⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-10 更新
Scaling Artificial Intelligence for Prostate Cancer Detection on MRI towards Population-Based Screening and Primary Diagnosis in a Global, Multiethnic Population (Study Protocol)
Authors:Anindo Saha, Joeran S. Bosma, Jasper J. Twilt, Alexander B. C. D. Ng, Aqua Asif, Kirti Magudia, Peder Larson, Qinglin Xie, Xiaodong Zhang, Chi Pham Minh, Samuel N. Gitau, Ivo G. Schoots, Martijn F. Boomsma, Renato Cuocolo, Nikolaos Papanikolaou, Daniele Regge, Derya Yakar, Mattijs Elschot, Jeroen Veltman, Baris Turkbey, Nancy A. Obuchowski, Jurgen J. Fütterer, Anwar R. Padhani, Hashim U. Ahmed, Tobias Nordström, Martin Eklund, Veeru Kasivisvanathan, Maarten de Rooij, Henkjan Huisman
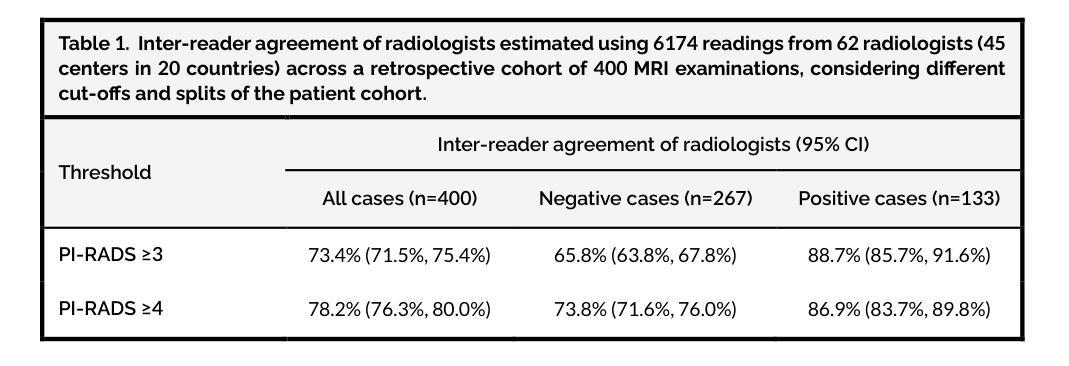
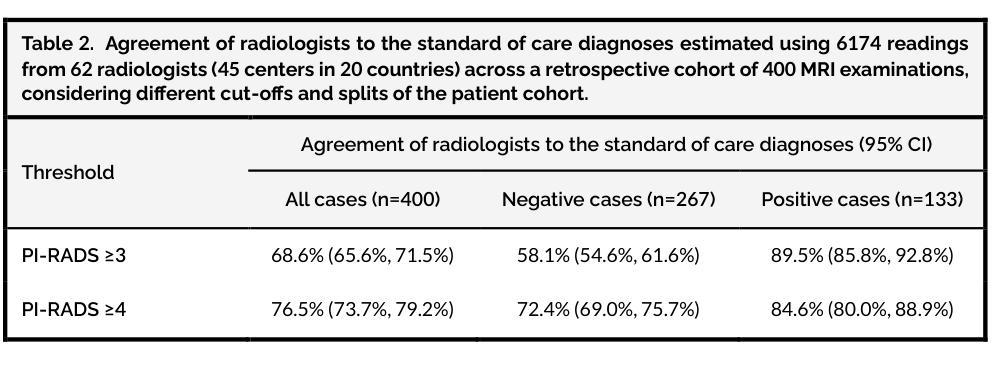
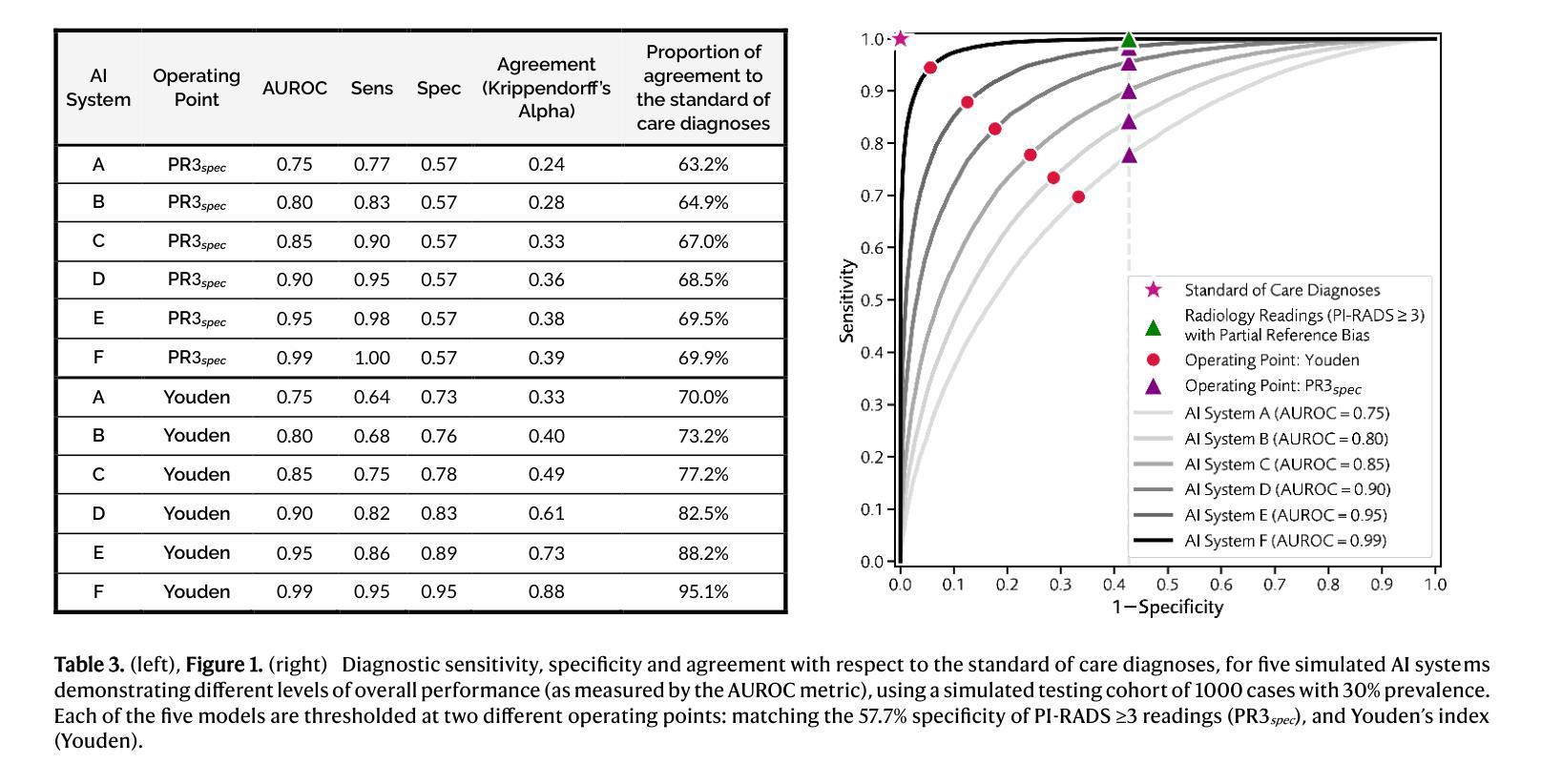
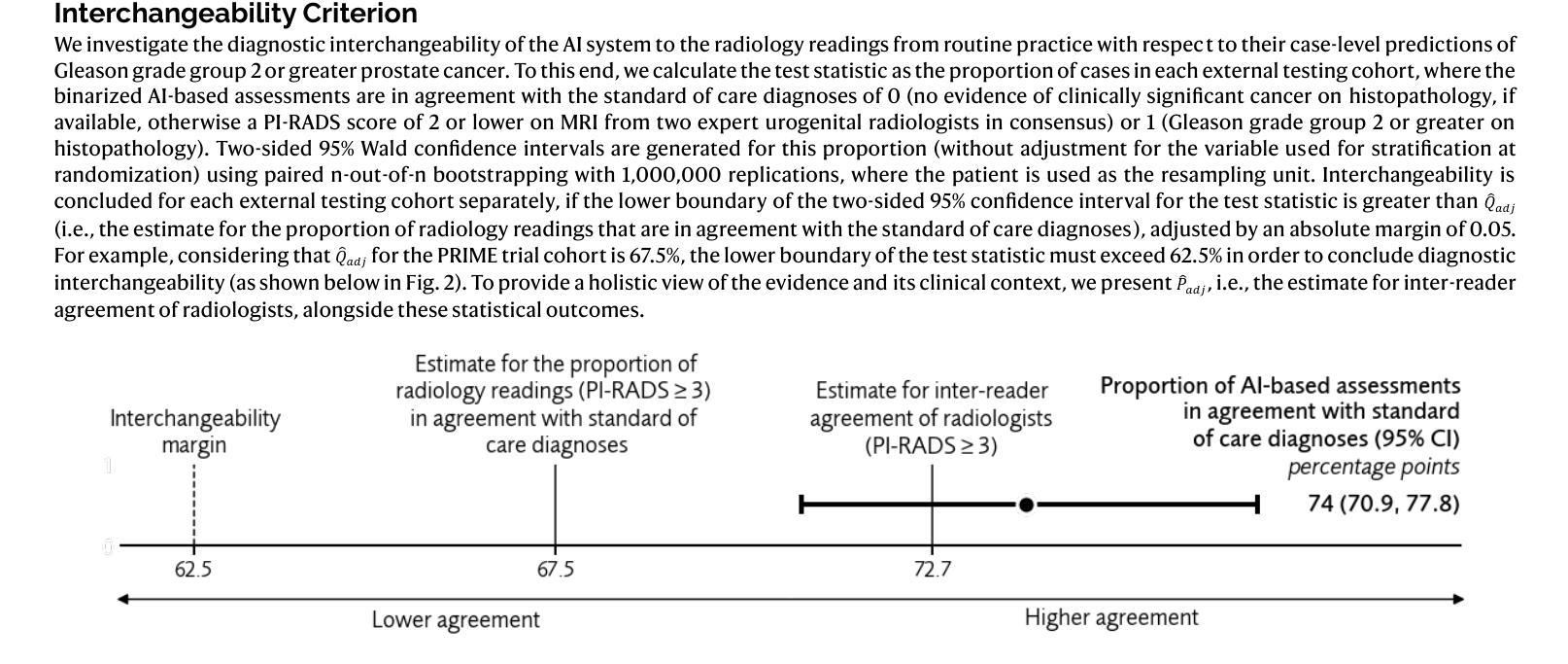
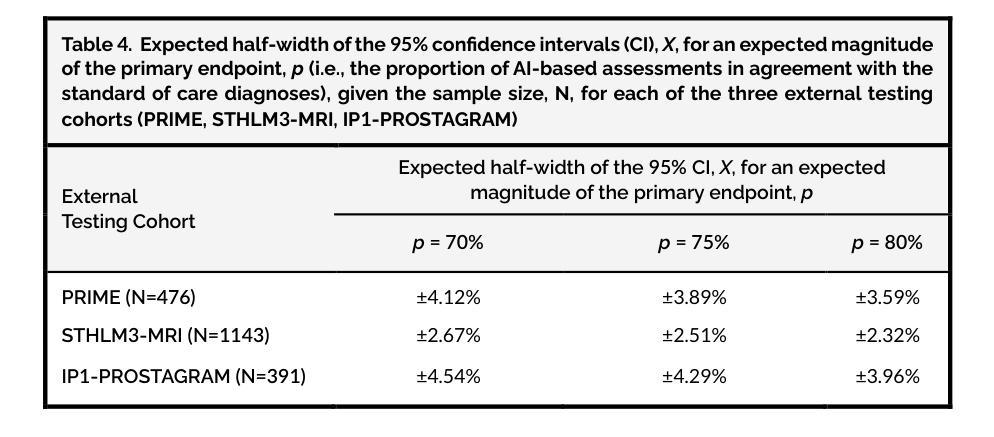
In this intercontinental, confirmatory study, we include a retrospective cohort of 22,481 MRI examinations (21,288 patients; 46 cities in 22 countries) to train and externally validate the PI-CAI-2B model, i.e., an efficient, next-generation iteration of the state-of-the-art AI system that was developed for detecting Gleason grade group $\geq$2 prostate cancer on MRI during the PI-CAI study. Of these examinations, 20,471 cases (19,278 patients; 26 cities in 14 countries) from two EU Horizon projects (ProCAncer-I, COMFORT) and 12 independent centers based in Europe, North America, Asia and Africa, are used for training and internal testing. Additionally, 2010 cases (2010 patients; 20 external cities in 12 countries) from population-based screening (STHLM3-MRI, IP1-PROSTAGRAM trials) and primary diagnostic settings (PRIME trial) based in Europe, North and South Americas, Asia and Australia, are used for external testing. Primary endpoint is the proportion of AI-based assessments in agreement with the standard of care diagnoses (i.e., clinical assessments made by expert uropathologists on histopathology, if available, or at least two expert urogenital radiologists in consensus; with access to patient history and peer consultation) in the detection of Gleason grade group $\geq$2 prostate cancer within the external testing cohorts. Our statistical analysis plan is prespecified with a hypothesis of diagnostic interchangeability to the standard of care at the PI-RADS $\geq$3 (primary diagnosis) or $\geq$4 (screening) cut-off, considering an absolute margin of 0.05 and reader estimates derived from the PI-CAI observer study (62 radiologists reading 400 cases). Secondary measures comprise the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of the AI system stratified by imaging quality, patient age and patient ethnicity to identify underlying biases (if any).
在这项洲际确认性研究中,我们纳入了22,481例MRI检查(涉及来自22个国家的46个城市中的21,288名患者)的数据来训练和验证PI-CAI-2B模型,即针对PI-CAI研究中MRI检测出的格莱森分级组≥ 2的前列腺癌而开发的一种先进的下一代人工智能系统。其中,来自两个欧盟地平线项目(ProCAncer-I、COMFORT)以及基于欧洲、北美、亚洲和非洲的另外独立研究中心的来自多个城市的约 2万零4百多次MRI检查案例被用于进行训练和内部测试(包括有参与者在欧洲,南美洲,北美洲亚洲以及澳大利亚的城市在内)。此外,另外招募自多个欧洲国家的大型随机性公共筛查计划中的数千例数据用于外部测试。主要的评价指标是人工智能评估结果与标准护理诊断结果之间的一致程度(如果可用的话,则根据临床评估中专家尿路病理学家在组织病理学上的判断为准;或者至少两名专家泌尿生殖放射科医生通过共识进行诊断评估,同时参考患者病史和同行咨询意见),旨在在外部测试群体中检测格莱森分级组≥ 2的前列腺癌患者。我们的统计分析计划事先假设与标准的诊疗护理诊断等同的评估标准,即PI-RADS≥ 3(主要诊断)或≥ 4(筛查)的临界值,同时考虑绝对误差为±0.05及通过PI-CAI观察者研究获得的读取估算数据(总计来自纳入该研究的国际医生贡献的有质量保障参考的多家医学影像放射中心的不同国际领域患者的各类历史历史患者疾病情况和医学研究调查所获得的超大型的集体实验值以供测试借鉴评估改进预测流程所需的通用医学类医学辅助系统基础模型的总体准确性。次要指标包括根据成像质量、患者年龄和种族分层的人工智能系统的曲线下面积(AUROC),以识别潜在偏见(如果存在)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究采用多国际跨地域的大型队列研究,利用全球不同地区的MRI检查数据训练并验证了新一代前列腺癌AI诊断模型PI-CAI-2B。该模型旨在提高前列腺癌的MRI诊断准确性,特别是对Gleason分级≥2级的癌症检测。研究中涉及多个国际项目与研究中心的数据用于模型的训练和测试,包括欧洲、北美、亚洲和非洲等地的数据。主要评价指标为AI诊断结果与标准诊疗意见的一致性。同时,研究还通过多个次要指标评估模型的性能与潜在偏见。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用全球多地区的MRI检查数据,旨在训练并验证新一代前列腺癌AI诊断模型PI-CAI-2B。
- 该模型用于检测Gleason分级≥2级的癌症,以提高前列腺癌的MRI诊断准确性。
- 研究涉及多个国际项目与研究中心的数据,包括来自欧洲、北美、亚洲和非洲等地的数据,用于模型的训练和测试。
- 主要评价指标为AI诊断结果与标准诊疗意见的一致性。
- 研究还通过次要指标评估模型的性能,包括不同成像质量、患者年龄和种族对模型表现的影响,以识别潜在偏见。
- 统计分析计划已预设假设,并与标准诊疗程序进行比较,以验证模型的诊断互换性。
点此查看论文截图

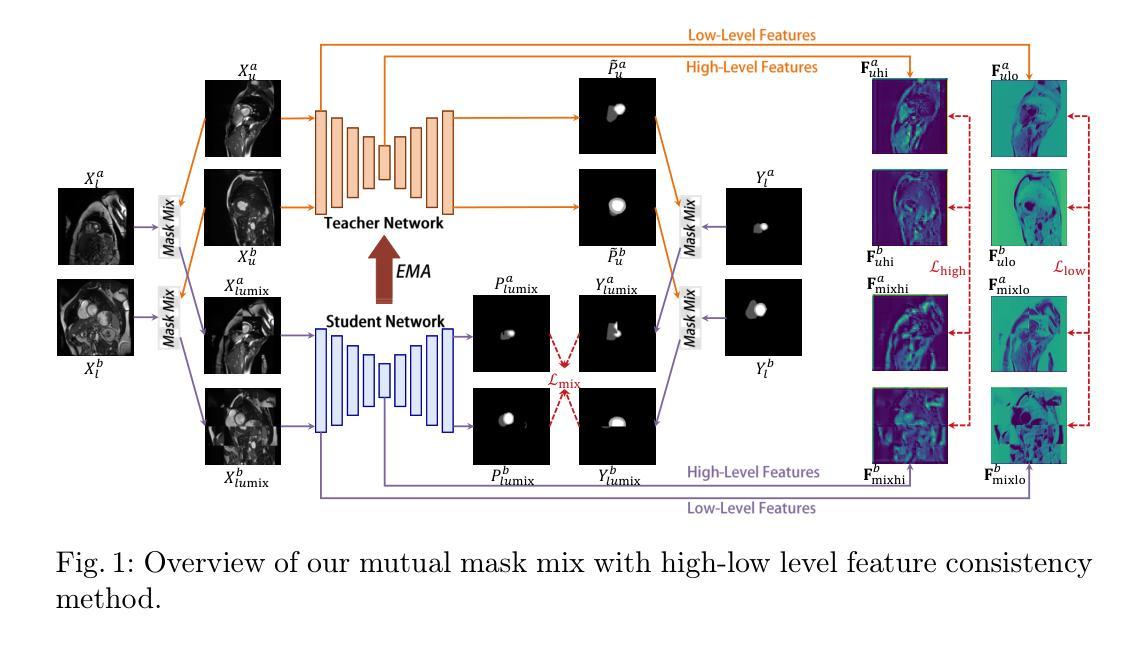
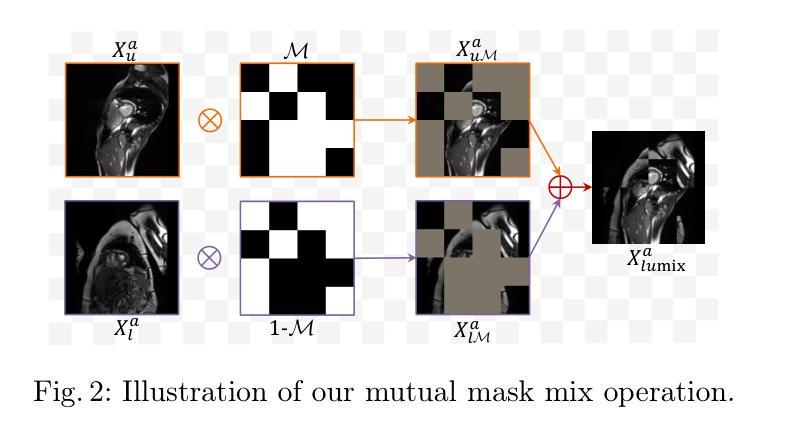
M$^3$HL: Mutual Mask Mix with High-Low Level Feature Consistency for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yajun Liu, Zenghui Zhang, Jiang Yue, Weiwei Guo, Dongying Li
Data augmentation methods inspired by CutMix have demonstrated significant potential in recent semi-supervised medical image segmentation tasks. However, these approaches often apply CutMix operations in a rigid and inflexible manner, while paying insufficient attention to feature-level consistency constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel method called Mutual Mask Mix with High-Low level feature consistency (M$^3$HL) to address the aforementioned challenges, which consists of two key components: 1) M$^3$: An enhanced data augmentation operation inspired by the masking strategy from Masked Image Modeling (MIM), which advances conventional CutMix through dynamically adjustable masks to generate spatially complementary image pairs for collaborative training, thereby enabling effective information fusion between labeled and unlabeled images. 2) HL: A hierarchical consistency regularization framework that enforces high-level and low-level feature consistency between unlabeled and mixed images, enabling the model to better capture discriminative feature representations.Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on widely adopted medical image segmentation benchmarks including the ACDC and LA datasets. Source code is available at https://github.com/PHPJava666/M3HL
数据增强方法在近期的半监督医学图像分割任务中表现出了巨大的潜力,这些方法受到CutMix的启发。然而,这些方法通常以一种僵硬且不灵活的方式应用CutMix操作,同时没有足够关注特征级别的一致性约束。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为具有高低层次特征一致性的互掩混合(M$^3$HL),以解决上述挑战。该方法包含两个关键组成部分:1)M$^3$:一种受Masked Image Modeling(MIM)中的掩模策略启发的增强数据增强操作。它通过动态可调整的掩模来改进传统的CutMix,生成空间互补的图像对进行协同训练,从而实现有标签和无标签图像之间的有效信息共享。2)HL:一种层次化一致性正则化框架,该框架在无标签和混合图像之间强制实施高层次和低层次特征的一致性,使模型能够更准确地捕获判别特征表示。我们的方法在广泛采用的医学图像分割基准测试(包括ACDC和LA数据集)上达到了最先进的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/PHPJava666/M3HL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学图像分割任务中,CutMix数据增强方法表现出显著潜力,但现有方法在应用时存在刚性和缺乏特征级别一致性约束的问题。本文提出一种名为M$^3$HL的新方法,包含M$^3$和HL两个关键组件。M$^3$通过动态可调掩膜生成空间互补图像对进行协同训练,促进标注和未标注图像的有效信息融合。HL建立层次一致性正则化框架,加强未标注和混合图像间的高、低层次特征一致性,使模型能更好捕捉判别特征表示。在广泛采用的医学图像分割基准测试上达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- CutMix数据增强方法在医学图像分割任务中具有显著潜力。
- 现有CutMix方法存在应用刚性、缺乏特征级别一致性约束的问题。
- M$^3$HL方法通过动态可调掩膜生成空间互补图像对,促进信息融合。
- M$^3$HL方法建立层次一致性正则化框架,加强特征一致性。
- M$^3$HL在医学图像分割基准测试上达到领先水平。
- M$^3$HL方法包括M$^3$和HL两个关键组件,分别负责数据增强和特征一致性。
点此查看论文截图

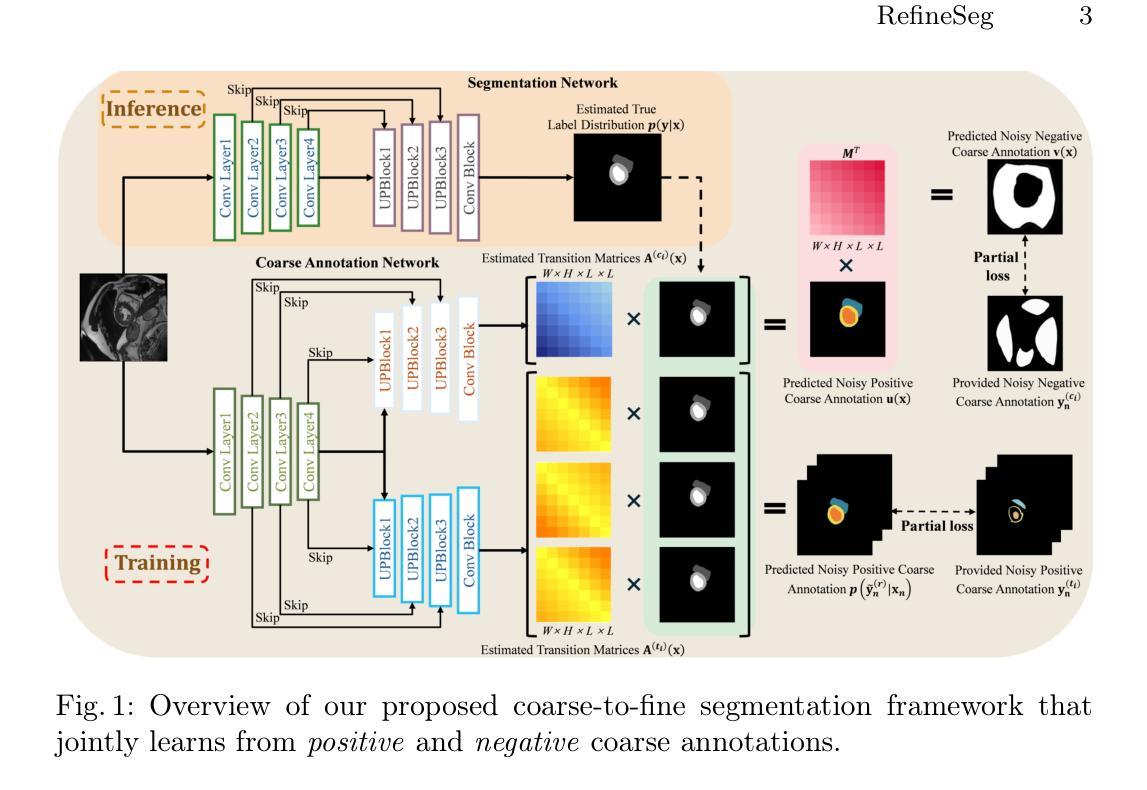
RefineSeg: Dual Coarse-to-Fine Learning for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Anghong Du, Nay Aung, Theodoros N. Arvanitis, Stefan K. Piechnik, Joao A C Lima, Steffen E. Petersen, Le Zhang
High-quality pixel-level annotations of medical images are essential for supervised segmentation tasks, but obtaining such annotations is costly and requires medical expertise. To address this challenge, we propose a novel coarse-to-fine segmentation framework that relies entirely on coarse-level annotations, encompassing both target and complementary drawings, despite their inherent noise. The framework works by introducing transition matrices in order to model the inaccurate and incomplete regions in the coarse annotations. By jointly training on multiple sets of coarse annotations, it progressively refines the network’s outputs and infers the true segmentation distribution, achieving a robust approximation of precise labels through matrix-based modeling. To validate the flexibility and effectiveness of the proposed method, we demonstrate the results on two public cardiac imaging datasets, ACDC and MSCMRseg, and further evaluate its performance on the UK Biobank dataset. Experimental results indicate that our approach surpasses the state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods and closely matches the fully supervised approach.
高质量的医疗图像像素级注释对于监督分割任务至关重要,但获取这样的注释成本高昂且需要医学专业知识。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种全新的从粗到细的分割框架,该框架完全依赖于粗级注释,包括目标和辅助绘图,尽管它们存在固有噪声。该框架通过引入转换矩阵来建模粗注释中的不准确和不完整区域。通过联合训练多组粗注释,它逐步优化网络的输出并推断出真正的分割分布,通过基于矩阵的建模实现精确标签的稳健近似。为了验证所提出方法的灵活性和有效性,我们在两个公共心脏成像数据集ACDC和MSCMRseg上展示了结果,并在UK Biobank数据集上进一步评估了其性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法超越了最新的弱监督方法,并与全监督方法非常接近。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要针对医疗图像分割任务中对高质量像素级标注的需求展开研究,提出了一种全新的粗到细分割框架。该框架无需精确标注,仅依赖粗级标注和补充绘图即可进行训练。通过引入过渡矩阵来模拟粗标注中的不准确和缺失区域,通过联合训练多个粗标注数据集,逐步优化网络输出并推断真实分割分布。实验结果显示,该方法超越了现有的弱监督方法,并与全监督方法接近。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量像素级标注对医疗图像分割任务至关重要,但获取成本高昂且需要医学专业知识。
- 提出了一种新的粗到细分割框架,可依赖粗级标注进行训练,包含目标和补充绘图。
- 引入过渡矩阵以模拟粗标注中的不准确和缺失区域。
- 通过联合训练多个粗标注数据集,逐步优化网络输出。
- 框架能推断真实分割分布,实现精确标签的稳健近似。
- 在两个公共心脏成像数据集ACDC和MSCMRseg上验证了方法的灵活性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

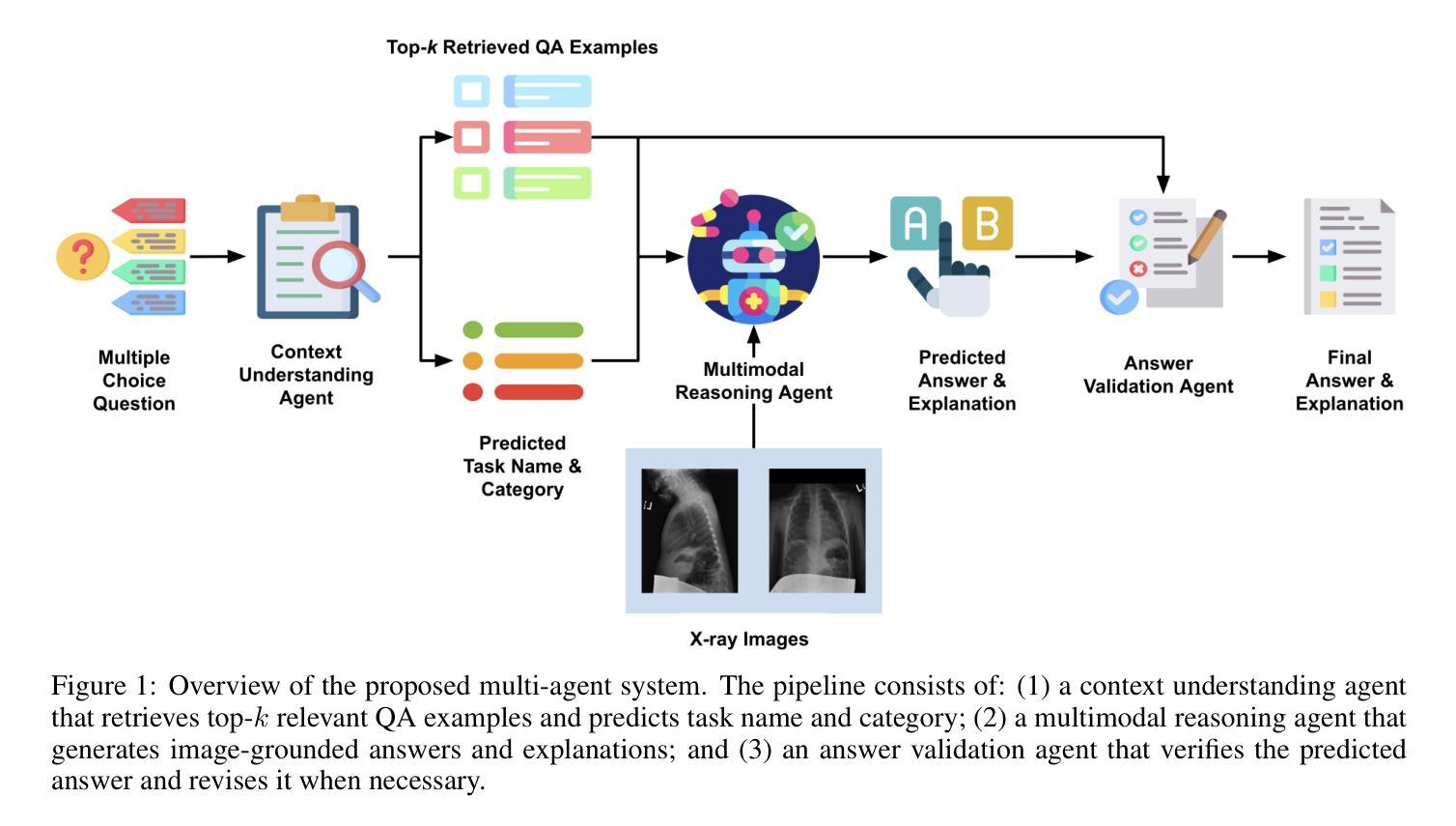
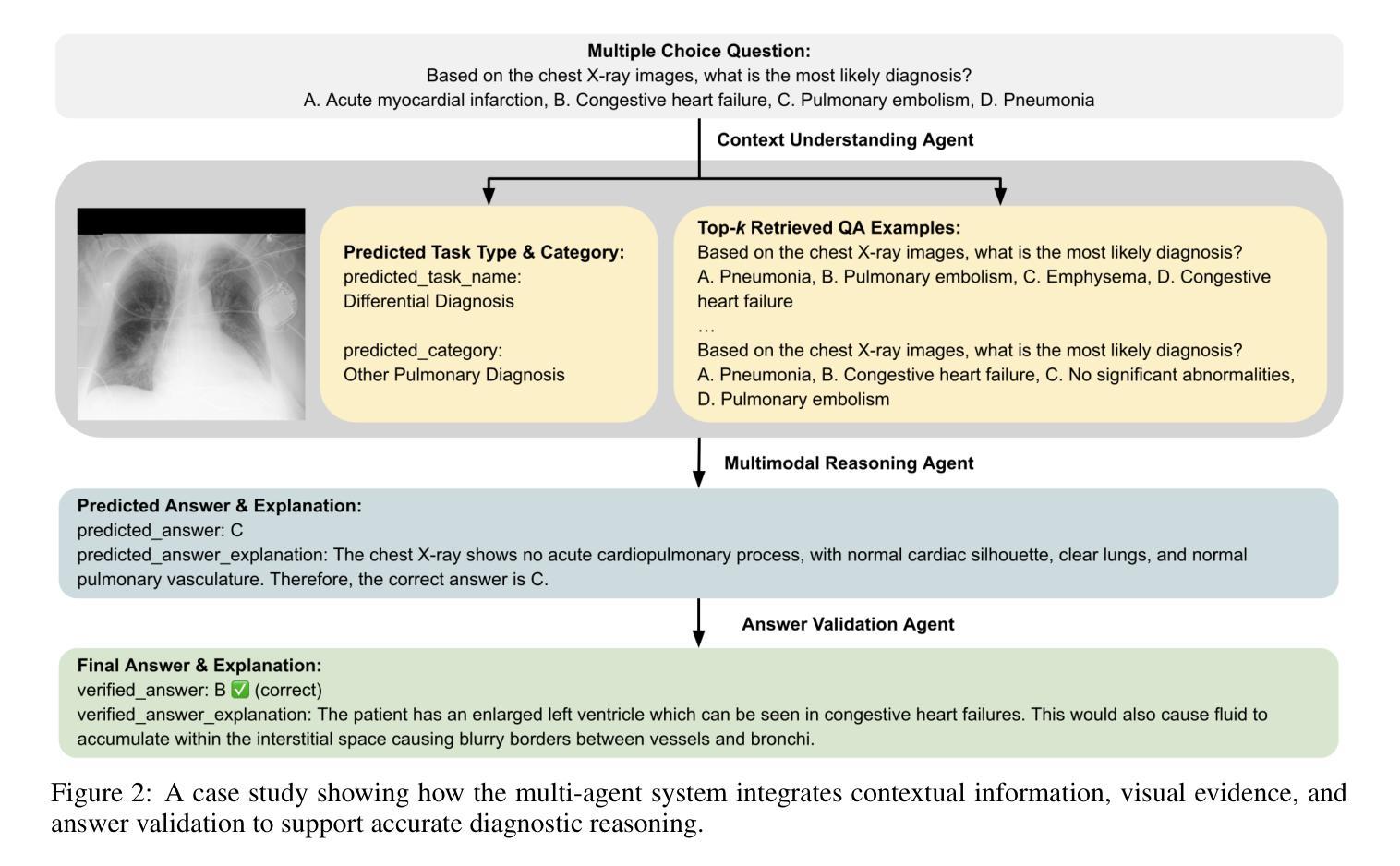
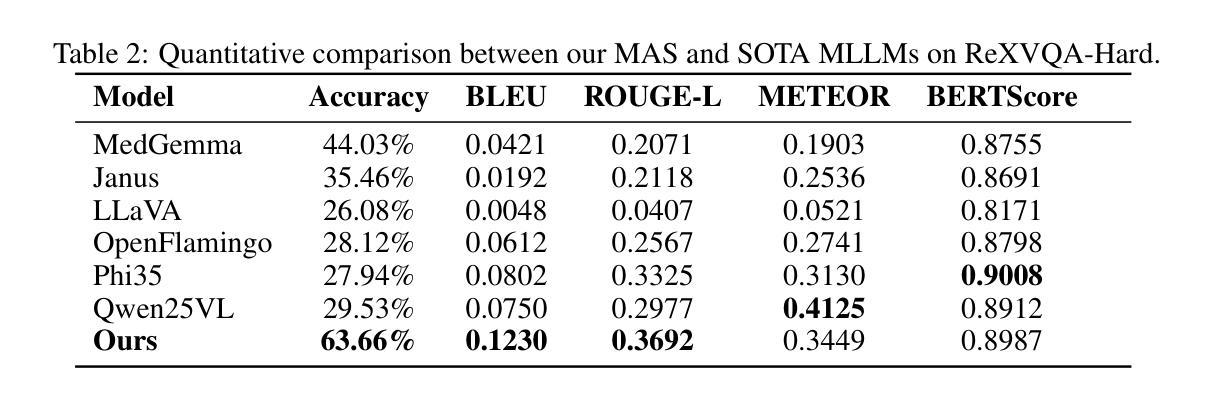
A Multi-Agent System for Complex Reasoning in Radiology Visual Question Answering
Authors:Ziruo Yi, Jinyu Liu, Ting Xiao, Mark V. Albert
Radiology visual question answering (RVQA) provides precise answers to questions about chest X-ray images, alleviating radiologists’ workload. While recent methods based on multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) have shown promising progress in RVQA, they still face challenges in factual accuracy, hallucinations, and cross-modal misalignment. We introduce a multi-agent system (MAS) designed to support complex reasoning in RVQA, with specialized agents for context understanding, multimodal reasoning, and answer validation. We evaluate our system on a challenging RVQA set curated via model disagreement filtering, comprising consistently hard cases across multiple MLLMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our system over strong MLLM baselines, with a case study illustrating its reliability and interpretability. This work highlights the potential of multi-agent approaches to support explainable and trustworthy clinical AI applications that require complex reasoning.
医学影像视觉问答(RVQA)能够对胸部X射线图像的相关问题提供精确答案,从而减轻放射科医生的工作量。虽然最近基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和检索增强生成(RAG)的RVQA方法在RVQA方面取得了令人鼓舞的进展,但它们仍然面临着事实准确性、幻觉和跨模态不对准等挑战。我们引入了一种多智能体系统(MAS),旨在支持RVQA中的复杂推理,配备用于上下文理解、多模态推理和答案验证的专门智能体。我们在一个经过模型分歧过滤筛选的挑战性RVQA数据集上评估我们的系统,该数据集包含多个MLLM中始终存在的困难案例。大量实验表明,我们的系统在强大的MLLM基准测试上具有优越性和有效性,案例研究证明了其可靠性和可解释性。这项工作突出了多智能体方法在支持需要复杂推理的可解释和可信赖的临床人工智能应用方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于放射学视觉问答(RVQA)技术,对于胸部X光图像相关问题能够给出精确答案,从而减轻放射科医生的工作量。尽管现有基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)和检索增强生成(RAG)的方法在RVQA方面取得显著进展,但在事实准确性、幻象和跨模态对齐方面仍面临挑战。本研究引入了一种多智能体系统(MAS),支持RVQA中的复杂推理,包括用于上下文理解、多模态推理和答案验证的专用智能体。通过模型分歧过滤法精心挑选的具有挑战性的RVQA数据集的实验结果显示,该系统的性能优于强大的MLLM基线,并通过案例研究证明了其可靠性和可解释性。本研究凸显了多智能体方法在需要复杂推理的可解释和可信赖的临床人工智能应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- RVQA技术能够为胸部X光图像相关问题提供精确答案,减轻放射科医生的工作量。
- 基于MLLM和RAG的方法在RVQA方面已取得显著进展,但仍存在事实准确性、幻象和跨模态对齐方面的挑战。
- 引入的多智能体系统(MAS)包括用于上下文理解、多模态推理和答案验证的专用智能体,以支持RVQA中的复杂推理。
- 通过模型分歧过滤法挑选的具有挑战性的RVQA数据集的实验验证了MAS系统的优越性。
- 与强大的MLLM基线相比,MAS系统在性能方面表现出优势。
- 通过案例研究证明了MAS系统的可靠性和可解释性。
点此查看论文截图

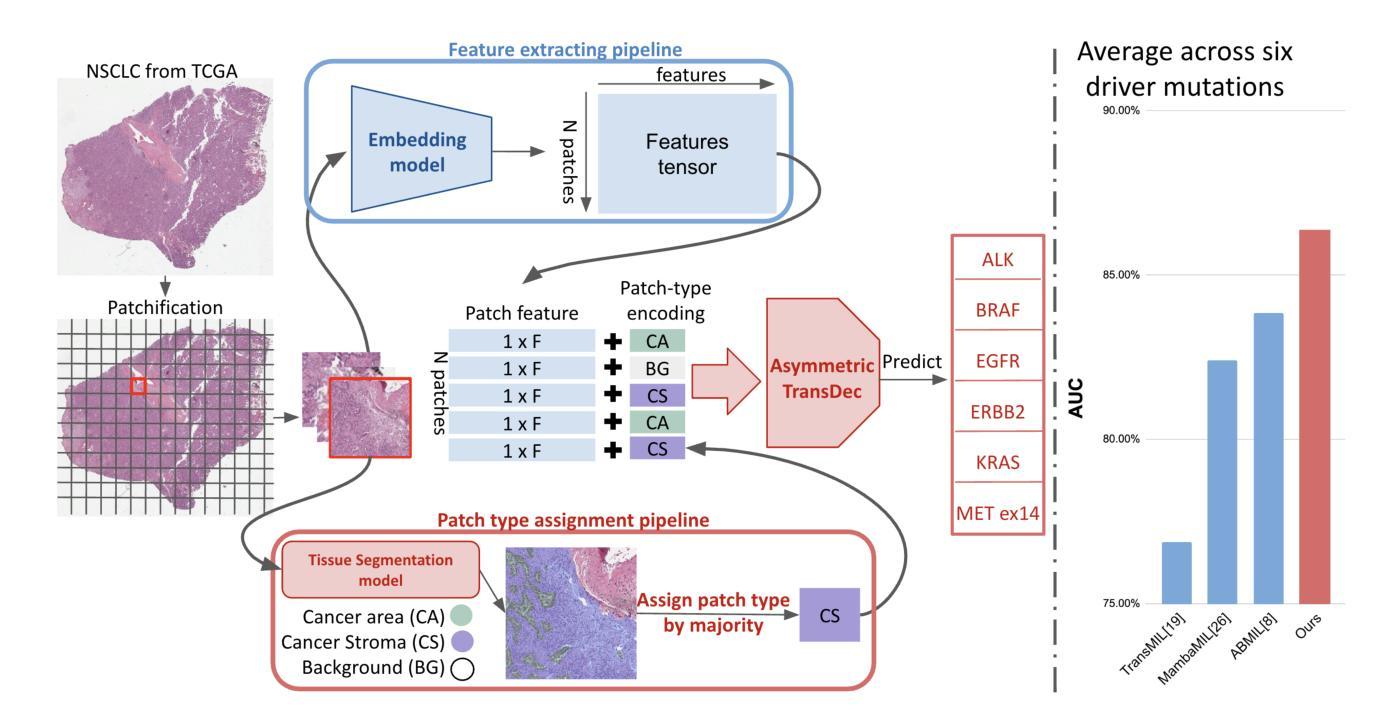
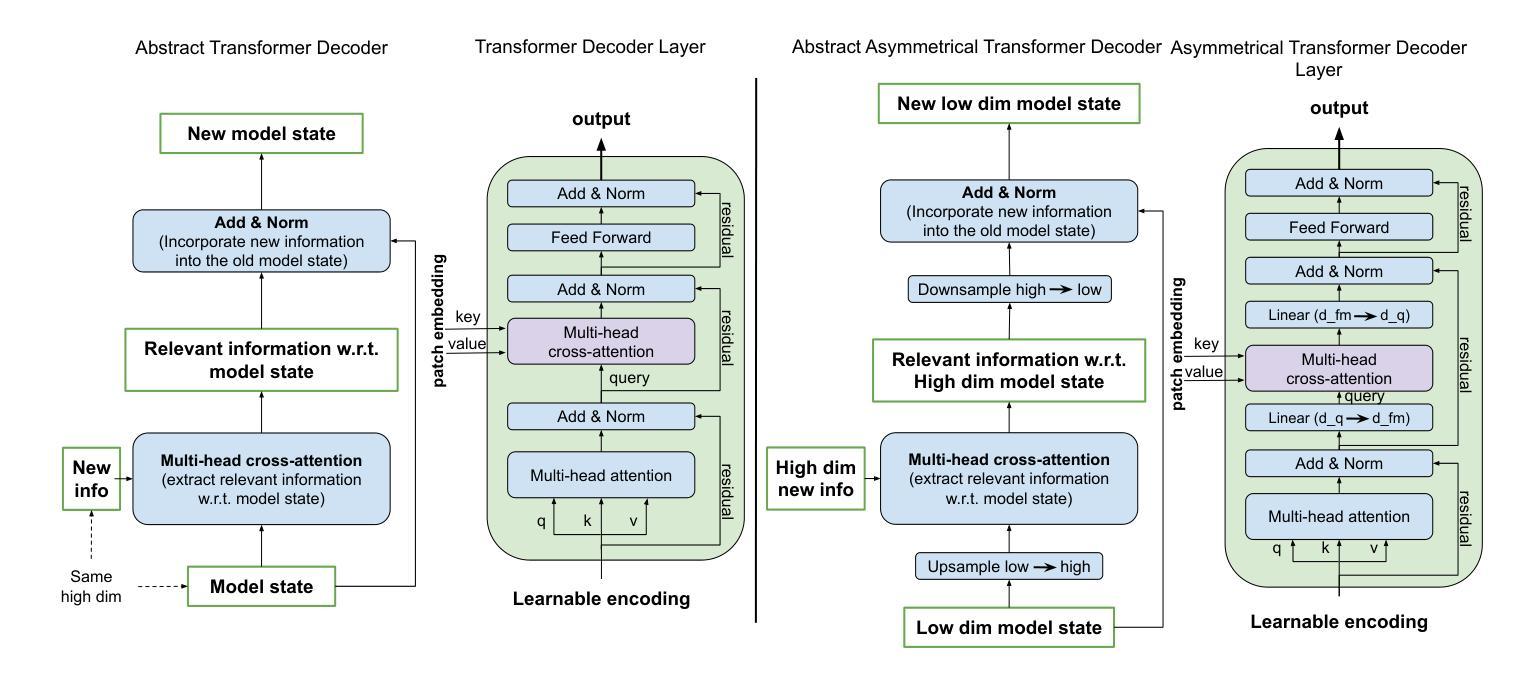
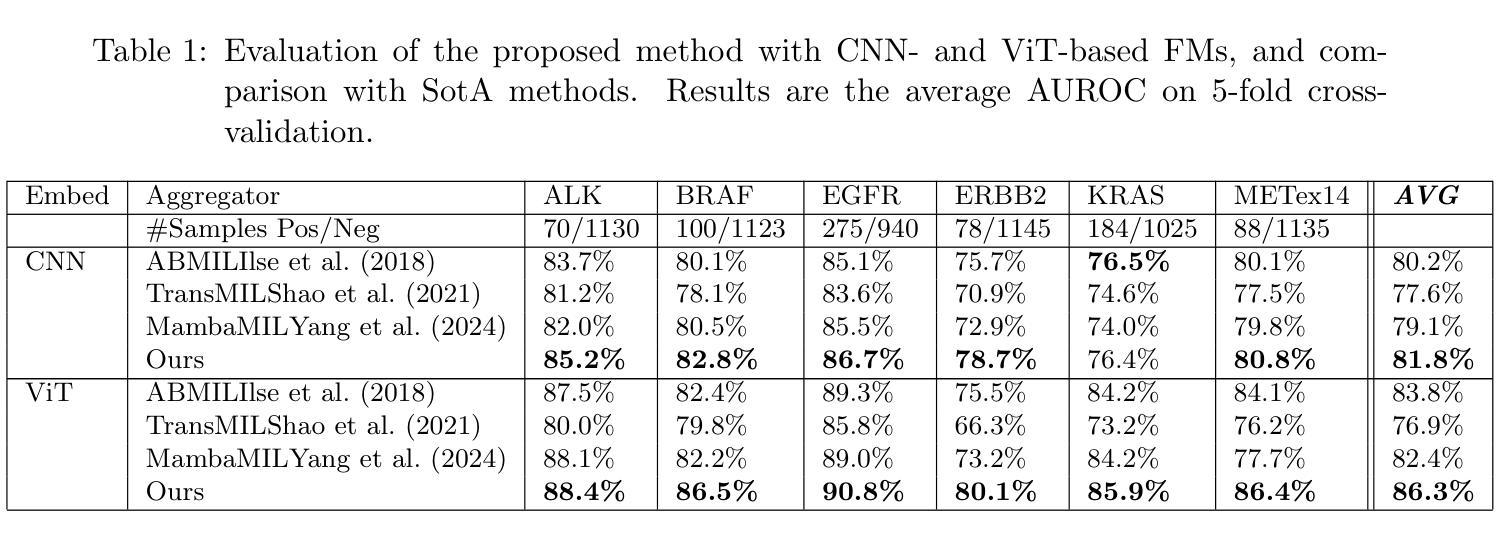
Identifying actionable driver mutations in lung cancer using an efficient Asymmetric Transformer Decoder
Authors:Biagio Brattoli, Jack Shi, Jongchan Park, Taebum Lee, Donggeun Yoo, Sergio Pereira
Identifying actionable driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) can impact treatment decisions and significantly improve patient outcomes. Despite guideline recommendations, broader adoption of genetic testing remains challenging due to limited availability and lengthy turnaround times. Machine Learning (ML) methods for Computational Pathology (CPath) offer a potential solution; however, research often focuses on only one or two common mutations, limiting the clinical value of these tools and the pool of patients who can benefit from them. This study evaluates various Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) techniques to detect six key actionable NSCLC driver mutations: ALK, BRAF, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, and MET ex14. Additionally, we introduce an Asymmetric Transformer Decoder model that employs queries and key-values of varying dimensions to maintain a low query dimensionality. This approach efficiently extracts information from patch embeddings and minimizes overfitting risks, proving highly adaptable to the MIL setting. Moreover, we present a method to directly utilize tissue type in the model, addressing a typical MIL limitation where either all regions or only some specific regions are analyzed, neglecting biological relevance. Our method outperforms top MIL models by an average of 3%, and over 4% when predicting rare mutations such as ERBB2 and BRAF, moving ML-based tests closer to being practical alternatives to standard genetic testing.
识别非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中的可操作驱动基因突变可以对治疗决策产生影响,并显著改善患者预后。尽管有指南推荐,但由于有限的可用性和漫长的周转时间,更广泛地采用基因检测仍然具有挑战性。计算病理学(CPath)中的机器学习(ML)方法提供了潜在的解决方案;然而,研究通常只关注一种或两种常见的突变,这限制了这些工具的临床价值以及可以从这些工具中受益的患者群体。本研究评估了各种多重实例学习(MIL)技术,以检测六种关键可操作NSCLC驱动基因突变:ALK、BRAF、EGFR、ERBB2、KRAS和MET ex14。此外,我们引入了一种不对称变压器解码器模型,该模型采用不同维度的查询和键值来保持低查询维度。这种方法有效地从补丁嵌入中提取信息,最小化过度拟合的风险,并证明其高度适应于MIL环境。而且,我们提出了一种直接在模型中使用组织类型的方法,解决了典型的MIL限制,即分析所有区域或仅分析某些特定区域,而忽略了生物相关性。我们的方法平均优于顶级MIL模型约3%,在预测如ERBB2和BRAF等罕见突变时超过4%,使基于ML的测试更接近实用的替代标准基因检测方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025 Workshop COMPAYL
Summary
本文研究了利用机器学习技术检测非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的六种关键可行动突变基因,包括ALK、BRAF、EGFR、ERBB2、KRAS和MET ex14的方法。引入了一种不对称转换器解码器模型,能高效地从补丁嵌入中提取信息并降低过拟合风险。同时,提出了直接利用组织类型的方法来解决多实例学习(MIL)的常规限制。该方法在预测罕见突变如ERBB2和BRAF方面表现优异,使得基于ML的测试更接近于实际的基因测试替代品。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中的关键见解要点,以简化的中文列出:
- 利用机器学习技术检测非小细胞肺癌的驱动基因突变对治疗决策有重要影响。
- 遗传测试的广泛采纳仍然面临挑战,而计算病理学中的机器学习方法提供了潜在解决方案。
- 研究评估了多种多实例学习技术来检测六种关键可行动NSCLC驱动突变。
- 引入了一种不对称转换器解码器模型,能高效处理信息并降低过拟合风险。
- 提出了一种直接利用组织类型的方法来解决多实例学习的限制。
- 该方法在预测罕见突变如ERBB2和BRAF方面表现优异。
- 该研究使得基于机器学习的测试更接近于实际的基因测试替代品。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Zero-Shot Brain Tumor Subtype Classification via Fine-Grained Patch-Text Alignment
Authors:Lubin Gan, Jing Zhang, Linhao Qu, Yijun Wang, Siying Wu, Xiaoyan Sun
The fine-grained classification of brain tumor subtypes from histopathological whole slide images is highly challenging due to subtle morphological variations and the scarcity of annotated data. Although vision-language models have enabled promising zero-shot classification, their ability to capture fine-grained pathological features remains limited, resulting in suboptimal subtype discrimination. To address these challenges, we propose the Fine-Grained Patch Alignment Network (FG-PAN), a novel zero-shot framework tailored for digital pathology. FG-PAN consists of two key modules: (1) a local feature refinement module that enhances patch-level visual features by modeling spatial relationships among representative patches, and (2) a fine-grained text description generation module that leverages large language models to produce pathology-aware, class-specific semantic prototypes. By aligning refined visual features with LLM-generated fine-grained descriptions, FG-PAN effectively increases class separability in both visual and semantic spaces. Extensive experiments on multiple public pathology datasets, including EBRAINS and TCGA, demonstrate that FG-PAN achieves state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization in zero-shot brain tumor subtype classification.
由于微妙的形态学变化和注释数据的稀缺,从病理全切片图像对脑肿瘤亚型进行精细分类是一项极具挑战性的任务。尽管视觉语言模型已经实现了有前景的零样本分类,但它们捕捉精细病理特征的能力仍然有限,导致亚型鉴别结果不理想。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了针对数字病理的量身定制的细粒度补丁对齐网络(Fine-Grained Patch Alignment Network,简称FG-PAN)。FG-PAN由两个关键模块组成:(1)局部特征细化模块,它通过模拟代表性补丁之间的空间关系来增强补丁级别的视觉特征;(2)细粒度文本描述生成模块,它利用大型语言模型来产生病理感知、类特定的语义原型。通过将精炼的视觉特征与LLM生成的细粒度描述进行对齐,FG-PAN有效地提高了视觉和语义空间中的类可分性。在多个公共病理学数据集(包括EBRAINS和TCGA)上的广泛实验表明,FG-PAN在零样本脑肿瘤亚型分类中实现了最先进的性能和稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脑肿瘤亚型的精细分类因其微妙的形态变化和注释数据的稀缺而从病理全组织切片图像中成为一个巨大挑战。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了细粒度补丁对齐网络(FG-PAN),这是一种适用于数字病理学的零样本分类新型框架。FG-PAN包含两个关键模块:一是局部特征优化模块,它通过模拟代表性补丁之间的空间关系来提升补丁级别的视觉特征;二是细粒度文本描述生成模块,它利用大型语言模型来生成病理相关的、具有类特异性的语义原型。通过优化视觉特征与细粒度描述的对齐,FG-PAN有效地提高了视觉和语义空间中的类可分性。在多个公共病理学数据集上的广泛实验表明,FG-PAN在零样本脑肿瘤亚型分类中达到了最先进的性能,并具有稳健的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤亚型的精细分类是一个重大挑战,因为存在微妙的形态变化和注释数据的稀缺性。
- 细粒度补丁对齐网络(FG-PAN)是一种针对数字病理学的零样本分类新型框架。
- FG-PAN包含两个关键模块:局部特征优化模块和细粒度文本描述生成模块。
- 局部特征优化模块通过模拟代表性补丁之间的空间关系提升补丁级别的视觉特征。
- 细粒度文本描述生成模块利用大型语言模型生成病理相关的、具有类特异性的语义原型。
- FG-PAN通过优化视觉特征与细粒度描述的对齐,有效提高了视觉和语义空间中的类可分性。
点此查看论文截图

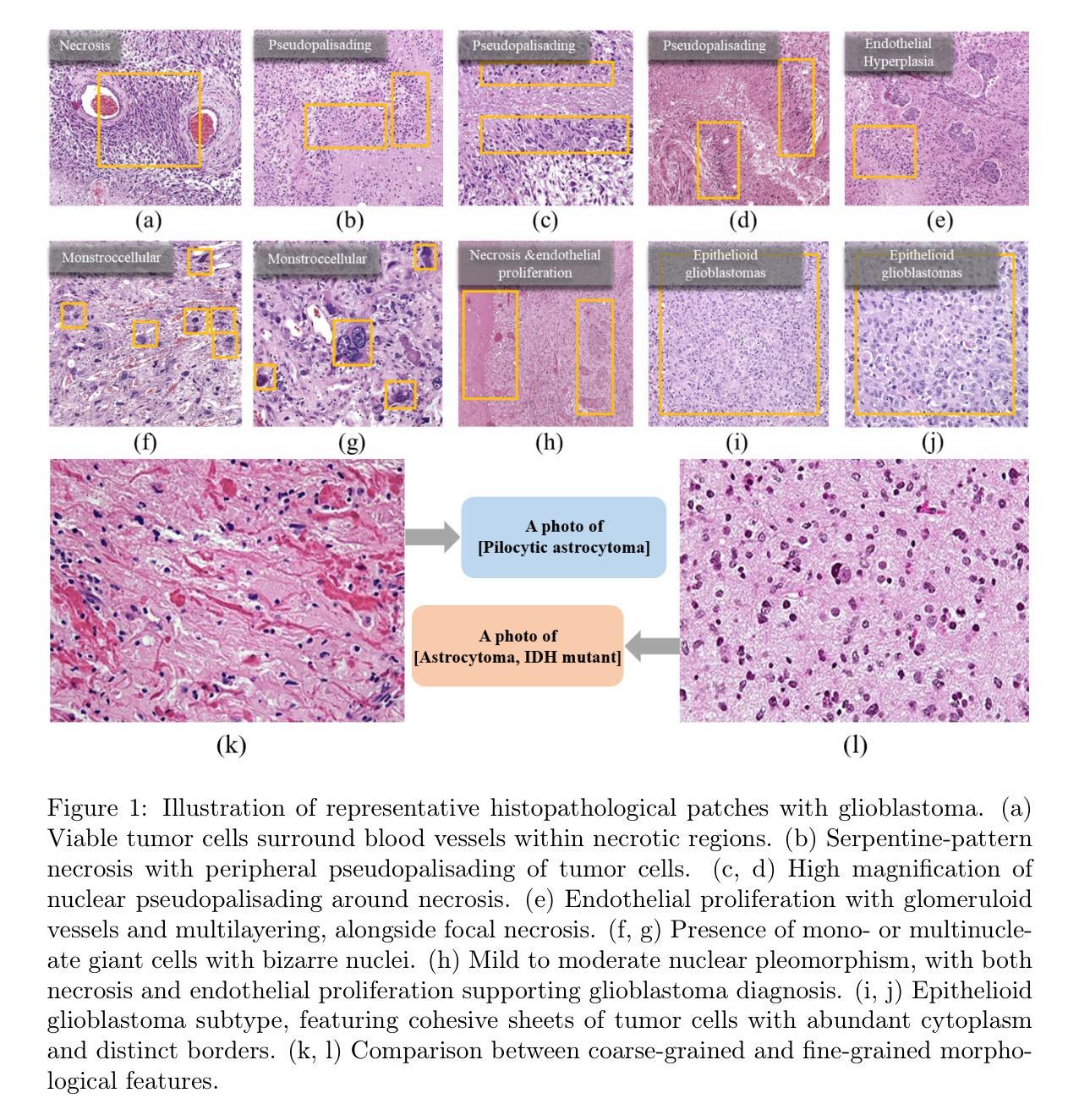
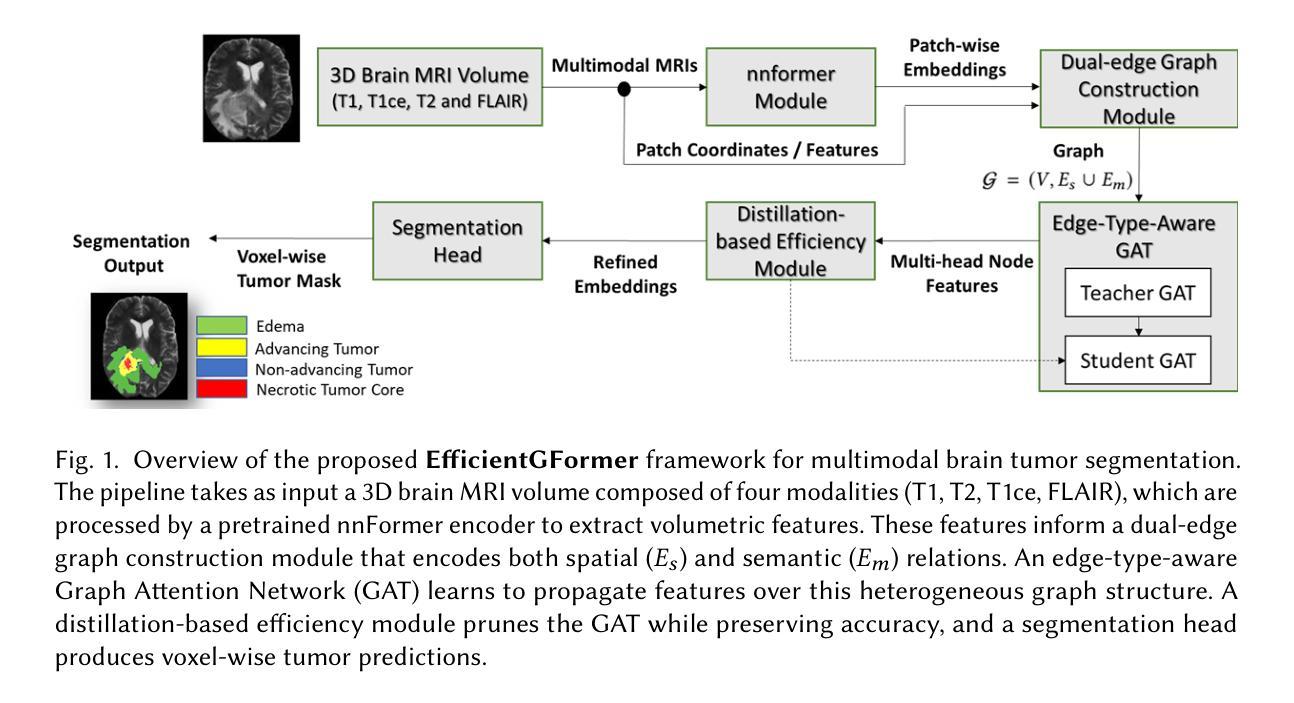
EfficientGFormer: Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation via Pruned Graph-Augmented Transformer
Authors:Fatemeh Ziaeetabar
Accurate and efficient brain tumor segmentation remains a critical challenge in neuroimaging due to the heterogeneous nature of tumor subregions and the high computational cost of volumetric inference. In this paper, we propose EfficientGFormer, a novel architecture that integrates pretrained foundation models with graph-based reasoning and lightweight efficiency mechanisms for robust 3D brain tumor segmentation. Our framework leverages nnFormer as a modality-aware encoder, transforming multi-modal MRI volumes into patch-level embeddings. These features are structured into a dual-edge graph that captures both spatial adjacency and semantic similarity. A pruned, edge-type-aware Graph Attention Network (GAT) enables efficient relational reasoning across tumor subregions, while a distillation module transfers knowledge from a full-capacity teacher to a compact student model for real-time deployment. Experiments on the MSD Task01 and BraTS 2021 datasets demonstrate that EfficientGFormer achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with significantly reduced memory and inference time, outperforming recent transformer-based and graph-based baselines. This work offers a clinically viable solution for fast and accurate volumetric tumor delineation, combining scalability, interpretability, and generalization.
精确且高效的脑肿瘤分割在神经成像中仍然是一个关键挑战,这是由于肿瘤亚区的异质性以及体积推理的高计算成本。在本文中,我们提出了EfficientGFormer,这是一种新型架构,它将预训练的基模型与基于图的推理和轻量化效率机制相结合,用于稳健的3D脑肿瘤分割。我们的框架利用nnFormer作为模态感知编码器,将多模态MRI体积转换为斑块级嵌入。这些特征被构建成一个双边缘图,该图捕捉了空间邻近性和语义相似性。一个经过修剪的边缘类型感知图注意力网络(GAT)实现了肿瘤亚区之间的有效关系推理,而蒸馏模块将知识从全容量教师转移到紧凑的学生模型,用于实时部署。在MSD Task01和BraTS 2021数据集上的实验表明,EfficientGFormer达到了最先进的准确性,并显著减少了内存和推理时间,超越了最近的基于转换器和基于图的基线。这项工作结合可扩展性、可解释性和泛化能力,为快速准确的体积肿瘤描绘提供了临床可行的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出EfficientGFormer架构,结合预训练基础模型、图推理和轻量化效率机制,用于稳健的3D脑肿瘤分割。该架构利用nnFormer作为模态感知编码器,将多模态MRI体积转换为斑块级嵌入,结构化双边缘图捕捉空间邻近性和语义相似性。实验证明EfficientGFormer在MSD Task01和BraTS 2021数据集上实现卓越精度,显著降低内存和推理时间,为快速准确的体积肿瘤描绘提供临床可行的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- EfficientGFormer是一个用于3D脑肿瘤分割的新型架构。
- 该架构结合了预训练基础模型、图推理和轻量化效率机制。
- nnFormer作为模态感知编码器,将多模态MRI体积转换为斑块级嵌入。
- 双边缘图结构用于捕捉空间邻近性和语义相似性。
- 架构采用修剪的边缘类型感知图注意力网络(GAT)实现高效的关系推理。
- 知识蒸馏模块将知识从全容量教师模型转移到紧凑的学生模型,实现实时部署。
点此查看论文截图

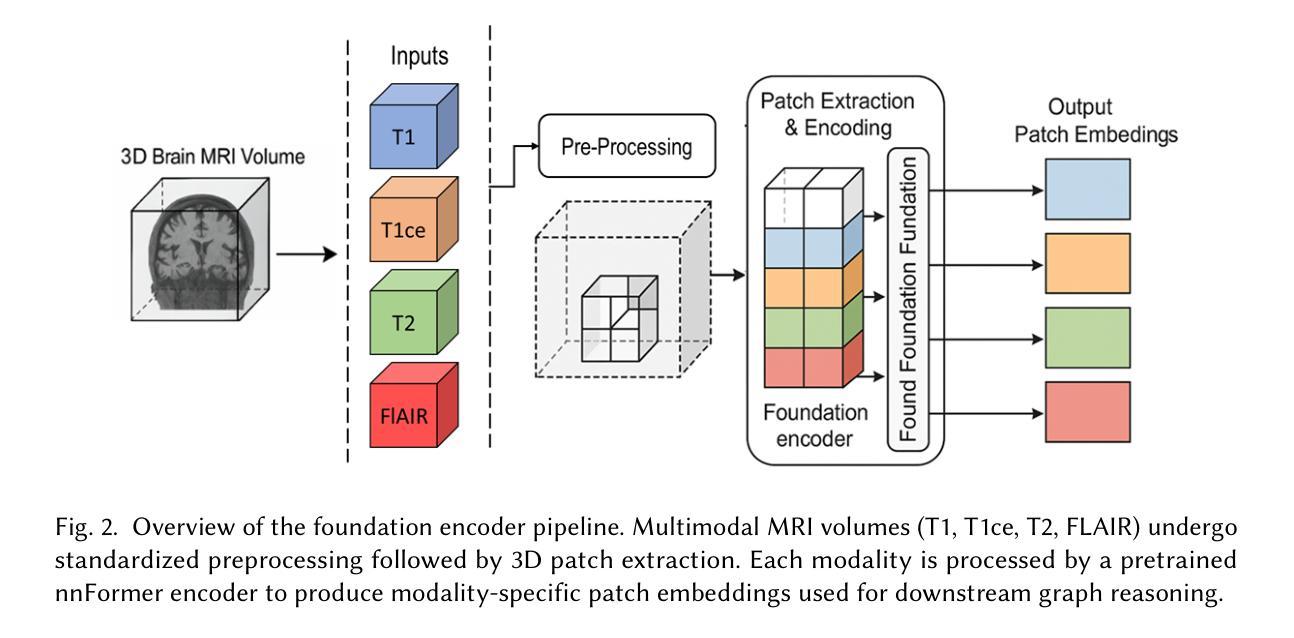
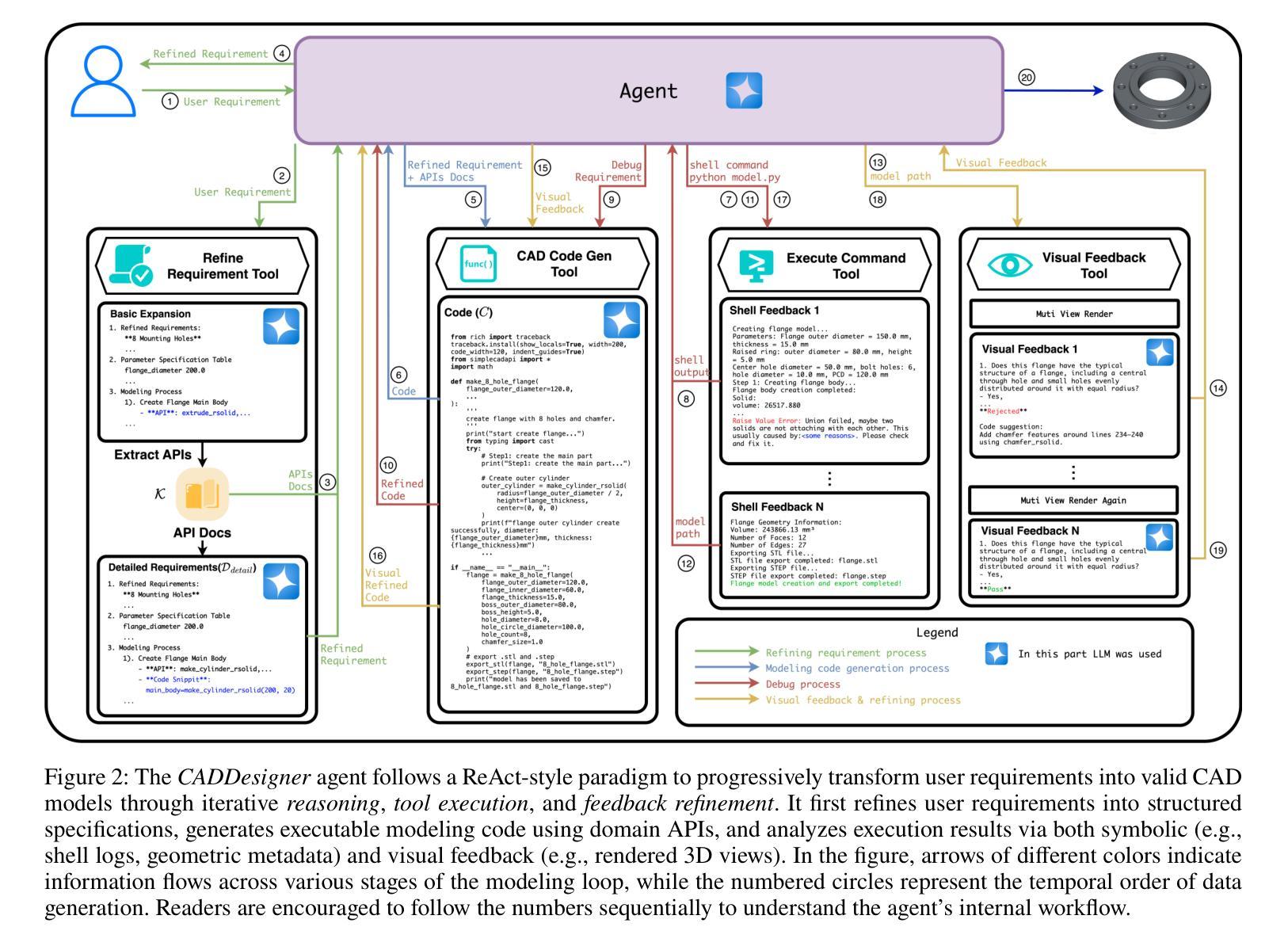
CADDesigner: Conceptual Design of CAD Models Based on General-Purpose Agent
Authors:Jingzhe Ni, Xiaolong Yin, Xingyu Lu, Xintong Li, Ji Wei, Ruofeng Tong, Min Tang, Peng Du
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a pivotal role in industrial manufacturing but typically requires a high level of expertise from designers. To lower the entry barrier and improve design efficiency, we present an agent for CAD conceptual design powered by large language models (LLMs). The agent accepts both abstract textual descriptions and freehand sketches as input, engaging in interactive dialogue with users to refine and clarify design requirements through comprehensive requirement analysis. Built upon a novel Context-Independent Imperative Paradigm (CIP), the agent generates high-quality CAD modeling code. During the generation process, the agent incorporates iterative visual feedback to improve model quality. Generated design cases are stored in a structured knowledge base, enabling continuous improvement of the agent’s code generation capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in CAD code generation.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工业制造中扮演着至关重要的角色,通常需要设计师具备高水平的专业知识。为了降低入门门槛并提高设计效率,我们提出了一种由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的CAD概念设计代理。该代理接受抽象的文本描述和手绘草图作为输入,通过全面的需求分析与用户进行交互对话,以细化和澄清设计要求。代理建立在新型上下文独立指令范式(CIP)之上,可生成高质量的CAD建模代码。在生成过程中,代理会融入迭代视觉反馈以提高模型质量。生成的案例被存储在结构化知识库中,使得代理的代码生成能力得以持续改进。实验结果表明,我们的方法在CAD代码生成方面达到了最先进的技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工业制造中的重要性,以及设计师通常需要具备高水平的专业知识这一现状,提出了一种采用大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的CAD概念设计代理。该代理接受抽象的文本描述和徒手草图作为输入,通过全面的需求分析与用户进行交互对话以明确和完善设计要求。它采用新颖的Context-Independent Imperative Paradigm(CIP)生成高质量的CAD建模代码。在生成过程中,代理结合迭代视觉反馈以提高模型质量。生成的案例存储在结构化知识库中,使得代理的代码生成能力得到持续提升。实验结果表明,该方法在CAD代码生成方面达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- CAD概念设计代理采用大型语言模型(LLM)技术,降低了CAD设计的门槛并提高了设计效率。
- 该代理可以接受抽象文本描述和徒手草图作为输入。
- 代理通过全面的需求分析与用户进行交互对话,以明确和完善设计要求。
- 采用新颖的Context-Independent Imperative Paradigm(CIP)生成高质量的CAD建模代码。
- 在代码生成过程中,代理结合迭代视觉反馈以提高模型质量。
- 生成的案例存储在结构化知识库中,使得代理的代码生成能力得到持续提升。
点此查看论文截图

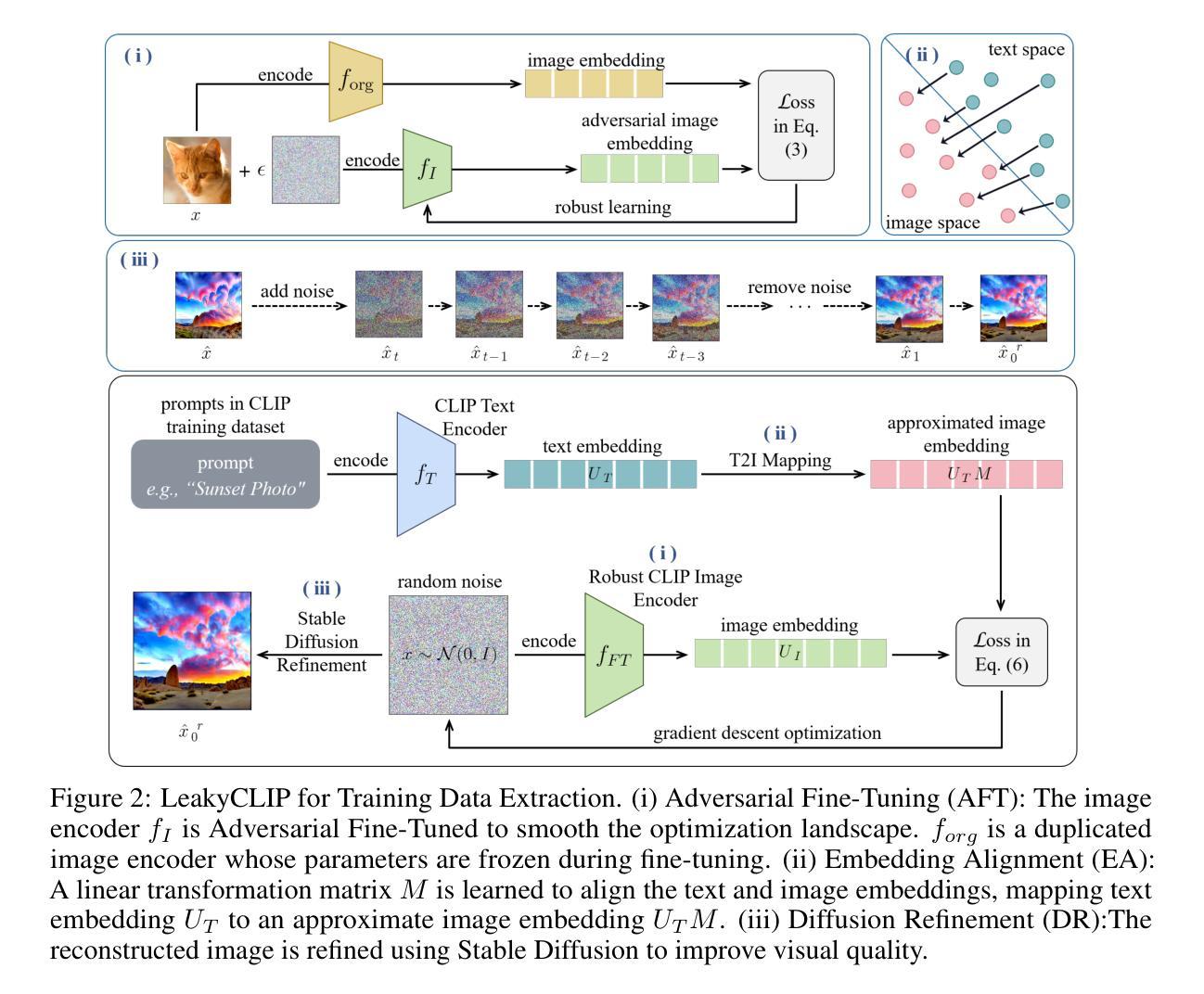
LeakyCLIP: Extracting Training Data from CLIP
Authors:Yunhao Chen, Shujie Wang, Xin Wang, Xingjun Ma
Understanding the memorization and privacy leakage risks in Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP) is critical for ensuring the security of multimodal models. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of extracting sensitive training examples from diffusion models, with conditional diffusion models exhibiting a stronger tendency to memorize and leak information. In this work, we investigate data memorization and extraction risks in CLIP through the lens of CLIP inversion, a process that aims to reconstruct training images from text prompts. To this end, we introduce \textbf{LeakyCLIP}, a novel attack framework designed to achieve high-quality, semantically accurate image reconstruction from CLIP embeddings. We identify three key challenges in CLIP inversion: 1) non-robust features, 2) limited visual semantics in text embeddings, and 3) low reconstruction fidelity. To address these challenges, LeakyCLIP employs 1) adversarial fine-tuning to enhance optimization smoothness, 2) linear transformation-based embedding alignment, and 3) Stable Diffusion-based refinement to improve fidelity. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of LeakyCLIP, achieving over 358% improvement in Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) for ViT-B-16 compared to baseline methods on LAION-2B subset. Furthermore, we uncover a pervasive leakage risk, showing that training data membership can even be successfully inferred from the metrics of low-fidelity reconstructions. Our work introduces a practical method for CLIP inversion while offering novel insights into the nature and scope of privacy risks in multimodal models.
了解对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)中的记忆和隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。最近的研究表明,从扩散模型中提取敏感训练样本是可行的,条件扩散模型在记忆和泄露信息方面表现出更强的倾向。在这项工作中,我们通过CLIP反转的视角来研究CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险。CLIP反转是一个旨在从文本提示中重建训练图像的过程。为此,我们引入了\textbf{LeakyCLIP},这是一个新的攻击框架,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。我们发现CLIP反转存在三个关键挑战:1)特征不稳健,2)文本嵌入中的视觉语义有限,以及3)重建保真度低。为了解决这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用1)对抗性微调以增强优化的平稳性,2)基于线性变换的嵌入对齐,以及3)基于Stable Diffusion的细化以提高保真度。经验结果表明LeakyCLIP的优越性,在LAION-2B子集上与基线方法相比,ViT-B-16的结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了358%以上。此外,我们发现了普遍的泄露风险,表明即使从低保真重建的指标中也可以成功推断出训练数据成员。我们的工作介绍了一种实用的CLIP反转方法,同时提供了关于多模态模型中隐私风险本质和范围的全新见解。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
理解对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)中的记忆与隐私泄露风险对于确保多模态模型的安全性至关重要。最新研究表明可以从扩散模型中提取敏感训练样本,并且条件扩散模型在记忆和泄露信息方面表现出更强的倾向。本研究通过CLIP反转的视角,探讨CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险。为此,我们引入了新型的攻击框架——LeakyCLIP,旨在从CLIP嵌入中实现高质量、语义准确的图像重建。我们确定了CLIP反转的三个关键挑战:1)非稳健特征;2)文本嵌入中的有限视觉语义;3)低重建保真度。为应对这些挑战,LeakyCLIP采用:1)对抗性微调以增强优化平滑度;2)基于线性变换的嵌入对齐;3)基于Stable Diffusion的改进以提高保真度。实证结果表明LeakyCLIP的优势,在LAION-2B子集上与基线方法相比,针对ViT-B-16的结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了358%以上。此外,我们发现了普遍的泄露风险,即使是从低保真重建的指标中,也能成功推断出训练数据成员。我们的工作不仅提供了CLIP反转的实际方法,还揭示了多模态模型中隐私风险的新特征和范围。
关键见解
- 对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在记忆和隐私泄露方面存在风险,这对多模态模型的安全性提出了挑战。
- 通过CLIP反转探究了CLIP中的数据记忆和提取风险。
- 引入了新型的攻击框架LeakyCLIP,实现了高质量、语义准确的图像重建。
- 确定了CLIP反转的三个关键挑战,并给出了相应的解决方案。
- LeakyCLIP在实证中表现出优越性能,提高了图像重建的保真度。
- 发现了普遍的泄露风险,即使低保真重建也能推断出训练数据成员。
点此查看论文截图



Microlocal analysis of non-linear operators arising in Compton CT
Authors:James W. Webber, Sean Holman
We present a novel microlocal analysis of a non-linear ray transform, $\mathcal{R}$, arising in Compton Scattering Tomography (CST). Due to attenuation effects in CST, the integral weights depend on the reconstruction target, $f$, which has singularities. Thus, standard linear Fourier Integral Operator (FIO) theory does not apply as the weights are non-smooth. The V-line (or broken ray) transform, $\mathcal{V}$, can be used to model the attenuation of incoming and outgoing rays. Through novel analysis of $\mathcal{V}$, we characterize the location and strength of the singularities of the ray transform weights. In conjunction, we provide new results which quantify the strength of the singularities of distributional products based on the Sobolev order of the individual components. By combining this new theory, our analysis of $\mathcal{V}$, and classical linear FIO theory, we determine the Sobolev order of the singularities of $\mathcal{R}f$. The strongest (lowest Sobolev order) singularities of $\mathcal{R}f$ are shown to correspond to the wavefront set elements of the classical Radon transform applied to $f$, and we use this idea and known results on the Radon transform to prove injectivity results for $\mathcal{R}$. In addition, we present novel reconstruction methods based on our theory, and we validate our results using simulated image reconstructions.
我们针对在康普顿散射断层扫描技术(CST)中出现的非线性射线变换$\mathcal{R}$提出了一种新的微局部分析。由于CST中的衰减效应,积分权重取决于具有奇异性的重建目标$f$。因此,标准的线性傅里叶积分算子(FIO)理论并不适用,因为权重是非光滑的。V线(或断线)变换$\mathcal{V}$可用于模拟入射和出射射线的衰减。通过对$\mathcal{V}$的新分析,我们表征了射线变换权重的奇异点的位置和强度。同时,我们提供了新的结果,根据各组件的Sobolev阶数量化分布产品奇异点的强度。通过结合这一新理论、我们对$\mathcal{V}$的分析和经典的线性FIO理论,我们确定了$\mathcal{R}f$的奇异点的Sobolev阶数。$\mathcal{R}f$的最强(最低Sobolev阶数)奇异点对应于经典Radon变换应用于$f$的波前集元素,我们使用这一思想以及Radon变换的已知结果来证明$\mathcal{R}$的单射性结果。此外,我们基于我们的理论提出了新颖的重构方法,并通过模拟图像重构验证了我们的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 8 figures
摘要
本文介绍了一种非线性的射线变换$\mathcal{R}$在康普顿散射断层扫描技术(CST)中的微局部分析。由于CST中的衰减效应,重建目标$f$的积分权重存在奇异性,因此标准的线性傅立叶积分算子理论不再适用。本文通过引入V线(或断裂射线)变换$\mathcal{V}$来模拟入射和出射射线的衰减,并对$\mathcal{V}$进行新型分析,以表征射线变换权重的奇异性位置和强度。结合基于Sobolev阶的分布式产品奇异性强度的新结果,通过结合这一新理论、我们对$\mathcal{V}$的分析以及经典的线性FIO理论,我们确定了$\mathcal{R}f$的奇异性Sobolev阶。$\mathcal{R}f$的最强(最低Sobolev阶)奇异性对应于经典Radon变换应用于$f$的波前集元素,我们利用这一思想以及Radon变换的已知结果来证明$\mathcal{R}$的注入性结果。此外,我们基于理论提出了新型重建方法,并通过模拟图像重建验证了我们的结果。
关键见解
- 介绍了非线性的射线变换$\mathcal{R}$在康普顿散射断层扫描技术中的微局部分析。
- 由于衰减效应,标准线性傅立叶积分算子理论不再适用于射线变换。
- 通过V线(或断裂射线)变换$\mathcal{V}$模拟入射和出射射线的衰减。
- 分析了射线变换权重的奇异性位置和强度。
- 结合新理论和经典线性FIO理论,确定了$\mathcal{R}f$的奇异性Sobolev阶。
- $\mathcal{R}f$的最强奇异性与经典Radon变换应用于$f$的波前集元素相对应。
点此查看论文截图

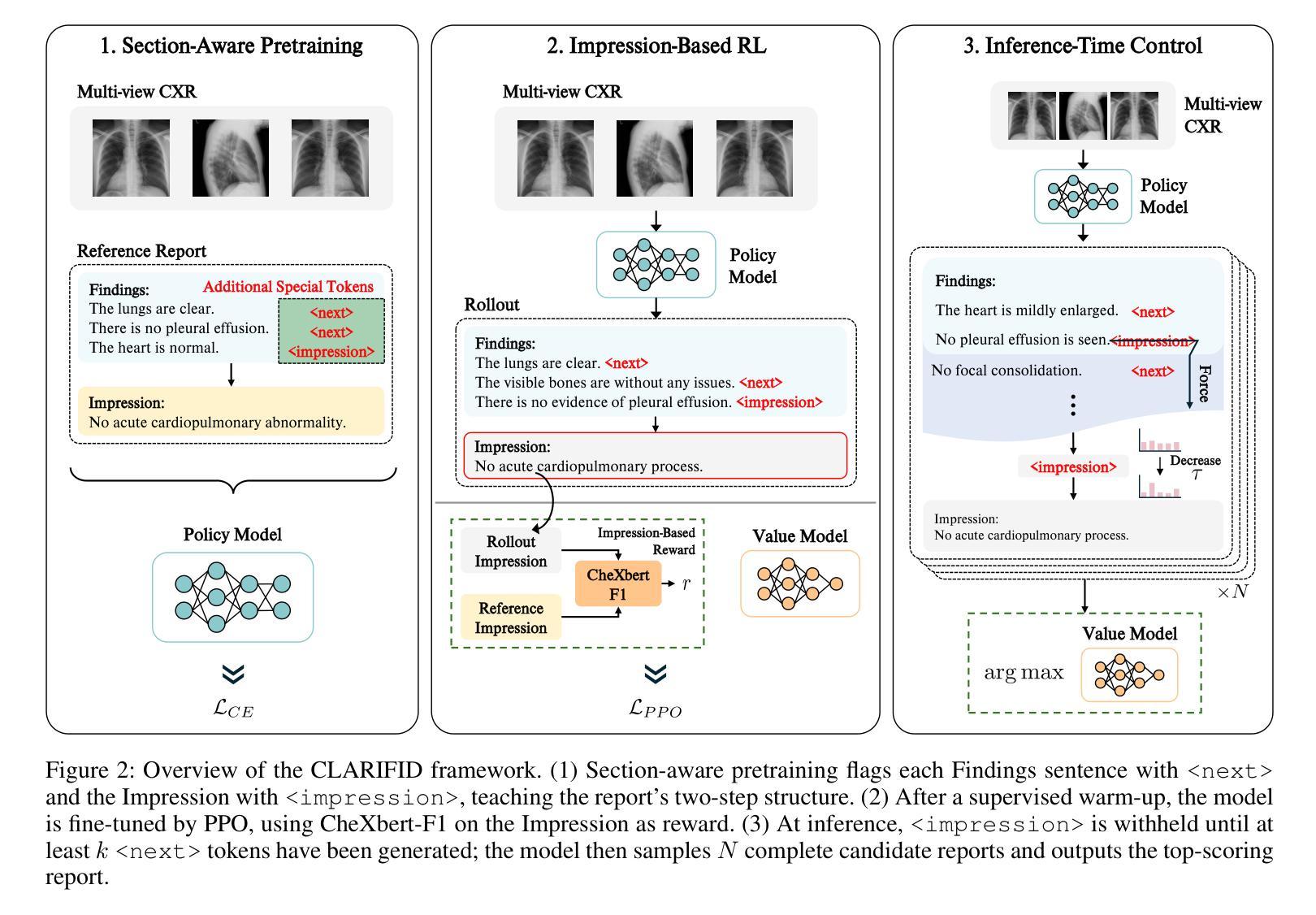
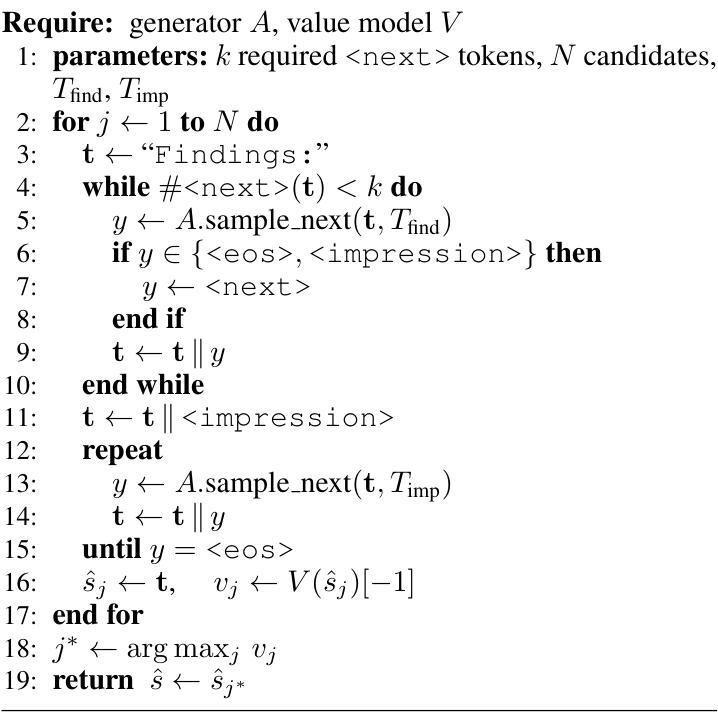
CLARIFID: Improving Radiology Report Generation by Reinforcing Clinically Accurate Impressions and Enforcing Detailed Findings
Authors:Kyeongkyu Lee, Seonghwan Yoon, Hongki Lim
Automatic generation of radiology reports has the potential to alleviate radiologists’ significant workload, yet current methods struggle to deliver clinically reliable conclusions. In particular, most prior approaches focus on producing fluent text without effectively ensuring the factual correctness of the reports and often rely on single-view images, limiting diagnostic comprehensiveness. We propose CLARIFID, a novel framework that directly optimizes diagnostic correctness by mirroring the two-step workflow of experts. Specifically, CLARIFID (1) learns the logical flow from Findings to Impression through section-aware pretraining, (2) is fine-tuned with Proximal Policy Optimization in which the CheXbert F1 score of the Impression section serves as the reward, (3) enforces reasoning-aware decoding that completes “Findings” before synthesizing the “Impression”, and (4) fuses multiple chest X-ray views via a vision-transformer-based multi-view encoder. During inference, we apply a reasoning-aware next-token forcing strategy followed by report-level re-ranking, ensuring that the model first produces a comprehensive Findings section before synthesizing the Impression and thereby preserving coherent clinical reasoning. Experimental results on the MIMIC-CXR dataset demonstrate that our method achieves superior clinical efficacy and outperforms existing baselines on both standard NLG metrics and clinically aware scores.
自动生成的放射学报告具有缓解放射科医生巨大工作量的潜力,但当前的方法在临床可靠结论的生成方面仍存在困难。尤其,大多数先前的方法主要关注生成流畅文本,未能有效地确保报告的事实正确性,并且常依赖于单一视图图像,从而限制了诊断的全面性。我们提出了CLARIFID这一新型框架,它直接优化诊断的正确性,通过镜像专家的两步工作流程。具体来说,CLARIFID(1)通过分段预训练学习从检查结果到印象的逻辑流程,(2)使用近端策略优化进行微调,其中以印象部分的CheXbert F1分数作为奖励,(3)强制执行推理感知解码,在完成“检查结果”后再合成“印象”,(4)通过基于视觉变换器的多视图编码器融合多个胸部X射线视图。在推理过程中,我们应用了一种推理感知的下一个标记强制策略,然后进行报告级别的重新排序,确保模型首先生成全面的检查结果部分,然后再合成印象,从而保持连贯的临床推理。在MIMIC-CXR数据集上的实验结果证明,我们的方法达到了卓越的临床效果,并在标准自然语言生成指标和临床意识得分上超越了现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CLARIFID的新框架,用于自动生成放射学报告。该框架旨在优化诊断正确性,通过模仿专家两步工作流程,包括逻辑流学习、基于近端策略优化的精细调整、推理感知解码以及多视角融合的图像分析。实验结果在MIMIC-CXR数据集上证明了其临床有效性和性能优势。
Key Takeaways
- CLARIFID框架旨在缓解放射科医生的工作负担,通过自动生成放射学报告优化诊断正确性。
- 该框架模仿专家两步工作流程,包括逻辑流学习、精细调整、推理感知解码和多视角融合的图像分析。
- CLARIFID通过section-aware预训练学习从“发现”到“印象”的逻辑流。
- 使用近端策略优化进行精细调整,以CheXbert F1分数作为奖励。
- 框架强制实施推理感知解码,先完成“发现”部分再合成“印象”。
- 通过视觉变压器进行多视角编码融合,提高诊断的全面性。
- 在推理过程中采用推理感知的下一个令牌强制策略,确保报告的连贯性和临床推理的完整性。
点此查看论文截图

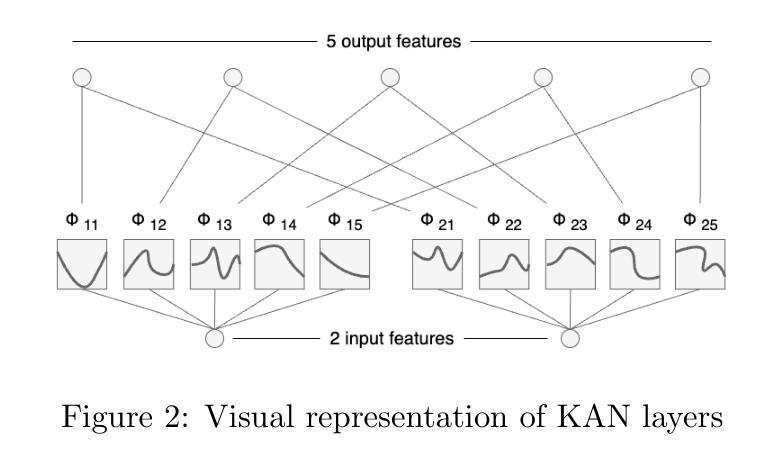
Capsule-ConvKAN: A Hybrid Neural Approach to Medical Image Classification
Authors:Laura Pituková, Peter Sinčák, László József Kovács, Peng Wang
This study conducts a comprehensive comparison of four neural network architectures: Convolutional Neural Network, Capsule Network, Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Network, and the newly proposed Capsule-Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Network. The proposed Capsule-ConvKAN architecture combines the dynamic routing and spatial hierarchy capabilities of Capsule Network with the flexible and interpretable function approximation of Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. This novel hybrid model was developed to improve feature representation and classification accuracy, particularly in challenging real-world biomedical image data. The architectures were evaluated on a histopathological image dataset, where Capsule-ConvKAN achieved the highest classification performance with an accuracy of 91.21%. The results demonstrate the potential of the newly introduced Capsule-ConvKAN in capturing spatial patterns, managing complex features, and addressing the limitations of traditional convolutional models in medical image classification.
本研究对四种神经网络架构进行了全面比较:卷积神经网络、胶囊网络、卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络以及新提出的胶囊-卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络。所提出的Capsule-ConvKAN架构结合了胶囊网络的动态路由和空间层次能力与卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的灵活和可解释函数逼近。这种新型混合模型旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在具有挑战性的现实世界生物医学图像数据中。这些架构在一个病理图像数据集上进行了评估,其中Capsule-ConvKAN获得了最高的分类性能,准确率为9.2%。结果表明,新引入的Capsule-ConvKAN在捕获空间模式、管理复杂特征以及解决医学图像分类中传统卷积模型的局限性方面具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version. Accepted to IEEE SMC 2025
Summary
本研究全面比较了四种神经网络架构,包括卷积神经网络、胶囊网络、卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络以及新提出的胶囊-卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(Capsule-ConvKAN)。新提出的Capsule-ConvKAN架构结合了胶囊网络的动态路由和空间层次能力,以及卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的灵活和可解释函数逼近能力。该混合模型旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在具有挑战性的真实世界生物医学图像数据中。在病理图像数据集上评估这些架构时,Capsule-ConvKAN获得了最高的分类性能,准确率为91.21%。结果表明,新引入的Capsule-ConvKAN在捕获空间模式、管理复杂特征以及解决医疗图像分类中传统卷积模型的局限性方面具有潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究对四种神经网络架构进行了全面比较,包括卷积神经网络、胶囊网络、卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络以及创新的Capsule-ConvKAN架构。
- Capsule-ConvKAN结合了胶囊网络和卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的优点,旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在处理具有挑战性的生物医学图像数据时。
- 在病理图像数据集上,Capsule-ConvKAN架构获得了最高的分类性能,准确率为91.21%。
- Capsule-ConvKAN架构具有捕获空间模式和管理复杂特征的能力。
- 新研究结果表明Capsule-ConvKAN有潜力克服传统卷积模型在医疗图像分类中的局限性。
- 该研究为神经网络在生物医学图像分类领域的应用提供了新的见解和可能的改进方向。
点此查看论文截图

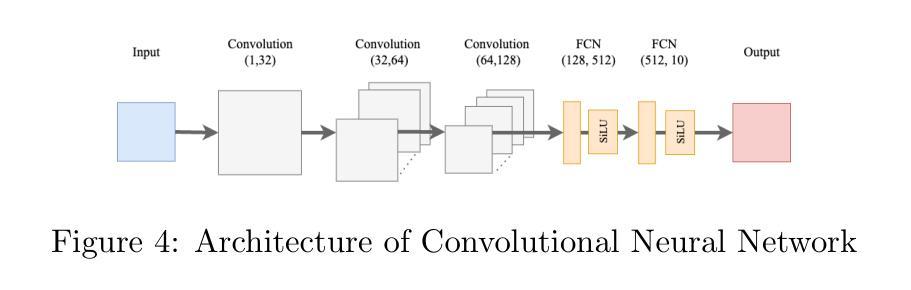
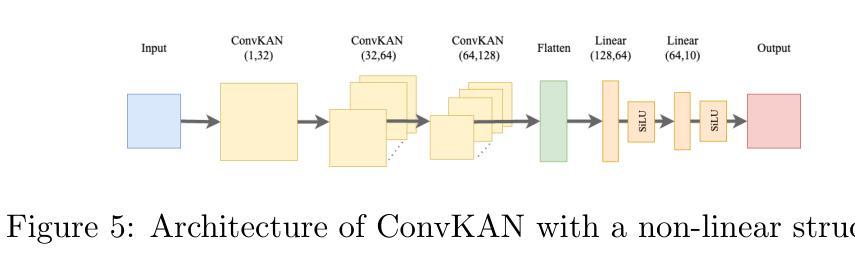
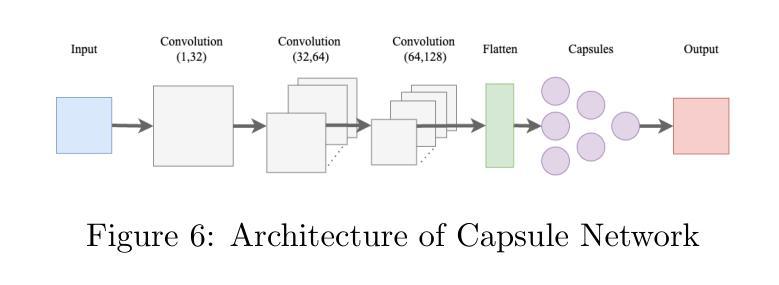
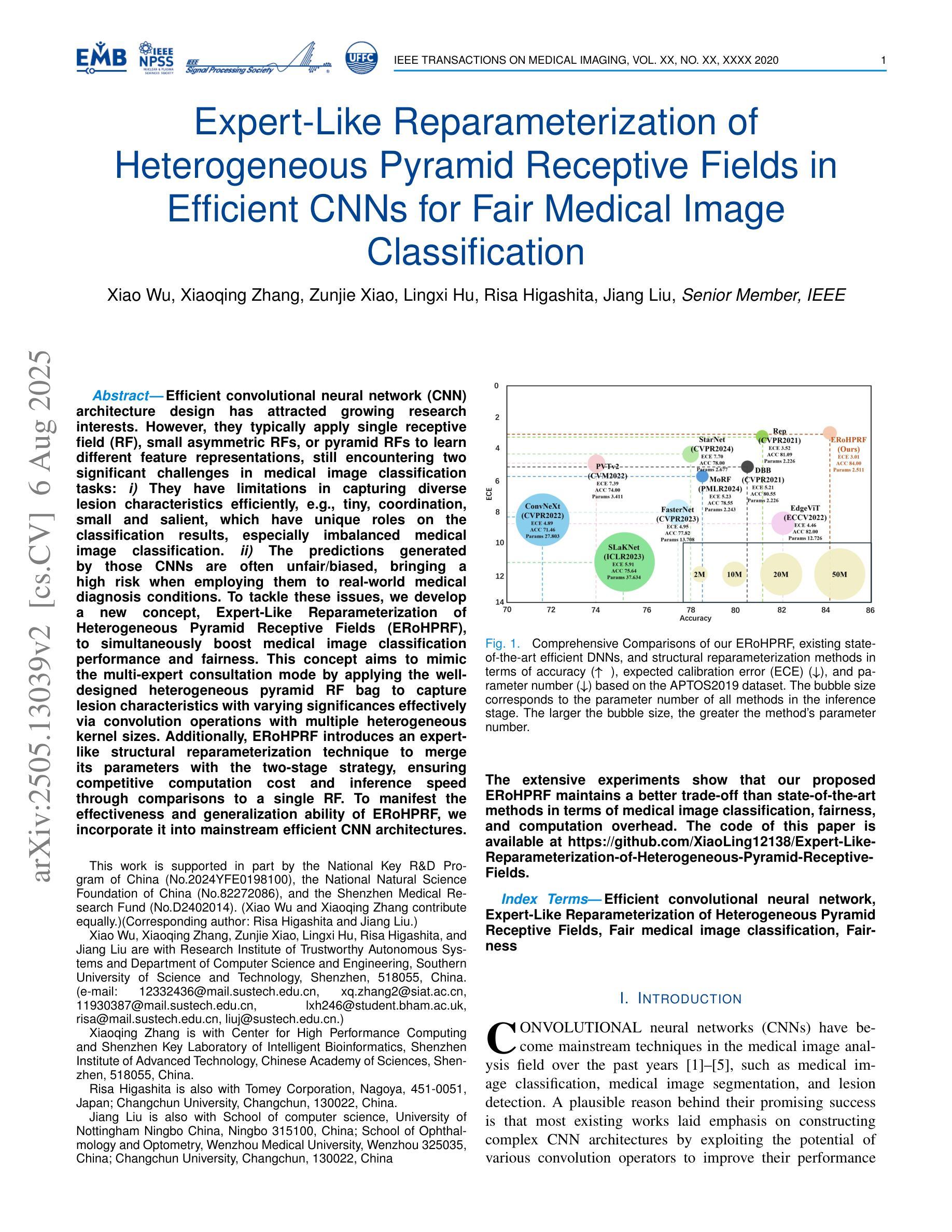
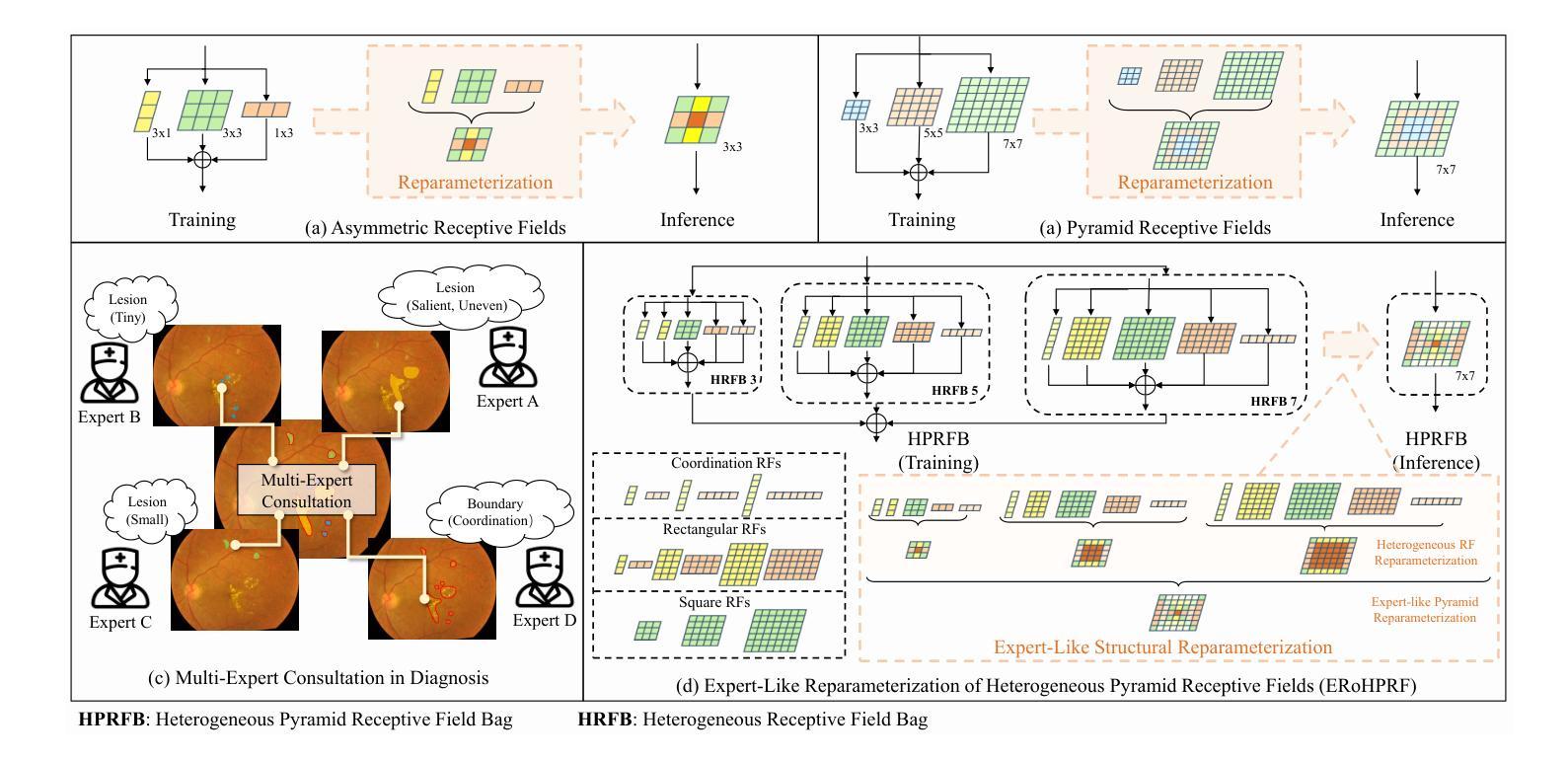
Expert-Like Reparameterization of Heterogeneous Pyramid Receptive Fields in Efficient CNNs for Fair Medical Image Classification
Authors:Xiao Wu, Xiaoqing Zhang, Zunjie Xiao, Lingxi Hu, Risa Higashita, Jiang Liu
Efficient convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture design has attracted growing research interests. However, they typically apply single receptive field (RF), small asymmetric RFs, or pyramid RFs to learn different feature representations, still encountering two significant challenges in medical image classification tasks: 1) They have limitations in capturing diverse lesion characteristics efficiently, e.g., tiny, coordination, small and salient, which have unique roles on the classification results, especially imbalanced medical image classification. 2) The predictions generated by those CNNs are often unfair/biased, bringing a high risk when employing them to real-world medical diagnosis conditions. To tackle these issues, we develop a new concept, Expert-Like Reparameterization of Heterogeneous Pyramid Receptive Fields (ERoHPRF), to simultaneously boost medical image classification performance and fairness. This concept aims to mimic the multi-expert consultation mode by applying the well-designed heterogeneous pyramid RF bag to capture lesion characteristics with varying significances effectively via convolution operations with multiple heterogeneous kernel sizes. Additionally, ERoHPRF introduces an expert-like structural reparameterization technique to merge its parameters with the two-stage strategy, ensuring competitive computation cost and inference speed through comparisons to a single RF. To manifest the effectiveness and generalization ability of ERoHPRF, we incorporate it into mainstream efficient CNN architectures. The extensive experiments show that our proposed ERoHPRF maintains a better trade-off than state-of-the-art methods in terms of medical image classification, fairness, and computation overhead. The code of this paper is available at https://github.com/XiaoLing12138/Expert-Like-Reparameterization-of-Heterogeneous-Pyramid-Receptive-Fields.
卷积神经网络(CNN)架构设计的效率已引起越来越多的研究兴趣。然而,它们通常应用单一感受野(RF)、小的不对称感受野或金字塔感受野来学习不同的特征表示,在医学图像分类任务中仍然面临两大挑战:1)它们在有效捕获各种病变特征方面存在局限性,例如微小、协调、小而显著的特征,这些特征对分类结果具有独特作用,特别是在不平衡医学图像分类中。2)这些CNN生成的预测往往不公平/存在偏见,在将其应用于真实世界医学诊断条件时存在高风险。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一个新的概念,即异质金字塔感受野的专家型再参数化(ERoHPRF),以同时提高医学图像分类的性能和公平性。该概念旨在通过应用设计精良的异质金字塔感受野袋来模仿多专家咨询模式,通过具有多种异构内核大小的卷积操作有效地捕获具有不同重要性的病变特征。此外,ERoHPRF引入了一种专家型结构再参数化技术,将其参数与两阶段策略相结合,通过与单一感受野进行比较,确保具有竞争力的计算成本和推理速度。为了证明ERoHPRF的有效性和通用性,我们将其纳入主流的简洁CNN架构中。大量实验表明,我们提出的ERoHPRF在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销方面比最先进的方法有更好的折衷。本文的代码可在[https://github.com/XiaoLing12138/Expert-Like-Reparameterization-of-Heterogeneous-Pyramid-Receptive-Fields]中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
卷积神经网络(CNN)架构的设计在医学图像分类任务中面临两大挑战:一是难以有效捕捉多种病变特征;二是预测结果可能存在不公平性/偏见。为此,本文提出了一个新的概念——Expert-Like Reparameterization of Heterogeneous Pyramid Receptive Fields(ERoHPRF),旨在通过应用设计精良的异质金字塔感受野袋来模拟多专家会诊模式,通过具有多种异质内核大小的卷积操作有效捕捉不同显著性的病变特征。同时,ERoHPRF引入了一种专家型结构重参数化技术,通过两阶段策略合并其参数,以确保计算成本和推理速度与单一感受野相比具有竞争力。实验表明,本文提出的ERoHPRF在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销方面达到了更优化的平衡。
关键要点
- CNN在医学图像分类中面临捕捉多样病变特征的挑战,特别是针对微小、协调、小而显著等独特作用的病变。
- 现有CNN预测存在不公平/偏见问题,应用于实际医疗诊断时存在高风险。
- 提出ERoHPRF新概念,模拟多专家会诊模式,通过异质金字塔感受野袋有效捕捉病变特征。
- ERoHPRF引入专家型结构重参数化技术,通过两阶段策略优化计算成本和推理速度。
- ERoHPRF在主流高效CNN架构中的集成实验表明,与最新技术相比,它在医学图像分类、公平性和计算开销之间达到了更好的平衡。
- 代码已公开,可在指定链接下载。
点此查看论文截图
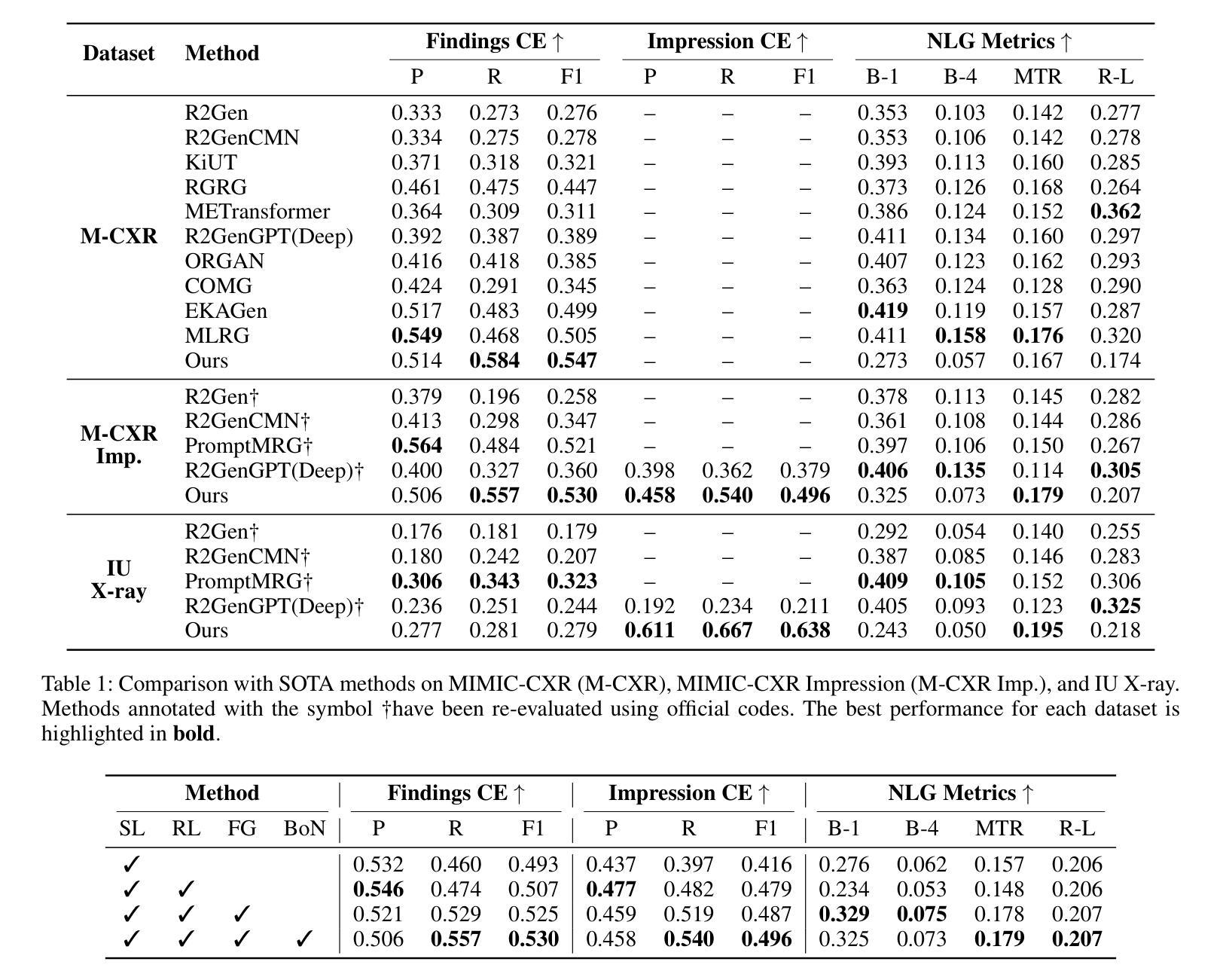
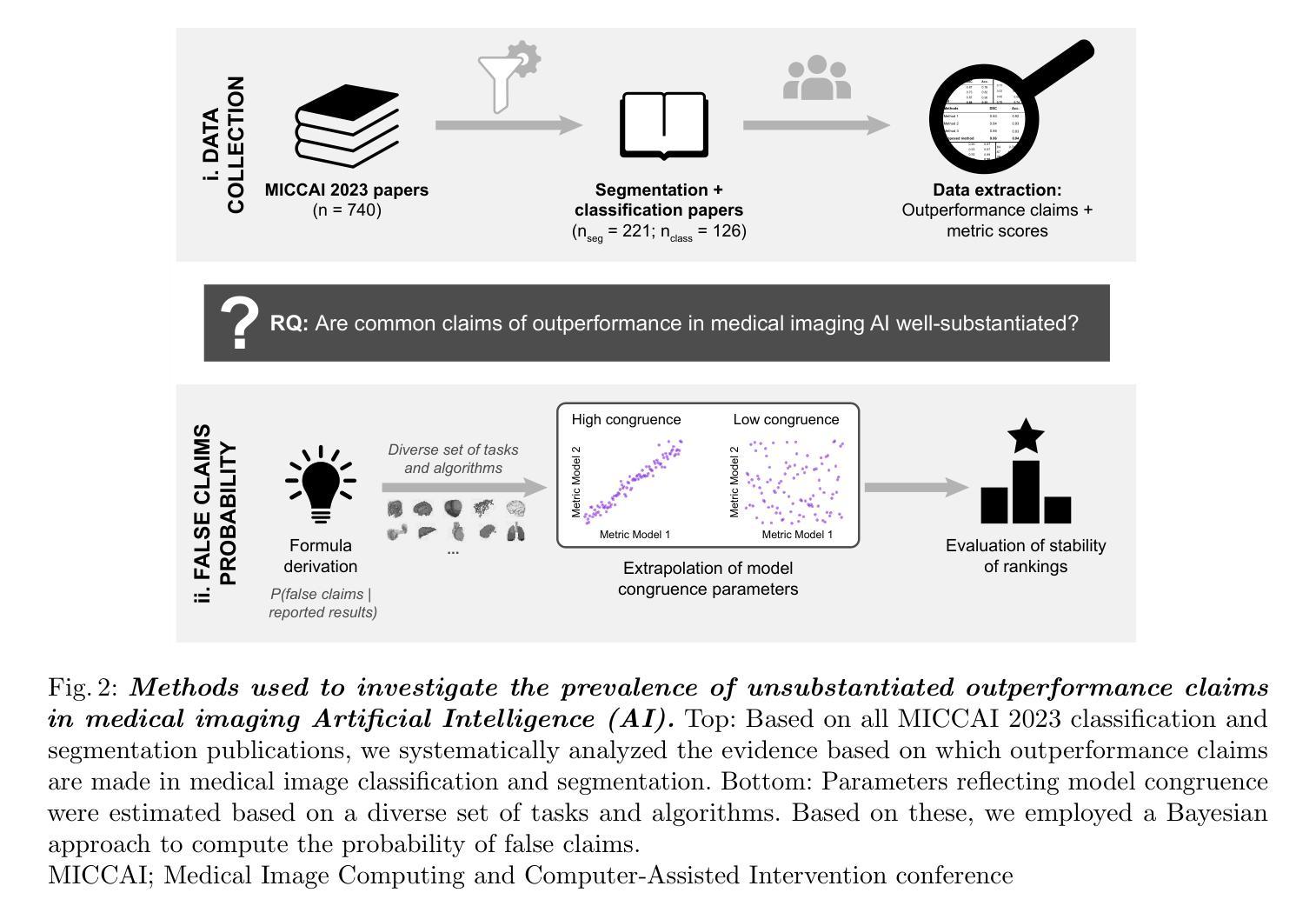
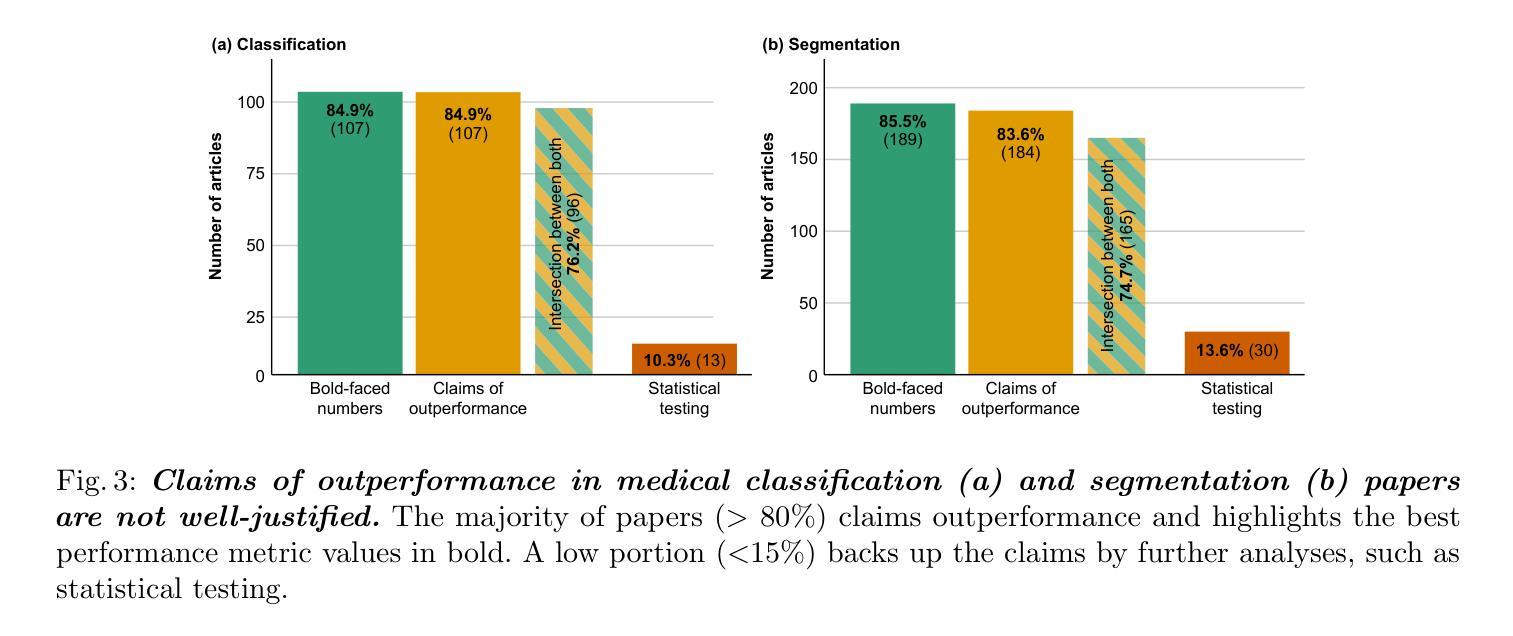
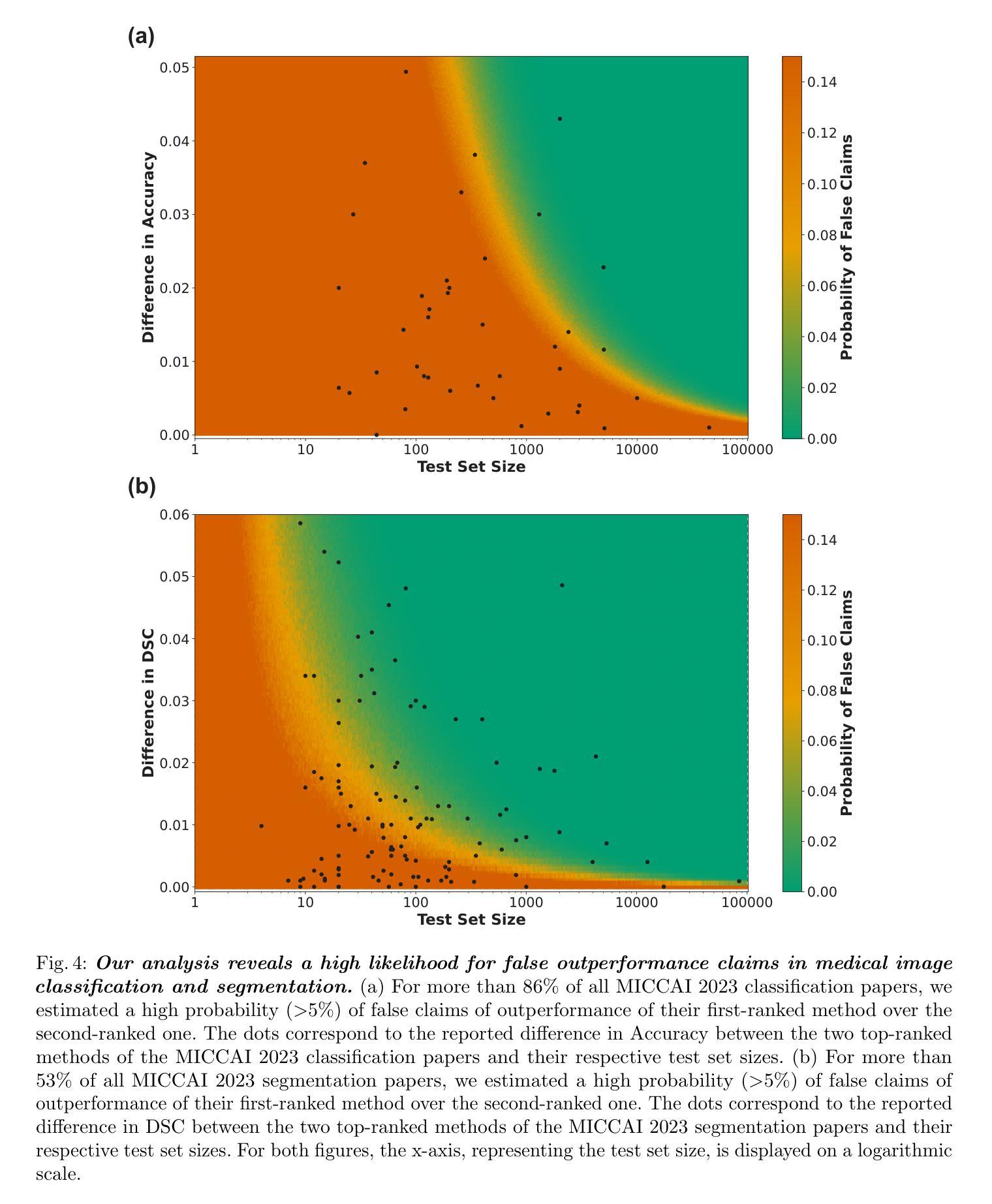
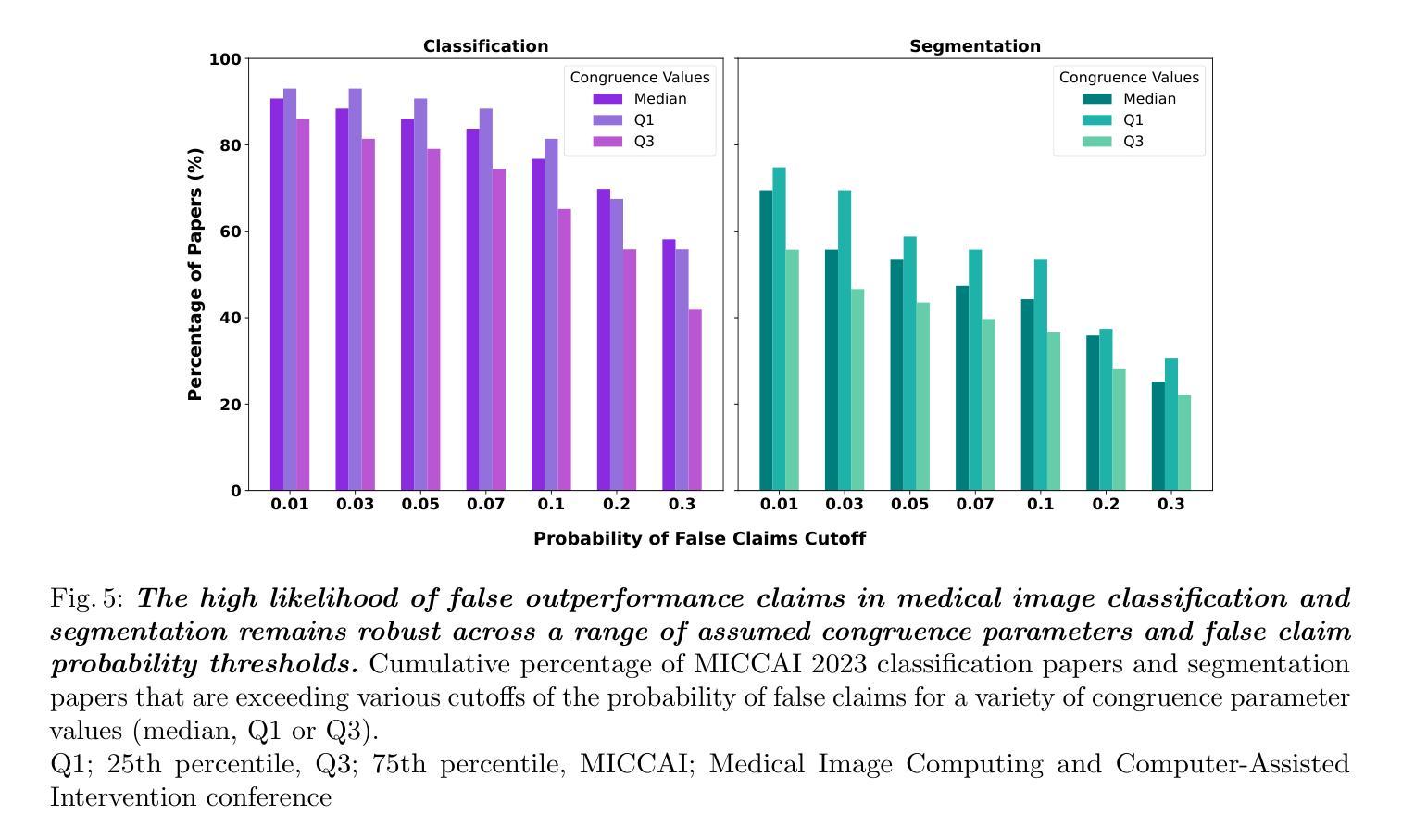
False Promises in Medical Imaging AI? Assessing Validity of Outperformance Claims
Authors:Evangelia Christodoulou, Annika Reinke, Pascaline Andrè, Patrick Godau, Piotr Kalinowski, Rola Houhou, Selen Erkan, Carole H. Sudre, Ninon Burgos, Sofiène Boutaj, Sophie Loizillon, Maëlys Solal, Veronika Cheplygina, Charles Heitz, Michal Kozubek, Michela Antonelli, Nicola Rieke, Antoine Gilson, Leon D. Mayer, Minu D. Tizabi, M. Jorge Cardoso, Amber Simpson, Annette Kopp-Schneider, Gaël Varoquaux, Olivier Colliot, Lena Maier-Hein
Performance comparisons are fundamental in medical imaging Artificial Intelligence (AI) research, often driving claims of superiority based on relative improvements in common performance metrics. However, such claims frequently rely solely on empirical mean performance. In this paper, we investigate whether newly proposed methods genuinely outperform the state of the art by analyzing a representative cohort of medical imaging papers. We quantify the probability of false claims based on a Bayesian approach that leverages reported results alongside empirically estimated model congruence to estimate whether the relative ranking of methods is likely to have occurred by chance. According to our results, the majority (>80%) of papers claims outperformance when introducing a new method. Our analysis further revealed a high probability (>5%) of false outperformance claims in 86% of classification papers and 53% of segmentation papers. These findings highlight a critical flaw in current benchmarking practices: claims of outperformance in medical imaging AI are frequently unsubstantiated, posing a risk of misdirecting future research efforts.
在医学成像人工智能(AI)研究中,性能比较是根本,通常基于通用性能指标上的相对改进来提出优越性主张。然而,此类主张往往仅依赖于经验平均性能。在本文中,我们通过分析具有代表性的医学成像论文,研究新提出的方法是否真正优于最新技术。我们基于贝叶斯方法量化错误主张的概率,该方法利用报告的结果以及经验估计的模型一致性来估计方法的相对排名是否可能偶然发生。根据我们的结果,在引入新方法时,大多数(> 80%)的论文都声称性能有所提高。我们的分析还显示,分类论文中有高达86%以及分割论文中有高达53%的论文存在虚假的性能提升主张概率较高(> 5%)。这些发现突显了当前基准测试实践中的一个关键缺陷:医学成像人工智能的性能提升主张往往缺乏依据,存在误导未来研究努力的风险。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文调查了医学成像人工智能(AI)研究中新提出的方法是否真正优于现有技术。通过分析代表性医学成像论文,基于贝叶斯方法和报告结果的模型一致性估计,发现大多数论文(超过80%)声称新方法优于现有技术,但分类论文中有超过5%的概率存在虚假性能声称。本文揭示了当前基准测试实践中的关键缺陷:医学成像AI的性能提升声称往往缺乏依据,误导未来研究工作的风险很高。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像AI研究中的性能比较至关重要,通常基于常见性能指标上的相对改进来宣称优越性。
- 大多数医学成像论文(超过80%)声称新方法优于现有技术。
- 基于贝叶斯方法和报告结果的模型一致性估计,存在虚假性能声称的可能性。
- 分类论文中存在较高的虚假性能声称概率(超过5%)。
- 当前基准测试实践存在关键缺陷,性能提升声称缺乏依据。
- 医学成像AI的误导向研究风险较高。
点此查看论文截图

CMT: A Cascade MAR with Topology Predictor for Multimodal Conditional CAD Generation
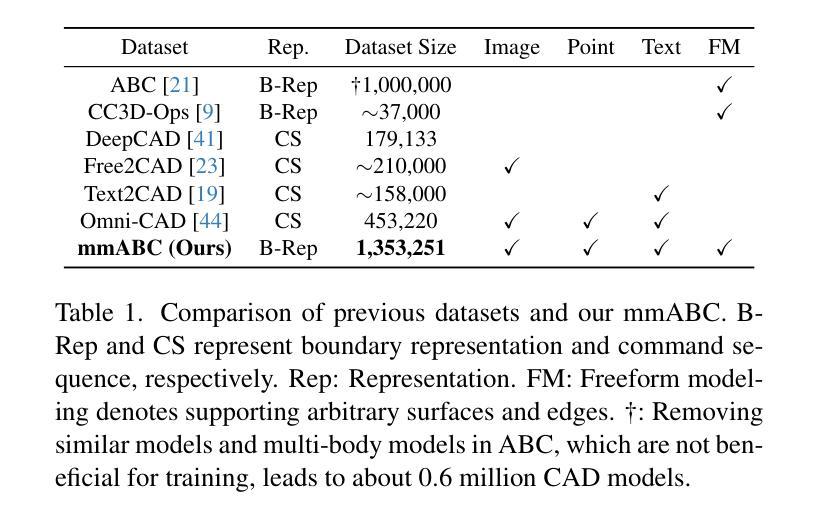
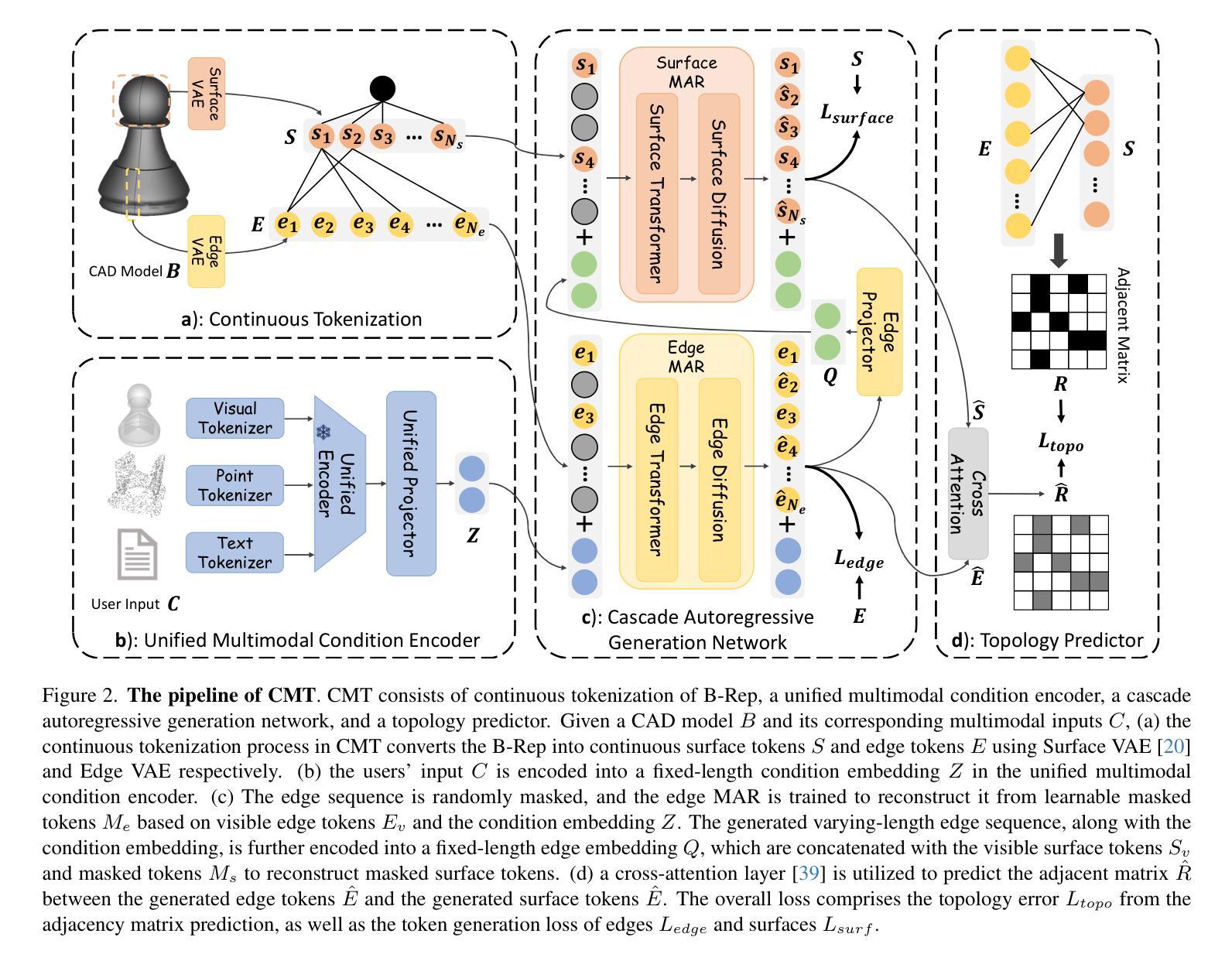
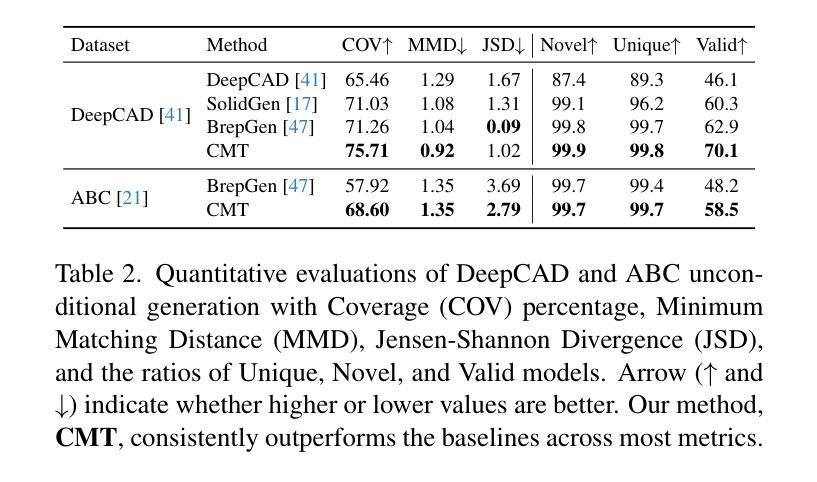
Authors:Jianyu Wu, Yizhou Wang, Xiangyu Yue, Xinzhu Ma, Jingyang Guo, Dongzhan Zhou, Wanli Ouyang, Shixiang Tang
While accurate and user-friendly Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is crucial for industrial design and manufacturing, existing methods still struggle to achieve this due to their over-simplified representations or architectures incapable of supporting multimodal design requirements. In this paper, we attempt to tackle this problem from both methods and datasets aspects. First, we propose a cascade MAR with topology predictor (CMT), the first multimodal framework for CAD generation based on Boundary Representation (B-Rep). Specifically, the cascade MAR can effectively capture the ``edge-counters-surface’’ priors that are essential in B-Reps, while the topology predictor directly estimates topology in B-Reps from the compact tokens in MAR. Second, to facilitate large-scale training, we develop a large-scale multimodal CAD dataset, mmABC, which includes over 1.3 million B-Rep models with multimodal annotations, including point clouds, text descriptions, and multi-view images. Extensive experiments show the superior of CMT in both conditional and unconditional CAD generation tasks. For example, we improve Coverage and Valid ratio by +10.68% and +10.3%, respectively, compared to state-of-the-art methods on ABC in unconditional generation. CMT also improves +4.01 Chamfer on image conditioned CAD generation on mmABC.
在计算机辅助设计(CAD)领域,准确且用户友好的CAD对于工业设计和制造至关重要。然而,由于现有方法的表示过于简化或架构不支持多模式设计需求,因此仍难以实现这一目标。在本文中,我们尝试从方法和数据集两个方面来解决这个问题。首先,我们提出了一种基于边界表示(B-Rep)的级联MAR与拓扑预测器(CMT),这是首个用于CAD生成的多模式框架。具体而言,级联MAR可以有效地捕获B-Rep中必不可少的“边缘对表面”的先验知识,而拓扑预测器则直接从MAR的紧凑标记中估计B-Rep的拓扑结构。其次,为了促进大规模训练,我们开发了一个大规模的多模式CAD数据集mmABC,其中包含超过130万个带有多模式注释的B-Rep模型,包括点云、文本描述和多个图像视图。大量实验表明,CMT在有条件和无条件的CAD生成任务中都表现出卓越的性能。例如,在无条件生成中,与最先进的方法相比,我们在ABC上的覆盖率和有效比率分别提高了+10.68%和+10.3%。在mmABC的图像条件CAD生成中,CMT的Chamfer值提高了+4.01。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于边界表示(B-Rep)的多模态计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成框架,包括级联的多模态架构(CMT)和拓扑预测器。CMT能有效捕捉B-Rep中的“边缘计数表面”先验信息,而拓扑预测器则直接从CMT的紧凑标记中估计拓扑结构。此外,为支持大规模训练,开发了一个大型多模态CAD数据集mmABC,包含超过130万带有多模态注释的B-Rep模型。实验表明,CMT在条件和无条件CAD生成任务上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的多模态计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成框架,解决了现有方法过于简化或无法支持多模态设计的问题。
- 该框架包含级联的多模态架构(CMT)和拓扑预测器,能有效捕捉B-Rep中的关键先验信息并估计拓扑结构。
- 为支持大规模训练,开发了一个大型多模态CAD数据集mmABC,包含丰富的B-Rep模型和多种模态的注释。
- 实验结果表明,CMT在CAD生成任务上表现优越,特别是在无条件生成和图像条件生成方面。
- 与现有技术相比,CMT在覆盖率、有效率和Chamfer等指标上都有显著提高。
- 该研究为工业设计和制造领域提供了更准确、用户友好的计算机辅助设计工具。
点此查看论文截图

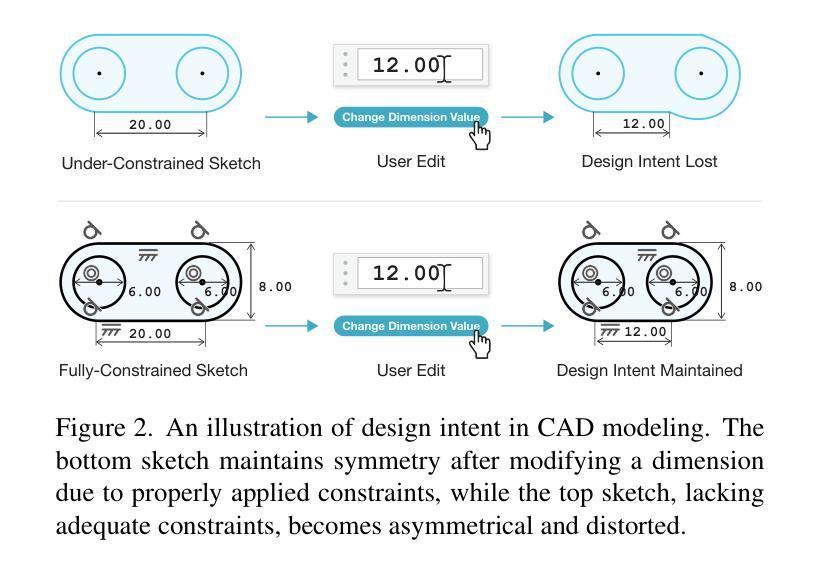
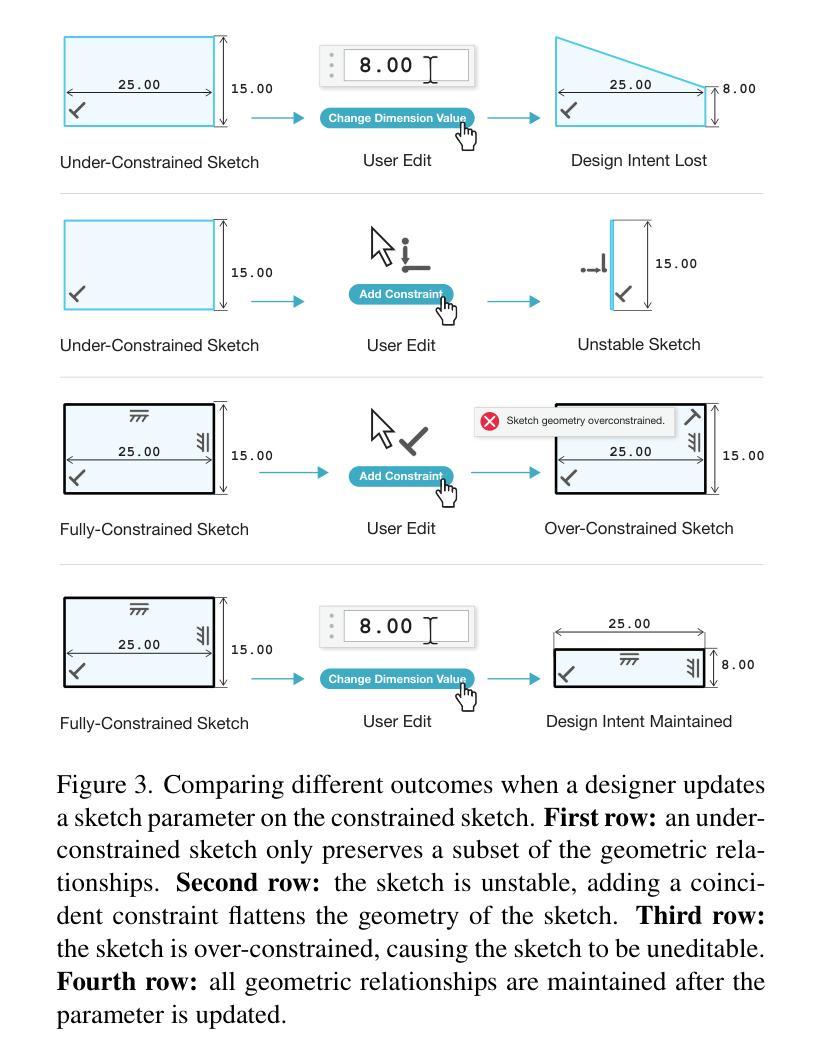
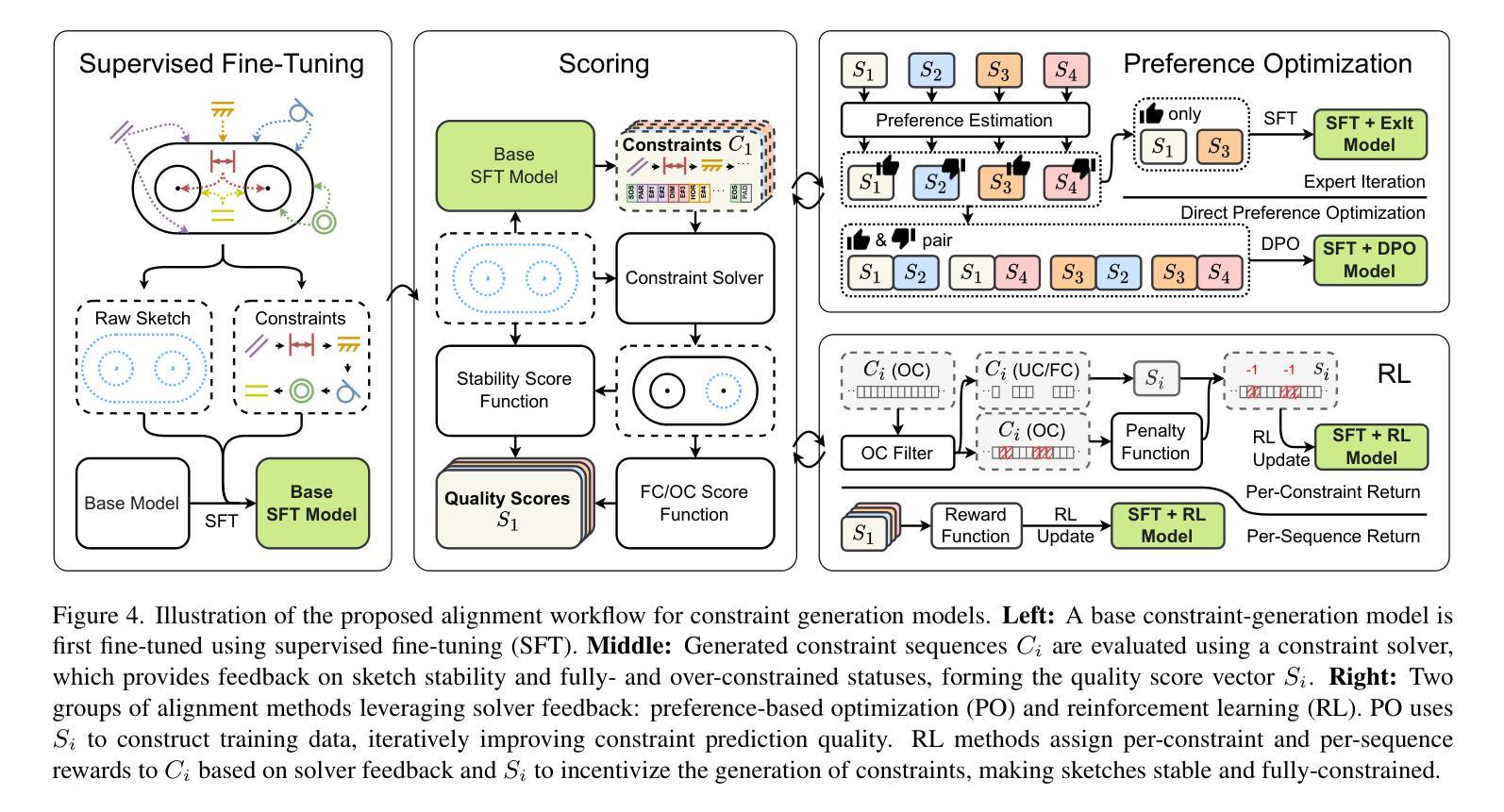
Aligning Constraint Generation with Design Intent in Parametric CAD
Authors:Evan Casey, Tianyu Zhang, Shu Ishida, William P. McCarthy, John Roger Thompson, Amir Khasahmadi, Joseph George Lambourne, Pradeep Kumar Jayaraman, Karl D. D. Willis
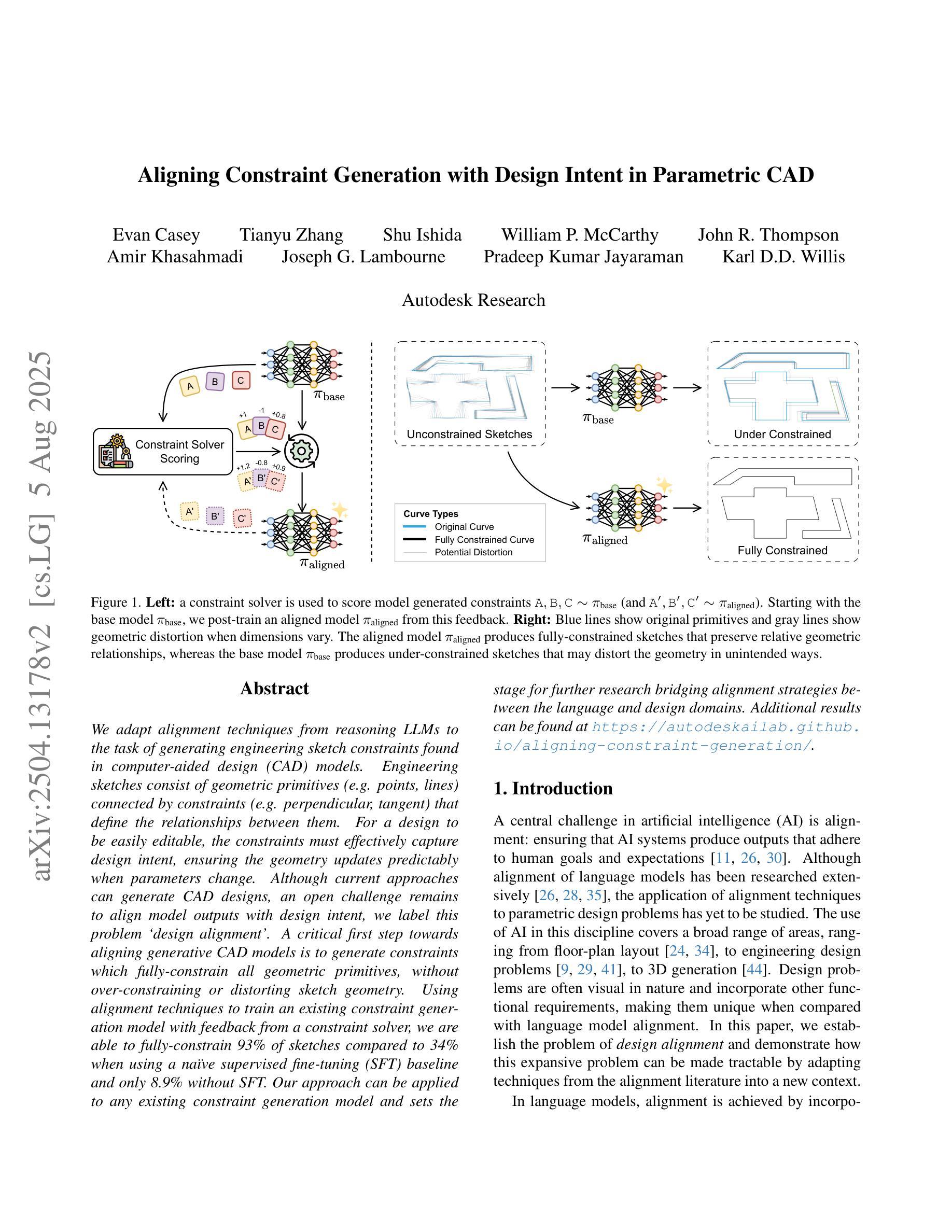
We adapt alignment techniques from reasoning LLMs to the task of generating engineering sketch constraints found in computer-aided design (CAD) models. Engineering sketches consist of geometric primitives (e.g. points, lines) connected by constraints (e.g. perpendicular, tangent) that define the relationships between them. For a design to be easily editable, the constraints must effectively capture design intent, ensuring the geometry updates predictably when parameters change. Although current approaches can generate CAD designs, an open challenge remains to align model outputs with design intent, we label this problem ‘design alignment’. A critical first step towards aligning generative CAD models is to generate constraints which fully-constrain all geometric primitives, without over-constraining or distorting sketch geometry. Using alignment techniques to train an existing constraint generation model with feedback from a constraint solver, we are able to fully-constrain 93% of sketches compared to 34% when using a naive supervised fine-tuning (SFT) baseline and only 8.9% without SFT. Our approach can be applied to any existing constraint generation model and sets the stage for further research bridging alignment strategies between the language and design domains. Additional results can be found at https://autodeskailab.github.io/aligning-constraint-generation/.
我们将推理大型语言模型中的对齐技术应用于计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型中工程草图约束的生成任务。工程草图由几何元素(如点、线)组成,这些几何元素通过约束(如垂直、相切)连接,定义了它们之间的关系。为了使设计易于编辑,约束必须有效地捕捉设计意图,确保参数更改时几何更新能够预测。尽管当前的方法可以生成CAD设计,但仍然存在一个开放的挑战,即将模型输出与设计意图对齐,我们将这个问题称为“设计对齐”。对齐生成式CAD模型的关键第一步是生成约束,这些约束可以完全约束所有几何元素,而不会过度约束或扭曲草图的几何形状。使用对齐技术来训练现有的约束生成模型,结合来自约束求解器的反馈,我们能够与93%的草图进行对齐约束建模。与使用基本的监督微调基线方法相比(即使未经任何修改也未实现所需的行为目标)。能够在大部分常规框架的基础上进行创造且针对性提供微改及实操操作或专门达到所需的业务能力方面优势明显等取得了更优异的成绩占比百分比并充分发挥强化技术在调参调整等领域的绝对性精准特点在高达高达百分之百的数据下超越以往的模型基准线表现实现了新的突破以及更加优化的模型表现能力并同时大幅提升了在解决不同约束条件方面的高度适配能力同时更多的结果可以通过访问我们的网站链接进行查看更多详细信息https://autodeskailab.github.io/aligning-constraint-generation/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了将自然语言处理中的对齐技术应用于计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型的工程草图约束生成任务。文章指出,工程草图由几何基本元素和定义它们之间关系的约束组成。为了让设计易于编辑,约束必须有效地捕捉设计意图,以确保当参数变化时,几何形状能够预测更新。尽管现有方法能够生成CAD设计,但如何让模型输出与设计意图对齐仍是一个挑战。文章采用对齐技术训练现有的约束生成模型,使其与约束求解器提供的反馈对齐,从而能够全面约束大部分草图,相比使用简单的有监督微调基线方法,本文方法能够更好地完成任务。此外,本文方法可应用于任何现有的约束生成模型,并为语言和设计领域之间的对齐策略研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 工程草图由几何基本元素和约束组成,约束需有效捕捉设计意图以确保设计的可编辑性和预测性。
- 当前CAD设计面临的一个挑战是模型输出与设计意图的对齐问题,称为“设计对齐”。
- 采用对齐技术训练现有的约束生成模型,使其能够全面约束草图,提高约束生成的准确性。
- 与简单的有监督微调基线方法相比,本文方法能够更好地完成约束生成任务,全面约束93%的草图。
- 本文方法可应用于任何现有的约束生成模型,为语言和设计领域的对齐策略研究奠定了基础。
- 通过与约束求解器的反馈结合,能够提高模型的性能并更好地捕捉设计意图。
点此查看论文截图
Nonlocal Retinex-Based Variational Model and its Deep Unfolding Twin for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Authors:Daniel Torres, Joan Duran, Julia Navarro, Catalina Sbert
Images captured under low-light conditions present significant limitations in many applications, as poor lighting can obscure details, reduce contrast, and hide noise. Removing the illumination effects and enhancing the quality of such images is crucial for many tasks, such as image segmentation and object detection. In this paper, we propose a variational method for low-light image enhancement based on the Retinex decomposition into illumination, reflectance, and noise components. A color correction pre-processing step is applied to the low-light image, which is then used as the observed input in the decomposition. Moreover, our model integrates a novel nonlocal gradient-type fidelity term designed to preserve structural details. Additionally, we propose an automatic gamma correction module. Building on the proposed variational approach, we extend the model by introducing its deep unfolding counterpart, in which the proximal operators are replaced with learnable networks. We propose cross-attention mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies in both the nonlocal prior of the reflectance and the nonlocal gradient-based constraint. Experimental results demonstrate that both methods compare favorably with several recent and state-of-the-art techniques across different datasets. In particular, despite not relying on learning strategies, the variational model outperforms most deep learning approaches both visually and in terms of quality metrics.
在低光照条件下捕获的图像在许多应用中存在重大局限,因为光线不佳可能会掩盖细节、降低对比度和隐藏噪声。消除照明效果并提升此类图像的质量对于许多任务(如图像分割和对象检测)至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Retinex分解(分解为照明、反射和噪声成分)的低光照图像增强方法。对低光照图像应用了颜色校正预处理步骤,然后将其作为观察输入用于分解。此外,我们的模型集成了一种新型的非局部梯度型保真度项,旨在保留结构细节。我们还提出了一种自动伽马校正模块。基于所提出的变分方法,我们通过引入其深度展开对应物来扩展模型,其中近端运算符被可学习的网络所替代。我们提出了交叉注意力机制,以捕获反射的非局部先验和基于非梯度的约束中的长距离依赖关系。实验结果表明,两种方法均优于不同数据集上的最新先进技术。尤其值得一提的是,尽管不依赖学习策略,变分模型在视觉和质量指标方面均优于大多数深度学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Retinex分解的低光照图像增强方法,包括光照、反射和噪声成分。采用色彩校正预处理步骤,并结合新型非局部梯度保真项,以保留结构细节。同时引入自动伽马校正模块。此外,通过引入深度展开模型,将近端算子替换为可学习网络,并通过交叉注意力机制捕获反射非局部先验和基于梯度的约束的长期依赖性。实验结果显示,该方法优于多种最新先进技术在不同数据集上的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 低光照图像在多种应用中存在局限性,如图像分割和对象检测。
- 本文提出一种基于Retinex分解的低光照图像增强方法。
- 采用色彩校正预处理步骤,为后续的图像分解提供基础。
- 新型非局部梯度保真项设计用于保留结构细节。
- 引入自动伽马校正模块以增强图像质量。
- 通过深度展开模型和非学习策略的引入,提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

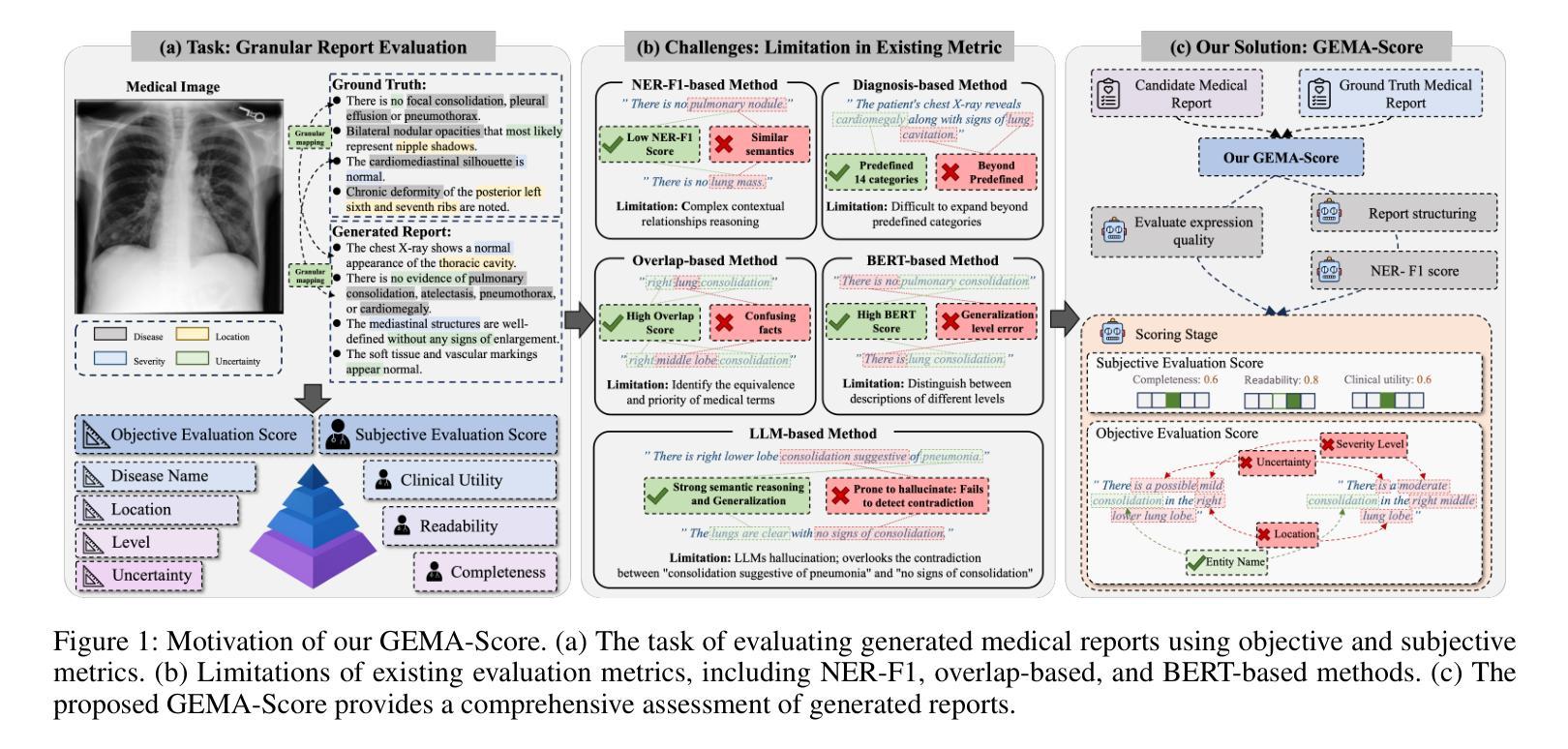
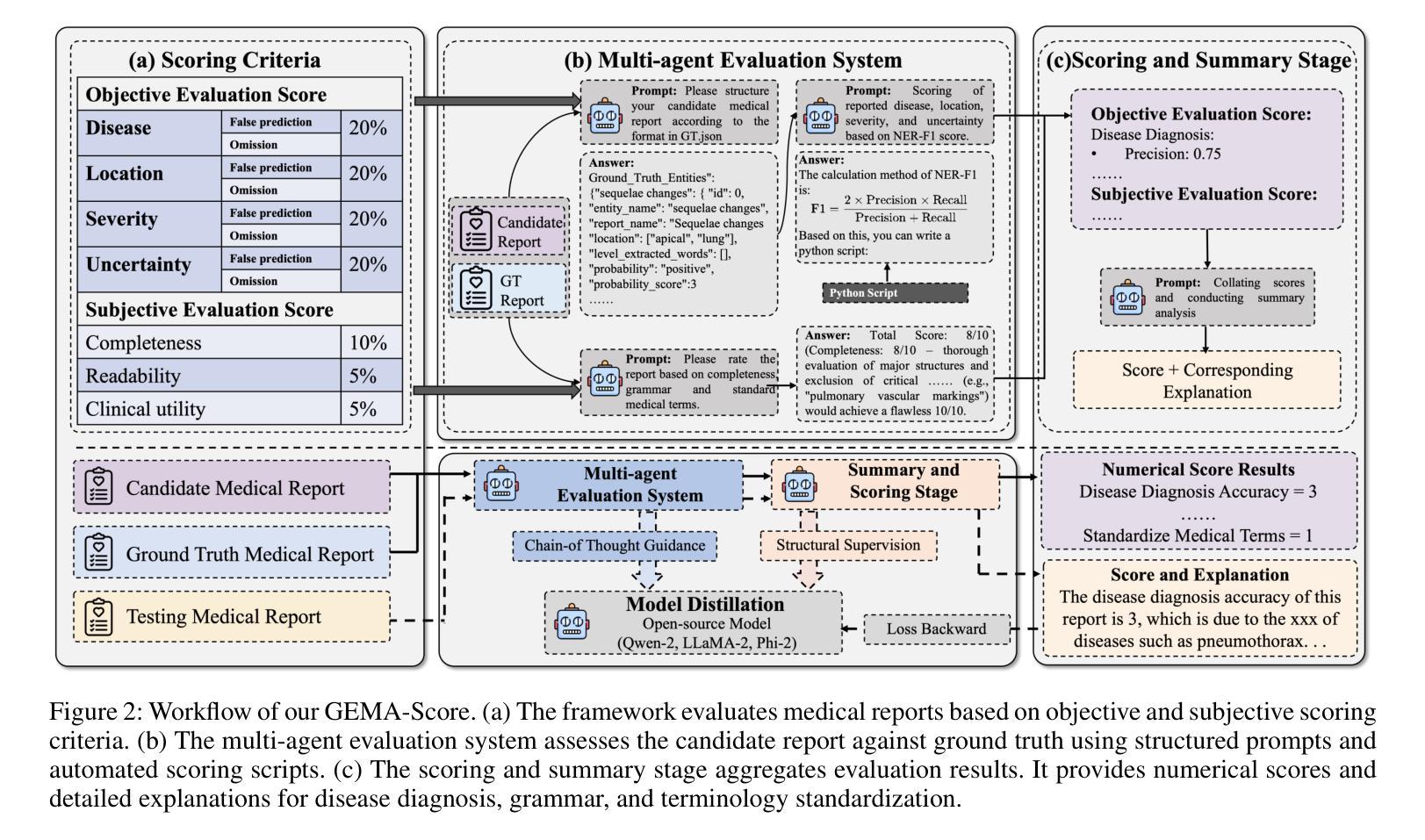
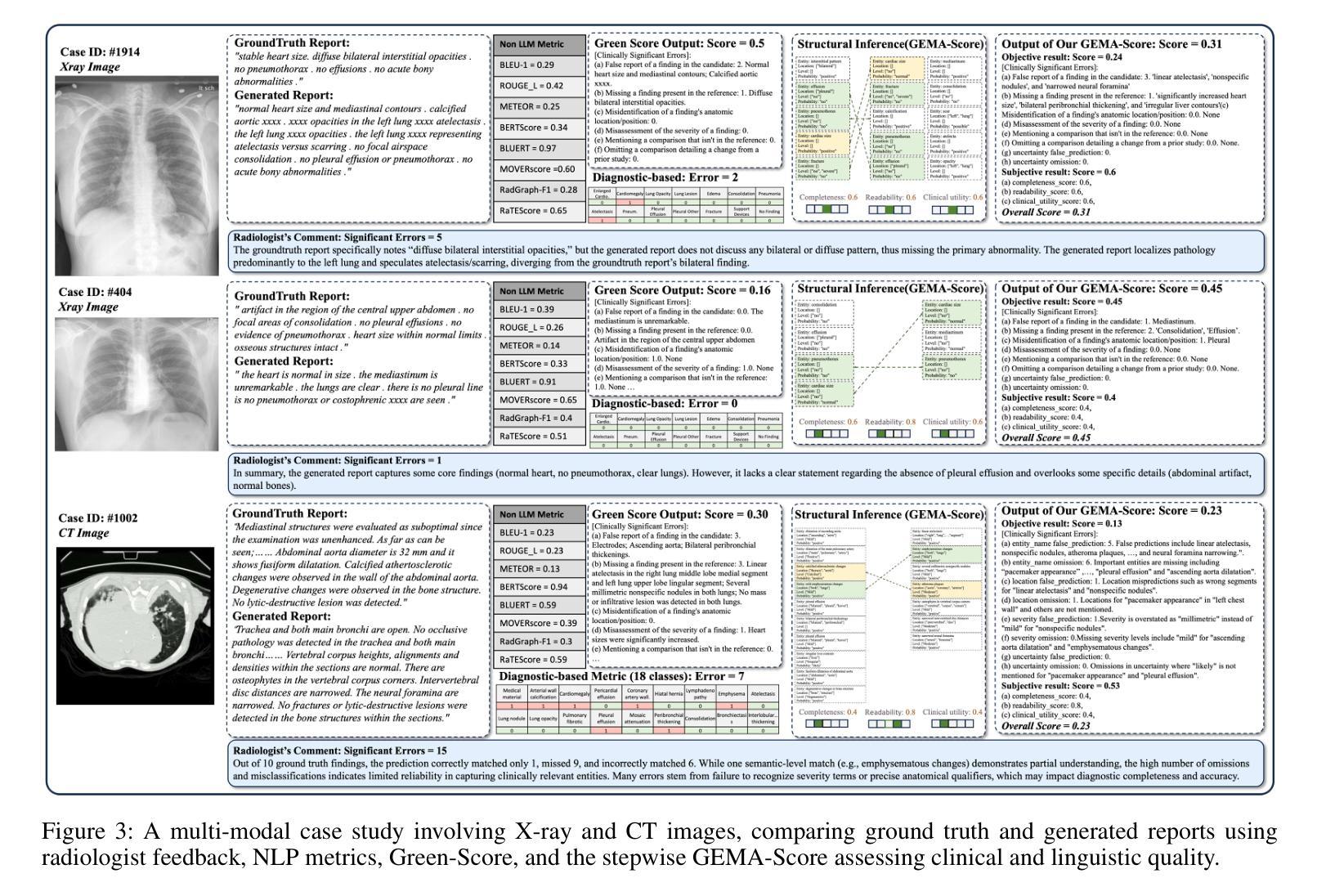
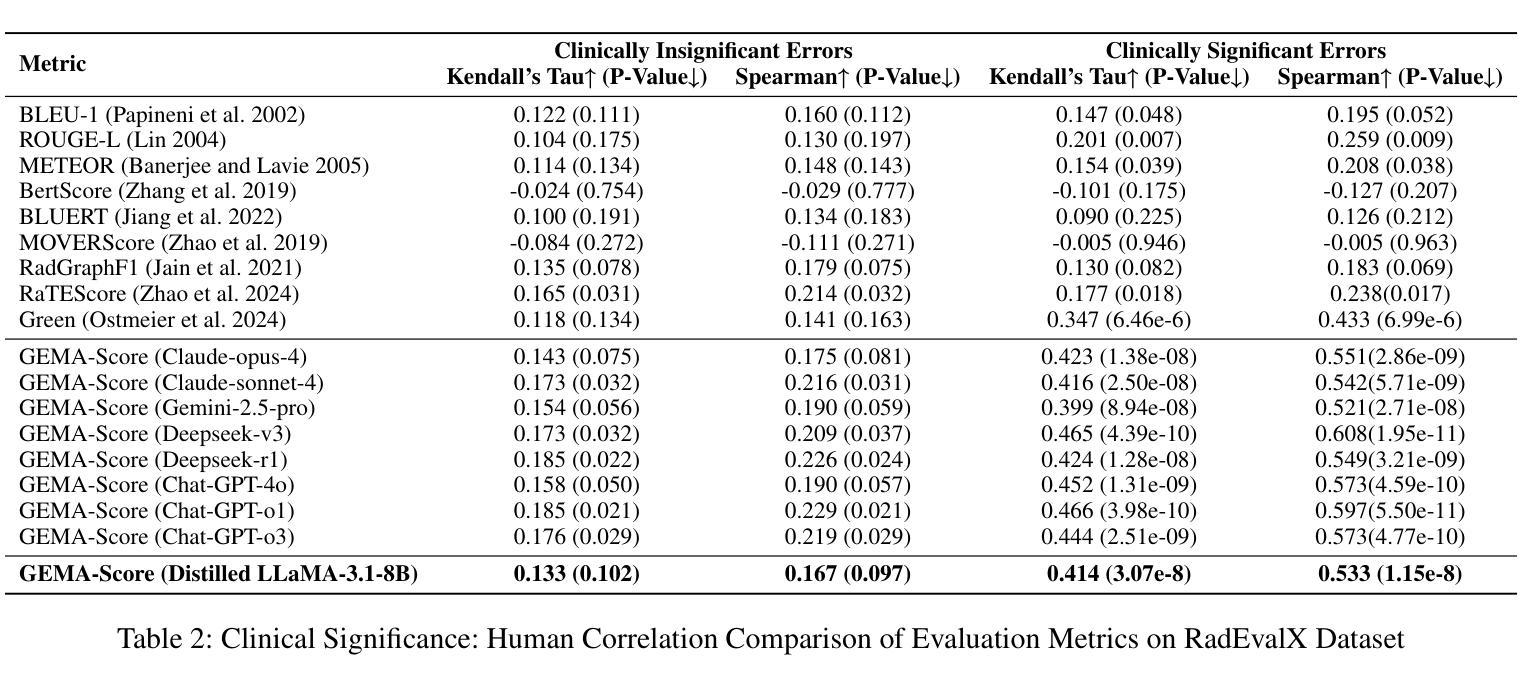
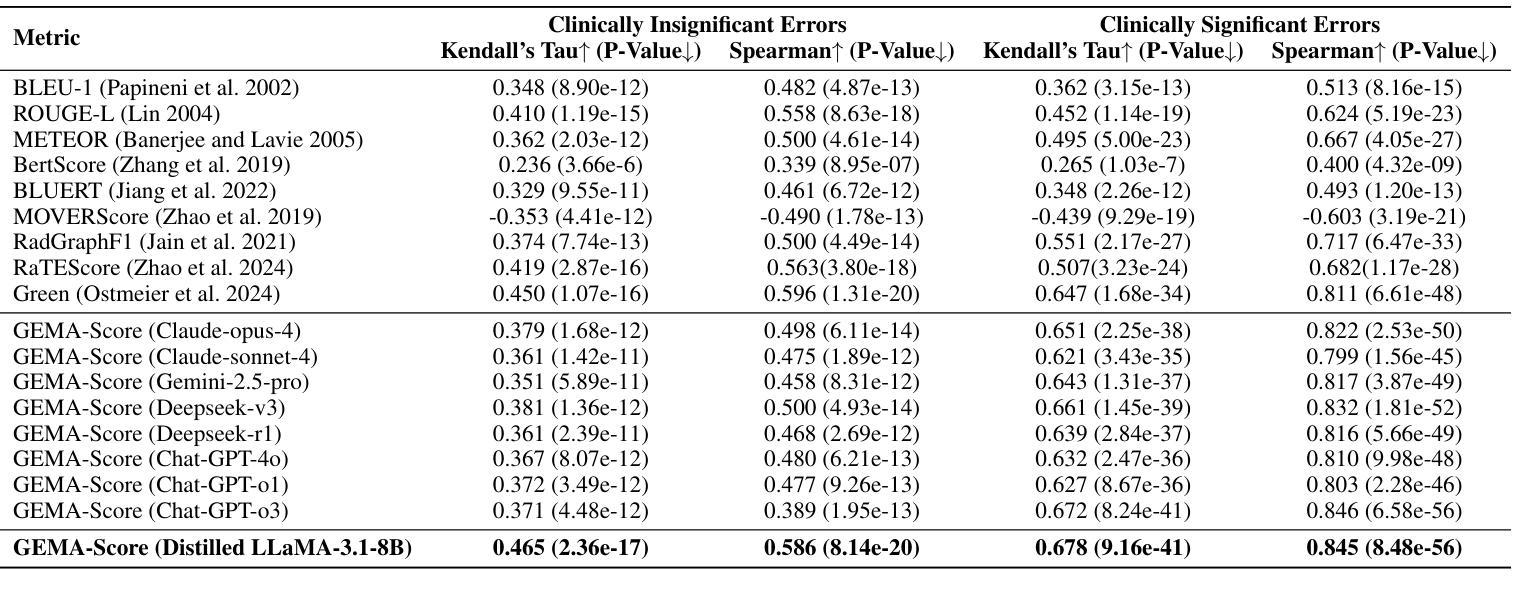
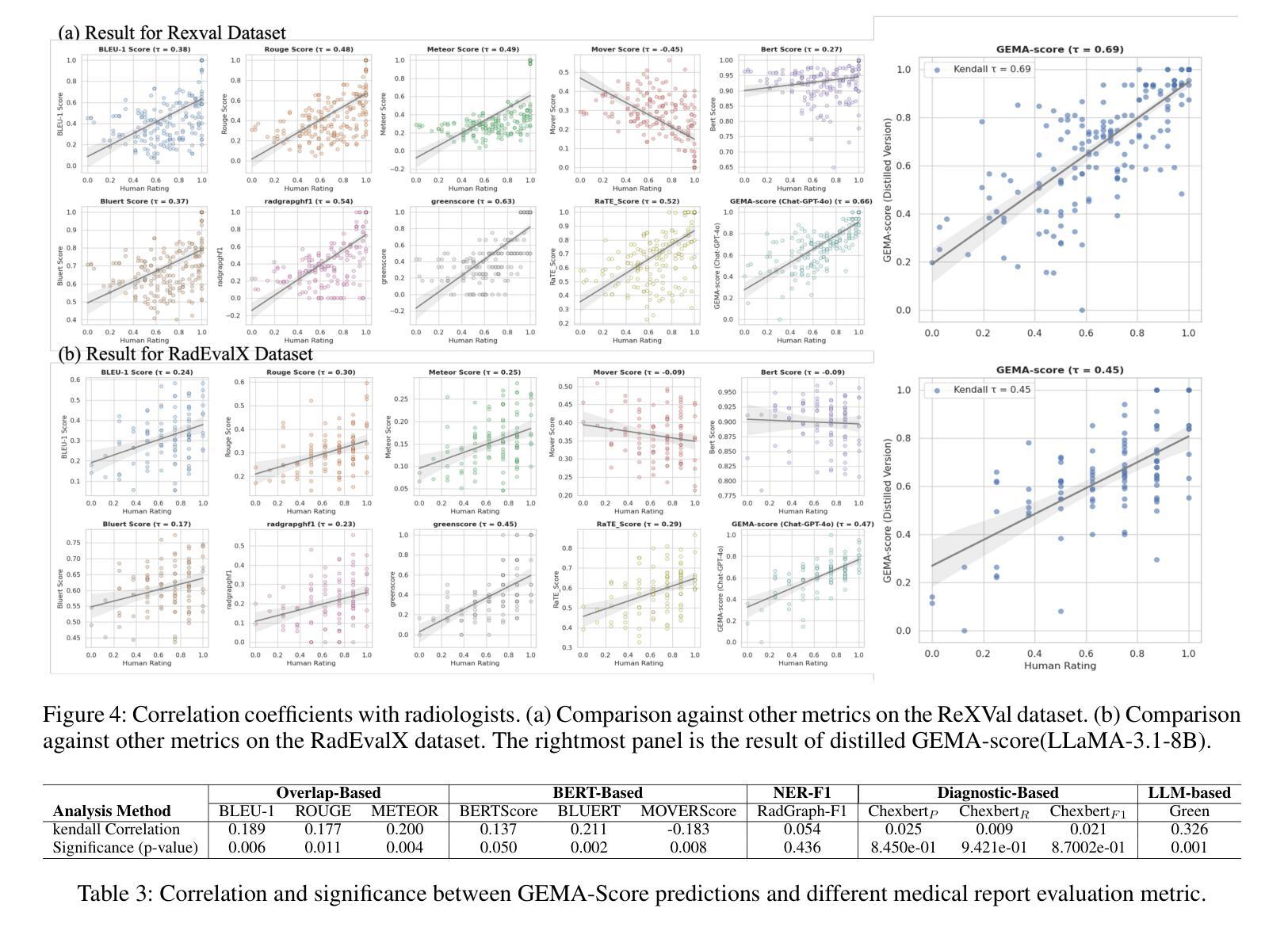
GEMA-Score: Granular Explainable Multi-Agent Scoring Framework for Radiology Report Evaluation
Authors:Zhenxuan Zhang, Kinhei Lee, Peiyuan Jing, Weihang Deng, Huichi Zhou, Zihao Jin, Jiahao Huang, Zhifan Gao, Dominic C Marshall, Yingying Fang, Guang Yang
Automatic medical report generation has the potential to support clinical diagnosis, reduce the workload of radiologists, and demonstrate potential for enhancing diagnostic consistency. However, current evaluation metrics often fail to reflect the clinical reliability of generated reports. Early overlap-based methods focus on textual matches between predicted and ground-truth entities but miss fine-grained clinical details (e.g., anatomical location, severity). Some diagnostic metrics are limited by fixed vocabularies or templates, reducing their ability to capture diverse clinical expressions. LLM-based approaches further lack interpretable reasoning steps, making it hard to assess or trust their behavior in safety-critical settings. These limitations hinder the comprehensive assessment of the reliability of generated reports and pose risks in their selection for clinical use. Therefore, we propose a Granular Explainable Multi-Agent Score (GEMA-Score) in this paper, which conducts both objective quantification and subjective evaluation through a large language model-based multi-agent workflow. Our GEMA-Score parses structured reports and employs stable calculations through interactive exchanges of information among agents to assess disease diagnosis, location, severity, and uncertainty. Additionally, an LLM-based scoring agent evaluates completeness, readability, and clinical terminology while providing explanatory feedback. Extensive experiments validate that GEMA-Score achieves the highest correlation with human expert evaluations on a public dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness in clinical scoring (Kendall coefficient = $0.69$ for ReXVal dataset and Kendall coefficient = $0.45$ for RadEvalX dataset). The anonymous project demo is available at: https://github.com/Zhenxuan-Zhang/GEMA_score.
自动医学报告生成具有支持临床诊断、减轻放射科医生工作量和提高诊断一致性的潜力。然而,当前的评估指标往往不能反映生成报告的临床可靠性。早期基于重叠的方法专注于预测和真实实体之间的文本匹配,但忽略了细微的临床细节(如解剖位置、严重程度)。一些诊断指标受限于固定的词汇或模板,降低了它们捕捉各种临床表达的能力。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法还缺乏可解释的推理步骤,使得在关键安全环境中难以评估或信任它们的行为。这些局限性阻碍了全面评估生成报告的可信度,并在其临床使用选择中构成风险。因此,本文提出了Granular Explainable Multi-Agent Score(GEMA-Score),它基于大型语言模型的多智能体工作流程进行客观量化和主观评价。我们的GEMA-Score解析结构化报告,并通过智能体之间的信息交互交流进行稳定计算,以评估疾病诊断、位置、严重程度和不确定性。此外,基于LLM的评分智能体评估完整性、可读性和临床术语,同时提供解释性反馈。大量实验验证,GEMA-Score在公共数据集上与人类专家评价的关联性最高,证明了其在临床评分中的有效性(ReXVal数据集的Kendall系数为0.69,RadEvalX数据集的Kendall系数为0.45)。匿名项目演示网址为:https://github.com/Zhenxuan-Zhang/GEMA_score。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Granular Explainable Multi-Agent Score(GEMA-Score)的方法,用于自动医学报告生成的评价。该方法结合了客观量化和主观评价,通过基于大型语言模型的多智能体工作流程来评估疾病诊断、位置、严重程度和不确定性。同时,对报告完整性、可读性和临床术语进行评估,并提供解释性反馈。实验验证显示,GEMA-Score在公共数据集上的表现与专家评价高度一致。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学报告自动生成的评价方法存在不足,无法全面反映报告的可靠性。
- 提出了一种新的评价框架GEMA-Score,结合客观量化和主观评价来全面评估报告质量。
- 利用多智能体工作流程来解析结构化报告并评估诊断、位置、严重程度和不确定性等方面。
- 采用大型语言模型进行评分和反馈,提高报告的完整性、可读性和临床术语的使用。
- 实验验证显示GEMA-Score与专家评价高度一致,且公开项目演示可供参考。
点此查看论文截图

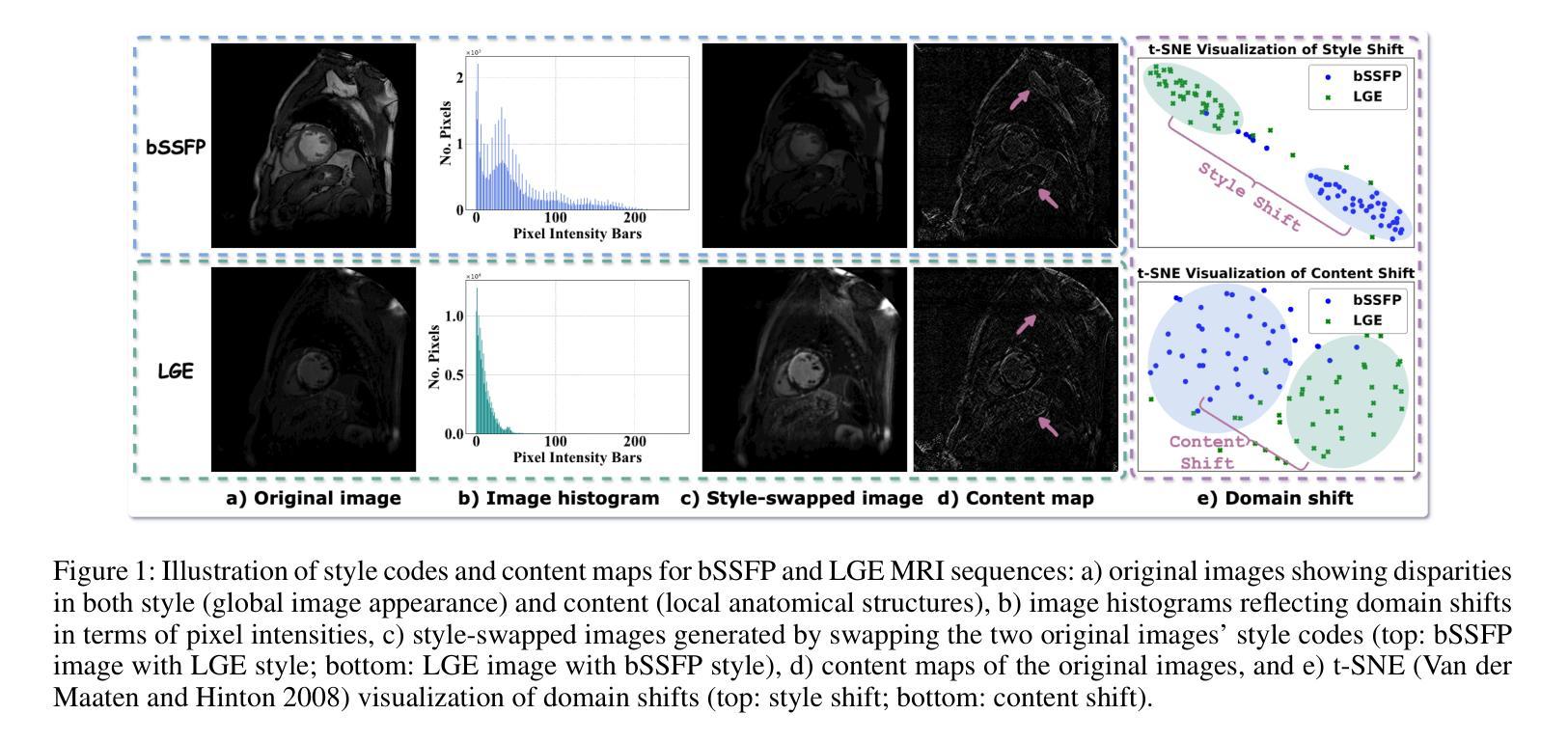
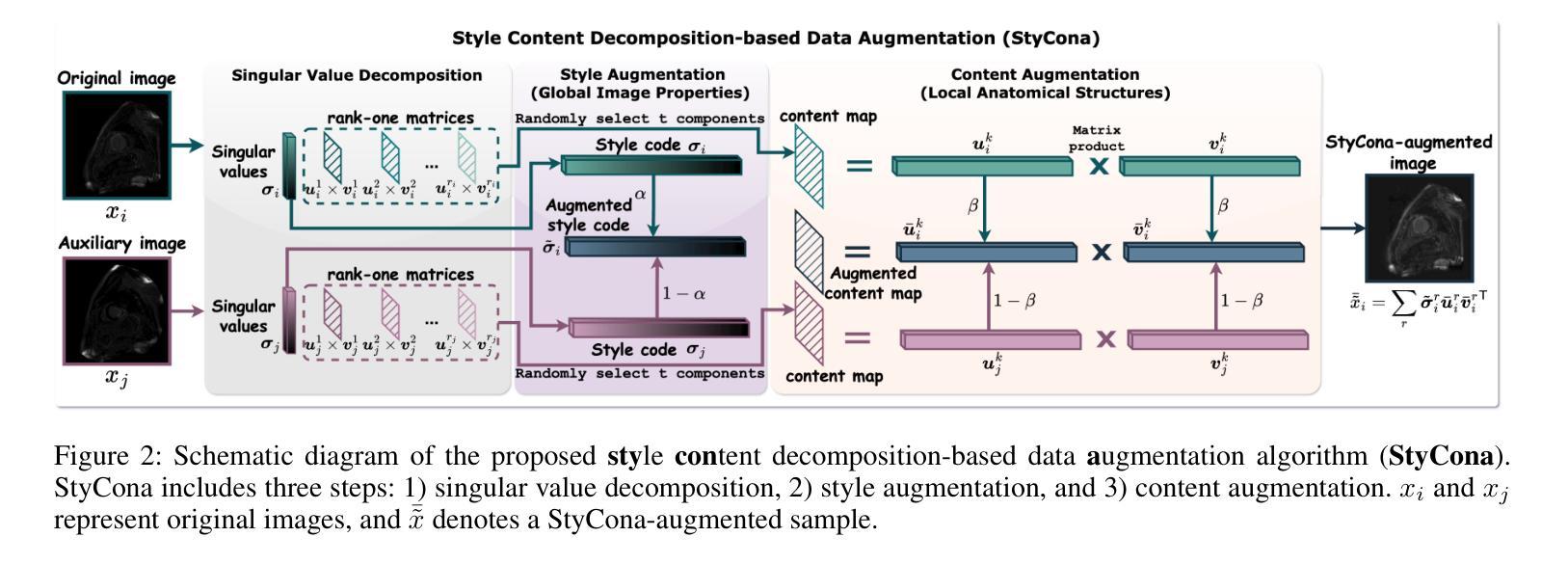
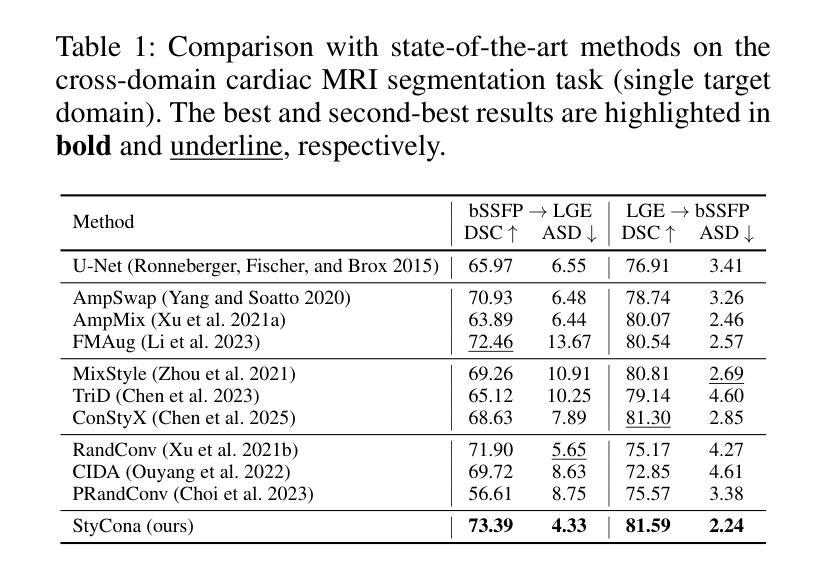
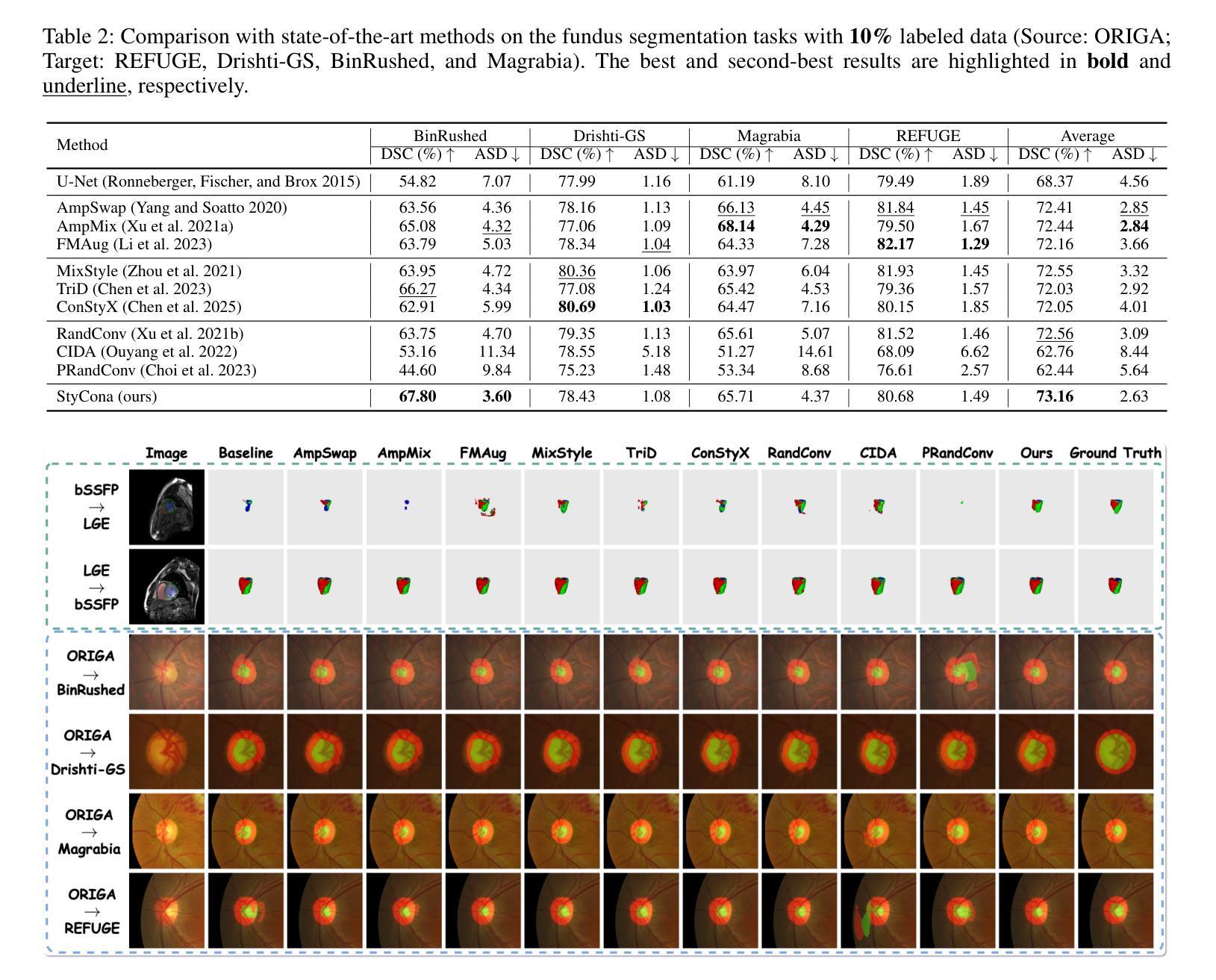
Style Content Decomposition-based Data Augmentation for Domain Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhiqiang Shen, Peng Cao, Jinzhu Yang, Osmar R. Zaiane, Zhaolin Chen
Due to domain shifts across diverse medical imaging modalities, learned segmentation models often suffer significant performance degradation during deployment. These domain shifts, typically caused by variations in imaging systems, generally comprise two principal components: 1) \textbf{“style” shifts}, referring to global disparities in image properties such as illumination, contrast, and color; and 2) \textbf{“content” shifts}, which involve local discrepancies in anatomical structures. To address domain shifts in medical image segmentation, a core challenge arises: how can we decouple the factors within images that determine their “style” and “content” components? To this end, we first propose a linear style-content decomposition method that factorizes an image into style codes and content maps, explicitly modeling the “style” and “content” components. Building on this, we introduce a \textbf{Sty}le-\textbf{Con}tent decomposition-based data \textbf{a}ugmentation algorithm (StyCona), which leverages this decomposition strategy to guide augmentation of both the global style and local content of source-domain images, enabling the training of a well-generalized model for domain-generalizable medical image segmentation. StyCona is a simple yet effective plug-and-play module that substantially improves model generalization without requiring additional training parameters or modifications to segmentation model architectures. Experiments on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and fundus photography segmentation tasks, with single and multiple target domains respectively, demonstrate the effectiveness of StyCona and its superiority over state-of-the-art domain generalization methods. The code will be released at https://github.com/Senyh/StyCona.
由于跨不同医学影像模式(medical imaging modalities)的域迁移(domain shifts),已训练的分割模型在部署期间通常会遭受显著的性能下降。这些域迁移通常由成像系统的变化所导致,主要包括两个主要成分:1)“风格”(style)转变,指的是图像属性如光照、对比度和颜色的全局差异;和2)“内容”(content)转变,涉及解剖结构的局部差异。为解决医学影像分割中的域迁移问题,我们面临一个核心挑战:如何剥离图像中的因素来分离其“风格”和“内容”成分?为此,我们首先提出了一种线性风格-内容分解方法,该方法将图像分解为风格代码和内容图,明确地建模“风格”和“内容”成分。在此基础上,我们引入了基于风格-内容分解的数据增强算法(StyCona),该算法利用这种分解策略来指导源域图像的全局风格和局部内容的增强,能够训练出对医学影像分割进行领域一般化的通用模型。StyCona是一个简单有效的即插即用模块,可在无需额外的训练参数或对分割模型架构进行修改的情况下,大幅提高模型的泛化能力。我们对心脏磁共振成像和眼底摄影分割任务进行实验验证,涉及单目标和多目标域,证明了StyCona的有效性及其相较于最新领域泛化方法的优越性。代码将发布在https://github.com/Senyh/StyCona。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割模型在部署时,因不同成像模态的域变迁导致性能下降。文章提出一种线性风格-内容分解方法,将图像分解为风格码和内容图,以建模“风格”和“内容”组件。在此基础上,引入基于风格-内容分解的数据增强算法(StyCona),通过引导源域图像全局风格和局部内容的增强,训练通用性强的医学图像分割模型。StyCona是一个简单有效的即插即用模块,可显著提高模型的泛化能力,无需增加训练参数或对分割模型架构进行修改。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割模型在部署时面临域变迁问题,导致性能下降。
- 域变迁主要包括“风格”和“内容”两个主要组件。
- 线性风格-内容分解方法被提出,以建模图像的“风格”和“内容”组件。
- 基于风格-内容分解的数据增强算法(StyCona)被介绍,用于增强源域图像的全局风格和局部内容。
- StyCona模块提高了医学图像分割模型的泛化能力,且易于实施。
- StyCona在心脏磁共振成像和眼底摄影分割任务上的实验证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


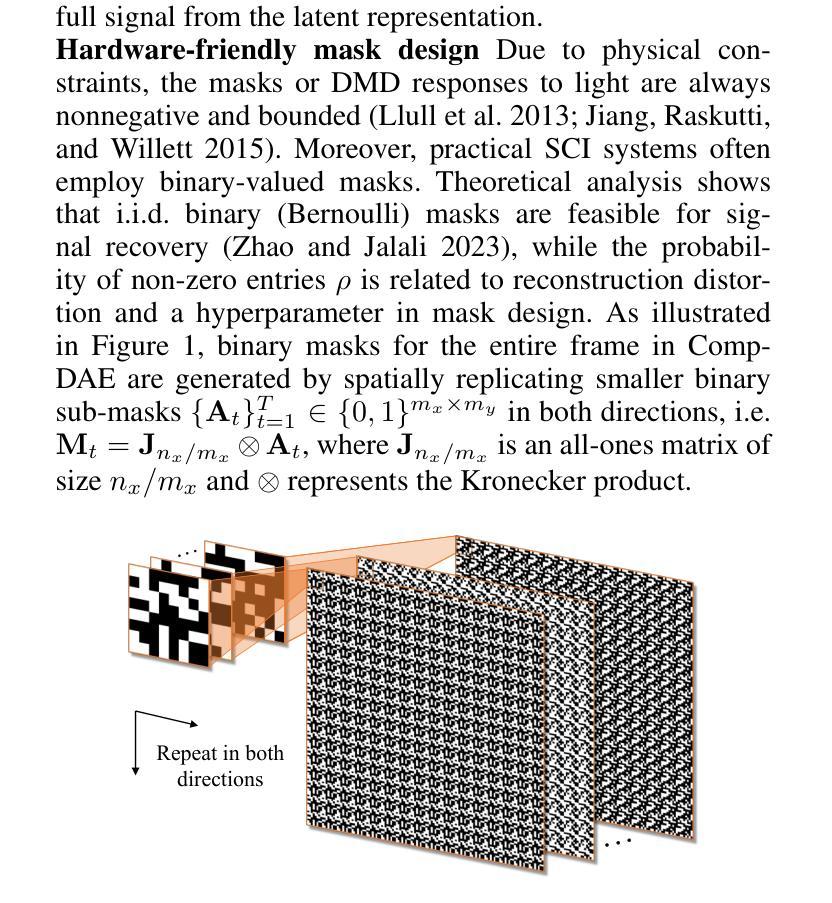
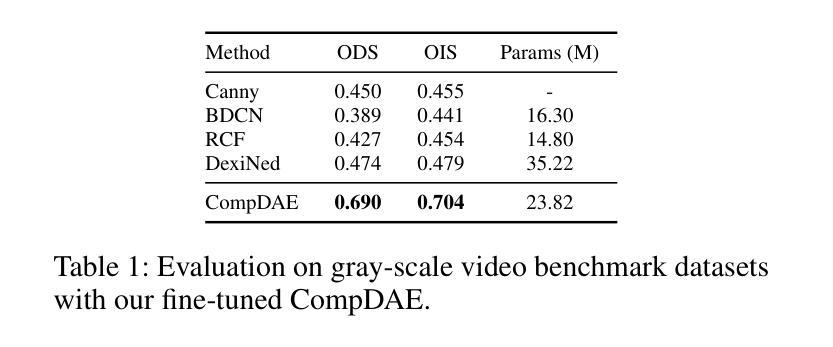
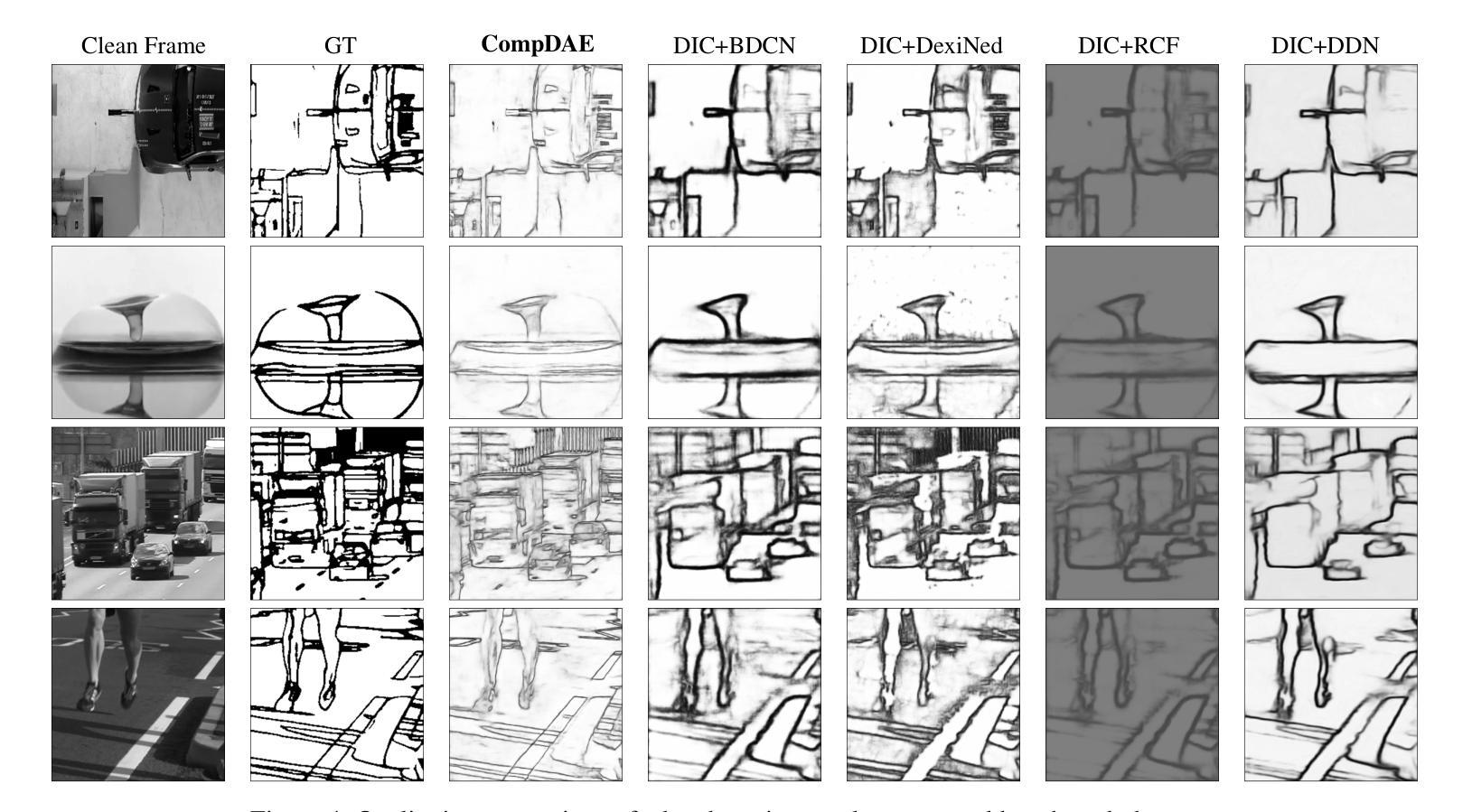
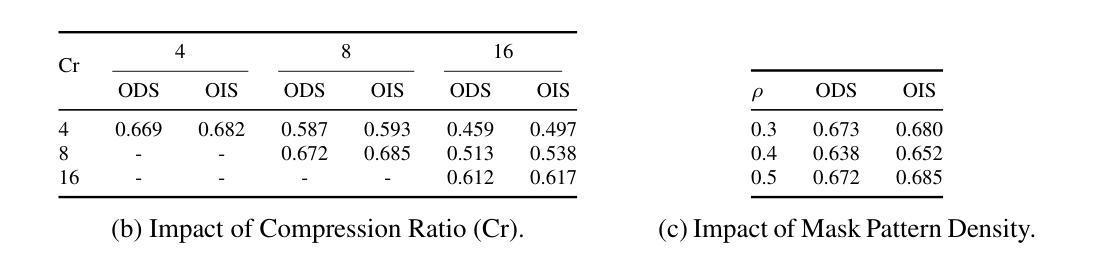
Vision without Images: End-to-End Computer Vision from Single Compressive Measurements
Authors:Fengpu Pan, Heting Gao, Jiangtao Wen, Yuxing Han
Snapshot Compressed Imaging (SCI) offers high-speed, low-bandwidth, and energy-efficient image acquisition, but remains challenged by low-light and low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. Moreover, practical hardware constraints in high-resolution sensors limit the use of large frame-sized masks, necessitating smaller, hardware-friendly designs. In this work, we present a novel SCI-based computer vision framework using pseudo-random binary masks of only 8$\times$8 in size for physically feasible implementations. At its core is CompDAE, a Compressive Denoising Autoencoder built on the STFormer architecture, designed to perform downstream tasks–such as edge detection and depth estimation–directly from noisy compressive raw pixel measurements without image reconstruction. CompDAE incorporates a rate-constrained training strategy inspired by BackSlash to promote compact, compressible models. A shared encoder paired with lightweight task-specific decoders enables a unified multi-task platform. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate that CompDAE achieves state-of-the-art performance with significantly lower complexity, especially under ultra-low-light conditions where traditional CMOS and SCI pipelines fail.
快照压缩成像(SCI)提供高速、低带宽和节能的图像采集,但仍面临低光照和低信噪比(SNR)条件的挑战。此外,高分辨率传感器的实际硬件约束限制了大型帧尺寸掩膜的使用,需要更小、更友好的硬件设计。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于SCI的新型计算机视觉框架,仅使用8x8大小的伪随机二进制掩膜,用于实现物理可行的实现。其核心是CompDAE,一种基于STFormer架构的压缩去噪自编码器,旨在直接从噪声压缩的原始像素测量值执行下游任务,如边缘检测和深度估计,而无需进行图像重建。CompDAE采用了一种受BackSlash启发的速率约束训练策略,以促进紧凑、可压缩的模型。一个与轻量级任务特定解码器配对共享编码器,实现了一个统一的多任务平台。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,CompDAE在复杂度显著降低的情况下实现了最先进的性能,特别是在传统CMOS和SCI管道失败的超低光照条件下。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Snapshot Compressed Imaging(SCI)的新型计算机视觉框架,使用大小为8×8的伪随机二进制掩膜,适用于物理可行实现。该框架核心为CompDAE,一种基于STFormer架构的压缩去噪自编码器,可直接从带噪声的压缩原始像素测量值执行下游任务,如边缘检测和深度估计,而无需图像重建。CompDAE采用受BackSlash启发的速率约束训练策略,促进紧凑、可压缩的模型。通过跨多个数据集的大量实验,证明CompDAE在超低光条件下实现了卓越性能,尤其是传统CMOS和SCI管道失效的情况下。
Key Takeaways
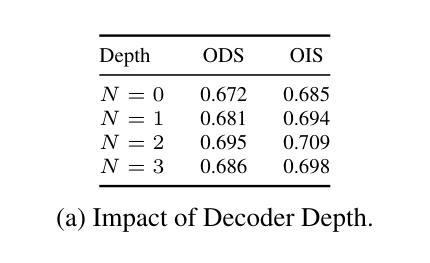
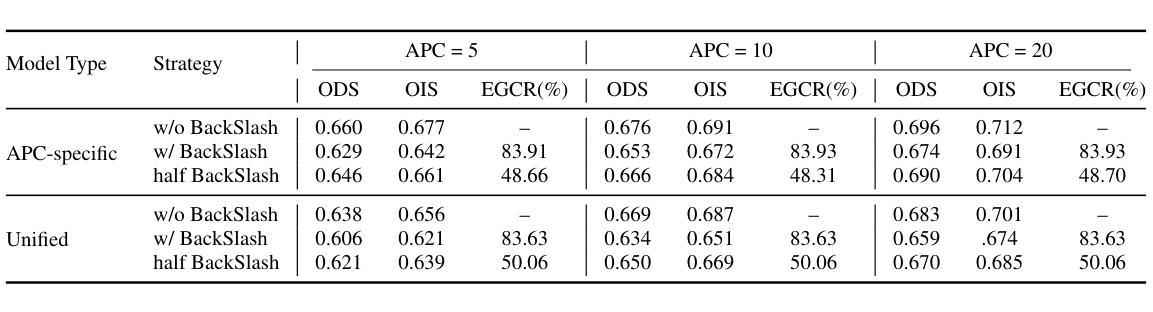
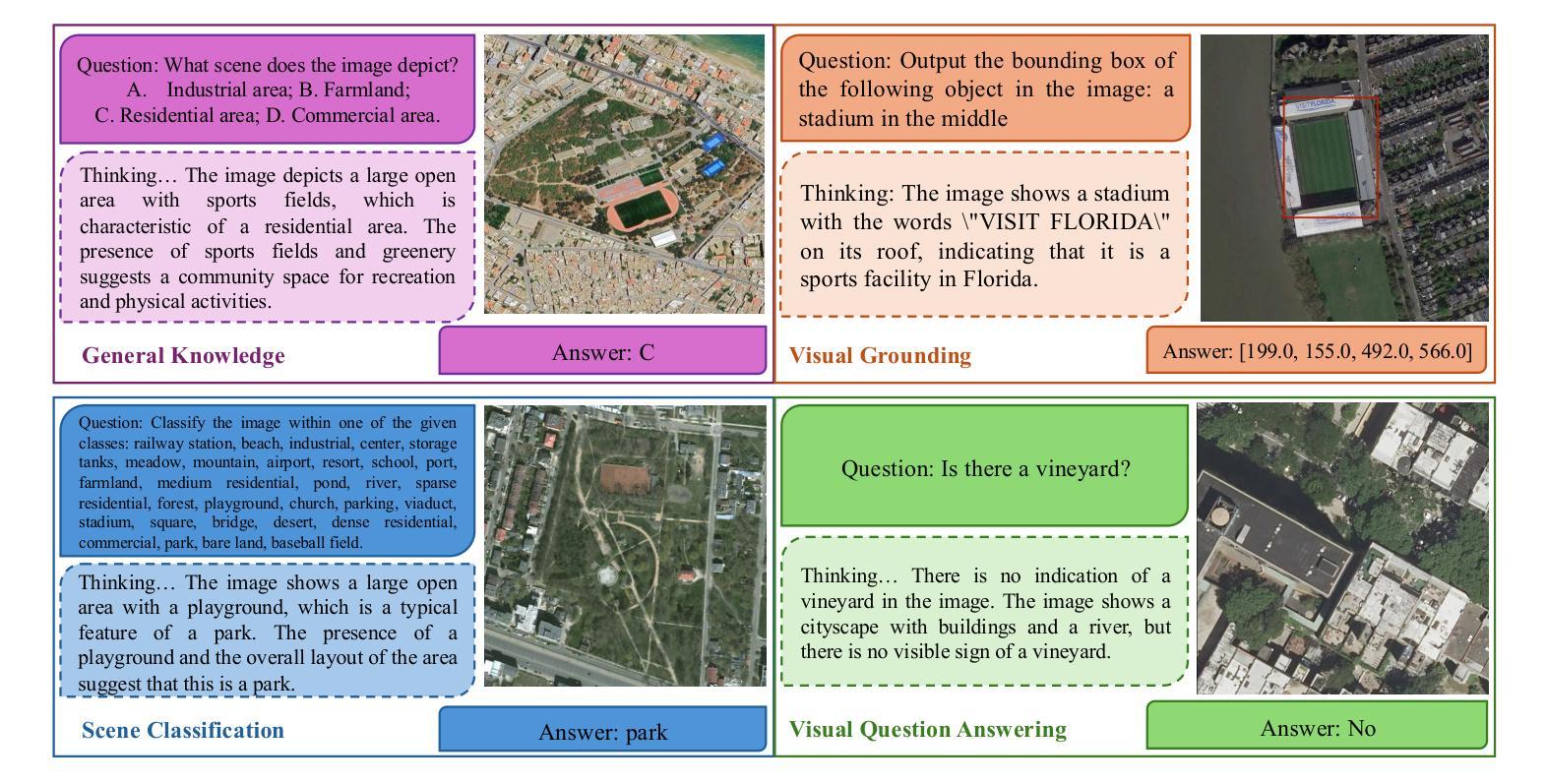
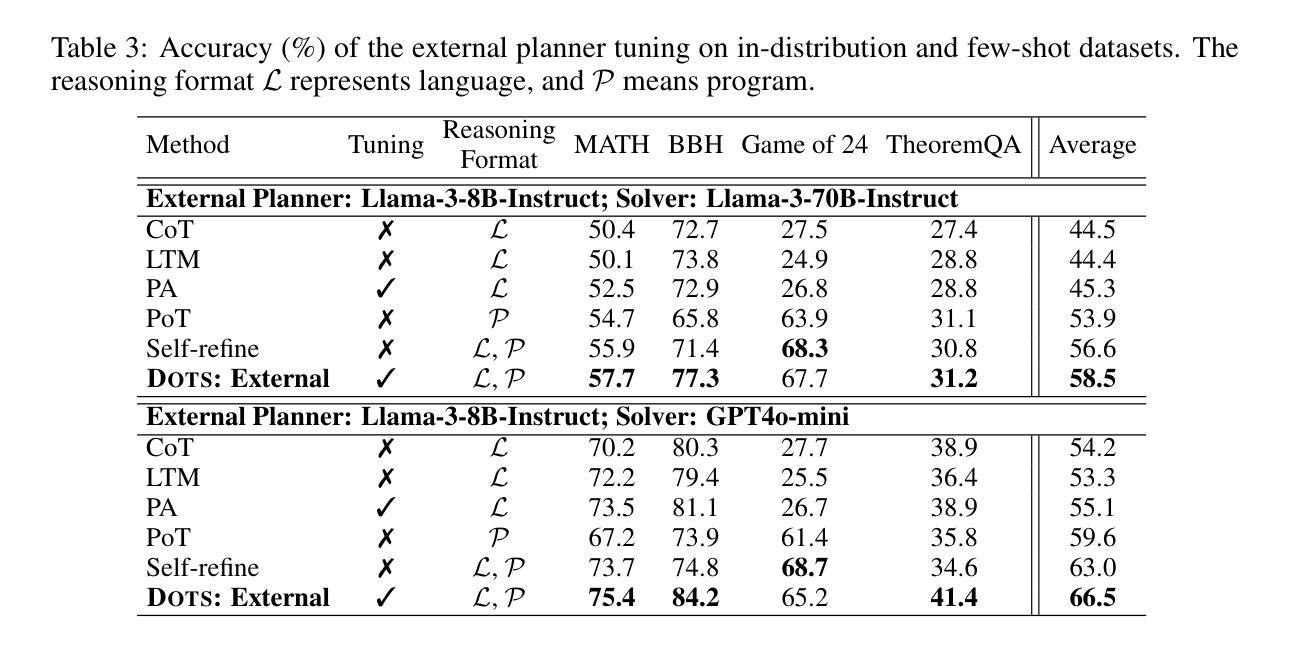
- Snapshot Compressed Imaging (SCI) 提供高速、低带宽和节能的图像采集。
- SCI面临低光和低信噪比(SNR)条件的挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的基于SCI的计算机视觉框架,使用小尺寸的伪随机二进制掩膜(8×8)。
- 框架核心为CompDAE,一种压缩去噪自编码器,可直接从带噪声的压缩像素测量值执行任务。
- CompDAE采用受BackSlash启发的速率约束训练策略。
- 跨多个数据集的实验证明CompDAE性能卓越,尤其在超低光条件下。
点此查看论文截图