⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
Speech LLMs in Low-Resource Scenarios: Data Volume Requirements and the Impact of Pretraining on High-Resource Languages
Authors:Seraphina Fong, Marco Matassoni, Alessio Brutti
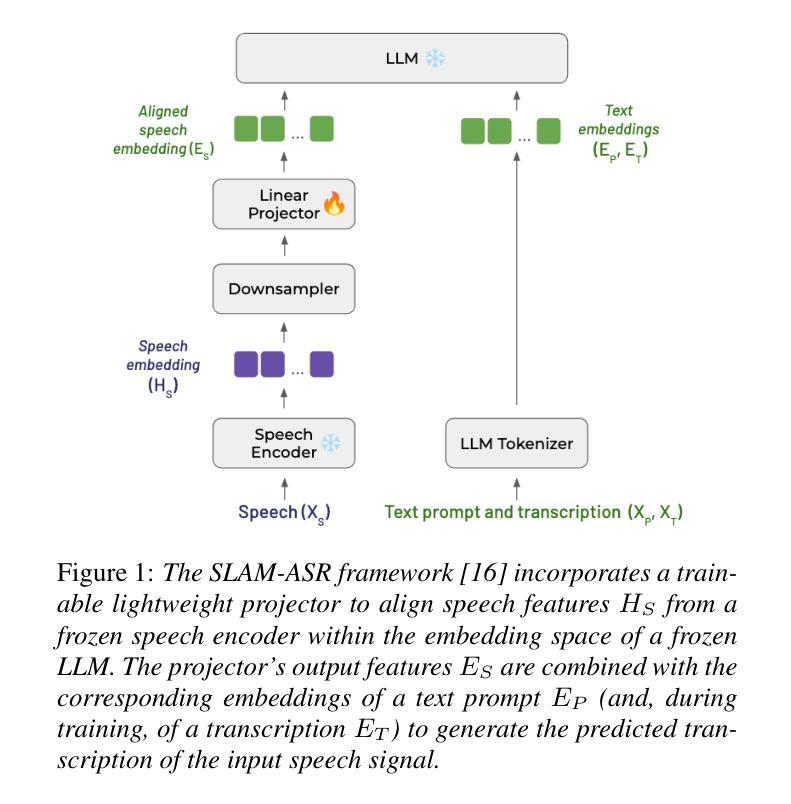
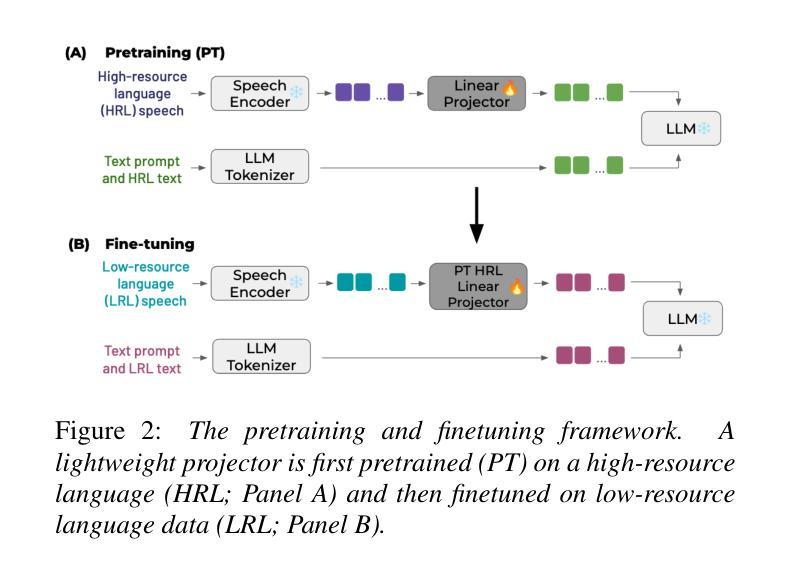
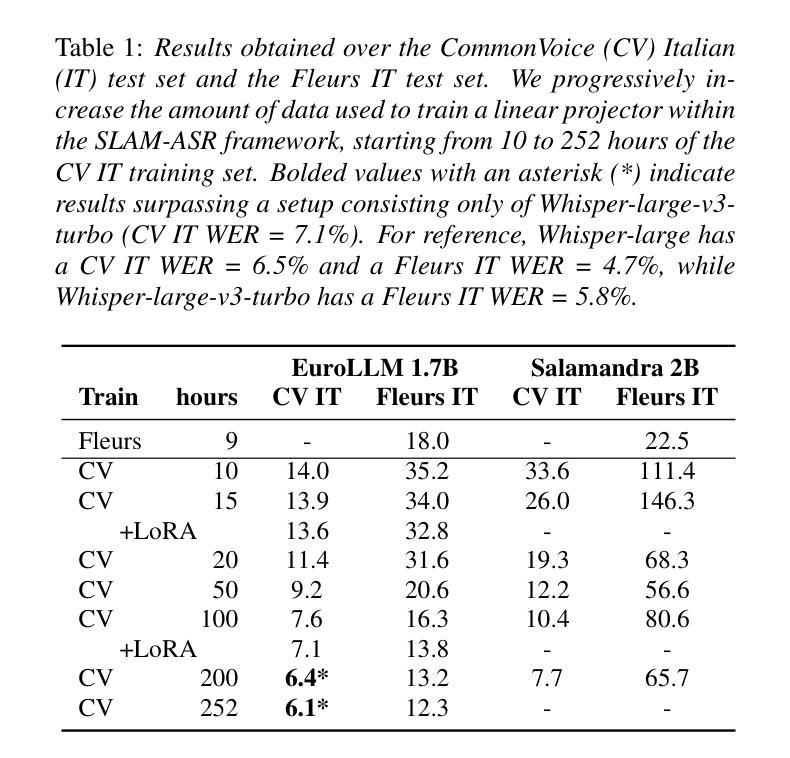
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated potential in handling spoken inputs for high-resource languages, reaching state-of-the-art performance in various tasks. However, their applicability is still less explored in low-resource settings. This work investigates the use of Speech LLMs for low-resource Automatic Speech Recognition using the SLAM-ASR framework, where a trainable lightweight projector connects a speech encoder and a LLM. Firstly, we assess training data volume requirements to match Whisper-only performance, re-emphasizing the challenges of limited data. Secondly, we show that leveraging mono- or multilingual projectors pretrained on high-resource languages reduces the impact of data scarcity, especially with small training sets. Using multilingual LLMs (EuroLLM, Salamandra) with whisper-large-v3-turbo, we evaluate performance on several public benchmarks, providing insights for future research on optimizing Speech LLMs for low-resource languages and multilinguality.
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理高资源语言的口语输入方面已显示出潜力,在各种任务中达到了最新技术性能。然而,它们在低资源环境中的适用性仍研究较少。本研究利用SLAM-ASR框架探索了语音LLM在资源低下的自动语音识别(ASR)中的应用,其中可训练的轻量级投影仪连接了语音编码器LLM。首先,我们评估了达到仅whisper性能所需的训练数据量,再次强调有限数据的挑战。其次,我们表明利用在高资源语言上预训练的单语或多语投影仪可以减少数据稀缺的影响,尤其是使用小型训练集时。使用多语言LLM(EuroLLM、Salamandra)与whisper-large-v3-turbo,我们在多个公共基准测试集上评估性能,为未来优化用于低资源语言和多种语言的语音LLM的研究提供见解。
论文及项目相关链接
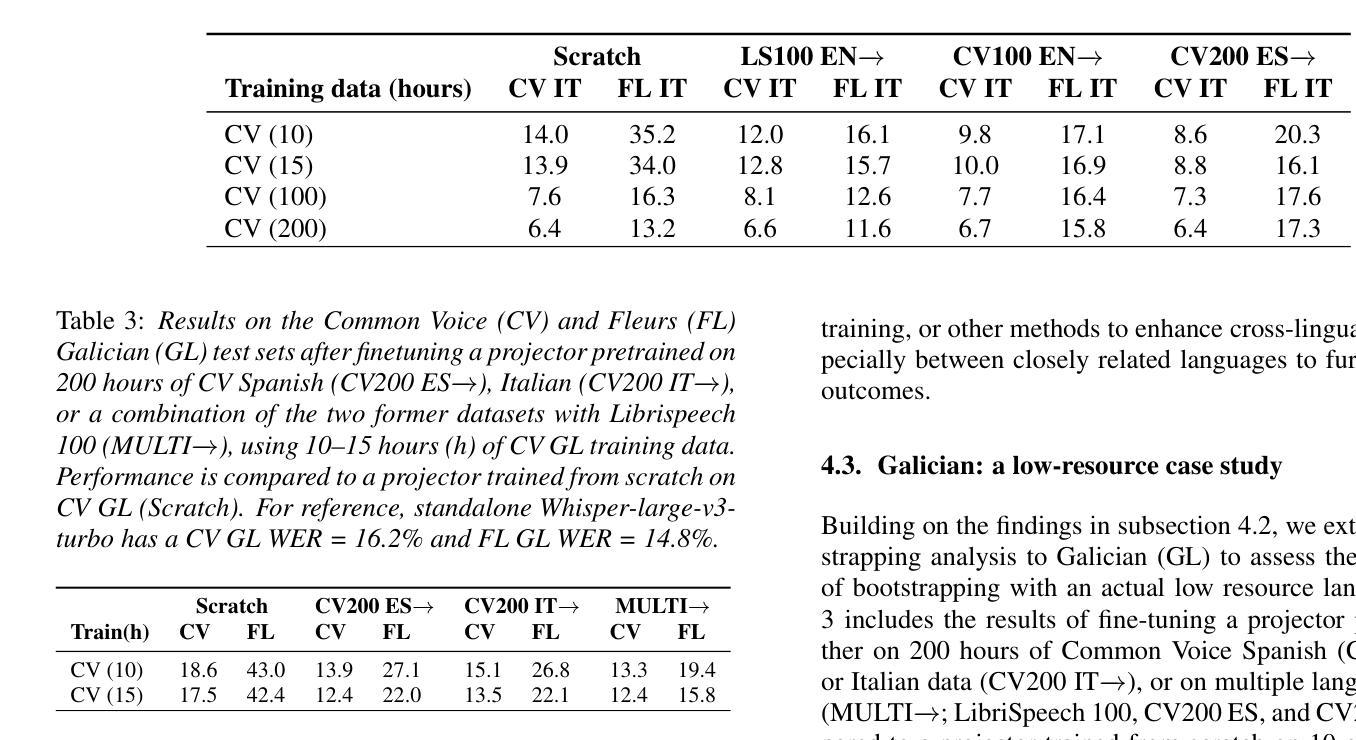
PDF Accepted at Interspeech 2025. 5 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
总结
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在处理高资源语言的口语输入方面显示出巨大潜力,并在各种任务中达到最新技术水平。然而,它们在低资源环境中的适用性仍然有待探索。本研究使用SLAM-ASR框架探讨了低资源自动语音识别中使用语音LLMs的问题。一个可训练的轻量级投影仪连接语音编码器与LLM。首先,我们评估了达到whisper-only性能所需的训练数据量,再次强调了数据有限的挑战。其次,我们展示了利用单语种或多语种预训练在高资源语言上的投影仪能够减少数据稀缺的影响,特别是小训练集情况下更为明显。通过使用多语种LLM(EuroLLM、Salamandra)与whisper-large-v3-turbo,我们在多个公共基准测试上评估性能,为未来优化语音LLMs在低资源语言和多语种方面的应用提供见解。
关键见解
- 大规模语言模型在高资源语言的口语处理方面表现出卓越性能,但在低资源环境中其适用性有待进一步探索。
- 使用SLAM-ASR框架研究语音LLMs在自动语音识别方面的应用。
- 训练数据量对达到whisper-only性能至关重要,突显数据有限的挑战。
- 利用预训练的单语种或多语种投影仪在高资源语言上可以减少数据稀缺的影响。
- 多语种LLMs在语音识别方面具有优势,尤其是在处理小训练集时效果更为显著。
- 在多个公共基准测试上对性能进行评估,为后续优化提供参照。
点此查看论文截图

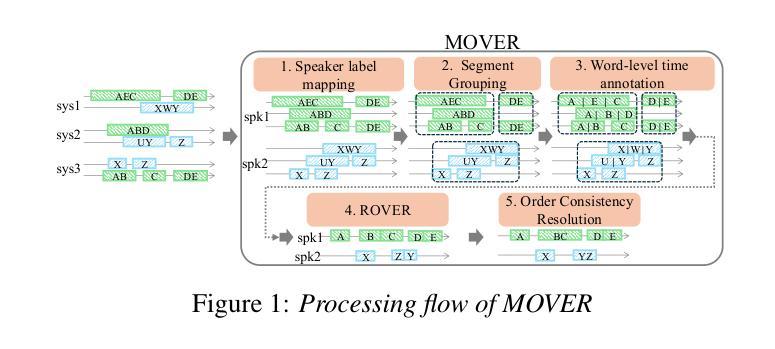
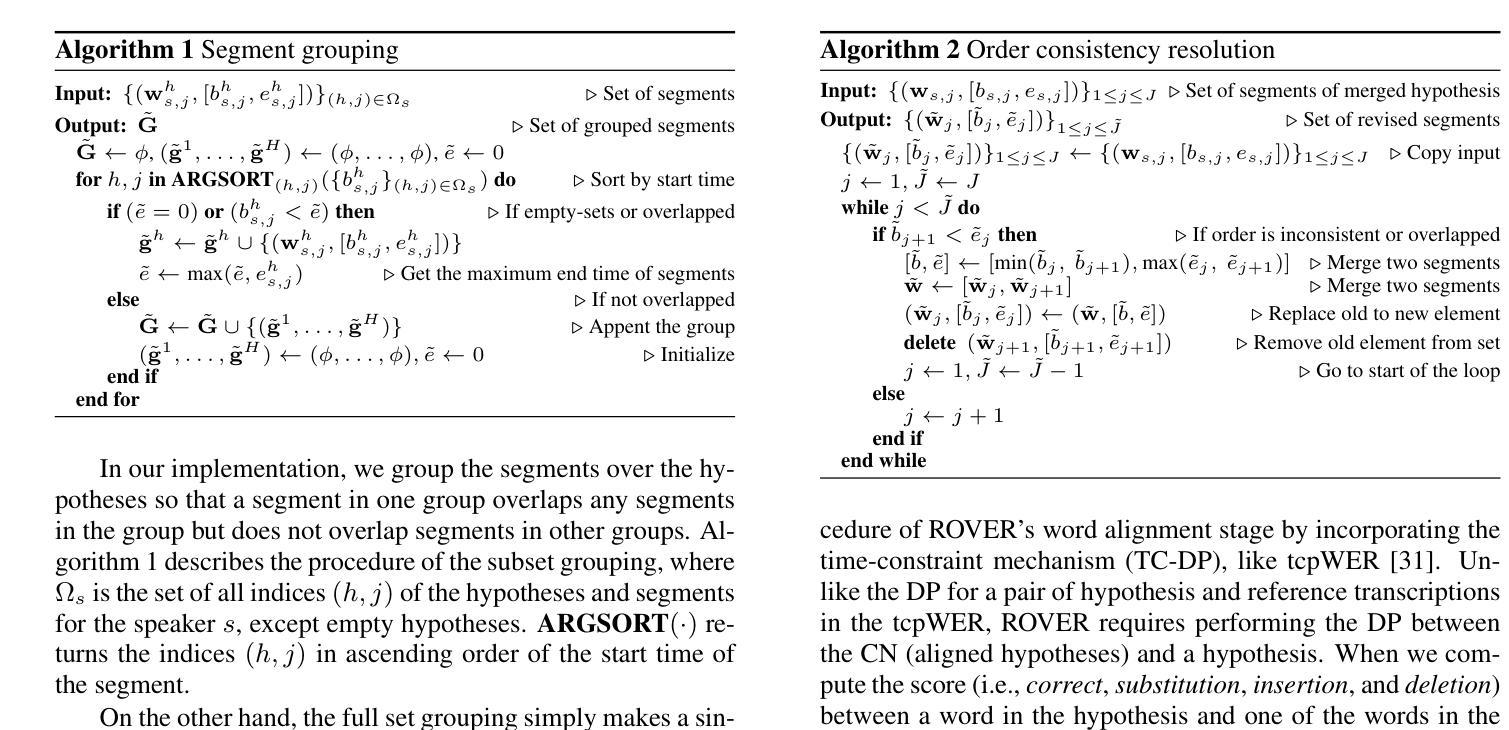
MOVER: Combining Multiple Meeting Recognition Systems
Authors:Naoyuki Kamo, Tsubasa Ochiai, Marc Delcroix, Tomohiro Nakatani
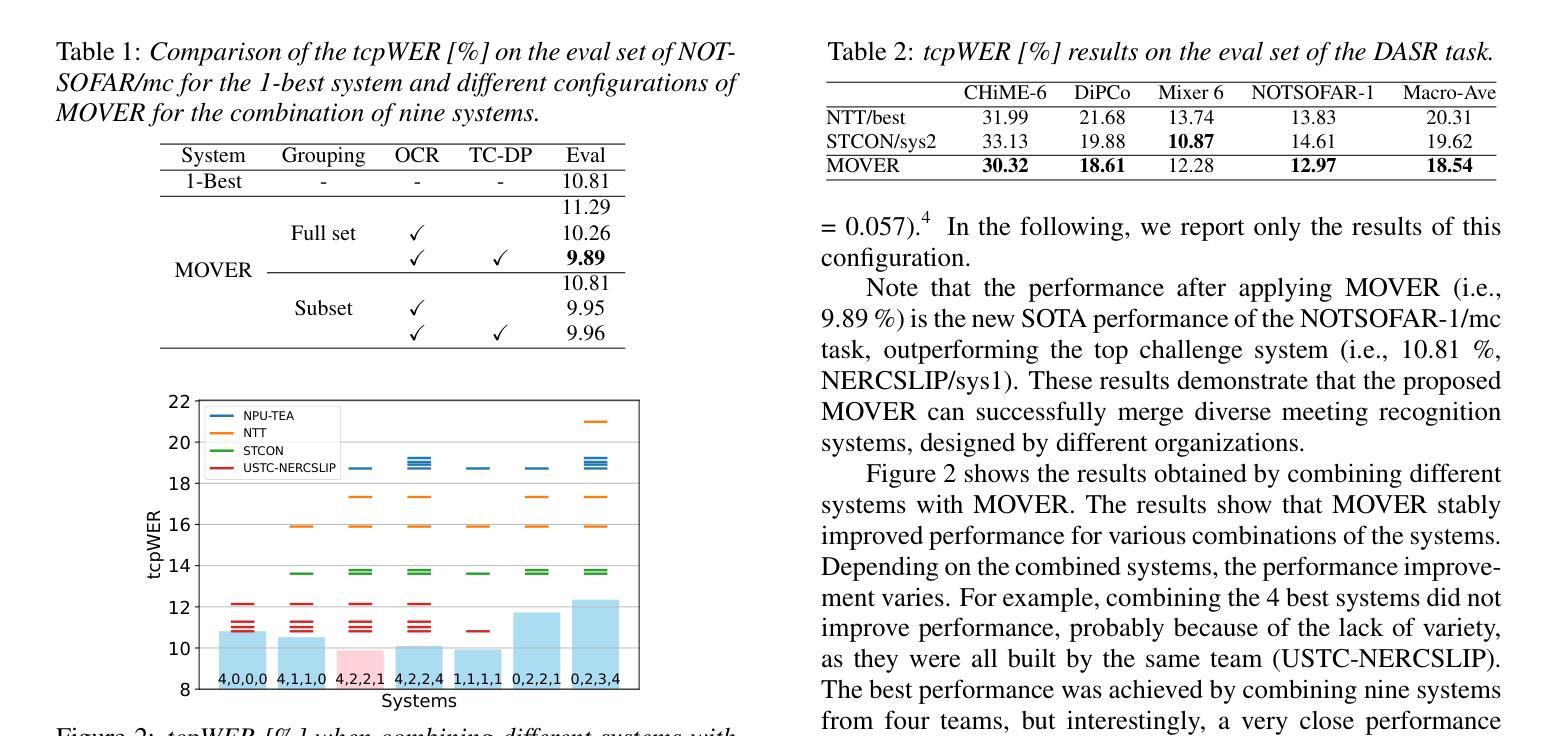
In this paper, we propose Meeting recognizer Output Voting Error Reduction (MOVER), a novel system combination method for meeting recognition tasks. Although there are methods to combine the output of diarization (e.g., DOVER) or automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems (e.g., ROVER), MOVER is the first approach that can combine the outputs of meeting recognition systems that differ in terms of both diarization and ASR. MOVER combines hypotheses with different time intervals and speaker labels through a five-stage process that includes speaker alignment, segment grouping, word and timing combination, etc. Experimental results on the CHiME-8 DASR task and the multi-channel track of the NOTSOFAR-1 task demonstrate that MOVER can successfully combine multiple meeting recognition systems with diverse diarization and recognition outputs, achieving relative tcpWER improvements of 9.55 % and 8.51 % over the state-of-the-art systems for both tasks.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了会议识别输出投票误差减少(MOVER)方法,这是一种用于会议识别任务的新型系统组合方法。尽管有方法可以将日记化(例如DOVER)或自动语音识别(ASR)系统的输出进行组合(例如ROVER),但MOVER是首个能够结合在日记化和ASR方面有所不同的会议识别系统输出的方法。MOVER通过包括说话人对齐、段落分组、词汇和时序组合等五个阶段的流程,将具有不同时间间隔和说话人标签的假设进行结合。在CHiME-8 DASR任务和NOTSOFAR-1任务的多通道轨道上的实验结果表明,MOVER能够成功地将多个会议识别系统进行组合,这些系统具有多样化的日记化和识别输出,相对于当前先进系统,实现了9.55%和8.51%的tcpWER改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
会议识别输出投票误差减少(MOVER)是一种新颖的会议识别任务系统组合方法。它结合不同时间段和说话人标签的假设,通过五阶段过程,包括说话人对齐、分段分组、词语和时间组合等。在CHiME-8 DASR任务和NOTSOFAR-1多通道任务的实验中,MOVER成功结合了多个会议识别系统,实现了相对tcpWER的改进,超过了现有系统的表现。
Key Takeaways
- MOVER是一种用于会议识别任务的全新系统组合方法。
- MOVER结合了不同时间段和说话人标签的假设。
- MOVER包含五阶段过程:说话人对齐、分段分组、词语和时间组合等。
- CHiME-8 DASR任务和NOTSOFAR-1多通道任务的实验验证了MOVER的有效性。
- MOVER能够成功结合多个会议识别系统,这些系统可能在迪亚里化和识别输出方面有所不同。
- 与现有系统相比,MOVER在相对tcpWER方面实现了显著的改进,分别为9.55%和8.51%。
- MOVER方法为会议识别任务的系统组合提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

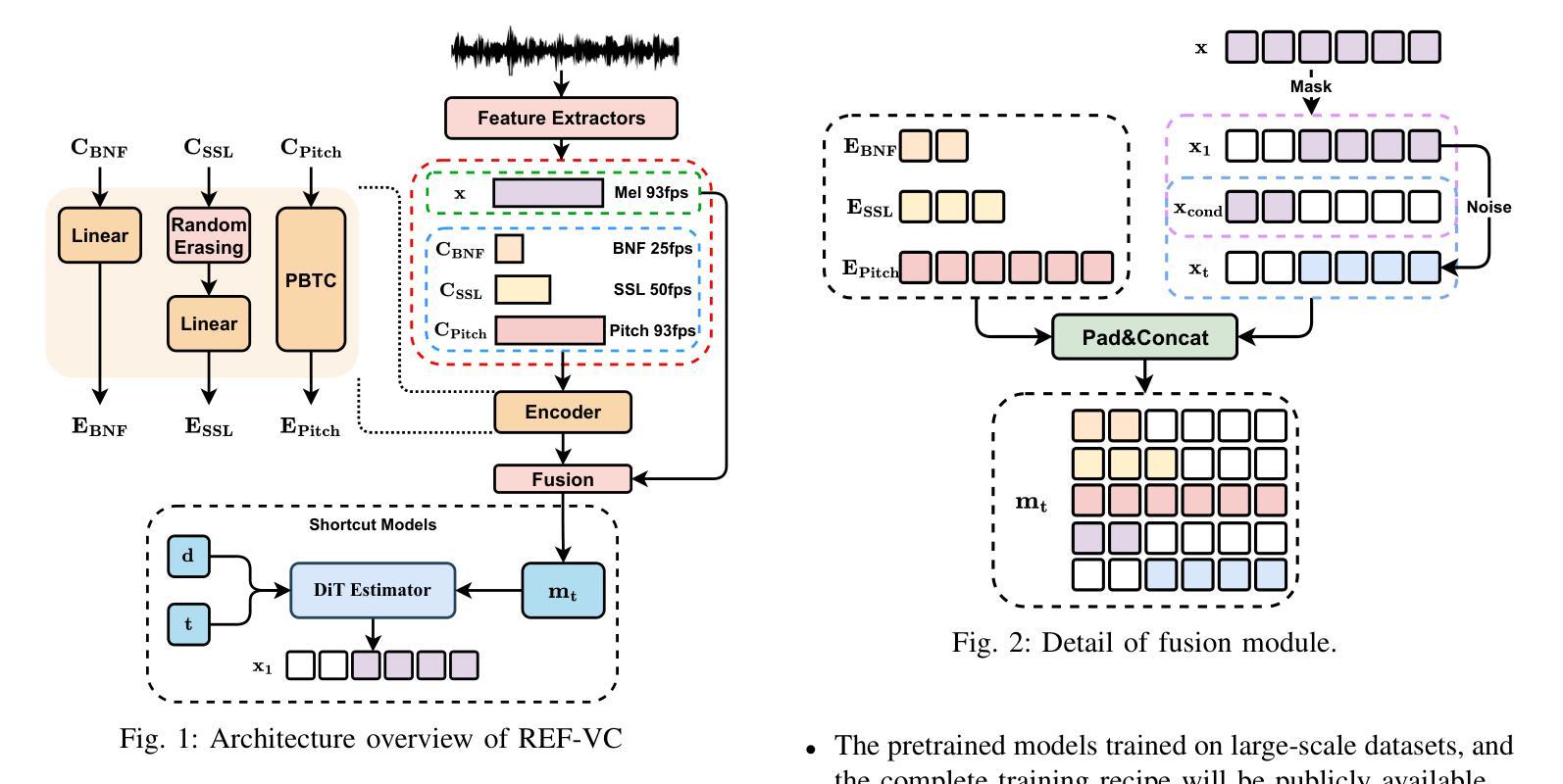
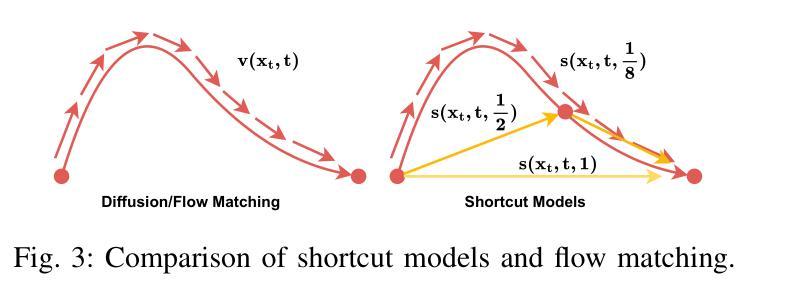
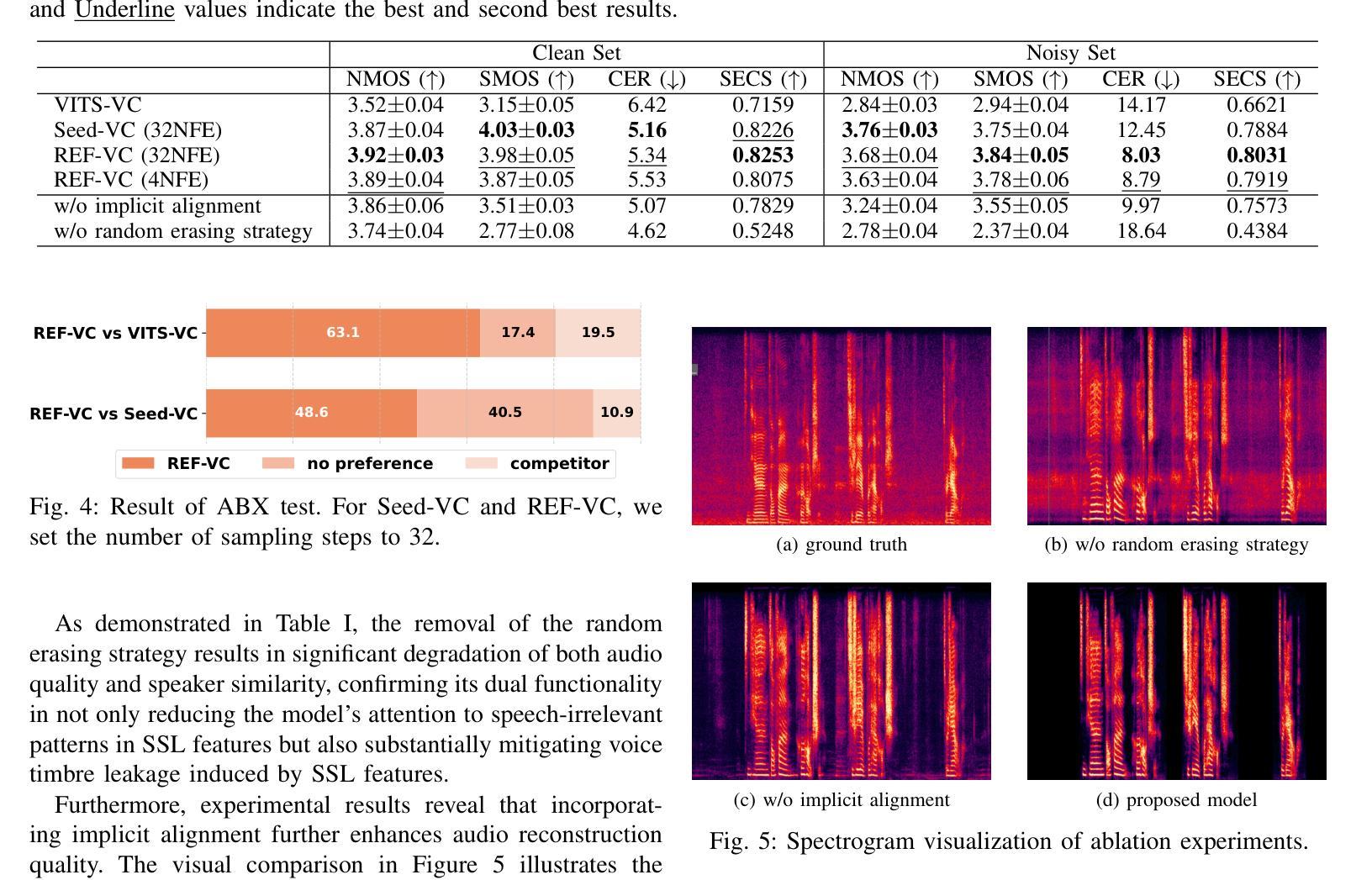
REF-VC: Robust, Expressive and Fast Zero-Shot Voice Conversion with Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Yuepeng Jiang, Ziqian Ning, Shuai Wang, Chengjia Wang, Mengxiao Bi, Pengcheng Zhu, Lei Xie, Zhonghua Fu
In real-world voice conversion applications, environmental noise in source speech and user demands for expressive output pose critical challenges. Traditional ASR-based methods ensure noise robustness but suppress prosody, while SSL-based models improve expressiveness but suffer from timbre leakage and noise sensitivity. This paper proposes REF-VC, a noise-robust expressive voice conversion system. Key innovations include: (1) A random erasing strategy to mitigate the information redundancy inherent in SSL feature, enhancing noise robustness and expressiveness; (2) Implicit alignment inspired by E2TTS to suppress non-essential feature reconstruction; (3) Integration of Shortcut Models to accelerate flow matching inference, significantly reducing to 4 steps. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms baselines such as Seed-VC in zero-shot scenarios on the noisy set, while also performing comparably to Seed-VC on the clean set. In addition, REF-VC can be compatible with singing voice conversion within one model.
在真实世界的声音转换应用中,源语音中的环境噪声以及用户对表现力输出的需求构成了关键的挑战。基于传统ASR的方法虽然能保证噪声稳健性,但会抑制韵律,而基于SSL的模型虽然能提高表现力,但却存在音色泄露和噪声敏感的问题。本文提出了REF-VC,一种噪声鲁棒性强的语音转换系统。主要创新点包括:(1)采用随机擦除策略,减轻SSL特征中的信息冗余,增强噪声稳健性和表现力;(2)受E2TTS启发的隐对齐方式,抑制非关键特征重建;(3)集成快捷模型,加速匹配流推理,大大缩短至4步。实验结果表明,我们的模型在噪声集上的零样本场景中优于基线方法(如Seed-VC),同时在清洁集上的表现与Seed-VC相当。此外,REF-VC可以在一个模型内兼容歌声转换。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对真实世界语音转换应用,源语音中的环境噪声和用户对于表达输出的需求构成了重大挑战。传统基于自动语音识别(ASR)的方法确保了噪声鲁棒性,但抑制了韵律;而基于自监督学习(SSL)的模型则提高了表达性,但存在音色泄漏和噪声敏感性。本文提出REF-VC,一种噪声鲁棒性强的表达性语音转换系统。主要创新包括:(1)采用随机擦除策略,减轻SSL特征中的信息冗余,增强噪声鲁棒性和表达性;(2)借鉴E2TTS的隐对齐方式,抑制非必要特征重建;(3)集成Shortcut Models加速流匹配推理,减少至4步。实验结果表明,我们的模型在噪声集上的零样本场景中优于基线方法如Seed-VC,同时在清洁集上的表现与Seed-VC相当。此外,REF-VC可以在一个模型内兼容歌唱语音转换。
要点解析
- 真实世界语音转换面临环境噪声和表达性需求两大挑战。
- 传统ASR方法虽噪声鲁棒但抑制韵律,而SSL模型虽表达性强却存在音色泄漏和噪声敏感问题。
- REF-VC系统提出随机擦除策略,旨在平衡噪声鲁棒性和表达性。
- 隐对齐方式和非必要特征抑制进一步提升了系统的性能。
- 集成Shortcut Models加速推理过程,减少计算步骤。
- 实验显示REF-VC在噪声环境下的性能优于基线方法,同时在清洁环境下表现相当。
点此查看论文截图

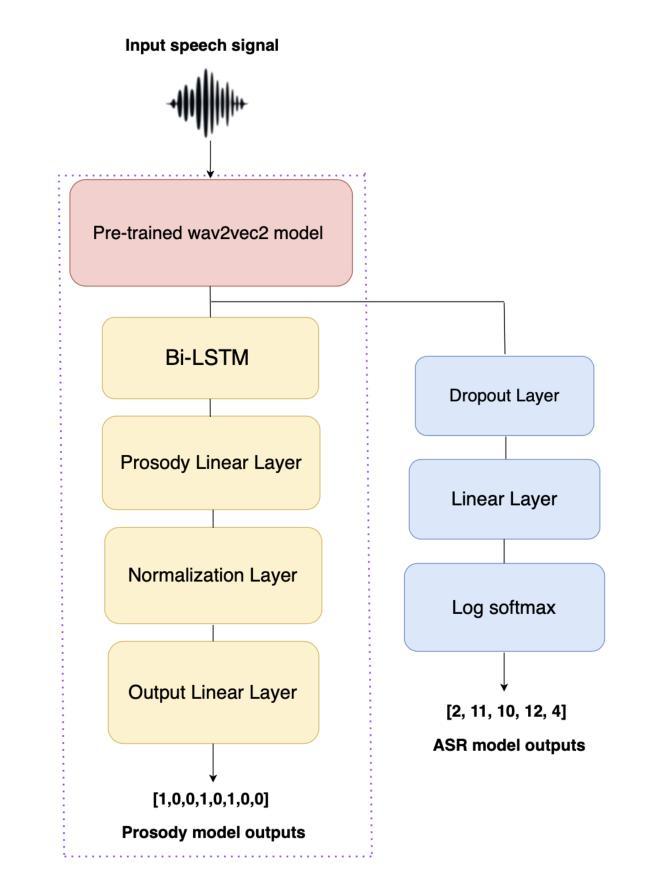
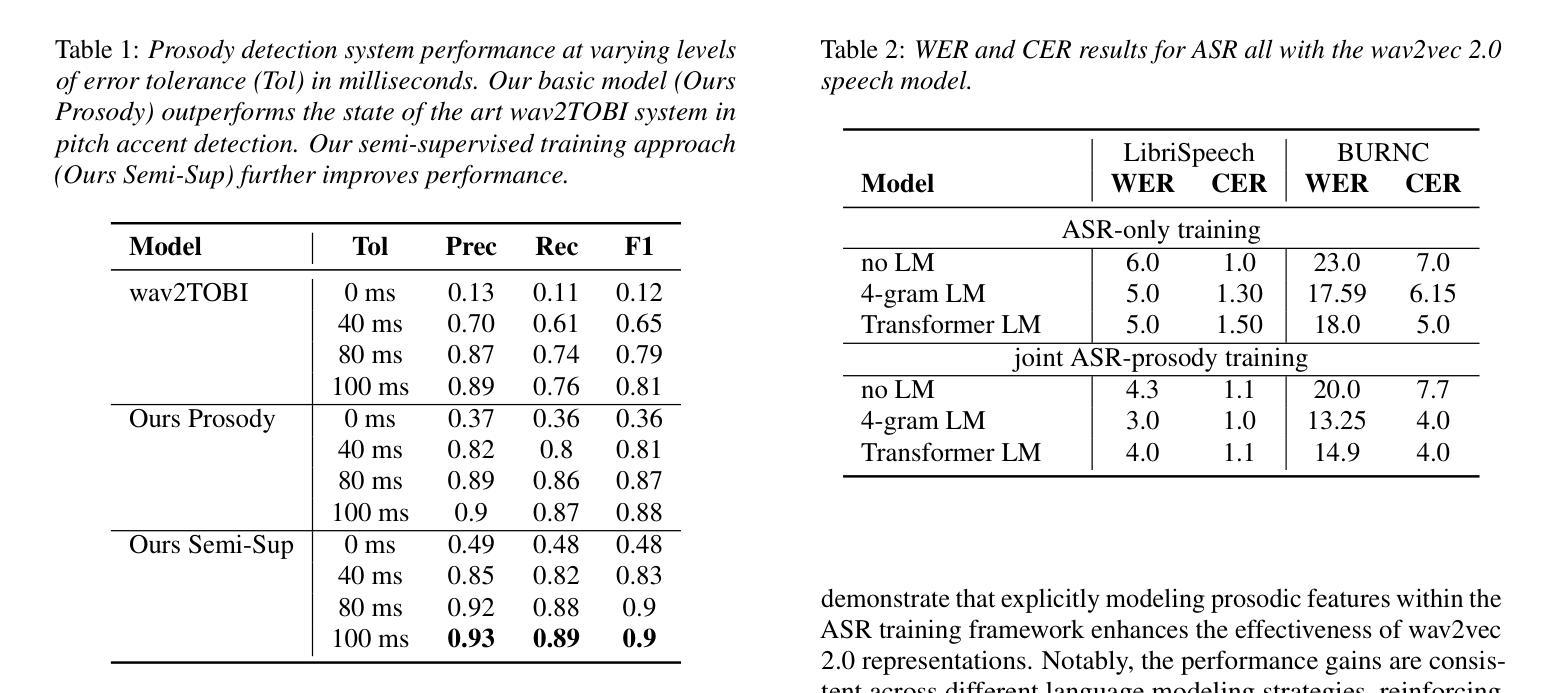
Pitch Accent Detection improves Pretrained Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:David Sasu, Natalie Schluter
We show the performance of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems that use semi-supervised speech representations can be boosted by a complimentary pitch accent detection module, by introducing a joint ASR and pitch accent detection model. The pitch accent detection component of our model achieves a significant improvement on the state-of-the-art for the task, closing the gap in F1-score by 41%. Additionally, the ASR performance in joint training decreases WER by 28.3% on LibriSpeech, under limited resource fine-tuning. With these results, we show the importance of extending pretrained speech models to retain or re-learn important prosodic cues such as pitch accent.
我们展示了通过使用半监督语音表示,结合一个辅助的音调重音检测模块,可以提高自动语音识别(ASR)系统的性能。通过引入一个联合ASR和音调重音检测模型,我们的模型的音调重音检测部分在该任务上取得了显著改进,在F1分数上缩小了41%的差距。此外,在联合训练中,ASR的性能在LibriSpeech上通过有限的资源微调降低了28.3%的词错误率。这些结果表明,扩展预训练的语音模型以保留或重新学习重要的韵律线索(如音调重音)的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
使用半监督语音表示的自动语音识别(ASR)系统的性能可以通过引入联合ASR和音调重音检测模型得到提升。该模型的音调重音检测部分在任务上实现了显著改进,F1得分提高了41%。此外,在LibriSpeech上进行联合训练后,ASR性能在有限资源微调的情况下降低了28.3%的词错误率。这证明了扩展预训练语音模型以保留或重新学习如音调重音等重要韵律特征的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入联合ASR和音调重音检测模型可以提升ASR系统的性能。
- 模型的音调重音检测部分在任务上实现了显著改进,F1得分提高了41%。
- 在LibriSpeech数据集上,联合训练后ASR性能得到显著提高,词错误率降低了28.3%。
- 在有限资源微调的情况下,该模型依然表现出较好的性能提升。
- 扩展预训练语音模型有助于保留或重新学习重要的韵律特征。
- 保留或重新学习如音调重音等韵律特征对提升ASR系统性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

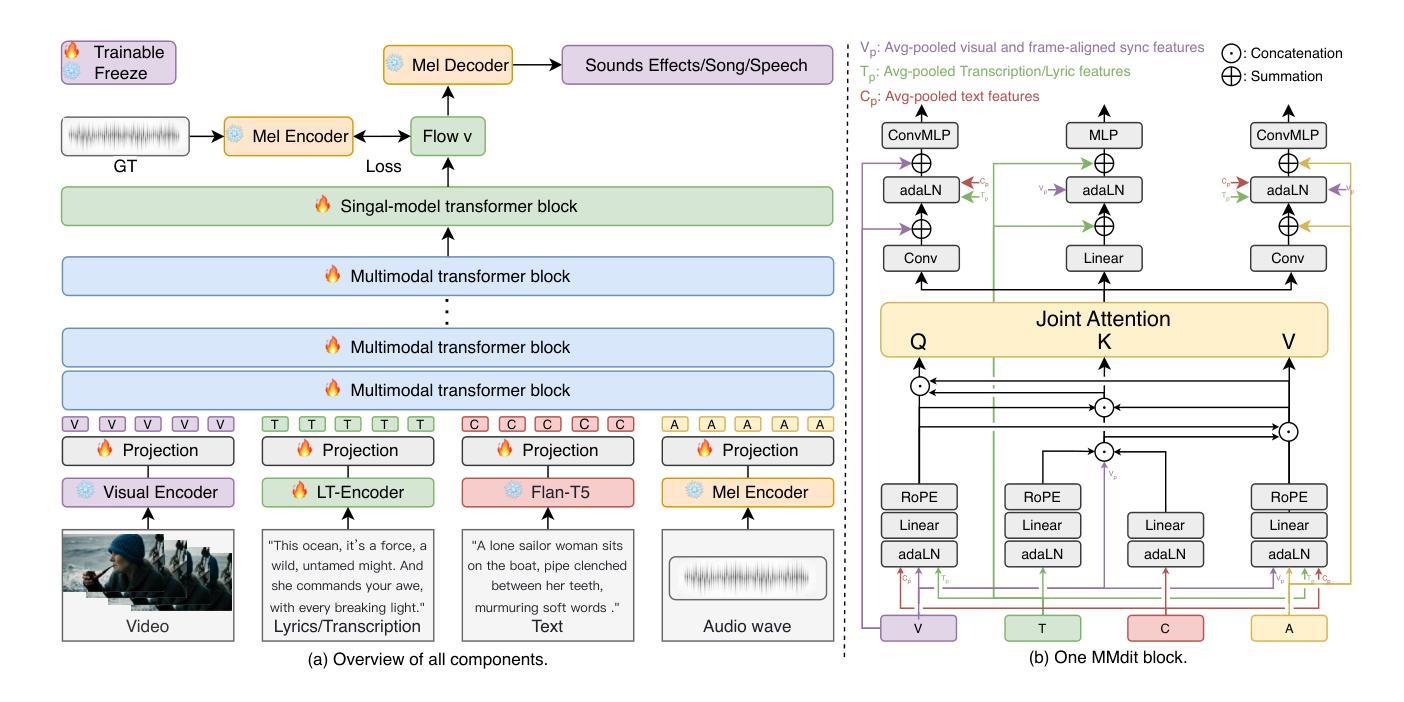
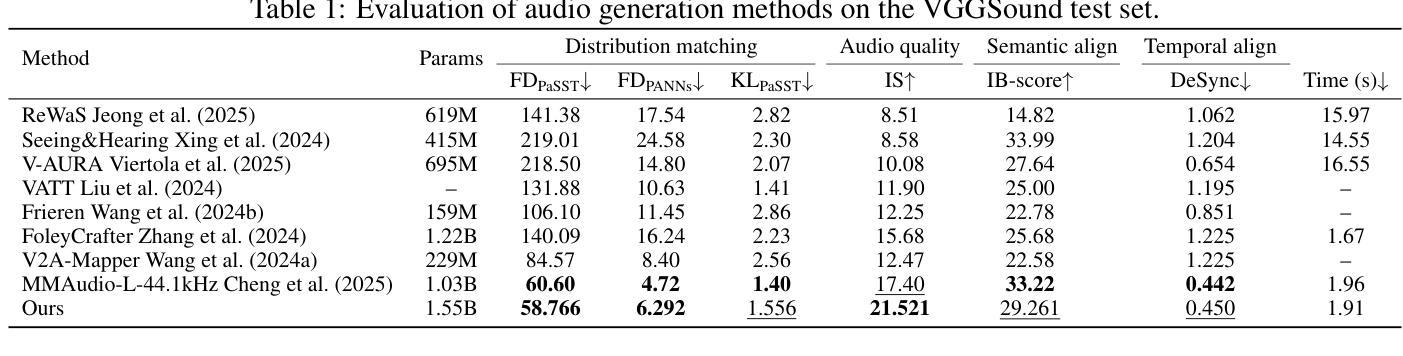
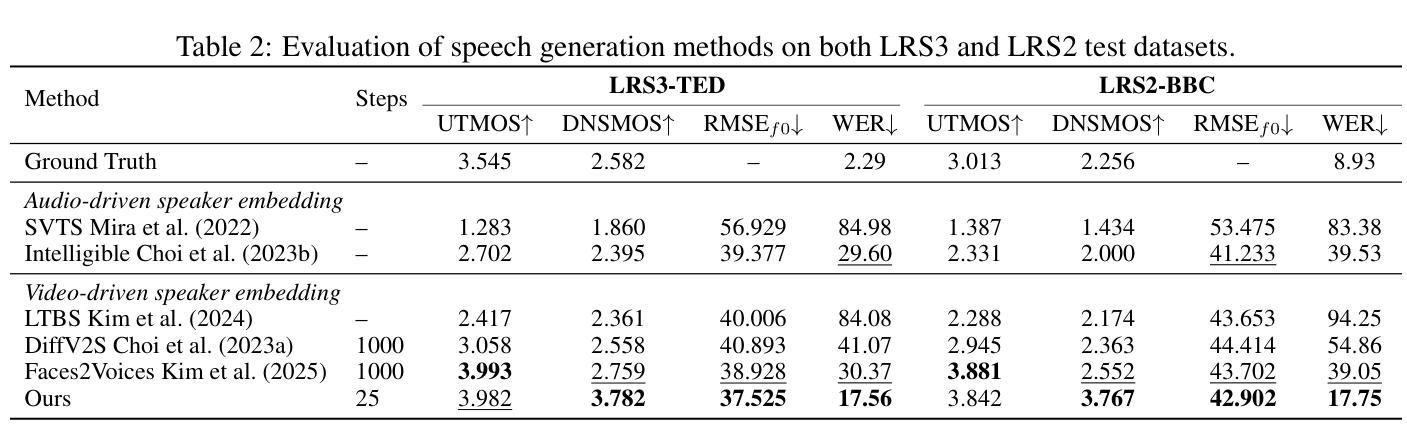
AudioGen-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Video-Synchronized Audio, Speech, and Song Generation
Authors:Le Wang, Jun Wang, Chunyu Qiang, Feng Deng, Chen Zhang, Di Zhang, Kun Gai
We present AudioGen-Omni - a unified approach based on multimodal diffusion transformers (MMDit), capable of generating high-fidelity audio, speech, and song coherently synchronized with the input video. AudioGen-Omni introduces a novel joint training paradigm that seamlessly integrates large-scale video-text-audio corpora, enabling a model capable of generating semantically rich, acoustically diverse audio conditioned on multimodal inputs and adaptable to a wide range of audio generation tasks. AudioGen-Omni employs a unified lyrics-transcription encoder that encodes graphemes and phonemes from both song and spoken inputs into dense frame-level representations. Dense frame-level representations are fused using an AdaLN-based joint attention mechanism enhanced with phase-aligned anisotropic positional infusion (PAAPI), wherein RoPE is selectively applied to temporally structured modalities to ensure precise and robust cross-modal alignment. By unfreezing all modalities and masking missing inputs, AudioGen-Omni mitigates the semantic constraints of text-frozen paradigms, enabling effective cross-modal conditioning. This joint training approach enhances audio quality, semantic alignment, and lip-sync accuracy, while also achieving state-of-the-art results on Text-to-Audio/Speech/Song tasks. With an inference time of 1.91 seconds for 8 seconds of audio, it offers substantial improvements in both efficiency and generality.
我们提出了AudioGen-Omni——一种基于多模式扩散变压器(MMDit)的统一方法,能够生成与输入视频同步的高保真音频、语音和歌曲。AudioGen-Omni引入了一种新的联合训练模式,该模式无缝集成了大规模的视频-文本-音频语料库,使模型能够在多模式输入条件下生成语义丰富、声音多样的音频,并适应广泛的音频生成任务。AudioGen-Omni采用统一的歌词-转录编码器,将歌曲和口语输入中的字母和音素编码成密集的帧级表示。密集的帧级表示通过使用基于AdaLN的联合注意力机制进行融合,增强阶段对齐的定向位置注入(PAAPI),其中RoPE被选择性应用于临时结构模态,以确保精确和稳健的跨模态对齐。通过解冻所有模态并屏蔽缺失的输入,AudioGen-Omni减轻了文本冻结模式的语义约束,实现了有效的跨模态条件设置。这种联合训练方法提高了音频质量、语义对齐和唇部同步准确性,同时在文本到音频/语音/歌曲任务上取得了最先进的成果。其推理时间为1.91秒可生成8秒的音频,在效率和通用性方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 figures
Summary
基于多模态扩散变压器(MMDit)的AudioGen-Omni统一方法,能够生成与输入视频同步的高保真音频、语音和歌曲。它通过无缝集成大规模视频-文本-音频语料库,实现了一种能够基于多模态输入生成语义丰富、声音多样的音频的模型,并适应广泛的音频生成任务。
Key Takeaways
- AudioGen-Omni是一种基于多模态扩散变压器(MMDit)的统一方法,能够生成高保真音频、语音和歌曲,与输入视频同步。
- 引入了一种新型联合训练范式,集成大规模视频-文本-音频语料库。
- 通过统一歌词-转录编码器,将歌曲和口语的字母和音素编码为密集帧级表示。
- 使用基于AdaLN的联合注意机制融合了密集帧级表示,增强了相位对齐的异构定位灌注(PAAPI)。
- RoPE选择性应用于具有时间结构的模态,实现精确和稳健的跨模态对齐。
- 通过解冻所有模态和掩盖缺失输入,缓解文本冻结范式的语义约束,实现有效的跨模态条件。
- 联合训练提高了音频质量、语义对齐和唇同步精度,并在文本到音频/语音/歌曲任务上实现最新结果。
点此查看论文截图

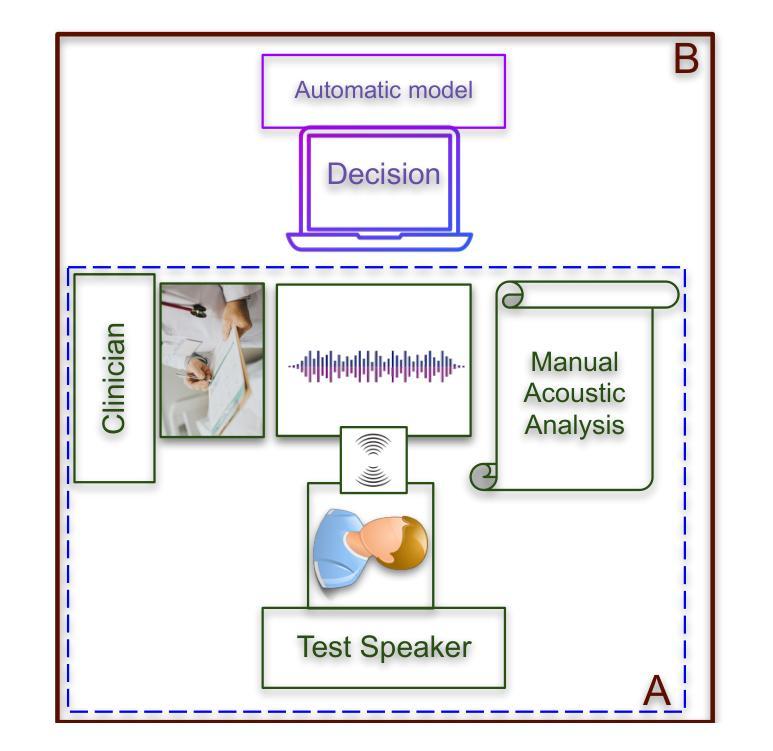
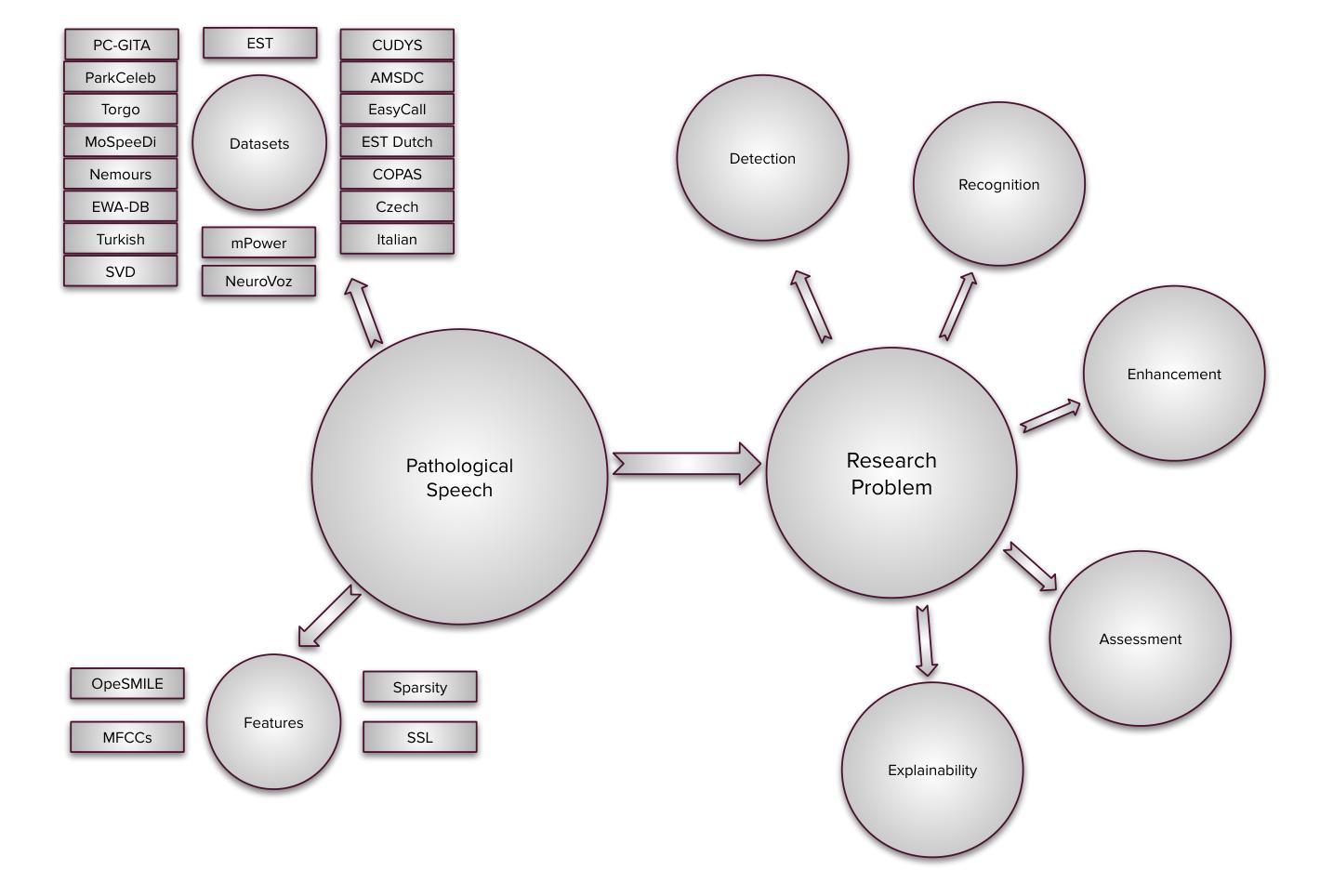
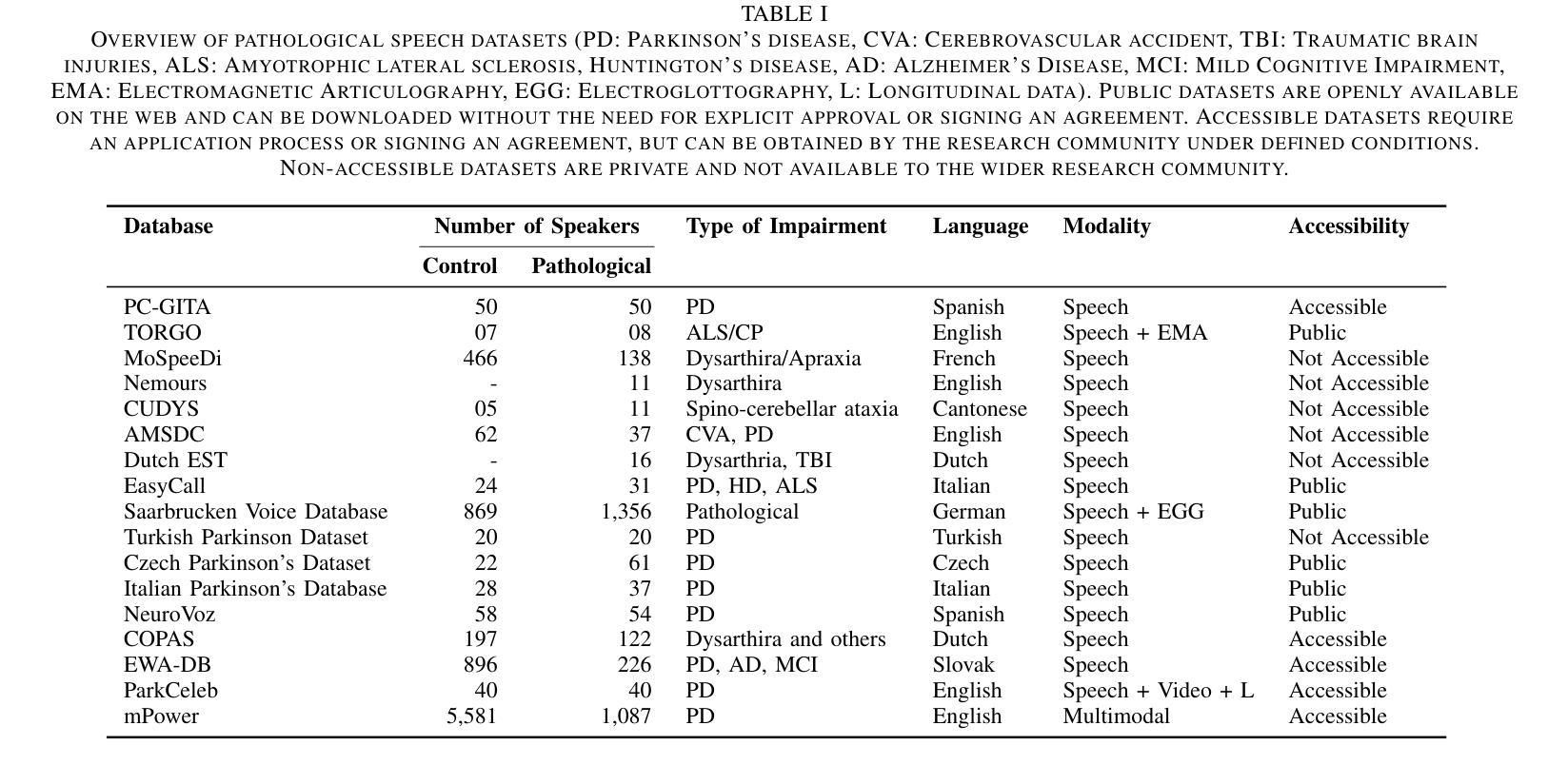
Overview of Automatic Speech Analysis and Technologies for Neurodegenerative Disorders: Diagnosis and Assistive Applications
Authors:Shakeel A. Sheikh, Md. Sahidullah, Ina Kodrasi
Advancements in spoken language technologies for neurodegenerative speech disorders are crucial for meeting both clinical and technological needs. This overview paper is vital for advancing the field, as it presents a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art methods in pathological speech detection, automatic speech recognition, pathological speech intelligibility enhancement, intelligibility and severity assessment, and data augmentation approaches for pathological speech. It also highlights key challenges, such as ensuring robustness, privacy, and interpretability. The paper concludes by exploring promising future directions, including the adoption of multimodal approaches and the integration of large language models to further advance speech technologies for neurodegenerative speech disorders.
口语技术在神经退行性疾病所致言语障碍方面的进展对于满足临床和技术需求至关重要。这篇综述论文对推进该领域具有重要意义,因为它全面回顾了病理性言语检测、自动语音识别、病理性言语清晰度增强、清晰度和严重程度评估以及病理性言语数据增强方法的最新方法。它还强调了确保稳健性、隐私性和可解释性等关键挑战。论文最后探讨了有前途的未来方向,包括采用多模式方法以及整合大型语言模型,以进一步推进神经退行性疾病所致言语障碍的口语技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing
Summary
这篇论文概述了神经退行性疾病语音技术的最新进展,涵盖了病理语音检测、自动语音识别、语音清晰度提升、语音清晰度和严重程度评估以及数据扩充等方面的先进方法。论文强调了关键挑战,如确保技术的稳健性、隐私性和可解释性,并探讨了未来采用多模式方法和整合大型语言模型等有望推动该领域进一步发展的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 论文全面回顾了神经退行性疾病语音技术的最新进展。
- 介绍了包括病理语音检测、自动语音识别等方面的先进方法。
- 论文强调了提高技术稳健性、隐私性和可解释性的关键挑战。
- 论文指出未来发展方向包括采用多模式方法和整合大型语言模型。
- 该论文对于推动神经退行性疾病语音技术的发展具有重要意义。
- 论文涉及语音清晰度提升和语音清晰度和严重程度评估等方面的内容。
点此查看论文截图

Recent Advances in Speech Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Wenqian Cui, Dianzhi Yu, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Guangyan Zhang, Qichao Wang, Yiwen Guo, Irwin King
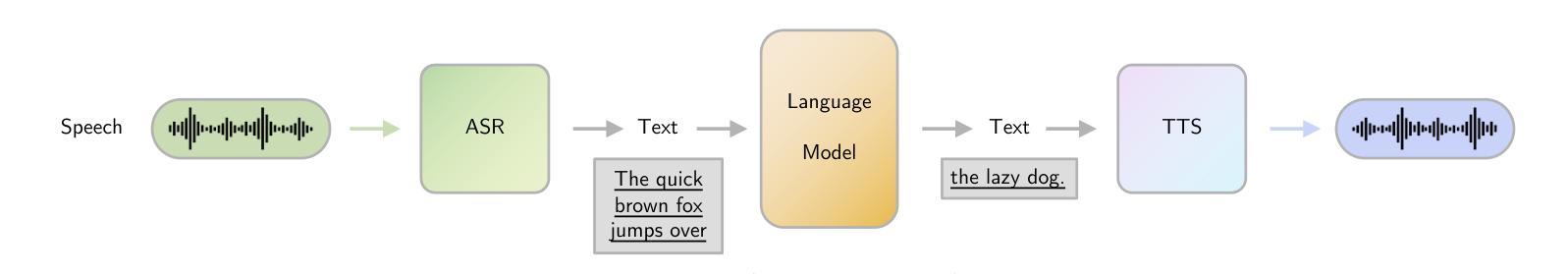
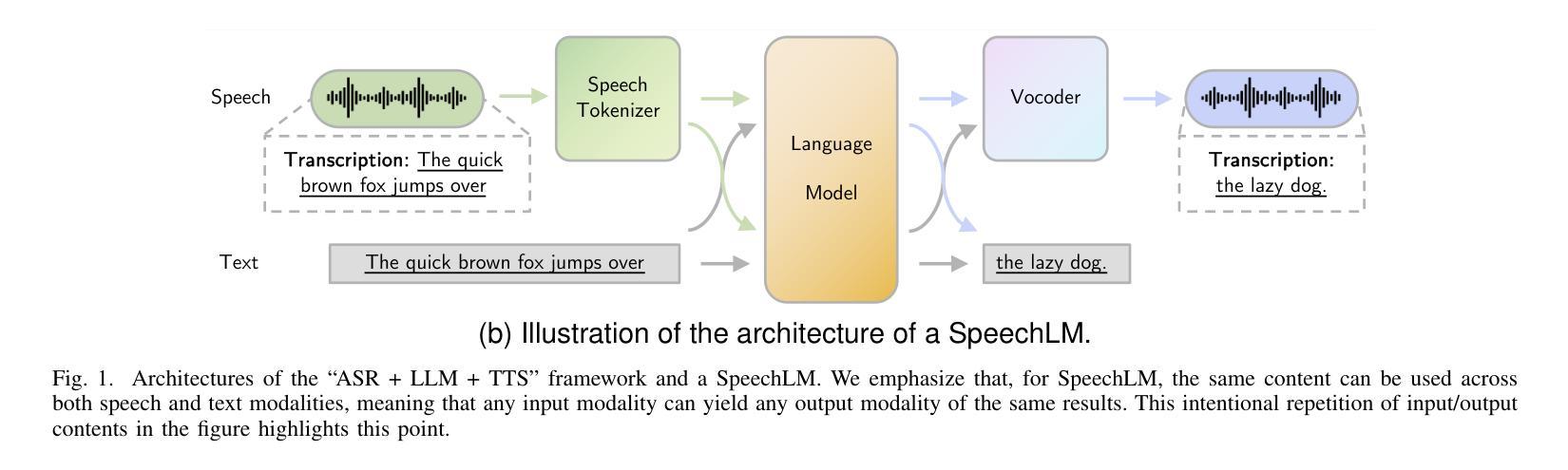
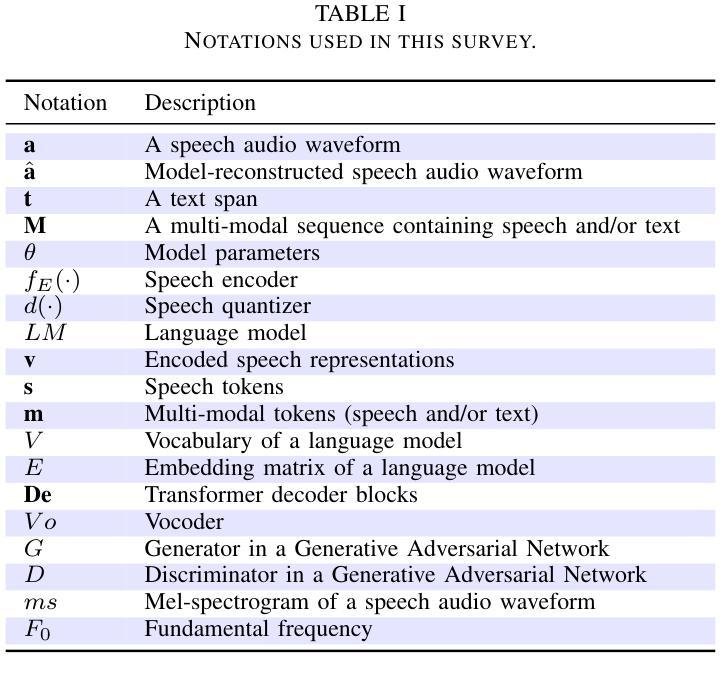
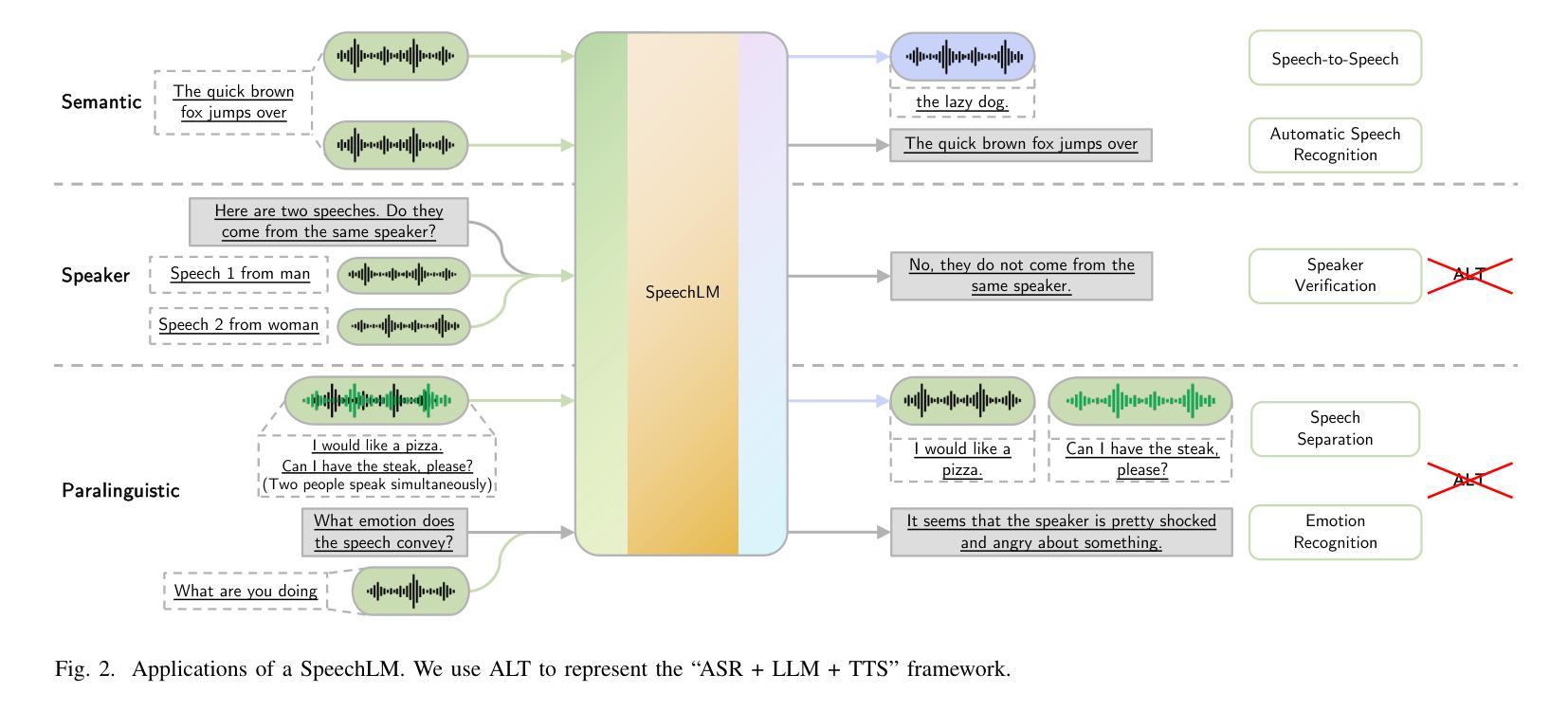
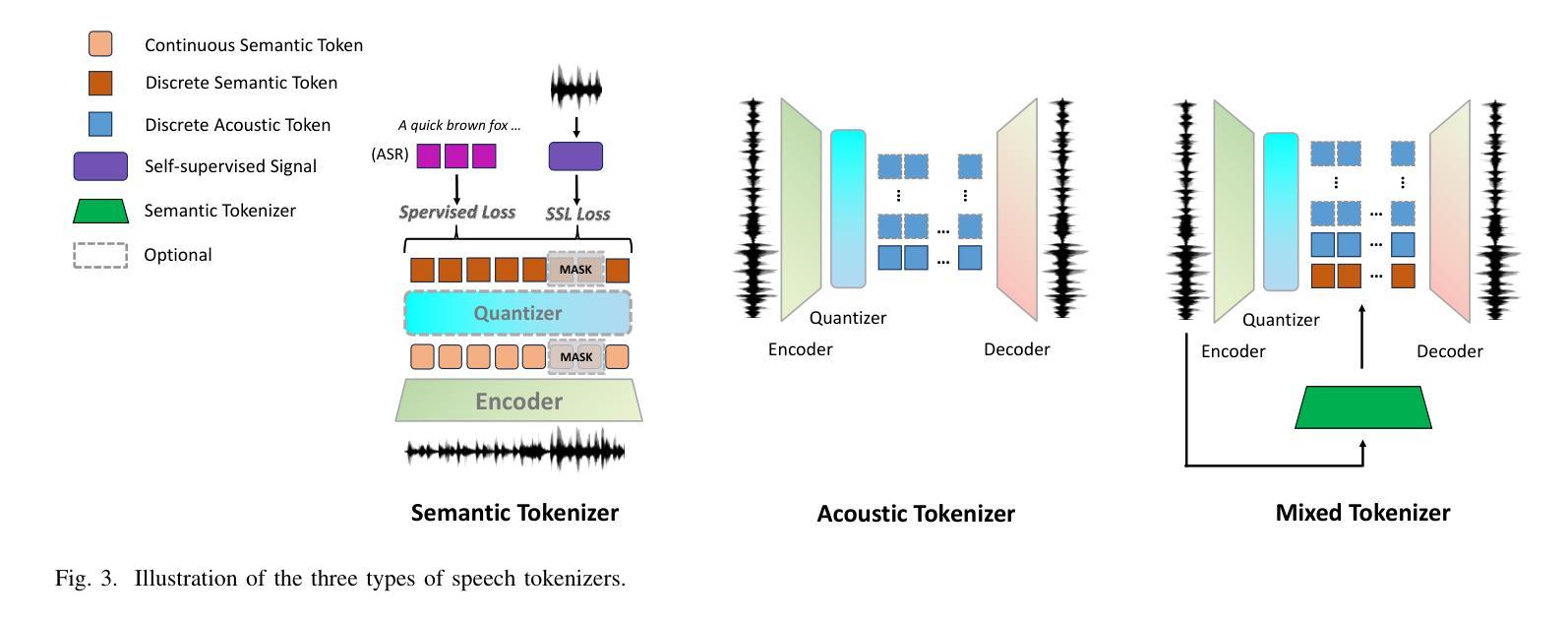
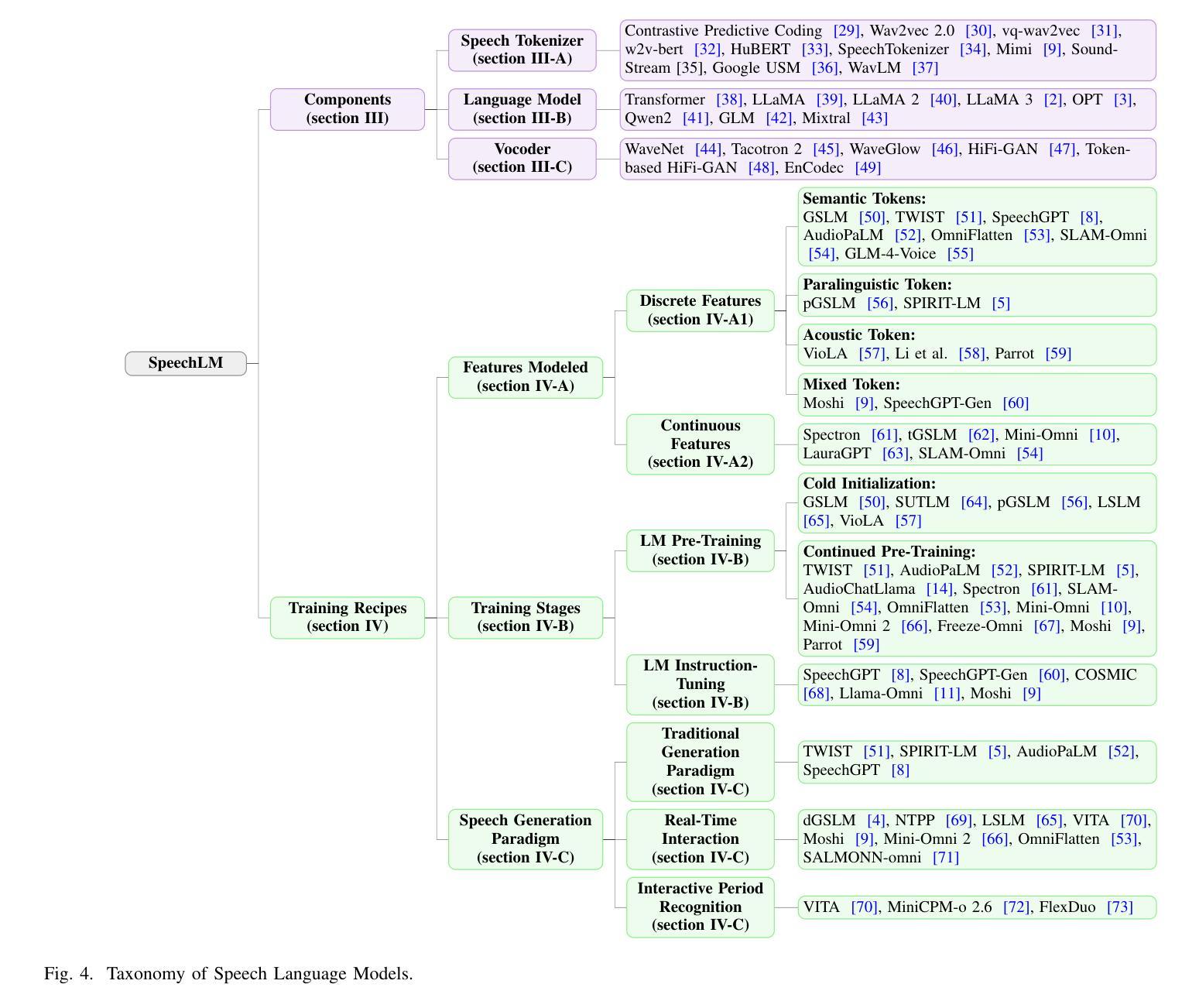
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently garnered significant attention, primarily for their capabilities in text-based interactions. However, natural human interaction often relies on speech, necessitating a shift towards voice-based models. A straightforward approach to achieve this involves a pipeline of ``Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) + LLM + Text-to-Speech (TTS)”, where input speech is transcribed to text, processed by an LLM, and then converted back to speech. Despite being straightforward, this method suffers from inherent limitations, such as information loss during modality conversion, significant latency due to the complex pipeline, and error accumulation across the three stages. To address these issues, Speech Language Models (SpeechLMs) – end-to-end models that generate speech without converting from text – have emerged as a promising alternative. This survey paper provides the first comprehensive overview of recent methodologies for constructing SpeechLMs, detailing the key components of their architecture and the various training recipes integral to their development. Additionally, we systematically survey the various capabilities of SpeechLMs, categorize their evaluation metrics, and discuss the challenges and future research directions in this rapidly evolving field. The GitHub repository is available at https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey
大型语言模型(LLM)近期引起了广泛关注,主要因其基于文本的交互能力。然而,自然人机交互通常依赖于语音,因此需要使用语音模型进行转换。一种实现此目标的直接方法是通过“自动语音识别(ASR)+ LLM +文本到语音(TTS)”的流程,将输入语音转录为文本,由LLM进行处理,然后再转回语音。尽管这种方法很直接,但它存在固有的局限性,例如在模态转换过程中的信息丢失、复杂的管道带来的显著延迟以及在三个阶段中的错误累积。为了解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLM)出现了——一种能够在不转换为文本的情况下生成语音的端到端模型。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了构建SpeechLM的最新方法,详细介绍了其关键组件和对其开发至关重要的各种培训配方。此外,我们还系统地概述了SpeechLM的各种功能,对其评估指标进行了分类,并讨论了这一快速发展的领域的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The reduced version of this paper has been accepted at ACL 2025
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)已受到广泛关注,但基于文本的交互方式忽略了自然人类交互通常依赖于语音的特性。因此,需要转向语音模型。尽管自动语音识别(ASR)+ LLM +文本转语音(TTS)方法可实现此目标,但存在信息损失、延迟和误差累积等问题。为解决这些问题,出现了语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)——无需从文本转换即可生成语音的端到端模型。本文首次全面概述了SpeechLMs的最新方法,详细介绍了其架构的关键组件和开发过程中不可或缺的训练食谱。此外,我们还系统地调查了SpeechLMs的各项功能、分类了评估指标,并讨论了这一快速发展领域的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库地址为:https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然人机交互中需考虑语音交互的重要性。
- 语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)作为端到端模型,可直接生成语音,避免了信息损失和复杂管道带来的延迟问题。
- SpeechLMs的关键组件包括架构设计和训练食谱,其中涉及多种技术和方法。
- SpeechLMs具有多种功能,如语音识别、语音合成、对话系统等,其评估指标包括准确性、自然度等。
- 目前SpeechLMs面临挑战,如数据标注、模型规模与效率平衡等,并需要未来进一步研究和改进。
- 读者可以通过访问GitHub仓库(https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey)获取更多关于SpeechLMs的详细信息和研究资源。
点此查看论文截图

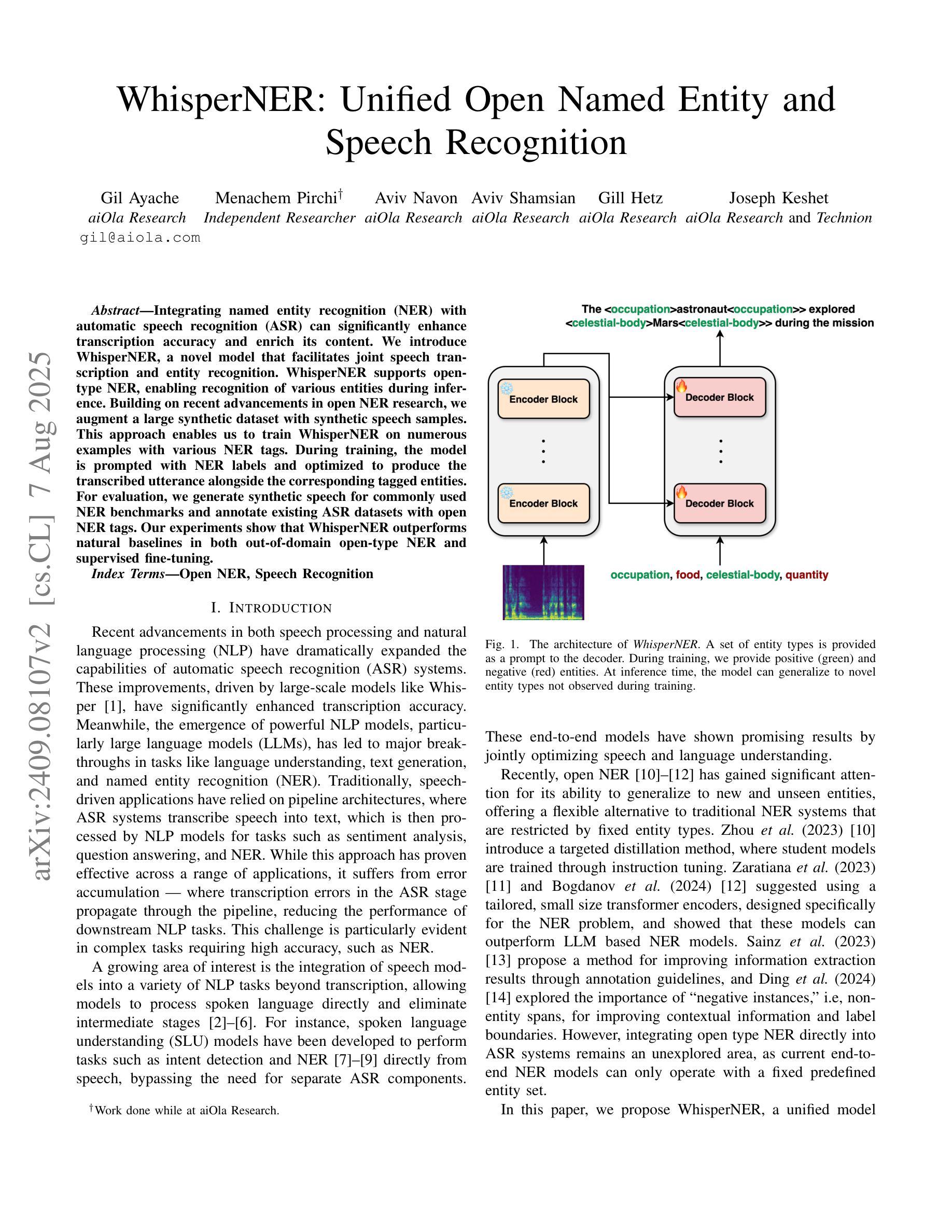
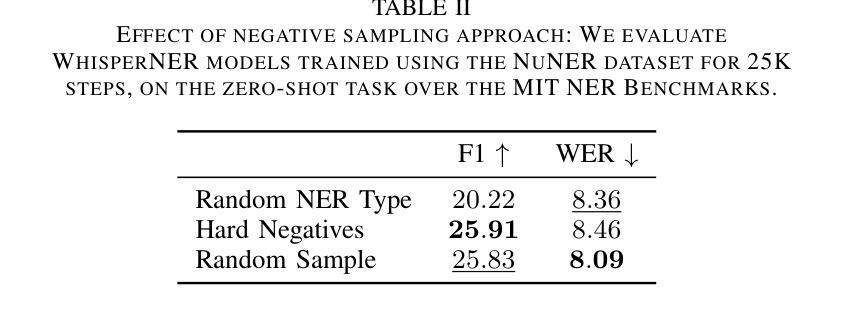
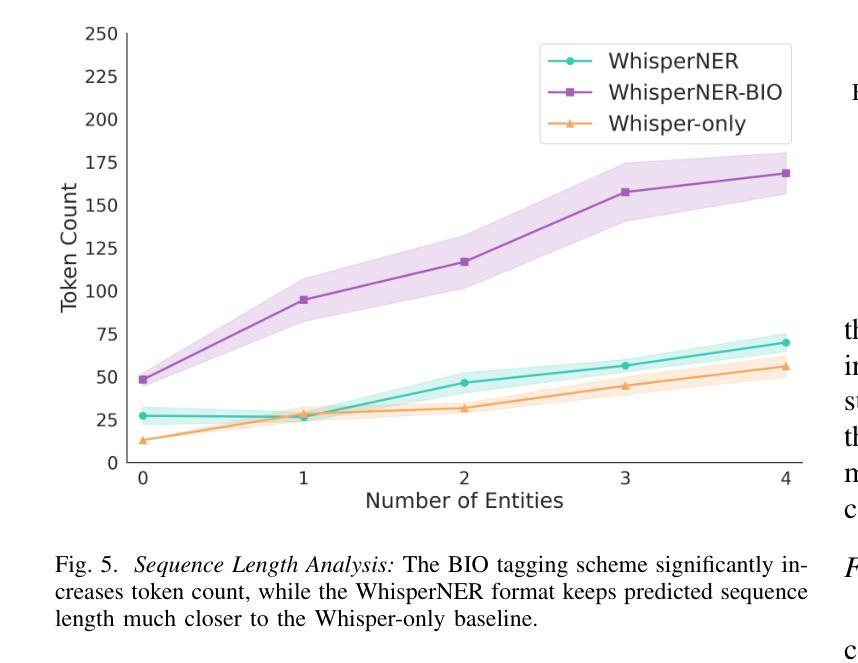
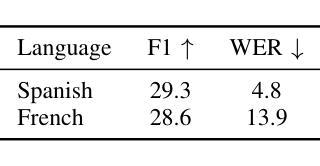
WhisperNER: Unified Open Named Entity and Speech Recognition
Authors:Gil Ayache, Menachem Pirchi, Aviv Navon, Aviv Shamsian, Gill Hetz, Joseph Keshet
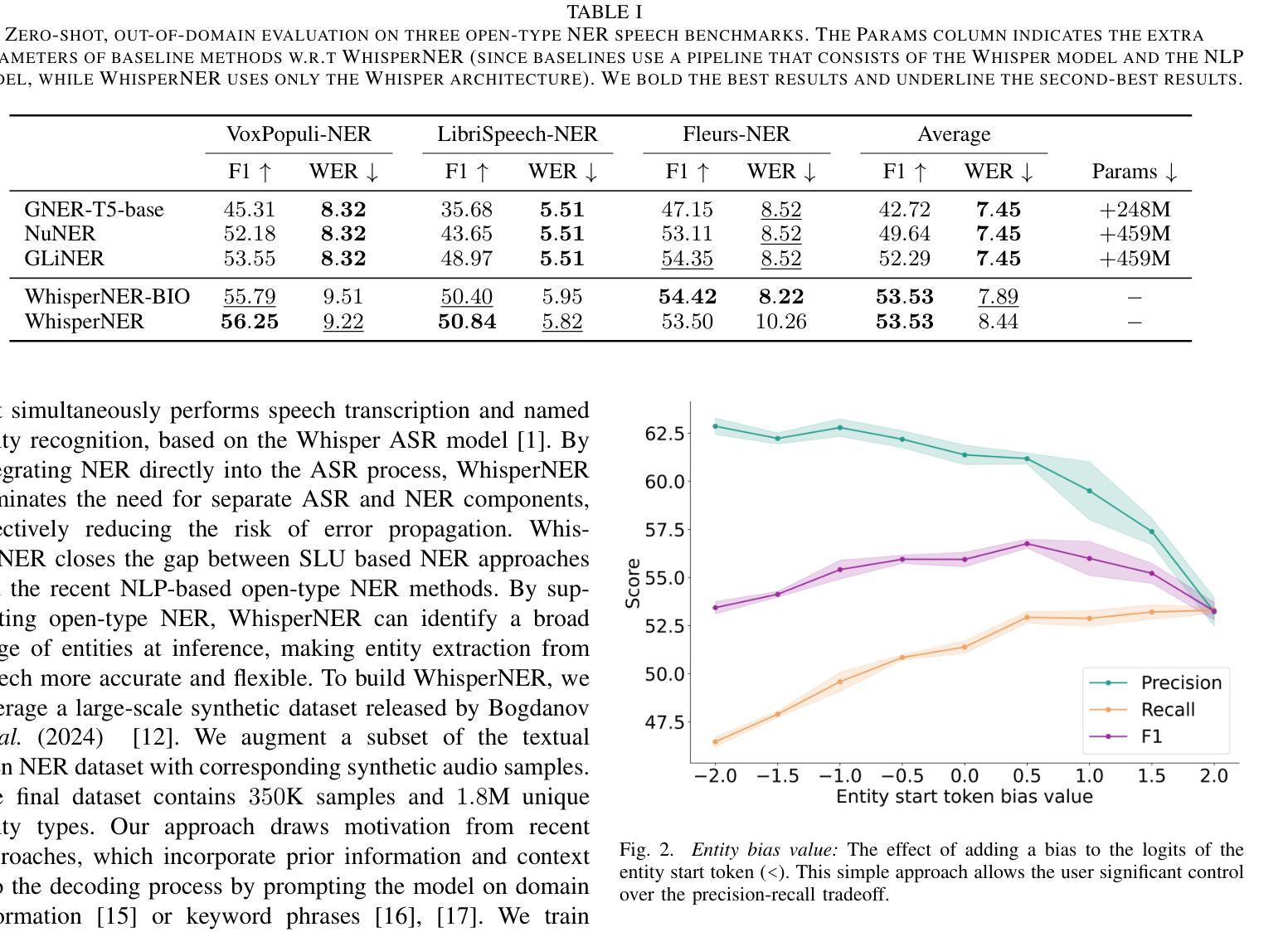
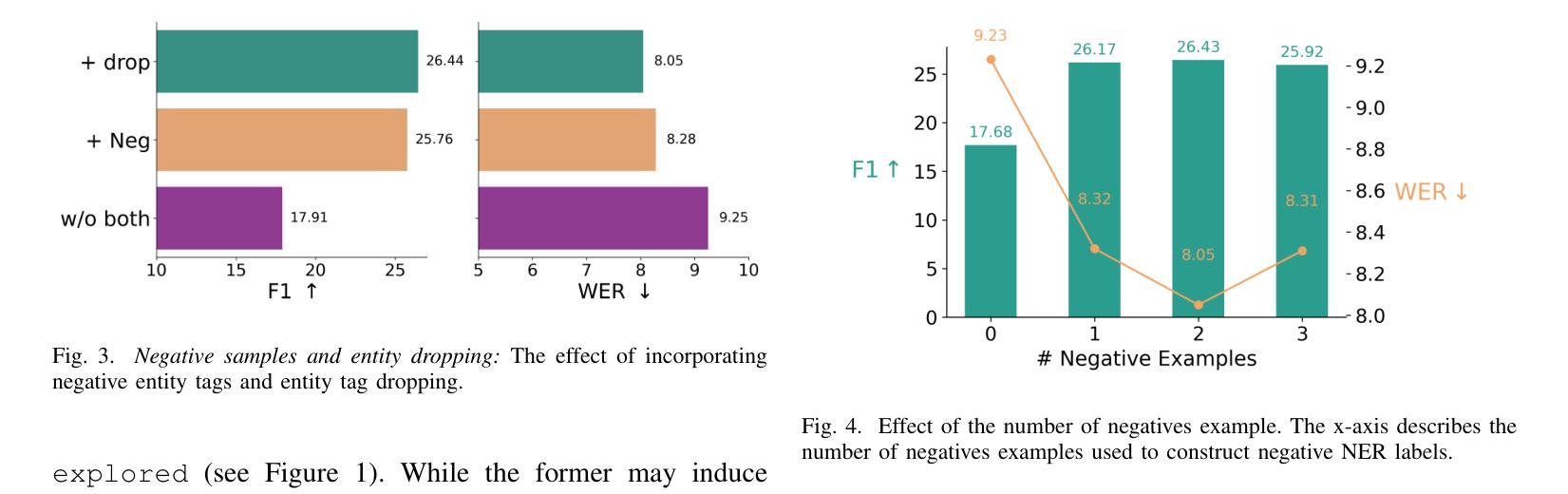
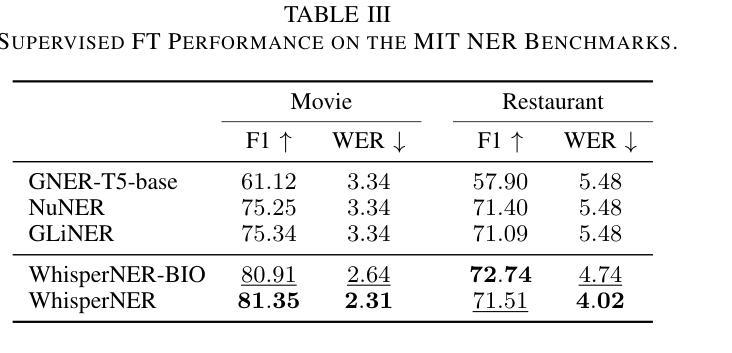
Integrating named entity recognition (NER) with automatic speech recognition (ASR) can significantly enhance transcription accuracy and informativeness. In this paper, we introduce WhisperNER, a novel model that allows joint speech transcription and entity recognition. WhisperNER supports open-type NER, enabling recognition of diverse and evolving entities at inference. Building on recent advancements in open NER research, we augment a large synthetic dataset with synthetic speech samples. This allows us to train WhisperNER on a large number of examples with diverse NER tags. During training, the model is prompted with NER labels and optimized to output the transcribed utterance along with the corresponding tagged entities. To evaluate WhisperNER, we generate synthetic speech for commonly used NER benchmarks and annotate existing ASR datasets with open NER tags. Our experiments demonstrate that WhisperNER outperforms natural baselines on both out-of-domain open type NER and supervised finetuning.
将命名实体识别(NER)与自动语音识别(ASR)相结合,可以显著提高转录准确性和信息量。在本文中,我们介绍了WhisperNER,这是一种允许联合语音转录和实体识别的新型模型。WhisperNER支持开放型NER,能够在推理过程中识别多样且不断发展的实体。基于最新的开放型NER研究,我们通过合成语音样本扩充了一个大型合成数据集。这使得我们能够在大量的带有不同NER标签的样本上训练WhisperNER。在训练过程中,模型会提示NER标签并进行优化,以输出转录的话语和相应的标记实体。为了评估WhisperNER的性能,我们为常用的NER基准生成合成语音,并使用开放型NER标签标注现有的ASR数据集。我们的实验表明,无论是在离域开放型NER还是监督微调上,WhisperNER的表现都优于自然基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ASRU 2025, IEEE
Summary
融合命名实体识别(NER)与自动语音识别(ASR)可有效提升转录准确性和信息量。本文介绍了一种新型模型WhisperNER,它可联合进行语音转录和实体识别。WhisperNER支持开放型NER,可在推理过程中识别多样且不断发展的实体。基于最新的开放型NER研究成果,我们利用合成的大型数据集与合成语音样本进行训练,使WhisperNER能够在大量样本上训练,并涵盖多样的NER标签。在训练过程中,模型通过NER标签进行提示,并优化输出带相应标签实体的转录语音。为评估WhisperNER性能,我们为常用的NER基准测试生成合成语音,并对现有的ASR数据集使用开放型NER标签进行标注。实验表明,WhisperNER在开放型NER和经过监督微调的任务上均优于自然基线。
Key Takeaways
- 整合命名实体识别(NER)与自动语音识别(ASR)能显著提升转录准确性和信息量。
- WhisperNER是一种新型模型,可同时实现语音转录和实体识别。
- WhisperNER支持开放型NER,能够识别多样且不断发展的实体。
- 利用合成的大型数据集与合成语音样本进行训练,增强WhisperNER模型的泛化能力。
- 模型在训练过程中通过NER标签提示,并优化输出带相应标签实体的转录语音。
- 合成语音生成和现有ASR数据集的开放型NER标签标注方法用于评估WhisperNER性能。
点此查看论文截图