⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
Decision-Making with Deliberation: Meta-reviewing as a Document-grounded Dialogue
Authors:Sukannya Purkayastha, Nils Dycke, Anne Lauscher, Iryna Gurevych
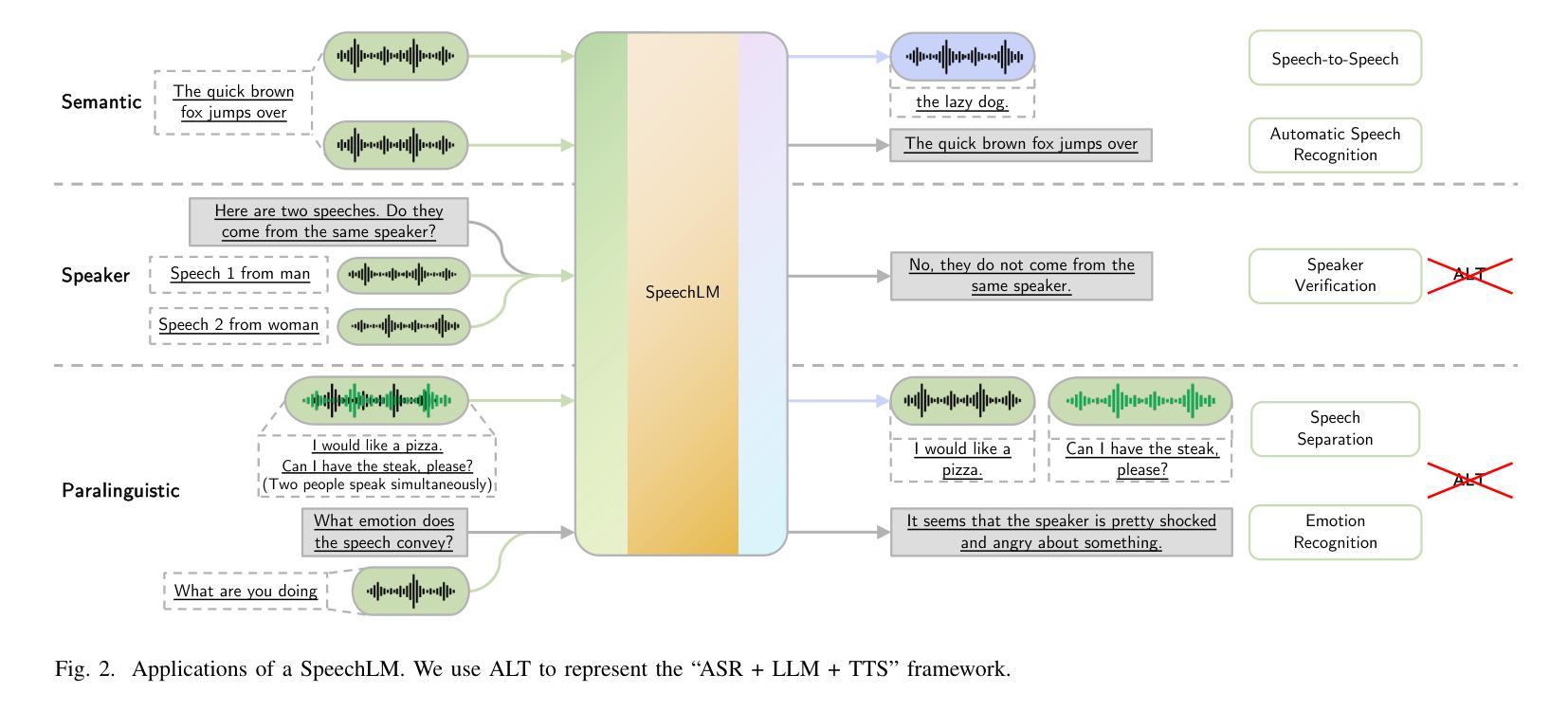
Meta-reviewing is a pivotal stage in the peer-review process, serving as the final step in determining whether a paper is recommended for acceptance. Prior research on meta-reviewing has treated this as a summarization problem over review reports. However, complementary to this perspective, meta-reviewing is a decision-making process that requires weighing reviewer arguments and placing them within a broader context. Prior research has demonstrated that decision-makers can be effectively assisted in such scenarios via dialogue agents. In line with this framing, we explore the practical challenges for realizing dialog agents that can effectively assist meta-reviewers. Concretely, we first address the issue of data scarcity for training dialogue agents by generating synthetic data using Large Language Models (LLMs) based on a self-refinement strategy to improve the relevance of these dialogues to expert domains. Our experiments demonstrate that this method produces higher-quality synthetic data and can serve as a valuable resource towards training meta-reviewing assistants. Subsequently, we utilize this data to train dialogue agents tailored for meta-reviewing and find that these agents outperform \emph{off-the-shelf} LLM-based assistants for this task. Finally, we apply our agents in real-world meta-reviewing scenarios and confirm their effectiveness in enhancing the efficiency of meta-reviewing.\footnote{Code and Data: https://github.com/UKPLab/arxiv2025-meta-review-as-dialog
元评审是同行评审过程中的一个关键阶段,是确定论文是否被推荐接受的最后一步。之前关于元评审的研究通常将其视为对评审报告的总结问题。然而,与这一观点相补充的是,元评审是一个决策过程,需要权衡评审者的观点并将它们放在更广泛的背景下。以往的研究表明,决策者可以在此类场景中通过对话代理进行有效的辅助。在此基础上,我们探索了实现可以有效辅助元评审的对话代理的实际挑战。具体来说,我们首先通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成合成数据来解决训练对话代理的数据稀缺问题,采用自我完善策略来提高这些对话与专家领域的关联性。我们的实验表明,该方法可产生高质量的合成数据,可作为训练元评审助理的宝贵资源。随后,我们利用这些数据训练了针对元评审的对话代理,发现这些代理在此任务上的表现优于现成的LLM助理。最后,我们将这些代理应用于真实的元评审场景中,并验证了它们在提高元评审效率方面的有效性。请注意查阅相关代码和数据集资源:【网址】。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages, 16 tables, 13 figures
Summary
本文探讨了元评审过程中的重要环节,指出元评审不仅是总结评审报告,更是决策过程。研究通过对话代理有效辅助决策者进行元评审决策,解决数据稀缺问题,采用基于自我完善策略的大型语言模型生成合成数据,训练针对元评审的对话代理,并在实际场景中验证其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 元评审是同行评审过程中的关键阶段,不仅是总结,更是决策过程。
- 对话代理可以有效辅助决策者在元评审过程中的决策。
- 数据稀缺是训练对话代理的难题,采用基于自我完善策略的大型语言模型生成合成数据是解决方案。
- 通过实验证明,该方法能生成高质量合成数据,对训练元评审助理有重要作用。
- 专门训练的对话代理在元评审任务中表现优于通用的大型语言模型助理。
- 将对话代理应用于实际元评审场景,验证了其在提高元评审效率方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction via Structural Entropy Minimization Partitioning
Authors:Kun Peng, Cong Cao, Hao Peng, Zhifeng Hao, Lei Jiang, Kongjing Gu, Yanbing Liu, Philip S. Yu
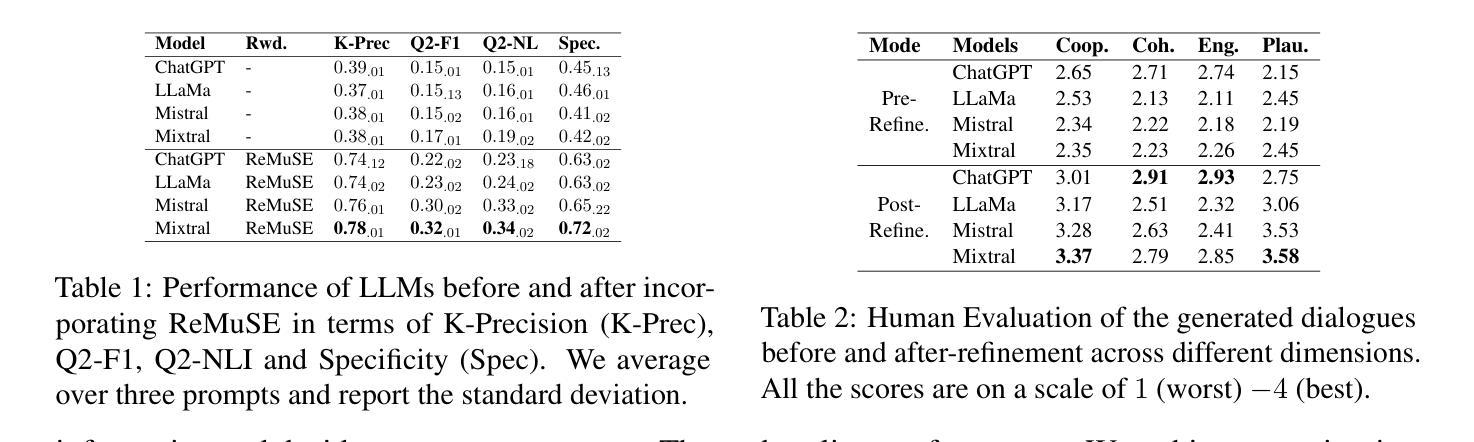
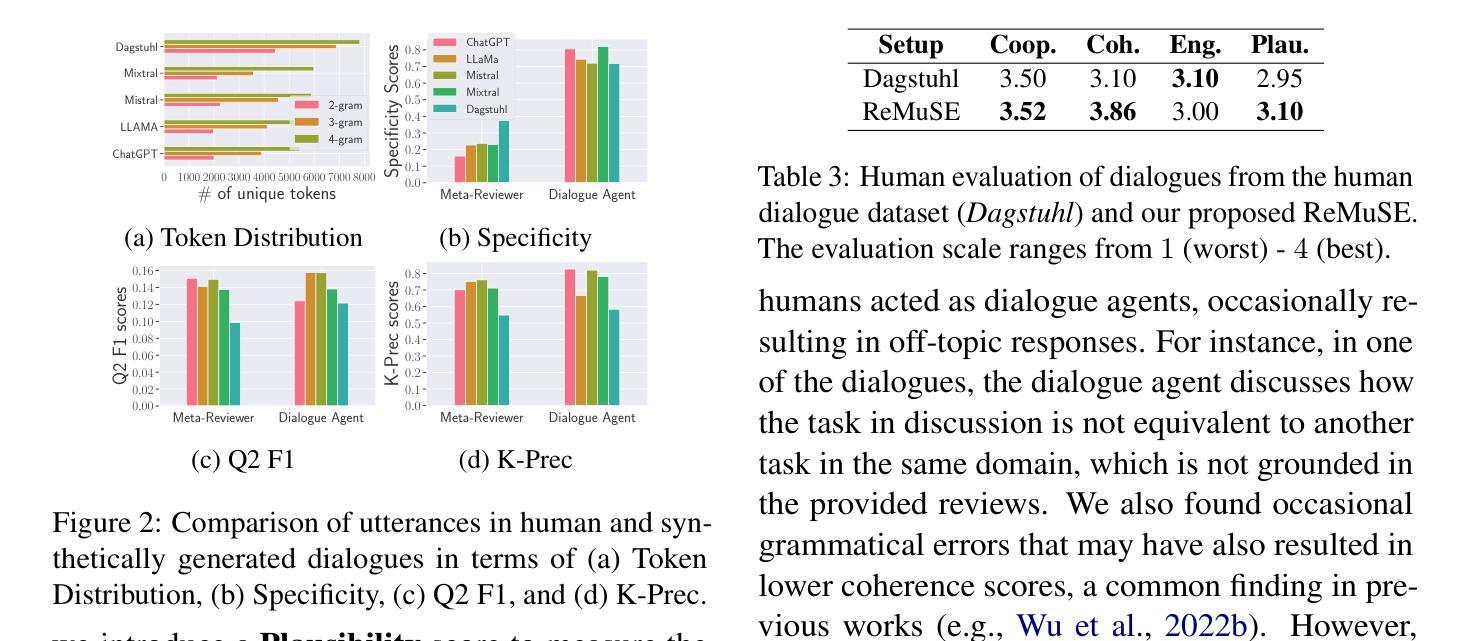
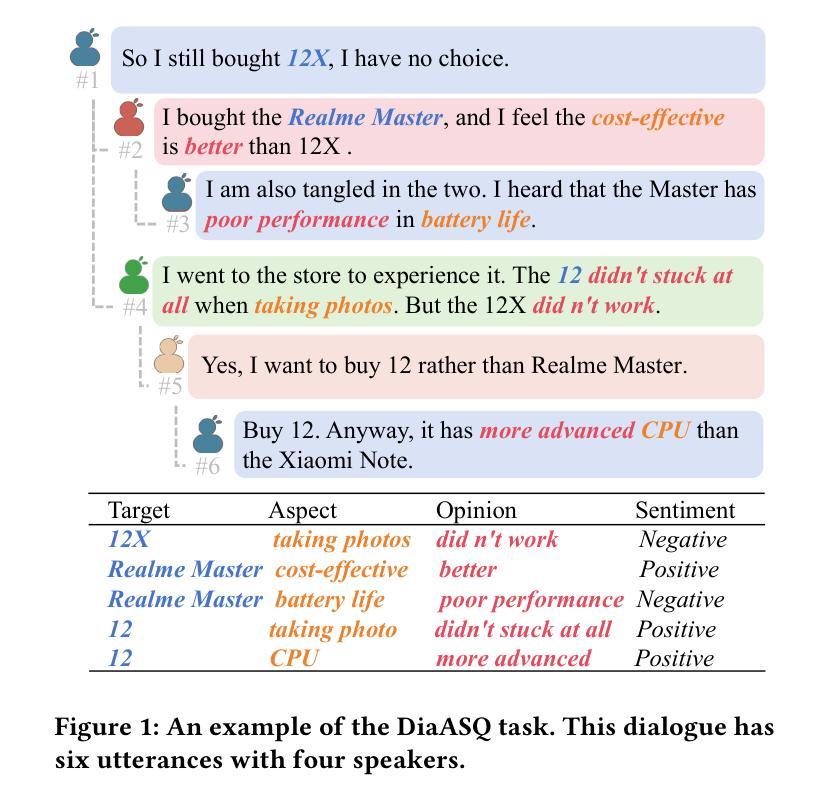
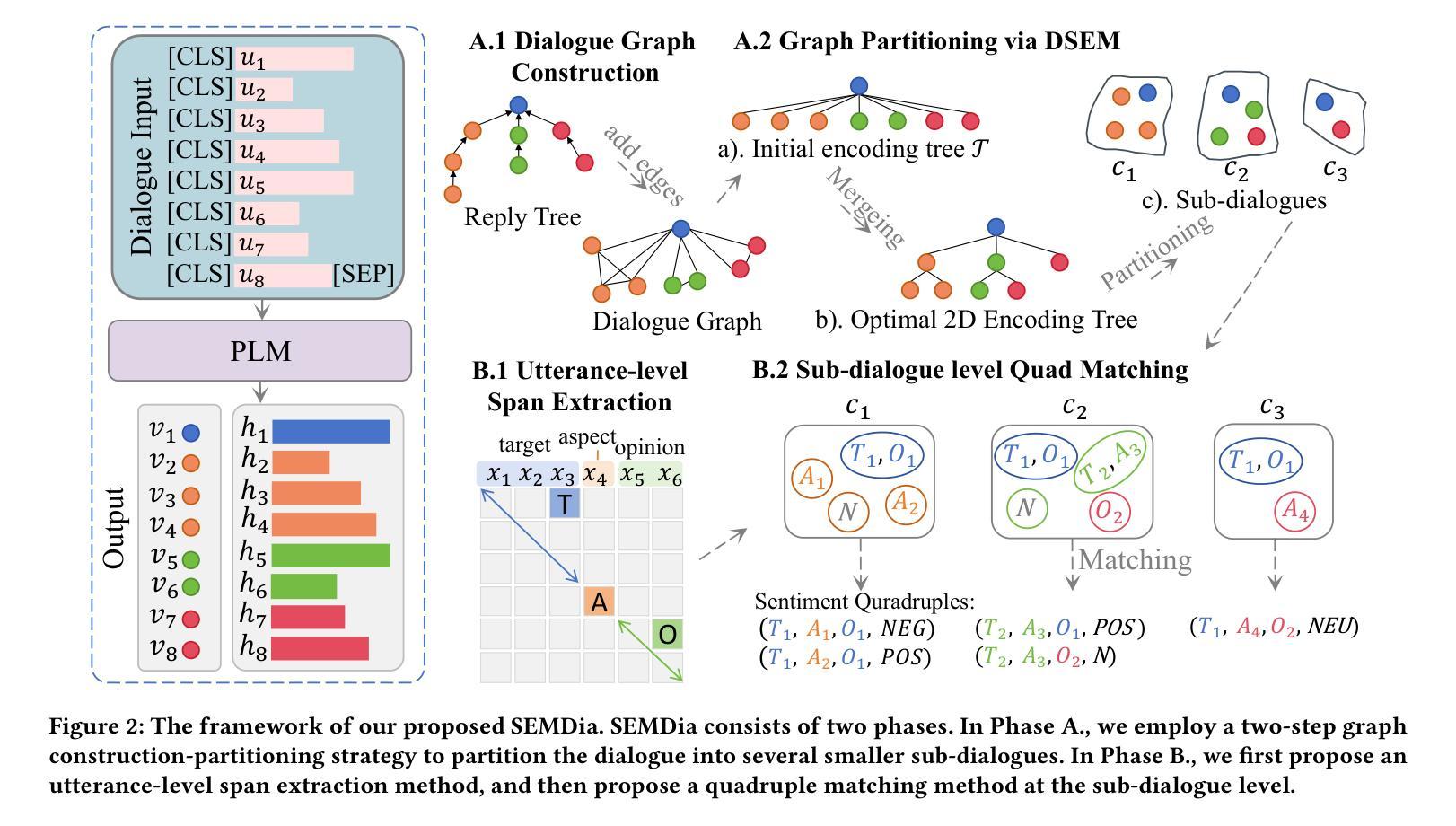
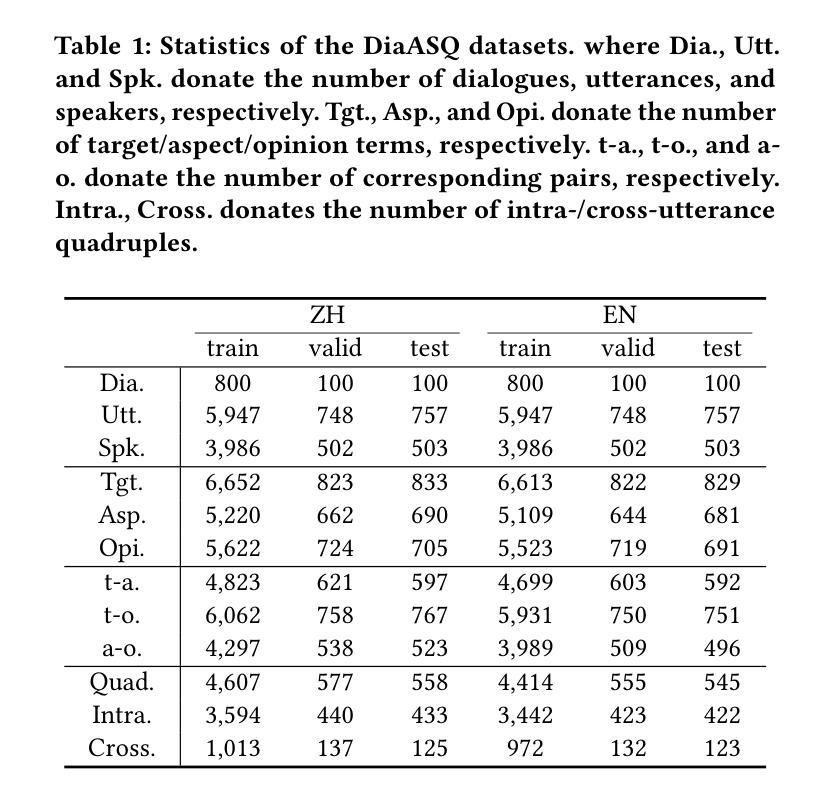
Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction (DiaASQ) aims to extract all target-aspect-opinion-sentiment quadruples from a given multi-round, multi-participant dialogue. Existing methods typically learn word relations across entire dialogues, assuming a uniform distribution of sentiment elements. However, we find that dialogues often contain multiple semantically independent sub-dialogues without clear dependencies between them. Therefore, learning word relationships across the entire dialogue inevitably introduces additional noise into the extraction process. To address this, our method focuses on partitioning dialogues into semantically independent sub-dialogues. Achieving completeness while minimizing these sub-dialogues presents a significant challenge. Simply partitioning based on reply relationships is ineffective. Instead, we propose utilizing a structural entropy minimization algorithm to partition the dialogues. This approach aims to preserve relevant utterances while distinguishing irrelevant ones as much as possible. Furthermore, we introduce a two-step framework for quadruple extraction: first extracting individual sentiment elements at the utterance level, then matching quadruples at the sub-dialogue level. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in DiaASQ with much lower computational costs.
对话基于方面的情感四重提取(DiaASQ)旨在从给定的多轮、多参与者的对话中提取所有的目标-方面-观点-情感四重关系。现有方法通常学习整个对话中的词关系,并假设情感元素呈均匀分布。然而,我们发现对话通常包含多个语义上独立的子对话,它们之间没有明确的依赖关系。因此,在整个对话中学习词关系不可避免地会为提取过程引入额外的噪音。为了解决这一问题,我们的方法专注于将对话分割成语义独立的子对话。在保持完整性的同时最小化这些子对话,这构成了一个巨大的挑战。仅基于回复关系进行分区是无效的。相反,我们提出了一种结构熵最小化算法来进行对话分割。这种方法旨在保留相关的言论,同时尽可能区分不相关的言论。此外,我们为四重提取引入了两步框架:首先在话语级别提取单个情感元素,然后在子对话级别匹配四重关系。大量实验表明,我们的方法在DiaASQ上实现了最先进的性能,同时计算成本更低。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CIKM2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对对话情感分析中目标-方面-观点-情感四元组提取的新方法。现有方法通常在整个对话中学习词关系,但对话中常包含多个语义独立的子对话,因此提出将对话划分为子对话并分别处理。采用结构熵最小化算法进行对话划分,旨在保留相关话语并尽可能区分不相关话语。同时,引入两步框架进行四元组提取,首先提取单句级别的情感元素,然后匹配子对话级别的四元组。实验表明,该方法在降低计算成本的同时实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Dialogues Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Extraction (DiaASQ)旨在从多轮、多参与者的对话中提取所有目标-方面-观点-情感四元组。
- 现有方法在整个对话中学习词关系,但对话中常含有多个语义独立的子对话。
- 简单的基于回复关系的划分方法无效,因此提出使用结构熵最小化算法进行对话划分。
- 该算法旨在保留相关话语并尽可能区分不相关话语。
- 引入两步框架进行四元组提取:首先提取单句级别的情感元素,然后匹配子对话级别的四元组。
- 实验证明该方法在DiaASQ上实现了卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图


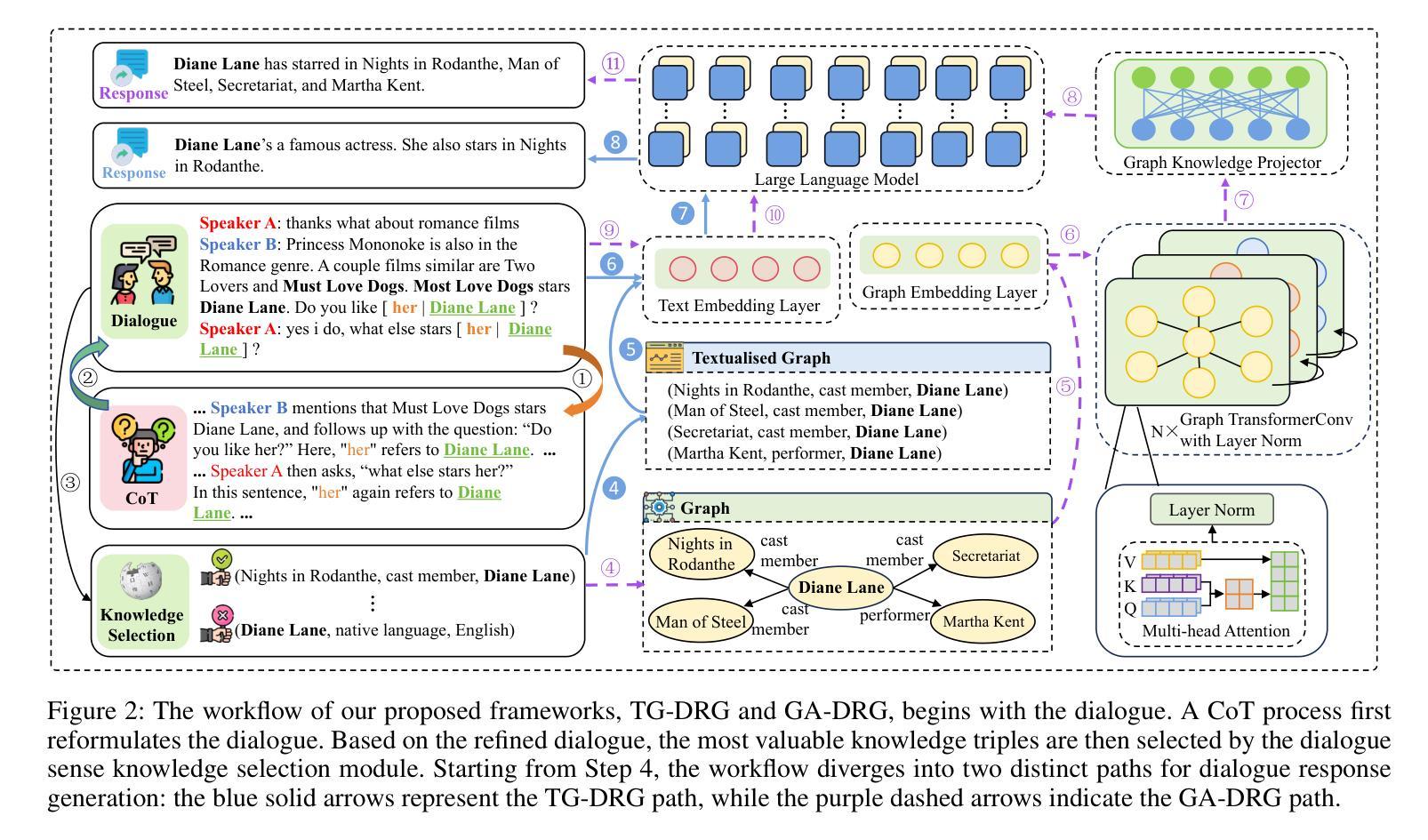
Improving Factuality for Dialogue Response Generation via Graph-Based Knowledge Augmentation
Authors:Xiangyan Chen, Yujian Gan, Yimeng Gu, Matthew Purver
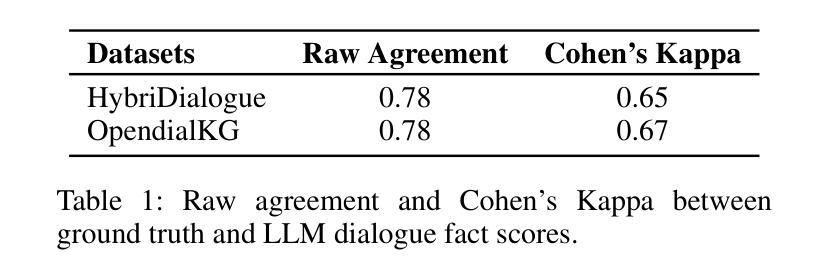
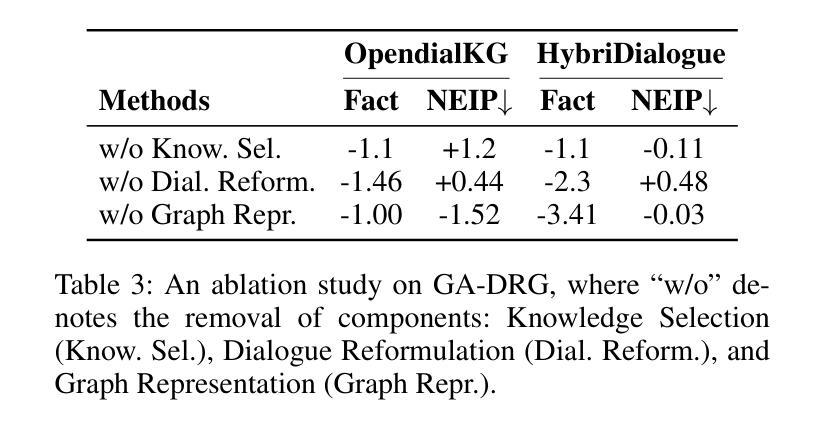
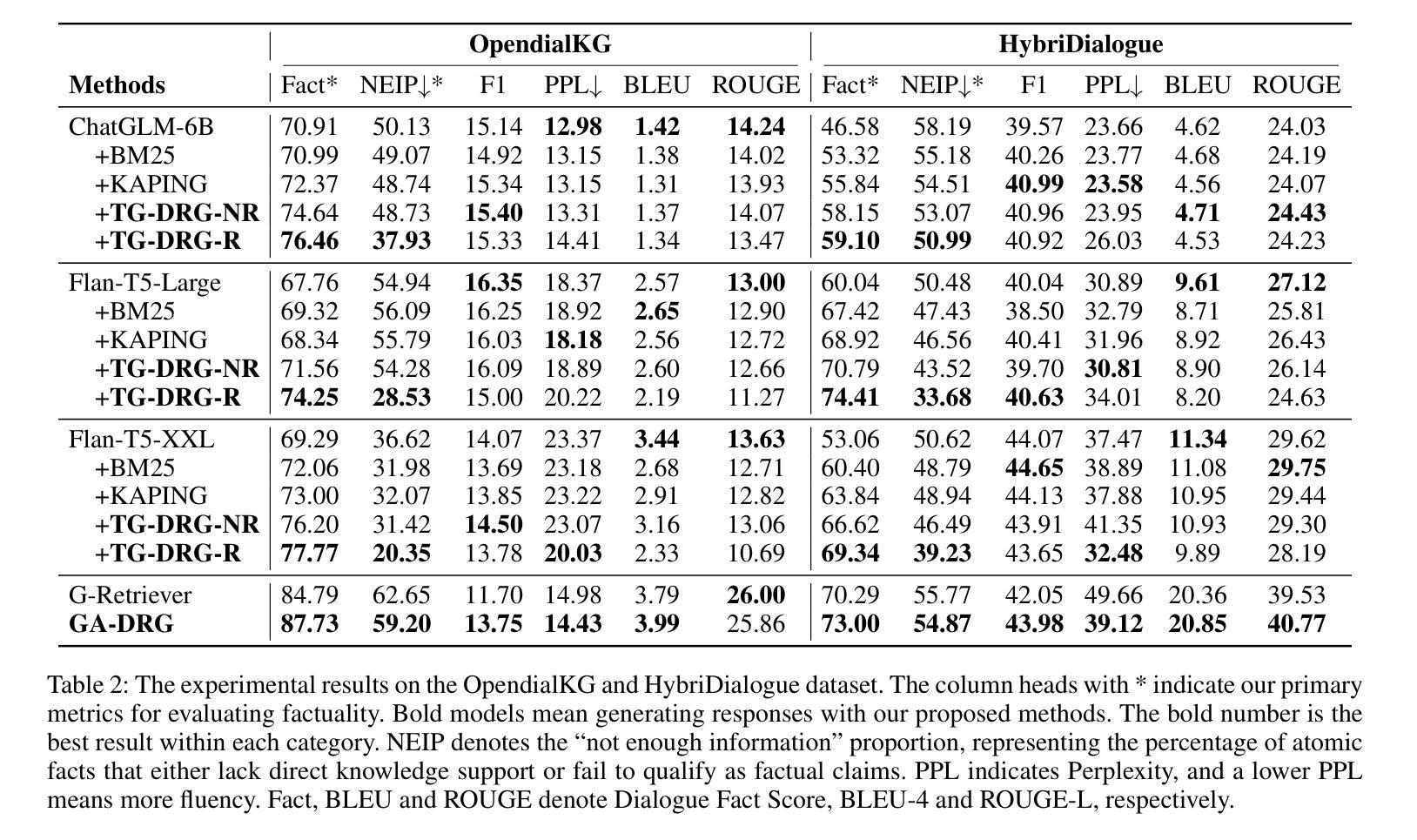
Large Language Models (LLMs) succeed in many natural language processing tasks. However, their tendency to hallucinate - generate plausible but inconsistent or factually incorrect text - can cause significant problems in certain tasks, including response generation in dialogue. To mitigate this issue, we propose two novel graph knowledge-augmented frameworks, Dialogue Response Generation via Textualised Graphs (TG-DRG) and Graph-Aware Dialogue Response Generation (GA-DRG), which combine reasoning-guided dialogue reformulation, dialogue sense knowledge selection, and graph-enhanced response generation to improve the factuality of dialogue responses. To evaluate the factuality of generated responses, we propose a dialogue fact score that addresses the limitations of existing fact-score methods in dialogue settings, providing a more reliable assessment of factual consistency. We evaluate our methods using different baselines on the OpendialKG and HybriDialogue datasets. Our methods noticeably improve factuality compared to other graph knowledge-augmentation baselines, including the state-of-the-art G-retriever, achieving improvements of 3.47% on OpendialKG and 3.12% on HybriDialogue in terms of dialogue fact score. The code will be released on GitHub.
大型语言模型(LLM)在许多自然语言处理任务中取得了成功。然而,它们倾向于产生合理但自相矛盾或事实错误的文本,这在某些任务中包括对话生成会引发严重问题。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了两种新型的图知识增强框架,即基于文本图的对话响应生成(TG-DRG)和图感知对话响应生成(GA-DRG)。这两个框架结合了推理引导的对话重构、对话常识知识选择和图增强响应生成,以提高对话响应的事实性。为了评估生成响应的事实性,我们提出了对话事实得分,解决了现有事实得分方法在对话环境中的局限性,为事实一致性提供了更可靠的评估。我们在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上使用了不同的基线来评估我们的方法。与包括当前最先进的G-检索器在内的其他图知识增强基线相比,我们的方法在事实性方面有了显著的提高,在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue上的对话事实得分分别提高了3.47%和3.12%。代码将在GitHub上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但在对话生成等任务中存在虚构倾向。为解决这一问题,本文提出两种新型图文知识增强框架:文本化图表对话响应生成(TG-DRG)和图形感知对话响应生成(GA-DRG)。它们结合推理引导对话重构、对话感知知识选择和图形增强响应生成,以提高对话响应的事实性。为评估生成响应的事实性,本文提出对话事实评分方法,解决了现有事实评分方法在对话设置中的局限性。在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上评估,与图形知识增强基线方法相比,所提方法显著提高了事实性,改进幅度达3.47%和3.12%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自然语言处理任务中表现优秀,但在对话生成任务中存在虚构问题。
- 提出两种新型的图知识增强框架:TG-DRG和GA-DRG,结合多种技术提高对话响应的事实性。
- 引入对话事实评分方法,更可靠地评估生成响应的事实性。
- 所提方法在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上评估,较图形知识增强基线有显著改善。
- 所提方法提高了3.47%和3.12%的事实性,显示出所提方法的有效性。
- 将在GitHub上发布代码。
- 通过对语言模型的改进,有助于更准确地生成对话响应,提高用户体验。
点此查看论文截图