⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
Mixture of Experts Guided by Gaussian Splatters Matters: A new Approach to Weakly-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection
Authors:Giacomo D’Amicantonio, Snehashis Majhi, Quan Kong, Lorenzo Garattoni, Gianpiero Francesca, François Bremond, Egor Bondarev
Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) is a challenging task due to the variability of anomalous events and the limited availability of labeled data. Under the Weakly-Supervised VAD (WSVAD) paradigm, only video-level labels are provided during training, while predictions are made at the frame level. Although state-of-the-art models perform well on simple anomalies (e.g., explosions), they struggle with complex real-world events (e.g., shoplifting). This difficulty stems from two key issues: (1) the inability of current models to address the diversity of anomaly types, as they process all categories with a shared model, overlooking category-specific features; and (2) the weak supervision signal, which lacks precise temporal information, limiting the ability to capture nuanced anomalous patterns blended with normal events. To address these challenges, we propose Gaussian Splatting-guided Mixture of Experts (GS-MoE), a novel framework that employs a set of expert models, each specialized in capturing specific anomaly types. These experts are guided by a temporal Gaussian splatting loss, enabling the model to leverage temporal consistency and enhance weak supervision. The Gaussian splatting approach encourages a more precise and comprehensive representation of anomalies by focusing on temporal segments most likely to contain abnormal events. The predictions from these specialized experts are integrated through a mixture-of-experts mechanism to model complex relationships across diverse anomaly patterns. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a 91.58% AUC on the UCF-Crime dataset, and demonstrates superior results on XD-Violence and MSAD datasets. By leveraging category-specific expertise and temporal guidance, GS-MoE sets a new benchmark for VAD under weak supervision.
视频异常检测(VAD)是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为异常事件的多样性和标注数据的有限性。在弱监督VAD(WSVAD)模式下,训练时仅提供视频级别的标签,而预测则在帧级别进行。虽然最先进的模型在简单异常(例如爆炸)方面表现良好,但在复杂现实世界事件(例如行窃)方面却表现困难。这种困难源于两个关键问题:(1)当前模型无法处理异常类型的多样性,因为它们使用共享模型处理所有类别,忽略了特定类别的特征;(2)弱监督信号缺乏精确的时间信息,限制了捕捉与正常事件混合的微妙异常模式的能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了高斯涂抹引导混合专家(GS-MoE),这是一种新型框架,采用一组专家模型,每个模型专门用于捕获特定的异常类型。这些专家由时间高斯涂抹损失引导,使模型能够利用时间一致性并增强弱监督。高斯涂抹方法通过关注最可能包含异常事件的时间段,鼓励对异常进行更精确和全面的表示。这些专业专家的预测通过混合专家机制进行集成,以模拟不同异常模式之间的复杂关系。我们的方法在UCF-Crime数据集上实现了91.58%的AUC,并在XD-Violence和MSAD数据集上展示了优越的结果。通过利用特定类别的专业知识和时间指导,GS-MoE为弱监督下的VAD设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
弱监督视频异常检测(WSVAD)面临多样异常事件和标签数据有限的挑战。现有模型在处理简单异常事件(如爆炸)时表现良好,但在处理复杂真实事件(如店内行窃)时遇到困难。为应对挑战,提出高斯溅射引导混合专家(GS-MoE)框架,采用一系列专家模型,每个模型专门捕捉特定异常类型。这些专家受时间高斯溅射损失的引导,提高捕捉微妙异常模式的能力。GS-MoE在UCF-Crime数据集上取得了91.58%的AUC,并在XD-Violence和MSAD数据集上展现出卓越结果。
Key Takeaways
- VAD任务因异常事件的多样性和标签数据的有限性而具有挑战性。
- 当前模型在处理复杂真实世界的异常事件时遇到困难,主要原因是无法处理异常类型的多样性和弱监督信号的缺乏。
- GS-MoE框架采用一系列专家模型,每个模型专门捕捉特定异常类型,解决了上述问题。
- 专家模型受时间高斯溅射损失的引导,利用时间一致性提高模型的性能。
- 高斯溅射方法鼓励更精确和全面的异常表示,专注于最可能包含异常事件的临时片段。
- GS-MoE通过混合专家机制的预测建模了各种异常模式的复杂关系。
点此查看论文截图

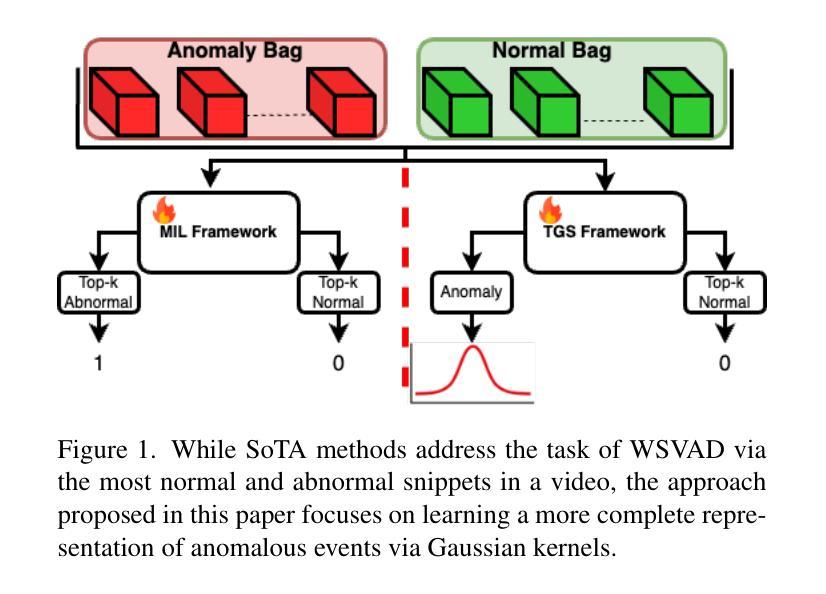
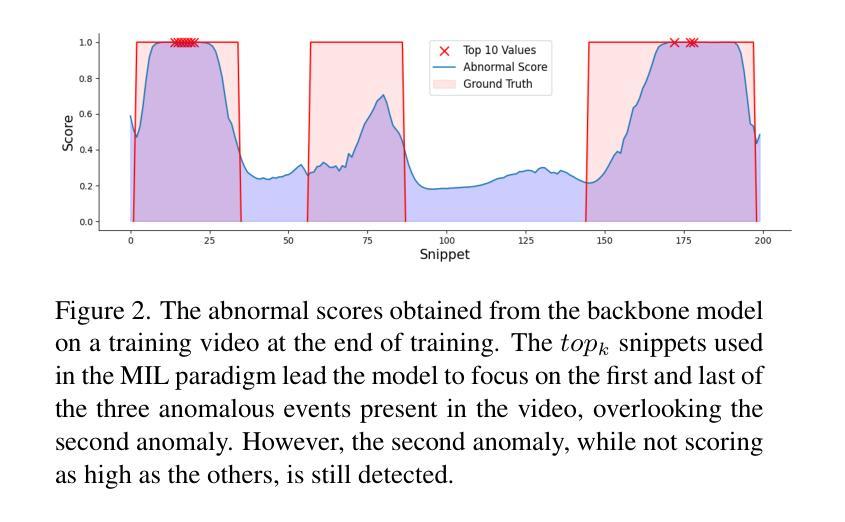
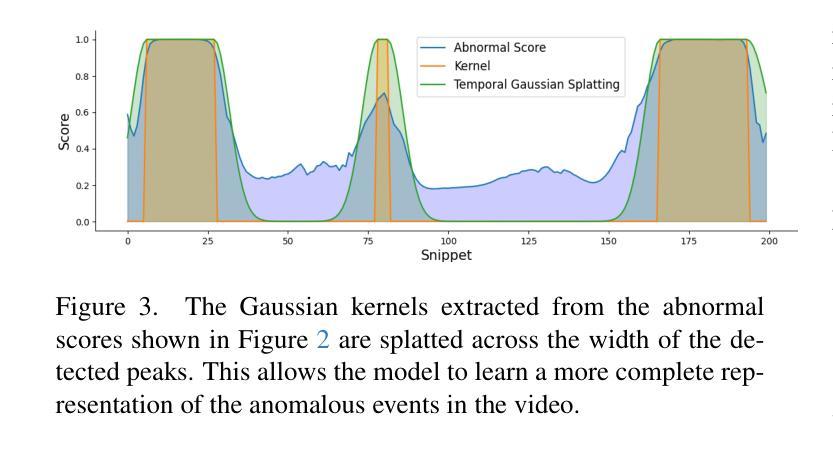
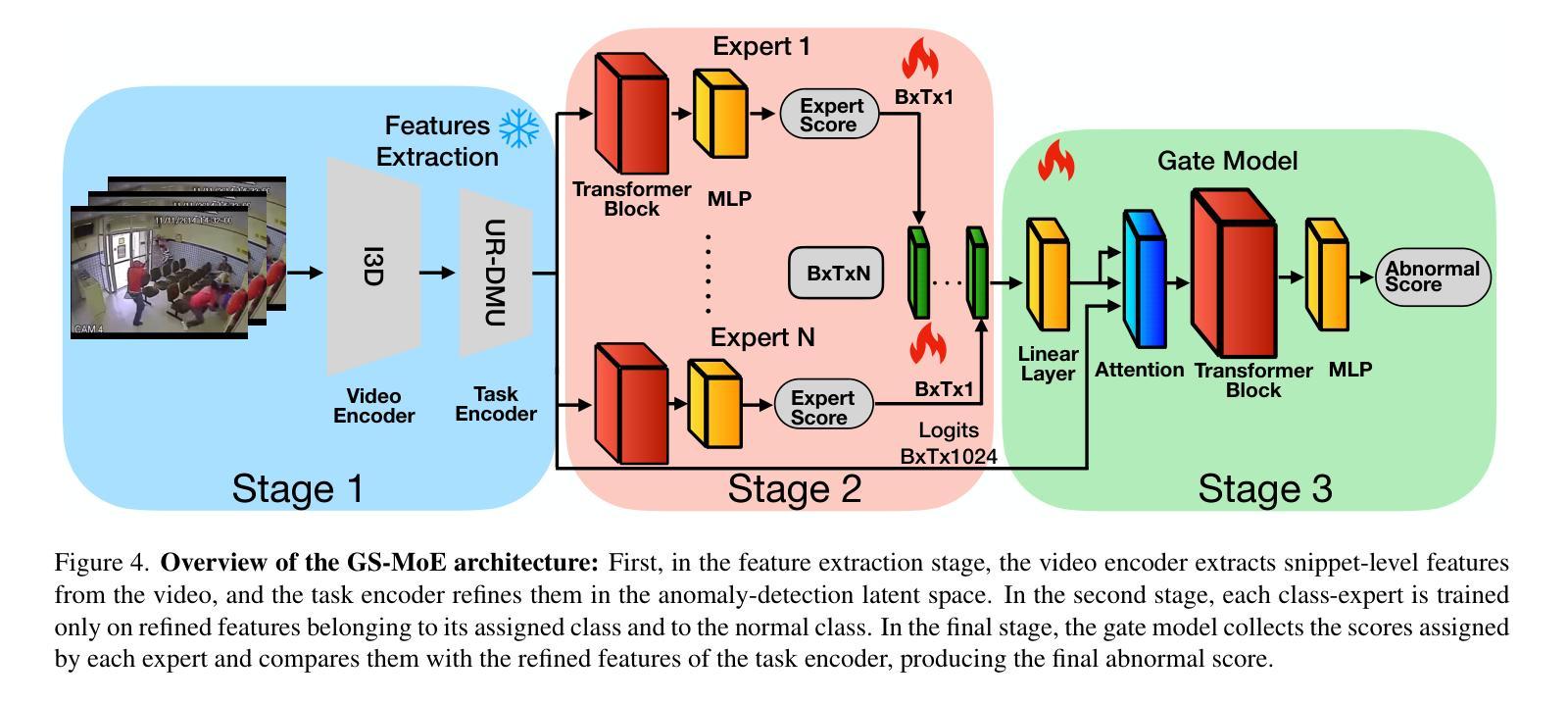
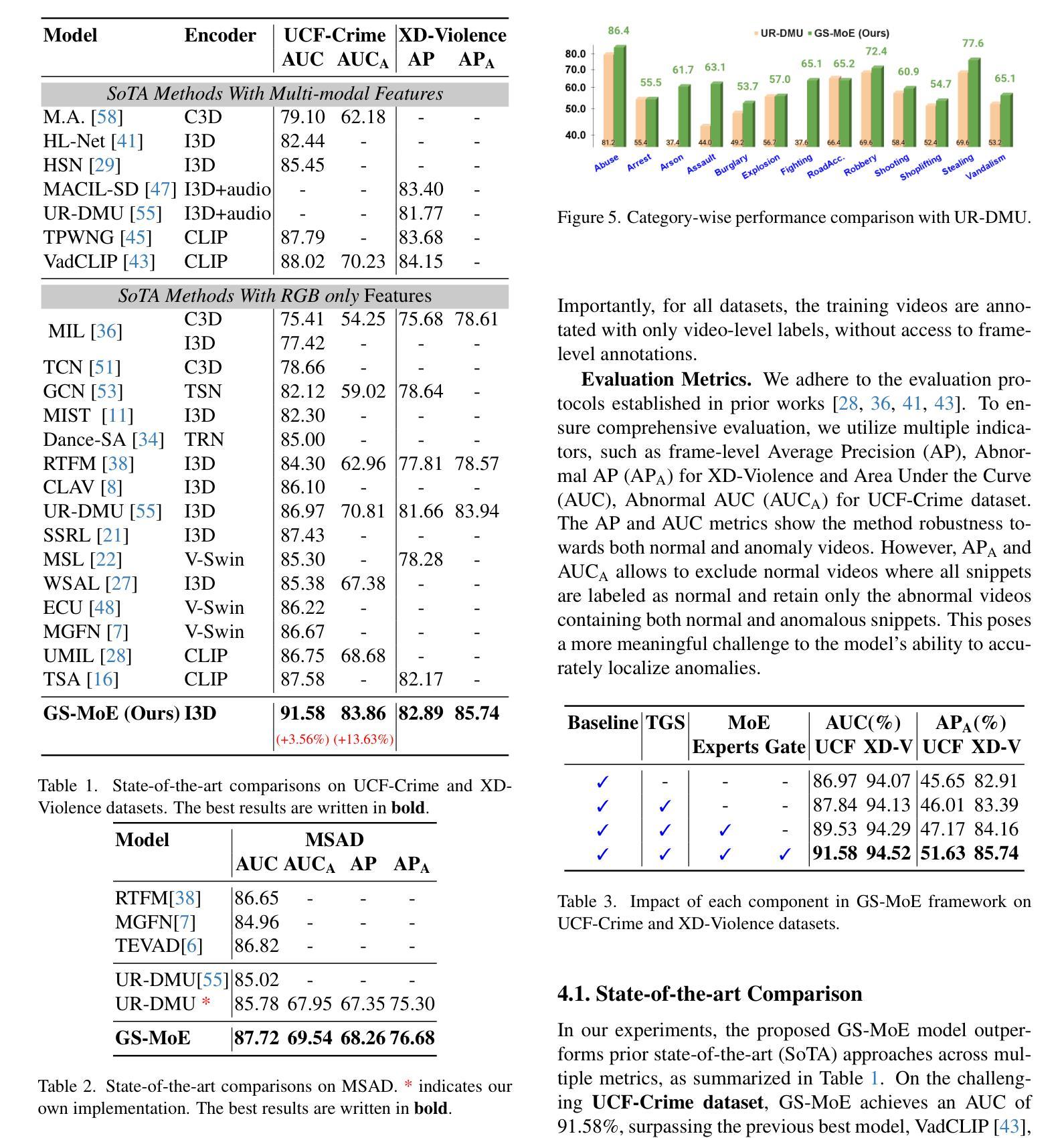
Roll Your Eyes: Gaze Redirection via Explicit 3D Eyeball Rotation
Authors:YoungChan Choi, HengFei Wang, YiHua Cheng, Boeun Kim, Hyung Jin Chang, YoungGeun Choi, Sang-Il Choi
We propose a novel 3D gaze redirection framework that leverages an explicit 3D eyeball structure. Existing gaze redirection methods are typically based on neural radiance fields, which employ implicit neural representations via volume rendering. Unlike these NeRF-based approaches, where the rotation and translation of 3D representations are not explicitly modeled, we introduce a dedicated 3D eyeball structure to represent the eyeballs with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our method generates photorealistic images that faithfully reproduce the desired gaze direction by explicitly rotating and translating the 3D eyeball structure. In addition, we propose an adaptive deformation module that enables the replication of subtle muscle movements around the eyes. Through experiments conducted on the ETH-XGaze dataset, we demonstrate that our framework is capable of generating diverse novel gaze images, achieving superior image quality and gaze estimation accuracy compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
我们提出了一种新型的3D眼神重定向框架,该框架利用明确的3D眼球结构。现有的眼神重定向方法通常基于神经辐射场,通过体积渲染采用隐式神经表示。与这些基于NeRF的方法不同,后者没有明确地建模3D表示的旋转和平移,我们引入了一个专门的3D眼球结构,使用3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)来表示眼球。我们的方法可以生成逼真的图像,通过明确地旋转和平移3D眼球结构,忠实地再现所需的眼神方向。此外,我们提出了一种自适应变形模块,能够实现眼睛周围微妙肌肉运动的复制。我们在ETH-XGaze数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的框架能够生成多种新颖的眼神图像,与现有最先进的方法相比,图像质量和眼神估计准确性更高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, ACM Multimeida 2025 accepted
摘要
本文提出了一种新型的3D视线重定向框架,该框架利用明确的3D眼球结构。现有视线重定向方法通常基于神经辐射场,采用隐式神经表示和体积渲染技术。与这些基于NeRF的方法不同,我们的方法引入了专门的3D眼球结构来表示眼球,采用3D高斯喷绘技术(3DGS)。该方法可生成逼真的图像,通过明确旋转和翻译3D眼球结构来忠实再现期望的视线方向。此外,还提出了一种自适应变形模块,能够复制眼睛周围肌肉的细微运动。在ETH-XGaze数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的框架能够生成多样化的新型视线图像,与现有最先进的方法相比,图像质量和视线估计准确性更高。
要点掌握
- 引入了一种新型的3D视线重定向框架,该框架利用明确的3D眼球结构。
- 与基于NeRF的方法不同,该框架采用3D高斯喷绘技术(3DGS)表示眼球。
- 该方法可以生成逼真的图像,并通过明确旋转和翻译3D眼球结构来展现视线方向。
- 提出了一种自适应变形模块,可以复制眼睛周围肌肉的细微运动。
- 在ETH-XGaze数据集上进行了实验验证,生成了多样化的新型视线图像。
- 与现有方法相比,该框架在图像质量和视线估计准确性方面表现更优。
- 该研究为视线重定向领域提供了一种新的、高效的方法。
点此查看论文截图

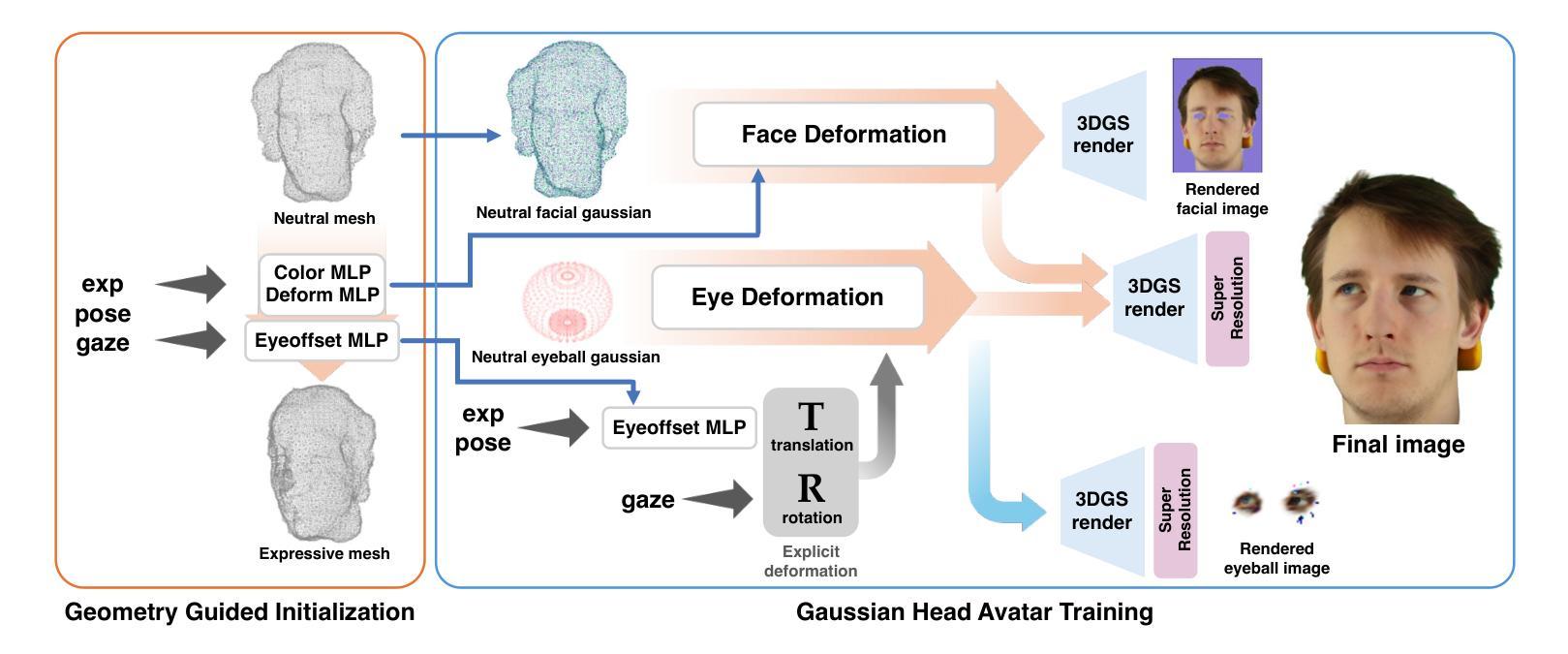
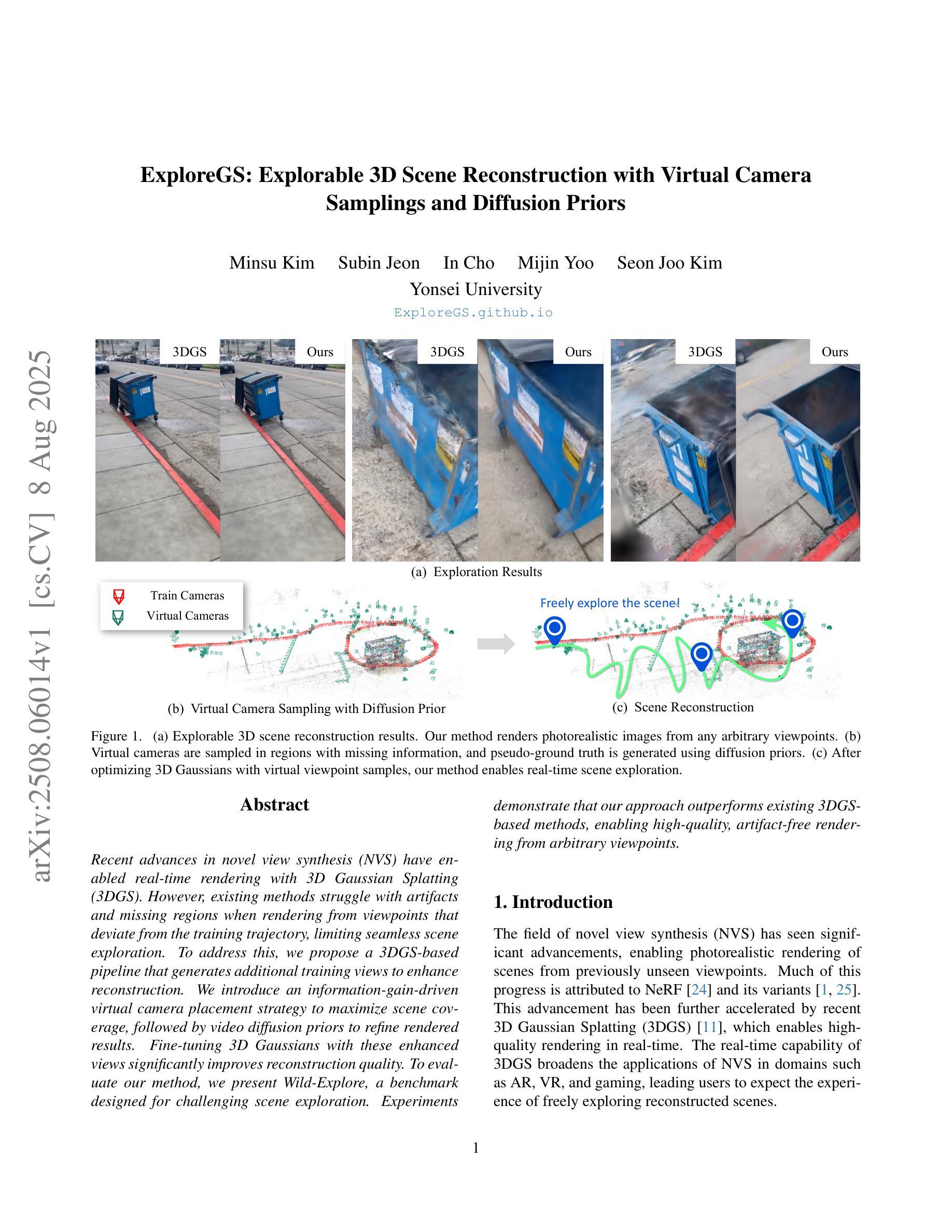
ExploreGS: Explorable 3D Scene Reconstruction with Virtual Camera Samplings and Diffusion Priors
Authors:Minsu Kim, Subin Jeon, In Cho, Mijin Yoo, Seon Joo Kim
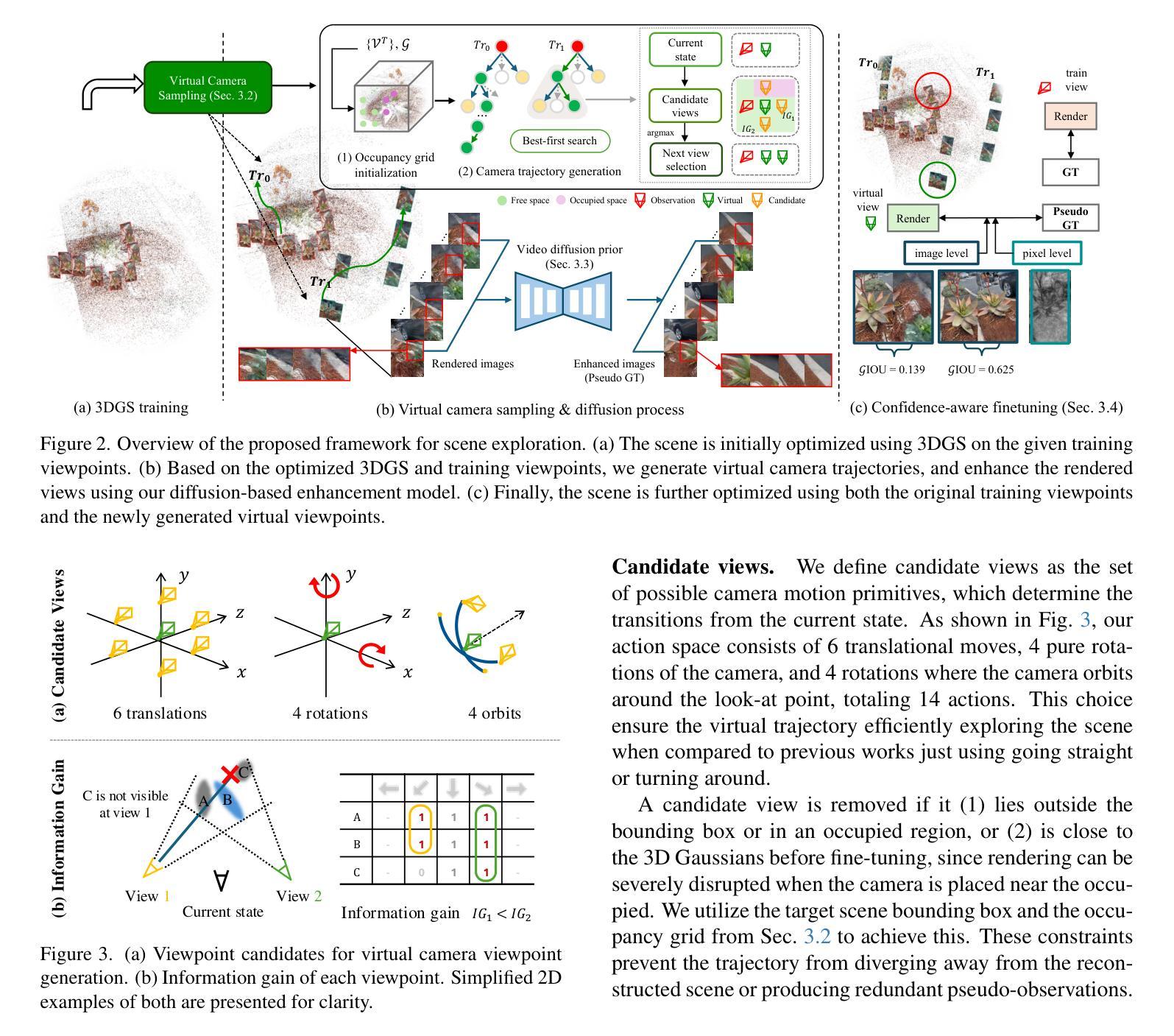
Recent advances in novel view synthesis (NVS) have enabled real-time rendering with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). However, existing methods struggle with artifacts and missing regions when rendering from viewpoints that deviate from the training trajectory, limiting seamless scene exploration. To address this, we propose a 3DGS-based pipeline that generates additional training views to enhance reconstruction. We introduce an information-gain-driven virtual camera placement strategy to maximize scene coverage, followed by video diffusion priors to refine rendered results. Fine-tuning 3D Gaussians with these enhanced views significantly improves reconstruction quality. To evaluate our method, we present Wild-Explore, a benchmark designed for challenging scene exploration. Experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing 3DGS-based methods, enabling high-quality, artifact-free rendering from arbitrary viewpoints. https://exploregs.github.io
近期新型视图合成(NVS)的进展已经实现了使用3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)进行实时渲染。然而,当从偏离训练轨迹的视角进行渲染时,现有方法往往会出现伪影和缺失区域,限制了无缝场景的探索。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于3DGS的管道,通过生成额外的训练视图来提高重建效果。我们引入了一种以信息增益驱动的虚拟相机放置策略,以最大化场景覆盖,然后利用视频扩散先验来优化渲染结果。使用这些增强视图对3D高斯进行微调,可以显著提高重建质量。为了评估我们的方法,我们推出了Wild-Explore,这是一个为具有挑战性的场景探索而设计的基准测试。实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的基于3DGS的方法,能够实现从任意视角进行的高质量、无伪影渲染。想了解更多信息请访问:[https://exploregs.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 Figures, ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于实时渲染技术的最新进展,使用三维高斯映射(3DGS)合成新的视角。文章提出了一种基于信息增益驱动的虚拟相机放置策略来最大化场景覆盖,并使用视频扩散先验技术改进渲染结果。该研究设计了一个名为Wild-Explore的基准测试平台,用于评估场景探索的挑战性。实验证明,该方法在任意视角的渲染质量上优于现有的三维高斯映射方法,能够实现高质量、无瑕疵的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 新视角合成技术结合三维高斯映射(3DGS)实现了实时渲染。
- 提出了一种基于信息增益驱动的虚拟相机放置策略,以最大化场景覆盖。
- 采用视频扩散先验技术改进了渲染结果。
- 设计了名为Wild-Explore的基准测试平台,用于评估场景探索的挑战性。
- 方法在任意视角的渲染质量上超越了现有的三维高斯映射方法。
- 实现的高质量渲染无显著瑕疵。
点此查看论文截图
A 3DGS-Diffusion Self-Supervised Framework for Normal Estimation from a Single Image
Authors:Yanxing Liang, Yinghui Wang, Jinlong Yang, Wei Li
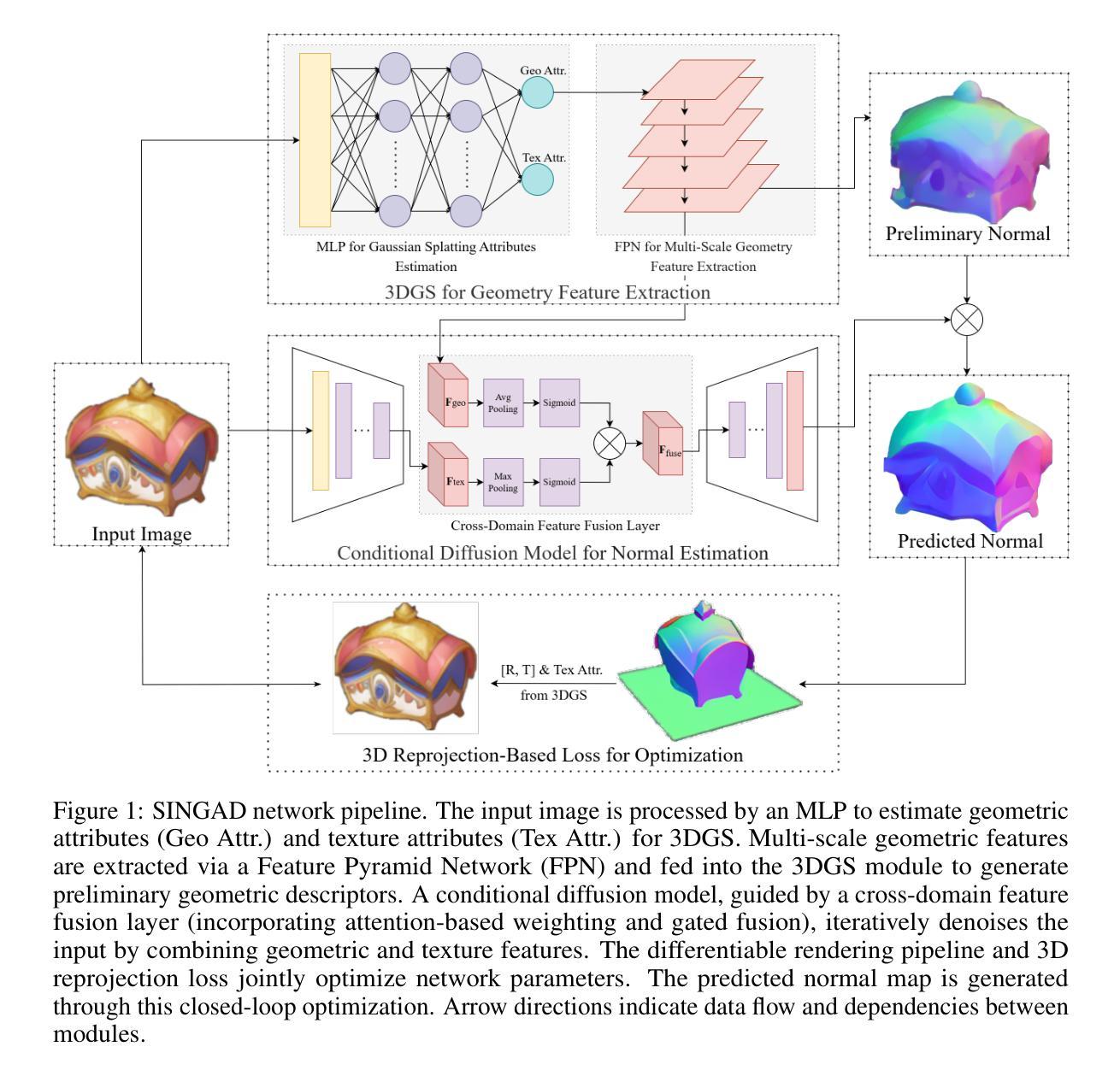
The lack of spatial dimensional information remains a challenge in normal estimation from a single image. Recent diffusion-based methods have demonstrated significant potential in 2D-to-3D implicit mapping, they rely on data-driven statistical priors and miss the explicit modeling of light-surface interaction, leading to multi-view normal direction conflicts. Moreover, the discrete sampling mechanism of diffusion models causes gradient discontinuity in differentiable rendering reconstruction modules, preventing 3D geometric errors from being backpropagated to the normal generation network, thereby forcing existing methods to depend on dense normal annotations. This paper proposes SINGAD, a novel Self-supervised framework from a single Image for Normal estimation via 3D GAussian splatting guided Diffusion. By integrating physics-driven light-interaction modeling and a differentiable rendering-based reprojection strategy, our framework directly converts 3D geometric errors into normal optimization signals, solving the challenges of multi-view geometric inconsistency and data dependency. Specifically, the framework constructs a light-interaction-driven 3DGS reparameterization model to generate multi-scale geometric features consistent with light transport principles, ensuring multi-view normal consistency. A cross-domain feature fusion module is designed within a conditional diffusion model, embedding geometric priors to constrain normal generation while maintaining accurate geometric error propagation. Furthermore, a differentiable 3D reprojection loss strategy is introduced for self-supervised optimization that minimizes geometric error between the reconstructed and input image, eliminating dependence on annotated normal datasets. Quantitative evaluations on the Google Scanned Objects dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches across multiple metrics.
缺乏空间维度信息仍然是单图像正常估计中的一个挑战。最近的基于扩散的方法在二维到三维隐式映射方面显示出巨大潜力,但它们依赖于数据驱动的统计先验,并忽略了光面交互的显式建模,从而导致多视角法线方向冲突。此外,扩散模型的离散采样机制导致可微分渲染重建模块中的梯度不连续,阻止三维几何误差反向传播到法线生成网络,从而迫使现有方法依赖于密集法线注释。本文提出了SINGAD,一种新型的自监督框架,用于通过三维高斯拼贴引导扩散从单图像进行法线估计。通过集成物理驱动的光交互建模和基于可微分渲染的重投影策略,我们的框架直接将三维几何误差转换为法线优化信号,解决了多视角几何不一致和数据依赖性的挑战。具体来说,该框架构建了一个由光交互驱动的3DGS重参数化模型,以生成符合光传输原理的多尺度几何特征,确保多视角法线一致性。在条件扩散模型中设计了一个跨域特征融合模块,嵌入几何先验以约束法线生成,同时保持准确的几何误差传播。此外,引入了一种可微分的三维重投影损失策略进行自监督优化,最小化重建图像与输入图像之间的几何误差,消除对注释法线数据集的依赖。在Google扫描对象数据集上的定量评估表明,我们的方法在多个指标上优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于单图像的自监督框架SINGAD,用于法线估计。该框架结合了物理驱动的光交互建模和基于可微分渲染的重投影策略,解决了多视角几何不一致性和数据依赖性问题。通过构建光交互驱动的3DGS重参数化模型,实现多尺度几何特征的一致性生成,确保多视角法线一致性。在Google扫描物体数据集上的定量评估表明,该方法优于其他最新技术方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新型自监督框架SINGAD用于单图像法线估计。
- 结合物理驱动的光交互建模和可微分渲染的重投影策略,解决多视角几何不一致性和数据依赖问题。
- 通过构建光交互驱动的3DGS重参数化模型,生成与光传输原理一致的多尺度几何特征。
- 设计了跨域特征融合模块,在条件扩散模型中嵌入几何先验以约束法线生成,同时保持准确的几何误差传播。
- 引入可微分的3D重投影损失策略进行自监督优化,减少了重建图像与输入图像之间的几何误差。
点此查看论文截图

Optimization-Free Style Transfer for 3D Gaussian Splats
Authors:Raphael Du Sablon, David Hart
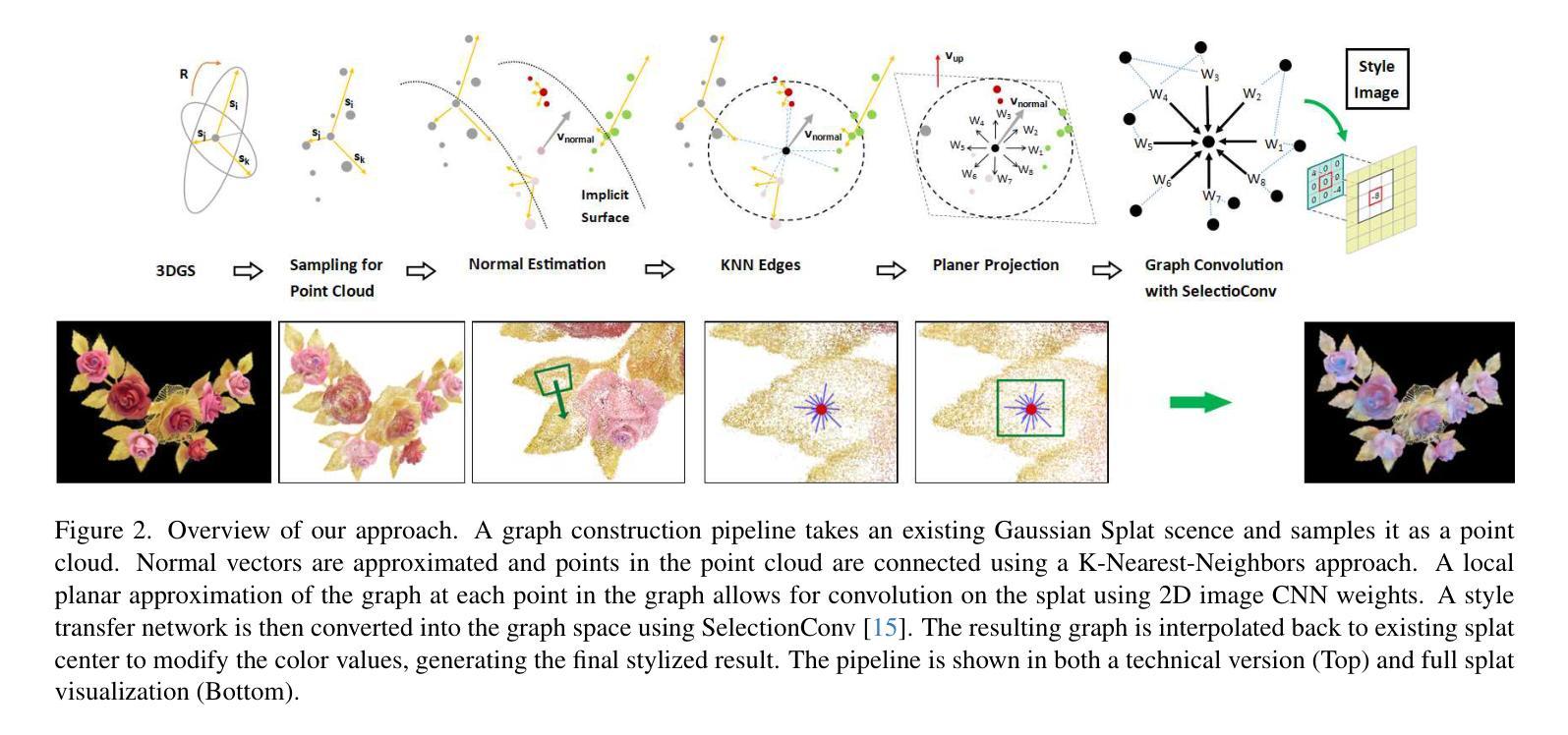
The task of style transfer for 3D Gaussian splats has been explored in many previous works, but these require reconstructing or fine-tuning the splat while incorporating style information or optimizing a feature extraction network on the splat representation. We propose a reconstruction- and optimization-free approach to stylizing 3D Gaussian splats. This is done by generating a graph structure across the implicit surface of the splat representation. A feed-forward, surface-based stylization method is then used and interpolated back to the individual splats in the scene. This allows for any style image and 3D Gaussian splat to be used without any additional training or optimization. This also allows for fast stylization of splats, achieving speeds under 2 minutes even on consumer-grade hardware. We demonstrate the quality results this approach achieves and compare to other 3D Gaussian splat style transfer methods. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/davidmhart/FastSplatStyler.
关于3D高斯斑点(splat)的风格转换任务,在之前的研究中已经进行了许多探索,但这些研究要求在融入风格信息的同时重建或微调斑点,或者在斑点表示上优化特征提取网络。我们提出了一种无需重建和优化的3D高斯斑点风格化方法。这是通过在斑点的隐式表面之间生成图形结构来实现的。然后,使用前馈、基于表面的风格化方法,并将其插值回场景中的各个斑点。这使得任何风格图像和3D高斯斑点都可以使用,无需任何额外的训练或优化。这也允许快速地对斑点进行风格化,即使在消费级硬件上也能达到低于2分钟的速度。我们展示了这种方法所达到的高质量结果,并将其与其他3D高斯斑点风格转换方法进行了比较。代码可在https://github.com/davidmhart/FastSplatStyler公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种无需重建和优化,基于图结构和表面样式的快速三维高斯样条风格化方法。该方法生成样条表示隐表面的图结构,使用前馈表面样式化方法,并插值回场景中的各个样条。这种方法可以适用于任意风格图像和三维高斯样条,无需额外训练或优化,具有快速风格化样条的能力,甚至能在消费级硬件上实现两分钟内完成。本文展示了此方法的结果质量,并与其它三维高斯样条风格迁移方法进行了比较。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的三维高斯样条风格化方法,无需重建和优化。
- 通过生成样条隐表面的图结构来实现样式化。
- 使用前馈表面样式化方法,并插值回场景中的各个样条。
- 适用于任意风格图像和三维高斯样条,具有广泛适用性。
- 无需额外训练或优化,具有快速风格化样条的能力。
- 在消费级硬件上实现两分钟内完成风格化,具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图




CF3: Compact and Fast 3D Feature Fields
Authors:Hyunjoon Lee, Joonkyu Min, Jaesik Park
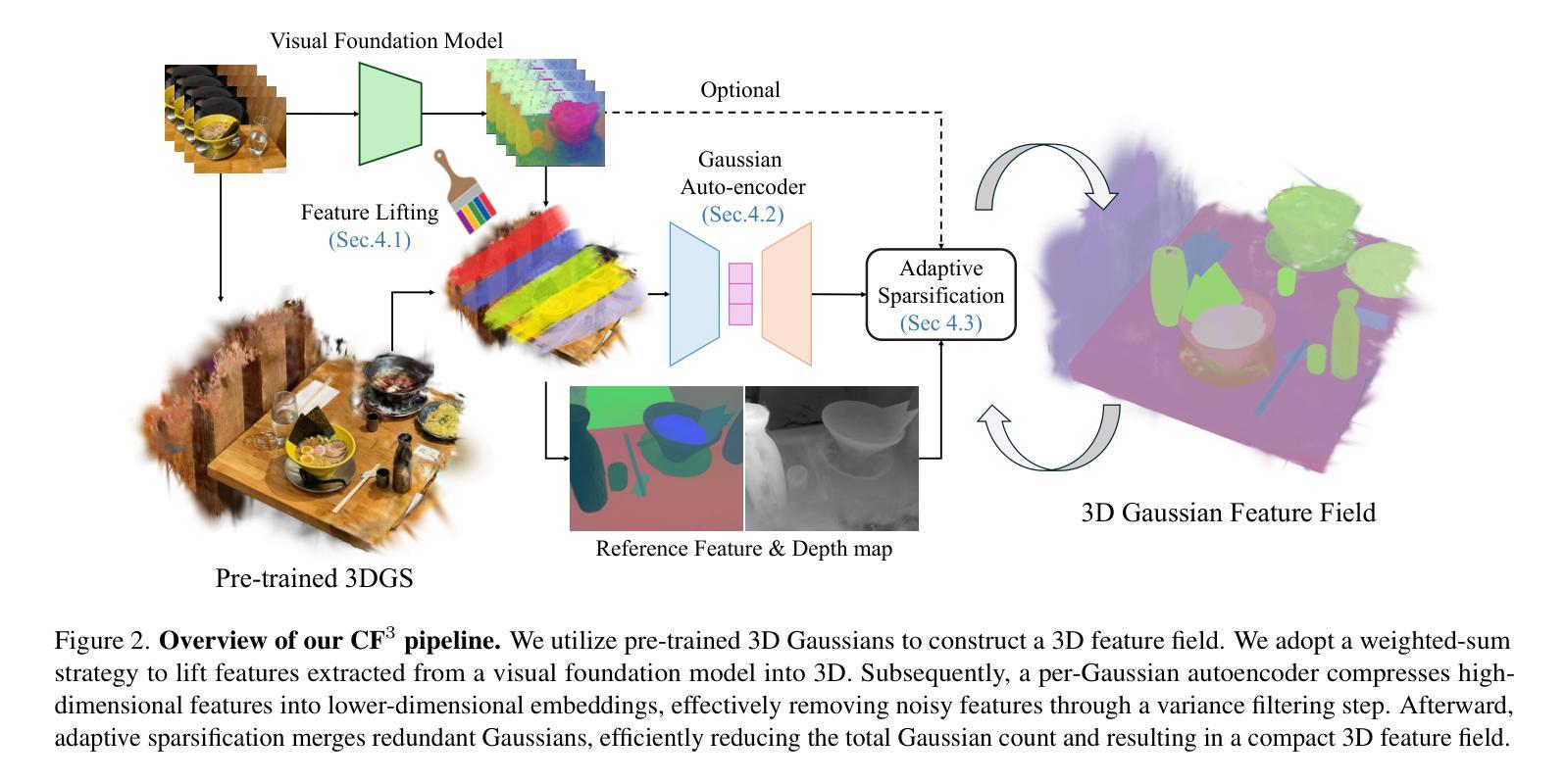
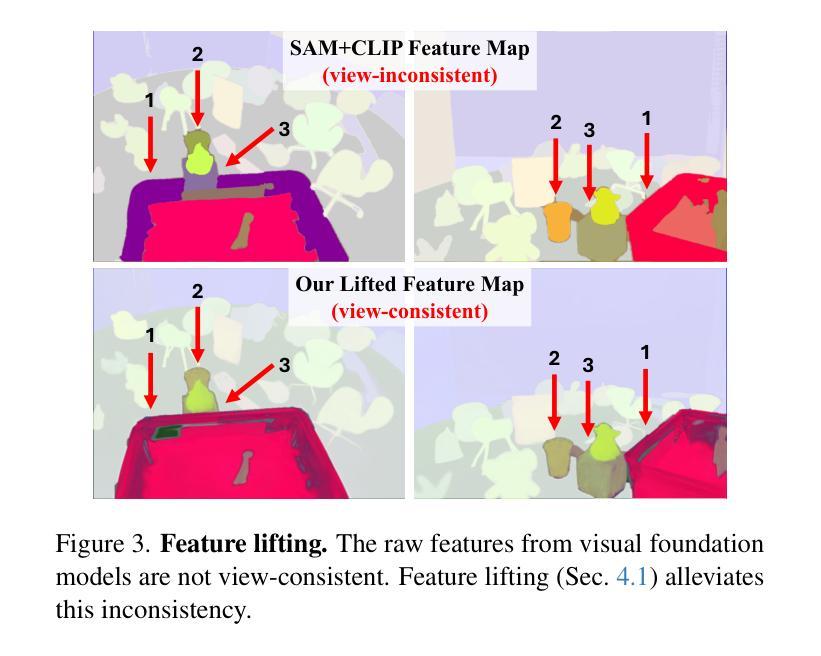
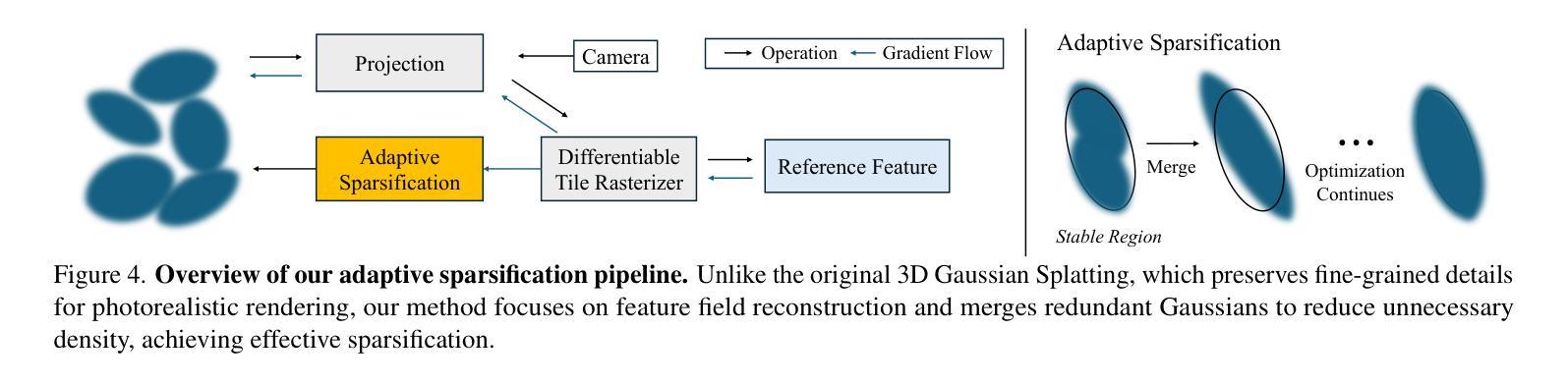
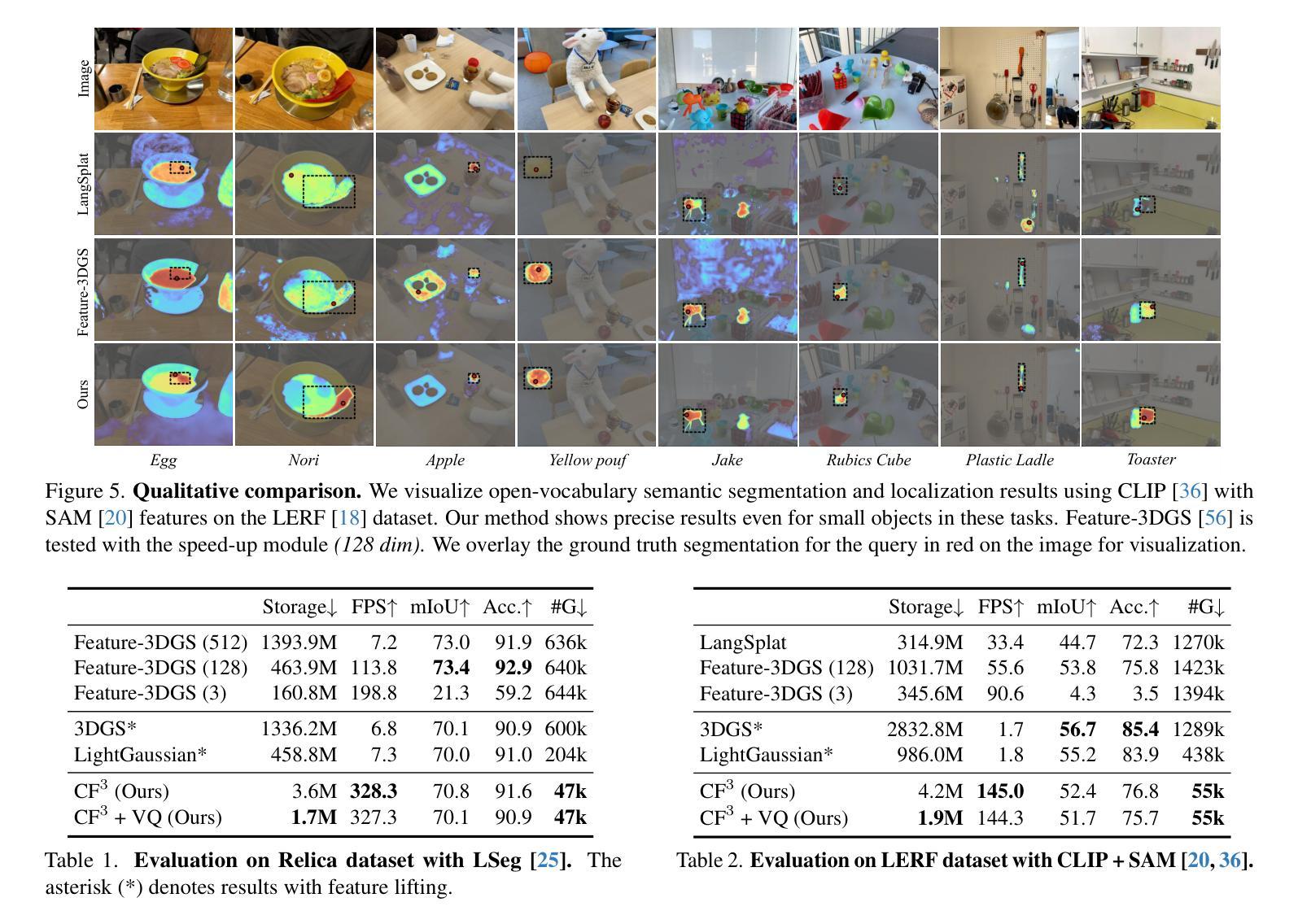
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has begun incorporating rich information from 2D foundation models. However, most approaches rely on a bottom-up optimization process that treats raw 2D features as ground truth, incurring increased computational costs. We propose a top-down pipeline for constructing compact and fast 3D Gaussian feature fields, namely, CF3. We first perform a fast weighted fusion of multi-view 2D features with pre-trained Gaussians. This approach enables training a per-Gaussian autoencoder directly on the lifted features, instead of training autoencoders in the 2D domain. As a result, the autoencoder better aligns with the feature distribution. More importantly, we introduce an adaptive sparsification method that optimizes the Gaussian attributes of the feature field while pruning and merging the redundant Gaussians, constructing an efficient representation with preserved geometric details. Our approach achieves a competitive 3D feature field using as little as 5% of the Gaussians compared to Feature-3DGS.
3D高斯展开技术(3DGS)已经开始融合来自二维基础模型的丰富信息。然而,大多数方法依赖于自下而上的优化过程,将原始二维特征视为真实依据,导致计算成本增加。我们提出了一种自上而下的构建紧凑快速的3D高斯特征场流水线,称为CF3。我们首先使用预训练的高斯对多视角二维特征进行快速加权融合。这种方法允许直接在提取的特征上训练高斯自编码器,而不是在二维域中训练自编码器。因此,自编码器与特征分布更加匹配。更重要的是,我们引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,该方法在剔除和合并冗余高斯的同时优化特征场的高斯属性,从而构建了保留几何细节的有效表示。我们的方法仅使用高斯数的5%,便构建了具有竞争力的三维特征场,相较于Feature-3DGS有所超越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
3DGS开始融合来自二维基础模型的丰富信息。然而,大多数方法采用自下而上的优化过程,将原始二维特征视为真实值,增加了计算成本。本文提出了一种构建紧凑快速的3D高斯特征场的自上而下方法——CF3。通过快速加权融合多维度的二维特征与预训练的高斯模型,可以直接在提取的特征上训练单个高斯自动编码器,使自动编码器更好地适应特征分布。更重要的是,引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,在优化特征场的高斯属性的同时删除并合并冗余的高斯模型,构建了一个具有保留几何细节的高效表示。与Feature-3DGS相比,该方法仅使用5%的高斯即可实现具有竞争力的三维特征场。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS开始融合二维基础模型的丰富信息以提升性能。
- 现有方法多采用自下而上的优化过程,导致计算成本较高。
- 提出了一种新的自上而下构建高效三维高斯特征场的方法——CF3。
- 通过快速加权融合多维度的二维特征与预训练的高斯模型,直接训练高斯自动编码器。
- 引入自适应稀疏化方法,优化特征场的高斯属性并删除冗余高斯模型。
点此查看论文截图


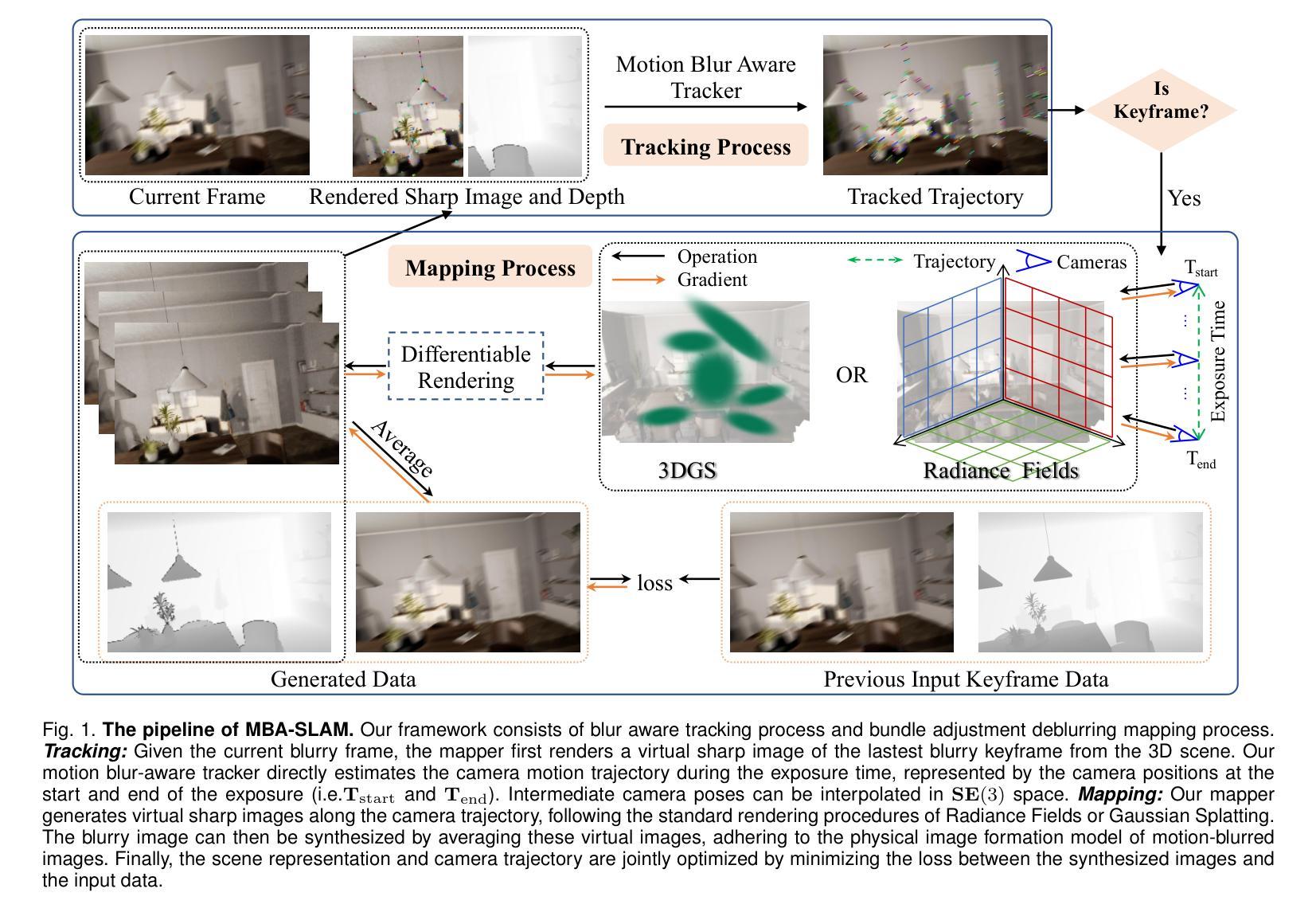
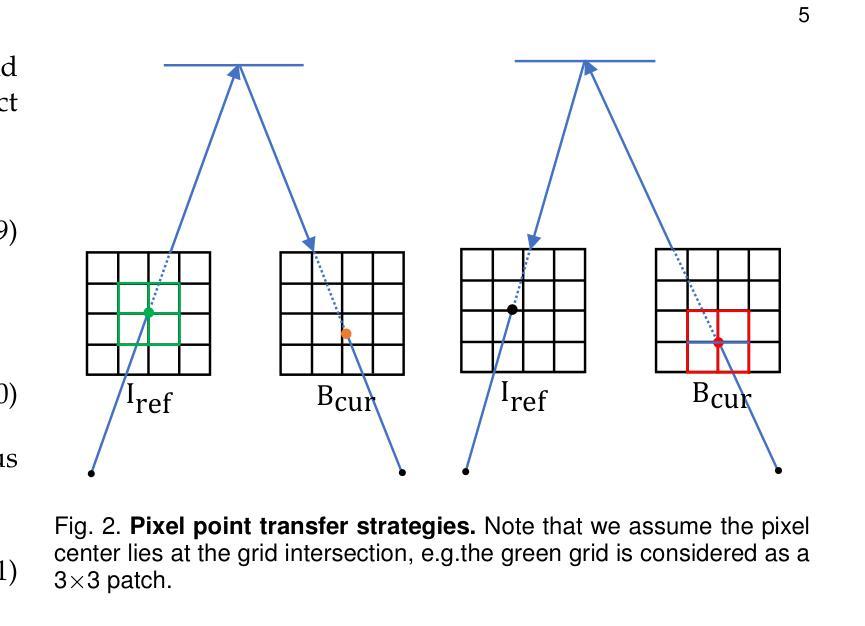
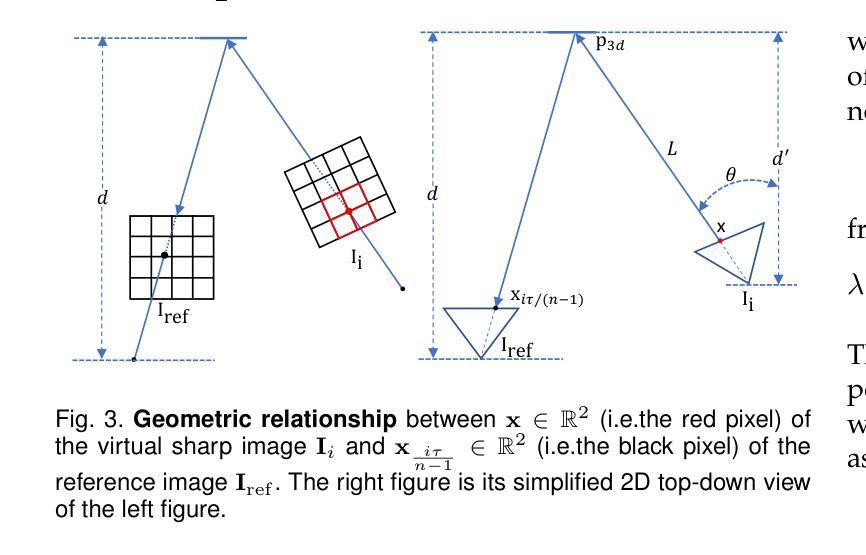
MBA-SLAM: Motion Blur Aware Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Authors:Peng Wang, Lingzhe Zhao, Yin Zhang, Shiyu Zhao, Peidong Liu
Emerging 3D scene representations, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), have demonstrated their effectiveness in Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) for photo-realistic rendering, particularly when using high-quality video sequences as input. However, existing methods struggle with motion-blurred frames, which are common in real-world scenarios like low-light or long-exposure conditions. This often results in a significant reduction in both camera localization accuracy and map reconstruction quality. To address this challenge, we propose a dense visual deblur SLAM pipeline (i.e. MBA-SLAM) to handle severe motion-blurred inputs and enhance image deblurring. Our approach integrates an efficient motion blur-aware tracker with either neural radiance fields or Gaussian Splatting based mapper. By accurately modeling the physical image formation process of motion-blurred images, our method simultaneously learns 3D scene representation and estimates the cameras’ local trajectory during exposure time, enabling proactive compensation for motion blur caused by camera movement. In our experiments, we demonstrate that MBA-SLAM surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods in both camera localization and map reconstruction, showcasing superior performance across a range of datasets, including synthetic and real datasets featuring sharp images as well as those affected by motion blur, highlighting the versatility and robustness of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/WU-CVGL/MBA-SLAM.
新兴的3D场景表示方法,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),在用于照片级真实渲染的同时定位和地图绘制(SLAM)中已经表现出了其有效性,特别是在使用高质量视频序列作为输入时。然而,现有方法在处理运动模糊帧时面临困难,这在现实世界场景中很常见,例如在低光或长时间曝光条件下。这通常会导致相机定位精度和地图重建质量的显著降低。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种密集的视觉去模糊SLAM管道(即MBA-SLAM),以处理严重的运动模糊输入并增强图像去模糊。我们的方法将高效的动态模糊感知跟踪器与基于神经辐射场或高斯拼贴的映射器相结合。通过精确建模运动模糊图像的物理成像过程,我们的方法同时学习3D场景表示并在曝光期间估计相机的局部轨迹,从而能够对由相机移动造成的运动模糊进行积极补偿。在我们的实验中,我们证明了MBA-SLAM在相机定位和地图重建方面都超越了之前的最先进方法,展示了我们方法在多个数据集上的卓越性能,包括合成数据集和受运动模糊影响的数据集,突出了我们的方法的通用性和稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/WU-CVGL/MBA-SLAM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TPAMI; Deblur Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Summary
本文提出一种针对运动模糊输入的密集视觉去模糊SLAM管道(MBA-SLAM),该管道能够有效处理新兴的三维场景表示技术,如神经辐射场和三维高斯喷绘,在同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)中的运动模糊问题。MBA-SLAM通过准确建模运动模糊图像的物理成像过程,同时学习三维场景表示并估计相机在曝光期间的局部轨迹,以主动补偿由相机移动引起的运动模糊。实验表明,MBA-SLAM在相机定位和地图构建方面超越了现有技术,并在多个数据集上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
1.新兴三维场景表示技术如Neural Radiance Fields和3D Gaussian Splatting在SLAM中的光栅化渲染方面表现出效果。
2.现有方法在处理运动模糊帧时存在困难,这在低光或长时间曝光等现实场景中很常见。
3.MBA-SLAM被提出以解决运动模糊输入的处理问题,它整合了一个高效的动态模糊感知追踪器。
4.MBA-SLAM能够同时学习三维场景表示并估计相机在曝光期间的局部轨迹,以主动补偿运动模糊。
5.MBA-SLAM在相机定位和地图构建方面超越了现有技术,并在多个数据集上展示优越性能。
6.MBA-SLAM方法具有通用性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图