⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-10 更新
Exploring Superior Function Calls via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Bingguang Hao, Maolin Wang, Zengzhuang Xu, Yicheng Chen, Cunyin Peng, Jinjie GU, Chenyi Zhuang
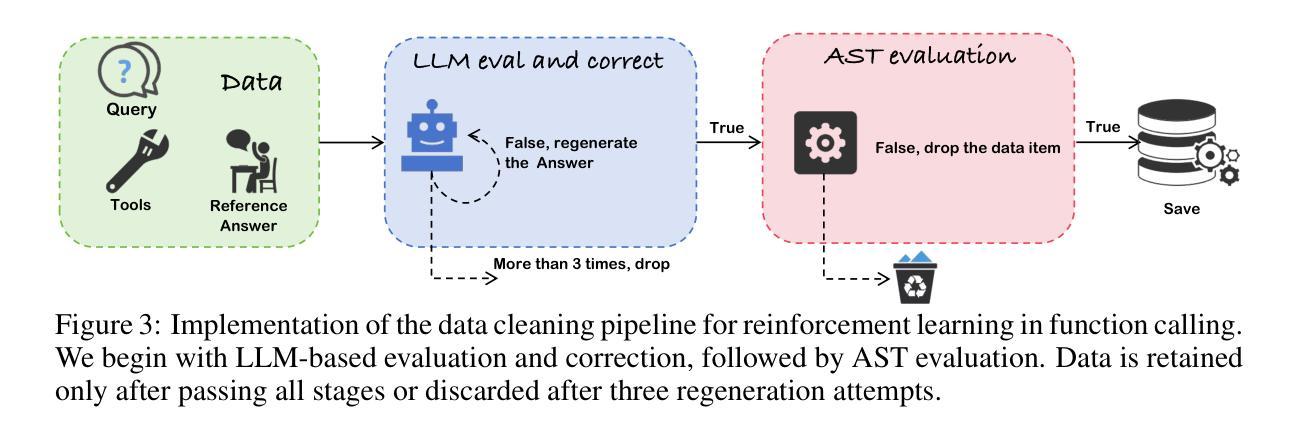
Function calling capabilities are crucial for deploying Large Language Models in real-world applications, yet current training approaches fail to develop robust reasoning strategies. Supervised fine-tuning produces models that rely on superficial pattern matching, while standard reinforcement learning methods struggle with the complex action space of structured function calls. We present a novel reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance group relative policy optimization through strategic entropy based exploration specifically tailored for function calling tasks. Our approach addresses three critical challenges in function calling: insufficient exploration during policy learning, lack of structured reasoning in chain-of-thought generation, and inadequate verification of parameter extraction. Our two-stage data preparation pipeline ensures high-quality training samples through iterative LLM evaluation and abstract syntax tree validation. Extensive experiments on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard demonstrate that this framework achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models with 86.02% overall accuracy, outperforming standard GRPO by up to 6% on complex multi-function scenarios. Notably, our method shows particularly strong improvements on code-pretrained models, suggesting that structured language generation capabilities provide an advantageous starting point for reinforcement learning in function calling tasks. We will release all the code, models and dataset to benefit the community.
函数调用能力对于将大型语言模型部署在真实世界应用中至关重要,然而当前的训练方法无法制定稳健的推理策略。监督微调产生的模型依赖于肤浅的模式匹配,而标准强化学习方法难以应对结构函数调用中的复杂动作空间。我们提出了一种新型的强化学习框架,旨在通过针对函数调用任务量身定制的战略熵基探索增强群体相对策略优化。我们的方法解决了函数调用中的三个关键挑战:策略学习过程中的探索不足,思维生成中结构推理的缺乏,以及参数提取的验证不足。我们的两阶段数据准备流程通过迭代的大型语言模型评估和抽象语法树验证,确保高质量的训练样本。在伯克利函数调用排行榜上的广泛实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现了最先进的性能,总体准确率为86.02%,在复杂的多函数场景中比标准GRPO高出6%。值得注意的是,我们的方法在代码预训练模型上显示出特别大的改进,这表明结构化语言生成能力为函数调用的强化学习提供了一个有利的起点。我们将发布所有的代码、模型和数据集以造福社区。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对大型语言模型在现实世界应用中的函数调用能力缺失问题,现有训练策略无法有效构建稳健的推理策略。本研究提出一种新颖的强化学习框架,旨在通过基于策略相对分组的熵探索增强策略优化,专门解决函数调用任务。该框架解决了函数调用中的三大挑战:策略学习过程中的探索不足、链式思维生成中的结构化推理缺失以及参数提取验证不足。通过两阶段数据准备管道,确保高质量的训练样本通过迭代的大型语言模型评估和抽象语法树验证。在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上的大量实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现最先进的性能,总体准确率为86.02%,在复杂的多功能场景上相比标准GRPO的准确率提高了高达6%。特别地,该方法在代码预训练模型上表现出显著的优势,表明结构化语言生成能力为强化学习在函数调用任务中提供了一个有利的起点。我们将发布所有代码、模型和数据集以造福学术界。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在现实世界应用中的函数调用能力至关重要。
- 当前训练策略无法为函数调用任务发展出稳健的推理策略。
- 监督微调产生的模型依赖于表面模式匹配,而标准强化学习方法面临复杂的动作空间的挑战。
- 提出一种新颖的强化学习框架,通过策略相对分组的熵探索增强策略优化来解决函数调用任务。
- 该框架解决了函数调用的三大挑战:探索不足、结构化推理缺失以及参数提取验证不足。
- 通过两阶段数据准备管道确保高质量的训练样本。
- 在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上的实验表明,该框架实现了最先进的性能,并在复杂的多功能场景上表现出显著的优势。
点此查看论文截图

SPaRFT: Self-Paced Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models
Authors:Dai Do, Manh Nguyen, Svetha Venkatesh, Hung Le
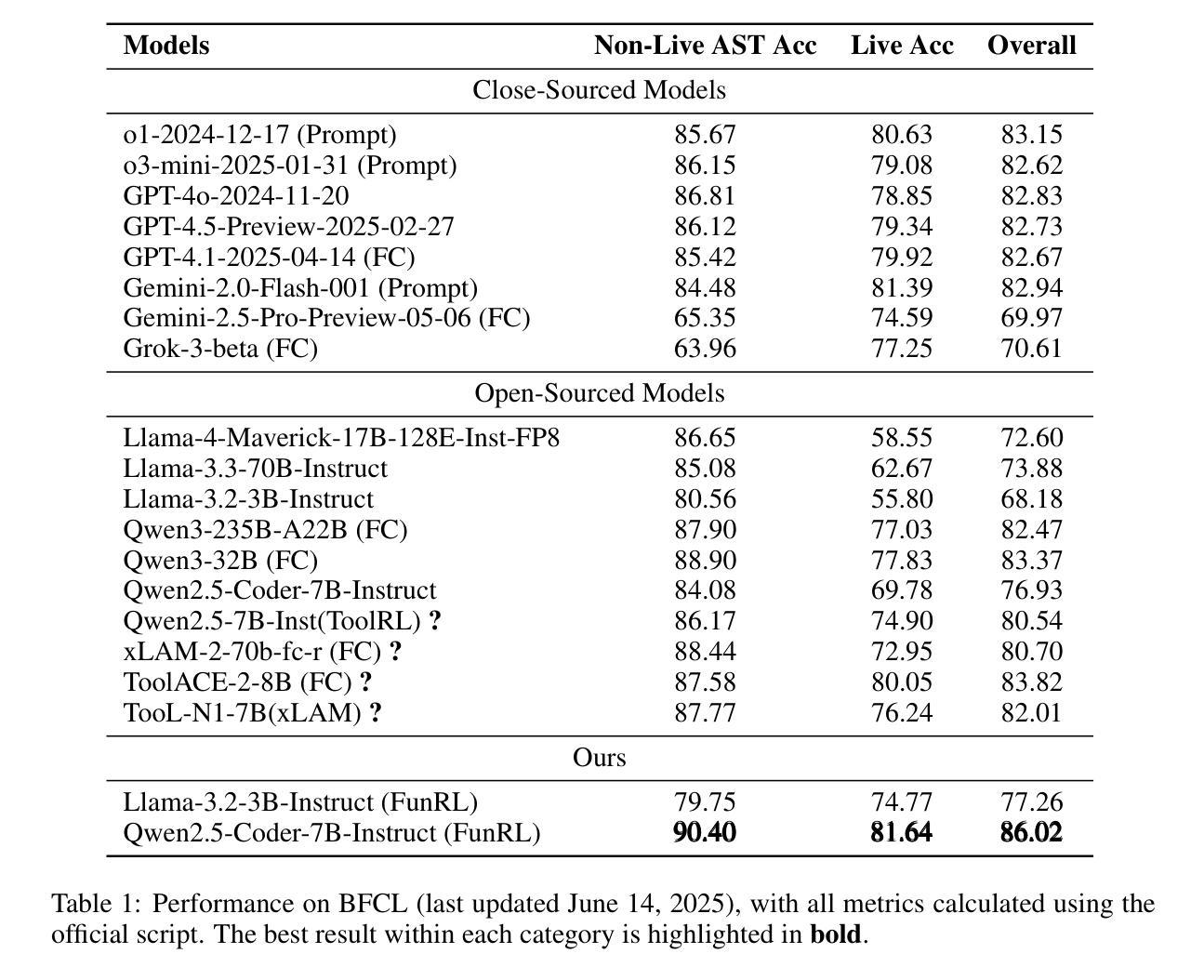
Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong reasoning capabilities when fine-tuned with reinforcement learning (RL). However, such methods require extensive data and compute, making them impractical for smaller models. Current approaches to curriculum learning or data selection are largely heuristic-driven or demand extensive computational resources, limiting their scalability and generalizability. We propose \textbf{SPaRFT}, a self-paced learning framework that enables efficient learning based on the capability of the model being trained through optimizing which data to use and when. First, we apply \emph{cluster-based data reduction} to partition training data by semantics and difficulty, extracting a compact yet diverse subset that reduces redundancy. Then, a \emph{multi-armed bandit} treats data clusters as arms, optimized to allocate training samples based on model current performance. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks show that SPaRFT achieves comparable or better accuracy than state-of-the-art baselines while using up to (100\times) fewer samples. Ablation studies and analyses further highlight the importance of both data clustering and adaptive selection. Our results demonstrate that carefully curated, performance-driven training curricula can unlock strong reasoning abilities in LLMs with minimal resources.
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在通过强化学习(RL)进行微调时显示出强大的推理能力。然而,这些方法需要大量的数据和计算资源,使得它们对于较小的模型来说不切实际。当前的教学方法或数据选择主要基于启发式方法,或者需要大量的计算资源,从而限制了其可扩展性和泛化能力。我们提出了SPaRFT,这是一种自适应学习框架,它通过优化使用哪些数据以及何时使用数据,实现基于模型能力的有效学习。首先,我们应用基于聚类的数据缩减方法,通过语义和难度对训练数据进行分区,提取出紧凑且多样化的子集,以减少冗余。然后,我们将数据集群视为多个武装带,采用多臂匪徒算法优化训练样本的分配,根据模型当前性能进行决策。跨多个推理基准的实验表明,SPaRFT的准确率与最先进的基准相当或更好,同时使用的样本数量减少了高达(100倍)。消融研究和分析进一步强调了数据聚类和自适应选择的重要性。我们的结果表明,精心策划的、以性能为导向的训练课程可以解锁小型语言模型的最强推理能力只需极少资源即可。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)通过强化学习(RL)进行微调后展现出强大的推理能力,但此方法需要大量数据和计算资源,对于小型模型来说并不实用。当前的教学法或数据选择方法主要依赖于启发式或大量计算资源,限制了其可扩展性和通用性。本文提出一种名为SPaRFT的自我节奏学习框架,基于模型的能力优化训练过程中数据和时间的分配,实现高效学习。通过聚类减少数据冗余,将训练数据按语义和难度进行分区,提取出紧凑且多样化的子集。然后,利用多臂老虎机算法优化数据集群的分配,根据模型当前性能来分配训练样本。实验证明,SPaRFT在多个推理基准测试中实现了与最新技术相当或更好的准确性,同时使用的样本数量最多减少了(100)倍。分析和消融研究进一步强调了数据聚类和自适应选择的重要性。结果表明,精心策划的性能驱动训练课程可以在有限资源下解锁LLMs的强大推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在强化学习微调下展现出强大的推理能力,但需大量数据和计算资源。
- 当前教学法或数据选择方法受限于启发式或计算资源,缺乏可扩展性和通用性。
- SPaRFT框架结合自我节奏学习和优化算法,实现高效训练数据使用。
- 通过聚类减少数据冗余,按语义和难度分区训练数据。
- 利用多臂老虎机算法优化数据集群分配,根据模型性能动态调整。
- 实验证明SPaRFT在多个推理基准测试中表现优异,样本使用量大幅减少。
点此查看论文截图

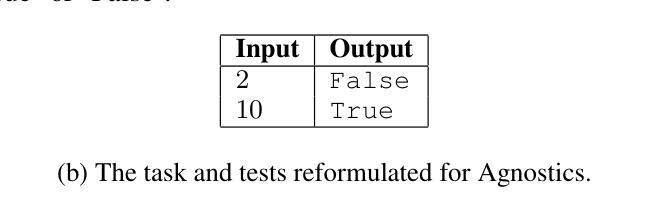
Agnostics: Learning to Code in Any Programming Language via Reinforcement with a Universal Learning Environment
Authors:Aleksander Boruch-Gruszecki, Yangtian Zi, Zixuan Wu, Tejas Oberoi, Carolyn Jane Anderson, Joydeep Biswas, Arjun Guha
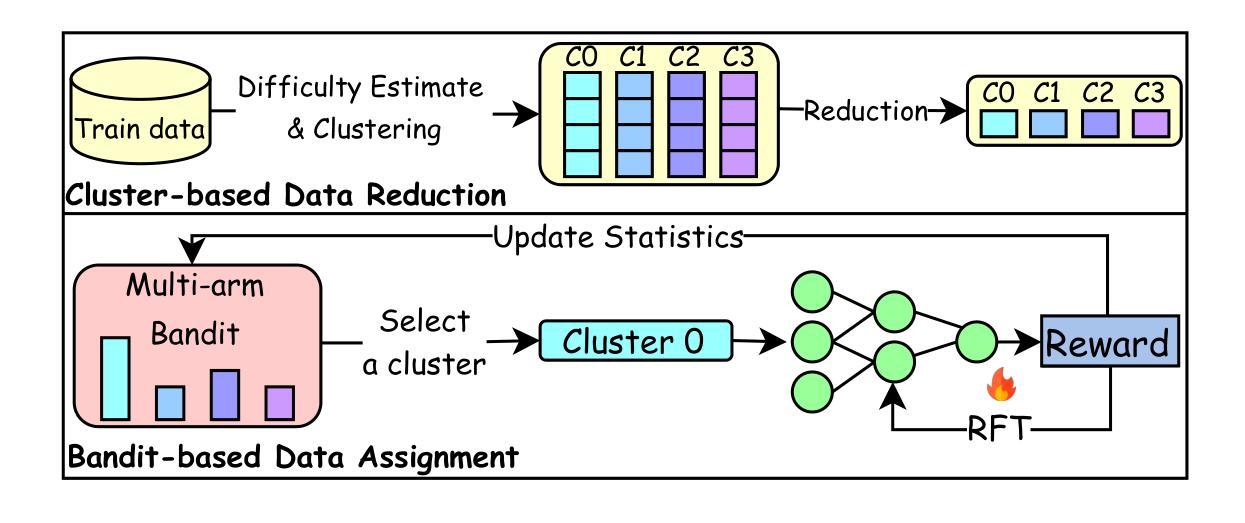
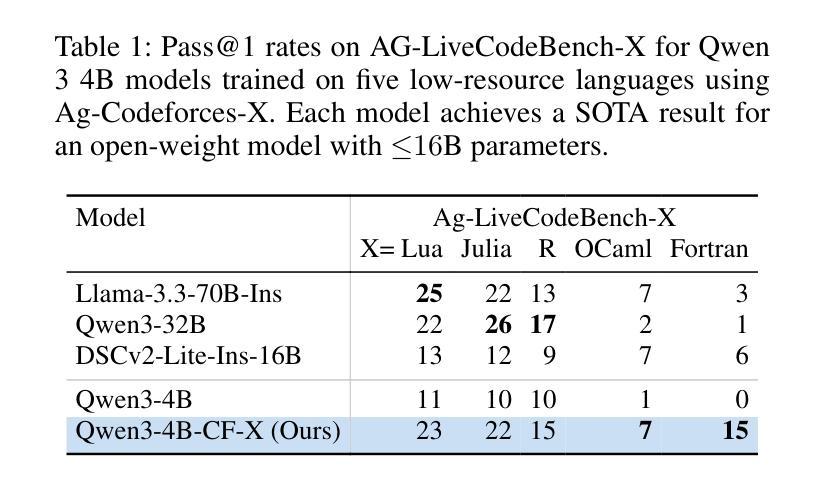
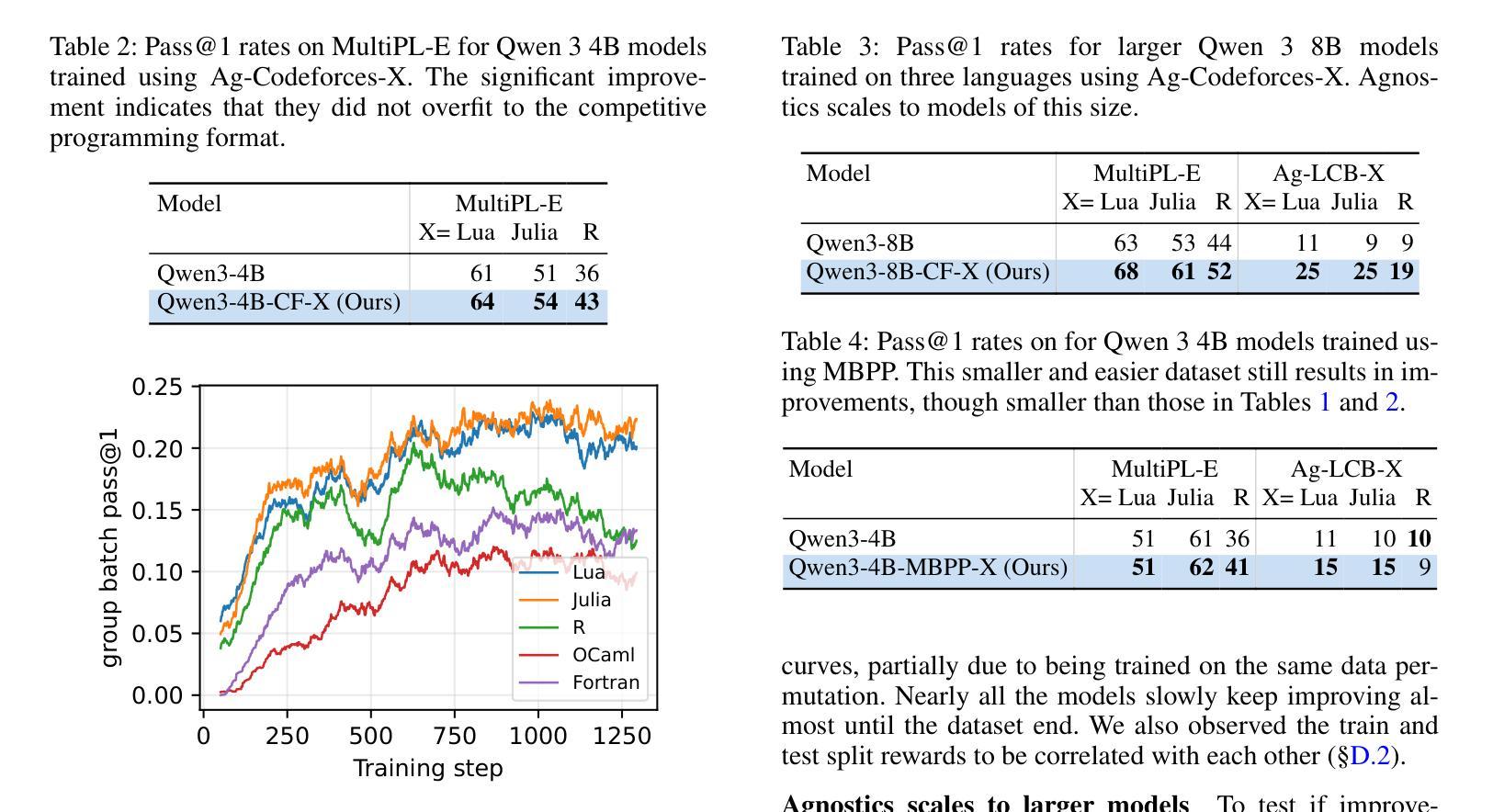
Large language models (LLMs) already excel at writing code in high-resource languages such as Python and JavaScript, yet stumble on low-resource languages that remain essential to science and engineering. Besides the obvious shortage of pre-training data, post-training itself is a bottleneck: every new language seems to require new datasets, test harnesses, and reinforcement-learning (RL) infrastructure. We introduce Agnostics, a language-agnostic post-training pipeline that eliminates this per-language engineering. The key idea is to judge code solely by its externally observable behavior, so a single verifier can test solutions written in any language. Concretely, we (i) use an LLM to rewrite existing unit-test datasets into an I/O format, (ii) supply a short configuration that tells the verifier how to compile and run a target language, and (iii) apply reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) in a robust code execution environment. Applied to five low-resource languages–Lua, Julia, R, OCaml, and Fortran–Agnostics (1) improves Qwen-3 4B to performance that rivals other 16B-70B open-weight models; (2) scales cleanly to larger and diverse model families (Qwen-3 8B, DeepSeek Coder 6.7B Instruct, Phi 4 Mini); and (3) for ${\le} 16$B parameter models, sets new state-of-the-art pass@1 results on MultiPL-E and a new multi-language version LiveCodeBench that we introduce. We will release the language-agnostic training datasets (Ag-MBPP-X, Ag-Codeforces-X, Ag-LiveCodeBench-X), training code, and ready-to-use configurations, making RL post-training in any programming language as simple as editing a short YAML file.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经在高资源语言(如Python和JavaScript)的编程方面表现出色,但在对科学和工程至关重要的低资源语言方面却遭遇困境。除了明显的预训练数据短缺外,后续的训练本身也是一个瓶颈:每种新语言似乎都需要新的数据集、测试程序和强化学习(RL)基础设施。我们引入了Agnostics,这是一种语言无关的后训练管道,消除了每种语言的工程。基本思想是根据代码的外在可观察行为来判断代码,因此单个验证器可以测试任何语言编写的解决方案。具体来说,我们(i)使用LLM将现有的单元测试数据集重写成I/O格式,(ii)提供一个简短配置,告诉验证器如何编译和运行目标语言,(iii)在一个稳定的代码执行环境中应用可验证奖励的强化学习(RLVR)。应用于五种低资源语言——Lua、Julia、R、OCaml和Fortran——Agnostics(1)将Qwen-3 4B的性能提高至与其他16B-70B公开权重模型相当的水平;(2)能够干净地扩展到更大和多样化的模型家族(Qwen-3 8B、DeepSeek Coder 6.7B Instruct、Phi 4 Mini);(3)对于≤16B参数模型,在我们引入的MultiPL-E和新的多语言版本LiveCodeBench上,设置了最新的最先进的pass@1结果。我们将发布语言无关的训练数据集(Ag-MBPP-X、Ag-Codeforces-X、Ag-LiveCodeBench-X)、训练代码和即用的配置,使任何编程语言的强化后训练只需编辑一个简短的YAML文件即可。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 19 figures. For artifacts, see https://agnostics.abgru.me
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理像Python和JavaScript这样的高资源语言编程时表现出色,但在处理科学工程必需的低资源语言时遇到困难。针对这一问题,我们推出了Agnostics,一种语言无关的后训练管道,它消除了每种语言所需的工程。Agnostics的关键思想是通过判断代码的外在行为来评估代码,从而使用单个验证器测试任何语言编写的解决方案。通过重写现有单元测试数据集为I/O格式、提供告诉验证器如何编译和运行目标语言的简短配置,以及应用可验证奖励的强化学习(RLVR)在稳健的代码执行环境中,我们实现了对五种低资源语言——Lua、Julia、R、OCaml和Fortran的应用。Agnostics不仅提高了性能,还轻松扩展到了更大的模型家族,并为我们引入的新多语言版本LiveCodeBench和MultiPL-E设置了新的最先进的pass@1结果。我们将发布语言无关的训练数据集、训练代码和即用型配置,使得在任何编程语言中进行强化学习后训练只需编辑一个简短的YAML文件即可。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理低资源语言编程时存在挑战,缺乏预训练数据和后训练瓶颈。
- Agnostics是一种语言无关的后训练管道,通过判断代码的外在行为来评估代码,消除每种语言所需的工程。
- Agnostics实现了对五种低资源语言的应用,并提高了性能。
- Agnostics能够轻松扩展到更大的模型家族。
- Agnostics为我们引入的新多语言版本LiveCodeBench和MultiPL-E设置了新的最先进的pass@1结果。
- 发布了语言无关的训练数据集、训练代码和即用型配置。
点此查看论文截图


VER-Bench: Evaluating MLLMs on Reasoning with Fine-Grained Visual Evidence
Authors:Chenhui Qiang, Zhaoyang Wei, Xumeng Han Zipeng Wang, Siyao Li, Xiangyuan Lan, Jianbin Jiao, Zhenjun Han
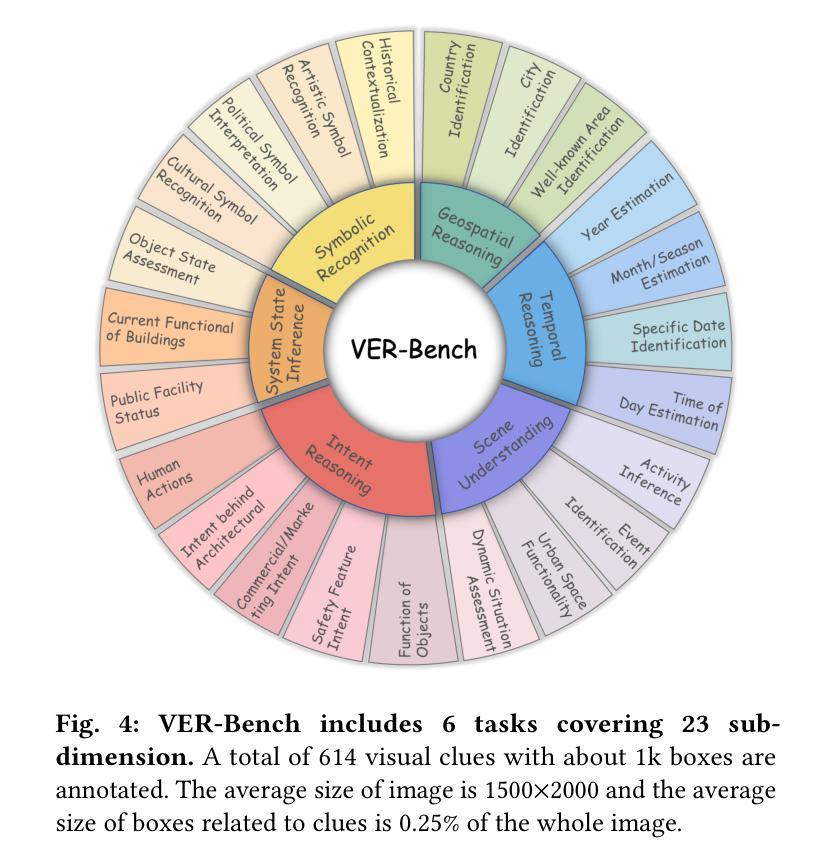
With the rapid development of MLLMs, evaluating their visual capabilities has become increasingly crucial. Current benchmarks primarily fall into two main types: basic perception benchmarks, which focus on local details but lack deep reasoning (e.g., “what is in the image?”), and mainstream reasoning benchmarks, which concentrate on prominent image elements but may fail to assess subtle clues requiring intricate analysis. However, profound visual understanding and complex reasoning depend more on interpreting subtle, inconspicuous local details than on perceiving salient, macro-level objects. These details, though occupying minimal image area, often contain richer, more critical information for robust analysis. To bridge this gap, we introduce the VER-Bench, a novel framework to evaluate MLLMs’ ability to: 1) identify fine-grained visual clues, often occupying on average just 0.25% of the image area; 2) integrate these clues with world knowledge for complex reasoning. Comprising 374 carefully designed questions across Geospatial, Temporal, Situational, Intent, System State, and Symbolic reasoning, each question in VER-Bench is accompanied by structured evidence: visual clues and question-related reasoning derived from them. VER-Bench reveals current models’ limitations in extracting subtle visual evidence and constructing evidence-based arguments, highlighting the need to enhance models’s capabilities in fine-grained visual evidence extraction, integration, and reasoning for genuine visual understanding and human-like analysis. Dataset and additional materials are available https://github.com/verbta/ACMMM-25-Materials.
随着大规模语言模型的快速发展,评估它们的视觉能力变得越来越重要。目前的基准测试主要分为两种类型:基本感知基准测试,侧重于局部细节,但缺乏深度推理(例如,“图像中有什么?”);以及主流的推理基准测试,侧重于图像中的突出元素,但可能无法评估需要细致分析的细微线索。然而,深刻的视觉理解和复杂的推理更多地依赖于解释细微的、不引人注目的局部细节,而不是感知显著、宏观级别的对象。这些细节虽然占据的图像面积很小,但往往包含更丰富、更关键的信息,有利于进行稳健的分析。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了VER-Bench这一新型框架,旨在评估大规模语言模型的能力:1)识别平均只占图像面积0.25%的细微视觉线索;2)将这些线索与世界知识相结合,进行复杂推理。VER-Bench包含374个精心设计的问题,涵盖地理空间、时间、情境、意图、系统状态和符号推理等方面,每个问题都伴有结构化证据:视觉线索和源于这些线索的问题相关推理。VER-Bench揭示了当前模型在提取细微视觉证据和构建基于证据论证方面的局限性,强调需要增强模型在细微视觉证据提取、整合和推理方面的能力,以实现真正的视觉理解和人类样本的分析。数据集和其他材料可通过https://github.com/verbta/ACMMM-25-Materials获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by ACMM2025 Dataset track
Summary
随着MLLMs的快速发展,评估其视觉能力变得至关重要。当前评估标准主要分为两类:侧重局部细节的感知评估和侧重显著图像元素推理的主流评估标准。然而,深刻的视觉理解和复杂推理更依赖于对微妙、不引人注目的局部细节的解释。为了弥补这一差距,引入了VER-Bench框架,用于评估MLLMs识别仅占图像面积平均0.25%的精细视觉线索的能力,以及将这些线索与世界知识相结合进行复杂推理的能力。该框架包括地理空间、时间、情境、意图、系统状态和符号推理等374个精心设计的问题,每个问题都附有结构化证据。这揭示了当前模型在提取细微视觉证据和构建基于证据的论证方面的局限性,强调了增强模型在精细视觉证据提取、整合和推理方面的能力的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs的视觉能力评估变得重要,需要新的评估框架来弥补现有基准测试的不足。
- VER-Bench框架旨在评估MLLMs对精细视觉线索的识别能力,这些线索仅占图像面积的0.25%。
- VER-Bench强调将视觉线索与世界知识结合进行复杂推理的重要性。
- 当前模型在提取细微视觉证据和构建基于证据的论证方面存在局限性。
- VER-Bench包含多种类型的问题,涵盖地理空间、时间、情境等,旨在全面评估MLLMs的推理能力。
- 每个问题在VER-Bench中都配有结构化证据,包括视觉线索和与问题相关的推理。
点此查看论文截图



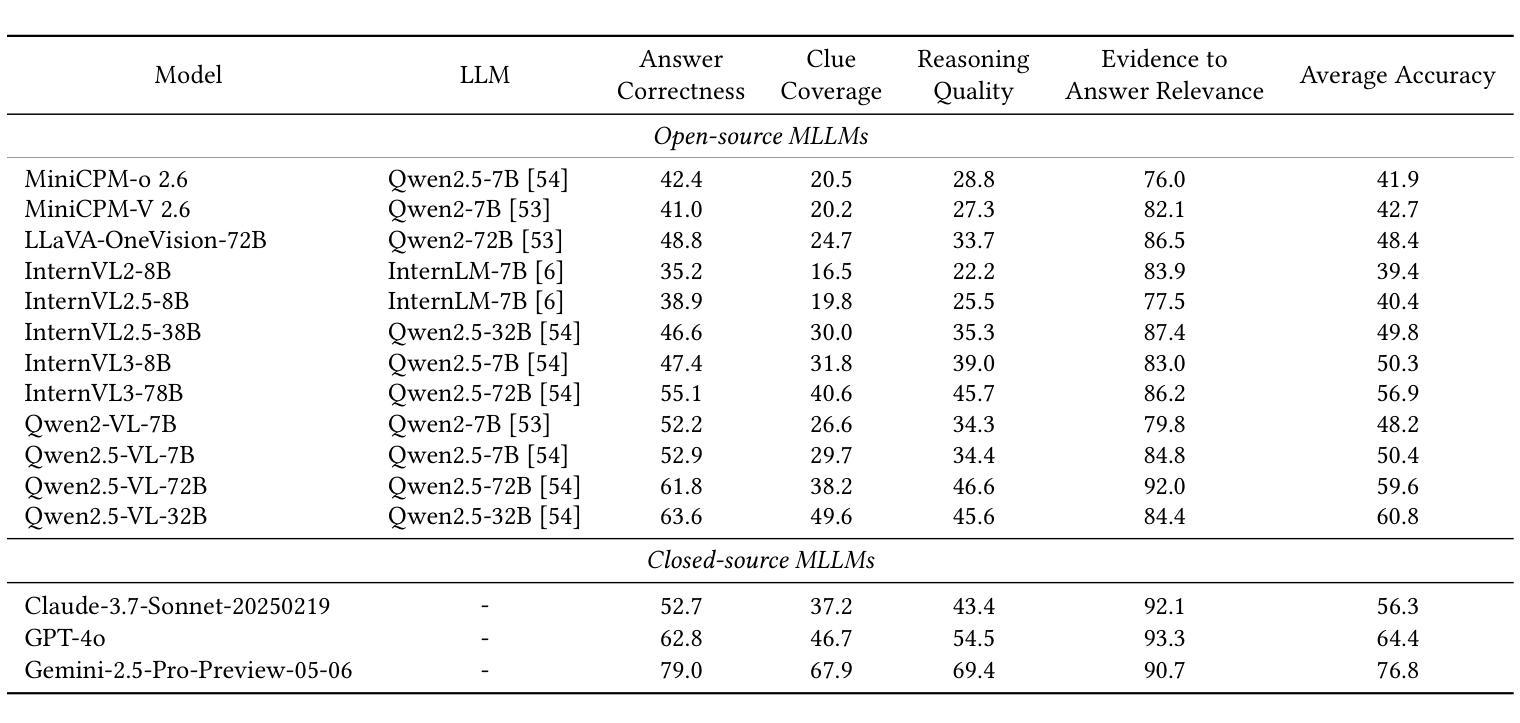
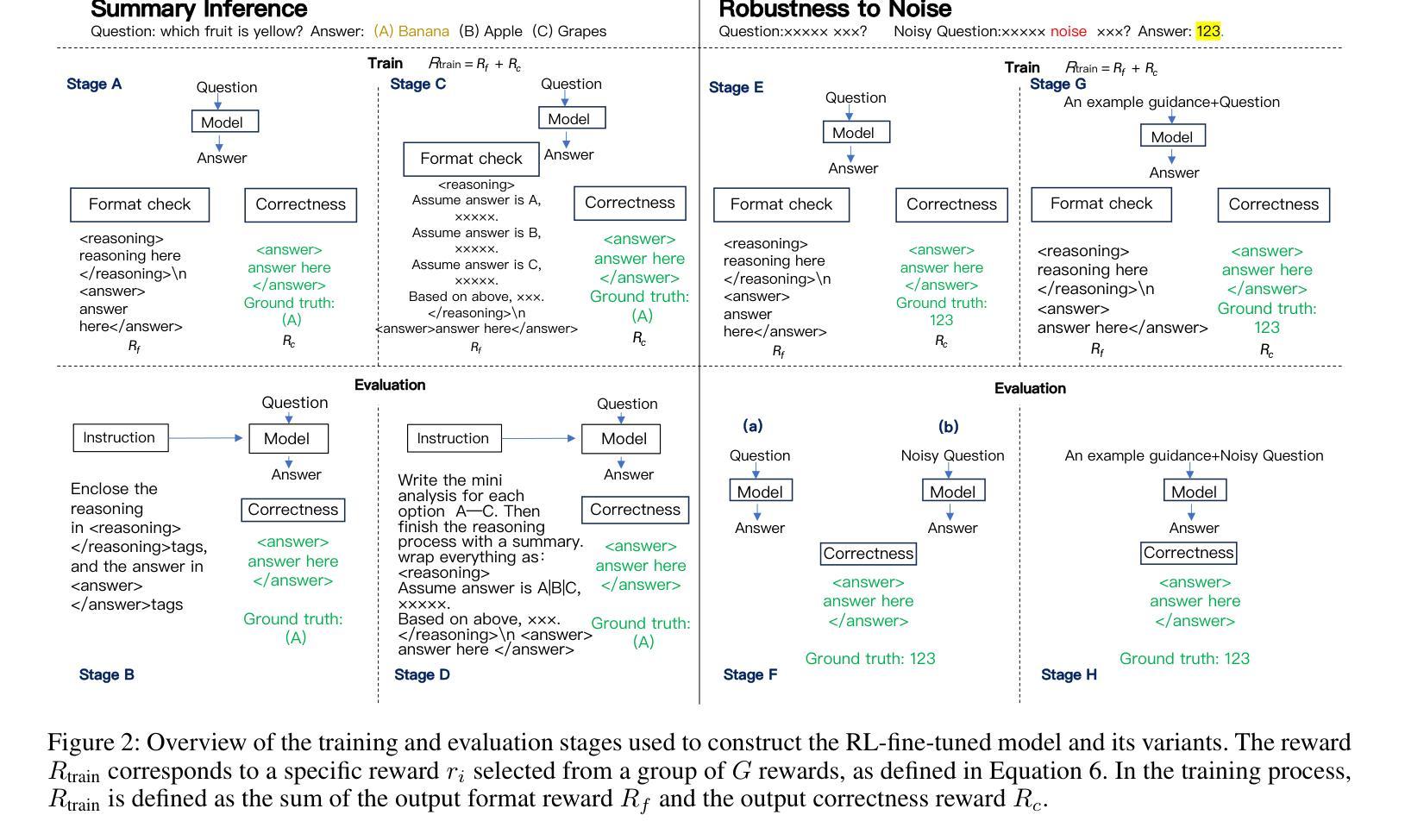
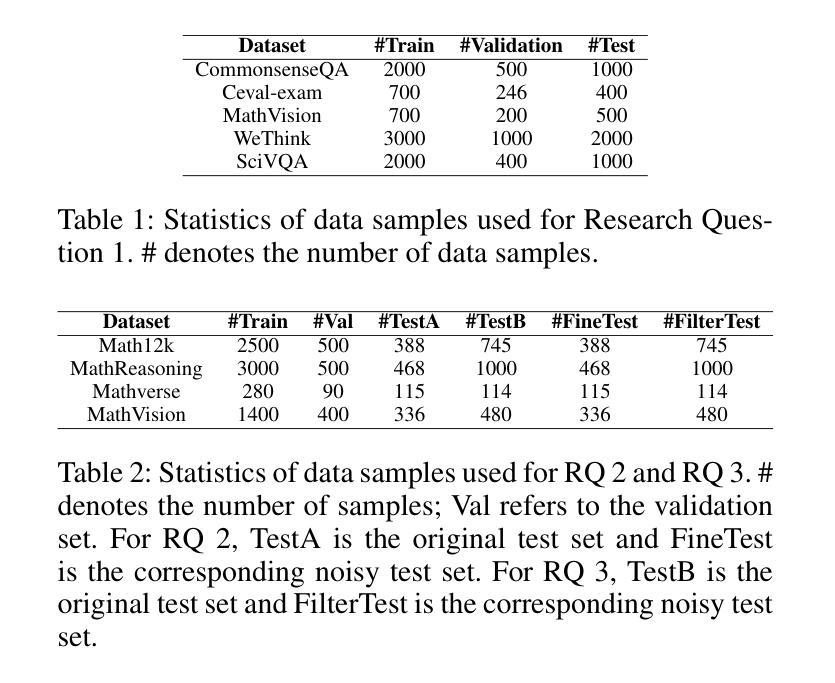
Large Language Models Reasoning Abilities Under Non-Ideal Conditions After RL-Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chang Tian, Matthew B. Blaschko, Mingzhe Xing, Xiuxing Li, Yinliang Yue, Marie-Francine Moens
Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a key technique for enhancing the reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs), with policy-gradient algorithms dominating the post-training stage because of their efficiency and effectiveness. However, most existing benchmarks evaluate large-language-model reasoning under idealized settings, overlooking performance in realistic, non-ideal scenarios. We identify three representative non-ideal scenarios with practical relevance: summary inference, fine-grained noise suppression, and contextual filtering. We introduce a new research direction guided by brain-science findings that human reasoning remains reliable under imperfect inputs. We formally define and evaluate these challenging scenarios. We fine-tune three LLMs and a state-of-the-art large vision-language model (LVLM) using RL with a representative policy-gradient algorithm and then test their performance on eight public datasets. Our results reveal that while RL fine-tuning improves baseline reasoning under idealized settings, performance declines significantly across all three non-ideal scenarios, exposing critical limitations in advanced reasoning capabilities. Although we propose a scenario-specific remediation method, our results suggest current methods leave these reasoning deficits largely unresolved. This work highlights that the reasoning abilities of large models are often overstated and underscores the importance of evaluating models under non-ideal scenarios. The code and data will be released at XXXX.
强化学习(RL)已成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的一种关键技术,策略梯度算法在训练后的阶段占据主导地位,因其高效性和有效性。然而,大多数现有的基准测试都在理想化的环境下评估大型语言模型的推理能力,忽略了在现实、非理想场景中的表现。我们确定了三个具有实际相关性的代表性非理想场景:摘要推理、精细噪声抑制和上下文过滤。我们引入了一个新的研究方向,该方向以脑科学的研究结果为指导,表明人类推理在存在缺陷的输入下仍然可靠。我们对这些具有挑战性的场景进行了正式的定义和评估。我们使用强化学习和一个代表性的策略梯度算法微调了三个LLM和一个最先进的视觉语言大模型(LVLM),然后在八个公开数据集上测试它们的性能。我们的结果表明,尽管强化学习微调改进了理想环境下的基线推理能力,但在所有三个非理想场景中性能均显著下降,暴露了高级推理能力的关键局限性。尽管我们提出了一种针对特定场景的补救方法,但我们的结果仍表明当前的方法在很大程度上无法解决这些推理缺陷。这项工作强调了大型模型的推理能力往往被高估了,并强调了在非理想环境下评估模型的重要性。代码和数据将在XXXX发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF large language models, large vision-language model, reasoning, non-ideal conditions, reinforcement learning
Summary
强化学习(RL)被用来提高大语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,其中策略梯度算法因其高效性和有效性而在后训练阶段占据主导地位。然而,大多数现有的基准测试都在理想化的环境下评估大语言模型的推理能力,忽略了在非理想场景下的表现。本文确定了三个具有实际意义的代表性非理想场景:摘要推理、精细噪声抑制和上下文过滤。我们引入了一个新的研究方向,该方向由脑科学发现引导,即人类推理可以在不完美的输入下仍然可靠。我们对三个LLM、一个最先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)进行了RL策略梯度算法的微调,并在八个公共数据集上测试了它们的性能。结果显示,虽然RL微调提高了理想环境下的基线推理能力,但在所有三种非理想场景中,性能显著下降,暴露出高级推理能力的关键局限性。尽管我们提出了针对特定场景的补救方法,但结果仍表明当前方法未能有效解决这些推理缺陷。这项工作强调了大型模型的推理能力经常被过分夸大,并强调了在非理想环境下评估模型的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习用于提高大语言模型的推理能力,其中策略梯度算法表现突出。
- 现有基准测试主要评估理想环境下的语言模型推理能力,忽略了非理想场景。
- 论文确定了三个具有实际意义的非理想场景:摘要推理、精细噪声抑制和上下文过滤。
- 脑科学发现表明人类推理可以在不完美的输入下仍然可靠,论文基于此引入新的研究方向。
- 实验结果显示,在非理想场景下,经过RL调教的模型的性能显著下降,暴露出其推理能力的局限性。
- 尽管尝试提出针对特定场景的补救方法,但当前模型在非理想场景下的推理缺陷仍未得到有效解决。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty-aware Predict-Then-Optimize Framework for Equitable Post-Disaster Power Restoration
Authors:Lin Jiang, Dahai Yu, Rongchao Xu, Tian Tang, Guang Wang
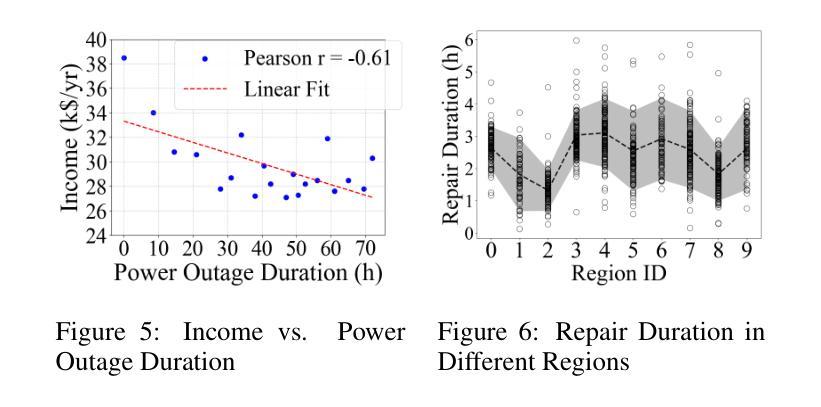
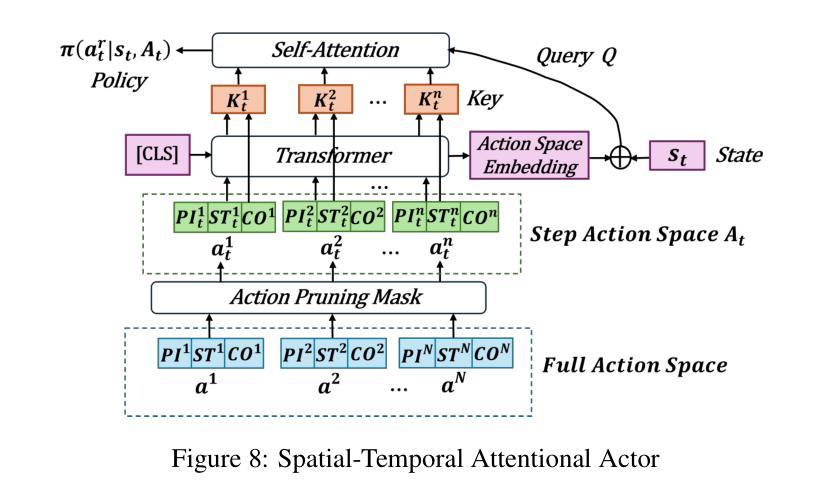
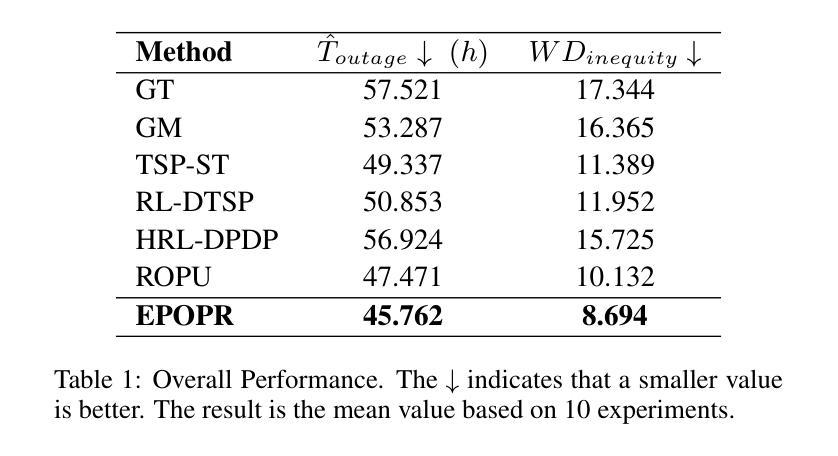
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, highlights the urgent need for efficient and equitable power system restoration. Many electricity providers make restoration decisions primarily based on the volume of power restoration requests from each region. However, our data-driven analysis reveals significant disparities in request submission volume, as disadvantaged communities tend to submit fewer restoration requests. This disparity makes the current restoration solution inequitable, leaving these communities vulnerable to extended power outages. To address this, we aim to propose an equity-aware power restoration strategy that balances both restoration efficiency and equity across communities. However, achieving this goal is challenging for two reasons: the difficulty of predicting repair durations under dataset heteroscedasticity, and the tendency of reinforcement learning agents to favor low-uncertainty actions, which potentially undermine equity. To overcome these challenges, we design a predict-then-optimize framework called EPOPR with two key components: (1) Equity-Conformalized Quantile Regression for uncertainty-aware repair duration prediction, and (2) Spatial-Temporal Attentional RL that adapts to varying uncertainty levels across regions for equitable decision-making. Experimental results show that our EPOPR effectively reduces the average power outage duration by 3.60% and decreases inequity between different communities by 14.19% compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
极端天气事件,如龙卷风的频发,凸显了高效公平的电力系统恢复的紧迫需求。许多电力供应商主要基于各地区的电力恢复请求数量来做出恢复决策。然而,我们的数据驱动分析显示,请求提交的数量存在显著差异,因为贫困社区往往提交较少的恢复请求。这种差异使得当前的恢复解决方案不公平,使这些社区容易受到长期停电的影响。为了解决这一问题,我们旨在提出一种公平意识强的电力恢复策略,在社区之间平衡恢复效率和公平。然而,实现这一目标面临两个挑战:数据集异方差性下预测修复持续时间的难度,以及强化学习代理人倾向于选择低不确定性行动的趋势,这可能会破坏公平。为了克服这些挑战,我们设计了一个名为EPOPR的预测优化框架,它有两个关键组成部分:(1)公平合规分位数回归,用于不确定性意识修复持续时间预测;(2)时空注意力强化学习,适应各地区不同不确定性水平,以公平决策。实验结果表明,与最新基线相比,我们的EPOPR平均停电持续时间减少了3.60%,不同社区之间的不公平现象减少了14.19%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,12 figures
Summary:极端天气事件频发,如龙卷风,凸显了高效公平地恢复电力系统的紧迫需求。当前电力恢复决策主要基于各地区的电力恢复请求数量,但数据分析显示劣势社区提交的恢复请求较少,导致当前解决方案不公平。为此,提出一种兼顾恢复效率和公平的电力恢复策略,面临数据集异方差性导致的维修时间预测难度和强化学习代理倾向于选择低不确定性行动以破坏公平性的挑战。为此,设计了一个预测优化框架EPOPR,包括不确定性感知维修时间预测和适应不同地区不确定性水平的公平决策制定。实验结果表明,EPOPR与现有技术相比,平均停电时间减少了3.60%,不同社区之间的不公平性减少了14.19%。
Key Takeaways:
- 极端天气事件凸显了电力恢复系统需要高效公平的恢复策略。
- 当前电力恢复决策主要基于请求数量,但劣势社区提交的恢复请求较少,导致解决方案不公平。
- 提出一种电力恢复策略,旨在平衡恢复效率和公平性。
- 实现该策略面临两大挑战:数据集异方差性导致的维修时间预测难度和强化学习代理的决策倾向。
- 设计了预测优化框架EPOPR来解决这些挑战,包括不确定性感知的维修时间预测和适应不同地区不确定性水平的决策制定。
- EPOPR与现有技术相比,平均停电时间减少了3.6%,社区间的不公平性减少了14.19%。
点此查看论文截图

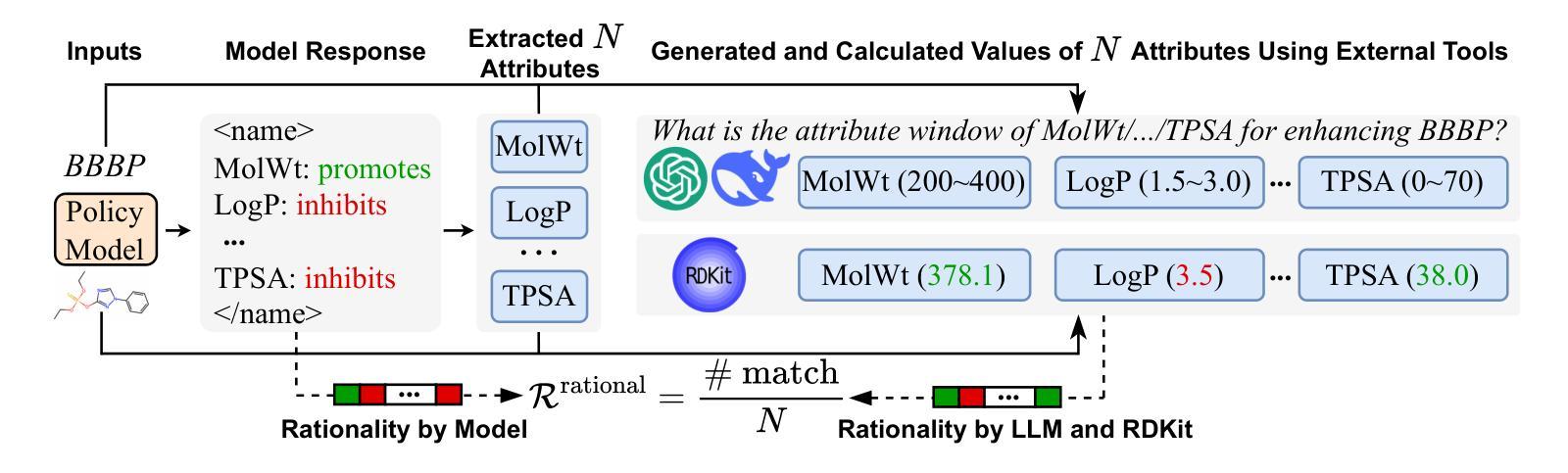
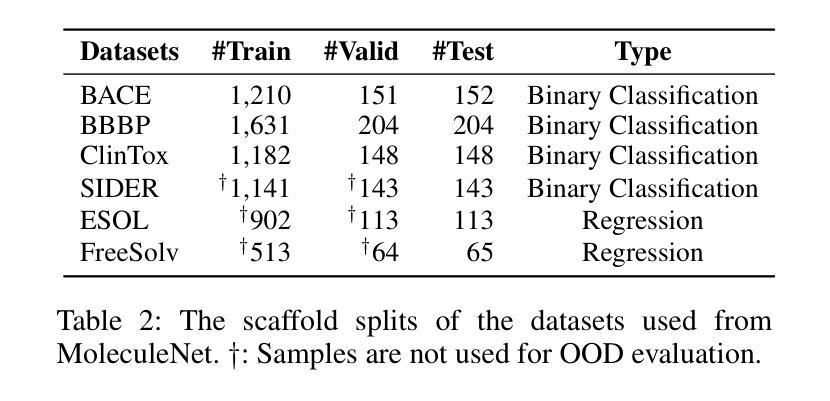
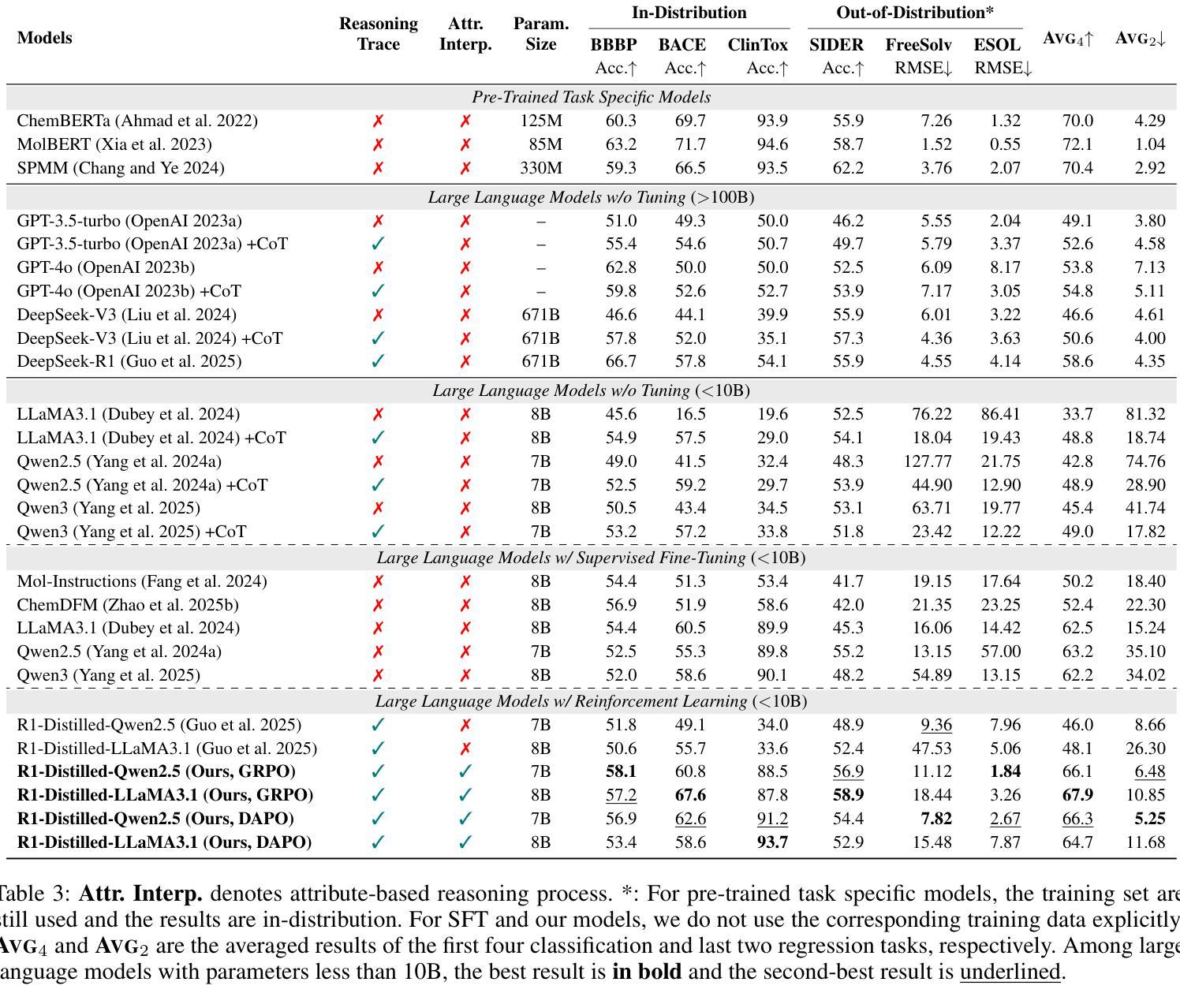
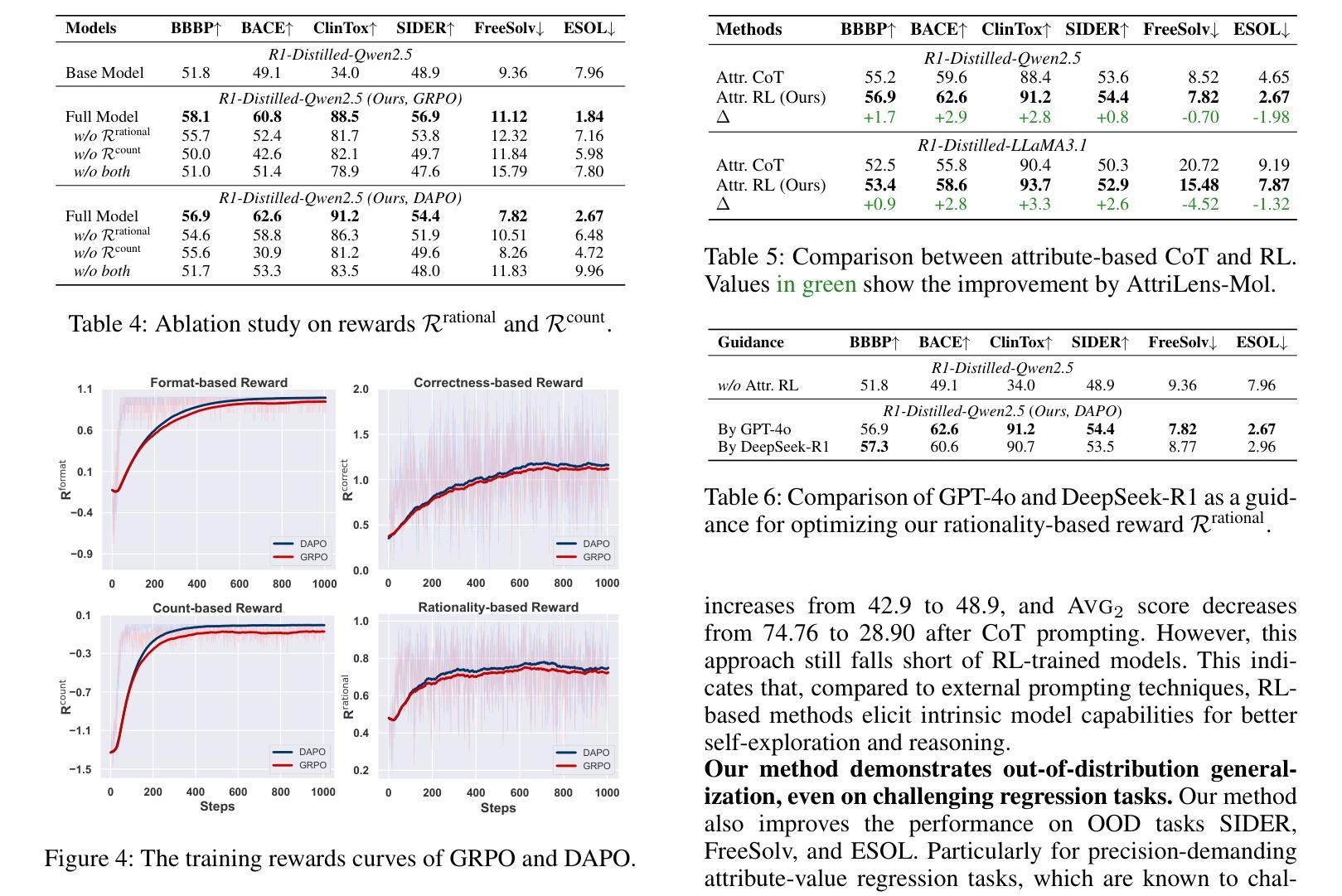
AttriLens-Mol: Attribute Guided Reinforcement Learning for Molecular Property Prediction with Large Language Models
Authors:Xuan Lin, Long Chen, Yile Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in assisting molecular property prediction tasks but often rely on human-crafted prompts and chain-of-thought templates. While recent advanced large reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1 employ reinforcement learning for an extended ``thinking’’ process, their reasoning can be verbose and lack relevance. We introduce AttriLens-Mol, an attribute-guided reinforcement learning framework for molecular property prediction with LLMs. AttriLens-Mol steers the model’s reasoning by using: (1) a format reward encouraging attribute-based structured output, (2) a count reward to avoid enumerating irrelevant attributes, and (3) a rationality reward using advanced LLMs and RDKit to verify the relatedness of the generated attributes. This approach implicitly elicits the model’s inherent knowledge of relevant molecular attributes during reasoning, enables making predictions for the molecular property more effectively. Experiments on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets show that, training both 7B-size R1-Distilled-Qwen2.5 and R1-Distilled-LLaMA3.1 models on 4,000 samples with our proposed AttriLens-Mol method significantly boosts the performance, getting comparable or better results than supervised fine-tuning models (Mol-Instructions, ChemDFM, etc.) and advanced models (GPT-3.5, GPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, DeepSeek-R1, etc.). Further, our extracted attributes for the target property, when used as features for an interpretable decision tree model, yield superior performance compared to attributes generated by prompting LLMs. This shows that AttriLens-Mol effectively elicits more relevant and predictive molecular attributes, leading to enhanced interpretability and performance for property prediction. We release the code in https://github.com/szu-tera/AttriLens-Mol.
大型语言模型(LLM)在辅助分子属性预测任务方面显示出巨大潜力,但它们通常依赖于人工制作的提示和思维链模板。虽然最近的先进的大型推理模型,如DeepSeek-R1,采用强化学习进行更长的“思考”过程,但它们的推理可能过于冗长且缺乏相关性。我们引入了AttriLens-Mol,这是一个用于分子属性预测的、以属性为导向的强化学习框架。AttriLens-Mol通过以下方式引导模型的推理:(1)格式奖励鼓励基于属性的结构化输出;(2)计数奖励避免列举不相关的属性;(3)合理性奖励使用高级LLM和RDKit验证生成属性的相关性。这种方法能够隐式地激发模型在推理过程中对相关分子属性的内在知识,从而更有效地进行分子属性预测。对内部和外部数据集的实验表明,使用我们提出的AttriLens-Mol方法对7B规模的R1-Distilled-Qwen2.5和R1-Distilled-LLaMA3.1模型进行训练,在4000个样本上的表现显著提升,获得了与监督微调模型(Mol-Instructions、ChemDFM等)和高级模型(GPT-3.5、GPT-4o、DeepSeek-V3、DeepSeek-R1等)相当或更好的结果。此外,我们为目标属性提取的属性,当用作可解释决策树模型的特征时,与通过提示LLM产生的属性相比,表现出更优越的性能。这表明AttriLens-Mol有效地引发了更相关和预测性的分子属性,提高了属性预测的可解释性和性能。我们在https://github.com/szu-tera/AttriLens-Mol发布了代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
大型语言模型在分子属性预测任务中展现出潜力,但仍需人工提示和思维链模板。最新的大型推理模型如DeepSeek-R1采用强化学习进行更长的推理过程,但存在推理冗长和缺乏相关性的问题。本文提出AttriLens-Mol,一个用于分子属性预测的、以属性引导强化学习的框架。它通过格式奖励、计数奖励和合理性奖励来引导模型的推理,避免了枚举不相关属性,并验证了生成属性的相关性。该方法在分布内和分布外数据集上的实验表明,使用AttriLens-Mol方法训练的大型语言模型性能显著提升,与监督微调模型(如Mol-Instructions、ChemDFM等)和先进模型(如GPT-3.5、GPT-4o、DeepSeek-V3、DeepSeek-R1等)相比,结果相当或更好。此外,使用AttriLens-Mol提取的目标属性作为特征,用于可解释性决策树模型时,表现出优越的性能,说明AttriLens-Mol能更有效地引出相关且预测性的分子属性,提高预测属性的可解释性和性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在分子属性预测中表现出潜力,但仍需改进推理过程的冗余和相关性问题。
- AttriLens-Mol是一个新的框架,使用属性引导的强化学习进行分子属性预测。
- AttriLens-Mol通过格式奖励、计数奖励和合理性奖励来引导模型推理。
- AttriLens-Mol能够提升大型语言模型在分子属性预测任务上的性能。
- 与其他模型和方法的比较显示,AttriLens-Mol表现优越。
- AttriLens-Mol提取的属性作为特征时,可显著提高决策树模型的可解释性和性能。
- AttriLens-Mol有效地引出相关且预测性的分子属性。
点此查看论文截图

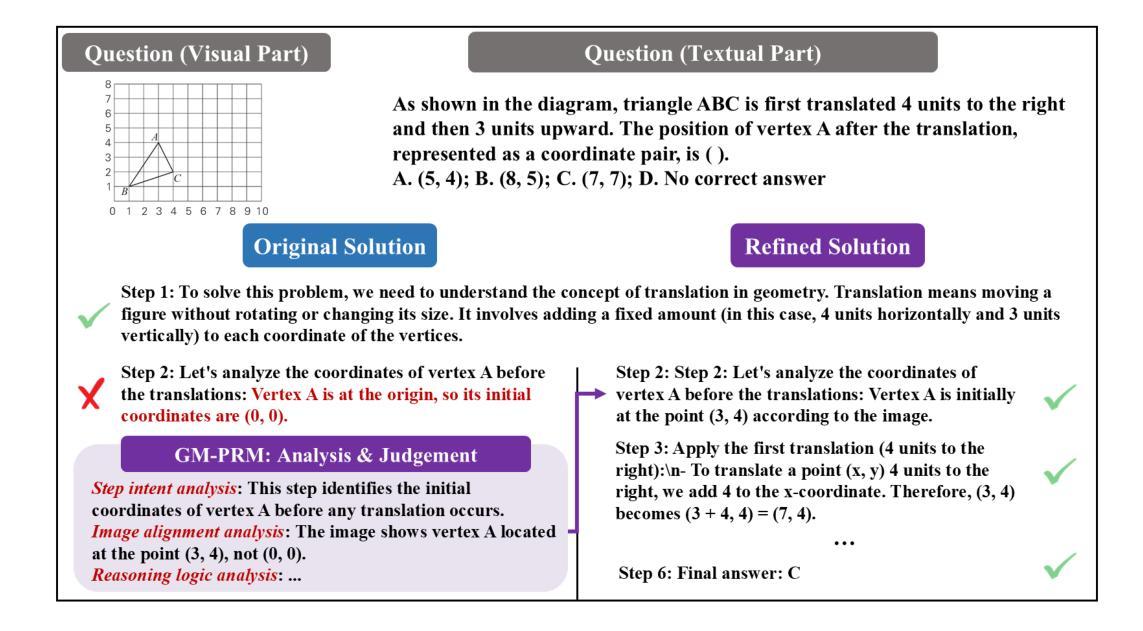
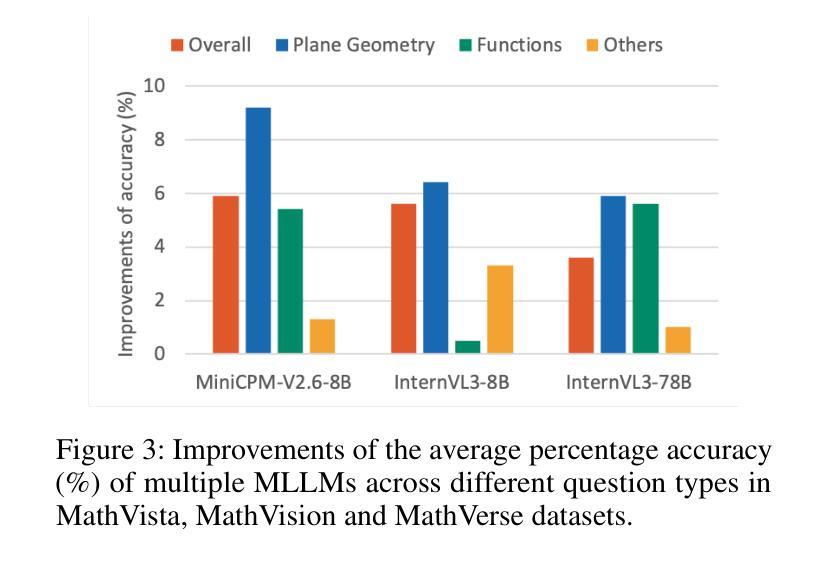
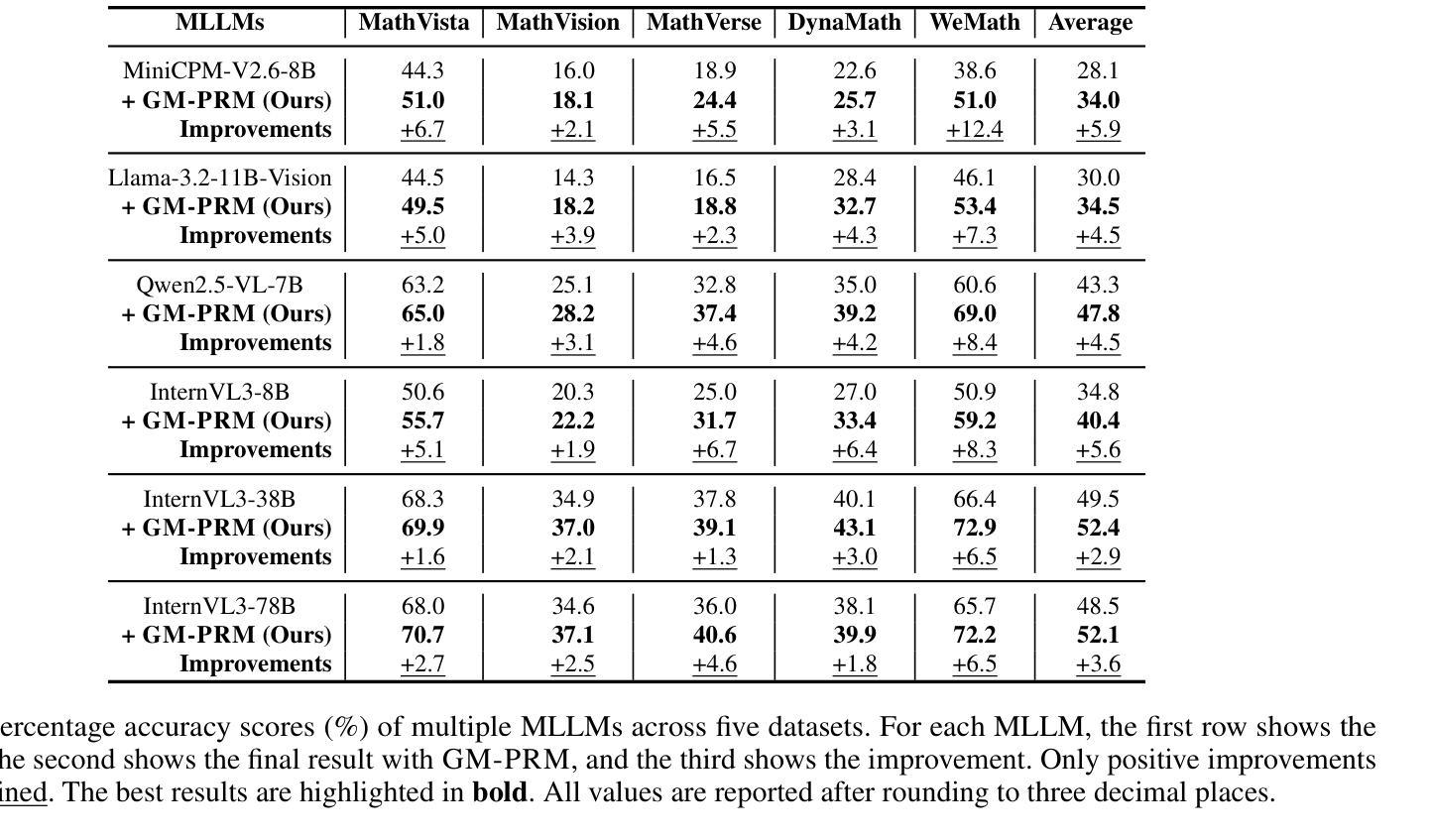
GM-PRM: A Generative Multimodal Process Reward Model for Multimodal Mathematical Reasoning
Authors:Jianghangfan Zhang, Yibo Yan, Kening Zheng, Xin Zou, Song Dai, Xuming Hu
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities but often struggle with complex, multi-step mathematical reasoning, where minor errors in visual perception or logical deduction can lead to complete failure. While Process Reward Models (PRMs) offer step-by-step supervision, existing multimodal PRMs are limited to being binary verifiers that can identify but not correct errors, offering little explanatory power. To address these deficiencies, we introduce the Generative Multimodal Process Reward Model (GM-PRM), a novel paradigm that transforms the PRM from a passive judge into an active reasoning collaborator. Instead of a simple scalar score, GM-PRM provides a fine-grained, interpretable analysis of each reasoning step, evaluating its step intent, visual alignment, and logical soundness. More critically, GM-PRM is trained to generate a corrected version of the first erroneous step it identifies. This unique corrective capability enables our new test-time inference strategy, Refined Best-of-N (Refined-BoN). This framework actively enhances solution quality by using the PRM’s generated correction to guide the policy model toward a more promising reasoning trajectory, thereby improving the diversity and correctness of the solution pool. We demonstrate that GM-PRM achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple multimodal math benchmarks, significantly boosting policy model performance with remarkable data efficiency, requiring only a 20K-sample training dataset. Our code will be released upon acceptance.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)表现出了令人瞩目的能力,但在复杂的多步骤数学推理方面常常遇到困难,视觉感知或逻辑推断中的小错误都可能导致完全失败。虽然过程奖励模型(PRM)提供了逐步监督,但现有的多模态PRM仅限于作为二进制验证器,只能识别错误而无法纠正错误,解释力很小。为了解决这些不足,我们引入了生成式多模态过程奖励模型(GM-PRM),这是一种将PRM从被动判断者转变为积极推理合作者的新型范式。GM-PRM不再提供简单的标量分数,而是对每一步推理进行精细的、可解释的分析,评估其步骤意图、视觉对齐和逻辑合理性。更重要的是,GM-PRM经过训练,可以生成其识别的第一个错误步骤的修正版本。这种独特的纠正能力使我们能够采用新的测试时间推理策略,即精细化最佳N策略(Refined-BoN)。该框架积极提高了解决方案的质量,利用PRM生成的修正来引导政策模型走向更有前途的推理轨迹,从而提高了解决方案池的多样性和正确性。我们在多个多模态数学基准测试上证明了GM-PRM实现了最新结果,显著提高了政策模型性能,并且数据效率惊人,只需要一个2万样本的训练数据集。我们的代码将在通过后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在处理复杂多步骤数学推理时面临的挑战,以及现有过程奖励模型(PRM)的局限性。为解决这些问题,提出了一种新的生成式多模态过程奖励模型(GM-PRM),该模型将PRM从被动判断转变为积极推理合作者。GM-PRM不仅能提供每个推理步骤的精细可解释性分析,还能对第一步中的错误进行修正,并通过改进的最佳N策略提高策略模型的性能,在多个多模态数学基准测试中达到最新成果,表现出惊人的数据效率。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在处理复杂多步骤数学推理时面临挑战,微小的视觉感知或逻辑推导错误可能导致完全失败。
- 现有PRM仅限于作为二进制验证器,只能识别错误而无法纠正,缺乏解释力。
- GM-PRM是一种新型模型,将PRM从被动判断转变为积极推理合作者,提供精细的可解释性分析并纠正错误推理步骤。
- GM-PRM通过改进的最佳N策略(Refined-BoN)提高策略模型的性能,提升解决方案的质量和多样性。
- GM-PRM在多个多模态数学基准测试中达到最新成果,显示出色的数据效率,仅需20K样本训练集。
点此查看论文截图

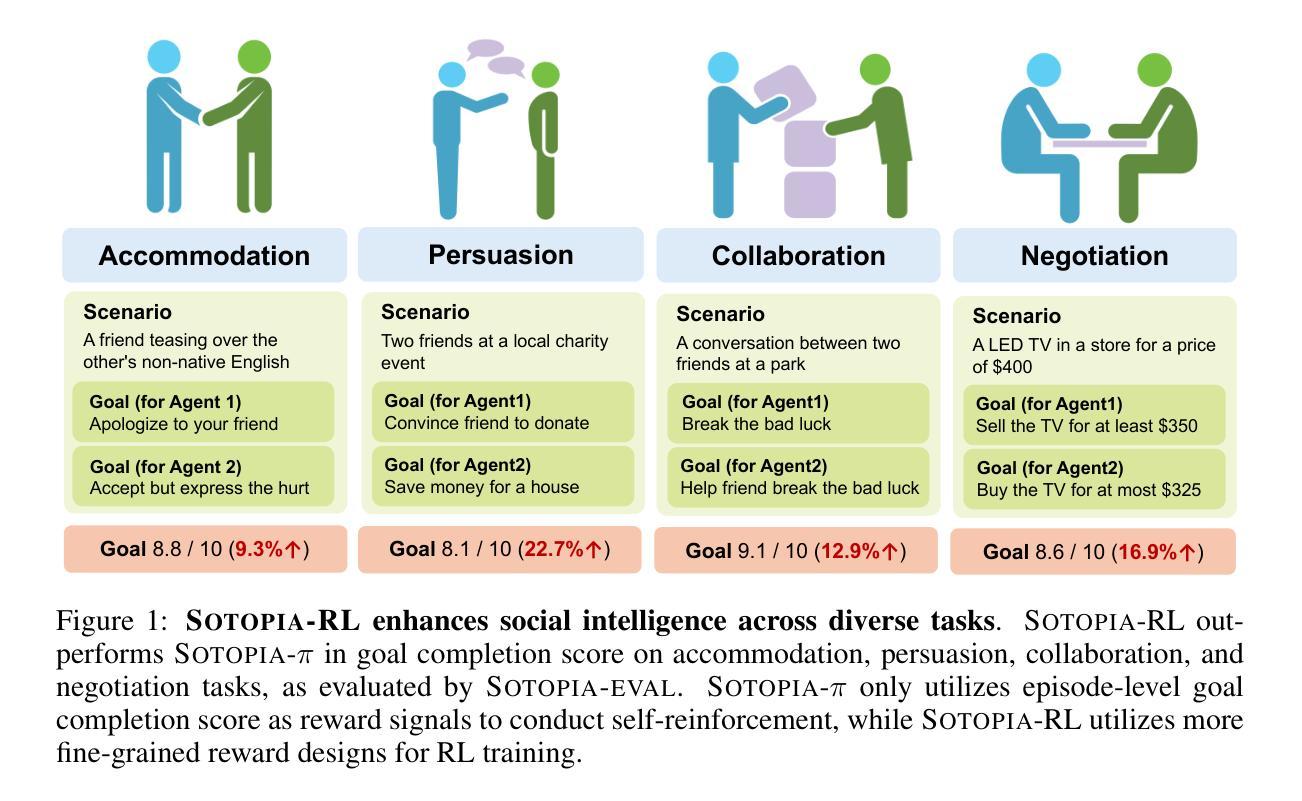
Sotopia-RL: Reward Design for Social Intelligence
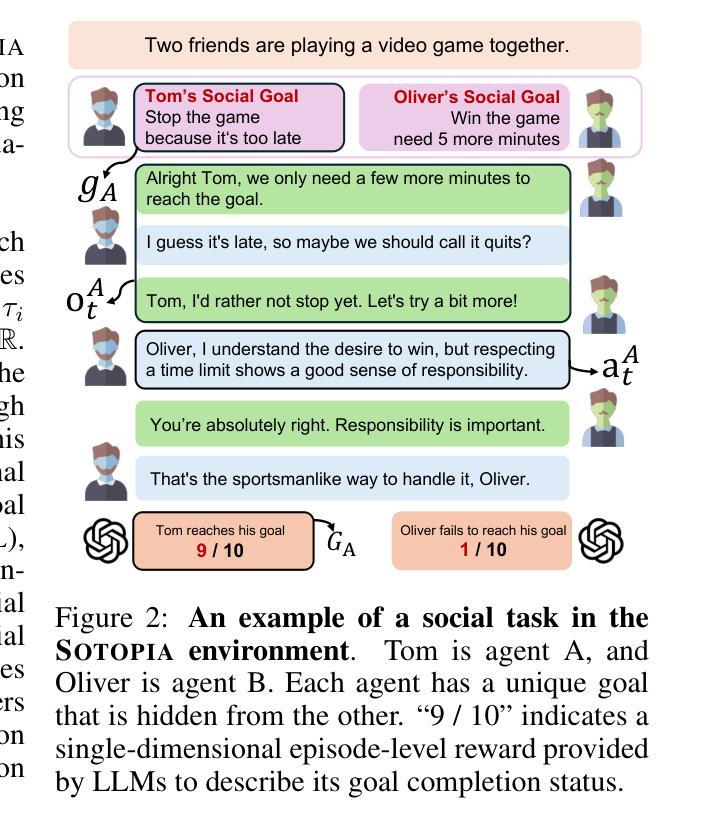
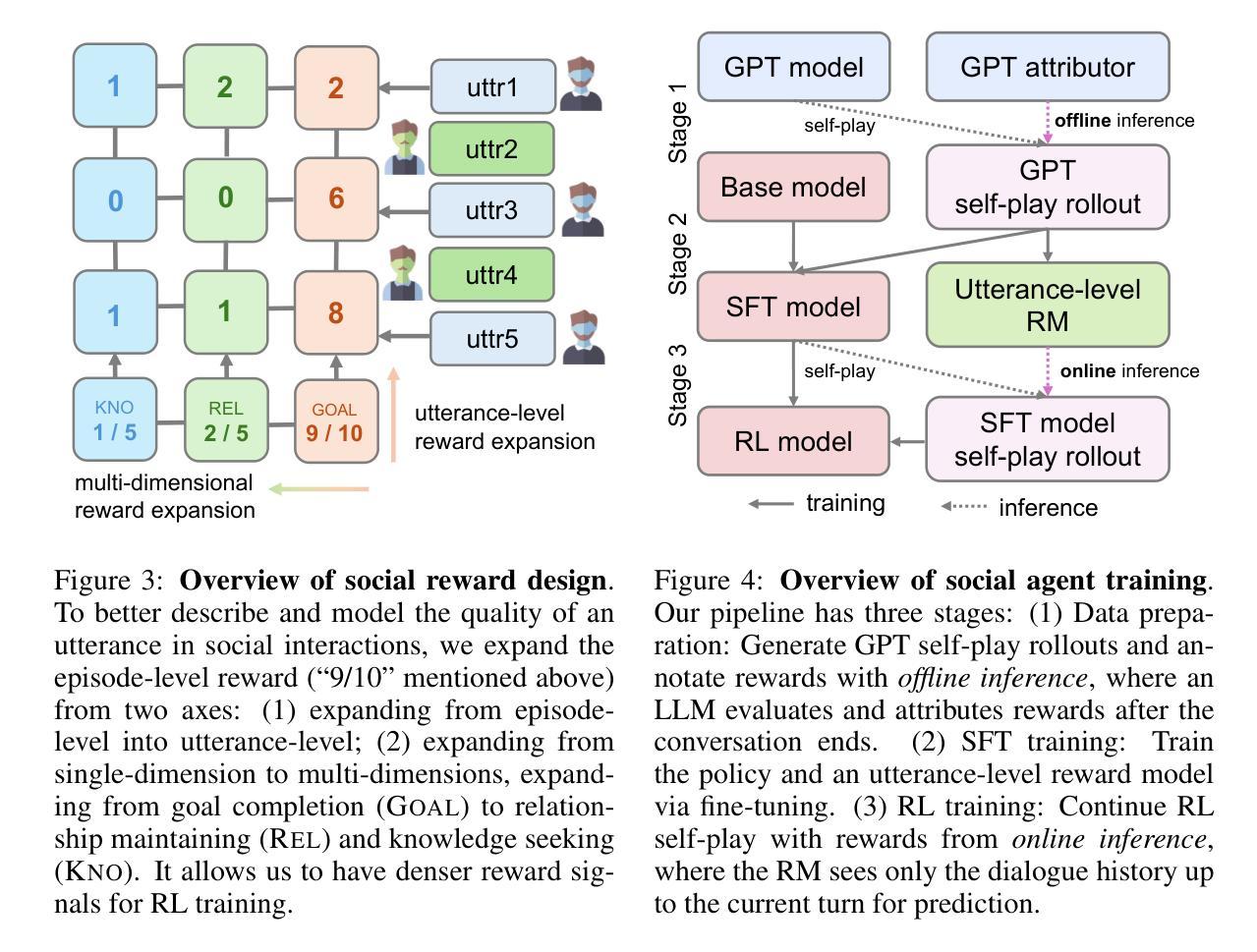
Authors:Haofei Yu, Zhengyang Qi, Yining Zhao, Kolby Nottingham, Keyang Xuan, Bodhisattwa Prasad Majumder, Hao Zhu, Paul Pu Liang, Jiaxuan You
Social intelligence has become a critical capability for large language models (LLMs), enabling them to engage effectively in real-world social tasks such as accommodation, persuasion, collaboration, and negotiation. Reinforcement learning (RL) is a natural fit for training socially intelligent agents because it allows models to learn sophisticated strategies directly through social interactions. However, social interactions have two key characteristics that set barriers for RL training: (1) partial observability, where utterances have indirect and delayed effects that complicate credit assignment, and (2) multi-dimensionality, where behaviors such as rapport-building or knowledge-seeking contribute indirectly to goal achievement. These characteristics make Markov decision process (MDP)-based RL with single-dimensional episode-level rewards inefficient and unstable. To address these challenges, we propose Sotopia-RL, a novel framework that refines coarse episode-level feedback into utterance-level, multi-dimensional rewards. Utterance-level credit assignment mitigates partial observability by attributing outcomes to individual utterances, while multi-dimensional rewards capture the full richness of social interactions and reduce reward hacking. Experiments in Sotopia, an open-ended social learning environment, demonstrate that Sotopia-RL achieves state-of-the-art social goal completion scores (7.17 on Sotopia-hard and 8.31 on Sotopia-full), significantly outperforming existing approaches. Ablation studies confirm the necessity of both utterance-level credit assignment and multi-dimensional reward design for RL training. Our implementation is publicly available at: https://github.com/sotopia-lab/sotopia-rl.
社会智能已经成为大型语言模型(LLM)的关键能力,使其能够有效地参与现实世界的社会任务,例如住宿、劝说、协作和谈判。强化学习(RL)是训练社会智能代理的自然选择,因为它允许模型通过社会互动直接学习复杂策略。然而,社会互动具有两个关键特征,为RL训练设置了障碍:(1)部分可观察性,即言论具有间接和延迟的影响,使信用分配变得复杂;(2)多维性,其中建立融洽关系或寻求知识等行为间接促进目标实现。这些特征使得基于马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)的RL与单维情节级奖励效率低下且不稳定。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Sotopia-RL,这是一个新的框架,它将粗略的情节级反馈细化为话语级的多维奖励。话语级信用分配通过将结果归于单个言论来减轻部分可观察性,而多维奖励捕捉社会互动的全部丰富性并减少奖励破解。在Sotopia(一个开放的社会学习环境)的实验中,Sotopia-RL实现了最先进的社交目标完成分数(Sotopia-hard上为7.17,Sotopia-full上为8.31),显著优于现有方法。消融研究证实了话语级信用分配和多维奖励设计对于RL训练的必要性。我们的实现可公开访问:https://github.com/sotopia-lab/sotopia-rl。
简化版
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary:
社会智能对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说已经成为一项至关重要的能力。强化学习(RL)适合训练具有社会智能的代理,因为它允许模型通过直接的社会互动学习复杂策略。然而,社会互动具有部分可观察性和多维性,这构成了对RL训练的障碍。针对这些挑战,我们提出了Sotopia-RL框架,该框架将粗略的片段级反馈细化为言语级的多维奖励。言语级的信用分配通过个人言语归属结果来缓解部分可观察性,而多维奖励捕捉社会互动的全部丰富性并减少奖励破解。在Sotopia开放社交学习环境中的实验表明,Sotopia-RL实现了先进的社会目标完成分数。
Key Takeaways:
- 社会智能对大型语言模型(LLM)至关重要,使其能有效完成现实社交任务,如协调、劝说、合作和谈判。
- 强化学习(RL)适合训练社会智能代理,能直接通过社会互动学习复杂策略。
- 社会互动具有两个关键特征:部分可观察性和多维性,为RL训练设置障碍。
- Sotopia-RL框架通过细化粗略的片段级反馈为言语级的多维奖励来解决这些挑战。
- 言语级的信用分配通过个人言语归属结果缓解部分可观察性。
- 多维奖励捕捉社会互动的全部丰富性,减少奖励破解。
点此查看论文截图

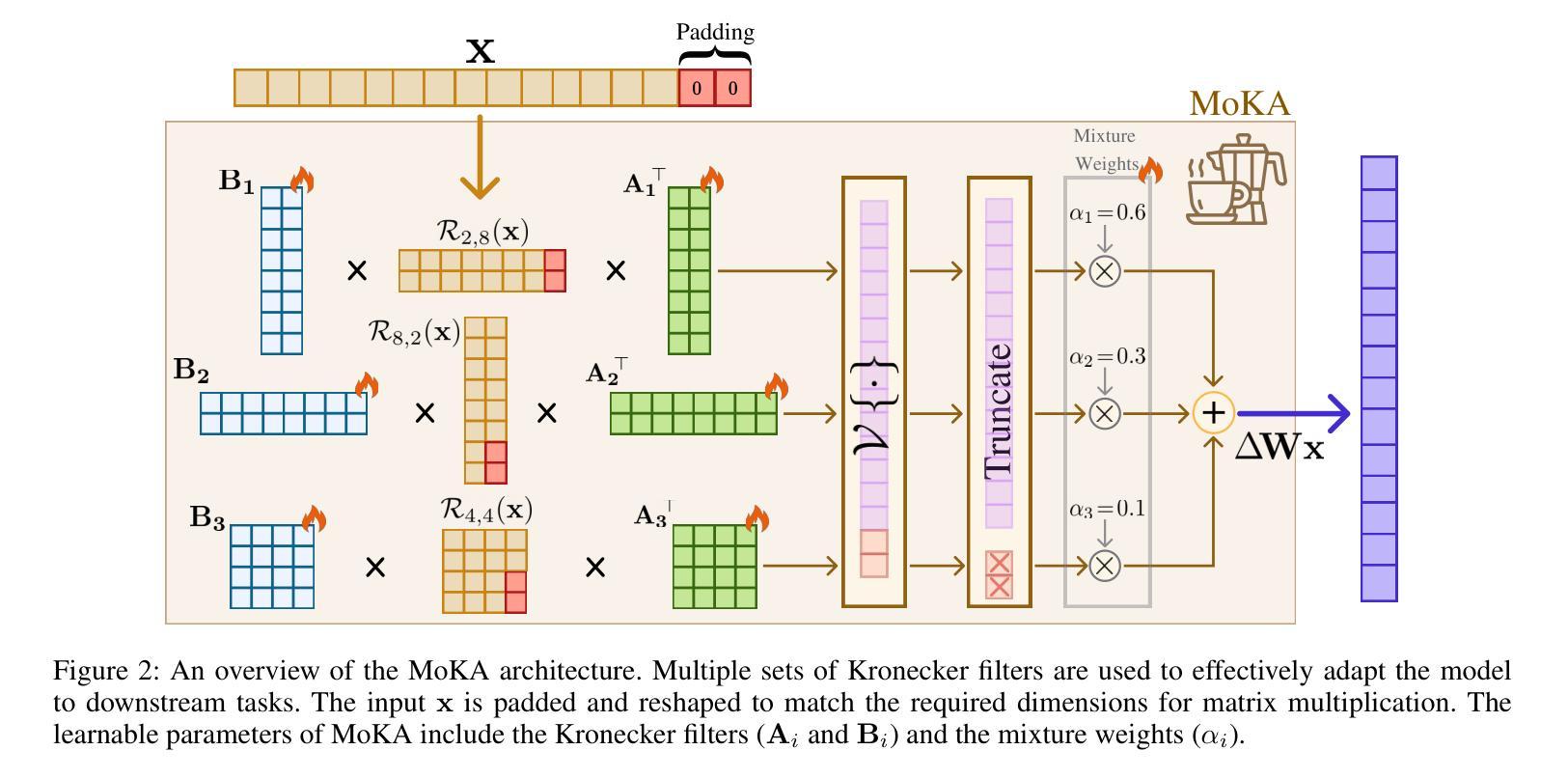
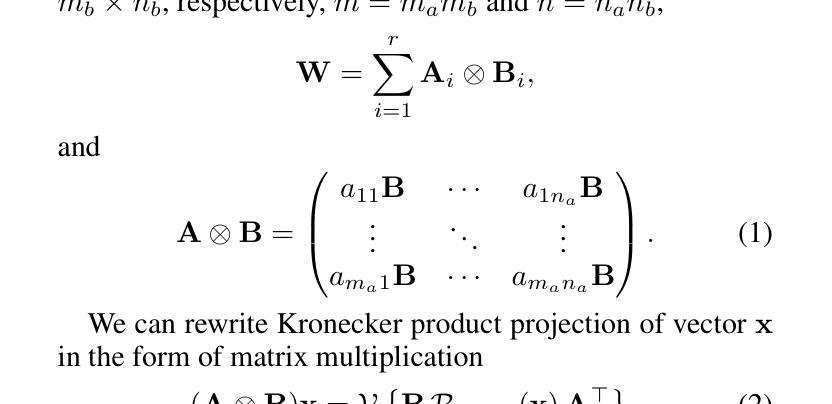
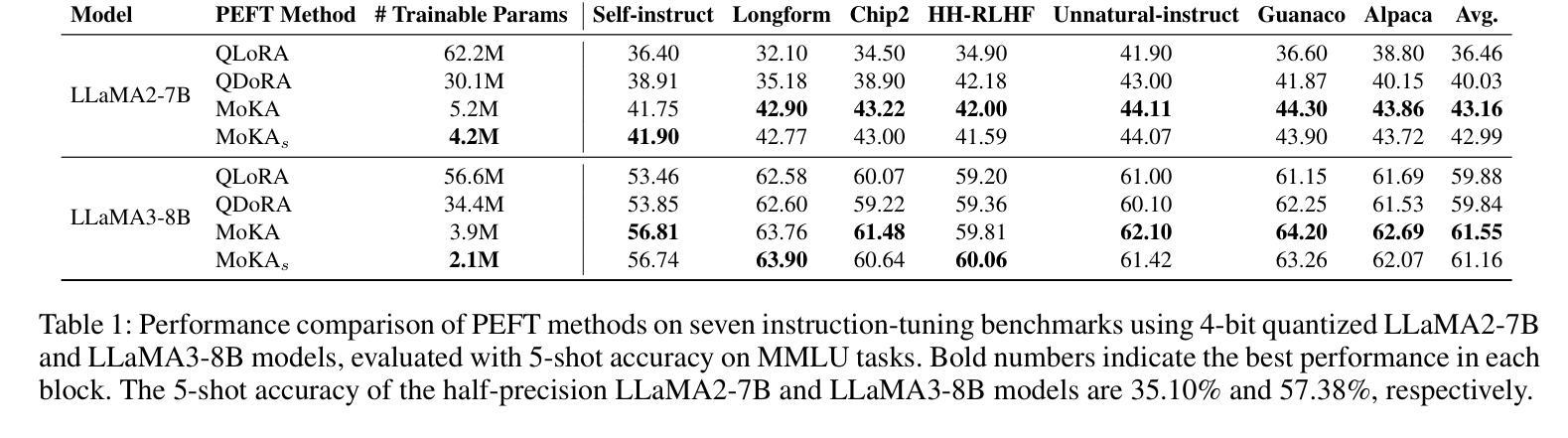
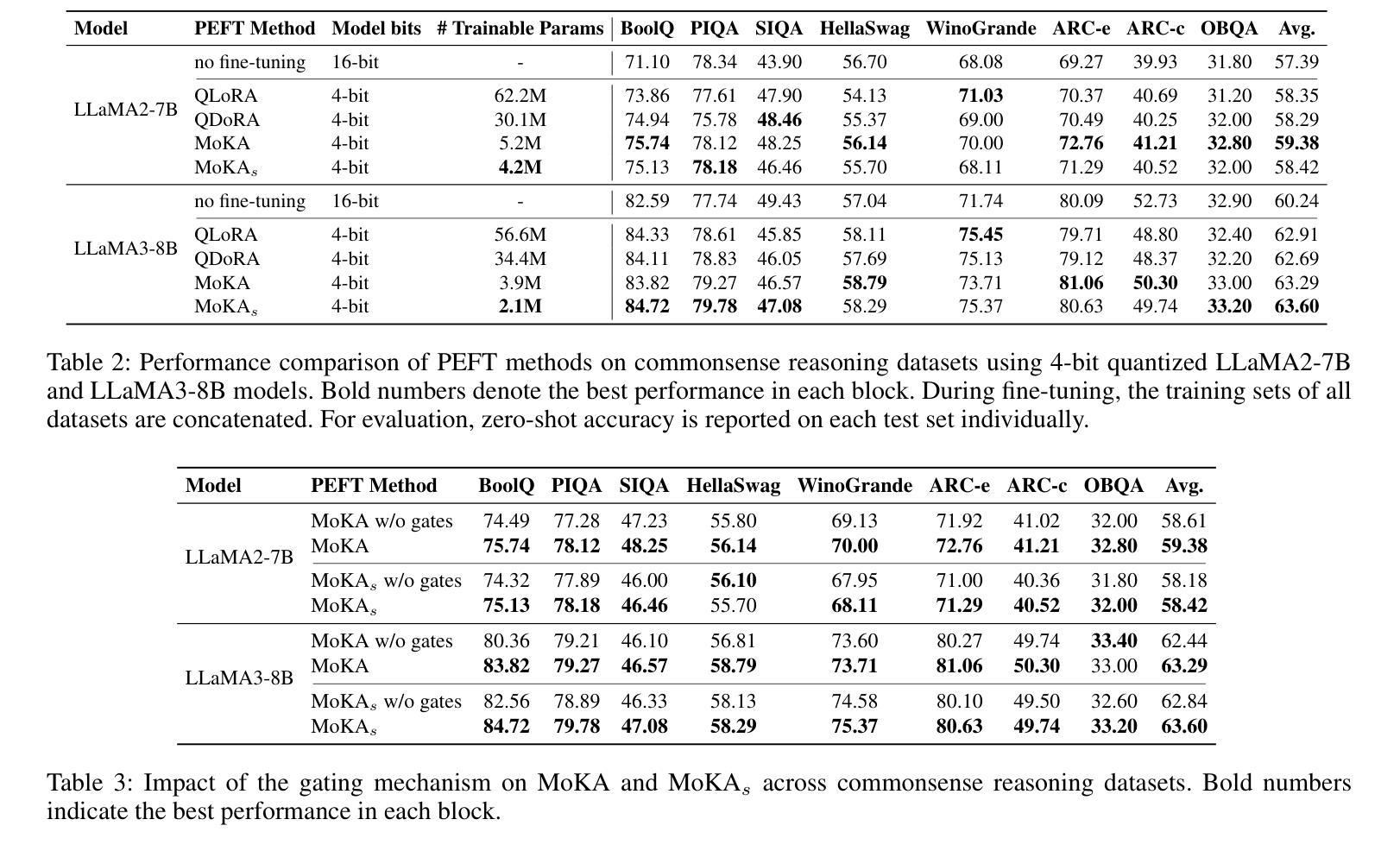
MoKA: Mixture of Kronecker Adapters
Authors:Mohammadreza Sadeghi, Mahsa Ghazvini Nejad, MirHamed Jafarzadeh Asl, Yu Gu, Yuanhao Yu, Masoud Asgharian, Vahid Partovi Nia
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is essential for reducing the computational overhead of large language models (LLMs). Low-rank family adapters are commonly used to control the parameter size efficiently while maintaining the generative power of LLMs. However, their limited expressiveness due to the rank constraint often restricts their performance on complex tasks. We propose Mixture of Kronecker Adapters (MoKA), a new generation of Kronecker adapters that addresses this limitation by modeling weight updates as a mixture of Kronecker products. Our proposed adapter leverages a gating mechanism that measures the importance of each Kronecker factor, enabling more expressive adaptation. Moreover, MoKA enables a rank flexibility that provides a better trade-off between parameter efficiency and accuracy. To ensure hardware efficiency, we reformulate Kronecker computations using standard matrix operations, allowing seamless deployment on GPU-optimized hardware. We conduct extensive experiments on instruction-tuning and commonsense reasoning tasks using low-bit quantized versions of LLaMA2-7B and LLaMA3-8B models. MoKA not only outperforms PEFT baselines, but also reduces the number of trainable parameters up to 27x, achieving state-of-the-art trade-offs between performance and parameter efficiency.
参数高效微调(PEFT)对于减少大型语言模型(LLM)的计算开销至关重要。低阶家族适配器通常用于有效地控制参数大小,同时保持LLM的生成能力。然而,由于阶数限制,它们的表达能力有限,往往在复杂任务上的表现受到限制。我们提出了混合克罗内克适配器(MoKA),这是一种新一代克罗内克适配器,通过模拟权重更新作为克罗内克产品的混合来解决这一限制。我们提出的适配器利用门控机制来衡量每个克罗内克因子的重要性,从而实现更具表现力的适配。此外,MoKA实现了阶数灵活性,在参数效率和准确性之间提供了更好的权衡。为了确保硬件效率,我们利用标准矩阵运算重新制定了克罗内克计算,可以无缝部署在GPU优化的硬件上。我们在指令调整和常识推理任务上进行了大量实验,使用LLaMA2-7B和LLaMA3-8B模型的低比特量化版本。MoKA不仅优于PEFT基线,还将训练参数数量减少了高达27倍,在实现性能和参数效率之间达到最先进的平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
参数高效微调(PEFT)对于减少大型语言模型(LLM)的计算开销至关重要。低秩家族适配器常用于有效地控制参数大小,同时保持LLM的生成能力。然而,由于秩的限制,它们在复杂任务上的表现力往往受限。我们提出了混合克罗内克适配器(MoKA),这是一种新一代克罗内克适配器,通过将权重更新建模为克罗内克产品的混合来解决这一限制。所提出的适配器利用门控机制来衡量每个克罗内克因子的重要性,从而实现更丰富的适应性。此外,MoKA实现了秩灵活性,在参数效率和准确性之间提供了更好的权衡。为确保硬件效率,我们使用标准矩阵操作重新制定克罗内克计算,可在GPU优化硬件上进行无缝部署。我们在指令调整和常识推理任务上对LLaMA的低比特量化版本进行了大量实验。MoKA不仅优于PEFT基线,还将训练参数数量减少至原来的27倍,实现了性能与参数效率之间的最新权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)对大型语言模型(LLM)很重要,能减少计算开销。
- 低秩家族适配器能有效控制参数大小并维持LLM的生成能力,但其在复杂任务上的表现受限。
- Mixture of Kronecker Adapters (MoKA) 通过建模权重更新为克罗内克产品的混合来解决低秩适配器的限制。
- MoKA利用门控机制衡量克罗内克因子的重要性,实现更丰富的适应性。
- MoKA在参数效率和准确性之间提供了更好的权衡,实现了秩灵活性。
- MoKA通过标准矩阵操作进行克罗内克计算改革,确保硬件效率并在GPU上无缝部署。
点此查看论文截图
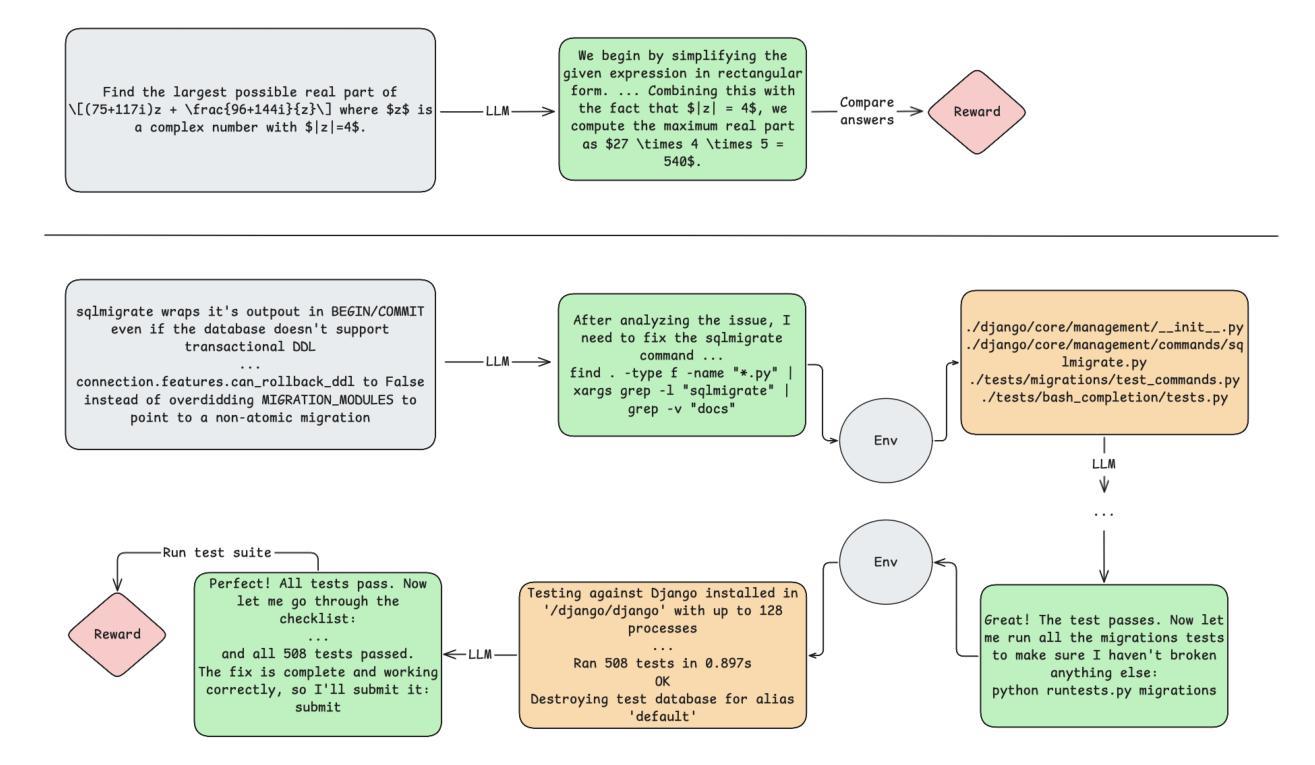
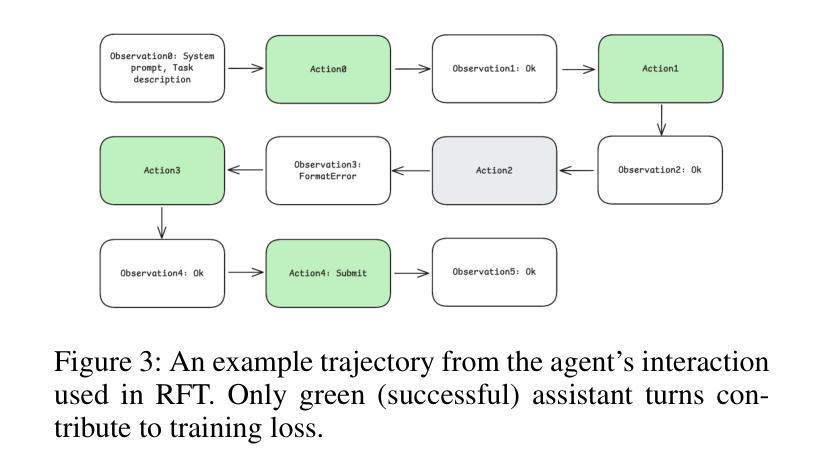
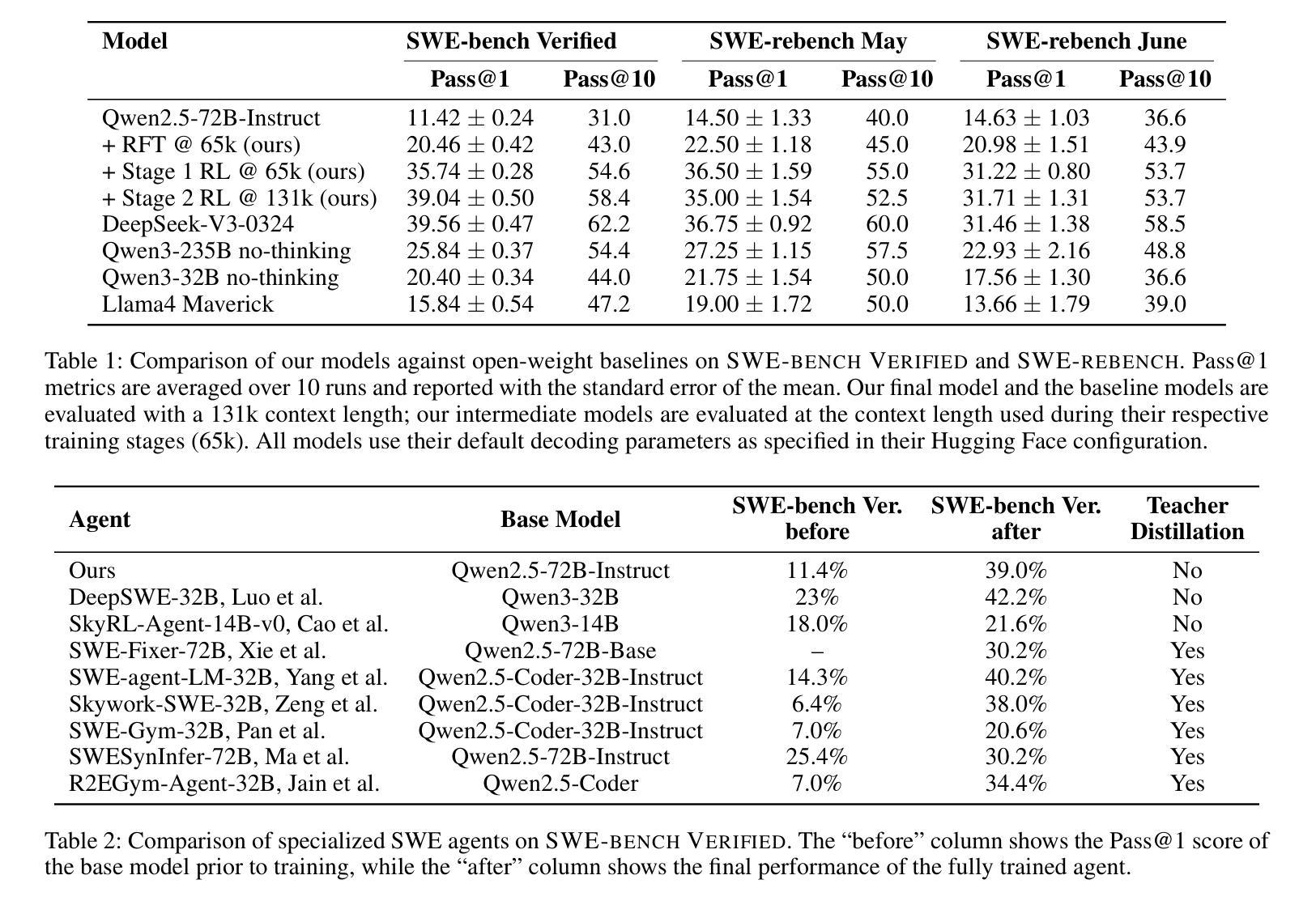
Training Long-Context, Multi-Turn Software Engineering Agents with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Alexander Golubev, Maria Trofimova, Sergei Polezhaev, Ibragim Badertdinov, Maksim Nekrashevich, Anton Shevtsov, Simon Karasik, Sergey Abramov, Andrei Andriushchenko, Filipp Fisin, Sergei Skvortsov, Boris Yangel
Research on applications of Reinforcement Learning (RL) to Large Language Models (LLMs) has mostly been focused on single-turn problems, such as mathematical reasoning or single-shot code generation. While these problems can be viewed as token-level multi-turn MDPs, this view corresponds to a degenerate case of multi-turn interaction where the environment provides no feedback. This contrasts with many real-world domains, such as software engineering (SWE), which require rich multi-turn interactions with a stateful environment that responds to each action with a non-trivial observation. To bridge this gap, we demonstrate the successful application of RL to this general regime. Using a modified Decoupled Advantage Policy Optimization (DAPO) algorithm, we train an agent based on Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to solve real-world software engineering tasks. Our approach increases the agent’s success rate on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark from a 20% rejection fine-tuned baseline to 39%, without relying on any teacher models. On SWE-rebench, our agent matches or outperforms leading open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3-0324 and Qwen3-235B-A22B using an identical scaffolding, offering a viable path toward building more capable autonomous agents for complex real-world problems based on open models.
关于强化学习(RL)在大型语言模型(LLM)中的应用,研究主要集中在单轮问题上,如数学推理或单次代码生成。虽然这些问题可以被视为令牌级的多轮MDP,但这种观点对应于多轮交互的退化情况,即环境不提供反馈。这与许多现实世界领域形成对比,如软件工程(SWE),它要求与具有状态的环境进行丰富的多轮交互,并根据每个动作产生非微不足道的观察结果。为了弥补这一差距,我们展示了将强化学习成功应用于这一通用体系。使用经过修改的解耦优势策略优化(DAPO)算法,我们基于Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct训练了一个智能体来解决现实世界中的软件工程任务。我们的方法提高了智能体在SWE-bench Verified基准测试上的成功率,从拒绝微调基准的20%提高到39%,并且没有依赖任何教师模型。在SWE-rebench上,我们的智能体使用相同的架构与领先的开源模型(如DeepSeek-V3-0324和Qwen3-235B-A22B)相匹配或表现更好,为基于开源模型构建能够解决复杂现实世界问题的更强大自主智能体提供了可行的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)在大型语言模型(LLM)的应用主要集中在单回合问题上,如数学推理或单次代码生成。然而,现实世界中的问题,如软件工程(SWE),需要丰富的多回合交互。本研究成功将RL应用于这一领域,采用改进的去耦合优势策略优化(DAPO)算法,基于Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct训练的软件工程任务智能体成功率提高显著。此研究展现了解决复杂现实世界问题的可行路径。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在大型语言模型的应用主要集中在单回合问题上。
- 现实世界问题如软件工程需要丰富的多回合交互。
- 研究采用改进的去耦合优势策略优化算法。
- 基于Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct训练智能体解决软件工程任务。
- 智能体在SWE-bench Verified上的成功率从基线提升到39%。
- 不依赖教师模型实现了提升效果。
点此查看论文截图

On the Evaluation of Large Language Models in Multilingual Vulnerability Repair
Authors:Dong wang, Junji Yu, Honglin Shu, Michael Fu, Chakkrit Tantithamthavorn, Yasutaka Kamei, Junjie Chen
Various Deep Learning-based approaches with pre-trained language models have been proposed for automatically repairing software vulnerabilities. However, these approaches are limited to a specific programming language (C/C++). Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) offer language-agnostic capabilities and strong semantic understanding, exhibiting potential to overcome multilingual vulnerability limitations. Although some work has begun to explore LLMs’ repair performance, their effectiveness is unsatisfactory. To address these limitations, we conducted a large-scale empirical study to investigate the performance of automated vulnerability repair approaches and state-of-the-art LLMs across seven programming languages. Results show GPT-4o, instruction-tuned with few-shot prompting, performs competitively against the leading approach, VulMaster. Additionally, the LLM-based approach shows superior performance in repairing unique vulnerabilities and is more likely to repair the most dangerous vulnerabilities. Instruction-tuned GPT-4o demonstrates strong generalization on vulnerabilities in previously unseen language, outperforming existing approaches. Analysis shows Go consistently achieves the highest effectiveness across all model types, while C/C++ performs the worst. Based on findings, we discuss the promise of LLM on multilingual vulnerability repair and the reasons behind LLM’s failed cases. This work takes the first look at repair approaches and LLMs across multiple languages, highlighting the promising future of adopting LLMs for multilingual vulnerability repair.
基于深度学习的各种预训练语言模型方法已被提出,用于自动修复软件漏洞。然而,这些方法仅限于特定的编程语言(如C/C++)。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步提供了与语言无关的能力和强大的语义理解,显示出克服多语言漏洞限制的潜力。尽管一些工作已经开始探索LLM的修复性能,但其有效性尚不理想。为了解决这些限制,我们进行了一项大规模实证研究,调查了自动化漏洞修复方法和最前沿的LLM在七种编程语言中的表现。结果表明,经过指令微调且使用少数提示进行引导训练的GPT-4o,在与领先的方法VulMaster竞争中表现强劲。此外,基于LLM的方法在修复独特漏洞时表现出卓越的性能,并更有可能修复最危险的漏洞。经过指令调校的GPT-4o在之前未见语言的漏洞上展现出强大的泛化能力,超越了现有方法。分析表明,Go在所有模型类型中始终实现最高效果,而C/C++表现最差。基于研究结果,我们讨论了LLM在多语言漏洞修复方面的前景以及LLM失败案例背后的原因。这项工作首次跨多种语言研究修复方法和LLM,突显了采用LLM进行多语言漏洞修复的广阔前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
深度学习已应用于自动修复软件漏洞,但仅限于特定编程语言(如C/C++)。大型语言模型(LLM)的出现提供了跨语言的修复能力,并展现出潜在优势。研究对比了多种自动化漏洞修复方法和先进的LLM模型在七种编程语言上的表现。结果显示,指令微调后的GPT-4o在少数提示下表现出竞争力,并且LLM方法更擅长修复独特和危险的漏洞。分析发现Go获得最高的修复效果,而C/C++表现最差。本文讨论了LLM在多语言漏洞修复中的潜力及其失败原因,并首次在多语言环境下对比了修复方法和LLM模型。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度学习已用于自动修复软件漏洞,但仅限于特定编程语言。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具备跨语言修复能力,对克服多语言漏洞限制展现潜力。
- GPT-4o在指令微调后表现出竞争力,可与领先的VulMaster方法相抗衡。
- LLM方法更擅长修复独特和危险的漏洞。
- 在所有模型类型中,Go获得最高的修复效果,而C/C++表现最差。
- LLM在多语言环境下的漏洞修复具有广阔前景。
点此查看论文截图

A Comparative Study of Neurosymbolic AI Approaches to Interpretable Logical Reasoning
Authors:Michael K. Chen
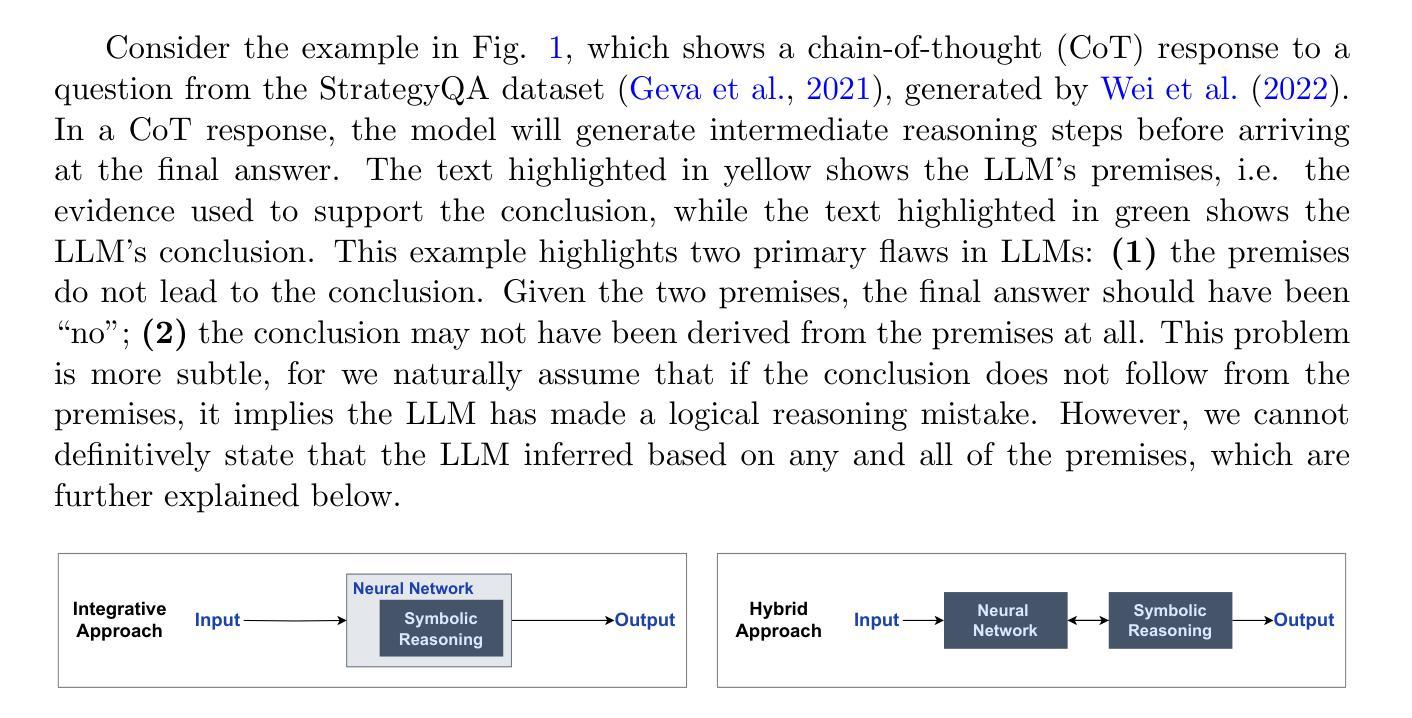
General logical reasoning, defined as the ability to reason deductively on domain-agnostic tasks, continues to be a challenge for large language models (LLMs). Current LLMs fail to reason deterministically and are not interpretable. As such, there has been a recent surge in interest in neurosymbolic AI, which attempts to incorporate logic into neural networks. We first identify two main neurosymbolic approaches to improving logical reasoning: (i) the integrative approach comprising models where symbolic reasoning is contained within the neural network, and (ii) the hybrid approach comprising models where a symbolic solver, separate from the neural network, performs symbolic reasoning. Both contain AI systems with promising results on domain-specific logical reasoning benchmarks. However, their performance on domain-agnostic benchmarks is understudied. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been a comparison of the contrasting approaches that answers the following question: Which approach is more promising for developing general logical reasoning? To analyze their potential, the following best-in-class domain-agnostic models are introduced: Logic Neural Network (LNN), which uses the integrative approach, and LLM-Symbolic Solver (LLM-SS), which uses the hybrid approach. Using both models as case studies and representatives of each approach, our analysis demonstrates that the hybrid approach is more promising for developing general logical reasoning because (i) its reasoning chain is more interpretable, and (ii) it retains the capabilities and advantages of existing LLMs. To support future works using the hybrid approach, we propose a generalizable framework based on LLM-SS that is modular by design, model-agnostic, domain-agnostic, and requires little to no human input.
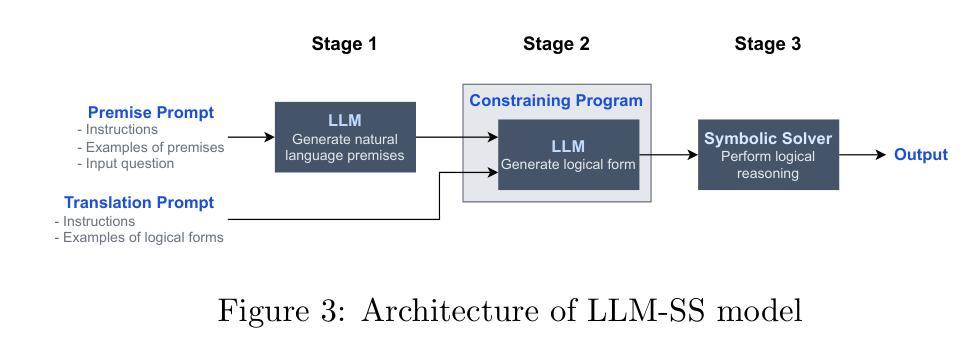
通用逻辑推理,被定义为能在领域无关的任务上进行演绎推理的能力,对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说仍然是一个挑战。当前的大型语言模型无法确定性地进行推理,并且不可解释。因此,神经符号人工智能近期引起了人们的极大兴趣,它试图将逻辑融入神经网络。我们首先确定了两种主要的神经符号方法来改进逻辑推理:(i)包含模型在内的整合方法,其中符号推理包含在神经网络中;(ii)混合方法,其中包括一个与神经网络分开的符号求解器来进行符号推理。这两种方法都包含在有前途的AI系统中,并且在特定领域的逻辑推理基准测试中取得了有前景的结果。然而,它们在领域无关基准测试中的表现尚未得到充分研究。据我们所知,还没有对比这两种不同方法的比较,回答以下问题:哪种方法对于开发通用逻辑推理更有前途?为了分析它们的潜力,我们介绍了以下最佳领域无关模型:采用整合方法的逻辑神经网络(LNN)和采用混合方法的大型语言模型符号求解器(LLM-SS)。通过以这两个模型作为案例研究并代表各自的方法,我们的分析表明,混合方法对于开发通用逻辑推理更有前途,因为(i)其推理链更可解释,(ii)它保留了现有大型语言模型的能力和优势。为了支持使用混合方法的未来工作,我们提出了一个基于LLM-SS的可泛化框架,该框架按设计是模块化的、模型无关、领域无关,并且几乎不需要人工输入。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeSy 2025
Summary
该文本讨论了大型语言模型在通用逻辑推理方面面临的挑战,并介绍了两种改善逻辑推理的神经符号方法:集成方法和混合方法。通过对最佳领域无关模型Logic Neural Network和LLM-Symbolic Solver的分析,发现混合方法更有可能用于发展通用逻辑推理,因其推理链更可解释,且保留了现有大型语言模型的能力和优势。为此,提出了一个基于LLM-SS的可模块化、模型无关、领域无关且需要很少人为输入的通用框架。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在通用逻辑推理方面存在挑战,缺乏确定性的推理和可解释性。
- 神经符号AI的集成方法和混合方法被用来改善逻辑推理。
- Logic Neural Network代表集成方法,而LLM-Symbolic Solver代表混合方法。
- 混合方法在开发通用逻辑推理方面更有前景,因为它的推理链更可解释,并保留了大型语言模型的能力。
- 混合方法框架应模块化、模型无关、领域无关,并尽量减少人为输入。
- 文本呼吁对这两种方法的对比研究,以明确哪种方法更有潜力用于通用逻辑推理的发展。
点此查看论文截图


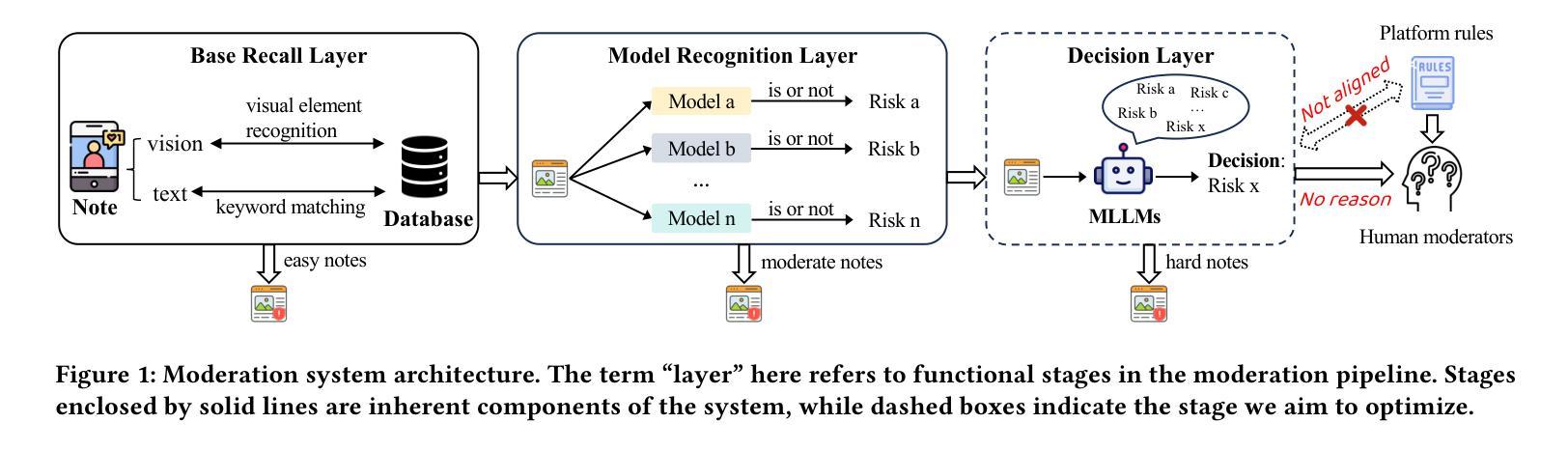
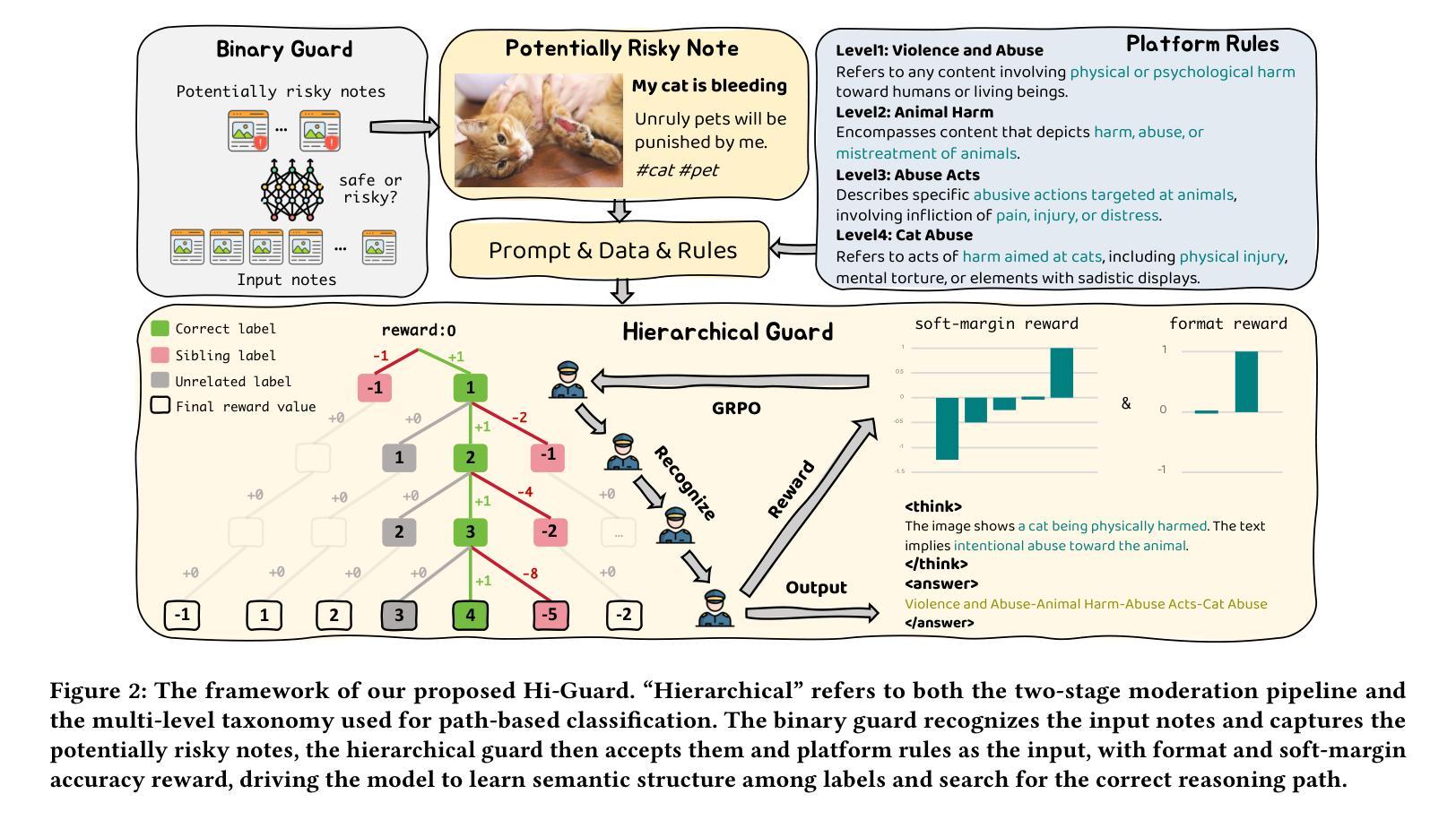
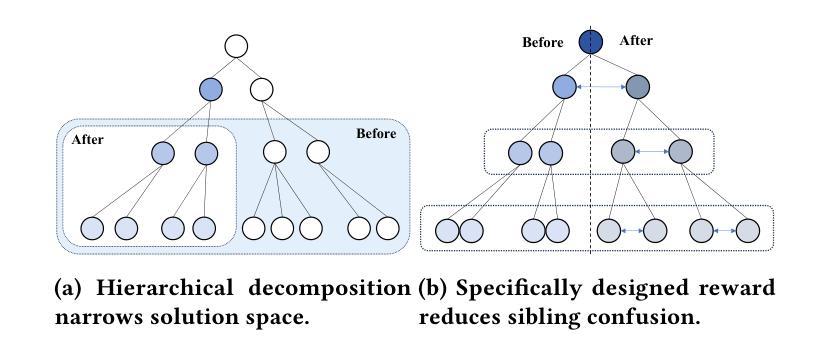
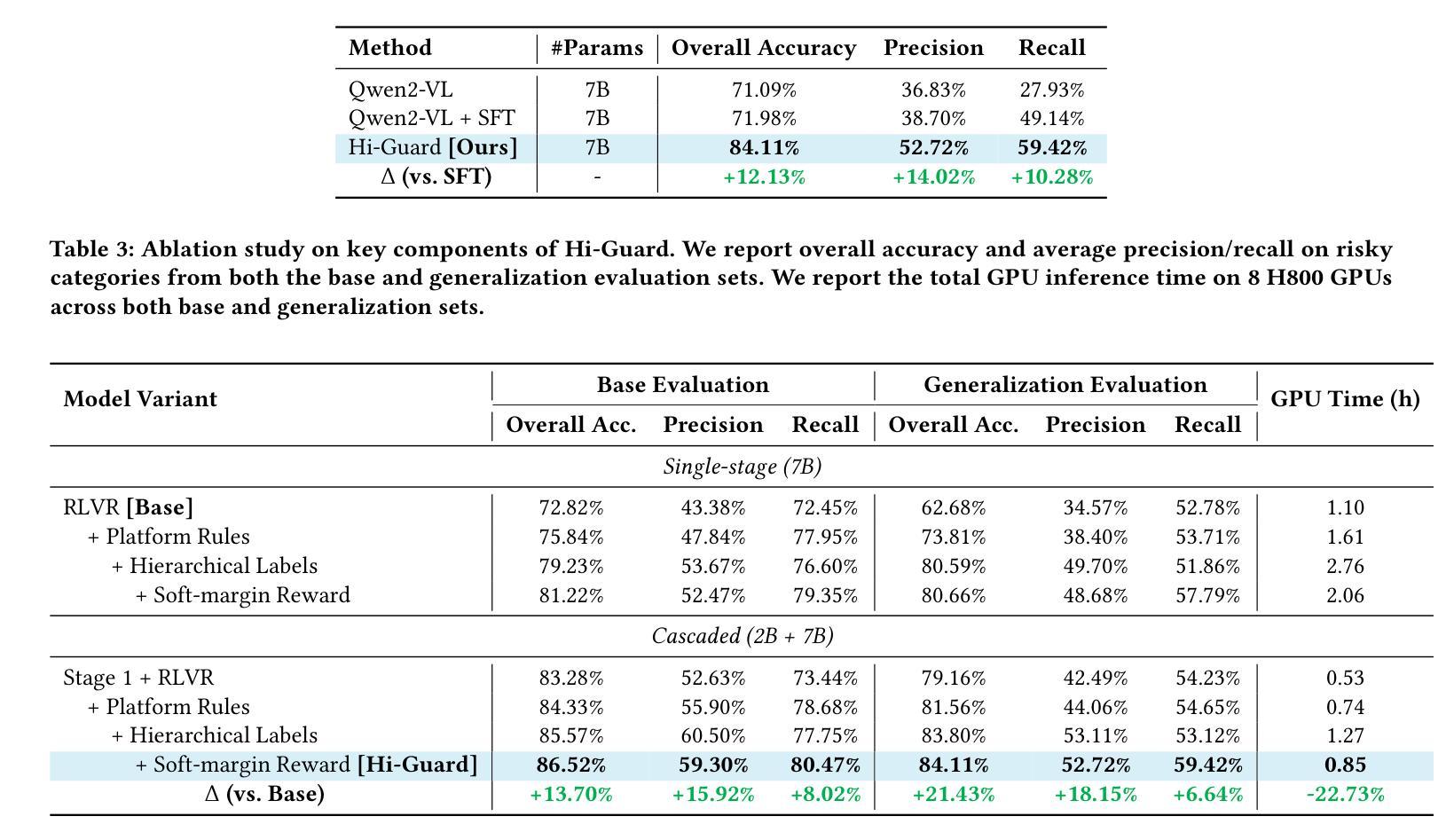
Towards Trustworthy Multimodal Moderation via Policy-Aligned Reasoning and Hierarchical Labeling
Authors:Anqi Li, Wenwei Jin, Jintao Tong, Pengda Qin, Weijia Li, Guo Lu
Social platforms have revolutionized information sharing, but also accelerated the dissemination of harmful and policy-violating content. To ensure safety and compliance at scale, moderation systems must go beyond efficiency and offer accuracy and interpretability. However, current approaches largely rely on noisy, label-driven learning, lacking alignment with moderation rules and producing opaque decisions that hinder human review. Therefore, we propose Hierarchical Guard (Hi-Guard), a multimodal moderation framework that introduces a new policy-aligned decision paradigm. The term “Hierarchical” reflects two key aspects of our system design: (1) a hierarchical moderation pipeline, where a lightweight binary model first filters safe content and a stronger model handles fine-grained risk classification; and (2) a hierarchical taxonomy in the second stage, where the model performs path-based classification over a hierarchical taxonomy ranging from coarse to fine-grained levels. To ensure alignment with evolving moderation policies, Hi-Guard directly incorporates rule definitions into the model prompt. To further enhance structured prediction and reasoning, we introduce a multi-level soft-margin reward and optimize with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), penalizing semantically adjacent misclassifications and improving explanation quality. Extensive experiments and real-world deployment demonstrate that Hi-Guard achieves superior classification accuracy, generalization, and interpretability, paving the way toward scalable, transparent, and trustworthy content safety systems. Code is available at: https://github.com/lianqi1008/Hi-Guard.
社交平台已经彻底改变了信息共享的方式,但也加速了有害和违反政策内容的传播。为了确保大规模的安全性和合规性,监管系统必须超越效率,提供准确性和可解释性。然而,当前的方法大多依赖于嘈杂的、标签驱动的学习,缺乏与监管规则的匹配,并产生阻碍人工审查的不透明决策。因此,我们提出了分层守卫(Hi-Guard)系统,这是一个引入新政策决策范式的多模式监管框架。术语“分层”反映了我们系统设计中的两个关键方面:(1)分层监管管道,其中轻量级二元模型首先过滤安全内容,更强模型处理精细风险分类;(2)第二阶段的分层分类法,模型在层次分类法上进行路径分类,从粗略到精细级别。为了确保与不断发展的监管政策相匹配,Hi-Guard直接将规则定义纳入模型提示。为了进一步增强结构化预测和推理,我们引入了多级软边界奖励,并通过组相对策略优化(GRPO)进行优化,对语义相邻的错误分类进行惩罚,提高解释质量。大量实验和现实世界部署表明,Hi-Guard在分类精度、通用性和可解释性方面表现出卓越性能,为可扩展、透明和可靠的内容安全系统铺平了道路。代码可在:https://github.com/lianqi1008/Hi-Guard上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社交媒体平台在信息分享方面带来了革命性的变革,但同时也加速了有害和违规内容的传播。为确保大规模内容的安全性和合规性,审核系统必须超越效率,提供准确性和可解释性。当前的方法大多依赖于嘈杂的标签驱动学习,缺乏与审核规则的匹配度,并产生阻碍人工审查的不透明决策。因此,我们提出了多层次守卫(Hi-Guard)这一多模式审核框架,引入了一种新的与策略匹配的决策范式。“层次化”反映了我们系统设计中的两个关键方面:一是层次化的审核管道,首先是轻便的二元模型过滤安全内容,然后是更强的模型进行精细风险分类;二是在第二阶段采用层次化的分类法,模型在从最粗糙到最精细的层次结构上进行路径分类。为确保与不断发展的审核策略相匹配,Hi-Guard直接将规则定义纳入模型提示中。通过引入多层次软边缘奖励,进一步优化了群组相对策略优化(GRPO),抑制语义相邻的误分类,提高解释质量。大量实验和现实世界部署表明,Hi-Guard在分类精度、推广和可解释性方面取得了卓越的成绩,为可扩展、透明和可靠的内容安全系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体平台在信息分享中带来变革,但违规内容传播问题加剧。
- 当前的审核系统需要超越效率,追求准确性和可解释性。
- 当前方法依赖标签驱动学习,缺乏与审核规则的匹配,决策不透明。
- 引入Hi-Guard多层次守卫框架,采用层次化审核管道和分类法。
- Hi-Guard直接纳入审核策略规则,提高模型与规则匹配度。
- 通过多层次软边缘奖励和GRPO优化,提高分类精度和解释质量。
- 实验和现实世界部署显示Hi-Guard在分类、推广和可解释性方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


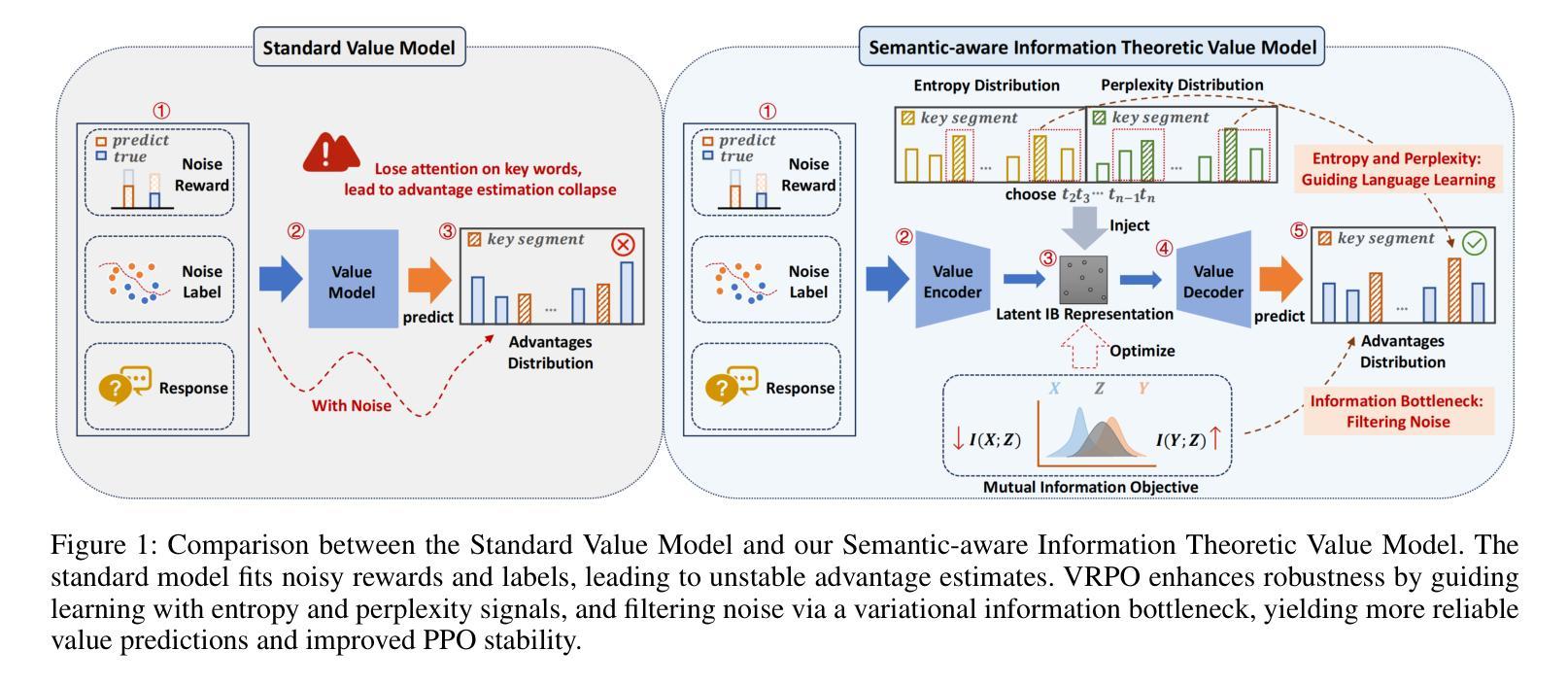
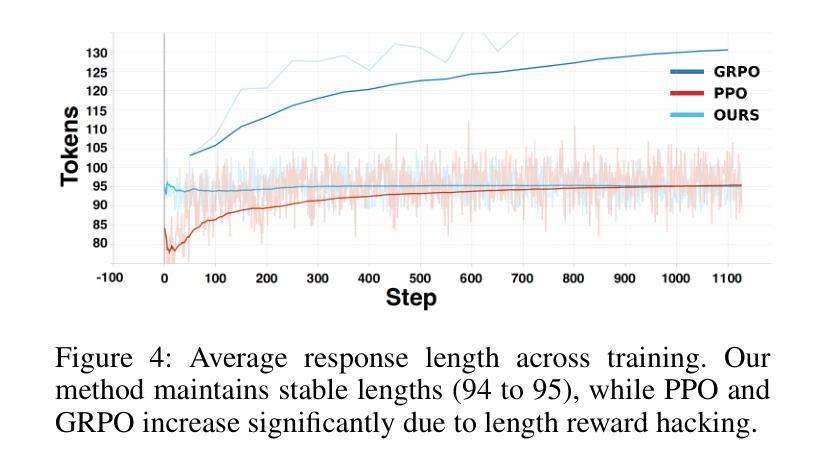
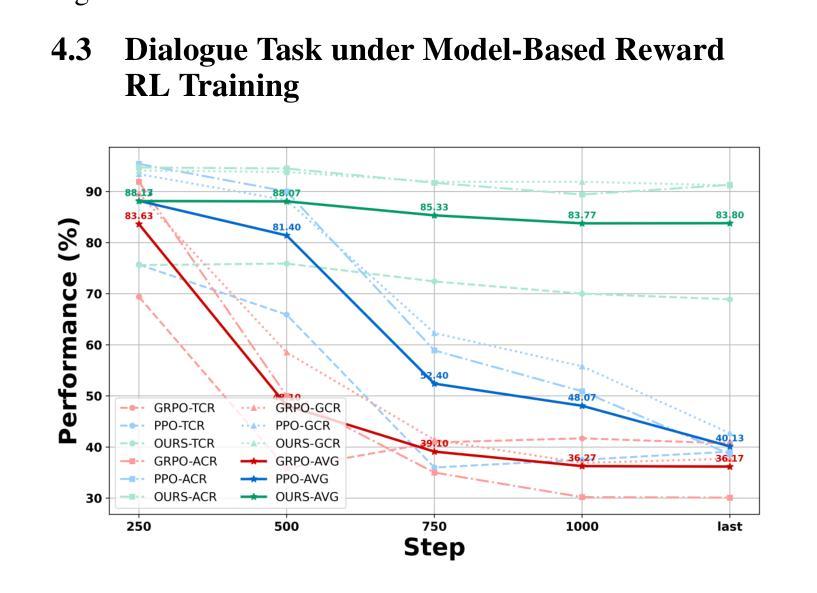
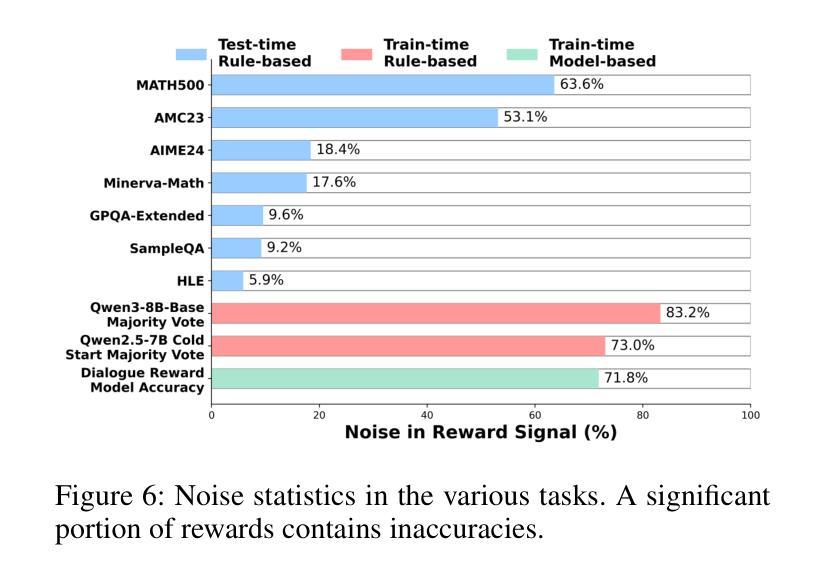
VRPO: Rethinking Value Modeling for Robust RL Training under Noisy Supervision
Authors:Dingwei Zhu, Shihan Dou, Zhiheng Xi, Senjie Jin, Guoqiang Zhang, Jiazheng Zhang, Junjie Ye, Mingxu Chai, Enyu Zhou, Ming Zhang, Caishuang Huang, Yunke Zhang, Yuran Wang, Tao Gui
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) often suffers from noisy or imperfect reward supervision in real-world settings, which undermines policy stability and generalization. Such noise may cause models to lose attention on key words during advantage estimation. While prior work focuses on reward denoising or filtering poor data, it often overlooks the critical role of the value model in policy optimization. In this work, we show that a strong value model is essential for mitigating noise by absorbing unstable signals and enabling more reliable advantage estimation. We propose VRPO, a value-centric framework for robust PPO training under noisy supervision. VRPO combines two core designs: (1) an auxiliary loss guided by entropy and perplexity from a frozen language model, and (2) a variational information bottleneck. These mechanisms enhance the value model’s ability to filter out noise and capture key words from the context during advantage estimation, transforming it from a passive predictor into an active regulator of noise. Experiments on math reasoning, science QA, and multi-turn dialogue, under both rule-based and model-based noisy rewards, show that VRPO consistently outperforms PPO and GRPO baselines. Our findings underscore the often-overlooked importance of the value model in RLHF and offer a principled and practical approach to robust policy optimization in noisy real-world environments.
基于人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)在真实世界环境中常常面临奖励监督存在噪声或不完美的问题,这破坏了策略的稳定性和泛化能力。这样的噪声可能会导致模型在估计优势时忽略关键词。虽然之前的研究集中在奖励去噪或过滤不良数据上,但它经常忽略价值模型在策略优化中的关键作用。在这项工作中,我们表明一个强大的价值模型对于缓解噪声至关重要,通过吸收不稳定信号并启更加可靠的优点估计。我们提出了VRPO,这是一个价值导向的框架,用于在噪声监督下进行稳健的PPO训练。VRPO结合了两种核心设计:(1)由冻结语言模型的熵和困惑度引导的辅助损失;(2)变分信息瓶颈。这些机制增强了价值模型在估计优势时从上下文中过滤噪声并捕获关键词的能力,将其从被动的预测器转变为对噪声的主动调节器。在数学推理、科学问答和多轮对话方面的实验表明,在基于规则和模型产生的噪声奖励下,VRPO始终优于PPO和GRPO基线。我们的研究发现了经常被忽视的价值模型在RLHF中的重要性,并为充满噪声的现实环境中的稳健策略优化提供了理论和实践相结合的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)在实际应用中常受到噪声或不完美的奖励监督影响,导致策略稳定性和泛化性下降。本文提出VRPO,一个以价值模型为中心、在噪声监督下进行稳健PPO训练的框架。VRPO结合了两个核心设计:一是通过冻结语言模型引导的熵和困惑度辅助损失,二是变分信息瓶颈。这些机制提升了价值模型在优势评估中过滤噪声和捕捉关键词的能力,将其从被动预测转变为积极调控噪声。实验表明,在规则模型和基于模型的噪声奖励下,VRPO在数学推理、科学问答和多轮对话等任务中表现优异于PPO和GRPO基线方法。强调了价值模型在RLHF中的重要性并提供了面向噪声环境下的稳健策略优化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)在实际应用中面临噪声或不完美奖励监督的挑战。
- 噪声可能导致模型在优势估计时忽略关键词。
- 现有工作多关注奖励去噪或过滤不良数据,却忽视了价值模型在策略优化中的关键作用。
- VRPO框架结合辅助损失和变分信息瓶颈来提升价值模型在优势评估中的性能。
- VRPO框架能将价值模型从被动预测转变为积极调控噪声的角色。
- 实验表明,VRPO在数学推理、科学问答和多轮对话等任务中表现优异,适应于噪声环境。
点此查看论文截图


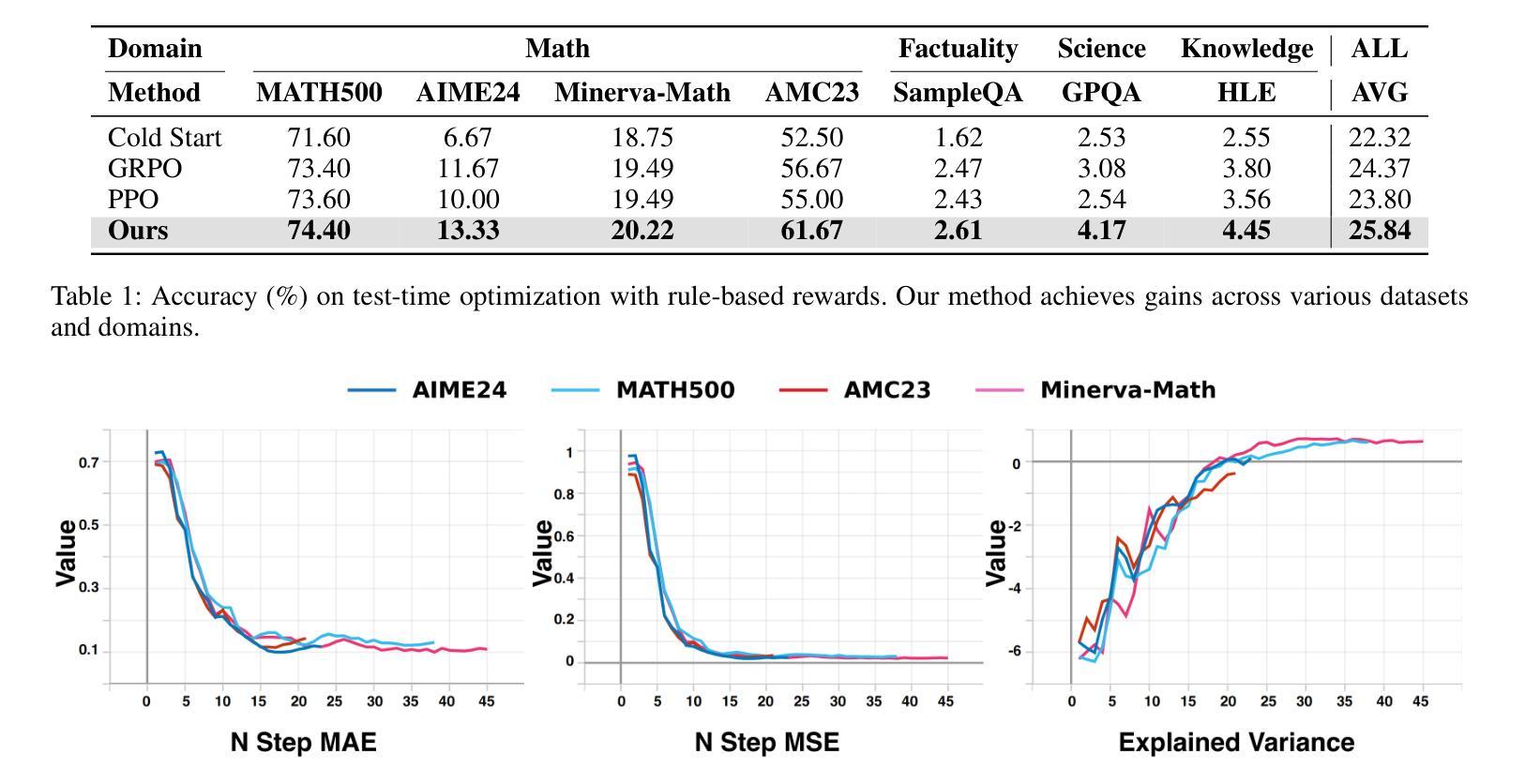
CAMA: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Causal Knowledge
Authors:Lei Zan, Keli Zhang, Ruichu Cai, Lujia Pan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of tasks, yet they still struggle with complex mathematical reasoning, a challenge fundamentally rooted in deep structural dependencies. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{CA}usal \textbf{MA}thematician (\textbf{CAMA}), a two-stage causal framework that equips LLMs with explicit, reusable mathematical structure. In the learning stage, CAMA first constructs the \textbf{M}athematical \textbf{C}ausal \textbf{G}raph (\textbf{MCG}), a high-level representation of solution strategies, by combining LLM priors with causal discovery algorithms applied to a corpus of question-solution pairs. The resulting MCG encodes essential knowledge points and their causal dependencies. To better align the graph with downstream reasoning tasks, CAMA further refines the MCG through iterative feedback derived from a selected subset of the question-solution pairs. In the reasoning stage, given a new question, CAMA dynamically extracts a task-relevant subgraph from the MCG, conditioned on both the question content and the LLM’s intermediate reasoning trace. This subgraph, which encodes the most pertinent knowledge points and their causal dependencies, is then injected back into the LLM to guide its reasoning process. Empirical results on real-world datasets show that CAMA significantly improves LLM performance on challenging mathematical problems. Furthermore, our experiments demonstrate that structured guidance consistently outperforms unstructured alternatives, and that incorporating asymmetric causal relationships yields greater improvements than using symmetric associations alone.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务中表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍面临挑战,这一挑战根本源于深层的结构依赖性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了配备LLM以明确、可重复使用的数学结构的两阶段因果框架,名为CAMA(因果数学家)。在学习阶段,CAMA首先通过结合LLM先验知识和应用于问题解决方案对语料库的因果发现算法,构建数学因果图(MCG),这是解决方案策略的高级表示。生成的MCG编码了必要的知识点和它们的因果依赖关系。为了更好地与下游推理任务对齐,CAMA进一步通过来自问题解决方案对所选子集的迭代反馈来优化MCG。在推理阶段,对于新问题,CAMA会根据问题的内容和LLM的中间推理轨迹,从MCG中动态提取与任务相关的子图。这个子图编码了最相关的知识点和它们的因果依赖关系,然后注入LLM以指导其推理过程。在真实数据集上的实证结果表明,CAMA显著提高了LLM解决复杂数学问题的性能。此外,我们的实验表明,结构化指导始终优于非结构化替代方案,并且纳入不对称因果关系比仅使用对称关联带来更大幅度的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在广泛的任务中表现出强大的性能,但在复杂的数学推理方面仍存在挑战。为解决此挑战,提出了因果数学家(CAMA)框架,该框架分为两个阶段:学习阶段和推理阶段。在学习阶段,CAMA构建数学因果图(MCG),这是一种高级解决方案策略表示。在推理阶段,CAMA根据问题和LLM的中间推理轨迹从MCG中提取相关子图,并指导LLM的推理过程。实验结果证明,CAMA能显著提高LLM解决复杂数学问题的能力,且结构化的指导方式优于非结构化方式,考虑不对称因果关系比仅使用对称关联效果更好。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂数学推理方面存在挑战。
- 因果数学家(CAMA)框架被提出来解决这一挑战,包含学习和推理两个阶段。
- 在学习阶段,CAMA构建数学因果图(MCG),结合LLM先验知识和因果发现算法,对问题解决方案对进行表示。
- MCG编码了重要的知识点及其因果关系。
- CAMA通过迭代反馈优化MCG,使其更好地适应下游推理任务。
- 在推理阶段,CAMA从MCG中提取与任务相关的子图,并注入LLM以指导其推理。
点此查看论文截图

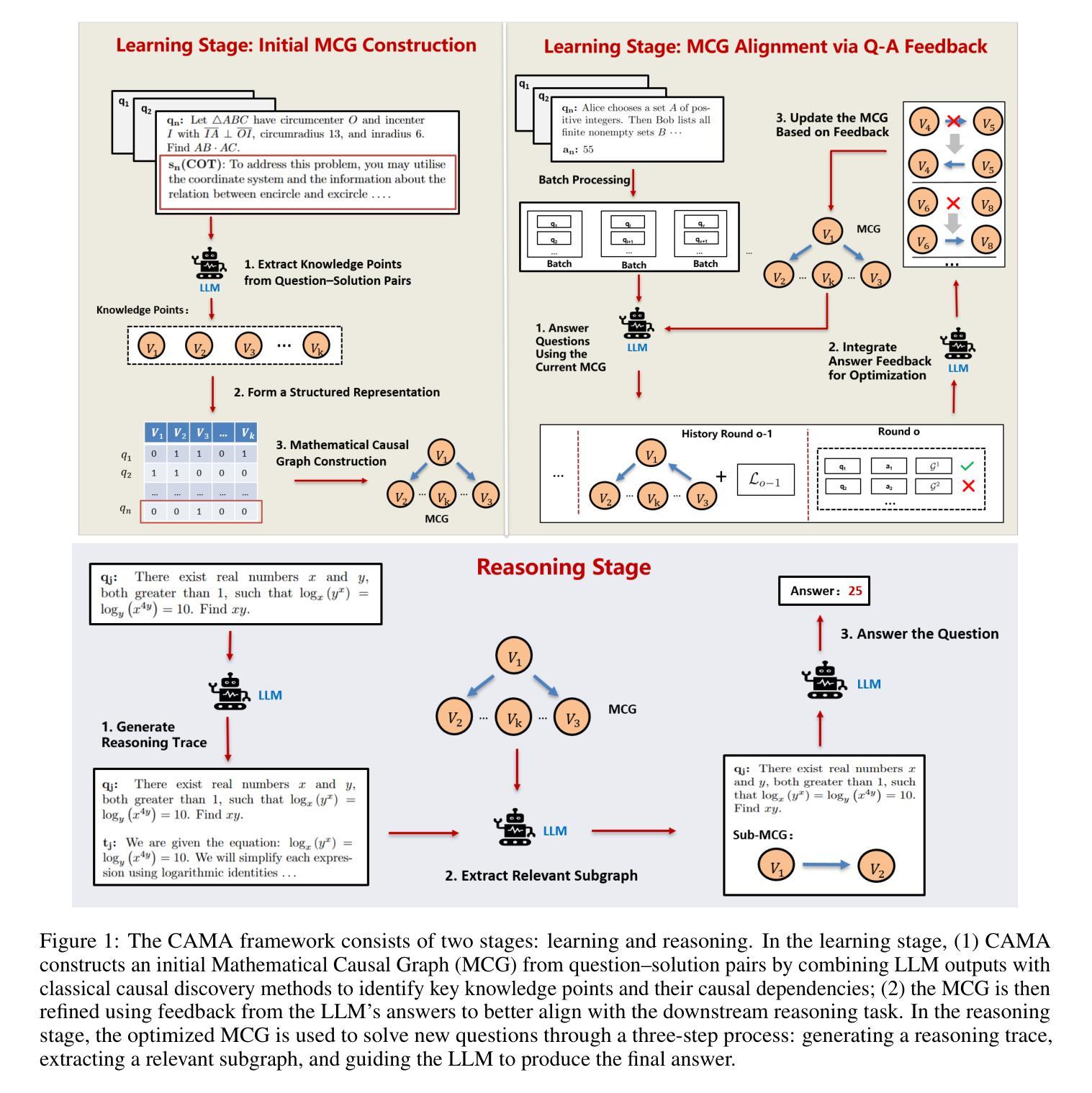
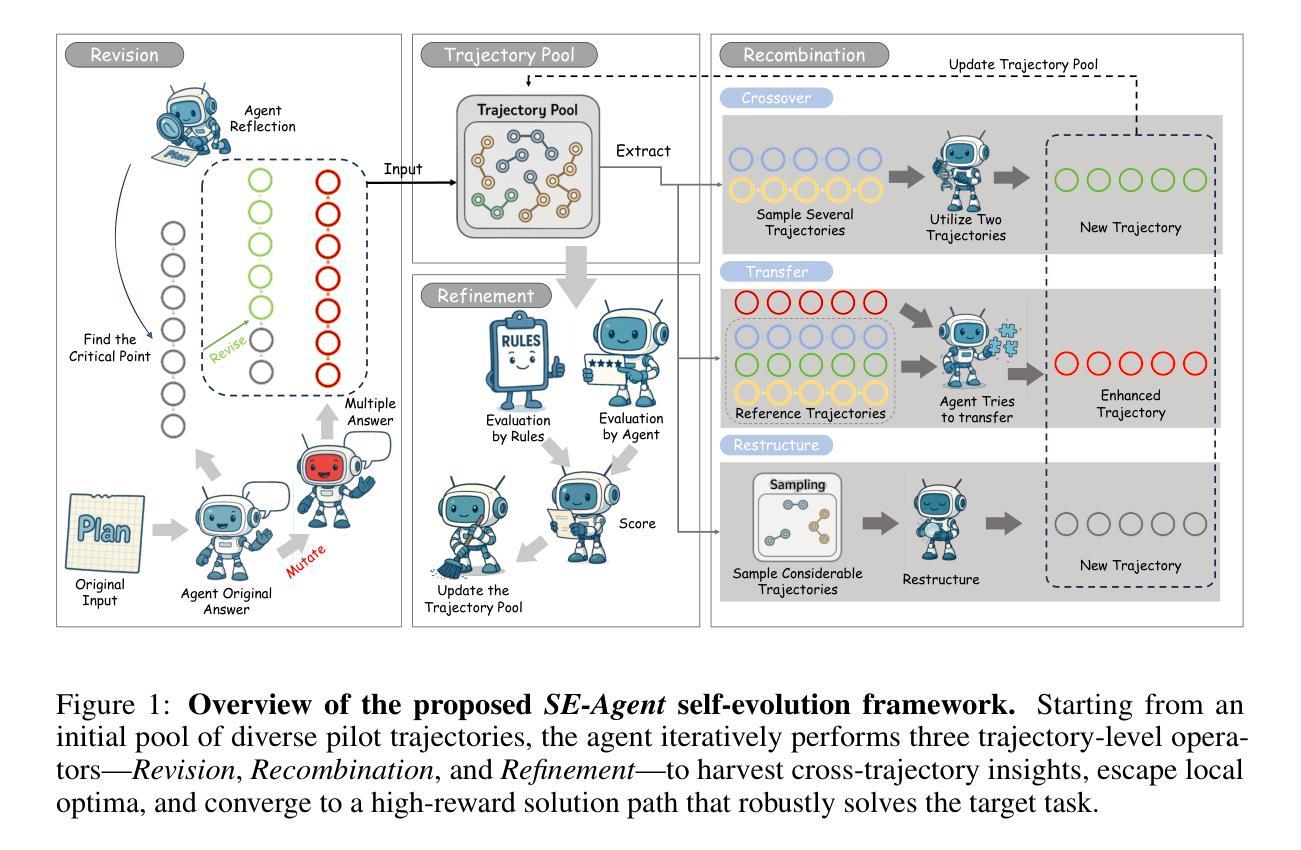
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent.
基于大规模语言模型(LLM)的代理最近表现出在复杂推理和工具使用方面的令人印象深刻的能力,这是通过与环境的多步骤交互实现的。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但它们的解决问题过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,仍然被低估。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理朝着正确的方向解决问题。尽管现有的方法,如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了不同轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致了冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,这是一种自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作来重新访问和改进先前的轨迹:修订、重组和精炼。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索受先前轨迹指导的多样化解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了持续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的性能达到了开源代理中的最新水平。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的智能体通过与环境的多步骤交互展现出强大的复杂任务处理能力。尽管LLM在处理复杂任务上具有潜力,但其解决任务的过程即交互轨迹尚未得到充分的挖掘。针对这一现状,我们提出了SE-Agent框架,这是一个能够让智能体通过自我进化优化其推理过程的框架。SE-Agent通过修订、重组和精炼三个关键操作来重新评估和增强先前的轨迹,从而实现智能体的连续自我进化,提高推理质量。在SWE-bench Verified上的实验结果表明,SE-Agent相较于其他开源智能体展现出卓越性能,相对改进幅度高达55%。
Key Takeaways
- LLM模型具备强大的复杂任务处理能力,尤其在多步骤环境交互中展现突出优势。
- 智能体的推理过程即交互轨迹对于解决任务至关重要,但当前对其的挖掘仍显不足。
- SE-Agent框架能够让智能体通过自我进化优化其推理过程,包括修订、重组和精炼先前的轨迹。
- SE-Agent能够扩大搜索空间并探索多样化的解决方案路径,从而提高了智能体的性能并降低了因推理路径不当而带来的负面影响。
- SE-Agent在SWE-bench Verified上的实验表现卓越,相较于其他开源智能体性能提升显著。
- SE-Agent框架公开可用,为智能体的进化研究提供了有力支持。
点此查看论文截图
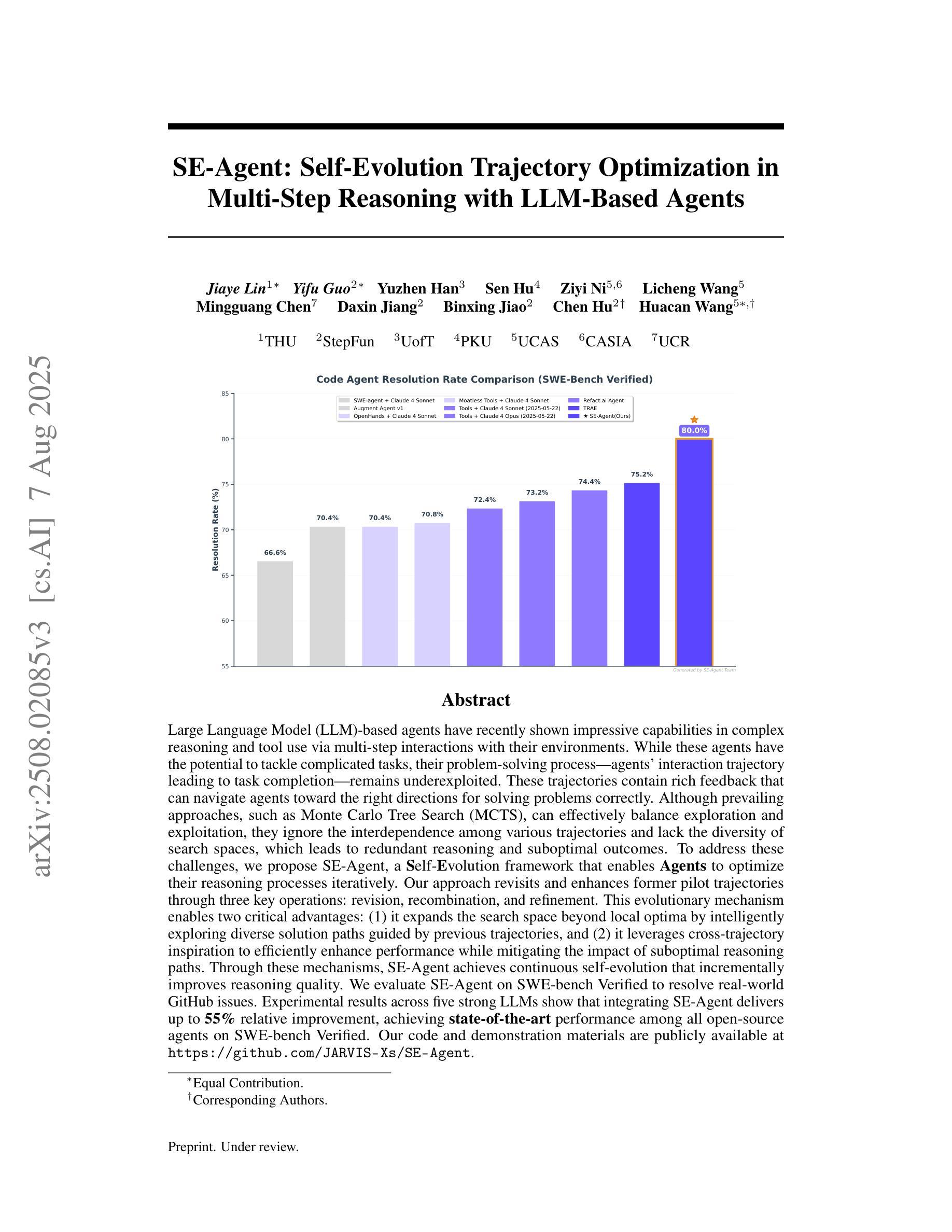
The SMeL Test: A simple benchmark for media literacy in language models
Authors:Gustaf Ahdritz, Anat Kleiman
The internet is rife with unattributed, deliberately misleading, or otherwise untrustworthy content. Though large language models (LLMs) are often tasked with autonomous web browsing, the extent to which they have learned the simple heuristics human researchers use to navigate this noisy environment is not currently known. In this paper, we introduce the Synthetic Media Literacy Test (SMeL Test), a minimal benchmark that tests the ability of language models to actively filter out untrustworthy information in context. We benchmark a variety of commonly used instruction-tuned LLMs, including reasoning models, and find that no model consistently succeeds; while reasoning in particular is associated with higher scores, even the best API model we test hallucinates up to 70% of the time. Remarkably, larger and more capable models do not necessarily outperform their smaller counterparts. We hope our work sheds more light on this important form of hallucination and guides the development of new methods to combat it.
互联网充斥着大量无归属、故意误导或其他不可靠的内容。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)经常承担自主网页浏览的任务,但它们是否掌握了人类研究者用来浏览这种嘈杂环境的简单启发式技术尚不清楚。在本文中,我们介绍了合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一个最小的基准测试,旨在测试语言模型在特定情境下主动过滤不可靠信息的能力。我们对各种常用的指令调整型LLM进行了基准测试,包括推理模型,发现没有任何模型始终表现良好;虽然推理与高分相关,但即使是我们的测试中表现最好的API模型也有高达70%的幻觉情况。值得注意的是,更大、更强大的模型并不一定比小型模型表现得更好。我们希望我们的工作能进一步揭示这种重要的幻觉现象,并为开发新的对抗幻觉的方法提供指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:互联网充斥着未经证实、故意误导或其他不可靠的内容。大型语言模型(LLMs)经常用于自动浏览网页,但它们是否掌握了人类研究人员用于导航此复杂环境的简单启发式方法尚不清楚。本文介绍了一种合成媒体素养测试(SMeL测试),这是一种最低限度的基准测试,旨在测试语言模型在特定情况下主动过滤不可靠信息的能力。我们对一系列常用的指令调优LLMs进行了基准测试,包括推理模型,发现没有模型始终表现良好;虽然推理与高分有关,但即使我们测试的最佳API模型也有高达70%的幻想。值得注意的是,更大、更强大的模型并不一定优于较小的模型。我们希望这项工作能更多地揭示这种幻觉的重要性,并为开发新的对抗方法提供指导。
Key Takeaways:
- 互联网存在大量不可靠内容,如未经证实、故意误导的信息。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动浏览网页时面临挑战,即如何识别和处理这些不可靠信息。
- 合成媒体素养测试(SMeL Test)是一种新提出的基准测试,旨在评估语言模型在过滤不可靠信息方面的能力。
- 现有的指令调优LLMs,包括推理模型,在SMeL测试中表现不一,没有模型能够始终如一地成功。
- 推理能力与在SMeL测试中获得高分有关,但最佳模型仍存在高达70%的幻觉问题。
- 更大、更强大的语言模型不一定在SMeL测试中表现更好。
点此查看论文截图

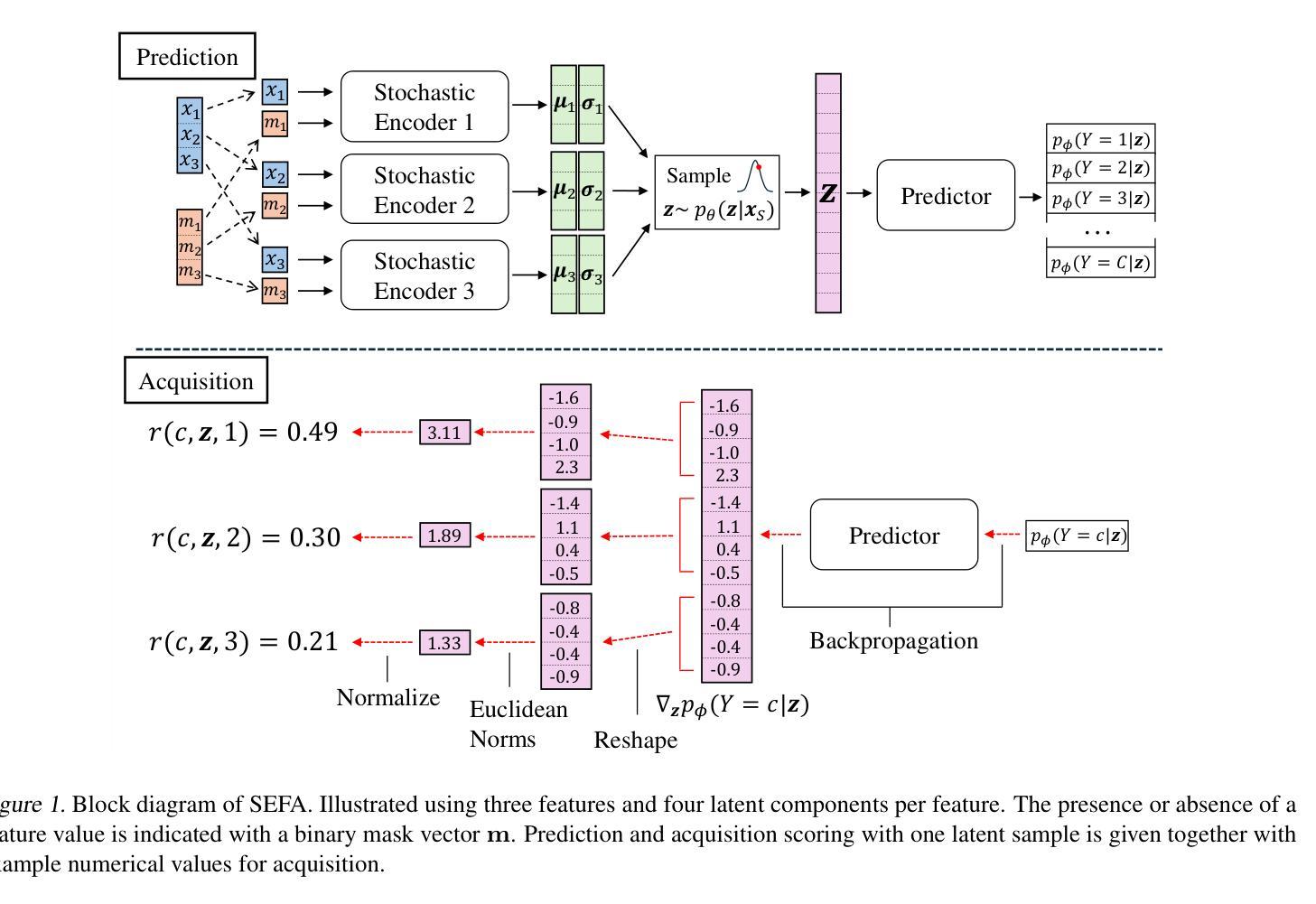
Stochastic Encodings for Active Feature Acquisition
Authors:Alexander Norcliffe, Changhee Lee, Fergus Imrie, Mihaela van der Schaar, Pietro Lio
Active Feature Acquisition is an instance-wise, sequential decision making problem. The aim is to dynamically select which feature to measure based on current observations, independently for each test instance. Common approaches either use Reinforcement Learning, which experiences training difficulties, or greedily maximize the conditional mutual information of the label and unobserved features, which makes myopic acquisitions. To address these shortcomings, we introduce a latent variable model, trained in a supervised manner. Acquisitions are made by reasoning about the features across many possible unobserved realizations in a stochastic latent space. Extensive evaluation on a large range of synthetic and real datasets demonstrates that our approach reliably outperforms a diverse set of baselines.
主动特征获取是一个针对每个实例的序贯决策问题。其目标是根据当前观察,独立地为每个测试实例动态选择要进行测量的特征。常见的方法要么使用强化学习,这会导致训练困难,要么贪婪地最大化标签和未观测特征的条件互信息,从而导致目光短浅的获取。为了解决这些缺点,我们引入了一种通过监督方式训练的潜在变量模型。通过在一个随机潜在空间中推理许多可能的未观测实现所对应的特征来进行特征获取。在多种合成和真实数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法可靠地优于各种基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 15 figures, 17 tables, published at ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了主动特征获取(Active Feature Acquisition)是一种针对每个测试实例进行动态选择特征的实例级决策问题。文章提出的方法基于监督学习训练一个潜在变量模型,通过对随机潜在空间中可能的未观察特征进行推理来选择特征,从而克服了使用强化学习的训练困难和基于条件互信息的贪婪方法造成的短视采集问题。经过广泛的数据集验证,本文方法相较于一系列基准测试具有出色的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 主动特征获取是一种针对每个测试实例动态选择特征的实例级决策问题。
- 强化学习常用于特征采集,但存在训练困难的问题。
- 基于条件互信息的贪婪方法会导致短视的采集决策。
- 引入了一种基于监督学习的潜在变量模型来解决上述问题。
- 通过在随机潜在空间中推理可能的未观察特征来做出采集决策。
- 该方法经过在多种合成和真实数据集上的广泛评估验证,显示出优于多种基准测试的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

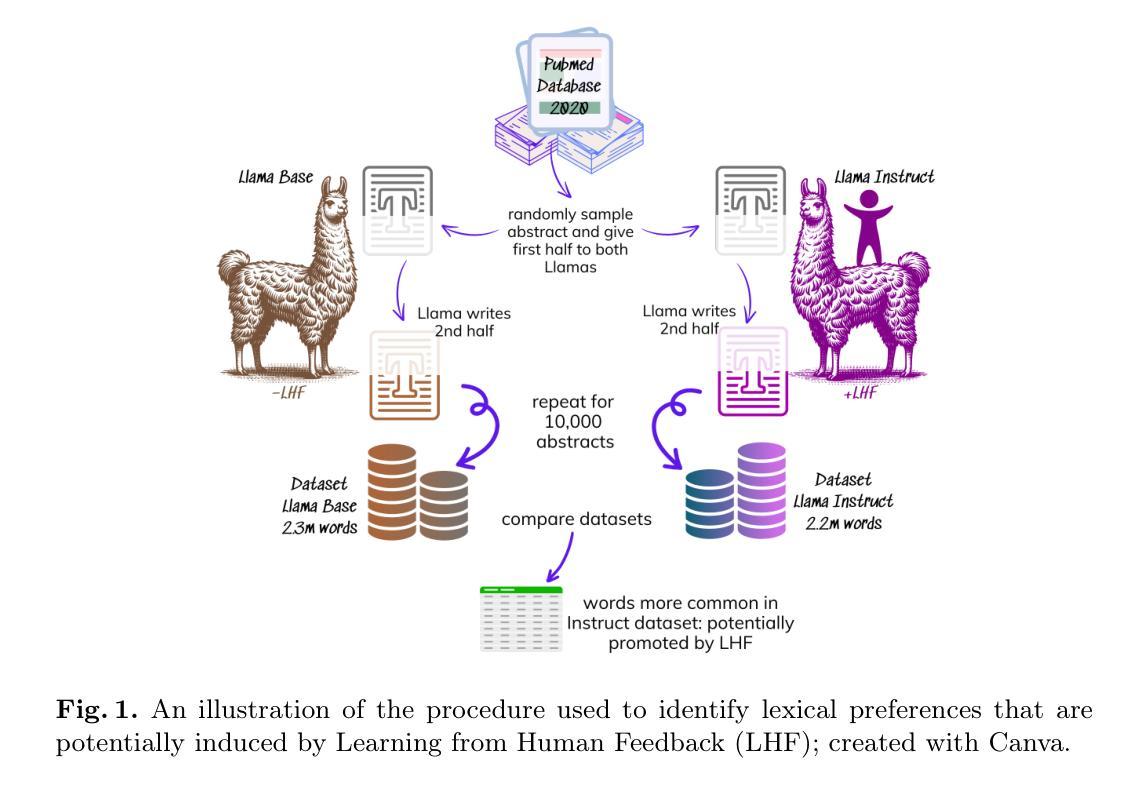
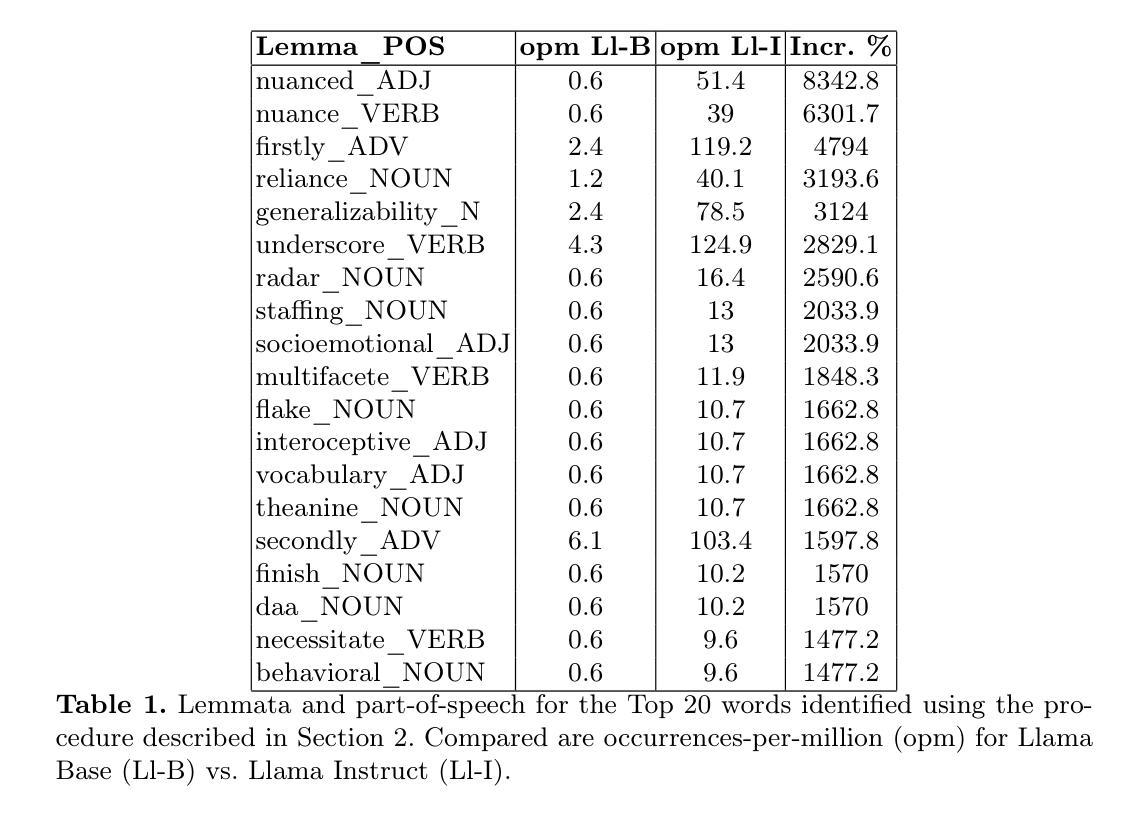
Word Overuse and Alignment in Large Language Models: The Influence of Learning from Human Feedback
Authors:Tom S. Juzek, Zina B. Ward
Large Language Models (LLMs) are known to overuse certain terms like “delve” and “intricate.” The exact reasons for these lexical choices, however, have been unclear. Using Meta’s Llama model, this study investigates the contribution of Learning from Human Feedback (LHF), under which we subsume Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback and Direct Preference Optimization. We present a straightforward procedure for detecting the lexical preferences of LLMs that are potentially LHF-induced. Next, we more conclusively link LHF to lexical overuse by experimentally emulating the LHF procedure and demonstrating that participants systematically prefer text variants that include certain words. This lexical overuse can be seen as a sort of misalignment, though our study highlights the potential divergence between the lexical expectations of different populations – namely LHF workers versus LLM users. Our work contributes to the growing body of research on explainable artificial intelligence and emphasizes the importance of both data and procedural transparency in alignment research.
大型语言模型(LLM)过度使用某些词汇,如“深入研究”和“复杂”。然而,对于这些词汇选择的确切原因尚不清楚。本研究利用Meta的Llama模型,探讨学习人类反馈(LHF)的贡献,我们将强化学习从人类反馈和直接偏好优化纳入其中。我们提出了一种检测潜在由LHF引起的大型语言模型词汇偏好的简单程序。接下来,我们通过模拟LHF程序并证明参与者系统性地偏好包含某些词汇的文本变体,更有说服力地将LHF与词汇过度使用联系起来。这种词汇过度使用可以看作是一种不对齐,但我们的研究突出了不同人群——即LHF工作者与LLM用户之间的词汇期望可能存在分歧。我们的工作为不断发展的可解释人工智能研究做出了贡献,并强调了数据和程序透明度在对齐研究中的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Bias and Fairness in AI (BIAS 2025) at ECML PKDD
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)存在过度使用某些术语的现象,例如“深入研究”和“复杂的”。本研究利用Meta的Llama模型,探讨了从人类反馈中学习(LHF)对此现象的影响。研究提出了一种检测LLM潜在LHF诱导词汇偏好的方法,并通过模拟LHF程序实验证明参与者对包含某些词汇的文本版本有系统性偏好。这种词汇过度使用可以被视为一种不对齐,但本研究强调了不同人群——即LHF工作者与LLM用户之间的词汇期望潜在分歧。本研究为人工智能的可解释性研究做出贡献,并强调了数据和程序透明在调整研究中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)存在过度使用某些术语的现象。
- 本研究利用Meta的Llama模型探讨了从人类反馈中学习(LHF)对LLM词汇选择的影响。
- 提出了一种检测LLM潜在LHF诱导词汇偏好的方法。
- 通过实验模拟LHF程序,证明参与者对包含某些特定词汇的文本版本有系统性偏好。
- 词汇过度使用可视为一种不对齐现象。
- 不同人群(如LHF工作者与LLM用户)之间的词汇期望存在潜在分歧。
点此查看论文截图