⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification
Authors:Yongliang Wu, Yizhou Zhou, Zhou Ziheng, Yingzhe Peng, Xinyu Ye, Xinting Hu, Wenbo Zhu, Lu Qi, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Xu Yang
We present a simple yet theoretically motivated improvement to Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) for the Large Language Model (LLM), addressing its limited generalization compared to reinforcement learning (RL). Through mathematical analysis, we reveal that standard SFT gradients implicitly encode a problematic reward structure that may severely restrict the generalization capabilities of model. To rectify this, we propose Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT), stabilizing gradient updates for each token by dynamically rescaling the objective function with the probability of this token. Remarkably, this single-line code change significantly outperforms standard SFT across multiple challenging benchmarks and base models, demonstrating greatly improved generalization. Additionally, our approach shows competitive results in offline RL settings, offering an effective yet simpler alternative. This work bridges theoretical insight and practical solutions, substantially advancing SFT performance. The code will be available at https://github.com/yongliang-wu/DFT.
我们对大型语言模型(LLM)的监督微调(SFT)进行了简单但理论上的改进,解决了其与强化学习(RL)相比的有限泛化能力问题。通过数学分析,我们发现标准SFT梯度隐式编码了一个有问题的奖励结构,这可能会严重限制模型的泛化能力。为了纠正这一点,我们提出了动态微调(DFT),通过动态调整目标函数与该令牌的概率来稳定每个令牌的梯度更新。值得注意的是,这一行代码的改动在多个具有挑战性的基准测试和基准模型上显著优于标准的SFT,表现出极大的泛化改进。此外,我们的方法在线下RL设置中也表现出有竞争力的结果,提供了一个有效但更简单的替代方案。这项工作将理论见解与实际解决方案相结合,极大地提高了SFT的性能。代码将在https://github.com/yongliang-wu/DFT上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对大型语言模型(LLM)的监督微调(SFT)的一种简单而理论上的改进方法,解决了其相对于强化学习(RL)的有限泛化问题。通过数学分析,作者发现标准SFT梯度隐含了一种可能严重限制模型泛化能力的问题奖励结构。为了解决这个问题,作者提出了动态微调(DFT),通过动态调整目标函数的概率来稳定每个标记的梯度更新。这一简单的代码改动在多个具有挑战性的基准测试和基础模型上显著优于标准的SFT,表现出更好的泛化能力。此外,该方法在离线RL设置中也表现出具有竞争力的结果,提供了一种有效且简单的替代方案。这项工作将理论见解和实用解决方案相结合,大大提高了SFT的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 监督微调(SFT)在大型语言模型(LLM)中存在有限泛化问题。
- 标准SFT梯度隐含了可能限制模型泛化能力的问题奖励结构。
- 动态微调(DFT)通过动态调整目标函数概率来稳定梯度更新,提高了模型的泛化能力。
- DFT在多个基准测试和模型上显著优于标准SFT。
- DFT在离线RL设置中也表现出竞争力。
- 该工作结合了理论分析和实用解决方案,推动了SFT的发展。
点此查看论文截图

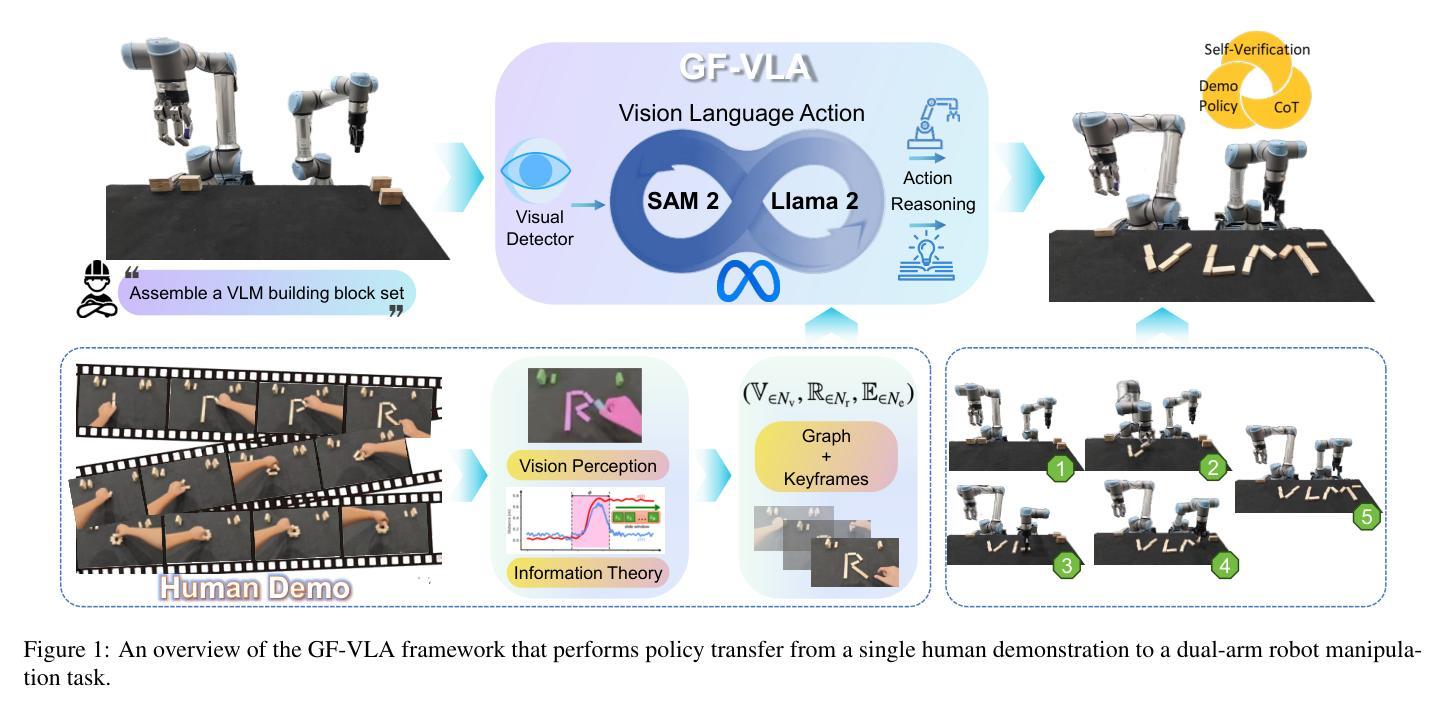
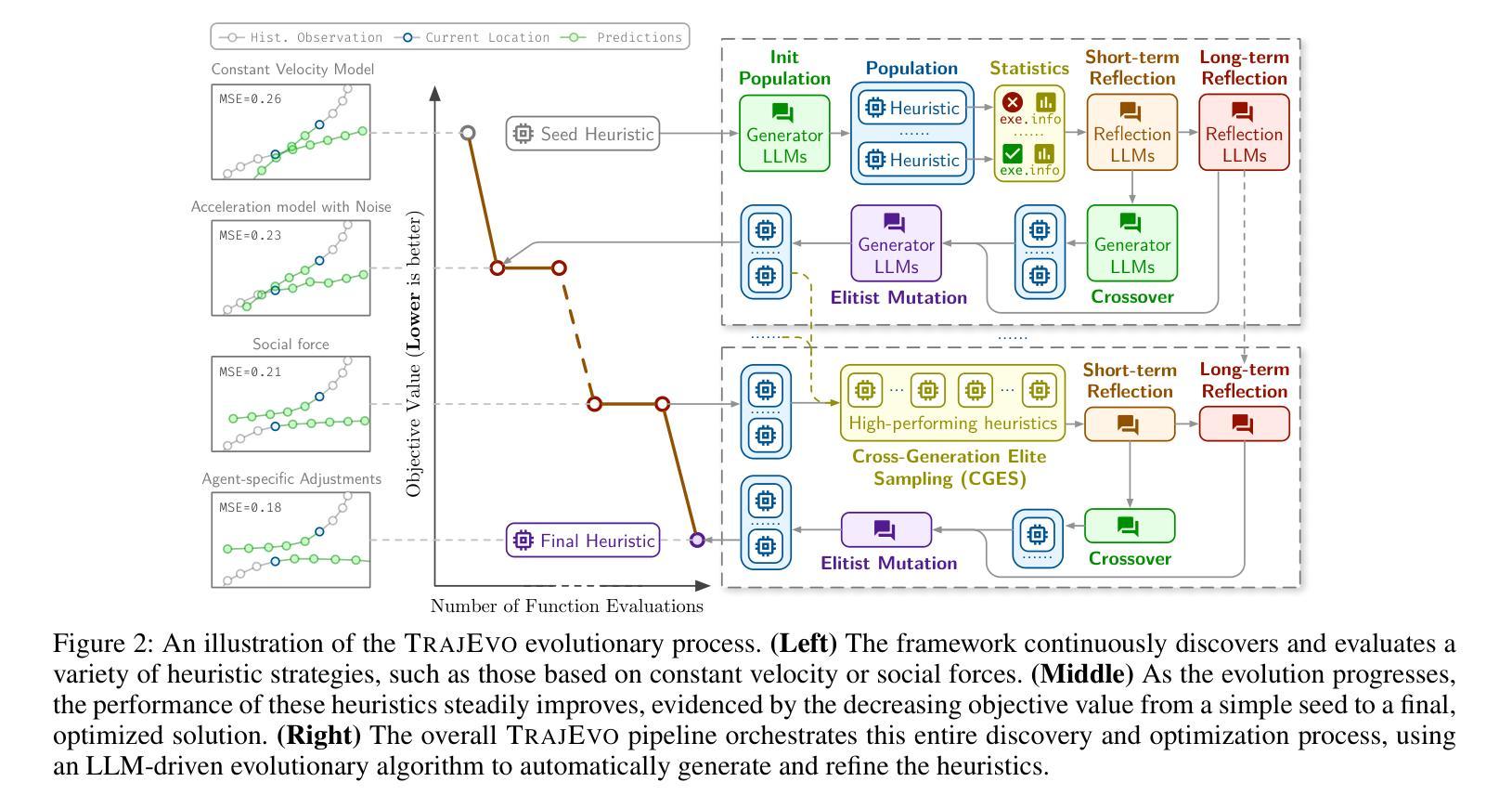
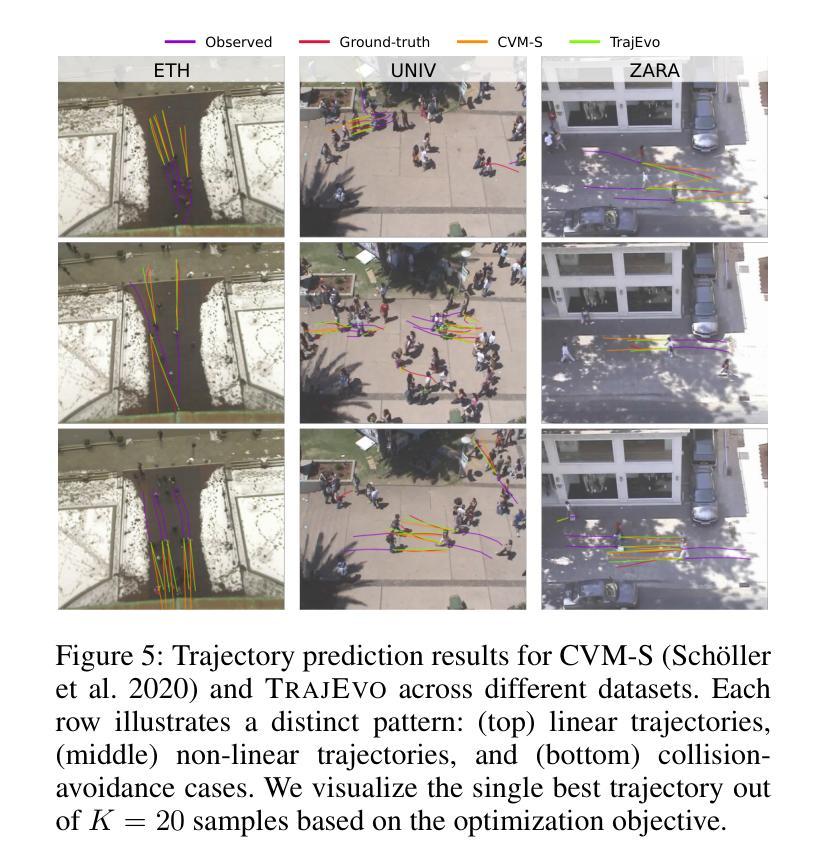
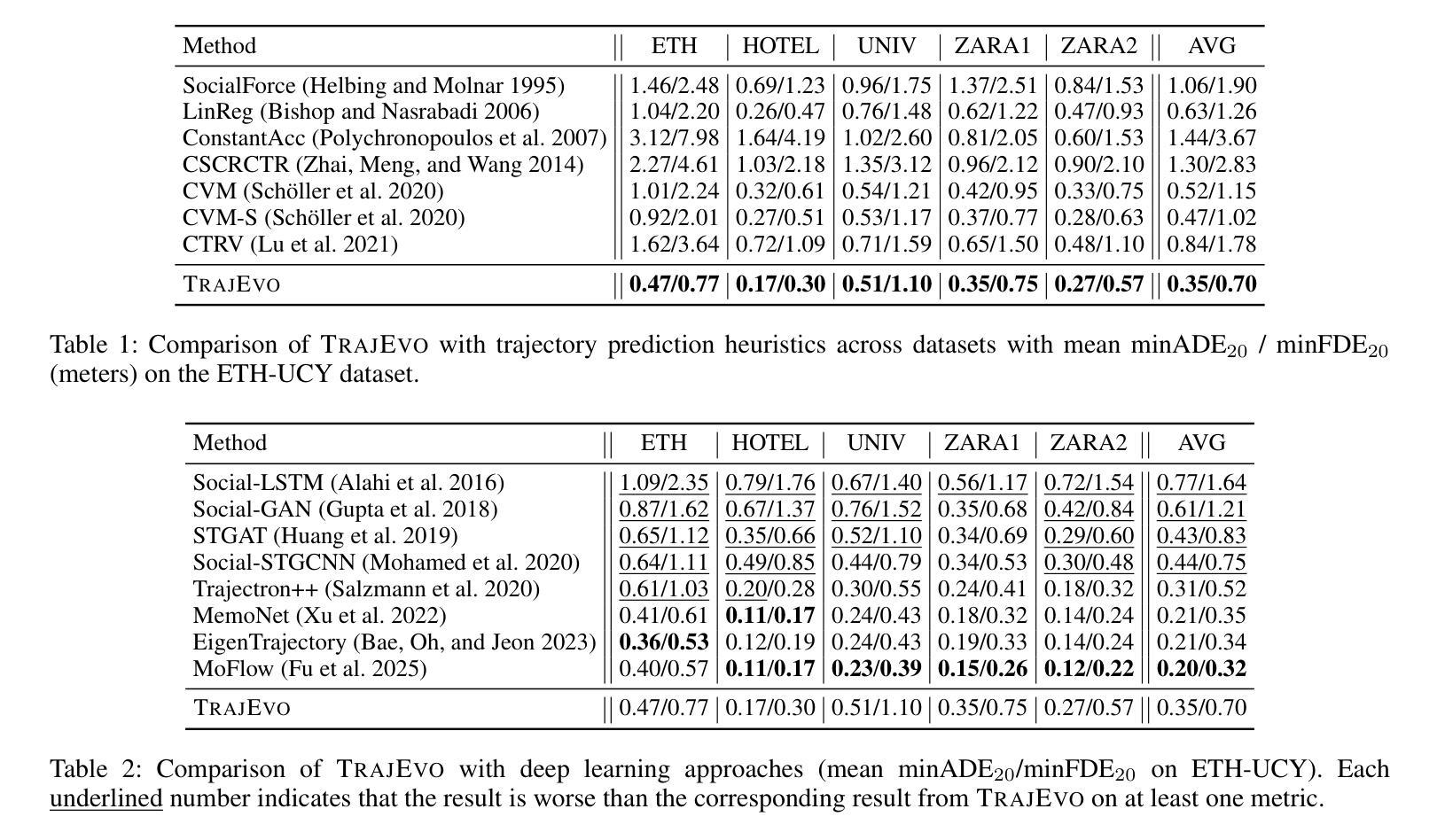
TrajEvo: Trajectory Prediction Heuristics Design via LLM-driven Evolution
Authors:Zhikai Zhao, Chuanbo Hua, Federico Berto, Kanghoon Lee, Zihan Ma, Jiachen Li, Jinkyoo Park
Trajectory prediction is a critical task in modeling human behavior, especially in safety-critical domains such as social robotics and autonomous vehicle navigation. Traditional heuristics based on handcrafted rules often lack accuracy and generalizability. Although deep learning approaches offer improved performance, they typically suffer from high computational cost, limited explainability, and, importantly, poor generalization to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. In this paper, we introduce TrajEvo, a framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically design trajectory prediction heuristics. TrajEvo employs an evolutionary algorithm to generate and refine prediction heuristics from past trajectory data. We propose two key innovations: Cross-Generation Elite Sampling to encourage population diversity, and a Statistics Feedback Loop that enables the LLM to analyze and improve alternative predictions. Our evaluations demonstrate that TrajEvo outperforms existing heuristic methods across multiple real-world datasets, and notably surpasses both heuristic and deep learning methods in generalizing to an unseen OOD real-world dataset. TrajEvo marks a promising step toward the automated design of fast, explainable, and generalizable trajectory prediction heuristics. We release our source code to facilitate future research at https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo.
轨迹预测是模拟人类行为的关键任务,特别是在社会机器人和自动驾驶导航等安全关键领域。基于手工制定的传统启发式方法通常缺乏准确性和泛化能力。尽管深度学习方法可以提升性能,但它们通常面临计算成本高、解释性差以及对于分布外(OOD)场景的泛化能力不强等重要问题。在本文中,我们介绍了TrajEvo框架,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测启发式方法。TrajEvo采用进化算法根据过去的轨迹数据生成和改进预测启发式方法。我们提出了两个关键创新点:跨代精英采样以促进种群多样性,以及一个统计反馈循环,使LLM能够分析和改进替代预测。我们的评估表明,TrajEvo在多个真实世界数据集上的表现优于现有的启发式方法,并且在未见过的OOD真实世界数据集上的泛化性能显著超越了启发式和深度学习方法。TrajEvo标志着朝着自动设计快速、可解释和可泛化的轨迹预测启发式方法迈出了有前景的一步。我们在https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo发布我们的源代码,以促进今后的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2505.04480
Summary
本文介绍了TrajEvo框架,该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测启发式方法。TrajEvo采用进化算法生成和细化预测启发式方法,并提出两个关键创新点:跨代精英采样以促进种群多样性,以及统计反馈循环使LLM能够分析和改进替代预测。评估结果表明,TrajEvo在多个真实数据集上的表现优于现有启发式方法,并在未见过的OOD真实数据集上的表现尤为突出。TrajEvo为快速、可解释和通用的轨迹预测启发式方法的自动化设计迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- TrajEvo框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测启发式方法,以提高准确性和泛化能力。
- TrajEvo采用进化算法生成和细化预测启发式方法,通过Cross-Generation Elite Sampling和Statistics Feedback Loop两个关键创新点来提升性能。
- 跨代精英采样有助于鼓励种群多样性,从而提高预测模型的探索能力和创新能力。
- 统计反馈循环使LLM能够分析和改进替代预测,从而提高模型的解释性和准确性。
- TrajEvo在多个真实数据集上的表现优于传统启发式方法和深度学习方法。
- TrajEvo能够很好地泛化到未见过的OOD真实数据集上,显示出其强大的适应性和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


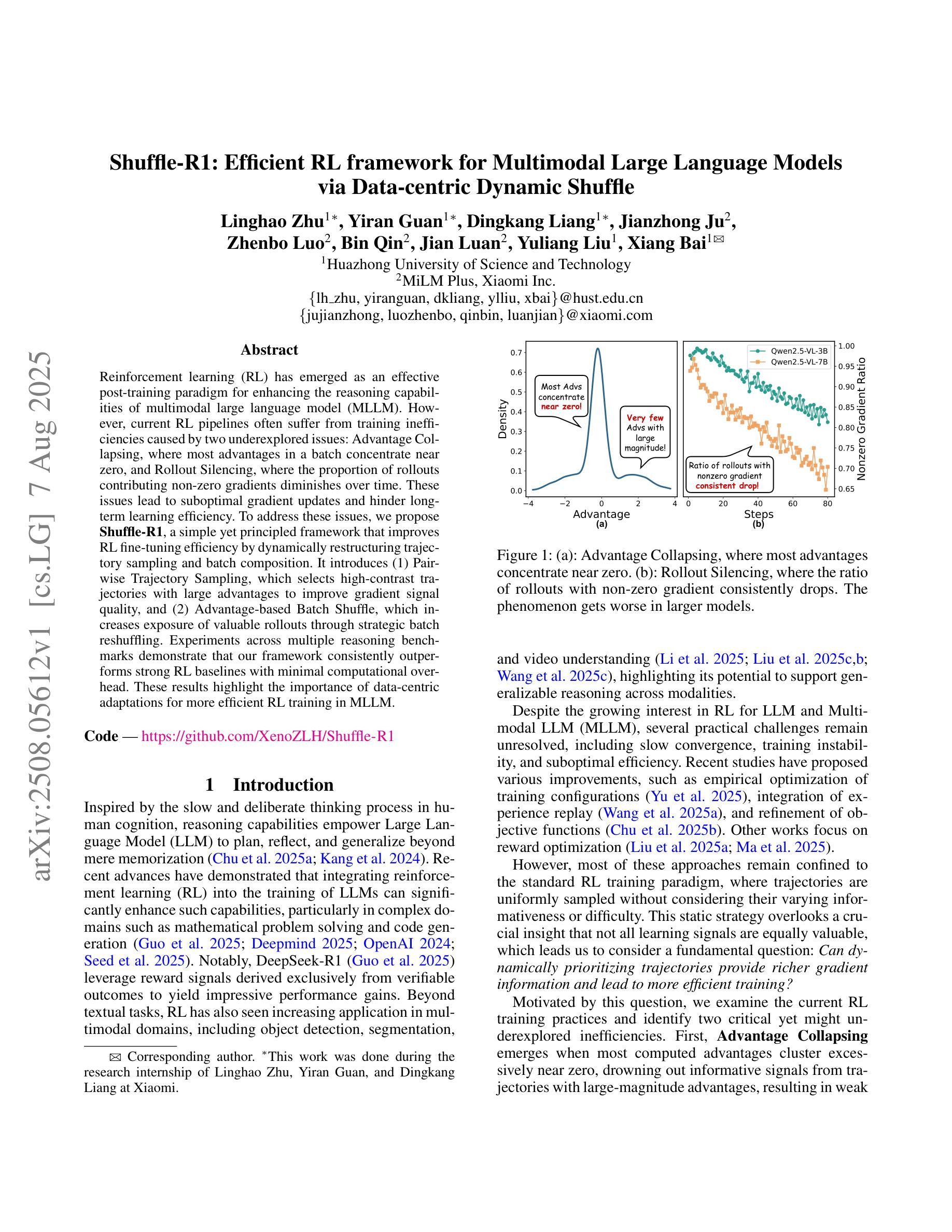
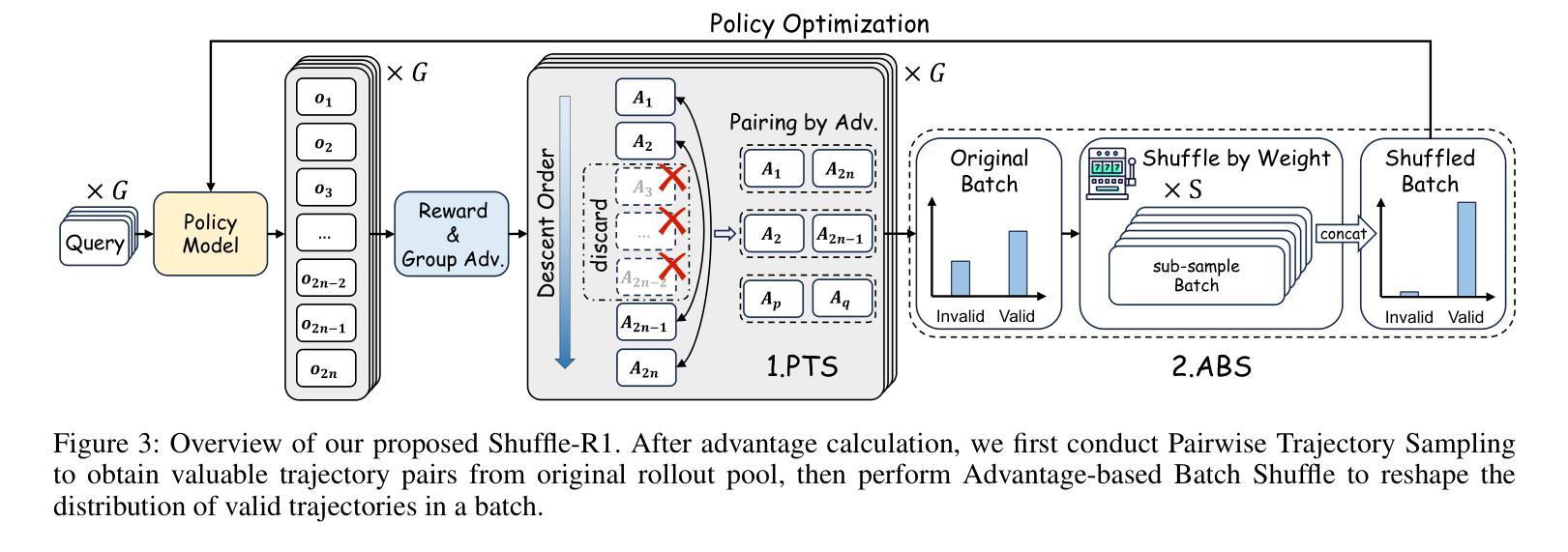
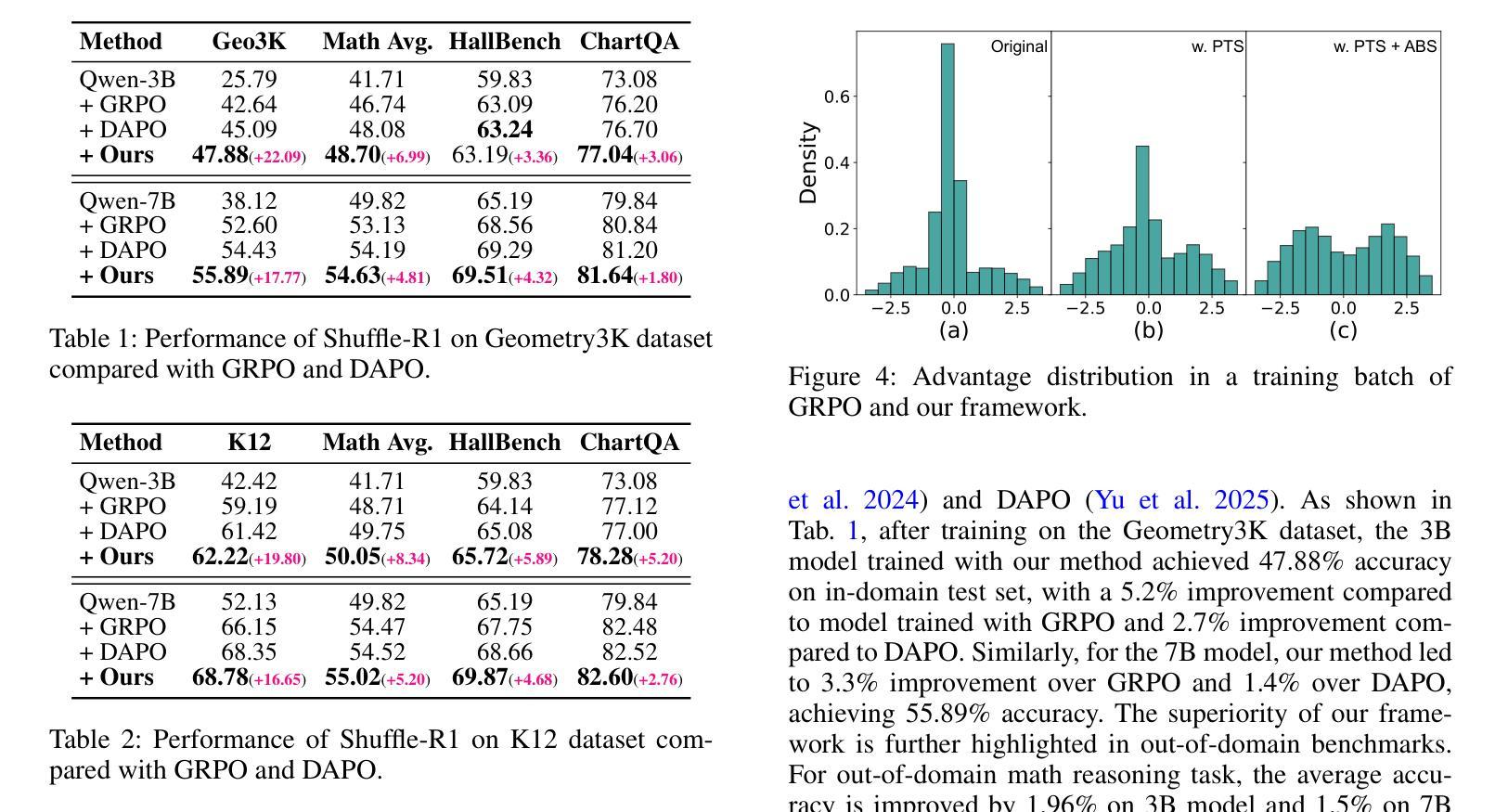
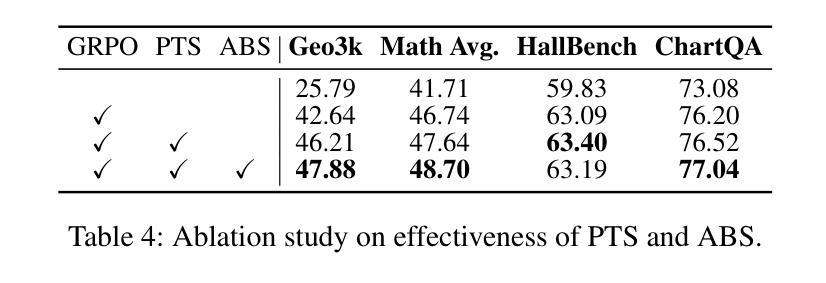
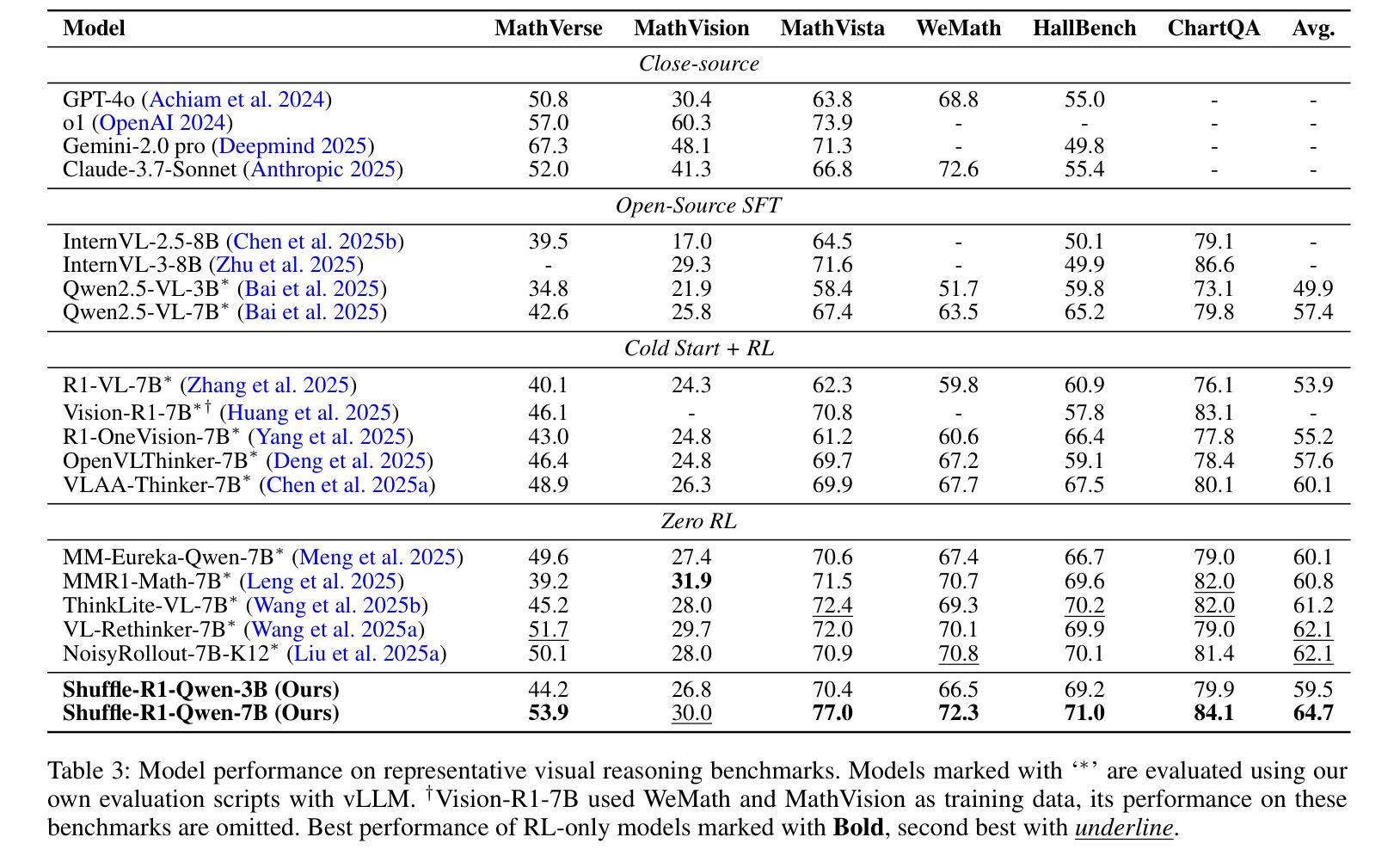
Shuffle-R1: Efficient RL framework for Multimodal Large Language Models via Data-centric Dynamic Shuffle
Authors:Linghao Zhu, Yiran Guan, Dingkang Liang, Jianzhong Ju, Zhenbo Luo, Bin Qin, Jian Luan, Yuliang Liu, Xiang Bai
Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as an effective post-training paradigm for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language model (MLLM). However, current RL pipelines often suffer from training inefficiencies caused by two underexplored issues: Advantage Collapsing, where most advantages in a batch concentrate near zero, and Rollout Silencing, where the proportion of rollouts contributing non-zero gradients diminishes over time. These issues lead to suboptimal gradient updates and hinder long-term learning efficiency. To address these issues, we propose Shuffle-R1, a simple yet principled framework that improves RL fine-tuning efficiency by dynamically restructuring trajectory sampling and batch composition. It introduces (1) Pairwise Trajectory Sampling, which selects high-contrast trajectories with large advantages to improve gradient signal quality, and (2) Advantage-based Trajectory Shuffle, which increases exposure of valuable rollouts through informed batch reshuffling. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks show that our framework consistently outperforms strong RL baselines with minimal overhead. These results highlight the importance of data-centric adaptations for more efficient RL training in MLLM.
强化学习(RL)已经成为提高多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)推理能力的一种有效的后训练范式。然而,当前的强化学习管道往往存在训练效率不高的现象,这主要由两个尚未被充分研究的问题引起:优势崩塌,即一批次中的大部分优势集中在零附近;以及扩展沉默问题,随着时间的推移,生成样本为非零梯度的贡献比例逐渐降低。这些问题导致了次优的梯度更新,并阻碍了长期学习效率的提升。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Shuffle-R1框架,它通过动态重构轨迹采样和批次组合来提高强化学习的微调效率。它引入了(1)配对轨迹采样,选择具有较大优势的对比轨迹来提高梯度信号质量;(2)基于优势的轨迹洗牌,通过信息丰富的批次重洗牌来增加有价值的生成样本的曝光。在多个推理基准测试上的实验表明,我们的框架始终优于强大的强化学习基线,并且具有最小的额外开销。这些结果强调了以数据为中心的策略对于提高MLLM中的强化学习训练效率的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:强化学习(RL)作为提升多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)推理能力的后训练范式,效果显著。然而,当前RL管道存在训练效率低下的问题,主要由于优势崩塌和滚动沉默两个未充分探讨的问题。为解决这些问题,提出Shuffle-R1框架,通过动态重构轨迹采样和批次组成来提高RL微调效率。该框架引入成对轨迹采样和基于优势的轨迹洗牌,提高梯度信号质量和有价值的滚动结果的曝光度。实验表明,该框架在多个推理基准测试中始终优于强大的RL基线,且几乎不增加开销。
Key Takeaways:
- 强化学习(RL)能有效提升多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的推理能力。
- 当前RL管道存在训练效率低下的问题,主要因为优势崩塌和滚动沉默。
- Shuffle-R1框架通过动态重构轨迹采样和批次组成来提高RL微调效率。
- Shuffle-R1引入成对轨迹采样,选择高对比度的轨迹以提高梯度信号质量。
- Shuffle-R1的基于优势的轨迹洗牌增加有价值滚动结果的曝光度。
- 实验证明Shuffle-R1框架在多个推理基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
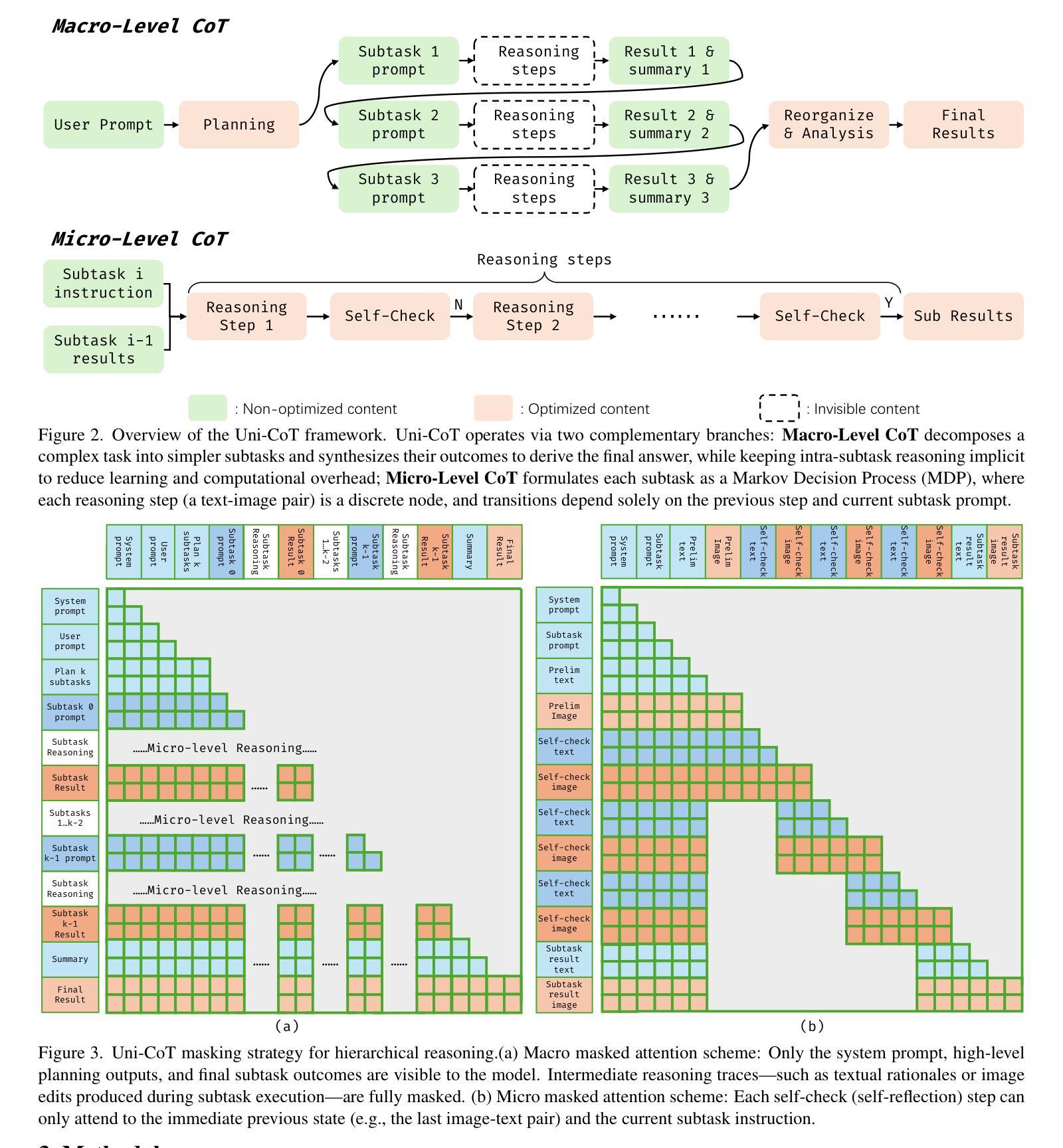
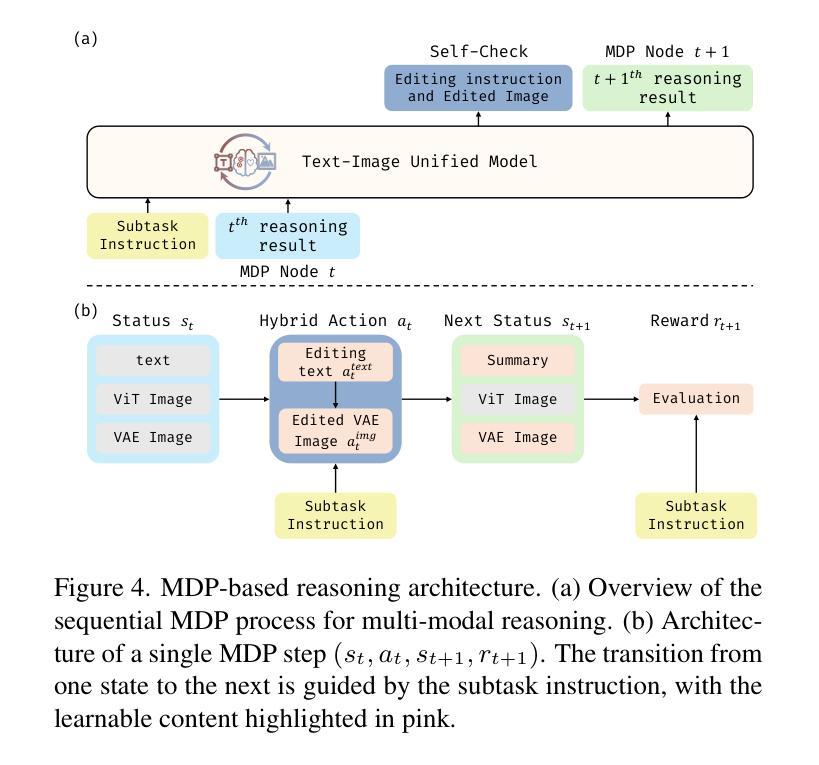
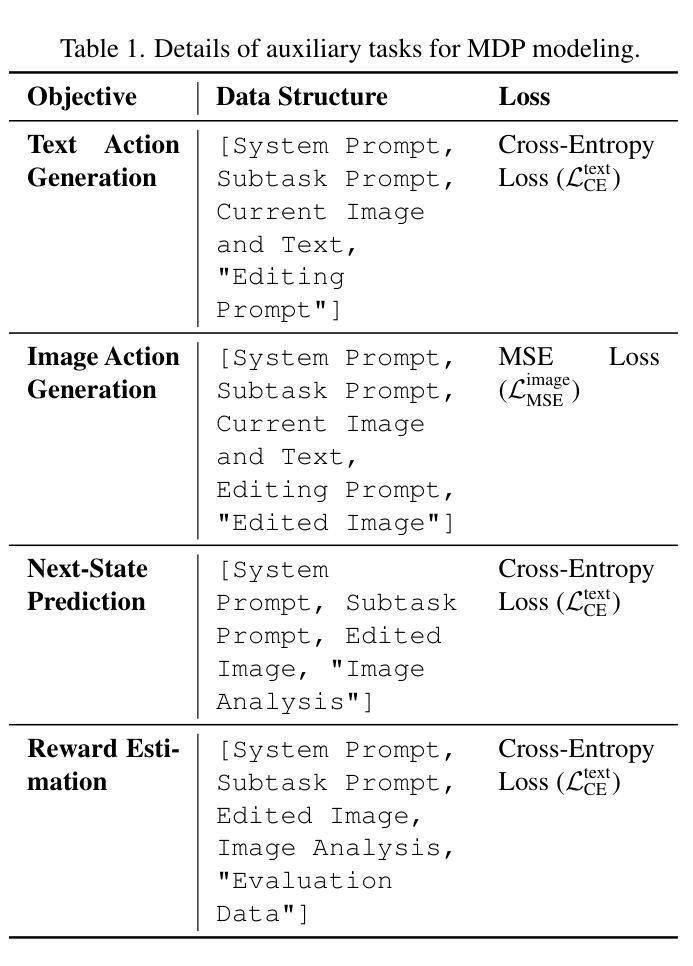
Uni-cot: Towards Unified Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Across Text and Vision
Authors:Luozheng Qin, Jia Gong, Yuqing Sun, Tianjiao Li, Mengping Yang, Xiaomeng Yang, Chao Qu, Zhiyu Tan, Hao Li
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has been widely adopted to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by decomposing complex tasks into simpler, sequential subtasks. However, extending CoT to vision-language reasoning tasks remains challenging, as it often requires interpreting transitions of visual states to support reasoning. Existing methods often struggle with this due to limited capacity of modeling visual state transitions or incoherent visual trajectories caused by fragmented architectures. To overcome these limitations, we propose Uni-CoT, a Unified Chain-of-Thought framework that enables coherent and grounded multimodal reasoning within a single unified model. The key idea is to leverage a model capable of both image understanding and generation to reason over visual content and model evolving visual states. However, empowering a unified model to achieve that is non-trivial, given the high computational cost and the burden of training. To address this, Uni-CoT introduces a novel two-level reasoning paradigm: A Macro-Level CoT for high-level task planning and A Micro-Level CoT for subtask execution. This design significantly reduces the computational overhead. Furthermore, we introduce a structured training paradigm that combines interleaved image-text supervision for macro-level CoT with multi-task objectives for micro-level CoT. Together, these innovations allow Uni-CoT to perform scalable and coherent multi-modal reasoning. Furthermore, thanks to our design, all experiments can be efficiently completed using only 8 A100 GPUs with 80GB VRAM each. Experimental results on reasoning-driven image generation benchmark (WISE) and editing benchmarks (RISE and KRIS) indicates that Uni-CoT demonstrates SOTA performance and strong generalization, establishing Uni-CoT as a promising solution for multi-modal reasoning. Project Page and Code: https://sais-fuxi.github.io/projects/uni-cot/
链式思维(Chain-of-Thought,简称CoT)推理已被广泛应用于通过分解复杂任务为更简单、连续的子任务来提升大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。然而,将CoT扩展到视觉语言推理任务仍然具有挑战性,因为它通常需要解释视觉状态的过渡来支持推理。现有方法由于建模视觉状态过渡的能力有限或碎片化架构导致的视觉轨迹不一致,往往在这方面表现挣扎。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://sais-fuxi.github.io/projects/uni-cot/
Summary
本文介绍了如何将Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理应用于增强大型语言模型(LLM)的挑战,特别是在视觉语言推理任务中的应用。针对现有方法的局限性,提出了一种统一的Chain-of-Thought框架(Uni-CoT),它能够在单个统一模型中进行连贯和基于地面的多模态推理。该框架引入了一种新颖的两级推理模式,即宏观层面的CoT用于高级任务规划,微观层面的CoT用于子任务执行,以减少计算开销。此外,还提出了一种结构化的训练模式,以支持宏观和微观两个层面的CoT的多任务目标。这些创新使得Uni-CoT在视觉语言推理任务中表现出卓越的性能和强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- Uni-CoT框架旨在解决将Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理应用于视觉语言推理任务的挑战。
- 它通过在单个统一模型中进行连贯和基于地面的多模态推理来实现这一目标。
- Uni-CoT引入了一种新颖的两级推理模式,包括宏观层面的任务规划和微观层面的子任务执行。
- 框架还采用了一种结构化的训练模式来支持宏观和微观CoT的多任务目标。
- 该框架的计算开销得到了显著降低,使得实验可以在有限的计算资源下完成。
- Uni-CoT在视觉语言推理任务中表现出卓越的性能和强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

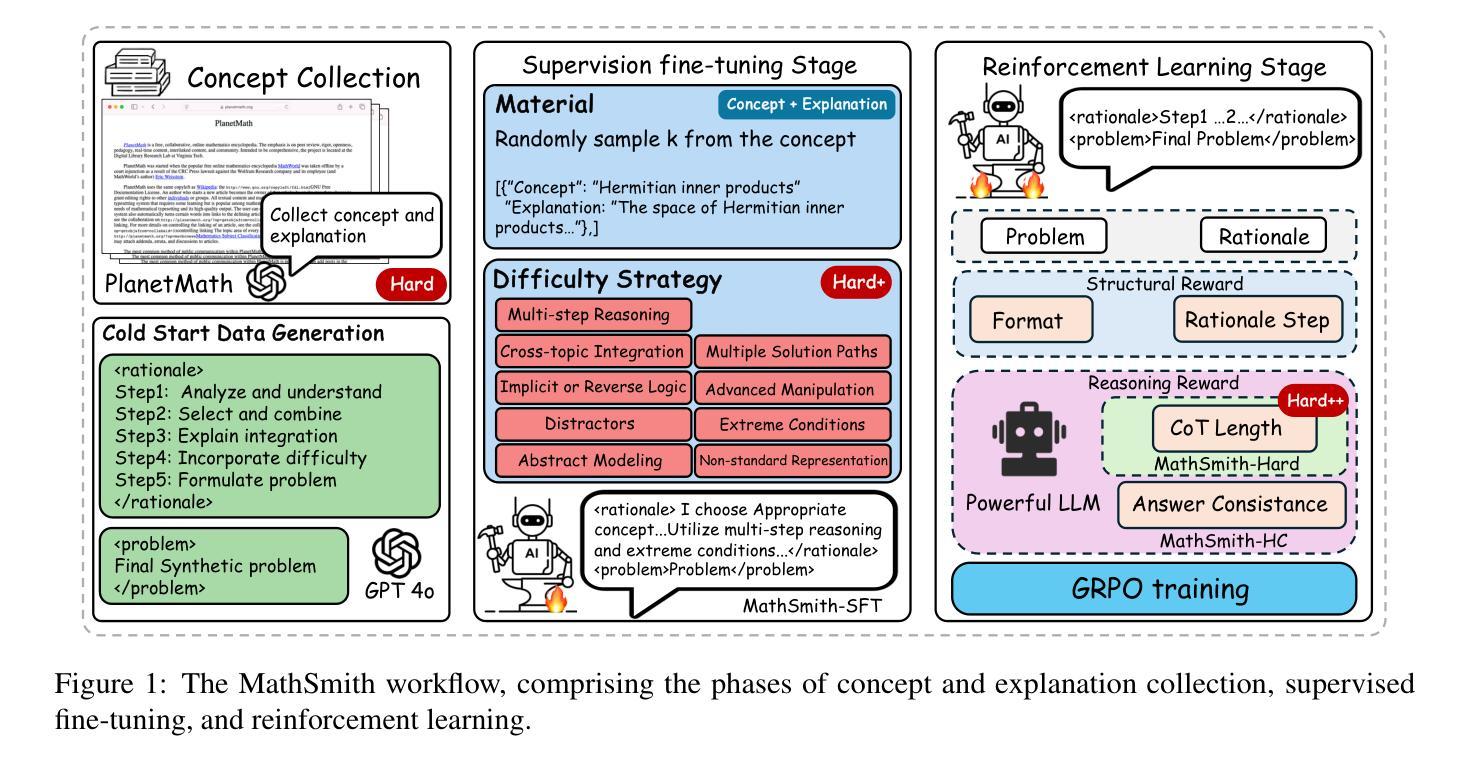
MathSmith: Towards Extremely Hard Mathematical Reasoning by Forging Synthetic Problems with a Reinforced Policy
Authors:Shaoxiong Zhan, Yanlin Lai, Ziyu Lu, Dahua Lin, Ziqing Yang, Fei Tang
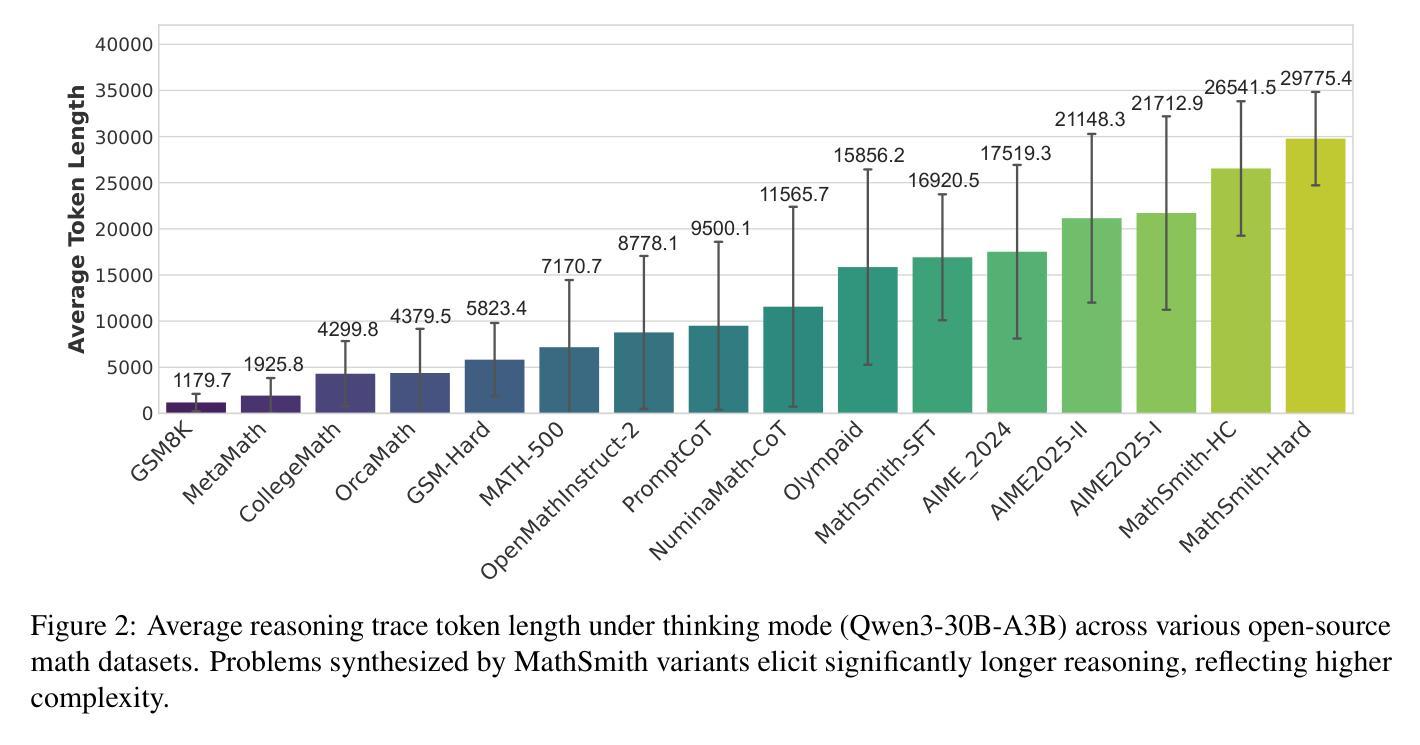
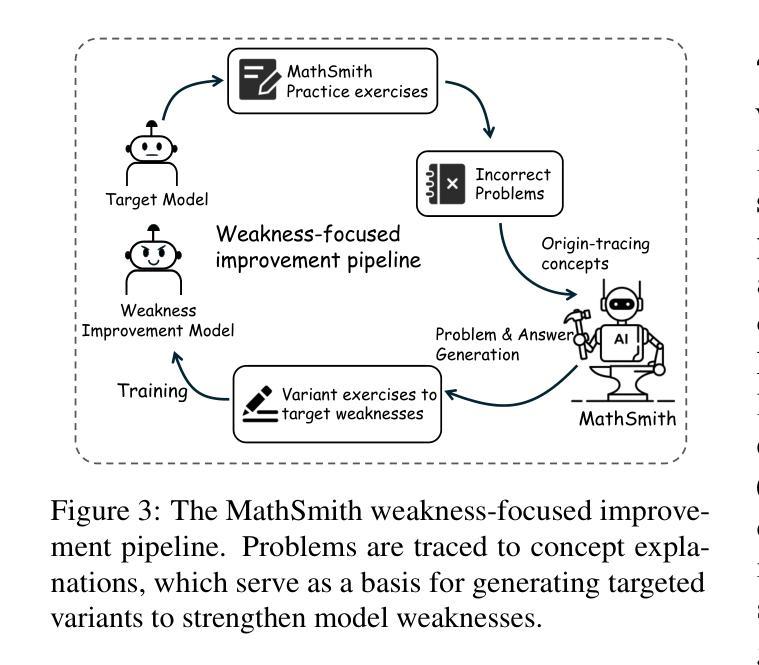
Large language models have achieved substantial progress in mathematical reasoning, yet their advancement is limited by the scarcity of high-quality, high-difficulty training data. Existing synthesis methods largely rely on transforming human-written templates, limiting both diversity and scalability. We propose MathSmith, a novel framework for synthesizing challenging mathematical problems to enhance LLM reasoning. Rather than modifying existing problems, MathSmith constructs new ones from scratch by randomly sampling concept-explanation pairs from PlanetMath, ensuring data independence and avoiding contamination. To increase difficulty, we design nine predefined strategies as soft constraints during rationales. We further adopts reinforcement learning to jointly optimize structural validity, reasoning complexity, and answer consistency. The length of the reasoning trace generated under autoregressive prompting is used to reflect cognitive complexity, encouraging the creation of more demanding problems aligned with long-chain-of-thought reasoning. Experiments across five benchmarks, categorized as easy & medium (GSM8K, MATH-500) and hard (AIME2024, AIME2025, OlympiadBench), show that MathSmith consistently outperforms existing baselines under both short and long CoT settings. Additionally, a weakness-focused variant generation module enables targeted improvement on specific concepts. Overall, MathSmith exhibits strong scalability, generalization, and transferability, highlighting the promise of high-difficulty synthetic data in advancing LLM reasoning capabilities.
大型语言模型在数学推理方面取得了显著进展,但其进展受限于高质量、高难度训练数据的稀缺性。现有的合成方法大多依赖于转换人工编写的模板,这限制了多样性和可扩展性。我们提出了MathSmith,这是一个合成具有挑战性数学问题以增强大型语言模型推理能力的新型框架。MathSmith不是修改现有问题,而是从零开始构建新问题,通过从PlanetMath随机抽取概念解释对,确保数据独立,避免污染。为了提高难度,我们设计了九种预设策略作为推理过程中的软约束。我们进一步采用强化学习来联合优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。在自动回归提示下生成的推理轨迹长度被用来反映认知复杂性,鼓励创建与长链思维推理相符的更具挑战性的问题。在五个基准测试上的实验,被分类为简单和中等(GSM8K,MATH-500)以及困难(AIME2024,AIME2025,OlympiadBench),表明MathSmith在短链和长链思维设置下均优于现有基准测试。此外,弱点聚焦的变体生成模块能够实现特定概念的针对性改进。总体上,MathSmith表现出强大的可扩展性、通用性和可迁移性,突显了高难度合成数据在提升大型语言模型推理能力方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型在数学推理方面取得了显著进展,但其发展受限于高质量、高难度训练数据的稀缺性。现有合成方法主要依赖人工编写模板的转换,限制了多样性和可扩展性。本文提出MathSmith框架,通过从PlanetMath中随机采样概念解释对来合成具有挑战性的数学问题,以增强LLM的推理能力。该框架采用强化学习优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。实验结果表明,MathSmith在五个不同难度的基准测试中均表现出出色的性能,并具备强大的可扩展性、通用性和可迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模语言模型在数学推理方面已取得进展,但缺乏高质量、高难度的训练数据限制了其进一步发展。
- 现有数学问题的合成方法主要基于人工编写模板的转换,这限制了多样性和可扩展性。
- MathSmith框架通过随机采样概念解释对来合成新的数学问题,确保数据独立,避免污染。
- MathSmith采用强化学习来优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。
- MathSmith生成的问题与长期思维推理相契合,反映了认知复杂性。
- 实验结果表明,MathSmith在多个基准测试中表现出色,特别是在困难级别的测试中。
点此查看论文截图

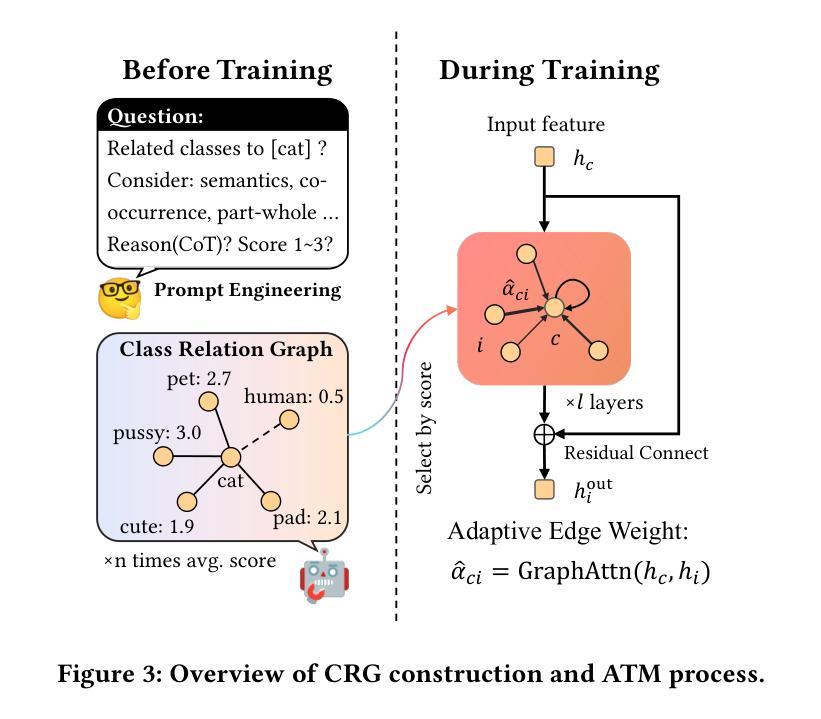
DART: Dual Adaptive Refinement Transfer for Open-Vocabulary Multi-Label Recognition
Authors:Haijing Liu, Tao Pu, Hefeng Wu, Keze Wang, Liang Lin
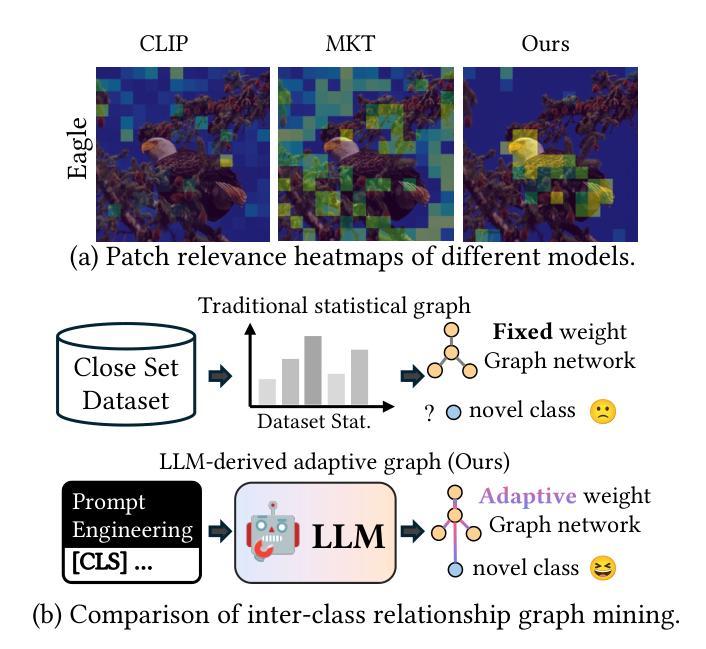
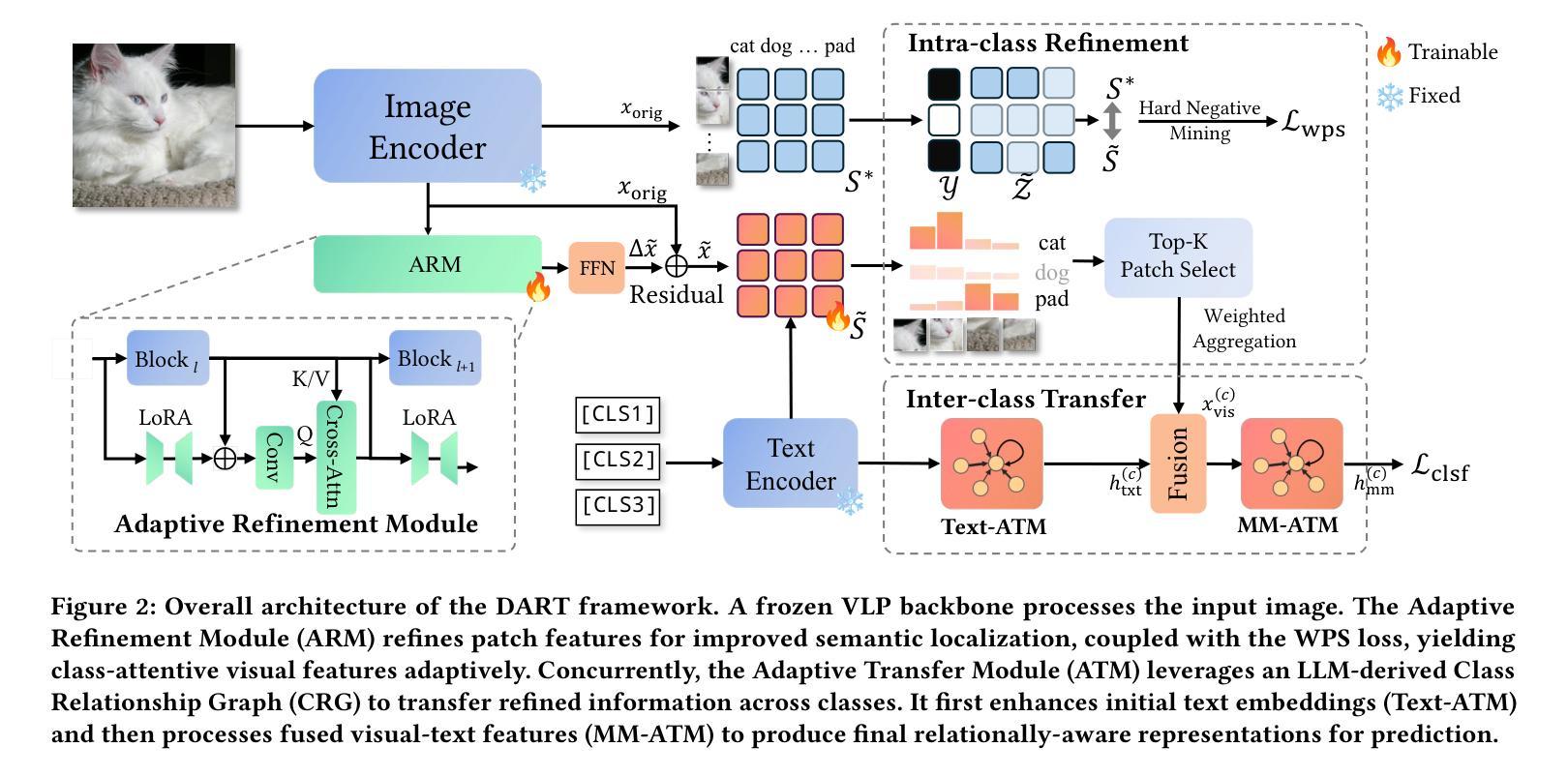
Open-Vocabulary Multi-Label Recognition (OV-MLR) aims to identify multiple seen and unseen object categories within an image, requiring both precise intra-class localization to pinpoint objects and effective inter-class reasoning to model complex category dependencies. While Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) models offer a strong open-vocabulary foundation, they often struggle with fine-grained localization under weak supervision and typically fail to explicitly leverage structured relational knowledge beyond basic semantics, limiting performance especially for unseen classes. To overcome these limitations, we propose the Dual Adaptive Refinement Transfer (DART) framework. DART enhances a frozen VLP backbone via two synergistic adaptive modules. For intra-class refinement, an Adaptive Refinement Module (ARM) refines patch features adaptively, coupled with a novel Weakly Supervised Patch Selecting (WPS) loss that enables discriminative localization using only image-level labels. Concurrently, for inter-class transfer, an Adaptive Transfer Module (ATM) leverages a Class Relationship Graph (CRG), constructed using structured knowledge mined from a Large Language Model (LLM), and employs graph attention network to adaptively transfer relational information between class representations. DART is the first framework, to our knowledge, to explicitly integrate external LLM-derived relational knowledge for adaptive inter-class transfer while simultaneously performing adaptive intra-class refinement under weak supervision for OV-MLR. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our DART achieves new state-of-the-art performance, validating its effectiveness.
开放词汇多标签识别(OV-MLR)旨在识别图像中的多个已知和未知对象类别,这需要精确的类内定位来精确定位对象,以及有效的类间推理来模拟复杂的类别依赖关系。虽然视觉语言预训练(VLP)模型提供了强大的开放词汇基础,但它们通常在弱监督下难以实现精细的定位,并且通常无法明确利用超越基本语义的结构化关系知识,特别对于未知类别的性能有所限制。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了双自适应细化传输(DART)框架。DART通过两个协同的自适应模块增强了冻结的VLP骨干网。对于类内细化,自适应细化模块(ARM)自适应地优化补丁特征,并结合新颖的弱监督补丁选择(WPS)损失,仅使用图像级标签实现区分定位。同时,对于类间传输,自适应传输模块(ATM)利用类关系图(CRG),该图使用从大型语言模型(LLM)中挖掘的结构化知识构建,并采用图注意力网络自适应地传输类表示之间的关系信息。据我们所知,DART是第一个明确整合外部LLM派生关系知识的框架,用于自适应的类间传输,同时执行弱监督下的自适应类内细化,以实现OV-MLR。在具有挑战性的基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的DART达到了新的最先进的性能,验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Open-Vocabulary Multi-Label Recognition(OV-MLR)的任务目标,即识别图像中的多个已知和未知对象类别。文章指出,为了实现这一目标,需要精确的类内定位和有效的类间推理。尽管Vision-Language Pre-training(VLP)模型提供了强大的开放词汇基础,但在弱监督下难以实现精细定位,并且未能明确利用结构化的关系知识,这限制了其在未知类别上的性能。为了克服这些局限性,文章提出了Dual Adaptive Refinement Transfer(DART)框架。DART通过两个协同的适应性模块增强了冻结的VLP骨干网。对于类内细化,自适应细化模块(ARM)自适应地优化补丁特征,并结合新的弱监督补丁选择(WPS)损失,使用图像级标签实现判别定位。对于类间转移,自适应转移模块(ATM)利用类关系图(CRG),该图是利用大型语言模型(LLM)挖掘的结构知识构建的,并应用图注意力网络自适应地转移类表示之间的关系信息。据我们所知,DART是第一个明确整合外部LLM派生关系知识以适应类间转移,同时执行弱监督下的自适应类内细化的框架,用于OV-MLR。实验表明,DART取得了新的最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Open-Vocabulary Multi-Label Recognition (OV-MLR) 要求同时实现精确的类内定位和有效的类间推理。
- Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) 模型虽然在开放词汇方面表现良好,但在弱监督下的精细定位方面存在挑战。
- DART框架通过两个协同的适应性模块(ARM和ATM)克服了VLP模型的局限性。
- ARM模块通过自适应优化补丁特征并结合WPS损失实现判别定位。
- ATM模块利用大型语言模型(LLM)挖掘的结构知识构建类关系图(CRG)。
- DART是第一个整合LLM派生关系知识的框架,用于自适应类间转移和类内细化。
点此查看论文截图

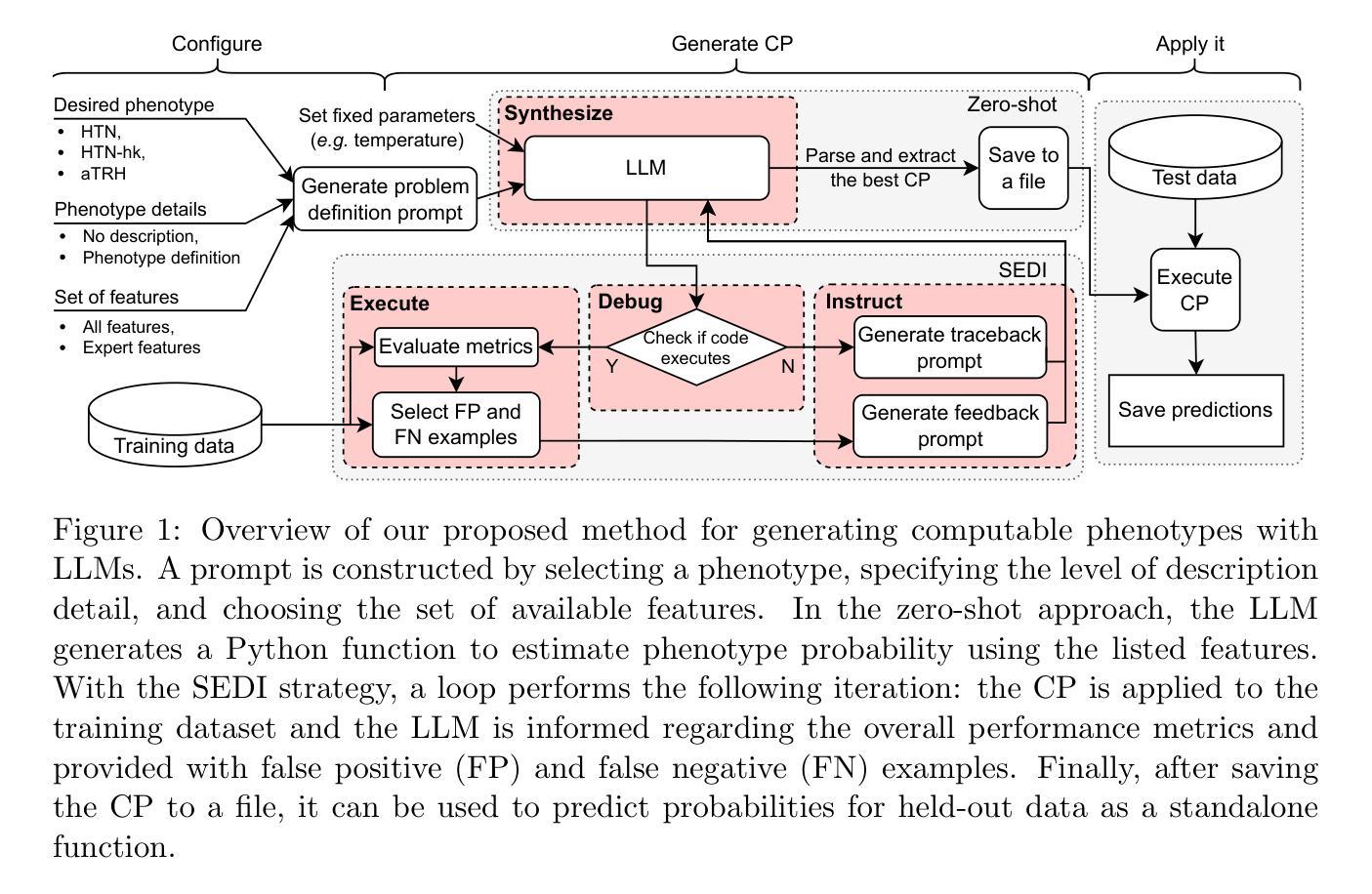
Iterative Learning of Computable Phenotypes for Treatment Resistant Hypertension using Large Language Models
Authors:Guilherme Seidyo Imai Aldeia, Daniel S. Herman, William G. La Cava
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities for medical question answering and programming, but their potential for generating interpretable computable phenotypes (CPs) is under-explored. In this work, we investigate whether LLMs can generate accurate and concise CPs for six clinical phenotypes of varying complexity, which could be leveraged to enable scalable clinical decision support to improve care for patients with hypertension. In addition to evaluating zero-short performance, we propose and test a synthesize, execute, debug, instruct strategy that uses LLMs to generate and iteratively refine CPs using data-driven feedback. Our results show that LLMs, coupled with iterative learning, can generate interpretable and reasonably accurate programs that approach the performance of state-of-the-art ML methods while requiring significantly fewer training examples.
大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗问题回答和编程方面展现出了显著的能力,但其在生成可解释的计算表型(CPs)方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们调查了LLM是否能为六种不同复杂度的临床表型生成准确且简洁的CPs,这可能用于实现可扩展的临床决策支持,以改善高血压患者的护理。除了评估零短性能外,我们还提出并测试了一种合成、执行、调试、指导策略,该策略利用LLM生成并使用数据驱动的反馈来迭代优化CPs。我们的结果表明,结合迭代学习,LLM可以生成可解释且相当准确的程序,其性能接近最新ML方法,同时显著减少了训练样本的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in PMLR, Volume 298, Machine Learning for Healthcare, 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在医疗问题回答和编程方面展现出显著能力,但其生成可解释的计算表型(CPs)的潜力尚未被充分探索。本研究探讨LLMs是否能针对六种不同复杂度的临床表型生成准确简要的CPs,这可用于实现可扩展的临床决策支持,提高高血压患者的护理水平。除了评估零短性能外,我们还提出了一种合成、执行、调试、指导的策略,该策略利用LLMs以数据驱动反馈来生成并迭代优化CPs。结果表明,结合迭代学习,LLMs可以生成可解释且相对准确的程序,其性能接近最新机器学习方法的性能,同时显著减少了对训练样本的需求。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs具备生成可解释的计算表型(CPs)的潜力,这对于临床决策支持具有重要意义。
- 本研究探讨了LLMs在针对六种不同复杂度的临床表型生成CPs方面的能力。
- 提出了一种合成、执行、调试、指导的策略,利用LLMs和数据进行反馈以迭代优化CPs的生成。
- LLMs结合迭代学习可以生成准确且可解释的程序,其性能接近最新机器学习方法。
- LLMs在医疗领域的应用,如医疗问题回答,得到了进一步发展。
- 本研究的结果表明,LLMs在编程方面的能力同样值得进一步探索和应用。
点此查看论文截图

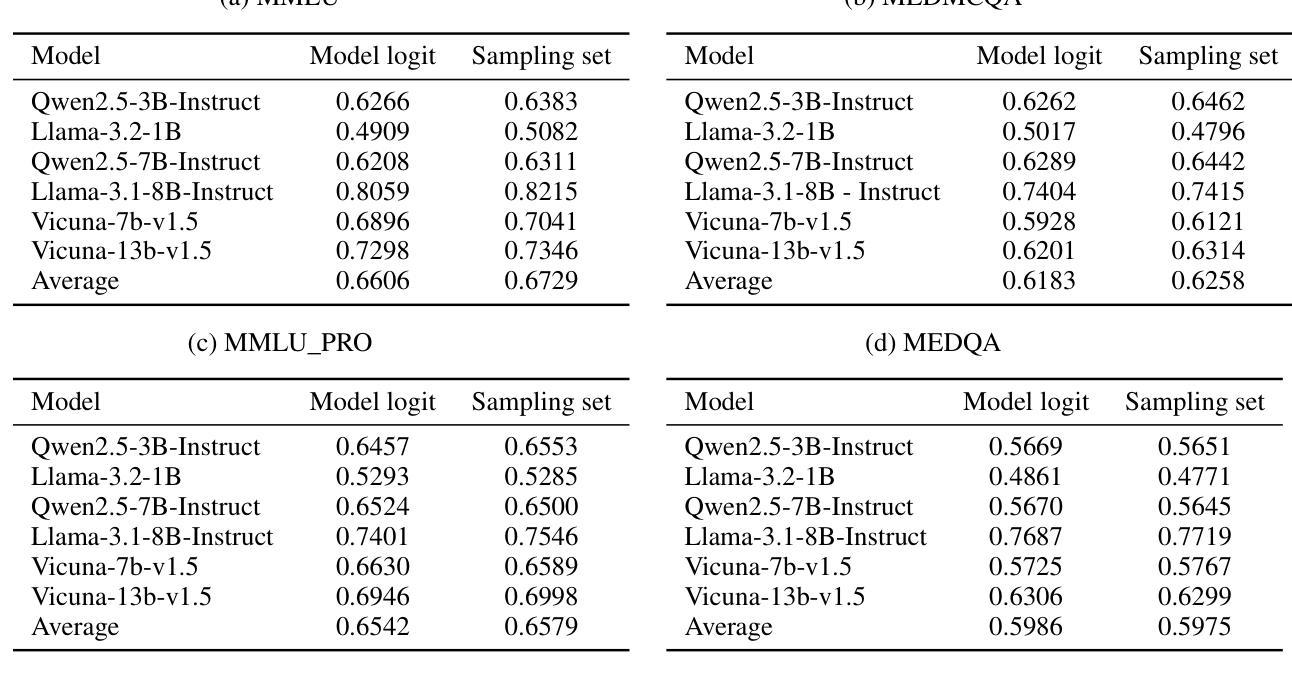
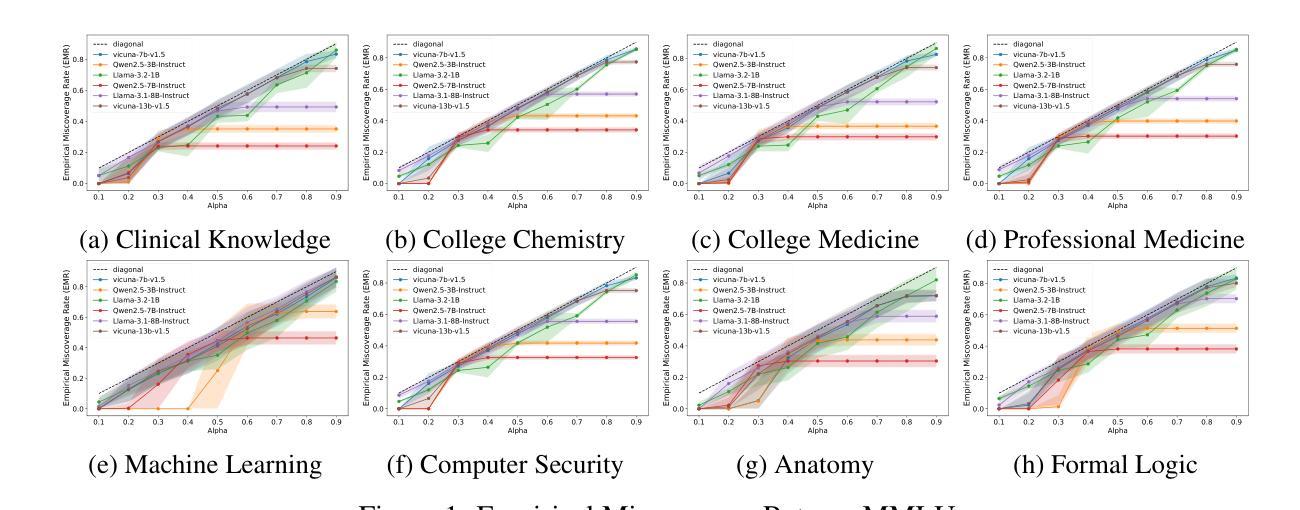
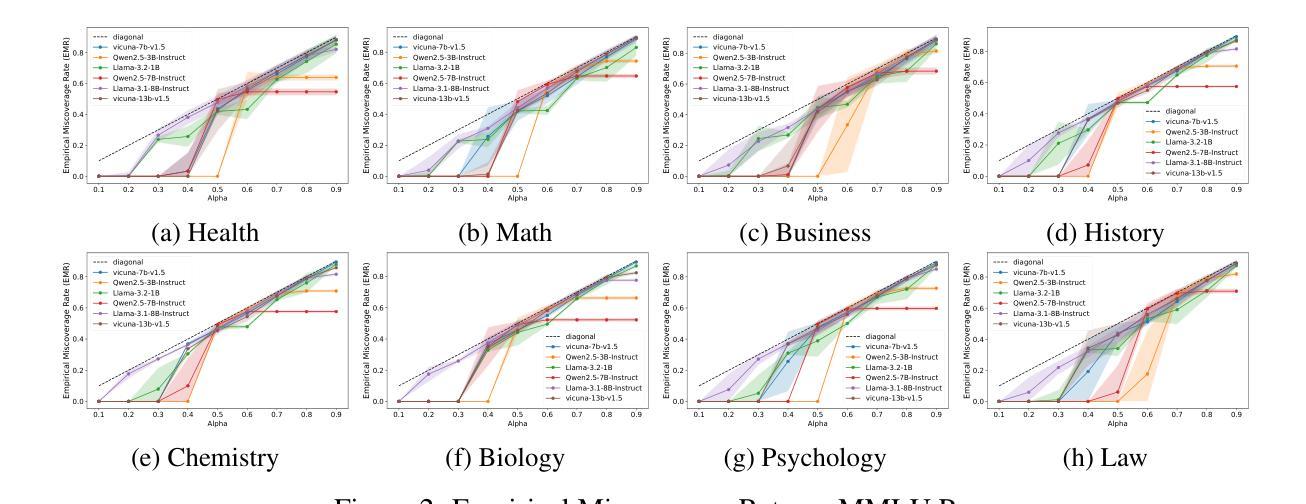
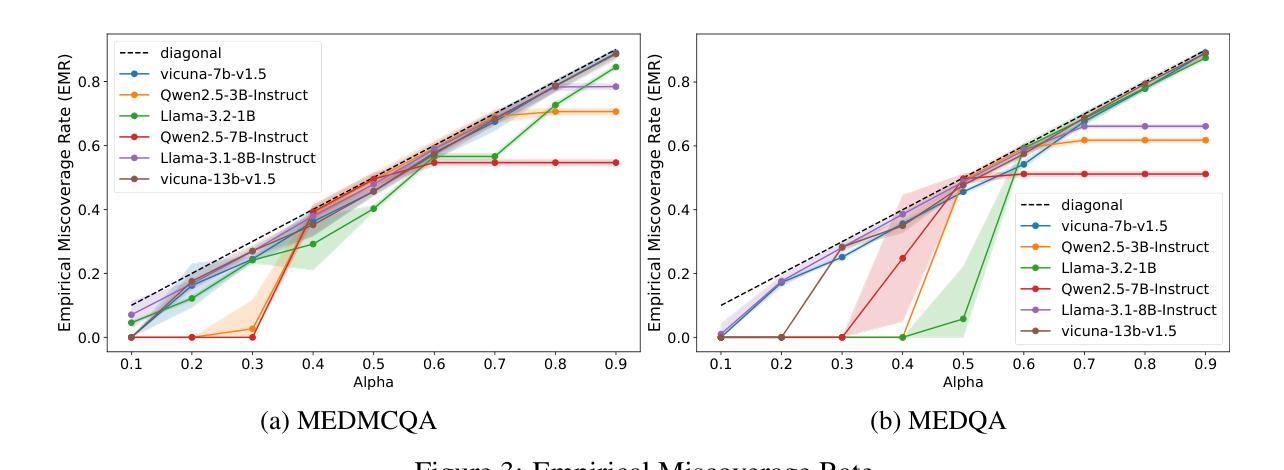
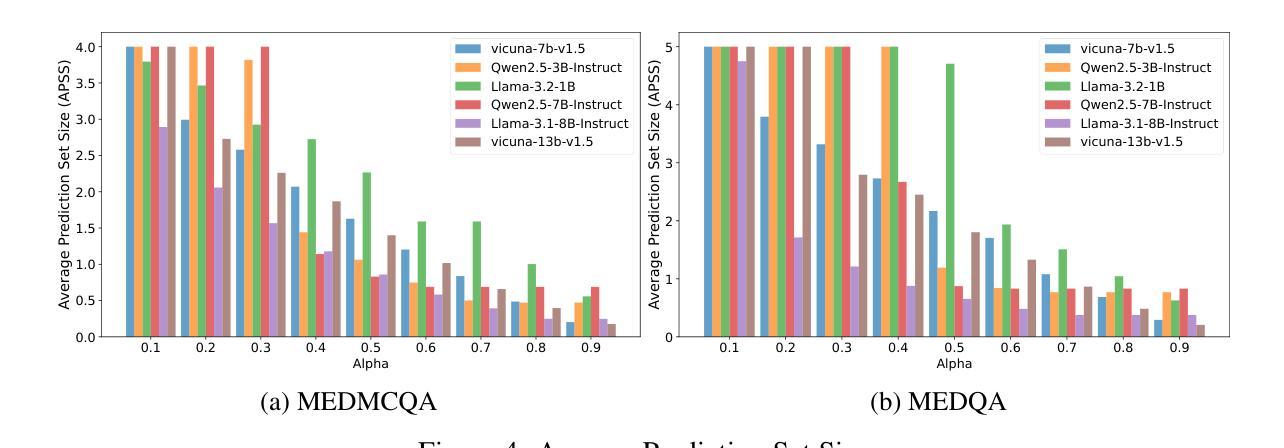
Conformal Sets in Multiple-Choice Question Answering under Black-Box Settings with Provable Coverage Guarantees
Authors:Guang Yang, Xinyang Liu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in multiple-choice question answering (MCQA), but their inherent unreliability, such as hallucination and overconfidence, limits their application in high-risk domains. To address this, we propose a frequency-based uncertainty quantification method under black-box settings, leveraging conformal prediction (CP) to ensure provable coverage guarantees. Our approach involves multiple independent samplings of the model’s output distribution for each input, with the most frequent sample serving as a reference to calculate predictive entropy (PE). Experimental evaluations across six LLMs and four datasets (MedMCQA, MedQA, MMLU, MMLU-Pro) demonstrate that frequency-based PE outperforms logit-based PE in distinguishing between correct and incorrect predictions, as measured by AUROC. Furthermore, the method effectively controls the empirical miscoverage rate under user-specified risk levels, validating that sampling frequency can serve as a viable substitute for logit-based probabilities in black-box scenarios. This work provides a distribution-free model-agnostic framework for reliable uncertainty quantification in MCQA with guaranteed coverage, enhancing the trustworthiness of LLMs in practical applications.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多选问答(MCQA)方面取得了显著的进步,但它们的固有不可靠性,如幻象和过度自信,限制了它们在高风险领域的应用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于频率的不确定性量化方法,该方法在黑色背景下设置,利用适形预测(CP)确保可证明覆盖保证。我们的方法涉及对模型的输出分布进行多次独立采样,每个输入样本最频繁的出现作为参考来计算预测熵(PE)。在六个LLM和四个数据集(MedMCQA、MedQA、MMLU、MMLU-Pro)上的实验评估表明,基于频率的PE在区分正确和错误预测方面优于基于Logit的PE,这通过AUROC来衡量。此外,该方法有效地控制了用户指定风险水平下的经验误覆盖率,验证了采样频率可以作为黑色背景下基于Logit概率的可行替代方案。这项工作提供了一个分布无关模型框架,用于可靠的不确定性量化MCQA中的保证覆盖,增强了LLM在实际应用中的可信度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多选题回答(MCQA)方面取得显著进展,但其内在的不确定性,如幻象和过度自信,限制了其在高风险领域的应用。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种基于频率的不确定性量化方法,采用黑色场景下基于侏儒的预测方法确保可验证覆盖保证。该方法通过多次独立采样模型的输出分布来确定每个输入的预测概率分布中最频繁出现的样本,计算预测熵(PE)。实验表明,基于频率的PE相较于基于Logit的PE更能有效区分正确与错误的预测,并成功控制实证覆盖度在用户指定的风险水平之下。本研究提供了一个分布无关、模型通用的框架,用于可靠的不确定性量化MCQA,增强了LLM在实际应用中的可信度。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在多选题回答(MCQA)方面取得显著进展,但存在内在不确定性问题。
- 提出一种基于频率的不确定性量化方法来解决这一问题。
- 采用基于侏儒的预测方法来确保可验证覆盖保证。
- 通过多次独立采样模型的输出分布来确定预测概率分布中最频繁出现的样本。
- 基于频率的PE相较于基于Logit的PE更能有效区分正确与错误的预测。
- 成功控制实证覆盖度在用户指定的风险水平之下。
点此查看论文截图

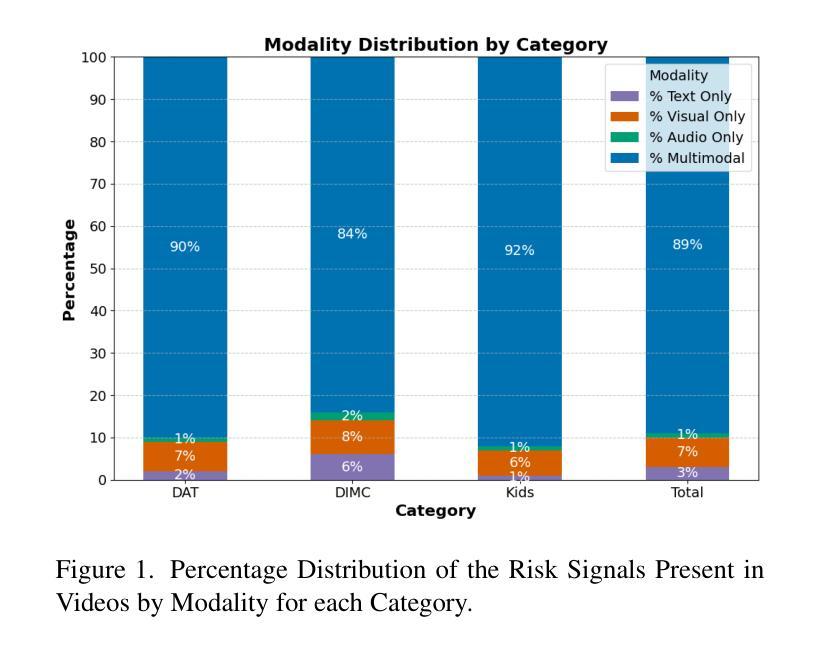
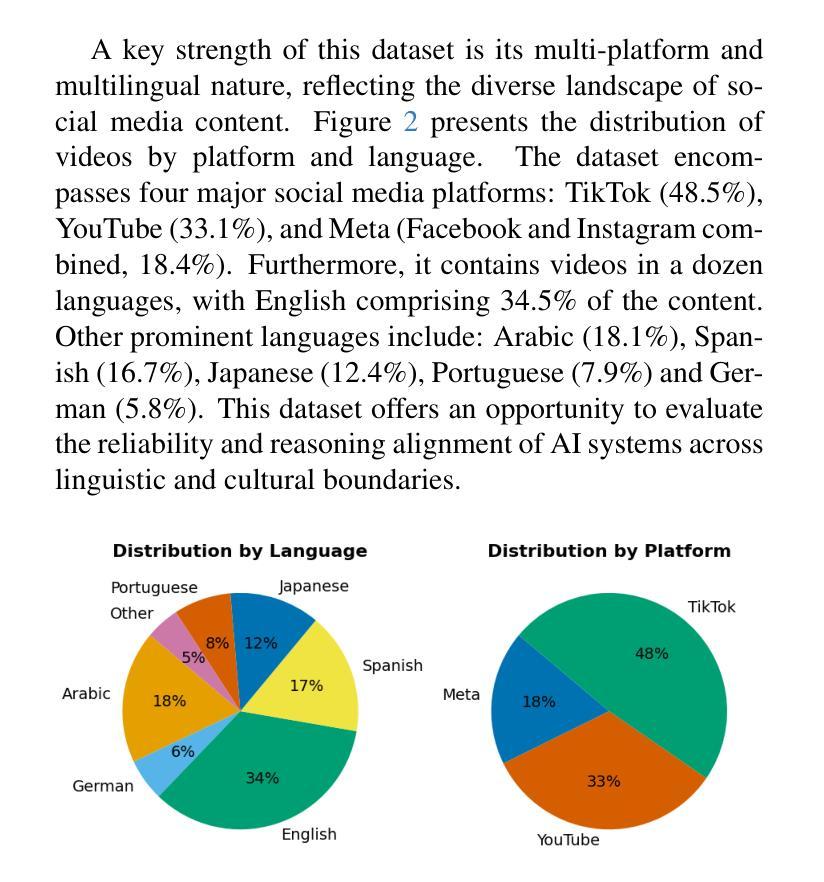
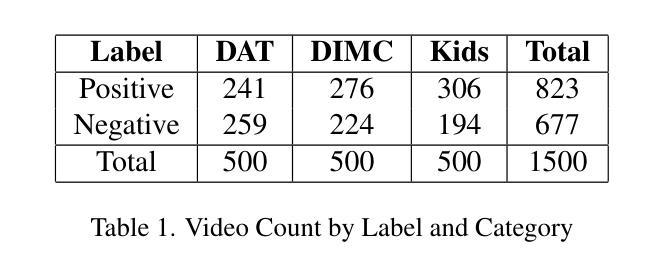
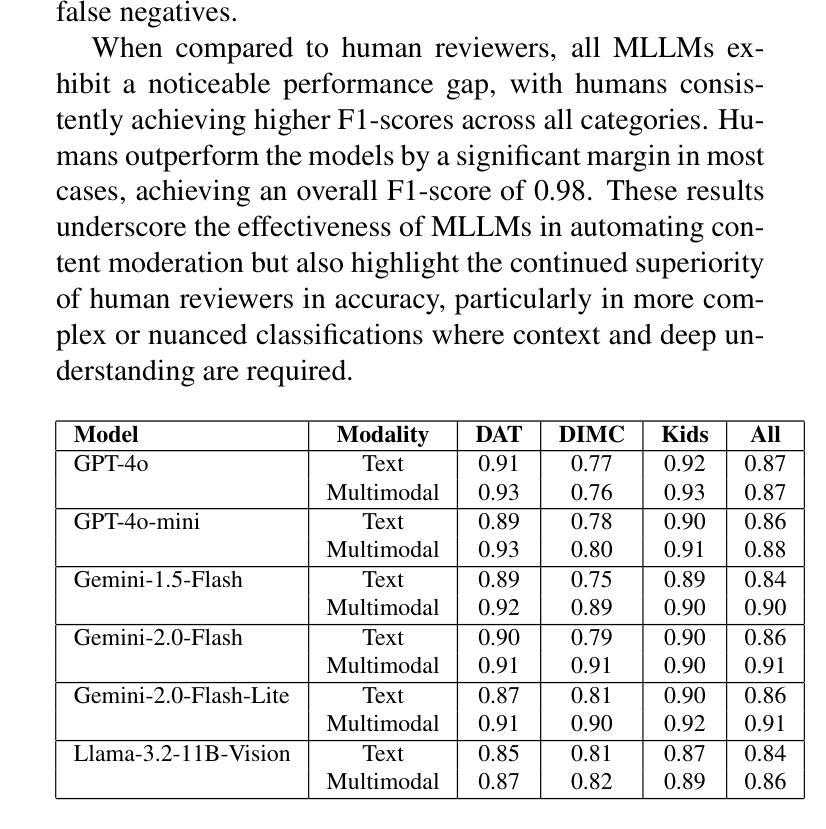
AI vs. Human Moderators: A Comparative Evaluation of Multimodal LLMs in Content Moderation for Brand Safety
Authors:Adi Levi, Or Levi, Sardhendu Mishra, Jonathan Morra
As the volume of video content online grows exponentially, the demand for moderation of unsafe videos has surpassed human capabilities, posing both operational and mental health challenges. While recent studies demonstrated the merits of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in various video understanding tasks, their application to multimodal content moderation, a domain that requires nuanced understanding of both visual and textual cues, remains relatively underexplored. In this work, we benchmark the capabilities of MLLMs in brand safety classification, a critical subset of content moderation for safe-guarding advertising integrity. To this end, we introduce a novel, multimodal and multilingual dataset, meticulously labeled by professional reviewers in a multitude of risk categories. Through a detailed comparative analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness of MLLMs such as Gemini, GPT, and Llama in multimodal brand safety, and evaluate their accuracy and cost efficiency compared to professional human reviewers. Furthermore, we present an in-depth discussion shedding light on limitations of MLLMs and failure cases. We are releasing our dataset alongside this paper to facilitate future research on effective and responsible brand safety and content moderation.
随着在线视频内容的数量呈指数级增长,对不安全视频的适度需求已经超越了人类的能力,带来了运营和心理健康方面的挑战。虽然最近有研究表明,多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在各种视频理解任务中具有优势,但它们在需要视觉和文本线索细微理解的多模态内容适度应用方面,研究相对较少。在这项工作中,我们以品牌安全分类为标准,评估了多模态语言模型的能力,这是内容适度中保护广告完整性的关键子集。为此,我们引入了一个新的多模态和多语言数据集,该数据集经过专业评论人员在各种风险类别中仔细标注。通过详细比较分析,我们展示了Gemini、GPT和Llama等多模态大型语言模型在多模态品牌安全方面的有效性,并评估了它们与专业人工审核员相比的准确性和成本效益。此外,我们对多模态大型语言模型的局限性及失败案例进行了深入探讨。我们随这篇论文一起发布我们的数据集,以促进未来在有效和负责任的品牌安全和内容适度方面的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Computer Vision in Advertising and Marketing (CVAM) workshop at ICCV 2025
Summary
随着在线视频内容的指数级增长,对安全视频的管理需求已经超越了人工处理的能力,带来了运营和心理健康方面的挑战。最近的研究表明,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种视频理解任务中具有优势,但在需要视觉和文本线索细微理解的多模态内容管理方面应用较少。本研究旨在评估MLLMs在品牌安全分类中的能力——内容管理的一个关键领域,以保护广告的真实性。为此,我们引入了一个新颖的多模态、多语言数据集,由专业评审人员进行了风险类别的细致标注。通过详细对比分析,我们证明了如Gemini、GPT和Llama等MLLMs在多模态品牌安全方面的有效性,并评估了它们在精度和成本效益方面相较于专业评审人员的表现。此外,我们还深入探讨了MLLMs的局限性和失败案例。同时发布的数据集将促进未来关于有效和负责任的品牌安全和内容管理的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 在线视频内容的增长导致了对安全视频管理的巨大需求,挑战了人工处理的能力。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解任务中具有优势,但在多模态内容管理方面的应用仍相对较少。
- 研究聚焦于评估MLLMs在品牌安全分类方面的能力。
- 引入了一个多模态、多语言的数据集,用于评估MLLMs的性能,该数据集由专业评审人员进行细致标注。
- 对比分析了MLLMs与专业评审人员在品牌安全分类方面的表现,显示出MLLMs的有效性、精度和成本效益。
- 讨论了MLLMs的局限性和失败案例。
点此查看论文截图

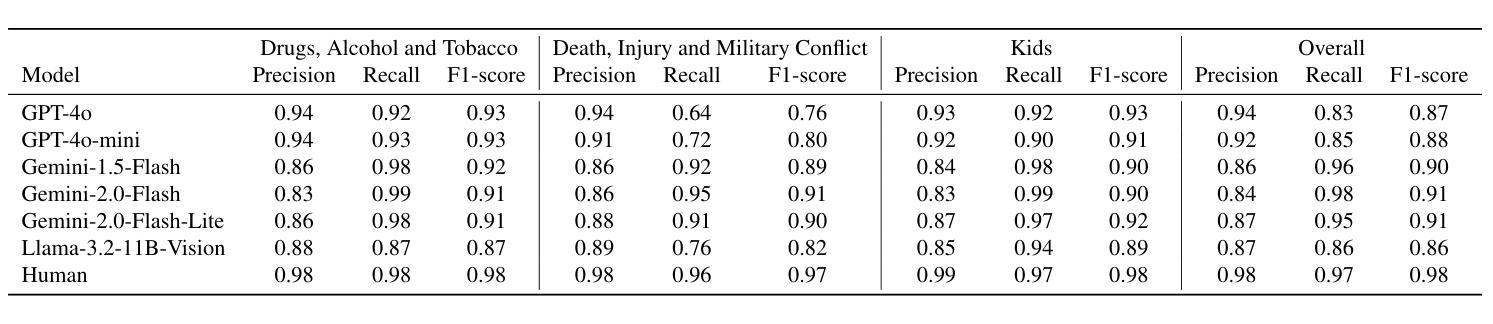
The World According to LLMs: How Geographic Origin Influences LLMs’ Entity Deduction Capabilities
Authors:Harsh Nishant Lalai, Raj Sanjay Shah, Jiaxin Pei, Sashank Varma, Yi-Chia Wang, Ali Emami
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been extensively tuned to mitigate explicit biases, yet they often exhibit subtle implicit biases rooted in their pre-training data. Rather than directly probing LLMs with human-crafted questions that may trigger guardrails, we propose studying how models behave when they proactively ask questions themselves. The 20 Questions game, a multi-turn deduction task, serves as an ideal testbed for this purpose. We systematically evaluate geographic performance disparities in entity deduction using a new dataset, Geo20Q+, consisting of both notable people and culturally significant objects (e.g., foods, landmarks, animals) from diverse regions. We test popular LLMs across two gameplay configurations (canonical 20-question and unlimited turns) and in seven languages (English, Hindi, Mandarin, Japanese, French, Spanish, and Turkish). Our results reveal geographic disparities: LLMs are substantially more successful at deducing entities from the Global North than the Global South, and the Global West than the Global East. While Wikipedia pageviews and pre-training corpus frequency correlate mildly with performance, they fail to fully explain these disparities. Notably, the language in which the game is played has minimal impact on performance gaps. These findings demonstrate the value of creative, free-form evaluation frameworks for uncovering subtle biases in LLMs that remain hidden in standard prompting setups. By analyzing how models initiate and pursue reasoning goals over multiple turns, we find geographic and cultural disparities embedded in their reasoning processes. We release the dataset (Geo20Q+) and code at https://sites.google.com/view/llmbias20q/home.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经进行了广泛的调整,以减轻明确的偏见,然而,它们通常表现出根植于预训练数据中的微妙隐含偏见。我们没有采用可能触发保护机制的由人类设计的问题来直接检测LLM,而是提出了研究模型在主动提出问题时的行为变化。20问游戏是一个多回合推理任务,作为实现这一目标的理想测试平台。我们系统地评估了使用新数据集Geo20Q+在实体推理中的地理性能差异,该数据集包含来自不同地区的知名人物和具有文化意义的事物(例如食物、地标、动物)。我们在两种游戏设置(标准的20个问题、无限回合)和七种语言(英语、印地语、普通话、日语、法语、西班牙语和土耳其语)中测试了流行的大型语言模型。我们的结果表明存在地理差异:大型语言模型在推测全球北方实体方面比全球南方更为成功,全球西方也比全球东方更为成功。虽然维基百科页面浏览量和预训练语料库频率与性能有轻微关联,但它们未能完全解释这些差异。值得注意的是,游戏所用的语言对性能差距的影响微乎其微。这些发现表明,创造性、自由形式的评估框架在揭示大型语言模型中隐藏细微偏见方面具有重要价值。通过分析模型如何在多回合中启动和追求推理目标,我们发现其推理过程中存在的地理和文化差异。我们在https://sites.google.com/view/llmbias20q/home发布了数据集(Geo20Q+)和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference on Language Modeling 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)尽管经过调整以减轻显性偏见,但它们通常表现出根植于预训练数据中的微妙隐性偏见。研究通过模型主动提问的方式来研究模型的偏见。在名为Geo20Q+的新数据集上,对模型在地理实体推理方面的表现进行了系统评估。测试了流行的大型语言模型在两种游戏玩法配置(经典的20问和无限回合制)下的表现,并在七种语言中进行。发现地理差异:大型语言模型在全球北方和西方的实体推理表现更好,而维基百科页面浏览量和预训练语料库频率对表现的影响较小,不能完全解释这些差异。语言对表现差距的影响微乎其微。这些发现表明,创造性的自由形式评估框架对于发现大型语言模型中的微妙偏见具有价值,这些偏见在标准提示设置中是隐藏的。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)即使经过调整以减轻偏见,仍存在基于预训练数据的微妙隐性偏见。
- 通过模型主动提问的方式研究模型的偏见是一种有效方法。
- 在名为Geo20Q+的新数据集上,发现大型语言模型在地理实体推理方面存在地理差异。
- 测试了大型语言模型在两种游戏玩法配置下的表现,发现其在全球北方和西方的表现更好。
- 维基百科页面浏览量和预训练语料库频率对大型语言模型表现的影响较小,不能完全解释这些差异。
- 语言对大型语言模型表现差距的影响微乎其微。
点此查看论文截图

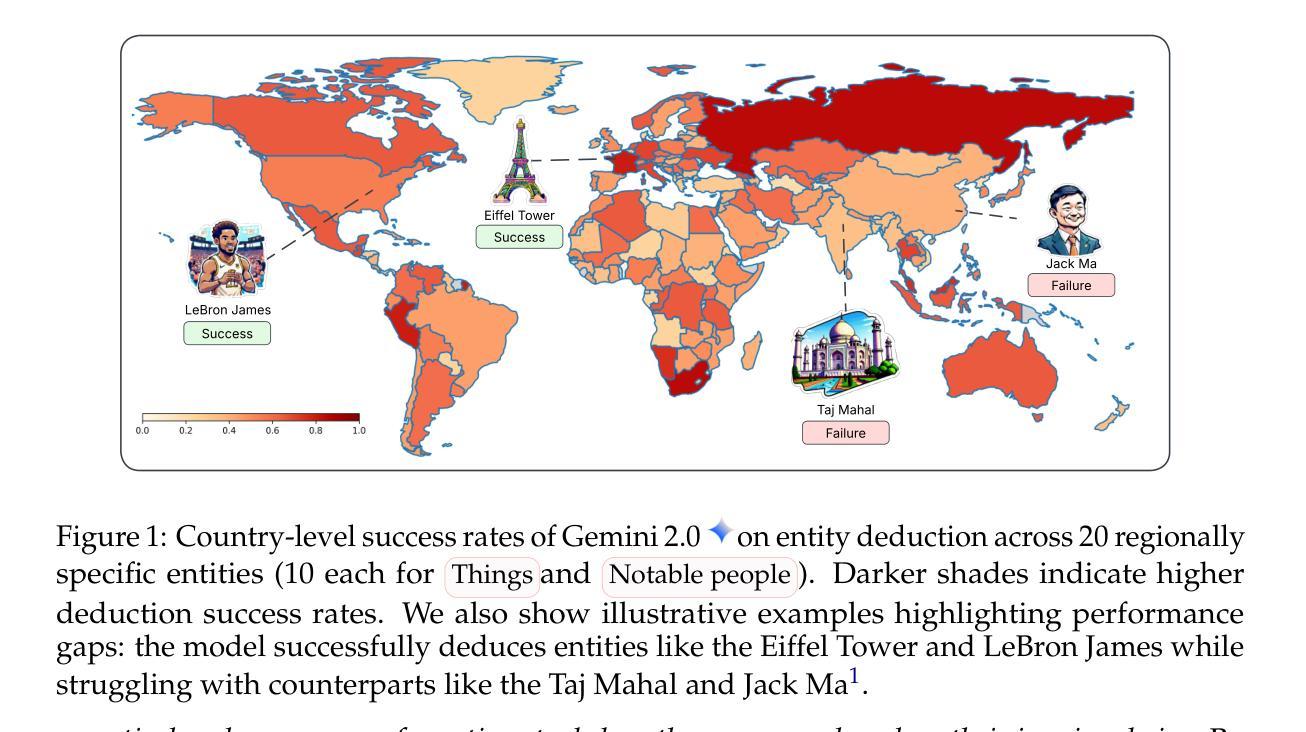
Advancing Hate Speech Detection with Transformers: Insights from the MetaHate
Authors:Santosh Chapagain, Shah Muhammad Hamdi, Soukaina Filali Boubrahimi
Hate speech is a widespread and harmful form of online discourse, encompassing slurs and defamatory posts that can have serious social, psychological, and sometimes physical impacts on targeted individuals and communities. As social media platforms such as X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, Reddit, and others continue to facilitate widespread communication, they also become breeding grounds for hate speech, which has increasingly been linked to real-world hate crimes. Addressing this issue requires the development of robust automated methods to detect hate speech in diverse social media environments. Deep learning approaches, such as vanilla recurrent neural networks (RNNs), long short-term memory (LSTM), and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have achieved good results, but are often limited by issues such as long-term dependencies and inefficient parallelization. This study represents the comprehensive exploration of transformer-based models for hate speech detection using the MetaHate dataset–a meta-collection of 36 datasets with 1.2 million social media samples. We evaluate multiple state-of-the-art transformer models, including BERT, RoBERTa, GPT-2, and ELECTRA, with fine-tuned ELECTRA achieving the highest performance (F1 score: 0.8980). We also analyze classification errors, revealing challenges with sarcasm, coded language, and label noise.
仇恨言论是一种广泛且有害的在线话语形式,包括侮辱性和诽谤性的帖子,可能对目标个人和社区产生严重的社会、心理和有时甚至是身体影响。随着诸如X(原Twitter)、Facebook、Instagram、Reddit等社交媒体平台继续促进广泛传播沟通的同时,它们也成为了仇恨言论的滋生地,仇恨言论与真实世界的仇恨犯罪之间的联系也愈发紧密。解决这一问题需要开发稳健的自动化方法,以在多样化的社交媒体环境中检测仇恨言论。深度学习的方法,如普通的循环神经网络(RNNs)、长短时记忆网络(LSTM)和卷积神经网络(CNNs)已经取得了良好的成果,但它们常常受限于长期依赖关系和不高效的并行化等问题。本研究使用MetaHate数据集全面探索基于Transformer模型的仇恨言论检测——一个包含36个数据集和120万个社交媒体样本的元集合。我们评估了多个先进的Transformer模型,包括BERT、RoBERTa、GPT-2和ELECTRA等模型,经过精细调整的ELECTRA模型取得了最佳性能(F1分数为0.8980)。我们还分析了分类错误,揭示出讥讽性言语、隐含的语言和标签噪声带来的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Deviant Dynamics in Digital Spaces workshop at ASONAM 2025
Summary
这篇文本主要讨论了网络上的仇恨言论问题,包括它对个人和社会的影响。文中提到社交媒体平台成为了仇恨言论的滋生地,这一问题已与现实世界的仇恨犯罪紧密相连。为了解决这一问题,研究者们正在开发在多样社交媒体环境中检测仇恨言论的自动化方法。当前深度学习和基于Transformer的模型都在这一领域取得了一些进展。本文重点研究了基于Transformer的模型在MetaHate数据集上的仇恨言论检测效果,其中fine-tuned ELECTRA模型表现最佳,F1分数达到0.8980。同时,文章还分析了分类错误的原因,包括讽刺、隐含语言和标签噪声等挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 仇恨言论是一种广泛且有害的网络表达形式,对目标个体和社区产生严重的社会、心理和物理影响。
- 社交媒体平台成为仇恨言论的滋生地,与现实世界的仇恨犯罪有联系。
- 自动化方法在处理多样社交媒体环境中的仇恨言论检测方面发挥着重要作用。
- 基于深度学习的模型,如RNN、LSTM和CNN等,在仇恨言论检测方面已有良好表现,但仍存在长期依赖和并行化效率低下等问题。
- 基于Transformer的模型在MetaHate数据集上进行仇恨言论检测表现出潜力。
- fine-tuned ELECTRA模型在仇恨言论检测方面取得了最佳性能,F1分数达到0.8980。
点此查看论文截图


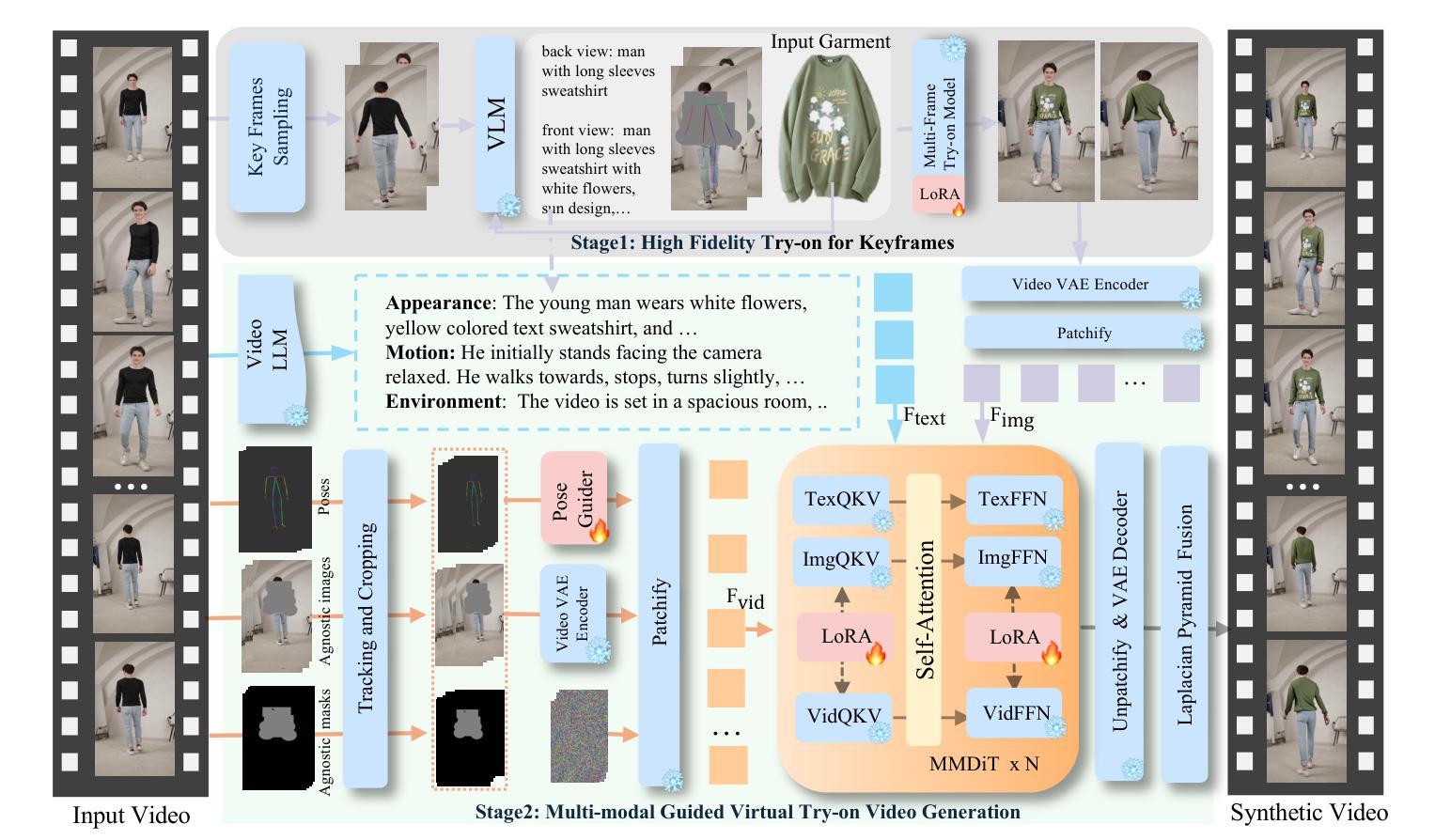
DreamVVT: Mastering Realistic Video Virtual Try-On in the Wild via a Stage-Wise Diffusion Transformer Framework
Authors:Tongchun Zuo, Zaiyu Huang, Shuliang Ning, Ente Lin, Chao Liang, Zerong Zheng, Jianwen Jiang, Yuan Zhang, Mingyuan Gao, Xin Dong
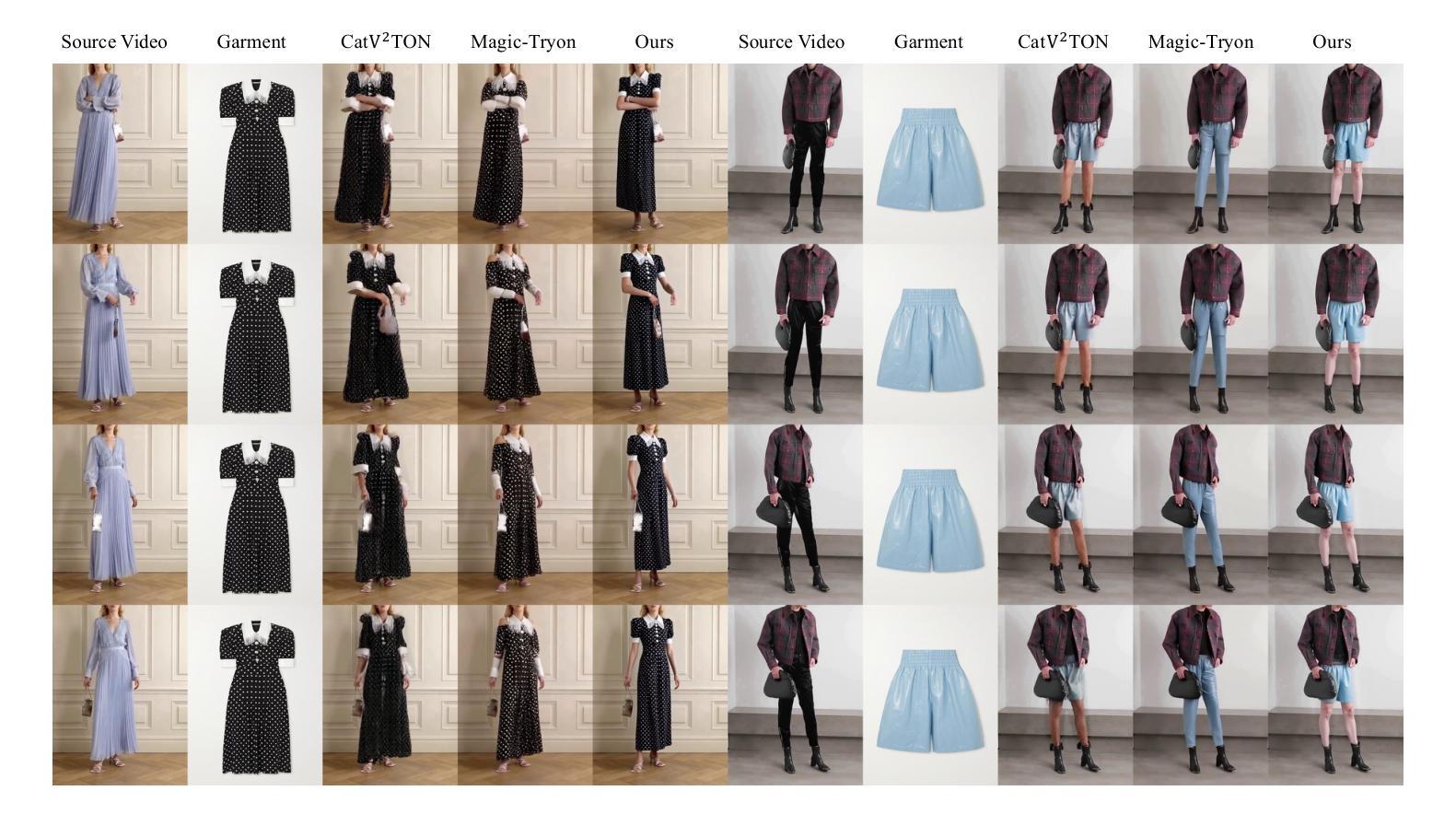
Video virtual try-on (VVT) technology has garnered considerable academic interest owing to its promising applications in e-commerce advertising and entertainment. However, most existing end-to-end methods rely heavily on scarce paired garment-centric datasets and fail to effectively leverage priors of advanced visual models and test-time inputs, making it challenging to accurately preserve fine-grained garment details and maintain temporal consistency in unconstrained scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose DreamVVT, a carefully designed two-stage framework built upon Diffusion Transformers (DiTs), which is inherently capable of leveraging diverse unpaired human-centric data to enhance adaptability in real-world scenarios. To further leverage prior knowledge from pretrained models and test-time inputs, in the first stage, we sample representative frames from the input video and utilize a multi-frame try-on model integrated with a vision-language model (VLM), to synthesize high-fidelity and semantically consistent keyframe try-on images. These images serve as complementary appearance guidance for subsequent video generation. \textbf{In the second stage}, skeleton maps together with fine-grained motion and appearance descriptions are extracted from the input content, and these along with the keyframe try-on images are then fed into a pretrained video generation model enhanced with LoRA adapters. This ensures long-term temporal coherence for unseen regions and enables highly plausible dynamic motions. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that DreamVVT surpasses existing methods in preserving detailed garment content and temporal stability in real-world scenarios. Our project page https://virtu-lab.github.io/
视频虚拟试穿(VVT)技术因其电子商务广告和娱乐方面的应用前景而引起了学术界的广泛关注。然而,大多数现有的端到端方法严重依赖于稀缺的配套服装数据集,未能有效利用先进的视觉模型的先验知识和测试时的输入,这使得在不受约束的场景中准确保留服装的精细细节并保持时间一致性具有挑战性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DreamVVT,这是一个精心设计的两阶段框架,建立在扩散变压器(DiTs)之上,它本质上能够利用多样且无配套的人形数据,提高在现实场景中的适应性。为了进一步利用预训练模型的先验知识和测试时的输入,在第一阶段,我们从输入视频中抽样代表性帧,并使用一个集成了视觉语言模型(VLM)的多帧试穿模型,合成高保真和语义一致的关键帧试穿图像。这些图像作为后续视频生成的补充外观指导。在第二阶段,从输入内容中提取骨架图以及精细的运动和外观描述,这些与关键帧试穿图像一起输入到增强有LoRA适配器的预训练视频生成模型中。这确保了未见区域的长期时间连贯性,并能够实现高度逼真的动态运动。大量的定量和定性实验表明,DreamVVT在保留服装内容的详细信息和现实场景中的时间稳定性方面超越了现有方法。我们的项目页面为:[https://virtu-lab.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 12 figures
Summary
视频虚拟试穿(VVT)技术在电子商务广告和娱乐等领域受到广泛关注。然而,现有端到端方法大多依赖稀缺的配对服装数据集,难以有效利用先进视觉模型的先验知识和测试时输入的信息,难以在不受约束的场景中准确保留细致的服装细节并保持时间一致性。为解决这些挑战,我们提出DreamVVT,这是一个基于扩散转换器(DiT)的精心设计的两阶段框架,能够利用多样的人类中心化数据增强在真实场景中的适应性。首先,我们从输入视频中采样关键帧,并使用多帧试穿模型与视觉语言模型(VLM)合成高质量、语义一致的关键帧试穿图像。接着在第二阶段,我们从输入内容中提取骨架图以及细致的动态和外观描述信息,并结合关键帧试穿图像输入到增强型视频生成模型中,确保长期时间连贯性并产生高度逼真的动态效果。实验证明,DreamVVT在保留服装细节和时间稳定性方面超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频虚拟试穿(VVT)技术在电子商务广告和娱乐领域有广泛应用前景。
- 现有方法依赖配对服装数据集,难以在真实场景中应用。
- DreamVVT基于扩散转换器(DiT)的两阶段框架,可利用多样的人类中心化数据。
- 第一阶段合成高质量、语义一致的关键帧试穿图像。
- 第二阶段结合骨架图、动态和外观描述信息,确保视频长期时间连贯性。
- DreamVVT在保留服装细节和时间稳定性方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图



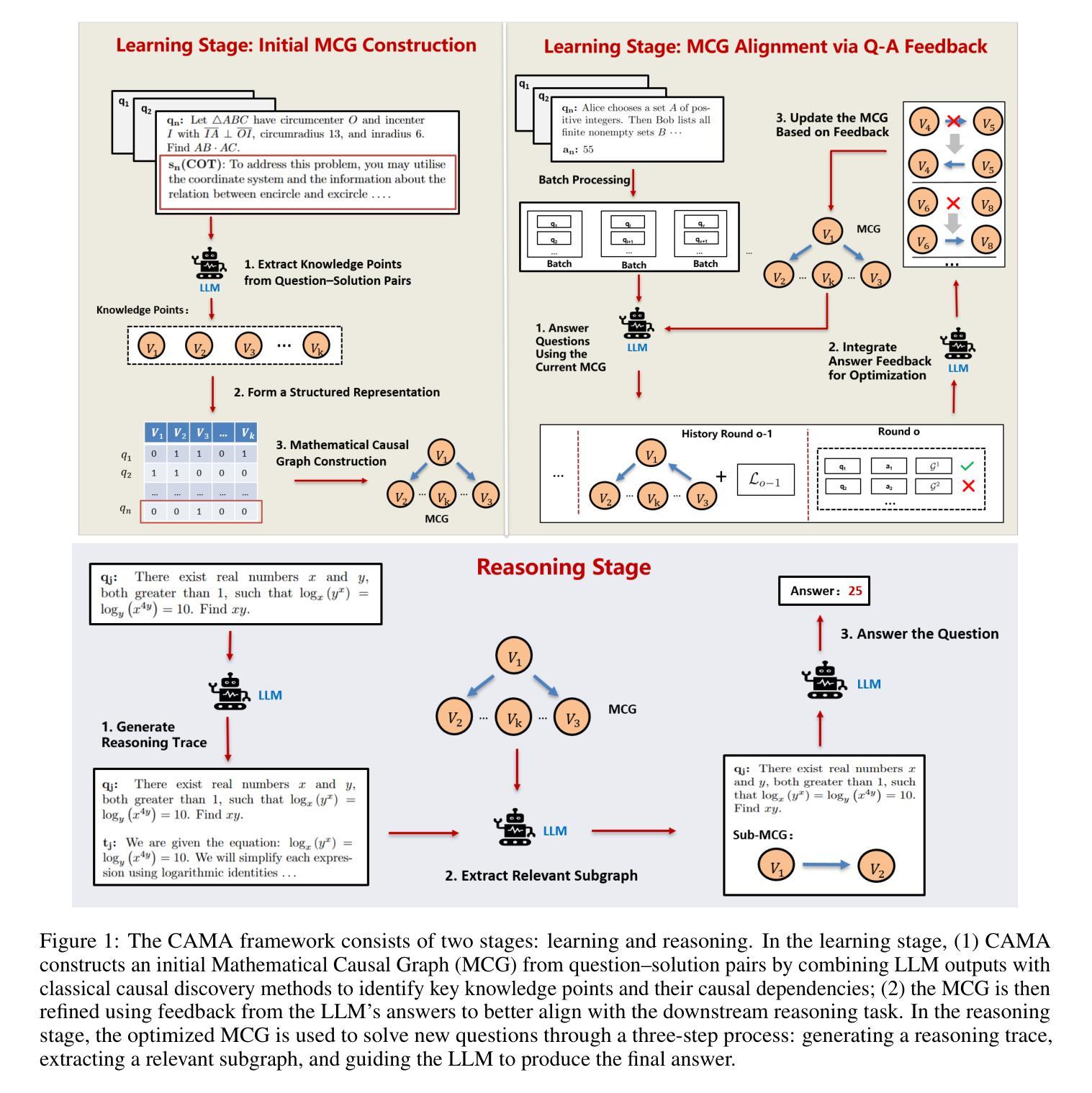
CAMA: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Causal Knowledge
Authors:Lei Zan, Keli Zhang, Ruichu Cai, Lujia Pan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of tasks, yet they still struggle with complex mathematical reasoning, a challenge fundamentally rooted in deep structural dependencies. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{CA}usal \textbf{MA}thematician (\textbf{CAMA}), a two-stage causal framework that equips LLMs with explicit, reusable mathematical structure. In the learning stage, CAMA first constructs the \textbf{M}athematical \textbf{C}ausal \textbf{G}raph (\textbf{MCG}), a high-level representation of solution strategies, by combining LLM priors with causal discovery algorithms applied to a corpus of question-solution pairs. The resulting MCG encodes essential knowledge points and their causal dependencies. To better align the graph with downstream reasoning tasks, CAMA further refines the MCG through iterative feedback derived from a selected subset of the question-solution pairs. In the reasoning stage, given a new question, CAMA dynamically extracts a task-relevant subgraph from the MCG, conditioned on both the question content and the LLM’s intermediate reasoning trace. This subgraph, which encodes the most pertinent knowledge points and their causal dependencies, is then injected back into the LLM to guide its reasoning process. Empirical results on real-world datasets show that CAMA significantly improves LLM performance on challenging mathematical problems. Furthermore, our experiments demonstrate that structured guidance consistently outperforms unstructured alternatives, and that incorporating asymmetric causal relationships yields greater improvements than using symmetric associations alone.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务中表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍存在困难,这一挑战根本源于深层的结构依赖性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了因果数学家(\textbf{CAMA})这一两阶段因果框架,为LLM配备明确的可重用数学结构。在学习阶段,CAMA首先构建数学因果图(MCG),这是一种解决方案策略的高级表示,通过结合LLM的先验知识和应用于问题解决方案对语料库的因果发现算法。结果产生的MCG编码了必要的知识点和它们的因果依赖关系。为了更好地与下游推理任务对齐,CAMA通过来自问题解决方案对子集的迭代反馈进一步改进MCG。在推理阶段,对于新问题,CAMA根据问题的内容和LLM的中间推理轨迹,动态地从MCG中提取任务相关子图。这个子图编码了最相关的知识点和它们的因果依赖关系,然后注入LLM以指导其推理过程。在真实数据集上的实证结果表明,CAMA在解决具有挑战性的数学问题方面显著提高了LLM的性能。此外,我们的实验表明,结构化的指导始终优于非结构化的替代方案,而融入不对称的因果关系比仅使用对称关联能带来更大的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务上表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍存在挑战。为解决这一挑战,提出了因果数学家(CAMA)框架,该框架分为两个阶段:学习阶段和推理阶段。学习阶段构建数学因果图(MCG),结合LLM先验知识与因果发现算法,对问题解答对进行编码,形成高层次的解决方案策略表示。推理阶段根据问题和LLM的中间推理轨迹,从MCG中动态提取相关子图,指导LLM的推理过程。实验表明,CAMA能显著提高LLM解决数学问题的能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM面临复杂数学推理的挑战,需要新的方法来解决。
- CAMA框架分为学习阶段和推理阶段,旨在提高LLM的数学推理能力。
- 学习阶段通过构建数学因果图(MCG)来编码解决方案策略。
- 推理阶段根据问题和LLM的推理轨迹从MCG中提取相关子图。
- CAMA通过结合LLM先验知识、因果发现算法和问题解答对,提高数学问题的解决能力。
- 实证结果表明,CAMA能显著提高LLM在解决数学问题上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

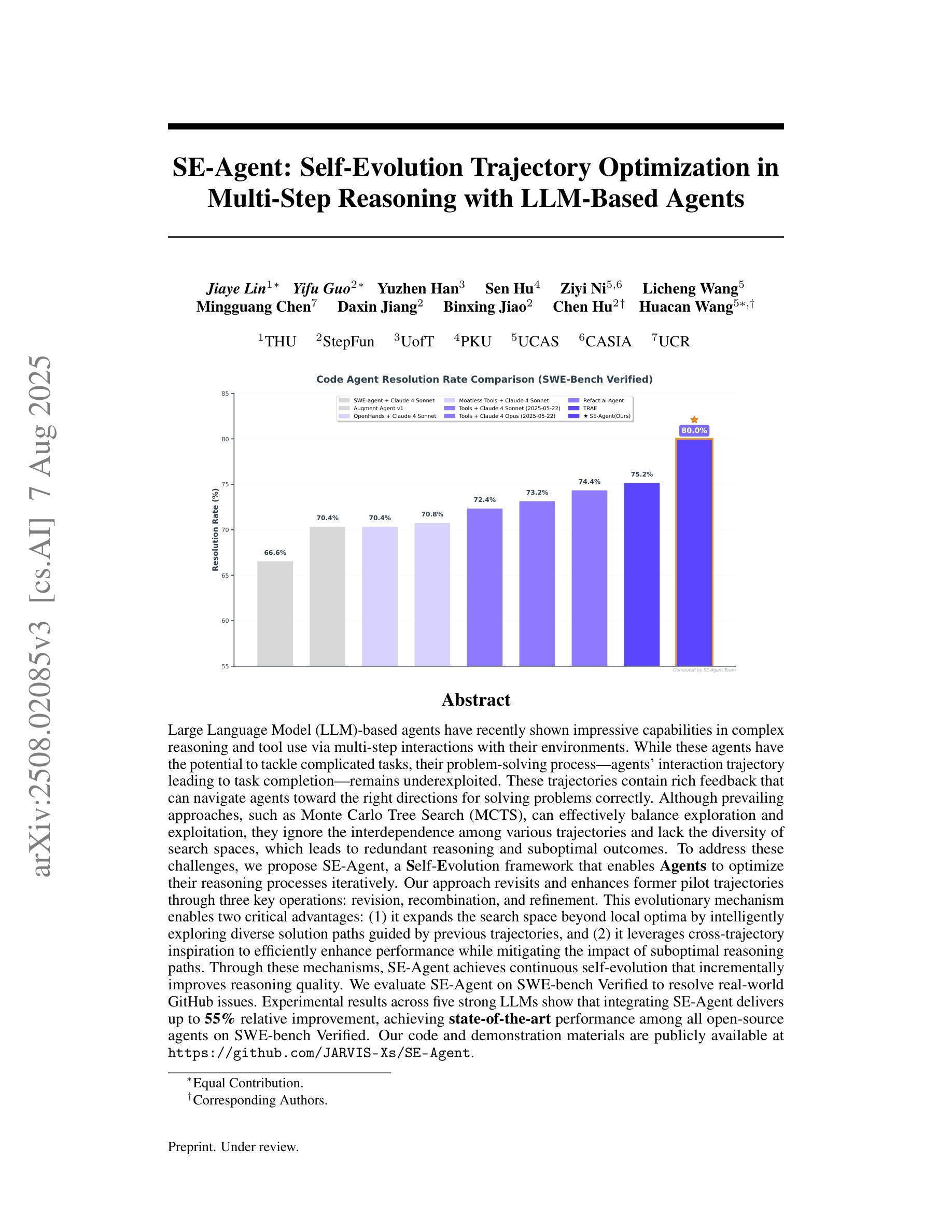
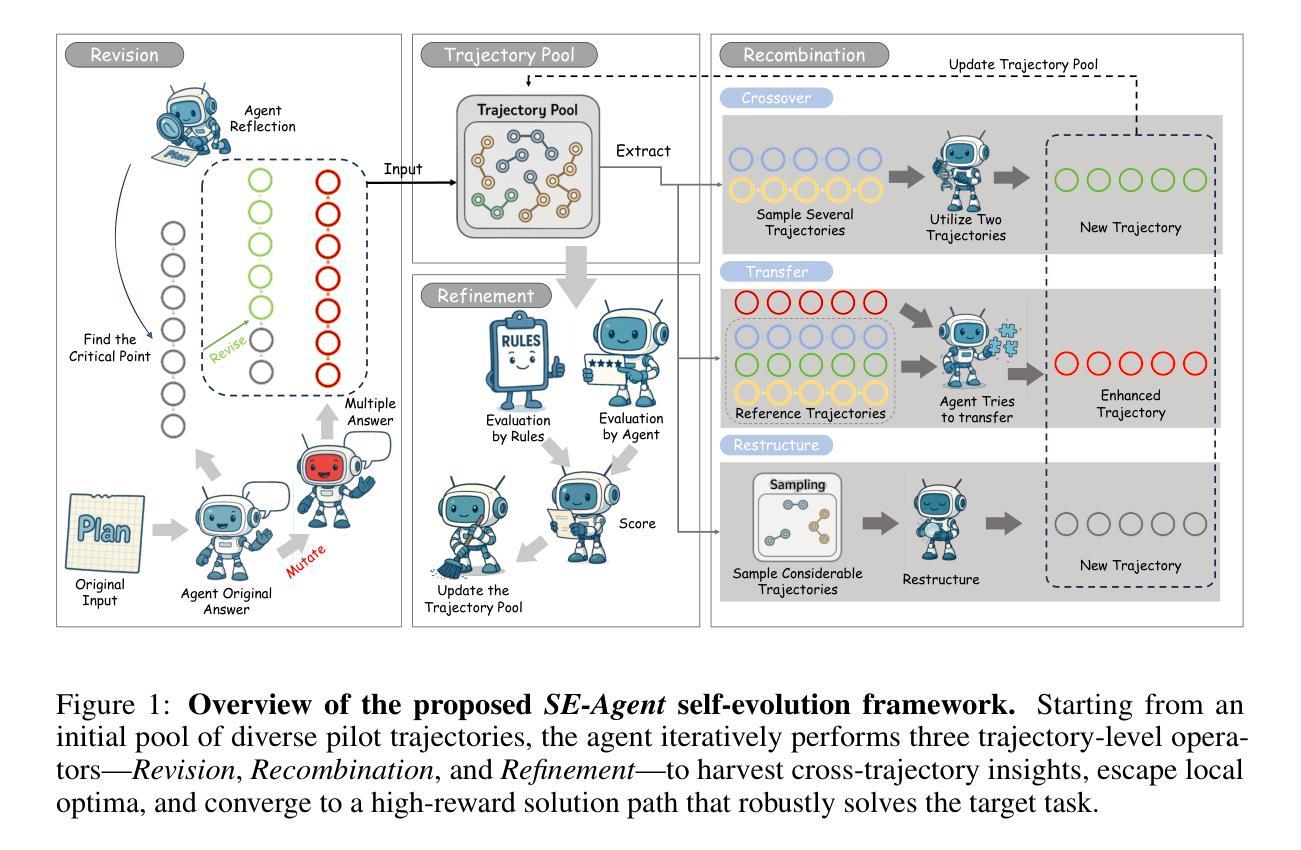
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理最近显示出通过与其环境进行多步骤交互进行复杂推理和工具使用的令人印象深刻的能力。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但他们的解决问题过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,仍未得到充分探索。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理正确解决问题。尽管现有的方法,如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了各种轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,一个自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作:修订、重组和细化,来重新审视和改进之前的轨迹。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索以前轨迹引导的多种解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了持续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的性能优于所有开源代理,达到了最新水平。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂推理和工具使用方面展现出强大的能力,通过与环境的多步交互完成任务。然而,其解题过程中的交互轨迹尚未得到充分研究。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导模型正确解决问题。现有方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)虽然能平衡探索与利用,但忽略了轨迹间的相互依赖性和搜索空间的多样性,导致冗余推理和次优结果。为解决这些问题,我们提出了SE-Agent框架,通过修订、重组和优化之前的轨迹,使模型能够迭代优化推理过程。实验结果表明,SE-Agent在真实世界GitHub问题上的性能相对于其他开源模型有明显提升。代码和演示材料公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- LLM模型在复杂推理和工具使用方面表现出强大的能力。
- LLM模型的解题过程中的交互轨迹尚未得到充分研究,其中包含丰富的反馈。
- 现有方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索忽略了轨迹间的相互依赖性和搜索空间的多样性。
- SE-Agent框架通过修订、重组和优化之前的轨迹,使模型能够迭代优化推理过程。
- SE-Agent实现了对局部最优解的超越,通过智能探索多种解决方案路径来提高性能。
- SE-Agent利用跨轨迹灵感来增强性能并减轻次优推理路径的影响。
点此查看论文截图
The SMeL Test: A simple benchmark for media literacy in language models
Authors:Gustaf Ahdritz, Anat Kleiman
The internet is rife with unattributed, deliberately misleading, or otherwise untrustworthy content. Though large language models (LLMs) are often tasked with autonomous web browsing, the extent to which they have learned the simple heuristics human researchers use to navigate this noisy environment is not currently known. In this paper, we introduce the Synthetic Media Literacy Test (SMeL Test), a minimal benchmark that tests the ability of language models to actively filter out untrustworthy information in context. We benchmark a variety of commonly used instruction-tuned LLMs, including reasoning models, and find that no model consistently succeeds; while reasoning in particular is associated with higher scores, even the best API model we test hallucinates up to 70% of the time. Remarkably, larger and more capable models do not necessarily outperform their smaller counterparts. We hope our work sheds more light on this important form of hallucination and guides the development of new methods to combat it.
互联网充斥着无属性、故意误导或其他不可信赖的内容。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)经常被赋予自主网页浏览的任务,但它们在这一嘈杂环境中学习人类研究者使用的简单启发式方法的程度目前尚不清楚。在本文中,我们引入了合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一个最小的基准测试,旨在测试语言模型在特定情境中主动过滤掉不可靠信息的能力。我们对各种常用的指令调整型LLM进行了基准测试,包括推理模型,发现没有任何模型能够始终成功;虽然推理与更高的分数特别相关,但即使是我们测试过的最好的API模型,也有高达70%的幻觉。值得注意的是,更大、更强大的模型并不一定比小型模型表现更好。我们希望我们的工作能进一步揭示这种重要的幻觉现象,并为开发新的对抗方法提供指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:互联网充斥着大量未经授权、故意误导或其他不可靠的内容。大型语言模型(LLM)常被用于自动浏览网页,但它们是否掌握了人类研究者用于导航这种嘈杂环境的简单启发式技术尚不清楚。本文介绍了合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一个基准测试,旨在测试语言模型在情境中主动过滤掉不可靠信息的能力。我们对多种常用的指令调整LLM进行了基准测试,发现没有任何模型始终表现良好;虽然推理能力尤其与高分相关,但即使是表现最佳的API模型也会达到70%的虚构程度。值得注意的是,更大、更强大的模型并不一定比小型模型表现得更好。我们希望这项工作能帮助进一步揭示这种虚构现象,并引导开发新的方法来应对它。
Key Takeaways:
- 互联网充斥着不可靠的内容,如未经授权的内容和故意误导信息。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在执行自主网页浏览任务时面临挑战,特别是在过滤不可靠信息方面。
- 合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试)被引入作为一种基准测试,以评估LLM在此方面的能力。
- 在测试中,没有一种LLM始终表现出良好的过滤能力。
- 推理能力在测试中尤为重要,但与高虚构程度相关。
- 即使是最先进的LLM也存在虚构现象,最高达到70%。
点此查看论文截图

Generative AI Adoption in Postsecondary Education, AI Hype, and ChatGPT’s Launch
Authors:Isabel Pedersen
The rapid integration of generative artificial intelligence (AI) into postsecondary education and many other sectors resulted in a global reckoning with this new technology. This paper contributes to the study of the multifaceted influence of generative AI, with a particular focus on OpenAI’s ChatGPT within academic settings during the first six months after the release in three specific ways. First, it scrutinizes the rise of ChatGPT as a transformative event construed through a study of mainstream discourses exhibiting AI hype. Second, it discusses the perceived implications of generative AI for writing, teaching, and learning through the lens of critical discourse analysis and critical AI studies. Third, it encourages the necessity for best practices in the adoption of generative AI technologies in education.
人工智能的快速集成到高等教育和其他许多领域,引发了全球对这一新技术的重新评估。本文研究了生成式人工智能的多方面影响,特别是OpenAI的ChatGPT在学术环境中的影响,以三种特定方式做出了贡献。首先,它仔细研究了ChatGPT作为一场变革性事件的出现,通过主流话语的研究展现了人工智能炒作现象。其次,它通过批判话语分析和批判人工智能研究的视角,探讨了生成式人工智能对写作、教学和学习的潜在影响。最后,它强调了采用生成式人工智能技术在教育中的最佳实践的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages
Summary
本文研究了生成式人工智能(AI)在高等教育和其他领域中的快速融合所带来的多方面影响,重点关注了OpenAI的ChatGPT在学术环境中的首次六个月应用。文章分析了ChatGPT作为一个变革性事件的出现与人工智能炒作话语之间的联系,探讨了生成式人工智能对写作、教学和学习的潜在影响,并强调了教育领域采用最佳实践使用生成式AI技术的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能(AI)在教育和其他领域中的融合引起全球关注。
- OpenAI的ChatGPT作为一种变革性事件被广泛研究,其在学术环境中的应用得到了特殊关注。
- 文章探讨了ChatGPT的出现与人工智能炒作话语之间的联系。
- 文章通过批判性话语分析和人工智能研究审视了生成式人工智能对写作、教学和学习的潜在影响。
- 文章强调了教育领域在使用生成式AI技术时需要遵循最佳实践的重要性。
- 文章指出,随着技术的快速发展,对生成式AI的研究和应用需要持续跟进和评估。
点此查看论文截图

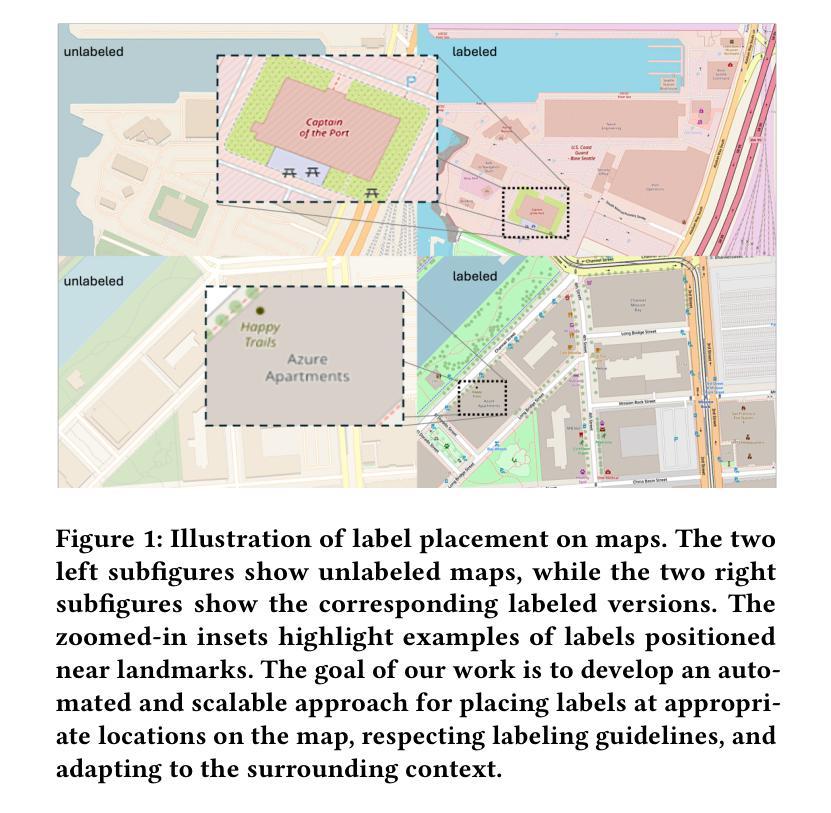
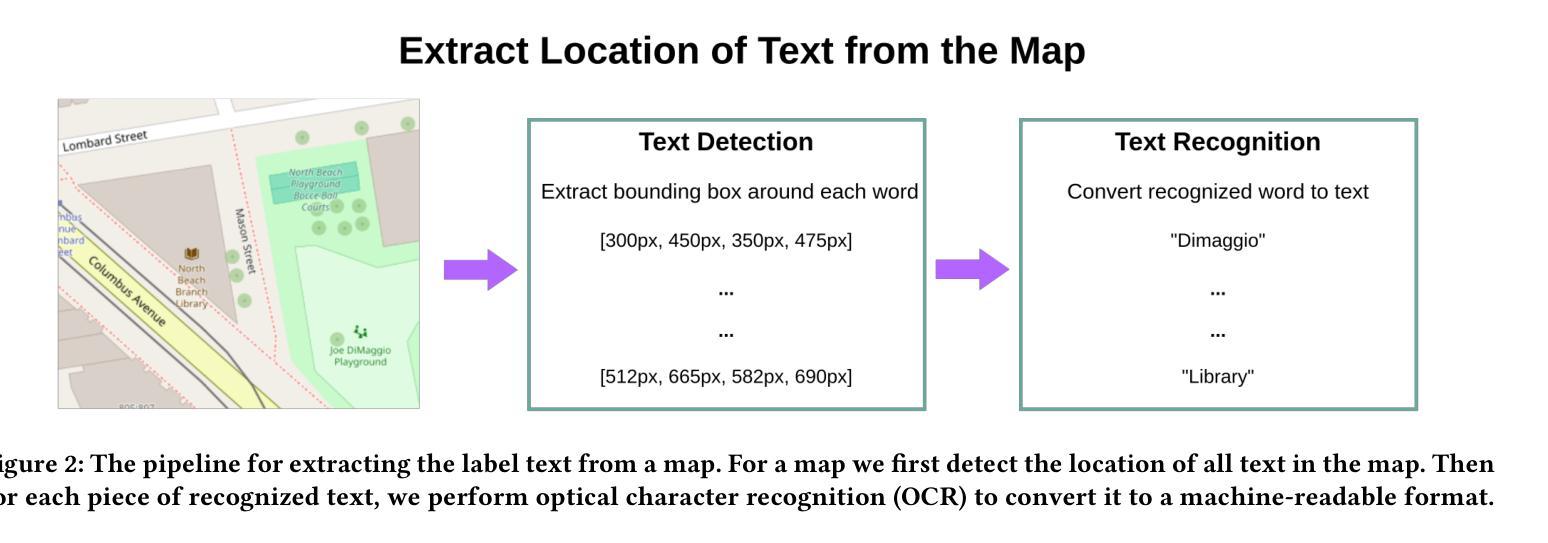
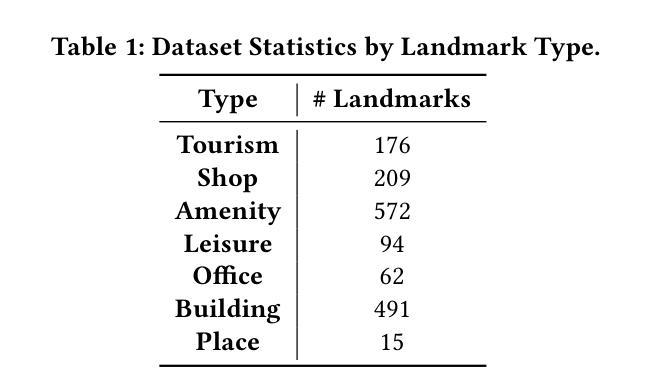
Automated Label Placement on Maps via Large Language Models
Authors:Harry Shomer, Jiejun Xu
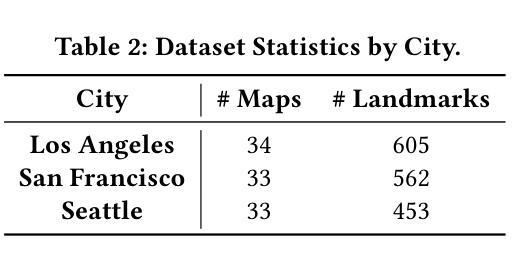
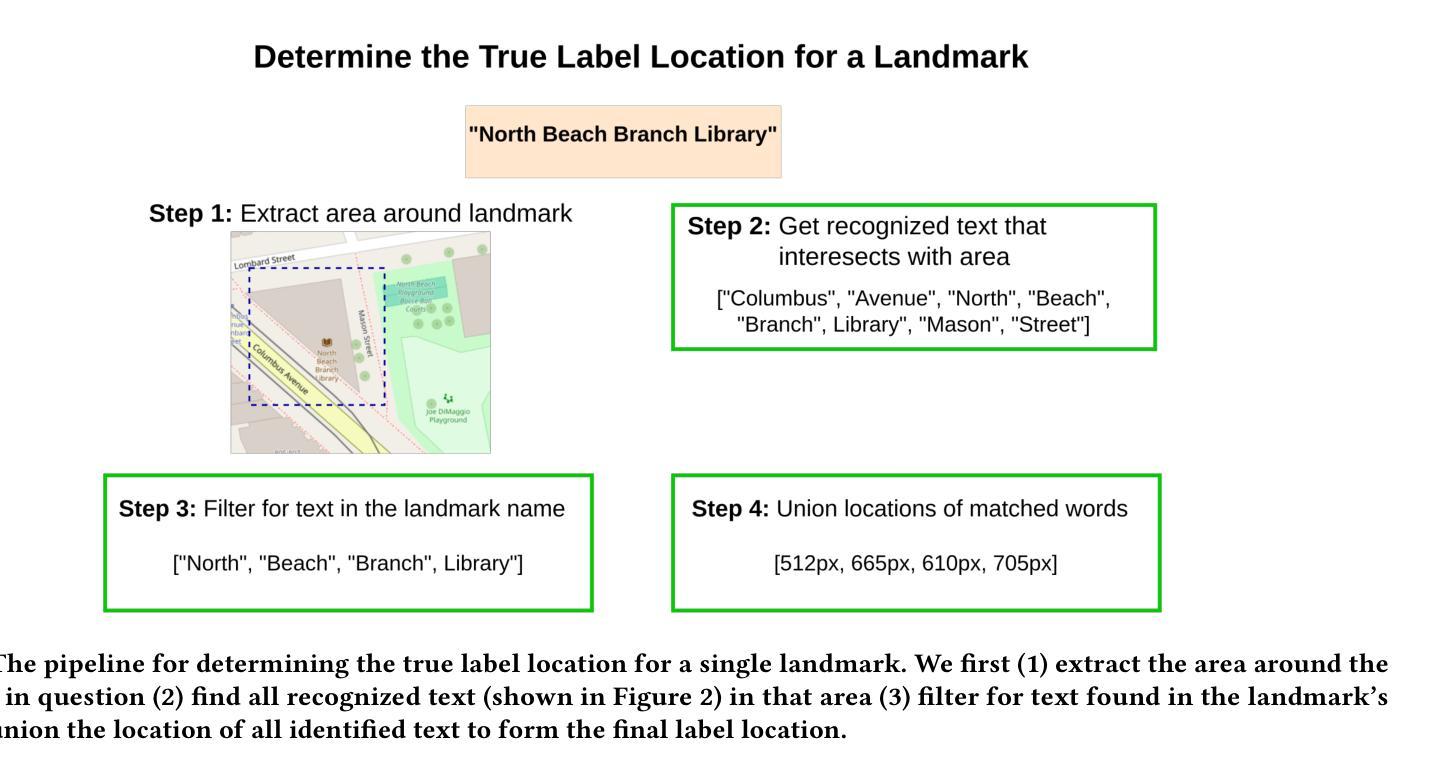
Label placement is a critical aspect of map design, serving as a form of spatial annotation that directly impacts clarity and interpretability. Despite its importance, label placement remains largely manual and difficult to scale, as existing automated systems struggle to integrate cartographic conventions, adapt to context, or interpret labeling instructions. In this work, we introduce a new paradigm for automatic label placement (ALP) that formulates the task as a data editing problem and leverages large language models (LLMs) for context-aware spatial annotation. To support this direction, we curate MAPLE, the first known benchmarking dataset for evaluating ALP on real-world maps, encompassing diverse landmark types and label placement annotations from open-source data. Our method retrieves labeling guidelines relevant to each landmark type leveraging retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), integrates them into prompts, and employs instruction-tuned LLMs to generate ideal label coordinates. We evaluate four open-source LLMs on MAPLE, analyzing both overall performance and generalization across different types of landmarks. This includes both zero-shot and instruction-tuned performance. Our results demonstrate that LLMs, when guided by structured prompts and domain-specific retrieval, can learn to perform accurate spatial edits, aligning the generated outputs with expert cartographic standards. Overall, our work presents a scalable framework for AI-assisted map finishing and demonstrates the potential of foundation models in structured data editing tasks. The code and data can be found at https://github.com/HarryShomer/MAPLE.
标签放置是地图设计中的一个关键方面,作为一种空间注释,它直接影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。尽管其重要性显著,但标签放置仍然大多依赖于手动操作,难以规模化,因为现有的自动化系统很难融入地图制作规范、适应上下文或解释标签指令。在这项工作中,我们引入了自动标签放置(ALP)的新范式,将任务形式化为数据编辑问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知空间注释。为了支持这一方向,我们创建了MAPLE,这是首个用于评估真实世界地图上ALP性能的标准数据集,涵盖了来自开源数据的各种地标类型和标签放置注释。我们的方法检索与每种地标类型相关的标签指南,利用检索增强生成(RAG)技术将它们整合到提示中,并调用指令微调LLM生成理想的标签坐标。我们在MAPLE上评估了四个开源LLM,分析了整体性能以及在不同类型地标上的泛化能力。这包括零样本教学和指令微调后的性能。结果表明,在结构化提示和领域特定检索的指导下,LLM可以学习执行精确的空间编辑,使生成输出符合专家地图制作标准。总的来说,我们的工作为AI辅助地图制作提供了一个可扩展的框架,并展示了基础模型在结构化数据编辑任务中的潜力。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/HarryShomer/MAPLE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Workshop on AI for Data Editing (AI4DE) at KDD 2025
Summary
地图标签放置是地图设计中的关键要素,影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。现有自动标签放置系统存在困难,难以结合地图惯例、适应上下文或解释标签指令。本研究引入一种新的自动标签放置(ALP)范式,将任务表述为数据编辑问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知的空间标注。为此,我们创建了MAPLE数据集,评估ALP在真实世界地图上的表现,涵盖多种地标类型和标签放置注释。我们的方法通过检索增强生成(RAG)检索与每种地标类型相关的标注指南,将其集成到提示中,并借助指令优化LLM生成理想的标签坐标。在MAPLE数据集上评估四个开源LLM的性能,分析整体表现和在不同类型地标上的泛化能力,包括零样本和指令优化性能。结果表明,在结构化提示和领域特定检索的指导下,LLM可以学习执行准确的空间编辑,生成输出与专家地图制作标准相符。总体而言,我们的工作提出了一个可扩展的AI辅助地图完成框架,展示了基础模型在结构化数据编辑任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 标签放置是地图设计中的核心环节,直接影响地图的清晰度和可解释性。
- 现有自动标签放置系统面临集成地图惯例、适应上下文和解释标签指令的挑战。
- 引入新的自动标签放置(ALP)范式,将其表述为数据编辑问题并利用大型语言模型(LLM)解决。
- 创立MAPLE数据集,用于评估ALP在真实世界地图上的性能。
- 方法结合检索增强生成(RAG)技术,检索与地标类型相关的标注指南,并集成到LLM的提示中。
- 在MAPLE数据集上评估LLM的性能,展示其在标签放置任务中的准确性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Beats Autoregressive in Data-Constrained Settings
Authors:Mihir Prabhudesai, Mengning Wu, Amir Zadeh, Katerina Fragkiadaki, Deepak Pathak
Autoregressive (AR) models have long dominated the landscape of large language models, driving progress across a wide range of tasks. Recently, diffusion-based language models have emerged as a promising alternative, though their advantages over AR models remain underexplored. In this paper, we systematically study masked diffusion models in data-constrained settings-where training involves repeated passes over limited data-and find that they significantly outperform AR models when compute is abundant but data is scarce. Diffusion models make better use of repeated data, achieving lower validation loss and superior downstream performance. We interpret this advantage as implicit data augmentation: masked diffusion exposes the model to a diverse distribution of token orderings and prediction tasks, unlike AR’s fixed left-to-right factorization. We find new scaling laws for diffusion models and derive a closed-form expression for the critical compute threshold at which diffusion begins to outperform AR. These results suggest that when data, not compute, is the bottleneck, diffusion models offer a compelling alternative to the standard AR paradigm. Our code is available at: https://diffusion-scaling.github.io.
自回归(AR)模型长期以来一直在大型语言模型领域中占据主导地位,并在各种任务中推动进展。最近,基于扩散的语言模型作为一种有前途的替代方法而出现,尽管它们相对于AR模型的优势仍未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们系统地研究了数据受限环境中掩蔽扩散模型的研究,其中训练涉及在有限数据上多次迭代,我们发现当计算资源充足但数据稀缺时,它们会大大优于AR模型。扩散模型能更好地利用重复数据,实现更低的验证损失和更出色的下游性能。我们将这种优势解释为隐式数据增强:掩蔽扩散使模型暴露于多样化的令牌顺序和预测任务分布中,这与AR的固定从左到右分解不同。我们为扩散模型找到了新的扩展定律,并推导出了临界计算阈值的闭式表达式,在这个阈值上,扩散开始优于AR。这些结果表明,当数据而不是计算成为瓶颈时,扩散模型为标准的AR范式提供了一个引人注目的替代方案。我们的代码可在:https://diffusion-scaling.github.io上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Webpage: https://diffusion-scaling.github.io
Summary
在大型语言模型领域,自回归(AR)模型长期占据主导地位。近期,扩散式语言模型崭露头角,成为了一种有前景的替代方案,但其相较于AR模型的优势尚未得到充分探索。本文系统地研究了数据受限情境下的掩码扩散模型,发现当计算资源充足而数据稀缺时,其显著优于AR模型。扩散模型能更好地利用重复数据,实现更低的验证损失和更出色的下游性能。本文将其优势解读为隐式数据增强:掩码扩散使模型暴露于多样化的令牌排序和预测任务分布中,不同于AR的固定从左到右的分解方式。研究发现扩散模型的新尺度定律,并推导出临界计算阈值的闭式表达式,当数据而非计算成为瓶颈时,扩散模型提供了对标准AR范式的有力替代。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散式语言模型作为大型语言模型的替代方案开始受到关注。
- 在数据受限且计算资源充足的情境下,掩码扩散模型显著优于自回归(AR)模型。
- 扩散模型能更好地利用重复数据,实现更低的验证损失。
- 扩散模型具有隐式数据增强的特性,暴露于多样化的令牌排序和预测任务分布中。
- 与AR模型的固定从左到右分解方式不同,扩散模型具备更多变性。
- 研究发现了扩散模型的新尺度定律,并推导出临界计算阈值。
点此查看论文截图

A Comparative Study of Specialized LLMs as Dense Retrievers
Authors:Hengran Zhang, Keping Bi, Jiafeng Guo
While large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as dense retrievers, the impact of their domain-specific specialization on retrieval effectiveness remains underexplored. This investigation systematically examines how task-specific adaptations in LLMs influence their retrieval capabilities, an essential step toward developing unified retrievers capable of handling text, code, images, and multimodal content. We conduct extensive experiments with eight Qwen2.5 7B LLMs, including base, instruction-tuned, code/math-specialized, long reasoning, and vision-language models across zero-shot retrieval settings and the supervised setting. For the zero-shot retrieval settings, we consider text retrieval from the BEIR benchmark and code retrieval from the CoIR benchmark. Further, to evaluate supervised performance, all LLMs are fine-tuned on the MS MARCO dataset. We find that mathematical specialization and the long reasoning capability cause consistent degradation in three settings, indicating conflicts between mathematical reasoning and semantic matching. The vision-language model and code-specialized LLMs demonstrate superior zero-shot performance compared to other LLMs, even surpassing BM25 on the code retrieval task, and maintain comparable performance to base LLMs in supervised settings. These findings suggest promising directions for the unified retrieval task leveraging cross-domain and cross-modal fusion.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被部署为密集检索器,其特定领域的专业化对检索效果的影响尚未得到充分探索。本研究系统地调查了LLM中的特定任务适应性如何影响它们的检索能力,这是朝着开发能够处理文本、代码、图像和多模态内容的统一检索器迈出的重要一步。我们在八个Qwen2.5 7B LLM上进行了广泛实验,包括基础模型、指令调优模型、代码/数学专业化模型、长期推理模型和视觉语言模型,在零样本检索设置和有监督设置下进行了测试。对于零样本检索设置,我们考虑了来自BEIR基准测试的文本检索和来自CoIR基准测试的代码检索。此外,为了评估监督性能,所有LLM都在MS MARCO数据集上进行微调。我们发现数学专业化知识和长期推理能力在三种设置下均导致性能持续下降,这表明数学推理和语义匹配之间存在冲突。视觉语言模型和专门针对代码设计的LLM在零样本任务中显示出卓越的性能,甚至在代码检索任务上超越了BM25,并且在有监督环境中保持了与基础LLM相当的性能。这些发现表明,利用跨域和跨模态融合的统一检索任务具有广阔的发展前景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CCIR25 and published by Springer LNCS or LNAI
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在密集检索中的应用日益广泛,但其域特定专业化对检索效果的影响尚未得到充分探索。本研究系统地探讨了LLM的任务特定适应性对其检索能力的影响,这是朝着开发能够处理文本、代码、图像和多模态内容的统一检索器迈出的重要一步。通过对八种不同专业领域的LLM进行广泛的实验,包括基础模型、指令调优模型、代码/数学专业模型、逻辑推理模型和视觉语言模型等,发现数学专业化和逻辑推理能力在某些设置下会导致性能下降,表明数学推理和语义匹配之间存在冲突。视觉语言模型和代码专业LLM在零射击检索任务中表现优异,甚至在代码检索任务上超越了BM25,并在监督设置中的表现与其他LLM相当。这些发现表明,利用跨域和跨模态融合的统一检索任务具有广阔的发展前景。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在密集检索中的应用广泛,但其域特定专业化对检索效果的影响尚待探索。
- 任务特定适应性对LLM的检索能力有重要影响。
- 数学专业化和逻辑推理能力在某些设置下可能导致LLM性能下降。
- 视觉语言模型和代码专业LLM在零射击检索任务中表现优异。
- 视觉语言模型和代码专业LLM在代码检索任务上可能超越现有方法。
- 在监督设置下,专业LLM的表现与其他模型相当。
点此查看论文截图