⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
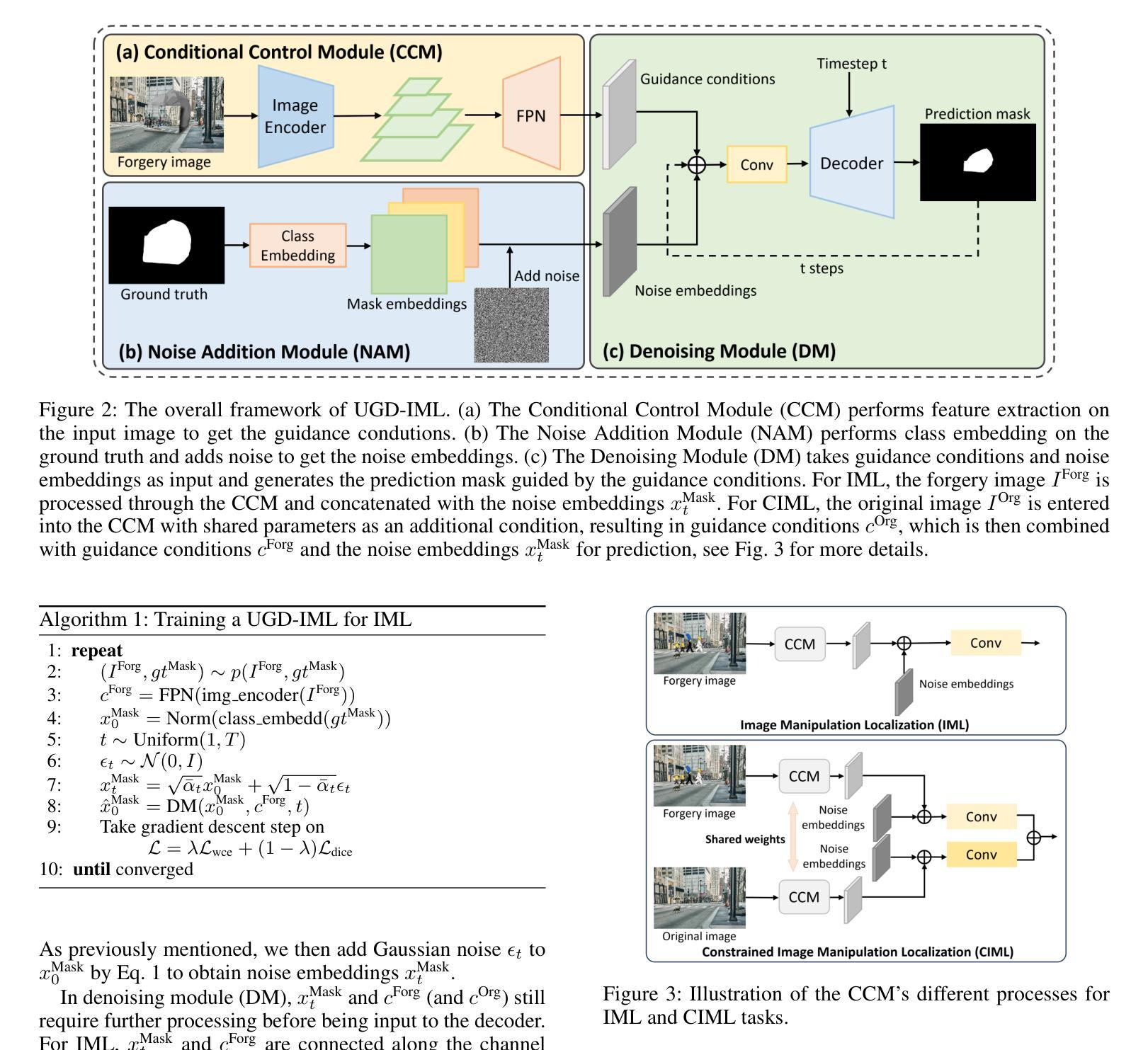
UGD-IML: A Unified Generative Diffusion-based Framework for Constrained and Unconstrained Image Manipulation Localization
Authors:Yachun Mi, Xingyang He, Shixin Sun, Yu Li, Yanting Li, Zhixuan Li, Jian Jin, Chen Hui, Shaohui Liu
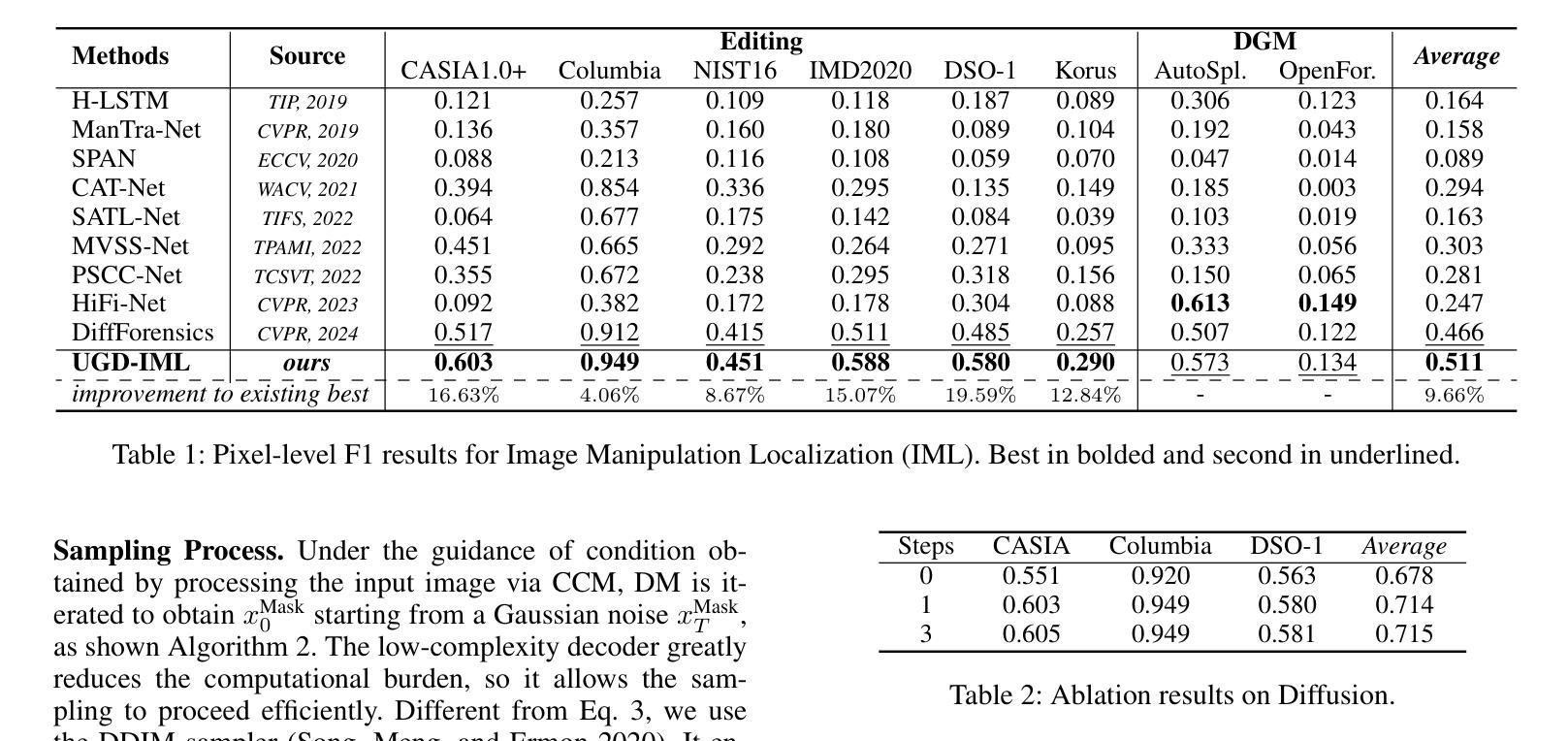
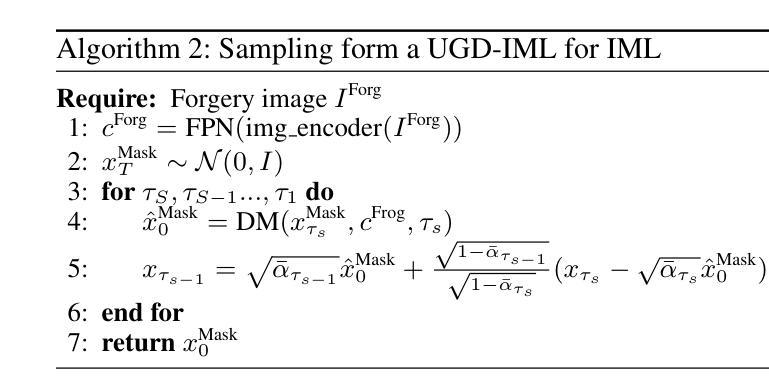
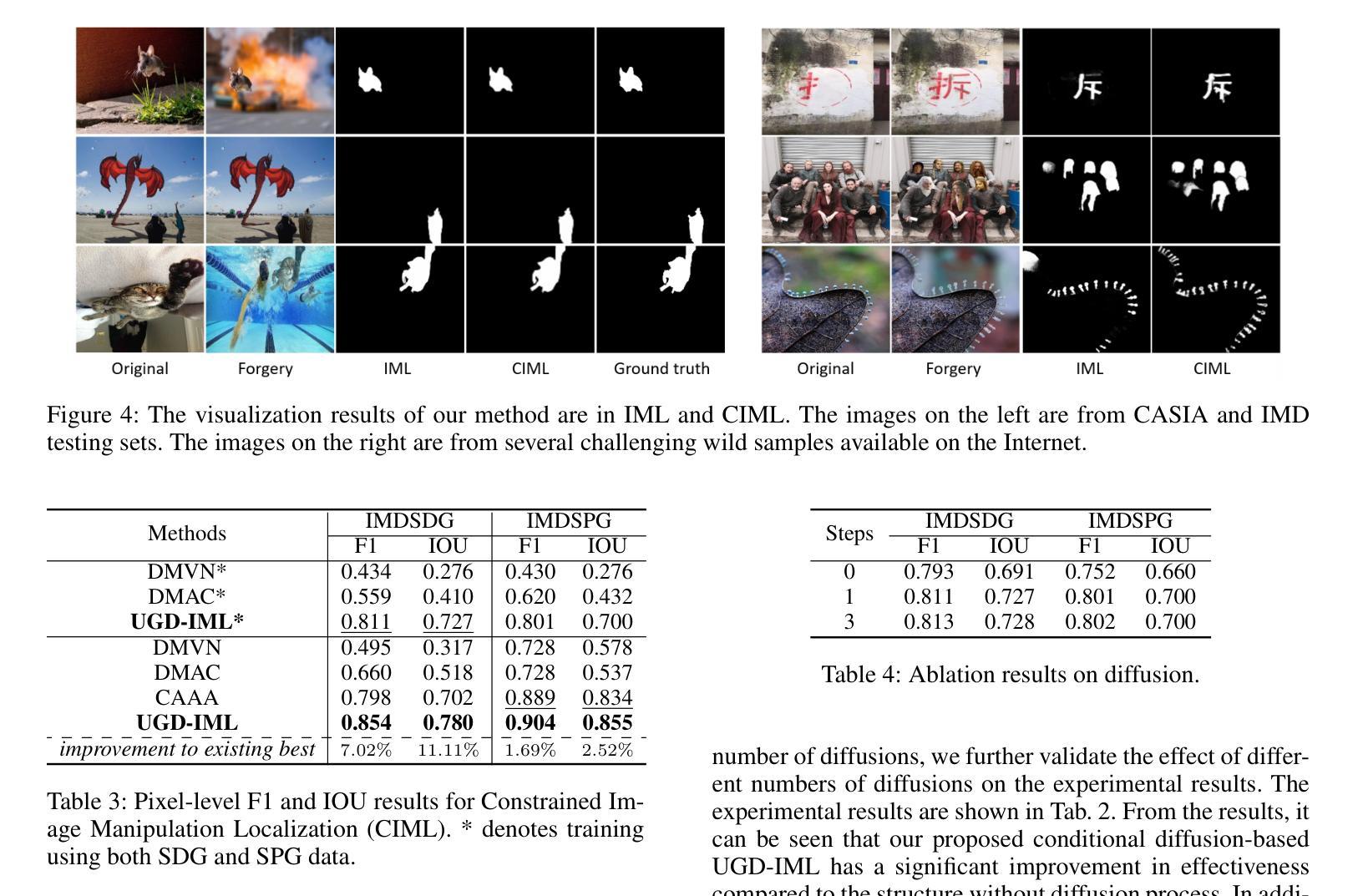
In the digital age, advanced image editing tools pose a serious threat to the integrity of visual content, making image forgery detection and localization a key research focus. Most existing Image Manipulation Localization (IML) methods rely on discriminative learning and require large, high-quality annotated datasets. However, current datasets lack sufficient scale and diversity, limiting model performance in real-world scenarios. To overcome this, recent studies have explored Constrained IML (CIML), which generates pixel-level annotations through algorithmic supervision. However, existing CIML approaches often depend on complex multi-stage pipelines, making the annotation process inefficient. In this work, we propose a novel generative framework based on diffusion models, named UGD-IML, which for the first time unifies both IML and CIML tasks within a single framework. By learning the underlying data distribution, generative diffusion models inherently reduce the reliance on large-scale labeled datasets, allowing our approach to perform effectively even under limited data conditions. In addition, by leveraging a class embedding mechanism and a parameter-sharing design, our model seamlessly switches between IML and CIML modes without extra components or training overhead. Furthermore, the end-to-end design enables our model to avoid cumbersome steps in the data annotation process. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that UGD-IML outperforms the SOTA methods by an average of 9.66 and 4.36 in terms of F1 metrics for IML and CIML tasks, respectively. Moreover, the proposed method also excels in uncertainty estimation, visualization and robustness.
在数字化时代,先进的图像编辑工具对视觉内容的完整性构成了严重威胁,使得图像篡改检测和定位成为关键的研究焦点。大多数现有的图像操纵定位(IML)方法依赖于判别学习,并需要大规模、高质量的有标注数据集。然而,当前的数据集缺乏足够的规模和多样性,限制了模型在现实世界场景中的性能。为了克服这一难题,近期的研究探索了约束IML(CIML),它通过算法监督生成像素级标注。然而,现有的CIML方法往往依赖于复杂的多阶段流水线,使得标注过程效率低下。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的统一生成框架UGD-IML,它结合了图像操纵本地化(IML)和约束IML(CIML)任务。该框架通过减少对数据集的依赖并提高数据利用效率,在有限数据条件下表现良好。此外,通过类嵌入机制和参数共享设计,UGD-IML可在IML和CIML模式之间无缝切换,简化了数据标注过程的繁琐步骤。实验结果表明,UGD-IML在IML和CIML任务上的F1指标平均优于现有方法9.66和4.36。此外,该方法在不确定性估计、可视化和鲁棒性方面也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的图像编辑工具对视觉内容的完整性构成严重威胁,促使图像伪造检测和定位成为研究重点。
- 当前图像操纵本地化(IML)方法依赖判别学习,需要大量高质量标注数据集,但现有数据集规模不足、多样性有限,限制了在现实场景中的表现。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了基于扩散模型的统一生成框架UGD-IML,结合IML和约束IML(CIML)任务。
- UGD-IML通过学习底层数据分布,减少了大规模标注数据集的依赖,在有限数据条件下表现良好。
- UGD-IML通过类嵌入机制和参数共享设计,实现IML和CIML模式之间的无缝切换,简化了数据标注过程。
- 实验结果表明,UGD-IML在IML和CIML任务上的F1指标显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Towards MR-Based Trochleoplasty Planning
Authors:Michael Wehrli, Alicia Durrer, Paul Friedrich, Sidaty El Hadramy, Edwin Li, Luana Brahaj, Carol C. Hasler, Philippe C. Cattin
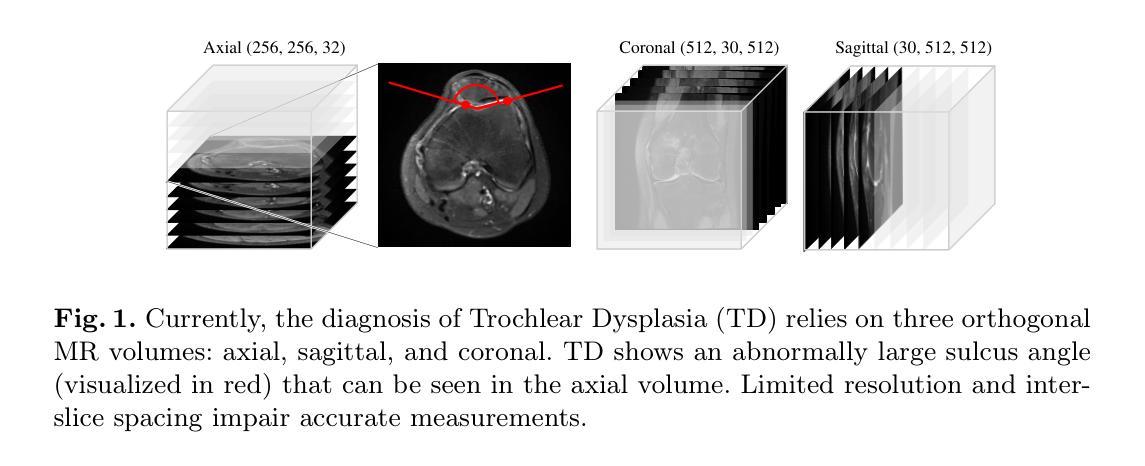
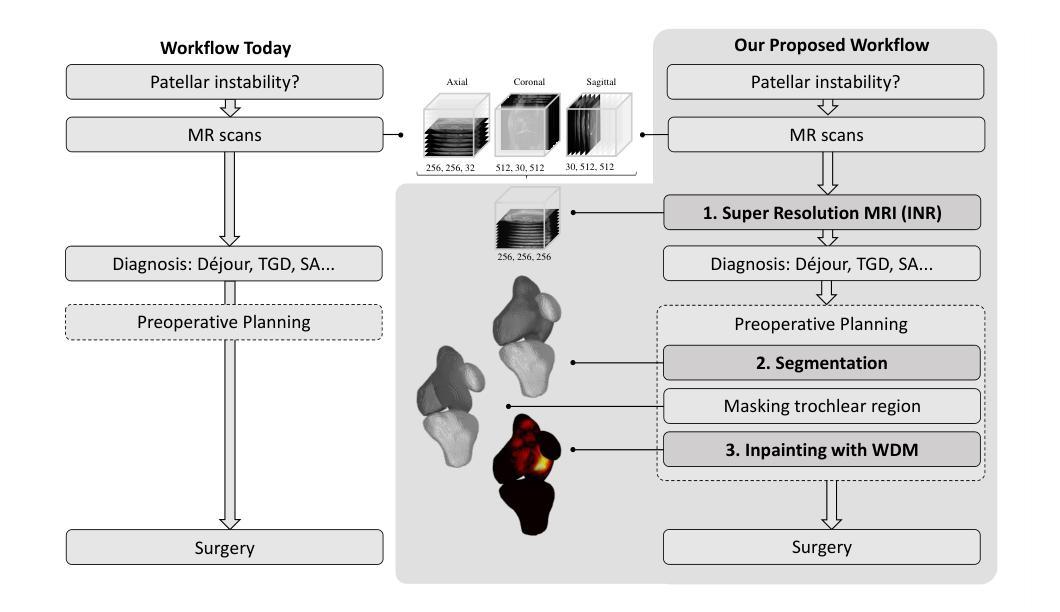
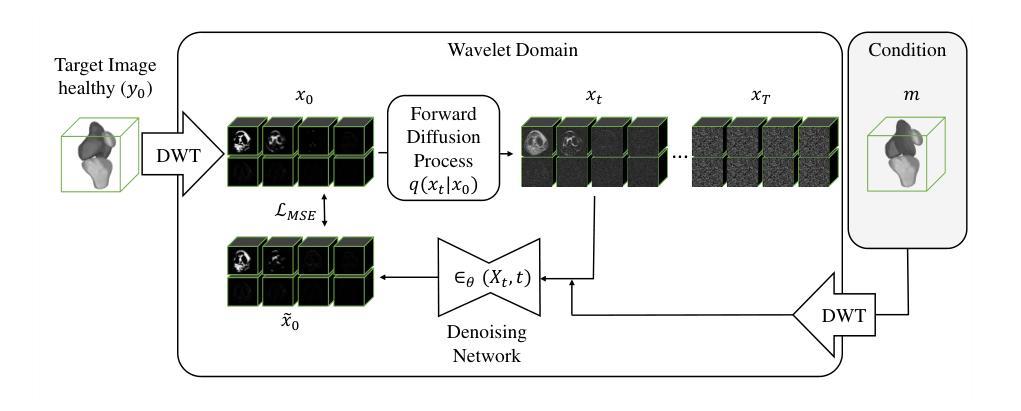
To treat Trochlear Dysplasia (TD), current approaches rely mainly on low-resolution clinical Magnetic Resonance (MR) scans and surgical intuition. The surgeries are planned based on surgeons experience, have limited adoption of minimally invasive techniques, and lead to inconsistent outcomes. We propose a pipeline that generates super-resolved, patient-specific 3D pseudo-healthy target morphologies from conventional clinical MR scans. First, we compute an isotropic super-resolved MR volume using an Implicit Neural Representation (INR). Next, we segment femur, tibia, patella, and fibula with a multi-label custom-trained network. Finally, we train a Wavelet Diffusion Model (WDM) to generate pseudo-healthy target morphologies of the trochlear region. In contrast to prior work producing pseudo-healthy low-resolution 3D MR images, our approach enables the generation of sub-millimeter resolved 3D shapes compatible for pre- and intraoperative use. These can serve as preoperative blueprints for reshaping the femoral groove while preserving the native patella articulation. Furthermore, and in contrast to other work, we do not require a CT for our pipeline - reducing the amount of radiation. We evaluated our approach on 25 TD patients and could show that our target morphologies significantly improve the sulcus angle (SA) and trochlear groove depth (TGD). The code and interactive visualization are available at https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/.
在处理Trochlear Dysplasia(TD)时,当前的方法主要依赖于低分辨率的临床磁共振(MR)扫描和手术直觉。手术计划是基于外科医生的经验制定的,较少采用微创技术,且手术结果不一。我们提出一个流程,该流程可从常规临床MR扫描生成超分辨率、患者专用的3D伪健康目标形态。首先,我们使用隐式神经表示(INR)计算各向同性超分辨率MR体积。接下来,我们使用多标签自定义训练网络对股骨、胫骨、髌骨和腓骨进行分割。最后,我们训练小波扩散模型(WDM),以生成Trochlear区域的伪健康目标形态。与之前产生伪健康低分辨率3D MR图像的工作相比,我们的方法能够生成兼容术前和术中的亚毫米分辨率的3D形态。这可以作为重塑股骨沟并保持原有髌骨关节的术前蓝图。此外,与其他工作相比,我们的流程不需要CT扫描,减少了辐射量。我们在25名TD患者上评估了我们的方法,并证明我们的目标形态能显著改善窝角(SA)和窝沟深度(TGD)。代码和交互式可视化内容可在https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI COLAS Workshop 2025. Code: https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/
Summary
本文介绍了一种治疗Trochlear Dysplasia(TD)的新方法。该方法利用隐式神经表示(INR)生成超分辨率的个性化三维伪健康目标形态,通过多标签定制网络分割骨骼结构,并使用小波扩散模型(WDM)生成伪健康目标形态。这种方法可以在术前和术中生成亚毫米级分辨率的三维形状,作为重塑股骨槽的术前蓝图,同时保留原髌骨关节。与其他方法相比,该方法不需要CT扫描,减少了辐射量。在25名TD患者上的实验结果表明,该方法能显著改善沟角(SA)和槽深(TGD)。相关代码和交互可视化在https://wehrlimi.github.io/sr-3d-planning/可供获取。
Key Takeaways
- 当前治疗Trochlear Dysplasia(TD)主要依赖于低分辨率的MR扫描和手术直觉,手术结果不一致。
- 提出了一个生成超分辨率、个性化三维伪健康目标形态的管道,该管道基于隐式神经表示(INR)。
- 通过多标签定制网络分割骨骼结构,包括股骨、胫骨、髌骨和腓骨。
- 使用小波扩散模型(WDM)生成伪健康目标形态,适用于术前和术中的高解析度三维形状生成。
- 该方法可作为重塑股骨槽的术前蓝图,同时保留原髌骨关节。
- 与其他方法相比,该管道不需要CT扫描,减少了辐射量。
点此查看论文截图

Learning 3D Texture-Aware Representations for Parsing Diverse Human Clothing and Body Parts
Authors:Kiran Chhatre, Christopher Peters, Srikrishna Karanam
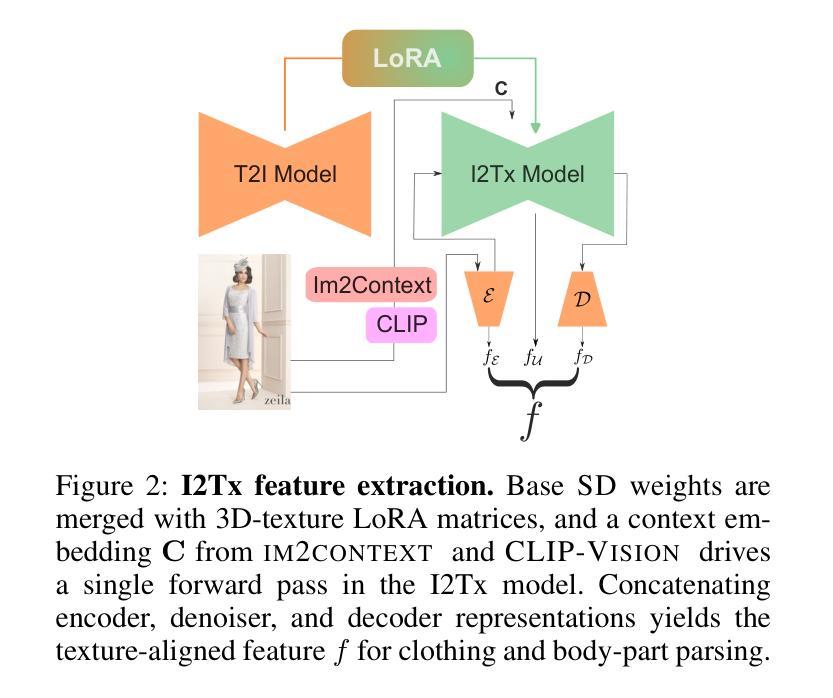
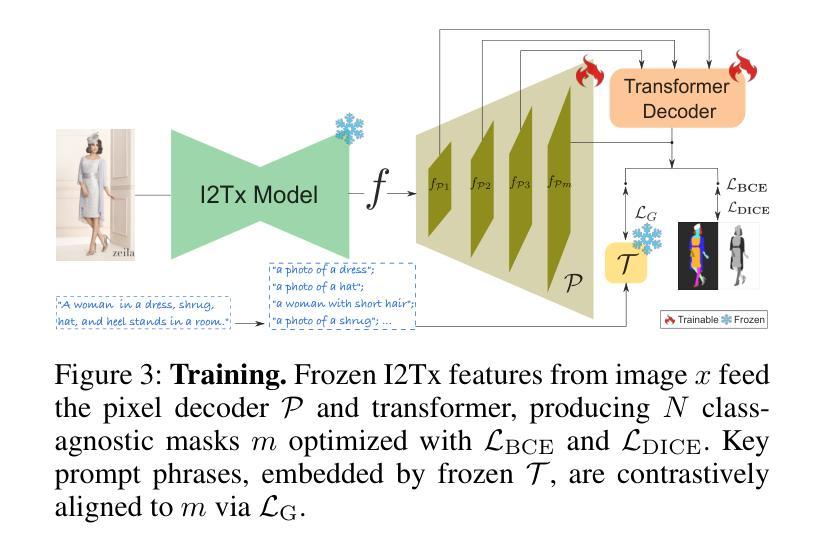
Existing methods for human parsing into body parts and clothing often use fixed mask categories with broad labels that obscure fine-grained clothing types. Recent open-vocabulary segmentation approaches leverage pretrained text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model features for strong zero-shot transfer, but typically group entire humans into a single person category, failing to distinguish diverse clothing or detailed body parts. To address this, we propose Spectrum, a unified network for part-level pixel parsing (body parts and clothing) and instance-level grouping. While diffusion-based open-vocabulary models generalize well across tasks, their internal representations are not specialized for detailed human parsing. We observe that, unlike diffusion models with broad representations, image-driven 3D texture generators maintain faithful correspondence to input images, enabling stronger representations for parsing diverse clothing and body parts. Spectrum introduces a novel repurposing of an Image-to-Texture (I2Tx) diffusion model – obtained by fine-tuning a T2I model on 3D human texture maps – for improved alignment with body parts and clothing. From an input image, we extract human-part internal features via the I2Tx diffusion model and generate semantically valid masks aligned to diverse clothing categories through prompt-guided grounding. Once trained, Spectrum produces semantic segmentation maps for every visible body part and clothing category, ignoring standalone garments or irrelevant objects, for any number of humans in the scene. We conduct extensive cross-dataset experiments – separately assessing body parts, clothing parts, unseen clothing categories, and full-body masks – and demonstrate that Spectrum consistently outperforms baseline methods in prompt-based segmentation.
现有的人类身体部位和服装解析方法通常使用具有广泛标签的固定掩膜类别,这掩盖了精细的服装类型。最近的开放词汇分割方法利用预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型特征进行强大的零样本迁移,但通常将整个人类归入单人类别,无法区分各种服装或详细的身体部位。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Spectrum,这是一个用于部分级别的像素解析(身体部位和服装)和实例级别的分组的统一网络。虽然基于扩散的开放词汇模型在各项任务中具有良好的通用性,但它们的内部表示并不适用于详细的人类解析。我们观察到,与具有广泛表示的扩散模型不同,图像驱动的3D纹理生成器保持对输入图像的忠实对应,能够为解析各种服装和身体部位提供更强大的表示。Spectrum引入了一种新颖的Image-to-Texture(I2Tx)扩散模型的重新利用方法——通过在对3D人类纹理图上进行微调得到的T2I模型——以改善与身体部位和服装的对齐。我们从输入图像中提取人体部位内部特征,通过I2Tx扩散模型生成与各种服装类别对齐的语义有效掩膜,通过提示引导定位。一旦训练完成,Spectrum就可以为场景中的每个人生成语义分割图,显示每个可见的身体部位和服装类别,同时忽略独立服装或无关物体。我们在多个数据集上进行了广泛的实验——分别评估身体部位、服装部位、未见过的服装类别和全身掩膜——并证明Spectrum在提示驱动的分割方面始终优于基准方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为Spectrum的统一网络,用于人体部位和服装的像素级解析以及实例级别的分组。文章指出,现有的方法在使用固定的掩膜类别时,通常使用宽泛的标签,忽略了精细的服装类型。虽然最近的开放词汇分割方法利用预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型特性进行零样本迁移,但它们通常将整个人类归为一个单一的人类别,无法区分多样化的服装或详细的身体部位。为解决这一问题,Spectrum结合了基于图像的3D纹理生成器的优点,并引入了一种新的图像到纹理(I2Tx)扩散模型的用途,该模型通过微调T2I模型获得,以改善与身体部位和服装的对齐。实验表明,Spectrum在基于提示的分割上表现优异,能生成与各种服装类别对齐的语义分割图。
Key Takeaways
1.现有方法在人体解析方面存在局限,如使用固定掩膜类别和宽泛标签导致的精细服装类型识别不足。
2.文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在零样本迁移方面表现出色,但难以区分多样化的服装和详细的身体部位。
3.Spectrum网络结合了T2I扩散模型和图像到纹理(I2Tx)模型的优势,实现了人体部位和服装的像素级解析以及实例级别的分组。
4.I2Tx扩散模型通过微调获得,能改善与身体部位和服装的对齐,提高语义分割图的生成质量。
5.Spectrum通过提取输入图像的人体部位内部特征,生成与各种服装类别对齐的语义分割图。
6.Spectrum在跨数据集实验中的表现优异,无论是评估身体部位、服装部分、未见过的服装类别还是全身掩膜。
点此查看论文截图




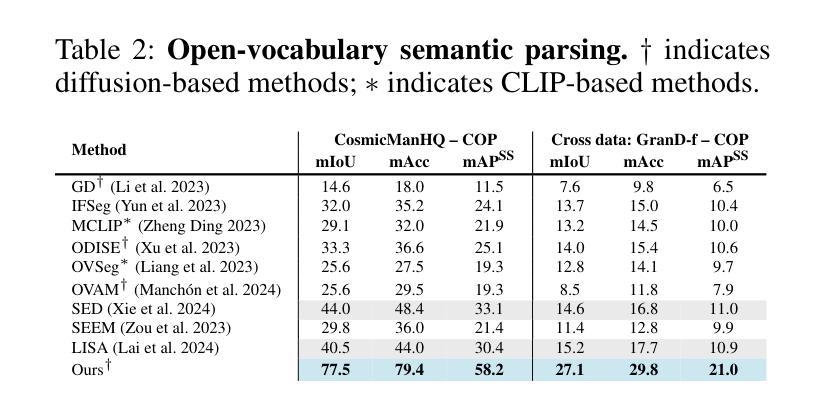
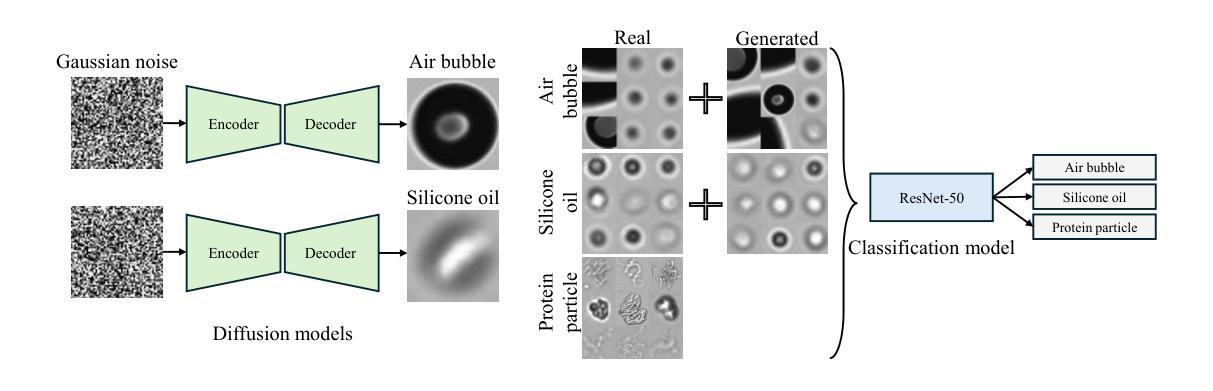
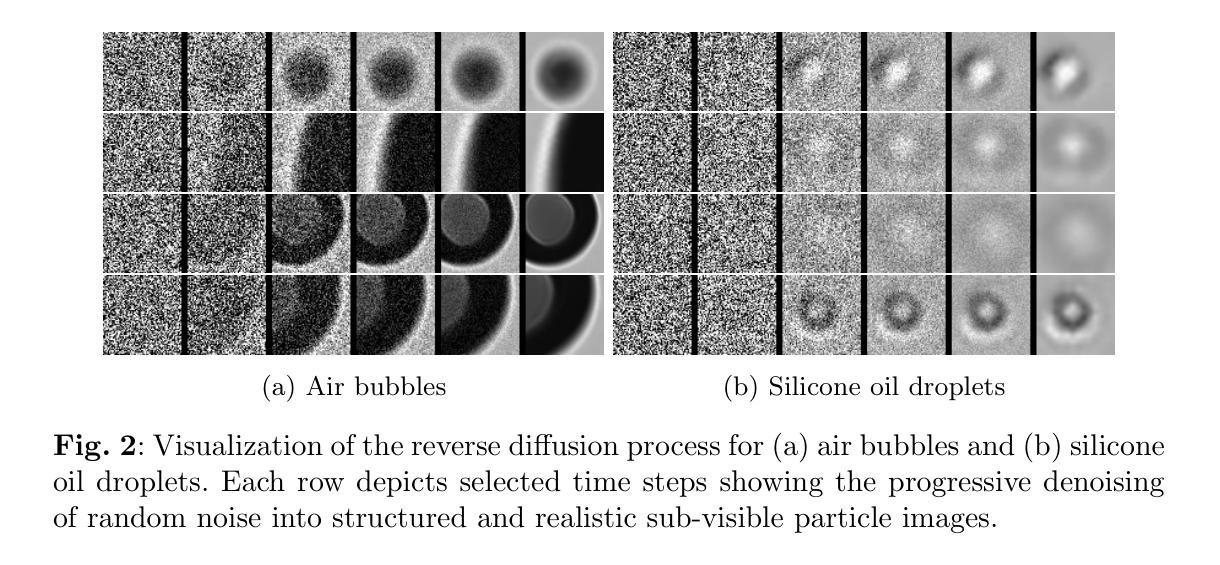
Improved Sub-Visible Particle Classification in Flow Imaging Microscopy via Generative AI-Based Image Synthesis
Authors:Utku Ozbulak, Michaela Cohrs, Hristo L. Svilenov, Joris Vankerschaver, Wesley De Neve
Sub-visible particle analysis using flow imaging microscopy combined with deep learning has proven effective in identifying particle types, enabling the distinction of harmless components such as silicone oil from protein particles. However, the scarcity of available data and severe imbalance between particle types within datasets remain substantial hurdles when applying multi-class classifiers to such problems, often forcing researchers to rely on less effective methods. The aforementioned issue is particularly challenging for particle types that appear unintentionally and in lower numbers, such as silicone oil and air bubbles, as opposed to protein particles, where obtaining large numbers of images through controlled settings is comparatively straightforward. In this work, we develop a state-of-the-art diffusion model to address data imbalance by generating high-fidelity images that can augment training datasets, enabling the effective training of multi-class deep neural networks. We validate this approach by demonstrating that the generated samples closely resemble real particle images in terms of visual quality and structure. To assess the effectiveness of using diffusion-generated images in training datasets, we conduct large-scale experiments on a validation dataset comprising 500,000 protein particle images and demonstrate that this approach improves classification performance with no negligible downside. Finally, to promote open research and reproducibility, we publicly release both our diffusion models and the trained multi-class deep neural network classifiers, along with a straightforward interface for easy integration into future studies, at https://github.com/utkuozbulak/svp-generative-ai.
使用流式成像显微镜结合深度学习进行亚可见粒子分析,已证明在识别粒子类型方面非常有效,能够区分硅胶油与蛋白质粒子等无害成分。然而,在将多类分类器应用于此类问题时,可用数据的稀缺性和数据集内粒子类型的严重不平衡仍然是巨大的障碍,这常常迫使研究人员不得不依赖效果较差的方法。对于硅胶油和气泡等非有意出现且数量较少的粒子类型,这一问题更具挑战性,相比之下,通过受控环境获取大量蛋白质粒子图像则相对容易。在这项工作中,我们开发了一种最先进的扩散模型,通过生成高保真图像来解决数据不平衡问题,这些图像可以扩充训练数据集,使得多类深度神经网络的训练更加有效。我们通过展示生成的样本在视觉质量和结构上与真实粒子图像非常相似来验证这种方法的有效性。为了评估在训练数据集中使用扩散生成图像的效果,我们在包含50万张蛋白质粒子图像的验证数据集上进行了大规模实验,并证明该方法在分类性能上有所提高,且没有明显的不利影响。最后,为了促进开放研究和可重复性,我们在https://github.com/utkuozbulak/svp-generative-ai上公开了我们的扩散模型和训练好的多类深度神经网络分类器,以及一个易于集成到未来研究中的简单接口。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用流成像显微镜结合深度学习进行亚可见粒子分析已被证明在识别粒子类型方面非常有效,能够区分如硅油与蛋白质颗粒等无害成分。然而,数据集可用数据的稀缺性和粒子类型之间的严重不平衡仍是应用多类分类器于此类问题的重大障碍。针对这一问题,本文开发了一种先进的扩散模型来解决数据不平衡问题,通过生成高质量图像来扩充训练数据集,为训练多类深度神经网络提供了有效方法。本文验证了所提出方法的有效性,并在包含50万蛋白质颗粒图像的大规模验证数据集上进行了实验。研究公开发布了扩散模型和训练好的多类深度神经网络分类器,便于未来研究的集成。
Key Takeaways
- 流成像显微镜结合深度学习在亚可见粒子分析中具有高识别能力。
- 数据稀缺和粒子类型不平衡是应用多类分类器的重大挑战。
- 扩散模型生成的高质量图像可以解决数据不平衡问题。
- 生成的样本在视觉质量和结构上与真实粒子图像相似。
- 在大规模验证数据集上验证了扩散模型的有效性,提高了分类性能。
- 研究公开的模型和分类器便于未来研究的集成。
点此查看论文截图

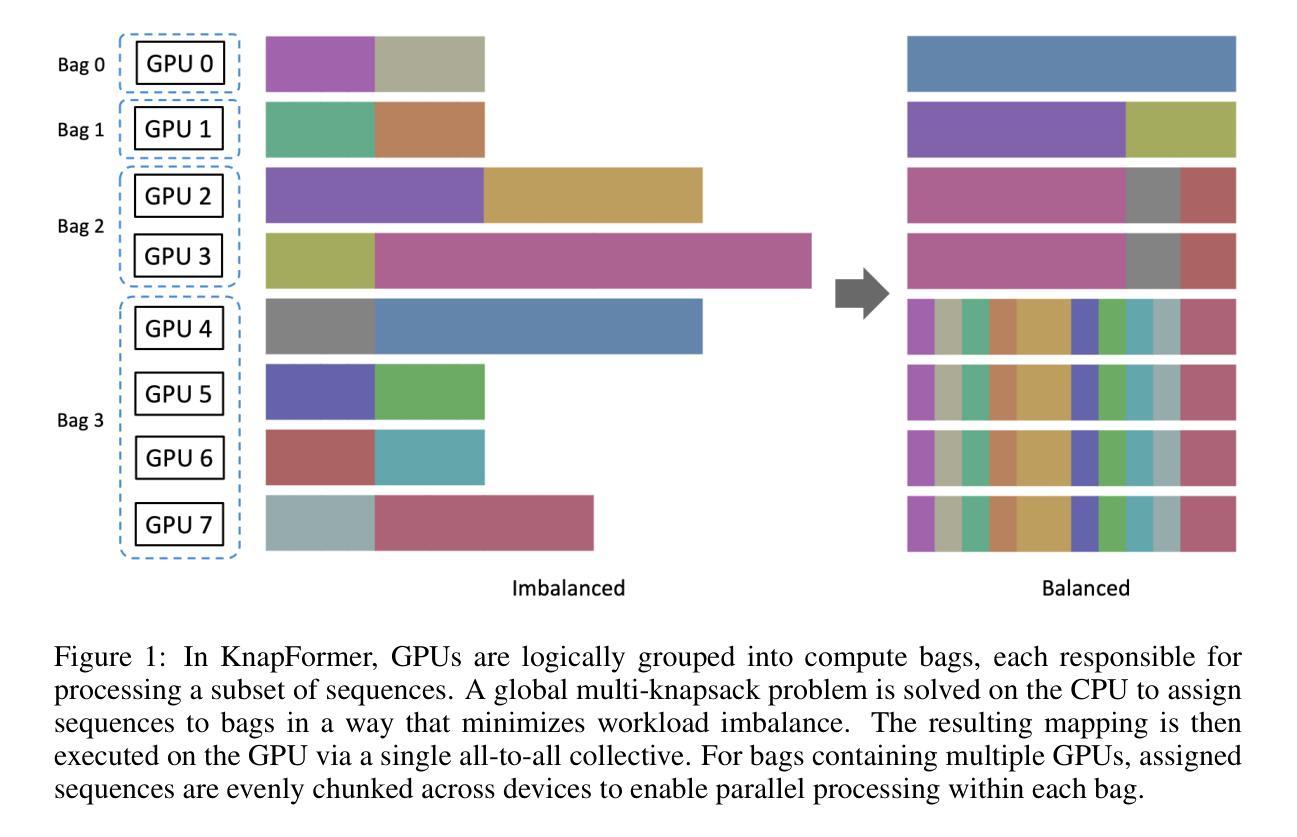
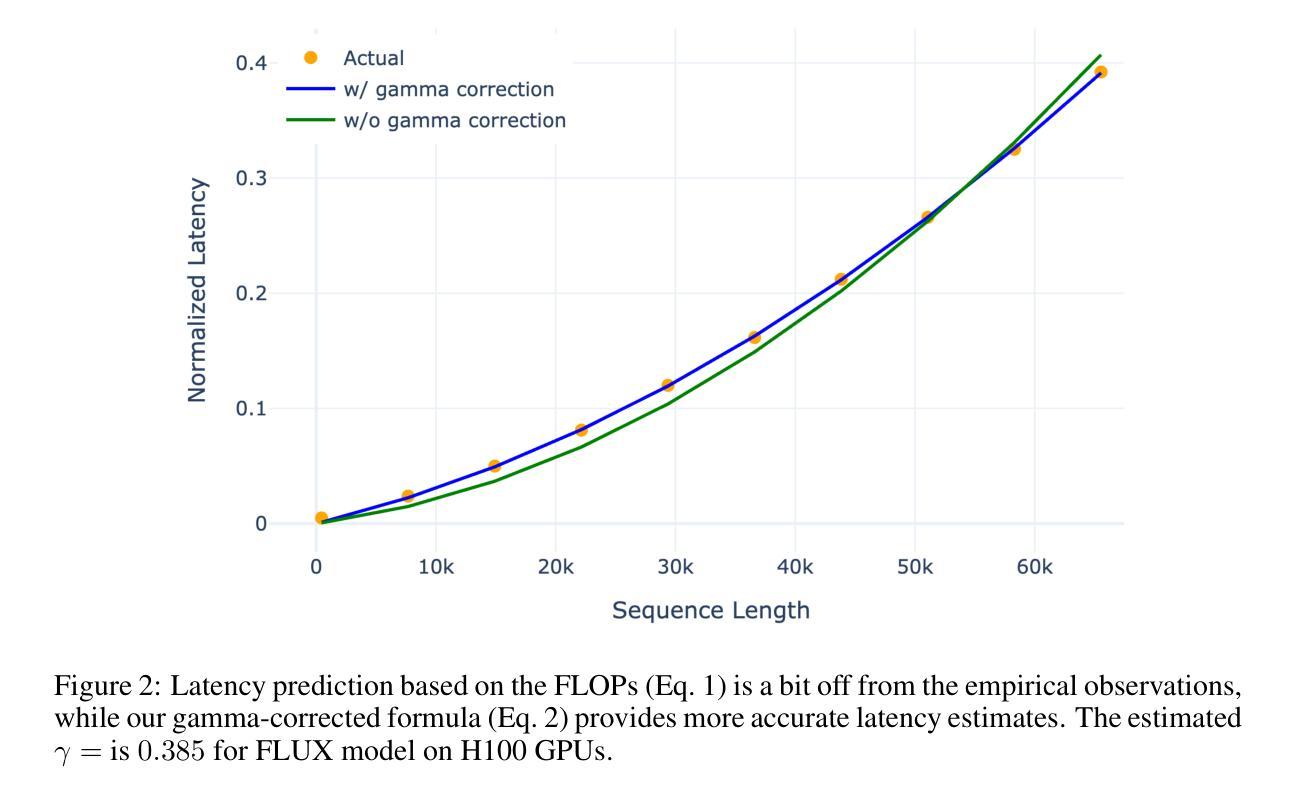
KnapFormer: An Online Load Balancer for Efficient Diffusion Transformers Training
Authors:Kai Zhang, Peng Wang, Sai Bi, Jianming Zhang, Yuanjun Xiong
We present KnapFormer, an efficient and versatile framework to combine workload balancing and sequence parallelism in distributed training of Diffusion Transformers (DiT). KnapFormer builds on the insight that strong synergy exists between sequence parallelism and the need to address the significant token imbalance across ranks. This imbalance arises from variable-length text inputs and varying visual token counts in mixed-resolution and image-video joint training. KnapFormer redistributes tokens by first gathering sequence length metadata across all ranks in a balancing group and solving a global knapsack problem. The solver aims to minimize the variances of total workload per-GPU, while accounting for the effect of sequence parallelism. By integrating DeepSpeed-Ulysees-based sequence parallelism in the load-balancing decision process and utilizing a simple semi-empirical workload model, KnapFormers achieves minimal communication overhead and less than 1% workload discrepancy in real-world training workloads with sequence length varying from a few hundred to tens of thousands. It eliminates straggler effects and achieves 2x to 3x speedup when training state-of-the-art diffusion models like FLUX on mixed-resolution and image-video joint data corpora. We open-source the KnapFormer implementation at https://github.com/Kai-46/KnapFormer/
我们提出了KnapFormer,这是一个高效且通用的框架,旨在结合工作量平衡和序列并行性,用于分布式训练扩散变压器(DiT)。KnapFormer建立在序列并行性与解决排名间显著令牌不平衡之间强烈协同作用的洞察之上。这种不平衡产生于混合分辨率和图像视频联合训练中可变长度的文本输入和视觉令牌计数。KnapFormer通过重新分配令牌来应对这一问题,首先收集平衡组中所有排名的序列长度元数据,并解决全局背包问题。求解器的目标是使每GPU的总工作量方差最小化,同时考虑序列并行性的影响。通过将基于DeepSpeed-Ulysses的序列并行性集成到负载均衡决策过程中,并利用简单的半经验工作量模型,KnapFormer在实际训练工作中实现了最小的通信开销和不到1%的工作量差异,序列长度从几百到数万不等。它消除了滞后效应,并在混合分辨率和图像视频联合数据集上训练最先进的扩散模型(如FLUX)时实现了2倍至3倍的加速效果。我们在https://github.com/Kai-46/KnapFormer/开源了KnapFormer实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/Kai-46/KnapFormer/
Summary
KnapFormer是一个针对Diffusion Transformers(DiT)进行分布式训练的高效且通用的框架,它通过解决全局背包问题实现了工作量平衡和序列并行性的结合。该框架解决了由不同长度文本输入和混合分辨率图像视频联合训练中的不同视觉令牌计数导致的令牌不平衡问题。通过集成DeepSpeed-Ulysees的序列并行性和负载均衡决策过程,并使用简单的工作负载模型,KnapFormer实现了最小的通信开销和真实训练场景中序列长度从几百到数万变化时的工作负载差异小于1%。它消除了滞后效应,并在混合分辨率和图像视频联合数据集上训练先进的扩散模型时实现了2倍至3倍的速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- KnapFormer是一个针对Diffusion Transformers的分布式训练框架,旨在结合工作量平衡和序列并行性。
- 该框架解决了由不同文本长度和混合分辨率图像视频联合训练中的视觉令牌计数不同导致的令牌不平衡问题。
- 通过集成DeepSpeed-Ulysees的序列并行性,KnapFormer实现了负载均衡决策过程。
- KnapFormer使用简单的工作负载模型,实现了最小的通信开销和工作负载差异小于1%。
- KnapFormer能够消除滞后效应,提高了训练效率。
- 在真实场景中,KnapFormer实现了在混合分辨率和图像视频联合数据集上训练先进的扩散模型时的高速性能提升,达到2倍至3倍的速度提升。
点此查看论文截图


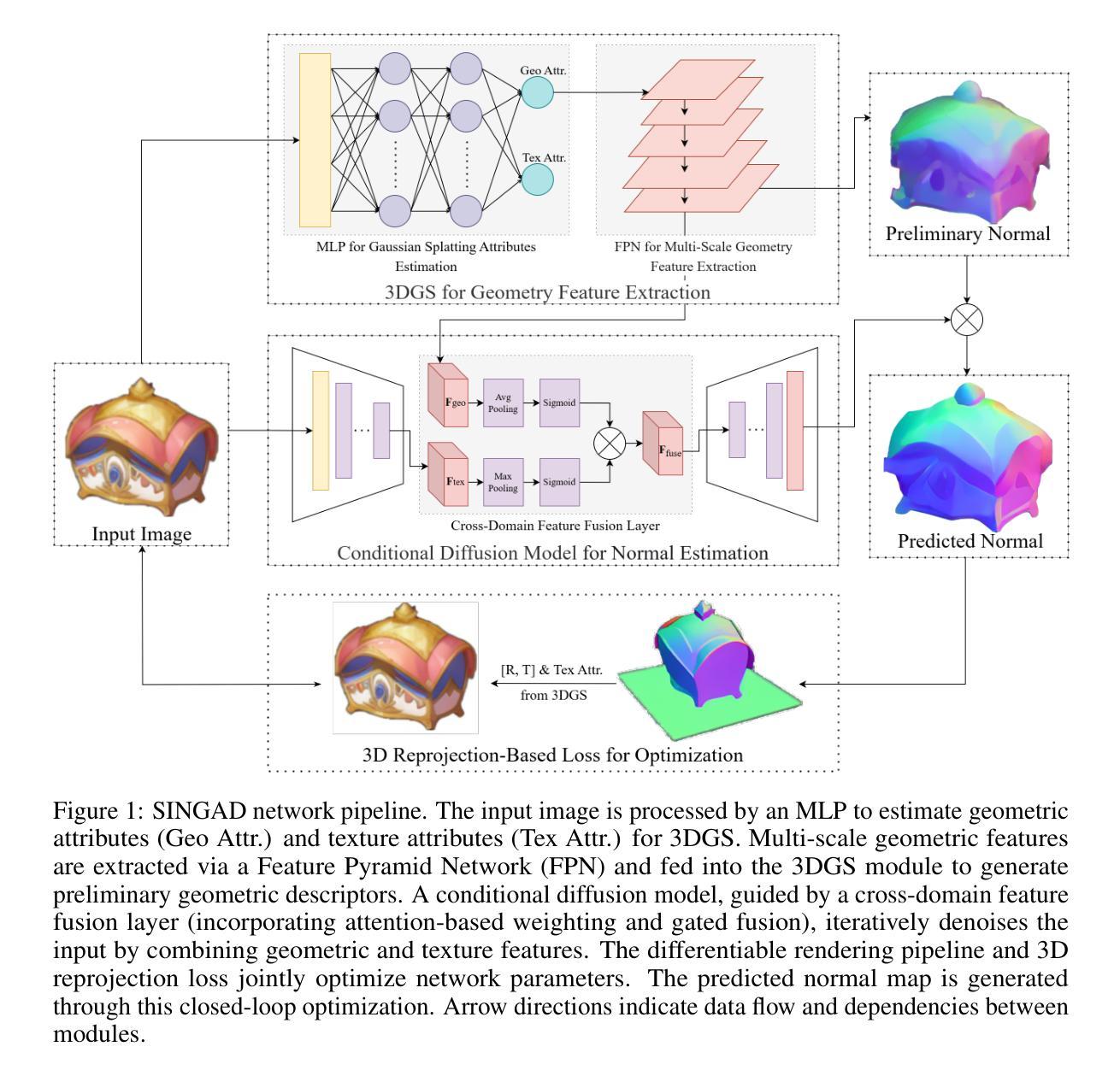
A 3DGS-Diffusion Self-Supervised Framework for Normal Estimation from a Single Image
Authors:Yanxing Liang, Yinghui Wang, Jinlong Yang, Wei Li
The lack of spatial dimensional information remains a challenge in normal estimation from a single image. Recent diffusion-based methods have demonstrated significant potential in 2D-to-3D implicit mapping, they rely on data-driven statistical priors and miss the explicit modeling of light-surface interaction, leading to multi-view normal direction conflicts. Moreover, the discrete sampling mechanism of diffusion models causes gradient discontinuity in differentiable rendering reconstruction modules, preventing 3D geometric errors from being backpropagated to the normal generation network, thereby forcing existing methods to depend on dense normal annotations. This paper proposes SINGAD, a novel Self-supervised framework from a single Image for Normal estimation via 3D GAussian splatting guided Diffusion. By integrating physics-driven light-interaction modeling and a differentiable rendering-based reprojection strategy, our framework directly converts 3D geometric errors into normal optimization signals, solving the challenges of multi-view geometric inconsistency and data dependency. Specifically, the framework constructs a light-interaction-driven 3DGS reparameterization model to generate multi-scale geometric features consistent with light transport principles, ensuring multi-view normal consistency. A cross-domain feature fusion module is designed within a conditional diffusion model, embedding geometric priors to constrain normal generation while maintaining accurate geometric error propagation. Furthermore, a differentiable 3D reprojection loss strategy is introduced for self-supervised optimization that minimizes geometric error between the reconstructed and input image, eliminating dependence on annotated normal datasets. Quantitative evaluations on the Google Scanned Objects dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches across multiple metrics.
由于缺乏空间维度信息,从单幅图像进行正常估算仍然是一个挑战。最近的基于扩散的方法在二维到三维隐式映射方面表现出了巨大的潜力,但它们依赖于数据驱动的统计先验知识,并忽略了光面交互的显式建模,从而导致多视角正常方向冲突。此外,扩散模型的离散采样机制导致可微分渲染重建模块中的梯度不连续,阻碍了将三维几何误差反向传播到正常生成网络,从而迫使现有方法依赖于密集的正常注释。本文提出了SINGAD,一种新型的自监督框架,通过以三维高斯喷射引导扩散从单幅图像进行正常估算。通过整合物理驱动的光交互建模和基于可微分渲染的重投影策略,我们的框架直接将三维几何误差转换为正常优化信号,解决了多视角几何不一致性和数据依赖性的挑战。具体来说,该框架构建了一个光交互驱动的3DGS重参数化模型,以生成符合光传输原理的多尺度几何特征,确保多视角正常的一致性。在条件扩散模型中设计了一个跨域特征融合模块,嵌入几何先验以约束正常的生成,同时保持准确的几何误差传播。此外,引入了一种可微分的三维重投影损失策略进行自监督优化,以最小化重建图像和输入图像之间的几何误差,从而消除对注释正常数据集依赖性。在Google扫描对象数据集上的定量评估表明,我们的方法在多指标上优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型自监督单图像法法向估计框架SINGAD。通过整合物理驱动的光交互建模和可微分渲染的重投影策略,框架直接转化3D几何误差为法向优化信号,解决多视角几何不一致和数据依赖问题。实验表明,该方法在Google扫描物体数据集上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在2D-to-3D隐式映射中具有巨大潜力,但仍面临空间维度信息缺失的挑战。
- 现有方法依赖数据驱动的统计先验,缺乏显式光面交互建模,导致多视角法向方向冲突。
- SINGAD框架通过结合物理驱动的光交互建模和可微分渲染策略,解决多视角几何不一致和数据依赖问题。
- 框架构建了一个光交互驱动的3DGS重参数化模型,生成与光传输原则一致的多尺度几何特征,确保多视角法向一致性。
- 框架设计了一个跨域特征融合模块,嵌入几何先验以约束法向生成并保持准确的几何误差传播。
- 引入可微分的3D重投影损失策略进行自监督优化,减少重建图像与输入图像之间的几何误差。
点此查看论文截图

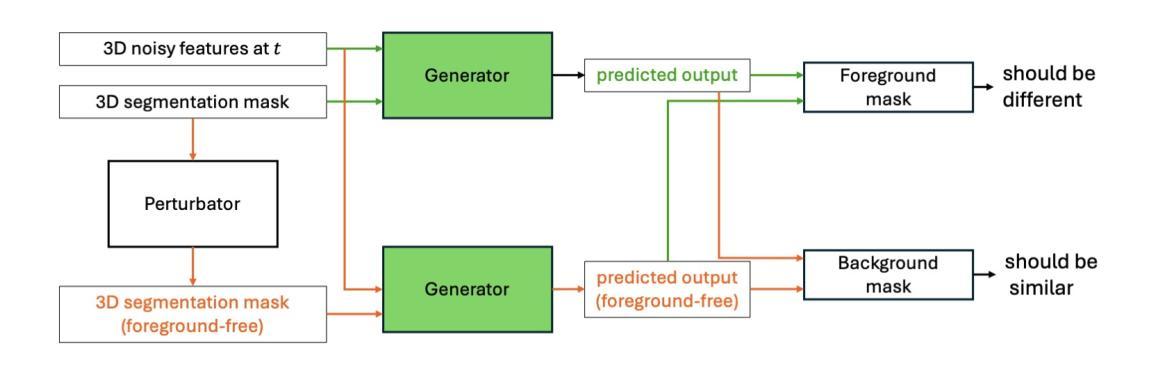
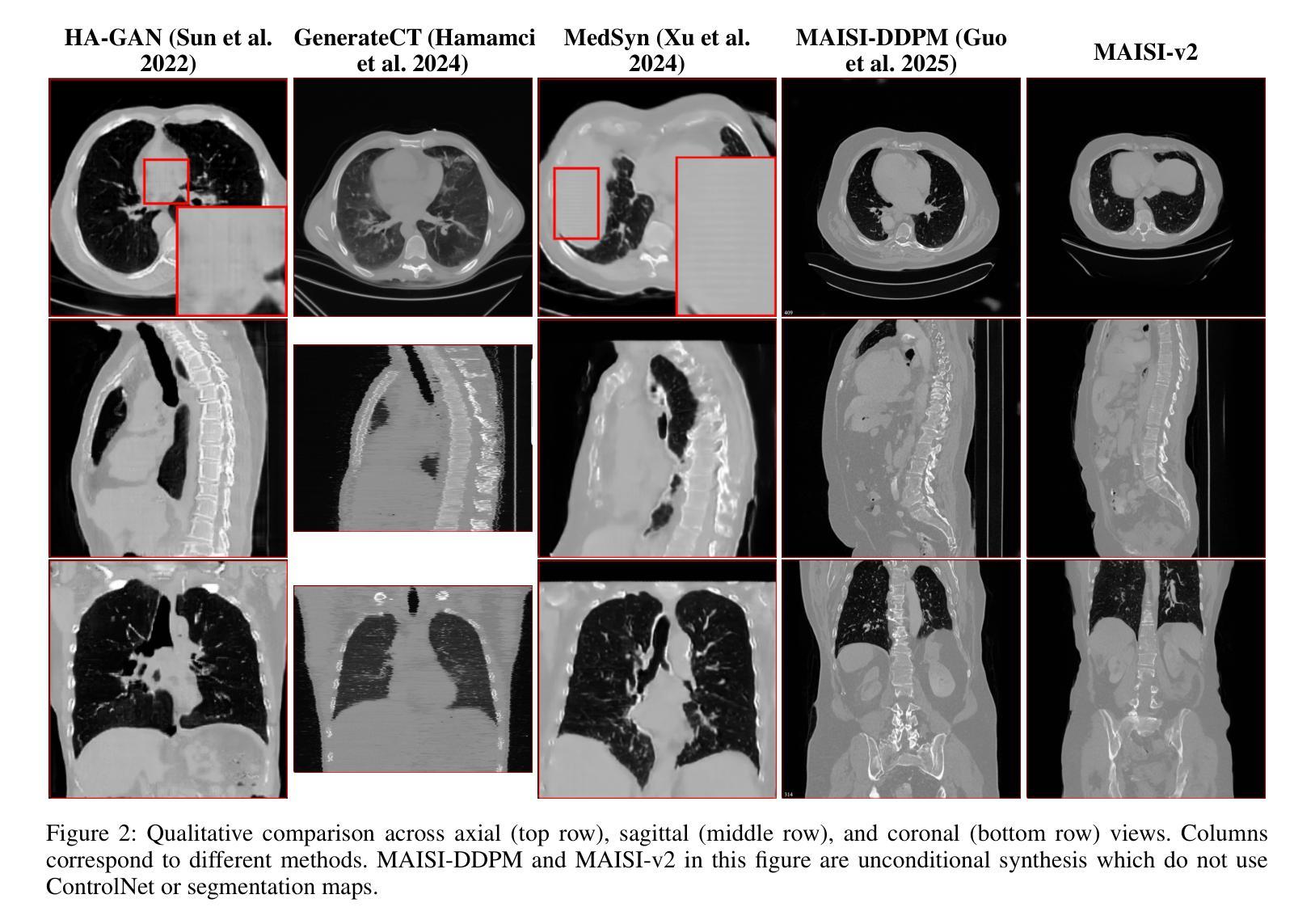
MAISI-v2: Accelerated 3D High-Resolution Medical Image Synthesis with Rectified Flow and Region-specific Contrastive Loss
Authors:Can Zhao, Pengfei Guo, Dong Yang, Yucheng Tang, Yufan He, Benjamin Simon, Mason Belue, Stephanie Harmon, Baris Turkbey, Daguang Xu
Medical image synthesis is an important topic for both clinical and research applications. Recently, diffusion models have become a leading approach in this area. Despite their strengths, many existing methods struggle with (1) limited generalizability that only work for specific body regions or voxel spacings, (2) slow inference, which is a common issue for diffusion models, and (3) weak alignment with input conditions, which is a critical issue for medical imaging. MAISI, a previously proposed framework, addresses generalizability issues but still suffers from slow inference and limited condition consistency. In this work, we present MAISI-v2, the first accelerated 3D medical image synthesis framework that integrates rectified flow to enable fast and high quality generation. To further enhance condition fidelity, we introduce a novel region-specific contrastive loss to enhance the sensitivity to region of interest. Our experiments show that MAISI-v2 can achieve SOTA image quality with $33 \times$ acceleration for latent diffusion model. We also conducted a downstream segmentation experiment to show that the synthetic images can be used for data augmentation. We release our code, training details, model weights, and a GUI demo to facilitate reproducibility and promote further development within the community.
医学图像合成在临床和研究应用中都是一个重要的话题。最近,扩散模型已成为该领域的主流方法。尽管它们具有优势,但许多现有方法仍然面临(1)通用性有限,仅适用于特定部位或体素间距;(2)推理速度慢,这是扩散模型的常见问题;(3)与输入条件对齐不佳,这对医学影像来说是关键问题。MAISI是一个先前提出的框架,解决了通用性问题,但仍然面临推理速度慢和条件一致性有限的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了MAISI-v2,这是第一个集成了矫正流的加速3D医学图像合成框架,能够实现快速和高质量的生成。为了进一步提高条件保真度,我们引入了一种新型的区域特异性对比损失,以提高对感兴趣区域的敏感性。我们的实验表明,MAISI-v2可以在潜在扩散模型上实现$33 \times$的加速,同时达到最佳图像质量。我们还进行了下游分割实验,以证明合成图像可用于数据增强。我们发布了我们的代码、训练细节、模型权重和GUI演示,以促进社区内的可重复性和进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医疗图像合成在临床和研究应用中均具有重要意义,扩散模型是这一领域的领先方法。虽然强大,但现有方法存在局限性,如通用性不足、推理速度慢以及与输入条件对齐不佳。MAISI-v2是解决这些问题的首个加速的3D医疗图像合成框架,它通过整合矫正流实现快速、高质量的生成。为进一步提高条件保真度,我们引入了一种新型的区域特异性对比损失,以提高对感兴趣区域的敏感性。实验表明,MAISI-v2可以在潜在扩散模型上实现$33 \times$的加速,同时达到最先进的图像质量。我们还进行了下游分割实验,以展示合成图像可用于数据增强。我们公开了代码、训练细节、模型权重和GUI演示,以促进社区内的可重复性和进一步发展。
要点摘要
- 医疗图像合成是临床和研究的重要应用之一,扩散模型是该领域的领先方法。
- 现有方法存在通用性不足的问题,仅适用于特定区域或体素间距。
- 扩散模型的常见问题是推理速度慢。
- 医疗成像中,与输入条件对齐不佳是一个关键问题。
- MAISI-v2是首个加速的3D医疗图像合成框架,通过整合矫正流实现快速高质量的生成。
- 为提高条件保真度,引入了新型区域特异性对比损失。
点此查看论文截图


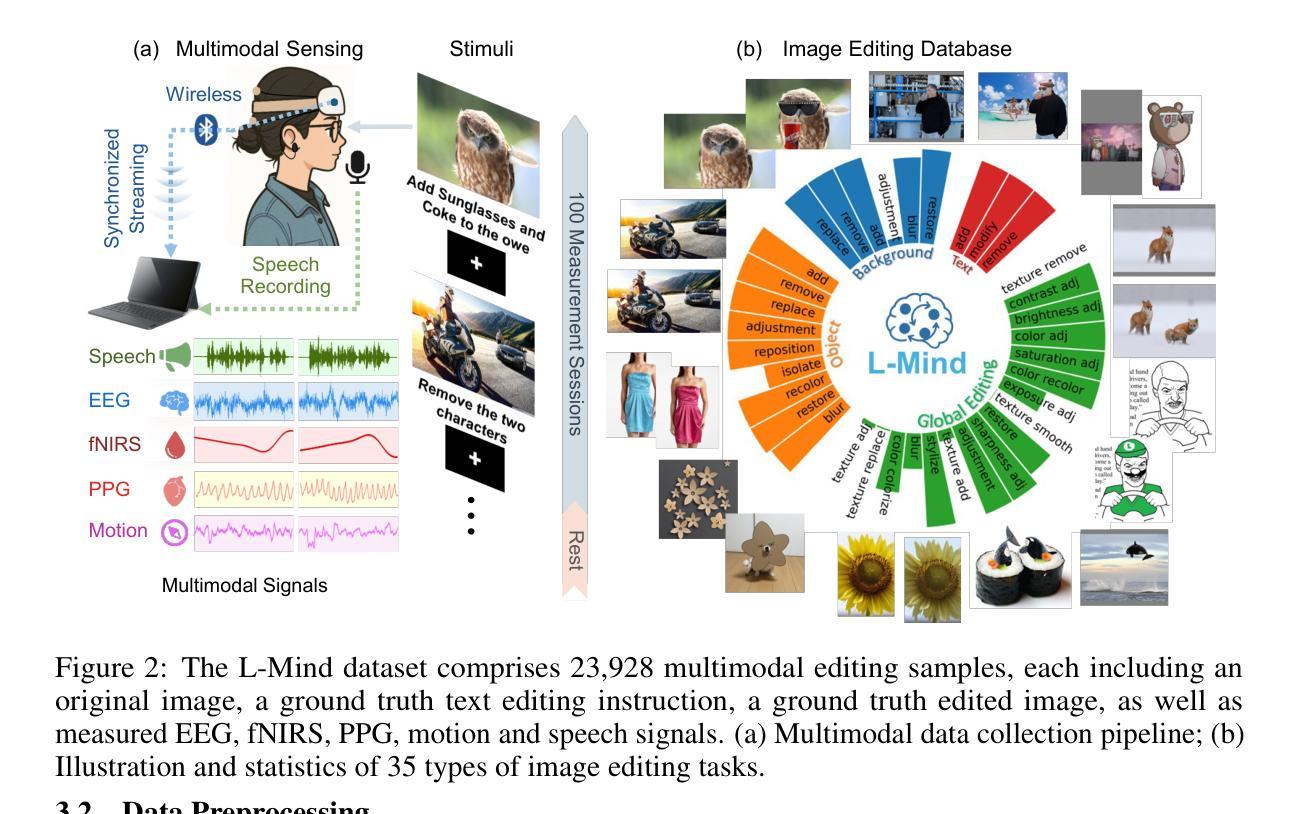
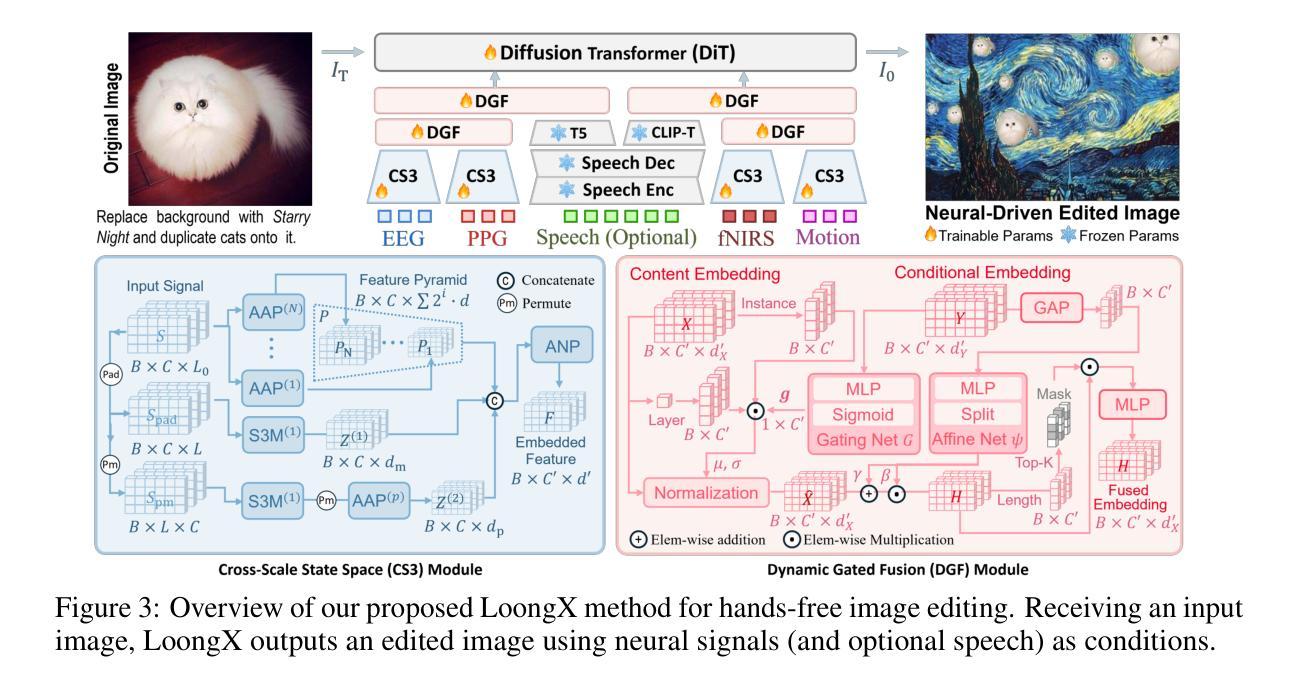
Neural-Driven Image Editing
Authors:Pengfei Zhou, Jie Xia, Xiaopeng Peng, Wangbo Zhao, Zilong Ye, Zekai Li, Suorong Yang, Jiadong Pan, Yuanxiang Chen, Ziqiao Wang, Kai Wang, Qian Zheng, Xiaojun Chang, Gang Pan, Shurong Dong, Kaipeng Zhang, Yang You
Traditional image editing typically relies on manual prompting, making it labor-intensive and inaccessible to individuals with limited motor control or language abilities. Leveraging recent advances in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and generative models, we propose LoongX, a hands-free image editing approach driven by multimodal neurophysiological signals. LoongX utilizes state-of-the-art diffusion models trained on a comprehensive dataset of 23,928 image editing pairs, each paired with synchronized electroencephalography (EEG), functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), photoplethysmography (PPG), and head motion signals that capture user intent. To effectively address the heterogeneity of these signals, LoongX integrates two key modules. The cross-scale state space (CS3) module encodes informative modality-specific features. The dynamic gated fusion (DGF) module further aggregates these features into a unified latent space, which is then aligned with edit semantics via fine-tuning on a diffusion transformer (DiT). Additionally, we pre-train the encoders using contrastive learning to align cognitive states with semantic intentions from embedded natural language. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LoongX achieves performance comparable to text-driven methods (CLIP-I: 0.6605 vs. 0.6558; DINO: 0.4812 vs. 0.4636) and outperforms them when neural signals are combined with speech (CLIP-T: 0.2588 vs. 0.2549). These results highlight the promise of neural-driven generative models in enabling accessible, intuitive image editing and open new directions for cognitive-driven creative technologies. Datasets and code will be released to support future work and foster progress in this emerging area.
传统图像编辑通常依赖于手动提示,这使得它劳动密集,对于运动控制或语言能力有限的个人来说难以接触。我们利用最近脑机接口(BCIs)和生成模型的进步,提出了LoongX,一种由多模态神经生理信号驱动的无接触图像编辑方法。LoongX利用最先进的扩散模型,在23928个图像编辑对上进行了训练,每个图像编辑对都与同步脑电图(EEG)、功能近红外光谱(fNIRS)、光电容积脉搏波(PPG)和头部运动信号配对,这些信号捕捉了用户意图。为了有效解决这些信号的异质性,LoongX集成了两个关键模块。跨尺度状态空间(CS3)模块编码具有信息性的模态特定特征。动态门控融合(DGF)模块进一步将这些特征聚合到统一的潜在空间中,然后通过微调扩散变压器(DiT)与编辑语义对齐。此外,我们使用对比学习对编码器进行预训练,将认知状态与嵌入的自然语言的语义意图对齐。大量实验表明,LoongX的性能与文本驱动的方法相当(CLIP-I:0.6605 vs. 0.6558;DINO:0.4812 vs. 0.4636),并在结合神经信号时表现出优越性(CLIP-T:0.2588 vs. 0.2549)。这些结果突显了神经驱动生成模型在图像编辑方面的潜力,并为认知驱动的创造性技术打开了新的发展方向。我们将发布数据集和代码以支持未来的工作并促进这一新兴领域的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 14 figures
Summary
基于先进的脑机接口技术和生成模型,提出一种名为LoongX的无手图像编辑方法,通过多模态神经生理信号驱动。该方法利用扩散模型,有效整合不同信号,实现用户意图与图像编辑的精准对接。
Key Takeaways
- LoongX利用先进的脑机接口技术,实现无手操作的图像编辑。
- 通过结合多模态神经生理信号(EEG、fNIRS、PPG等),捕获用户意图。
- LoongX通过CS3模块提取信号中的特定特征,并通过DGF模块将这些特征整合到统一潜在空间。
- 利用扩散变压器(DiT)与编辑语义对齐,通过微调实现潜在空间的精确操作。
- 通过对比实验,显示LoongX在性能上可与文本驱动方法相媲美,并在结合神经信号和语音时表现更优。
- LoongX的实现证明了神经驱动生成模型在图像编辑中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

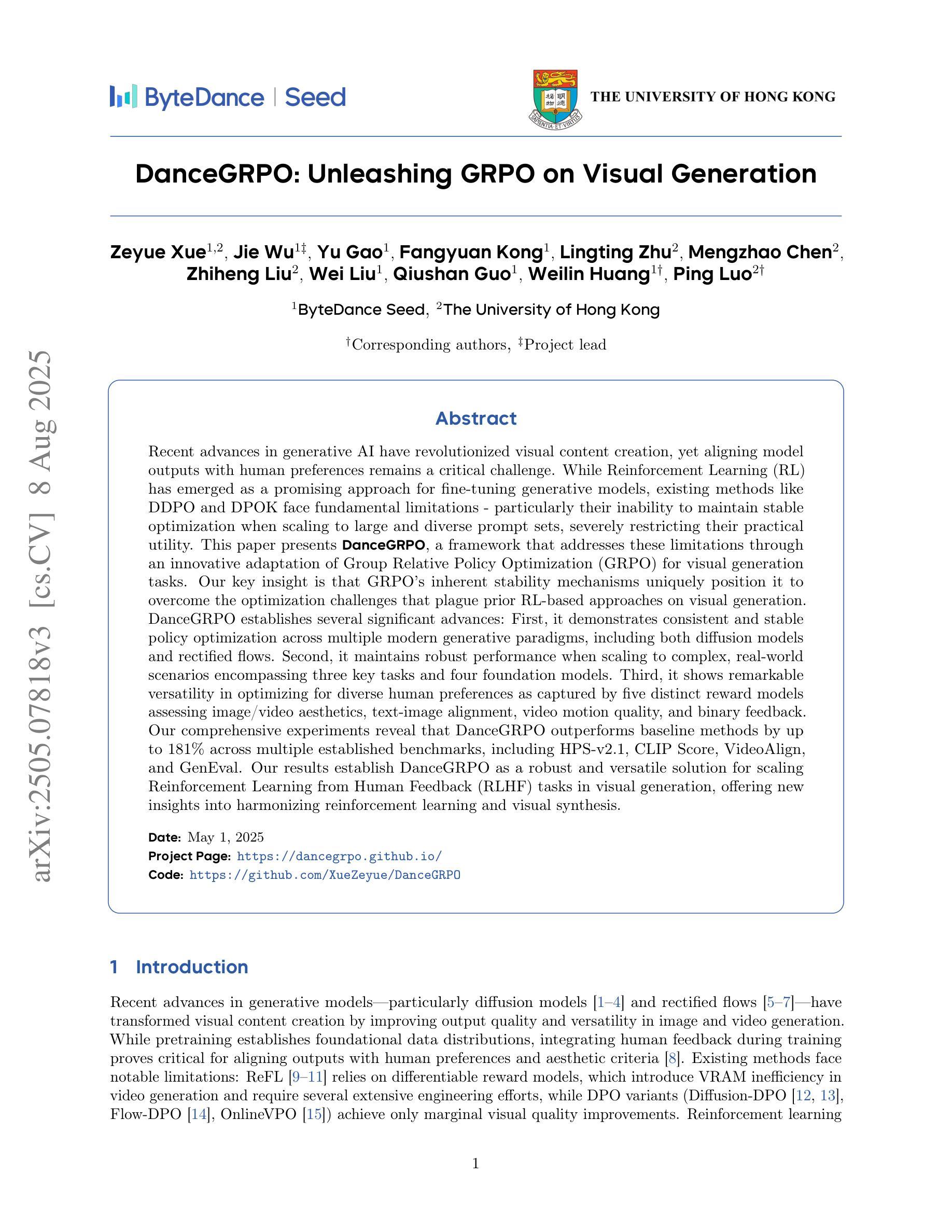
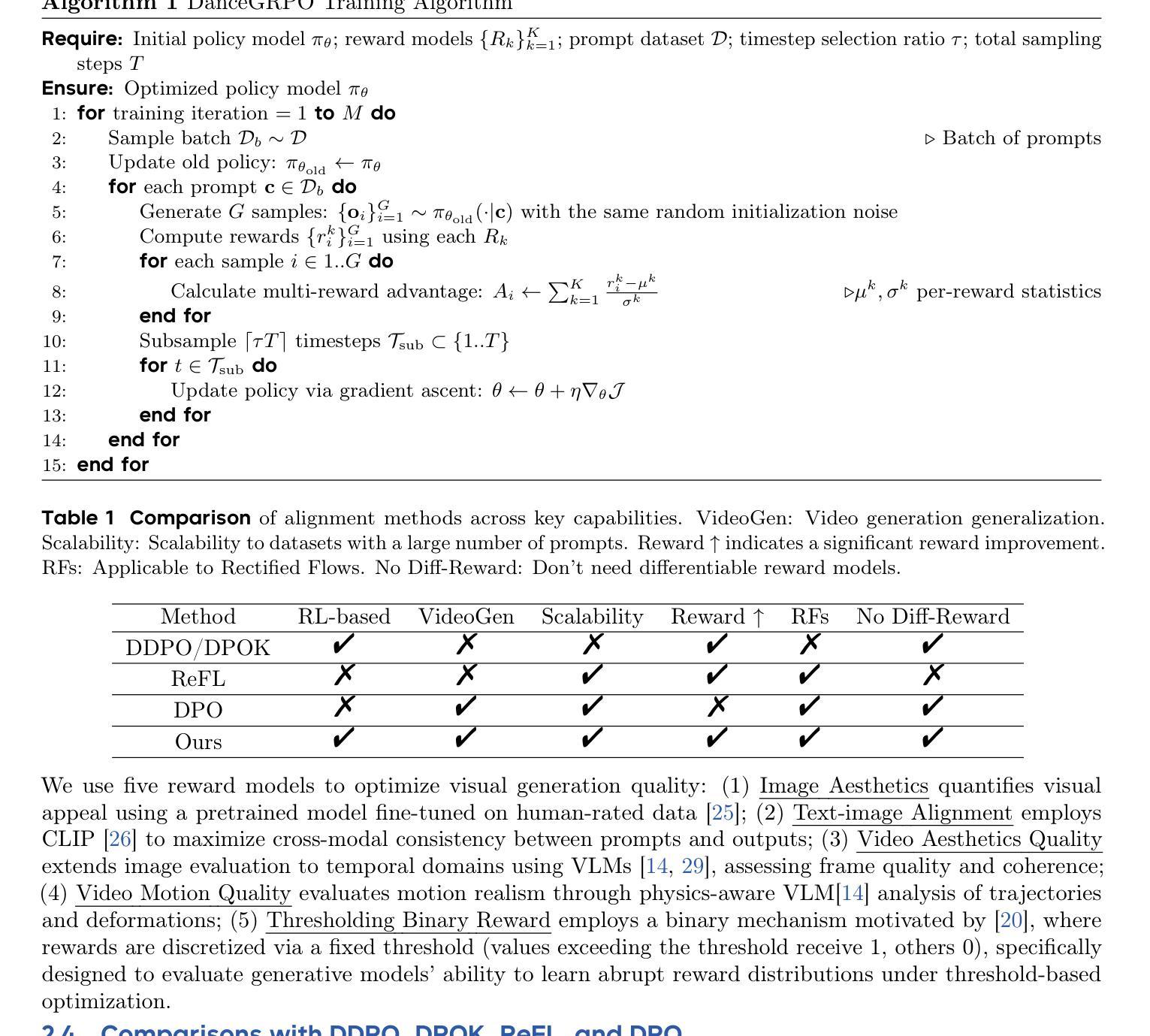
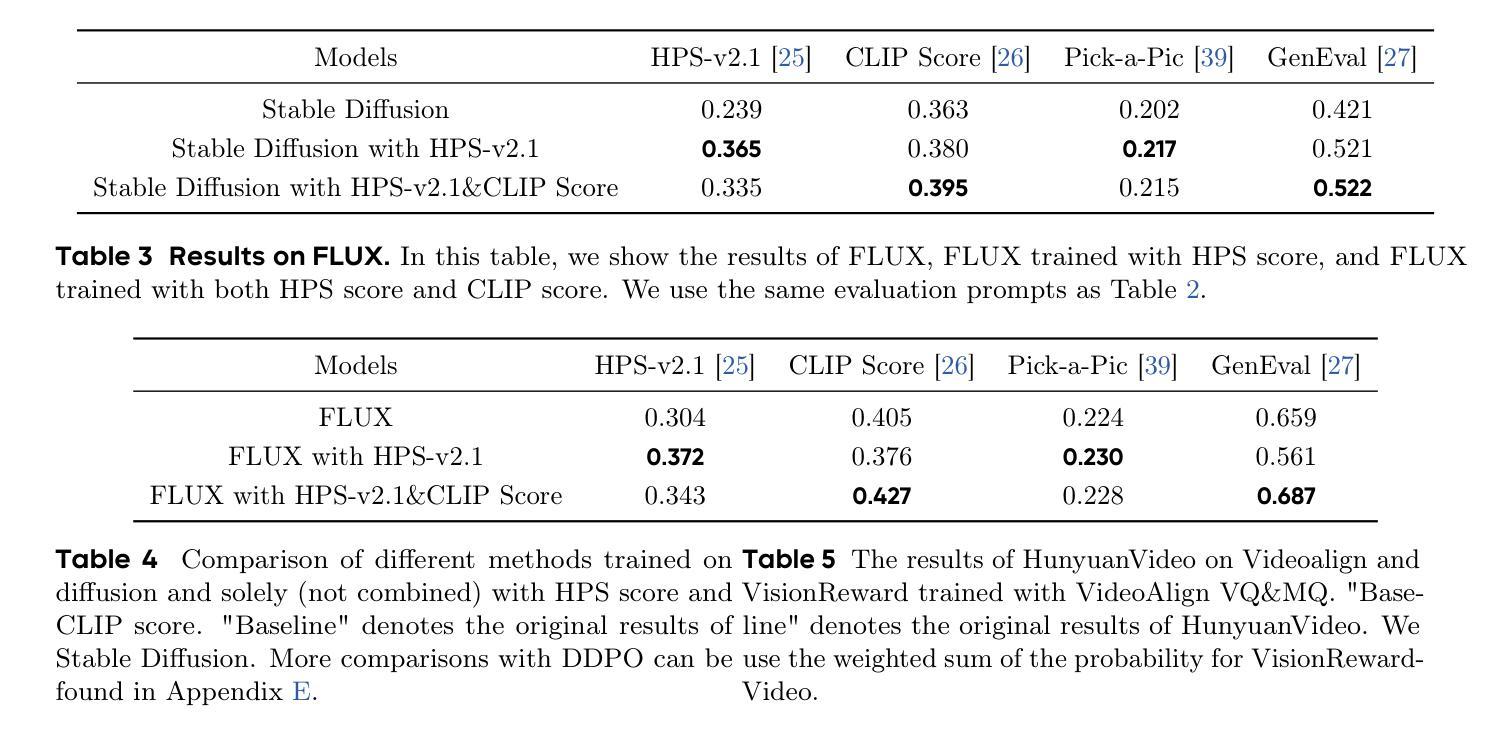
DanceGRPO: Unleashing GRPO on Visual Generation
Authors:Zeyue Xue, Jie Wu, Yu Gao, Fangyuan Kong, Lingting Zhu, Mengzhao Chen, Zhiheng Liu, Wei Liu, Qiushan Guo, Weilin Huang, Ping Luo
Recent advances in generative AI have revolutionized visual content creation, yet aligning model outputs with human preferences remains a critical challenge. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a promising approach for fine-tuning generative models, existing methods like DDPO and DPOK face fundamental limitations - particularly their inability to maintain stable optimization when scaling to large and diverse prompt sets, severely restricting their practical utility. This paper presents DanceGRPO, a framework that addresses these limitations through an innovative adaptation of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for visual generation tasks. Our key insight is that GRPO’s inherent stability mechanisms uniquely position it to overcome the optimization challenges that plague prior RL-based approaches on visual generation. DanceGRPO establishes several significant advances: First, it demonstrates consistent and stable policy optimization across multiple modern generative paradigms, including both diffusion models and rectified flows. Second, it maintains robust performance when scaling to complex, real-world scenarios encompassing three key tasks and four foundation models. Third, it shows remarkable versatility in optimizing for diverse human preferences as captured by five distinct reward models assessing image/video aesthetics, text-image alignment, video motion quality, and binary feedback. Our comprehensive experiments reveal that DanceGRPO outperforms baseline methods by up to 181% across multiple established benchmarks, including HPS-v2.1, CLIP Score, VideoAlign, and GenEval. Our results establish DanceGRPO as a robust and versatile solution for scaling Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) tasks in visual generation, offering new insights into harmonizing reinforcement learning and visual synthesis.
最近生成式人工智能的进步在视觉内容创作方面带来了革命性的变化,然而,将模型输出与人类偏好对齐仍然是一个巨大的挑战。尽管强化学习(RL)在微调生成模型方面显示出有前途的应用前景,但现有的方法如DDPO和DPOK面临基础性的局限——特别是在扩展到大型和多样化的提示集时无法维持稳定的优化,这严重限制了它们的实用性。本文提出了DanceGRPO框架,它通过针对视觉生成任务的Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)的创新性适应来解决这些局限性。我们的关键见解是GRPO的内在稳定性机制以其独特的方式克服了优化挑战,这些挑战一直困扰着先前的基于RL的视觉生成方法。DanceGRPO取得了几个重要进展:首先,它证明了在现代生成范式中的稳定政策优化一致性,包括扩散模型和校正流。其次,在扩展到包括三个关键任务和四个基础模型在内的复杂现实世界场景时,它保持了稳健的性能。第三,在优化五种不同奖励模型所捕捉到的不同人类偏好方面表现出卓越的通用性,这些奖励模型评估图像/视频美学、文本与图像的对齐方式、视频运动质量和二进制反馈。我们的综合实验表明,在多个既定基准测试中,DanceGRPO较基线方法高出181%,包括HPS-v2.1、CLIP Score、VideoAlign和GenEval。我们的结果证实,DanceGRPO是视觉生成领域中强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)任务扩展的稳健且通用的解决方案,为强化学习与视觉合成的和谐统一提供了新的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://dancegrpo.github.io/
Summary
最新进展的生成式人工智能在视觉内容创作领域掀起革命,但仍面临模型输出与人类偏好对齐的挑战。尽管强化学习(RL)在微调生成模型方面展现出巨大潜力,但现有方法如DDPO和DPOK存在根本性局限,难以在大规模且多样化的提示集上维持稳定的优化,限制了其实用性。本文提出DanceGRPO框架,通过集团相对政策优化(GRPO)的创新适应,解决这些挑战。DanceGRPO在视觉生成任务上实现了多项重要进展,包括在不同现代生成范式中持续稳定的政策优化、在复杂现实场景中的稳健性能以及优化多种人类偏好的灵活性。实验表明,DanceGRPO在多个基准测试中较基线方法高出181%,成为视觉生成领域中强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)任务的稳健且通用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI在视觉内容创作领域的进展及其面临的挑战。
- 强化学习在微调生成模型中的潜力与现有方法的局限。
- DanceGRPO框架通过集团相对政策优化(GRPO)解决现有挑战。
- DanceGRPO实现跨多种生成范式的稳定政策优化。
- DanceGRPO在复杂现实场景中的稳健性能。
- DanceGRPO优化多种人类偏好的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图
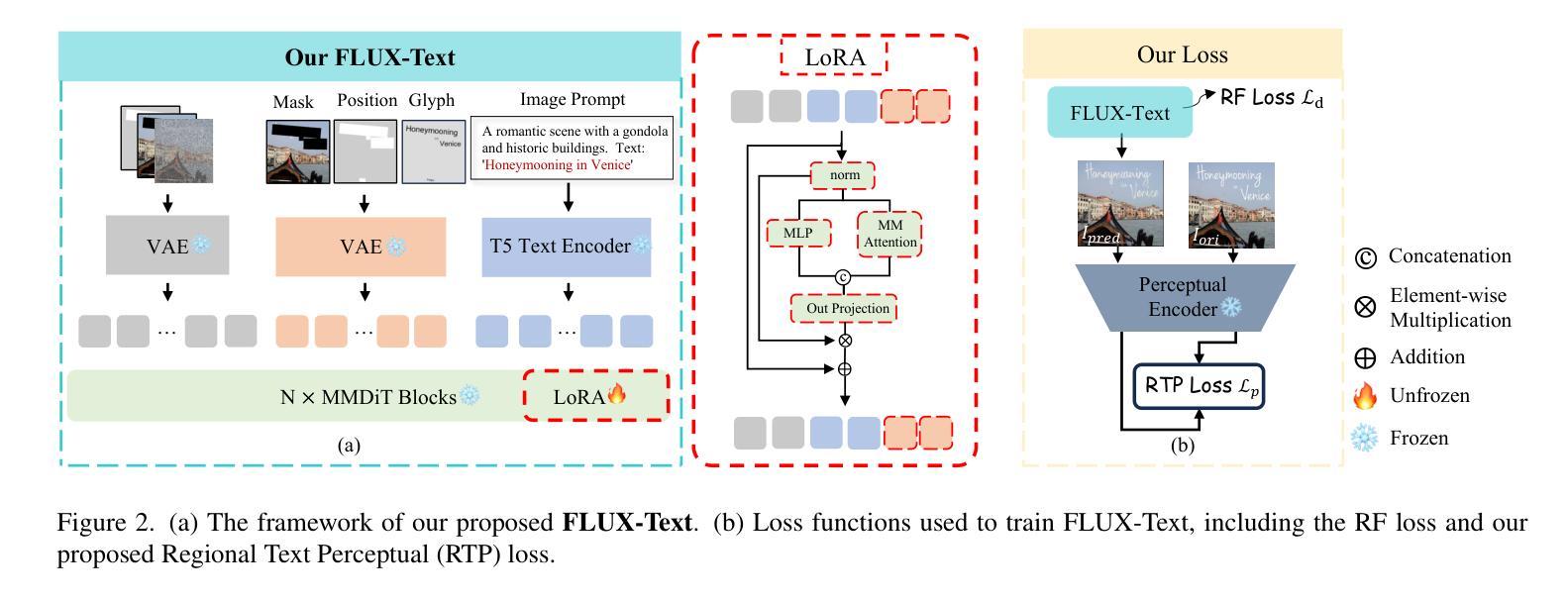
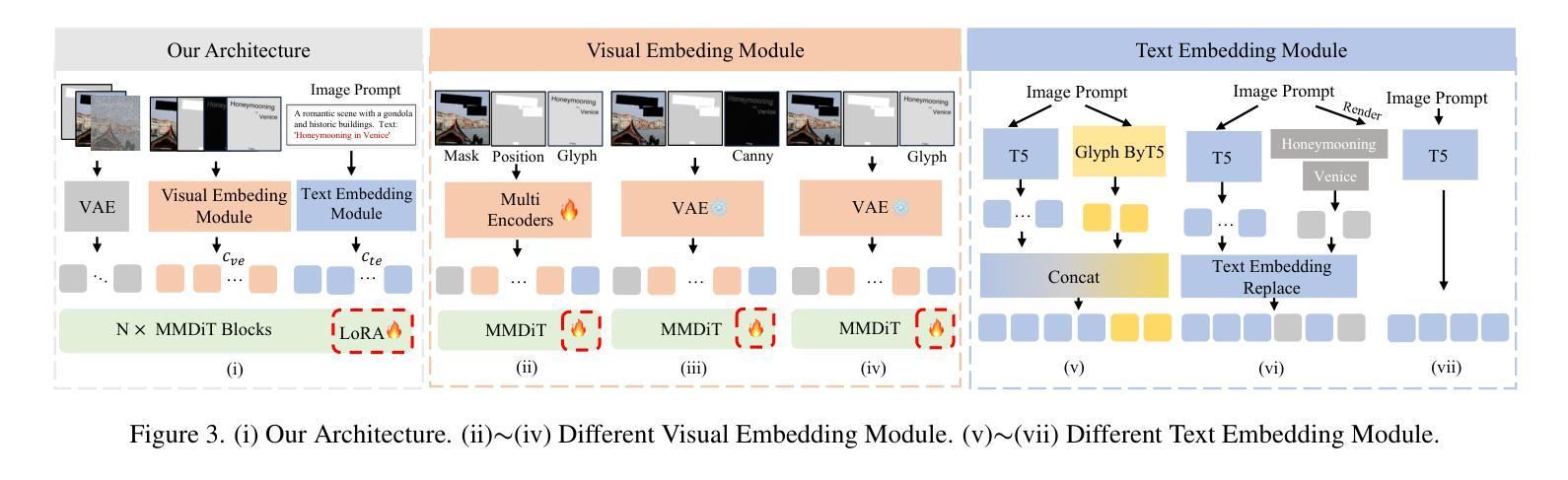
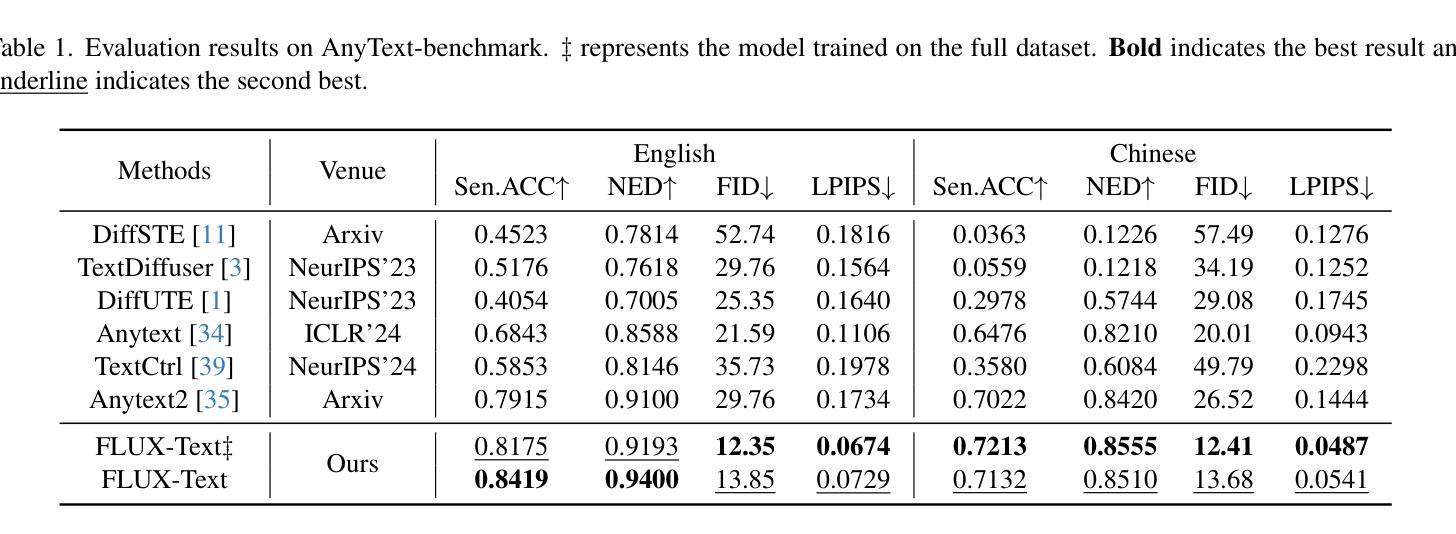
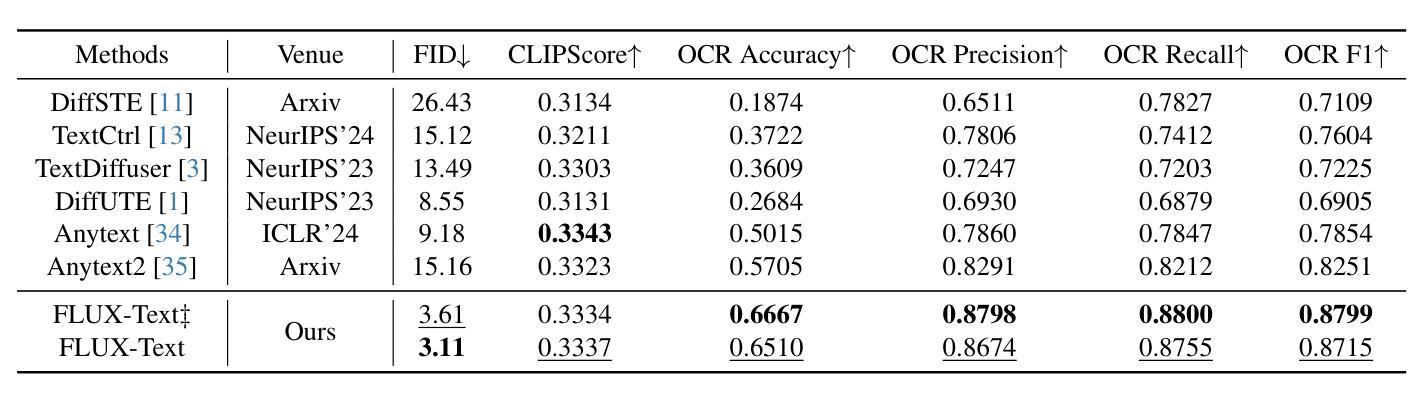
FLUX-Text: A Simple and Advanced Diffusion Transformer Baseline for Scene Text Editing
Authors:Rui Lan, Yancheng Bai, Xu Duan, Mingxing Li, Dongyang Jin, Ryan Xu, Lei Sun, Xiangxiang Chu
Scene text editing aims to modify or add texts on images while ensuring text fidelity and overall visual quality consistent with the background. Recent methods are primarily built on UNet-based diffusion models, which have improved scene text editing results, but still struggle with complex glyph structures, especially for non-Latin ones (\eg, Chinese, Korean, Japanese). To address these issues, we present \textbf{FLUX-Text}, a simple and advanced multilingual scene text editing DiT method. Specifically, our FLUX-Text enhances glyph understanding and generation through lightweight Visual and Text Embedding Modules, while preserving the original generative capability of FLUX. We further propose a Regional Text Perceptual Loss tailored for text regions, along with a matching two-stage training strategy to better balance text editing and overall image quality. Benefiting from the DiT-based architecture and lightweight feature injection modules, FLUX-Text can be trained with only $0.1$M training examples, a \textbf{97%} reduction compared to $2.9$M required by popular methods. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets, including English and Chinese benchmarks, demonstrate that our method surpasses other methods in visual quality and text fidelity. All the code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/FluxText.
场景文本编辑旨在在图像上修改或添加文本,同时确保文本忠诚度和与背景一致的整体视觉质量。最近的方法主要建立在基于UNet的扩散模型上,已经改善了场景文本编辑的结果,但在处理复杂的字形结构时仍然面临挑战,尤其是非拉丁语系(例如中文、韩语、日语)。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了FLUX-Text,这是一种简单先进的多元场景文本编辑DiT方法。具体来说,我们的FLUX-Text通过轻量级的视觉和文本嵌入模块增强了字形理解和生成,同时保留了FLUX的原始生成能力。我们还针对文本区域提出了区域文本感知损失,以及一个配套的两阶段训练策略,以更好地平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量。得益于DiT架构和轻量级特征注入模块,FLUX-Text仅需0.1M训练样本即可进行训练,与流行方法所需的2.9M相比,减少了97%。在多个公共数据集上的广泛实验,包括英语和中文基准测试,证明我们的方法在视觉质量和文本忠诚度方面超过了其他方法。所有代码可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/FluxText获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于UNet扩散模型的先进多语言场景文本编辑方法——FLUX-Text。该方法通过轻量级视觉和文本嵌入模块,增强了字形理解和生成能力,同时保持了FLUX的原始生成能力。此外,还提出了一种针对文本区域的区域性文本感知损失和相应的两阶段训练策略,以更好地平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量。FLUX-Text可在仅使用少量训练样本的情况下达到出色的性能,特别是在处理非拉丁语系(如中文)的复杂字形结构时表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- FLUX-Text是基于UNet扩散模型的先进多语言场景文本编辑方法。
- FLUX-Text通过轻量级视觉和文本嵌入模块增强了字形理解和生成能力。
- 提出了一种针对文本区域的区域性文本感知损失,以提高文本编辑的质量。
- 采用了两阶段训练策略,以平衡文本编辑和整体图像质量的优化。
- FLUX-Text可在仅使用少量训练样本的情况下达到出色的性能。
- FLUX-Text在处理非拉丁语系(如中文)的复杂字形结构时表现优异。
- 所有代码已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图


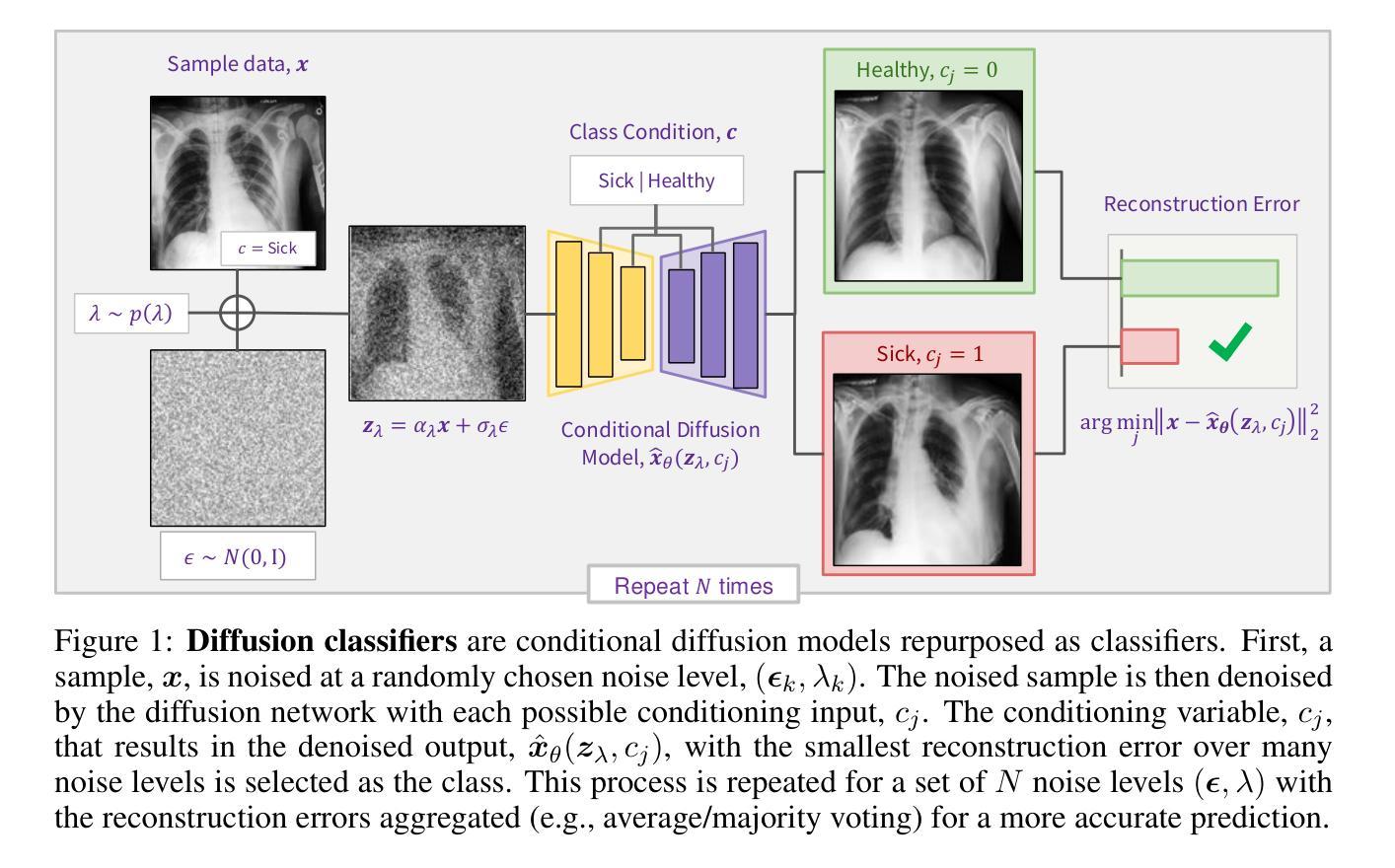
Conditional Diffusion Models are Medical Image Classifiers that Provide Explainability and Uncertainty for Free
Authors:Gian Mario Favero, Parham Saremi, Emily Kaczmarek, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel
Discriminative classifiers have become a foundational tool in deep learning for medical imaging, excelling at learning separable features of complex data distributions. However, these models often need careful design, augmentation, and training techniques to ensure safe and reliable deployment. Recently, diffusion models have become synonymous with generative modeling in 2D. These models showcase robustness across a range of tasks including natural image classification, where classification is performed by comparing reconstruction errors across images generated for each possible conditioning input. This work presents the first exploration of the potential of class conditional diffusion models for 2D medical image classification. First, we develop a novel majority voting scheme shown to improve the performance of medical diffusion classifiers. Next, extensive experiments on the CheXpert and ISIC Melanoma skin cancer datasets demonstrate that foundation and trained-from-scratch diffusion models achieve competitive performance against SOTA discriminative classifiers without the need for explicit supervision. In addition, we show that diffusion classifiers are intrinsically explainable, and can be used to quantify the uncertainty of their predictions, increasing their trustworthiness and reliability in safety-critical, clinical contexts. Further information is available on our project page: https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier.github.io/.
判别分类器已成为深度学习医学影像分析的基础工具,擅长学习复杂数据分布的分离特征。然而,为了确保安全可靠的部署,这些模型通常需要精心设计、增强和训练技术。最近,扩散模型已成为二维生成模型的代名词。这些模型在各种任务中表现出稳健性,包括自然图像分类,分类是通过比较每个可能的条件输入所生成的图像的重构误差来完成的。本文首次探索了类条件扩散模型在二维医学图像分类中的潜力。首先,我们开发了一种新型多数投票方案,该方案被证明可以提高医学扩散分类器的性能。接下来,在CheXpert和ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的大量实验表明,基础扩散模型和从头训练的扩散模型的性能与最新判别分类器相当,无需显式监督。此外,我们还表明,扩散分类器本质上是可解释的,可用于量化其预测的的不确定性,这在安全关键的临床环境中增加了其可信度和可靠性。更多信息请参见我们的项目页面:https://faverogian.github.io/med-diffusion-classifier.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025
Summary
本文首次探索了类条件扩散模型在二维医学影像分类中的潜力。研究团队发展了一种新型多数投票方案,用于提高医学影像扩散分类器的性能。实验结果显示,无论是在CheXpert还是ISIC黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上,基础扩散模型和从头训练的扩散模型都能达到与当前顶尖判别模型相竞争的性能,且无需显式监督。此外,扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性,可量化预测的不确定性,增加了其在安全关键的医疗环境中的可信度和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 类条件扩散模型首次被探索用于二维医学影像分类。
- 研究团队提出了新型多数投票方案以提高医学影像扩散分类器的性能。
- 扩散模型在医疗影像分类上表现出与顶尖判别模型相竞争的性能。
- 扩散模型无需显式监督,即可实现良好性能。
- 扩散分类器具有内在的可解释性。
- 扩散分类器可量化预测的不确定性。
- 扩散分类器的可信度和可靠性在医疗环境中尤为重要。
点此查看论文截图