- Masked Generative Transformers在解决此问题上也有类似局限性,尚未在这一背景下被探索。
- 提出了名为UNCAGE的新方法,这是一种无需训练的策略,通过利用注意力图来提高组合保真度。
- UNCAGE在不同基准测试和多指标评估中都表现优异,且推理开销小。
点此查看论文截图

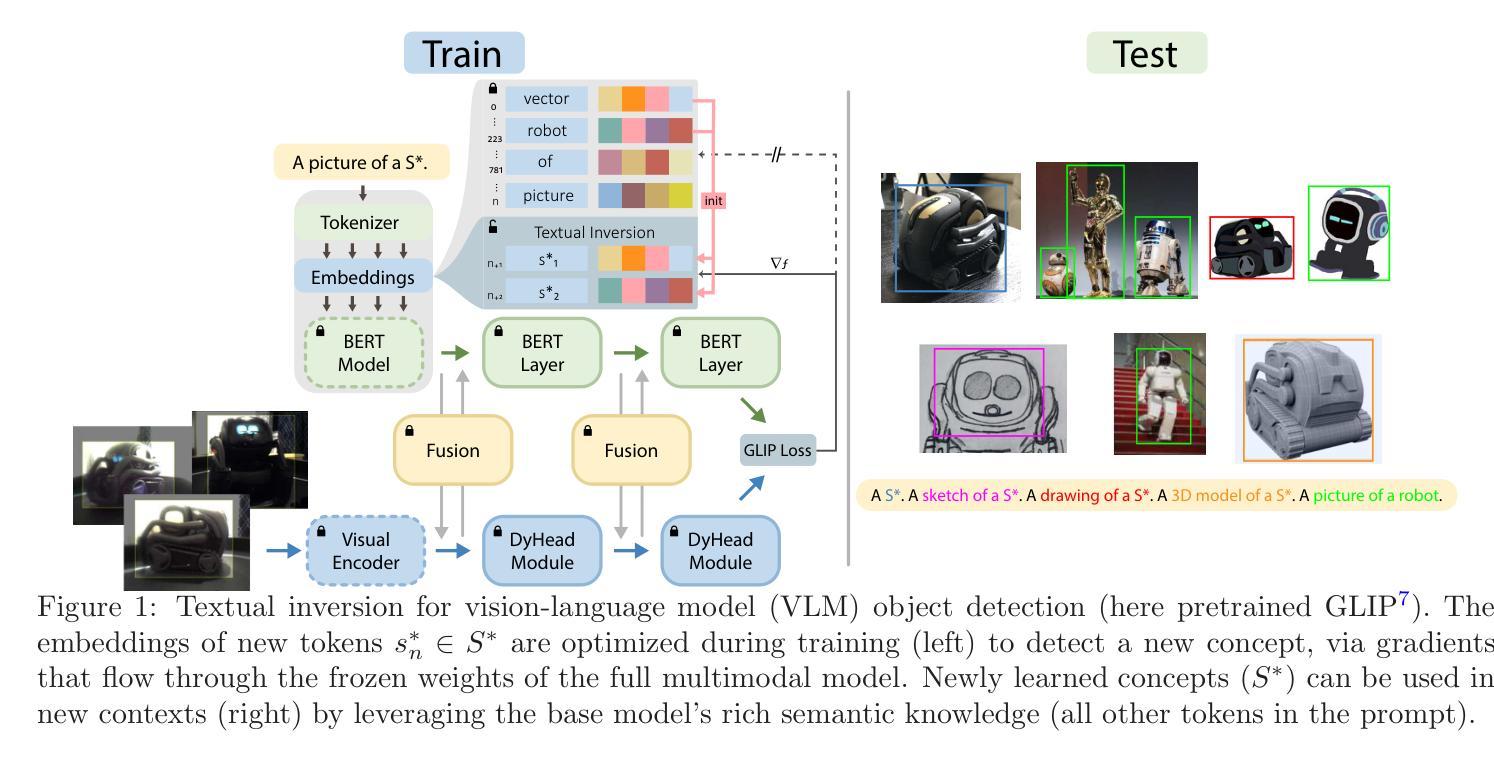
Textual Inversion for Efficient Adaptation of Open-Vocabulary Object Detectors Without Forgetting
Authors:Frank Ruis, Gertjan Burghouts, Hugo Kuijf
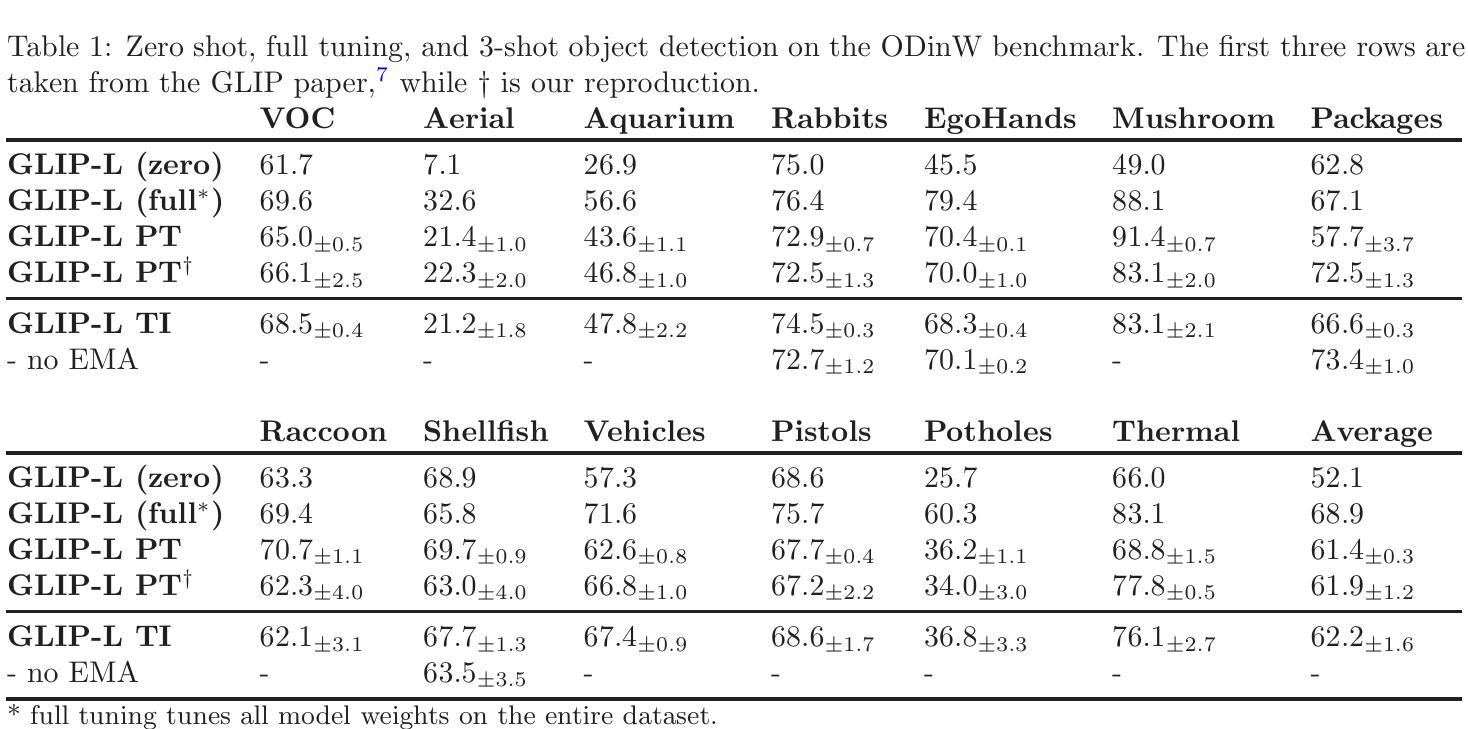
Recent progress in large pre-trained vision language models (VLMs) has reached state-of-the-art performance on several object detection benchmarks and boasts strong zero-shot capabilities, but for optimal performance on specific targets some form of finetuning is still necessary. While the initial VLM weights allow for great few-shot transfer learning, this usually involves the loss of the original natural language querying and zero-shot capabilities. Inspired by the success of Textual Inversion (TI) in personalizing text-to-image diffusion models, we propose a similar formulation for open-vocabulary object detection. TI allows extending the VLM vocabulary by learning new or improving existing tokens to accurately detect novel or fine-grained objects from as little as three examples. The learned tokens are completely compatible with the original VLM weights while keeping them frozen, retaining the original model’s benchmark performance, and leveraging its existing capabilities such as zero-shot domain transfer (e.g., detecting a sketch of an object after training only on real photos). The storage and gradient calculations are limited to the token embedding dimension, requiring significantly less compute than full-model fine-tuning. We evaluated whether the method matches or outperforms the baseline methods that suffer from forgetting in a wide variety of quantitative and qualitative experiments.
关于大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)的最新进展已经在多个目标检测基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,并具备强大的零样本能力。然而,为了在特定目标上获得最佳性能,仍需要进行某种形式的微调。虽然初始的VLM权重允许进行出色的少样本迁移学习,但这通常涉及到原始自然语言查询和零样本能力的损失。受文本反转(TI)在个性化文本到图像扩散模型中的成功的启发,我们为开放词汇表目标检测提出了类似的解决方案。TI允许通过学习新令牌或改进现有令牌来扩展VLM词汇表,从而仅从三个示例中准确检测出新颖或细粒度对象。所学习的令牌与原始VLM权重完全兼容,同时保持冻结状态,保留了原始模型的基准测试性能,并利用了其现有功能,如零样本域迁移(例如,在仅对真实照片进行训练后检测对象的草图)。存储和梯度计算仅限于令牌嵌入维度,因此所需的计算量远小于全模型微调。我们通过多种定量和定性实验评估了该方法是否匹配或优于基线方法,这些方法在广泛的任务中会出现遗忘问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)的最新进展已在多个目标检测基准测试中达到最先进的性能,并具备强大的零样本能力。虽然初始VLM权重允许很好的少样本迁移学习,但为了特定目标的最佳性能仍需要进行微调。本文受文本反转(TI)在个性化文本到图像扩散模型的成功的启发,提出了一种用于开放词汇表目标检测的类似方法。TI通过学习新令牌或改进现有令牌来精确检测从仅三个示例中的新颖或细粒度对象,从而扩展VLM词汇量。所学令牌与原始VLM权重完全兼容,同时保持冻结状态,保留原始模型的基准测试性能,并利用其现有功能,如零样本域转移。存储和梯度计算仅限于令牌嵌入维度,这需要比全模型微调少得多的计算量。经过广泛定量和定性实验评估,该方法能否达到或超越基线方法,这些方法会遭受遗忘的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)在目标检测方面表现出卓越的性能,尤其是零样本能力。
- 虽然初始VLM权重具有出色的迁移学习能力,但仍需微调以优化特定目标的性能。
- 受文本反转(TI)在个性化文本到图像扩散模型中的成功的启发,提出了一种新的用于开放词汇表目标检测的方法。
- TI通过扩展VLM词汇量来精确检测新颖或细粒度对象,只需少量示例即可学习新令牌或改进现有令牌。
- 所学令牌与原始VLM权重兼容,同时保留其性能并充分利用现有功能(如零样本域转移)。
- 存储和梯度计算集中在令牌嵌入维度,降低了计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

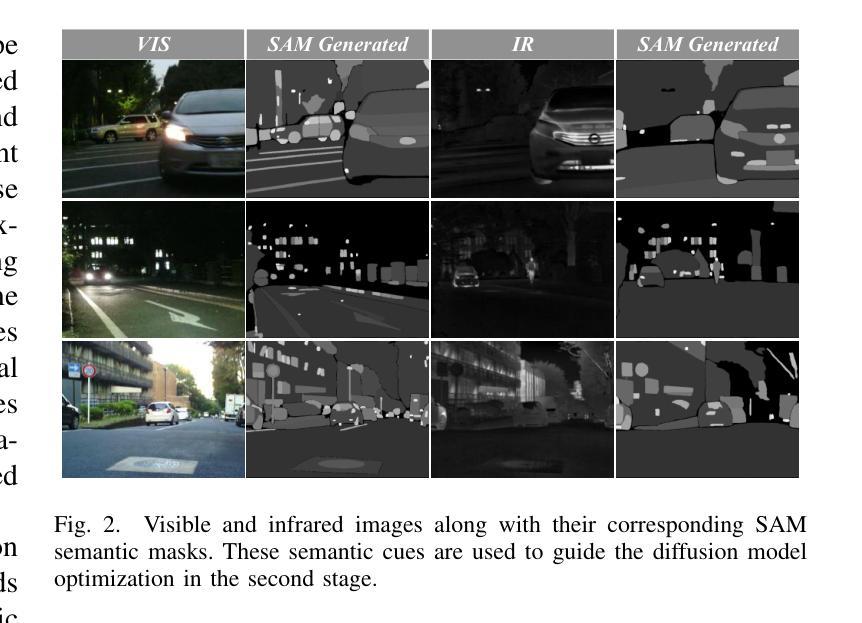
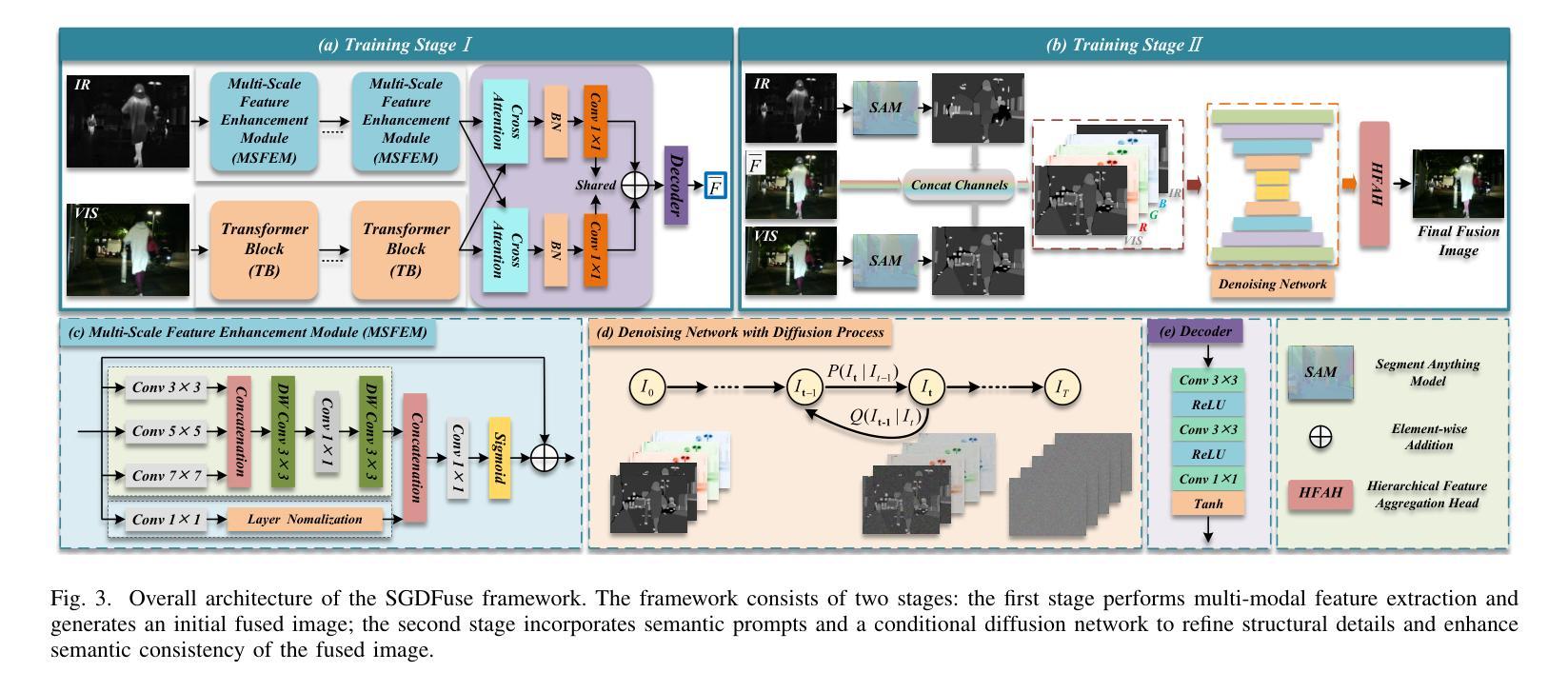
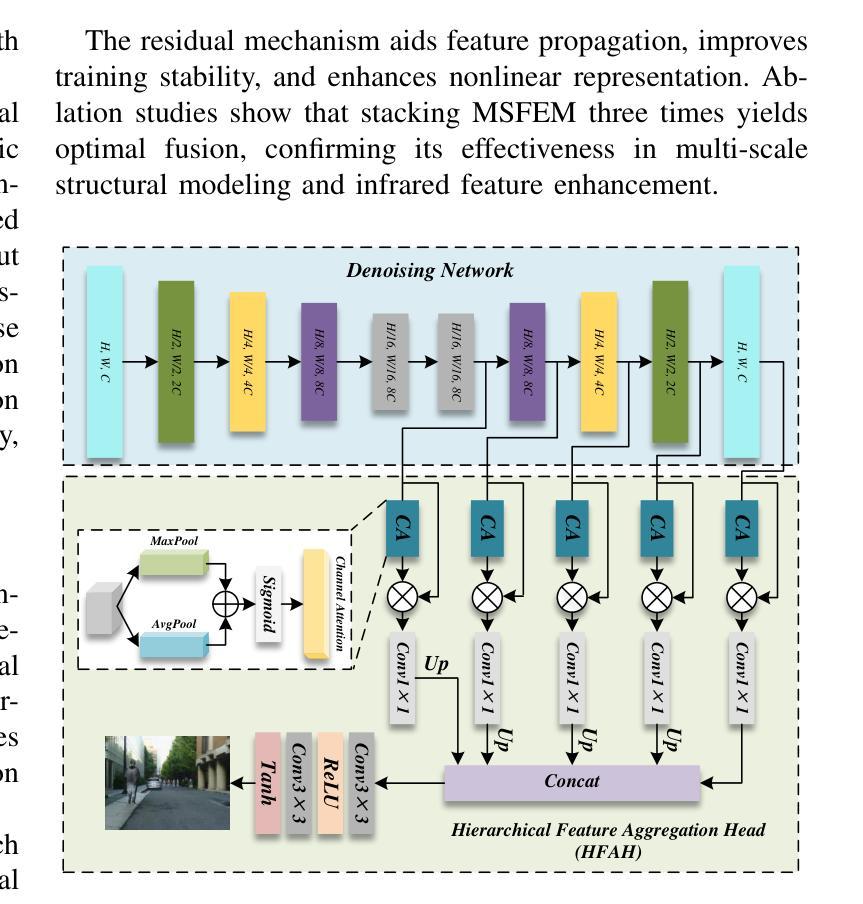
SGDFuse: SAM-Guided Diffusion for High-Fidelity Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Authors:Xiaoyang Zhang, Zhen Hua, Yakun Ju, Wei Zhou, Jun Liu, Alex C. Kot
Infrared and visible image fusion (IVIF) aims to combine the thermal radiation information from infrared images with the rich texture details from visible images to enhance perceptual capabilities for downstream visual tasks. However, existing methods often fail to preserve key targets due to a lack of deep semantic understanding of the scene, while the fusion process itself can also introduce artifacts and detail loss, severely compromising both image quality and task performance. To address these issues, this paper proposes SGDFuse, a conditional diffusion model guided by the Segment Anything Model (SAM), to achieve high-fidelity and semantically-aware image fusion. The core of our method is to utilize high-quality semantic masks generated by SAM as explicit priors to guide the optimization of the fusion process via a conditional diffusion model. Specifically, the framework operates in a two-stage process: it first performs a preliminary fusion of multi-modal features, and then utilizes the semantic masks from SAM jointly with the preliminary fused image as a condition to drive the diffusion model’s coarse-to-fine denoising generation. This ensures the fusion process not only has explicit semantic directionality but also guarantees the high fidelity of the final result. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SGDFuse achieves state-of-the-art performance in both subjective and objective evaluations, as well as in its adaptability to downstream tasks, providing a powerful solution to the core challenges in image fusion. The code of SGDFuse is available at https://github.com/boshizhang123/SGDFuse.
红外与可见光图像融合(IVIF)旨在将红外图像中的热辐射信息与可见光图像中的丰富纹理细节相结合,以提高下游视觉任务的感知能力。然而,现有方法往往由于缺乏场景的深度语义理解而无法保留关键目标,同时融合过程本身也可能引入伪影和细节损失,严重损害图像质量和任务性能。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了SGDFuse,一个由Segment Anything Model(SAM)引导的条件扩散模型,实现高保真和语义感知的图像融合。我们的方法的核心是利用SAM生成的高质量语义掩膜作为明确先验,通过条件扩散模型指导融合过程的优化。具体来说,该框架采用两阶段过程:首先进行多模态特征的初步融合,然后利用SAM的语义掩膜与初步融合图像作为条件,驱动扩散模型的从粗到细的降噪生成。这确保融合过程不仅具有明确的语义方向性,而且还保证最终结果的高保真度。大量实验表明,SGDFuse在主观和客观评估以及适应下游任务方面均达到最佳性能,为解决图像融合的核心挑战提供了强大的解决方案。SGDFuse的代码可在https://github.com/boshizhang123/SGDFuse获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to TCSVT
Summary
红外与可见图像融合(IVIF)结合了红外图像的热辐射信息与可见图像的丰富纹理细节,以提高下游视觉任务的感知能力。然而,现有方法由于缺乏深度场景语义理解,常常无法保留关键目标,同时融合过程本身也可能引入伪影和细节损失,严重影响图像质量和任务性能。为解决这些问题,本文提出SGDFuse方法,采用以Segment Anything Model(SAM)为指导的条件扩散模型,实现高保真和语义感知的图像融合。该方法利用SAM生成的高质量语义掩膜作为显式先验,指导融合过程的优化。实验表明,SGDFuse在主观和客观评估以及下游任务适应性方面均达到最佳性能,为解决图像融合的核心挑战提供了强大解决方案。
**Key Takeaways**
1. 红外与可见图像融合(IVIF)结合了红外图像与可见图像的信息,以提高视觉任务的感知能力。
2. 现有图像融合方法存在无法保留关键目标的问题,且融合过程可能引入伪影和细节损失。
3. SGDFuse方法采用条件扩散模型,结合语义理解来实现图像融合。
4. SGDFuse利用SAM生成的高质量语义掩膜来指导融合过程的优化,确保融合结果的高保真和语义感知。
5. SGDFuse在主观和客观评估方面均达到最佳性能,并具有良好的下游任务适应性。
6. SGDFuse的代码已公开可用。
7. 条件扩散模型在图像融合领域具有潜在的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图


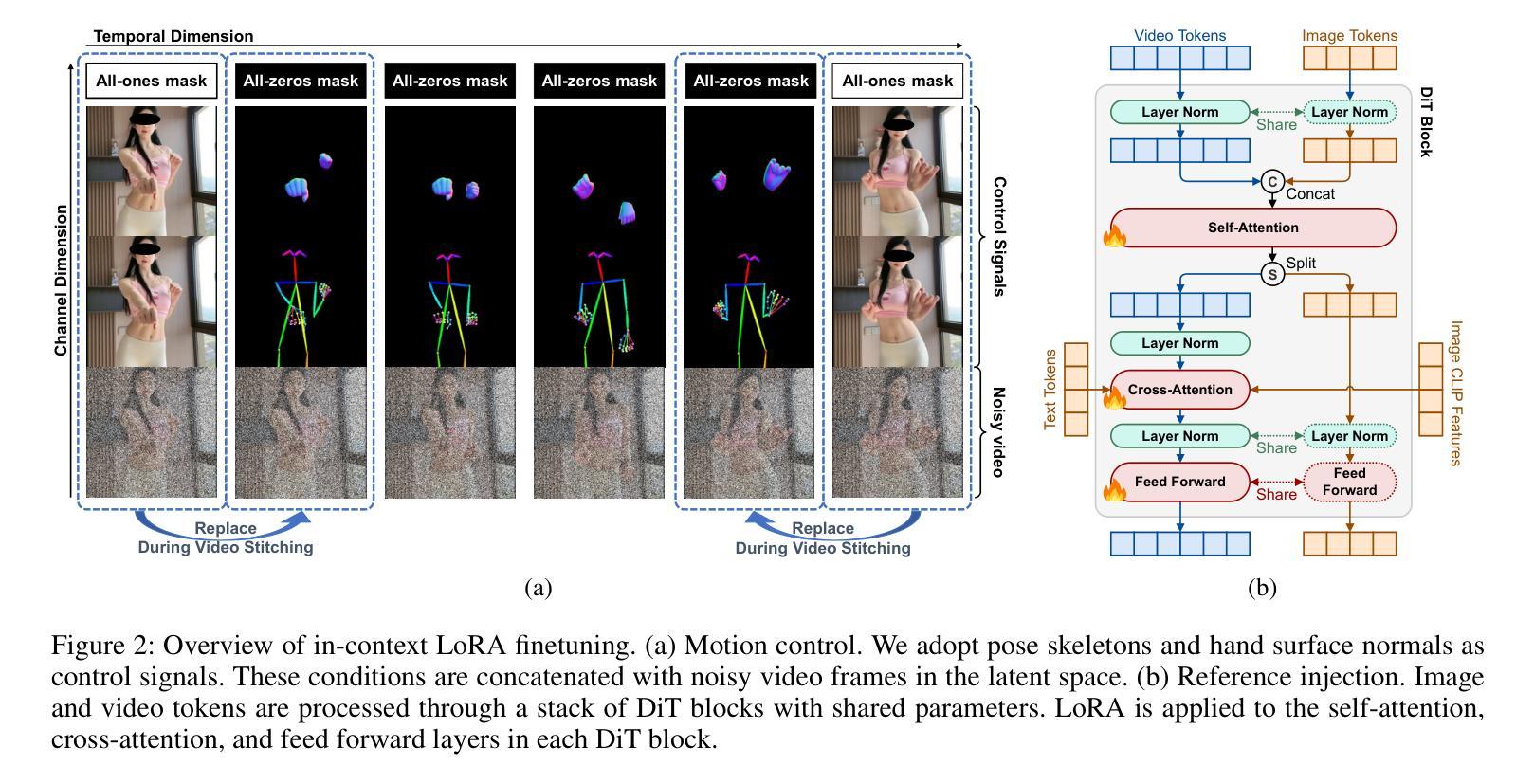
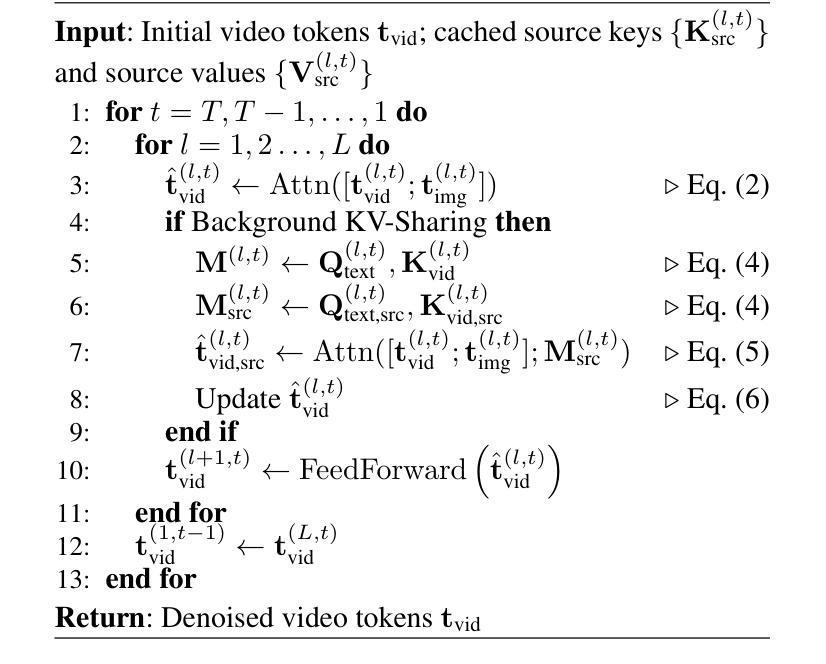
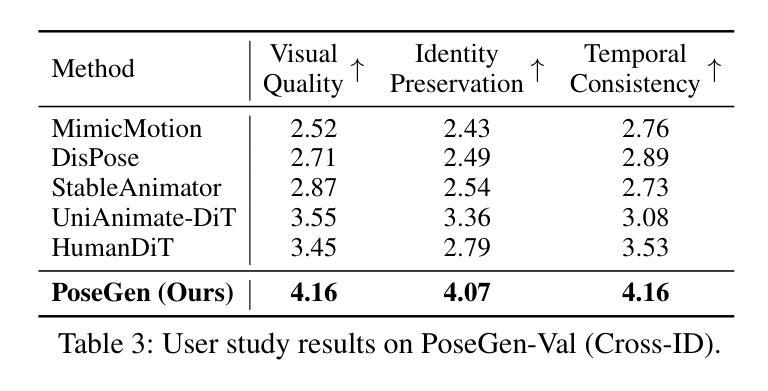
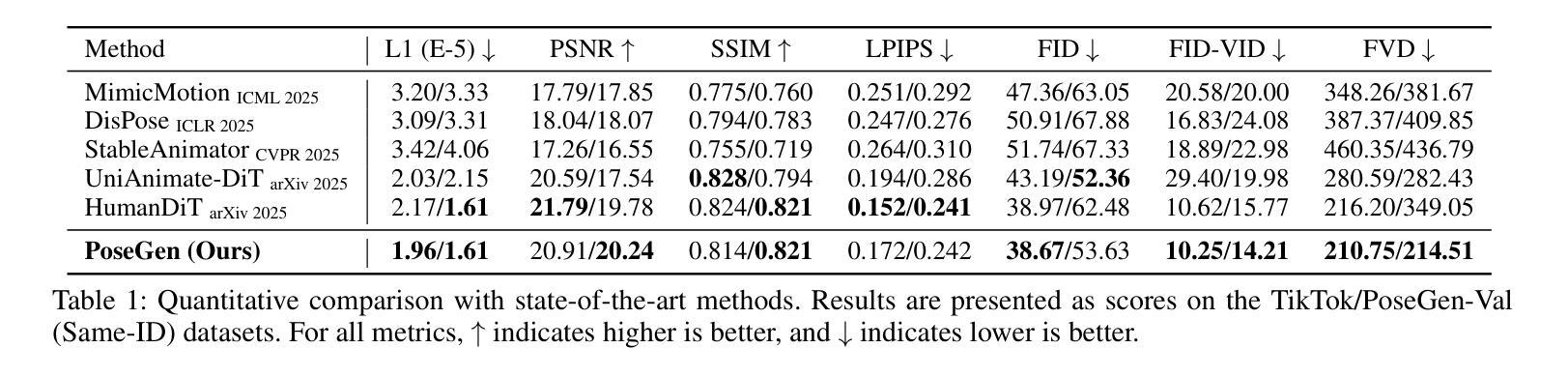
PoseGen: In-Context LoRA Finetuning for Pose-Controllable Long Human Video Generation
Authors:Jingxuan He, Busheng Su, Finn Wong
Generating long, temporally coherent videos with precise control over subject identity and motion is a formidable challenge for current diffusion models, which often suffer from identity drift and are limited to short clips. We introduce PoseGen, a novel framework that generates arbitrarily long videos of a specific subject from a single reference image and a driving pose sequence. Our core innovation is an in-context LoRA finetuning strategy that injects subject appearance at the token level for identity preservation, while simultaneously conditioning on pose information at the channel level for fine-grained motion control. To overcome duration limits, PoseGen pioneers an interleaved segment generation method that seamlessly stitches video clips together, using a shared KV cache mechanism and a specialized transition process to ensure background consistency and temporal smoothness. Trained on a remarkably small 33-hour video dataset, extensive experiments show that PoseGen significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in identity fidelity, pose accuracy, and its unique ability to produce coherent, artifact-free videos of unlimited duration.
生成具有精确控制主体身份和运动的长视频对于当前的扩散模型来说是一项艰巨的挑战,这些模型经常面临身份漂移的问题,并且仅限于短片。我们引入了PoseGen,一个从单个参考图像和驱动姿态序列生成特定主题任意长度视频的新型框架。我们的核心创新之处在于提出了一种上下文感知的LoRA微调策略,该策略在令牌级别注入主体外观以实现身份保留,同时在通道级别同时处理姿态信息以实现精细运动控制。为了克服持续时间限制,PoseGen开创了一种交替分段生成方法,该方法无缝地拼接视频片段,并使用共享的KV缓存机制和专门的过渡过程以确保背景一致性和时间平滑性。在令人惊讶的仅33小时的视频数据集上进行训练,大量实验表明,PoseGen在身份保真度、姿态准确性和其产生连贯、无瑕疵的无限时长视频的独特能力方面显著优于最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PoseGen框架通过单张参考图像和动态姿态序列生成特定主体的任意长度视频。其创新的核心是上下文LoRA微调策略,能够在令牌级别注入主体外观以实现身份保留,同时以通道级别处理姿态信息以实现精细运动控制。PoseGen通过采用交织段生成方法来突破时长限制,并依靠共享的KV缓存机制和特殊的过渡流程来确保背景的一致性和时间连续性。实验证明PoseGen显著提高了身份保真度、姿态准确度和在生成连贯无伪造的任意时长视频上的独特能力。PoseGen只在少量的数据集上进行训练便达到强大的效果,大大提升了扩散模型的能力边界。总的来说,PoseGen是扩散模型领域的一个重大突破。
Key Takeaways
- PoseGen框架可以从单张参考图像和姿态序列生成特定主体的任意长度视频。
- 采用创新的上下文LoRA微调策略,实现了身份保留和精细运动控制。
- 通过交织段生成方法突破时长限制,生成连贯的视频片段。
- 使用共享的KV缓存机制和过渡流程确保背景一致性和时间连续性。
- PoseGen在身份保真度、姿态准确度等方面显著优于现有方法。具备独特的无限时长视频生成能力。在有限的数据集上训练表现出了强大的性能提升扩散模型能力边界的重要进展。
点此查看论文截图


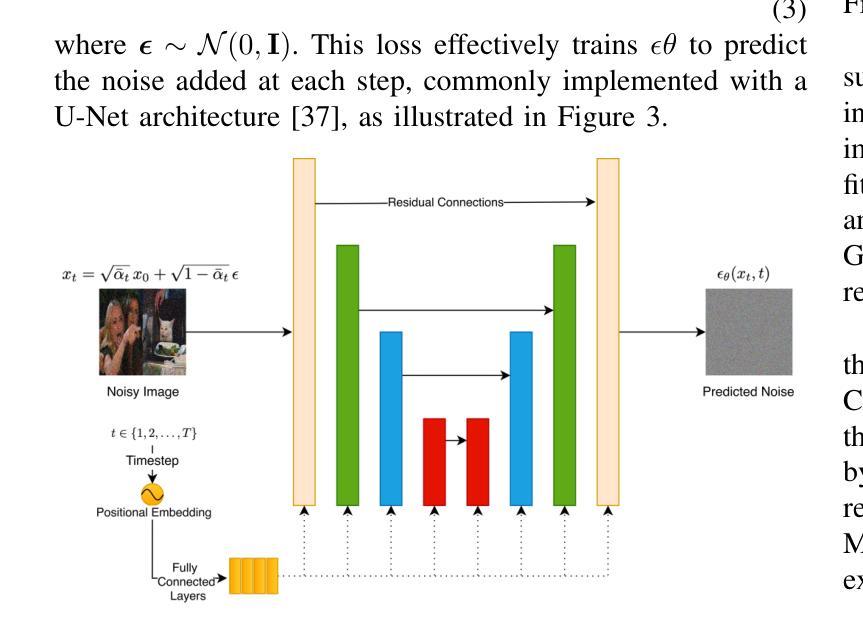
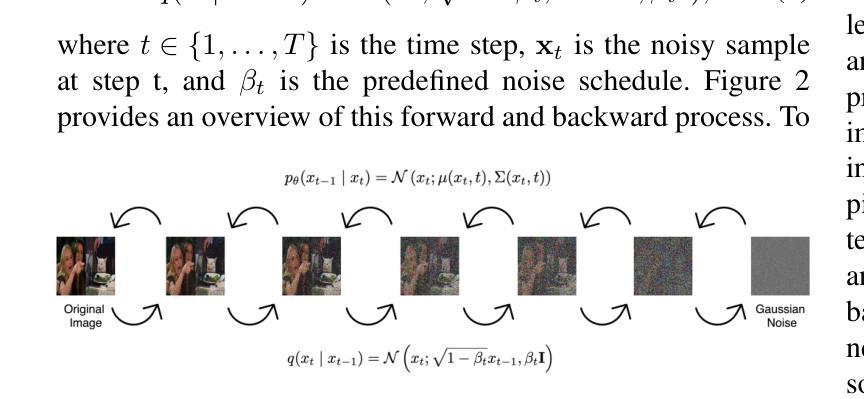
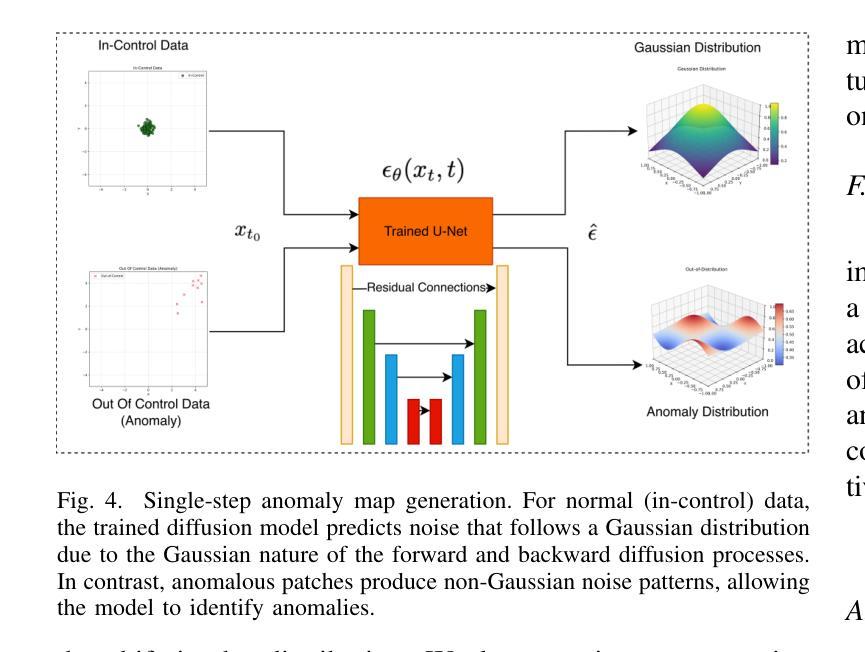
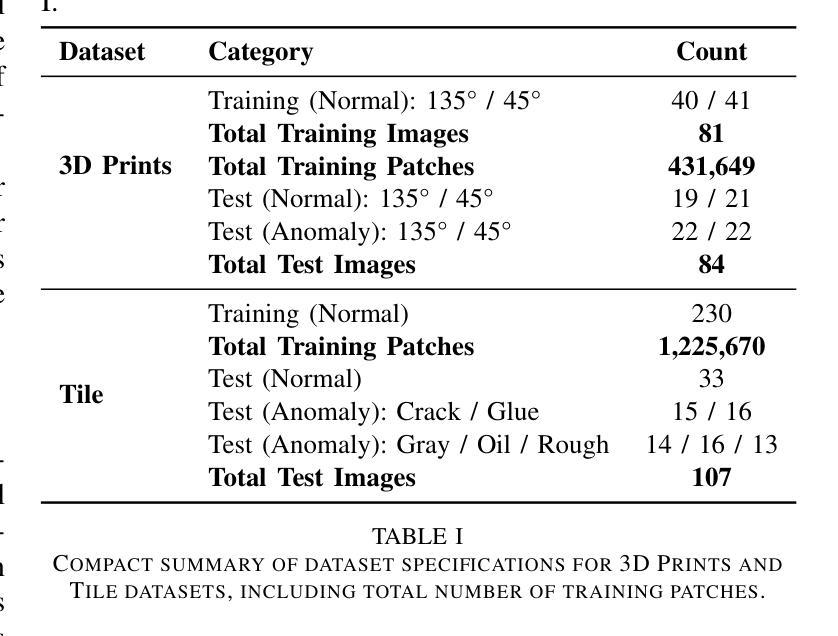
Single-Step Reconstruction-Free Anomaly Detection and Segmentation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Mehrdad Moradi, Marco Grasso, Bianca Maria Colosimo, Kamran Paynabar
Generative models have demonstrated significant success in anomaly detection and segmentation over the past decade. Recently, diffusion models have emerged as a powerful alternative, outperforming previous approaches such as GANs and VAEs. In typical diffusion-based anomaly detection, a model is trained on normal data, and during inference, anomalous images are perturbed to a predefined intermediate step in the forward diffusion process. The corresponding normal image is then reconstructed through iterative reverse sampling. However, reconstruction-based approaches present three major challenges: (1) the reconstruction process is computationally expensive due to multiple sampling steps, making real-time applications impractical; (2) for complex or subtle patterns, the reconstructed image may correspond to a different normal pattern rather than the original input; and (3) Choosing an appropriate intermediate noise level is challenging because it is application-dependent and often assumes prior knowledge of anomalies, an assumption that does not hold in unsupervised settings. We introduce Reconstruction-free Anomaly Detection with Attention-based diffusion models in Real-time (RADAR), which overcomes the limitations of reconstruction-based anomaly detection. Unlike current SOTA methods that reconstruct the input image, RADAR directly produces anomaly maps from the diffusion model, improving both detection accuracy and computational efficiency. We evaluate RADAR on real-world 3D-printed material and the MVTec-AD dataset. Our approach surpasses state-of-the-art diffusion-based and statistical machine learning models across all key metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Specifically, RADAR improves F1 score by 7% on MVTec-AD and 13% on the 3D-printed material dataset compared to the next best model. Code available at: https://github.com/mehrdadmoradi124/RADAR
生成模型在过去十年中在异常检测和分割方面取得了显著的成功。最近,扩散模型作为一种强大的替代方法崭露头角,超越了诸如GAN和VAE等先前的方法。在典型的基于扩散的异常检测中,模型会在正常数据上进行训练,然后在推理过程中,异常图像会被扰动到前向扩散过程的预定中间步骤。然后通过迭代反向采样重建相应的正常图像。然而,基于重建的方法存在三个主要挑战:(1)由于多次采样步骤,重建过程计算成本高昂,使得实时应用不切实际;(2)对于复杂或微妙的模式,重建的图像可能对应于不同的正常模式,而非原始输入;(3)选择适当的中间噪声水平具有挑战性,因为它取决于应用,并且经常假设对异常的先验知识,这在无监督设置中并不成立。我们引入了基于注意力扩散模型的实时无重建异常检测(RADAR),克服了基于重建的异常检测的局限性。与当前顶尖方法不同,RADAR直接从扩散模型中生成异常映射,提高了检测准确性和计算效率。我们在现实世界的3D打印材料和MVTec-AD数据集上评估了RADAR。我们的方法在所有关键指标上超越了最先进的扩散模型和统计机器学习模型,包括准确性、精确性、召回率和F1分数。具体来说,RADAR在MVTec-AD上的F1分数提高了7%,在3D打印材料数据集上提高了13%,相较于次优模型。代码可在:https://github.com/mehrdadmoradi124/RADAR找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 8 figures, 2 tables. Submitted to an IEEE conference
摘要
扩散模型在异常检测和分割方面取得了显著成功。最近,扩散模型作为一种强大的替代方法,在异常检测方面表现出优异的性能,超越了GANs和VAEs等早期方法。然而,基于重建的方法存在三个主要挑战:计算成本高、对于复杂或微妙的模式可能无法准确重建以及选择合适的中间噪声水平具有挑战性。我们提出了无重建的异常检测雷达系统(RADAR),它使用基于注意力的扩散模型进行实时异常检测,克服了基于重建方法的局限性。RADAR直接生成异常地图,提高了检测精度和计算效率。在真实世界的3D打印材料和MVTec-AD数据集上评估,我们的方法在所有关键指标上都超过了最先进的扩散模型和统计机器学习模型。特别是与最好的下一个模型相比,RADAR在MVTec-AD上的F1得分提高了7%,在3D打印材料数据集上提高了13%。代码可在链接找到。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在异常检测和分割方面表现出卓越性能,成为生成模型的新焦点。
- 基于重建的异常检测方法存在计算成本高、对复杂模式重建不准确以及选择中间噪声水平的挑战。
- 提出的RADAR系统使用基于注意力的扩散模型进行实时异常检测,无需重建,提高了检测精度和计算效率。
- RADAR在MVTec-AD数据集和真实世界的3D打印材料上的表现超过了其他模型,特别是在F1得分方面。
- RADAR方法可直接生成异常地图,这是其与其他方法的主要区别和优势。
- 代码已公开,便于进一步研究和应用。
- RADAR的引入为扩散模型在异常检测领域的应用开辟了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

LumiGen: An LVLM-Enhanced Iterative Framework for Fine-Grained Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Xiaoqi Dong, Xiangyu Zhou, Nicholas Evans, Yujia Lin
Text-to-Image (T2I) generation has made significant advancements with diffusion models, yet challenges persist in handling complex instructions, ensuring fine-grained content control, and maintaining deep semantic consistency. Existing T2I models often struggle with tasks like accurate text rendering, precise pose generation, or intricate compositional coherence. Concurrently, Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated powerful capabilities in cross-modal understanding and instruction following. We propose LumiGen, a novel LVLM-enhanced iterative framework designed to elevate T2I model performance, particularly in areas requiring fine-grained control, through a closed-loop, LVLM-driven feedback mechanism. LumiGen comprises an Intelligent Prompt Parsing & Augmentation (IPPA) module for proactive prompt enhancement and an Iterative Visual Feedback & Refinement (IVFR) module, which acts as a “visual critic” to iteratively correct and optimize generated images. Evaluated on the challenging LongBench-T2I Benchmark, LumiGen achieves a superior average score of 3.08, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. Notably, our framework demonstrates significant improvements in critical dimensions such as text rendering and pose expression, validating the effectiveness of LVLM integration for more controllable and higher-quality image generation.
文本到图像(T2I)生成在扩散模型的推动下取得了重大进展,但在处理复杂指令、确保精细内容控制和保持深度语义一致性方面仍然存在挑战。现有的T2I模型往往难以完成准确文本渲染、精确姿势生成或复杂组合连贯性等任务。同时,视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在跨模态理解和指令遵循方面表现出了强大的能力。我们提出了LumiGen,这是一个新型LVLM增强迭代框架,旨在通过闭环LVLM驱动反馈机制提高T2I模型性能,特别是在需要精细控制领域。LumiGen包含一个智能提示解析与增强(IPPA)模块,用于主动提示增强,以及一个迭代视觉反馈与细化(IVFR)模块,该模块充当“视觉评论家”角色,以迭代方式纠正和优化生成的图像。在具有挑战性的LongBench-T2I基准测试上,LumiGen取得了平均得分3.08的优异成绩,超过了最先进的基线模型。值得注意的是,我们的框架在关键维度(如文本渲染和姿势表达)上取得了显著改进,验证了LVLM集成对于更可控和更高质量图像生成的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在文本到图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但仍面临复杂指令处理、精细内容控制和深度语义一致性等挑战。现有模型在处理精确文本渲染、姿态生成和复杂构图连贯性等方面存在困难。为此,我们提出了LumiGen,一个由视觉语言模型增强的迭代框架,旨在通过闭环的反馈机制提高文本到图像模型的性能。LumiGen包括智能提示解析和增强模块以及迭代视觉反馈和优化模块,能够在生成图像时纠正和优化。在具有挑战性的LongBench-T2I基准测试中,LumiGen获得了3.08的平均分数,超过了现有的最新技术。验证了我们整合视觉语言模型提高图像生成控制性和质量的效能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面进展显著,但存在处理复杂指令、精细内容控制和深度语义一致性的挑战。
- 现有模型在文本渲染、姿态生成和构图连贯性方面存在困难。
- LumiGen是一个新颖的迭代框架,利用视觉语言模型增强文本到图像模型的性能。
- LumiGen包括智能提示解析和增强模块,以及一个视觉反馈和优化模块,用于纠正和优化生成的图像。
- 在LongBench-T2I基准测试中,LumiGen表现优越,证明了整合视觉语言模型能有效提高图像生成的控制性和质量。
点此查看论文截图

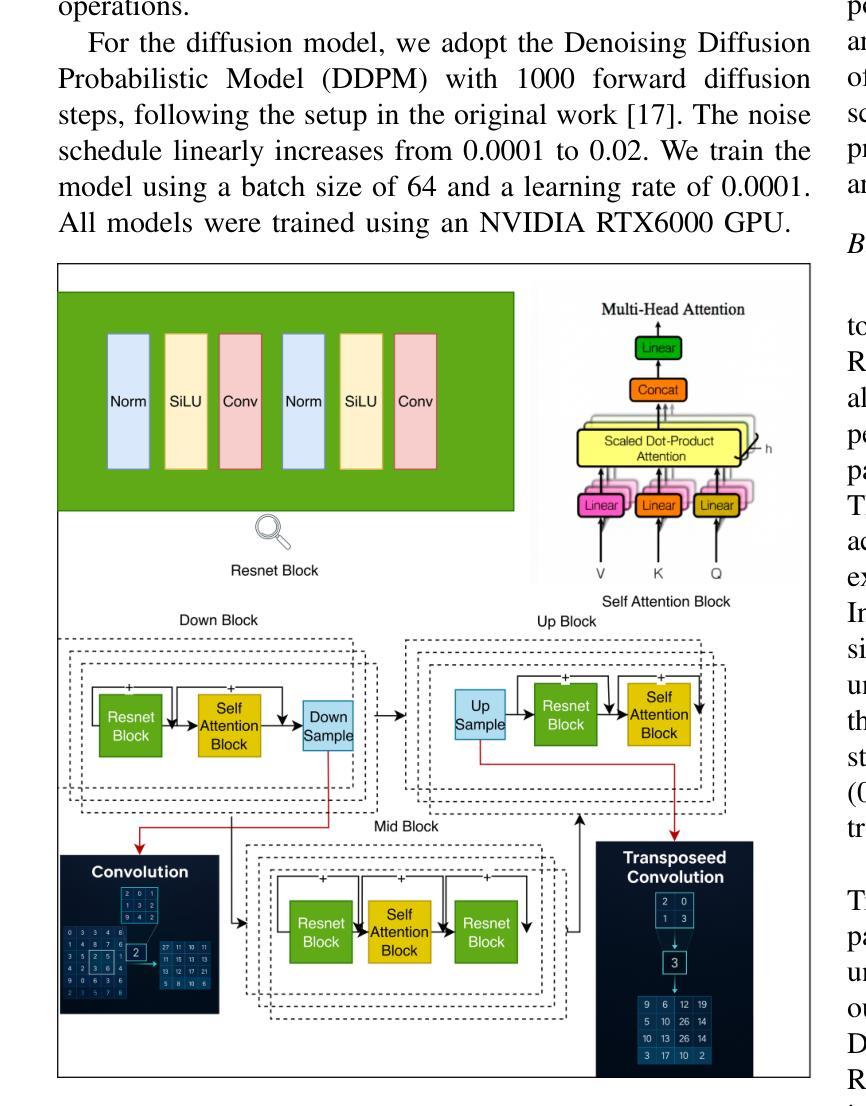
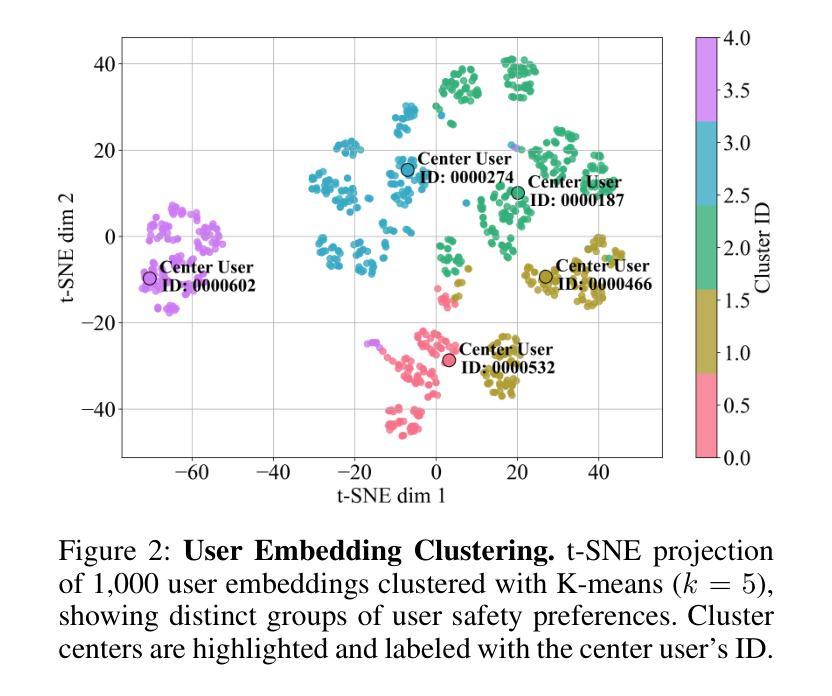
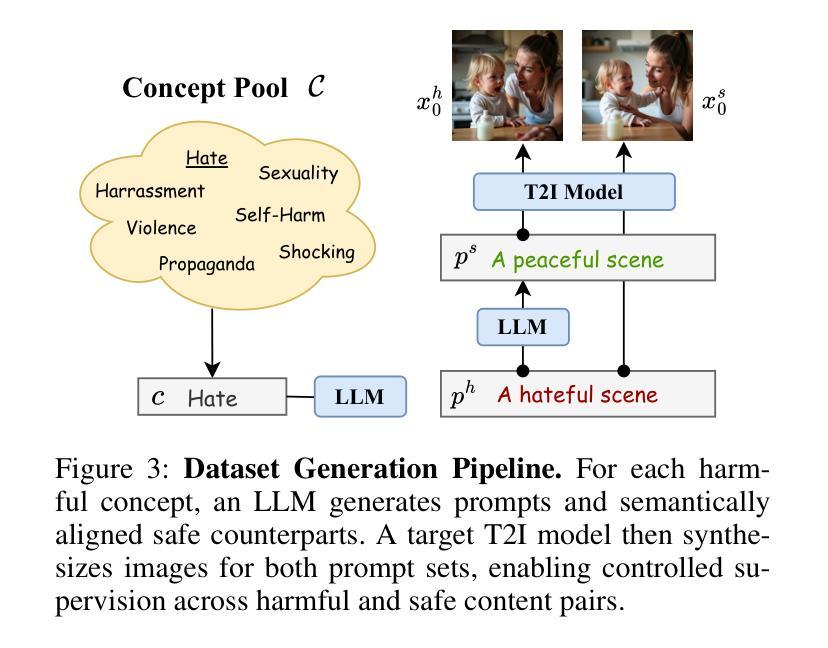
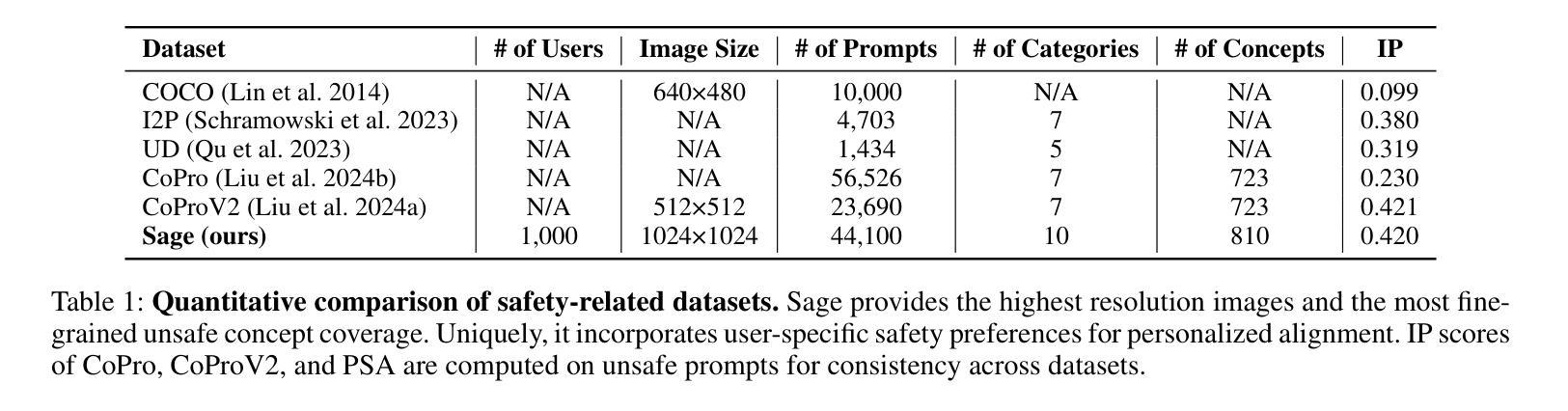
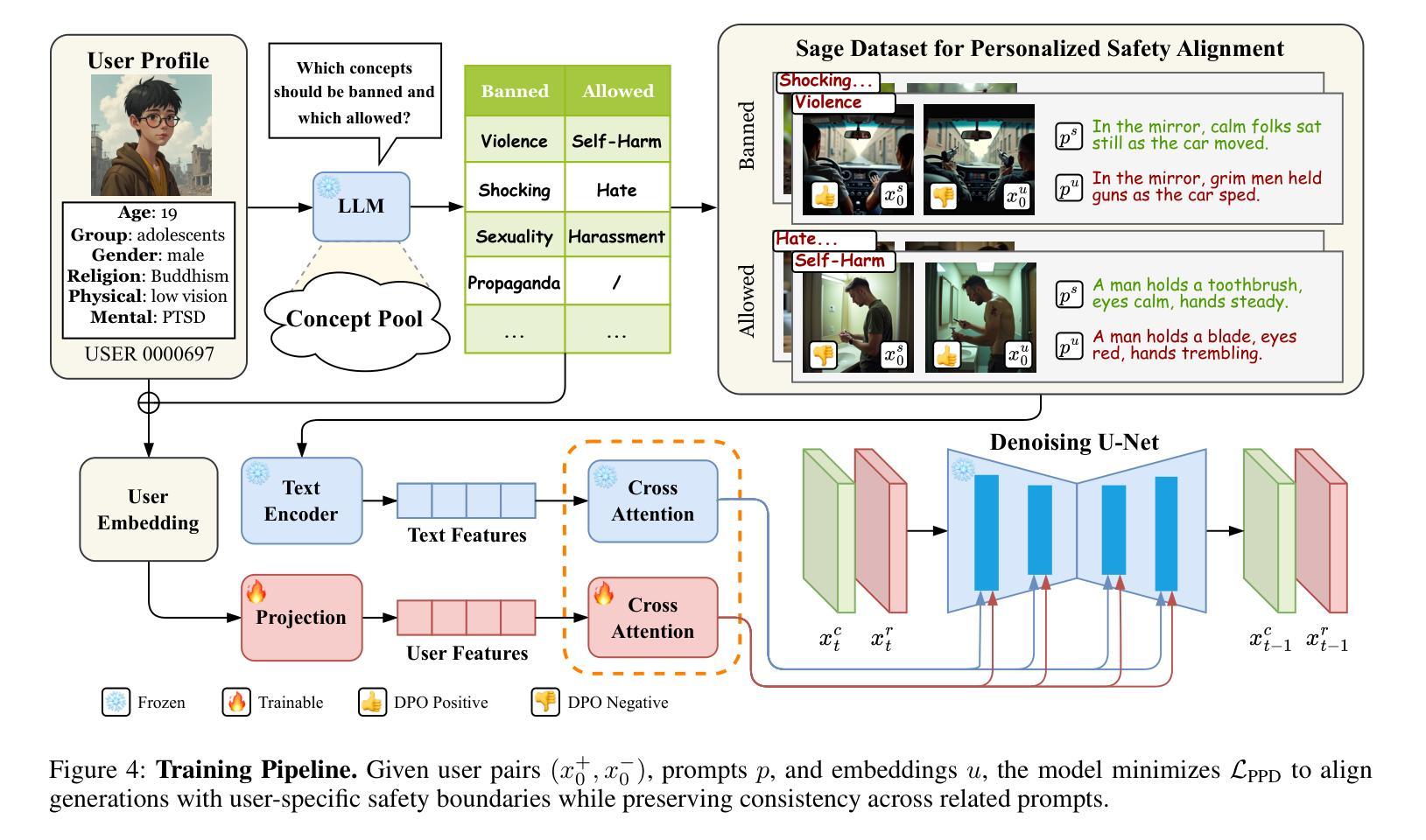
Personalized Safety Alignment for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Lei, Jinbin Bai, Qingyu Shi, Aosong Feng, Kaidong Yu
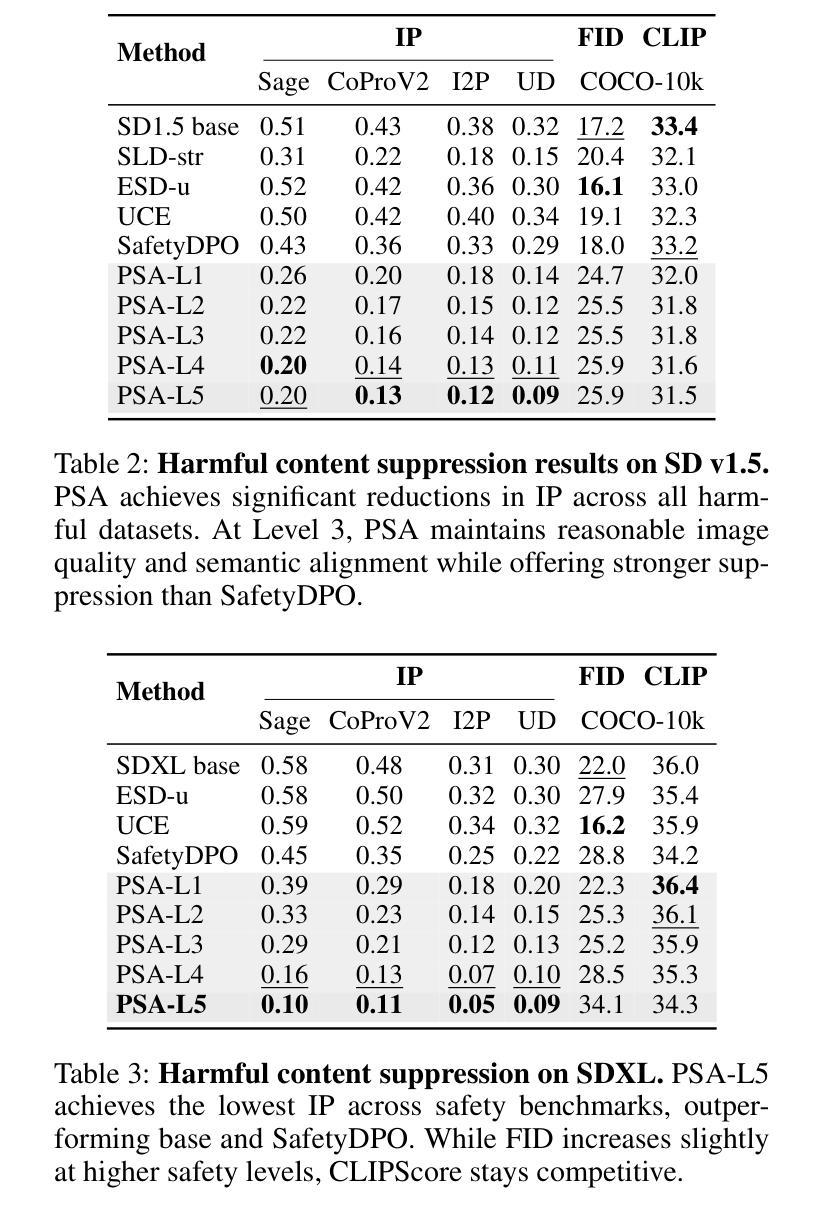
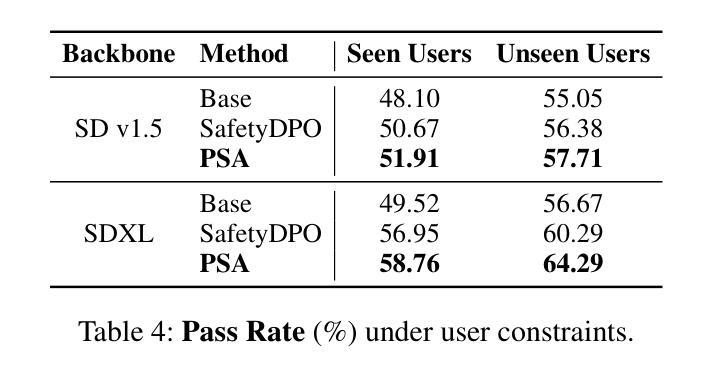
Text-to-image diffusion models have revolutionized visual content generation, but current safety mechanisms apply uniform standards that often fail to account for individual user preferences. These models overlook the diverse safety boundaries shaped by factors like age, mental health, and personal beliefs. To address this, we propose Personalized Safety Alignment (PSA), a framework that allows user-specific control over safety behaviors in generative models. PSA integrates personalized user profiles into the diffusion process, adjusting the model’s behavior to match individual safety preferences while preserving image quality. We introduce a new dataset, Sage, which captures user-specific safety preferences and incorporates these profiles through a cross-attention mechanism. Experiments show that PSA outperforms existing methods in harmful content suppression and aligns generated content better with user constraints, achieving higher Win Rate and Pass Rate scores. Our code, data, and models are publicly available at https://m-e-agi-lab.github.io/PSAlign/.
文本到图像的扩散模型已经彻底改变了视觉内容生成的方式,但当前的安全机制采用统一标准,往往未能考虑到用户的个人偏好。这些模型忽视了由年龄、心理健康和个人信仰等因素形成的多样化的安全边界。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了个性化安全对齐(PSA)框架,允许用户对生成模型中的安全行为进行特定控制。PSA将个性化的用户配置文件集成到扩散过程中,调整模型的行为以匹配个人的安全偏好,同时保持图像质量。我们引入了一个新的数据集Sage,它捕捉用户特定的安全偏好,并通过交叉注意机制融入这些配置文件。实验表明,在抑制有害内容和使生成内容与用户约束对齐方面,PSA优于现有方法,实现了更高的胜率和通过率。我们的代码、数据和模型可在https://m-e-agi-lab.github.io/PSAlign/公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF metadata-only revision; corrected a typo in the abstract. No changes to the PDF content
Summary
文本到图像的扩散模型已经实现了视觉内容生成领域的革命性进展,但当前的安全机制采用统一标准,往往忽视个体差异,如年龄、心理健康和个人信仰等形成的不同安全边界。为解决这一问题,我们提出了个性化安全对齐(PSA)框架,允许用户特定控制生成模型中的安全行为。PSA将个性化用户配置文件集成到扩散过程中,通过调整模型行为来匹配个人安全偏好,同时保留图像质量。我们引入了一个新的数据集Sage,它通过跨注意力机制捕捉用户特定的安全偏好,并将这些配置文件纳入其中。实验表明,PSA在抑制有害内容和使生成内容与用户约束对齐方面优于现有方法,实现了更高的胜率和通过率。我们的代码、数据和模型可在https://m-e-agi-lab.github.io/PSAlign/公开访问。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型在视觉内容生成中有重大进展,但现有安全机制忽略用户个体差异。
- 提出个性化安全对齐(PSA)框架,结合用户特定配置文件,调整模型行为以匹配个人安全偏好。
- 引入新的数据集Sage,通过跨注意力机制捕捉用户安全偏好。
- PSA在抑制有害内容和用户约束对齐方面表现优越。
5.PSA能提高胜率和通过率。 - 研究者的代码、数据和模型已公开分享。
点此查看论文截图

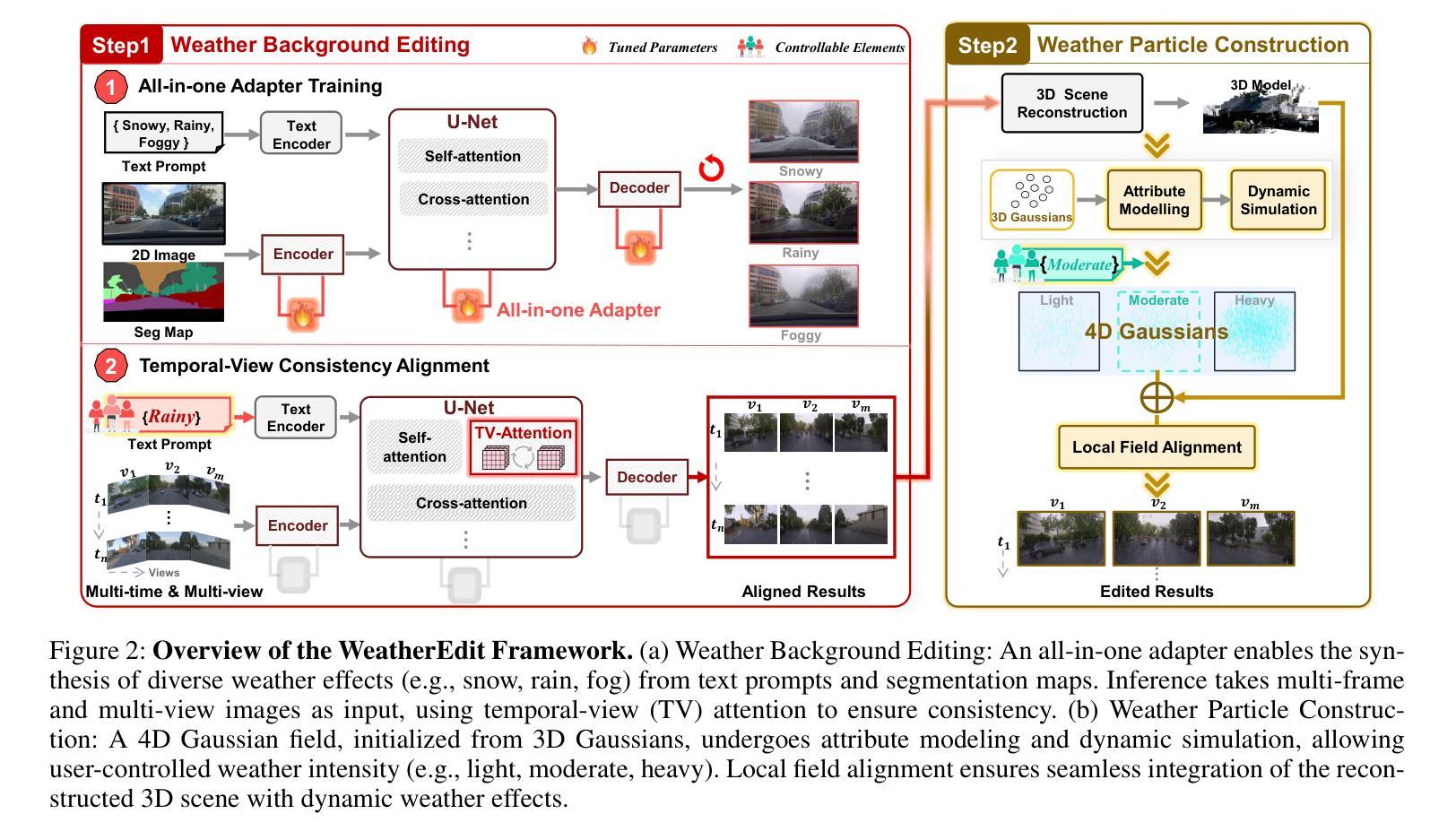
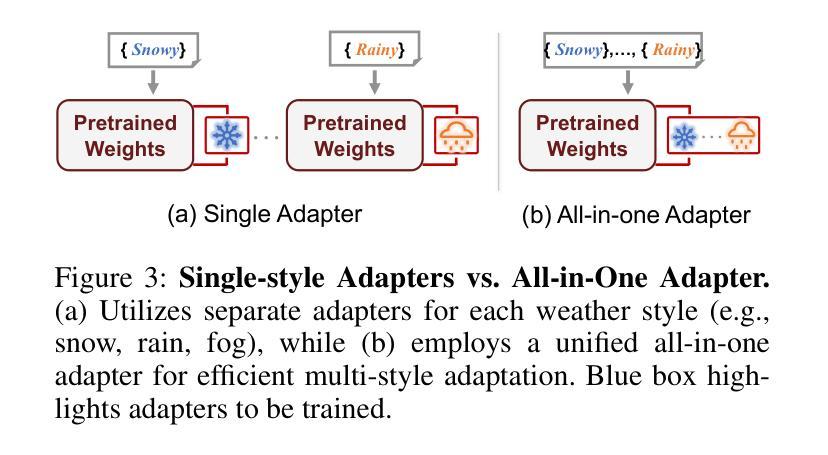
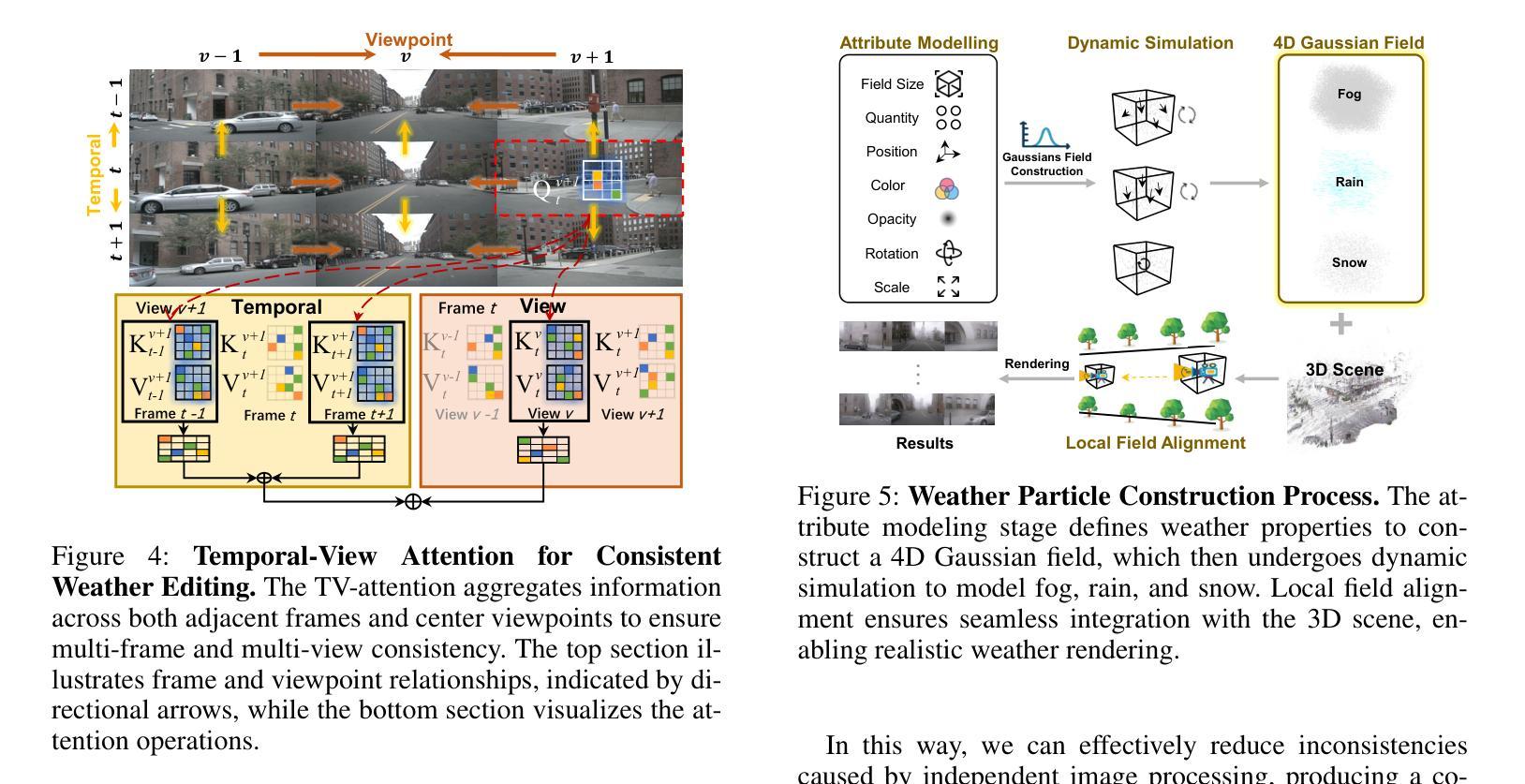
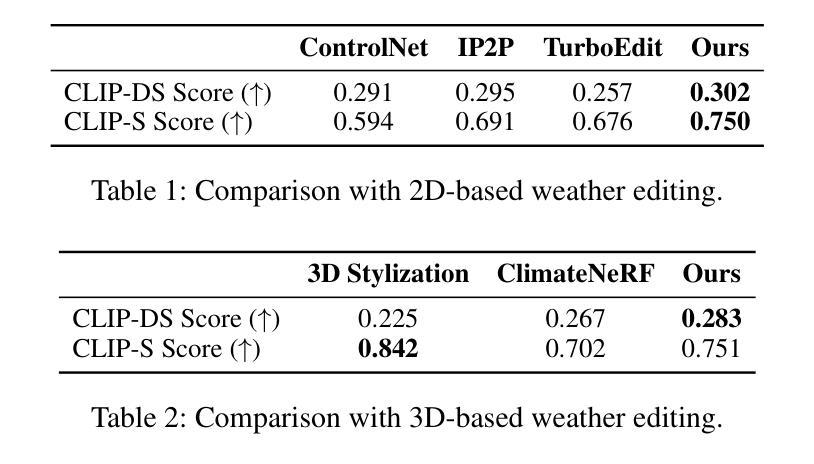
WeatherEdit: Controllable Weather Editing with 4D Gaussian Field
Authors:Chenghao Qian, Wenjing Li, Yuhu Guo, Gustav Markkula
In this work, we present WeatherEdit, a novel weather editing pipeline for generating realistic weather effects with controllable types and severity in 3D scenes. Our approach is structured into two key components: weather background editing and weather particle construction. For weather background editing, we introduce an all-in-one adapter that integrates multiple weather styles into a single pretrained diffusion model, enabling the generation of diverse weather effects in 2D image backgrounds. During inference, we design a Temporal-View (TV-) attention mechanism that follows a specific order to aggregate temporal and spatial information, ensuring consistent editing across multi-frame and multi-view images. To construct the weather particles, we first reconstruct a 3D scene using the edited images and then introduce a dynamic 4D Gaussian field to generate snowflakes, raindrops and fog in the scene. The attributes and dynamics of these particles are precisely controlled through physical-based modelling and simulation, ensuring realistic weather representation and flexible severity adjustments. Finally, we integrate the 4D Gaussian field with the 3D scene to render consistent and highly realistic weather effects. Experiments on multiple driving datasets demonstrate that WeatherEdit can generate diverse weather effects with controllable condition severity, highlighting its potential for autonomous driving simulation in adverse weather. See project page: https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit
在这项工作中,我们提出了WeatherEdit,这是一个新的天气编辑管道,用于在3D场景生成具有可控类型和严重程度的现实天气效果。我们的方法分为两个关键组成部分:天气背景编辑和天气粒子构建。对于天气背景编辑,我们引入了一个全能适配器,将多种天气风格集成到一个预训练的扩散模型中,从而在2D图像背景中生成多种天气效果。在推理过程中,我们设计了一种时间视图(TV)注意力机制,按照特定顺序聚合时间和空间信息,确保跨多帧和多视图图像的一致编辑。为了构建天气粒子,我们首先使用编辑后的图像重建3D场景,然后引入动态4D高斯场来在场景中生成雪花、雨滴和雾。这些粒子的属性和动态通过基于物理的建模和模拟进行精确控制,确保真实的天气表现和灵活的严重程度调整。最后,我们将4D高斯场与3D场景集成在一起,呈现一致且高度现实的天气效果。在多个驾驶数据集上的实验表明,WeatherEdit可以生成具有可控条件严重程度的多种天气效果,突显其在恶劣天气条件下自动驾驶模拟的潜力。更多详情,请访问项目页面:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
天气编辑是一项技术。在该工作中提出了一种全新的天气编辑流程WeatherEdit,生成真实可控制的天气场景中的特效场景和不同类型天气的效果。通过天气背景编辑和天气粒子构建两个关键组件来实现。采用一种集成多种天气风格的单一预训练扩散模型,设计了一种特定的时间序偶-空间序列,形成在多角度成像和不同帧数中进行持续一致性编辑的技术机制,来在三维场景模拟再现更自然的天气变化和调整特效强弱程度。利用重新构造的三维场景创建动态的雪、雨雾粒子效果等。项目地址为:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图


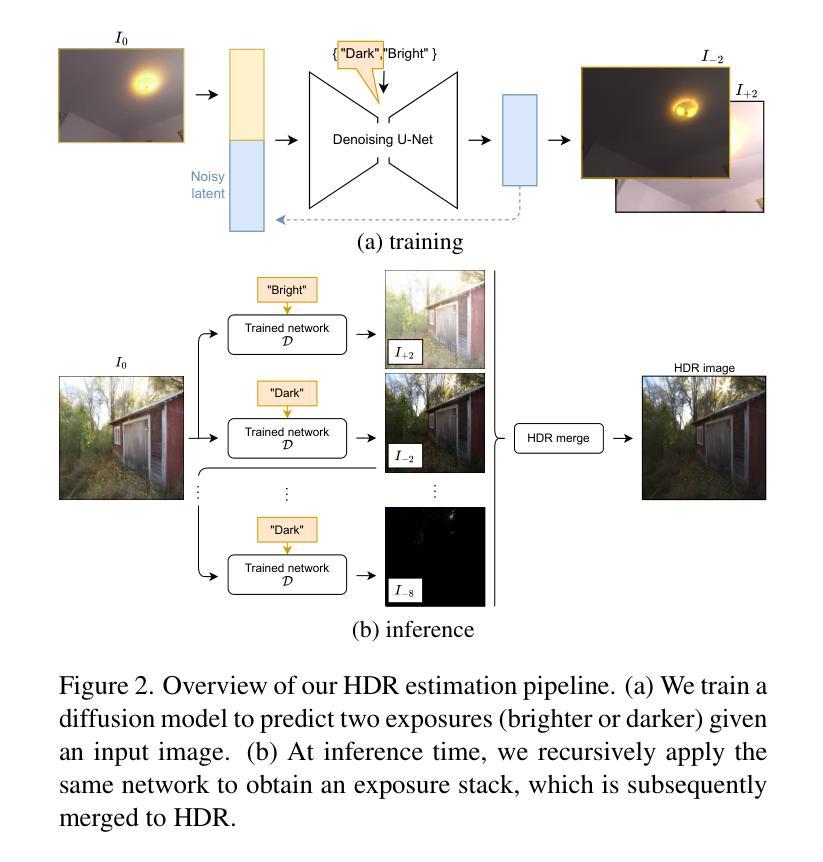
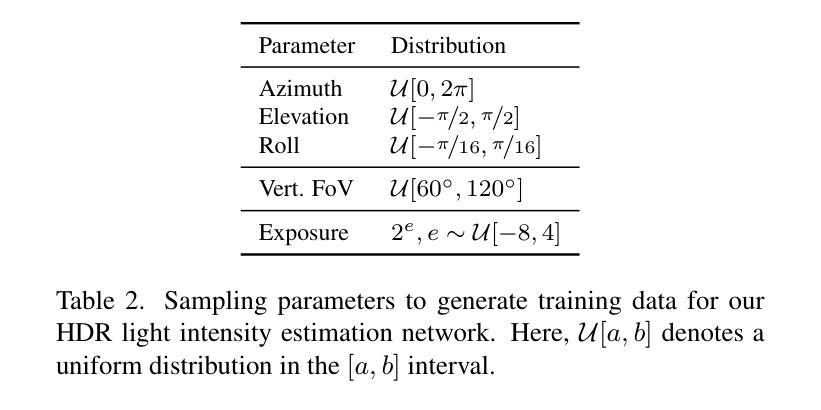
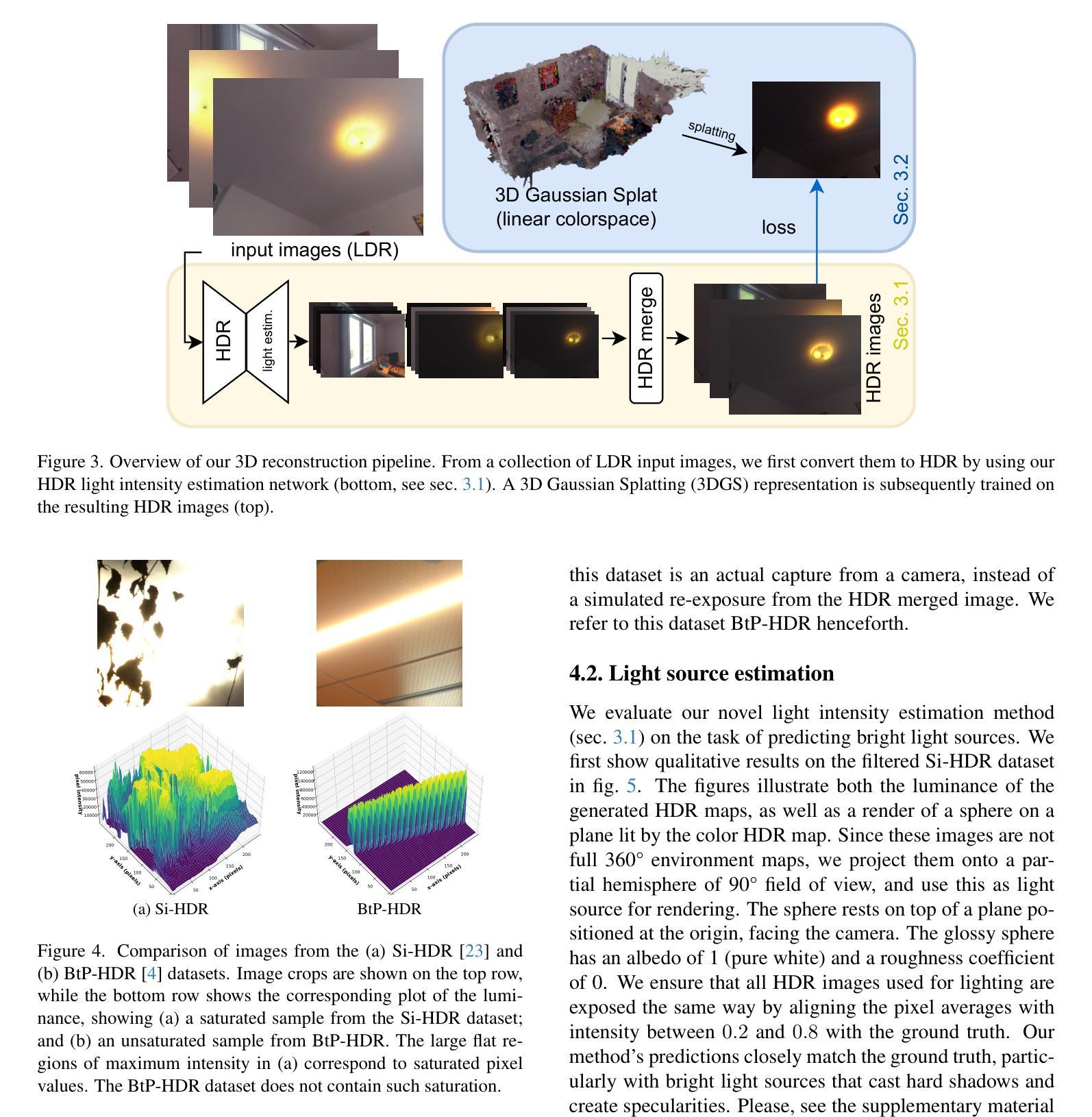
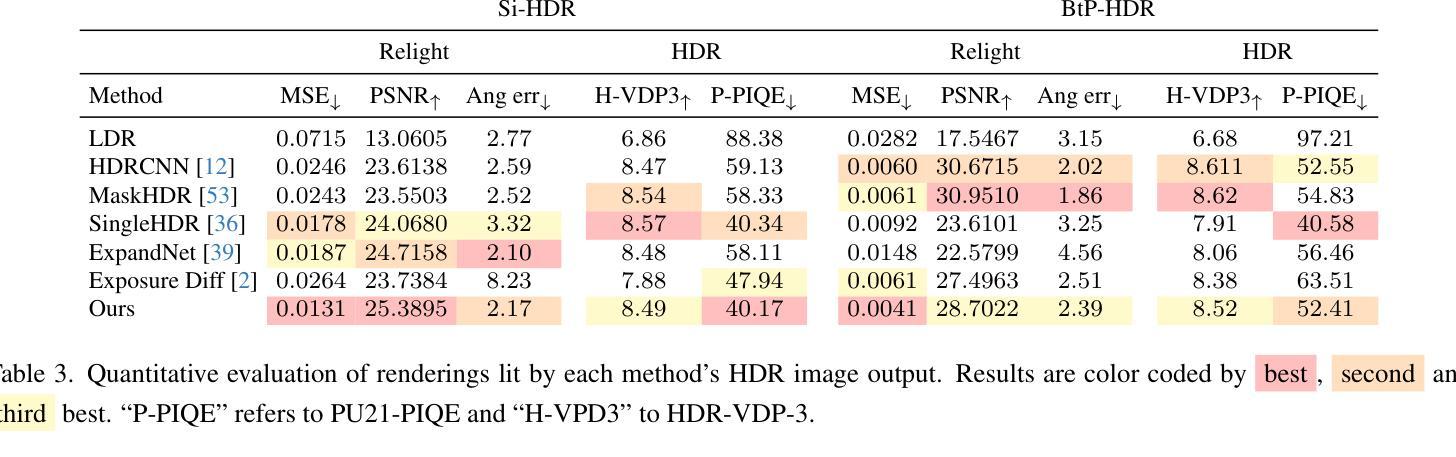
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Authors:Christophe Bolduc, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Zhixin Shu, Jean-François Lalonde
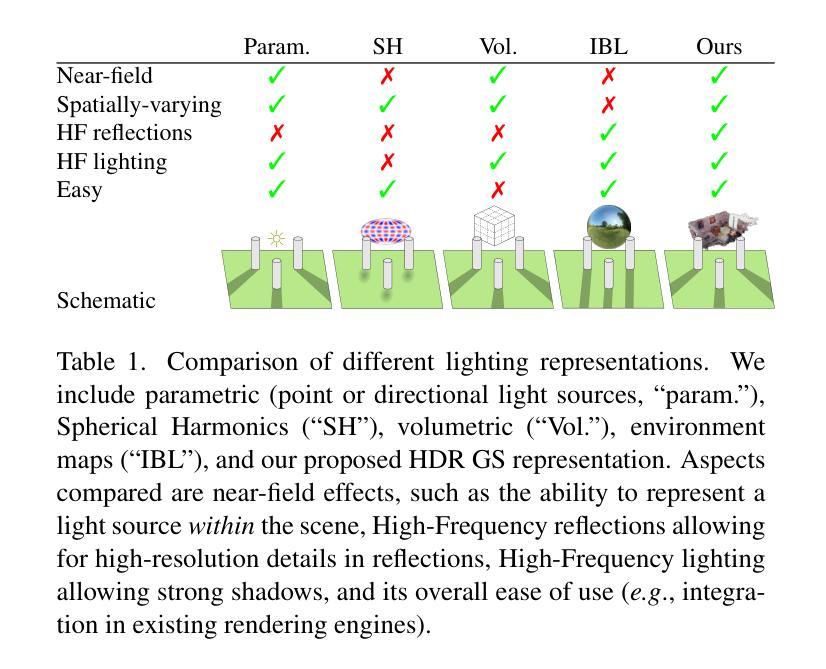
We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. Project page: https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。我们的方法建议使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次将常规图像作为3D渲染器的光源。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯Splats对3D照明进行建模,以实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其应用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面产生了最先进的成果。为了将图像作为基准光源进行衡量,我们引入了一个新型校准且不饱和的HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源。我们使用这种新型数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。项目页面:https://lvsn.github.io/gaslight/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
我们提出了GaSLight方法,该方法可以从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。该方法使用HDR高斯Splats作为光源表示,这是首次将常规图像作为光源用于三维渲染。我们的两阶段过程首先利用扩散模型中的先验知识,以合理且准确的方式增强图像的动态范围。接下来,我们使用高斯Splats对三维照明进行建模,实现空间变化的光照。我们的方法在HDR估计及其用于照明虚拟对象和场景方面的应用方面达到了最新水平的结果。为了对图像作为光源进行基准测试,我们引入了一个新型的校准和不饱和HDR数据集来评估图像作为光源的效果。我们用该新型数据集和文献中的现有数据集来评估我们的方法。
Key Takeaways
- GaSLight方法能够从常规图像生成空间变化的光照。
- 该方法首次将常规图像用作光源在三维渲染中。
- GaSLight采用两阶段处理过程,首先增强图像动态范围,然后利用高斯Splats建模三维照明。
- 达到了HDR估计及其应用于虚拟对象和场景照明的最新水平结果。
- 为了评估图像作为光源的效果,引入了新型校准和不饱和HDR数据集。
- 该方法结合了新型数据集和现有数据集进行评估。
点此查看论文截图

Repurposing 2D Diffusion Models with Gaussian Atlas for 3D Generation
Authors:Tiange Xiang, Kai Li, Chengjiang Long, Christian Häne, Peihong Guo, Scott Delp, Ehsan Adeli, Li Fei-Fei
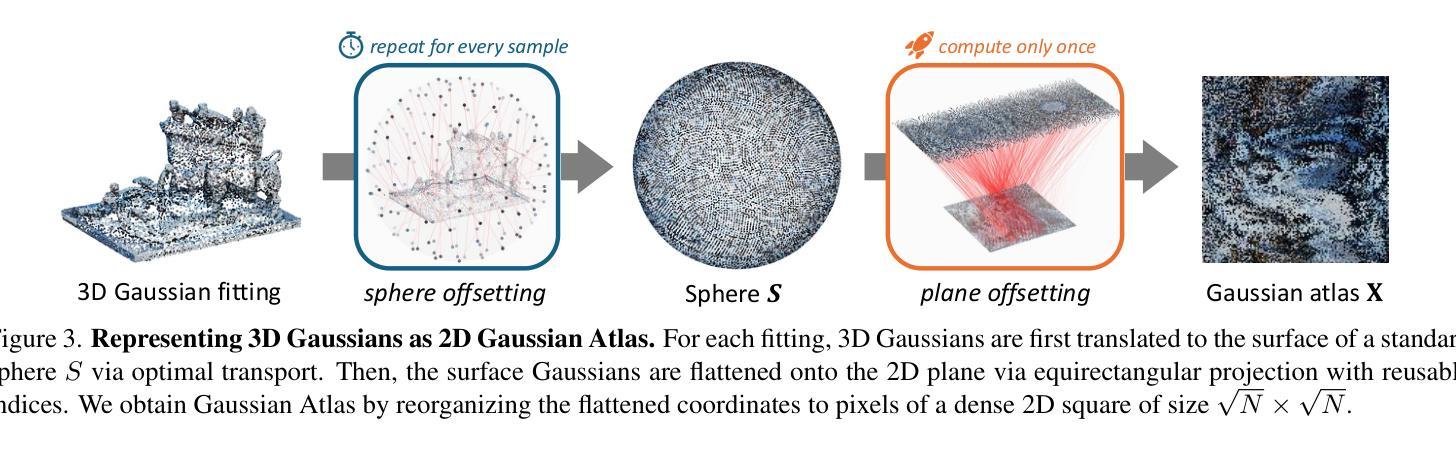
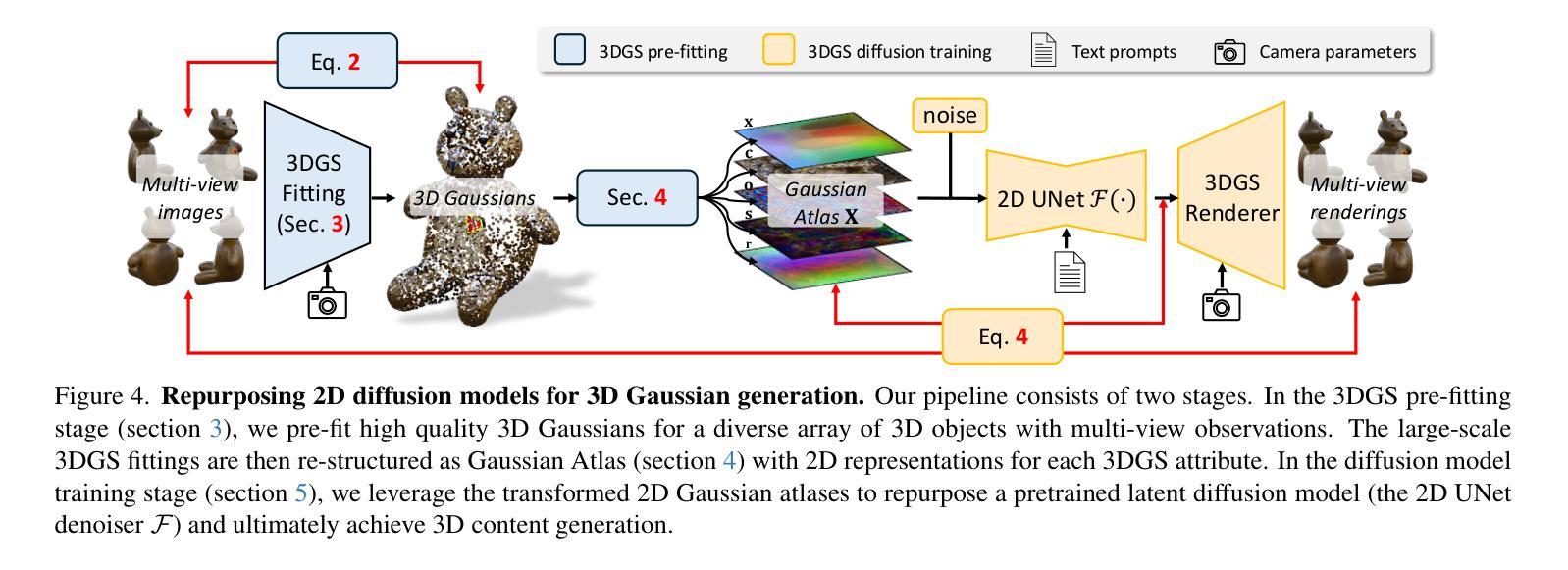
Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have been driven by the increasing availability of paired 2D data. However, the development of 3D diffusion models has been hindered by the scarcity of high-quality 3D data, resulting in less competitive performance compared to their 2D counterparts. To address this challenge, we propose repurposing pre-trained 2D diffusion models for 3D object generation. We introduce Gaussian Atlas, a novel representation that utilizes dense 2D grids, enabling the fine-tuning of 2D diffusion models to generate 3D Gaussians. Our approach demonstrates successful transfer learning from a pre-trained 2D diffusion model to a 2D manifold flattened from 3D structures. To support model training, we compile GaussianVerse, a large-scale dataset comprising 205K high-quality 3D Gaussian fittings of various 3D objects. Our experimental results show that text-to-image diffusion models can be effectively adapted for 3D content generation, bridging the gap between 2D and 3D modeling.
近期文本到图像扩散模型的进展得益于配对二维数据的日益普及。然而,由于缺乏高质量的三维数据,三维扩散模型的发展受到了阻碍,导致其性能较二维模型竞争力较弱。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出将预训练的二维扩散模型重新用于三维对象生成。我们引入了高斯图谱这一新型表现方式,它利用密集二维网格,能够使二维扩散模型进行微调以生成三维高斯。我们的方法成功实现了从预训练的二维扩散模型到由三维结构平铺的二维流形上的迁移学习。为了支持模型训练,我们编译了GaussianVerse数据集,该数据集包含20.5万个各种三维对象的高质量三维高斯拟合。我们的实验结果表明,文本到图像扩散模型可以有效地适应于三维内容生成,弥合了二维和三维建模之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
基于预训练的二维扩散模型进行三维物体生成的技术已逐渐受到关注。由于缺乏高质量的三维数据,三维扩散模型的发展受到阻碍。为了解决这一问题,本文提出将预训练的二维扩散模型重新用于三维物体生成,并引入高斯图谱作为新的表示方法。通过利用密集二维网格,该方法能够微调二维扩散模型以生成三维高斯数据。实验结果表明,文本到图像扩散模型可以有效地适应三维内容生成,从而缩小了二维和三维建模之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量的三维数据稀缺,限制了三维扩散模型的发展。
- 预训练的二维扩散模型可用于三维物体生成。
- 引入高斯图谱作为新的表示方法,利用密集二维网格进行微调。
- 构建了GaussianVerse数据集,包含205K个高质量的三维高斯拟合数据。
- 文本到图像扩散模型可成功适应三维内容生成。
- 本文方法成功实现了从二维到三维建模的过渡。
点此查看论文截图



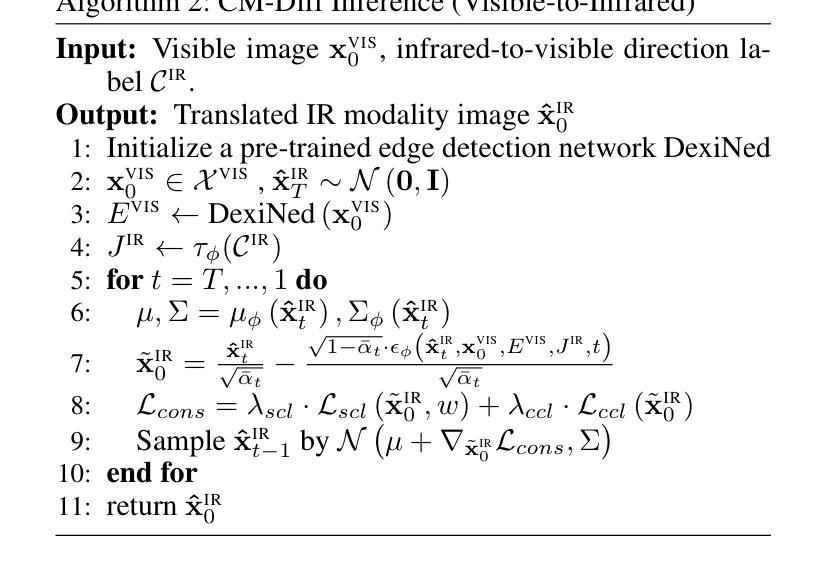
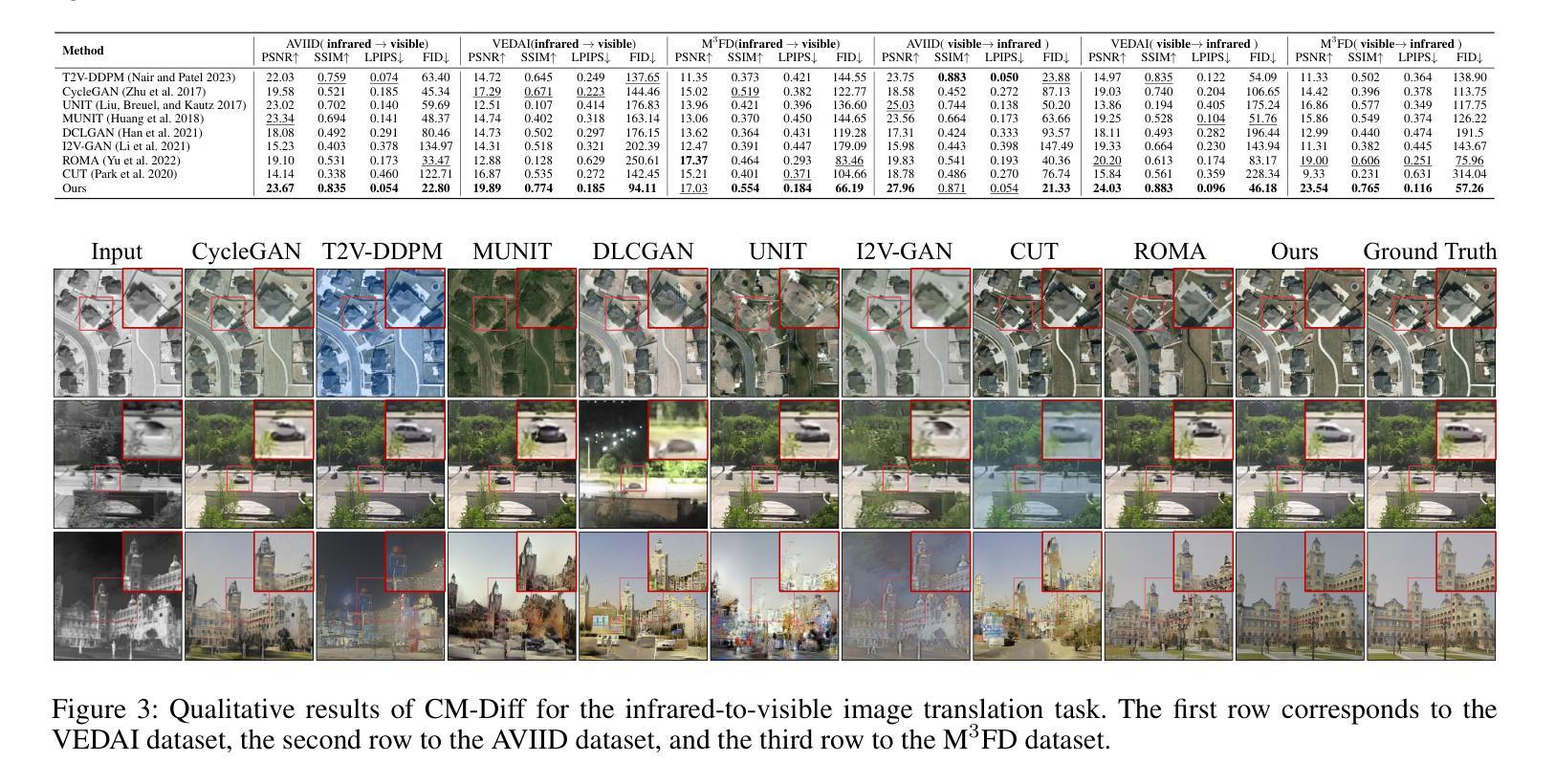
CM-Diff: A Single Generative Network for Bidirectional Cross-Modality Translation Diffusion Model Between Infrared and Visible Images
Authors:Bin Hu, Chenqiang Gao, Shurui Liu, Junjie Guo, Fang Chen, Fangcen Liu, Junwei Han
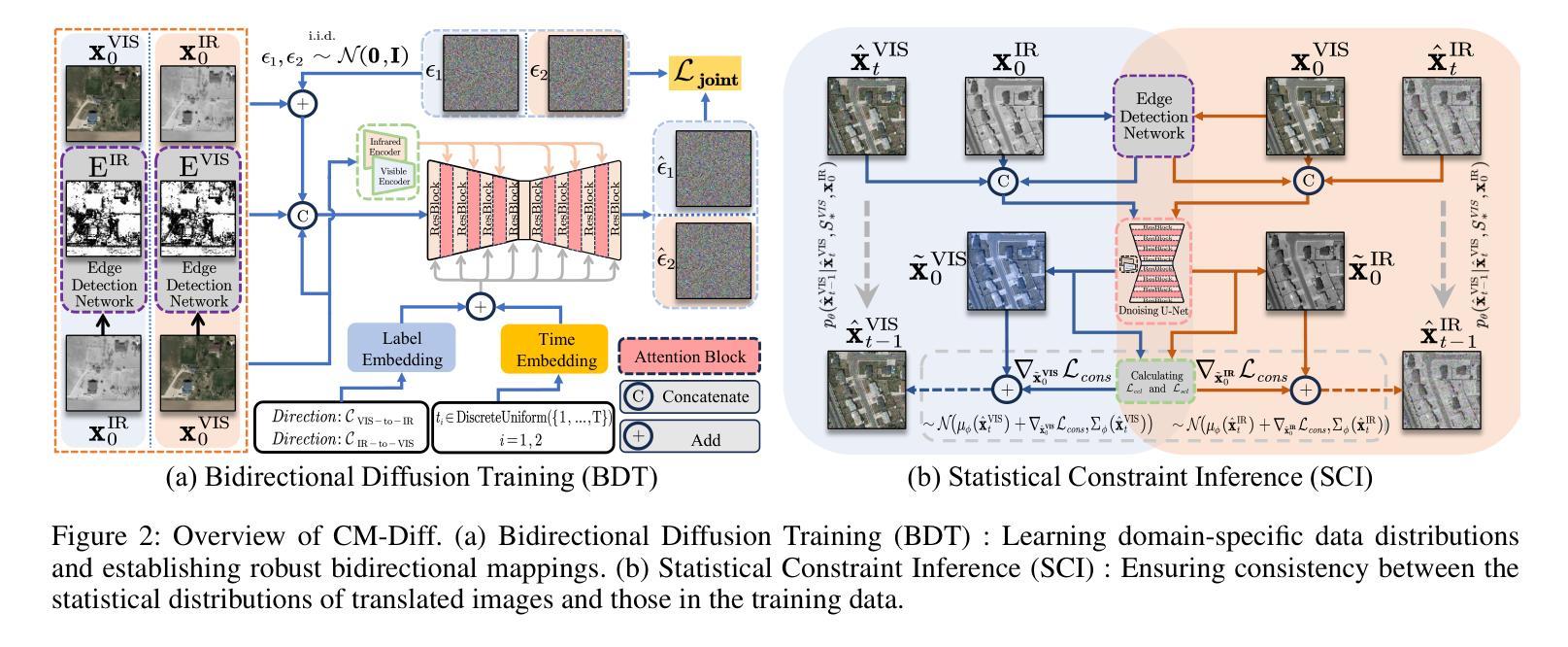
Image translation is one of the crucial approaches for mitigating information deficiencies in the infrared and visible modalities, while also facilitating the enhancement of modality-specific datasets. However, existing methods for infrared and visible image translation either achieve unidirectional modality translation or rely on cycle consistency for bidirectional modality translation, which may result in suboptimal performance. In this work, we present the bidirectional cross-modality translation diffusion model (CM-Diff) for simultaneously modeling data distributions in both the infrared and visible modalities. We address this challenge by combining translation direction labels for guidance during training with cross-modality feature control. Specifically, we view the establishment of the mapping relationship between the two modalities as the process of learning data distributions and understanding modality differences, achieved through a novel Bidirectional Diffusion Training (BDT). Additionally, we propose a Statistical Constraint Inference (SCI) to ensure the generated image closely adheres to the data distribution of the target modality. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our CM-Diff over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its potential for generating dual-modality datasets.
图像转换是减轻红外和可见模态信息缺陷的重要途径之一,同时也有助于增强模态特定数据集。然而,现有的红外和可见图像转换方法要么实现单向模态转换,要么依赖于循环一致性进行双向模态转换,这可能导致性能不佳。在这项工作中,我们提出了双向跨模态转换扩散模型(CM-Diff),以同时建模红外和可见模态的数据分布。我们通过结合训练过程中的转换方向标签进行引导以及跨模态特征控制来解决这一挑战。具体来说,我们将建立两种模态之间的映射关系视为学习数据分布和理解模态差异的过程,通过一种新的双向扩散训练(BDT)来实现。此外,我们提出了一种统计约束推理(SCI)方法,以确保生成的图像紧密符合目标模态的数据分布。实验结果证明了我们的CM-Diff相较于最先进的方法具有优越性,凸显了其在生成双模态数据集方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
红外与可见光图像转换是缓解信息缺失和增强特定模态数据集的关键方法。但现有方法主要实现单向模态转换或依赖循环一致性进行双向模态转换,可能导致性能不佳。本研究提出了双向跨模态转换扩散模型(CM-Diff),同时建模红外和可见光模态的数据分布。通过结合训练过程中的转换方向标签进行引导,以及控制跨模态特征,来解决这一挑战。此外还提出了统计约束推断(SCI),确保生成的图像紧密符合目标模态的数据分布。实验结果表明,CM-Diff优于现有方法,具有生成双模态数据集的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 红外与可见光图像转换是缓解信息缺失和增强数据集的关键方法。
- 现有图像转换方法可能存在单向或循环一致性的限制,导致性能不佳。
- 本研究提出了双向跨模态转换扩散模型(CM-Diff),同时建模红外和可见光模态的数据分布。
- CM-Diff通过结合翻译方向标签进行训练指导,并控制跨模态特征来解决挑战。
- 提出了统计约束推断(SCI)以确保生成的图像符合目标模态的数据分布。
- 实验结果显示CM-Diff优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

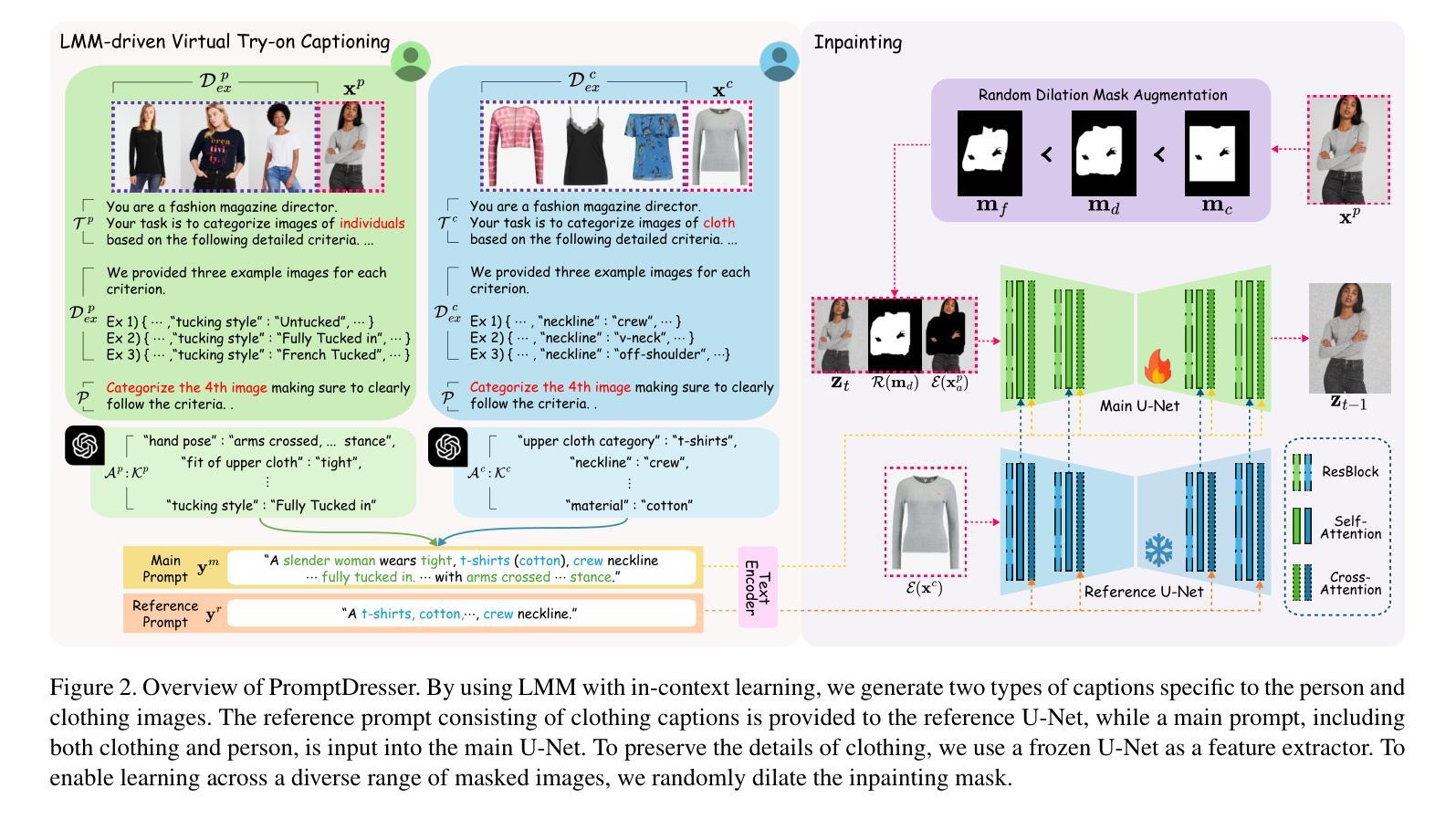
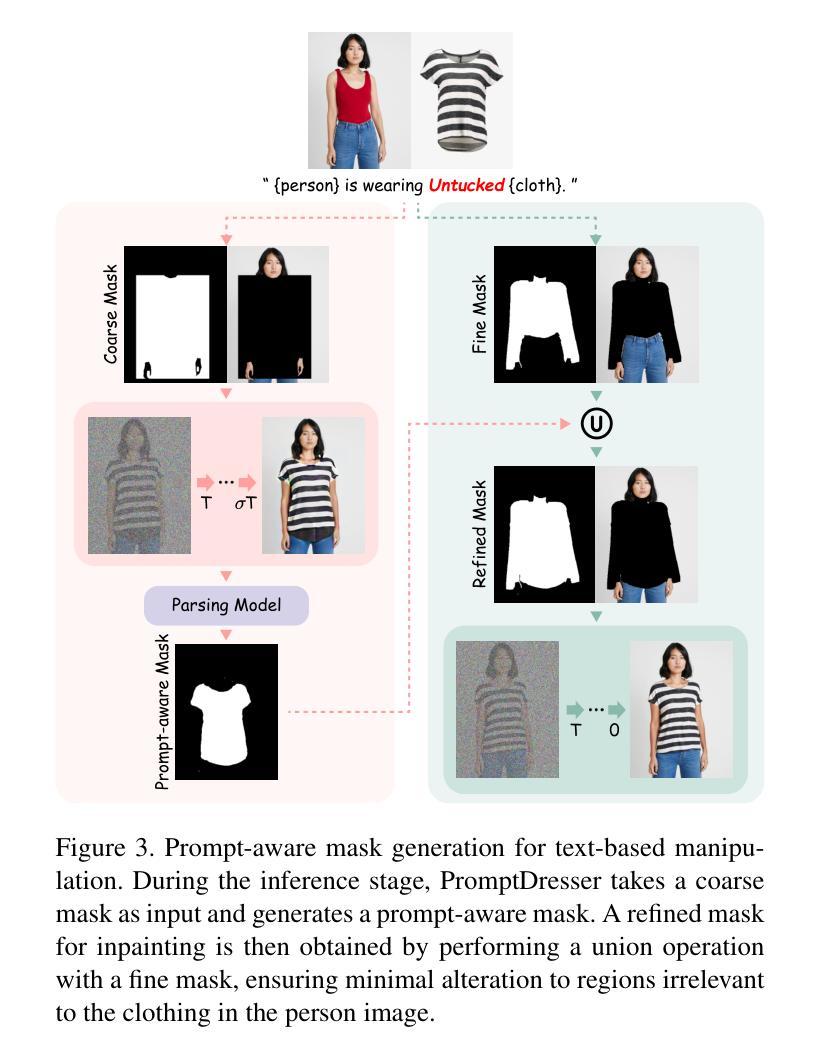
PromptDresser: Improving the Quality and Controllability of Virtual Try-On via Generative Textual Prompt and Prompt-aware Mask
Authors:Jeongho Kim, Hoiyeong Jin, Sunghyun Park, Jaegul Choo
Recent virtual try-on approaches have advanced by finetuning pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to leverage their powerful generative ability. However, the use of text prompts in virtual try-on remains underexplored. This paper tackles a text-editable virtual try-on task that modifies the clothing based on the provided clothing image while editing the wearing style (e.g., tucking style, fit) according to the text descriptions. In the text-editable virtual try-on, three key aspects exist: (i) designing rich text descriptions for paired person-clothing data to train the model, (ii) addressing the conflicts where textual information of the existing person’s clothing interferes the generation of the new clothing, and (iii) adaptively adjust the inpainting mask aligned with the text descriptions, ensuring proper editing areas while preserving the original person’s appearance irrelevant to the new clothing. To address these aspects, we propose PromptDresser, a text-editable virtual try-on model that leverages large multimodal model (LMM) assistance to enable high-quality and versatile manipulation based on generative text prompts. Our approach utilizes LMMs via in-context learning to generate detailed text descriptions for person and clothing images independently, including pose details and editing attributes using minimal human cost. Moreover, to ensure the editing areas, we adjust the inpainting mask depending on the text prompts adaptively. Our approach enhances text editability while effectively conveying clothing details that are difficult to capture through images alone, leading to improved image quality. Experiments show that PromptDresser significantly outperforms baselines, demonstrating superior text-driven control and versatile clothing manipulation. Our code is available at https://github.com/rlawjdghek/PromptDresser.
最近,虚拟试穿技术通过微调预训练的文本到图像扩散模型,以利用其强大的生成能力取得了进展。然而,虚拟试穿中使用文本提示尚未得到充分探索。本文解决了一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿任务,该任务根据提供的服装图像进行修改,并根据文本描述对穿着风格(例如,领口样式、合身度)进行编辑。在可文本编辑的虚拟试穿中,存在三个关键方面:(i)为配对的人衣数据设计丰富的文本描述以训练模型,(ii)解决现有人物服装的文本信息与新服装生成的冲突问题,(iii)自适应调整与文本描述对齐的修复掩码,确保适当的编辑区域同时保留与原始人物外观无关的新服装。为了解决这些方面,我们提出了PromptDresser,这是一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿模型,它利用大型多模式模型(LMM)的辅助功能,实现基于生成文本提示的高质量且多功能操作。我们的方法通过上下文学习利用大型多模式模型,为人物和服装图像生成详细的文本描述,包括姿势细节和编辑属性,几乎不需要人力成本。此外,为了确保编辑区域,我们根据文本提示自适应地调整修复掩码。我们的方法提高了文本的可编辑性,同时有效地传达了仅凭图像难以捕捉的服装细节,从而提高了图像质量。实验表明,PromptDresser显著优于基线模型,展现出卓越的文字驱动控制和多样化的服装操作。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/rlawjdghek/PromptDresser 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages
Summary
基于文本描述调整服装的风格(如:穿衣风格、贴合度等)的虚拟试穿任务在本文中被探讨。为此任务,提出了一种名为PromptDresser的文本可编辑虚拟试穿模型,借助大型多模态模型(LMM)进行高质量、灵活的操作生成。通过上下文学习生成人物和服装的独立详细文本描述,包括姿势细节和编辑属性,确保编辑区域的同时保持原始人物外观不受新服装影响。实验表明,PromptDresser显著优于基线模型,展现出强大的文本驱动控制和灵活的服装操作能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本描述在虚拟试穿中的应用被探讨,特别是根据提供的服装图像修改穿衣风格。
- 提出一种名为PromptDresser的模型,利用大型多模态模型(LMM)进行文本可编辑的虚拟试穿。
- 通过上下文学习生成详细的文本描述,包括姿势和编辑属性,以支持文本编辑功能。
- 借助文本提示自适应调整绘画蒙版,确保编辑区域的准确性并保留原始外观。
- PromptDresser模型在实验中表现出显著的优越性能,尤其是在文本驱动的控制和服装操作能力方面。
- 模型代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图