⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-11 更新
Can open source large language models be used for tumor documentation in Germany? – An evaluation on urological doctors’ notes
Authors:Stefan Lenz, Arsenij Ustjanzew, Marco Jeray, Meike Ressing, Torsten Panholzer
Tumor documentation in Germany is largely done manually, requiring reading patient records and entering data into structured databases. Large language models (LLMs) could potentially enhance this process by improving efficiency and reliability. This evaluation tests eleven different open source LLMs with sizes ranging from 1-70 billion model parameters on three basic tasks of the tumor documentation process: identifying tumor diagnoses, assigning ICD-10 codes, and extracting the date of first diagnosis. For evaluating the LLMs on these tasks, a dataset of annotated text snippets based on anonymized doctors’ notes from urology was prepared. Different prompting strategies were used to investigate the effect of the number of examples in few-shot prompting and to explore the capabilities of the LLMs in general. The models Llama 3.1 8B, Mistral 7B, and Mistral NeMo 12 B performed comparably well in the tasks. Models with less extensive training data or having fewer than 7 billion parameters showed notably lower performance, while larger models did not display performance gains. Examples from a different medical domain than urology could also improve the outcome in few-shot prompting, which demonstrates the ability of LLMs to handle tasks needed for tumor documentation. Open source LLMs show a strong potential for automating tumor documentation. Models from 7-12 billion parameters could offer an optimal balance between performance and resource efficiency. With tailored fine-tuning and well-designed prompting, these models might become important tools for clinical documentation in the future. The code for the evaluation is available from https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval. We also release the dataset as a new valuable resource that addresses the shortage of authentic and easily accessible benchmarks in German-language medical NLP.
德国的肿瘤记录大多是通过手动完成的,需要阅读患者病历并将数据输入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLMs)有望通过提高效率可靠性增强这一流程。本次评估对三种基本任务(识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期)测试了11种不同规模(从1亿到70亿模型参数)的开源LLMs。为了评估这些LLMs在这些任务上的表现,我们准备了一个基于泌尿科匿名医生笔记的注释文本片段数据集。使用了不同的提示策略来探究在少数案例提示中示例数量对模型的影响,并探索LLMs的一般能力。Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务中表现良好。具有较少训练数据或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而更大的模型并未显示出性能提升。来自不同于泌尿科的医学领域的例子也能在少数案例提示中改善结果,这证明了LLMs处理肿瘤记录所需任务的能力。开源LLMs在自动化肿瘤记录方面显示出巨大潜力。具有7-12亿参数的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间提供最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调和精心设计的提示,这些模型可能会成为未来临床记录的重要工具。评估的代码可从https://github.com/stefan-m-lenz/UroLlmEval获取。我们还发布了该数据集作为新的宝贵资源,以解决德国医学NLP领域中真实且易于访问的基准测试数据不足的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 53 pages, 5 figures
Summary
在德国的肿瘤记录过程中,主要依赖于手动操作,涉及阅读患者记录并输入结构化数据库。大型语言模型(LLMs)有潜力通过提高效率和可靠性来改进这一过程。本评估使用基于匿名泌尿科医生笔记的数据集,测试了11种不同规模的大型语言模型(从1亿到70亿模型参数)在肿瘤记录过程中的三项基本任务上的表现:识别肿瘤诊断、分配ICD-10代码和提取首次诊断日期。评估结果显示,Llama 3.1 8B、Mistral 7B和Mistral NeMo 12B等模型在这些任务上表现良好。训练数据不足或参数少于7亿的模型表现明显较差,而更大的模型并没有显示出性能提升。此外,不同医学领域的数据也有助于改进少样本提示的效果,证明了大型语言模型处理肿瘤记录任务的能力。开源大型语言模型在自动化肿瘤记录方面显示出巨大潜力,具有7-12亿参数的模型可能在性能和资源效率之间达到最佳平衡。通过有针对性的微调(fine-tuning)和精心设计提示(prompting),这些模型可能成为未来临床记录的重要工具。该评估的代码和数据集已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在肿瘤记录过程中具有改善效率和可靠性的潜力。
- 对不同规模的大型语言模型进行了评估,发现具有7-12亿参数的模型在性能和资源效率之间表现出最佳平衡。
- 在肿瘤诊断记录、ICD-10代码分配和首次诊断日期提取等任务上,部分模型表现良好。
- 模型在少样本提示场景下的表现受到所使用医学领域数据的影响。
- 通过有针对性的微调(fine-tuning)和精心设计提示(prompting),大型语言模型可能成为未来临床文档处理的重要工具。
- 数据集的公开有助于解决德国语言医学自然语言处理领域缺乏真实和易于访问的基准测试数据的问题。
点此查看论文截图

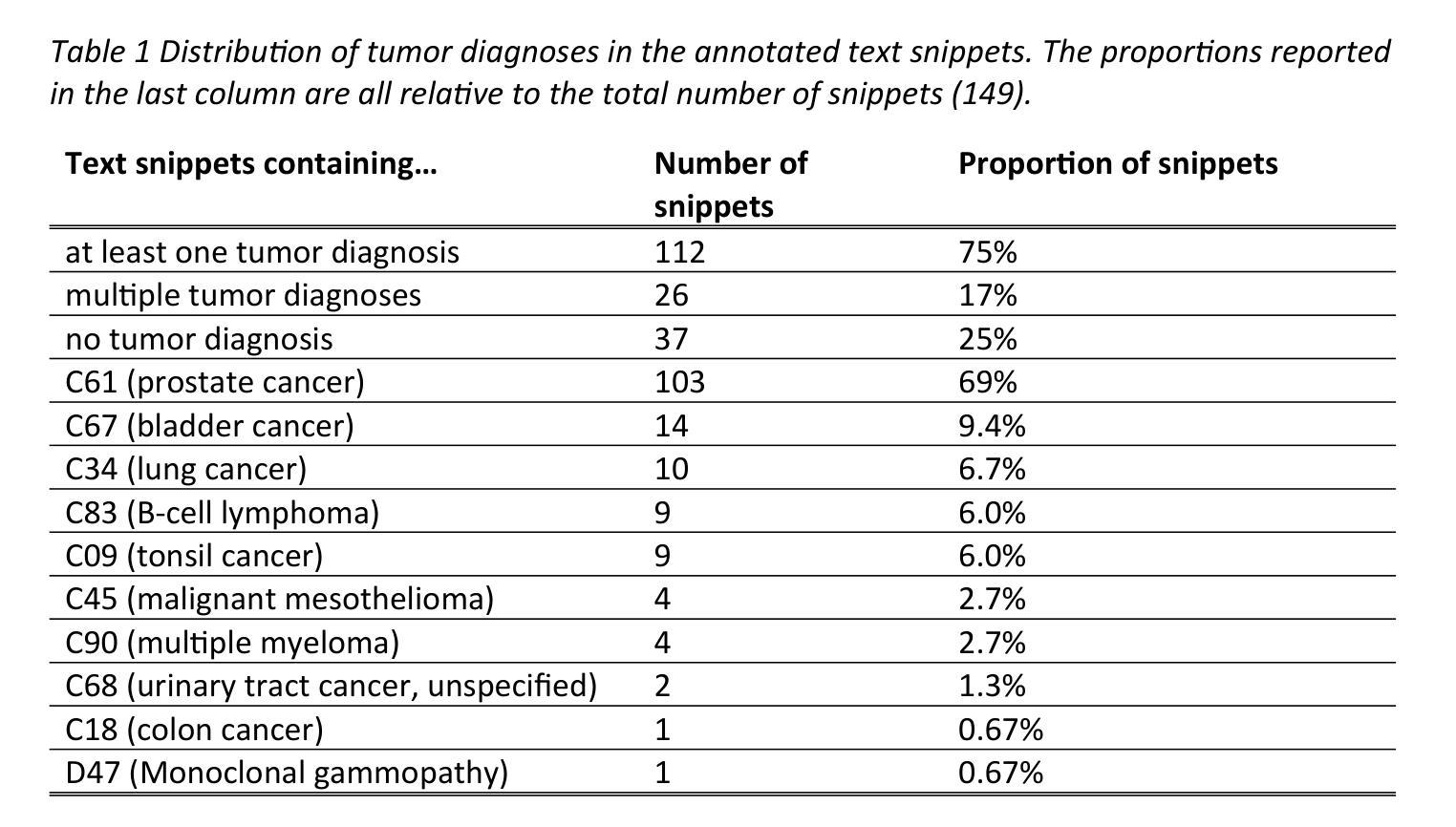
FedSemiDG: Domain Generalized Federated Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhipeng Deng, Zhe Xu, Tsuyoshi Isshiki, Yefeng Zheng
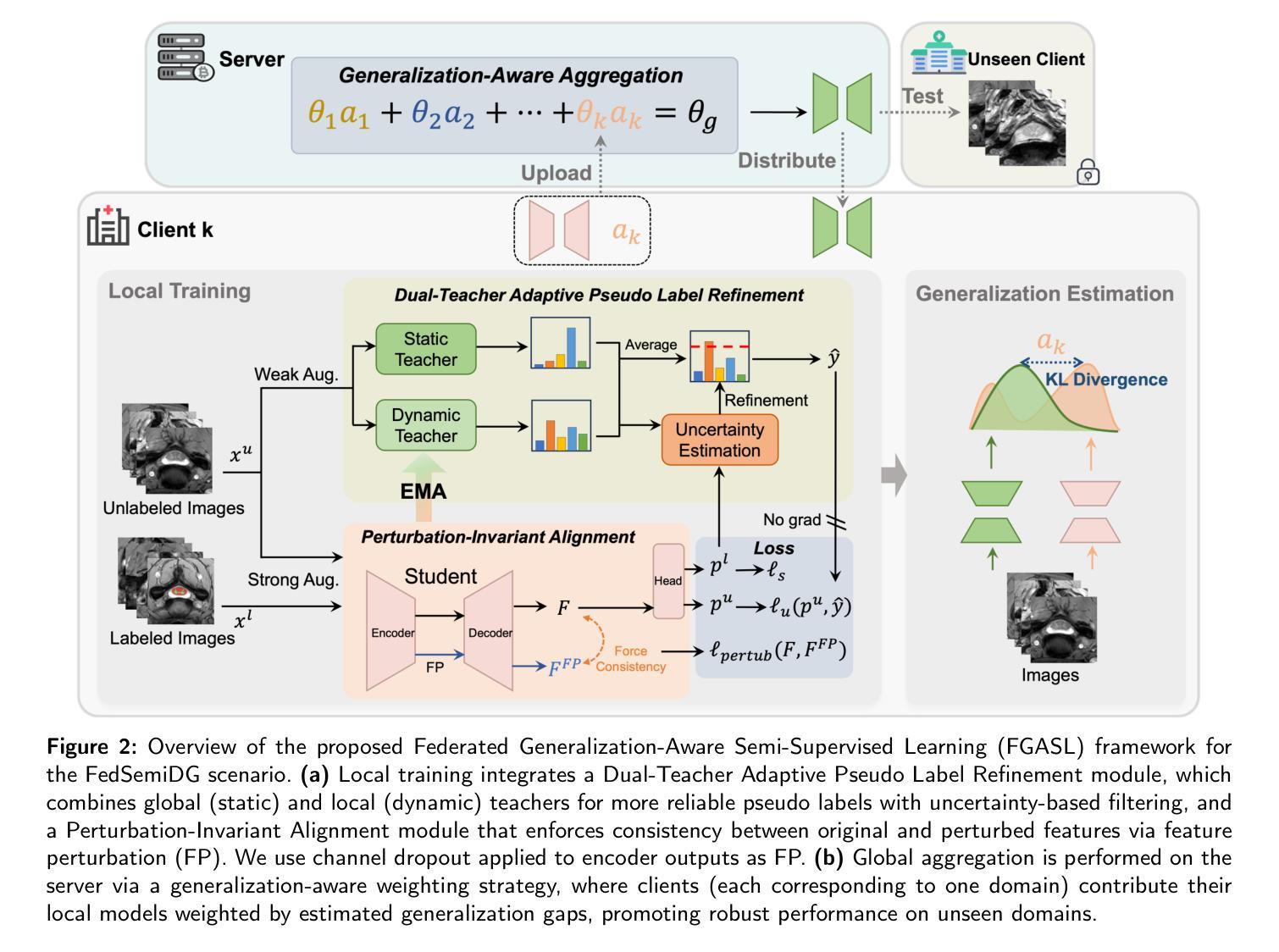
Medical image segmentation is challenging due to the diversity of medical images and the lack of labeled data, which motivates recent developments in federated semi-supervised learning (FSSL) to leverage a large amount of unlabeled data from multiple centers for model training without sharing raw data. However, what remains under-explored in FSSL is the domain shift problem which may cause suboptimal model aggregation and low effectivity of the utilization of unlabeled data, eventually leading to unsatisfactory performance in unseen domains. In this paper, we explore this previously ignored scenario, namely domain generalized federated semi-supervised learning (FedSemiDG), which aims to learn a model in a distributed manner from multiple domains with limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data such that the model can generalize well to unseen domains. We present a novel framework, Federated Generalization-Aware SemiSupervised Learning (FGASL), to address the challenges in FedSemiDG by effectively tackling critical issues at both global and local levels. Globally, we introduce Generalization-Aware Aggregation (GAA), assigning adaptive weights to local models based on their generalization performance. Locally, we use a Dual-Teacher Adaptive Pseudo Label Refinement (DR) strategy to combine global and domain-specific knowledge, generating more reliable pseudo labels. Additionally, Perturbation-Invariant Alignment (PIA) enforces feature consistency under perturbations, promoting domain-invariant learning. Extensive experiments on four medical segmentation tasks (cardiac MRI, spine MRI, bladder cancer MRI and colorectal polyp) demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art FSSL and domain generalization approaches, achieving robust generalization on unseen domains.
医学图像分割是一个充满挑战的任务,因为医学图像具有多样性且缺乏标记数据。这促使了联邦半监督学习(FSSL)的近期发展,以利用多个中心的大量未标记数据进行模型训练,而无需共享原始数据。然而,在FSSL中仍未得到充分探索的是域偏移问题,它可能导致模型聚合不佳以及利用未标记数据的效果低下,最终在未见的域上导致性能不佳。在本文中,我们探索了以前被忽略的场景,即领域通用联邦半监督学习(FedSemiDG),其目标是从多个领域以分布式方式学习模型,使用有限的标记数据和丰富的未标记数据,以便模型能够很好地推广未见领域。我们提出了一种新的框架,名为联邦泛化感知半监督学习(FGASL),以解决FedSemiDG中的挑战,在全局和局部层面有效地解决关键问题。在全局层面,我们引入了泛化感知聚合(GAA),根据局部模型的泛化性能分配自适应权重。在局部层面,我们使用双教师自适应伪标签细化(DR)策略来结合全局和领域特定知识,生成更可靠的伪标签。此外,扰动不变对齐(PIA)强制在扰动下保持特征一致性,促进领域不变学习。在四个医学分割任务(心脏MRI、脊柱MRI、膀胱癌MRI和结肠息肉)上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法显著优于最新的FSSL和领域通用方法,在未见的域上实现了稳健的泛化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages
摘要
本文探讨了联邦半监督学习(FSSL)在医学图像分割中的域偏移问题。由于医学图像的多样性和标记数据的缺乏,FSSL在模型训练时面临挑战。本文提出了一个新的场景:域泛化联邦半监督学习(FedSemiDG),旨在从多个领域以分布式方式学习模型,用有限的标记数据和大量的无标记数据,使模型能够在未见领域上良好泛化。为了解决FedSemiDG中的挑战,本文提出了一种新的框架——联邦泛化感知半监督学习(FGASL),在全球和地方层面有效地解决关键问题。全球层面,我们引入了感知泛化聚合(GAA),根据局部模型的泛化性能分配自适应权重。地方层面,我们使用双教师自适应伪标签细化(DR)策略,结合全局和领域特定知识,生成更可靠的伪标签。此外,扰动不变对齐(PIA)在扰动下强制执行特征一致性,促进领域不变学习。在四个医学分割任务上的实验表明,本文的方法显著优于最新的FSSL和域泛化方法,在未见领域上实现了稳健的泛化。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割面临多样性及标记数据缺乏的挑战。
- 联邦半监督学习(FSSL)在利用无标记数据方面展现出优势,但域偏移问题尚未被充分探索。
- 提出了一种新的场景:域泛化联邦半监督学习(FedSemiDG),旨在学习能适应未见领域的模型。
- 引入了一种新的框架:联邦泛化感知半监督学习(FGASL)来解决FedSemiDG中的挑战。
- 在全球层面,通过感知泛化聚合(GAA)根据泛化性能分配自适应权重。
- 在地方层面,使用双教师自适应伪标签细化(DR)生成更可靠的伪标签。
点此查看论文截图

TokenFlow: Unified Image Tokenizer for Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Authors:Liao Qu, Huichao Zhang, Yiheng Liu, Xu Wang, Yi Jiang, Yiming Gao, Hu Ye, Daniel K. Du, Zehuan Yuan, Xinglong Wu
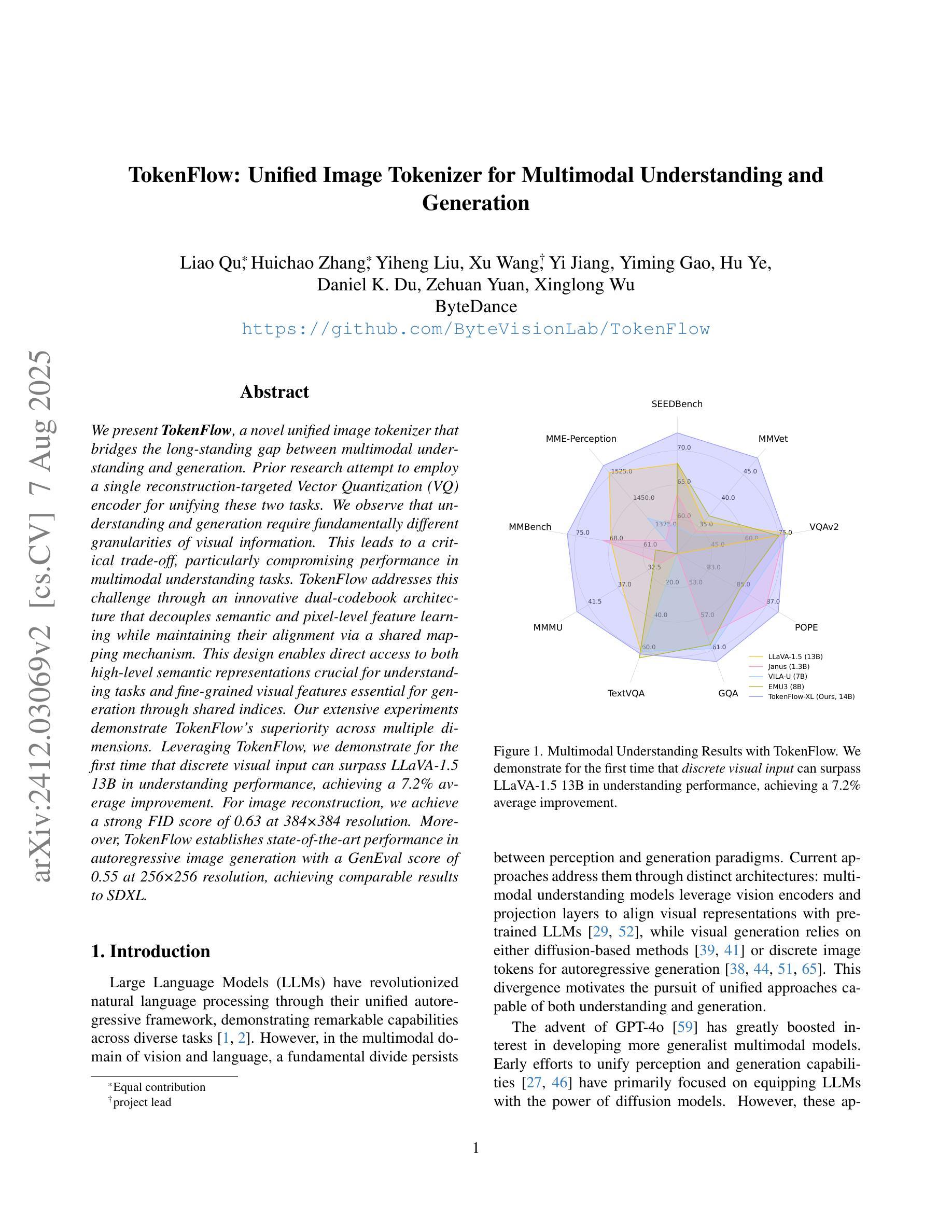
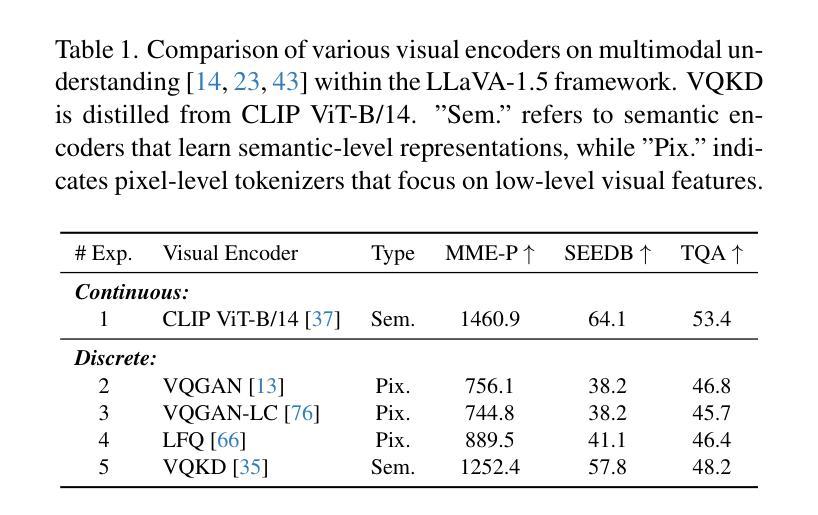
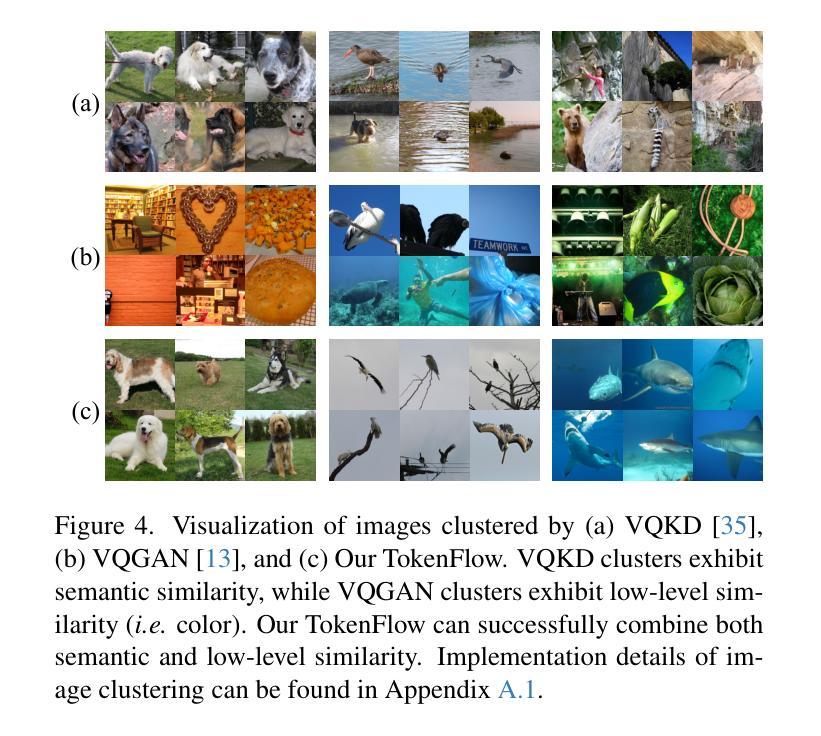
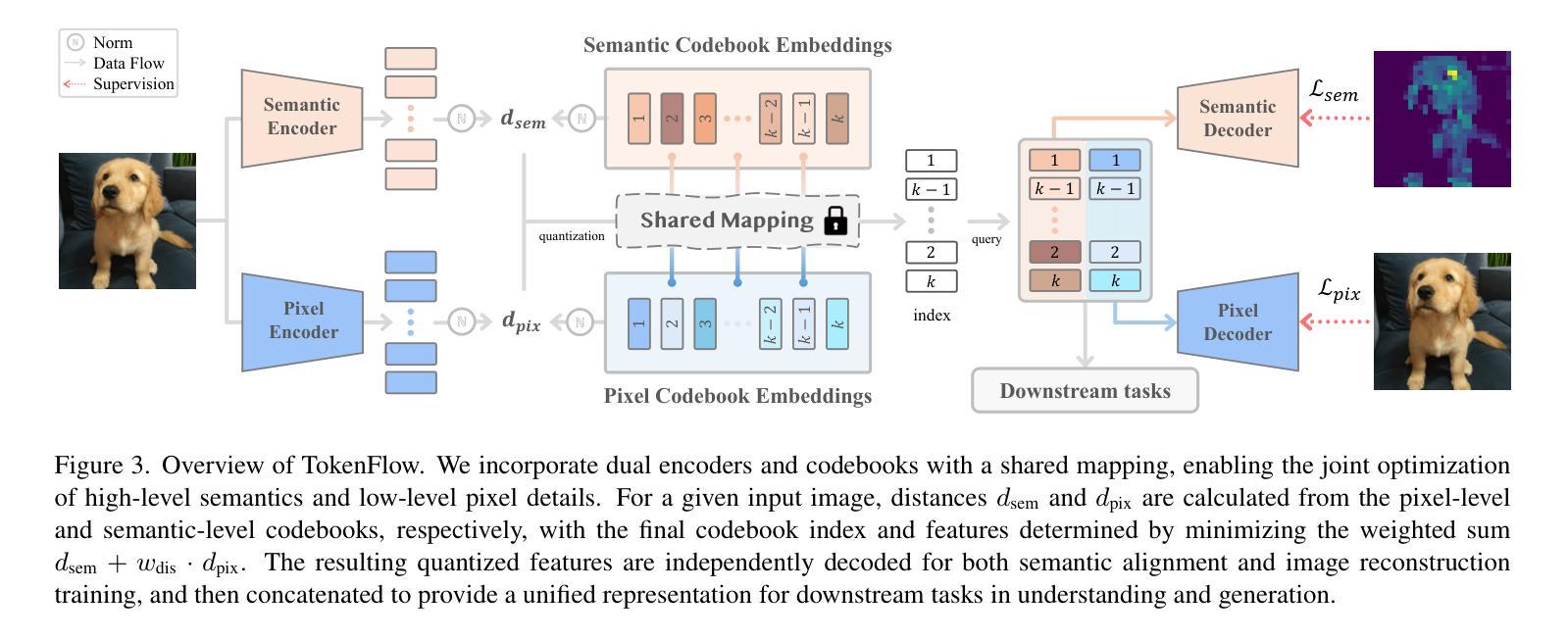
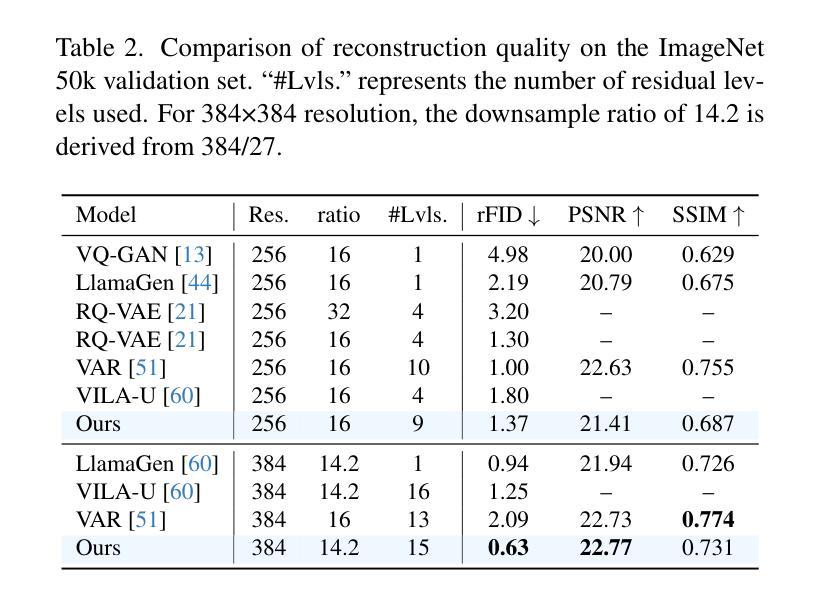
We present TokenFlow, a novel unified image tokenizer that bridges the long-standing gap between multimodal understanding and generation. Prior research attempt to employ a single reconstruction-targeted Vector Quantization (VQ) encoder for unifying these two tasks. We observe that understanding and generation require fundamentally different granularities of visual information. This leads to a critical trade-off, particularly compromising performance in multimodal understanding tasks. TokenFlow addresses this challenge through an innovative dual-codebook architecture that decouples semantic and pixel-level feature learning while maintaining their alignment via a shared mapping mechanism. This design enables direct access to both high-level semantic representations crucial for understanding tasks and fine-grained visual features essential for generation through shared indices. Our extensive experiments demonstrate TokenFlow’s superiority across multiple dimensions. Leveraging TokenFlow, we demonstrate for the first time that discrete visual input can surpass LLaVA-1.5 13B in understanding performance, achieving a 7.2% average improvement. For image reconstruction, we achieve a strong FID score of 0.63 at 384384 resolution. Moreover, TokenFlow establishes state-of-the-art performance in autoregressive image generation with a GenEval score of 0.55 at 256256 resolution, achieving comparable results to SDXL.
我们提出了TokenFlow,这是一种新的统一图像分词器,它缩小了长期以来存在于多模态理解和生成之间的鸿沟。先前的研究试图采用以重建为目标的向量量化(VQ)编码器来统一这两个任务。我们发现,理解和生成需要不同粒度的视觉信息。这导致了一个关键的权衡问题,特别是在多模态理解任务中的性能妥协。TokenFlow通过创新的双码本架构来解决这一挑战,该架构将语义和像素级特征学习解耦,同时通过共享映射机制保持它们的一致性。这种设计使得我们可以直接访问对理解任务至关重要的高级语义表示以及通过共享索引对生成至关重要的精细视觉特征。我们的广泛实验证明了TokenFlow在多个维度上的优越性。利用TokenFlow,我们首次证明离散视觉输入可以在理解性能上超越LLaVA-1.5 13B,平均提高7.2%。在图像重建方面,我们在384*384分辨率下取得了0.63的强FID分数。此外,TokenFlow在自回归图像生成方面建立了最先进的性能,在256*256分辨率下达到了GenEval得分0.55,实现了与SDXL相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025; Code and models: https://github.com/ByteVisionLab/TokenFlow
Summary
本文介绍了TokenFlow,一种新型的统一图像分词器,能够弥合长久以来多模态理解和生成之间的鸿沟。TokenFlow采用创新的双码本架构,解决了理解和生成需要不同粒度的视觉信息的问题,实现了语义和像素级特征学习的解耦,同时通过共享映射机制保持其对齐。实验表明,TokenFlow在多个维度上表现出卓越的性能,特别是在图像理解和重建方面。
Key Takeaways
- TokenFlow是一种新型图像分词器,能够弥合多模态理解和生成之间的鸿沟。
- 现有研究尝试使用单一重建目标的向量量化编码器来统一这两个任务,但理解和生成需要不同粒度的视觉信息。
- TokenFlow通过双码本架构解决这一问题,实现语义和像素级特征学习的解耦。
- TokenFlow通过共享索引,实现高级语义表示和精细视觉特征的直接访问。
- 在多个维度上,TokenFlow的实验表现出卓越的性能。
- 在理解性能方面,TokenFlow超越了LLaVA-1.5 13B,平均改进了7.2%。
点此查看论文截图


Automatic brain tumor segmentation in 2D intra-operative ultrasound images using magnetic resonance imaging tumor annotations
Authors:Mathilde Faanes, Ragnhild Holden Helland, Ole Solheim, Sébastien Muller, Ingerid Reinertsen
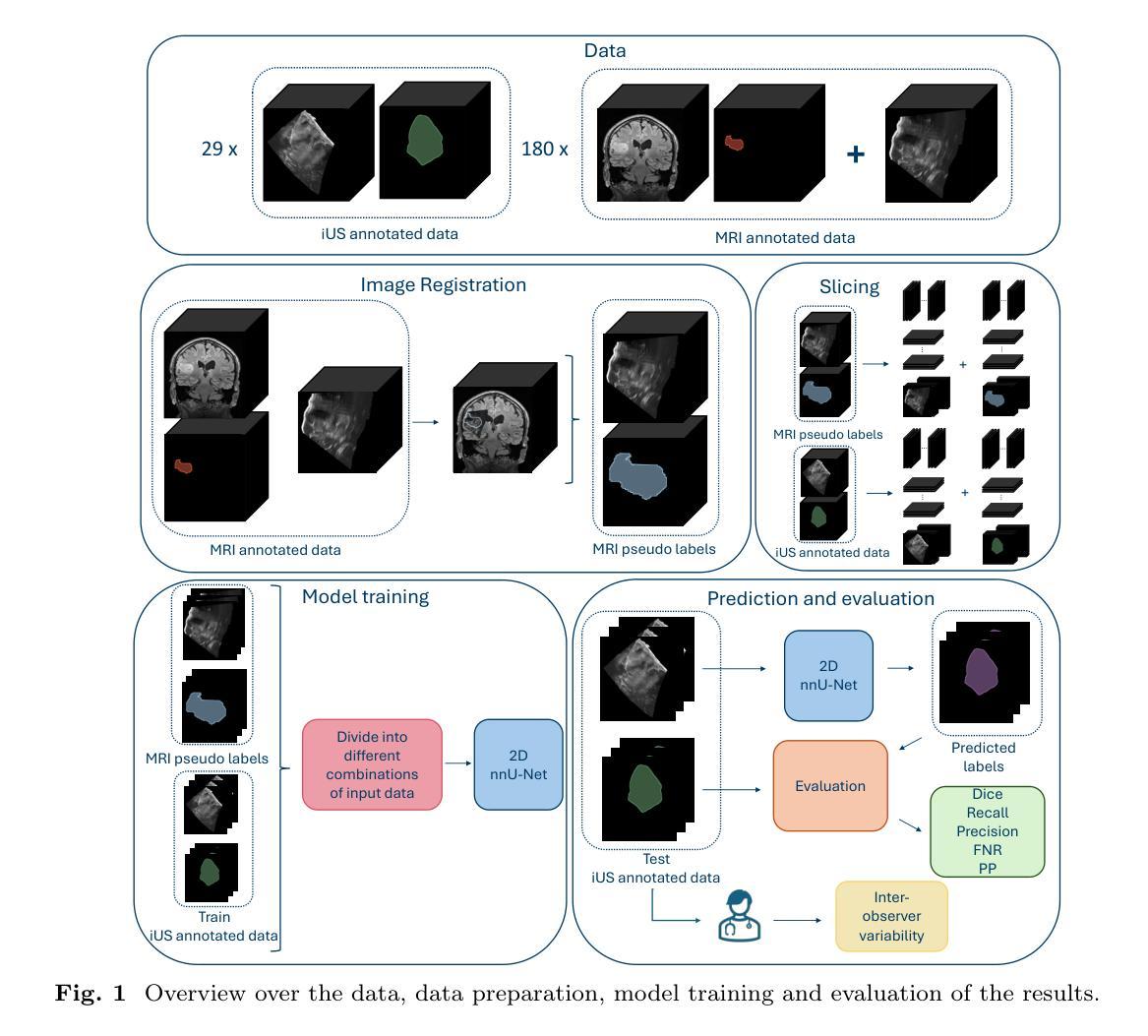
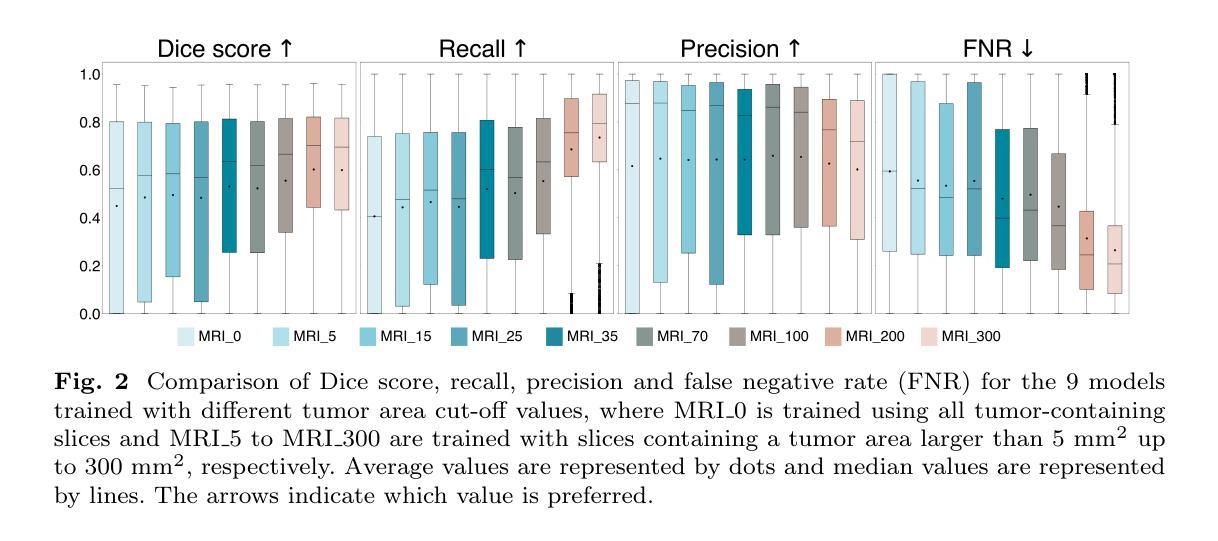
Automatic segmentation of brain tumors in intra-operative ultrasound (iUS) images could facilitate localization of tumor tissue during resection surgery. The lack of large annotated datasets limits the current models performances. In this paper, we investigated the use of tumor annotations in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, which are more accessible than annotations in iUS images, for training of deep learning models for iUS brain tumor segmentation. We used 180 annotated MRI scans with corresponding unannotated iUS images, and 29 annotated iUS images. Image registration was performed to transfer the MRI annotations to the corresponding iUS images before training the nnU-Net model with different configurations of the data and label origins. The results showed no significant difference in Dice score for a model trained with only MRI annotated tumors compared to models trained with only iUS annotations and both, and to expert annotations, indicating that MRI tumor annotations can be used as a substitute for iUS tumor annotations to train a deep learning model for automatic brain tumor segmentation in iUS images. The best model obtained an average Dice score of $0.62\pm0.31$, compared to $0.67\pm0.25$ for an expert neurosurgeon, where the performance on larger tumors were similar, but lower for the models on smaller tumors. In addition, the results showed that removing smaller tumors from the training sets improved the results. The main models are available here: https://github.com/mathildefaanes/us_brain_tumor_segmentation/tree/main
在术中超声(iUS)图像中自动分割脑肿瘤可以有助于在切除手术期间定位肿瘤组织。缺乏大量标注数据集限制了当前模型的表现。在本文中,我们研究了在磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中使用肿瘤标注的方法,这些标注比iUS图像中的标注更容易获得,用于训练深度学习模型进行iUS脑肿瘤分割。我们使用180个标注的MRI扫描和相应的未标注iUS图像,以及29个标注的iUS图像。在将MRI标注转移到相应的iUS图像之前,进行了图像配准,然后使用不同配置的数据和标签来源训练nnU-Net模型。结果表明,与仅使用iUS标注、同时使用MRI和iUS标注以及专家标注训练的模型相比,仅使用MRI标注的肿瘤训练的模型的Dice得分没有显著差异,这表明MRI肿瘤标注可以作为替代iUS肿瘤标注来训练深度学习模型,以自动进行iUS图像中的脑肿瘤分割。最佳模型获得的平均Dice得分为$0.62\pm0.31$,而专家神经外科医生的得分为$0.67\pm0.25$,对于较大的肿瘤,两者性能相似,但对较小肿瘤的模型性能较低。此外,结果还表明,从训练集中去除较小的肿瘤可以提高结果。主要模型可在此处找到:https://github.com/mathildefaanes/us_brain_tumor_segmentation/tree/main
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14, 5figures. This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文探讨了利用磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中的肿瘤注释信息训练深度学习模型,以在术中超声(iUS)图像中实现自动脑肿瘤分割的可能性。研究采用MRI扫描中的肿瘤注释信息替代iUS图像中的肿瘤注释信息,并发现训练出的模型性能与专家注释相当。最佳模型的平均Dice系数为$0.62±0.31$,与专家神经外科医生的性能接近。此外,研究还发现去除训练集中的小肿瘤可以提高模型性能。此项目的主要模型已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 利用MRI扫描中的肿瘤注释信息训练深度学习模型以实现术中超声图像中的脑肿瘤自动分割。
- 使用MRI肿瘤注释信息作为替代iUS肿瘤注释信息训练模型,性能与专家注释相当。
- 最佳模型的平均Dice系数为$0.62±0.31$,与专家神经外科医生性能接近。
- 模型在大肿瘤上的性能良好,但在小肿瘤上的性能较低。
- 去除训练集中的小肿瘤可以提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

CAD-MLLM: Unifying Multimodality-Conditioned CAD Generation With MLLM
Authors:Jingwei Xu, Chenyu Wang, Zibo Zhao, Wen Liu, Yi Ma, Shenghua Gao
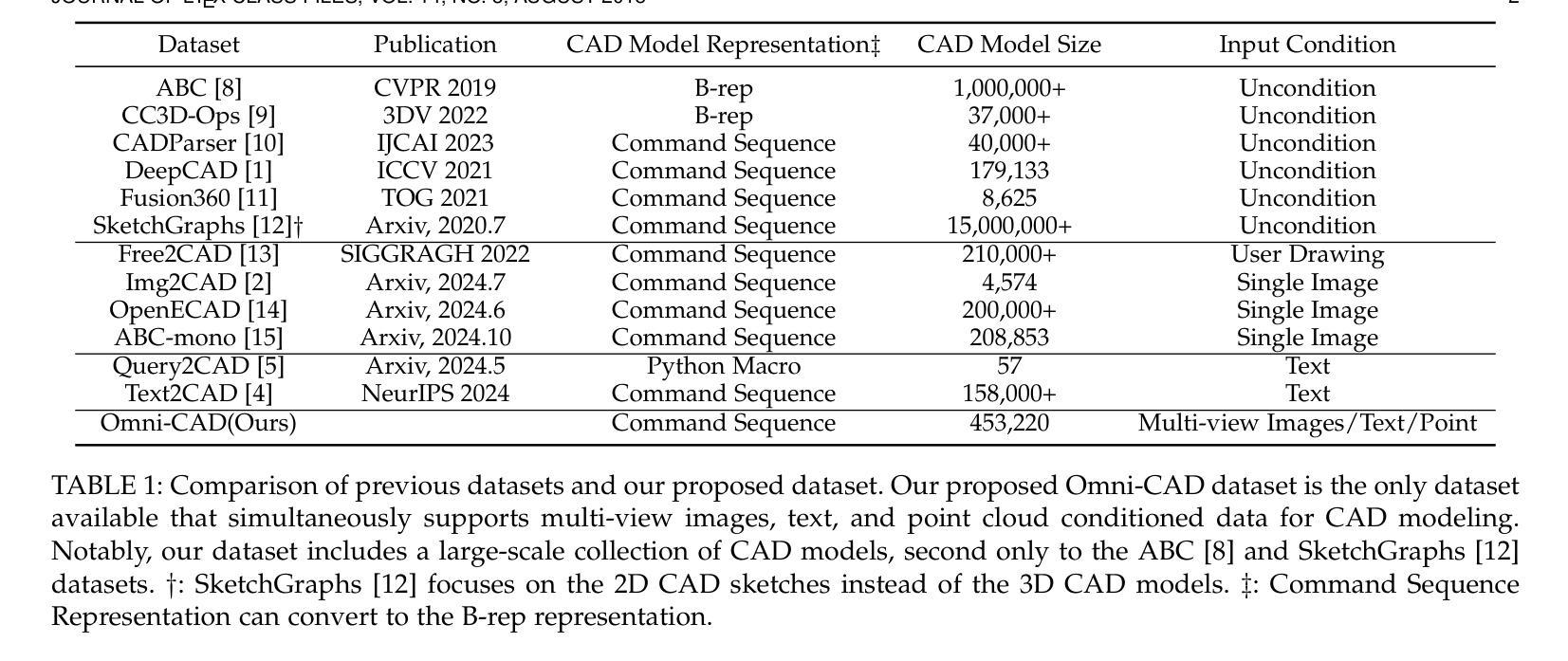
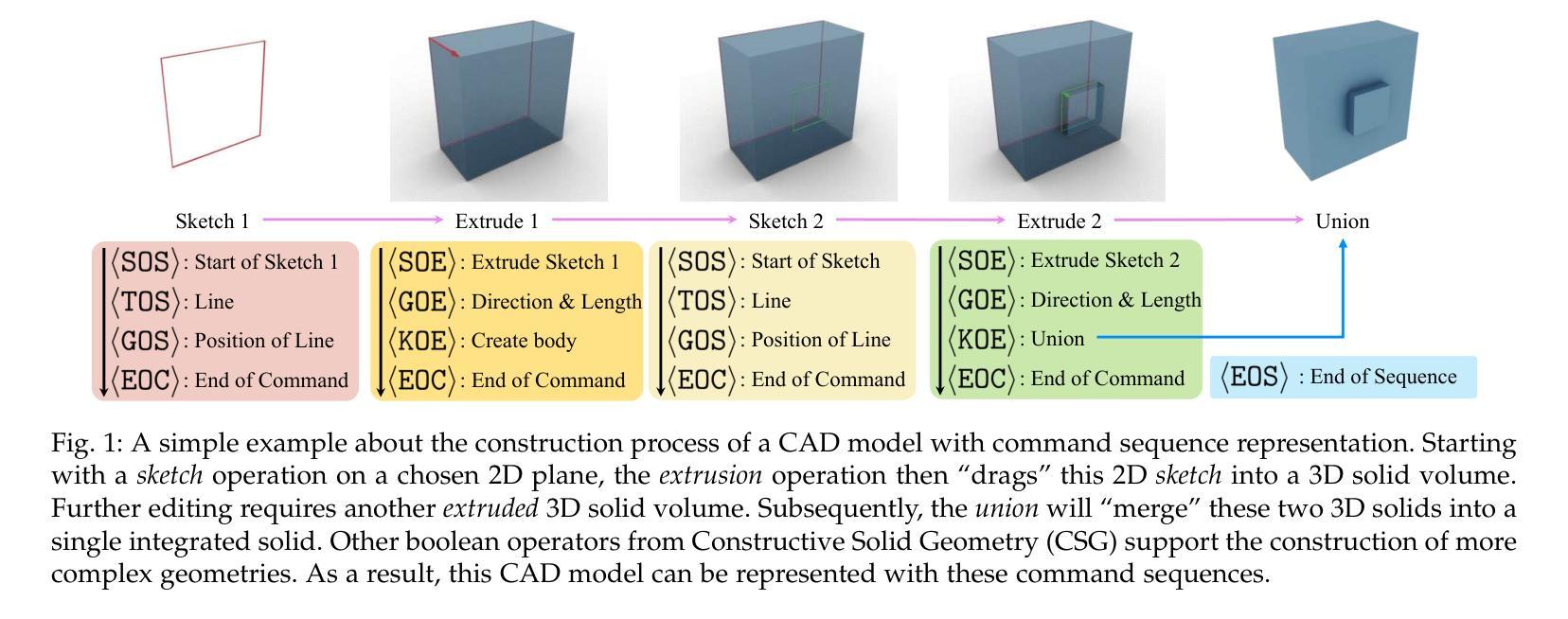
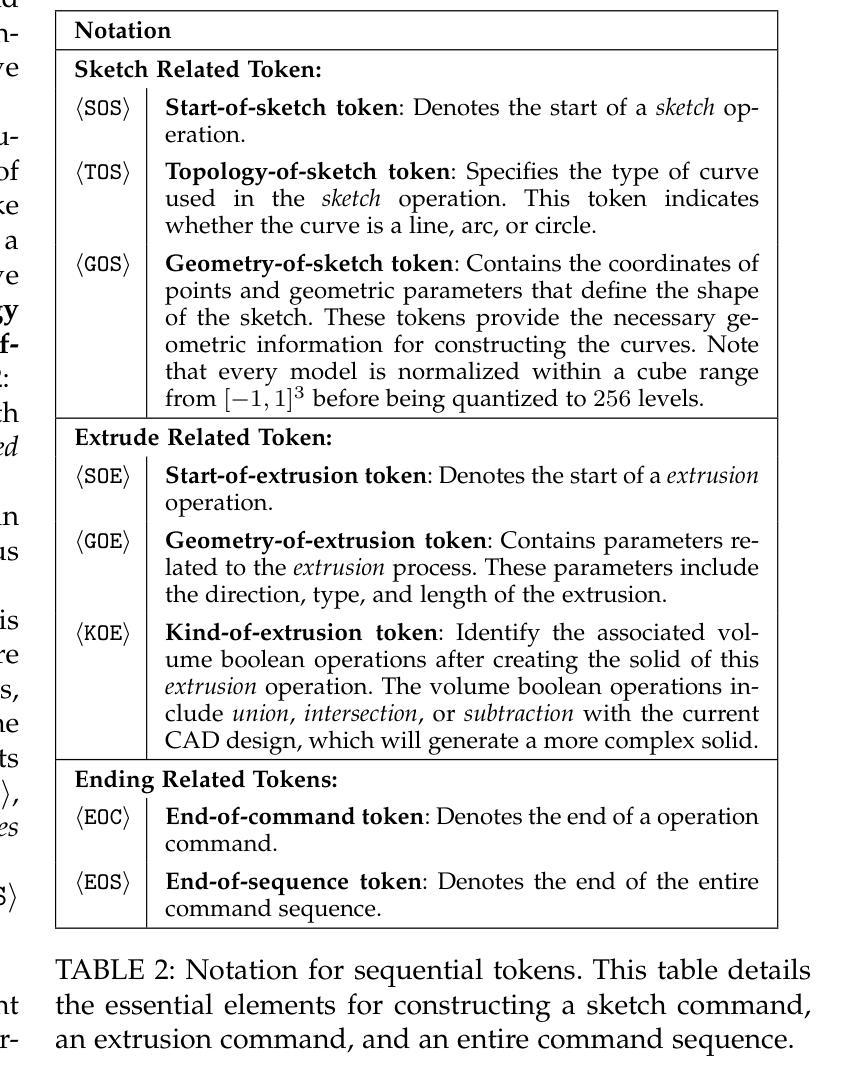
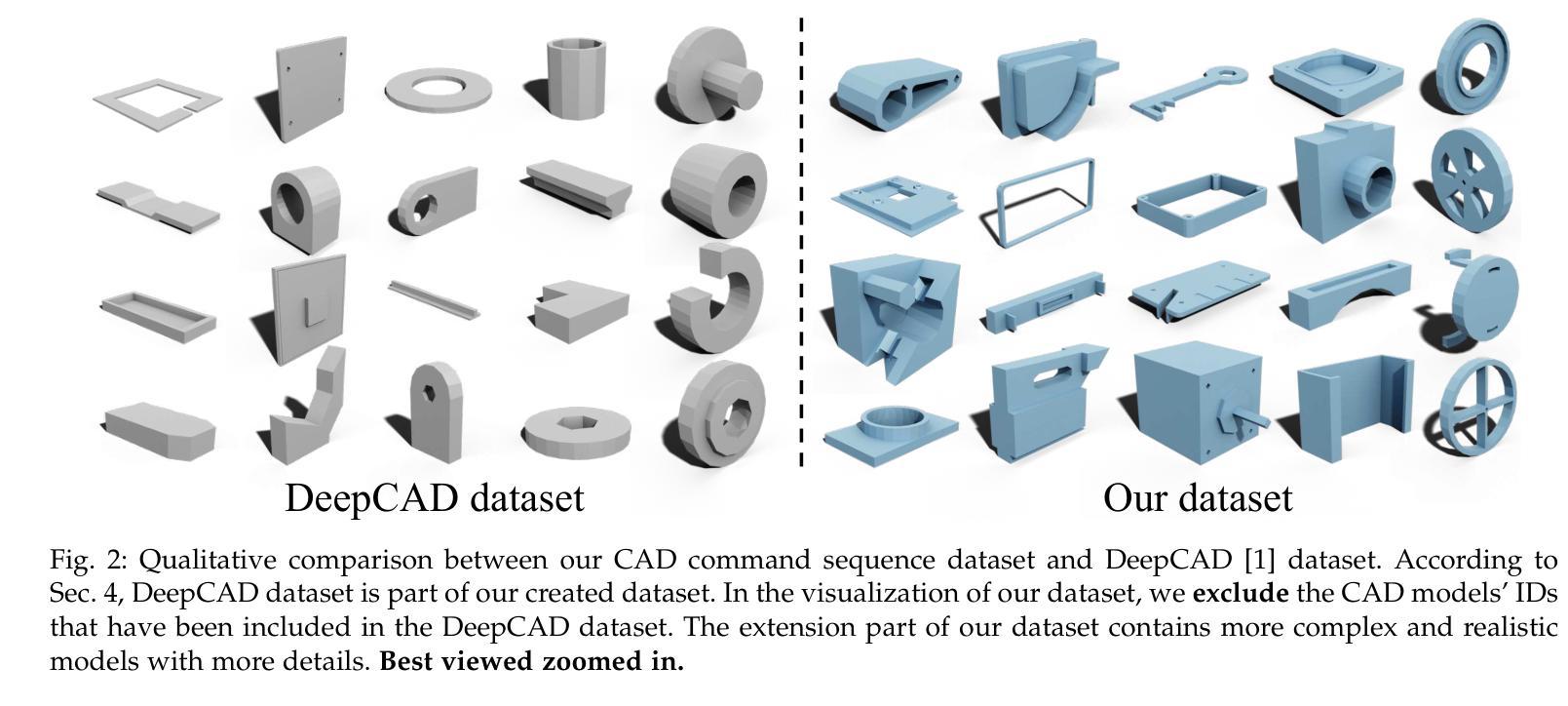
This paper aims to design a unified Computer-Aided Design (CAD) generation system that can easily generate CAD models based on the user’s inputs in the form of textual description, images, point clouds, or even a combination of them. Towards this goal, we introduce the CAD-MLLM, the first system capable of generating parametric CAD models conditioned on the multimodal input. Specifically, within the CAD-MLLM framework, we leverage the command sequences of CAD models and then employ advanced large language models (LLMs) to align the feature space across these diverse multi-modalities data and CAD models’ vectorized representations. To facilitate the model training, we design a comprehensive data construction and annotation pipeline that equips each CAD model with corresponding multimodal data. Our resulting dataset, named Omni-CAD, is the first multimodal CAD dataset that contains textual description, multi-view images, points, and command sequence for each CAD model. It contains approximately 450K instances and their CAD construction sequences. To thoroughly evaluate the quality of our generated CAD models, we go beyond current evaluation metrics that focus on reconstruction quality by introducing additional metrics that assess topology quality and surface enclosure extent. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that CAD-MLLM significantly outperforms existing conditional generative methods and remains highly robust to noises and missing points. The project page and more visualizations can be found at: https://cad-mllm.github.io/
本文旨在设计一个统一的计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成系统,该系统能够轻松根据用户的文本描述、图像、点云甚至它们的组合形式等输入来生成CAD模型。为实现这一目标,我们引入了CAD-MLLM系统,这是第一个能够根据多模式输入生成参数化CAD模型的系统。具体而言,在CAD-MLLM框架内,我们利用CAD模型的命令序列,然后采用先进的大型语言模型(LLM)来对齐这些多样化的多模式数据以及CAD模型的向量表示的特征空间。为了促进模型训练,我们设计了一个综合的数据构建和注释管道,使每个CAD模型都配备相应的多模式数据。我们由此构建的数据集名为Omni-CAD,它是第一个包含文本描述、多视角图像、点和每个CAD模型的命令序列的多模式CAD数据集。它包含大约45万实例及其CAD构建序列。为了全面评估我们生成的CAD模型的质量,我们超越了当前以重建质量为重点的评价指标,引入了其他评估拓扑质量和表面封闭程度的指标。大量的实验结果证明,CAD-MLLM显著优于现有的条件生成方法,并对噪声和缺失点具有高度鲁棒性。项目页面和更多可视化内容可在:https://cad-mllm.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cad-mllm.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了一个统一计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成系统,该系统能够根据用户的文本描述、图像、点云或它们的组合作为输入,轻松生成CAD模型。为实现这一目标,引入了CAD-MLLM系统,它是第一个能够根据多模式输入生成参数化CAD模型的系统。该系统利用CAD模型的命令序列,并采用先进的大型语言模型(LLM)来对齐各种多模式数据和CAD模型的向量表示的特征空间。为帮助模型训练,设计了一个全面的数据构建和注释管道,为每个CAD模型配备相应的多模式数据,构建了名为Omni-CAD的多模式CAD数据集。此外,还引入了拓扑质量和表面封闭程度等评估指标来全面评估生成的CAD模型的质量。实验结果表明,CAD-MLLM显著优于现有的条件生成方法,对噪声和缺失点具有高度鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文旨在设计一个统一的CAD生成系统,能够根据用户的多种输入(文本描述、图像、点云等)轻松生成CAD模型。
- 引入了CAD-MLLM系统,首次实现基于多模式输入的条件化CAD模型生成。
- CAD-MLLM利用CAD模型的命令序列,并采用大型语言模型进行特征空间对齐。
- 为支持模型训练,构建了一个全面的数据构建和注释管道,并创建了Omni-CAD多模式CAD数据集。
- 提出的评估方法不仅关注重建质量,还考虑了拓扑质量和表面封闭程度。
- 实验结果表明,CAD-MLLM在性能上显著优于现有条件生成方法。
点此查看论文截图

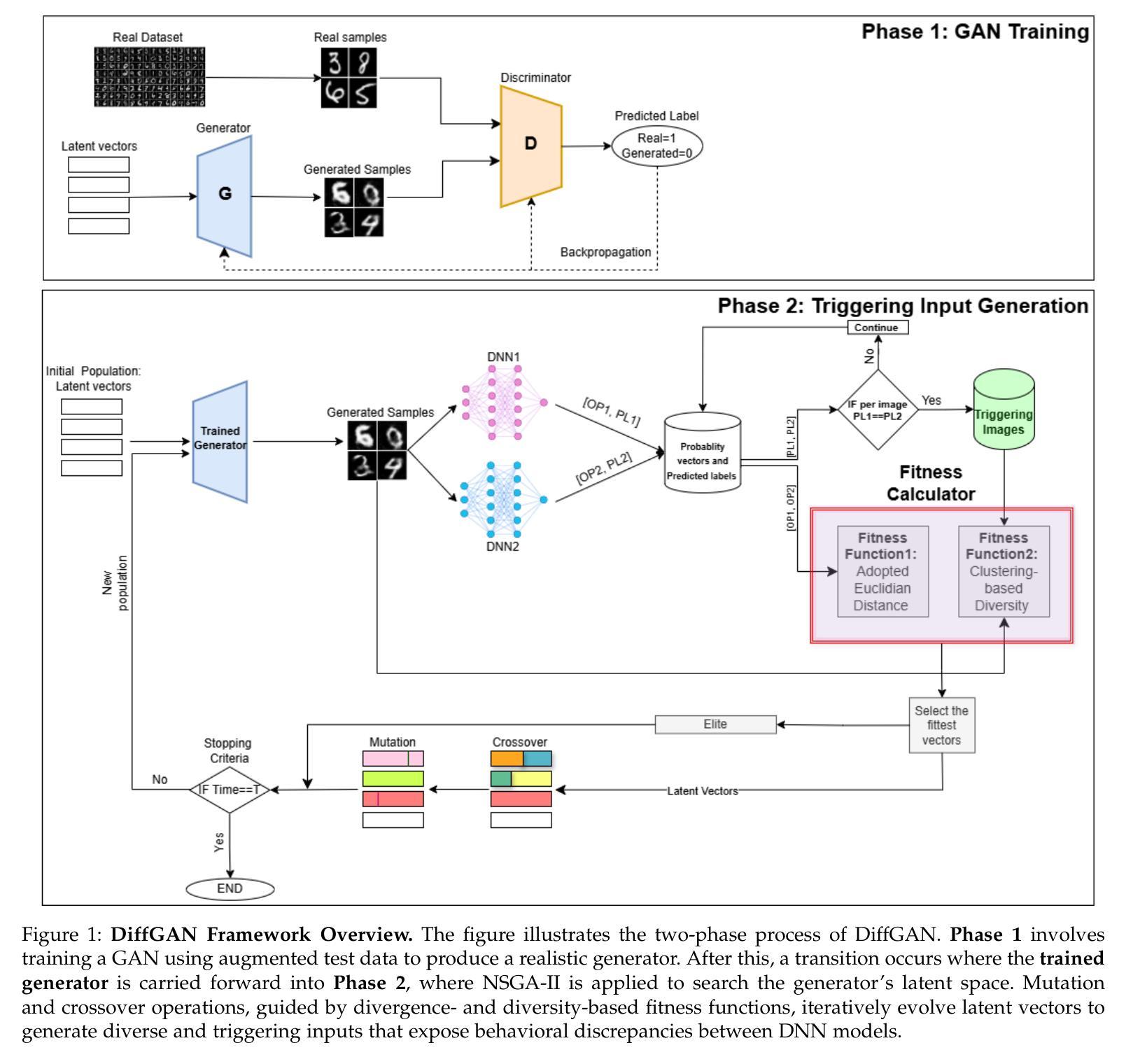
DiffGAN: A Test Generation Approach for Differential Testing of Deep Neural Networks for Image Analysis
Authors:Zohreh Aghababaeyan, Manel Abdellatif, Lionel Briand, Ramesh S
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are increasingly deployed across applications. However, ensuring their reliability remains a challenge, and in many situations, alternative models with similar functionality and accuracy are available. Traditional accuracy-based evaluations often fail to capture behavioral differences between models, especially with limited test datasets, making it difficult to select or combine models effectively. Differential testing addresses this by generating test inputs that expose discrepancies in DNN model behavior. However, existing approaches face significant limitations: many rely on model internals or are constrained by available seed inputs. To address these challenges, we propose DiffGAN, a black-box test image generation approach for differential testing of DNN models. DiffGAN leverages a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II to generate diverse and valid triggering inputs that reveal behavioral discrepancies between models. DiffGAN employs two custom fitness functions, focusing on diversity and divergence, to guide the exploration of the GAN input space and identify discrepancies between models’ outputs. By strategically searching this space, DiffGAN generates inputs with specific features that trigger differences in model behavior. DiffGAN is black-box, making it applicable in more situations. We evaluate DiffGAN on eight DNN model pairs trained on widely used image datasets. Our results show DiffGAN significantly outperforms a SOTA baseline, generating four times more triggering inputs, with greater diversity and validity, within the same budget. Additionally, the generated inputs improve the accuracy of a machine learning-based model selection mechanism, which selects the best-performing model based on input characteristics and can serve as a smart output voting mechanism when using alternative models.
深度神经网络(DNNs)在各应用领域中的应用越来越广泛。然而,确保其可靠性仍然是一个挑战,而且在许多情况下,存在具有相似功能和准确性的替代模型。传统的基于准确性的评估往往无法捕捉到模型之间的行为差异,尤其是在有限的测试数据集的情况下,使得难以有效地选择或组合模型。差分测试通过生成测试输入来解决这个问题,这些输入能够暴露DNN模型行为之间的差异。然而,现有方法存在重大局限性:许多方法依赖于模型内部信息或受到可用种子输入的约束。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DiffGAN,这是一种用于DNN模型差分测试的黑色盒子测试图像生成方法。DiffGAN利用生成对抗网络(GAN)和非支配排序遗传算法II来生成多样且有效的触发输入,这些输入能够揭示模型之间的行为差异。DiffGAN采用两个自定义的适应度函数,侧重于多样性和发散性,以指导GAN输入空间的探索并识别模型输出之间的差异。通过有针对性地搜索这个空间,DiffGAN生成具有特定特征的输入,这些输入能够触发模型行为的差异。DiffGAN是黑色盒子的,使其能在更多情况下适用。我们在使用广泛使用的图像数据集训练的八个DNN模型对上评估了DiffGAN。结果表明,DiffGAN显著优于最新技术基线,在相同的预算内,生成了四倍多的触发输入,具有更大的多样性和有效性。此外,生成的输入提高了基于机器学习模型的选型机制的准确性,该机制根据输入特征选择性能最佳的模型,当使用替代模型时,它可以作为智能输出投票机制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)和非支配排序遗传算法II的差分测试方法(DiffGAN),用于对深度神经网络(DNN)模型进行行为差异测试。DiffGAN旨在生成能够揭示模型行为差异的触发输入,通过两个自定义的适应度函数(多样性和发散性)来指导GAN输入空间的探索。DiffGAN具有黑盒特性,适用于更多场景。在广泛使用的图像数据集上训练的八个DNN模型对的评估显示,DiffGAN显著优于现有技术,生成了更多触发输入,并提高了机器学习模型选择机制的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- Deep Neural Networks (DNNs)的可靠性保证是一个挑战,特别是在有限测试数据集的情况下。
- 差异测试通过生成测试输入来揭示DNN模型之间的差异,但现有方法存在局限性。
- DiffGAN是一种针对DNN模型的差分测试新方法,利用生成对抗网络(GAN)和非支配排序遗传算法II生成触发输入。
- DiffGAN具有黑盒特性,适用于更多场景。
- DiffGAN通过两个自定义的适应度函数(多样性和发散性)来指导GAN输入空间的探索,以发现模型行为差异。
- 与现有技术相比,DiffGAN生成的触发输入数量更多、更具多样性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图