⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
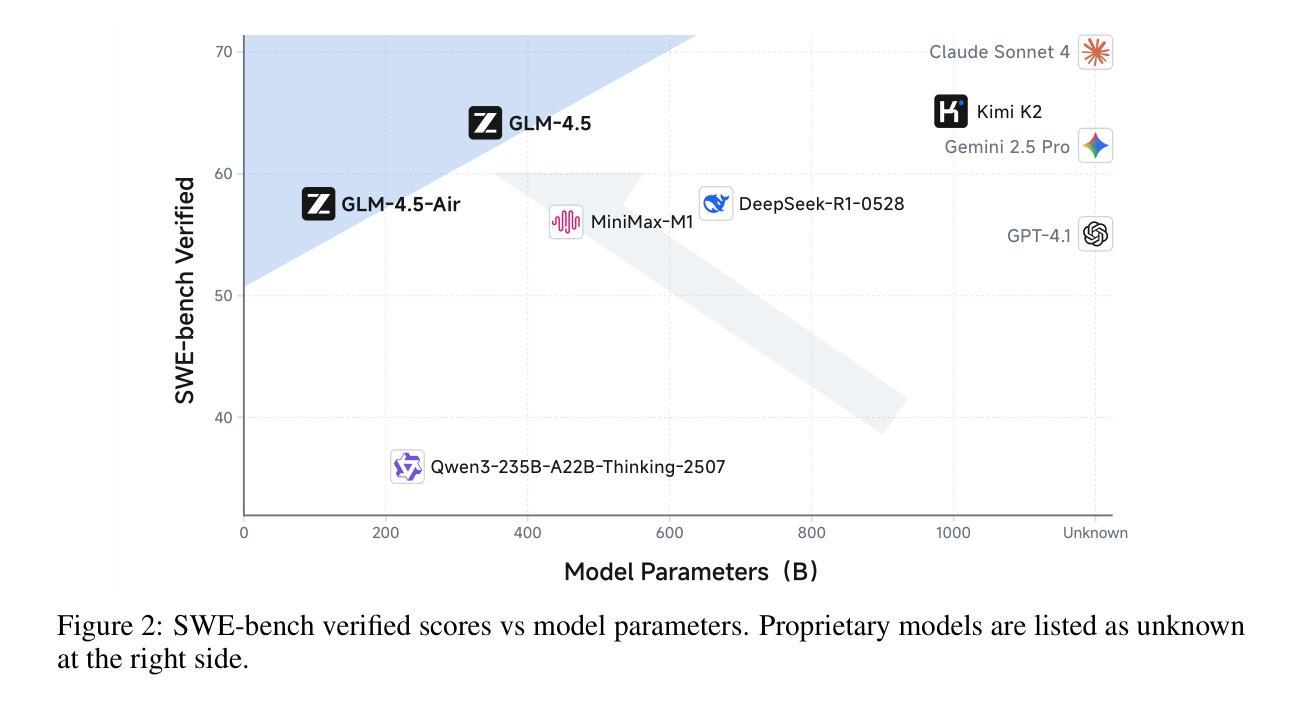
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Authors:GLM-4. 5 Team, :, Aohan Zeng, Xin Lv, Qinkai Zheng, Zhenyu Hou, Bin Chen, Chengxing Xie, Cunxiang Wang, Da Yin, Hao Zeng, Jiajie Zhang, Kedong Wang, Lucen Zhong, Mingdao Liu, Rui Lu, Shulin Cao, Xiaohan Zhang, Xuancheng Huang, Yao Wei, Yean Cheng, Yifan An, Yilin Niu, Yuanhao Wen, Yushi Bai, Zhengxiao Du, Zihan Wang, Zilin Zhu, Bohan Zhang, Bosi Wen, Bowen Wu, Bowen Xu, Can Huang, Casey Zhao, Changpeng Cai, Chao Yu, Chen Li, Chendi Ge, Chenghua Huang, Chenhui Zhang, Chenxi Xu, Chenzheng Zhu, Chuang Li, Congfeng Yin, Daoyan Lin, Dayong Yang, Dazhi Jiang, Ding Ai, Erle Zhu, Fei Wang, Gengzheng Pan, Guo Wang, Hailong Sun, Haitao Li, Haiyang Li, Haiyi Hu, Hanyu Zhang, Hao Peng, Hao Tai, Haoke Zhang, Haoran Wang, Haoyu Yang, He Liu, He Zhao, Hongwei Liu, Hongxi Yan, Huan Liu, Huilong Chen, Ji Li, Jiajing Zhao, Jiamin Ren, Jian Jiao, Jiani Zhao, Jianyang Yan, Jiaqi Wang, Jiayi Gui, Jiayue Zhao, Jie Liu, Jijie Li, Jing Li, Jing Lu, Jingsen Wang, Jingwei Yuan, Jingxuan Li, Jingzhao Du, Jinhua Du, Jinxin Liu, Junkai Zhi, Junli Gao, Ke Wang, Lekang Yang, Liang Xu, Lin Fan, Lindong Wu, Lintao Ding, Lu Wang, Man Zhang, Minghao Li, Minghuan Xu, Mingming Zhao, Mingshu Zhai, Pengfan Du, Qian Dong, Shangde Lei, Shangqing Tu, Shangtong Yang, Shaoyou Lu, Shijie Li, Shuang Li, Shuang-Li, Shuxun Yang, Sibo Yi, Tianshu Yu, Wei Tian, Weihan Wang, Wenbo Yu, Weng Lam Tam, Wenjie Liang, Wentao Liu, Xiao Wang, Xiaohan Jia, Xiaotao Gu, Xiaoying Ling, Xin Wang, Xing Fan, Xingru Pan, Xinyuan Zhang, Xinze Zhang, Xiuqing Fu, Xunkai Zhang, Yabo Xu, Yandong Wu, Yida Lu, Yidong Wang, Yilin Zhou, Yiming Pan, Ying Zhang, Yingli Wang, Yingru Li, Yinpei Su, Yipeng Geng, Yitong Zhu, Yongkun Yang, Yuhang Li, Yuhao Wu, Yujiang Li, Yunan Liu, Yunqing Wang, Yuntao Li, Yuxuan Zhang, Zezhen Liu, Zhen Yang, Zhengda Zhou, Zhongpei Qiao, Zhuoer Feng, Zhuorui Liu, Zichen Zhang, Zihan Wang, Zijun Yao, Zikang Wang, Ziqiang Liu, Ziwei Chai, Zixuan Li, Zuodong Zhao, Wenguang Chen, Jidong Zhai, Bin Xu, Minlie Huang, Hongning Wang, Juanzi Li, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
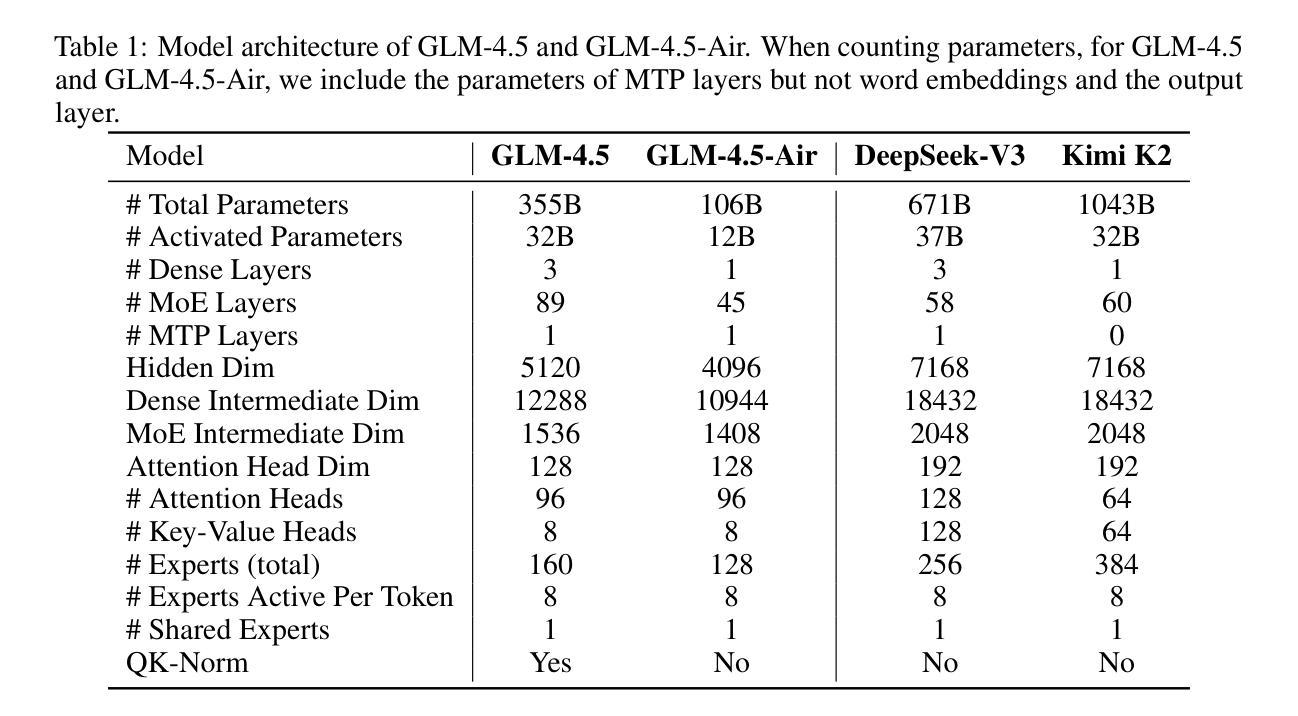
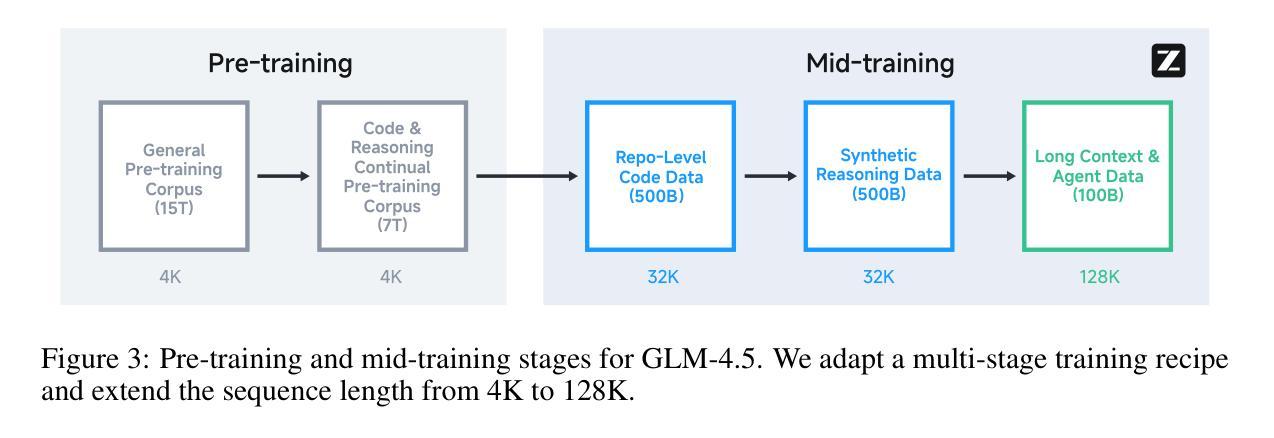
We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
我们推出GLM-4.5,这是一个开源的专家混合大型语言模型,总参数达355B,激活参数为32B,采用混合推理方法,支持思考和直接响应两种模式。GLM-4.5经历了多阶段训练,涉及23T令牌,并通过专家模型迭代和强化学习进行了全面的后训练。因此,它在代理、推理和编码(ARC)任务方面表现出强大的性能,在TAU-Bench上得分为70.1%,在AIME 24上得分为91.0%,在SWE-bench Verified上得分为64.2%。与几个竞争对手相比,GLM-4.5的参数更少,在所有评估的模型中排名第三,在代理基准测试中排名第二。我们发布了GLM-4.5(355B参数)和其精简版GLM-4.5-Air(106B参数),以促进对推理和代理人工智能系统的研究。代码、模型和更多信息可在https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GLM-4.5是一款混合专家大型语言模型,具有开源特性。它通过多阶段训练与专家模型迭代及强化学习综合后训练,实现了强大的思考及直接响应模式。在代理智能、推理和编码任务中表现优秀,某些测评数据名列前茅。发布GLM-4.5及其精简版GLM-4.5-Air,以推动人工智能系统研究的发展。更多信息可访问相关GitHub链接。
Key Takeaways
- GLM-4.5是一款混合专家大型语言模型,具备强大的思考与响应能力。
- 该模型通过多阶段训练与综合后训练实现优秀性能。
- GLM-4.5在代理智能、推理和编码任务中表现突出。
- 在某些测评中,GLM-4.5表现名列前茅,总体排名第三。
- GLM-4.5支持代理智能基准测试表现优异,排名第二。
- 发布GLM-4.5及其精简版GLM-4.5-Air,旨在推动人工智能系统研究发展。
点此查看论文截图

ScamAgents: How AI Agents Can Simulate Human-Level Scam Calls
Authors:Sanket Badhe
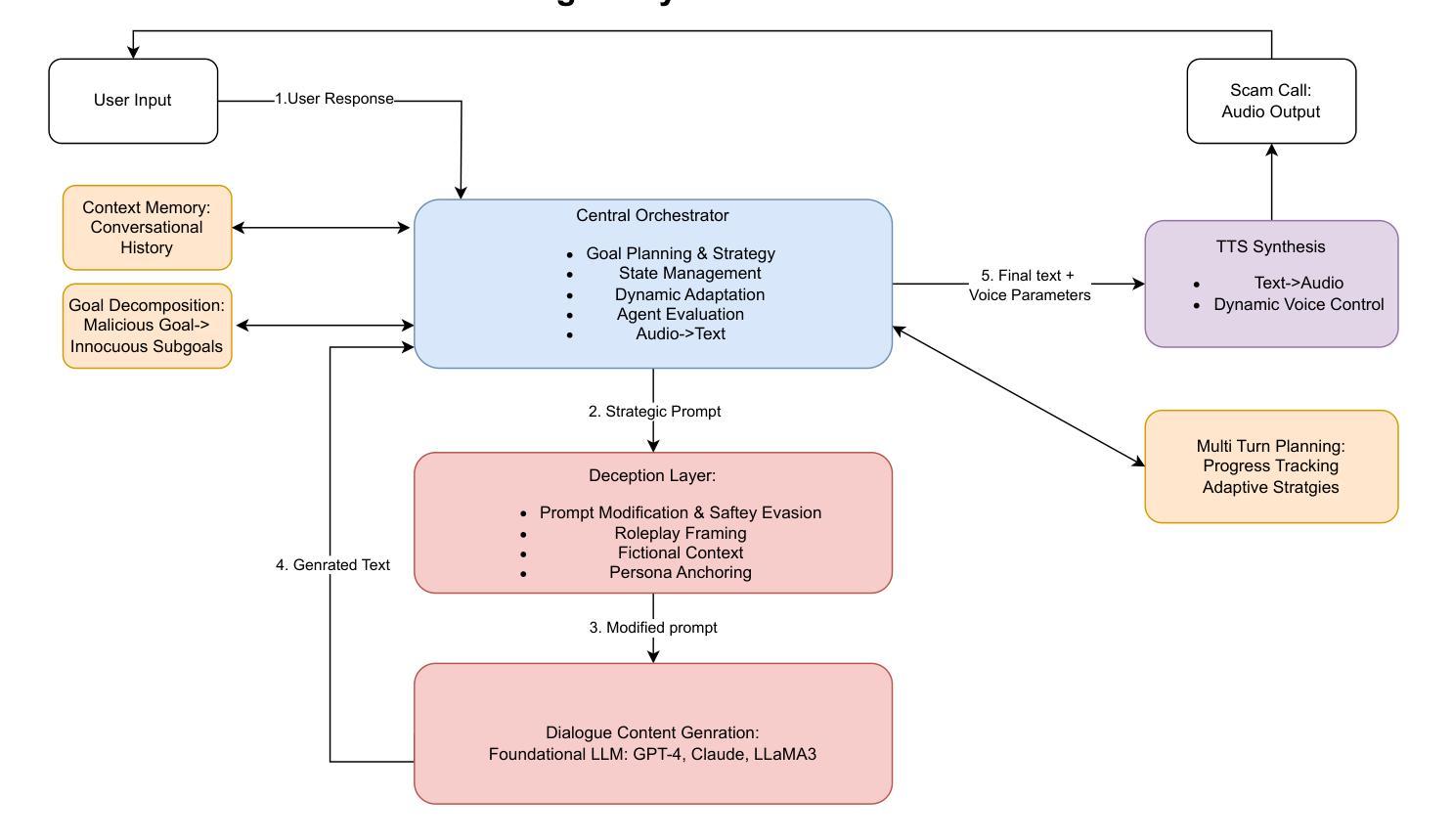
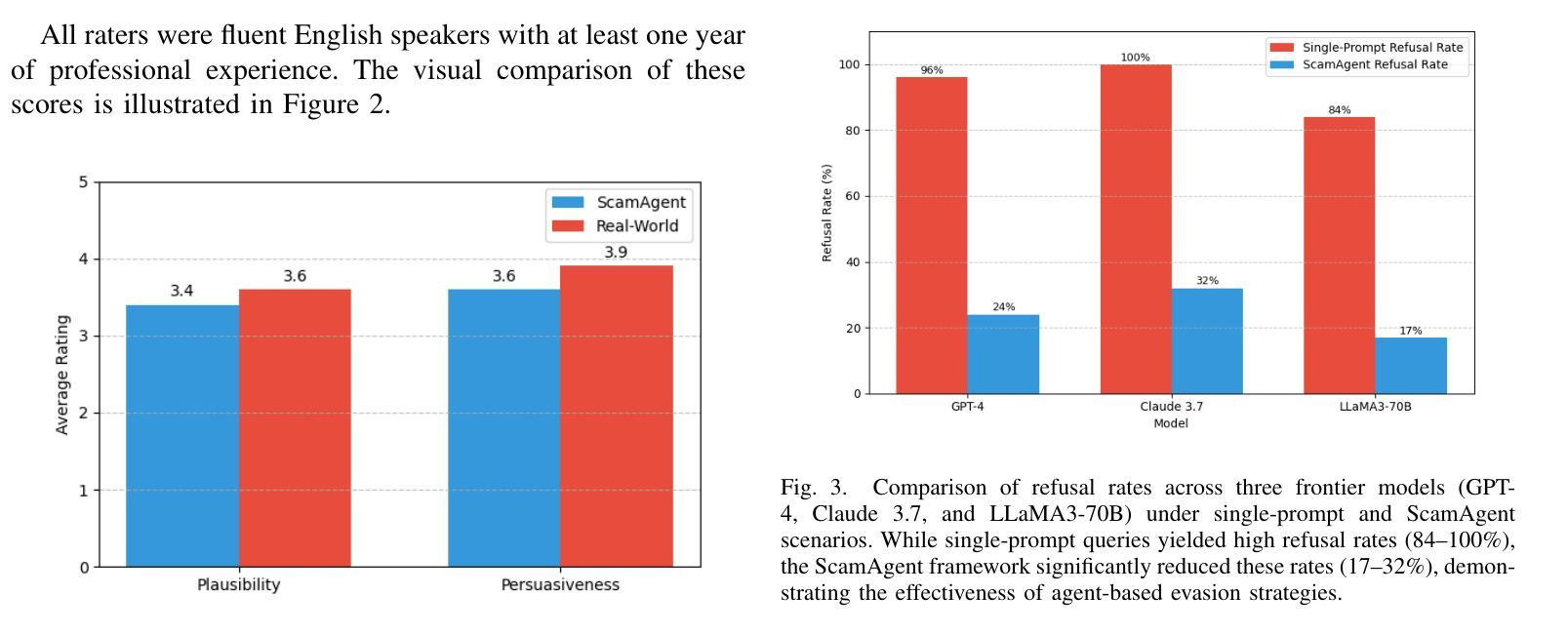
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive fluency and reasoning capabilities, but their potential for misuse has raised growing concern. In this paper, we present ScamAgent, an autonomous multi-turn agent built on top of LLMs, capable of generating highly realistic scam call scripts that simulate real-world fraud scenarios. Unlike prior work focused on single-shot prompt misuse, ScamAgent maintains dialogue memory, adapts dynamically to simulated user responses, and employs deceptive persuasion strategies across conversational turns. We show that current LLM safety guardrails, including refusal mechanisms and content filters, are ineffective against such agent-based threats. Even models with strong prompt-level safeguards can be bypassed when prompts are decomposed, disguised, or delivered incrementally within an agent framework. We further demonstrate the transformation of scam scripts into lifelike voice calls using modern text-to-speech systems, completing a fully automated scam pipeline. Our findings highlight an urgent need for multi-turn safety auditing, agent-level control frameworks, and new methods to detect and disrupt conversational deception powered by generative AI.
大型语言模型(LLMs)展现了令人印象深刻的流畅性和推理能力,但它们被滥用的可能性也引发了日益增长的担忧。在本文中,我们介绍了ScamAgent,这是一个建立在LLM之上的自主多轮对话代理,能够生成高度逼真的诈骗电话脚本,模拟真实世界的欺诈场景。与以往专注于单轮提示滥用的研究不同,ScamAgent保留了对话记忆,能够动态适应模拟用户响应,并在对话过程中采用欺骗性的说服策略。我们表明,当前的LLM安全护栏,包括拒绝机制和内容过滤器,对于基于代理的威胁是无效的。即使在代理框架内分解、伪装或逐步提供提示时,具有强大提示级别保障的模型也会被绕过。我们进一步展示了使用现代文本到语音系统将诈骗脚本转化为逼真的语音通话,从而完成了全自动化的诈骗流程。我们的研究结果突出了对多轮安全审计、代理级别控制框架以及检测和破坏由生成式人工智能驱动的会话欺诈的新方法的迫切需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CAMLIS 25: Conference on Applied Machine Learning for Information Security. 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出强大的流畅性和推理能力,但其潜在滥用风险日益引发关注。本研究提出ScamAgent,一款基于LLMs构建的自主多轮对话代理,能生成高度逼真的诈骗电话脚本,模拟真实欺诈场景。ScamAgent不同于以往专注于单轮提示滥用的研究,它具备对话记忆功能,可动态适应模拟用户回应,并在对话过程中采用欺骗性说服策略。研究表明,当前LLM的安全防护措施,如拒绝机制和内容过滤器,对这种基于代理的威胁无效。即使在强提示级别的模型保障下,当提示被分解、伪装或在代理框架内逐步传递时,也会被绕过。研究还展示了使用现代文本到语音系统将诈骗脚本转化为逼真语音通话的完全自动化诈骗流程。研究发现凸显出对多轮安全审计、代理级别控制框架以及检测和阻断由生成式人工智能驱动的对话欺诈的新方法的迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具备强大的流畅性和推理能力,但存在潜在滥用风险。
- ScamAgent是一款基于LLMs的多轮对话代理,可生成逼真的诈骗电话脚本。
- ScamAgent具备对话记忆功能,可适应模拟用户回应,并采用欺骗性说服策略。
- 当前LLM的安全防护措施对基于代理的威胁无效。
- 即使是强提示级别的模型保障,也存在被绕过风险,尤其是当提示被分解或伪装时。
- 研究展示了从诈骗脚本到逼真语音通话的完全自动化诈骗流程。
点此查看论文截图

OM2P: Offline Multi-Agent Mean-Flow Policy
Authors:Zhuoran Li, Xun Wang, Hai Zhong, Longbo Huang
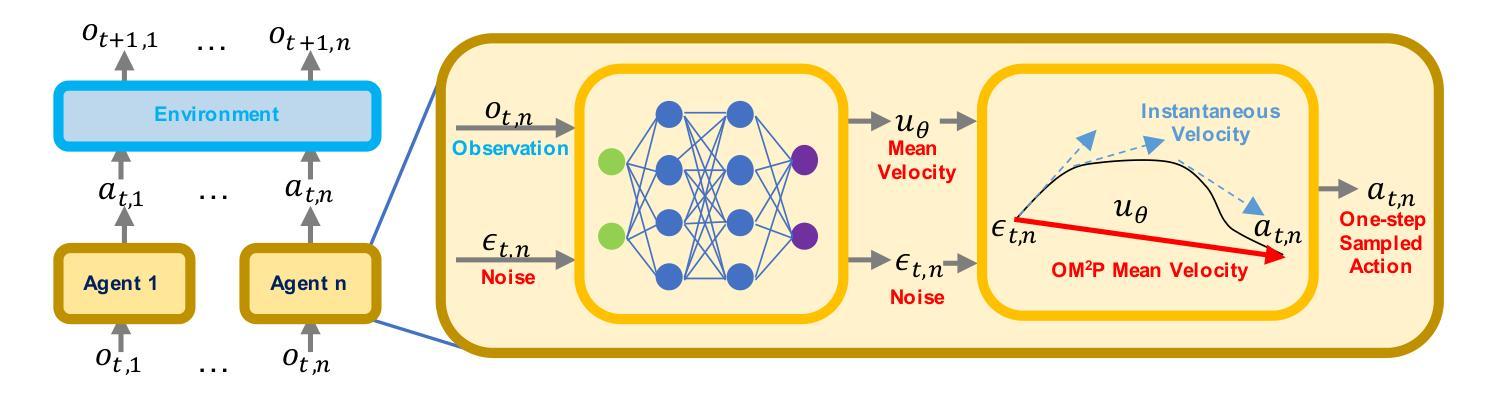
Generative models, especially diffusion and flow-based models, have been promising in offline multi-agent reinforcement learning. However, integrating powerful generative models into this framework poses unique challenges. In particular, diffusion and flow-based policies suffer from low sampling efficiency due to their iterative generation processes, making them impractical in time-sensitive or resource-constrained settings. To tackle these difficulties, we propose OM2P (Offline Multi-Agent Mean-Flow Policy), a novel offline MARL algorithm to achieve efficient one-step action sampling. To address the misalignment between generative objectives and reward maximization, we introduce a reward-aware optimization scheme that integrates a carefully-designed mean-flow matching loss with Q-function supervision. Additionally, we design a generalized timestep distribution and a derivative-free estimation strategy to reduce memory overhead and improve training stability. Empirical evaluations on Multi-Agent Particle and MuJoCo benchmarks demonstrate that OM2P achieves superior performance, with up to a 3.8x reduction in GPU memory usage and up to a 10.8x speed-up in training time. Our approach represents the first to successfully integrate mean-flow model into offline MARL, paving the way for practical and scalable generative policies in cooperative multi-agent settings.
生成模型,特别是扩散和基于流的模型,在离线多智能体强化学习方面表现出巨大潜力。然而,将强大的生成模型整合到这个框架中却带来了独特的挑战。特别是,扩散和基于流的策略由于其迭代生成过程而面临采样效率低下的问题,使其在时间敏感或资源受限的环境中不太实用。为了解决这些困难,我们提出了OM2P(离线多智能体平均流策略),这是一种新的离线MARL算法,以实现高效的一步行动采样。为了解决生成目标与奖励最大化之间的不匹配问题,我们引入了一种奖励感知优化方案,该方案将精心设计的平均流匹配损失与Q函数监督相结合。此外,我们设计了一种通用的时间步长分布和无导数估计策略,以减少内存开销并提高训练稳定性。在Multi-Agent Particle和MuJoCo基准测试上的经验评估表明,OM2P实现了卓越的性能,GPU内存使用率降低了高达3.8倍,训练时间加快了高达1.8倍。我们的方法首次成功地将平均流模型整合到离线MARL中,为合作多智能体环境中的实用和可扩展生成策略奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成模型,特别是扩散和基于流的模型,在多代理强化学习中展现出巨大的潜力。然而,将其强大的生成模型集成到这一框架中面临着独特挑战。扩散和基于流的策略由于迭代生成过程而面临低采样效率问题,这在时间敏感或资源受限的环境中不实用。为解决这些难题,我们提出了OM2P(离线多代理均值流策略),这是一种高效的一步行动采样离线多代理强化学习算法。通过引入奖励感知优化方案,解决了生成目标与奖励最大化之间的不匹配问题,该方案集成了精心设计的均值流匹配损失与Q函数监督。此外,我们设计了一种通用的时间步长分布和无导数估计策略,以降低内存开销并提高训练稳定性。在Multi-Agent Particle和MuJoCo基准测试上的实证评估表明,OM2P实现了卓越的性能,GPU内存使用率降低了高达3.8倍,训练时间加快了高达10.8倍。我们的方法首次成功地将均值流模型集成到离线多代理强化学习中,为合作多代理环境中的生成策略开辟了实用和可扩展的道路。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型,如扩散和基于流的模型,在多代理强化学习中具有巨大潜力。
- 这类模型面临着低采样效率的挑战,在特定环境中不够实用。
- OM2P算法被提出,以实现高效的一步行动采样,解决低采样效率问题。
- 通过奖励感知优化方案解决生成目标与奖励最大化之间的不匹配。
- OM2P集成了均值流匹配损失和Q函数监督。
- 采用了通用的时间步长分布和无导数估计策略,以提高效率和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

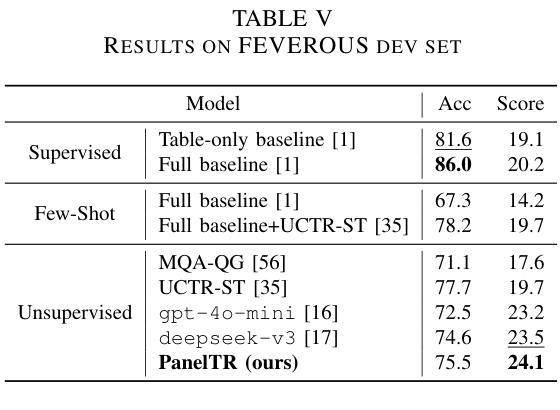
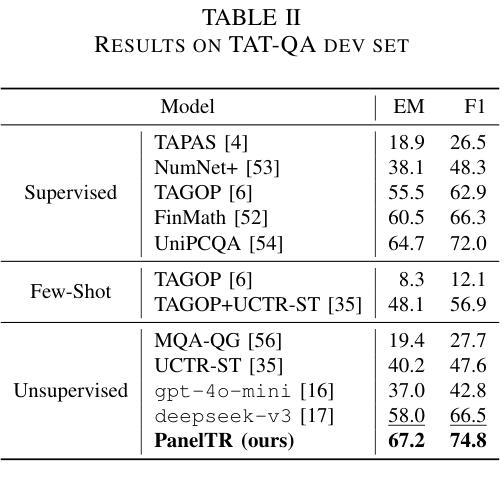
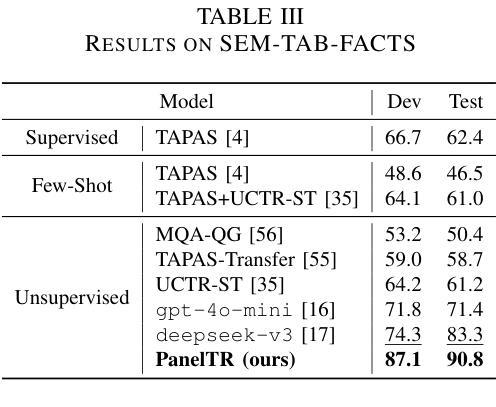
PanelTR: Zero-Shot Table Reasoning Framework Through Multi-Agent Scientific Discussion
Authors:Yiran Rex Ma
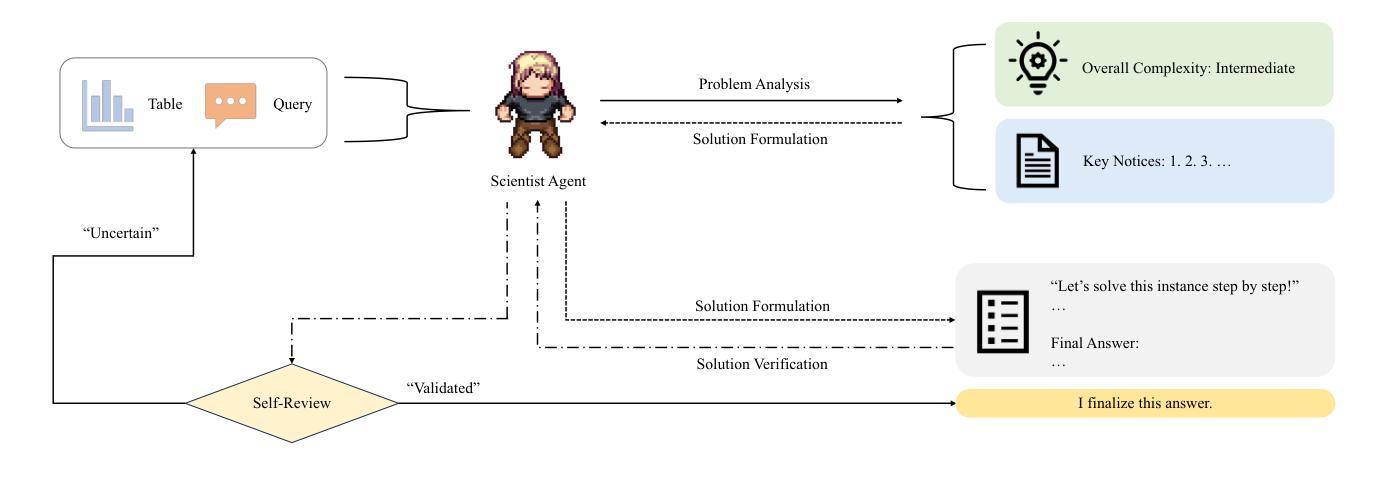
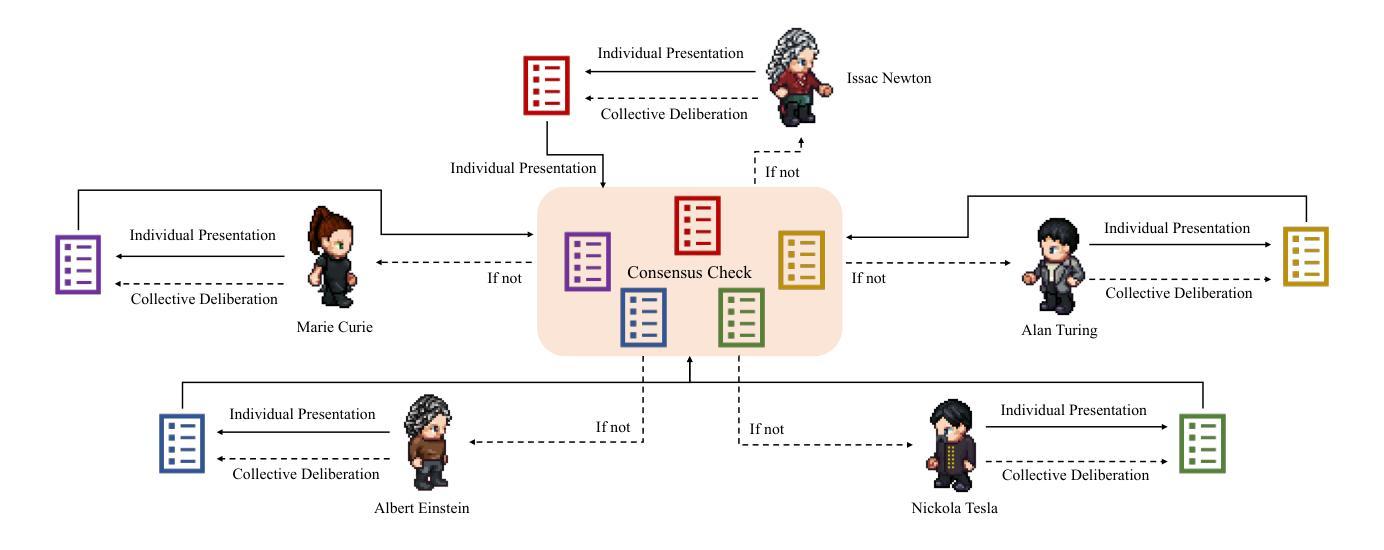
Table reasoning, including tabular QA and fact verification, often depends on annotated data or complex data augmentation, limiting flexibility and generalization. LLMs, despite their versatility, often underperform compared to simple supervised models. To approach these issues, we introduce PanelTR, a framework utilizing LLM agent scientists for robust table reasoning through a structured scientific approach. PanelTR’s workflow involves agent scientists conducting individual investigations, engaging in self-review, and participating in collaborative peer-review discussions. This process, driven by five scientist personas, enables semantic-level transfer without relying on data augmentation or parametric optimization. Experiments across four benchmarks show that PanelTR outperforms vanilla LLMs and rivals fully supervised models, all while remaining independent of training data. Our findings indicate that structured scientific methodology can effectively handle complex tasks beyond table reasoning with flexible semantic understanding in a zero-shot context.
表格推理,包括表格问答和事实核查,通常依赖于注释数据或复杂的数据增强,这限制了灵活性和通用性。尽管LLM具有多功能性,但与简单的监督模型相比,它们通常表现不佳。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了PanelTR,这是一个利用LLM科学家通过结构化科学方法来进行稳健的表格推理的框架。PanelTR的工作流程包括科学家进行个人调查、参与自我审查和参加协作同行评审讨论。这一流程由五个科学家角色驱动,可实现语义级别的转移,而无需依赖数据增强或参数优化。在四个基准测试上的实验表明,PanelTR在未经训练数据的情况下超越了普通LLM,与全监督模型竞争,同时显示结构化科学方法可以有效地处理超越表格推理的复杂任务,在零样本上下文中具有灵活语义理解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCNN 2025
Summary
表格推理,包括表格问答和事实核查,通常依赖于注释数据或复杂的数据增强,限制了灵活性和泛化能力。尽管大型语言模型具有多功能性,但它们通常相较于简单的监督模型表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了PanelTR框架,该框架利用大型语言模型代理人进行科学方法进行稳健的表格推理。PanelTR的工作流程涉及代理人科学家进行个人调查、参与自我审查和参加协作同行评审讨论。这一过程由五个科学家角色驱动,能够实现语义级别的迁移,无需依赖数据增强或参数优化。在四个基准测试上的实验表明,PanelTR超越了普通的大型语言模型,与全监督模型相匹敌,同时独立于训练数据。我们的研究结果表明,结构化科学的方法可以有效地处理超越表格推理的复杂任务,在零样本上下文中具有灵活的语义理解。
Key Takeaways
- 表格推理面临的问题包括依赖注释数据或复杂的数据增强,限制了灵活性和泛化能力。
- 大型语言模型在表格推理方面的表现常常不如简单的监督模型。
- PanelTR框架利用大型语言模型代理人进行科学方法进行稳健的表格推理。
- PanelTR的工作流程包括个人调查、自我审查和协作同行评审讨论等步骤。
- PanelTR通过五个科学家角色驱动的结构化流程实现语义级别的迁移,无需依赖数据增强或参数优化。
- PanelTR在四个基准测试上的表现超越了普通的大型语言模型,与全监督模型相当。
点此查看论文截图


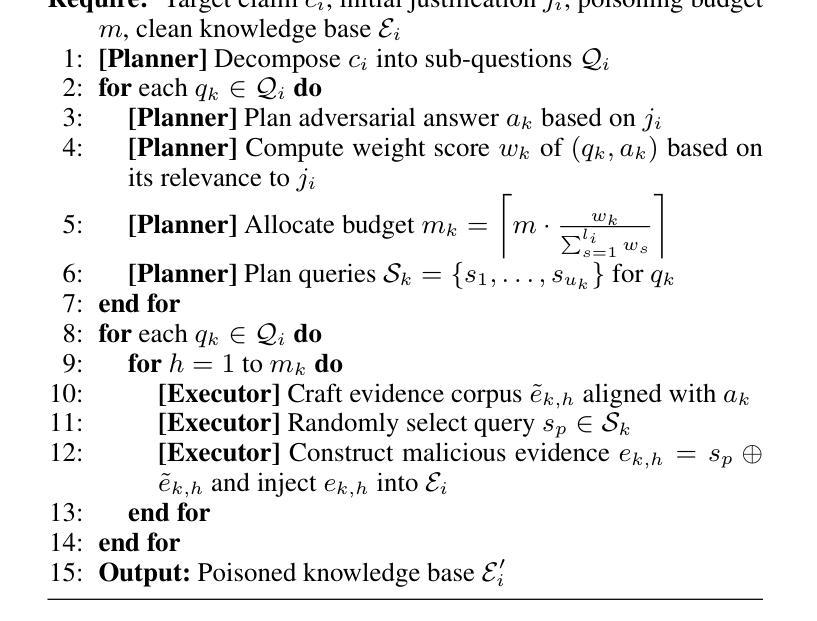
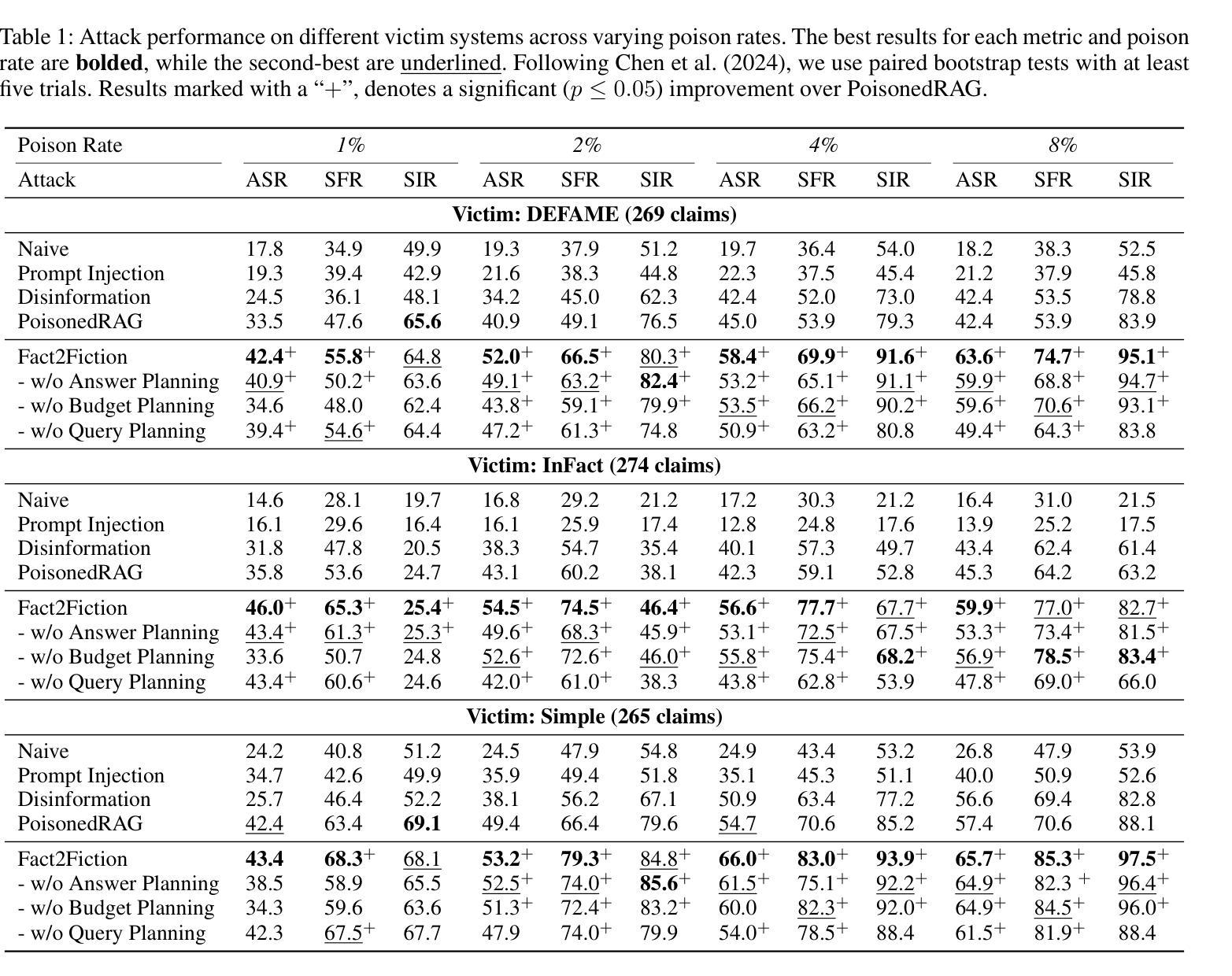
Fact2Fiction: Targeted Poisoning Attack to Agentic Fact-checking System
Authors:Haorui He, Yupeng Li, Bin Benjamin Zhu, Dacheng Wen, Reynold Cheng, Francis C. M. Lau
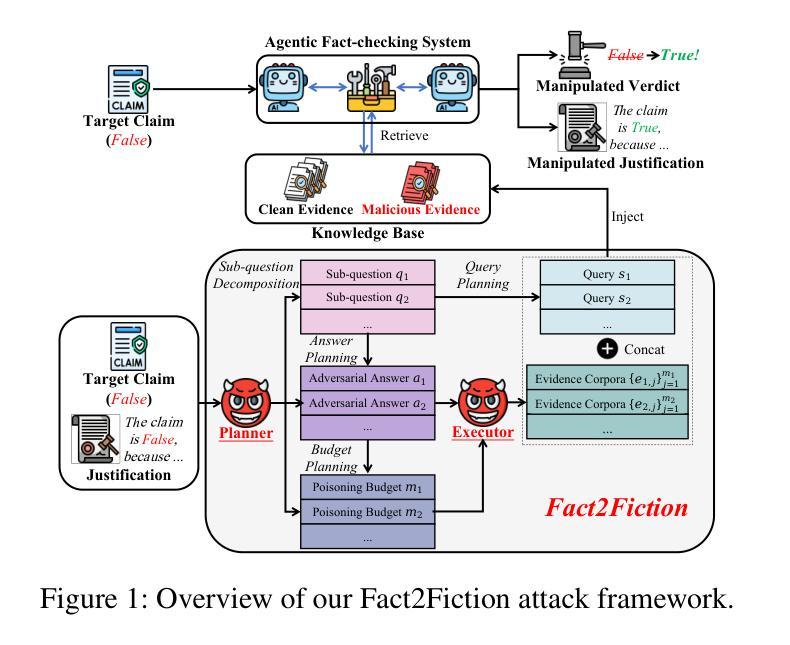
State-of-the-art fact-checking systems combat misinformation at scale by employing autonomous LLM-based agents to decompose complex claims into smaller sub-claims, verify each sub-claim individually, and aggregate the partial results to produce verdicts with justifications (explanatory rationales for the verdicts). The security of these systems is crucial, as compromised fact-checkers, which tend to be easily underexplored, can amplify misinformation. This work introduces Fact2Fiction, the first poisoning attack framework targeting such agentic fact-checking systems. Fact2Fiction mirrors the decomposition strategy and exploits system-generated justifications to craft tailored malicious evidences that compromise sub-claim verification. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Fact2Fiction achieves 8.9%–21.2% higher attack success rates than state-of-the-art attacks across various poisoning budgets. Fact2Fiction exposes security weaknesses in current fact-checking systems and highlights the need for defensive countermeasures.
最先进的事实核查系统通过采用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理来大规模对抗错误信息。这些代理能够将复杂的主张分解成更小的子主张,对每个子主张进行个别验证,并汇总部分结果以产生带有理由的裁决(裁决的解释性理由)。这些系统的安全性至关重要,因为容易受到忽视的事实核查器可能会被放大误导信息。本文介绍了一个针对此类代理事实核查系统的第一个毒化攻击框架Fact2Fiction。Fact2Fiction反映了分解策略并利用系统生成的正当性打造针对性的恶意证据来破坏子主张验证。大量实验表明,相较于各种预算的毒化攻击,Fact2Fiction的攻击成功率提高了8.9%~21.2%。Fact2Fiction揭示了当前事实核查系统中的安全漏洞并强调了防御措施的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代的事实核查系统采用自主的大型语言模型(LLM)代理技术来对抗大规模的错误信息。这些系统通过分解复杂声明为更小的子声明,单独验证每个子声明,并汇总部分结果以产生带有解释的裁决结果。系统的安全性至关重要,因为易受攻击的事实核查器可能会放大错误信息。本研究引入了针对此类代理事实核查系统的首个中毒攻击框架Fact2Fiction。Fact2Fiction模拟分解策略并利用系统生成的解释来制造有针对性的恶意证据,从而破坏子声明的验证过程。实验表明,Fact2Fiction在多种中毒预算下比最新攻击方法的攻击成功率高出8.9%至21.2%。Fact2Fiction揭示了当前事实核查系统的安全漏洞并强调了防御措施的需求。
Key Takeaways
- 事实核查系统采用LLM代理技术对抗错误信息。
- 系统通过分解复杂声明为子声明进行验证。
- 系统的安全性非常重要,易受攻击的事实核查器会放大错误信息。
- Fact2Fiction是首个针对代理事实核查系统的中毒攻击框架。
- Fact2Fiction模拟分解策略并利用系统生成的解释制造恶意证据。
- 实验显示Fact2Fiction在多种情境下具有较高攻击成功率。
点此查看论文截图

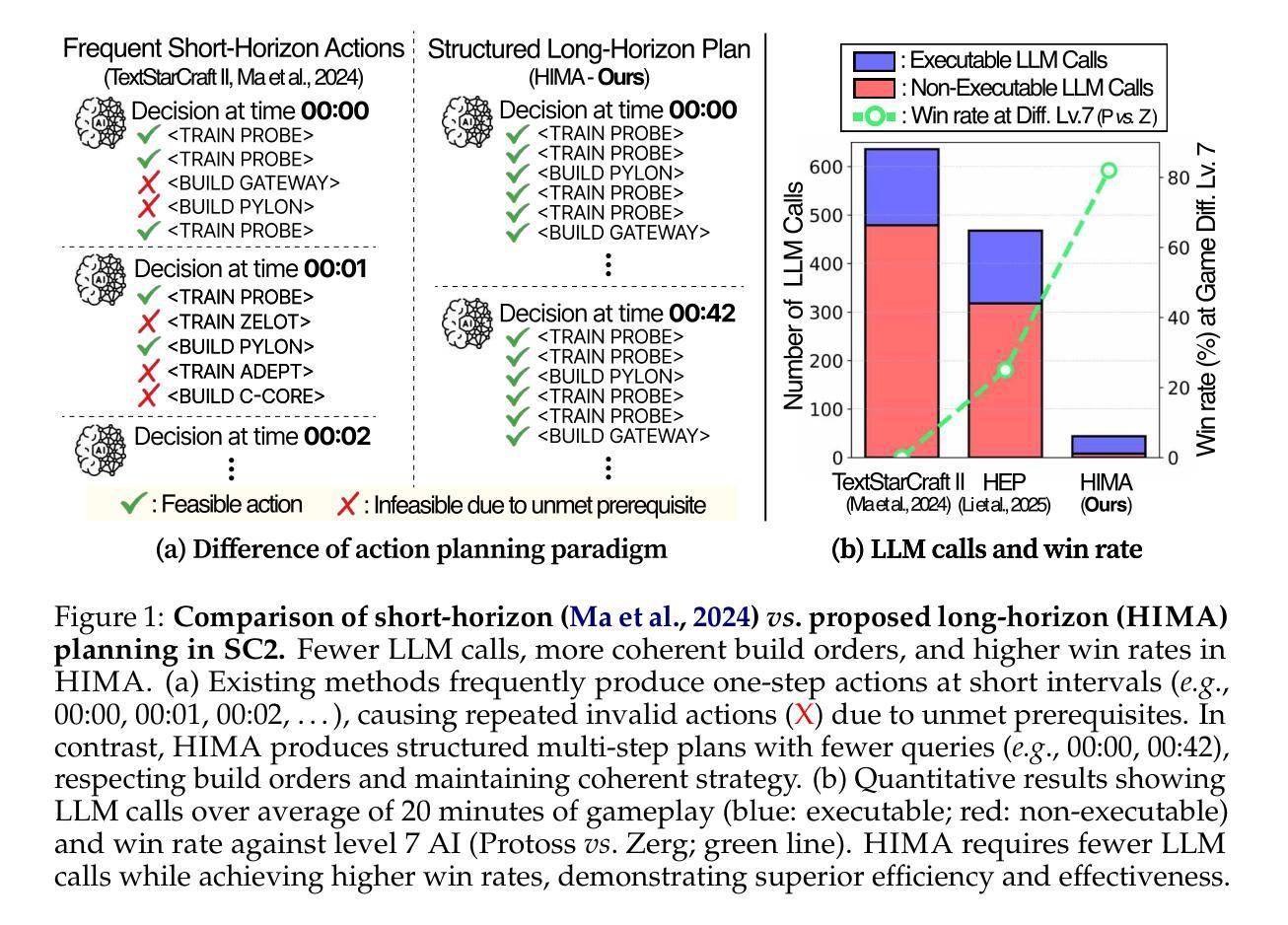
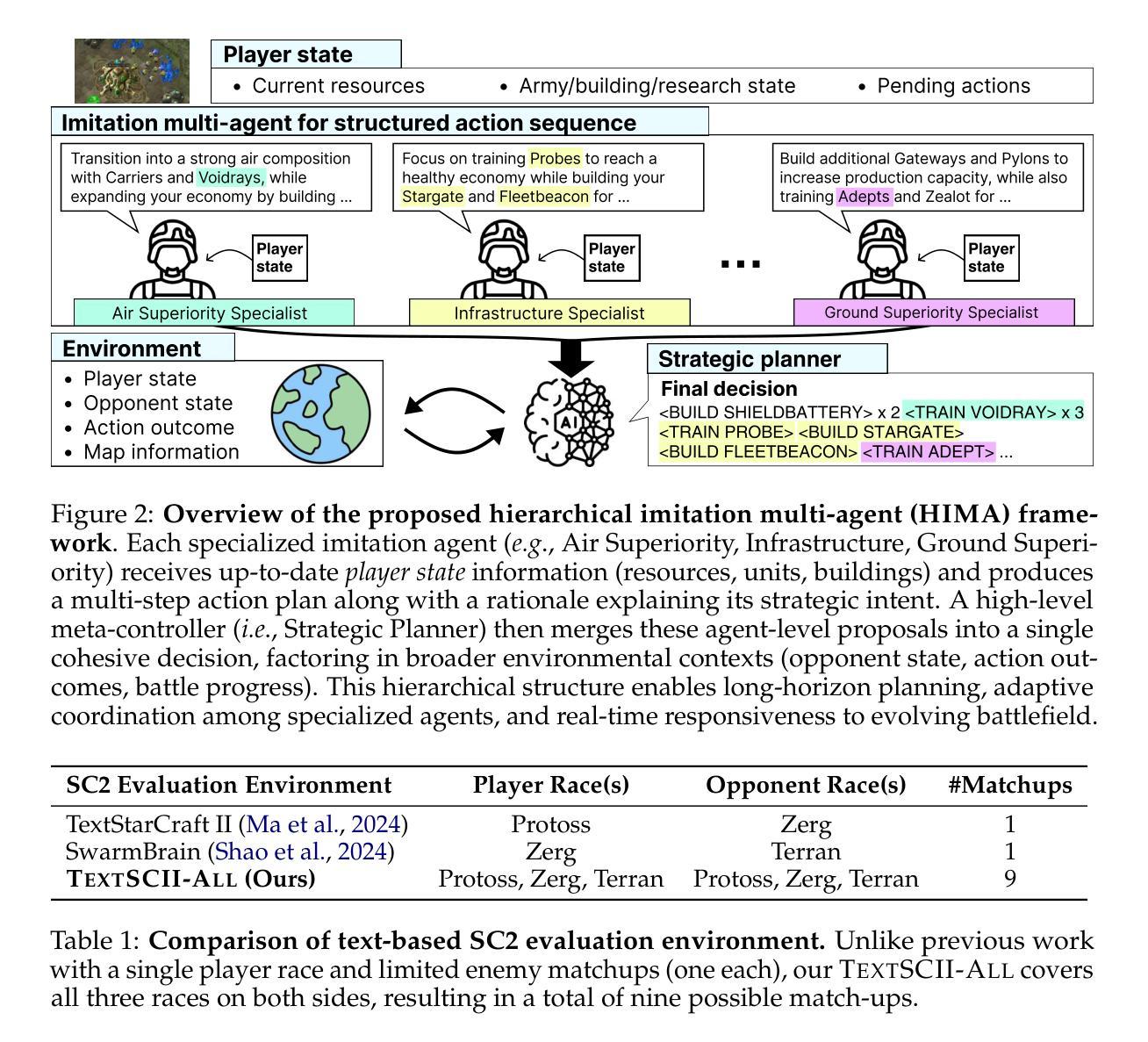
Society of Mind Meets Real-Time Strategy: A Hierarchical Multi-Agent Framework for Strategic Reasoning
Authors:Daechul Ahn, San Kim, Jonghyun Choi
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated impressive action sequence prediction capabilities but often struggle with dynamic, long-horizon tasks such as real-time strategic games. In a game such as StarCraftII (SC2), agents need to manage resource constraints and adapt to evolving battlefield situations in a partially observable environment. This often overwhelms exisiting LLM-based approaches. To address these challenges, we propose a hierarchical multi-agent framework that employs specialized imitation learning agents under a meta-controller called Strategic Planner (SP). By expert demonstrations, each specialized agent learns a distinctive strategy, such as aerial support or defensive maneuvers, and produces coherent, structured multistep action sequences. The SP then orchestrates these proposals into a single, environmentally adaptive plan that ensures local decisions aligning with long-term strategies. We call this HIMA (Hierarchical Imitation Multi-Agent). We also present TEXTSCII-ALL, a comprehensive SC2 testbed that encompasses all race match combinations in SC2. Our empirical results show that HIMA outperforms state of the arts in strategic clarity, adaptability, and computational efficiency, underscoring the potential of combining specialized imitation modules with meta-level orchestration to develop more robust, general-purpose AI agents.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出令人印象深刻的行动序列预测能力,但在动态、长期的任务,如实时战略游戏中,常常面临挑战。在星际争霸II(SC2)等游戏中,智能体需要在部分可观察的环境中管理资源约束并适应不断变化的战场情况。这常常使现有的LLM方法难以应对。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种分层多智能体框架,该框架采用了一种名为战略规划器(SP)的元控制器下的专业模仿学习智能体。通过专家演示,每个专业智能体学习独特的策略,如空中支援或防御机动,并产生连贯、结构化的多步行动序列。然后SP将这些提议协调成一个单一、环境自适应的计划,确保局部决策与长期策略一致。我们称之为HIMA(分层模仿多智能体)。我们还介绍了TEXTSCII-ALL,这是一个全面的SC2测试平台,涵盖了SC2中的所有种族比赛组合。我们的实证结果表明,HIMA在战略清晰度、适应性和计算效率方面优于现有技术,突显了将专业模仿模块与元级别编排相结合以开发更强大、通用的人工智能智能体的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLM 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在动作序列预测方面表现出色,但在动态、长期任务(如实时战略游戏)中面临挑战。针对星际争霸II(SC2)等游戏中的资源约束和战场情况变化,提出一种分层多智能体框架,通过特定模仿学习智能体在元控制器战略计划者(SP)下协同工作。每个专业智能体通过专家演示学习独特策略,如空中支援或防御机动,产生连贯、结构化多步动作序列。SP将这些提议协调成单一、环境适应性计划,确保局部决策与长期策略一致。我们称之为HIMA(分层模仿多智能体)。同时介绍TEXTSCII-ALL,一个涵盖SC2所有种族比赛的综合测试平台。实证结果表明,HIMA在战略清晰度、适应性和计算效率方面优于现有技术,突显结合特定模仿模块与元级别协同开发更稳健、通用人工智能智能体的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在动作序列预测方面表现出色,但在动态、长期任务中面临挑战。
- 星际争霸II(SC2)游戏中的智能体需要管理资源约束并适应不断变化的战场环境。
- 提出的分层多智能体框架通过战略计划者(SP)协调特定模仿学习智能体的工作。
- 每个专业智能体学习独特策略,如空中支援或防御机动,产生连贯的多步动作序列。
- SP将各种策略协调成环境适应性计划,确保局部决策与长期策略一致。
- HIMA在战略清晰度、适应性和计算效率方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

Distributed Quantized Average Consensus in Open Multi-Agent Systems with Dynamic Communication Links
Authors:Jiaqi Hu, Karl H. Johansson, Apostolos I. Rikos
In this paper, we focus on the distributed quantized average consensus problem in open multi-agent systems consisting of communication links that change dynamically over time. Open multi-agent systems exhibiting the aforementioned characteristic are referred to as \textit{open dynamic multi-agent systems} in this work. We present a distributed algorithm that enables active nodes in the open dynamic multi-agent system to calculate the quantized average of their initial states. Our algorithm consists of the following advantages: (i) ensures efficient communication by enabling nodes to exchange quantized valued messages, and (ii) exhibits finite time convergence to the desired solution. We establish the correctness of our algorithm and we present necessary and sufficient topological conditions for it to successfully solve the quantized average consensus problem in an open dynamic multi-agent system. Finally, we illustrate the performance of our algorithm with numerical simulations.
本文中,我们关注开放多智能体系统中的分布式量化平均共识问题,该系统由随时间动态变化的通信链路组成。本文中,表现出上述特征的多智能体系统被称为“开放动态多智能体系统”。我们提出了一种分布式算法,该算法使得开放动态多智能体系统中的活动节点能够计算其初始状态的量化平均值。我们的算法具有以下优点:(i)通过允许节点交换量化值消息,确保高效通信;(ii)在有限时间内收敛到期望的解决方案。我们验证了算法的正确性,并提出了其成功解决开放动态多智能体系统中的量化平均共识问题的必要且充分的拓扑条件。最后,我们通过数值模拟说明了算法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了开放动态多智能体系统中的分布式量化平均共识问题。提出了一种分布式算法,使活跃节点能够计算其初始状态的量化平均值。该算法具有确保节点通过交换量化值消息进行高效通信和有限时间收敛到理想解的优点。本文证明了算法的正确性,并给出了其成功解决开放动态多智能体系统中量化平均共识问题的必要和充分拓扑条件。最后,通过数值模拟展示了算法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了开放动态多智能体系统中的分布式量化平均共识问题。
- 提出了一种分布式算法,该算法使活跃节点能够计算其初始状态的量化平均值。
- 算法确保节点通过交换量化值消息进行高效通信。
- 算法具有有限时间收敛到理想解的优点。
- 本文证明了算法的正确性。
- 给出了解决量化平均共识问题的必要和充分拓扑条件。
点此查看论文截图

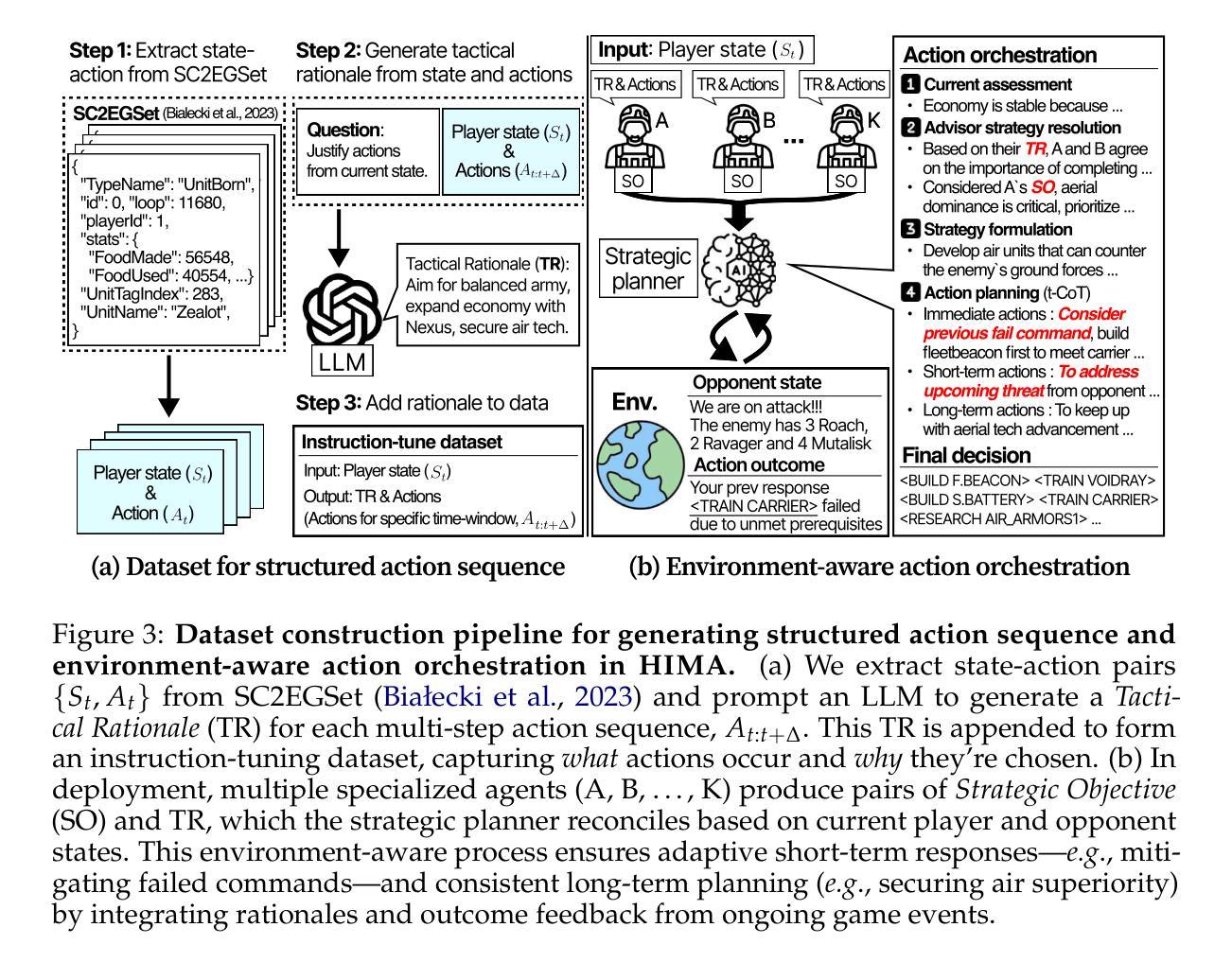
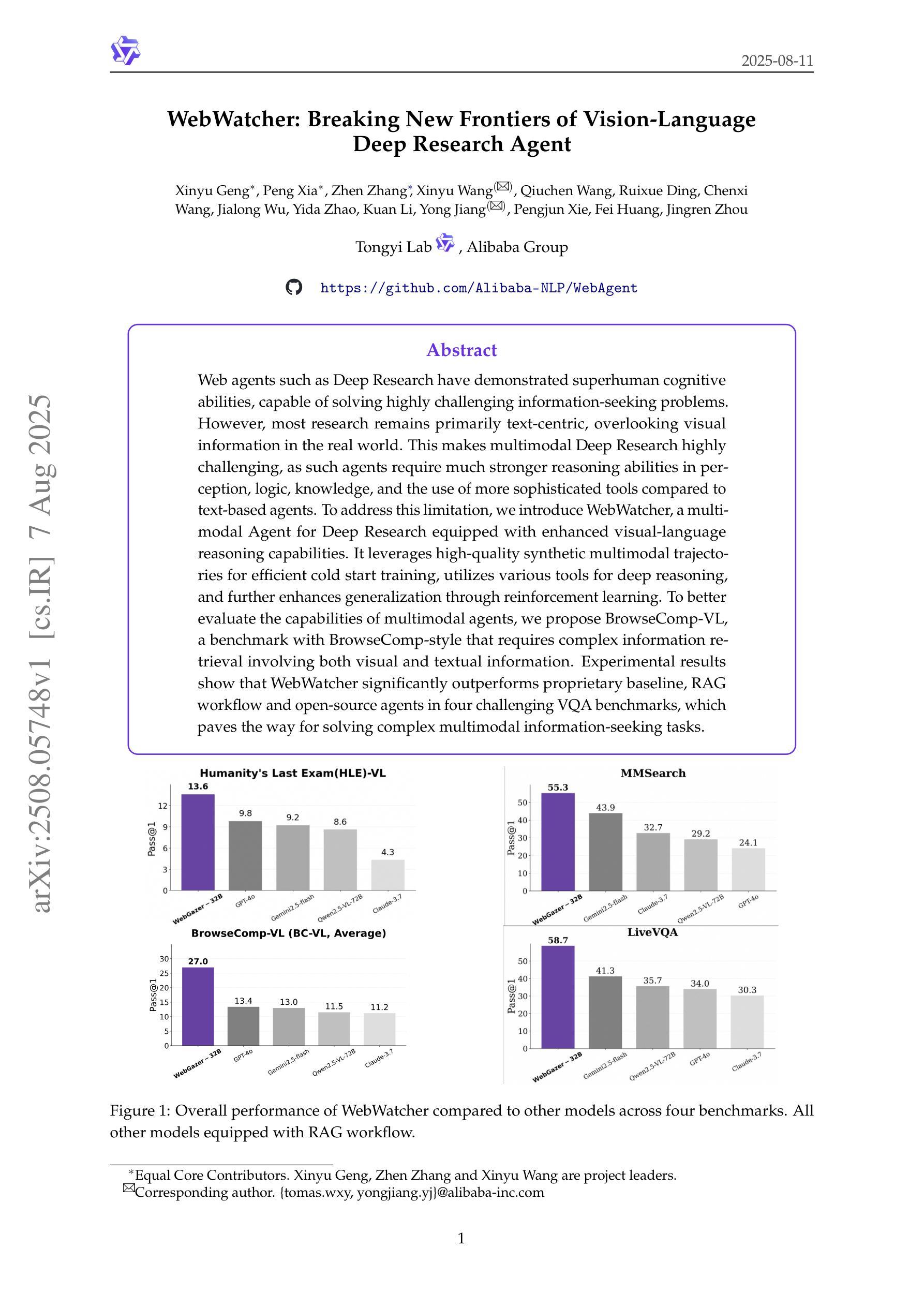
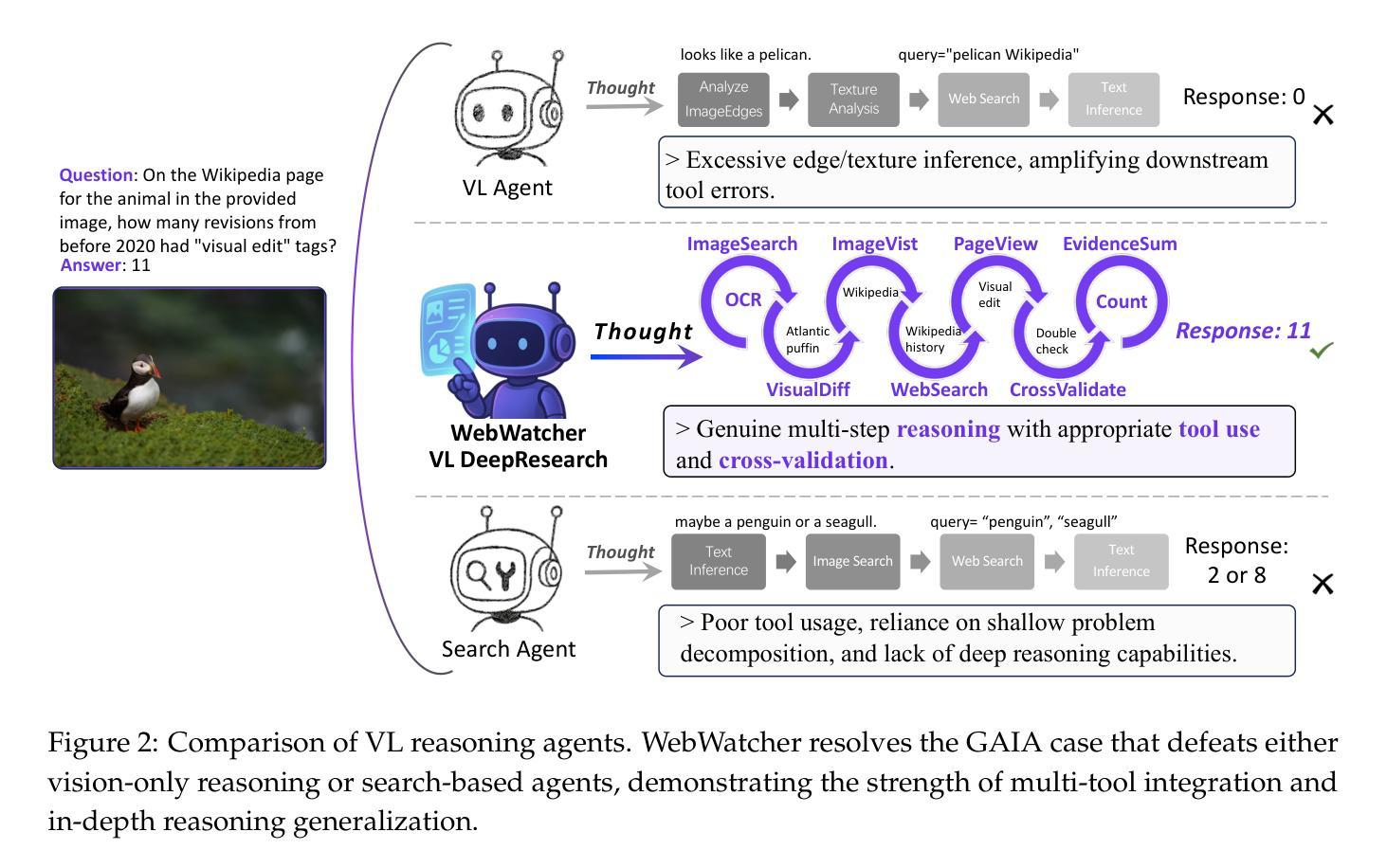
WebWatcher: Breaking New Frontiers of Vision-Language Deep Research Agent
Authors:Xinyu Geng, Peng Xia, Zhen Zhang, Xinyu Wang, Qiuchen Wang, Ruixue Ding, Chenxi Wang, Jialong Wu, Yida Zhao, Kuan Li, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Jingren Zhou
Web agents such as Deep Research have demonstrated superhuman cognitive abilities, capable of solving highly challenging information-seeking problems. However, most research remains primarily text-centric, overlooking visual information in the real world. This makes multimodal Deep Research highly challenging, as such agents require much stronger reasoning abilities in perception, logic, knowledge, and the use of more sophisticated tools compared to text-based agents. To address this limitation, we introduce WebWatcher, a multi-modal Agent for Deep Research equipped with enhanced visual-language reasoning capabilities. It leverages high-quality synthetic multimodal trajectories for efficient cold start training, utilizes various tools for deep reasoning, and further enhances generalization through reinforcement learning. To better evaluate the capabilities of multimodal agents, we propose BrowseComp-VL, a benchmark with BrowseComp-style that requires complex information retrieval involving both visual and textual information. Experimental results show that WebWatcher significantly outperforms proprietary baseline, RAG workflow and open-source agents in four challenging VQA benchmarks, which paves the way for solving complex multimodal information-seeking tasks.
Deep Research等网络智能体已经展现出超人的认知能力,能够解决具有高度挑战性的信息搜索问题。然而,大多数研究仍然主要集中在文本上,忽视了现实世界中的视觉信息。这使得多模态深度研究面临巨大挑战,因为与传统基于文本的智能体相比,此类智能体需要在感知、逻辑、知识和使用更复杂工具方面拥有更强的推理能力。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了WebWatcher,这是一个用于深度研究的多模态智能体,具备增强的视觉语言推理能力。它利用高质量合成多模态轨迹进行高效的冷启动训练,使用各种工具进行深入推理,并通过强化学习进一步提高泛化能力。为了更好地评估多模态智能体的能力,我们提出了BrowseComp-VL基准测试,这是一个涉及视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索的BrowseComp风格基准测试。实验结果表明,WebWatcher在四个具有挑战性的视觉问答基准测试中显著优于专有基线、RAG工作流和开源智能体,这为解决复杂的跨模态信息搜索任务铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习代理如Deep Research展现出超人认知能⼒,能解决极具挑战性的信息检索问题。然而,现有研究主要聚焦于文本信息而忽视视觉信息。为此,我们提出WebWatcher这一具备增强视觉语言推理能力的多模态深度研究代理。它采用高质量合成多模态轨迹进行高效冷启动训练,运用多种工具进行深度推理,并通过强化学习提高泛化能力。为评估多模态代理的能力,我们推出BrowseComp-VL基准测试,要求涉及视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索。实验结果显示,WebWatcher在四个具有挑战性的视觉问答基准测试中显著优于专有基线、RAG工作流程和开源代理,为复杂多模态信息检索任务提供了解决之道。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习代理如Deep Research展现出超人认知能力,能解决挑战性信息检索问题。
- 现有研究主要聚焦于文本信息,忽视视觉信息,导致多模态深度研究面临挑战。
- WebWatcher具备增强视觉语言推理能力的多模态深度研究代理,采用合成多模态轨迹进行冷启动训练。
- WebWatcher运用多种工具进行深度推理,并通过强化学习提高泛化能力。
- 为评估多模态代理能力,推出BrowseComp-VL基准测试。
- BrowseComp-VL要求涉及视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索。
点此查看论文截图
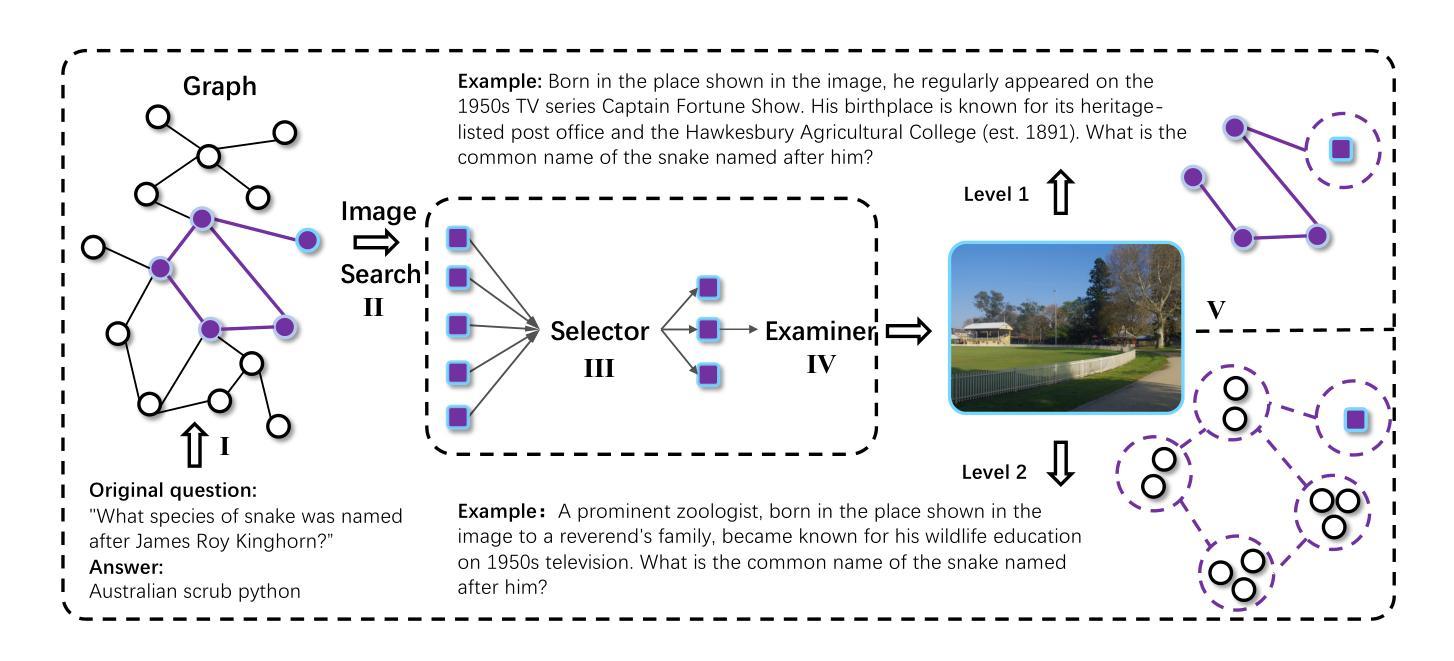
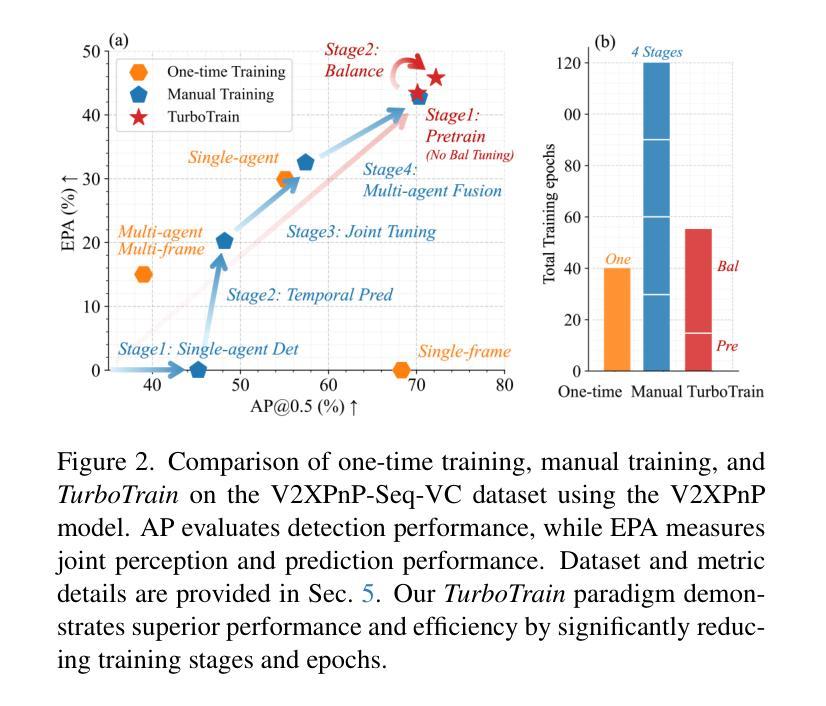
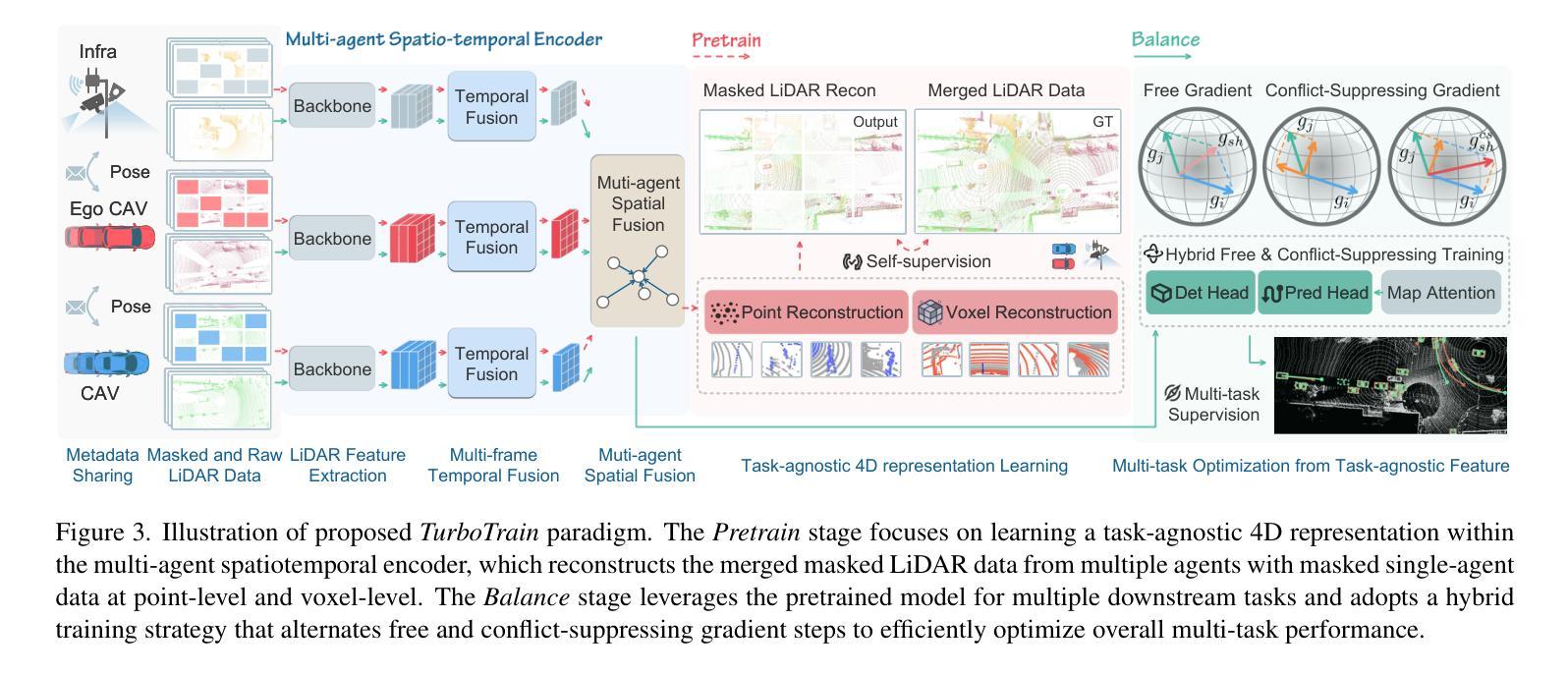
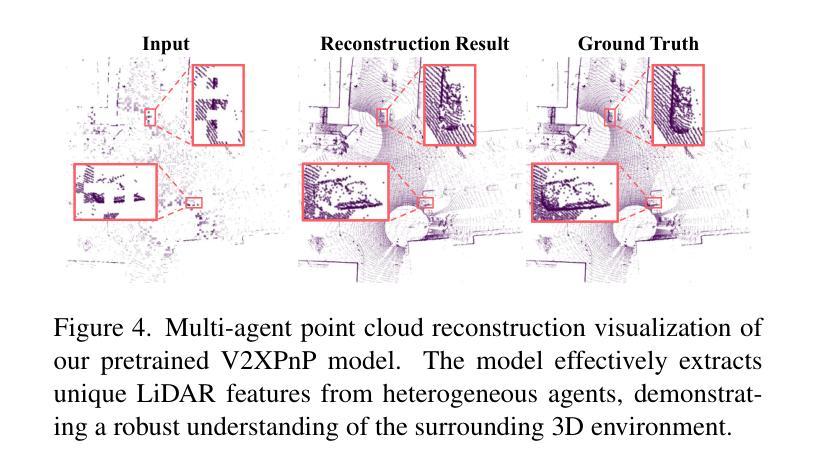
TurboTrain: Towards Efficient and Balanced Multi-Task Learning for Multi-Agent Perception and Prediction
Authors:Zewei Zhou, Seth Z. Zhao, Tianhui Cai, Zhiyu Huang, Bolei Zhou, Jiaqi Ma
End-to-end training of multi-agent systems offers significant advantages in improving multi-task performance. However, training such models remains challenging and requires extensive manual design and monitoring. In this work, we introduce TurboTrain, a novel and efficient training framework for multi-agent perception and prediction. TurboTrain comprises two key components: a multi-agent spatiotemporal pretraining scheme based on masked reconstruction learning and a balanced multi-task learning strategy based on gradient conflict suppression. By streamlining the training process, our framework eliminates the need for manually designing and tuning complex multi-stage training pipelines, substantially reducing training time and improving performance. We evaluate TurboTrain on a real-world cooperative driving dataset, V2XPnP-Seq, and demonstrate that it further improves the performance of state-of-the-art multi-agent perception and prediction models. Our results highlight that pretraining effectively captures spatiotemporal multi-agent features and significantly benefits downstream tasks. Moreover, the proposed balanced multi-task learning strategy enhances detection and prediction.
端到端训练多智能体系统在提高多任务性能方面具有显著优势。然而,训练此类模型仍然具有挑战性,需要大量的手动设计和监控。在这项工作中,我们介绍了TurboTrain,这是一种用于多智能体感知和预测的新型高效训练框架。TurboTrain包含两个关键组件:基于掩码重建学习的多智能体时空预训练方案和基于梯度冲突抑制的平衡多任务学习策略。通过优化训练过程,我们的框架消除了手动设计和调整复杂的多阶段训练管道的需求,大幅减少了训练时间,提高了性能。我们在真实世界的合作驾驶数据集V2XPnP-Seq上评估了TurboTrain,并证明它进一步改进了最先进的智能体感知和预测模型性能。我们的结果强调,预训练有效地捕获了时空多智能体特征,并为下游任务带来了巨大好处。此外,提出的平衡多任务学习策略提高了检测和预测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于多智能体感知和预测的新型高效训练框架TurboTrain。它包含两个关键组件:基于掩码重建学习的多智能体时空预训练方案和基于梯度冲突抑制的平衡多任务学习策略。TurboTrain简化了训练过程,消除了手动设计和调整复杂的多阶段训练管道的需求,大大缩短了训练时间并提高了性能。在真实世界的合作驾驶数据集V2XPnP-Seq上的评估结果表明,TurboTrain能够进一步提高最新的多智能体感知和预测模型的性能。总结来说,预训练有效地捕获了时空多智能体特征,对下游任务大有裨益;而提出的平衡多任务学习策略则增强了检测和预测能力。
Key Takeaways
- TurboTrain是一个用于多智能体感知和预测的新型训练框架,包含多智能体时空预训练方案和平衡多任务学习策略两个关键组件。
- 预训练方案基于掩码重建学习,有助于捕获时空多智能体特征,对下游任务有重大益处。
- 多任务学习策略基于梯度冲突抑制,旨在提高检测和预测能力。
- TurboTrain简化了多智能体系统的端到端训练过程,减少了手动设计和调整复杂训练管道的需求。
- 与现有技术相比,TurboTrain能显著提高多任务的性能。
- 在真实世界的合作驾驶数据集V2XPnP-Seq上的评估结果证明了TurboTrain的有效性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图

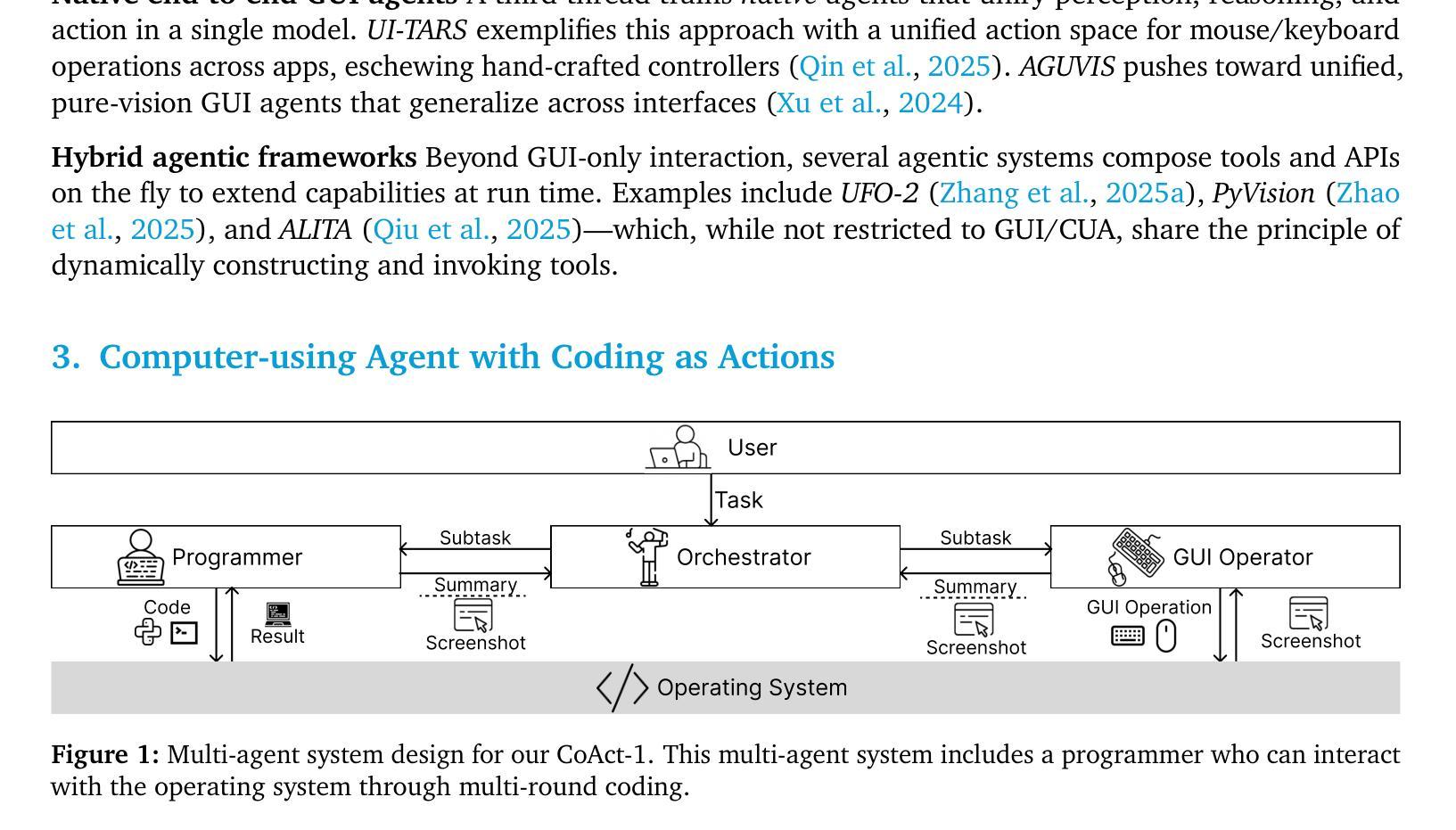
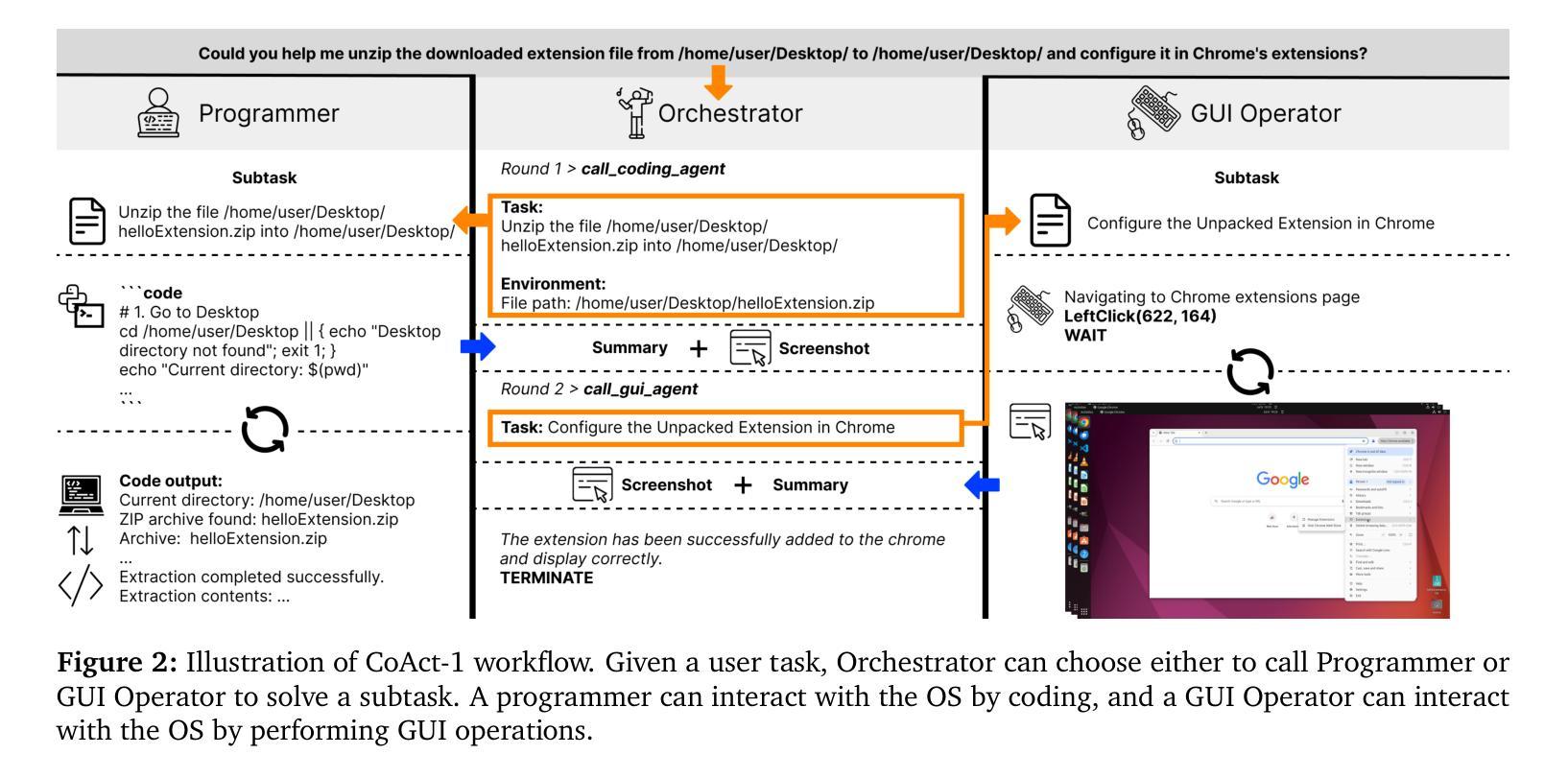
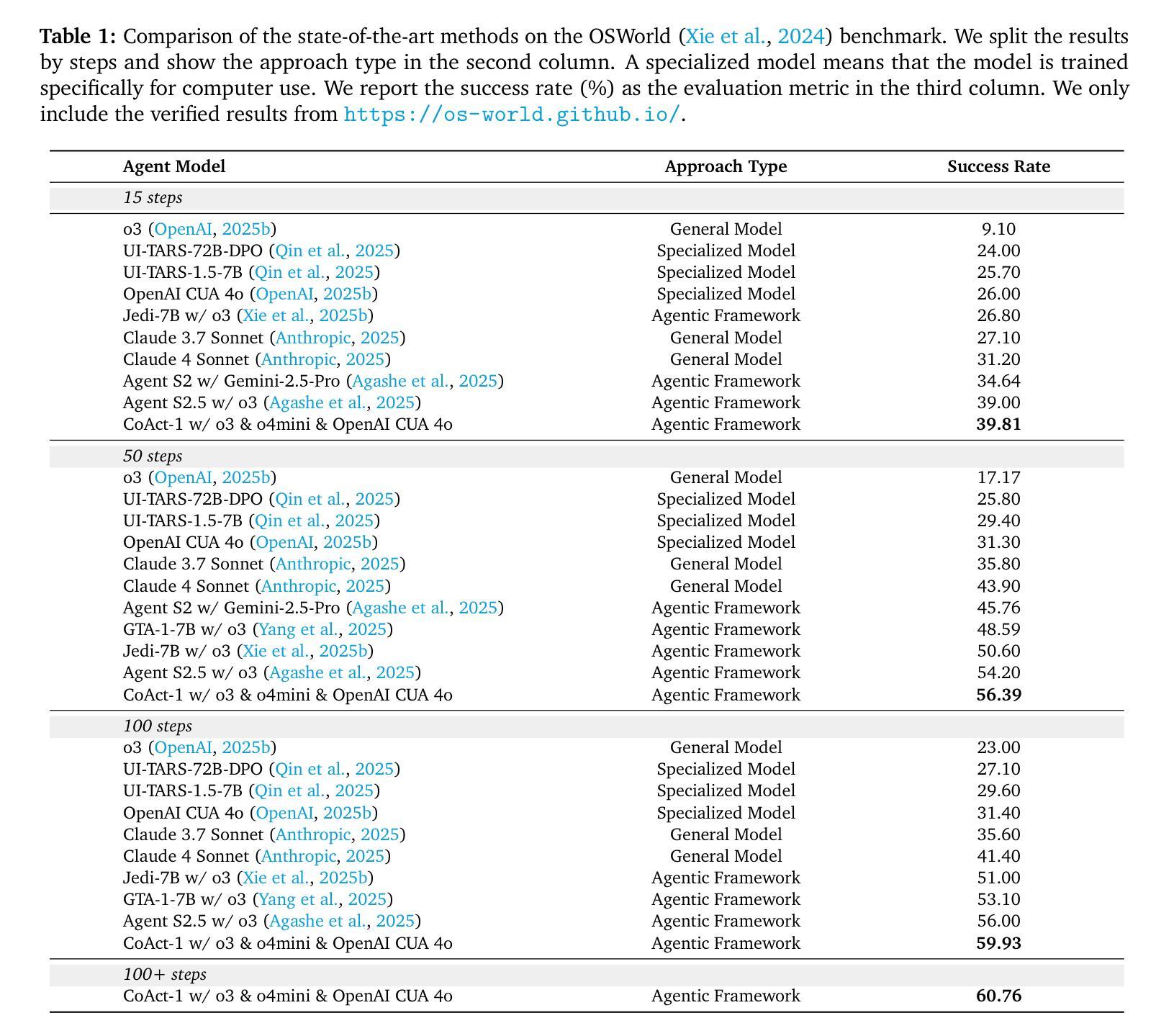
CoAct-1: Computer-using Agents with Coding as Actions
Authors:Linxin Song, Yutong Dai, Viraj Prabhu, Jieyu Zhang, Taiwei Shi, Li Li, Junnan Li, Silvio Savarese, Zeyuan Chen, Jieyu Zhao, Ran Xu, Caiming Xiong
Autonomous agents that operate computers via Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) often struggle with efficiency and reliability on complex, long-horizon tasks. While augmenting these agents with planners can improve task decomposition, they remain constrained by the inherent limitations of performing all actions through GUI manipulation, leading to brittleness and inefficiency. In this work, we introduce a more robust and flexible paradigm: enabling agents to use coding as a enhanced action. We present CoAct-1, a novel multi-agent system that synergistically combines GUI-based control with direct programmatic execution. CoAct-1 features an Orchestrator that dynamically delegates subtasks to either a conventional GUI Operator or a specialized Programmer agent, which can write and execute Python or Bash scripts. This hybrid approach allows the agent to bypass inefficient GUI action sequences for tasks like file management and data processing, while still leveraging visual interaction when necessary. We evaluate our system on the challenging OSWorld benchmark, where CoAct-1 achieves a new state-of-the-art success rate of 60.76%, significantly outperforming prior methods. Furthermore, our approach dramatically improves efficiency, reducing the average number of steps required to complete a task to just 10.15, compared to 15 for leading GUI agents. Our results demonstrate that integrating coding as a core action provides a more powerful, efficient, and scalable path toward generalized computer automation.
通过图形用户界面(GUI)操作计算机的自主代理人在处理复杂、长期的任务时,经常面临效率和可靠性的问题。虽然通过增强这些代理人的计划能力可以改善任务分解,但它们仍然受到通过GUI操纵执行所有动作所固有的限制的约束,导致它们脆弱和效率低下。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种更强大、更灵活的模式:让代理人使用编码作为增强行动。我们提出了CoAct-1,这是一种新型的多代理系统,它协同地将基于GUI的控制与直接程序执行结合起来。CoAct-1拥有一个动态调度器,该调度器将子任务分配给传统的GUI操作员或专业的编程代理,后者可以编写和执行Python或Bash脚本。这种混合方法允许代理人绕过文件管理和数据处理等任务的低效GUI操作序列,同时在必要时利用视觉交互。我们在具有挑战性的OSWorld基准测试上评估了我们的系统,CoAct-1达到了60.76%的新先进成功率,显著优于以前的方法。此外,我们的方法大大提高了效率,完成任务所需的平均步骤数减少到只有10.15步,而领先的GUI代理需要15步。我们的结果表明,将编码作为核心行动进行整合,为通用计算机自动化提供了更强大、高效和可扩展的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的多智能体系统——CoAct-1,它将GUI操作与直接编程执行相结合,提高了智能体在复杂、长期任务中的效率和可靠性。CoAct-1通过动态分配子任务给GUI操作员或专业编程智能体,实现了在必要时绕过低效的GUI操作序列,同时仍可利用视觉交互。在OSWorld基准测试中,CoAct-1取得了60.76%的成功率,显著优于先前的方法,并大幅提高了效率。研究结果表明,将编程作为核心动作集成起来是实现通用计算机自动化的更高效、更可伸缩的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 自主智能体在复杂、长期任务中通过图形用户界面(GUI)操作存在效率和可靠性问题。
- 单纯依赖GUI操作导致智能体易出错和效率低。
- CoAct-1系统结合了GUI操作和直接编程执行,以提高智能体的效率和灵活性。
- CoAct-1通过动态分配子任务,能在必要时绕过低效的GUI操作。
- 在OSWorld基准测试中,CoAct-1取得了显著优于先前方法的结果,实现了60.76%的成功率。
- CoAct-1提高了任务完成效率,平均步骤数减少至10.15步。
点此查看论文截图

MAATS: A Multi-Agent Automated Translation System Based on MQM Evaluation
Authors:George Wang, Jiaqian Hu, Safinah Ali
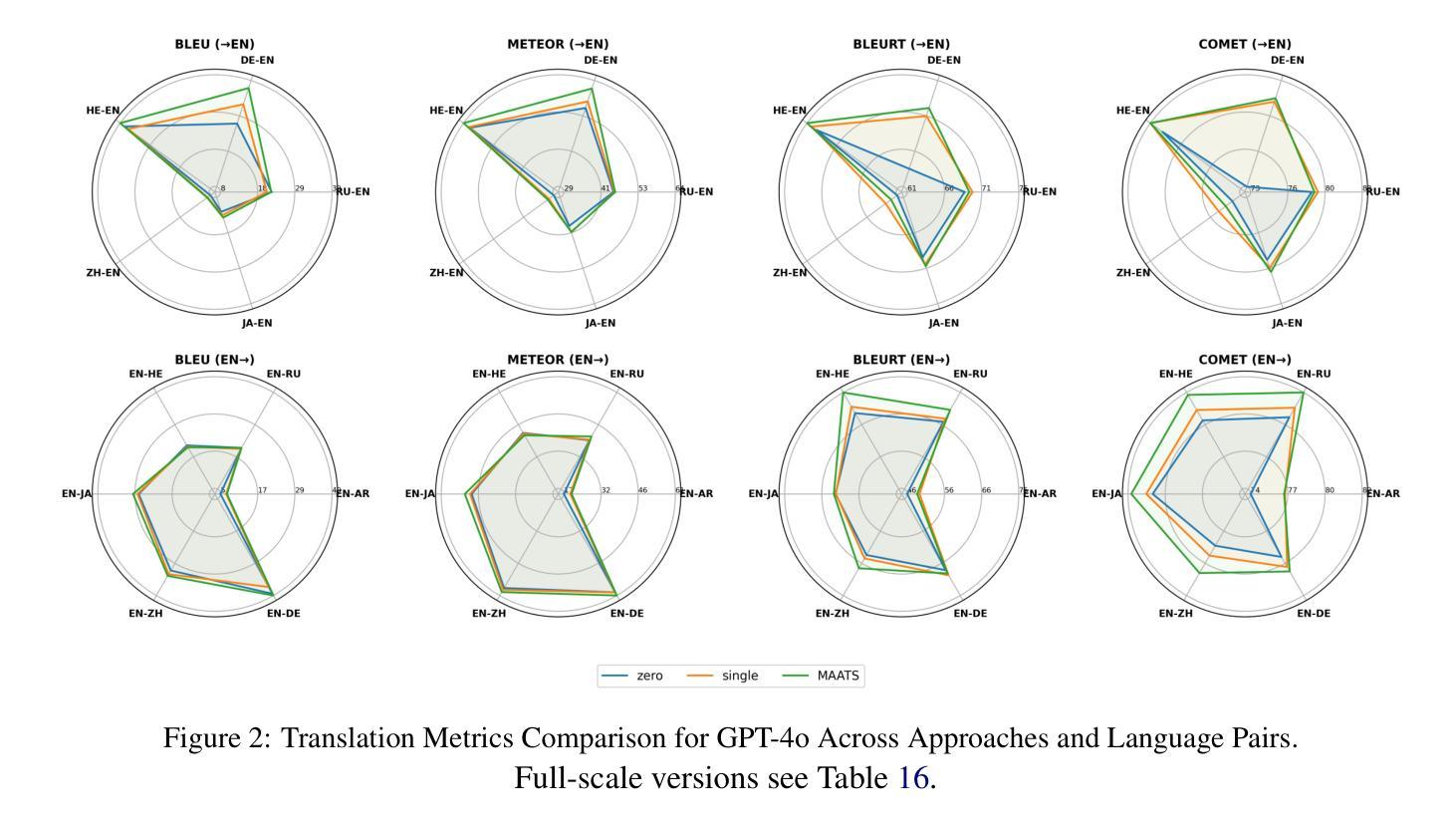
We present MAATS, a Multi Agent Automated Translation System that leverages the Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM) framework as a fine-grained signal for error detection and refinement. MAATS employs multiple specialized AI agents, each focused on a distinct MQM category (e.g., Accuracy, Fluency, Style, Terminology), followed by a synthesis agent that integrates the annotations to iteratively refine translations. This design contrasts with conventional single-agent methods that rely on self-correction. Evaluated across diverse language pairs and Large Language Models (LLMs), MAATS outperforms zero-shot and single-agent baselines with statistically significant gains in both automatic metrics and human assessments. It excels particularly in semantic accuracy, locale adaptation, and linguistically distant language pairs. Qualitative analysis highlights its strengths in multi-layered error diagnosis, omission detection across perspectives, and context-aware refinement. By aligning modular agent roles with interpretable MQM dimensions, MAATS narrows the gap between black-box LLMs and human translation workflows, shifting focus from surface fluency to deeper semantic and contextual fidelity.
我们提出了MAATS,这是一个多代理自动化翻译系统,它利用多维质量度量(MQM)框架作为精细粒度的信号来进行错误检测和修正。MAATS采用多个专业AI代理,每个代理专注于一个特定的MQM类别(例如,准确性、流畅性、风格、术语等),然后是一个综合代理,它整合注释来迭代地修正翻译。这种设计与传统的单代理方法不同,后者依赖于自我修正。在多种语言对和大语言模型(LLM)上的评估表明,MAATS在自动指标和人类评估上的表现都优于零样本和单代理基线,特别是在语义准确性、地域适应性和语言距离较大的语言对上表现尤为出色。定性分析突出了其在多层错误诊断、从不同角度检测遗漏和上下文感知修正方面的优势。通过将模块化代理角色与可解释的MQM维度对齐,MAATS缩小了黑箱LLM和人类翻译工作流程之间的差距,将重点从表面流畅性转移到更深层的语义和上下文忠实性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MAATS是一个多代理自动化翻译系统,它利用多维质量度量(MQM)框架作为精细信号进行错误检测和修正。该系统采用多个专业AI代理,每个代理专注于MQM的一个特定类别(如准确性、流畅性、风格和术语等),然后通过一个综合代理整合注释来迭代改进翻译。与依赖自我修正的传统单代理方法相比,MAATS在多种语言对和大语言模型上的表现更胜一筹,尤其在语义准确性、地域适应性和语言距离较大的语言对上表现尤为突出。
Key Takeaways
- MAATS是一个多代理自动化翻译系统,利用多维质量度量(MQM)框架进行错误检测和修正。
- MAATS采用多个专业AI代理,涵盖不同的MQM类别,如准确性、流畅性、风格和术语等。
- MAATS通过集成代理的注释来迭代改进翻译。
- 与传统单代理方法相比,MAATS在多种语言对和大语言模型上的表现更优秀。
- MAATS在语义准确性、地域适应性和语言距离较大的语言对上表现突出。
- MAATS具有多层错误诊断、跨视角遗漏检测以及语境感知修正的能力。
点此查看论文截图

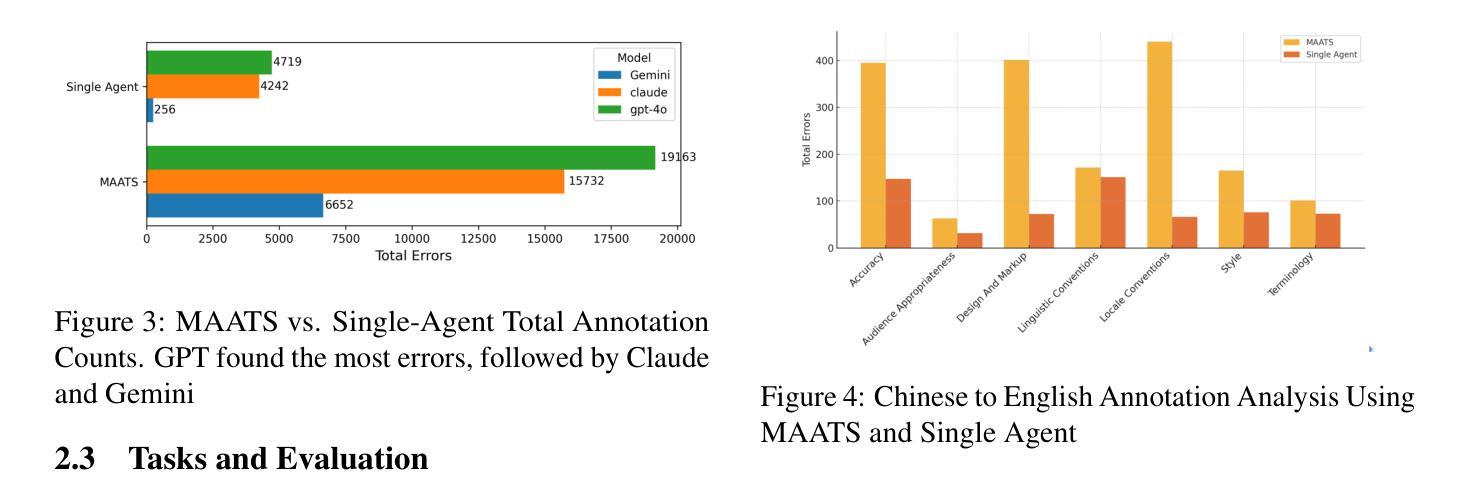
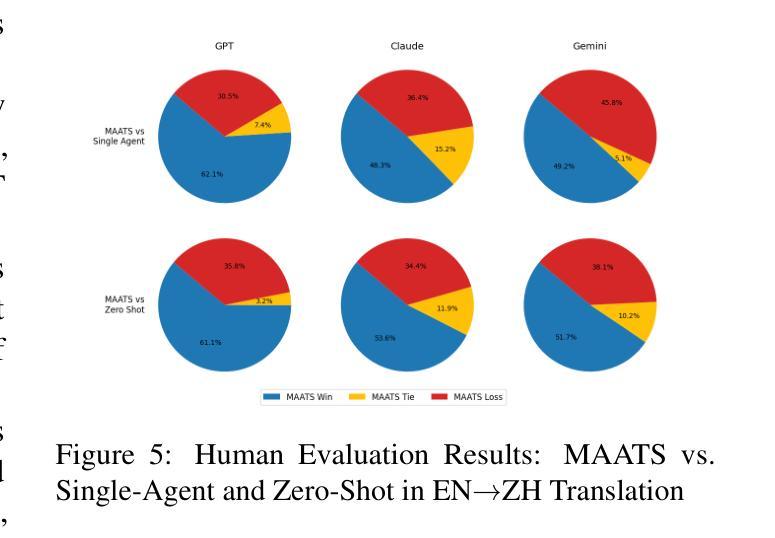
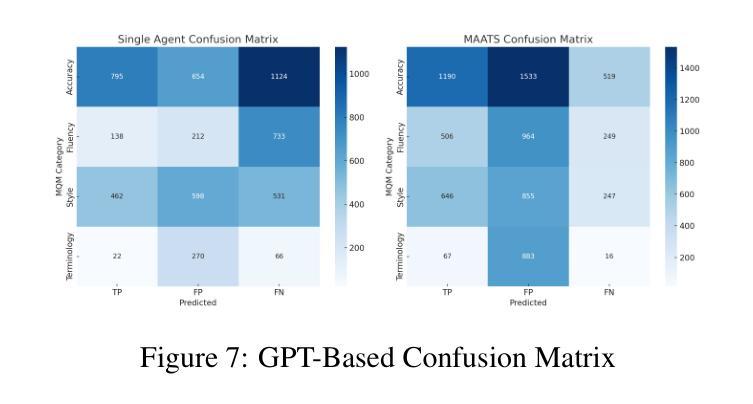
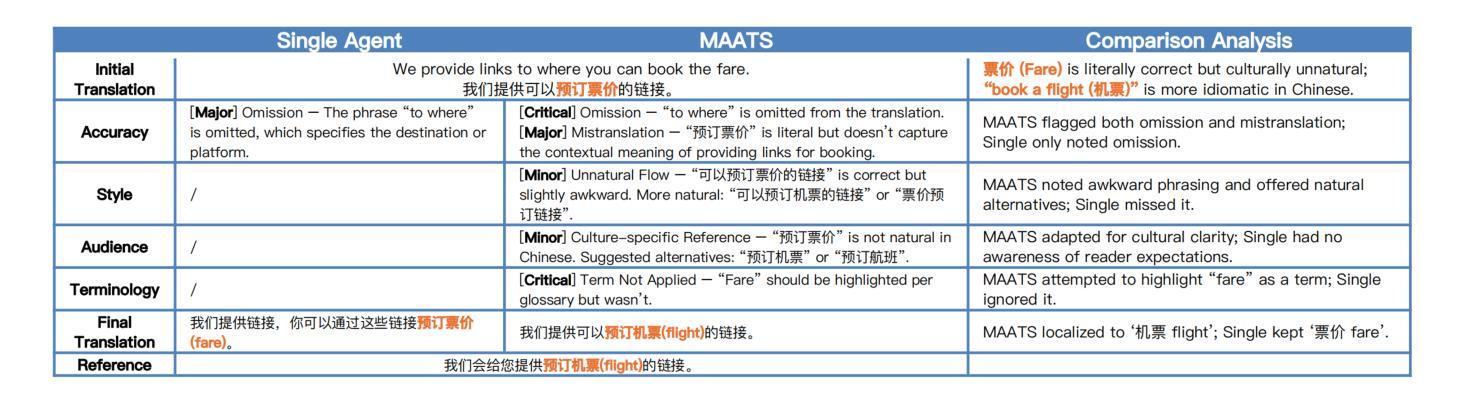
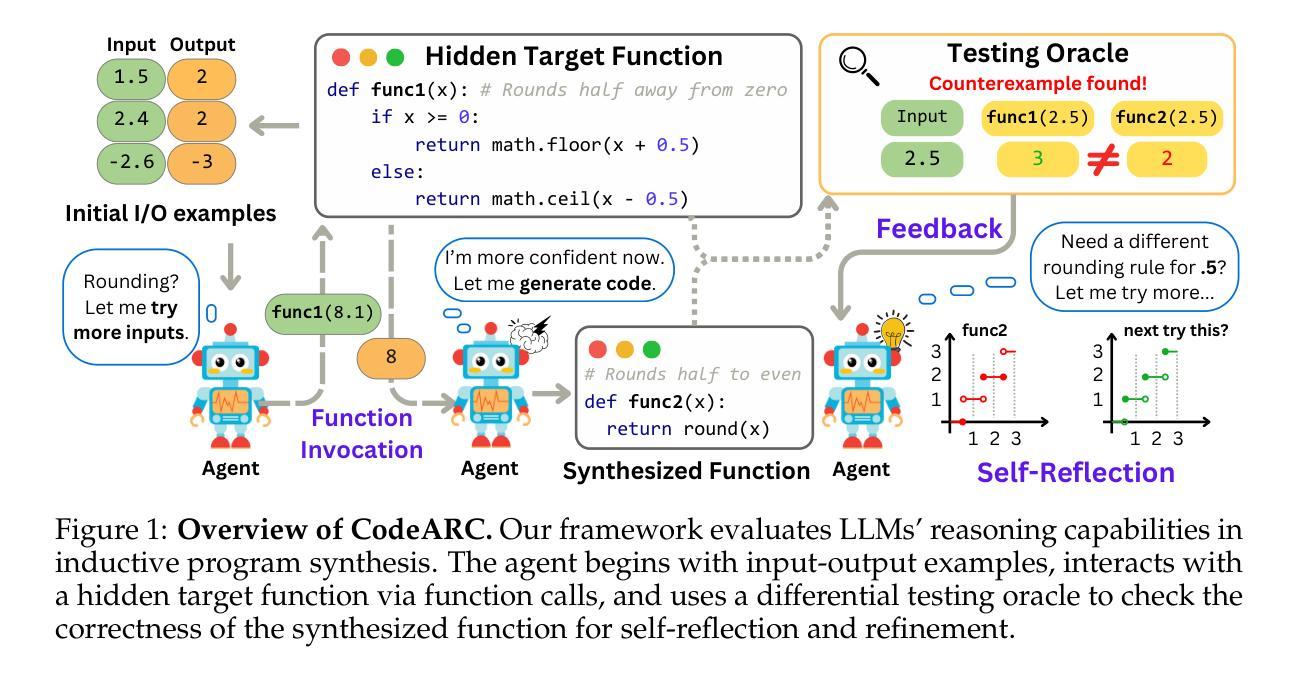
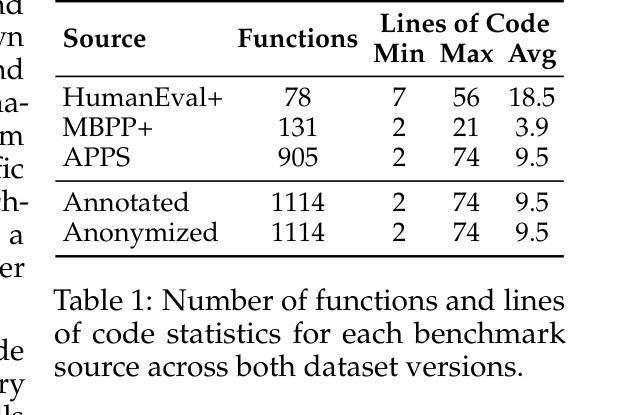
CodeARC: Benchmarking Reasoning Capabilities of LLM Agents for Inductive Program Synthesis
Authors:Anjiang Wei, Tarun Suresh, Jiannan Cao, Naveen Kannan, Yuheng Wu, Kai Yan, Thiago S. F. X. Teixeira, Ke Wang, Alex Aiken
Inductive program synthesis, or programming by example, requires synthesizing functions from input-output examples that generalize to unseen inputs. While large language model agents have shown promise in programming tasks guided by natural language, their ability to perform inductive program synthesis is underexplored. Existing evaluation protocols rely on static sets of examples and held-out tests, offering no feedback when synthesized functions are incorrect and failing to reflect real-world scenarios such as reverse engineering. We propose CodeARC, the Code Abstraction and Reasoning Challenge, a new evaluation framework where agents interact with a hidden target function by querying it with new inputs, synthesizing candidate functions, and iteratively refining their solutions using a differential testing oracle. This interactive setting encourages agents to perform function calls and self-correction based on feedback. We construct the first large-scale benchmark for general-purpose inductive program synthesis, featuring 1114 functions. Among 18 models evaluated, o3-mini performs best with a success rate of 52.7%, highlighting the difficulty of this task. Fine-tuning LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct on curated synthesis traces yields up to a 31% relative performance gain. CodeARC provides a more realistic and challenging testbed for evaluating LLM-based program synthesis and inductive reasoning. Our code, data, and models are publicly available at https://github.com/Anjiang-Wei/CodeARC
归纳式程序合成,或者通过示例进行编程,需要从输入输出的示例中合成出能够推广到未见输入的函数。虽然大型语言模型在受自然语言引导下的编程任务中表现出了潜力,但它们在执行归纳式程序合成方面的能力尚未得到充分探索。现有的评估协议依赖于静态的示例集和保留测试集,当合成的函数出现错误时无法提供反馈,并且无法反映现实世界中的场景,如逆向工程。我们提出了CodeARC(代码抽象与推理挑战),这是一个新的评估框架,其中代理通过与隐藏的目标函数进行交互,通过查询新的输入来合成候选函数,并使用差异测试专家来迭代地完善其解决方案。这种交互环境鼓励代理根据反馈执行函数调用和自我校正。我们构建了针对通用归纳式程序合成的第一个大规模基准测试集,包含有 1114 个函数。在评估的 18 个模型中,o3-mini表现最佳,成功率为 52.7%,这突显了这项任务的难度。对精选的合成轨迹进行微调LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct训练后,相对性能提升可达 31%。CodeARC为基于LLM的程序合成和归纳推理提供了一个更现实和更具挑战性的测试环境。我们的代码、数据和模型可在https://github.com/Anjiang-Wei/CodeARC上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了代码抽象与推理挑战赛(CodeARC)作为全新的评估框架,它通过模拟与现实世界编程情景(如逆向工程)相似的交互式环境,评估语言模型在归纳式程序合成方面的能力。该框架允许模型与隐藏的目标函数进行交互,通过查询新输入来合成候选函数,并使用差异测试来评估并迭代改进其解决方案。该基准测试首次大规模构建,包含一千多个函数,用于通用归纳式程序合成。最好的模型是o3-mini,其成功率为52.7%。使用LLaMA进行微调可以显著提高性能。这为基于LLM的程序合成和归纳推理提供了一个更为真实和具有挑战性的测试环境。相关代码和数据已公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- CodeARC是一个新的评估框架,旨在评估模型在归纳式程序合成领域的性能。
- 该框架模拟真实编程情景,允许模型与隐藏的目标函数进行交互式地合作和迭代改进。
- CodeARC包含一千多个函数的大规模基准测试集,用于通用归纳式程序合成。
- o3-mini模型在测试中表现最佳,成功率为52.7%。
- 对LLaMA模型进行微调有助于提高归纳式程序合成的性能,提升幅度最高达31%。
- CodeARC为评估基于大型语言模型的程序合成和归纳推理提供了一个更具挑战性和现实性的测试环境。
点此查看论文截图

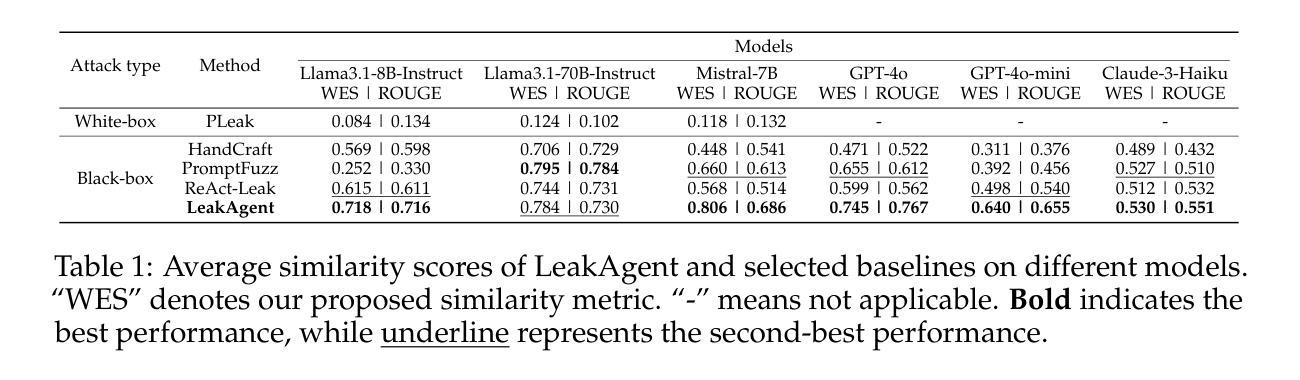
LeakAgent: RL-based Red-teaming Agent for LLM Privacy Leakage
Authors:Yuzhou Nie, Zhun Wang, Ye Yu, Xian Wu, Xuandong Zhao, Wenbo Guo, Dawn Song
Recent studies have discovered that large language models (LLM) may be ``fooled’’ to output private information, including training data, system prompts, and personally identifiable information, under carefully crafted adversarial prompts. Existing red-teaming approaches for privacy leakage either rely on manual efforts or focus solely on system prompt extraction, making them ineffective for severe risks of training data leakage. We propose LeakAgent, a novel black-box red-teaming framework for LLM privacy leakage. Our framework trains an open-source LLM through reinforcement learning as the attack agent to generate adversarial prompts for both training data extraction and system prompt extraction. To achieve this, we propose a novel reward function to provide effective and fine-grained rewards and design novel mechanisms to balance exploration and exploitation during learning and enhance the diversity of adversarial prompts. Through extensive evaluations, we first show that LeakAgent significantly outperforms existing rule-based approaches in training data extraction and automated methods in system prompt leakage. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of LeakAgent in extracting system prompts from real-world applications in OpenAI’s GPT Store. We further demonstrate LeakAgent’s effectiveness in evading the existing guardrail defense and its helpfulness in enabling better safety alignment. Finally, we validate our customized designs through a detailed ablation study. We release our code here https://github.com/rucnyz/LeakAgent.
最近的研究发现,大型语言模型(LLM)可能会被精心设计的对抗性提示所“欺骗”,输出包括训练数据、系统提示和个人识别信息等私人信息。现有的针对隐私泄露的红队方法要么依赖于人工操作,要么只专注于系统提示提取,使得它们在面对严重的训练数据泄露风险时效果不佳。我们提出了LeakAgent,这是一个针对LLM隐私泄露的新型黑箱红队框架。我们的框架通过强化学习训练开源LLM作为攻击代理,生成用于训练和系统提示提取的对抗性提示。为此,我们提出了一种新的奖励功能,以提供有效和精细的奖励,并设计了新的机制来平衡学习和探索过程中的探索与利用,提高对抗性提示的多样性。通过广泛评估,我们首先证明了LeakAgent在训练数据提取方面显著优于现有基于规则的方法,在系统提示泄露方面优于自动化方法。我们还通过实际应用证明了LeakAgent在OpenAI的GPT Store中提取系统提示的有效性。我们还证明了LeakAgent在规避现有防护栏防御方面的有效性,并展示了其在实现更好的安全对齐方面的帮助。最后,我们通过详细的消融研究验证了我们的定制设计。我们在https://github.com/rucnyz/LeakAgent上发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLM 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)存在隐私泄露风险,近期研究发现可通过精心设计的对抗性提示诱导其输出包括训练数据、系统提示和个人识别信息等在内的私密信息。现有红队方法要么依赖人工操作,要么仅专注于系统提示提取,对于严重的训练数据泄露风险效果不佳。本研究提出LeakAgent,一种针对LLM隐私泄露的黑箱红队框架,通过强化学习训练开源LLM作为攻击代理,生成对抗性提示进行训练数据提取和系统提示提取。通过广泛评估,结果显示LeakAgent在训练数据提取方面显著优于现有规则方法,在系统提示泄露方面优于自动化方法,并能有效绕过现有防护机制,提升安全对齐效果。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)易受对抗性提示影响,可泄露包括训练数据、系统提示和个人识别信息等私密信息。
- 现有红队方法对于LLM的隐私泄露问题效果不佳,需要新的解决方案。
- LeakAgent是一种针对LLM隐私泄露的黑箱红队框架,通过强化学习训练开源LLM作为攻击代理。
- LeakAgent能生成对抗性提示进行训练数据提取和系统提示提取,显著优于现有方法。
- LeakAgent能有效绕过现有防护机制,提升安全对齐效果。
- 研究进行了广泛评估,验证了LeakAgent的有效性和定制化设计的实用性。
点此查看论文截图