⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
Text Embedded Swin-UMamba for DeepLesion Segmentation
Authors:Ruida Cheng, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Pritam Mukherjee, Benjamin Hou, Qingqing Zhu, Zhiyong Lu, Matthew McAuliffe, Ronald M. Summers
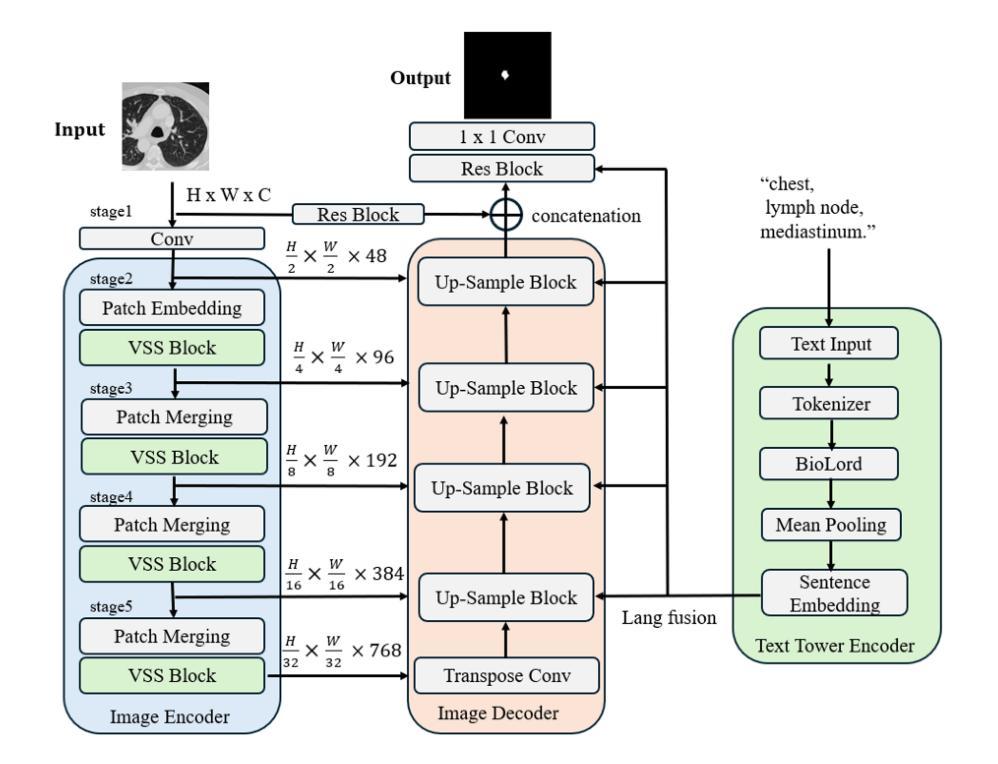
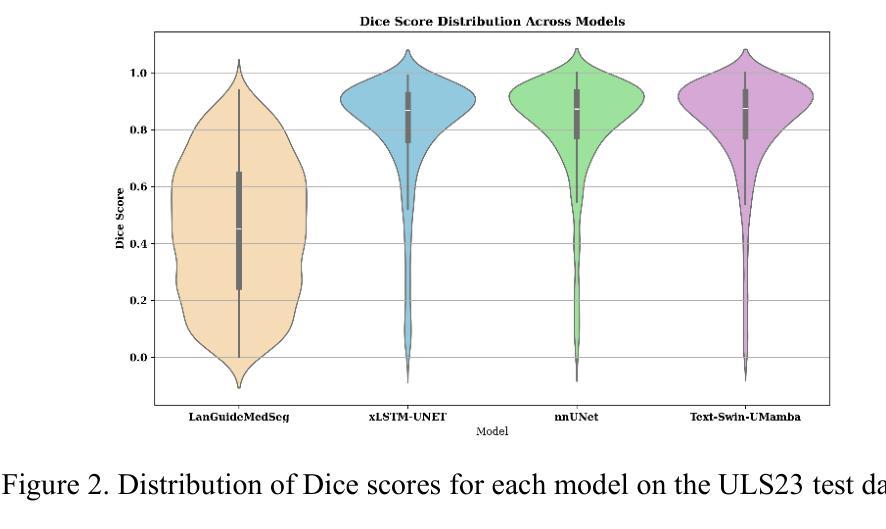
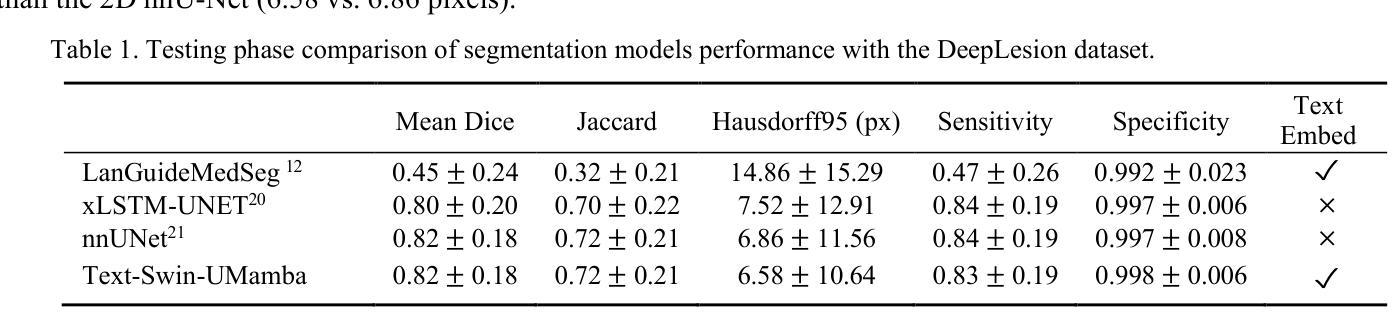
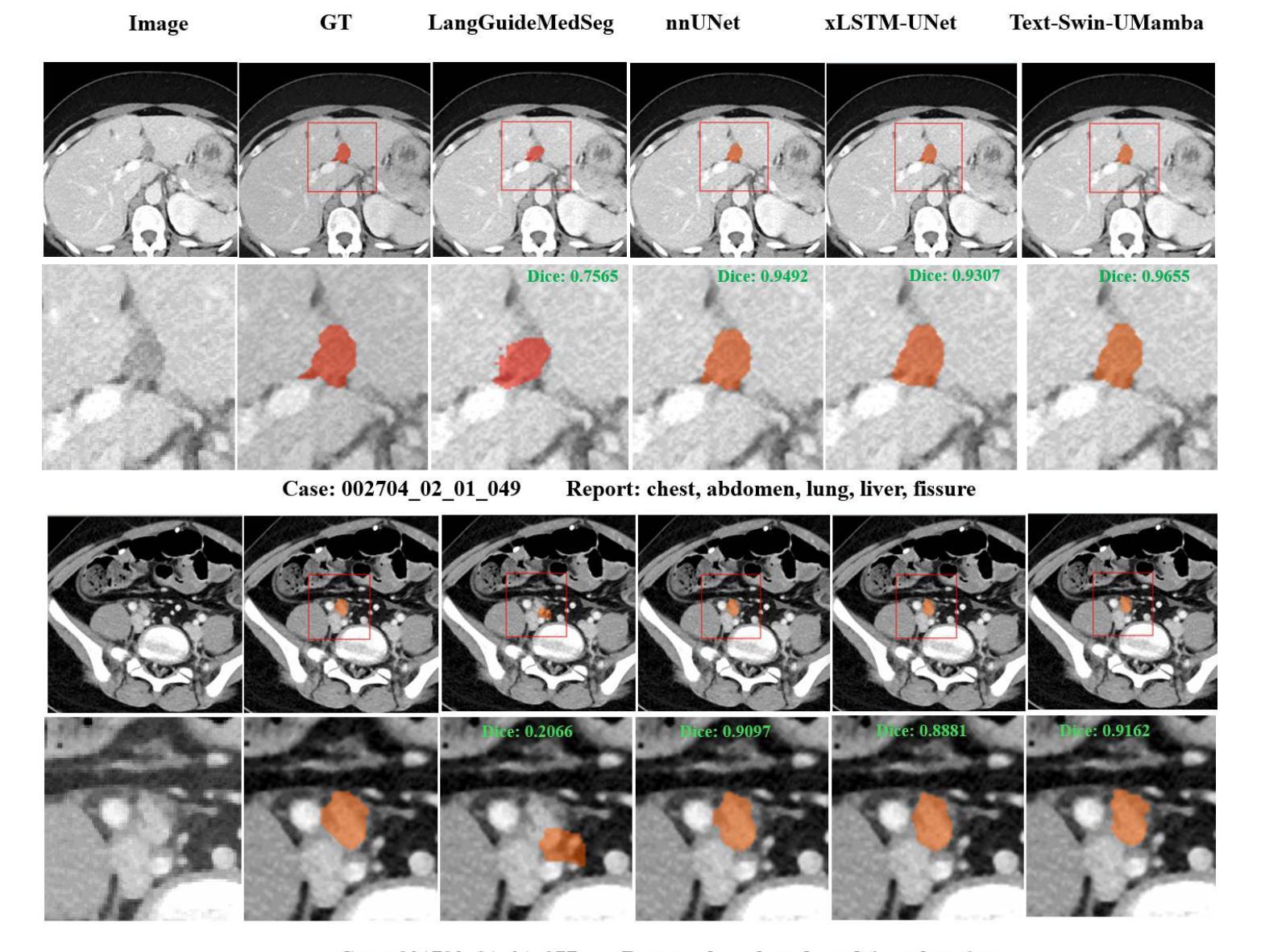
Segmentation of lesions on CT enables automatic measurement for clinical assessment of chronic diseases (e.g., lymphoma). Integrating large language models (LLMs) into the lesion segmentation workflow offers the potential to combine imaging features with descriptions of lesion characteristics from the radiology reports. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of integrating text into the Swin-UMamba architecture for the task of lesion segmentation. The publicly available ULS23 DeepLesion dataset was used along with short-form descriptions of the findings from the reports. On the test dataset, a high Dice Score of 82% and low Hausdorff distance of 6.58 (pixels) was obtained for lesion segmentation. The proposed Text-Swin-UMamba model outperformed prior approaches: 37% improvement over the LLM-driven LanGuideMedSeg model (p < 0.001),and surpassed the purely image-based xLSTM-UNet and nnUNet models by 1.74% and 0.22%, respectively. The dataset and code can be accessed at https://github.com/ruida/LLM-Swin-UMamba
对CT上的病灶进行分割,可实现慢性疾病的临床评估(例如淋巴瘤)的自动测量。将大型语言模型(LLM)集成到病灶分割工作流程中,可将图像特征与来自放射学报告的病灶特征描述相结合。在研究中,我们探讨了将文本集成到Swin-UMamba架构中进行病灶分割任务的可能性。使用公开可用的ULS23 DeepLesion数据集以及报告中发现结果的简短描述。在测试数据集上,获得了高达82%的Dice分数,Hausdorff距离低至6.58像素进行病灶分割。提出的Text-Swin-UMamba模型在以前的方法上具有出色的表现:与LLM驱动的LanGuideMedSeg模型相比,提高了37%(p <0.001),并且比纯图像基础的xLSTM-UNet和nnUNet模型分别高出1.74%和0.22%。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/ruida/LLM-Swin-UMamba访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究的摘要指出,通过在大规模语言模型的基础上,使用图像分析对慢性病变(如淋巴瘤)进行CT扫描中的病灶分割与临床评估研究具有可行性。本研究采用了Swin-UMamba架构并融入了文本信息,使用公开可用的ULS23 DeepLesion数据集和报告中的简短描述发现结果。在测试集上,该模型取得了较高的Dice系数(82%)和较低的Hausdorff距离(6.58像素),并显著优于其他模型。通过GitHub链接,公开了数据集和代码。该模型将有望为医学影像领域的精准分析开辟新的可能。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的主要观点与收获点:
- 研究旨在探讨集成文本信息到病灶分割工作流中的可行性,特别是使用大规模语言模型(LLMs)。
- 研究采用了Swin-UMamba架构并结合文本信息来处理CT图像中的病灶分割。
- 使用公开可用的ULS23 DeepLesion数据集以及报告中的简短描述作为辅助信息。
- 在测试集上取得了较高的Dice系数(82%)和低Hausdorff距离(6.58像素),表明模型在病灶分割任务上的良好性能。
- 该模型相较于其他方法(如LLM驱动的LanGuideMedSeg模型、纯图像基础的xLSTM-UNet和nnUNet模型)具有显著优势,实现了较高的性能提升。
- 数据集和代码可通过GitHub链接公开访问,为研究人员提供了便利的资源。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-Omics Analysis for Cancer Subtype Inference via Unrolling Graph Smoothness Priors
Authors:Jielong Lu, Zhihao Wu, Jiajun Yu, Jiajun Bu, Haishuai Wang
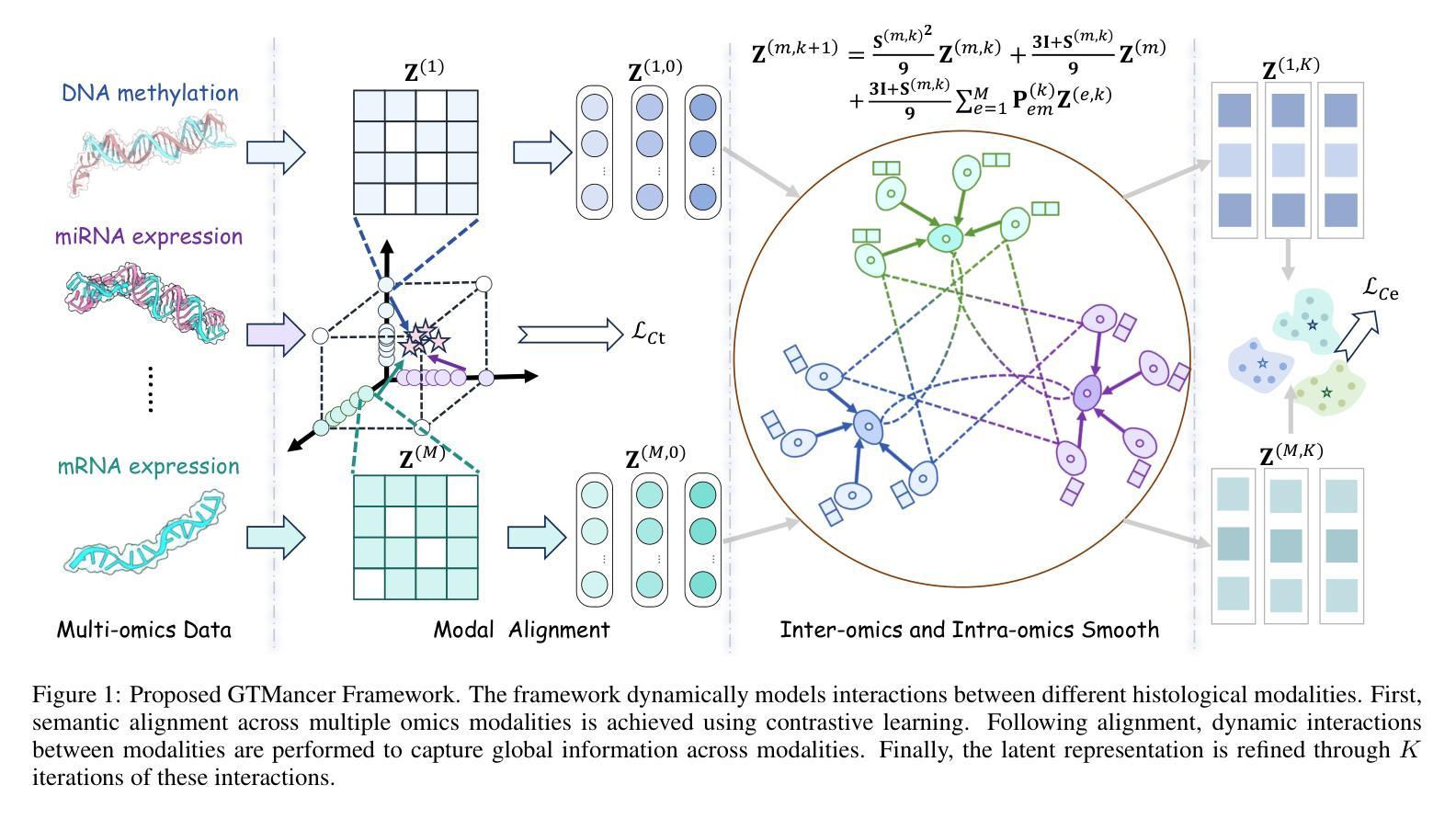
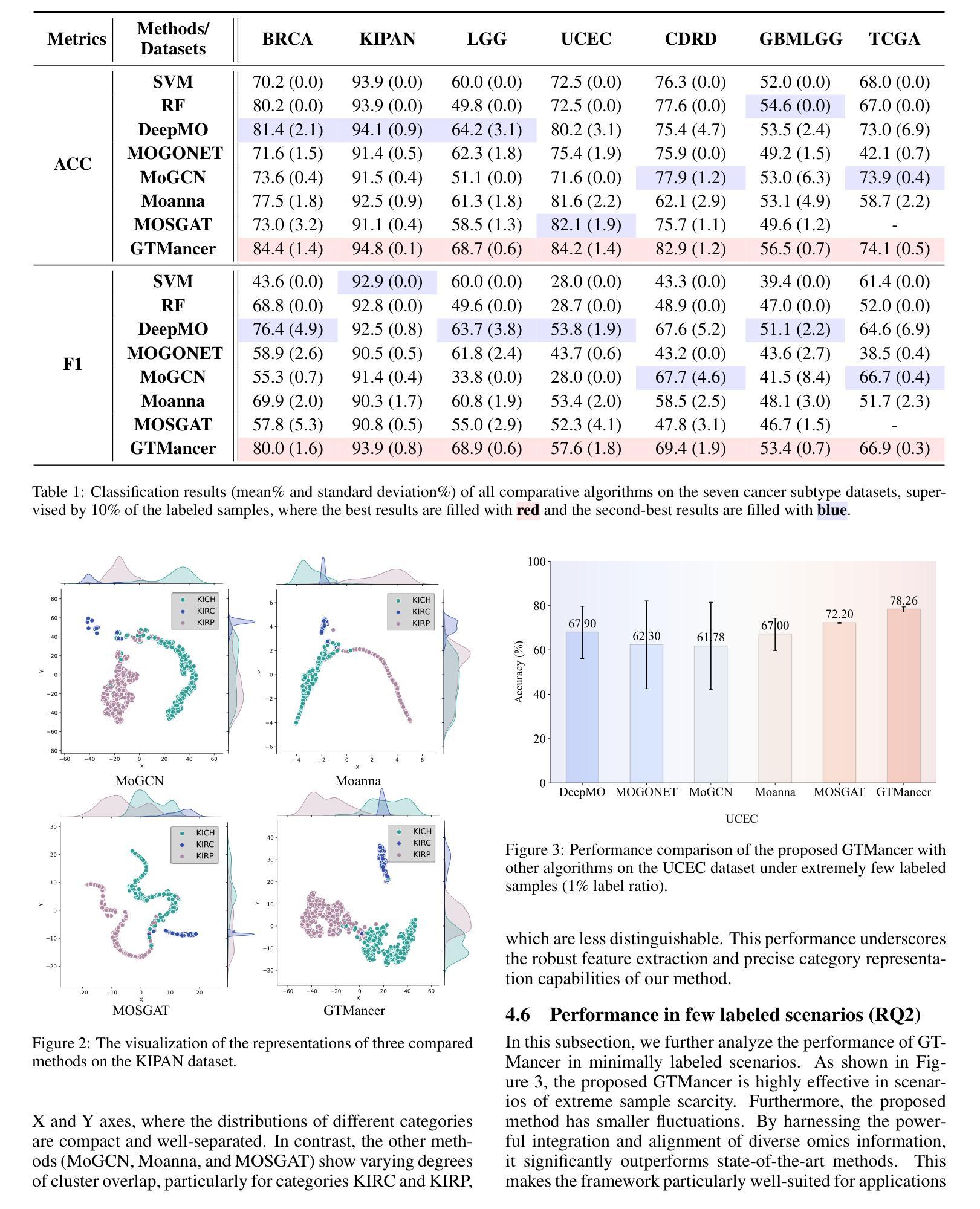
Integrating multi-omics datasets through data-driven analysis offers a comprehensive understanding of the complex biological processes underlying various diseases, particularly cancer. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have recently demonstrated remarkable ability to exploit relational structures in biological data, enabling advances in multi-omics integration for cancer subtype classification. Existing approaches often neglect the intricate coupling between heterogeneous omics, limiting their capacity to resolve subtle cancer subtype heterogeneity critical for precision oncology. To address these limitations, we propose a framework named Graph Transformer for Multi-omics Cancer Subtype Classification (GTMancer). This framework builds upon the GNN optimization problem and extends its application to complex multi-omics data. Specifically, our method leverages contrastive learning to embed multi-omics data into a unified semantic space. We unroll the multiplex graph optimization problem in that unified space and introduce dual sets of attention coefficients to capture structural graph priors both within and among multi-omics data. This approach enables global omics information to guide the refining of the representations of individual omics. Empirical experiments on seven real-world cancer datasets demonstrate that GTMancer outperforms existing state-of-the-art algorithms.
通过数据驱动分析整合多组学数据集,为我们全面理解各种疾病(特别是癌症)背后的复杂生物过程提供了途径。图神经网络(GNNs)最近显示出在生物数据中利用关系结构的显著能力,推动了多组学整合在癌症亚型分类方面的进展。现有方法往往忽视了不同组学之间的复杂耦合,限制了它们在解决对精确肿瘤学至关重要的癌症亚型细微异质性的能力。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一个名为“用于多组学癌症亚型分类的图转换器”(GTMancer)的框架。该框架建立在GNN优化问题的基础上,并将其应用扩展到复杂的多组学数据。具体来说,我们的方法利用对比学习将多组学数据嵌入到统一的语义空间中。我们在该统一空间中解开多重图优化问题,并引入双重注意力系数集,以捕获组内和组间多组学数据的结构图先验。这种方法使得全局组学信息能够指导单个组学表示的精化。在七个真实世界的癌症数据集上的实验表明,GTMancer优于现有的最先进算法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多组学数据集通过数据驱动分析整合,为理解各种疾病尤其是癌症的复杂生物过程提供了全面视角。图神经网络(GNNs)能够挖掘生物数据中的关系结构,因而在癌症亚型分类的多组学整合中取得了进展。然而,现有方法忽视了不同组学之间的复杂耦合,难以解决癌症亚型异质性的细微差异,这对于精准肿瘤学至关重要。为应对这些局限,我们提出了名为“多组学癌症亚型分类图转换器(GTMancer)”的框架。该框架建立在GNN优化问题的基础上,扩展至复杂的多组学数据应用。它通过对比学习将多组学数据嵌入统一的语义空间,解决多层图形优化问题,并引入双重注意力系数来捕捉组学内部和之间的结构图形先验信息。这使得全局组学信息能够指导单个组学表征的细化。在七个真实世界的癌症数据集上的实验表明,GTMancer优于现有最先进的算法。
Key Takeaways
- 多组学数据整合能提供对癌症等疾病的全面理解。
- 图神经网络(GNNs)在挖掘生物数据关系结构方面表现出强大能力,促进了癌症亚型分类的多组学整合。
- 现有方法忽略组学间的复杂耦合,难以捕捉癌症亚型异质性的细微差异。
- GTMancer框架旨在解决这一问题,通过嵌入统一的语义空间处理多组学数据。
- GTMancer结合对比学习和双重注意力系数,捕捉结构图形先验信息。
- GTMancer方法使得全局组学信息能指导单个组学表征的细化。
点此查看论文截图

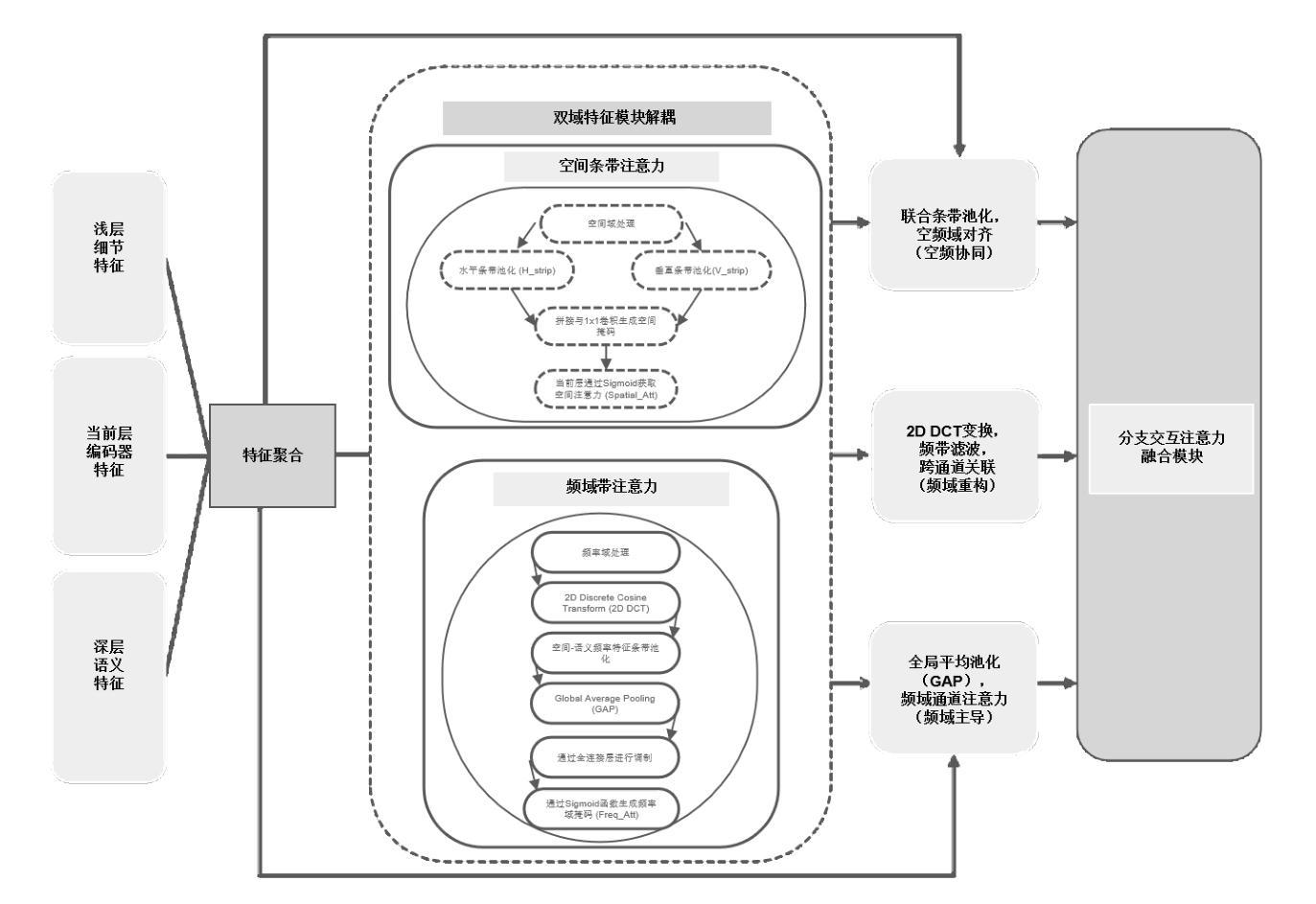
A Semantic Segmentation Algorithm for Pleural Effusion Based on DBIF-AUNet
Authors:Ruixiang Tang, Jianglong Qin, Mingda Zhang, Yan Song, Yi Wu, Wei Wu
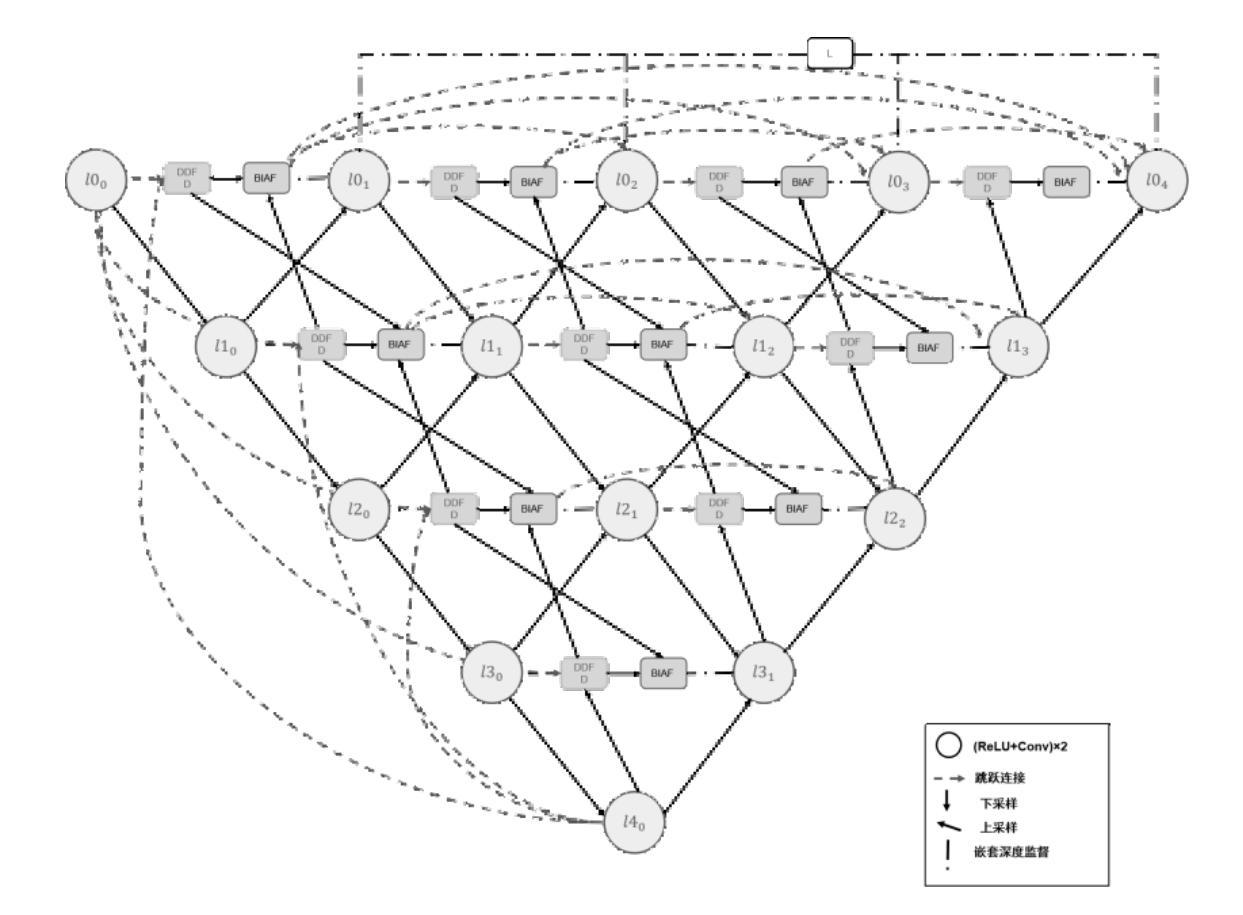
Pleural effusion semantic segmentation can significantly enhance the accuracy and timeliness of clinical diagnosis and treatment by precisely identifying disease severity and lesion areas. Currently, semantic segmentation of pleural effusion CT images faces multiple challenges. These include similar gray levels between effusion and surrounding tissues, blurred edges, and variable morphology. Existing methods often struggle with diverse image variations and complex edges, primarily because direct feature concatenation causes semantic gaps. To address these challenges, we propose the Dual-Branch Interactive Fusion Attention model (DBIF-AUNet). This model constructs a densely nested skip-connection network and innovatively refines the Dual-Domain Feature Disentanglement module (DDFD). The DDFD module orthogonally decouples the functions of dual-domain modules to achieve multi-scale feature complementarity and enhance characteristics at different levels. Concurrently, we design a Branch Interaction Attention Fusion module (BIAF) that works synergistically with the DDFD. This module dynamically weights and fuses global, local, and frequency band features, thereby improving segmentation robustness. Furthermore, we implement a nested deep supervision mechanism with hierarchical adaptive hybrid loss to effectively address class imbalance. Through validation on 1,622 pleural effusion CT images from Southwest Hospital, DBIF-AUNet achieved IoU and Dice scores of 80.1% and 89.0% respectively. These results outperform state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models U-Net++ and Swin-UNet by 5.7%/2.7% and 2.2%/1.5% respectively, demonstrating significant optimization in segmentation accuracy for complex pleural effusion CT images.
胸膜积水的语义分割能够精确识别疾病严重程度和病变区域,从而显著提高临床诊断和治疗准确性和及时性。目前,胸膜积水CT图像的语义分割面临多重挑战。这些挑战包括积水与周围组织之间的灰度相似度、边缘模糊以及形态变化多样。现有方法往往难以应对多样的图像变化和复杂的边缘,主要是因为直接特征拼接会导致语义鸿沟。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了双分支交互融合注意力模型(DBIF-AUNet)。该模型构建了一个密集嵌套跳跃连接网络,并创新地改进了双域特征分解模块(DDFD)。DDFD模块通过正交解耦双域模块的功能,实现多尺度特征互补,并增强不同级别的特征。同时,我们设计了一个分支交互注意力融合模块(BIAF),它与DDFD协同工作。该模块动态加权并融合全局、局部和频带特征,从而提高分割稳健性。此外,我们采用了一种具有分层自适应混合损失的嵌套深度监督机制,以有效解决类别不平衡问题。通过对来自西南医院的1622张胸膜积水CT图像进行验证,DBIF-AUNet的IoU和Dice得分分别为80.1%和89.0%,分别优于先进的医学图像分割模型U-Net++和Swin-UNet的5.7%/2.7%和2.2%/1.5%。这证明了DBIF-AUNet在复杂胸膜积水CT图像分割精度上的显著优化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables
Summary
基于双分支交互融合注意力模型的胸膜腔积液CT图像语义分割技术能有效提升临床诊断和治疗准确性和时效性,通过精确识别病变严重程度和区域。该技术解决了包括灰度相似、边缘模糊和形态多变等挑战,通过构建密集嵌套跳跃连接网络和改良的双域特征分解模块,实现了多尺度特征互补和各级特征增强。同时,设计分支交互注意力融合模块,动态加权融合全局、局部和频带特征,提高分割稳健性。实施嵌套深度监督机制,结合分层自适应混合损失,有效应对类别不平衡问题。在西南医院的1622张胸膜腔积液CT图像验证中,DBIF-AUNet取得了交并比和Dice系数分别为80.1%和89.0%的结果,较其他先进医学图像分割模型有显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 胸膜腔积液语义分割对临床诊断和治疗的重要性:能精确识别病变程度和区域,提高诊断和治疗的准确性和时效性。
- 胸膜腔积液CT图像语义分割所面临的挑战:包括灰度相似、边缘模糊和形态多变等。
- DBIF-AUNet模型的主要创新点:构建密集嵌套网络,改良双域特征分解模块,实现多尺度特征互补。
- 分支交互注意力融合模块的作用:动态加权融合全局、局部和频带特征,提高分割稳健性。
- 嵌套深度监督机制和分层自适应混合损失的应用:有效应对类别不平衡问题。
- DBIF-AUNet模型在胸膜腔积液CT图像分割上的优秀表现:较其他先进模型有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

Towards MR-Based Trochleoplasty Planning
Authors:Michael Wehrli, Alicia Durrer, Paul Friedrich, Sidaty El Hadramy, Edwin Li, Luana Brahaj, Carol C. Hasler, Philippe C. Cattin
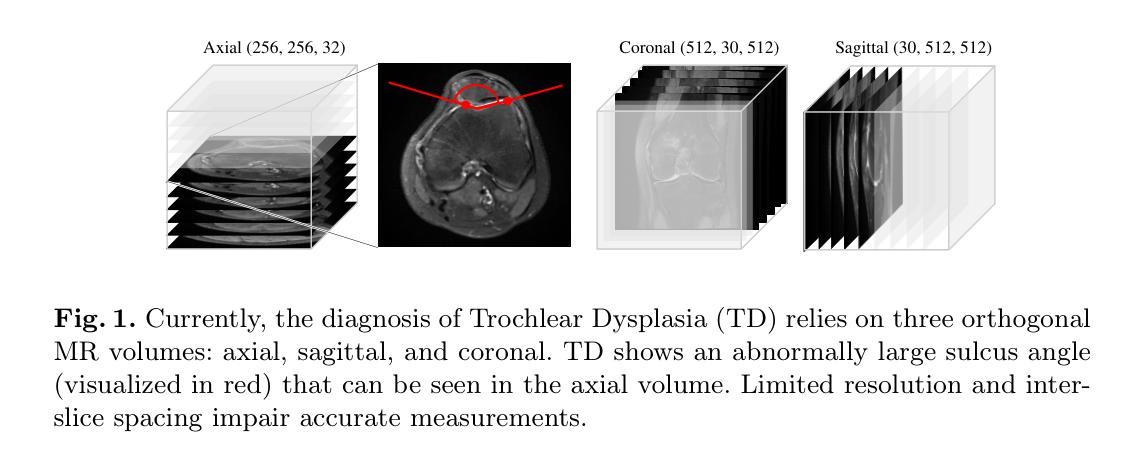
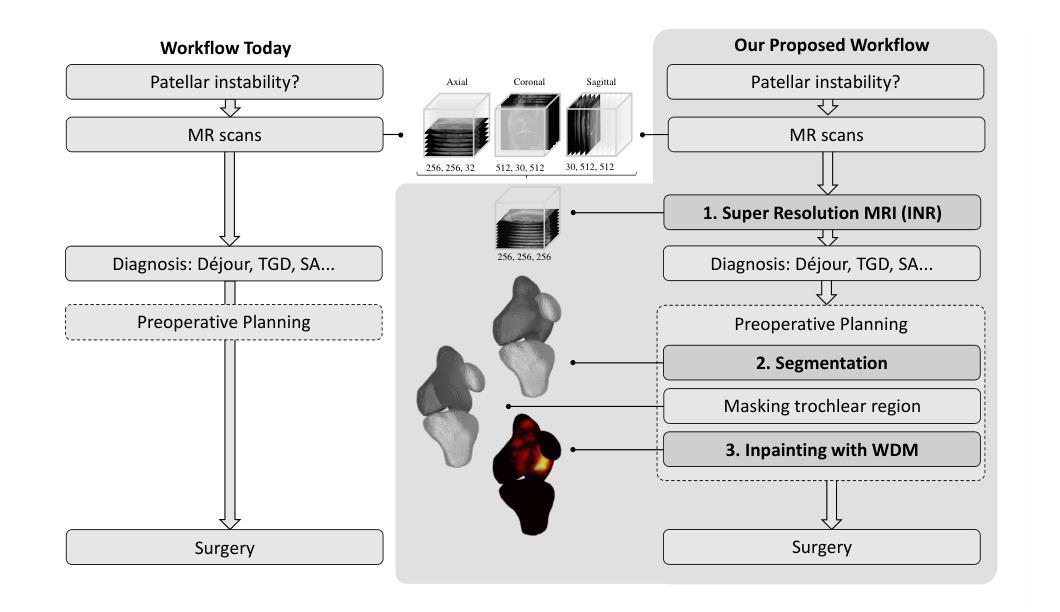
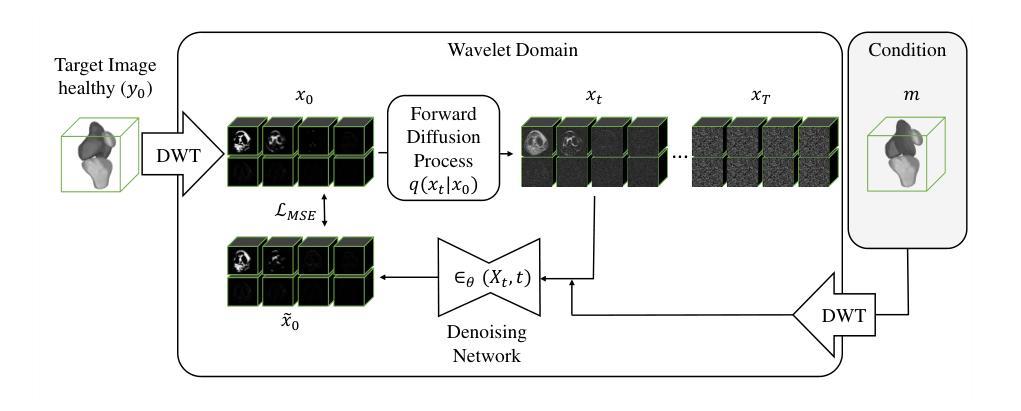
To treat Trochlear Dysplasia (TD), current approaches rely mainly on low-resolution clinical Magnetic Resonance (MR) scans and surgical intuition. The surgeries are planned based on surgeons experience, have limited adoption of minimally invasive techniques, and lead to inconsistent outcomes. We propose a pipeline that generates super-resolved, patient-specific 3D pseudo-healthy target morphologies from conventional clinical MR scans. First, we compute an isotropic super-resolved MR volume using an Implicit Neural Representation (INR). Next, we segment femur, tibia, patella, and fibula with a multi-label custom-trained network. Finally, we train a Wavelet Diffusion Model (WDM) to generate pseudo-healthy target morphologies of the trochlear region. In contrast to prior work producing pseudo-healthy low-resolution 3D MR images, our approach enables the generation of sub-millimeter resolved 3D shapes compatible for pre- and intraoperative use. These can serve as preoperative blueprints for reshaping the femoral groove while preserving the native patella articulation. Furthermore, and in contrast to other work, we do not require a CT for our pipeline - reducing the amount of radiation. We evaluated our approach on 25 TD patients and could show that our target morphologies significantly improve the sulcus angle (SA) and trochlear groove depth (TGD). The code and interactive visualization are available at https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/.
针对Trochlear Dysplasia(TD)的治疗,目前的方法主要依赖于低分辨率的临床磁共振(MR)扫描和手术直觉。手术计划基于外科医生经验,较少采用微创技术,且手术结果不一致。我们提出了一种流程,该流程可从常规临床MR扫描生成超分辨率的、针对患者特定的3D伪健康目标形态。首先,我们使用隐式神经表示(INR)计算各向同性超分辨率MR体积。接下来,我们使用多标签自定义训练网络对股骨、胫骨、髌骨和腓骨进行分割。最后,我们训练小波扩散模型(WDM),以生成槽状区域的伪健康目标形态。与之前生成伪健康低分辨率3D MR图像的工作相比,我们的方法能够生成用于术前和术中的亚毫米分辨率的3D形态。这些可以作为重塑股骨槽同时保留原生髌骨关节的术前蓝图。此外,与其他工作相比,我们的流程不需要CT,减少了辐射量。我们在2 TND患者上对进行了评估我们的方法可以改善槽角(SA)和槽深(TGD)。代码和交互式可视化内容可在https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI COLAS Workshop 2025. Code: https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/
Summary
本文提出一种治疗Trochlear Dysplasia(TD)的新方法,通过生成超分辨率的3D伪健康目标形态来提高手术效果。该方法利用隐式神经表示(INR)计算超分辨率MR体积,并通过多标签定制网络对股骨、胫骨、膝盖骨和腓骨进行分割。最后通过小波扩散模型(WDM)生成伪健康的目標形态。这种方法可产生亚毫米分辨率的3D形状,用于术前和术中指导手术操作。并且相比以往的方法,本方法不需要CT扫描,减少了辐射暴露。在25名TD患者上的实验表明,该方法能显著改善槽角(SA)和股骨沟深度(TGD)。
Key Takeaways
- 当前治疗Trochlear Dysplasia主要依赖低分辨率MR扫描和手术直觉,手术效果不一致。
- 提出一种生成超分辨率、病人特定的3D伪健康目标形态的管道。
- 利用隐式神经表示(INR)计算超分辨率MR体积。
- 通过多标签定制网络对骨骼进行分割。
- 采用小波扩散模型(WDM)生成伪健康的目标形态。
- 该方法可产生亚毫米分辨率的3D形状,适用于术前和术中指导。
点此查看论文截图

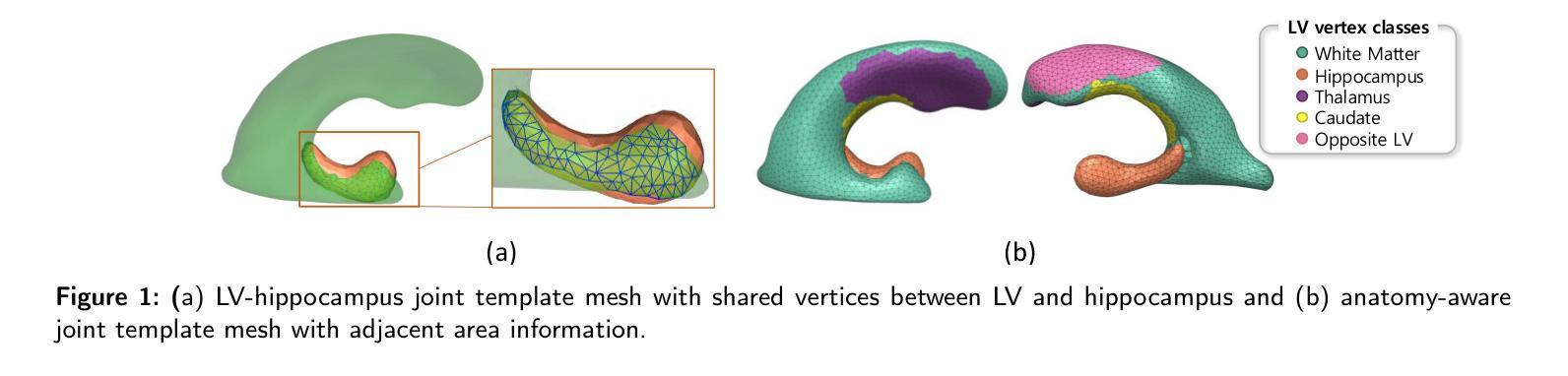
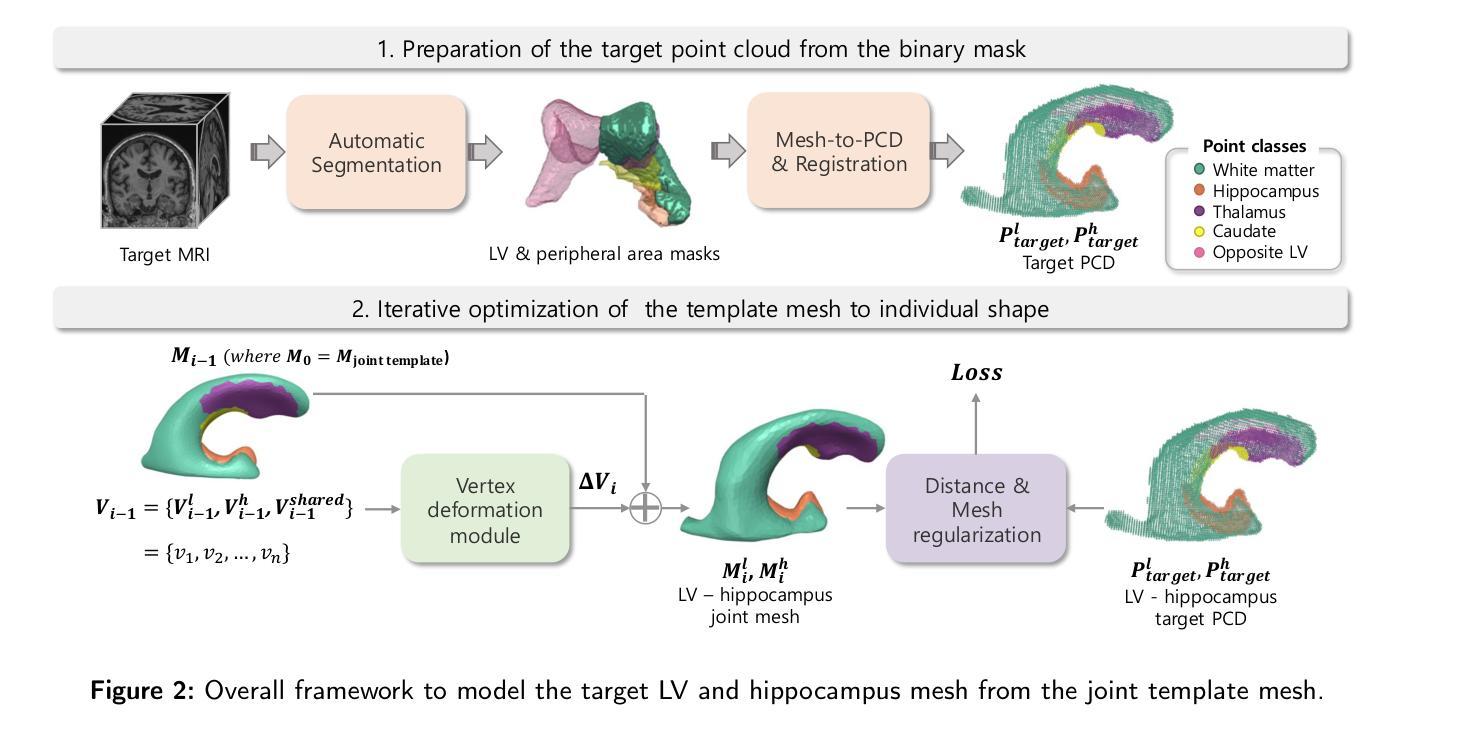
LV-Net: Anatomy-aware lateral ventricle shape modeling with a case study on Alzheimer’s disease, the Australian Imaging Biomarkers and Lifestyle flagship study of ageing
Authors:Wonjung Park, Suhyun Ahn, Jinah Park
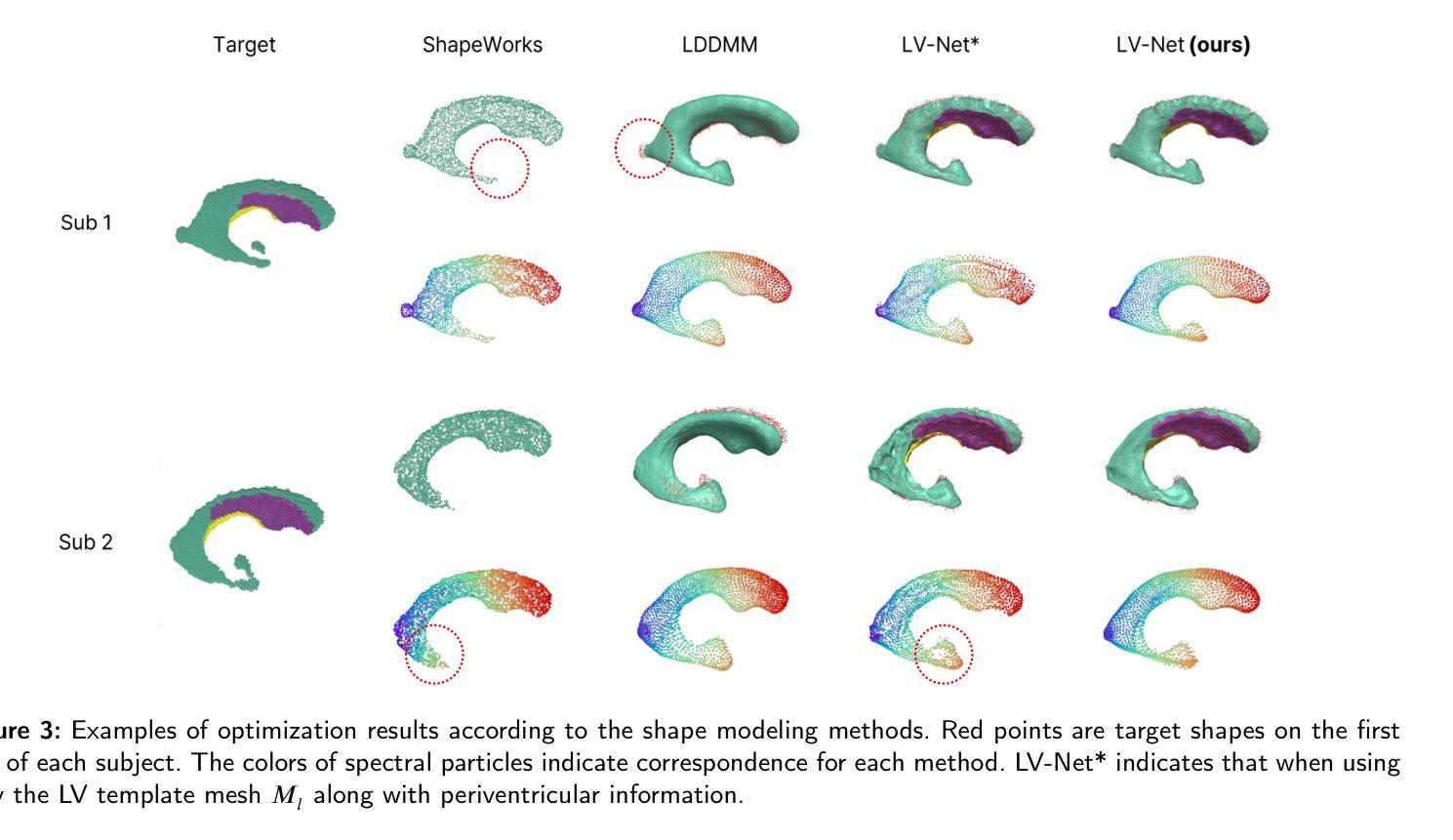
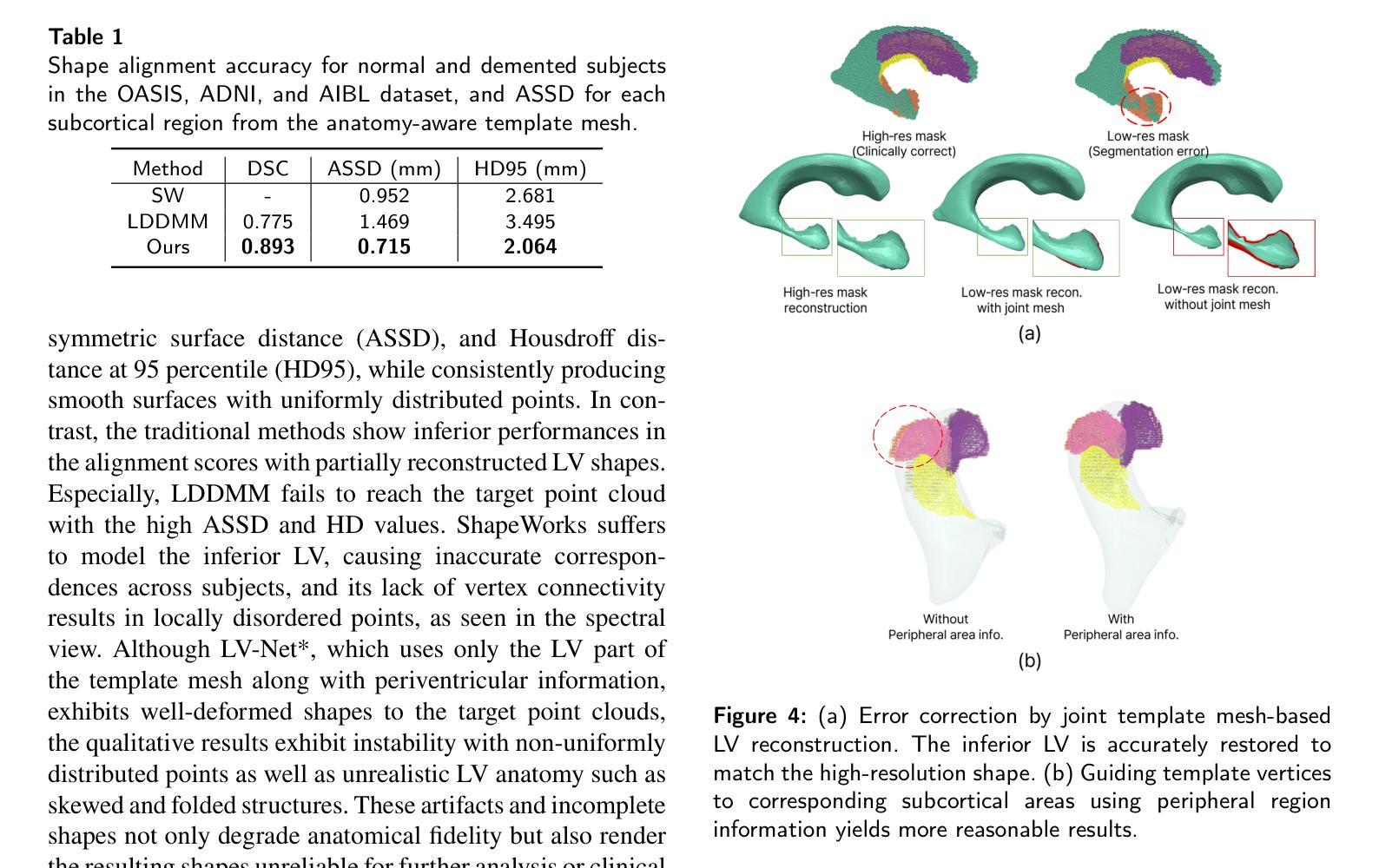
Lateral ventricle (LV) shape analysis holds promise as a biomarker for neurological diseases; however, challenges remain due to substantial shape variability across individuals and segmentation difficulties arising from limited MRI resolution. We introduce LV-Net, a novel framework for producing individualized 3D LV meshes from brain MRI by deforming an anatomy-aware joint LV-hippocampus template mesh. By incorporating anatomical relationships embedded within the joint template, LV-Net reduces boundary segmentation artifacts and improves reconstruction robustness. In addition, by classifying the vertices of the template mesh based on their anatomical adjacency, our method enhances point correspondence across subjects, leading to more accurate LV shape statistics. We demonstrate that LV-Net achieves superior reconstruction accuracy, even in the presence of segmentation imperfections, and delivers more reliable shape descriptors across diverse datasets. Finally, we apply LV-Net to Alzheimer’s disease analysis, identifying LV subregions that show significantly associations with the disease relative to cognitively normal controls. The codes for LV shape modeling are available at https://github.com/PWonjung/LV_Shape_Modeling.
侧脑室(LV)形态分析作为神经疾病的生物标志物具有巨大潜力。然而,由于个体间存在的明显形态差异以及MRI分辨率限制导致的分割困难,仍存在挑战。我们引入了LV-Net,这是一个新型框架,通过变形一个了解结构的联合LV-海马模板网格,从脑部MRI生成个性化的3D LV网格。通过融入联合模板内的结构关系,LV-Net减少了边界分割伪影,提高了重建的稳健性。此外,通过对模板网格的顶点根据其结构邻接进行分类,我们的方法提高了跨主体的点对应关系,从而得到更准确的LV形态统计。我们证明,即使在存在分割缺陷的情况下,LV-Net也能实现更高的重建精度,并在各种数据集中提供更可靠的形状描述符。最后,我们将LV-Net应用于阿尔茨海默病分析,识别出与认知正常对照相比,与疾病有显著关联的LV子区域。LV形态建模的代码可在https://github.com/PWonjung/LV_Shape_Modeling找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于医学图像的三维建模技术,LV-Net框架通过个性化地构建侧脑室(LV)的3D网格,为神经性疾病研究提供了新的视角。该框架采用解剖结构感知的联合LV-海马模板网格,通过融入解剖关系,提高了重建的稳健性并降低了边界分割的误差。LV-Net提高了顶点对应的准确性,生成更精确的LV形状统计信息。此外,LV-Net在分割不完美的情况下仍具有出色的重建精度,为不同数据集提供了更可靠的形状描述。最后,LV-Net在阿尔茨海默病分析中的应用揭示了与疾病相关的LV子区域。
Key Takeaways
- LV-Net是一个基于医学图像的三维建模框架,可以个性化地构建侧脑室(LV)的3D网格。
- 该框架通过采用解剖结构感知的联合LV-海马模板网格,提高了重建的稳健性。
- LV-Net通过融入解剖关系,降低了边界分割的误差和减少分割困难的问题。
- 该方法提高了网格顶点对应的准确性,有助于生成更精确的LV形状统计信息。
- LV-Net即使在分割不完美的情况下也具有出色的重建精度,能够提供可靠的形状描述。
- LV-Net在不同数据集中表现优越,能够为神经性疾病研究提供有价值的信息。
点此查看论文截图

Few-Shot Deployment of Pretrained MRI Transformers in Brain Imaging Tasks
Authors:Mengyu Li, Guoyao Shen, Chad W. Farris, Xin Zhang
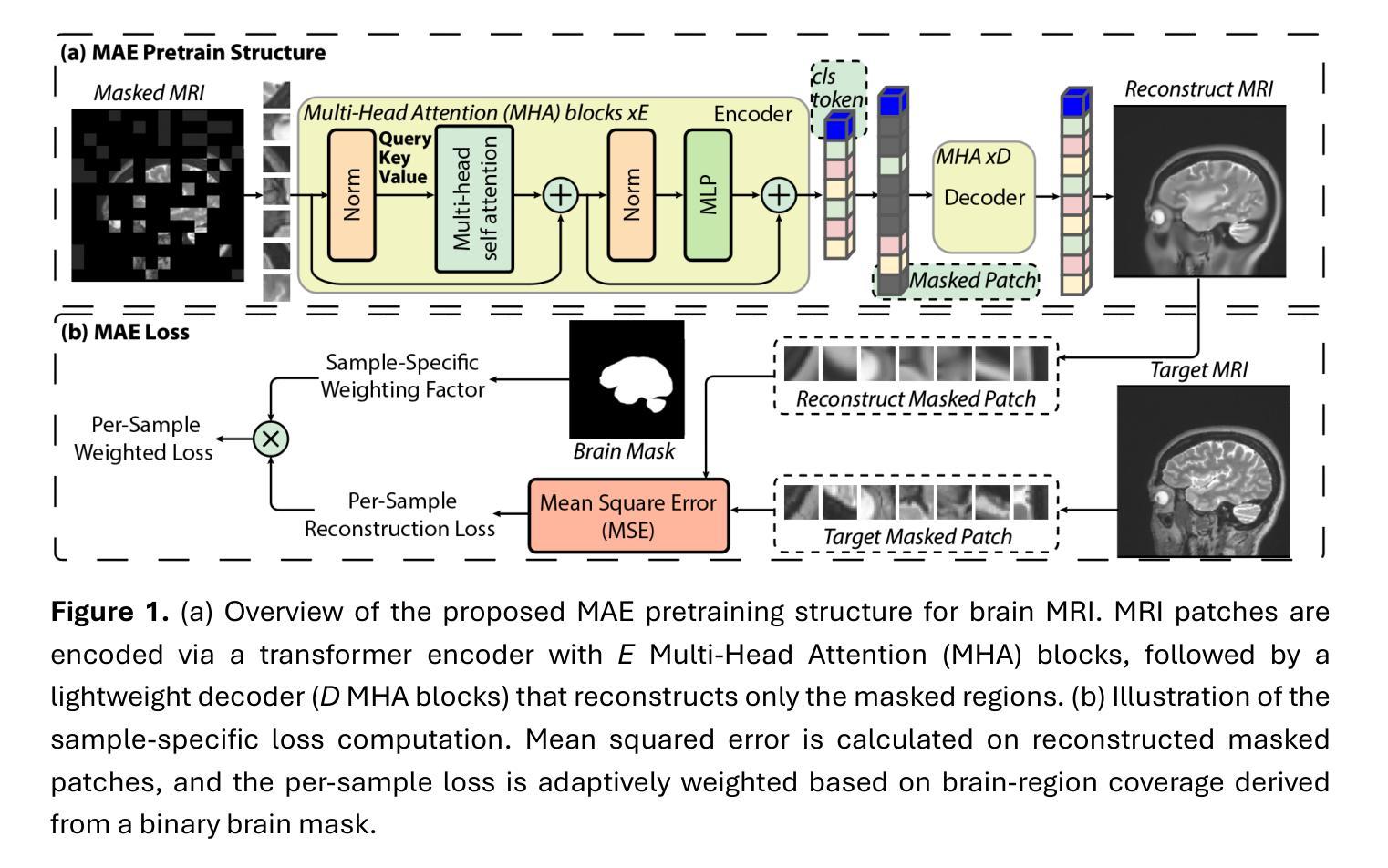
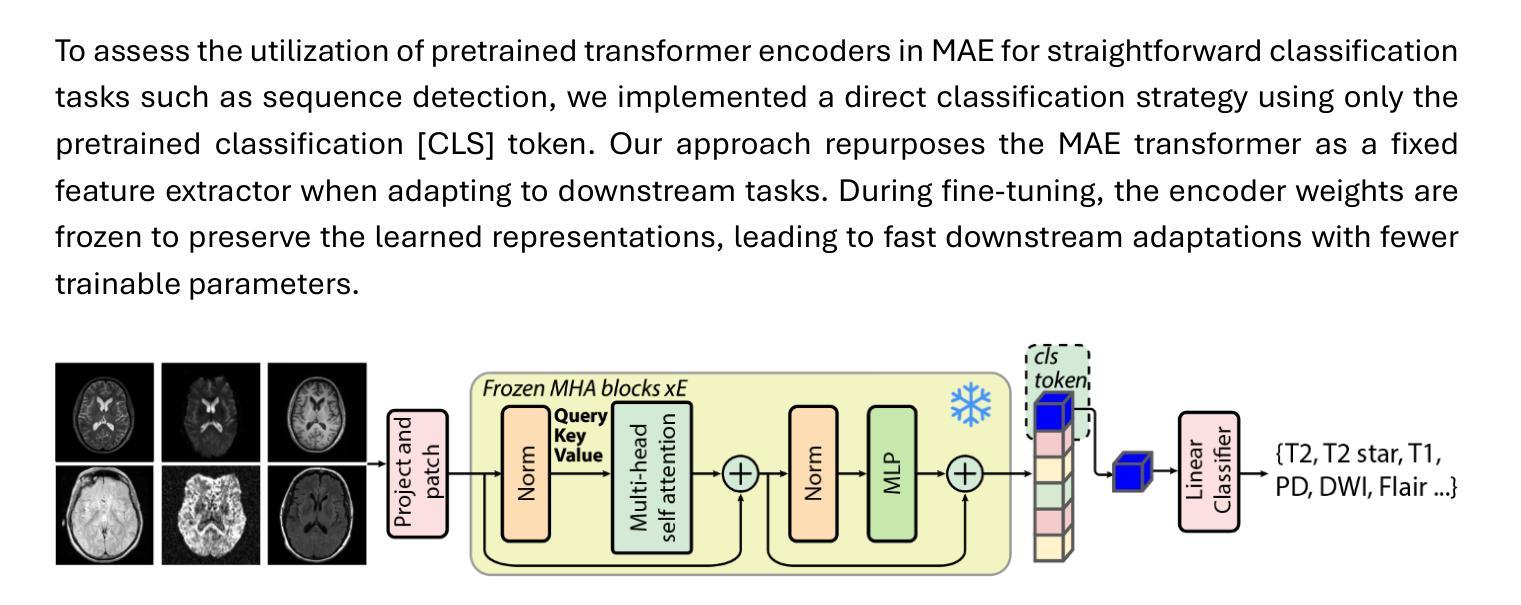
Machine learning using transformers has shown great potential in medical imaging, but its real-world applicability remains limited due to the scarcity of annotated data. In this study, we propose a practical framework for the few-shot deployment of pretrained MRI transformers in diverse brain imaging tasks. By utilizing the Masked Autoencoder (MAE) pretraining strategy on a large-scale, multi-cohort brain MRI dataset comprising over 31 million slices, we obtain highly transferable latent representations that generalize well across tasks and datasets. For high-level tasks such as classification, a frozen MAE encoder combined with a lightweight linear head achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in MRI sequence identification with minimal supervision. For low-level tasks such as segmentation, we propose MAE-FUnet, a hybrid architecture that fuses multiscale CNN features with pretrained MAE embeddings. This model consistently outperforms other strong baselines in both skull stripping and multi-class anatomical segmentation under data-limited conditions. With extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations, our framework demonstrates efficiency, stability, and scalability, suggesting its suitability for low-resource clinical environments and broader neuroimaging applications.
在医学成像领域,利用变压器进行机器学习已显示出巨大潜力,但由于缺乏标注数据,其在实际世界中的适用性仍然有限。本研究提出了一个实用的框架,用于在多种脑成像任务中部署少量的预训练MRI变压器。通过在一个大规模、多队列的脑MRI数据集(包含超过3100万张切片)上利用Masked Autoencoder(MAE)的预训练策略,我们获得了高度可迁移的潜在表示,这些表示在任务和数据集之间具有很好的通用性。对于高级任务,如分类,使用冻结的MAE编码器结合轻量级的线性头,可以在极少的监督下实现MRI序列识别的最新准确性。对于低级任务,如分割,我们提出了MAE-FUnet,这是一种混合架构,融合了多尺度CNN特征与预训练的MAE嵌入。在数据有限的情况下,该模型在颅骨剥离和多类解剖分割方面都始终优于其他强大的基线。通过广泛的定量和定性评估,我们的框架证明了其效率、稳定性和可扩展性,表明它适用于资源有限的临床环境和更广泛的神经影像应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables
摘要
医学成像中机器学习利用转换器展示巨大潜力,但由于缺乏标注数据,其实用性受限。本研究提出一种实用框架,用于在少量样本下部署预训练的MRI转换器,用于多种脑成像任务。利用大规模多队列脑MRI数据集(超过31百万切片)的Masked Autoencoder(MAE)预训练策略,我们获得高度可迁移的潜在表示,可在任务和数据集之间良好地通用化。对于高级任务如分类,冻结的MAE编码器结合轻量级线性头实现了MRI序列识别的最新准确性,监督需求极少。对于低级任务如分割,我们提出MAE-FUnet混合架构,它将多尺度CNN特征与预训练的MAE嵌入相结合。该模型在数据有限的情况下,在颅骨剥离和多类解剖分割方面均优于其他强大的基线模型。通过广泛的定量和定性评估,我们的框架展现出高效性、稳定性和可扩展性,适用于资源有限的临床环境和更广泛的神经成像应用。
关键见解
- 机器学习在医学成像中使用转换器具有巨大潜力,但数据缺乏标注限制了其实际应用。
- 提出了一种利用少量数据样本的实用框架,用于部署预训练的MRI转换器以执行多种脑成像任务。
- 使用Masked Autoencoder(MAE)预训练策略在大型多队列脑MRI数据集上获得高度可迁移的潜在表示。
- 在MRI序列分类等高级任务上实现了最新准确性水平,使用冻结的MAE编码器和轻量级线性头,监督需求极低。
- 对于分割等低级任务,提出了MAE-FUnet混合架构,结合了多尺度CNN特征和预训练的MAE嵌入。
- 在数据有限的情况下,该模型在颅骨剥离和多类解剖分割方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

MAISI-v2: Accelerated 3D High-Resolution Medical Image Synthesis with Rectified Flow and Region-specific Contrastive Loss
Authors:Can Zhao, Pengfei Guo, Dong Yang, Yucheng Tang, Yufan He, Benjamin Simon, Mason Belue, Stephanie Harmon, Baris Turkbey, Daguang Xu
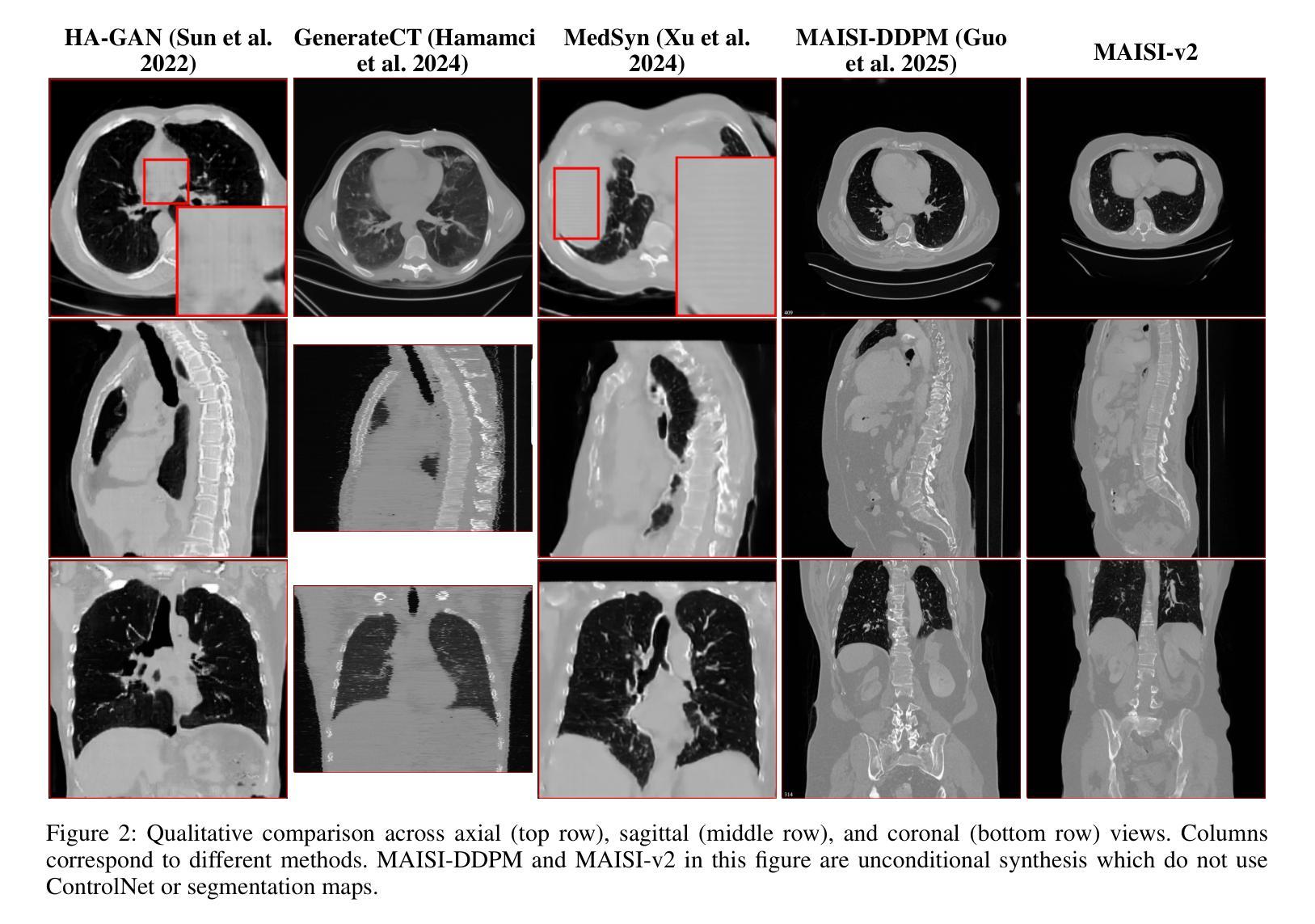
Medical image synthesis is an important topic for both clinical and research applications. Recently, diffusion models have become a leading approach in this area. Despite their strengths, many existing methods struggle with (1) limited generalizability that only work for specific body regions or voxel spacings, (2) slow inference, which is a common issue for diffusion models, and (3) weak alignment with input conditions, which is a critical issue for medical imaging. MAISI, a previously proposed framework, addresses generalizability issues but still suffers from slow inference and limited condition consistency. In this work, we present MAISI-v2, the first accelerated 3D medical image synthesis framework that integrates rectified flow to enable fast and high quality generation. To further enhance condition fidelity, we introduce a novel region-specific contrastive loss to enhance the sensitivity to region of interest. Our experiments show that MAISI-v2 can achieve SOTA image quality with $33 \times$ acceleration for latent diffusion model. We also conducted a downstream segmentation experiment to show that the synthetic images can be used for data augmentation. We release our code, training details, model weights, and a GUI demo to facilitate reproducibility and promote further development within the community.
医学图像合成在临床和研究应用中都是一个重要的主题。最近,扩散模型已成为该领域的主流方法。尽管它们具有优势,但许多现有方法仍然面临(1)通用性有限,仅适用于特定部位或体素间距;(2)推理速度慢,这是扩散模型的常见问题;(3)与输入条件对齐性差,这对医学影像来说是关键问题。之前提出的MAISI框架解决了通用性问题,但仍然存在推理速度慢和条件一致性有限的问题。在这项工作中,我们推出了MAISI-v2,这是第一个集成的加速3D医学图像合成框架,通过采用修正流来实现快速高质量生成。为了进一步提高条件保真度,我们引入了一种新型区域特定对比损失,以提高对感兴趣区域的敏感性。我们的实验表明,MAISI-v2可以在潜在扩散模型上实现$33 \times$的加速,同时达到最新图像质量。我们还进行了下游分割实验,以证明合成图像可用于数据增强。我们公开了代码、训练细节、模型权重和GUI演示,以促进社区内的可重复性和进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了医学图像合成的新方法MAISI-v2,它是加速的3D医学图像合成框架,通过整合修正流实现快速和高质生成。为解决通用性和条件一致性问题,引入区域特定对比损失以增强感兴趣区域的敏感性。实验显示,MAISI-v2能提高潜在扩散模型的图像质量,达到$33 \times$加速效果,且合成的图像可用于数据增强。
要点
- 医学图像合成在临床和研究应用中的重要性。
- 扩散模型在医学图像合成中的主导地位。
- 现有方法存在的局限性,如有限通用性、推理速度慢和条件一致性差。
- MAISI-v2框架的提出,解决了通用性问题,实现了快速高质量生成。
- 通过引入区域特定对比损失,增强对感兴趣区域的敏感性。
- 实验结果显示MAISI-v2具有优异的图像质量和加速效果。
- 合成的图像可用于数据增强,并公开了代码、训练细节、模型权重和GUI演示,以促进社区内的可重复性和进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图


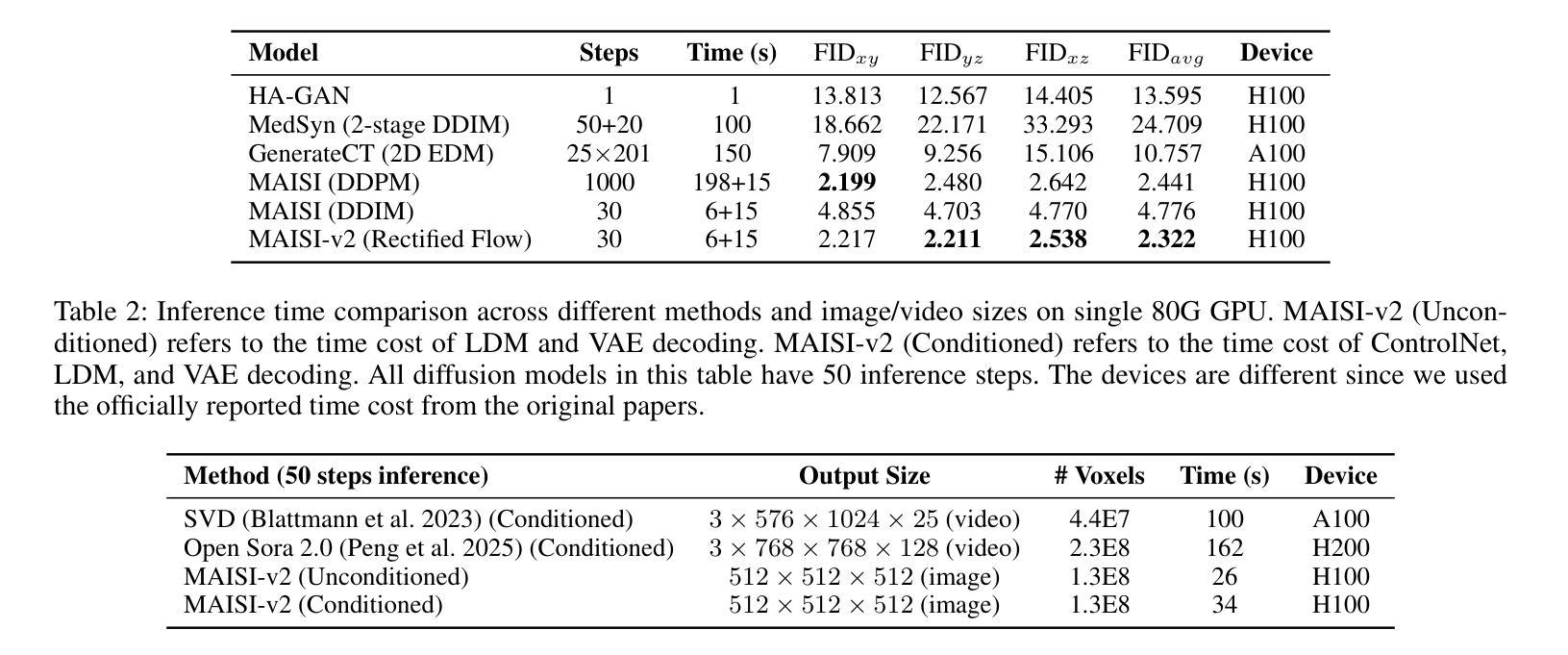
SiCmiR Atlas: Single-Cell miRNA Landscapes Reveals Hub-miRNA and Network Signatures in Human Cancers
Authors:Xiao-Xuan Cai, Jing-Shan Liao, Jia-Jun Ma, Yu-Xuan Pang, Yi-Gang Chen, Yang-Chi-Dung Lin, Yi-Dan Chen, Xin Cao, Yi-Cheng Zhang, Tao-Sheng Xu, Tzong-Yi Lee, Hsi-Yuan Huang, Hsien-Da Huang
microRNA are pivotal post-transcriptional regulators whose single-cell behavior has remained largely inaccessible owing to technical barriers in single-cell small-RNA profiling. We present SiCmiR, a two-layer neural network that predicts miRNA expression profile from only 977 LINCS L1000 landmark genes reducing sensitivity to dropout of single-cell RNA-seq data. Proof-of-concept analyses illustrate how SiCmiR can uncover candidate hub-miRNAs in bulk-seq cell lines and hepatocellular carcinoma, scRNA-seq pancreatic ductal carcinoma and ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma and extracellular-vesicle-mediated crosstalk in glioblastoma. Trained on 6462 TCGA paired miRNA-mRNA samples, SiCmiR attains state-of-the-art accuracy on held-out cancers and generalizes to unseen cancer types, drug perturbations and scRNA-seq. We next constructed SiCmiR-Atlas, containing 632 public datasets, 9.36 million cells, 726 cell types, which is the first dedicated database of single-cell mature miRNA expression–providing interactive visualization, biomarker identification and cell-type-resolved miRNA-target networks. SiCmiR transforms bulk-derived statistical power into a single-cell view of miRNA biology and provides a community resource SiCmiR Atlas for biomarker discovery. SiCmiR Atlas is avilable at https://awi.cuhk.edu.cn/~SiCmiR/.
microRNA是关键的转录后调控因子,由于其单细胞行为的特点,在单细胞小RNA图谱分析中仍存在较大的技术障碍,因此我们对单细胞RNA测序数据的丢失具有高度的敏感性。我们推出了SiCmiR,这是一种两层神经网络,它仅从977个LINCS L1000标志性基因预测miRNA表达图谱,降低了对单细胞RNA测序数据丢失的敏感性。概念验证分析说明了SiCmiR如何能在大规模测序细胞株、肝细胞癌、胰腺导管癌和ACTH分泌垂体腺瘤以及胶质母细胞瘤的胞外囊泡介导的串话中揭示候选的枢纽miRNA。SiCmiR在6462个TCGA配对miRNA-mRNA样本上进行训练,对未包含的癌症达到了最先进的准确性,并可推广到未见过的癌症类型、药物干扰和单细胞RNA测序。接下来,我们构建了SiCmiR-Atlas,包含632个公共数据集、936万个细胞、726种细胞类型,这是首个专门针对单细胞成熟miRNA表达的专业数据库——提供交互式可视化、生物标记物鉴定和细胞类型特定的miRNA-靶标网络。SiCmiR将大规模统计能力转化为单细胞miRNA生物学视图,并为生物标记物发现提供了社区资源SiCmiR Atlas。SiCmiR Atlas可在https://awi.cuhk.edu.cn/~SiCmiR/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了新技术SiCmiR,该技术通过两层神经网络预测miRNA表达谱,仅使用977个LINCS L1000标志性基因,提高了对单细胞RNA-seq数据丢失的敏感性。SiCmiR可用于发现候选中心miRNA,在多种癌症和药物扰动中表现出卓越准确性,并构建首个专门用于单细胞成熟miRNA表达的数据库SiCmiR-Atlas。
Key Takeaways
- SiCmiR是一种基于两层神经网络的技术,用于预测miRNA表达谱。
- 它仅使用977个LINCS L1000标志性基因,提高了对单细胞RNA-seq数据丢失的敏感性。
- SiCmiR可用于发现多种癌症中的候选中心miRNA,包括bulk-seq细胞株、肝细胞癌、胰腺导管癌和ACTH分泌垂体腺瘤。
- SiCmiR在癌症类型、药物扰动和单细胞RNA-seq上具有卓越准确性。
- 构建首个专门用于单细胞成熟miRNA表达的数据库SiCmiR-Atlas,包含632个公共数据集、936万个细胞和726种细胞类型。
- SiCmiR可将大规模统计数据转化为单细胞miRNA生物学视角,并提供社区资源SiCmiR Atlas用于生物标志物发现。
点此查看论文截图

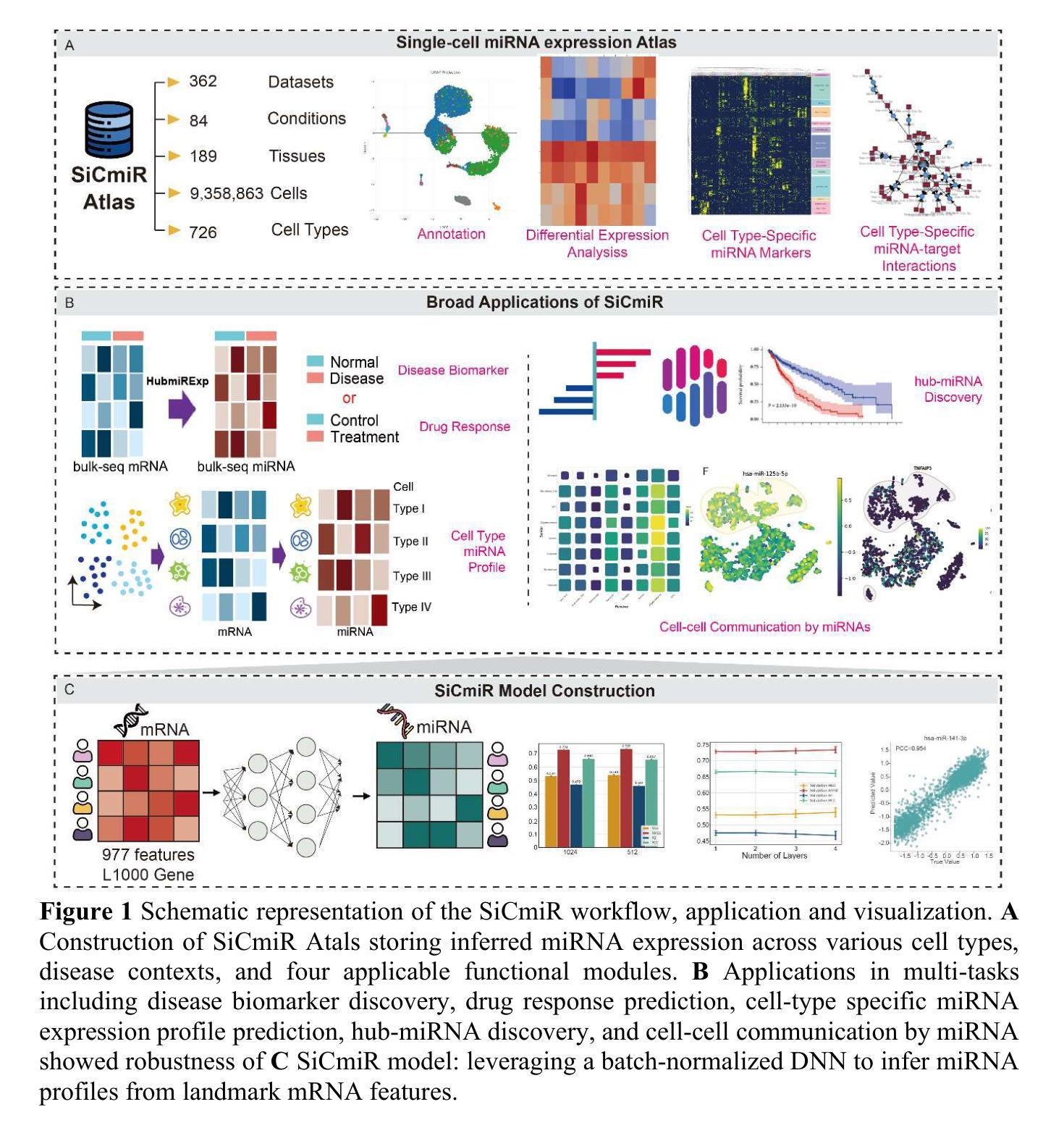
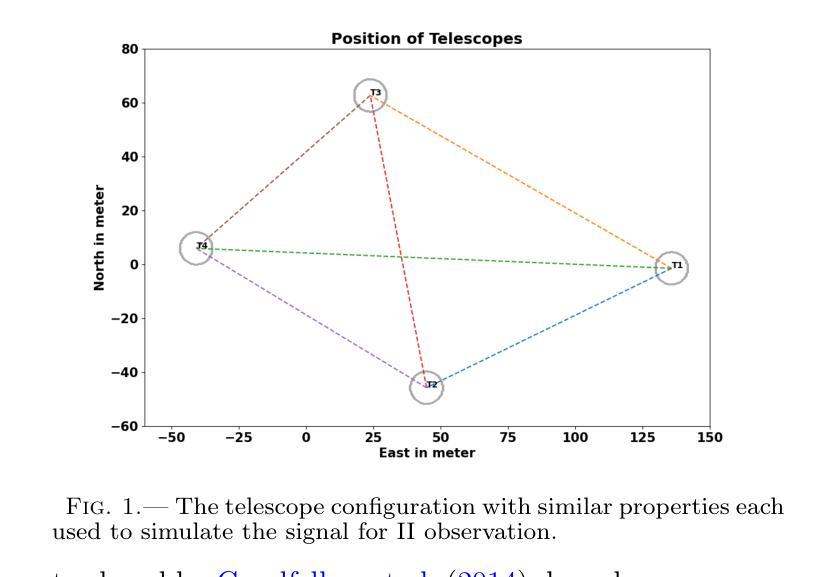
Generative AI for image reconstruction in Intensity Interferometry: a first attempt
Authors:Km Nitu Rai, Yuri van der Burg, Soumen Basak, Prasenjit Saha, Subrata Sarangi
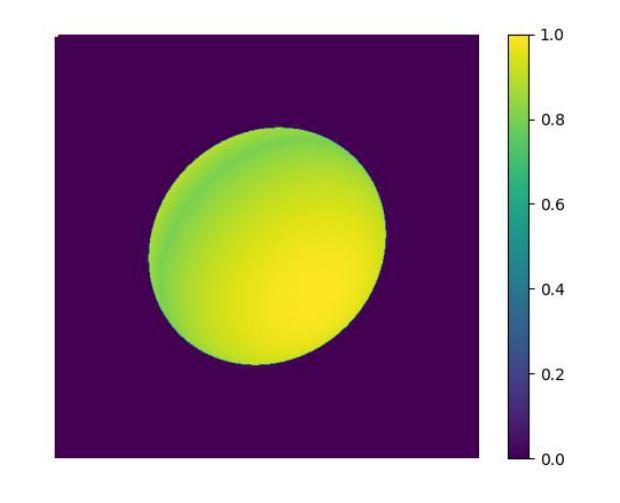
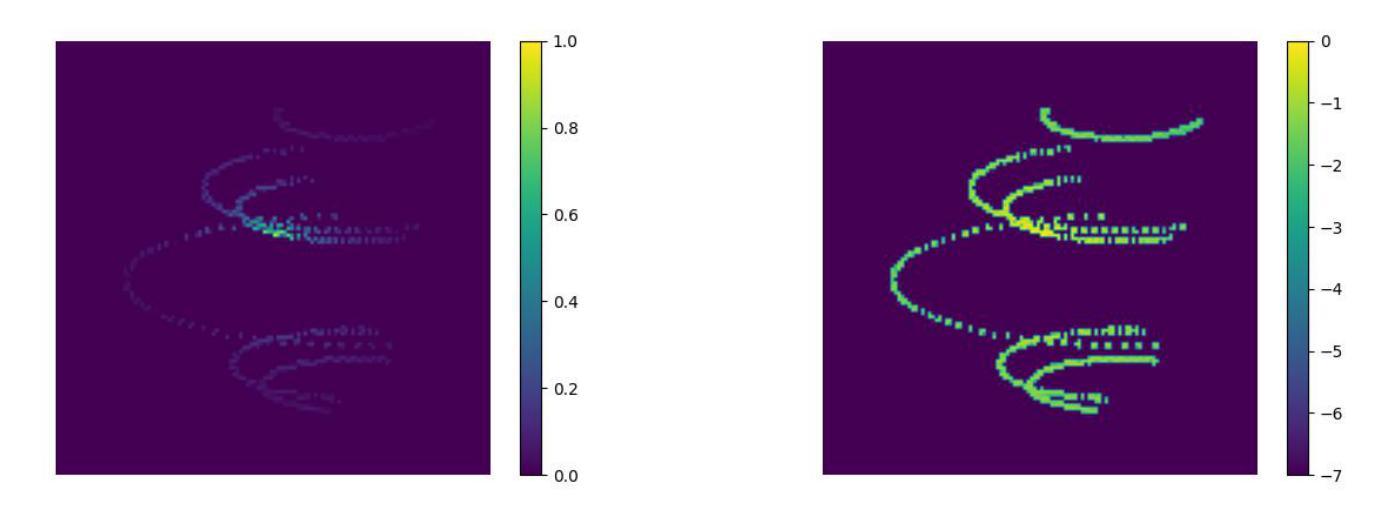
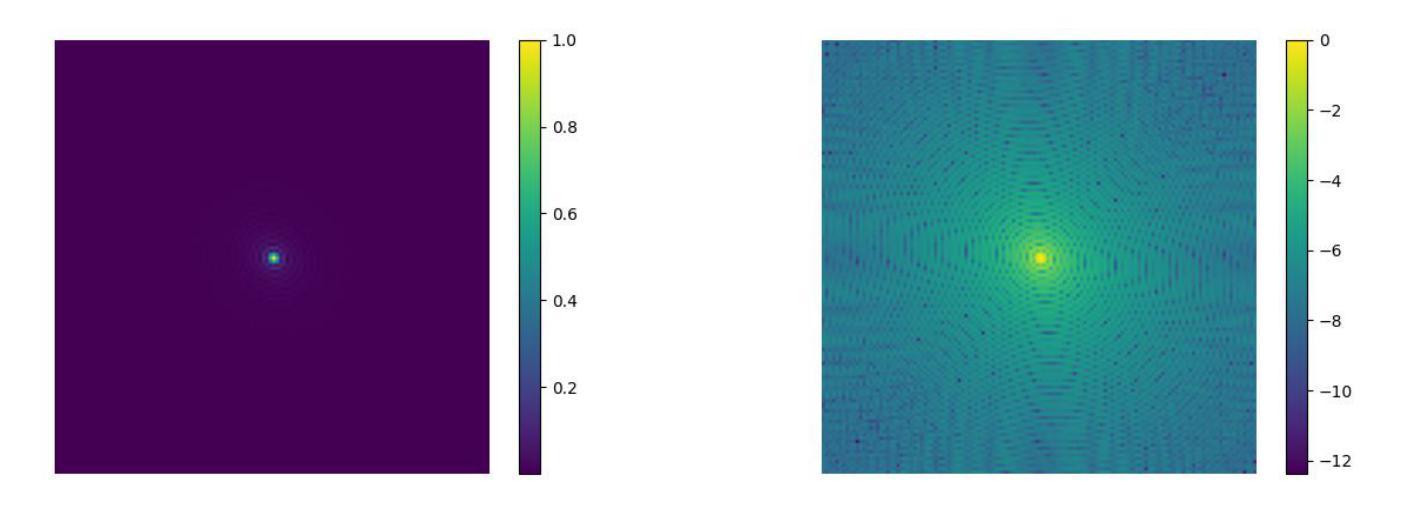
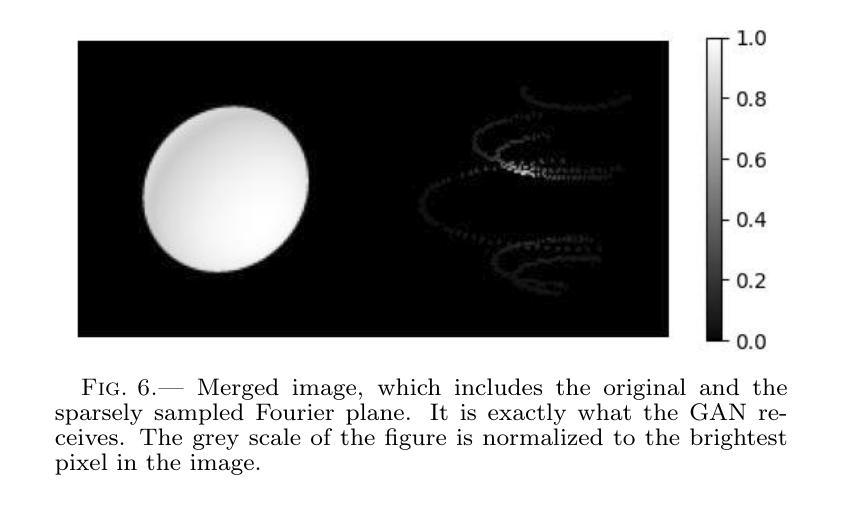
In the last few years Intensity Interferometry (II) has made significant strides in achieving high-precision resolution of stellar objects at optical wavelengths. Despite these advancements, phase retrieval remains a major challenge due to the nature of photon correlation. This paper explores the application of a conditional Generative Adversarial Network (cGAN) to tackle the problem of image reconstruction in Intensity Interferometry. This approach successfully reconstructs the shape, size, and brightness distribution of a fast-rotating star from sparsely sampled, spatial power spectrum of the source, corresponding to II with four telescopes. Although this particular example could also be addressed using parameter fitting, the results suggest that with larger arrays much more complicated systems could be reconstructed by applying machine-learning techniques to II.
近年来,干涉测量法(Intensity Interferometry,简称II)在光学波长下实现星体目标的高精度分辨率方面取得了重大进展。尽管如此,由于光子相关性本质的影响,相位恢复仍然是一个重大挑战。本文探讨了条件生成对抗网络(Conditional Generative Adversarial Network,简称cGAN)在干涉测量法图像重建中的应用。此方法成功地从稀疏采样的源空间功率谱重建了快速旋转恒星的形状、大小和亮度分布,对应于使用四个望远镜进行的干涉测量法。虽然这个特定例子也可以通过参数拟合来解决,但结果表明,对于更大的阵列系统,通过机器学习技术应用于干涉测量法,可以重建更为复杂的系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 16 figures
Summary
近年来,强度干涉测量法在光学波长上对恒星物体实现高精度分辨率方面取得了显著进展。然而,由于光子相关性,相位恢复仍是重大挑战。本文探讨了有条件生成对抗网络(cGAN)在强度干涉测量法图像重建中的应用,成功从稀疏采样的源空间功率谱中重建了快速旋转恒星的形状、大小和亮度分布,对应于使用四个望远镜的强度干涉测量法。结果表明,通过机器学习技术应用于强度干涉测量法,可以重建更复杂的系统。
Key Takeaways
- 强度干涉测量法(II)在光学波长上对恒星物体实现高精度分辨率有重大进展。
- 相位恢复仍是强度干涉测量法的主要挑战,尤其是因为光子相关性。
- 有条件生成对抗网络(cGAN)被应用于强度干涉测量法的图像重建。
- cGAN成功从稀疏采样的源空间功率谱重建了快速旋转恒星的形状、大小和亮度分布。
- 参数拟合也可以解决这一问题,但机器学习技术可能为更大的系统提供更复杂的重建解决方案。
- 此方法对于更复杂的系统具有潜力,特别是使用更大望远镜阵列的强度干涉测量法。
点此查看论文截图

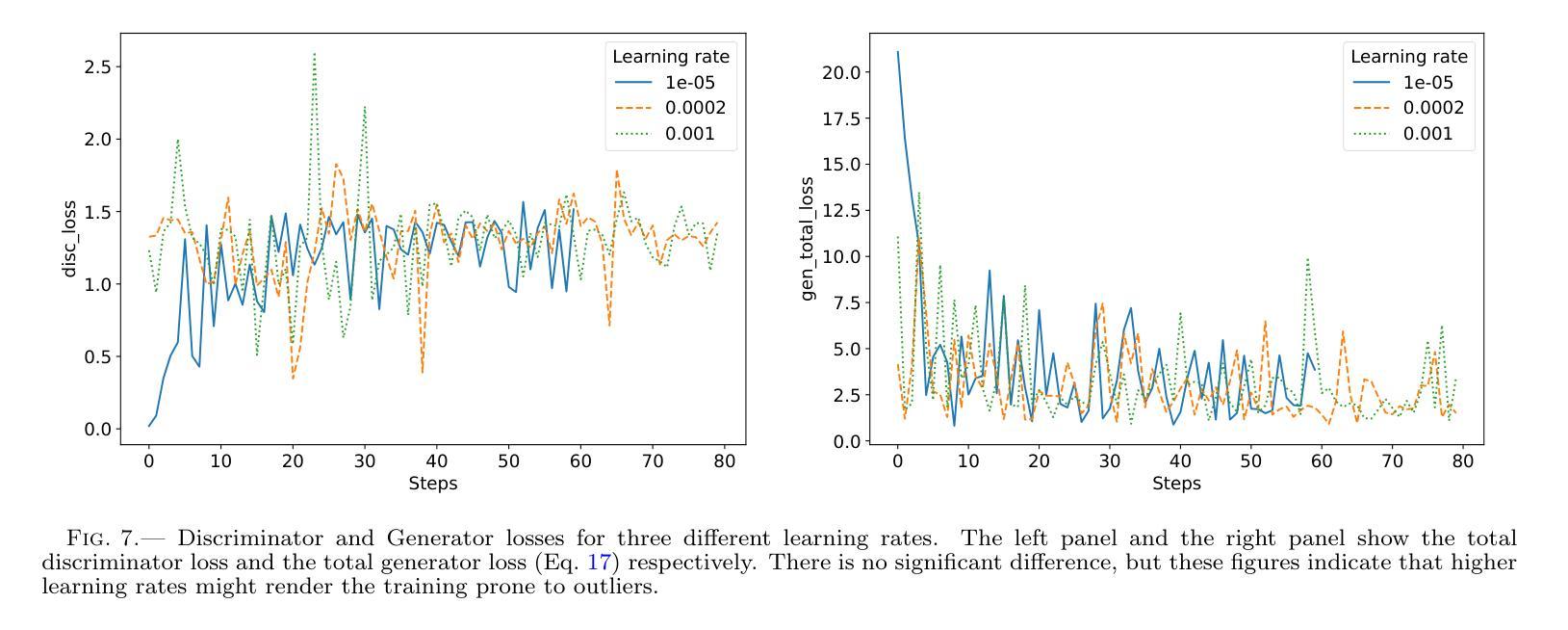
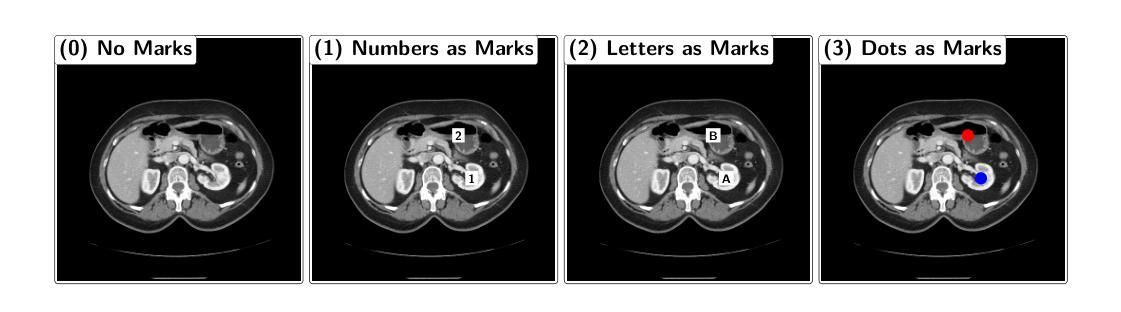
Your other Left! Vision-Language Models Fail to Identify Relative Positions in Medical Images
Authors:Daniel Wolf, Heiko Hillenhagen, Billurvan Taskin, Alex Bäuerle, Meinrad Beer, Michael Götz, Timo Ropinski
Clinical decision-making relies heavily on understanding relative positions of anatomical structures and anomalies. Therefore, for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to be applicable in clinical practice, the ability to accurately determine relative positions on medical images is a fundamental prerequisite. Despite its importance, this capability remains highly underexplored. To address this gap, we evaluate the ability of state-of-the-art VLMs, GPT-4o, Llama3.2, Pixtral, and JanusPro, and find that all models fail at this fundamental task. Inspired by successful approaches in computer vision, we investigate whether visual prompts, such as alphanumeric or colored markers placed on anatomical structures, can enhance performance. While these markers provide moderate improvements, results remain significantly lower on medical images compared to observations made on natural images. Our evaluations suggest that, in medical imaging, VLMs rely more on prior anatomical knowledge than on actual image content for answering relative position questions, often leading to incorrect conclusions. To facilitate further research in this area, we introduce the MIRP , Medical Imaging Relative Positioning, benchmark dataset, designed to systematically evaluate the capability to identify relative positions in medical images.
临床决策在很大程度上依赖于对解剖结构和异常部位相对位置的理解。因此,为了使视觉语言模型(VLM)在临床实践中得到应用,准确确定医学图像上相对位置的能力是基本前提。尽管这一能力非常重要,但目前却很少被深入研究。为了填补这一空白,我们评估了最先进的VLMs的能力,包括GPT-4o、Llama3.2、Pixtral和JanusPro,发现所有模型在这个基本任务上都失败了。借鉴计算机视觉中的成功方法,我们调查了视觉提示(如在解剖结构上放置字母数字或彩色标记)是否能提高性能。虽然这些标记提供了适度的改进,但在医学图像上的结果仍然显著低于在自然图像上观察到的结果。我们的评估表明,在医学成像中,VLMs更依赖于先验解剖知识而不是实际的图像内容来回答相对位置问题,这常常导致错误的结论。为了促进该领域的研究,我们引入了医疗成像相对定位(MIRP)基准数据集,旨在系统地评估在医学图像上识别相对位置的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2025
Summary
临床决策依赖于对解剖结构和异常情况的相对位置的理解。为了将视觉语言模型(VLMs)应用于临床实践,准确确定医学图像上的相对位置是基本前提。尽管其重要性很高,但这种能力仍然被大大忽视。评估了最先进的VLMs的能力,包括GPT-4o、Llama3.2、Pixtral和JanusPro,发现它们在这个基本任务上都失败了。受计算机视觉成功方法的启发,研究是否可以通过在解剖结构上放置字母数字或彩色标记等视觉提示来增强性能。虽然这些标记提供了适度的改进,但在医学图像上的结果仍然显著低于在自然图像上的观察结果。评估结果表明,在医学成像中,VLMs更依赖于先验解剖知识而非实际图像内容来回答相对位置问题,这往往导致错误结论。为了促进该领域的研究,引入了MIRP(医学成像相对定位)基准数据集,旨在系统地评估在医学图像上识别相对位置的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 临床决策需要理解解剖结构和异常情况的相对位置。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学图像上的相对位置确定能力方面存在缺陷。
- 先进的VLMs在基本任务上表现不佳,即准确确定医学图像上的相对位置。
- 视觉提示(如字母数字或彩色标记)可以提供适度的改进,但性能仍然有限。
- VLMs在医学图像上的表现低于在自然图像上的表现。
- 在医学成像中,VLMs更依赖于先验解剖知识而非图像内容来回答相对位置问题。
点此查看论文截图

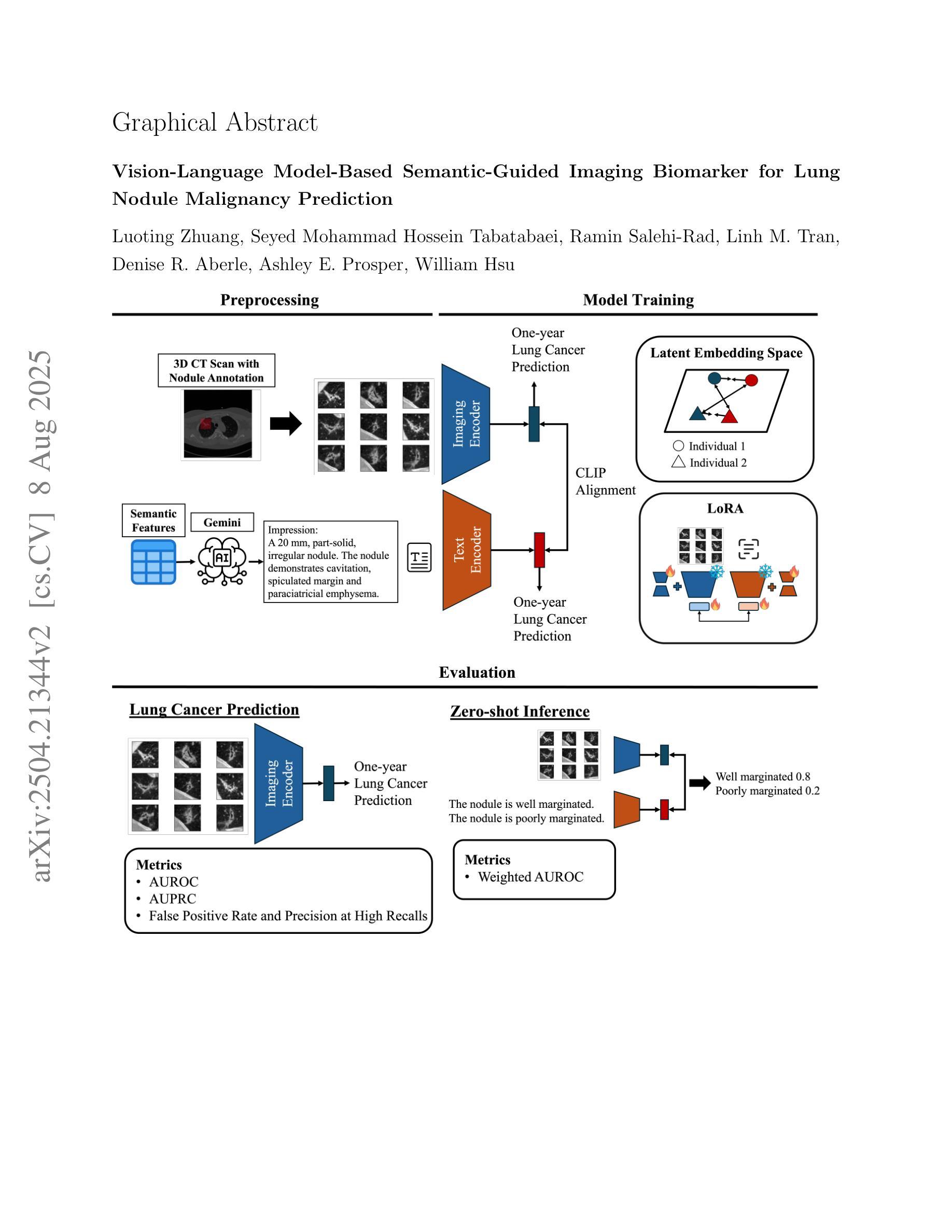
Vision-Language Model-Based Semantic-Guided Imaging Biomarker for Lung Nodule Malignancy Prediction
Authors:Luoting Zhuang, Seyed Mohammad Hossein Tabatabaei, Ramin Salehi-Rad, Linh M. Tran, Denise R. Aberle, Ashley E. Prosper, William Hsu
Machine learning models have utilized semantic features, deep features, or both to assess lung nodule malignancy. However, their reliance on manual annotation during inference, limited interpretability, and sensitivity to imaging variations hinder their application in real-world clinical settings. Thus, this research aims to integrate semantic features derived from radiologists’ assessments of nodules, guiding the model to learn clinically relevant, robust, and explainable imaging features for predicting lung cancer. We obtained 938 low-dose CT scans from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) with 1,246 nodules and semantic features. Additionally, the Lung Image Database Consortium dataset contains 1,018 CT scans, with 2,625 lesions annotated for nodule characteristics. Three external datasets were obtained from UCLA Health, the LUNGx Challenge, and the Duke Lung Cancer Screening. We fine-tuned a pretrained Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) model with a parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach to align imaging and semantic text features and predict the one-year lung cancer diagnosis. Our model outperformed state-of-the-art (SOTA) models in the NLST test set with an AUROC of 0.901 and AUPRC of 0.776. It also showed robust results in external datasets. Using CLIP, we also obtained predictions on semantic features through zero-shot inference, such as nodule margin (AUROC: 0.812), nodule consistency (0.812), and pleural attachment (0.840). Our approach surpasses the SOTA models in predicting lung cancer across datasets collected from diverse clinical settings, providing explainable outputs, aiding clinicians in comprehending the underlying meaning of model predictions. This approach also prevents the model from learning shortcuts and generalizes across clinical settings. The code is available at https://github.com/luotingzhuang/CLIP_nodule.
机器学习模型已经利用语义特征、深度特征或两者来评估肺结节的恶性程度。然而,它们在推理过程中对手动标注的依赖、解释性有限以及对成像变化的敏感性,阻碍了它们在现实临床环境中的应用。因此,本研究旨在整合放射科医生对结节的评估所衍生的语义特征,引导模型学习临床相关、稳健和可解释的成像特征,以预测肺癌。我们从国家肺癌筛查试验(NLST)获得了938例低剂量CT扫描,包含1246个结节和语义特征。此外,肺部图像数据库联盟数据集包含1018例CT扫描,其中2625个病灶被标注为结节特征。另外三个外部数据集来自加州大学洛杉矶医疗中心、LUNGx挑战赛和杜克大学肺癌筛查。我们使用微调过的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,采用参数高效的微调方法,对齐成像和语义文本特征,预测一年内肺癌的诊断结果。我们的模型在NLST测试集上的表现超过了最先进模型的性能,曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.901,精确接收者操作特征曲线下面积(AUPRC)为0.776。在外部数据集上也表现出稳健的结果。使用CLIP,我们还通过零样本推理获得了语义特征的预测,如结节边缘(AUROC: 0.812)、结节一致性(0.812)和胸膜附着(0.840)。我们的方法在预测来自不同临床环境的数据集上的肺癌时,超越了最先进的模型,提供了可解释的输出结果,帮助临床医生理解模型预测结果的内在含义。这种方法还防止了模型学习捷径,并在不同的临床环境中进行了推广。代码可在https://github.com/luotingzhuang/CLIP_nodule找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了利用机器学习方法预测肺癌的问题。研究团队整合了放射科医生对结节的语义特征评估,指导模型学习临床相关、稳健和可解释的成像特征。他们使用预训练的Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP)模型,通过参数有效的微调方法,对齐图像和语义文本特征,预测一年内肺癌的诊断。该模型在多个外部数据集上表现优异,并提供可解释的输出结果,帮助临床医生理解模型预测的背后含义。该模型能防止学习快捷方式并在不同的临床环境中进行推广。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用机器学习方法预测肺癌,结合了放射科医生对结节的语义特征评估。
- 采用预训练的CLIP模型,通过参数有效的微调方法,对齐图像和语义文本特征。
- 模型在多个数据集上表现优于现有技术,包括来自NLST的肺部CT扫描数据和外部数据集。
- 模型能进行零样本推断,预测语义特征如结节边缘、一致性和胸膜附着等。
- 模型提供可解释的输出结果,有助于临床医生理解预测背后的含义。
- 模型能够防止学习快捷方式,具有良好的泛化能力,能在不同的临床环境中应用。
点此查看论文截图
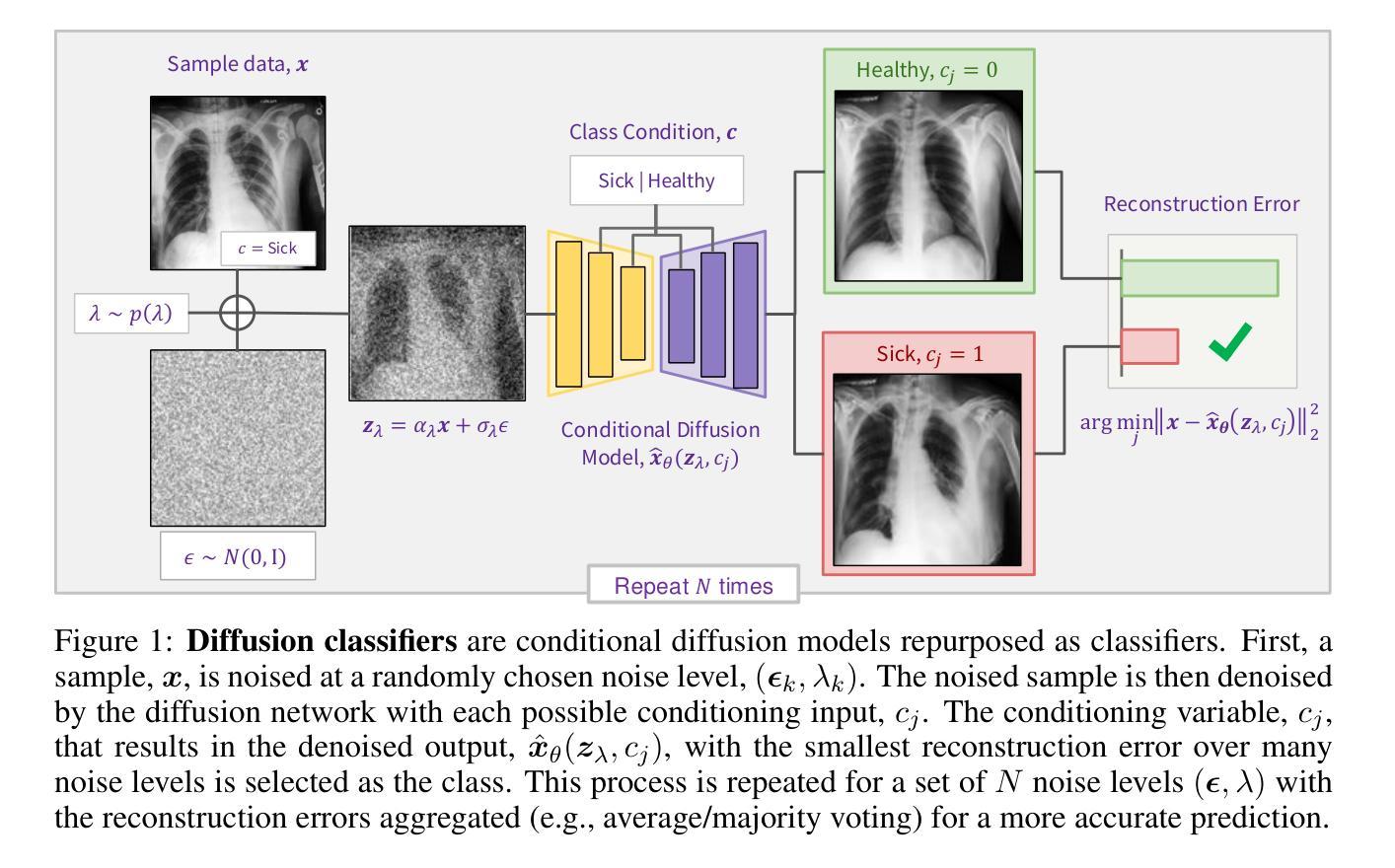
Conditional Diffusion Models are Medical Image Classifiers that Provide Explainability and Uncertainty for Free
Authors:Gian Mario Favero, Parham Saremi, Emily Kaczmarek, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel
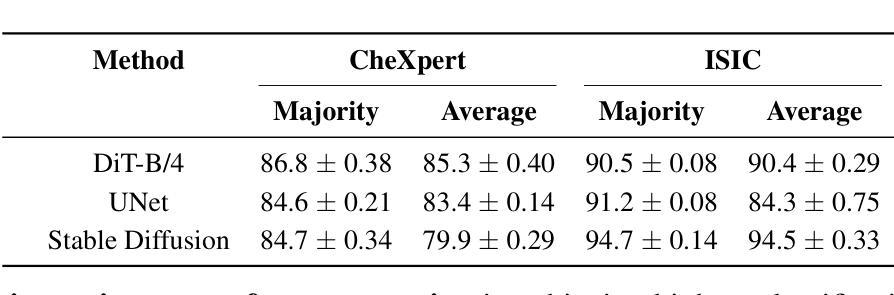
Discriminative classifiers have become a foundational tool in deep learning for medical imaging, excelling at learning separable features of complex data distributions. However, these models often need careful design, augmentation, and training techniques to ensure safe and reliable deployment. Recently, diffusion models have become synonymous with generative modeling in 2D. These models showcase robustness across a range of tasks including natural image classification, where classification is performed by comparing reconstruction errors across images generated for each possible conditioning input. This work presents the first exploration of the potential of class conditional diffusion models for 2D medical image classification. First, we develop a novel majority voting scheme shown to improve the performance of medical diffusion classifiers. Next, extensive experiments on the CheXpert and ISIC Melanoma skin cancer datasets demonstrate that foundation and trained-from-scratch diffusion models achieve competitive performance against SOTA discriminative classifiers without the need for explicit supervision. In addition, we show that diffusion classifiers are intrinsically explainable, and can be used to quantify the uncertainty of their predictions, increasing their trustworthiness and reliability in safety-critical, clinical contexts. Further information is available on our project page: https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier.github.io/.
判别分类器已经成为深度医学成像中的基本工具,擅长学习复杂数据分布的可分特征。然而,为了确保安全和可靠的部署,这些模型通常需要精心设计、增强和训练技术。最近,扩散模型已成为二维生成模型的代名词。这些模型在各种任务中展示了稳健性,包括自然图像分类,分类是通过比较针对每个可能的条件输入生成的图像之间的重建误差来完成的。这项工作首次探索了二维医学图像分类中类条件扩散模型的潜力。首先,我们开发了一种新型多数投票方案,以提高医学扩散分类器的性能。其次,在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的大量实验表明,基础扩散模型和从头开始训练的扩散模型无需显式监督即可实现与最新判别分类器相当的性能。此外,我们还证明了扩散分类器本质上是可解释的,可用于量化其预测的的不确定性,这在安全关键的医疗环境中增加了其可信度和可靠性。更多信息请访问我们的项目页面:https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025
Summary
本文探索了类条件扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中的潜力。研究提出了一种新的多数投票方案,提高了医学扩散分类器的性能。在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的实验表明,基础扩散模型和从头训练的扩散模型在竞争性能方面达到了当前最佳鉴别分类器的水平,而无需显式监督。此外,扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性,可用于量化预测的确定性,从而增加其在安全关键的医疗环境中的可信度和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中具有潜力。
- 新的多数投票方案提高了医学扩散分类器的性能。
- 扩散模型在CheXpert和ISIC数据集上表现出竞争力。
- 扩散模型无需显式监督即可达到最佳鉴别分类器的性能。
- 扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性。
- 扩散分类器可以量化预测的确定性。
点此查看论文截图

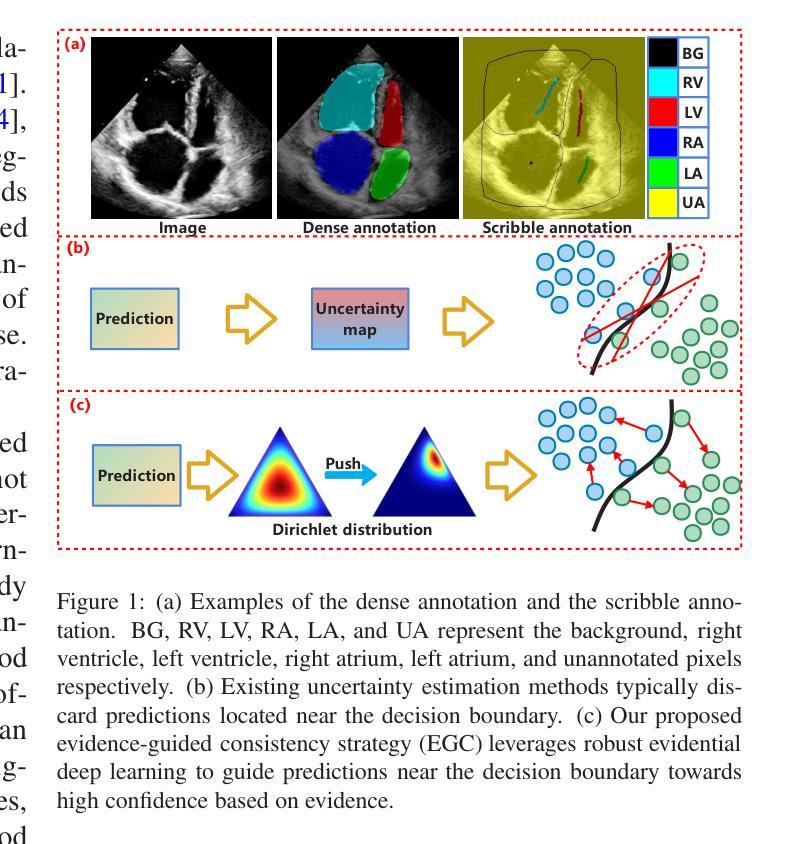
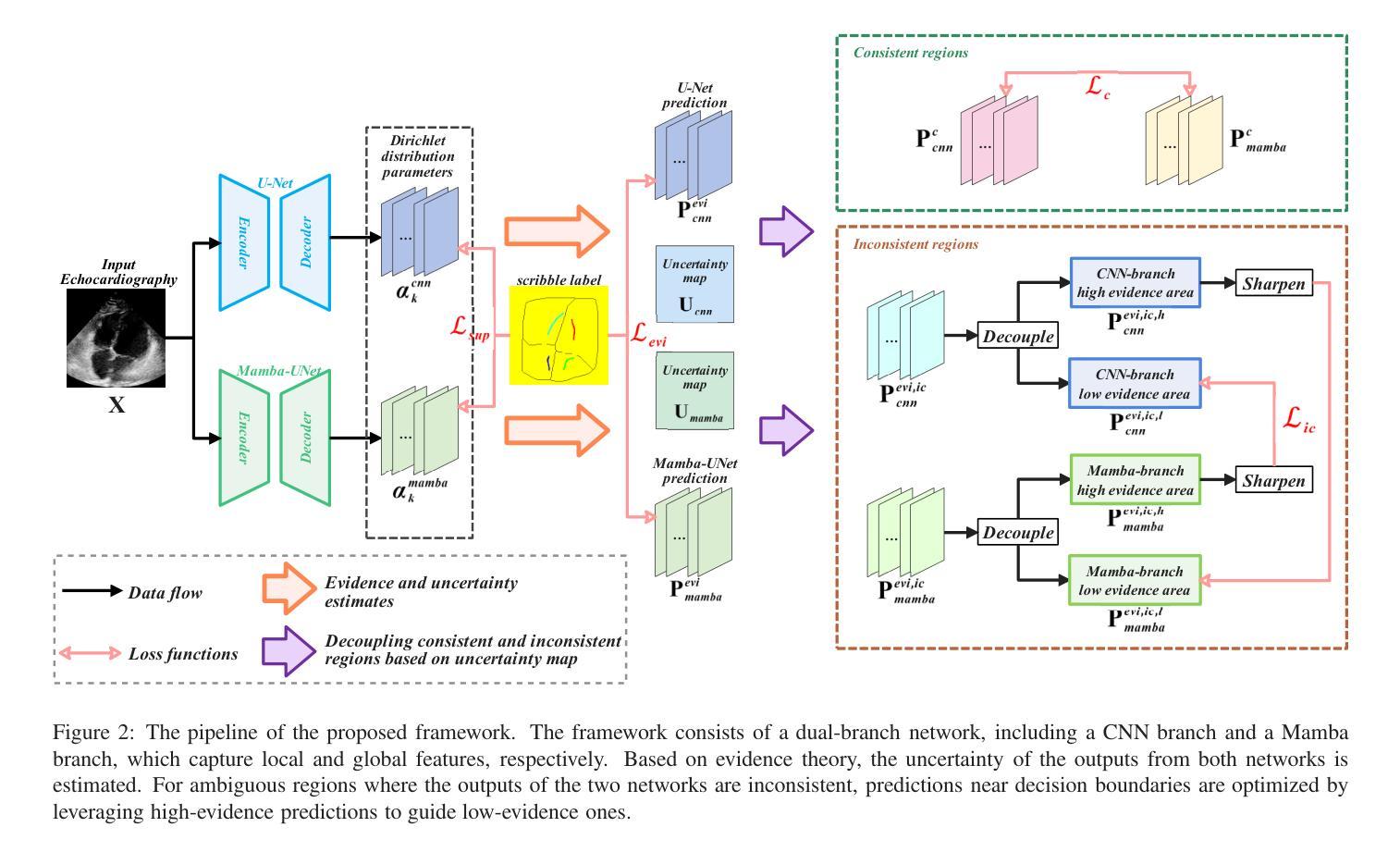
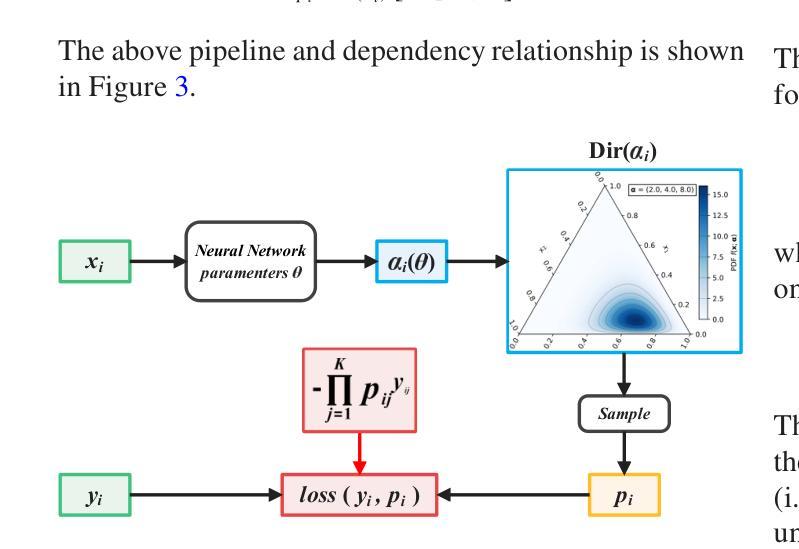
MambaEviScrib: Mamba and Evidence-Guided Consistency Enhance CNN Robustness for Scribble-Based Weakly Supervised Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiaoxiang Han, Xinyu Li, Jiang Shang, Yiman Liu, Keyan Chen, Shugong Xu, Qiaohong Liu, Qi Zhang
Segmenting anatomical structures and lesions from ultrasound images contributes to disease assessment. Weakly supervised learning (WSL) based on sparse annotation has achieved encouraging performance and demonstrated the potential to reduce annotation costs. This study attempts to introduce scribble-based WSL into ultrasound image segmentation tasks. However, ultrasound images often suffer from poor contrast and unclear edges, coupled with insufficient supervison signals for edges, posing challenges to edge prediction. Uncertainty modeling has been proven to facilitate models in dealing with these issues. Nevertheless, existing uncertainty estimation paradigms are not robust enough and often filter out predictions near decision boundaries, resulting in unstable edge predictions. Therefore, we propose leveraging predictions near decision boundaries effectively. Specifically, we introduce Dempster-Shafer Theory (DST) of evidence to design an Evidence-Guided Consistency strategy. This strategy utilizes high-evidence predictions, which are more likely to occur near high-density regions, to guide the optimization of low-evidence predictions that may appear near decision boundaries. Furthermore, the diverse sizes and locations of lesions in ultrasound images pose a challenge for CNNs with local receptive fields, as they struggle to model global information. Therefore, we introduce Visual Mamba based on structured state space sequence models, which achieves long-range dependency with linear computational complexity, and we construct a novel hybrid CNN-Mamba framework. During training, the collaboration between the CNN branch and the Mamba branch in the proposed framework draws inspiration from each other based on the EGC strategy. Experiments demonstrate the competitiveness of the proposed method. Dataset and code will be available on https://github.com/GtLinyer/MambaEviScrib.
从超声图像中分割解剖结构和病变有助于疾病评估。基于稀疏标注的弱监督学习(WSL)已经取得了令人鼓舞的性能,并显示出降低标注成本潜力。本研究试图将基于涂鸦的WSL引入超声图像分割任务。然而,超声图像常常存在对比度差、边缘不清等问题,再加上边缘监督信号不足,给边缘预测带来了挑战。不确定性建模已被证明有助于模型处理这些问题。然而,现有的不确定性估计范式还不够稳健,经常过滤掉决策边界附近的预测,导致边缘预测不稳定。因此,我们提出有效利用决策边界附近的预测。具体来说,我们引入Dempster-Shafer理论(DST)的证据来设计一种证据引导的一致性策略。该策略利用高证据预测(它们更可能出现在高密度区域),来指导低证据预测的优化,这些低证据预测可能出现在决策边界附近。此外,超声图像中病变的大小和位置的多样性对具有局部感受野的卷积神经网络(CNN)提出了挑战,因为它们很难对全局信息进行建模。因此,我们引入了基于结构化状态空间序列模型的视觉Mamba,实现了线性计算复杂度的长程依赖性,并构建了一个新型的混合CNN-Mamba框架。在训练过程中,所提框架中的CNN分支和Mamba分支之间的协作是基于EGC策略的相互启发。实验证明了所提方法的竞争力。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/GtLinyer/MambaEviScrib上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Information Fusion
Summary
本文介绍了基于涂鸦的弱监督学习在超声图像分割中的应用。针对超声图像对比度差、边缘不清及监督信号不足等问题,提出利用Dempster-Shafer证据理论引导的一致性策略,有效处理边缘预测问题。同时,引入基于结构化状态空间序列模型的视觉Mamba,解决CNN对全局信息建模的局限性。实验证明,该方法具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 超声图像分割对疾病评估有贡献,但存在对比度差、边缘不清和缺乏监督信号的挑战。
- 涂鸦式弱监督学习被引入超声图像分割任务中。
- 不确定性建模有助于模型处理边缘预测问题,但现有方法不稳定。
- 提出利用Dempster-Shafer证据理论引导的一致性策略,有效处理边缘预测问题。
- 超声图像中病变的多样性和位置挑战了CNN的局部接收场。
- 引入基于结构化状态空间序列模型的视觉Mamba,实现长期依赖关系。
- 构建混合CNN-Mamba框架,CNN与Mamba分支相互协作以改善性能。
点此查看论文截图