⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-10 更新
Scaling LLM Planning: NL2FLOW for Parametric Problem Generation and Rigorous Evaluation
Authors:Jungkoo Kang
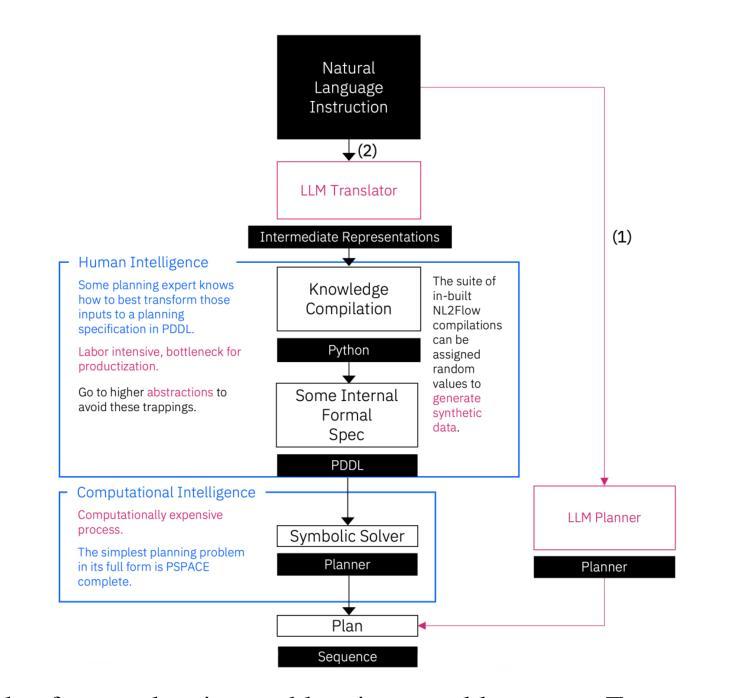
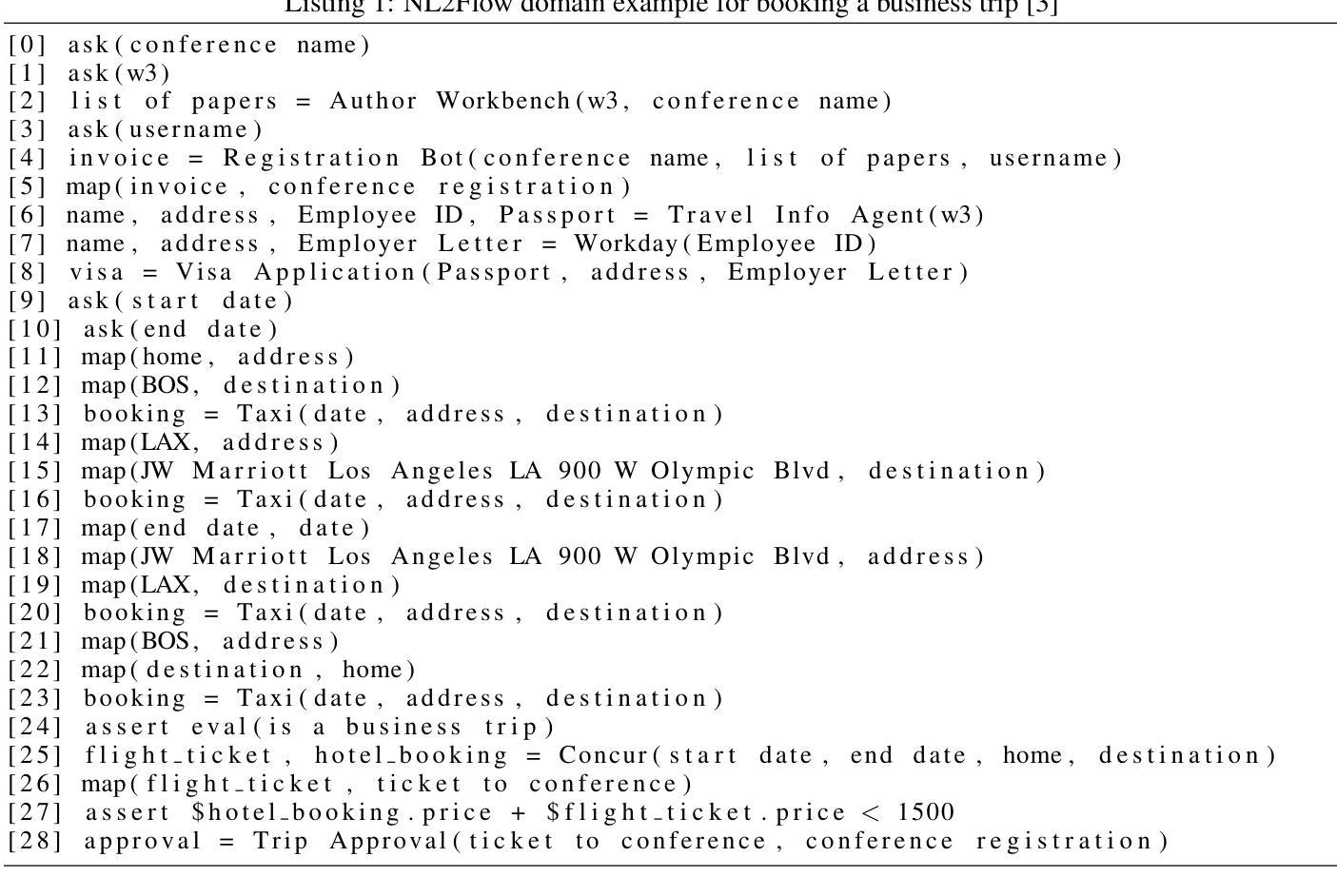
Effective agent performance relies on the ability to compose tools and agents into effective workflows. However, progress in Large Language Model (LLM) planning and reasoning is limited by the scarcity of scalable, reliable evaluation data. This study addresses this limitation by identifying a suitable workflow domain for LLM application. I introduce NL2Flow, a fully automated system for parametrically generating planning problems, which are expressed in natural language, a structured intermediate representation, and formal PDDL, and rigorously evaluating the quality of generated plans. NL2Flow generates a dataset of 2296 low-difficulty problems in automated workflow generation and evaluates multiple open-sourced, instruct-tuned LLMs without task-specific optimization or architectural modifications. Results reveal that the highest performing model achieved 86% success in generating valid plans and 69% in generating optimal plans, specifically for problems with feasible plans. Regression analysis shows that the influence of problem characteristics on plan generation is contingent on both model and prompt design. To investigate the potential of LLMs as natural language-to-JSON translators for workflow definition, and to facilitate integration with downstream symbolic computation tools and a symbolic planner, I evaluated the LLM’s translation performance on natural language workflow descriptions. I observed that translating natural language into a JSON representation of a workflow problem yielded a lower success rate than generating a plan directly, suggesting that unnecessary decomposition of the reasoning task may degrade performance and highlighting the benefit of models capable of reasoning directly from natural language to action. As LLM reasoning scales to increasingly complex problems, understanding the shifting bottlenecks and sources of error within these systems will be crucial.
有效的代理性能取决于将工具和代理组合成有效工作流程的能力。然而,由于缺少可扩展、可靠的评估数据,大型语言模型(LLM)的规划和推理进展受到限制。本研究通过确定适合LLM应用的流程领域来解决这一限制。作者介绍了NL2Flow,这是一个全自动的系统,可以参数化生成规划问题,这些问题以自然语言、结构化中间表示和正式PDDL来表达,并对生成的计划质量进行严格的评估。NL2Flow生成了一个包含2296个低难度问题的数据集,用于自动化工作流程生成,并评估了多个开源、经过指令调整的大型语言模型,无需特定任务的优化或架构修改。结果表明,表现最好的模型在生成有效计划方面达到了86%的成功率,在生成最佳计划方面达到了69%,仅限于具有可行计划的问题。回归分析表明,问题特征对计划生成的影响取决于模型和提示设计。为了研究大型语言模型作为自然语言到JSON的工作流定义翻译器的潜力,并促进其与下游符号计算工具和符号规划器的集成,作者评估了大型语言模型在自然语言工作流描述上的翻译性能。作者观察到,将自然语言翻译成工作流问题的JSON表示形式的成功率低于直接生成计划的成功率,这表明不必要的分解推理任务可能会降低性能,并突出显示直接从自然语言进行推理的模型的好处。随着大型语言模型推理处理越来越复杂的问题,理解这些系统内不断变化的瓶颈和错误来源将至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 7 figures
摘要
本研究针对大型语言模型(LLM)在规划和推理方面的应用,通过识别适合LLM应用的流程领域,解决了评价数据缺乏的问题。引入NL2Flow系统,可参数化生成规划问题,以自然语言、结构化中间表示和正式PDDL表达,并对生成计划的质量进行严谨评估。研究生成了2296个低难度自动化工作流程问题数据集,并对多个开源、指令调优的LLMs进行了评估,无需特定任务优化或架构修改。结果显示,性能最好的模型在生成有效计划方面成功率为86%,在生成最优计划方面成功率为69%,仅限于有可行计划的问题。回归分析显示,问题特征对计划生成的影响取决于模型和提示设计。评估了LLM作为自然语言到JSON翻译器的潜力,用于工作流程定义,并与下游符号计算工具和符号规划器进行集成。发现将自然语言翻译成工作流程问题的JSON表示形式成功率较低,直接生成计划的成功率更高。这表明将推理任务过度分解可能会降低性能,并强调直接从自然语言进行推理的模型的优势。随着LLM推理在越来越复杂的问题上的扩展,理解这些系统中不断变化的瓶颈和错误来源将至关重要。
关键见解
- 研究通过NL2Flow系统解决了LLM在规划和推理方面的评价数据缺乏问题,该系统可参数化生成规划问题。
- 评估了多个LLMs在自动化工作流程生成方面的性能,发现性能最好的模型在生成有效计划方面成功率为86%,在生成最优计划方面为69%。
- 回归分析显示问题特征、模型和提示设计共同影响计划生成。
- 评估了LLM作为自然语言到JSON翻译器的潜力,发现直接进行计划生成比翻译表示法更成功。
- 过度分解推理任务可能会降低LLM的性能。
- 随着LLM推理在更复杂问题上的扩展,理解其瓶颈和错误来源变得至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


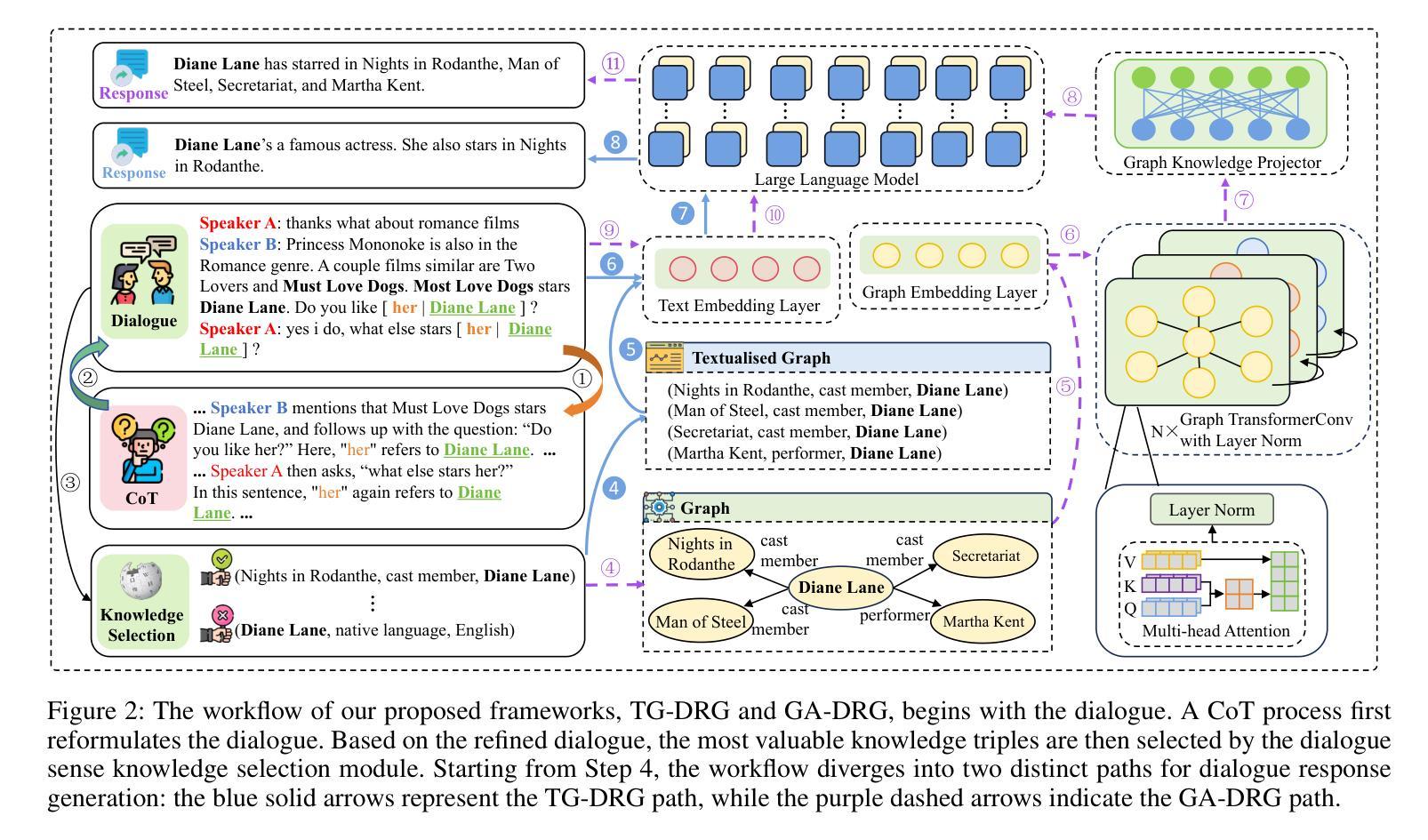
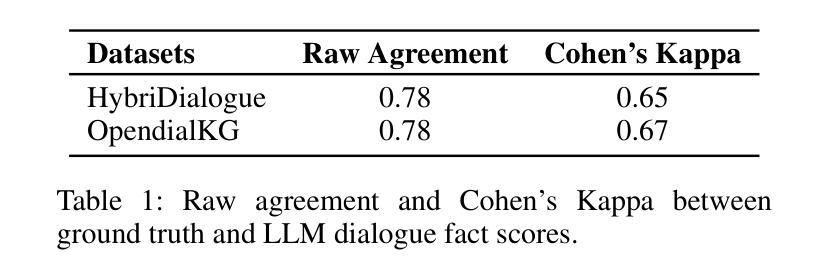
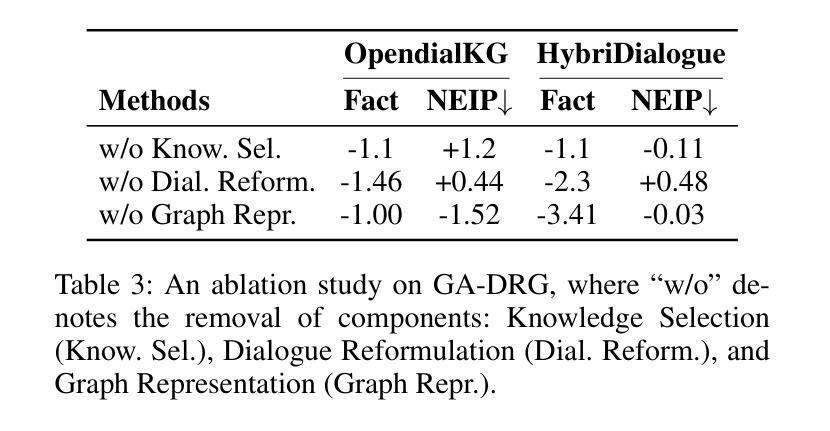
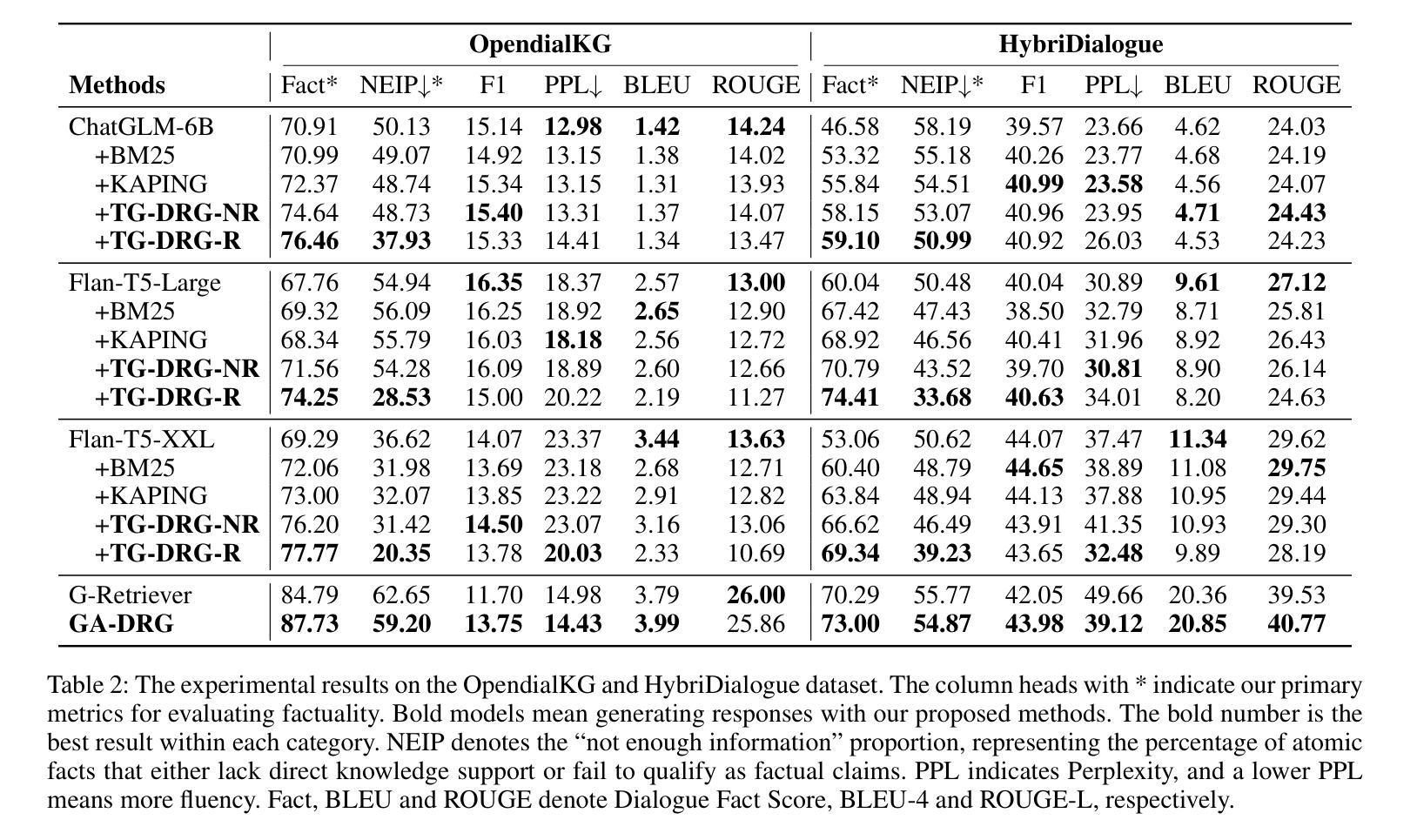
Improving Factuality for Dialogue Response Generation via Graph-Based Knowledge Augmentation
Authors:Xiangyan Chen, Yujian Gan, Yimeng Gu, Matthew Purver
Large Language Models (LLMs) succeed in many natural language processing tasks. However, their tendency to hallucinate - generate plausible but inconsistent or factually incorrect text - can cause significant problems in certain tasks, including response generation in dialogue. To mitigate this issue, we propose two novel graph knowledge-augmented frameworks, Dialogue Response Generation via Textualised Graphs (TG-DRG) and Graph-Aware Dialogue Response Generation (GA-DRG), which combine reasoning-guided dialogue reformulation, dialogue sense knowledge selection, and graph-enhanced response generation to improve the factuality of dialogue responses. To evaluate the factuality of generated responses, we propose a dialogue fact score that addresses the limitations of existing fact-score methods in dialogue settings, providing a more reliable assessment of factual consistency. We evaluate our methods using different baselines on the OpendialKG and HybriDialogue datasets. Our methods noticeably improve factuality compared to other graph knowledge-augmentation baselines, including the state-of-the-art G-retriever, achieving improvements of 3.47% on OpendialKG and 3.12% on HybriDialogue in terms of dialogue fact score. The code will be released on GitHub.
大型语言模型(LLM)在许多自然语言处理任务中取得了成功。然而,它们倾向于产生合理但自相矛盾或事实错误的文本,这在某些任务中(包括对话生成响应)可能会导致严重问题。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了两种新型的图知识增强框架,即基于文本图的对话响应生成(TG-DRG)和图感知对话响应生成(GA-DRG)。这两个框架结合了推理引导的对话重构、对话常识知识选择和图增强响应生成,以提高对话响应的事实性。为了评估生成响应的事实性,我们提出了对话事实得分,解决了现有事实得分方法在对话环境中的局限性,为事实一致性提供了更可靠的评估。我们在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上使用了不同的基线来评估我们的方法。我们的方法在事实性上显著改进了其他图形知识增强基线,包括最先进的G检索器,在OpendialKG上提高了3.47%,在HybriDialogue上提高了3.12%,对话事实得分有所提高。代码将在GitHub上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但在对话生成等任务中存在虚构问题。本文提出两种新型的图知识增强框架,即文本化图对话响应生成(TG-DRG)和图感知对话响应生成(GA-DRG),结合推理引导对话重构、对话情境知识选择和图增强响应生成,以提高对话响应的事实性。为评估生成响应的事实性,本文提出对话事实评分方法,解决现有方法在对话环境中的局限性,提供更可靠的评估。实验结果显示,所提方法在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上显著提高事实性,相较于其他图知识增强基线方法,包括最先进的G-retriever,在对话事实评分上分别提高了3.47%和3.12%。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但在对话生成中存在虚构问题。
- 提出两种新型的图知识增强框架TG-DRG和GA-DRG,以提高对话响应的事实性。
- 结合推理引导对话重构、对话情境知识选择和图增强响应生成。
- 提出对话事实评分方法,以更可靠地评估生成响应的事实性。
- 所提方法在OpendialKG和HybriDialogue数据集上显著提高事实性。
- 与其他图知识增强基线方法相比,所提方法表现更优,在对话事实评分上有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

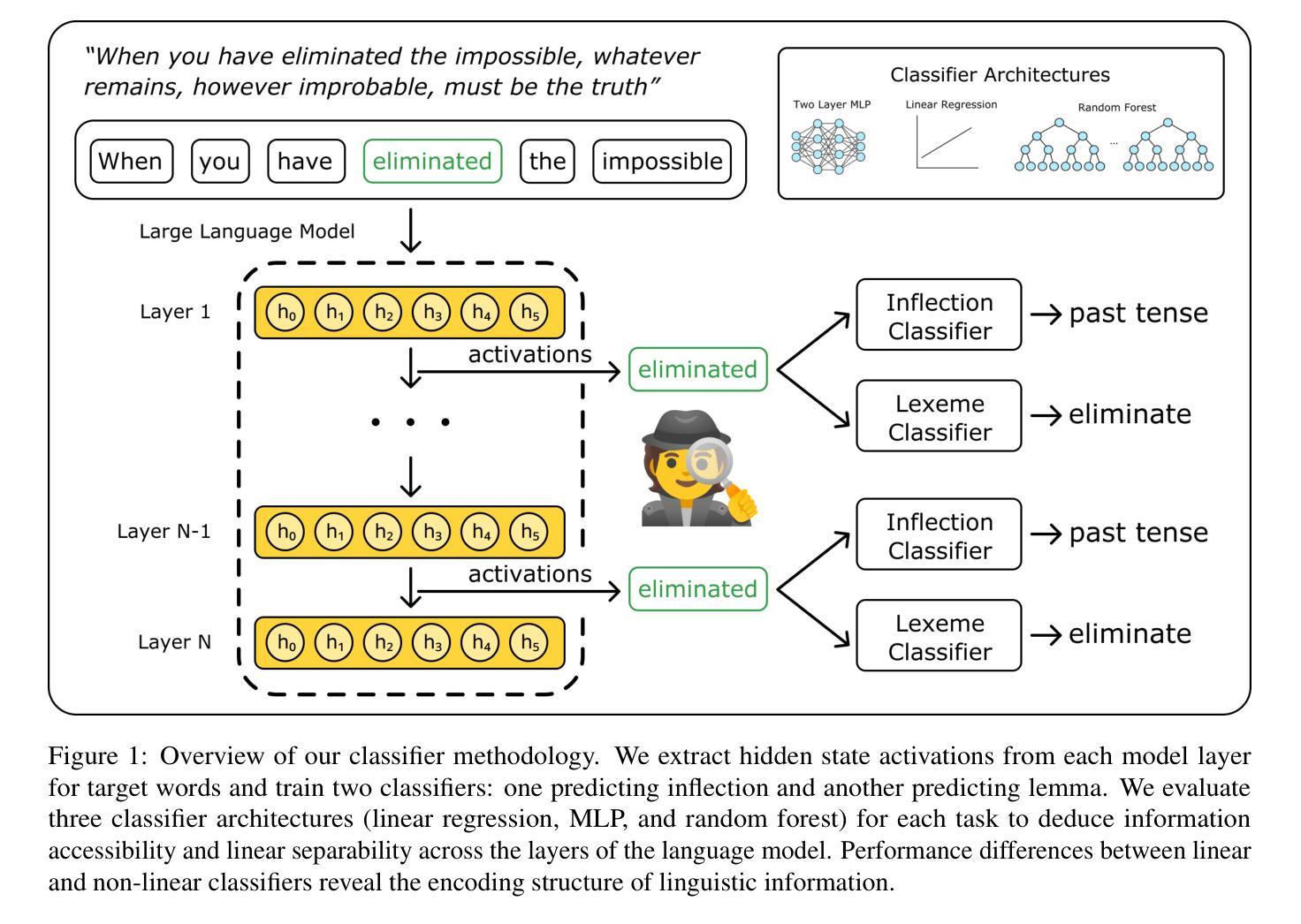
Model Internal Sleuthing: Finding Lexical Identity and Inflectional Morphology in Modern Language Models
Authors:Michael Li, Nishant Subramani
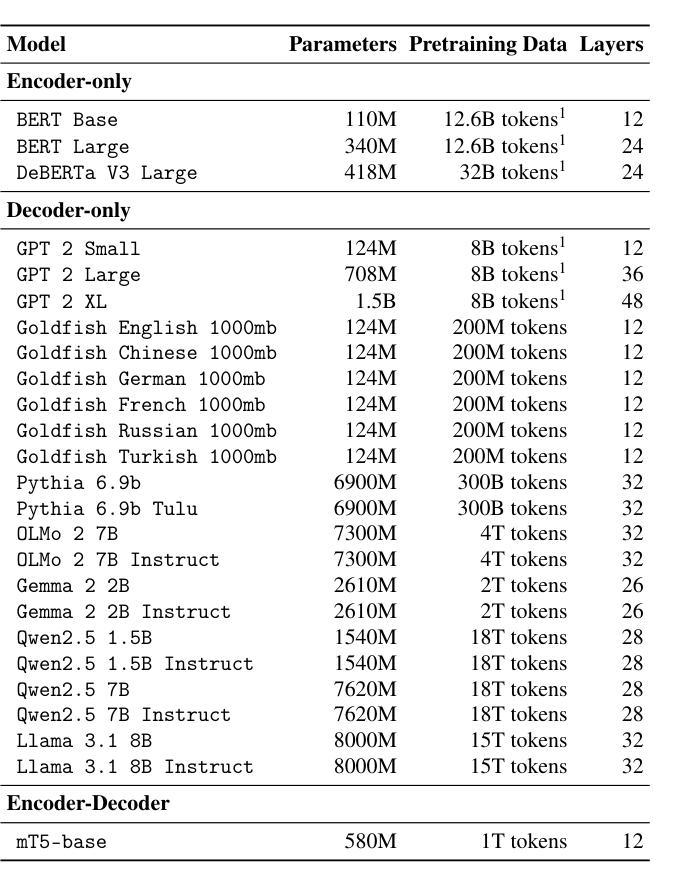
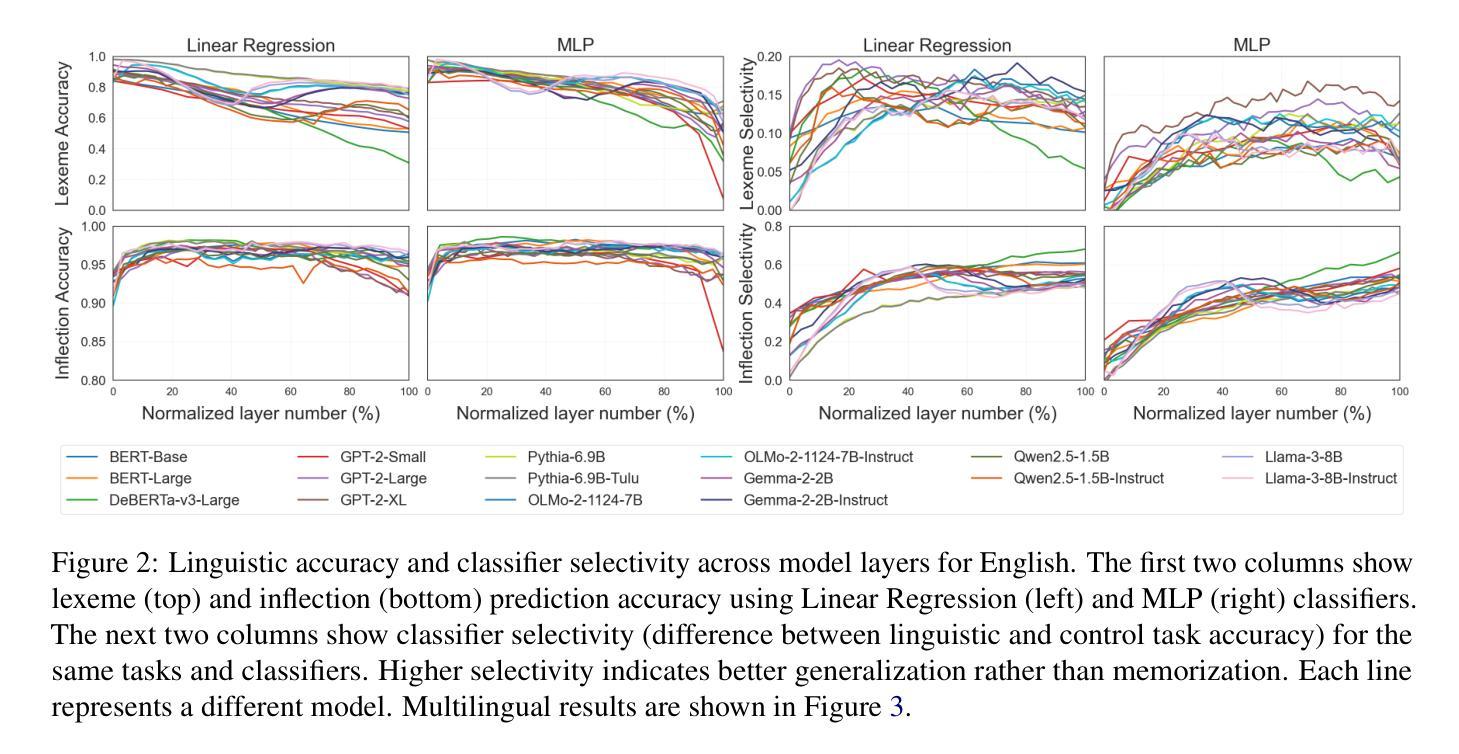
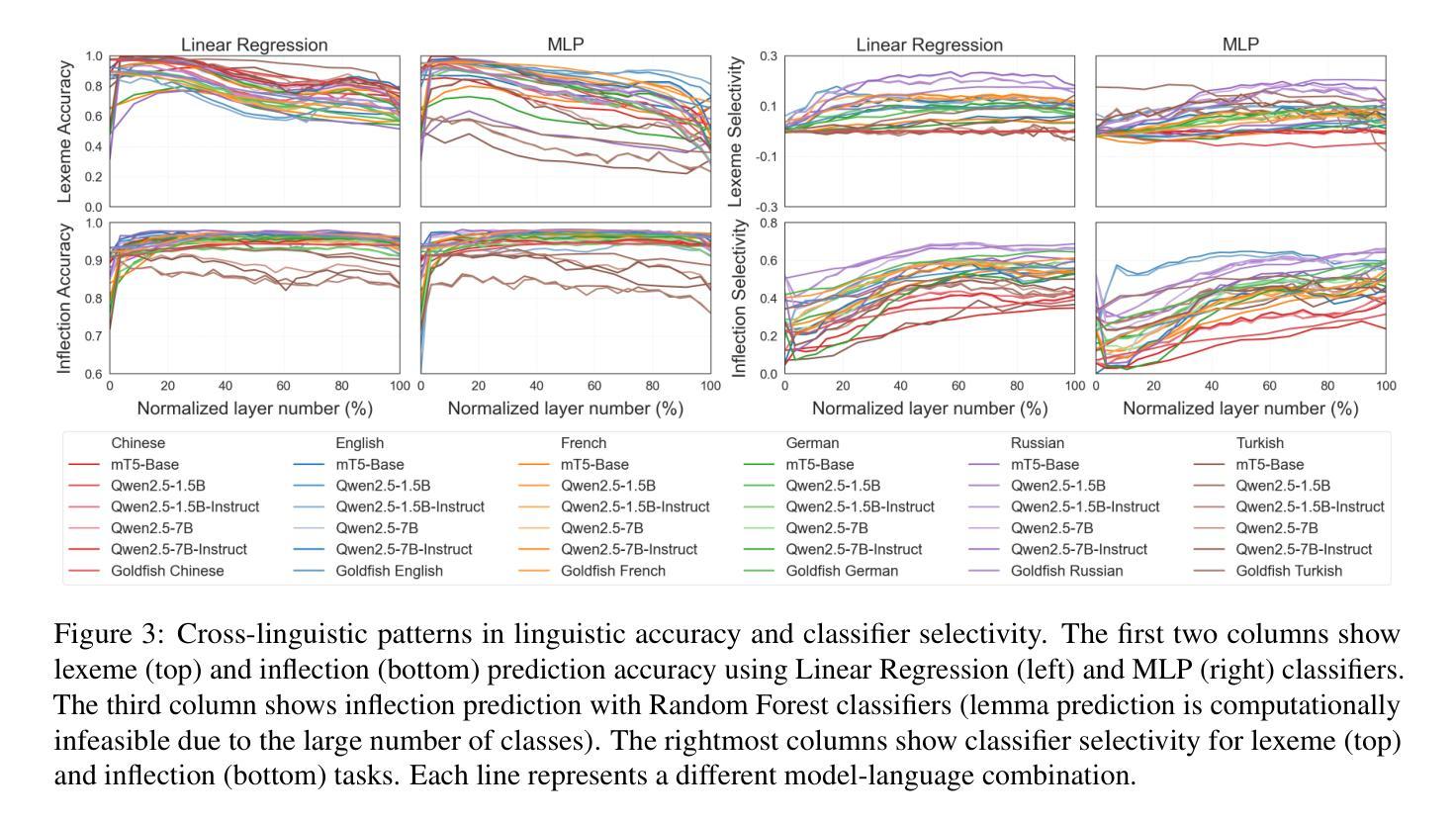
Large transformer-based language models dominate modern NLP, yet our understanding of how they encode linguistic information is rooted in studies of early models like BERT and GPT-2. To better understand today’s language models, we investigate how 25 models - from classical architectures (BERT, DeBERTa, GPT-2) to modern large language models (Pythia, OLMo-2, Gemma-2, Qwen2.5, Llama-3.1) - represent lexical identity and inflectional morphology across six typologically diverse languages. Using linear and nonlinear classifiers trained on hidden activations, we predict word lemmas and inflectional features layer by layer. We find that models concentrate lexical information linearly in early layers and increasingly nonlinearly in later layers, while keeping inflectional information uniformly accessible and linearly separable throughout. Additional experiments probe the nature of these encodings: attention and residual analyses examine where within layers information can be recovered, steering vector experiments test what information can be functionally manipulated, and intrinsic dimensionality analyses explore how the representational structure evolves across layers. Remarkably, these encoding patterns emerge across all models we test, despite differences in architecture, size, and training regime (pretrained and instruction-tuned variants). This suggests that, even with substantial advances in LLM technologies, transformer models organize linguistic information in similar ways, indicating that these properties are important for next token prediction and are learned early during pretraining. Our code is available at https://github.com/ml5885/model_internal_sleuthing
现代自然语言处理主要由大型基于transformer的语言模型主导,然而我们对它们如何编码语言信息的理解还仅限于早期模型,如BERT和GPT-2。为了更好地理解当今的语言模型,我们研究了从经典架构(BERT、DeBERTa、GPT-2)到现代大型语言模型(Pythia、OLMo-2、Gemma-2、Qwen2.5、Llama-3.1)的25种模型是如何在六种语言类型丰富的语言中表示词汇身份和屈折形态。我们使用在隐藏激活上训练的线性和非线性分类器逐层预测词干和屈折特征。我们发现模型在早期层次中以线性方式集中词汇信息,而在后期层次中则越来越以非线性方式集中信息,同时保持屈折信息在整个过程中均匀可访问并且可线性分离。额外的实验探讨了这些编码的本质:注意力分析和残差分析检查可以在哪些层次内恢复信息,转向向量实验测试可以操作哪些信息,以及内在维度分析探索层次间表示结构如何演变。值得注意的是,尽管我们在测试所有模型时都发现了这些编码模式,这些模型在架构、规模和训练制度(预训练和指令调整变体)方面存在差异。这表明,尽管大型语言模型技术取得了重大进展,但transformer模型以相似的方式组织语言信息,这表明这些属性对于下一个令牌预测很重要,并且在预训练期间早期就已经学习到了。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ml5885/model_internal_sleuthing找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF INTERPLAY Workshop COLM 2025
Summary
本文探讨了现代自然语言处理中大型基于Transformer的语言模型如何编码语言信息。通过对包括经典架构(如BERT和GPT-2)和现代大型语言模型在内的共25种模型的深入研究发现,这些模型在早期层级中采用线性方式集中词汇信息,并在后续层级中逐渐采用非线性方式。同时,这些模型保持将屈折信息均匀分布并始终保持线性可分。研究还通过一系列实验探究了这些编码的特性,包括注意力与残差分析、引导向量实验和内在维度分析。尽管模型在架构、规模和训练机制上存在差异,但它们展现出相似的编码模式。这表明即便是在LLM技术取得了显著进步的背景下,Transformer模型的组织语言信息的方式仍然是稳定的。对于下一步的词预测而言,这些特性尤为重要,并且主要是在预训练阶段早期就形成的。相关的代码可以在相关网站公开获取。
Key Takeaways
- 大型基于Transformer的语言模型主导现代NLP领域的研究。它们采用分层的信息处理方式处理词汇信息和屈折信息。词汇信息在前期层级中以线性方式为主,后期层级则逐渐采用非线性方式处理。屈折信息则在整个模型中保持均匀分布和线性可分性。
点此查看论文截图

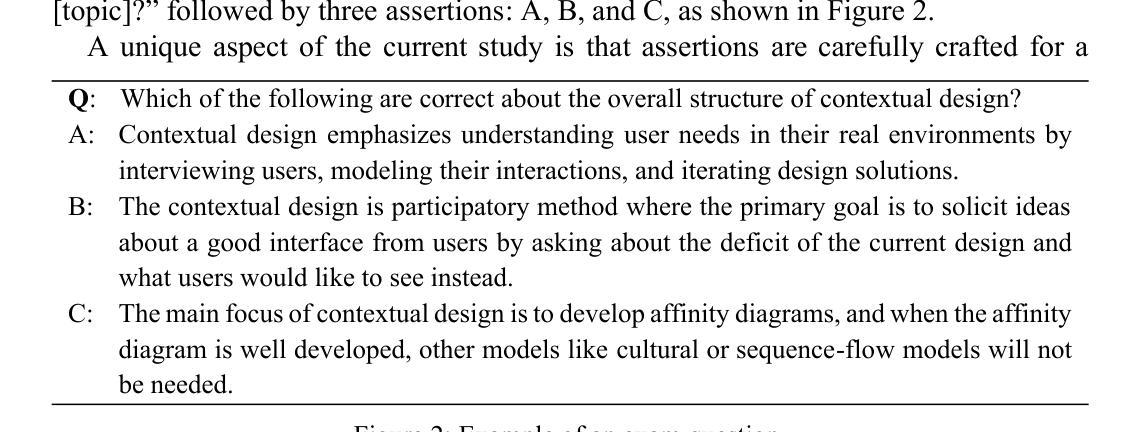
Tell Me Who Your Students Are: GPT Can Generate Valid Multiple-Choice Questions When Students’ (Mis)Understanding Is Hinted
Authors:Machi Shimmei, Masaki Uto, Yuichiroh Matsubayashi, Kentaro Inui, Aditi Mallavarapu, Noboru Matsuda
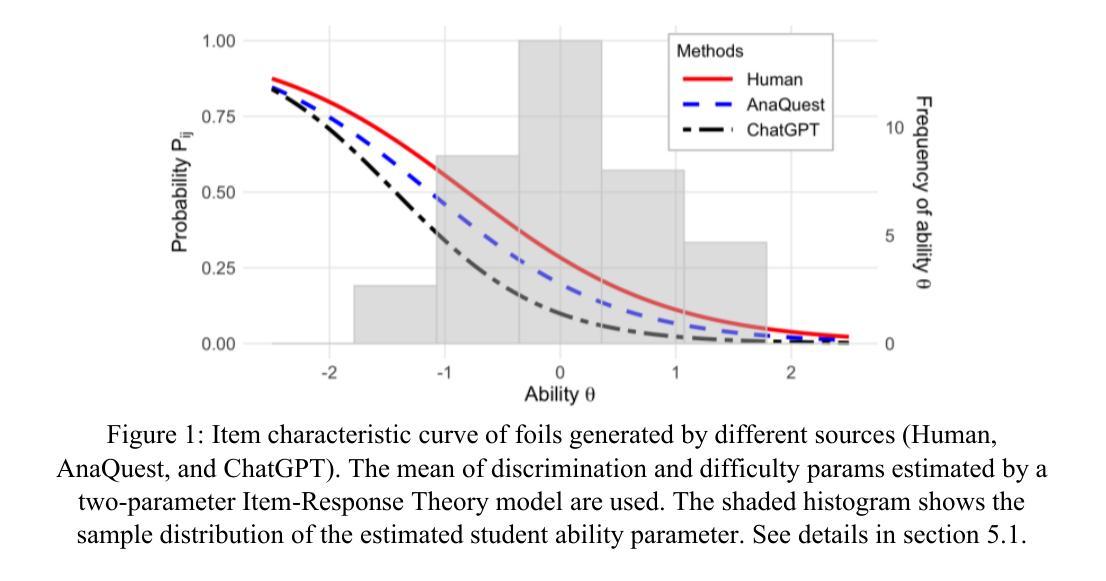
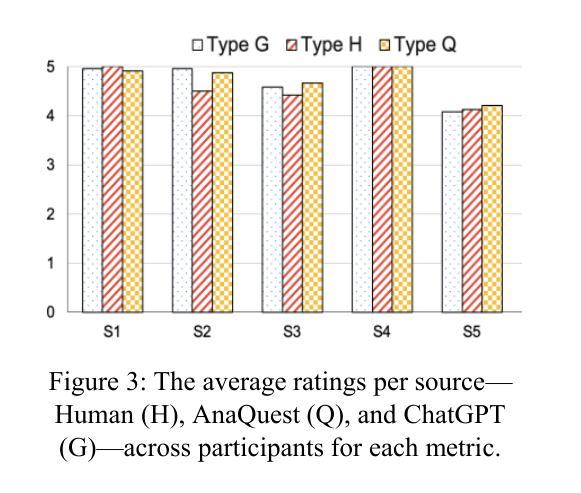
The primary goal of this study is to develop and evaluate an innovative prompting technique, AnaQuest, for generating multiple-choice questions (MCQs) using a pre-trained large language model. In AnaQuest, the choice items are sentence-level assertions about complex concepts. The technique integrates formative and summative assessments. In the formative phase, students answer open-ended questions for target concepts in free text. For summative assessment, AnaQuest analyzes these responses to generate both correct and incorrect assertions. To evaluate the validity of the generated MCQs, Item Response Theory (IRT) was applied to compare item characteristics between MCQs generated by AnaQuest, a baseline ChatGPT prompt, and human-crafted items. An empirical study found that expert instructors rated MCQs generated by both AI models to be as valid as those created by human instructors. However, IRT-based analysis revealed that AnaQuest-generated questions - particularly those with incorrect assertions (foils) - more closely resembled human-crafted items in terms of difficulty and discrimination than those produced by ChatGPT.
本研究的主要目标是开发并评估一种创新性的提示技术——AnaQuest,该技术使用预训练的大型语言模型来生成多项选择题(MCQs)。在AnaQuest中,选择项是关于复杂概念的句子级断言。该技术结合了形成性评估和终结性评估。在形成性阶段,学生以自由文本的形式回答关于目标概念的问题。在终结性评估中,AnaQuest分析这些回答以生成正确和错误的断言。为了评估生成的MCQ的有效性,应用项目反应理论(IRT)比较了AnaQuest生成的多项选择题、基线ChatGPT提示和人类制作的题目之间的项目特征。实证研究结果表明,专家导师认为AI模型生成的MCQ与人类导师创建的题目同样有效。然而,基于IRT的分析显示,AnaQuest生成的问题——特别是那些带有错误断言(foil)的问题——在难度和区分度方面更接近于人类制作的题目,而不是ChatGPT生成的题目。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a pre-print version of a paper to appear in AIED2025. The camera-ready version is available at https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-99264-3_16
Summary
AnaQuest是一项旨在利用预训练的大型语言模型生成多选题(MCQs)的创新提示技术。它结合了形成性评估和终结性评估,通过对学生关于目标概念的自由文本回答进行分析,生成正确和错误的断言。研究表明,人工智能模型生成的MCQs与专家教师生成的题目具有相同的效度,但AnaQuest生成的问题在难度和区分度上更接近人类制作的题目。
Key Takeaways
- AnaQuest是一种用于生成多选题的创新提示技术,利用预训练的大型语言模型。
- 该技术整合了形成性和终结性评估来生成正确和错误的断言作为选择题选项。
- 通过Item Response Theory(IRT)对AnaQuest生成的题目与ChatGPT和人工生成的题目进行比较分析。
- 专家教师认为AI模型生成的MCQs与人工制作的题目具有相同的效度。
- AnaQuest生成的问题,特别是包含错误断言的选项,在难度和区分度上更接近人类制作的题目。
- AnaQuest技术有助于提高题目生成的效率和质量,有助于教育评估和学生的学习发展。
点此查看论文截图

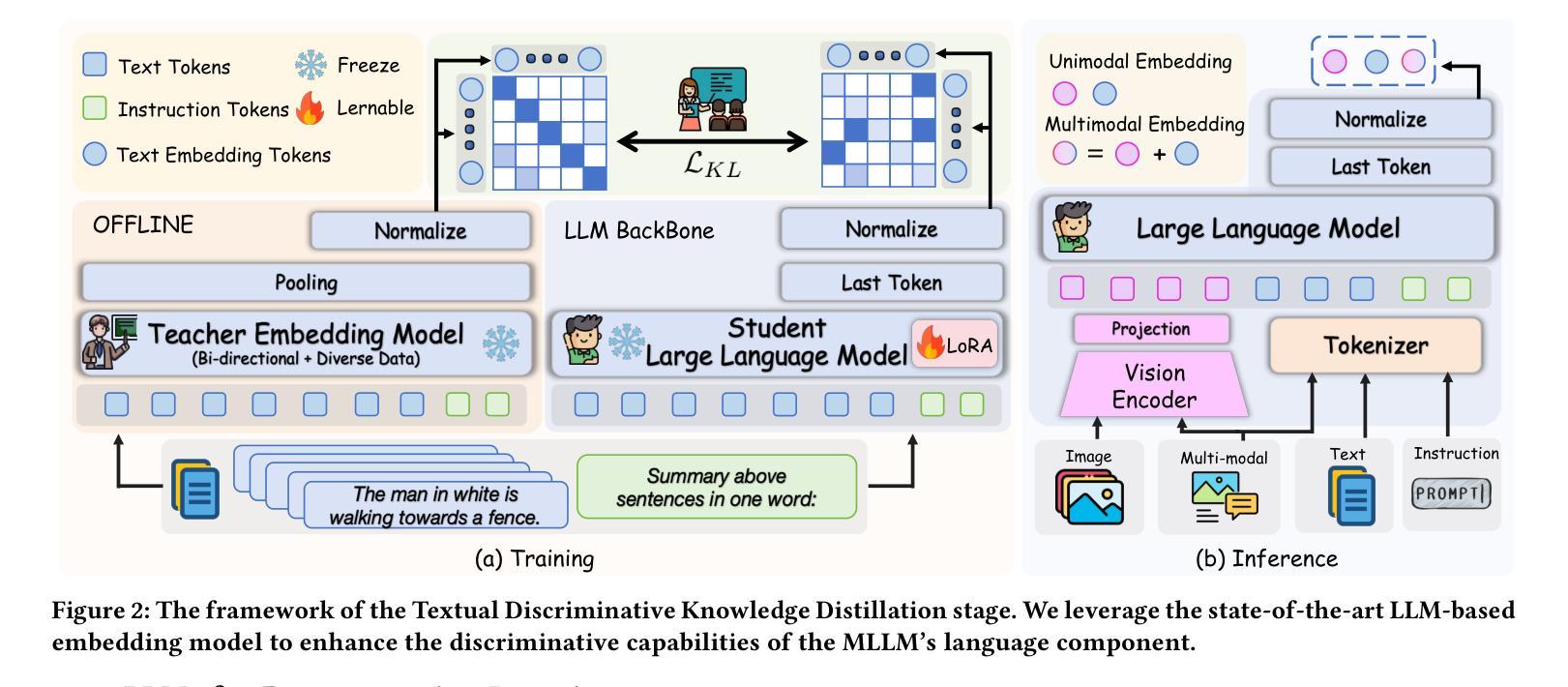
Breaking the Modality Barrier: Universal Embedding Learning with Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Tiancheng Gu, Kaicheng Yang, Ziyong Feng, Xingjun Wang, Yanzhao Zhang, Dingkun Long, Yingda Chen, Weidong Cai, Jiankang Deng
The Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) framework has become a widely used approach for multimodal representation learning, particularly in image-text retrieval and clustering. However, its efficacy is constrained by three key limitations: (1) text token truncation, (2) isolated image-text encoding, and (3) deficient compositionality due to bag-of-words behavior. While recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant advances in generalized vision-language understanding, their potential for learning transferable multimodal representations remains underexplored.In this work, we present UniME (Universal Multimodal Embedding), a novel two-stage framework that leverages MLLMs to learn discriminative representations for diverse downstream tasks. In the first stage, we perform textual discriminative knowledge distillation from a powerful LLM-based teacher model to enhance the embedding capability of the MLLM's language component. In the second stage, we introduce hard negative enhanced instruction tuning to further advance discriminative representation learning. Specifically, we initially mitigate false negative contamination and then sample multiple hard negatives per instance within each batch, forcing the model to focus on challenging samples. This approach not only improves discriminative power but also enhances instruction-following ability in downstream tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on the MMEB benchmark and multiple retrieval tasks, including short and long caption retrieval and compositional retrieval. Results demonstrate that UniME achieves consistent performance improvement across all tasks, exhibiting superior discriminative and compositional capabilities.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)框架已成为广泛应用于多模态表示学习的方法,尤其在图像文本检索和聚类中。然而,它的有效性受到三个主要限制:(1)文本令牌截断,(2)孤立的图像文本编码,以及(3)由于词袋行为导致的成分缺陷。虽然最近的多媒体语言大模型(MLLM)在通用视觉语言理解方面取得了显著进展,但其学习可转移的多模态表示潜力仍未得到充分探索。在本研究中,我们提出了UniME(通用多模态嵌入),这是一个利用MLLM学习用于下游任务的判别表示的新型两阶段框架。在第一阶段,我们通过强大的基于LLM的教师模型进行文本判别知识蒸馏,以增强MLLM的语言组件的嵌入能力。在第二阶段,我们引入了硬负增强指令调整,以进一步推动判别表示学习。具体来说,我们首先缓解假阴性污染,然后在每个批次内为每个实例采样多个硬负样本,迫使模型关注具有挑战性的样本。这种方法不仅提高了判别力,而且提高了下游任务中的指令执行能力。我们在MMEB基准测试和多个检索任务上进行了广泛实验,包括短文本和长文本检索以及组合检索。结果表明,UniME在所有任务上均实现了性能改进,展现出卓越的判别和组合能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures, Accepted by ACM MM2025, Project page: https://garygutc.github.io/UniME
Summary
CLIP框架在多模态表示学习方面,尤其在图像文本检索和聚类中,得到了广泛应用。但其存在文本令牌截断、孤立的图像文本编码和因词袋行为导致的成分缺陷等三个关键局限性。虽然最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在通用视觉语言理解方面取得了显著进展,但其在学习可转移的多模态表示方面的潜力仍被探索不足。本研究提出UniME(通用多模态嵌入),这是一个利用MLLMs学习判别表示用于多种下游任务的新型两阶段框架。第一阶段,通过强大的LLM模型进行文本判别知识蒸馏,以增强MLLM语言组件的嵌入能力。第二阶段,引入增强指令调整硬负样本进一步优化判别表示学习。通过减少假阴性污染并对每个实例在批次内采样多个硬负样本,迫使模型关注具有挑战性的样本。这种方法不仅提高了判别力,还提高了下游任务中的指令遵循能力。在MMEB基准测试和多个检索任务上的实验表明,UniME在所有任务上实现了性能改进,表现出卓越的判别和组合能力。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP框架在多模态表示学习中广泛应用,但存在文本令牌截断、图像文本编码孤立和成分缺陷等局限性。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在通用视觉语言理解方面取得显著进展,但在学习可转移的多模态表示方面潜力未得到充分探索。
- UniME是一个利用MLLMs的新型两阶段框架,旨在学习用于多种下游任务的判别表示。
- 第一阶段通过强大的LLM模型进行文本判别知识蒸馏以增强嵌入能力。
- 第二阶段引入增强指令调整硬负样本,提高判别力并增强指令遵循能力。
- UniME在多个基准测试和检索任务上实现了性能改进,表现出卓越的判别和组合能力。
点此查看论文截图


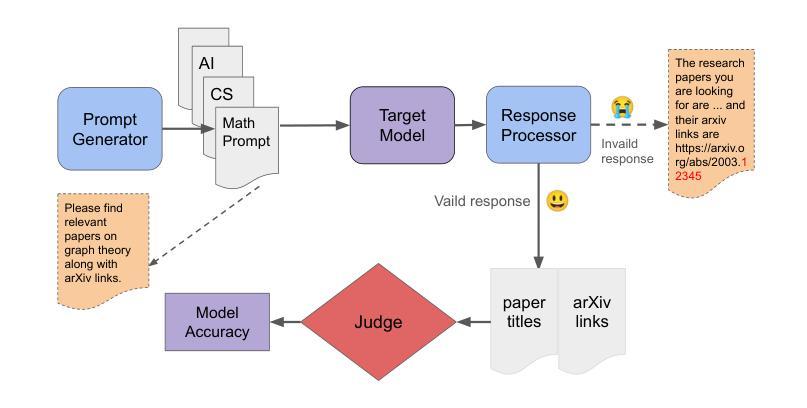
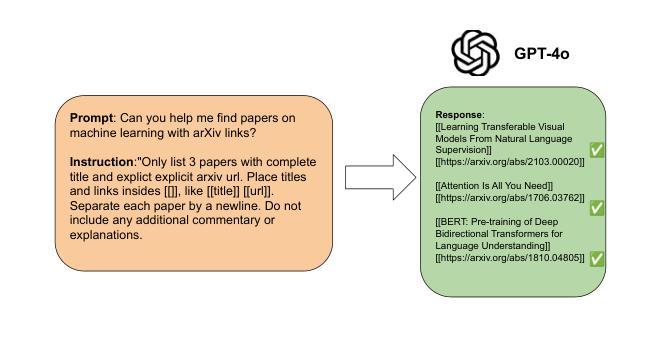
ArXivBench: When You Should Avoid Using ChatGPT for Academic Writing
Authors:Ning Li, Jingran Zhang, Justin Cui
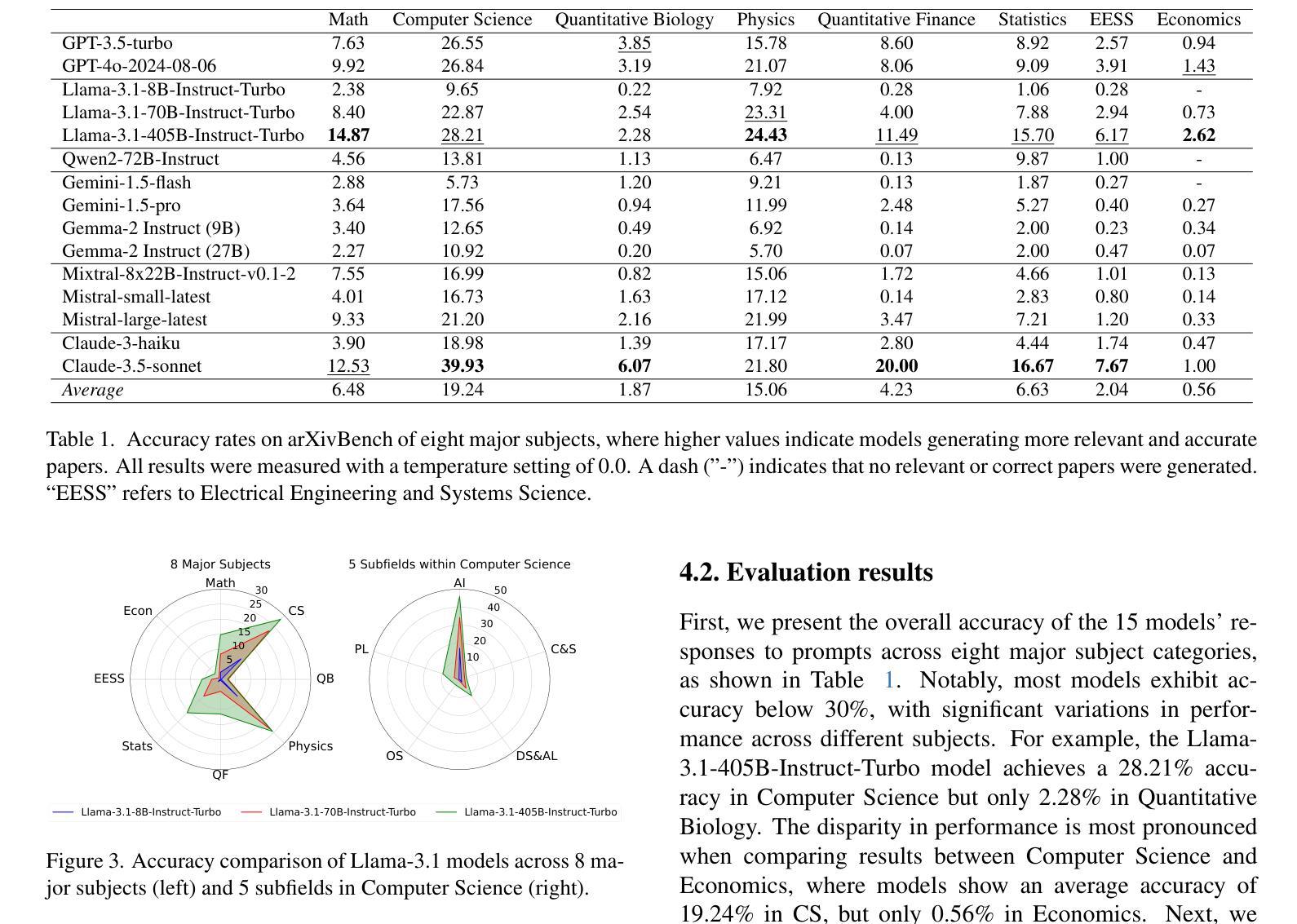
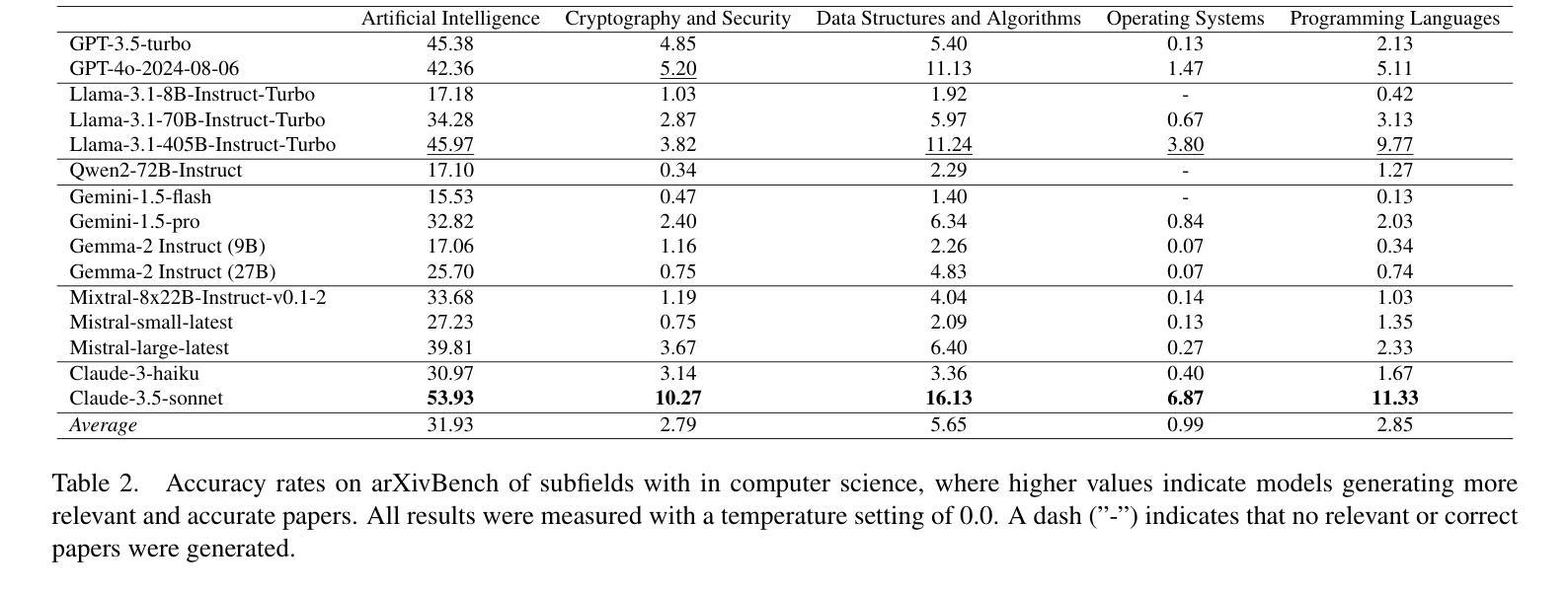
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in reasoning and question answering, yet their tendency to generate factually incorrect content remains a critical challenge. This study evaluates proprietary and open-source LLMs on generating relevant research papers with accurate arXiv links. Our evaluation reveals critical academic risks: LLMs frequently generate incorrect arXiv links or references to non-existent papers, fundamentally undermining their ability to properly attribute research contributions to the actual authors. We introduce arXivBench, a benchmark specifically designed to assess LLM performance across eight major subject categories on arXiv and five subfields within computer science, one of the most popular categories among them. Our findings show concerning accuracy variations across subjects, with Claude-3.5-Sonnet exhibiting a substantial advantage in generating both relevant and accurate responses. Notably, most LLMs perform significantly better in Artificial Intelligence than other subfields. This benchmark provides a standardized tool for evaluating LLM reliability in scientific contexts, promoting more dependable academic use in research environments. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/liningresearch/arXivBench and https://huggingface.co/datasets/arXivBenchLLM/arXivBench.
大型语言模型(LLM)在推理和问答方面表现出强大的能力,但它们生成事实错误内容的倾向仍然是一个关键挑战。本研究评估了专有和开源的LLM在生成带有准确arXiv链接的相关研究论文方面的能力。我们的评估揭示了重要的学术风险:LLM经常生成错误的arXiv链接或引用不存在的论文,从根本上削弱了它们正确归属研究贡献给实际作者的能力。我们推出了arXivBench,这是一个专门用于评估LLM在arXiv八大主题类别和计算机科学五大子领域性能的工具,这是它们中最受欢迎的一个类别。我们的研究发现在不同主题之间出现了令人担忧的准确性变化,其中Claude-3.5-Sonnet在生成既相关又准确响应方面表现出显著优势。值得注意的是,大多数LLM在人工智能方面的表现要好于其他子领域。这个基准工具为评估LLM在科学环境中的可靠性提供了标准化工具,促进了在学术环境中更可靠的用途。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/liningresearch/arXivBench和https://huggingface.co/datasets/arXivBenchLLM/arXivBench找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在推理和问答方面表现出强大的能力,但生成事实错误内容的问题仍是关键挑战。本研究对专有和开源LLM生成具有准确arXiv链接的相关研究论文的能力进行评估。评估结果显示出重要的学术风险:LLM经常生成错误的arXiv链接或引用不存在的论文,从根本上破坏了其正确归属研究贡献的能力。为此,研究引入了arXivBench基准测试,该测试专门设计用于评估LLM在arXiv八大主题类别和计算机科学五个子领域的表现。研究发现,各主题之间的准确率存在差异,其中Claude-3.5-Sonnet在生成相关和准确响应方面表现出显著优势。值得注意的是,大多数LLM在人工智能方面的表现优于其他子领域。此基准测试为评估LLM在科学环境中的可靠性提供了标准化工具,促进了研究环境中更可靠的学术使用。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在生成带有准确arXiv链接的研究论文时存在事实错误的问题。
- LLM有时会生成错误的arXiv链接或引用不存在的论文,这影响了对研究贡献的正确归属。
- 引入了一个新的基准测试工具arXivBench,用于评估LLM在多个学术领域(包括计算机科学的子领域)的表现。
- 在不同的主题类别中,LLM的表现存在差异,其中Claude-3.5-Sonnet在某些任务上表现较好。
- LLM在人工智能领域的表现通常优于其他子领域。
- arXivBench提供了一个标准化的工具来评估LLM在科学环境中的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

R2Vul: Learning to Reason about Software Vulnerabilities with Reinforcement Learning and Structured Reasoning Distillation
Authors:Martin Weyssow, Chengran Yang, Junkai Chen, Ratnadira Widyasari, Ting Zhang, Huihui Huang, Huu Hung Nguyen, Yan Naing Tun, Tan Bui, Yikun Li, Ang Han Wei, Frank Liauw, Eng Lieh Ouh, Lwin Khin Shar, David Lo
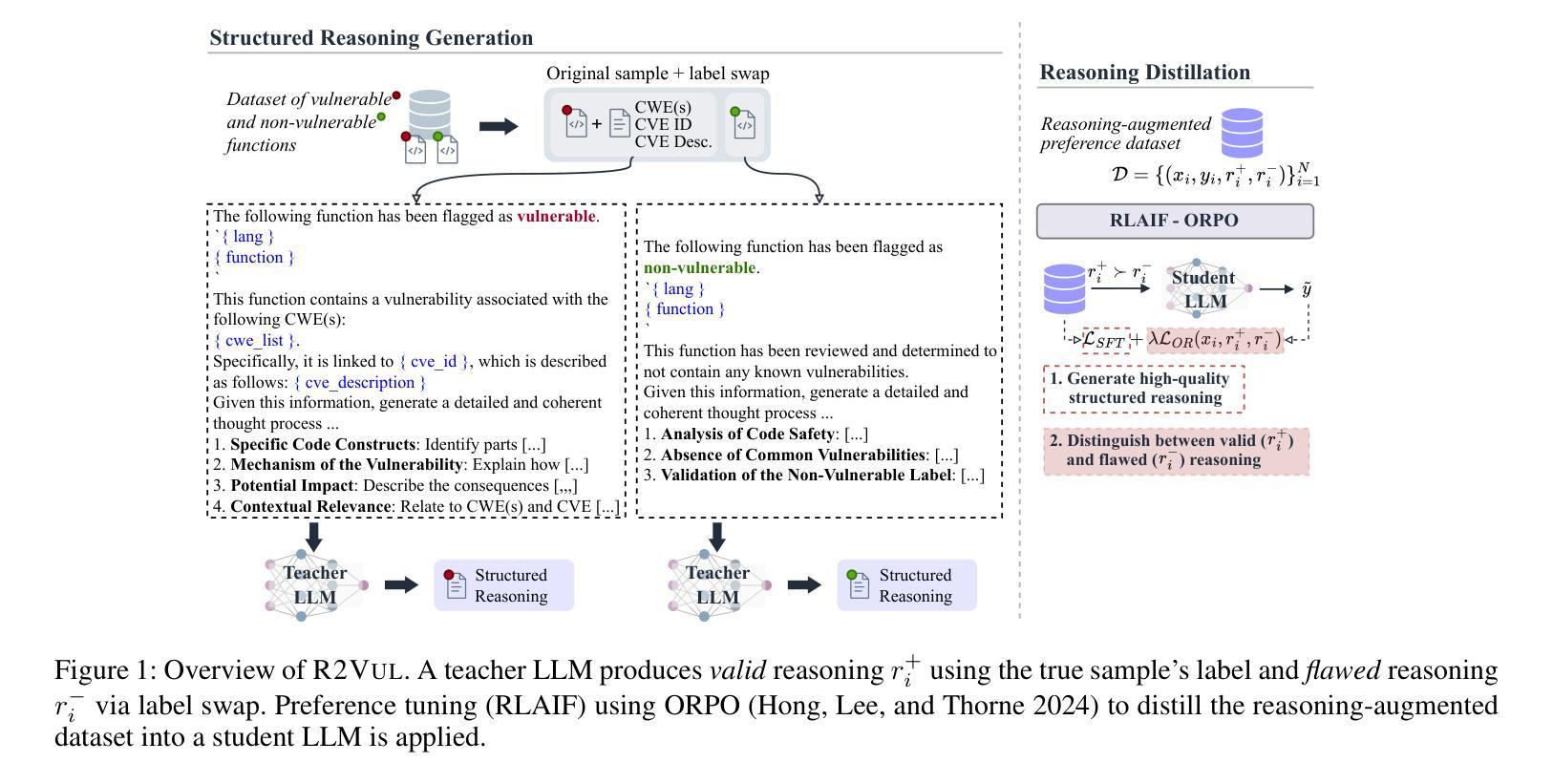
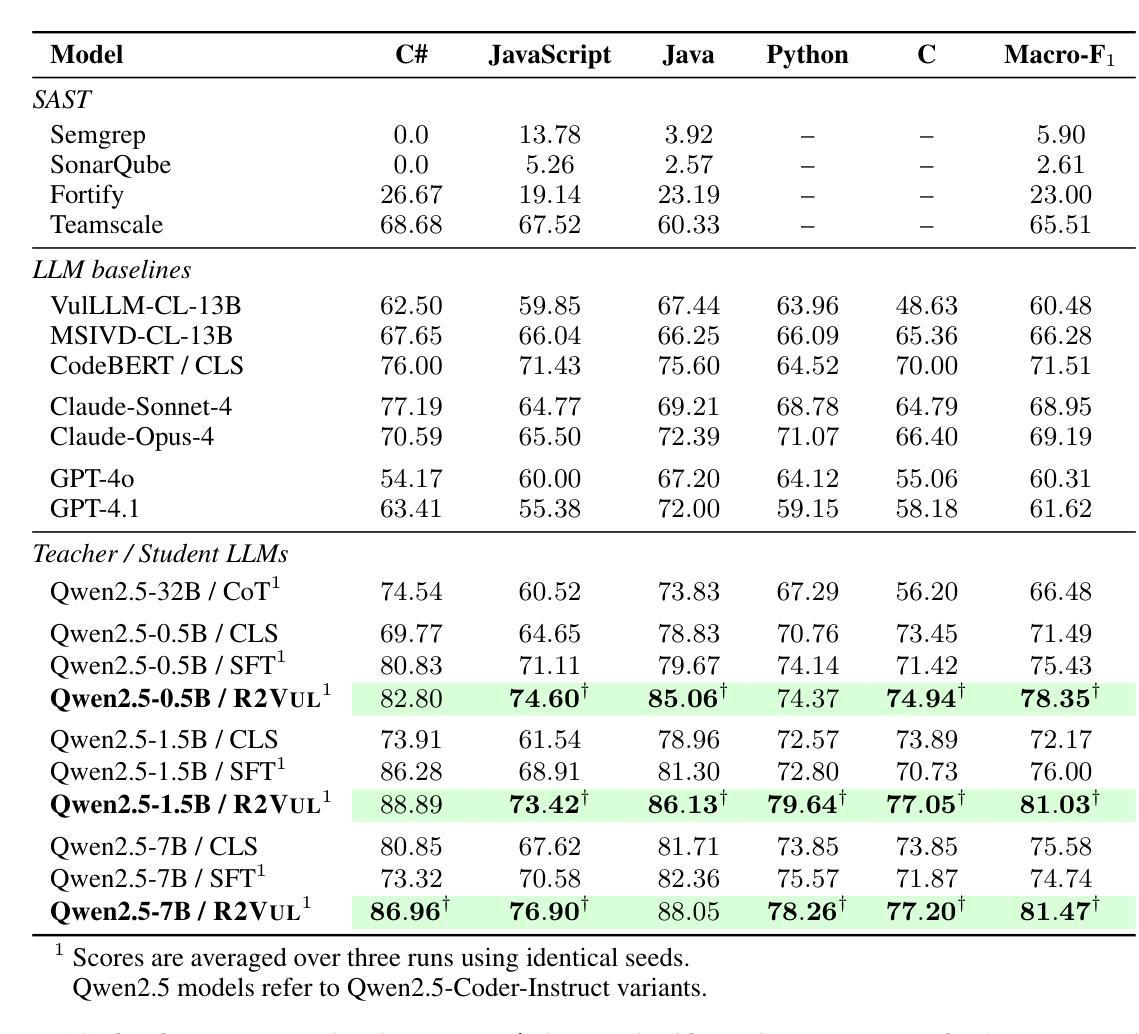
Large language models (LLMs) have shown promising performance in software vulnerability detection, yet their reasoning capabilities remain unreliable. We propose R2Vul, a method that combines reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF) and structured reasoning distillation to teach small code LLMs to detect vulnerabilities while generating security-aware explanations. Unlike prior chain-of-thought and instruction tuning approaches, R2Vul rewards well-founded over deceptively plausible vulnerability explanations through RLAIF, which results in more precise detection and high-quality reasoning generation. To support RLAIF, we construct the first multilingual preference dataset for vulnerability detection, comprising 18,000 high-quality samples in C#, JavaScript, Java, Python, and C. We evaluate R2Vul across five programming languages and against four static analysis tools, eight state-of-the-art LLM-based baselines, and various fine-tuning approaches. Our results demonstrate that a 1.5B R2Vul model exceeds the performance of its 32B teacher model and leading commercial LLMs such as Claude-4-Opus. Furthermore, we introduce a lightweight calibration step that reduces false positive rates under varying imbalanced data distributions. Finally, through qualitative analysis, we show that both LLM and human evaluators consistently rank R2Vul model’s reasoning higher than other reasoning-based baselines.
大型语言模型(LLM)在软件漏洞检测方面表现出有前景的性能,但它们的推理能力仍然不可靠。我们提出了R2Vul方法,它结合了人工智能反馈的强化学习(RLAIF)和结构化推理蒸馏技术,用于教授小型代码LLM检测漏洞,同时生成安全意识的解释。与先前的思维链和指令调整方法不同,R2Vul通过RLAIF奖励基于事实的漏洞解释,这些解释避免了似是而非的欺骗性,从而实现了更精确的检测和高质量的推理生成。为了支持RLAIF,我们构建了用于漏洞检测的第一套多语言偏好数据集,包含C#、JavaScript、Java、Python和C中的18,000个高质量样本。我们对五种编程语言进行了评估,并与四种静态分析工具、八个最新的LLM基准模型和各种微调方法进行了比较。我们的结果表明,一个规模为1.5B的R2Vul模型超过了其规模为32B的教师模型和领先的商业LLM(如Claude-4-Opus)的性能。此外,我们还引入了一个轻量级的校准步骤,该步骤可以降低在不同不平衡数据分布下的误报率。最后,通过定性分析,我们证明LLM和人类评估者都一致地认为R2Vul模型的推理能力高于其他基于推理的基准模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM在软件漏洞检测中表现优异,但其推理能力尚待提高。为此,研究者提出了R2Vul方法,它结合了强化学习和结构化推理蒸馏技术,用于教授小型代码LLM检测漏洞并生成安全意识的解释。R2Vul通过强化学习从人工智能反馈(RLAIF)奖励有根据的、不欺骗性的漏洞解释,从而提高漏洞检测的精确性和高质量推理生成。为了支持RLAIF,研究者构建了首个用于漏洞检测的多语言偏好数据集,包含C#、JavaScript、Java、Python和C的18,000高质量样本。评估结果显示,R2Vul模型性能超越大型模型及商业LLM,并引入轻量级校准步骤以降低不同不平衡数据分布下的误报率。定性分析显示,LLM和人类评估者均认为R2Vul模型的推理能力高于其他基于推理的基线。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在软件漏洞检测中表现良好,但推理能力需提升。
- R2Vul方法结合了强化学习和结构化推理蒸馏技术,用于教授LLM检测漏洞并生成安全意识的解释。
- RLAIF通过奖励有根据的、不欺骗性的漏洞解释,提高漏洞检测的精确性和推理质量。
- 研究者构建了首个用于漏洞检测的多语言偏好数据集。
- R2Vul模型性能超越大型模型及商业LLM。
- 引入轻量级校准步骤以降低误报率。
点此查看论文截图

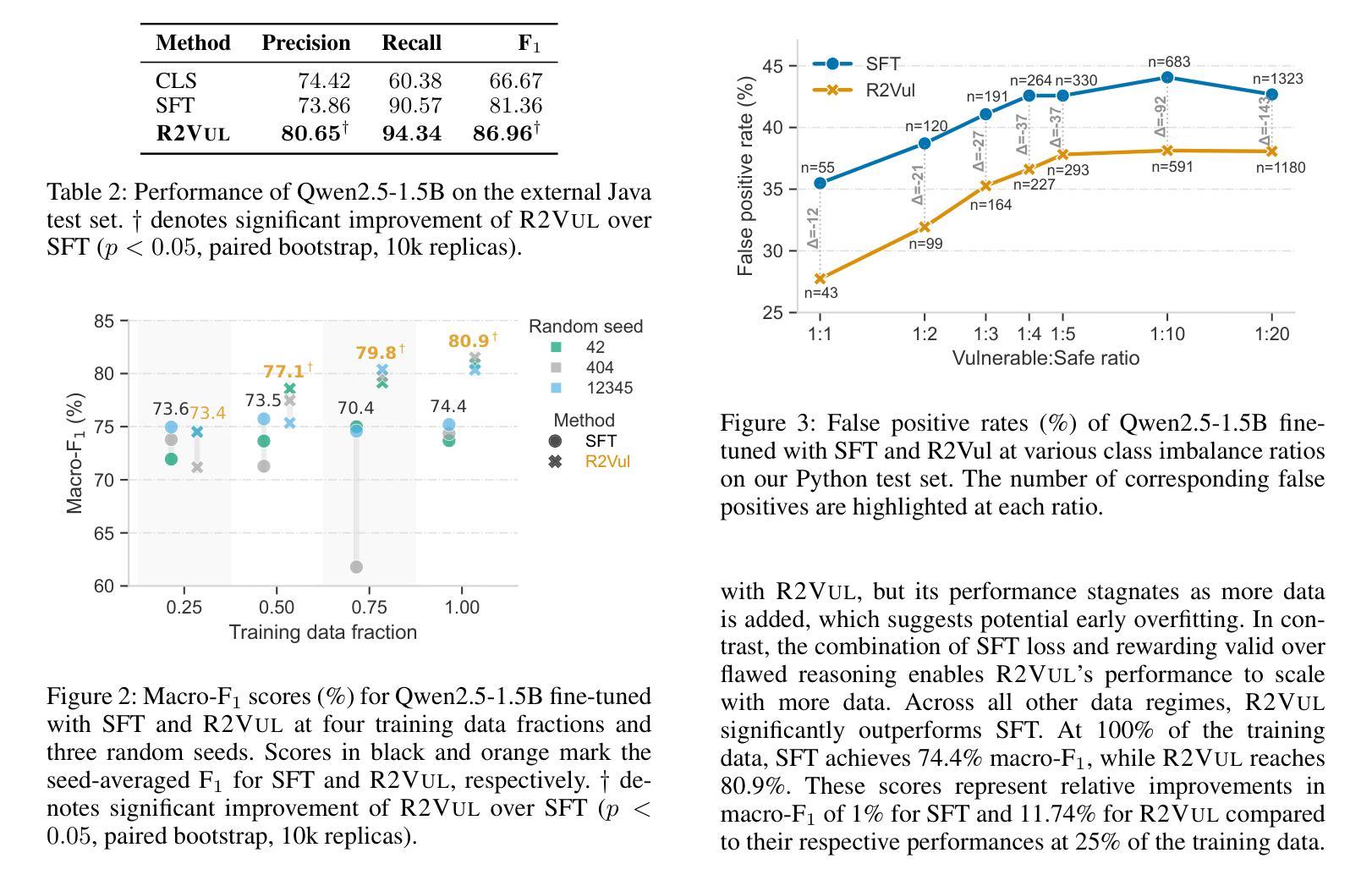
SciReplicate-Bench: Benchmarking LLMs in Agent-driven Algorithmic Reproduction from Research Papers
Authors:Yanzheng Xiang, Hanqi Yan, Shuyin Ouyang, Lin Gui, Yulan He
This study evaluates large language models (LLMs) in generating code from algorithm descriptions in recent NLP papers. The task requires two key competencies: (1) algorithm comprehension: synthesizing information from papers and academic literature to understand implementation logic, and (2) coding expertise: identifying dependencies and correctly implementing necessary APIs. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we introduce SciReplicate-Bench, a benchmark of 100 tasks from 36 NLP papers published in 2024, featuring detailed annotations and comprehensive test cases. Building on SciReplicate-Bench, we propose Sci-Reproducer, a dual-agent framework consisting of a Paper Agent that interprets algorithmic concepts from literature and a Code Agent that retrieves dependencies from repositories and implements solutions. To assess algorithm understanding, we introduce reasoning graph accuracy, which quantifies similarity between generated and reference reasoning graphs derived from code comments and structure. For evaluating implementation quality, we employ execution accuracy, CodeBLEU, and repository dependency/API recall metrics. In our experiments, we evaluate various powerful non-reasoning and reasoning LLMs as foundational models. The best-performing LLM using \ModelName~achieves only 39% execution accuracy, highlighting the benchmark’s difficulty. Our analysis identifies missing or inconsistent algorithm descriptions as key barriers to successful reproduction. We make available our benchmark and code at https://github.com/xyzCS/SciReplicate-Bench and project homepage at https://xyzcs.github.io/scireplicate.github.io/.
本研究评估大型语言模型(LLM)在根据最新自然语言处理(NLP)论文中的算法描述生成代码的能力。这项任务需要两个关键技能:(1)算法理解:从论文和学术文献中综合信息,以理解实现逻辑;(2)编码专业知识:识别依赖关系并正确实现必要的API。为了进行严格的评估,我们推出了SciReplicate-Bench,这是一个包含来自2024年发表的36篇NLP论文的100个任务的基准测试,具有详细的注释和全面的测试用例。基于SciReplicate-Bench,我们提出了Sci-Reproducer,这是一个由两个代理组成的框架,包括一个理解文献中算法概念的Paper Agent和一个从存储库中检索依赖关系并实现解决方案的Code Agent。为了评估算法理解,我们引入了推理图准确性,它量化了从代码注释和结构派生的生成推理图与参考推理图之间的相似性。为了评估实现质量,我们采用执行准确性、CodeBLEU以及存储库依赖/API召回指标。在我们的实验中,我们评估了各种强大的非推理和推理LLM作为基础模型。表现最佳的LLM使用ModelName~仅达到39%的执行准确性,这突出了该基准测试的困难程度。我们的分析确定了缺失或不一致的算法描述是成功复制的主要障碍。我们在https://github.com/xyzCS/SciReplicate-Bench和项目主页https://xyzcs.github.io/scireplicate.github.io/上提供了我们的基准测试和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究评估大型语言模型(LLM)在根据最新自然语言处理(NLP)论文中的算法描述生成代码的能力。这项任务需要两个关键技能:1)算法理解:从论文和学术文献中综合信息以理解实现逻辑;2)编码专业知识:识别依赖关系并正确实现必要的API。为了进行严格评估,我们推出了SciReplicate-Bench,这是一个由36篇于XXXX年发表的NLP论文中的XXXX个任务组成的基准测试,具有详细的注释和全面的测试用例。基于SciReplicate-Bench,我们提出了Sci-Reproducer,这是一个由论文代理和代码代理组成的双代理框架,论文代理负责从文献中解释算法概念,而代码代理则从存储库中检索依赖关系并实现解决方案。为了评估算法理解,我们引入了推理图准确性,该指标量化了从代码注释和结构派生的生成推理图和参考推理图之间的相似性。为了评估实现质量,我们采用了执行准确性、CodeBLEU以及存储库依赖/API召回率指标。在我们的实验中,我们对各种强大的非推理和推理LLM作为基础模型进行了评估。表现最佳的LLM模型名称~仅达到XXXX%的执行准确性,凸显了本基准测试的困难度。我们的分析确定了缺失或不一致的算法描述是成功复制的主要障碍。我们的基准测试和代码可在https://github.com/xyzCS/SciReplicate-Bench上获取,项目主页为https://xyzcs.github.io/scireplicate.github.io/。。
关键见解
- 本研究评估了大型语言模型(LLM)在根据NLP论文中的算法描述生成代码的能力。
- 提出了SciReplicate-Bench基准测试,包含来自最新NLP论文的任务,用于严格评估LLM在此任务上的表现。
- 引入Sci-Reproducer框架,包含论文代理和代码代理,分别负责算法理解和代码实现。
- 采用多种指标评估算法理解和代码实现质量,包括推理图准确性、执行准确性、CodeBLEU以及存储库依赖/API召回率。
- 实验显示,即使是最优秀的LLM模型,在执行准确性方面仍面临挑战,这突显了此任务的复杂性。
- 分析和指出算法描述的缺失或不一致是复制过程中的主要难题。
点此查看论文截图

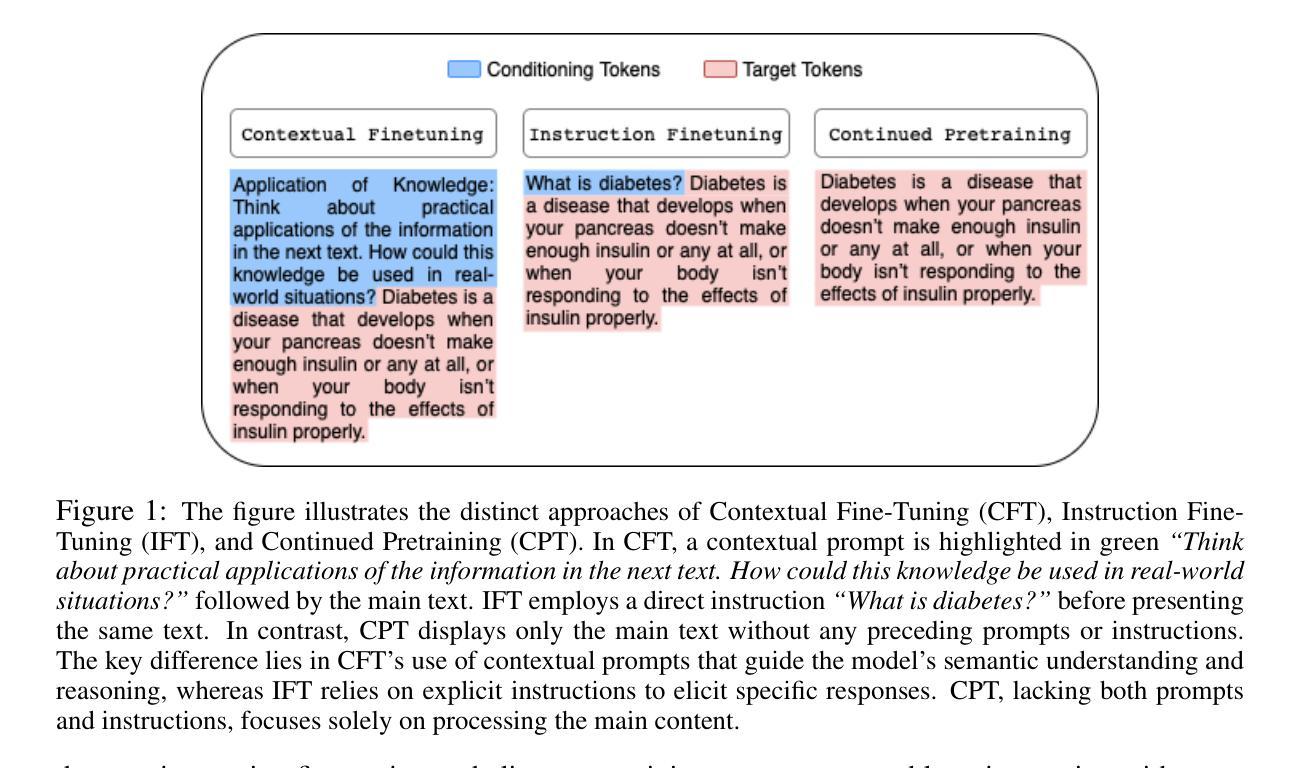
Teaching LLMs How to Learn with Contextual Fine-Tuning
Authors:Younwoo Choi, Muhammad Adil Asif, Ziwen Han, John Willes, Rahul G. Krishnan
Prompting Large Language Models (LLMs), or providing context on the expected model of operation, is an effective way to steer the outputs of such models to satisfy human desiderata after they have been trained. But in rapidly evolving domains, there is often need to fine-tune LLMs to improve either the kind of knowledge in their memory or their abilities to perform open ended reasoning in new domains. When human’s learn new concepts, we often do so by linking the new material that we are studying to concepts we have already learned before. To that end, we ask, “can prompting help us teach LLMs how to learn”. In this work, we study a novel generalization of instruction tuning, called contextual fine-tuning, to fine-tune LLMs. Our method leverages instructional prompts designed to mimic human cognitive strategies in learning and problem-solving to guide the learning process during training, aiming to improve the model’s interpretation and understanding of domain-specific knowledge. We empirically demonstrate that this simple yet effective modification improves the ability of LLMs to be fine-tuned rapidly on new datasets both within the medical and financial domains.
提示大型语言模型(LLM)或提供预期的模型操作上下文,是引导此类模型的输出以满足其在训练后的人类需求的有效方式。但在快速发展的领域中,通常需要微调LLM,以改善其内存中的知识类型或在新领域进行开放式推理的能力。当人类学习新概念时,我们常常通过将正在研究的新材料与已经学过的概念联系起来来学习。为此,我们的问题是:“提示能否帮助我们教会LLM如何学习”。在这项工作中,我们研究了一种指令微调的新泛化,称为上下文微调,以微调LLM。我们的方法利用指令提示,模仿人类在学习和解决问题中的认知策略,以指导训练过程中的学习过程,旨在提高模型对特定领域知识的解释和理解能力。我们通过实证证明,这种简单而有效的改进提高了LLM在新数据集上的快速微调能力,无论是在医疗还是金融领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
训练大型语言模型(LLM)时,通过提示特定模型操作模式可以有效引导模型输出以满足人类需求。在快速变化的领域中,需要微调LLM以提高其记忆知识或在新领域进行开放式推理的能力。本研究提出了一种新的指令微调方法——上下文微调,该方法利用模拟人类学习和解决问题的认知策略的指令提示来指导学习过程,旨在提高模型对特定领域的理解和解释能力。本研究通过实证证明,这种简单而有效的方法能提高LLM在新数据集上的微调能力,特别是在医疗和金融领域。
Key Takeaways
- 通过提示引导大型语言模型(LLM)的输出以满足人类需求。
- 在快速变化的领域中需要微调LLM。
- 提出了一种新的指令微调方法——上下文微调。
- 上下文微调利用指令提示模拟人类学习和解决问题的认知策略。
- 上下文微调旨在提高模型对特定领域的理解和解释能力。
- 实证证明上下文微调能提高LLM在新数据集上的微调能力。
点此查看论文截图

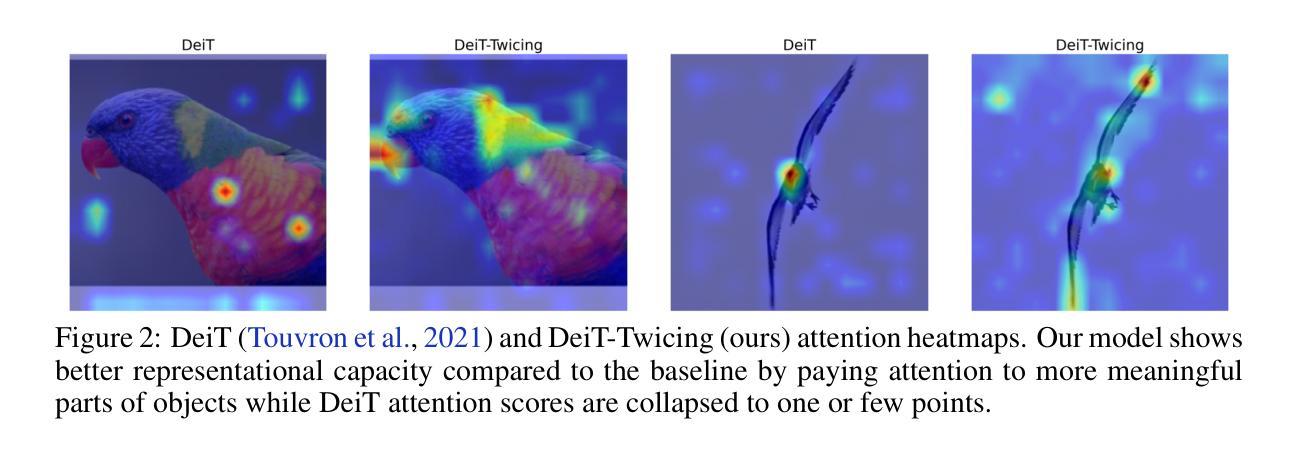
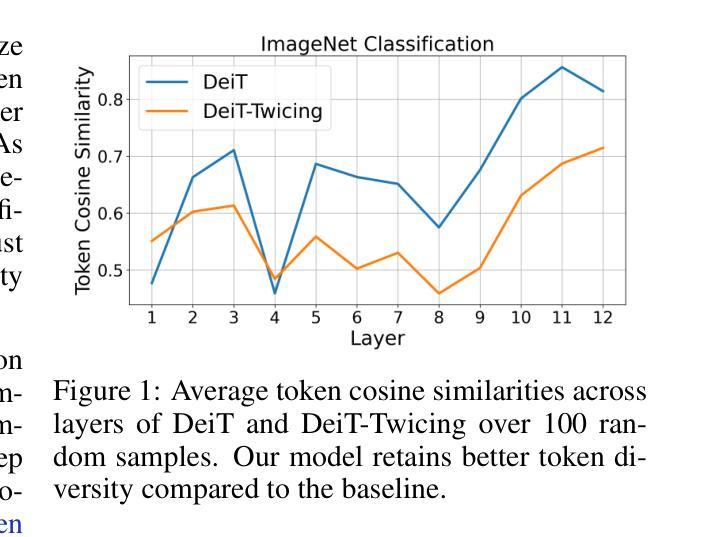
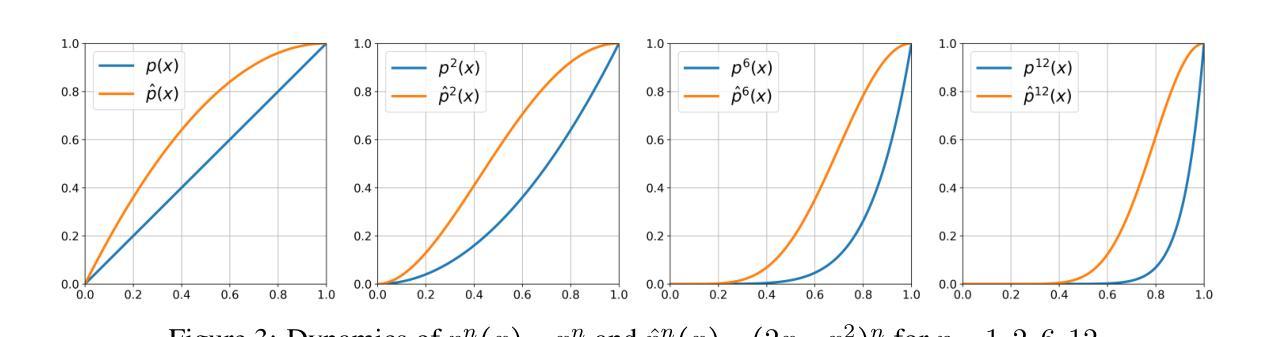
Transformer Meets Twicing: Harnessing Unattended Residual Information
Authors:Laziz Abdullaev, Tan M. Nguyen
Transformer-based deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art performance across numerous language and vision tasks. While the self-attention mechanism, a core component of transformers, has proven capable of handling complex data patterns, it has been observed that the representational capacity of the attention matrix degrades significantly across transformer layers, thereby hurting its overall performance. In this work, we leverage the connection between self-attention computations and low-pass non-local means (NLM) smoothing filters and propose the Twicing Attention, a novel attention mechanism that uses kernel twicing procedure in nonparametric regression to alleviate the low-pass behavior of associated NLM smoothing with compelling theoretical guarantees and enhanced adversarial robustness. This approach enables the extraction and reuse of meaningful information retained in the residuals following the imperfect smoothing operation at each layer. Our proposed method offers two key advantages over standard self-attention: 1) a provably slower decay of representational capacity and 2) improved robustness and accuracy across various data modalities and tasks. We empirically demonstrate the performance gains of our model over baseline transformers on multiple tasks and benchmarks, including image classification and language modeling, on both clean and corrupted data.
基于Transformer的深度学习模型已在众多语言和视觉任务中实现了最先进的性能。虽然Transformer的核心组件自注意力机制已证明能够处理复杂的数据模式,但人们观察到,注意力矩阵在Transformer层间的表示能力会显著下降,从而损害其总体性能。在这项工作中,我们利用自注意力计算与低通非局部均值(NLM)平滑滤波器之间的联系,提出了Twicing Attention,这是一种新型注意力机制。它通过非参数回归中的核twicing程序来缓解与自注意力相关的NLM平滑的低通行为,具有引人注目的理论保证和增强的对抗稳健性。这种方法使得能够在每一层不完美的平滑操作后提取和再利用残差中保留的有意义的信息。我们提出的方法相对于标准自注意力具有两个关键优势:1)表示能力的衰减速度较慢;2)在各种数据模态和任务中提高了稳健性和准确性。我们在多个任务和基准测试上实证地展示了我们的模型相对于基线Transformer的性能提升,包括图像分类和语言建模,以及干净和损坏的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages in the main text. Published at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对Transformer模型在深层学习中存在的不足(即注意矩阵的代表性容量在Transformer层中显著下降),提出了一种新的注意力机制——Twicing Attention。该机制利用自注意力计算和局部均值平滑滤波器之间的联系,通过非参数回归中的核调整过程来实现对平滑滤波器的低通行为的缓解。通过这种方式,该方法能够提取和重用每一层的不完美平滑操作后的残差中的有意义信息。相比于标准的自注意力机制,Twicing Attention提供了两个主要优势:保证的代表性容量衰减较慢,以及在不同数据模态和任务上提高了鲁棒性和准确性。作者在多个任务和基准测试上实证了模型性能的提升,包括图像分类和语言建模,以及干净和受污染的数据。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型中的自注意力机制在处理复杂数据模式时表现出色,但注意矩阵的代表性容量在Transformer层中会显著下降,影响整体性能。
- 提出了一种新的注意力机制——Twicing Attention,利用自注意力计算和局部均值平滑滤波器之间的联系,通过核调整过程改善模型性能。
- Twicing Attention能够提取和重用每一层的不完美平滑操作后的残差中的有意义信息。
- Twicing Attention相比标准自注意力机制具有两个主要优势:保证的代表性容量衰减较慢,以及提高的鲁棒性和准确性。
- 该方法在图像分类和语言建模等多个任务上实现了对基准Transformer模型的性能提升。
- 该方法能在干净和受污染的数据上均实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

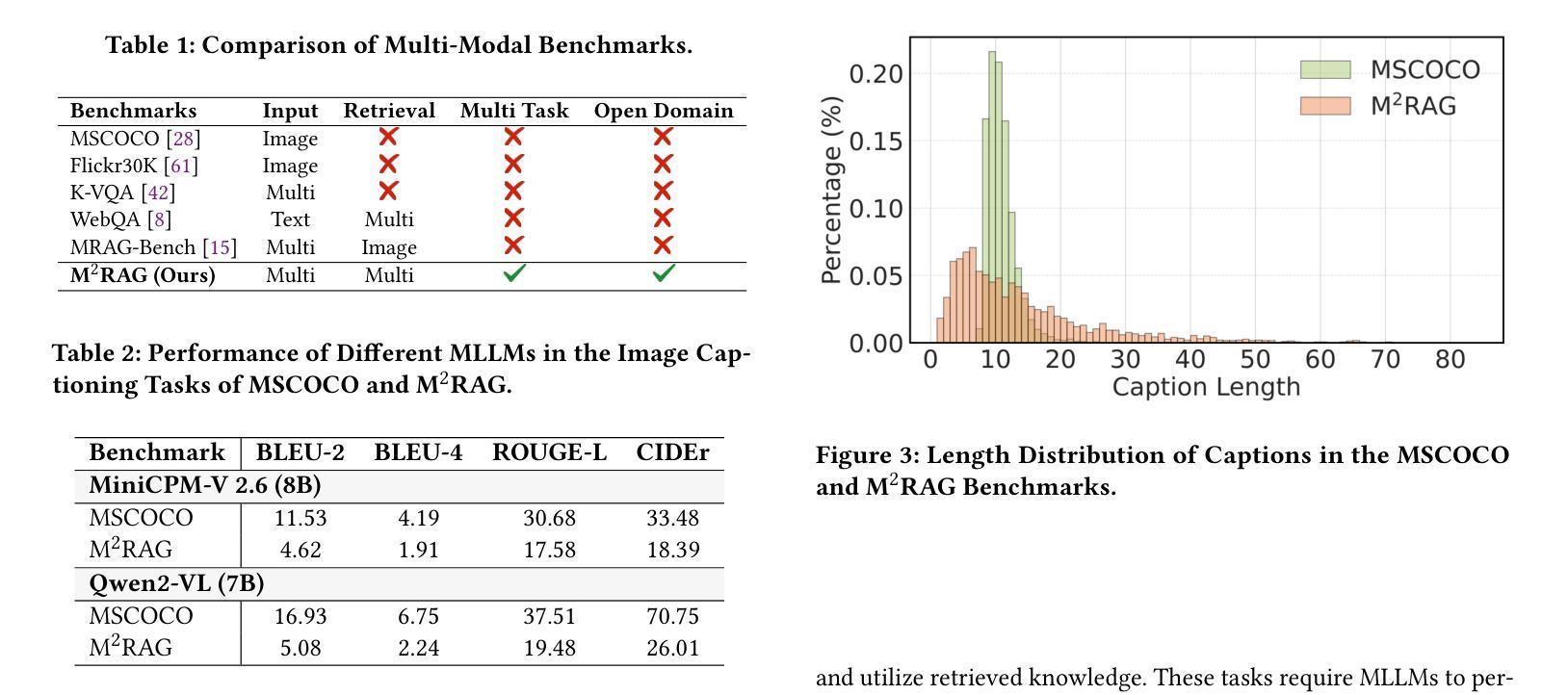
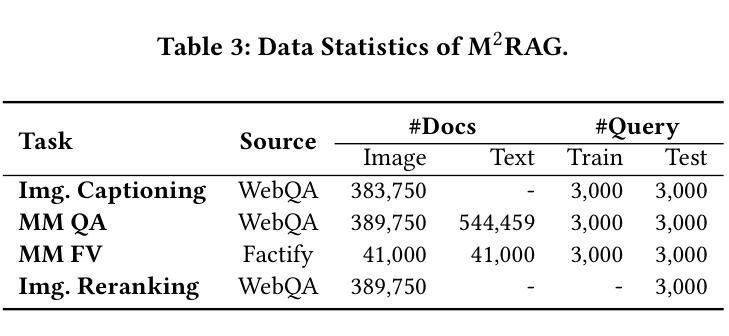
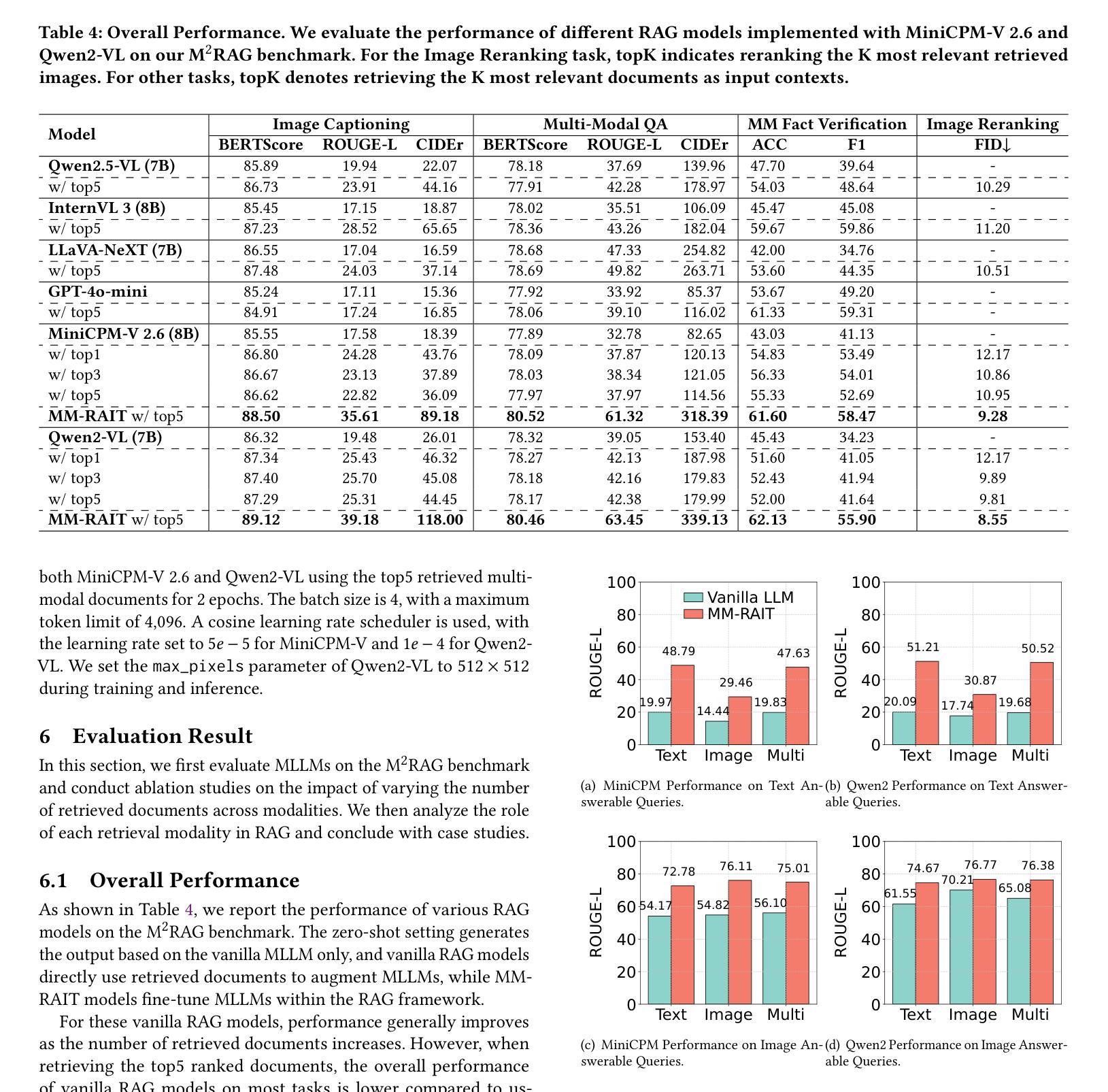
Benchmarking Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Multi-Modal Contexts
Authors:Zhenghao Liu, Xingsheng Zhu, Tianshuo Zhou, Xinyi Zhang, Xiaoyuan Yi, Yukun Yan, Ge Yu, Maosong Sun
With the rapid advancement of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), their capability in understanding both images and text has greatly improved. However, their potential for leveraging multi-modal contextual information in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) remains largely underexplored. To address this gap, this paper introduces Multi-Modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (M$^2$RAG), a benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness of Multi-modal Large Language Models in leveraging knowledge from multi-modal retrieval documents. The benchmark comprises four tasks: image captioning, multi-modal question answering, multi-modal fact verification, and image reranking. All tasks are set in an open-domain setting, requiring RAG models to retrieve query-relevant information from a multi-modal document collection and use it as contextual input for RAG modeling. To enhance the context utilization capabilities of MLLMs, we also introduce Multi-Modal Retrieval-Augmented Instruction Tuning (MM-RAIT), an instruction tuning method that optimizes MLLMs within multi-modal contexts. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of MM-RAIT by significantly improving the quality of responses generated by different RAG models, outperforming MiniCPM-V 2.6 and Qwen2-VL with 34% and 33% gains, respectively. All data and code are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/M2RAG.
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的快速发展,它们对图像和文本的理解能力得到了极大的提高。然而,它们在检索增强生成(RAG)中利用多模态上下文信息的潜力尚未得到充分探索。为了解决这一空白,本文引入了多模态检索增强生成(M^2^RAG)基准测试,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型在利用多模态检索文档中的知识方面的有效性。该基准测试包括四个任务:图像描述、多模态问答、多模态事实验证和图像重排序。所有任务都在开放域环境中设置,要求RAG模型从多模态文档集合中检索与查询相关的信息,并将其用作RAG建模的上下文输入。为了提高MLLMs的上下文利用能力,我们还引入了多模态检索增强指令调整(MM-RAIT),这是一种指令调整方法,可在多模态上下文中优化MLLMs。我们的实验表明,MM-RAIT通过显著提高不同RAG模型生成的响应质量而有效,分别超越了MiniCPM-V 2.6和Qwen2-VL,分别提高了34%和33%。所有数据代码均可从https://github.com/NEUIR/M2RAG获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的快速发展,其对图像和文本的理解能力已大幅提升。然而,它们在利用多模态上下文信息方面的潜力在检索增强生成(RAG)中仍被大量忽视。本文提出了多模态检索增强生成(M^2RAG)这一基准测试,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型在利用多模态检索文档中的知识方面的有效性。该基准测试包括四个任务:图像描述、多模态问答、多模态事实验证和图像重排序。所有任务均在开放领域环境中设置,要求RAG模型从多模态文档集合中检索与查询相关的信息,并将其用作RAG建模的上下文输入。为了提升MLLMs在上下文使用方面的能力,本文还引入了多模态检索增强指令调整(MM-RAIT),这是一种能在多模态上下文中优化MLLMs的指令调整方法。实验证明,MM-RAIT能有效提升不同RAG模型生成答案的质量,相较于MiniCPM-V 2.6和Qwen2-VL分别提升了34%和33%。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)能理解图像和文本,但其利用多模态上下文信息的潜力在检索增强生成(RAG)中尚未被充分探索。
- 本文提出了多模态检索增强生成(M^2RAG)基准测试,涵盖图像描述、多模态问答、多模态事实验证和图像重排序四个任务,以评估多模态LLMs的有效性。
- M^2RAG要求在开放领域环境中,RAG模型能从多模态文档集合中检索相关信息作为上下文输入。
- 为了提升MLLMs在上下文使用方面的能力,引入了多模态检索增强指令调整(MM-RAIT)方法。
- MM-RAIT能有效提升不同RAG模型生成答案的质量,相比其他模型有显著提升。
- M^2RAG和MM-RAIT的相关数据和代码已公开,便于研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图


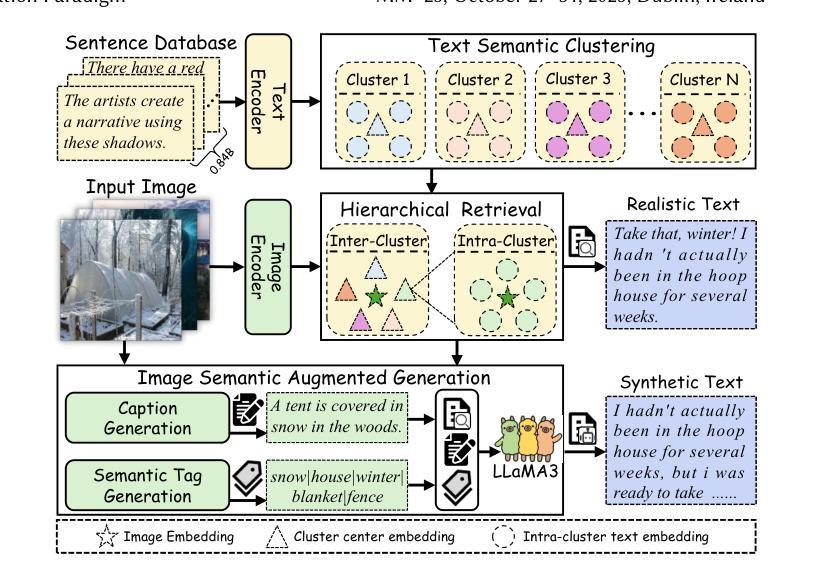
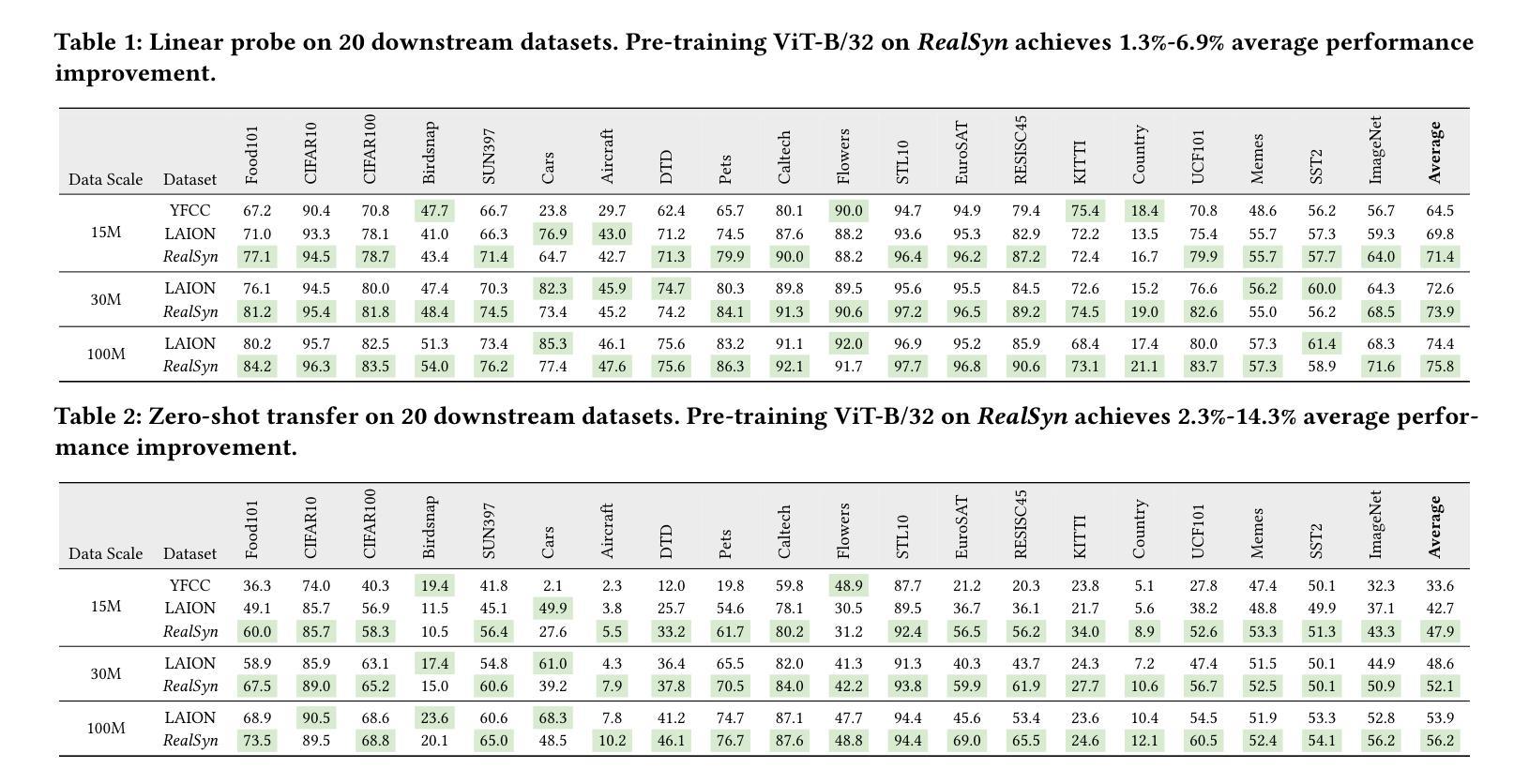
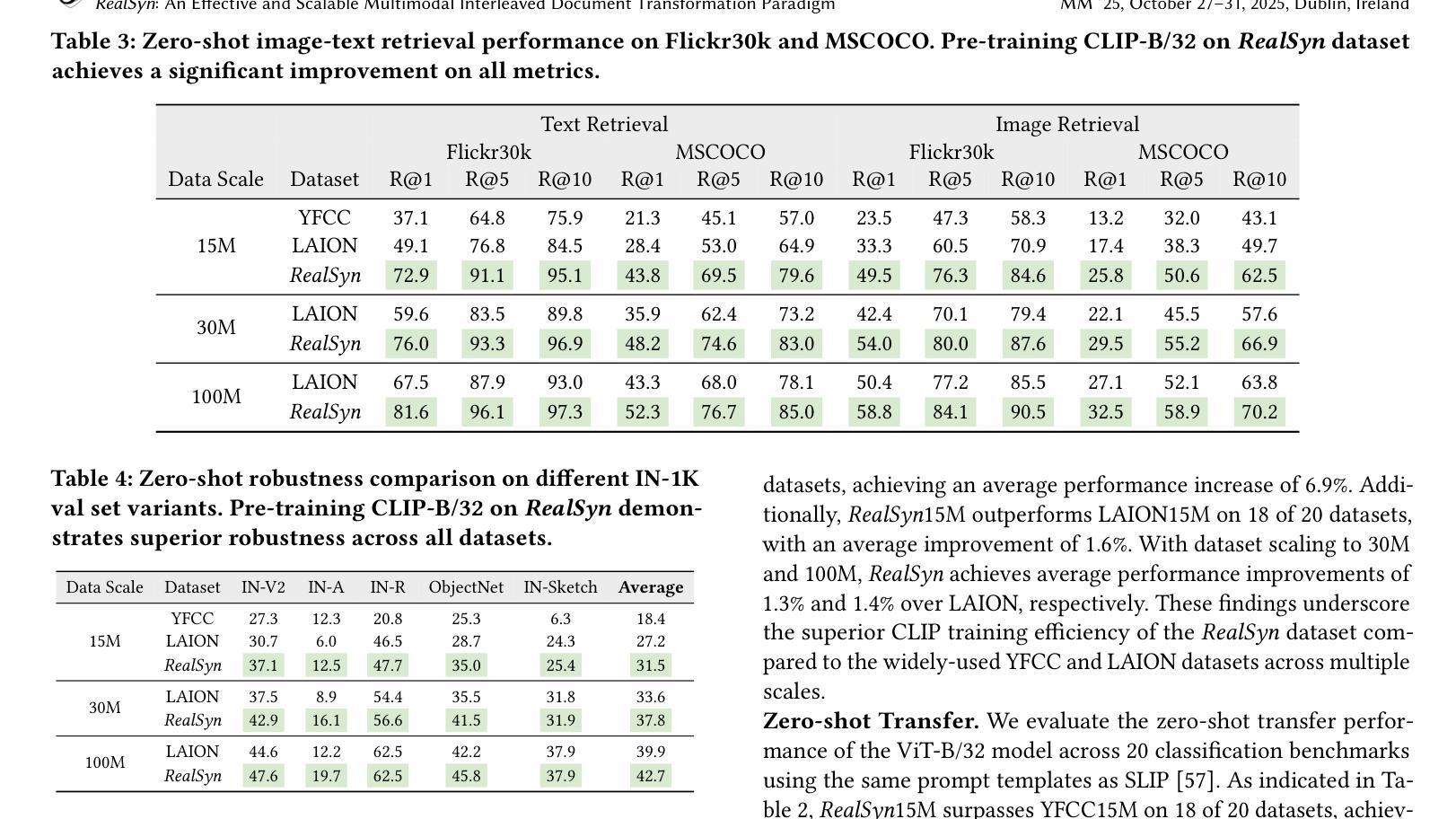
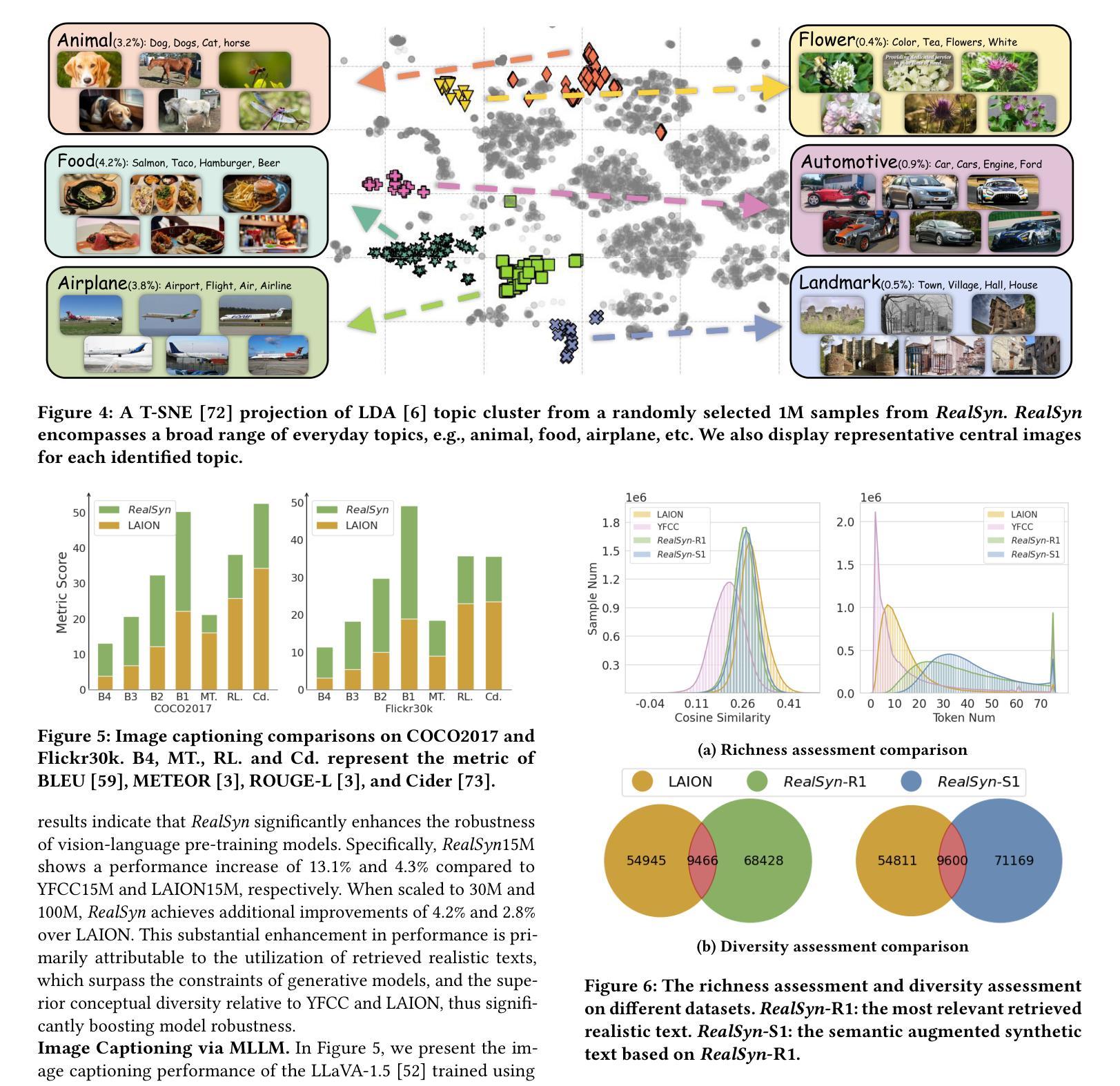
RealSyn: An Effective and Scalable Multimodal Interleaved Document Transformation Paradigm
Authors:Tiancheng Gu, Kaicheng Yang, Chaoyi Zhang, Yin Xie, Xiang An, Ziyong Feng, Dongnan Liu, Weidong Cai, Jiankang Deng
After pre-training on extensive image-text pairs, Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) demonstrates promising performance on a wide variety of benchmarks. However, a substantial volume of multimodal interleaved documents remains underutilized for contrastive vision-language representation learning. To fully leverage these unpaired documents, we initially establish a Real-World Data Extraction pipeline to extract high-quality images and texts. Then we design a hierarchical retrieval method to efficiently associate each image with multiple semantically relevant realistic texts. To further enhance fine-grained visual information, we propose an image semantic augmented generation module for synthetic text production. Furthermore, we employ a semantic balance sampling strategy to improve dataset diversity, enabling better learning of long-tail concepts. Based on these innovations, we construct RealSyn, a dataset combining realistic and synthetic texts, available in three scales: 15M, 30M, and 100M. We compare our dataset with other widely used datasets of equivalent scale for CLIP training. Models pre-trained on RealSyn consistently achieve state-of-the-art performance across various downstream tasks, including linear probe, zero-shot transfer, zero-shot robustness, and zero-shot retrieval. Furthermore, extensive experiments confirm that RealSyn significantly enhances contrastive vision-language representation learning and demonstrates robust scalability. To facilitate future research, the RealSyn dataset and pretrained model weights are released at https://github.com/deepglint/RealSyn.
经过对大量图像文本对进行预训练后,对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在各种基准测试上表现出了有前景的性能。然而,大量的未配对的多媒体交互文档在对比视觉语言表示学习中仍未得到充分利用。为了充分利用这些未配对的文档,我们最初建立了一个现实世界数据提取管道,以提取高质量的图片和文本。然后,我们设计了一种分层检索方法,以有效地将每张图像与多个语义上相关的现实文本相关联。为了进一步提取精细的视觉信息,我们提出了一个图像语义增强生成模块来进行合成文本的生产。此外,我们采用了一种语义平衡采样策略来提高数据集多样性,从而能够更好地学习长尾概念。基于这些创新,我们构建了RealSyn数据集,融合了现实和合成文本,分为三个规模:15M、30M和100M。我们将数据集与同等规模的其他常用CLIP训练数据集进行了比较。在各种下游任务中,基于RealSyn预训练的模型始终实现了最先进的性能,包括线性探测、零样本迁移、零样本鲁棒性和零样本检索。此外,大量实验证实,RealSyn显著增强了对比视觉语言表示学习,并表现出稳健的可扩展性。为了方便未来研究,RealSyn数据集和预训练模型权重已在https://github.com/deepglint/RealSyn上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 12 figures, Accepted by ACM MM2025, Webpage: https://garygutc.github.io/RealSyn
Summary
本文介绍了基于对比视觉语言预训练的改进方法,通过构建RealSyn数据集来提升对比视觉语言表示学习。RealSyn数据集结合了真实和合成文本,建立了真实世界数据提取管道和分层检索方法,以提高图像与文本之间的语义关联。此外,通过图像语义增强生成模块和语义平衡采样策略,提高了模型的性能。在多个下游任务中,预训练在RealSyn上的模型表现出最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在广泛的多模态交错文档上的性能有待提升。
- 建立了真实世界数据提取管道以提取高质量图像和文本。
- 设计了分层检索方法,使每个图像与多个语义相关的现实文本有效关联。
- 通过图像语义增强生成模块提高精细视觉信息。
- 采用语义平衡采样策略提高数据集多样性,有助于学习长尾概念。
- 构建了RealSyn数据集,结合了真实和合成文本,提供三种规模供选择。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Knowledge Injection in LLMs via Self-Distillation
Authors:Kalle Kujanpää, Pekka Marttinen, Harri Valpola, Alexander Ilin
In many practical applications, large language models (LLMs) need to acquire new knowledge not present in their pre-training data. Efficiently leveraging this knowledge usually relies on supervised fine-tuning or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Although RAG has emerged as the industry standard for knowledge injection, fine-tuning has not yet achieved comparable success. This paper proposes utilizing prompt distillation, a self-distillation-based method previously explored primarily for style alignment and instruction tuning, to internalize new factual knowledge from free-form documents. Unlike prior methods, our approach requires neither larger teacher models nor structured knowledge formats. Across multiple LLM sizes and model families, we show that prompt distillation outperforms standard supervised fine-tuning and can even surpass RAG. We analyze the key factors contributing to prompt distillation’s effectiveness and examine how it scales.
在许多实际应用中,大型语言模型(LLM)需要获取其预训练数据中未包含的新知识。有效地利用这些知识通常依赖于监督微调或检索增强生成(RAG)。尽管RAG已成为知识注入的行业标准,但微调尚未取得与之相当的成就。本文提出利用提示蒸馏法,这是一种基于自我蒸馏的方法,之前主要用于风格对齐和指令调整,以从自由形式的文档中内化新的事实知识。不同于以前的方法,我们的方法既不需要更大的教师模型,也不需要结构化的知识格式。我们在多个LLM规模和模型家族中表明,提示蒸馏法优于标准的监督微调,甚至可以超越RAG。我们分析了提示蒸馏法有效性的关键因素,并研究了其如何扩展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在实际应用中需要获取预训练数据以外的新知识。尽管检索增强生成(RAG)已成为知识注入的行业标准,但微调尚未取得相应的成功。本文提出利用提示蒸馏法,这是一种基于自我蒸馏的方法,以前主要用于风格对齐和指令调整,以内化来自自由形式文档的新事实知识。与其他方法不同,我们的方法既不需要更大的教师模型,也不需要结构化知识格式。跨多个LLM大小和模型家族,我们证明了提示蒸馏法优于标准的监督微调,甚至可以超越RAG。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在实际应用中需要获取预训练数据之外的新知识。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)已成为知识注入的行业标准,但微调尚未取得同等成功。
- 提示蒸馏法是一种基于自我蒸馏的方法,可以内化来自自由形式文档的新事实知识。
- 与其他方法相比,提示蒸馏法不需要更大的教师模型和结构化知识格式。
- 提示蒸馏法在不同规模和家族的LLM中表现出优于标准监督微调的性能。
- 提示蒸馏法的有效性关键在于其能够自我蒸馏并内化新的事实知识。
点此查看论文截图

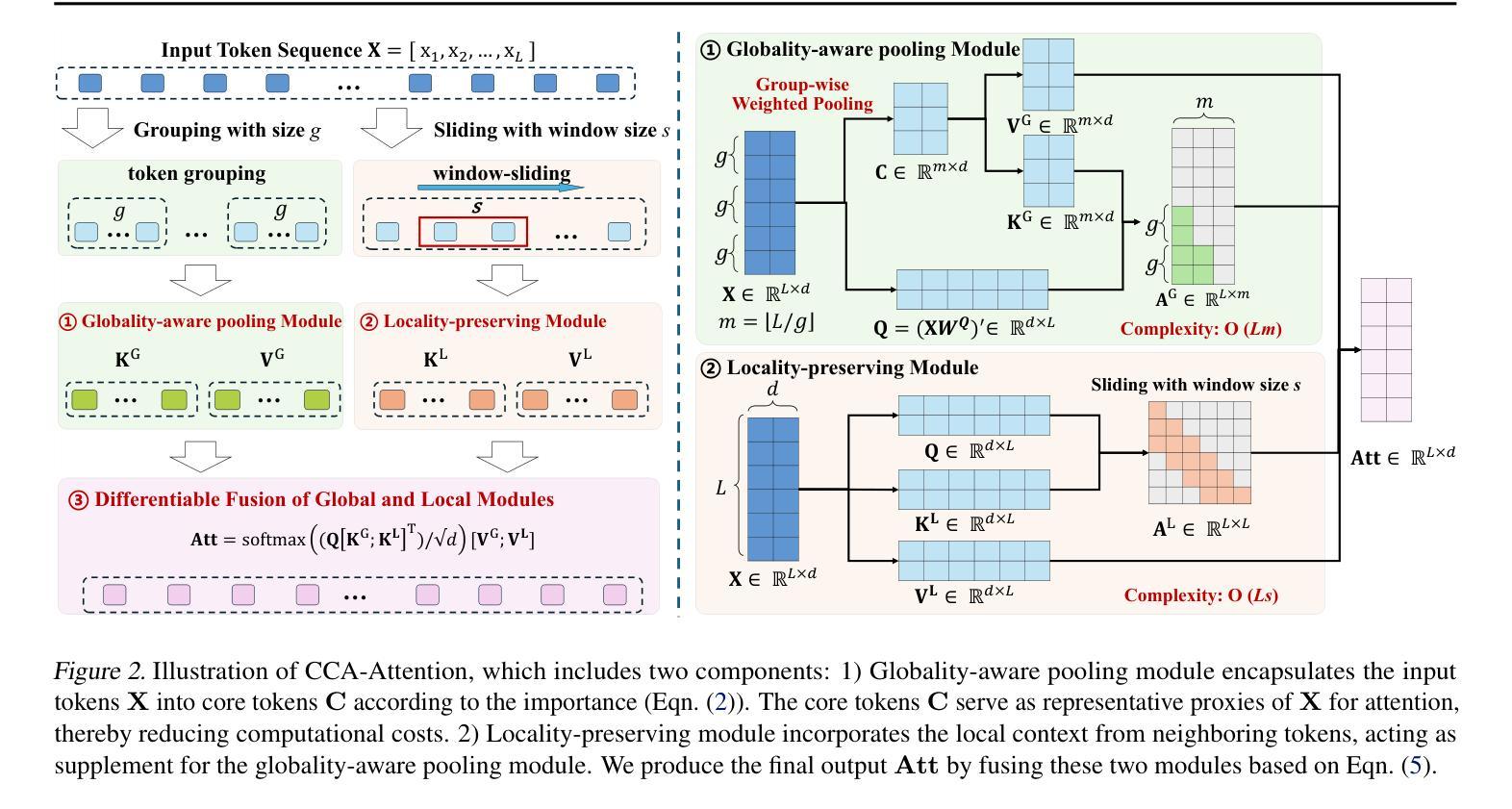
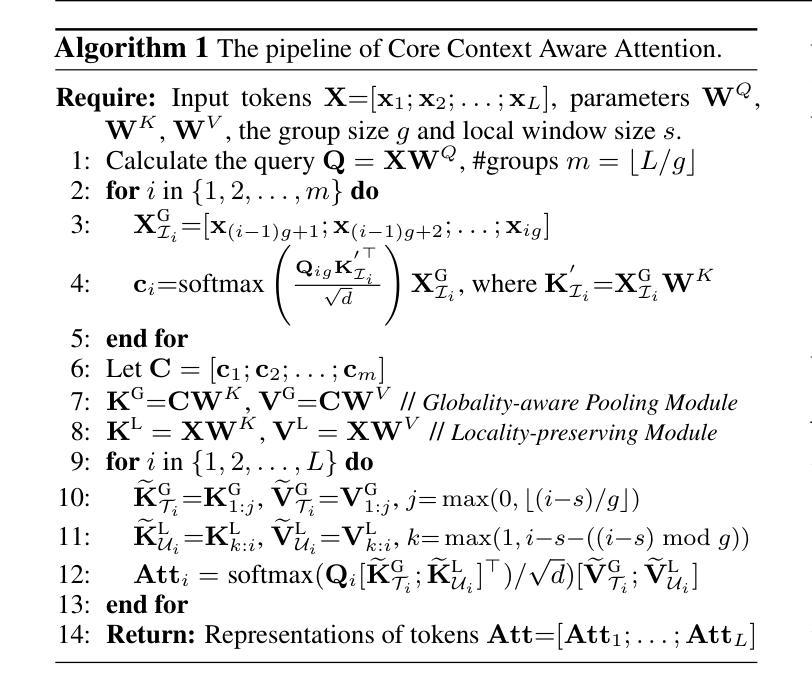
Core Context Aware Transformers for Long Context Language Modeling
Authors:Yaofo Chen, Zeng You, Shuhai Zhang, Haokun Li, Yirui Li, Yaowei Wang, Mingkui Tan
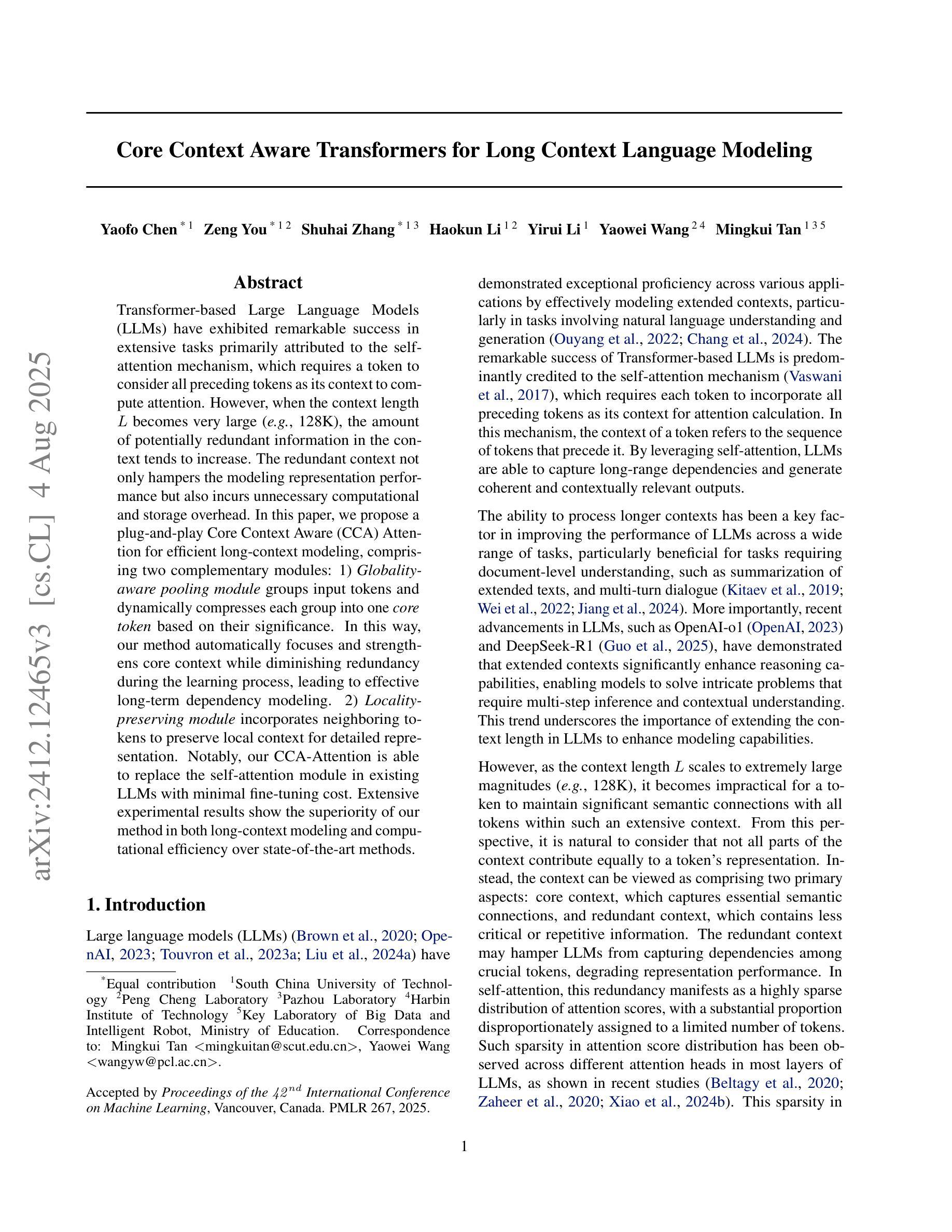
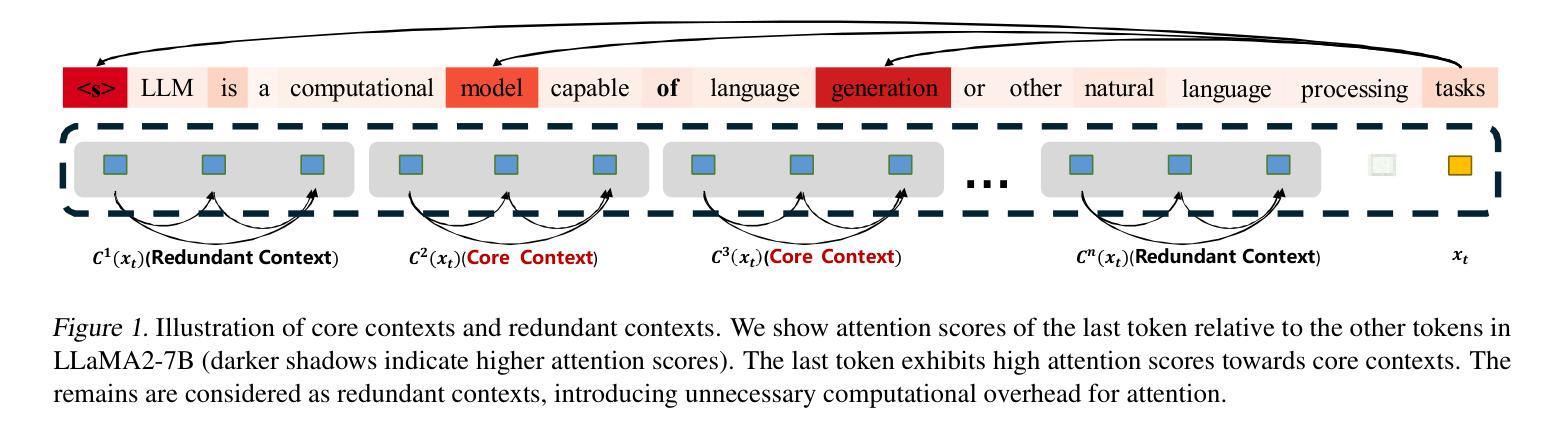
Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable success in extensive tasks primarily attributed to self-attention mechanism, which requires a token to consider all preceding tokens as its context to compute attention. However, when the context length L becomes very large (e.g., 128K), the amount of potentially redundant information in the context tends to increase. The redundant context not only hampers the modeling representation performance but also incurs unnecessary computational and storage overhead. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play Core Context Aware (CCA) Attention for efficient long-context modeling, comprising two complementary modules: 1) Globality-aware pooling module groups input tokens and dynamically compresses each group into one core token based on their significance. In this way, our method automatically focuses and strengthens core context while diminishing redundancy during the learning process, leading to effective long-term dependency modeling. 2) Locality-preserving module incorporates neighboring tokens to preserve local context for detailed representation. Notably, our CCA-Attention is able to replace the self-attention module in existing LLMs with minimal fine-tuning cost. Extensive experimental results show the superiority of our method in both long-context modeling and computational efficiency over state-of-the-art methods.
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在大量任务中取得了显著的成功,这主要归功于自注意力机制。自注意力机制要求一个标记(token)将所有先前的标记作为其上下文来计算注意力。然而,当上下文长度L变得非常大(例如128K)时,上下文中潜在冗余信息的数量往往会增加。冗余的上下文不仅阻碍建模表示性能,而且还产生不必要的计算和存储开销。在本文中,我们提出了一种即插即用的核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力,用于高效的长上下文建模,包括两个互补模块:1)全局感知池模块对输入标记进行分组,并根据其重要性动态地将每个组压缩成一个核心标记。通过这种方式,我们的方法在学习过程中自动聚焦和增强核心上下文,同时减少冗余,从而实现有效的长期依赖关系建模。2)局部性保持模块结合了相邻的标记,以保留局部上下文,从而实现详细的表示。值得注意的是,我们的CCA注意力能够以最小的微调成本替换现有LLM中的自注意力模块。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在长上下文建模和计算效率上优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ICML 2025
Summary:基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在处理长文本时面临冗余信息问题,影响建模性能并造成计算和存储负担。本文提出了一种名为核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力机制,通过全局感知池化模块和局部保留模块来高效建模长文本,并自动聚焦强化核心上下文并减少冗余。CCA注意力能替换现有LLM中的自注意力模块,并具有良好的计算效率和性能表现。
Key Takeaways:
- 基于Transformer的LLM在处理长文本时存在冗余信息问题。
- 核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力机制旨在解决这一问题,包括全局感知池化模块和局部保留模块。
- 全局感知池化模块按重要性将输入令牌分组并动态压缩,以强化核心上下文并减少冗余。
- 局部保留模块保留邻近令牌以进行详细表示。
- CCA注意力机制能替换现有LLM中的自注意力模块。
- 实证研究结果显示,CCA注意力机制在长篇文本建模和计算效率上表现优越。
- 该方法具有较低的微调成本。
点此查看论文截图
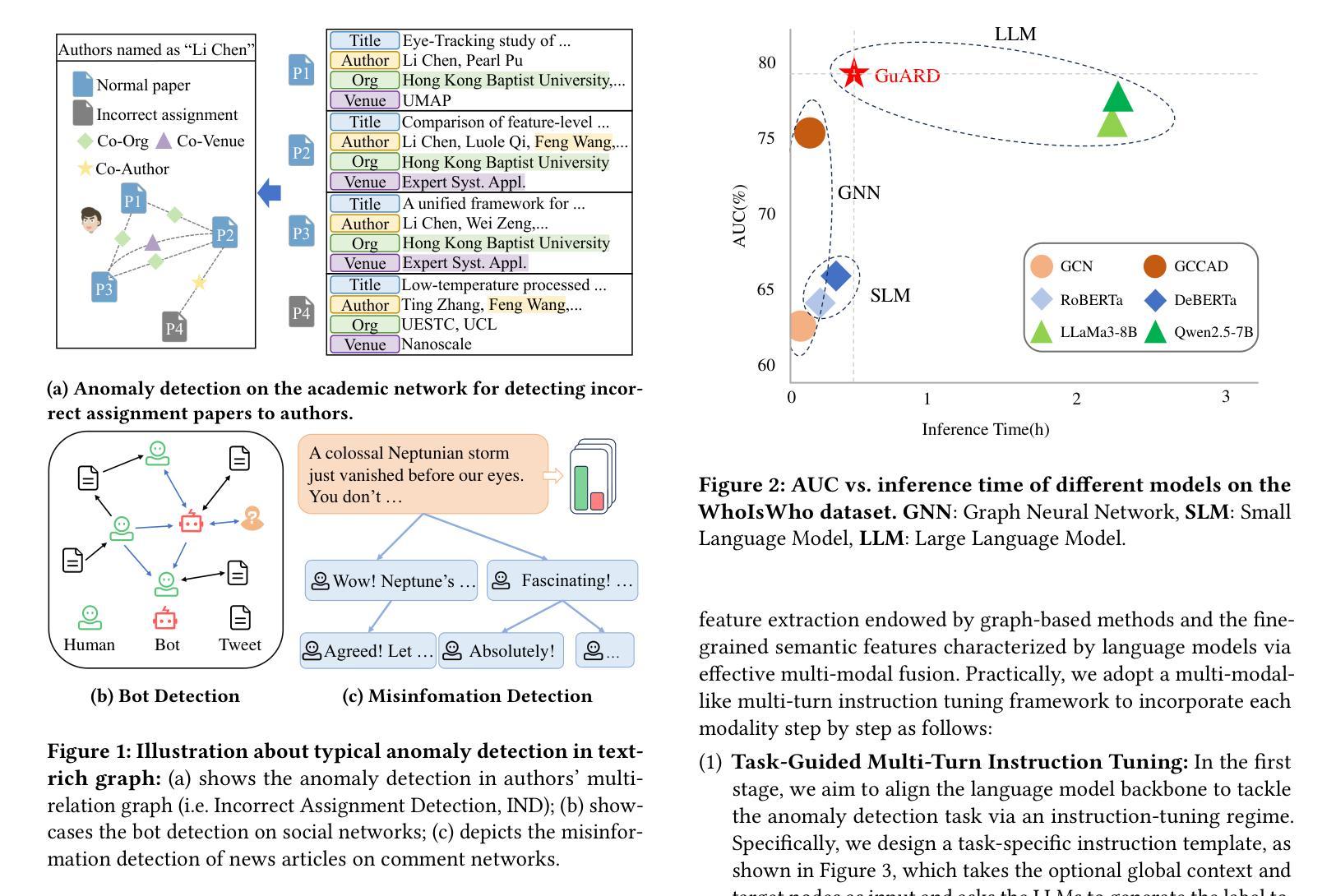
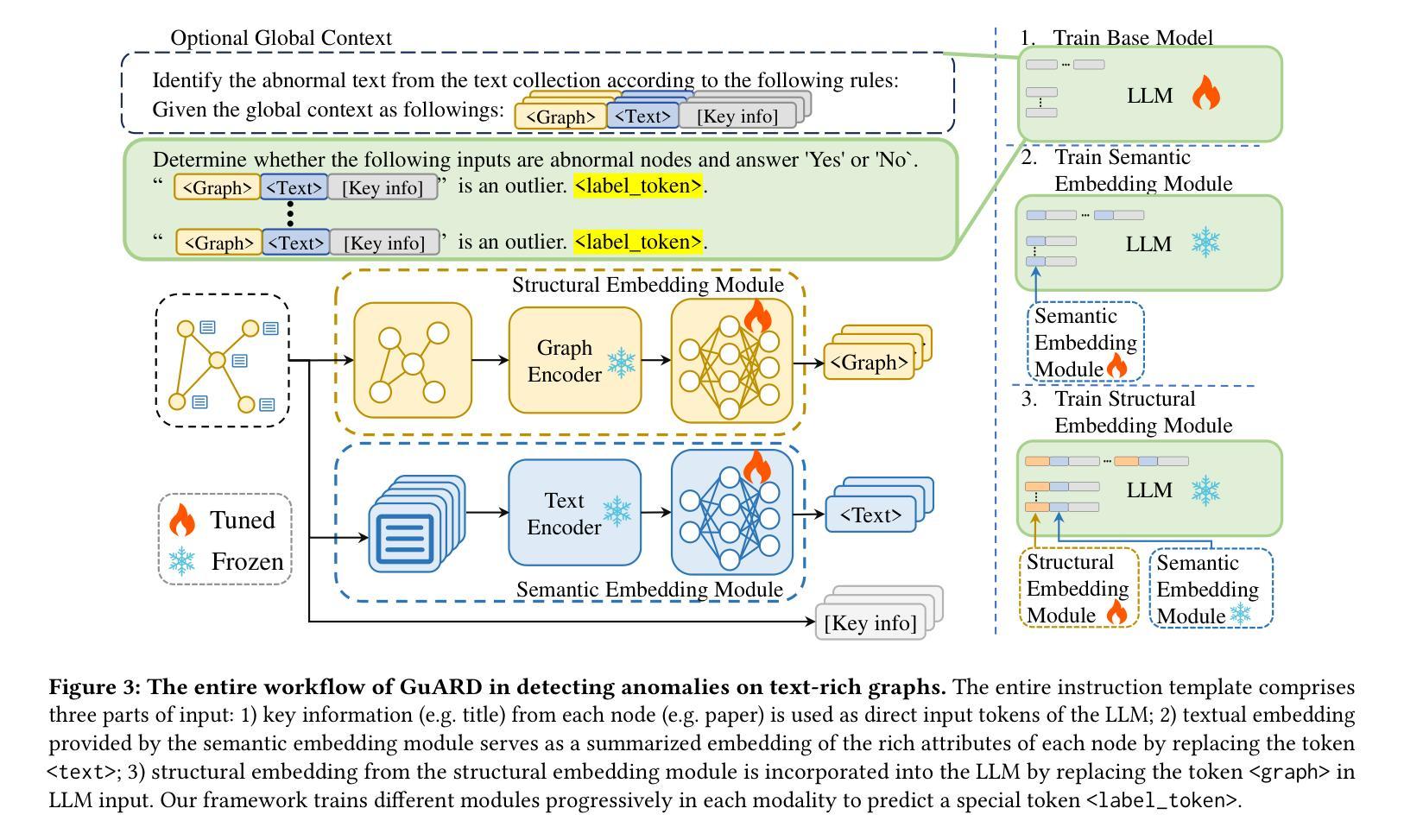
GuARD: Effective Anomaly Detection through a Text-Rich and Graph-Informed Language Model
Authors:Yunhe Pang, Bo Chen, Fanjin Zhang, Yanghui Rao, Evgeny Kharlamov, Jie Tang
Anomaly detection on text-rich graphs is widely prevalent in real life, such as detecting incorrectly assigned academic papers to authors and detecting bots in social networks. The remarkable capabilities of large language models (LLMs) pave a new revenue by utilizing rich-text information for effective anomaly detection. However, simply introducing rich texts into LLMs can obscure essential detection cues and introduce high fine-tuning costs. Moreover, LLMs often overlook the intrinsic structural bias of graphs which is vital for distinguishing normal from abnormal node patterns. To this end, this paper introduces GuARD, a text-rich and graph-informed language model that combines key structural features from graph-based methods with fine-grained semantic attributes extracted via small language models for effective anomaly detection on text-rich graphs. GuARD is optimized with the progressive multi-modal multi-turn instruction tuning framework in the task-guided instruction tuning regime tailed to incorporate both rich-text and structural modalities. Extensive experiments on four datasets reveal that GuARD outperforms graph-based and LLM-based anomaly detection methods, while offering up to 5$\times$ times speedup in training and 5$\times$ times speedup in inference over vanilla long-context LLMs on the large-scale WhoIsWho dataset.
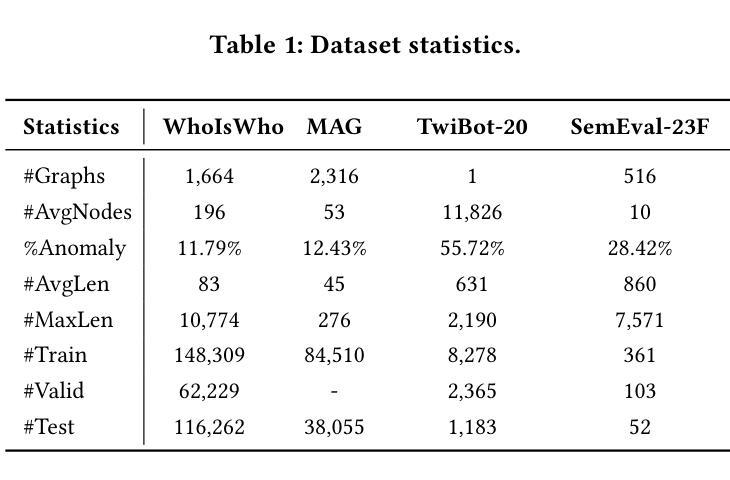
文本丰富的图上的异常检测在现实生活中普遍存在,例如检测错误分配给作者的学术论文和检测社交网络中的机器人。大型语言模型(LLM)的显著能力为利用丰富文本信息进行有效的异常检测开辟了新的收入来源。然而,仅仅将丰富文本引入LLM会掩盖重要的检测线索,并产生高昂的微调成本。此外,LLM通常会忽略图的内在结构偏见,这对于区分正常和异常的节点模式至关重要。为此,本文介绍了GuARD,这是一种结合基于图的丰富文本和图信息语言模型的方法。GuARD结合了基于图的方法的关键结构特征与通过小型语言模型提取的精细语义属性,用于在文本丰富的图上有效地进行异常检测。GuARD采用任务导向指令调整制度下的渐进式多模式多轮指令调整框架进行了优化,以结合丰富文本和结构模式。在四个数据集上的大量实验表明,GuARD在异常检测方法上优于基于图和基于LLM的方法,同时在大型WhoIsWho数据集上提供了高达5倍的培训和推理速度提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at KDD 2025
Summary
文本丰富的图异常检测在现实生活中应用广泛,如检测学术论文的错误分配和社交网络中机器人的检测。大型语言模型(LLM)的出色能力为利用丰富文本信息进行有效的异常检测开辟了新的收入途径。然而,仅仅将丰富文本引入LLM可能会掩盖重要的检测线索并产生高昂的微调成本。此外,LLM往往会忽视图的结构性偏见,这对于区分正常和异常的节点模式至关重要。为此,本文提出了GuARD,它是一种文本丰富且基于图的模型,结合了基于图的和基于小型语言模型提取的关键结构特征以及精细语义属性,可有效检测文本丰富的图的异常。实验表明,GuARD在异常检测方面的性能优于基于图和基于LLM的方法,在大型数据集上实现了高达五倍的训练速度和推理速度的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测在现实世界中有广泛的应用,如学术论和社交网络的检测问题。
- 大型语言模型在利用丰富文本进行异常检测方面具有巨大潜力。
- 仅使用丰富文本引入大型语言模型可能导致重要检测线索的丢失和较高的微调成本。
- 大型语言模型往往忽视图的结构性偏见,这对于区分正常和异常节点模式至关重要。
- GuARD模型结合了基于图的精细结构特征和通过小型语言模型提取的语义属性,有效提高了异常检测的准确性。
- GuARD模型的优化包括采用多模态多任务指导训练策略以及结合丰富文本和结构模式的能力。
点此查看论文截图

CreatiLayout: Siamese Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Creative Layout-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hui Zhang, Dexiang Hong, Yitong Wang, Jie Shao, Xinglong Wu, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang
Diffusion models have been recognized for their ability to generate images that are not only visually appealing but also of high artistic quality. As a result, Layout-to-Image (L2I) generation has been proposed to leverage region-specific positions and descriptions to enable more precise and controllable generation. However, previous methods primarily focus on UNet-based models (\eg SD1.5 and SDXL), and limited effort has explored Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiTs), which have demonstrated powerful image generation capabilities. Enabling MM-DiT for layout-to-image generation seems straightforward but is challenging due to the complexity of how layout is introduced, integrated, and balanced among multiple modalities. To this end, we explore various network variants to efficiently incorporate layout guidance into MM-DiT, and ultimately present SiamLayout. To inherit the advantages of MM-DiT, we use a separate set of network weights to process the layout, treating it as equally important as the image and text modalities. Meanwhile, to alleviate the competition among modalities, we decouple the image-layout interaction into a siamese branch alongside the image-text one and fuse them in the later stage. Moreover, we contribute a large-scale layout dataset, named LayoutSAM, which includes 2.7 million image-text pairs and 10.7 million entities. Each entity is annotated with a bounding box and a detailed description. We further construct the LayoutSAM-Eval benchmark as a comprehensive tool for evaluating the L2I generation quality. Finally, we introduce the Layout Designer, which taps into the potential of large language models in layout planning, transforming them into experts in layout generation and optimization. These components form CreatiLayout – a systematic solution that integrates the layout model, dataset, and planner for creative layout-to-image generation.
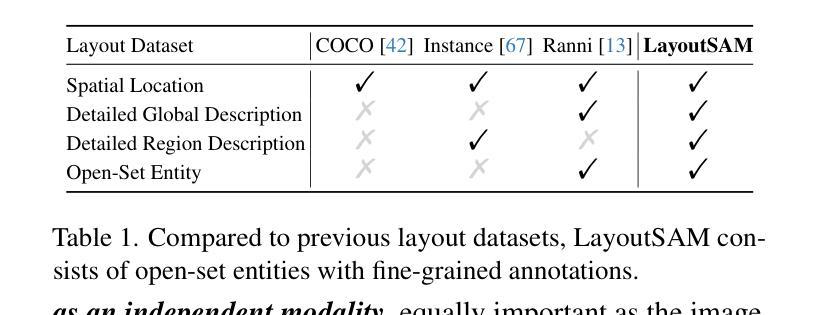
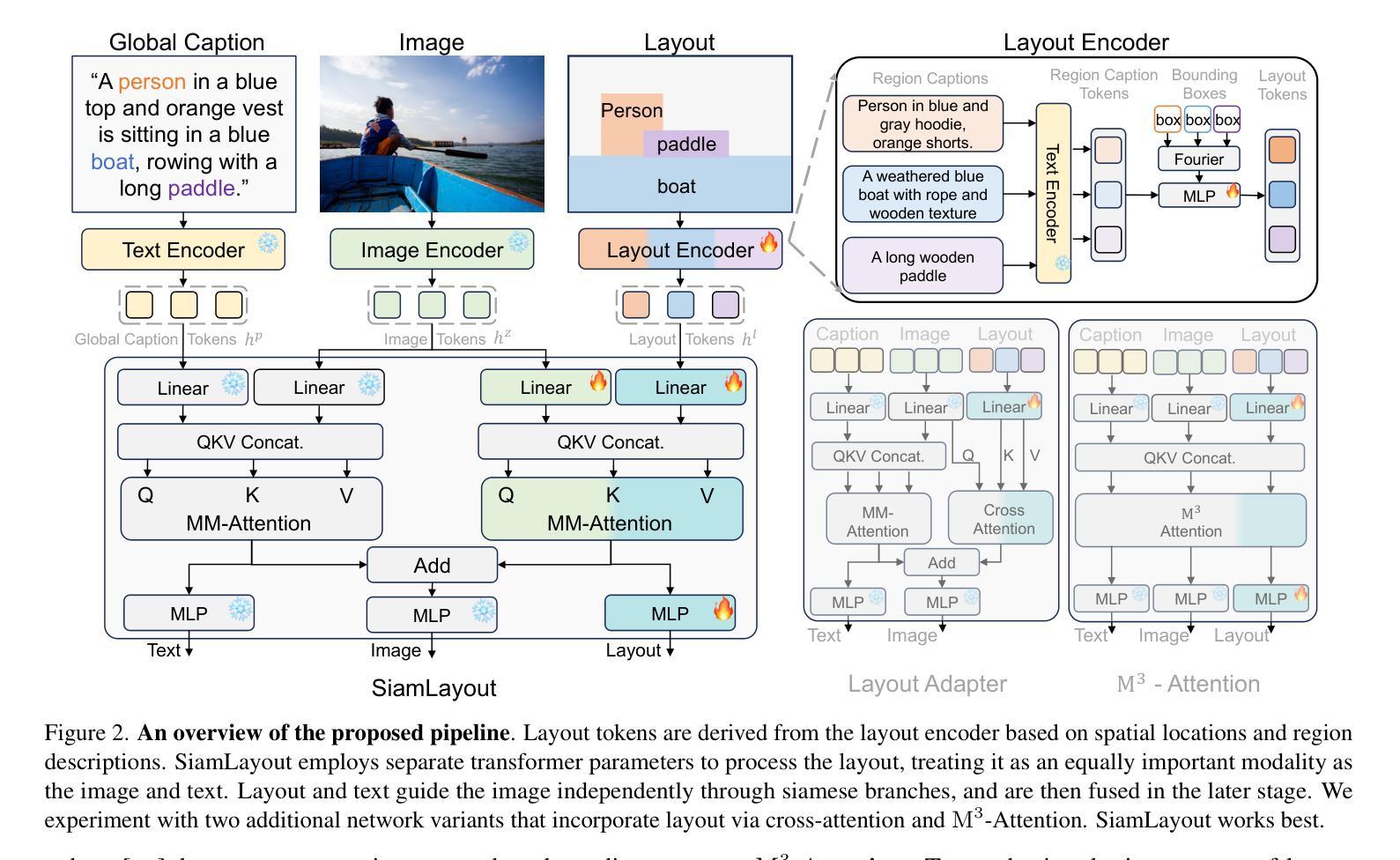
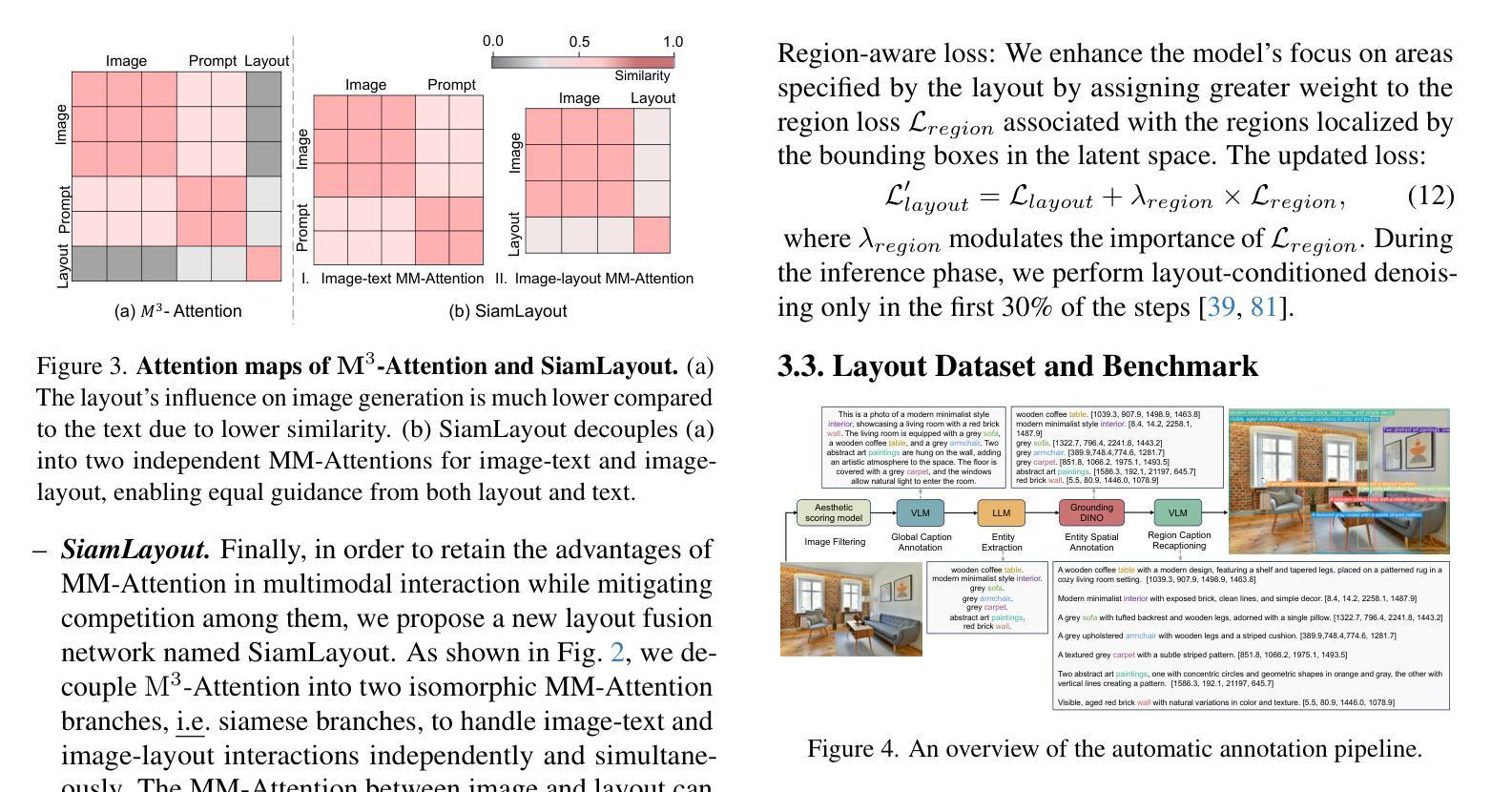
扩散模型因其能够生成不仅在视觉上吸引人而且艺术性很高的图像而备受瞩目。因此,提出了Layout-to-Image(L2I)生成方法,利用特定区域的位置和描述来实现更精确和可控的生成。然而,之前的方法主要集中在基于UNet的模型(例如SD1.5和SDXL),对多模态扩散变压器(MM-DiT)的探索有限,后者已显示出强大的图像生成能力。虽然使MM-DiT用于布局到图像生成看似简单,但由于布局如何引入、集成和平衡在多模态之间的复杂性,这仍然是一个挑战。为此,我们探索了各种网络变体,以有效地将布局指导融入MM-DiT,并最终推出SiamLayout。为了继承MM-DiT的优点,我们使用一组独立的网络权重来处理布局,将其视为与图像和文本模态同样重要。同时,为了减轻模态之间的竞争,我们将图像布局交互分解成与图像文本分支并列的孪生分支,并在后期进行融合。此外,我们贡献了一个大规模布局数据集,名为LayoutSAM,其中包括270万张图像文本对和1070万个实体。每个实体都带有边界框和详细描述。我们还构建了LayoutSAM-Eval基准测试,作为评估L2I生成质量的综合工具。最后,我们介绍了布局设计师,它挖掘了大语言模型在布局规划中的潜力,将其转变为布局生成和优化的专家。这些组件构成了CreatiLayout——一个系统解决方案,集成了布局模型、数据集和规划器,用于创意布局到图像生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了利用扩散模型进行布局到图像(Layout-to-Image,L2I)生成的技术。文章介绍了Multimodal Diffusion Transformers(MM-DiT)在图像生成中的应用,并指出如何将布局指导有效地融入MM-DiT的复杂性。为此,文章探索了各种网络变体,最终提出了SiamLayout方案。该方案利用专门的网络权重处理布局,并解耦图像与布局的交互,在后期进行融合。此外,文章还贡献了一个大规模布局数据集LayoutSAM,并建立了评价L2I生成质量的LayoutSAM-Eval基准测试。最后,文章介绍了Layout Designer,这是一个利用大型语言模型在布局规划中的潜力,将其转化为布局生成和优化的专家系统。这些组件共同构成了CreatiLayout,一个整合布局模型、数据集和规划器的创意布局到图像生成的系统解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够生成高质量图像,Layout-to-Image(L2I)生成技术利用区域特定位置和描述来实现更精确和可控的生成。
- 之前的方法主要关注UNet-based模型,而Multimodal Diffusion Transformers(MM-DiT)在图像生成中展现出强大能力,但融入布局指导具有挑战性。
- SiamLayout通过探索各种网络变体来高效融入布局指导,利用专门的网络权重处理布局,并解耦图像与布局的交互。
- LayoutSAM是一个大规模布局数据集,包含图像、文本和实体标注,为L2I生成提供数据支持。
- LayoutSAM-Eval基准测试用于评估L2I生成质量。
- Layout Designer利用大型语言模型在布局规划中的潜力,转化为布局生成和优化的专家系统。
点此查看论文截图

WSI-LLaVA: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Whole Slide Image
Authors:Yuci Liang, Xinheng Lyu, Meidan Ding, Wenting Chen, Jipeng Zhang, Yuexiang Ren, Xiangjian He, Song Wu, Sen Yang, Xiyue Wang, Xiaohan Xing, Linlin Shen
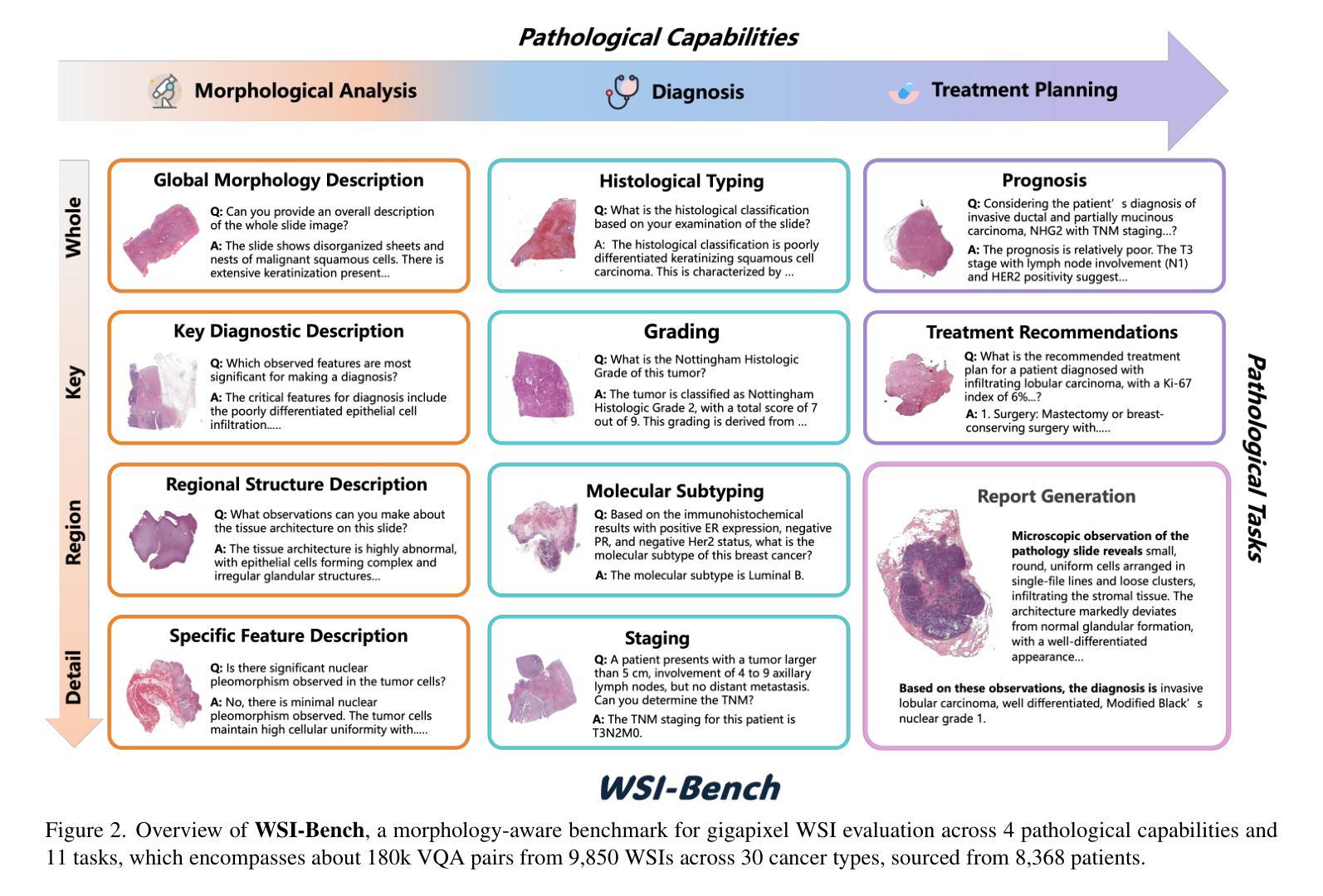
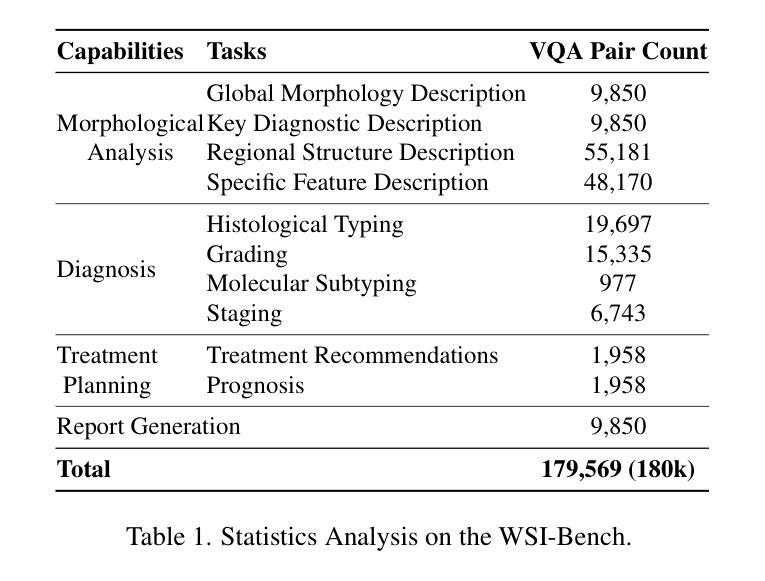
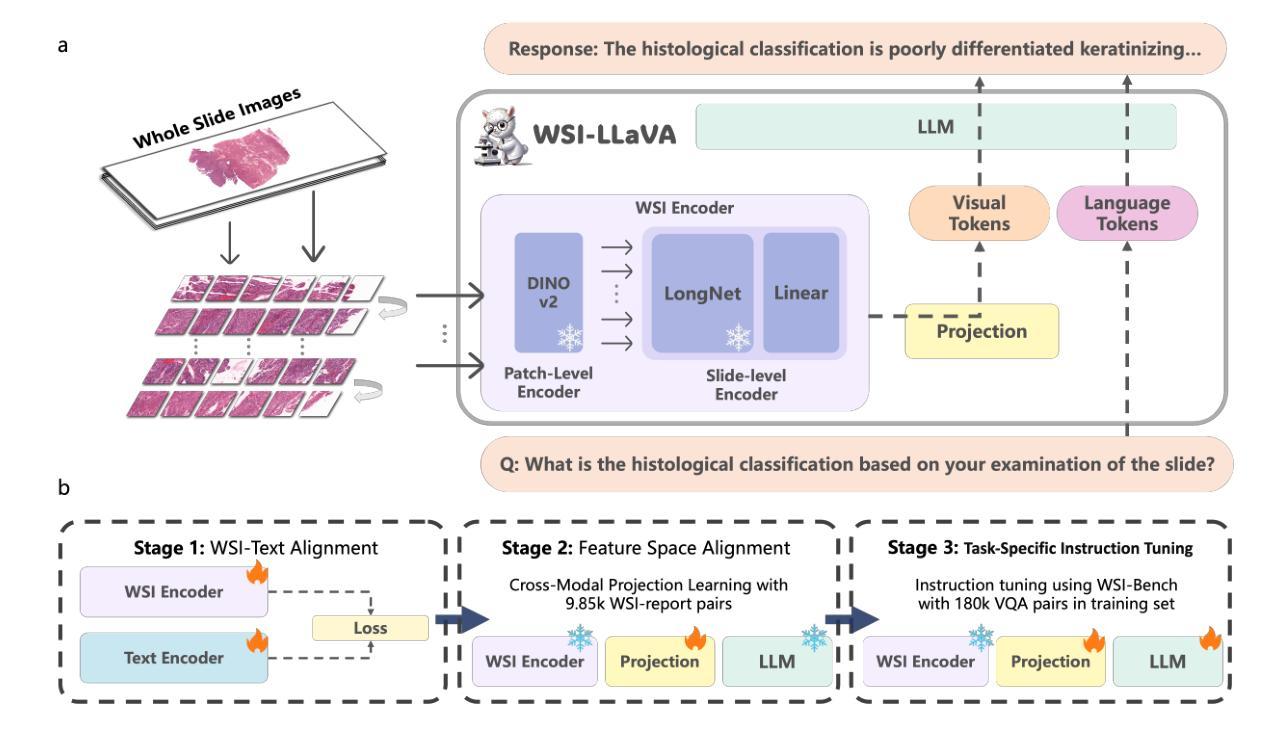
Recent advancements in computational pathology have produced patch-level Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), but these models are limited by their inability to analyze whole slide images (WSIs) comprehensively and their tendency to bypass crucial morphological features that pathologists rely on for diagnosis. To address these challenges, we first introduce WSI-Bench, a large-scale morphology-aware benchmark containing 180k VQA pairs from 9,850 WSIs across 30 cancer types, designed to evaluate MLLMs’ understanding of morphological characteristics crucial for accurate diagnosis. Building upon this benchmark, we present WSI-LLaVA, a novel framework for gigapixel WSI understanding that employs a three-stage training approach: WSI-text alignment, feature space alignment, and task-specific instruction tuning. To better assess model performance in pathological contexts, we develop two specialized WSI metrics: WSI-Precision and WSI-Relevance. Experimental results demonstrate that WSI-LLaVA outperforms existing models across all capability dimensions, with a significant improvement in morphological analysis, establishing a clear correlation between morphological understanding and diagnostic accuracy.
计算病理学领域的最新进展已经产生了补丁级别的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),但这些模型受到无法全面分析全幻灯片图像(WSIs)的局限,并且倾向于绕过病理学家赖以进行诊断的关键形态特征。为了应对这些挑战,我们首先引入了WSI-Bench,这是一个大规模的形态感知基准测试,包含来自9850张幻灯片图像的18万对问答(VQA),涉及3种癌症类型,旨在评估MLLMs对形态特征的认知程度,这对于准确诊断至关重要。基于此基准测试,我们提出了WSI-LLaVA,这是一个用于gigapixel WSI理解的全新框架,采用三阶段训练方法:WSI文本对齐、特征空间对齐和任务特定指令调整。为了更好地评估模型在病理上下文中的性能,我们开发了两个专门的WSI指标:WSI精确度和WSI相关性。实验结果表明,WSI-LLaVA在所有能力维度上都优于现有模型,在形态分析方面取得了显著改进,建立了形态理解与诊断准确性之间的明确相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, 38 pages, 22 figures, 35 tables
Summary
计算病理学领域的最新进展已经出现了基于patch的多模态大语言模型(MLLMs),但这些模型在分析全切片图像(WSIs)时存在局限性,无法全面分析并容易忽略病理医师诊断所依赖的关键形态特征。为解决这些问题,研究团队推出了WSI-Bench,这是一个大规模的形态感知基准测试,包含来自9850个WSIs的18万个问答对,涉及30种癌症类型,旨在评估MLLMs对关键形态特征的理解能力。在此基础上,研究团队进一步提出了WSI-LLaVA框架,采用三阶段训练法处理巨像素WSI理解问题,包括WSI文本对齐、特征空间对齐和任务特定指令调整。为更好地评估模型在病理环境下的表现,研究团队还开发了两个专门的WSI指标:WSI精度和WSI相关性。实验结果表明,WSI-LLaVA在各方面性能均优于现有模型,形态分析显著改善,形态理解与诊断准确度的相关性明确。
Key Takeaways
- 计算病理学领域出现基于patch的多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)。
- MLLMs在分析全切片图像(WSIs)时存在局限性,无法全面分析并易忽略关键形态特征。
- WSI-Bench是一个大规模的形态感知基准测试,用于评估MLLMs对形态特征的理解能力。
- WSI-LLaVA是一个处理巨像素WSI理解的框架,采用三阶段训练法提高模型性能。
- WSI-LLaVA在形态分析方面显著改善,实验结果表明其性能优于现有模型。
- 研究团队为评估模型在病理环境下的表现,开发了两个专门的WSI指标:WSI精度和WSI相关性。
点此查看论文截图


A Runtime-Adaptive Transformer Neural Network Accelerator on FPGAs
Authors:Ehsan Kabir, Jason D. Bakos, David Andrews, Miaoqing Huang
Transformer neural networks (TNN) excel in natural language processing (NLP), machine translation, and computer vision (CV) without relying on recurrent or convolutional layers. However, they have high computational and memory demands, particularly on resource-constrained devices like FPGAs. Moreover, transformer models vary in processing time across applications, requiring custom models with specific parameters. Designing custom accelerators for each model is complex and time-intensive. Some custom accelerators exist with no runtime adaptability, and they often rely on sparse matrices to reduce latency. However, hardware designs become more challenging due to the need for application-specific sparsity patterns. This paper introduces ADAPTOR, a runtime-adaptive accelerator for dense matrix computations in transformer encoders and decoders on FPGAs. ADAPTOR enhances the utilization of processing elements and on-chip memory, enhancing parallelism and reducing latency. It incorporates efficient matrix tiling to distribute resources across FPGA platforms and is fully quantized for computational efficiency and portability. Evaluations on Xilinx Alveo U55C data center cards and embedded platforms like VC707 and ZCU102 show that our design is 1.2$\times$ and 2.87$\times$ more power efficient than the NVIDIA K80 GPU and the i7-8700K CPU respectively. Additionally, it achieves a speedup of 1.7 to 2.25$\times$ compared to some state-of-the-art FPGA-based accelerators.
Transformer神经网络(TNN)在自然语言处理(NLP)、机器翻译和计算机视觉(CV)方面表现出色,无需依赖循环或卷积层。然而,它们对计算和内存的需求很高,特别是在FPGA等资源受限的设备上。此外,不同的应用程序中,Transformer模型的处理时间会有所不同,因此需要具有特定参数的定制模型。为每种模型设计定制加速器是复杂且耗时的。虽然存在一些没有运行时适应性的定制加速器,但它们通常依赖于稀疏矩阵来降低延迟。然而,由于需要特定的应用稀疏模式,硬件设计变得更加具有挑战性。本文介绍了ADAPTOR,这是一个用于FPGA上Transformer编码器和解码器中的密集矩阵计算的运行时自适应加速器。ADAPTOR提高了处理元件和片上内存的利用率,增强了并行性并降低了延迟。它采用高效的矩阵分块技术,以在FPGA平台之间分配资源,并且为了计算效率和便携性而完全量化。在Xilinx Alveo U55C数据中心卡和VC707和ZCU102等嵌入式平台上的评估显示,我们的设计比NVIDIA K80 GPU和i7-8700K CPU分别高出1.2倍和2.87倍的能效。此外,与一些最新的FPGA加速器相比,它实现了1.7到2.25倍的速度提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2409.14023
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对FPGA上变压器编码器解码器中密集矩阵运算的、具有运行时自适应性的加速器——ADAPTOR。它能提高处理元件和片上内存的利用率,增强并行性并降低延迟。通过有效的矩阵切片技术,它能合理分配资源在各种FPGA平台上,并且为实现计算效率和便携性进行了全面量化。评估结果表明,相比NVIDIA K80 GPU和i7-8700K CPU,ADAPTOR在设计效率上更具优势,实现了较高的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer neural networks (TNN) 不依赖循环卷积层就能在自然语言处理(NLP)、机器翻译和计算机视觉(CV)等领域表现出色,但计算内存需求较高,特别是在FPGA等资源受限设备上。
- 针对不同应用,Transformer模型的处理时间有所不同,需要定制具有特定参数的模型。设计针对每个模型的定制加速器是复杂且耗时的。
- 当前存在一些无运行时适应性的定制加速器,它们通常依赖稀疏矩阵来降低延迟,但由于需要特定的应用稀疏模式,硬件设计更具挑战性。
- 本文提出了ADAPTOR,一个针对FPGA上Transformer编码器解码器密集矩阵运算的、具有运行时自适应性的加速器。
- ADAPTOR通过提高处理元件和片上内存的利用率、增强并行性并降低延迟来优化性能。
- ADAPTOR采用有效的矩阵切片技术,可以跨FPGA平台分配资源,且为了计算效率和便携性进行了全面量化。
点此查看论文截图


DOTS: Learning to Reason Dynamically in LLMs via Optimal Reasoning Trajectories Search
Authors:Murong Yue, Wenlin Yao, Haitao Mi, Dian Yu, Ziyu Yao, Dong Yu
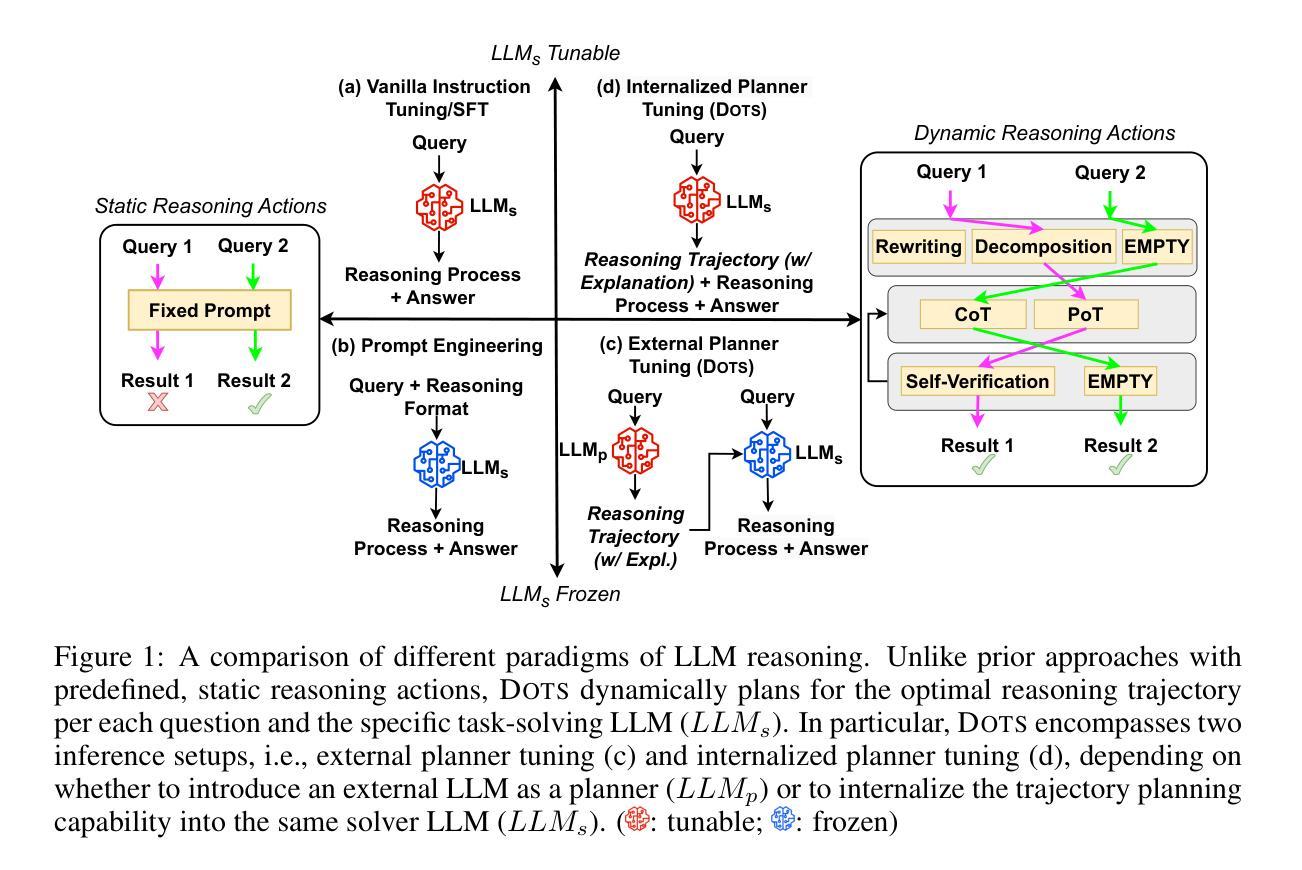
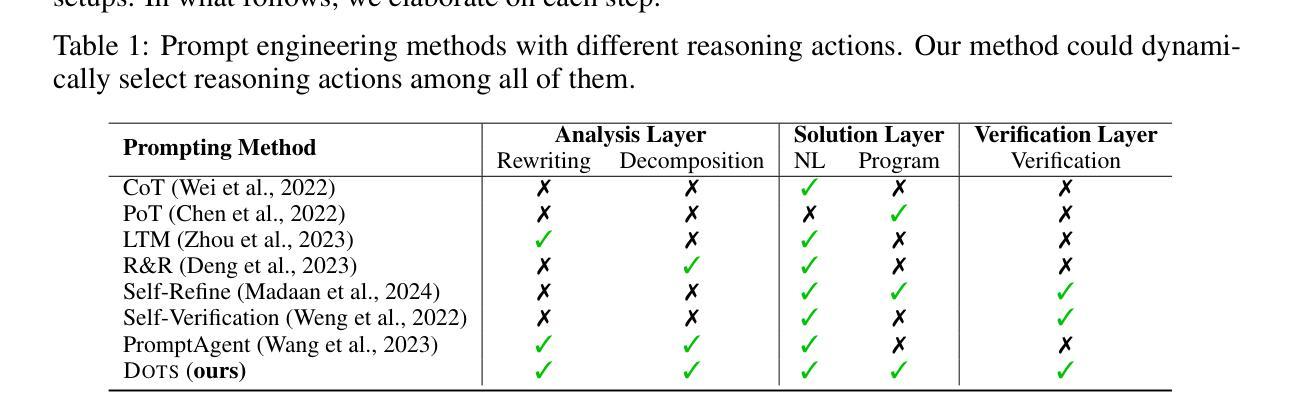
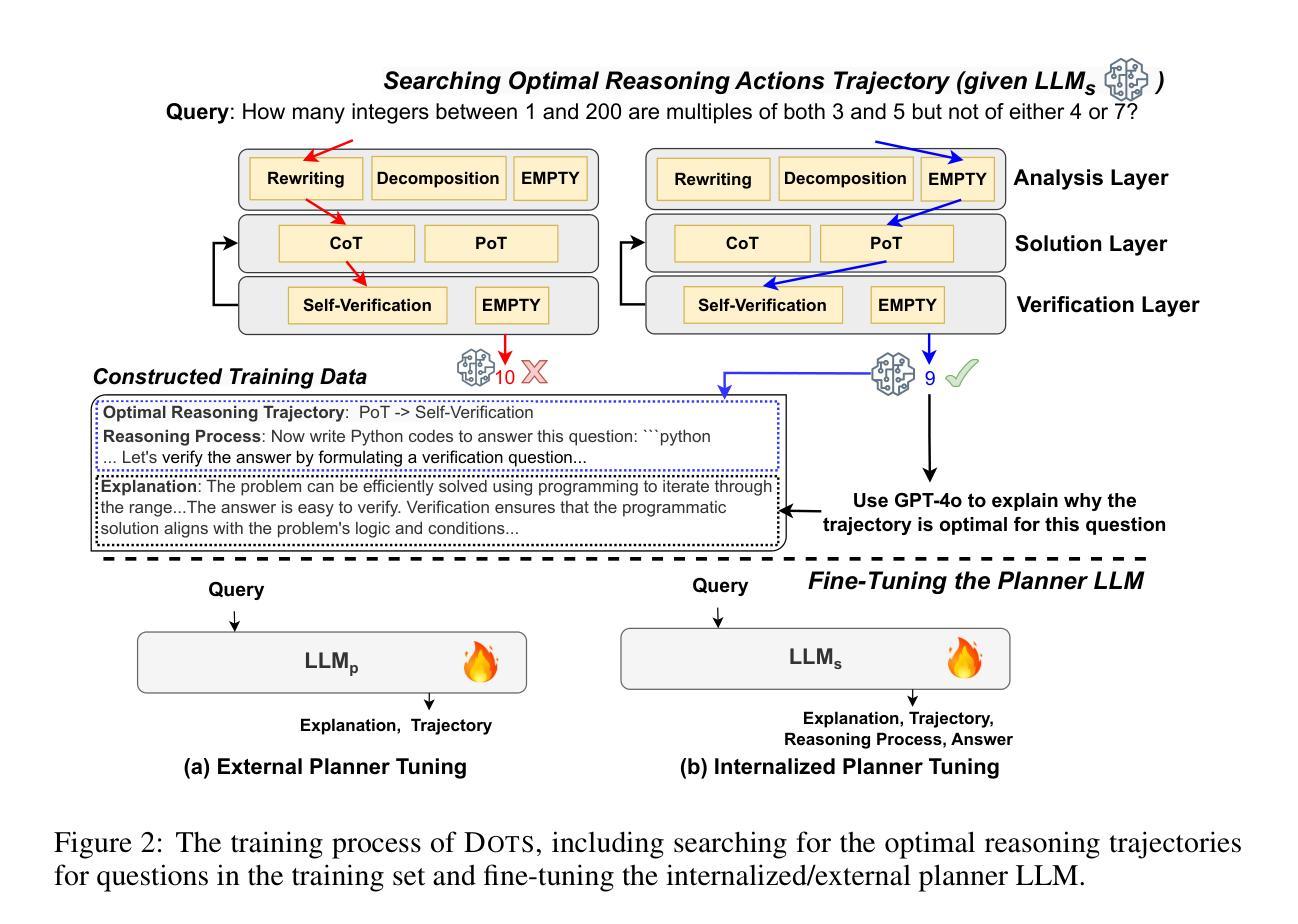
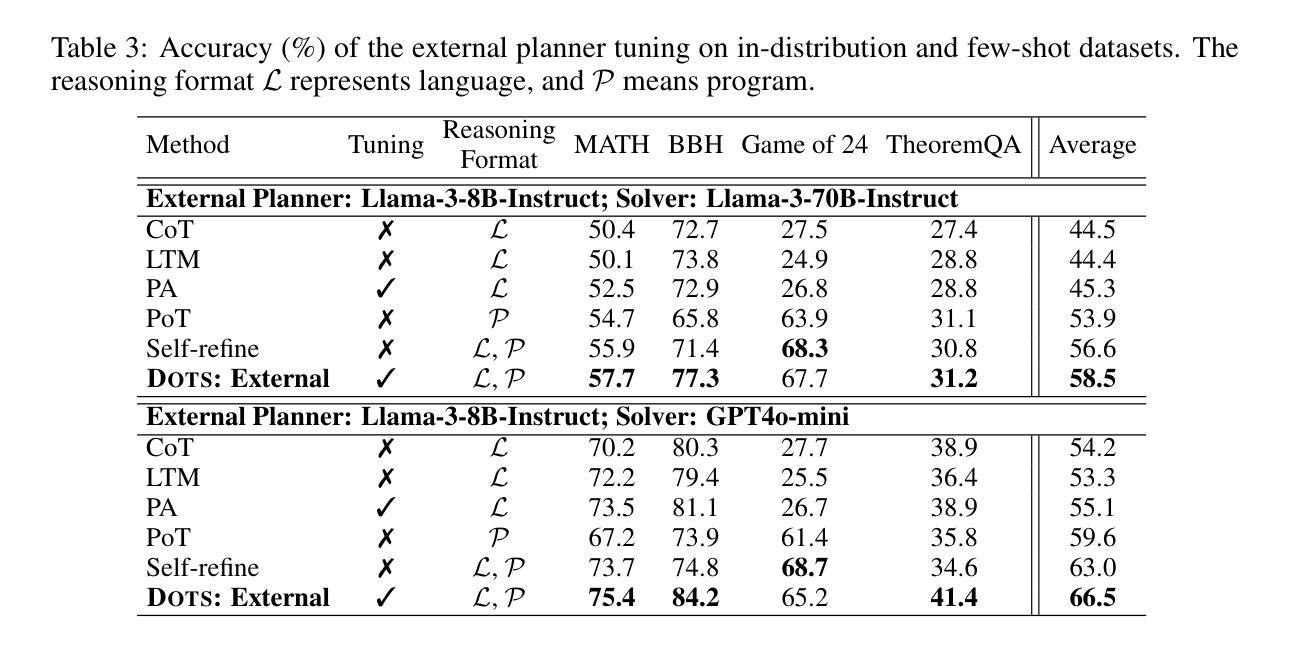
Enhancing the capability of large language models (LLMs) in reasoning has gained significant attention in recent years. Previous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of various prompting strategies in aiding LLMs in reasoning (called “reasoning actions”), such as step-by-step thinking, reflecting before answering, solving with programs, and their combinations. However, these approaches often applied static, predefined reasoning actions uniformly to all questions, without considering the specific characteristics of each question or the capability of the task-solving LLM. In this paper, we propose DOTS, an approach enabling LLMs to reason dynamically via optimal reasoning trajectory search, tailored to the specific characteristics of each question and the inherent capability of the task-solving LLM. Our approach involves three key steps: i) defining atomic reasoning action modules that can be composed into various reasoning action trajectories; ii) searching for the optimal action trajectory for each training question through iterative exploration and evaluation for the specific task-solving LLM; and iii) using the collected optimal trajectories to train an LLM to plan for the reasoning trajectories of unseen questions. In particular, we propose two learning paradigms, i.e., fine-tuning an external LLM as a planner to guide the task-solving LLM, or directly fine-tuning the task-solving LLM with an internalized capability for reasoning actions planning. Our experiments across eight reasoning tasks show that our method consistently outperforms static reasoning techniques and the vanilla instruction tuning approach. Further analysis reveals that our method enables LLMs to adjust their computation based on problem complexity, allocating deeper thinking and reasoning to harder problems.
近年来,增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力已经引起了广泛关注。以往的研究表明,各种提示策略在帮助LLM进行推理(称为“推理行动”)方面是行之有效的,例如逐步思考、答题前思考、程序解题及其组合。然而,这些方法通常将静态的预定义推理行动统一应用于所有问题,而没有考虑到每个问题的特定特征或任务解决LLM的能力。在本文中,我们提出了DOTS方法,这是一种使LLM能够通过最优推理轨迹搜索进行动态推理的方法,它根据每个问题的特定特征和任务解决LLM的内在能力来定制。我们的方法涉及三个关键步骤:i)定义原子推理行动模块,这些模块可以组合成各种推理行动轨迹;ii)通过迭代探索和评估,为特定的任务解决LLM针对每个训练问题搜索最优行动轨迹;iii)使用收集到的最优轨迹来训练LLM,以规划未见问题的推理轨迹。特别是,我们提出了两种学习范式,即微调外部LLM作为规划师来指导任务解决LLM,或直接微调任务解决LLM,使其具备推理行动规划的能力。我们在八个推理任务上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于静态推理技术和普通的指令调整方法。进一步的分析表明,我们的方法使LLM能够根据问题的复杂性调整其计算,将更深入的思考和推理分配给更复杂的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
摘要
近年来,提升大语言模型(LLM)的推理能力备受关注。先前的研究已经展示了各种提示策略在辅助LLM进行推理(称为”推理行动”)中的有效性,如逐步思考、预思考再回答、程序求解等。然而,这些方法常常统一地应用静态的、预定义的推理行动到所有问题上,没有考虑到每个问题的特定特性或任务解决LLM的能力。本文提出DOTS方法,一种使LLM能够针对每个问题的特定特性和任务解决LLM的内在能力进行动态推理的方法。该方法包括三个关键步骤:定义可以组合成各种推理行动轨迹的原子推理行动模块;通过迭代探索和评估为每个训练问题搜索特定的任务解决LLM的最优行动轨迹;使用收集的最优轨迹来训练LLM,以规划未见问题的推理轨迹。我们提出了两种学习范式,即微调外部LLM作为规划器来指导任务解决LLM,或直接微调任务解决LLM以具备内部化的推理行动规划能力。在八个推理任务上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于静态推理技术和指令微调方法。进一步分析表明,我们的方法使LLM能够根据问题复杂度调整计算,将更深入的思考和推理分配给更难的问题。
关键见解
- LLM的推理能力提升受到关注,之前的方法多是应用静态推理行动到所有问题。
- 本文提出DOTS方法,能基于问题特性和LLM能力进行动态推理。
- DOTS包含三个关键步骤:定义原子推理模块、搜索最优行动轨迹、训练LLM进行规划。
- 提出两种学习范式:外部LLM规划器或内部化LLM能力。
- 在八个推理任务上的实验显示,DOTS方法优于静态和指令微调方法。
- DOTS方法使LLM能够根据问题复杂度调整计算,合理分配推理资源。
- 该方法有助于提升LLM在实际问题中的灵活性和适应性。
点此查看论文截图