⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
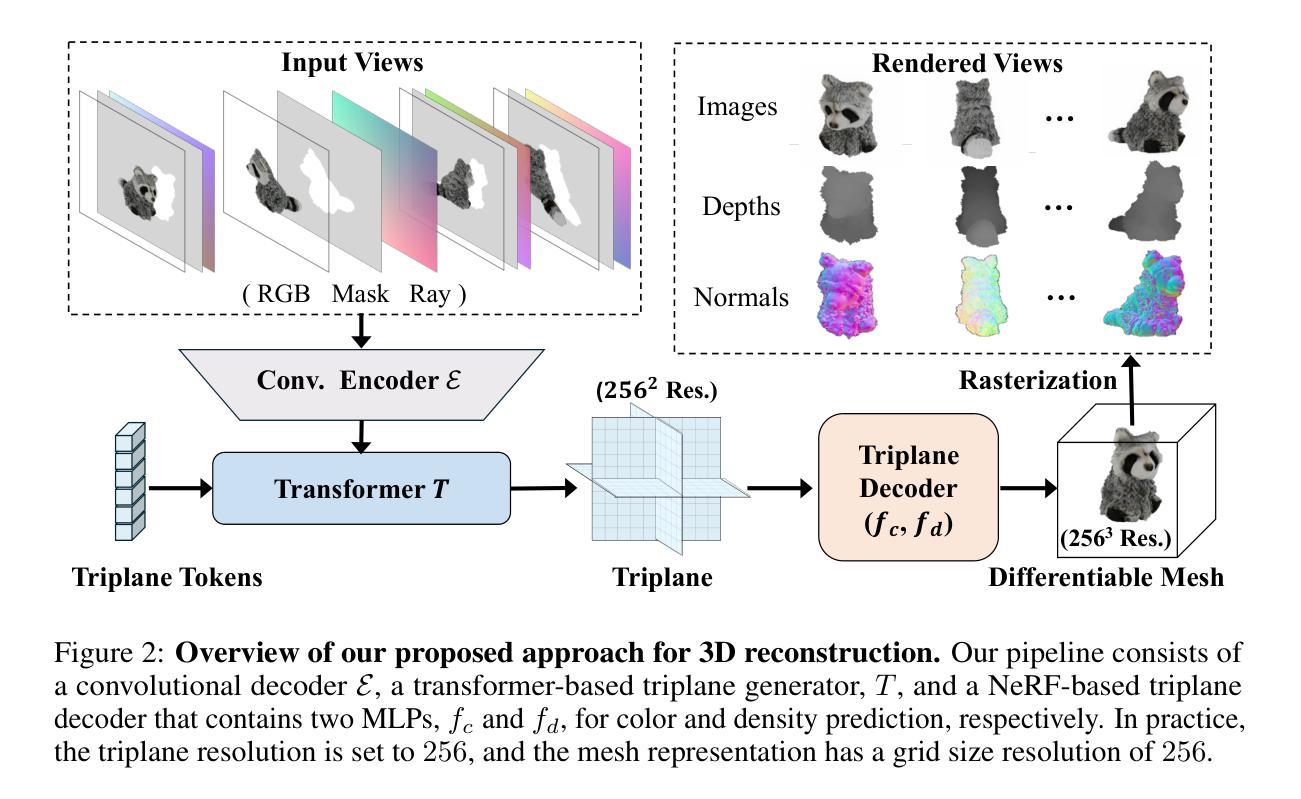
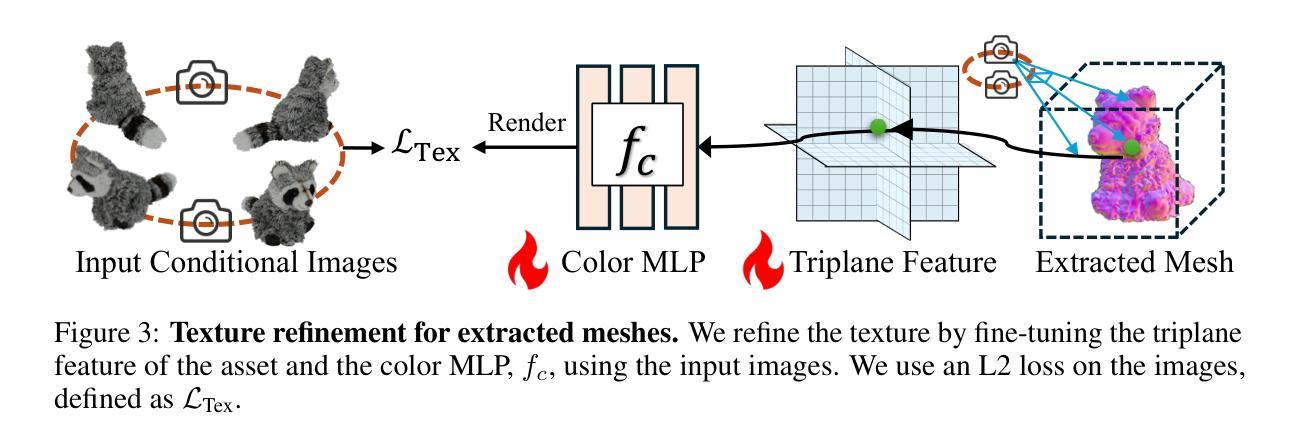
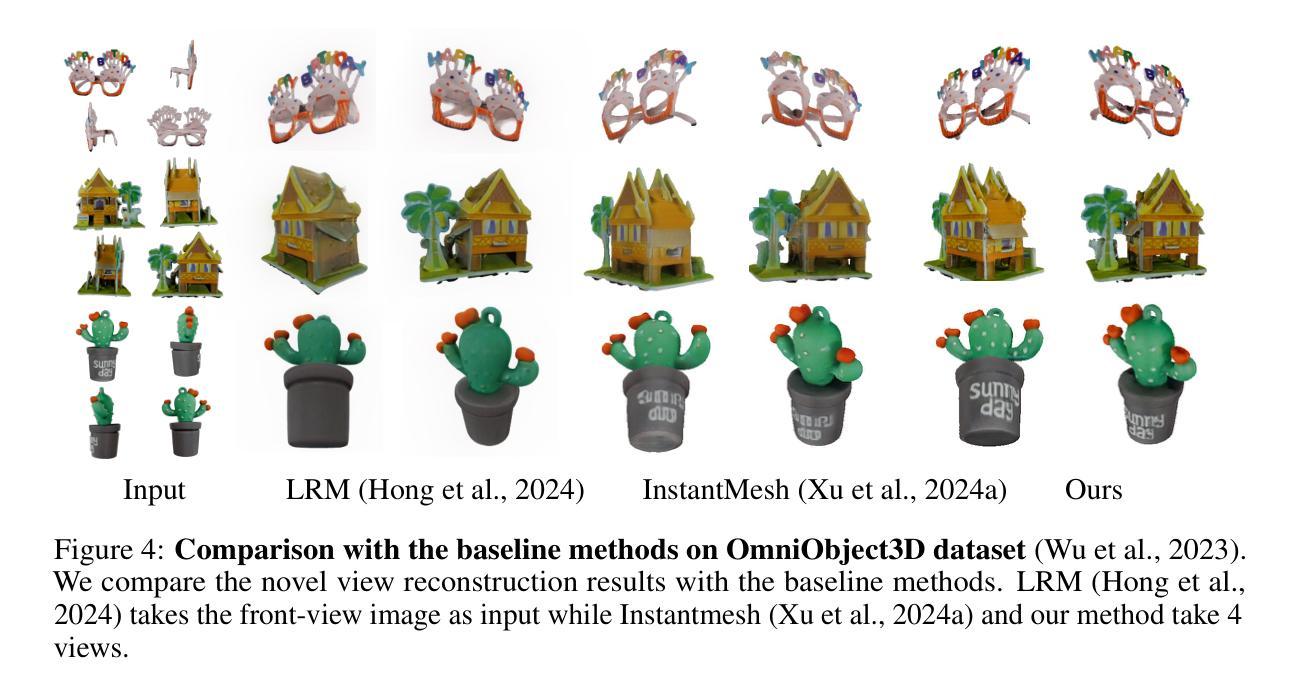
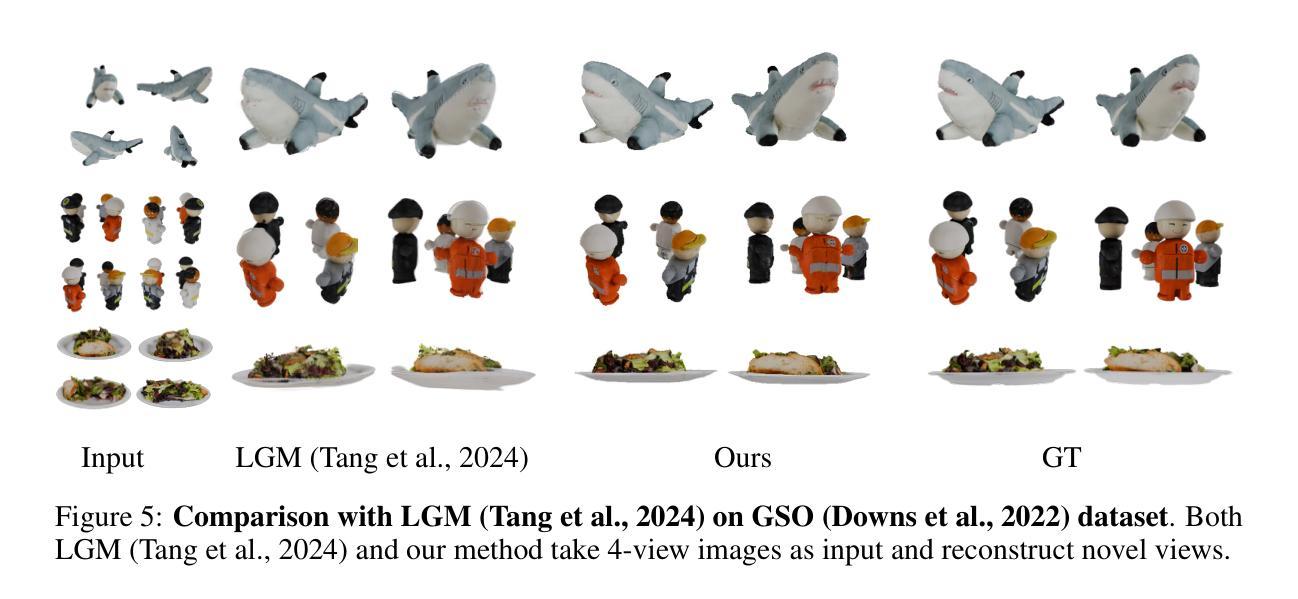
GTR: Improving Large 3D Reconstruction Models through Geometry and Texture Refinement
Authors:Peiye Zhuang, Songfang Han, Chaoyang Wang, Aliaksandr Siarohin, Jiaxu Zou, Michael Vasilkovsky, Vladislav Shakhrai, Sergey Korolev, Sergey Tulyakov, Hsin-Ying Lee
We propose a novel approach for 3D mesh reconstruction from multi-view images. Our method takes inspiration from large reconstruction models like LRM that use a transformer-based triplane generator and a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model trained on multi-view images. However, in our method, we introduce several important modifications that allow us to significantly enhance 3D reconstruction quality. First of all, we examine the original LRM architecture and find several shortcomings. Subsequently, we introduce respective modifications to the LRM architecture, which lead to improved multi-view image representation and more computationally efficient training. Second, in order to improve geometry reconstruction and enable supervision at full image resolution, we extract meshes from the NeRF field in a differentiable manner and fine-tune the NeRF model through mesh rendering. These modifications allow us to achieve state-of-the-art performance on both 2D and 3D evaluation metrics, such as a PSNR of 28.67 on Google Scanned Objects (GSO) dataset. Despite these superior results, our feed-forward model still struggles to reconstruct complex textures, such as text and portraits on assets. To address this, we introduce a lightweight per-instance texture refinement procedure. This procedure fine-tunes the triplane representation and the NeRF color estimation model on the mesh surface using the input multi-view images in just 4 seconds. This refinement improves the PSNR to 29.79 and achieves faithful reconstruction of complex textures, such as text. Additionally, our approach enables various downstream applications, including text- or image-to-3D generation.
我们提出了一种从多视角图像进行3D网格重建的新方法。我们的方法受到大型重建模型(如LRM)的启发,这些模型使用基于变压器的三平面生成器和在多个视角图像上训练好的神经辐射场(NeRF)模型。然而,在我们的方法中,我们引入了一些重要的改进,可以显著提高3D重建的质量。首先,我们研究了原始的LRM架构,并发现了几个缺点。随后,我们对LRM架构进行了相应的修改,以改进多视角图像表示并提高了计算效率的训练。其次,为了改进几何重建并在全图像分辨率上实现监督,我们以可区分的方式从NeRF场中提取网格,并通过网格渲染对NeRF模型进行微调。这些改进使我们能够在Google扫描对象(GSO)数据集上实现最先进的性能,在二维和三维评估指标上的PSNR达到28.67。尽管取得了这些出色的结果,我们的前馈模型在重建复杂纹理(如资产上的文字和肖像)方面仍然面临挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一种轻量级的按实例纹理细化程序。该程序使用输入的多视角图像在网格表面上对三平面表示和NeRF颜色估计模型进行微调,仅耗时4秒。这种细化将PSNR提高到29.79,并实现了复杂纹理(如文字)的真实重建。此外,我们的方法还支持各种下游应用,包括文本或图像到三维的生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 17 figures. Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/GTR/; Code: https://github.com/snap-research/snap_gtr/
摘要
本文提出了一种基于多视角图像的三维网格重建新方法。该方法受到大型重建模型(如LRM)的启发,使用基于变压器的三平面生成器和在多个视角图像上训练的神经辐射场(NeRF)模型。然而,在我们的方法中,进行了几项重要改进,显著提高了三维重建质量。我们对LRM架构进行了深入分析和改进,以优化多视角图像表示和计算效率。其次,为了改进几何重建并在全图像分辨率上实现监督,我们从NeRF场中提取网格并以可微的方式对其进行微调。这些改进使我们能够在二维和三维评估指标上实现卓越性能,如在Google扫描对象(GSO)数据集上的PSNR为28.67。尽管我们的前馈模型取得了这些出色结果,但在重建复杂纹理(如文本和肖像资产)时仍面临挑战。为解决此问题,我们引入了一种轻量级的按实例纹理细化程序。该程序仅使用输入的多视角图像,在4秒内对三平面表示和NeRF颜色估计模型进行微调。这种细化将PSNR提高到29.79,并实现了复杂纹理(如文本)的忠实重建。此外,我们的方法还支持文本或图像到三维的生成等下游应用。
要点
- 提出了一种基于多视角图像的三维网格重建新方法,受到LRM模型的启发并进行了改进。
- 对LRM架构进行了深入分析并进行了改进,以提高多视角图像表示和计算效率。
- 通过从NeRF场中提取网格并以可微方式进行微调,改进了几何重建,并实现了全图像分辨率上的监督。
- 在多个数据集上实现了卓越的性能,如在GSO数据集上的PSNR为28.67。
- 尽管在复杂纹理的重建上取得了进展,但仍面临一些挑战,因此引入了一种轻量级的按实例纹理细化程序。
- 细化程序能够在短时间内(4秒)提高PSNR并忠实重建复杂纹理。
点此查看论文截图

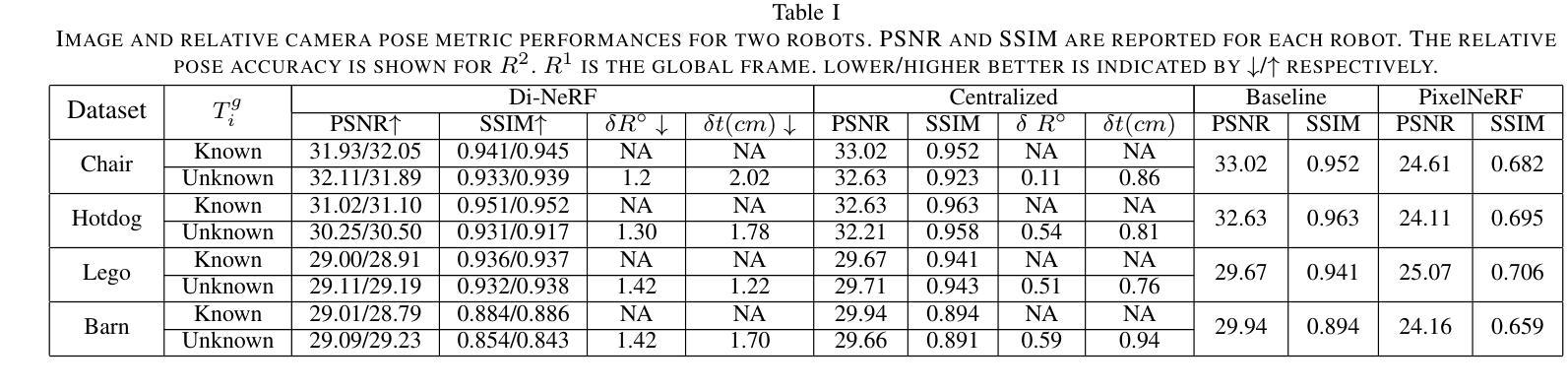
Di-NeRF: Distributed NeRF for Collaborative Learning with Relative Pose Refinement
Authors:Mahboubeh Asadi, Kourosh Zareinia, Sajad Saeedi
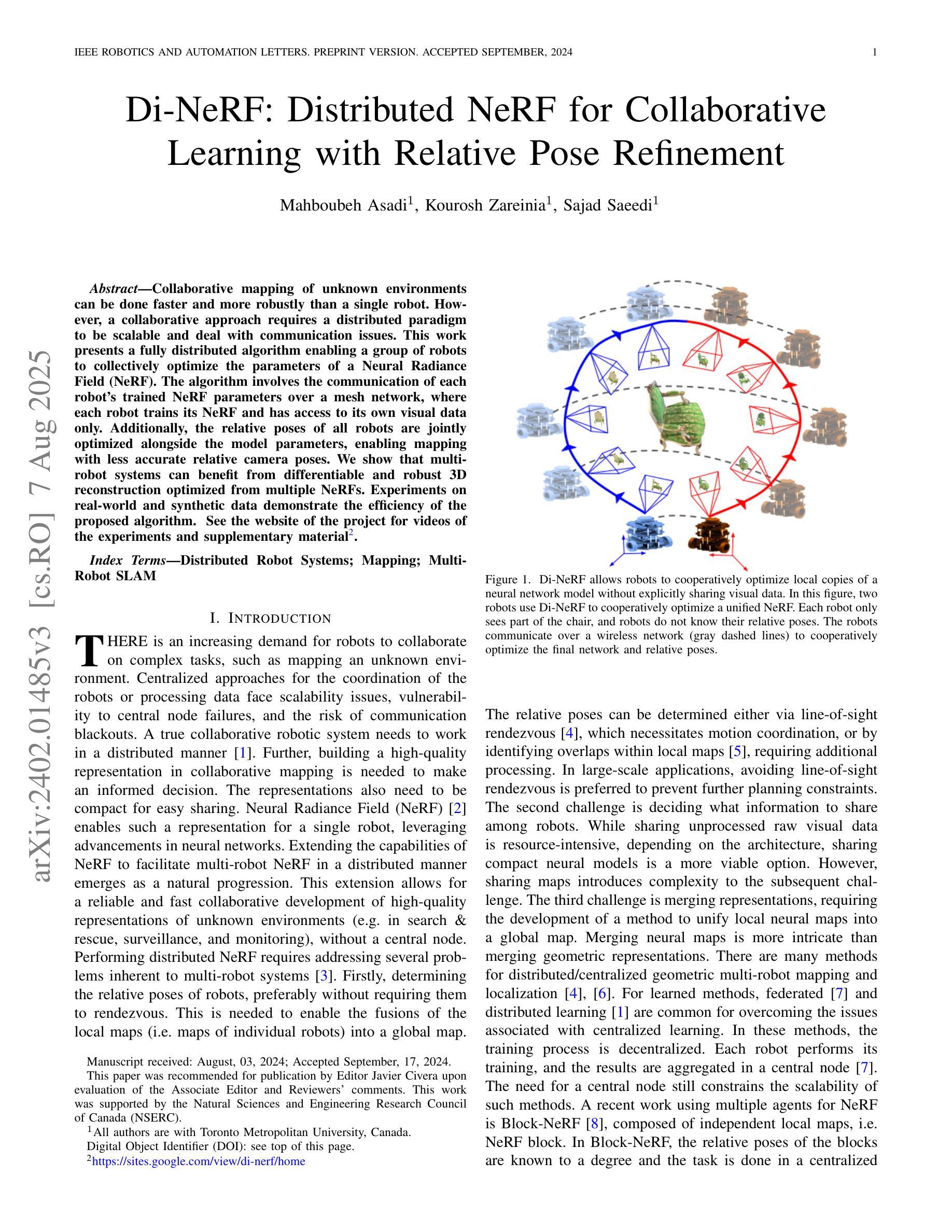
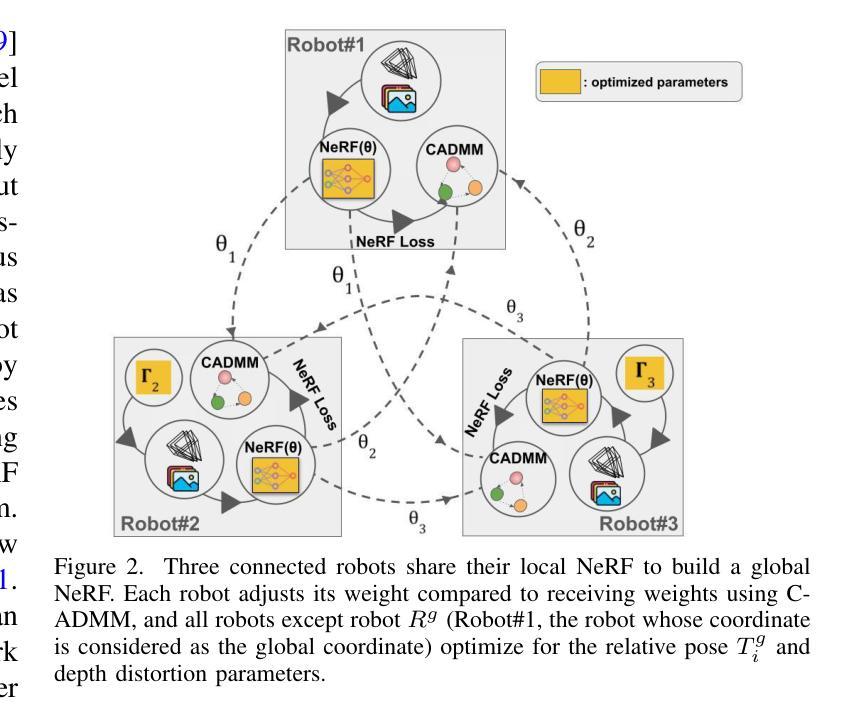
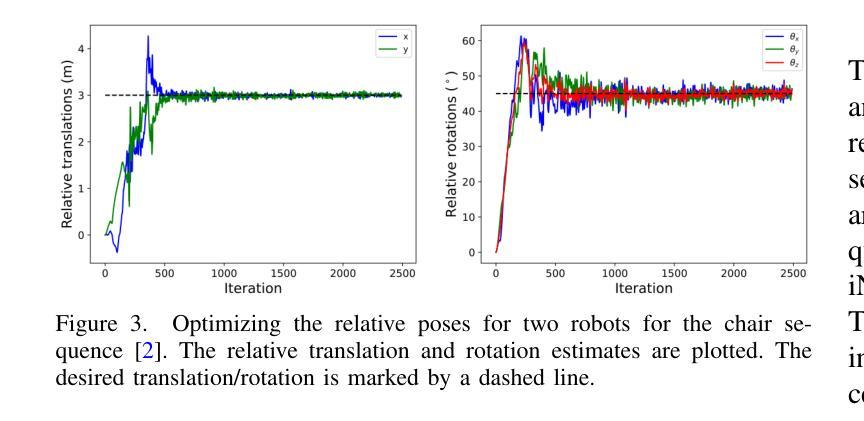
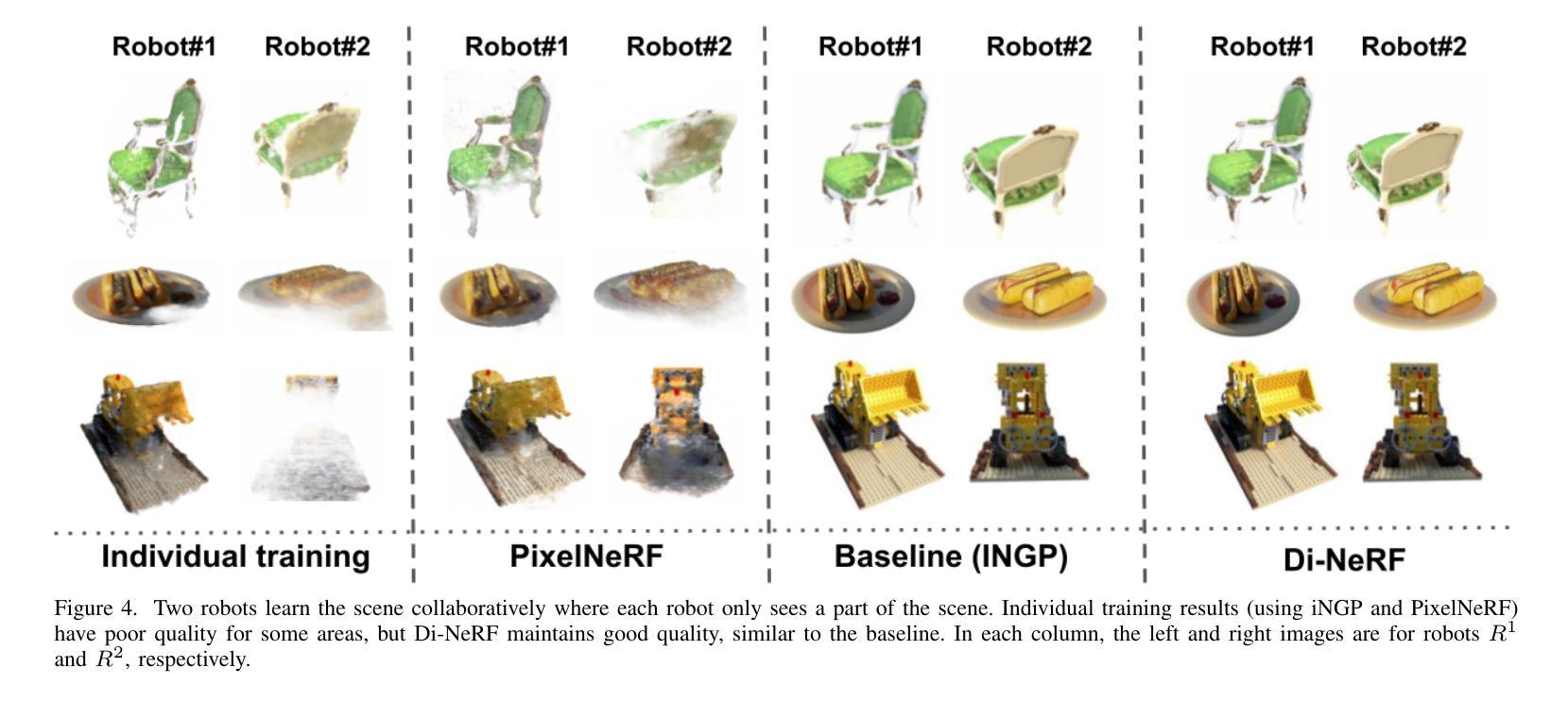
Collaborative mapping of unknown environments can be done faster and more robustly than a single robot. However, a collaborative approach requires a distributed paradigm to be scalable and deal with communication issues. This work presents a fully distributed algorithm enabling a group of robots to collectively optimize the parameters of a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF). The algorithm involves the communication of each robot’s trained NeRF parameters over a mesh network, where each robot trains its NeRF and has access to its own visual data only. Additionally, the relative poses of all robots are jointly optimized alongside the model parameters, enabling mapping with less accurate relative camera poses. We show that multi-robot systems can benefit from differentiable and robust 3D reconstruction optimized from multiple NeRFs. Experiments on real-world and synthetic data demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed algorithm. See the website of the project for videos of the experiments and supplementary material (https://sites.google.com/view/di-nerf/home).
协作式地图绘制未知环境相较于单一机器人来说,可以更快且更稳健地完成。然而,协作式方法需要一个分布式模式来实现扩展并解决通信问题。本研究提出了一种全分布式算法,该算法使得一组机器人能够协同优化神经网络辐射场(NeRF)的参数。该算法涉及通过网格网络进行每个机器人训练的NeRF参数的通信,其中每个机器人仅训练自己的NeRF并使用其自身的视觉数据。此外,所有机器人的相对姿态与模型参数一起进行联合优化,这使得即使使用不太精确的相对相机姿态也可以实现地图绘制。我们证明了多机器人系统受益于可从多个NeRF优化的可区分且稳健的3D重建。真实和合成数据的实验证明了所提出算法的效率。有关实验的录像和补充材料,请参见项目网站(https://sites.google.com/view/di-nerf/home)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 11 figures, Accepted in IEEE-RA-L
Summary
本文介绍了一种全分布式算法,该算法使机器人群体能够集体优化神经辐射场(NeRF)的参数,从而实现环境地图的协同构建。算法通过网格网络进行机器人间的NeRF参数通信,每个机器人仅使用自己的视觉数据进行训练。同时,相对机器人姿态与模型参数联合优化,可在相机姿态不太准确的情况下进行映射。实验表明,多机器人系统可从多个NeRF中获益,实现可微调的稳健三维重建。有关实验的更多内容,请参见项目网站(https://sites.google.com/view/di-nerf/home)。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人群体可通过全分布式算法协同构建环境地图,实现更快更稳健的映射。
- 该算法采用网格网络进行机器人间的NeRF参数通信。
- 每个机器人仅使用其视觉数据进行NeRF训练。
- 相对机器人姿态与模型参数联合优化,可在相机姿态不准确的情况下进行映射。
- 多机器人系统可从多个NeRF中获益,实现更精准的三维重建。
- 实验证明该算法在真实和合成数据上的有效性。
点此查看论文截图