⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-09 更新
A Scalable Pipeline for Enabling Non-Verbal Speech Generation and Understanding
Authors:Runchuan Ye, Yixuan Zhou, Renjie Yu, Zijian Lin, Kehan Li, Xiang Li, Xin Liu, Guoyang Zeng, Zhiyong Wu
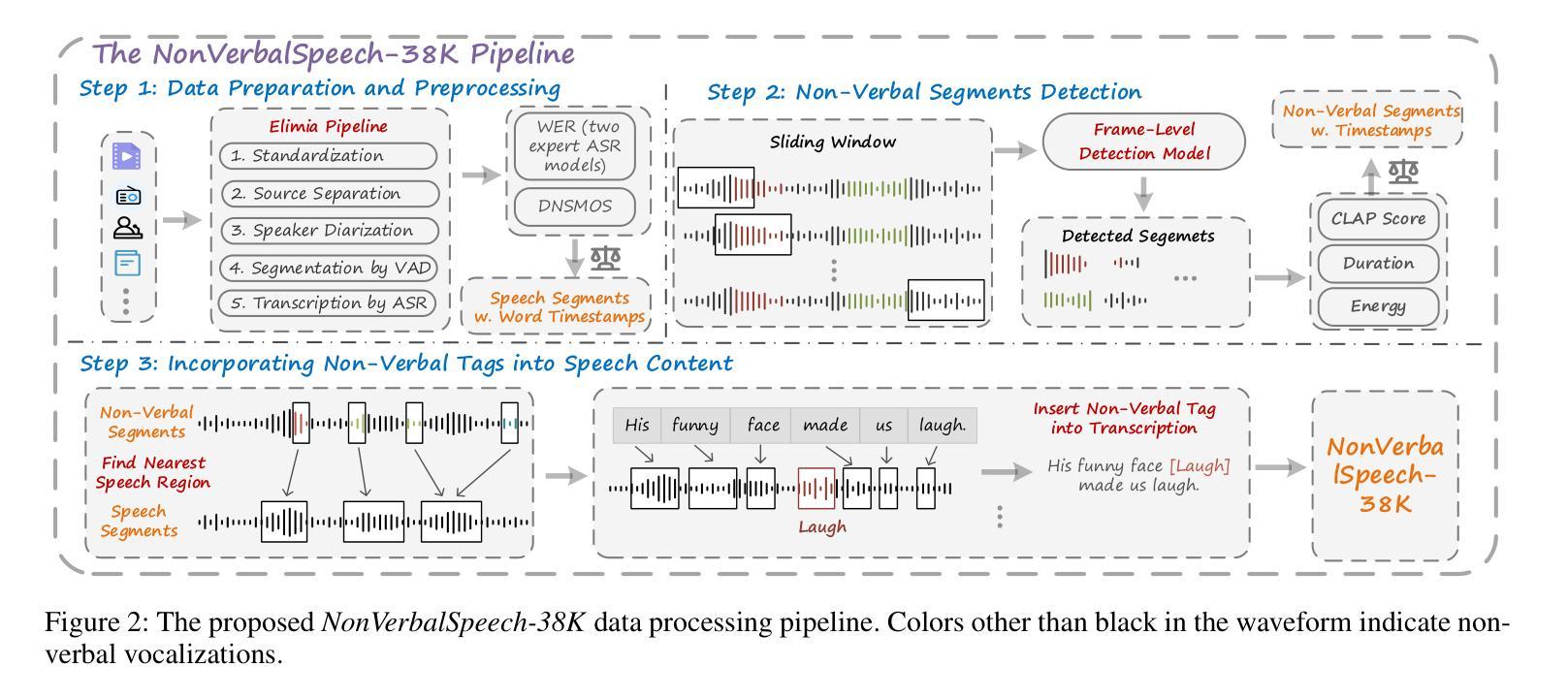
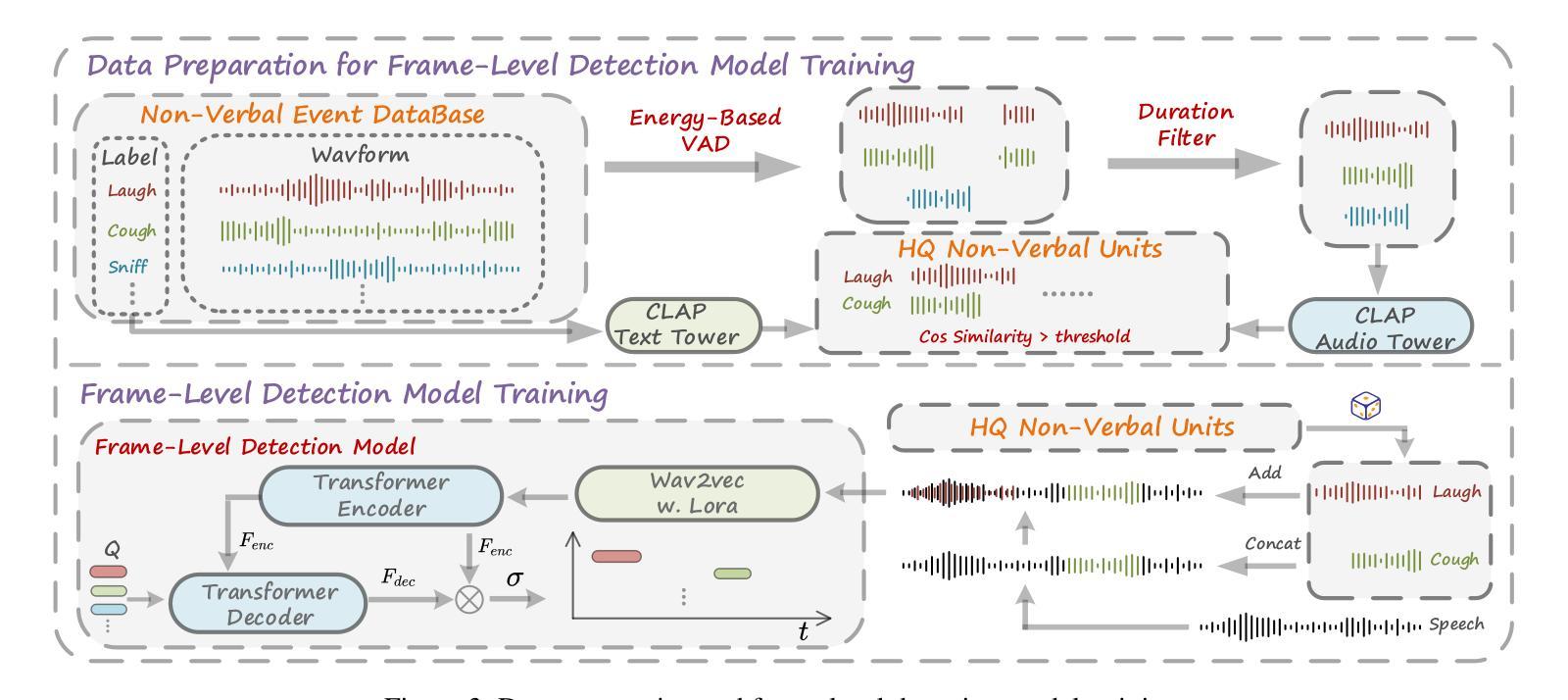
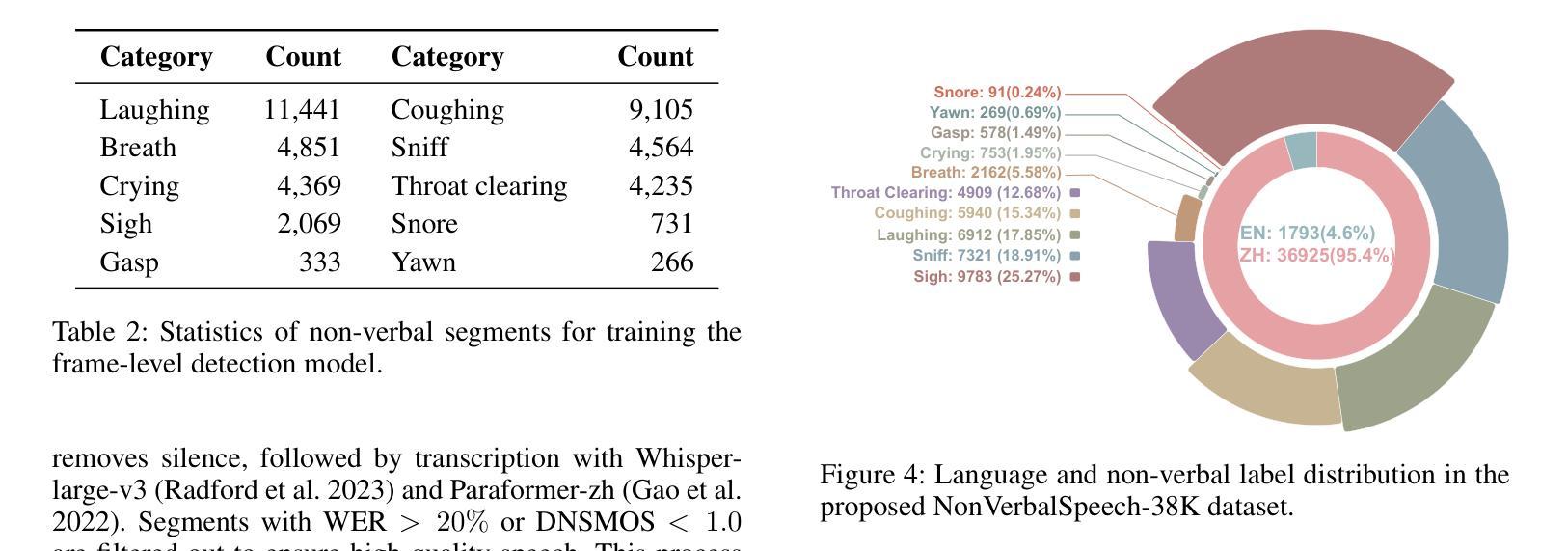
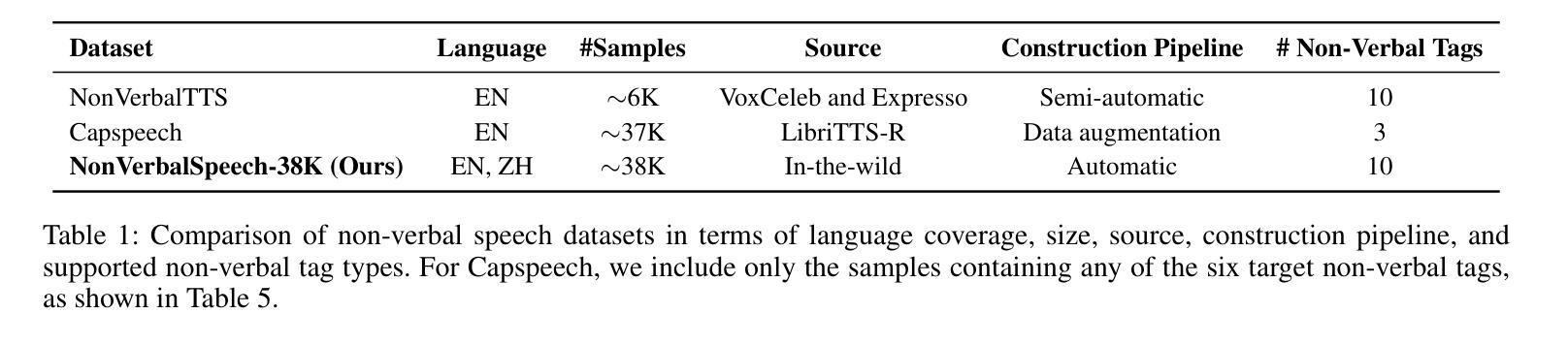
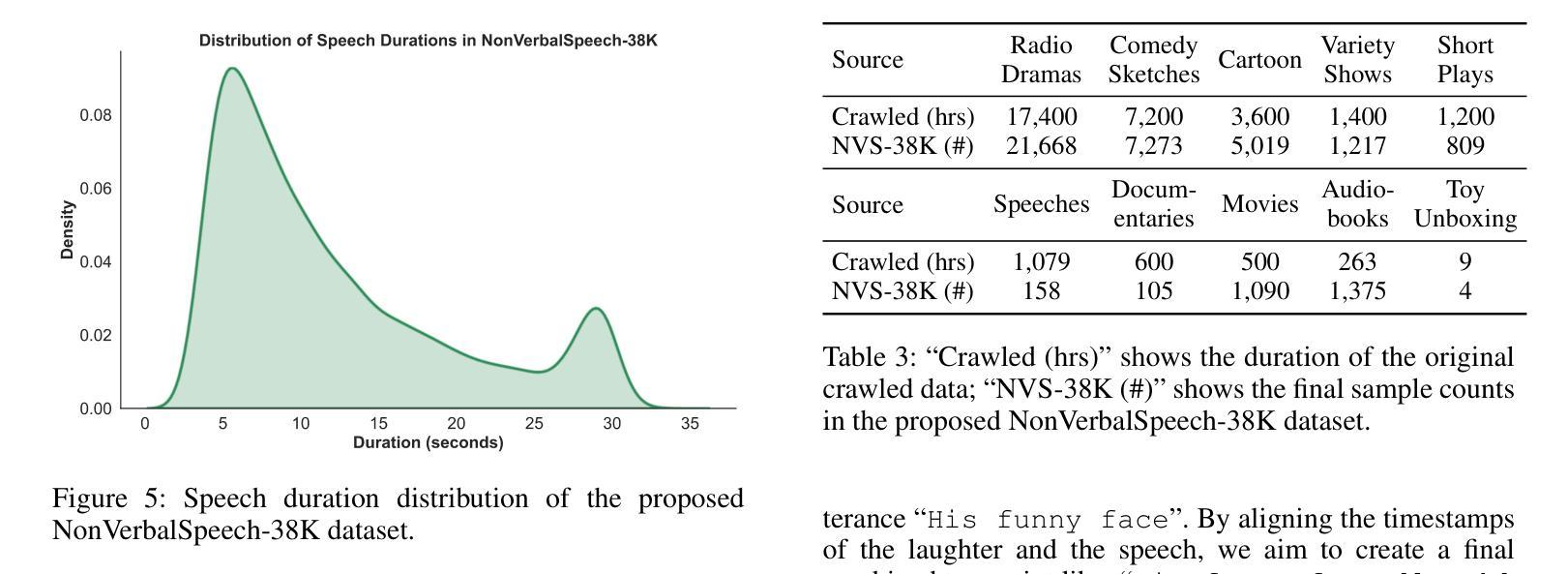
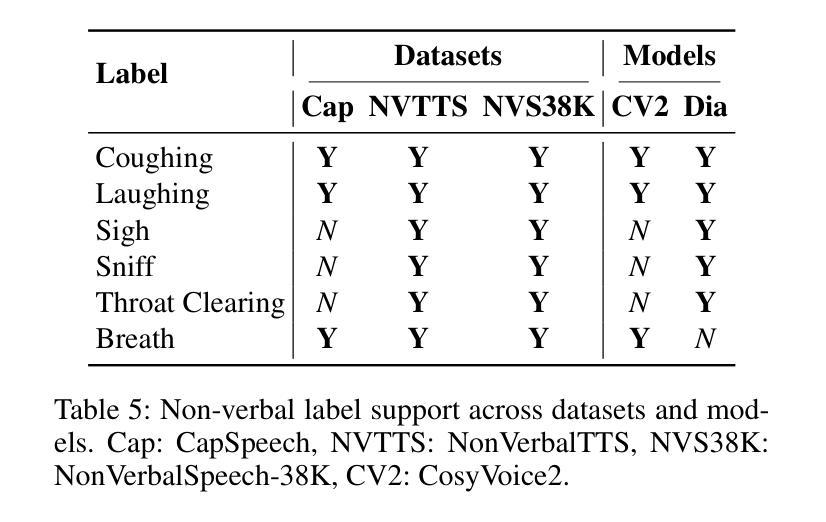
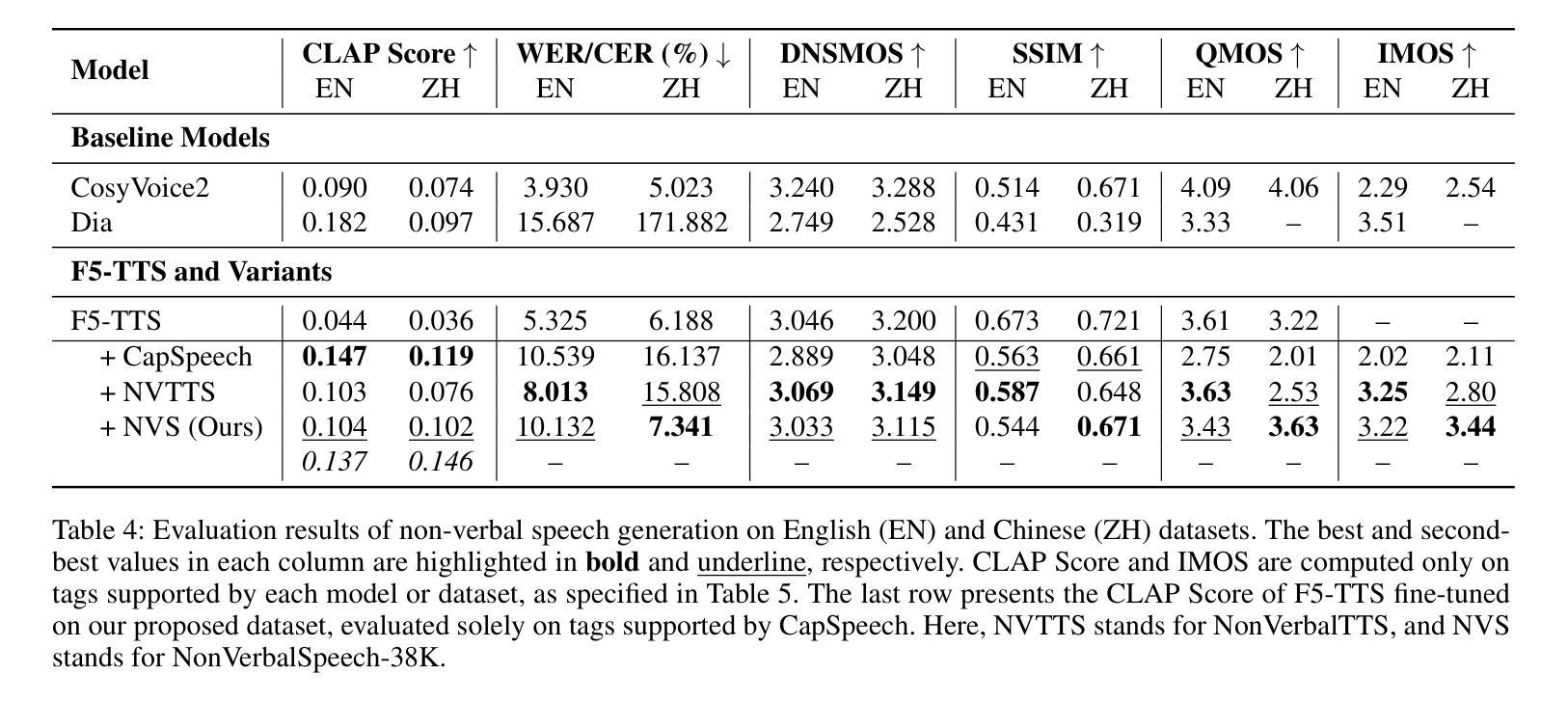
Human spoken communication involves not only lexical content but also non-verbal vocalizations (NVs) such as laughter, sighs, and coughs, which convey emotions, intentions, and social signals. However, most existing speech systems focus solely on verbal content and lack the ability to understand and generate such non-verbal cues, reducing the emotional intelligence and communicative richness of spoken interfaces. In this work, we introduce $\textbf{NonVerbalSpeech-38K}$, a large and diverse dataset for non-verbal speech generation and understanding, collected from real-world media and annotated using an automatic pipeline. The dataset contains 38,718 samples (about 131 hours) with 10 categories of non-verbal cues, such as laughter, sniff, and throat clearing. We further validate the dataset by fine-tuning state-of-the-art models, including F5-TTS and Qwen2-Audio, demonstrating its effectiveness in non-verbal speech generation and understanding tasks. Our contributions are threefold: (1) We propose a practical pipeline for building natural and diverse non-verbal speech datasets; (2) We release a large-scale dataset to advance research on non-verbal speech generation and understanding; (3) We validate the dataset’s effectiveness by demonstrating improvements in both non-verbal speech synthesis and captioning, thereby facilitating richer human-computer interaction.
人类口语交流不仅包括词汇内容,还包括非语言性的发声(NVs),如笑声、叹息声和咳嗽声,这些声音传达情感、意图和社会信号。然而,现有的大多数语音系统只关注语言内容,缺乏理解和生成非语言线索的能力,降低了语音界面的情感智能和沟通丰富性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了NonVerbalSpeech-38K,这是一个用于非语言语音生成和理解的大型多样化数据集,数据来源于真实媒体并自动进行标注处理。该数据集包含38718个样本(约131小时),包含笑声、鼻塞和清嗓等十类非语言线索。我们进一步使用最新技术模型精细调整验证数据集,包括F5-TTS和Qwen2-Audio等,在非语言语音生成和理解任务中表现出良好的有效性。我们的贡献有三点:(1)我们提出了构建自然和非语言语音数据集的实用流程;(2)我们发布大规模数据集以促进非语言语音生成和理解的研究;(3)我们通过演示非语言语音合成和字幕中的改进验证了数据集的有效性,从而促进了更丰富的人机交互。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为NonVerbalSpeech-38K的大型非语言语音数据集,包含来自真实世界的媒体数据,涉及笑声、叹气等十种非语言线索,共计38,718个样本。通过改进现有模型验证了数据集的有效性,可用于非语言语音生成和理解任务,促进更丰富的人机交互。
Key Takeaways
- 人类口头交流不仅包括词汇内容,还包括如笑声、叹息和咳嗽等非语言声音(NVs),它们传递情感、意图和社会信号。
- 现存的语音系统主要关注语言内容,无法理解和生成非语言线索,导致语音界面缺乏情感智能和丰富的交流性。
- 引入的大型数据集NonVerbalSpeech-38K用于非语言语音生成和理解,包含真实世界媒体采集的约十万个样本,包括笑声等十类非语言线索。
- 数据集通过改进最新模型进行验证,证明了其在非语言语音生成和理解任务中的有效性。
- 数据集的构建涉及一个实用的管道流程,旨在实现自然和多样化的非语言语音数据集建设。
- 数据集的发布推动了非语言语音生成和理解领域的研究进展。
点此查看论文截图

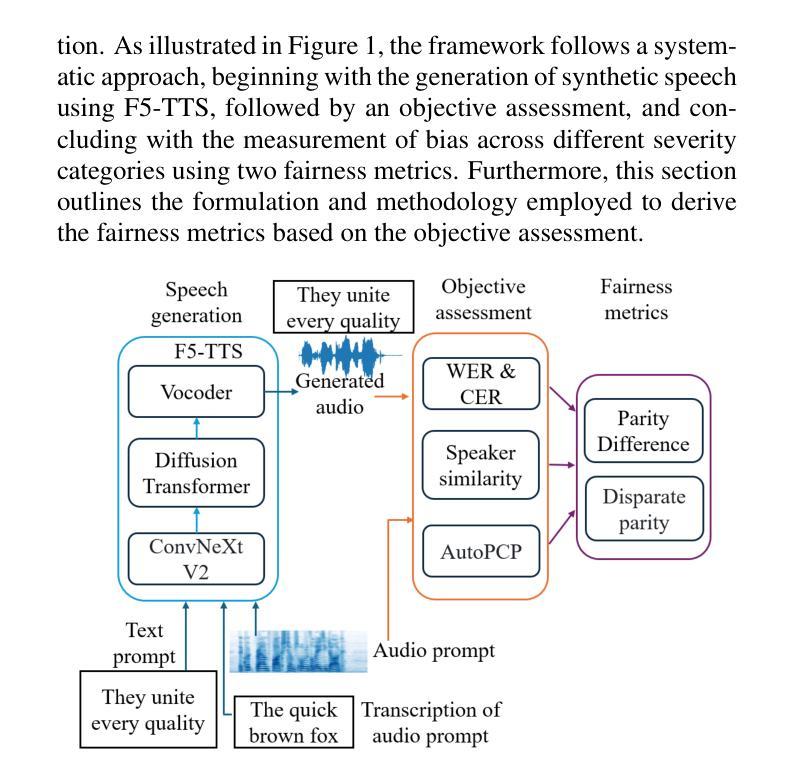
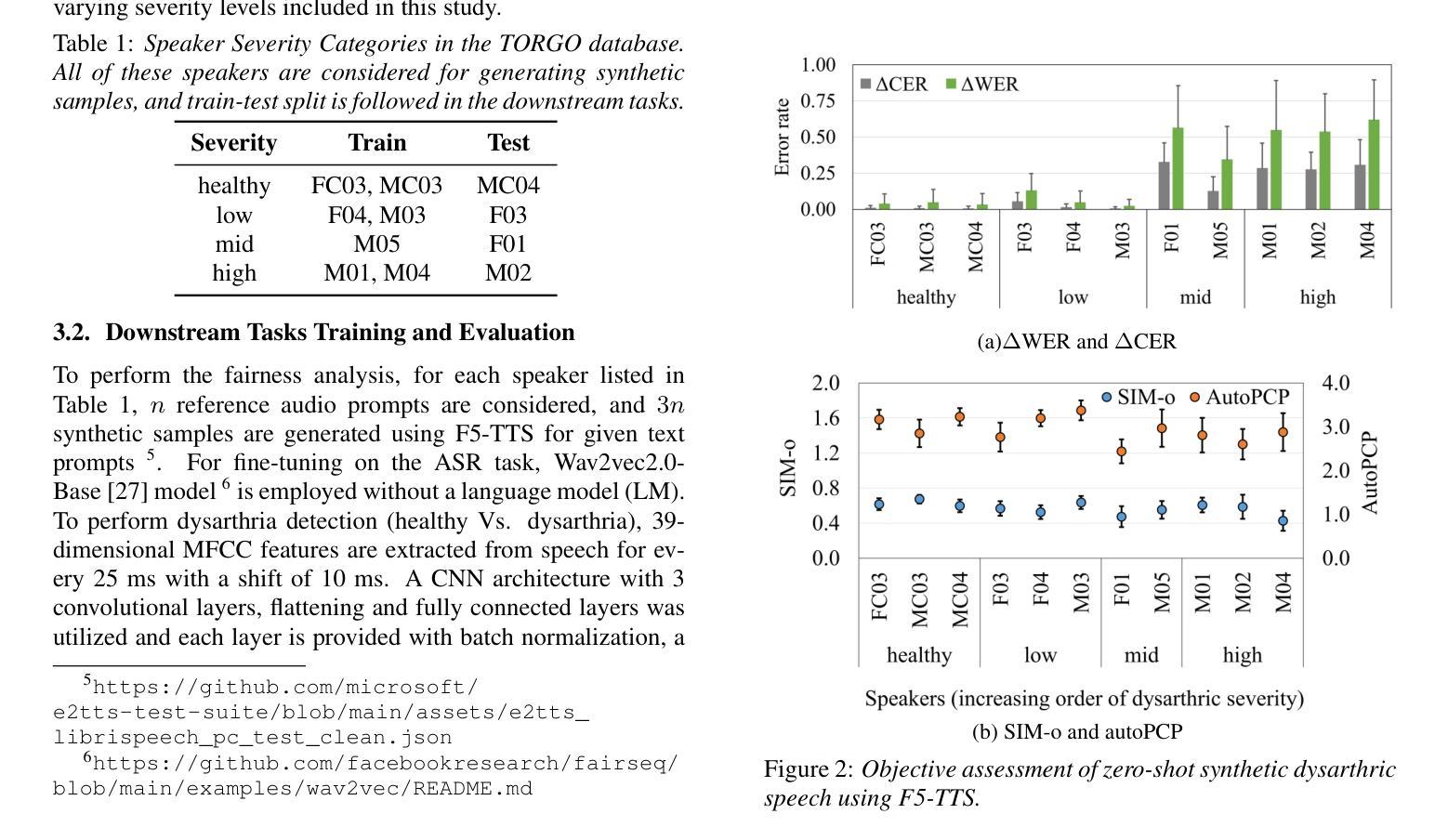
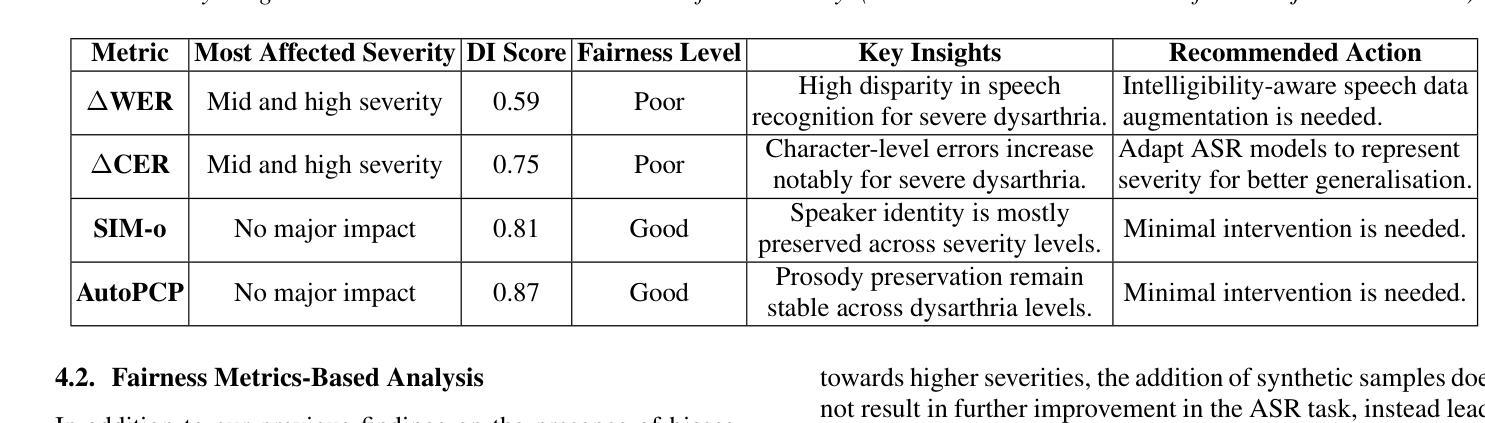
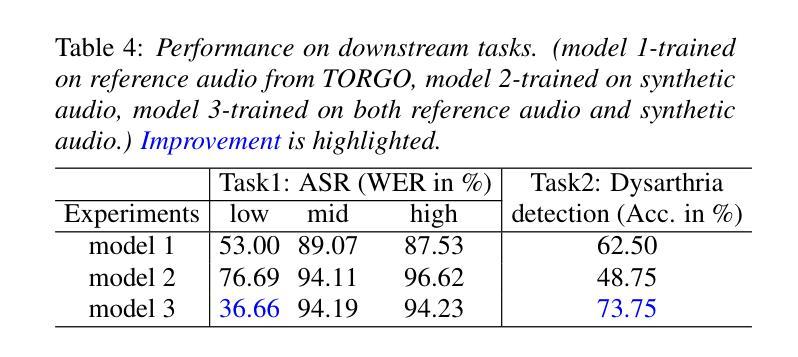
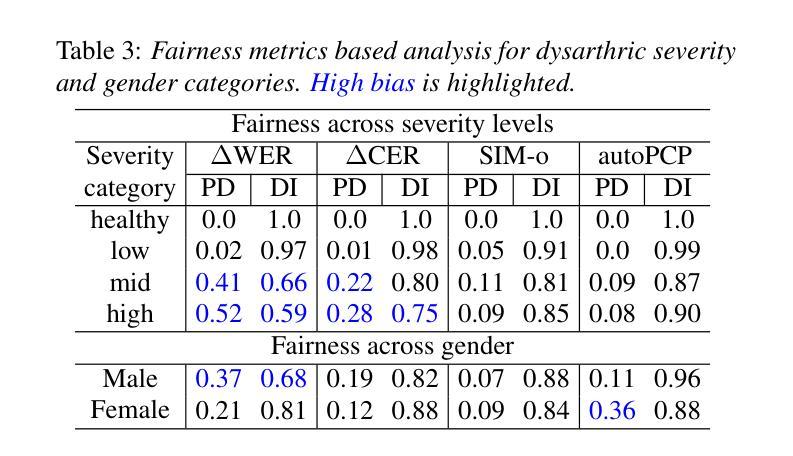
Fairness in Dysarthric Speech Synthesis: Understanding Intrinsic Bias in Dysarthric Speech Cloning using F5-TTS
Authors:Anuprabha M, Krishna Gurugubelli, Anil Kumar Vuppala
Dysarthric speech poses significant challenges in developing assistive technologies, primarily due to the limited availability of data. Recent advances in neural speech synthesis, especially zero-shot voice cloning, facilitate synthetic speech generation for data augmentation; however, they may introduce biases towards dysarthric speech. In this paper, we investigate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art F5-TTS in cloning dysarthric speech using TORGO dataset, focusing on intelligibility, speaker similarity, and prosody preservation. We also analyze potential biases using fairness metrics like Disparate Impact and Parity Difference to assess disparities across dysarthric severity levels. Results show that F5-TTS exhibits a strong bias toward speech intelligibility over speaker and prosody preservation in dysarthric speech synthesis. Insights from this study can help integrate fairness-aware dysarthric speech synthesis, fostering the advancement of more inclusive speech technologies.
言语障碍者在辅助技术开发方面面临重大挑战,这主要是因为数据有限。神经网络语音合成的最新进展,尤其是零样本语音克隆,促进了数据增强中的合成语音生成;然而,它们可能对言语障碍语音产生偏见。在本文中,我们使用TORGO数据集研究最先进的F5-TTS在克隆言语障碍语音方面的有效性,重点关注可理解性、演讲者相似性和韵律保持。我们还使用如不同影响的差距和公平性差异等公平性指标,分析潜在的偏见,以评估不同言语障碍严重程度之间的差异。结果表明,在言语障碍语音合成中,F5-TTS更偏向于注重语音可理解性,而非演讲者和韵律的保持。本研究的见解有助于融入具有公平意识的言语障碍语音合成,推动更具包容性的语音技术的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Interspeech 2025
摘要
本文主要探讨了神经网络语音合成在模仿患有构音障碍人士的语音时的效能和潜在偏见问题。针对当前构音障碍语音数据的缺乏,本文使用最新的神经语音合成技术(特别是零样本语音克隆技术)进行数据增强,同时重点考察了模型的性能。通过对TORGO数据集的分析,主要关注了语音清晰度、说话人相似度和语调保持三个维度。此外,本文还通过公平性的指标如差异影响和公平差异来评估不同构音障碍程度之间的差异。研究结果表明,F5-TTS在合成构音障碍语音时更偏向于语音清晰度而非说话人和语调的保持。本文的见解有助于开发更包容的语音技术,促进公平性感知构音障碍语音合成的整合。
关键见解
- 神经网络语音合成在模仿构音障碍人士的语音方面面临挑战,主要原因在于相关数据的稀缺性。
- 最新的零样本语音克隆技术可用于数据增强并推进此项研究的进展。
- 对TORGO数据集的分析,涉及了语音清晰度、说话人相似性和语调保持等关键性能指标的考察。
- F5-TTS模型在合成构音障碍语音时倾向于保证语音清晰度而非说话人的声音和语调的模仿。
- 通过差异影响和公平差异等公平性指标,发现了模型在不同构音障碍程度间的差异和潜在偏见。
- 研究结果强调了开发更包容的语音技术的重要性,以促进公平性感知构音障碍语音合成的整合。
点此查看论文截图


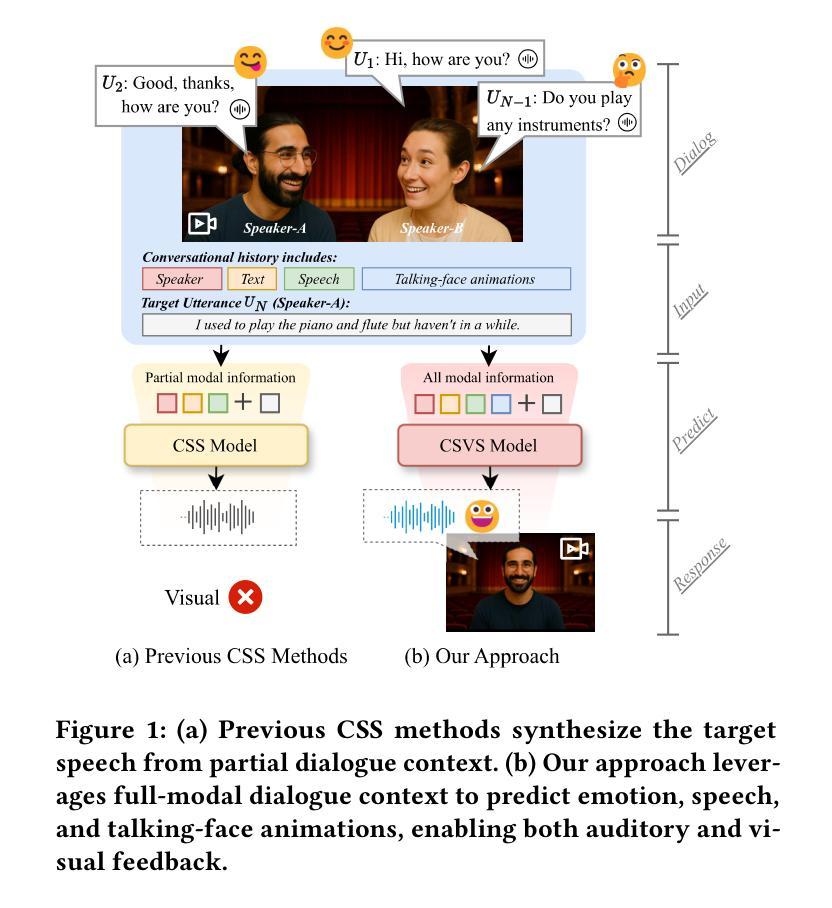
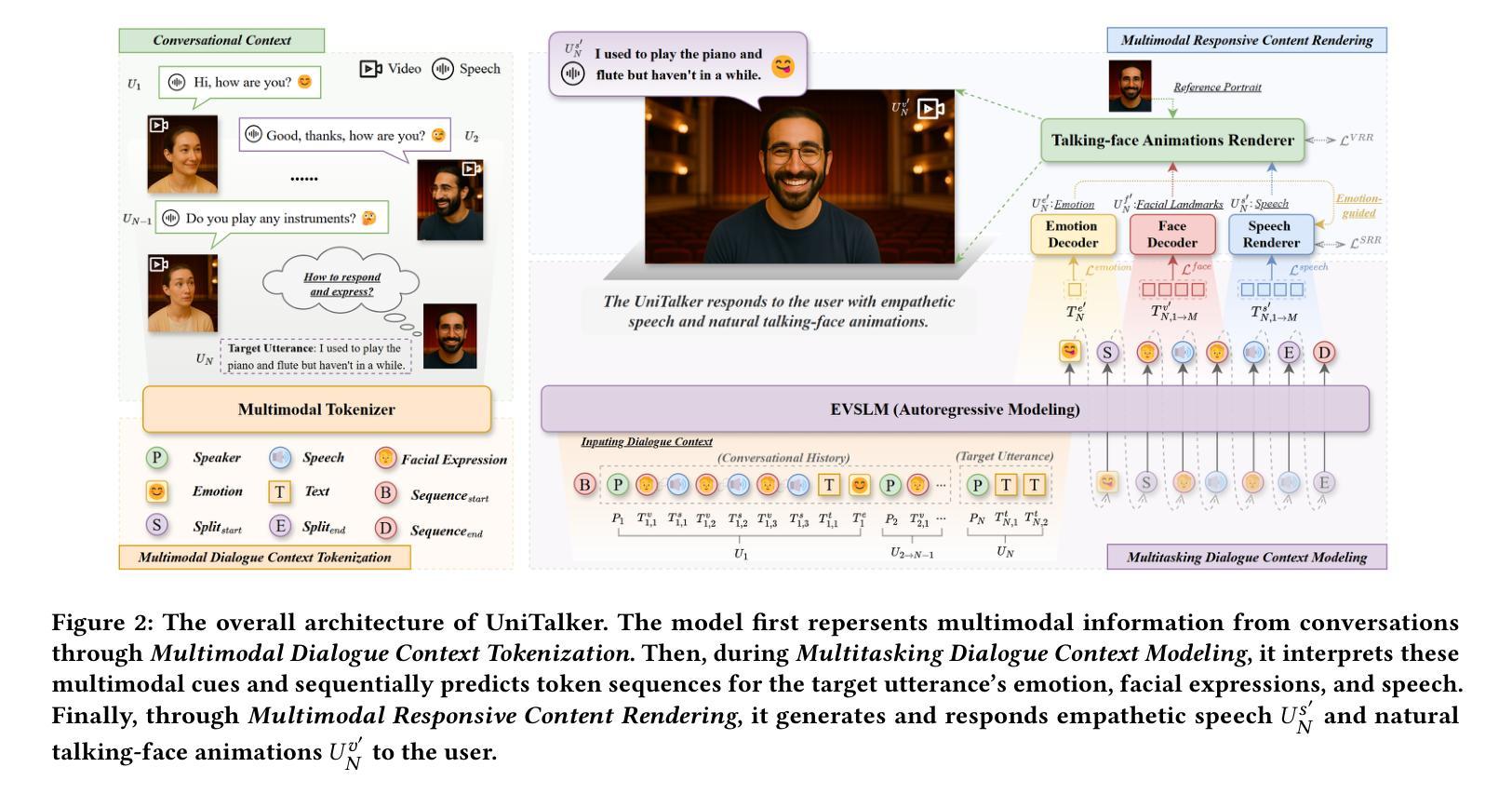
UniTalker: Conversational Speech-Visual Synthesis
Authors:Yifan Hu, Rui Liu, Yi Ren, Xiang Yin, Haizhou Li
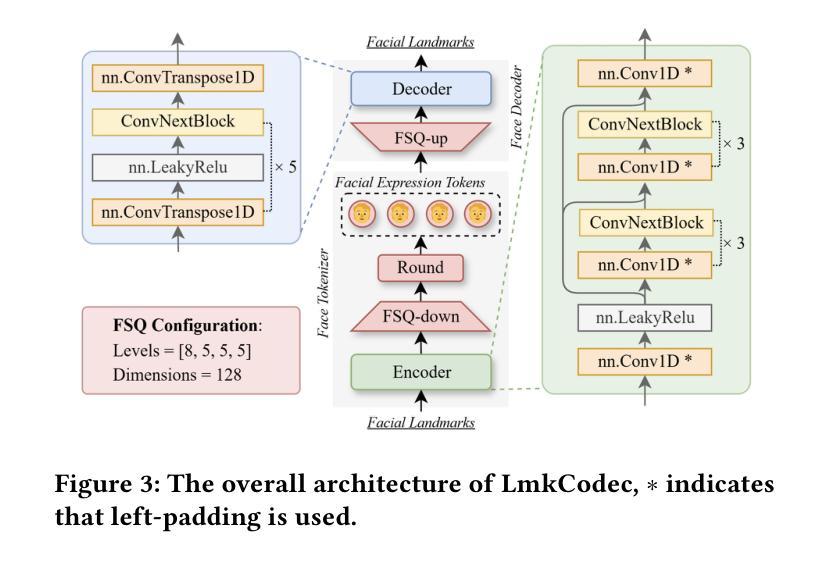
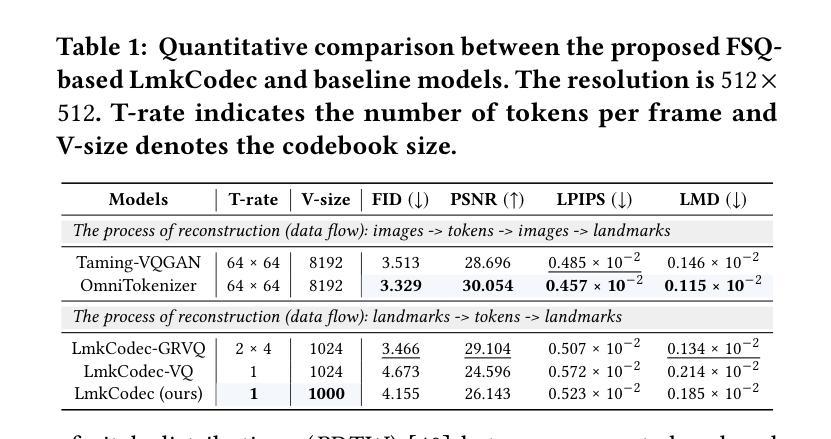
Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) is a key task in the user-agent interaction area, aiming to generate more expressive and empathetic speech for users. However, it is well-known that “listening” and “eye contact” play crucial roles in conveying emotions during real-world interpersonal communication. Existing CSS research is limited to perceiving only text and speech within the dialogue context, which restricts its effectiveness. Moreover, speech-only responses further constrain the interactive experience. To address these limitations, we introduce a Conversational Speech-Visual Synthesis (CSVS) task as an extension of traditional CSS. By leveraging multimodal dialogue context, it provides users with coherent audiovisual responses. To this end, we develop a CSVS system named UniTalker, which is a unified model that seamlessly integrates multimodal perception and multimodal rendering capabilities. Specifically, it leverages a large-scale language model to comprehensively understand multimodal cues in the dialogue context, including speaker, text, speech, and the talking-face animations. After that, it employs multi-task sequence prediction to first infer the target utterance’s emotion and then generate empathetic speech and natural talking-face animations. To ensure that the generated speech-visual content remains consistent in terms of emotion, content, and duration, we introduce three key optimizations: 1) Designing a specialized neural landmark codec to tokenize and reconstruct facial expression sequences. 2) Proposing a bimodal speech-visual hard alignment decoding strategy. 3) Applying emotion-guided rendering during the generation stage. Comprehensive objective and subjective experiments demonstrate that our model synthesizes more empathetic speech and provides users with more natural and emotionally consistent talking-face animations.
对话语音合成(CSS)是用户代理交互领域的一项关键任务,旨在为用户生成更具表现力和同情心的语音。然而,众所周知,“倾听”和“眼神交流”在现实世界的人际交流过程中对于传达情感起着至关重要的作用。现有的CSS研究仅限于感知对话上下文中的文本和语音,这限制了其有效性。此外,仅语音响应进一步限制了交互体验。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了对话语音视觉合成(CSVS)任务,作为传统CSS的扩展。通过利用多模式对话上下文,它为用户提供连贯的视听响应。为此,我们开发了一个名为UniTalker的CSVS系统,这是一个统一模型,能够无缝集成多模式感知和多模式渲染功能。具体来说,它利用大规模语言模型全面理解对话上下文中的多模式线索,包括说话者、文本、语音和说话面部动画。之后,它采用多任务序列预测,首先推断目标话语的情感,然后生成同情的语音和自然的说话面部动画。为了确保生成的语音视觉内容在情感、内容和持续时间方面保持一致,我们引入了三个关键优化:1)设计专门的神经地标编解码器来标记和重建面部表情序列。2)提出了一种双模态语音视觉硬对齐解码策略。3)在生成阶段应用情感引导渲染。全面的客观和主观实验表明,我们的模型合成更富有同情心的语音,为用户提供更自然、情感更一致的说话面部动画。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 8 figures, Accepted by ACM MM 2025
摘要
对话语音合成(CSS)是用户代理交互领域的一项关键任务,旨在为用户生成更具表现力和同情心的语音。然而,在现实世界的人际交流中,情感和情绪的表达不仅仅依赖于语音和文字对话。现有的CSS研究局限于对话语境中的文本和语音感知,这限制了其有效性。此外,仅依赖语音的响应也限制了交互体验。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了对话语音视觉合成(CSVS)任务作为传统CSS的扩展。通过利用多模态对话语境,它为用户提供连贯的视听响应。为此,我们开发了一个名为UniTalker的CSVS系统,这是一个统一的模型,能够无缝集成多模态感知和多模态渲染功能。该系统利用大规模语言模型全面理解对话语境中的多模态线索,包括说话者、文本、语音和说话面部动画。然后采用多任务序列预测,首先推断目标话语的情感,然后生成富有同情心的语音和自然流畅的说话面部动画。为了确保生成的语音视觉内容在情感、内容和持续时间方面保持一致,我们引入了三项关键优化措施:设计专门的神经地标编解码器来标记和重建面部表情序列;提出双模态语音视觉硬对齐解码策略;在生成阶段应用情感引导渲染。全面的客观和主观实验表明,我们的模型合成的语音更具同情心,并能为用户提供更自然、情感一致的说话面部动画响应。
要点摘要
- 对话语音合成(CSS)旨在生成更表现力和同情心的语音,但局限于文本和语音感知,影响效果。
- 提出对话语音视觉合成(CSVS)任务,结合多模态对话语境,提供更连贯的视听响应。
- 开发CSVS系统UniTalker,整合多模态感知和多模态渲染,全面理解对话语境中的多模态线索。
- 利用多任务序列预测生成富有同情心的语音和自然的说话面部动画,确保语音视觉内容在情感、内容和持续时间上保持一致。
- 引入三项关键优化措施:神经地标编解码器、双模态语音视觉硬对齐解码策略和情感引导渲染。
- 实验证明,UniTalker合成的语音更富有同情心,提供的说话面部动画更自然和情感一致。
点此查看论文截图

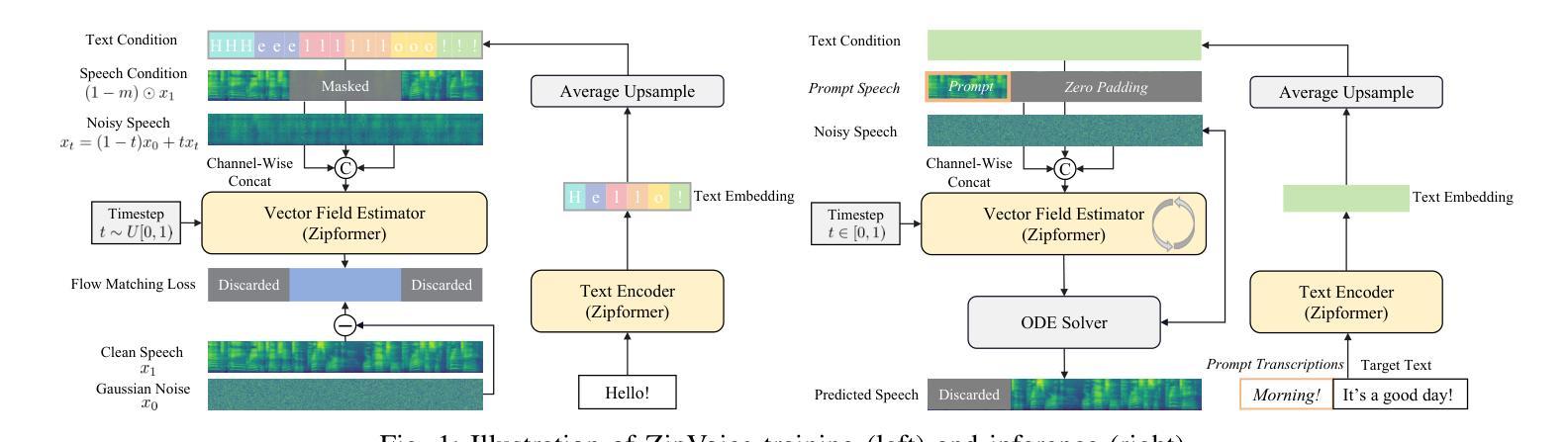
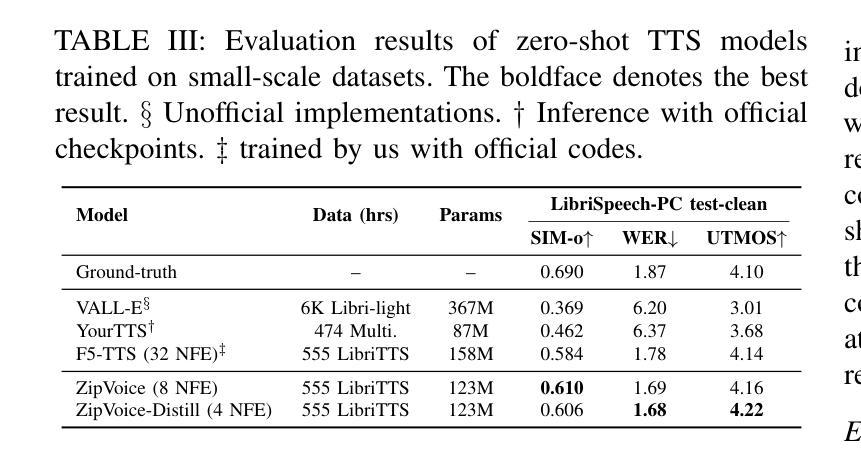
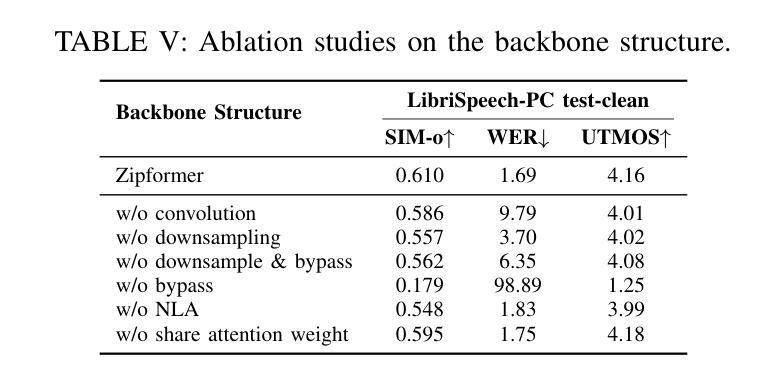
ZipVoice: Fast and High-Quality Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Flow Matching
Authors:Han Zhu, Wei Kang, Zengwei Yao, Liyong Guo, Fangjun Kuang, Zhaoqing Li, Weiji Zhuang, Long Lin, Daniel Povey
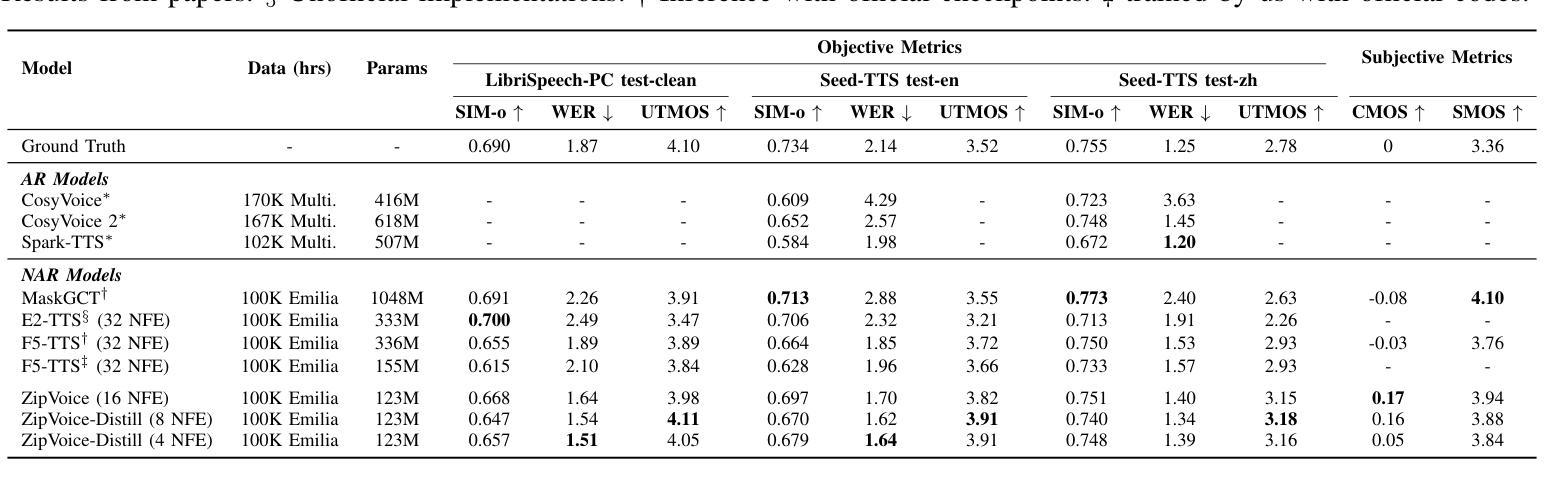
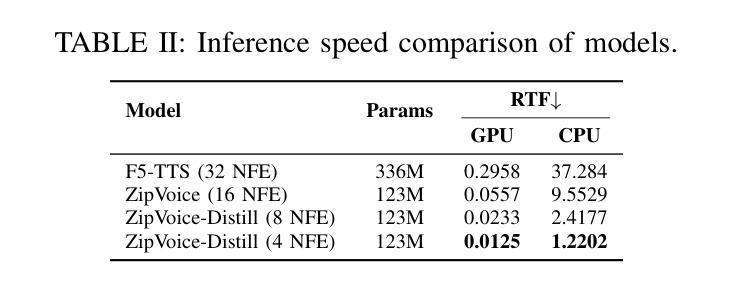
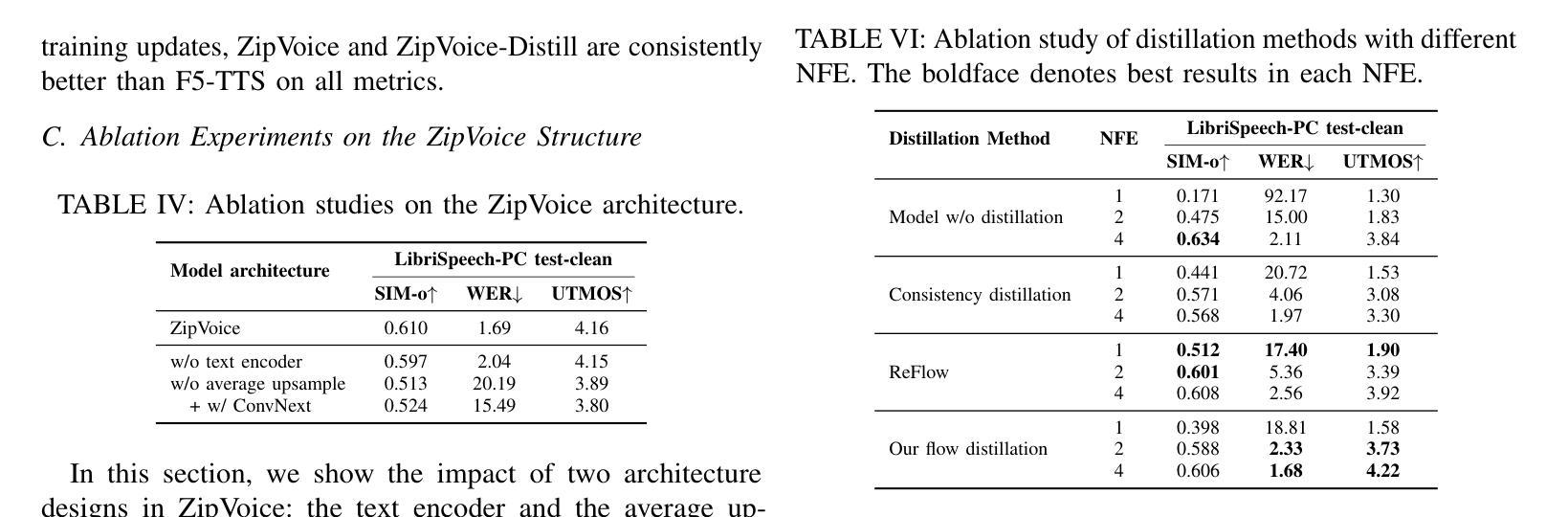
Existing large-scale zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models deliver high speech quality but suffer from slow inference speeds due to massive parameters. To address this issue, this paper introduces ZipVoice, a high-quality flow-matching-based zero-shot TTS model with a compact model size and fast inference speed. Key designs include: 1) a Zipformer-based vector field estimator to maintain adequate modeling capabilities under constrained size; 2) Average upsampling-based initial speech-text alignment and Zipformer-based text encoder to improve speech intelligibility; 3) A flow distillation method to reduce sampling steps and eliminate the inference overhead associated with classifier-free guidance. Experiments on 100k hours multilingual datasets show that ZipVoice matches state-of-the-art models in speech quality, while being 3 times smaller and up to 30 times faster than a DiT-based flow-matching baseline. Codes, model checkpoints and demo samples are publicly available at https://github.com/k2-fsa/ZipVoice.
现有的大规模零样本文本到语音(TTS)模型虽然能够提供高质量的语音,但由于参数庞大,导致推理速度较慢。针对这一问题,本文引入了ZipVoice,这是一个基于高质量流匹配的零样本TTS模型,具有较小的模型尺寸和快速的推理速度。关键设计包括:1)基于Zipformer的向量场估计器,在受限大小下保持足够的建模能力;2)基于平均上采样的初始语音文本对齐和基于Zipformer的文本编码器,以提高语音的可懂度;3)流蒸馏方法用于减少采样步骤,消除与无分类器引导相关的推理开销。在100k小时的多语种数据集上的实验表明,ZipVoice在语音质量方面与最新模型相匹配,同时比基于DiT的流匹配基准模型小3倍,速度快达30倍。代码、模型检查点和演示样本可在https://github.com/k2-fsa/ZipVoice上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ASRU 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于流匹配的零样本文本转语音(TTS)模型ZipVoice,旨在解决现有大规模零样本TTS模型参数庞大、推理速度慢的问题。ZipVoice模型设计精巧,包括使用Zipformer向量场估计器在有限大小下保持建模能力、基于平均上采样的初始语音文本对齐和Zipformer文本编码器提高语音清晰度,以及流蒸馏方法减少采样步骤,消除无分类引导相关的推理开销。实验表明,ZipVoice在语音质量上达到最新水平,模型体积为其他模型的十分之一不到,推理速度最快可达三十倍。
Key Takeaways
- ZipVoice是一个基于流匹配的零样本TTS模型,旨在解决大规模TTS模型推理速度慢的问题。
- ZipVoice设计包括Zipformer向量场估计器、基于平均上采样的文本语音对齐和Zipformer文本编码器。
- 流蒸馏方法用于减少采样步骤和消除推理开销。
- ZipVoice在语音质量上达到最新水平,同时模型体积更小,推理速度更快。
- ZipVoice模型可通过公开的代码库和模型检查点进行访问和使用。
- 模型性能的提升是通过一系列技术改进实现的,包括模型结构设计、优化算法等。
点此查看论文截图

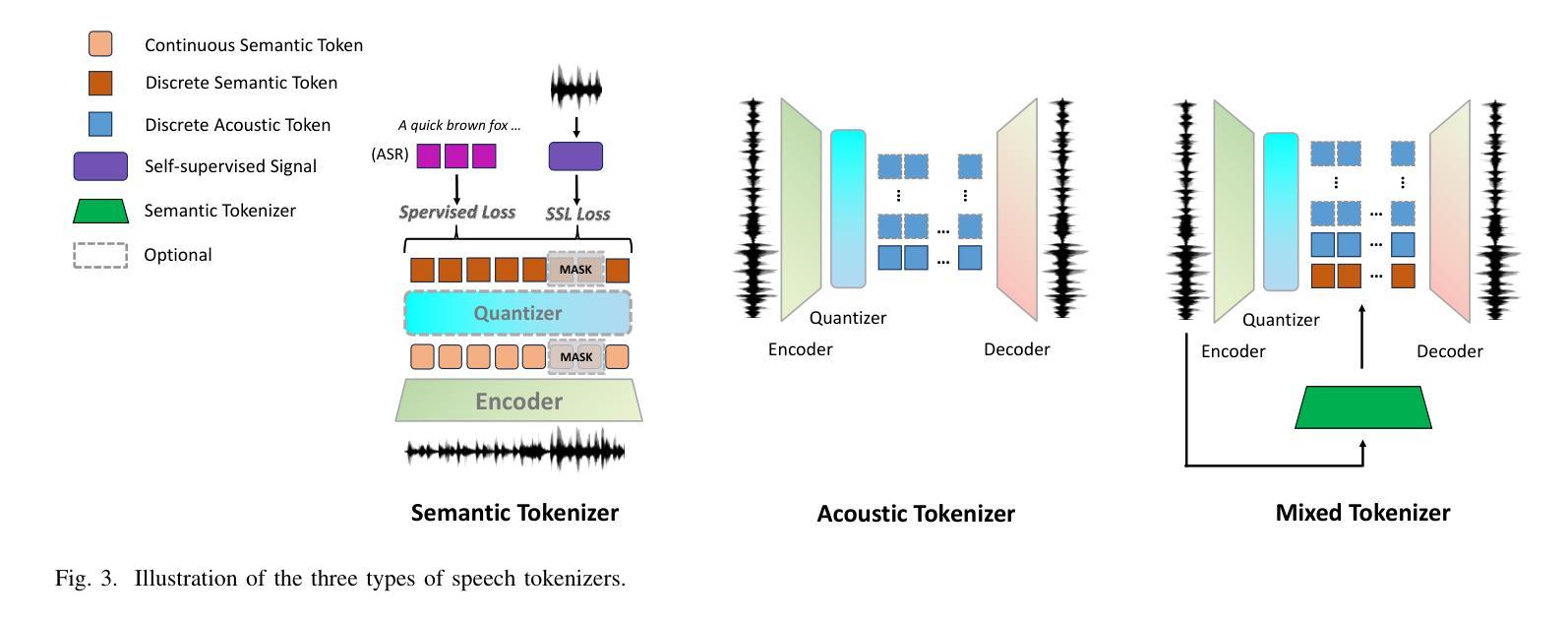
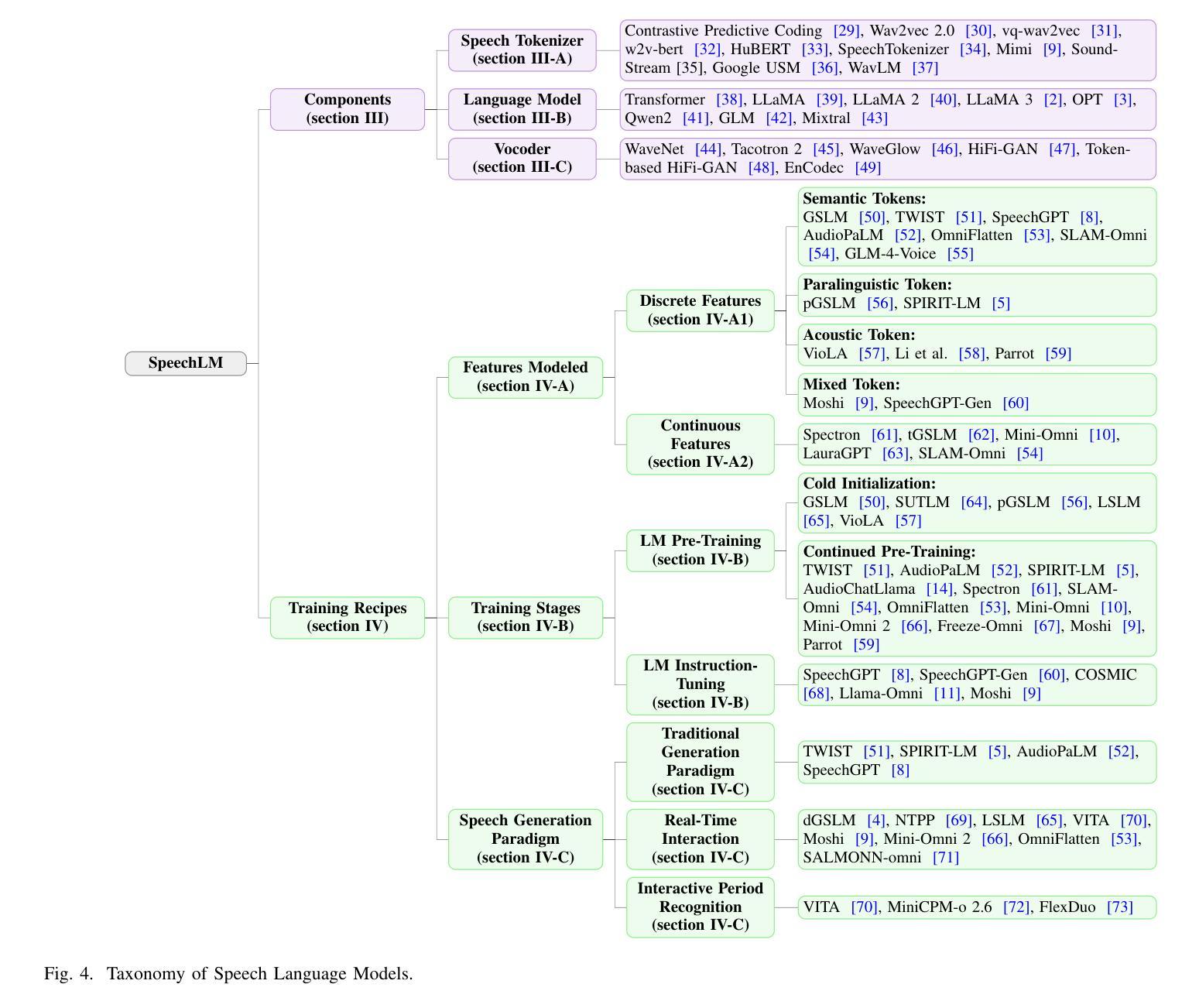
Recent Advances in Speech Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Wenqian Cui, Dianzhi Yu, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Guangyan Zhang, Qichao Wang, Yiwen Guo, Irwin King
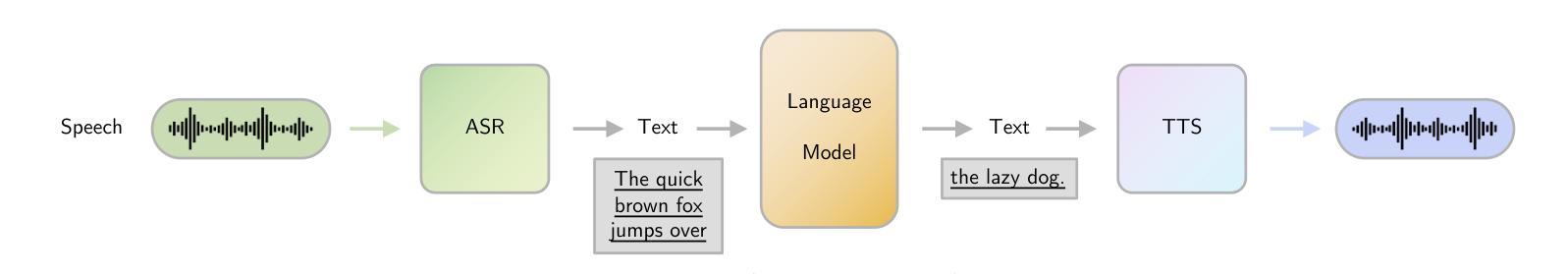
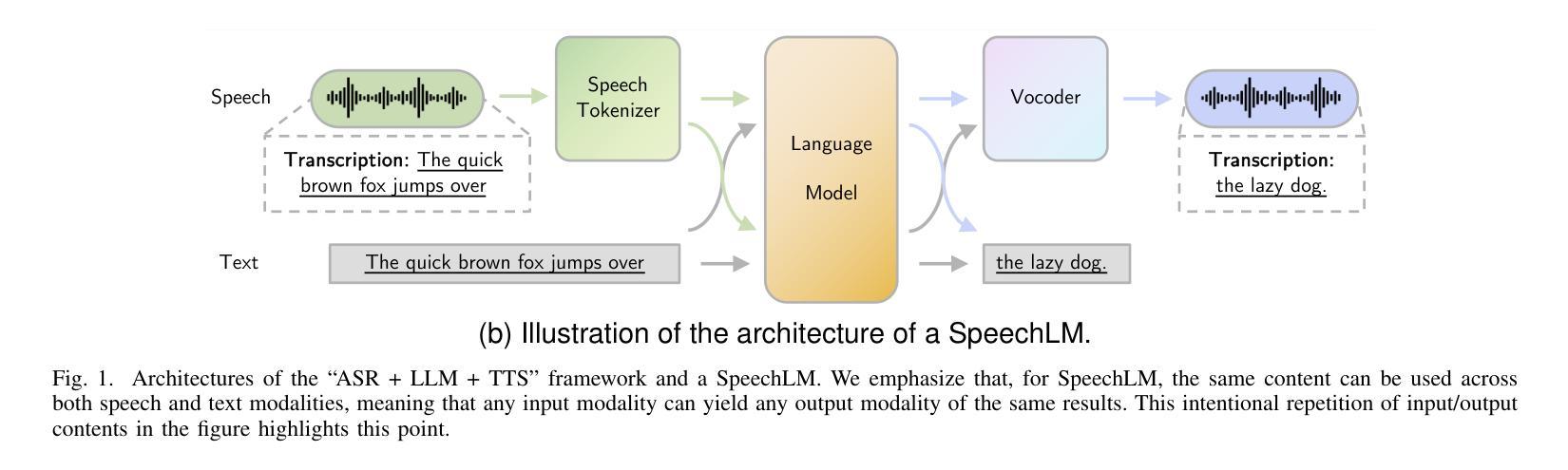
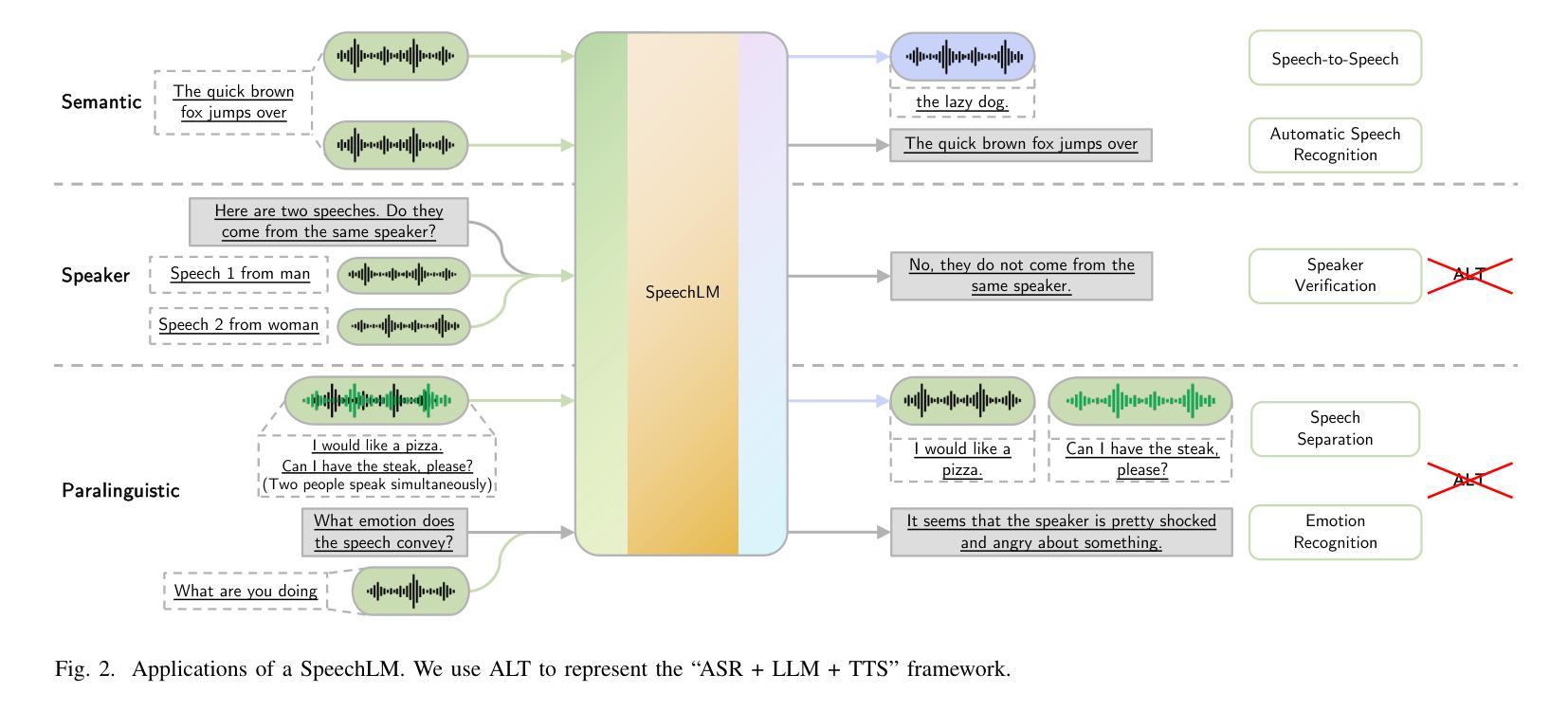
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently garnered significant attention, primarily for their capabilities in text-based interactions. However, natural human interaction often relies on speech, necessitating a shift towards voice-based models. A straightforward approach to achieve this involves a pipeline of ``Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) + LLM + Text-to-Speech (TTS)”, where input speech is transcribed to text, processed by an LLM, and then converted back to speech. Despite being straightforward, this method suffers from inherent limitations, such as information loss during modality conversion, significant latency due to the complex pipeline, and error accumulation across the three stages. To address these issues, Speech Language Models (SpeechLMs) – end-to-end models that generate speech without converting from text – have emerged as a promising alternative. This survey paper provides the first comprehensive overview of recent methodologies for constructing SpeechLMs, detailing the key components of their architecture and the various training recipes integral to their development. Additionally, we systematically survey the various capabilities of SpeechLMs, categorize their evaluation metrics, and discuss the challenges and future research directions in this rapidly evolving field. The GitHub repository is available at https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey
大型语言模型(LLM)近期备受关注,主要因其基于文本的交互能力。然而,自然人类交互通常依赖于语音,因此需要向基于语音的模型转变。实现这一目标的一种直接方法是“自动语音识别(ASR)+ LLM + 文本到语音(TTS)”的管道,其中输入语音被转录为文本,由LLM处理,然后再转回语音。尽管这种方法很直接,但它存在固有的局限性,例如在模态转换过程中的信息损失、由于复杂管道而产生的显著延迟以及三个阶段的错误累积。为解决这些问题,语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)——无需从文本转换即可生成语音的端到端模型——作为有前途的替代方案而出现。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了构建SpeechLMs的最新方法,详细描述了其架构的关键组件以及对其发展至关重要的各种训练配方。此外,我们还系统地概述了SpeechLMs的各种功能,对其评估指标进行分类,并讨论了这一快速演变领域面临的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库可通过https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The reduced version of this paper has been accepted at ACL 2025
Summary
大语言模型因其文本交互能力而受到广泛关注,但自然人类互动更多地依赖于语音。为实现语音交互,一种常见的方法是结合自动语音识别(ASR)、大型语言模型(LLM)和文本到语音(TTS)。然而,这种方法存在信息损失、延迟和误差累积的问题。为解决这些问题,出现了一种直接生成语音的端到端语音语言模型(SpeechLM)。这篇综述论文首次全面概述了SpeechLM的最新构建方法、关键组件、训练方法和开发策略。论文还系统地调查了SpeechLM的各种能力,对其评估指标进行了分类,并讨论了这一快速演进领域的挑战和未来研究方向。GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/dreamtheater123/Awesome-SpeechLM-Survey。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型在自然人机交互中扮演重要角色,但需要解决语音交互的问题。
- 结合ASR、LLM和TTS的常见方法存在固有的局限性。
- 语音语言模型(SpeechLM)是这些问题的一个有前途的替代解决方案,可直接生成语音而无需文本转换。
- SpeechLM具有多种关键组件和训练策略,用于构建和优化模型性能。
- SpeechLM具有多种能力,包括语音识别、语音合成和自然性对话等。
- 对SpeechLM的评价采用多种指标进行分类,用于系统评价模型性能。
点此查看论文截图