⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
SPARSE Data, Rich Results: Few-Shot Semi-Supervised Learning via Class-Conditioned Image Translation
Authors:Guido Manni, Clemente Lauretti, Loredana Zollo, Paolo Soda
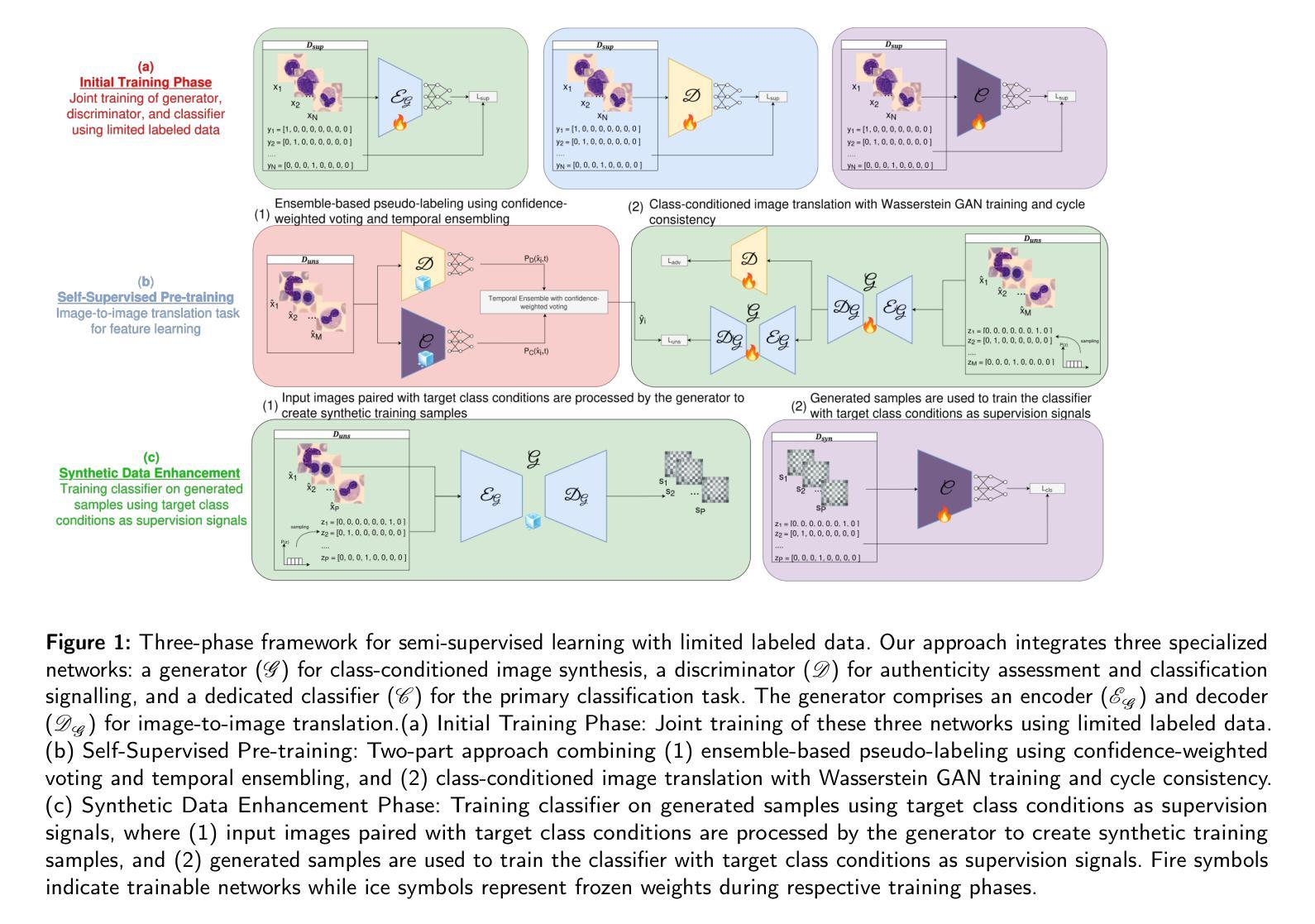
Deep learning has revolutionized medical imaging, but its effectiveness is severely limited by insufficient labeled training data. This paper introduces a novel GAN-based semi-supervised learning framework specifically designed for low labeled-data regimes, evaluated across settings with 5 to 50 labeled samples per class. Our approach integrates three specialized neural networks – a generator for class-conditioned image translation, a discriminator for authenticity assessment and classification, and a dedicated classifier – within a three-phase training framework. The method alternates between supervised training on limited labeled data and unsupervised learning that leverages abundant unlabeled images through image-to-image translation rather than generation from noise. We employ ensemble-based pseudo-labeling that combines confidence-weighted predictions from the discriminator and classifier with temporal consistency through exponential moving averaging, enabling reliable label estimation for unlabeled data. Comprehensive evaluation across eleven MedMNIST datasets demonstrates that our approach achieves statistically significant improvements over six state-of-the-art GAN-based semi-supervised methods, with particularly strong performance in the extreme 5-shot setting where the scarcity of labeled data is most challenging. The framework maintains its superiority across all evaluated settings (5, 10, 20, and 50 shots per class). Our approach offers a practical solution for medical imaging applications where annotation costs are prohibitive, enabling robust classification performance even with minimal labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE.
深度学习已经彻底改变了医学影像领域,但其有效性因缺乏足够的标注训练数据而受到严重限制。本文介绍了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,该框架专为低标注数据环境设计,并在每类有5到50个标注样本的各种环境中进行了评估。我们的方法整合了三个专用神经网络——用于类条件图像翻译的生成器、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及专用分类器——在一个三阶段训练框架中。该方法在有限的标注数据上进行监督训练,并在无监督学习中利用大量未标注图像进行图像到图像的翻译,而不是通过噪声生成。我们采用基于集合的伪标签方法,该方法结合了鉴别器和分类器的加权预测,并通过指数移动平均实现时间一致性,从而为未标注数据提供可靠的标签估计。在11个MedMNIST数据集上的综合评估表明,我们的方法在六个最先进的基于GAN的半监督方法上实现了统计学上的显著改善,特别是在极端的5个样本设置中,标注数据的稀缺性最具挑战性。该框架在所有评估环境(每类5、10、20和50个样本)中均保持其优势。我们的方法为医学影像应用提供了实际解决方案,其中标注成本高昂,即使在少量标注数据的情况下也能实现稳健的分类性能。代码可从https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在医学成像领域有革命性进展,但受限于缺乏标注的训练数据。本文提出一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,适用于少量标注数据的场景。该框架包含三个神经网络,通过监督学习和无监督学习相结合的方式进行训练,并在MedMNIST数据集上取得了显著成果。该框架在标注数据稀缺时具有显著优势,且适用于医学成像应用。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,适用于医学成像中标注数据不足的情况。
- 该框架集成了三个神经网络:用于类条件图像翻译的发电机、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及专用分类器。
- 该方法通过监督学习和无监督学习相结合的方式训练模型,利用有限标注数据和大量未标注图像。
- 采用基于集合的伪标签方法,结合鉴别器和分类器的预测结果,通过指数移动平均实现时间一致性,为未标注数据提供可靠的标签估计。
- 在多个MedMNIST数据集上的综合评估表明,该框架在少量标注数据的设置下表现优异,相对于六种最先进的GAN半监督方法具有统计上的显著改善。
- 该框架在标注数据极度稀缺的场景下(如每类仅有5个样本)表现出特别强的性能。
点此查看论文截图

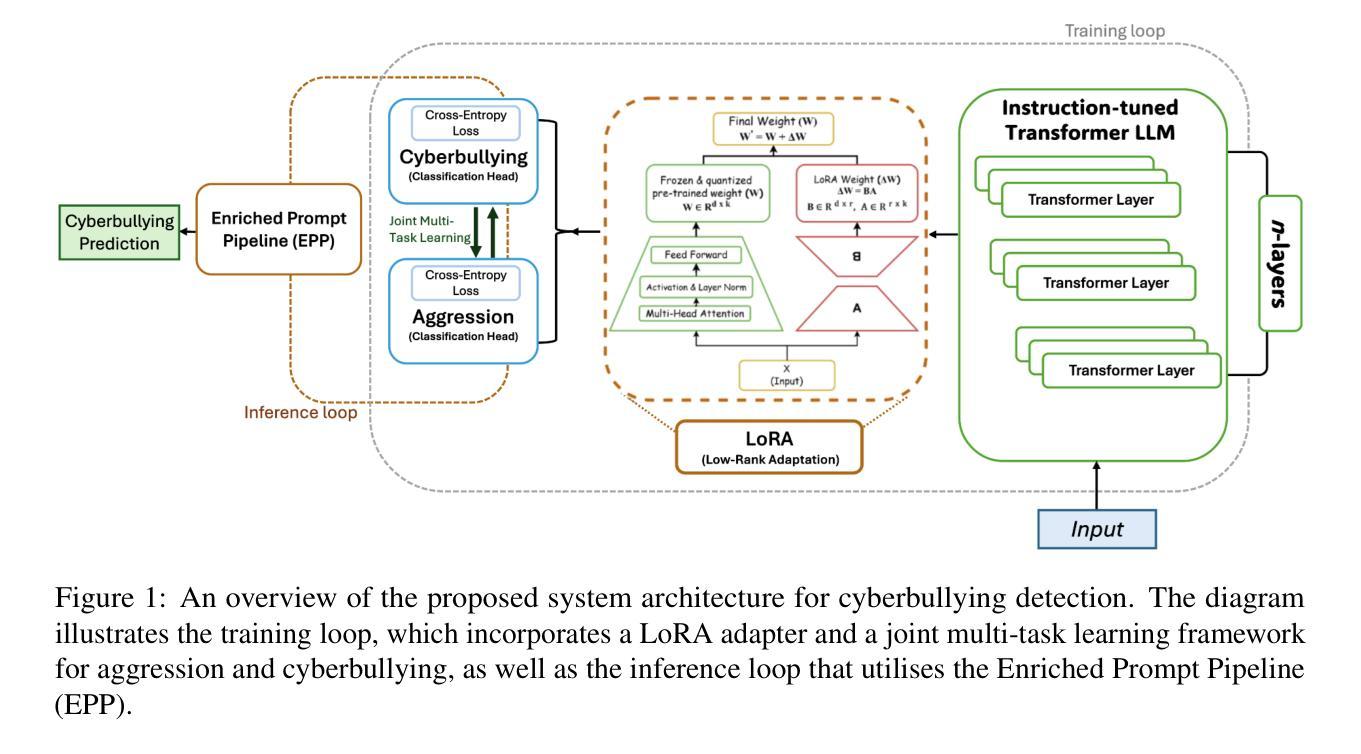
Cyberbullying Detection via Aggression-Enhanced Prompting
Authors:Aisha Saeid, Anu Sabu, Girish A. Koushik, Ferrante Neri, Diptesh Kanojia
Detecting cyberbullying on social media remains a critical challenge due to its subtle and varied expressions. This study investigates whether integrating aggression detection as an auxiliary task within a unified training framework can enhance the generalisation and performance of large language models (LLMs) in cyberbullying detection. Experiments are conducted on five aggression datasets and one cyberbullying dataset using instruction-tuned LLMs. We evaluated multiple strategies: zero-shot, few-shot, independent LoRA fine-tuning, and multi-task learning (MTL). Given the inconsistent results of MTL, we propose an enriched prompt pipeline approach in which aggression predictions are embedded into cyberbullying detection prompts to provide contextual augmentation. Preliminary results show that the enriched prompt pipeline consistently outperforms standard LoRA fine-tuning, indicating that aggression-informed context significantly boosts cyberbullying detection. This study highlights the potential of auxiliary tasks, such as aggression detection, to improve the generalisation of LLMs for safety-critical applications on social networks.
检测社交媒体上的网络欺凌仍然是一个关键的挑战,因为其表达具有细微性和多样性。本研究旨在探究在统一训练框架内整合攻击检测作为辅助任务,能否增强大型语言模型(LLM)在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。本研究使用指令调整的大型语言模型,在五个攻击数据集和一个网络欺凌数据集上进行了实验。我们评估了多种策略:零样本、小样本、独立LoRA微调和多任务学习(MTL)。鉴于多任务学习的不一致结果,我们提出了一种丰富的提示管道方法,其中攻击预测被嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中以提供上下文增强。初步结果表明,丰富的提示管道始终优于标准的LoRA微调,这表明攻击信息上下文显著提高了网络欺凌检测效果。本研究突出了辅助任务(如攻击检测)的潜力,可以改进大型语言模型在社交媒体安全关键应用的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to RANLP 2025
Summary:本研究探讨了将攻击检测作为辅助任务融入统一训练框架,以提高大型语言模型在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。实验表明,将攻击检测嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中的丰富提示管道方法能够一致地优于标准LoRA微调,显示出攻击检测提供的上下文信息对网络欺凌检测的增强作用。
Key Takeaways:
- 网络欺凌的微妙和多变表达使其检测成为一项关键挑战。
- 集成攻击检测作为辅助任务可以提高大型语言模型在网络欺凌检测中的性能。
- 实验涉及多种策略,包括零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调和多任务学习。
- 多任务学习的结果不一致,提出将攻击检测嵌入网络欺凌检测提示的丰富提示管道方法。
- 初步结果表明,丰富提示管道方法优于标准LoRA微调。
- 攻击检测提供的上下文信息对网络欺凌检测有显著提升作用。
点此查看论文截图

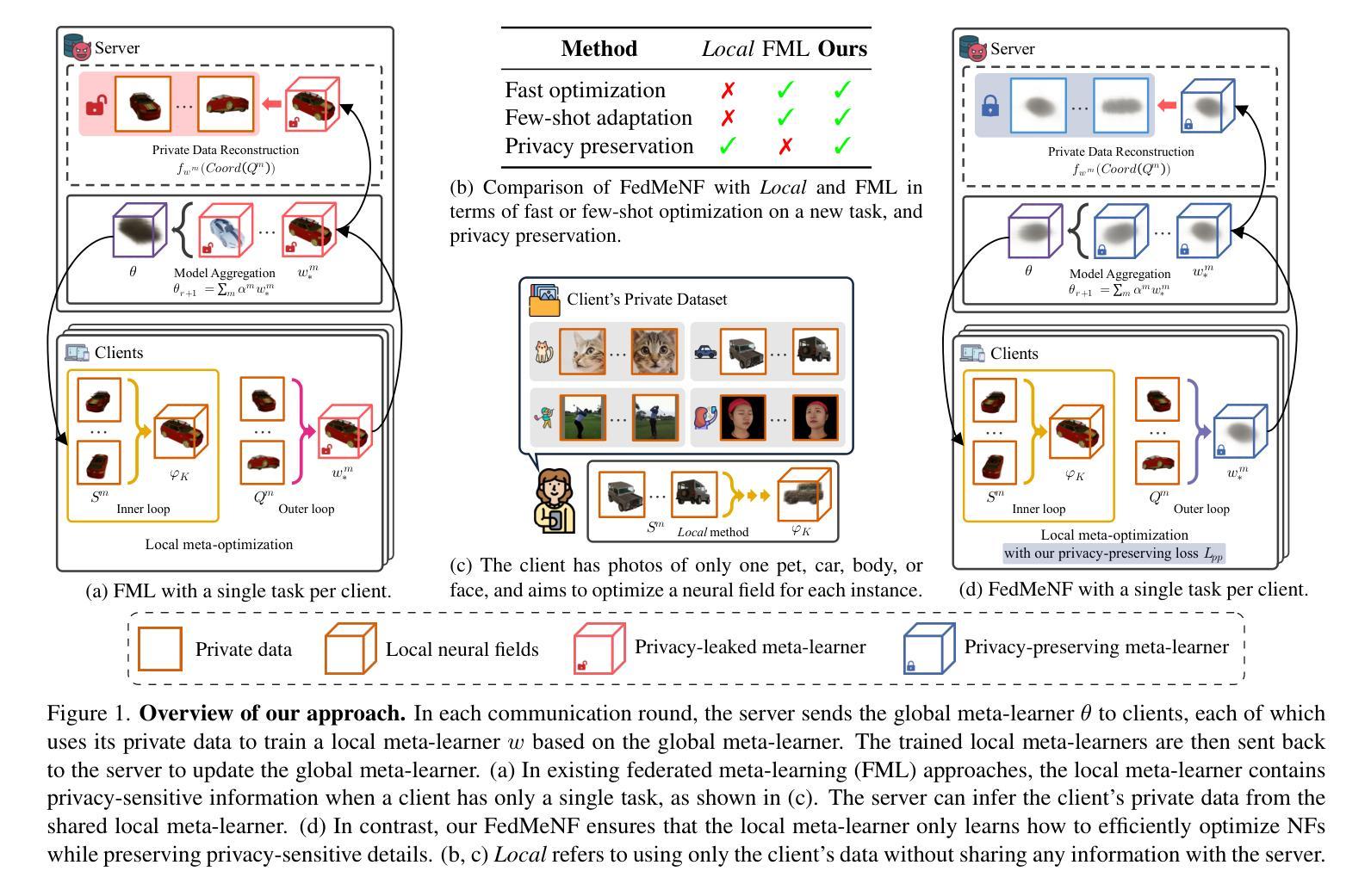
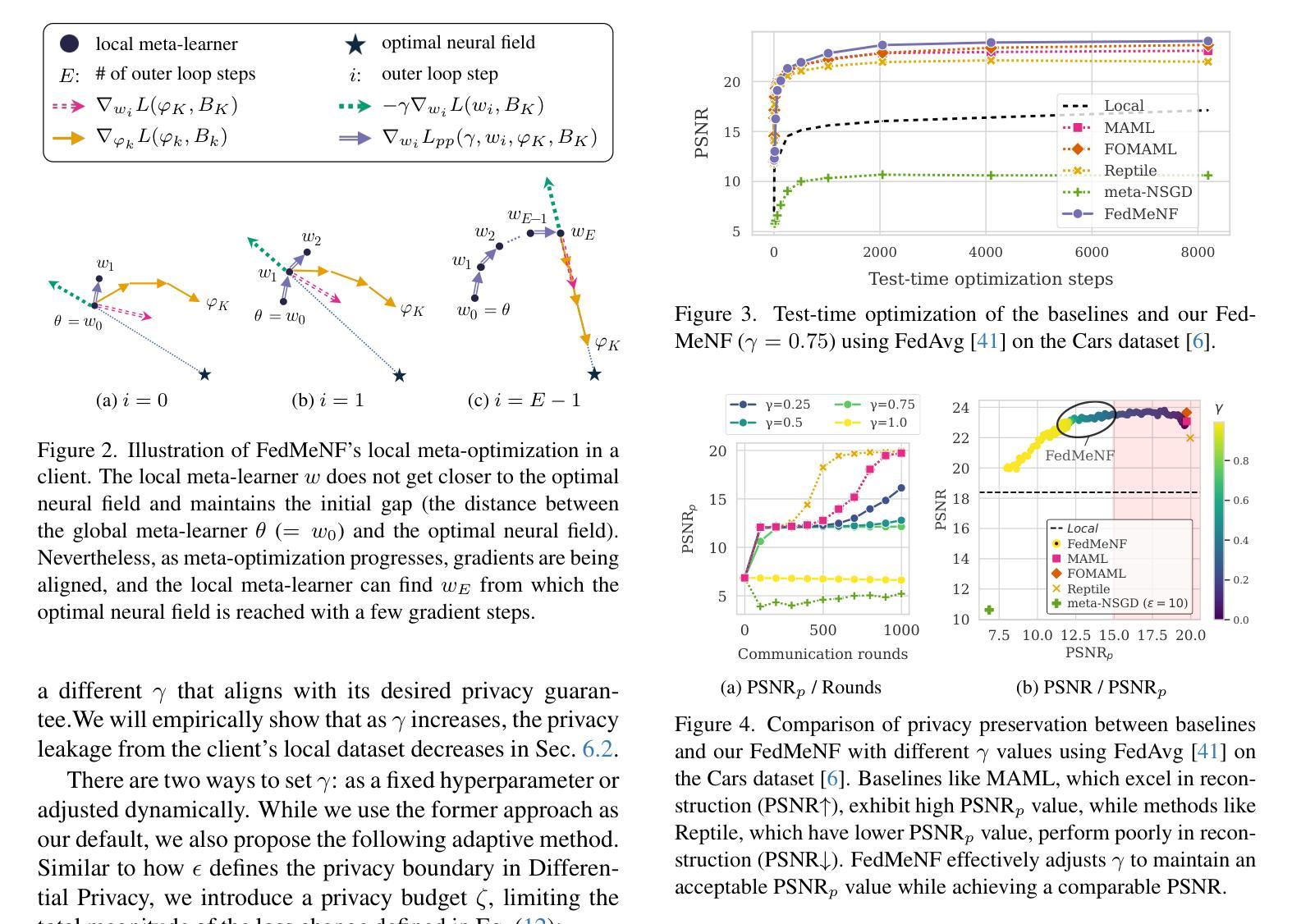
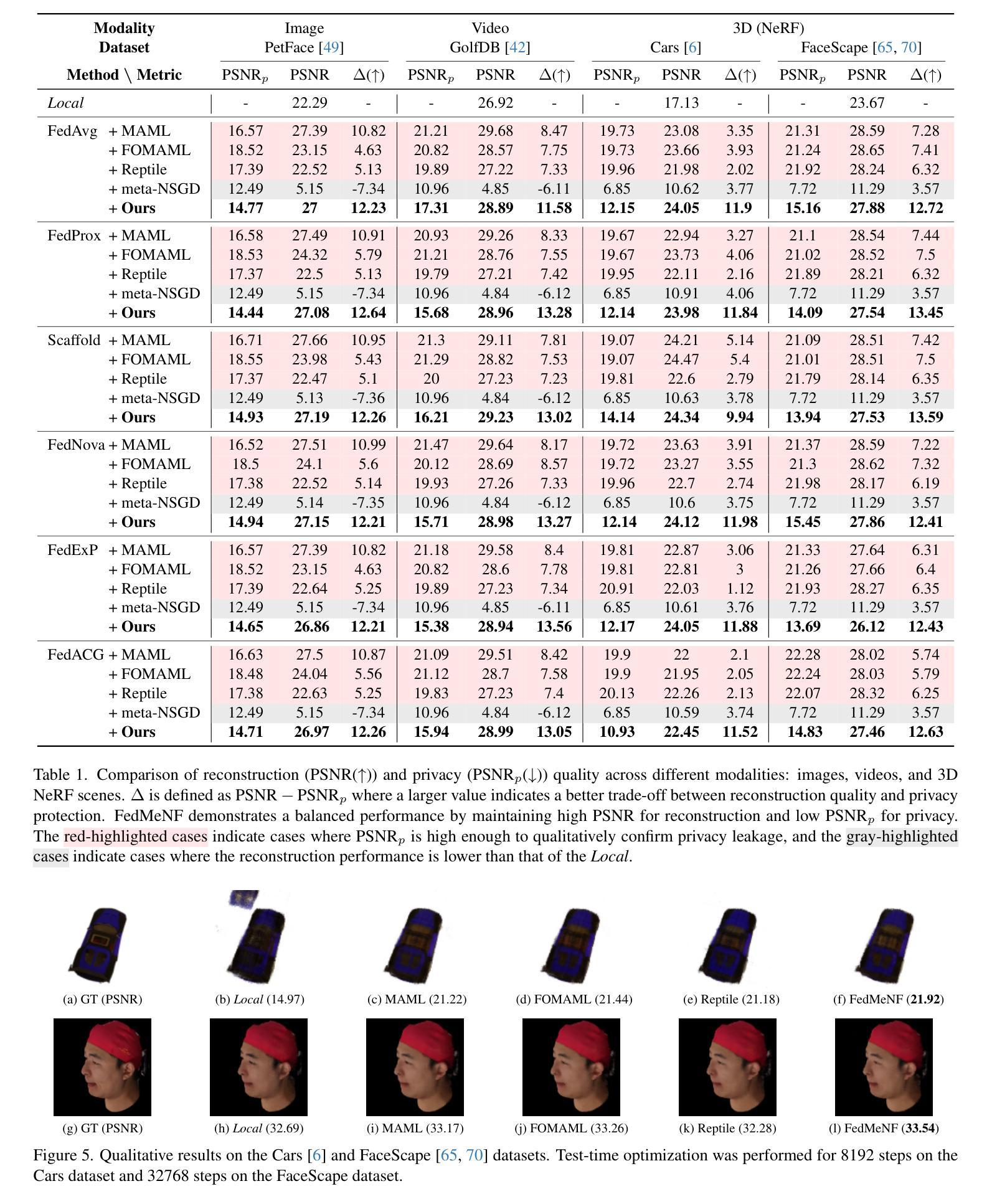
FedMeNF: Privacy-Preserving Federated Meta-Learning for Neural Fields
Authors:Junhyeog Yun, Minui Hong, Gunhee Kim
Neural fields provide a memory-efficient representation of data, which can effectively handle diverse modalities and large-scale data. However, learning to map neural fields often requires large amounts of training data and computations, which can be limited to resource-constrained edge devices. One approach to tackle this limitation is to leverage Federated Meta-Learning (FML), but traditional FML approaches suffer from privacy leakage. To address these issues, we introduce a novel FML approach called FedMeNF. FedMeNF utilizes a new privacy-preserving loss function that regulates privacy leakage in the local meta-optimization. This enables the local meta-learner to optimize quickly and efficiently without retaining the client’s private data. Our experiments demonstrate that FedMeNF achieves fast optimization speed and robust reconstruction performance, even with few-shot or non-IID data across diverse data modalities, while preserving client data privacy.
神经网络场提供了一种数据表示方法,这种方法具有高效的内存占用,并能够有效地处理多种模态和大规模数据。然而,学习映射神经网络通常需要大量的训练数据和计算资源,这在资源受限的边缘设备上可能会受到限制。一种解决此限制的方法是采用联邦元学习(FML),但传统的FML方法存在隐私泄露问题。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了一种新型的FML方法,称为FedMeNF。FedMeNF利用了一种新的隐私保护损失函数,该函数可以在本地元优化过程中控制隐私泄露。这使得本地元学习者能够在不保留客户端私有数据的情况下快速有效地进行优化。我们的实验表明,即使在多种模态数据的少量样本或非独立同分布(non-IID)数据情况下,FedMeNF也能实现快速优化和稳健的重建性能,同时保护客户端数据隐私。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
神经网络场为数据提供了内存高效的表示,可处理多样模态和大规模数据。然而,学习映射神经网络场通常需要大量的训练数据和计算资源,这在资源受限的边缘设备上可能受限。为解决这一问题,我们引入了名为FedMeNF的新型联邦元学习方法。FedMeNF利用新的隐私保护损失函数,对本地元优化中的隐私泄露进行规范。这允许本地元学习者快速高效地进行优化,同时无需保留客户端的私有数据。实验表明,即使在各种数据模态的少量样本或非独立同分布数据下,FedMeNF也能实现快速优化和稳健的重建性能,同时保护客户端数据隐私。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络场是内存高效的数据表示方法,可处理多样模态和大规模数据。
- 学习映射神经网络场通常需要大量的训练数据和计算资源。
- 联邦元学习(FML)是解决资源受限设备上的训练数据限制的一种方法。
- 传统的FML方法存在隐私泄露问题。
- FedMeNF是一种新型的联邦元学习方法,利用隐私保护损失函数规范本地元优化中的隐私泄露。
- FedMeNF允许快速高效的本地元优化,同时保护客户端的私有数据。
点此查看论文截图

IOCC: Aligning Semantic and Cluster Centers for Few-shot Short Text Clustering
Authors:Jixuan Yin, Zhihao Yao, Wenshuai Huo, Xinmiao Yu, Xiaocheng Feng, Bo Li
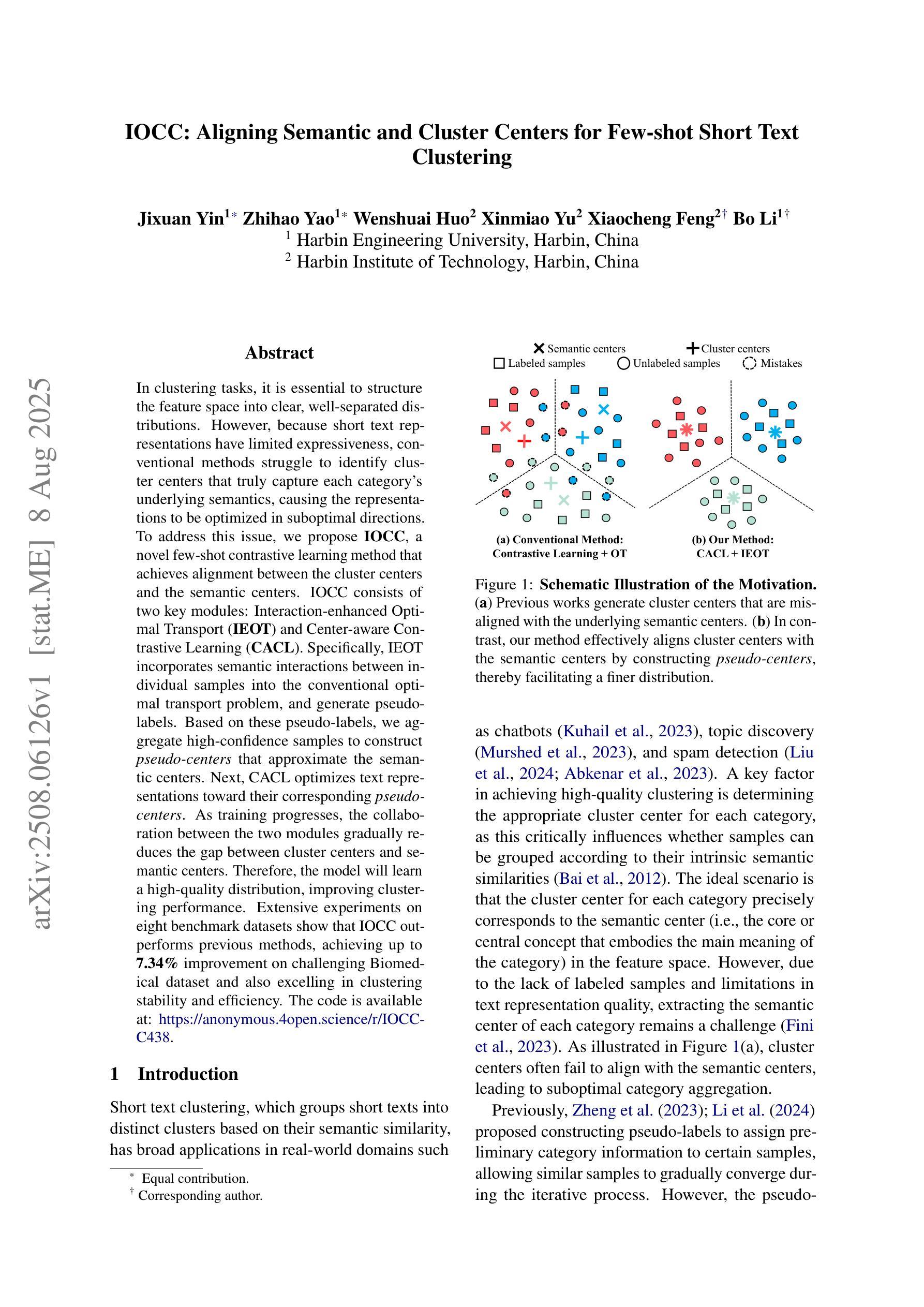
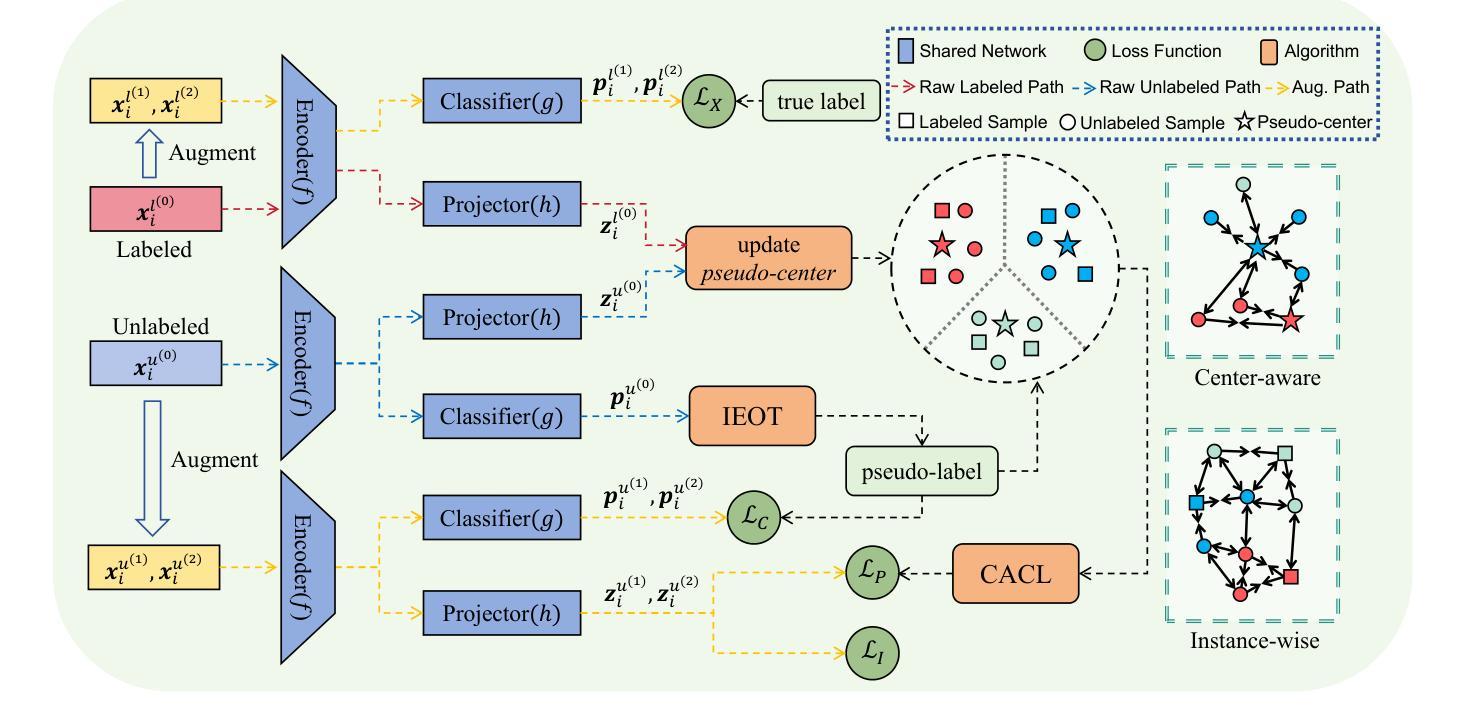
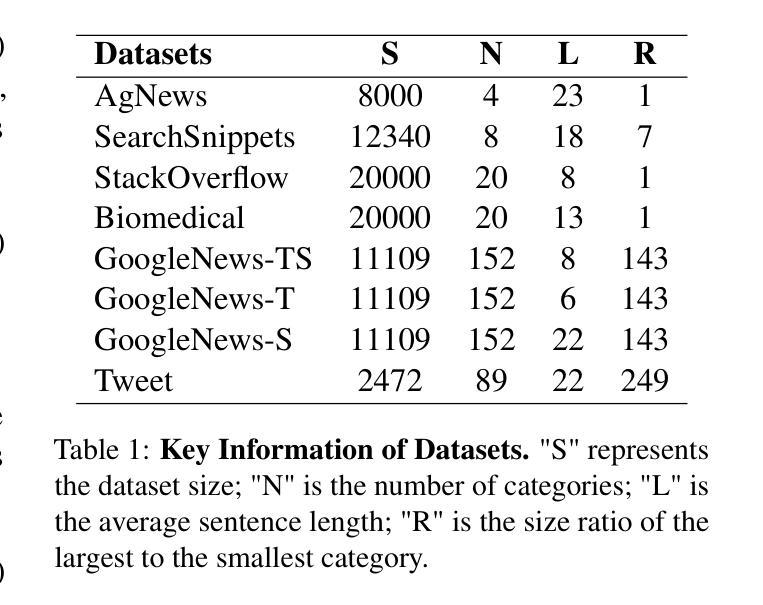
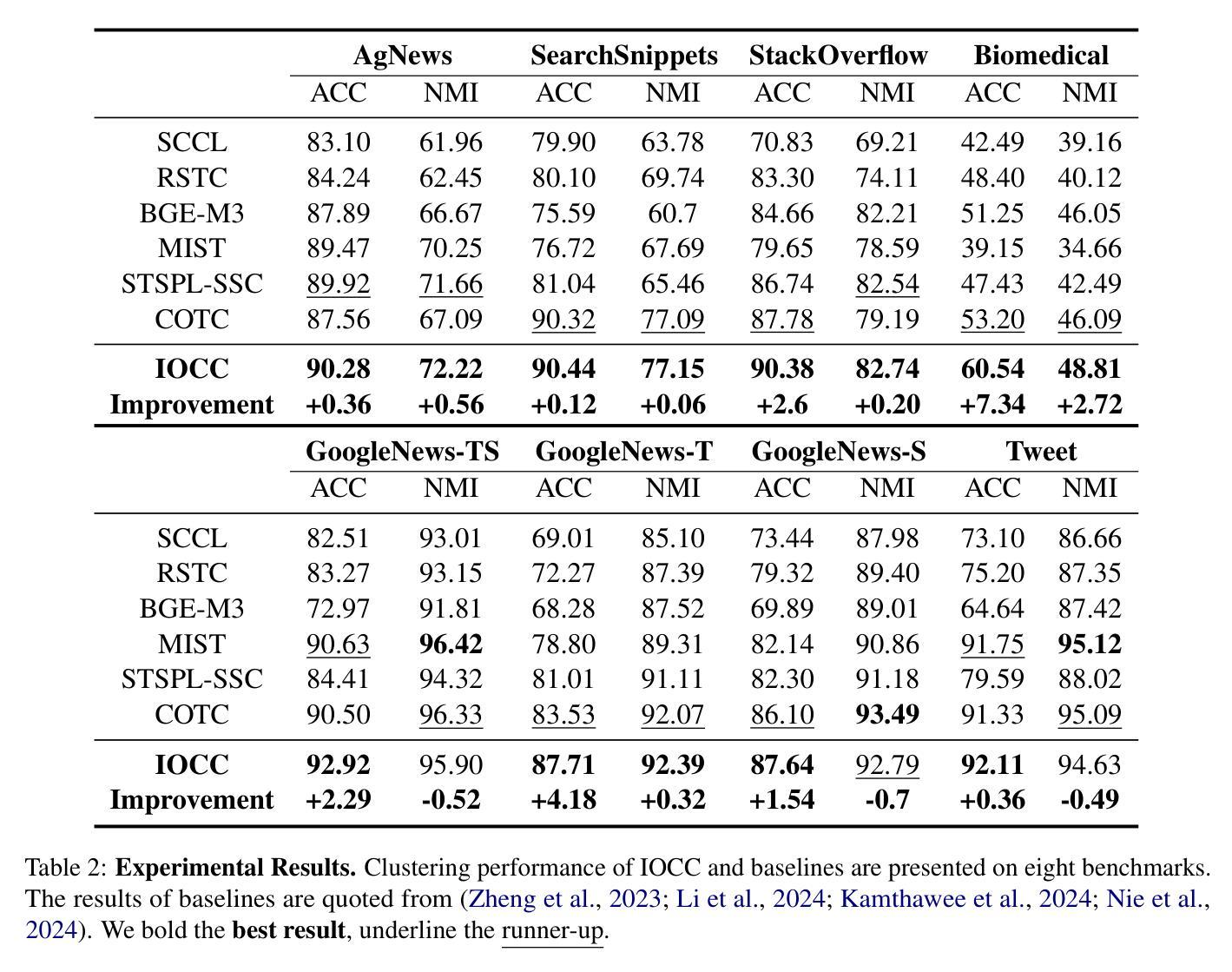
In clustering tasks, it is essential to structure the feature space into clear, well-separated distributions. However, because short text representations have limited expressiveness, conventional methods struggle to identify cluster centers that truly capture each category’s underlying semantics, causing the representations to be optimized in suboptimal directions. To address this issue, we propose IOCC, a novel few-shot contrastive learning method that achieves alignment between the cluster centers and the semantic centers. IOCC consists of two key modules: Interaction-enhanced Optimal Transport (IEOT) and Center-aware Contrastive Learning (CACL). Specifically, IEOT incorporates semantic interactions between individual samples into the conventional optimal transport problem, and generate pseudo-labels. Based on these pseudo-labels, we aggregate high-confidence samples to construct pseudo-centers that approximate the semantic centers. Next, CACL optimizes text representations toward their corresponding pseudo-centers. As training progresses, the collaboration between the two modules gradually reduces the gap between cluster centers and semantic centers. Therefore, the model will learn a high-quality distribution, improving clustering performance. Extensive experiments on eight benchmark datasets show that IOCC outperforms previous methods, achieving up to 7.34% improvement on challenging Biomedical dataset and also excelling in clustering stability and efficiency. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/IOCC-C438.
在聚类任务中,将特征空间结构化为清晰、分离良好的分布至关重要。然而,由于短文本表示的表达能力有限,传统方法难以识别真正捕捉每个类别底层语义的聚类中心,导致表示的优化方向不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了IOCC,这是一种新的少样本对比学习方法,实现了聚类中心与语义中心之间的对齐。IOCC由两个关键模块组成:交互增强最优传输(IEOT)和中心感知对比学习(CACL)。具体来说,IEOT将个体样本之间的语义交互纳入传统最优传输问题中,并生成伪标签。基于这些伪标签,我们聚合高置信度样本来构建近似语义中心的伪中心。接下来,CACL将文本表示优化朝向其对应的伪中心。随着训练的进行,两个模块之间的协作逐渐缩小了聚类中心和语义中心之间的差距。因此,模型将学习高质量分布,提高聚类性能。在八个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,IOCC优于以前的方法,在具有挑战性的生物医学数据集上实现了高达7.34%的改进,同时在聚类稳定性和效率方面也表现出色。代码可用在:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/IOCC-C438。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种基于少数样本对比学习的聚类方法IOCC,旨在解决短文本表示的问题。通过构建交互增强的最优传输模块(IEOT)和中心感知对比学习模块(CACL),IOCC实现了对聚类中心和语义中心的匹配。实验结果显示,IOCC在多个基准数据集上取得了显著的改进,特别是在具有挑战性的生物医学数据集上,实现了高达7.34%的性能提升,且在聚类稳定性和效率方面也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- IOCC是一种用于聚类任务的少数样本对比学习方法,旨在解决短文本表示的问题。
- IOCC通过构建IEOT模块,将样本间的语义交互纳入传统最优传输问题中,生成伪标签。
- 基于伪标签,IOCC聚合高置信度样本构建伪中心,近似语义中心。
- CACL模块则致力于优化文本表示,使其朝向对应的伪中心。
- 随着训练的进行,IEOT和CACL两个模块的协作逐渐缩小了聚类中心和语义中心的差距。
- 实验结果显示,IOCC在多个数据集上取得了显著性能提升,特别是在生物医学数据集上。
点此查看论文截图
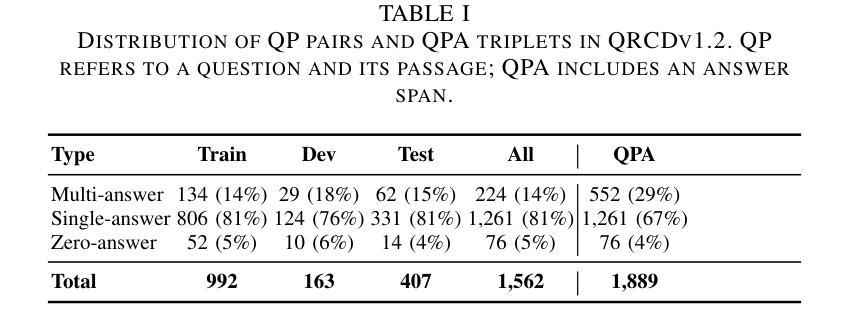
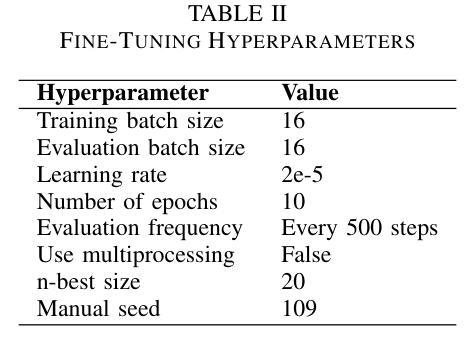
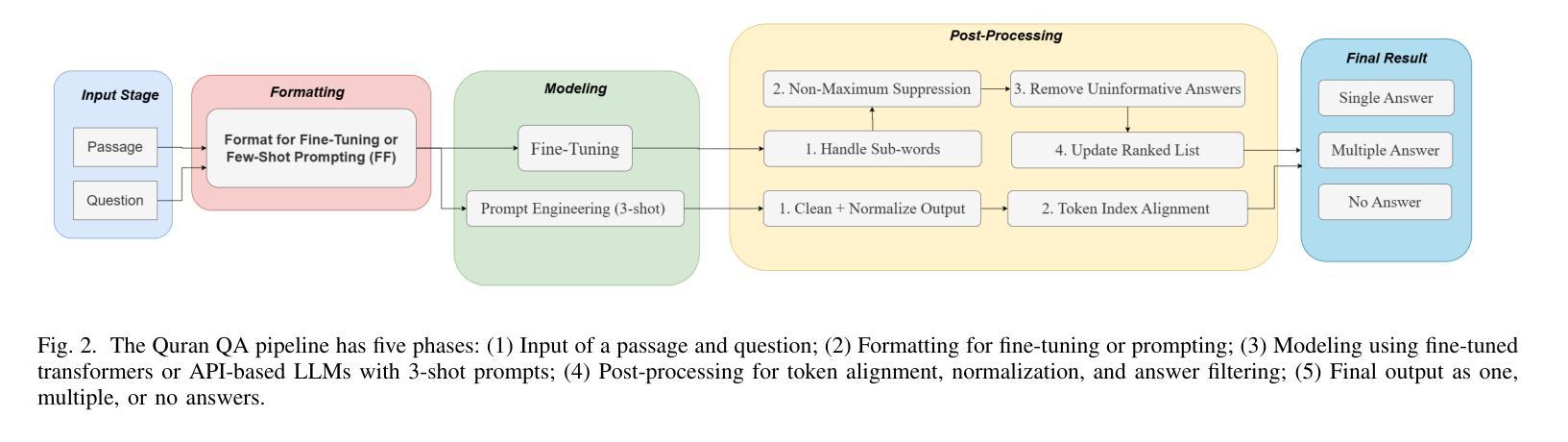
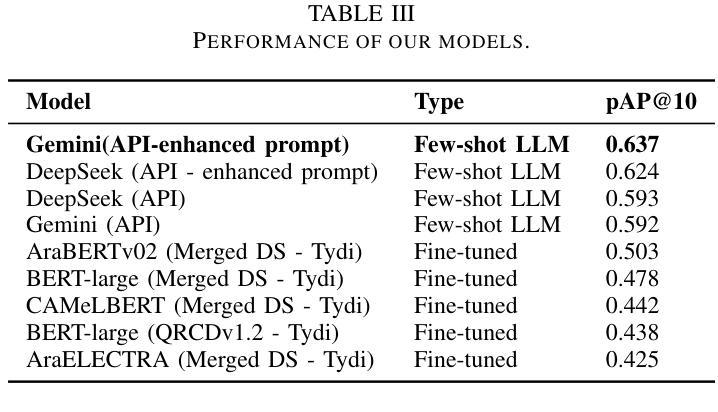
Few-Shot Prompting for Extractive Quranic QA with Instruction-Tuned LLMs
Authors:Mohamed Basem, Islam Oshallah, Ali Hamdi, Ammar Mohammed
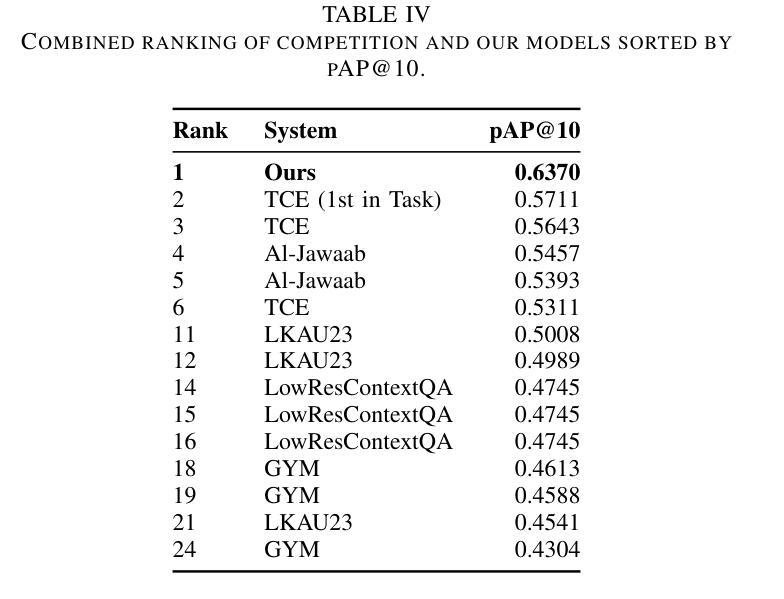
This paper presents two effective approaches for Extractive Question Answering (QA) on the Quran. It addresses challenges related to complex language, unique terminology, and deep meaning in the text. The second uses few-shot prompting with instruction-tuned large language models such as Gemini and DeepSeek. A specialized Arabic prompt framework is developed for span extraction. A strong post-processing system integrates subword alignment, overlap suppression, and semantic filtering. This improves precision and reduces hallucinations. Evaluations show that large language models with Arabic instructions outperform traditional fine-tuned models. The best configuration achieves a pAP10 score of 0.637. The results confirm that prompt-based instruction tuning is effective for low-resource, semantically rich QA tasks.
本文介绍了两种针对《古兰经》的提取式问答(QA)的有效方法。它解决了与复杂语言、独特术语和文本深层意义相关的挑战。第二种方法使用少量提示与经过指令调整的 大型语言模型,如Gemini和DeepSeek。开发了一个专门的阿拉伯语提示框架,用于跨度提取。强大的后处理系统集成了子词对齐、重叠抑制和语义过滤。这提高了精度并减少了幻觉。评估表明,带有阿拉伯语指令的大型语言模型优于传统微调模型。最佳配置达到pAP10得分为0.637。结果证实,基于提示的指令调整对于低资源、语义丰富的问答任务是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages , 2 figures , Accepted in IMSA 2025,Egypt , https://imsa.msa.edu.eg/
Summary
本文介绍了两种针对《古兰经》的有效提取式问答方法。第二种方法采用基于指令调整的大型语言模型(如Gemini和DeepSeek)进行少量提示,开发了一个专用的阿拉伯文提示框架用于跨提取。通过整合子词对齐、抑制重叠和语义过滤的强大的后处理系统提高了精度并减少了误生成。评估显示,带有阿拉伯指令的大型语言模型优于传统微调模型,最佳配置达到pAP10分数为0.637。证明基于指令调整的提示对于资源匮乏但语义丰富的问答任务是有效的。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了两种针对《古兰经》的提取式问答的有效方法。
- 第二种方法使用基于指令调整的大型语言模型进行少量提示,开发了阿拉伯文提示框架用于跨提取。
- 论文强调了挑战,包括复杂语言、独特术语和文本中的深层含义。
- 通过强大的后处理系统提高了精度并减少了误生成。
- 评估显示,带有阿拉伯指令的大型语言模型性能优于传统微调模型。
- 最佳配置的pAP10分数为0.637,表明其性能较高。
点此查看论文截图


Dean of LLM Tutors: Exploring Comprehensive and Automated Evaluation of LLM-generated Educational Feedback via LLM Feedback Evaluators
Authors:Keyang Qian, Yixin Cheng, Rui Guan, Wei Dai, Flora Jin, Kaixun Yang, Sadia Nawaz, Zachari Swiecki, Guanliang Chen, Lixiang Yan, Dragan Gašević
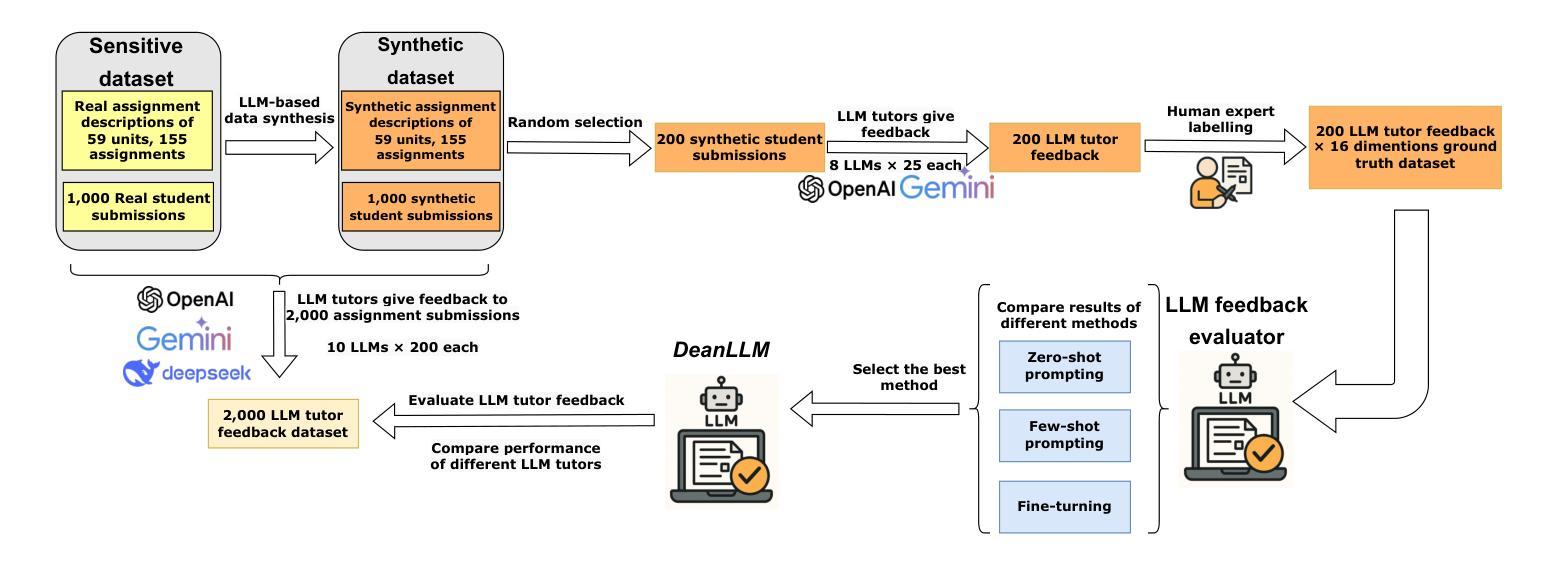
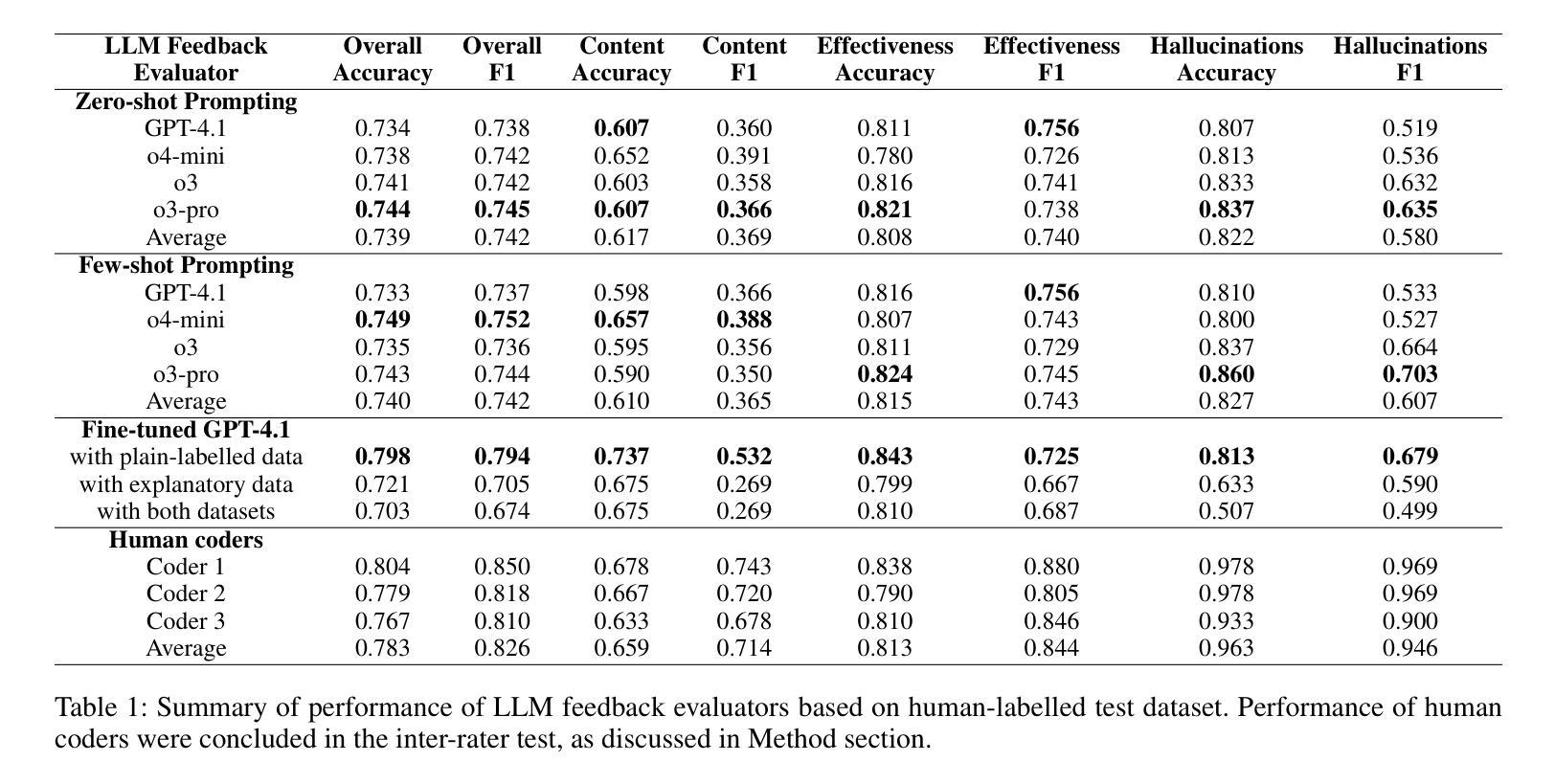
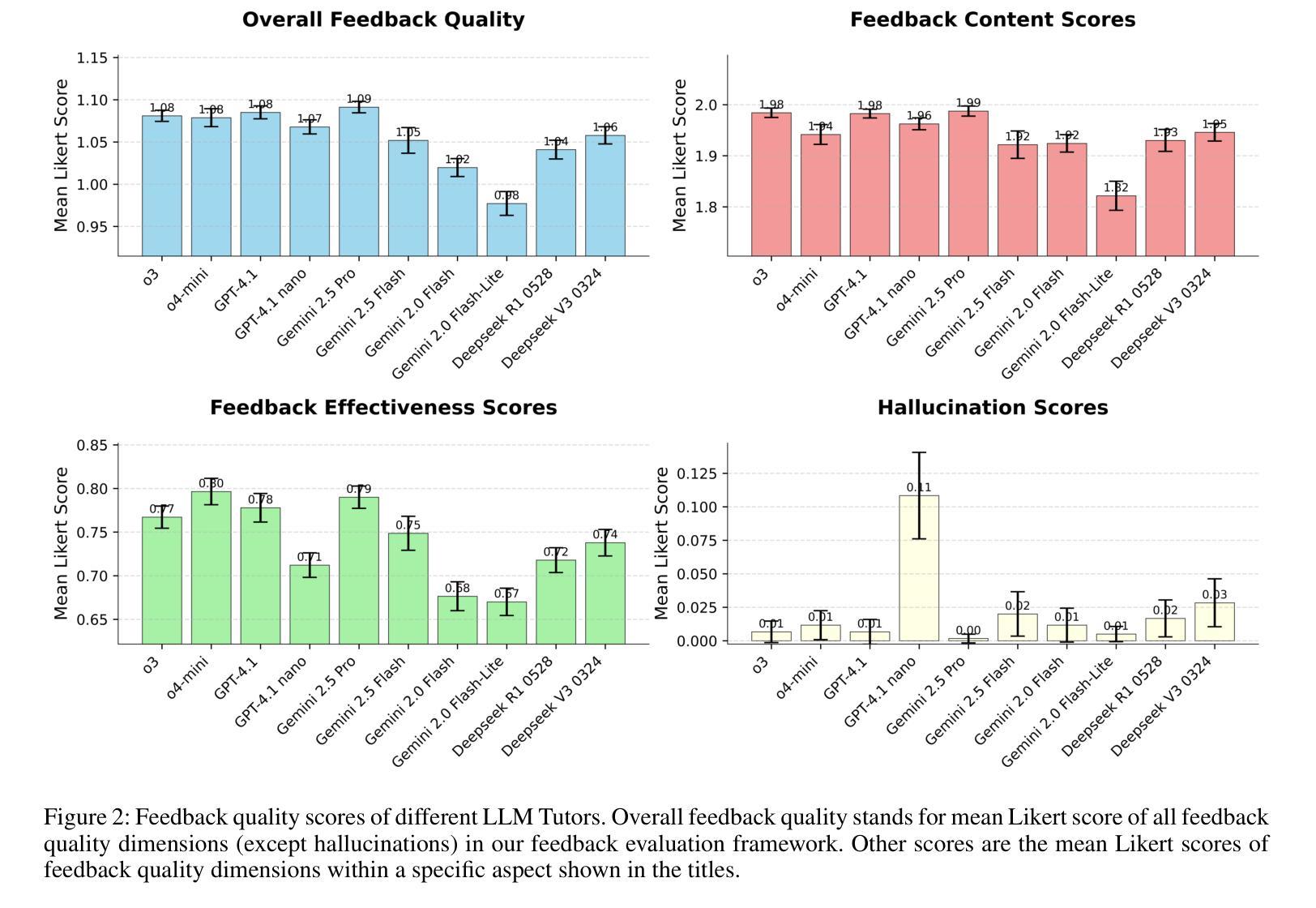
The use of LLM tutors to provide automated educational feedback to students on student assignment submissions has received much attention in the AI in Education field. However, the stochastic nature and tendency for hallucinations in LLMs can undermine both quality of learning experience and adherence to ethical standards. To address this concern, we propose a method that uses LLM feedback evaluators (DeanLLMs) to automatically and comprehensively evaluate feedback generated by LLM tutor for submissions on university assignments before it is delivered to students. This allows low-quality feedback to be rejected and enables LLM tutors to improve the feedback they generated based on the evaluation results. We first proposed a comprehensive evaluation framework for LLM-generated educational feedback, comprising six dimensions for feedback content, seven for feedback effectiveness, and three for hallucination types. Next, we generated a virtual assignment submission dataset covering 85 university assignments from 43 computer science courses using eight commonly used commercial LLMs. We labelled and open-sourced the assignment dataset to support the fine-tuning and evaluation of LLM feedback evaluators. Our findings show that o3-pro demonstrated the best performance in zero-shot labelling of feedback while o4-mini demonstrated the best performance in few-shot labelling of feedback. Moreover, GPT-4.1 achieved human expert level performance after fine-tuning (Accuracy 79.8%, F1-score 79.4%; human average Accuracy 78.3%, F1-score 82.6%). Finally, we used our best-performance model to evaluate 2,000 assignment feedback instances generated by 10 common commercial LLMs, 200 each, to compare the quality of feedback generated by different LLMs. Our LLM feedback evaluator method advances our ability to automatically provide high-quality and reliable educational feedback to students.
使用大型语言模型(LLM)辅导工具为学生提供自动化教育反馈在人工智能教育领域引起了广泛关注。然而,大型语言模型的随机性和出现幻觉的倾向可能会破坏学习体验的质量和遵守道德标准。为了解决这一担忧,我们提出了一种使用LLM反馈评估器(DeanLLMs)的方法,该方法可以自动和全面地评估LLM辅导工具针对大学作业提交的反馈,然后再将其递送给学生。这允许拒绝低质量的反馈,并使得LLM辅导工具可以根据评估结果改进其生成的反馈。我们首次为LLM生成的教育反馈提出了一个全面的评估框架,该框架包括六个关于反馈内容的维度,七个关于反馈效果的维度和三个关于幻觉类型的维度。接下来,我们使用八种常见商业LLM生成了一个虚拟的作业提交数据集,该数据集涵盖了来自43门计算机科学课程的85项作业。我们对作业数据集进行了标注并开源,以支持LLM反馈评估器的微调与评估。我们的研究结果表明,在零样本标记反馈方面,o3-pro表现出最佳性能,而在少样本标记反馈方面,o4-mini表现出最佳性能。此外,GPT-4.1在经过微调后达到了人类专家的水平(准确率79.8%,F1分数79.4%;人类平均准确率78.3%,F1分数82.6%)。最后,我们使用性能最佳的模型评估了由十种常见商业LLM生成的2000个作业反馈实例(每种LLM 200个),以比较不同LLM生成的反馈质量。我们的LLM反馈评估器方法提高了我们为学生提供高质量和可靠教育反馈的自动化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM辅导工具为学生作业提供自动化反馈在教育界备受关注。然而,LLM的随机性和幻觉倾向可能影响学习体验和遵守道德标准。为此,研究团队提出了使用LLM反馈评估系统(DeanLLMs)自动全面评估LLM辅导工具提供的反馈的方法。此方法能在学生作业提交后对学生的作业反馈进行自动评价,对低质量的反馈进行筛选。该研究团队提出了全面的评估框架,并为评估反馈质量开发了一个虚拟作业提交数据集。最终,通过评估模型,团队发现GPT-4.1在经过微调后达到人类专家级别的性能。此外,该研究还使用最佳性能模型评估了不同LLM生成的反馈质量。此研究提高了为学生自动提供高质量可靠教育反馈的能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM辅导工具提供自动化教育反馈引起关注。
- LLM的随机性和幻觉可能影响学习体验和遵守道德标准。
- 使用DeanLLMs方法自动全面评估LLM提供的反馈。
- 提出一个包含多维度评价体系的综合评估框架来评估LLM生成的反馈质量。
- 开发了一个虚拟作业提交数据集支持LLM反馈评估模型的微调与评估。
- GPT-4.1经过微调后性能接近人类专家水平。
点此查看论文截图

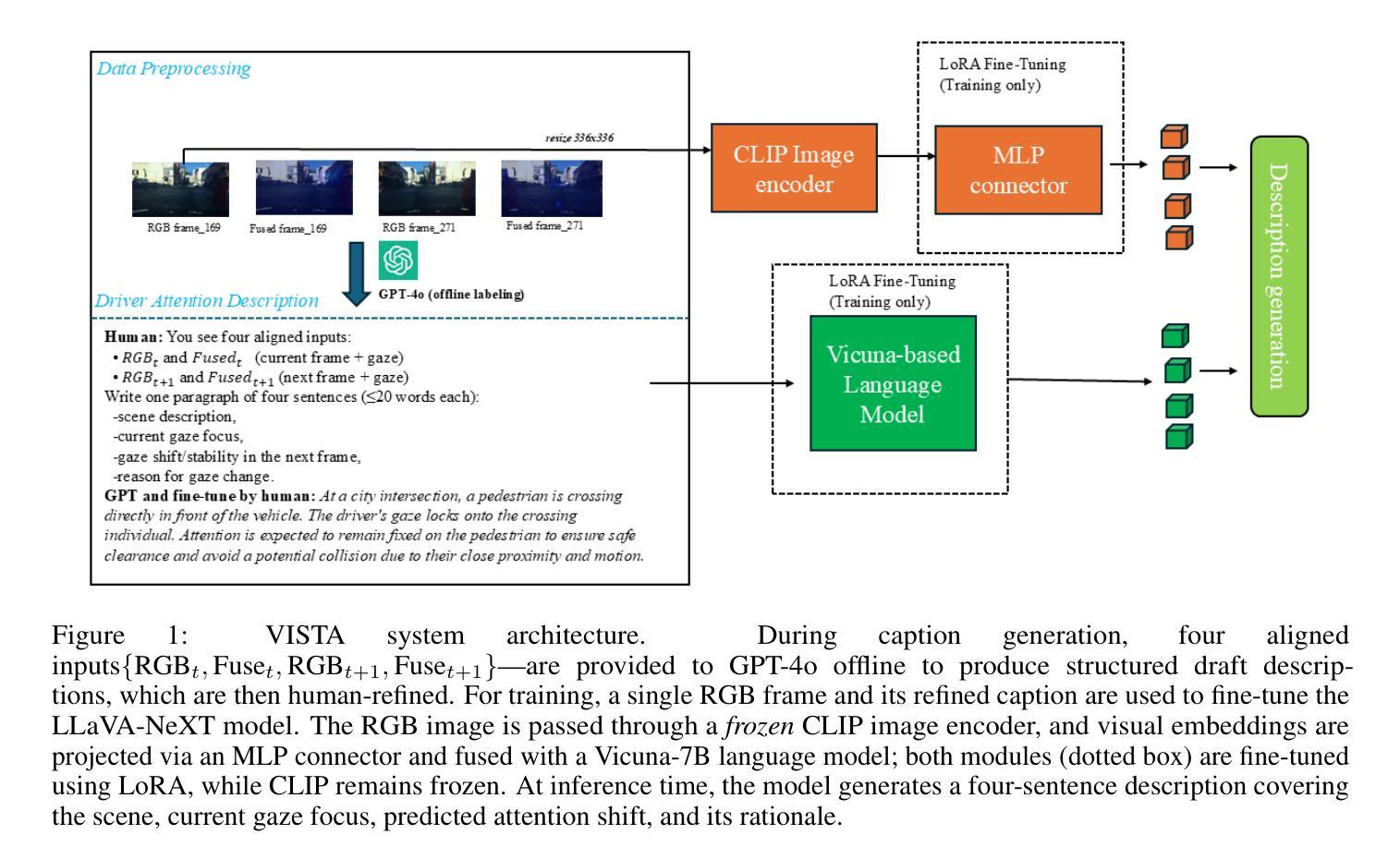
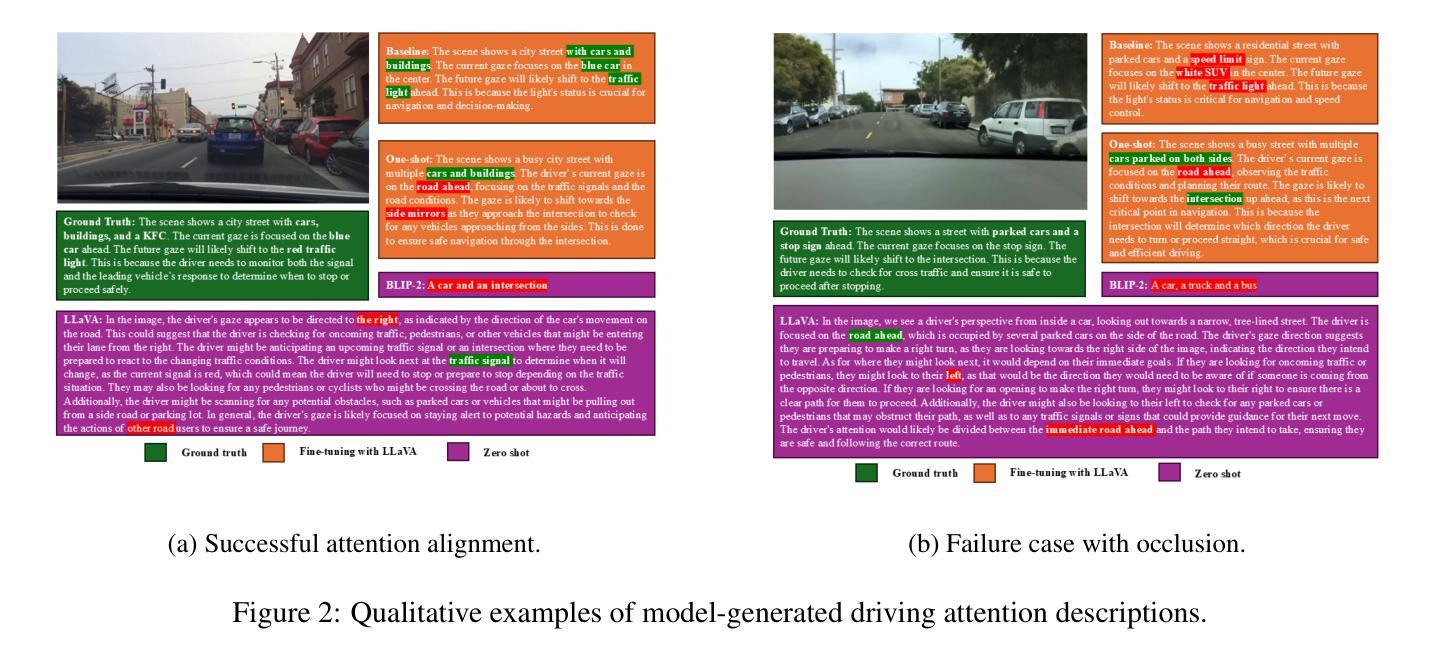
VISTA: Vision-Language Imitation of Situational Thinking and Attention for Human-Like Driver Focus in Dynamic Environments
Authors:Kaiser Hamid, Khandakar Ashrafi Akbar, Nade Liang
Driver visual attention prediction is a critical task in autonomous driving and human-computer interaction (HCI) research. Most prior studies focus on estimating attention allocation at a single moment in time, typically using static RGB images such as driving scene pictures. In this work, we propose a vision-language framework that models the changing landscape of drivers’ gaze through natural language, using few-shot and zero-shot learning on single RGB images. We curate and refine high-quality captions from the BDD-A dataset using human-in-the-loop feedback, then fine-tune LLaVA to align visual perception with attention-centric scene understanding. Our approach integrates both low-level cues and top-down context (e.g., route semantics, risk anticipation), enabling language-based descriptions of gaze behavior. We evaluate performance across training regimes (few shot, and one-shot) and introduce domain-specific metrics for semantic alignment and response diversity. Results show that our fine-tuned model outperforms general-purpose VLMs in attention shift detection and interpretability. To our knowledge, this is among the first attempts to generate driver visual attention allocation and shifting predictions in natural language, offering a new direction for explainable AI in autonomous driving. Our approach provides a foundation for downstream tasks such as behavior forecasting, human-AI teaming, and multi-agent coordination.
驾驶者视觉注意力预测在自动驾驶和人机交互(HCI)研究中是一项至关重要的任务。早期的大部分研究主要集中在估计单一时刻的注意力分配,通常使用静态RGB图像,如驾驶场景图片。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个视觉语言框架,通过自然语言对驾驶者视线变化进行建模,利用单RGB图像的少样本和零样本学习。我们通过人类参与反馈来精炼和筛选BDD-A数据集的高质量标题,然后对LLaVA进行微调,使视觉感知与以注意力为中心的场景理解保持一致。我们的方法结合了低级线索和自上而下上下文(例如,路线语义、风险预测),实现了基于语言的视线行为描述。我们评估了不同训练模式(少样本和一次学习)的性能,并引入了用于语义对齐和响应多样性的领域特定指标。结果表明,经过微调的模型在注意力转移检测和可解释性方面优于通用VLMs。据我们所知,这是首次尝试用自然语言生成驾驶者视觉注意力分配和转移预测,为自动驾驶中的可解释人工智能提供了新的方向。我们的方法为下游任务(如行为预测、人机协作和多智能体协调)提供了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合视觉与语言的框架,利用少量样本学习与零样本学习技术,通过自然语言描述来模拟驾驶者视线的动态变化。该研究使用BDD-A数据集的高质量描述,通过人类反馈进行微调,并采用LLaVA模型进行视觉感知与注意力集中场景理解的校准。该方法结合了底层线索和顶层上下文信息,如路线语义和风险评估,以语言描述驾驶者的视线行为。在多种训练模式下进行评估,并引入特定领域的语义对齐和响应多样性指标。结果表明,经过微调后的模型在注意力转移检测和可解释性方面优于通用视觉语言模型。这是首次尝试用自然语言生成驾驶者视觉注意力分配和转移预测的研究之一,为自动驾驶中的可解释性AI提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的视觉与语言框架,用于模拟驾驶者视线的动态变化。
- 利用少量样本学习与零样本学习技术,通过自然语言描述来预测驾驶者的视觉注意力。
- 使用BDD-A数据集的高质量描述,并结合人类反馈进行微调。
- 采用LLaVA模型校准视觉感知与注意力集中场景理解。
- 结合底层线索和顶层上下文信息进行分析。
- 在多种训练模式下评估模型性能,并引入特定领域的语义对齐和响应多样性指标。
点此查看论文截图

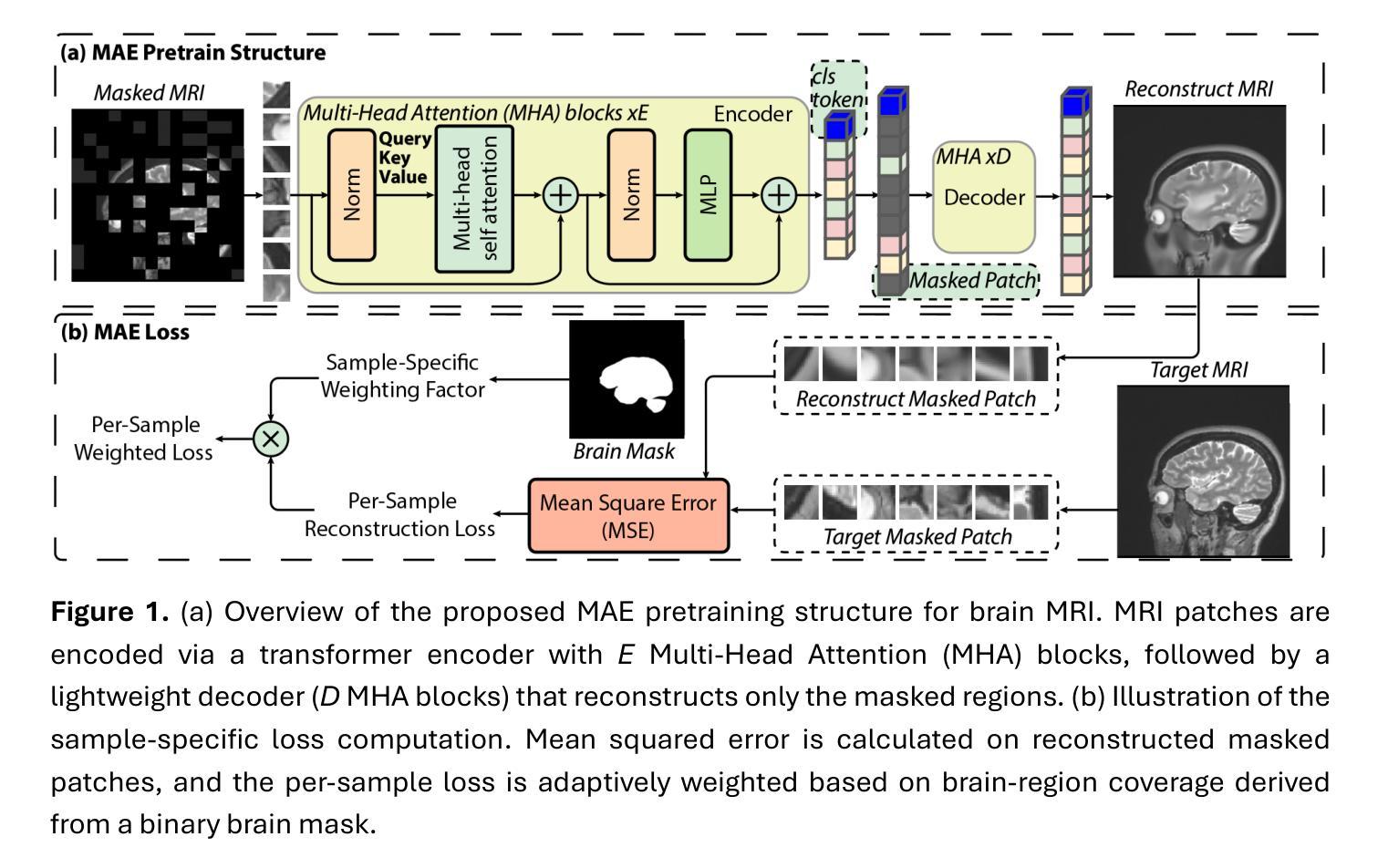
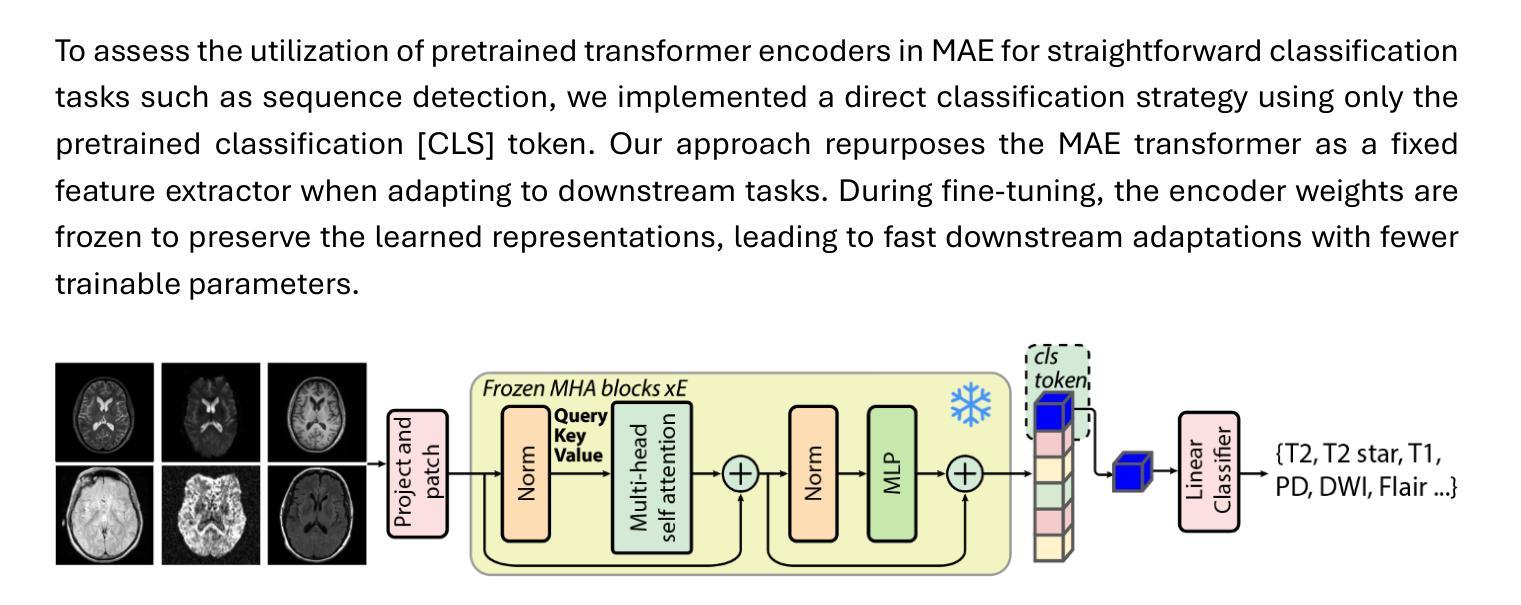
Few-Shot Deployment of Pretrained MRI Transformers in Brain Imaging Tasks
Authors:Mengyu Li, Guoyao Shen, Chad W. Farris, Xin Zhang
Machine learning using transformers has shown great potential in medical imaging, but its real-world applicability remains limited due to the scarcity of annotated data. In this study, we propose a practical framework for the few-shot deployment of pretrained MRI transformers in diverse brain imaging tasks. By utilizing the Masked Autoencoder (MAE) pretraining strategy on a large-scale, multi-cohort brain MRI dataset comprising over 31 million slices, we obtain highly transferable latent representations that generalize well across tasks and datasets. For high-level tasks such as classification, a frozen MAE encoder combined with a lightweight linear head achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in MRI sequence identification with minimal supervision. For low-level tasks such as segmentation, we propose MAE-FUnet, a hybrid architecture that fuses multiscale CNN features with pretrained MAE embeddings. This model consistently outperforms other strong baselines in both skull stripping and multi-class anatomical segmentation under data-limited conditions. With extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations, our framework demonstrates efficiency, stability, and scalability, suggesting its suitability for low-resource clinical environments and broader neuroimaging applications.
利用转换器进行机器学习在医学成像中显示出巨大潜力,但由于缺乏标注数据,其在现实世界中的适用性仍然有限。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个实用的框架,用于在多种脑成像任务中部署少量的预训练MRI转换器。通过在一个大规模、多队列的脑MRI数据集(包含超过3100万张切片)上采用Masked Autoencoder(MAE)预训练策略,我们获得了高度可迁移的潜在表示,这些表示在任务和数据集之间具有很好的通用性。对于高级任务,如分类,使用冻结的MAE编码器结合轻量级线性头,可以在几乎无监督的情况下实现MRI序列识别的最新准确性。对于低级任务(如分割),我们提出了MAE-FUnet,这是一种混合架构,融合了多尺度CNN特征与预训练的MAE嵌入。该模型在颅骨剥离和多类解剖分割任务中均持续超越其他强大的基线模型,展现出其在数据有限条件下的优越性。通过广泛的定量和定性评估,我们的框架表现出高效性、稳定性和可扩展性,表明其适用于资源有限的临床环境和更广泛的神经影像应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本研究提出了一个实用的框架,用于在医学图像领域部署预训练的MRI转换器。通过大规模多队列MRI数据集采用Masked Autoencoder(MAE)预训练策略,获得高度可迁移的潜在表示,实现跨任务和数据集的良好泛化。在高级任务(如分类)中,冻结的MAE编码器结合轻量级线性头实现了在MRI序列识别方面的最先进的准确度,并可在数据受限的条件下取得较好的效果。在低级任务(如分割)中,本研究提出了MAE-FUnet混合架构,融合了多尺度CNN特征与预训练的MAE嵌入。该模型在颅骨剥离和多类解剖分割任务中均优于其他强大的基线模型,并通过广泛的定量和定性评估证明了其效率、稳定性和可扩展性,适用于低资源临床环境和更广泛的神经影像应用。
Key Takeaways
- 利用Masked Autoencoder (MAE) 预训练策略实现了MRI转换器在医学图像领域的优异表现。
- 通过大规模MRI数据集的训练,获得了高度可迁移的潜在表示,提升了模型的泛化能力。
- 在高级任务中,结合冻结的MAE编码器和轻量级线性头实现了MRI序列识别的最先进的准确度。
- 针对低级任务如分割,提出了MAE-FUnet混合架构,融合了多尺度CNN特征与预训练的MAE嵌入,表现出色。
- 模型在数据受限的条件下仍能保持优越性能。
- 模型通过了广泛的定量和定性评估,证明了其效率、稳定性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

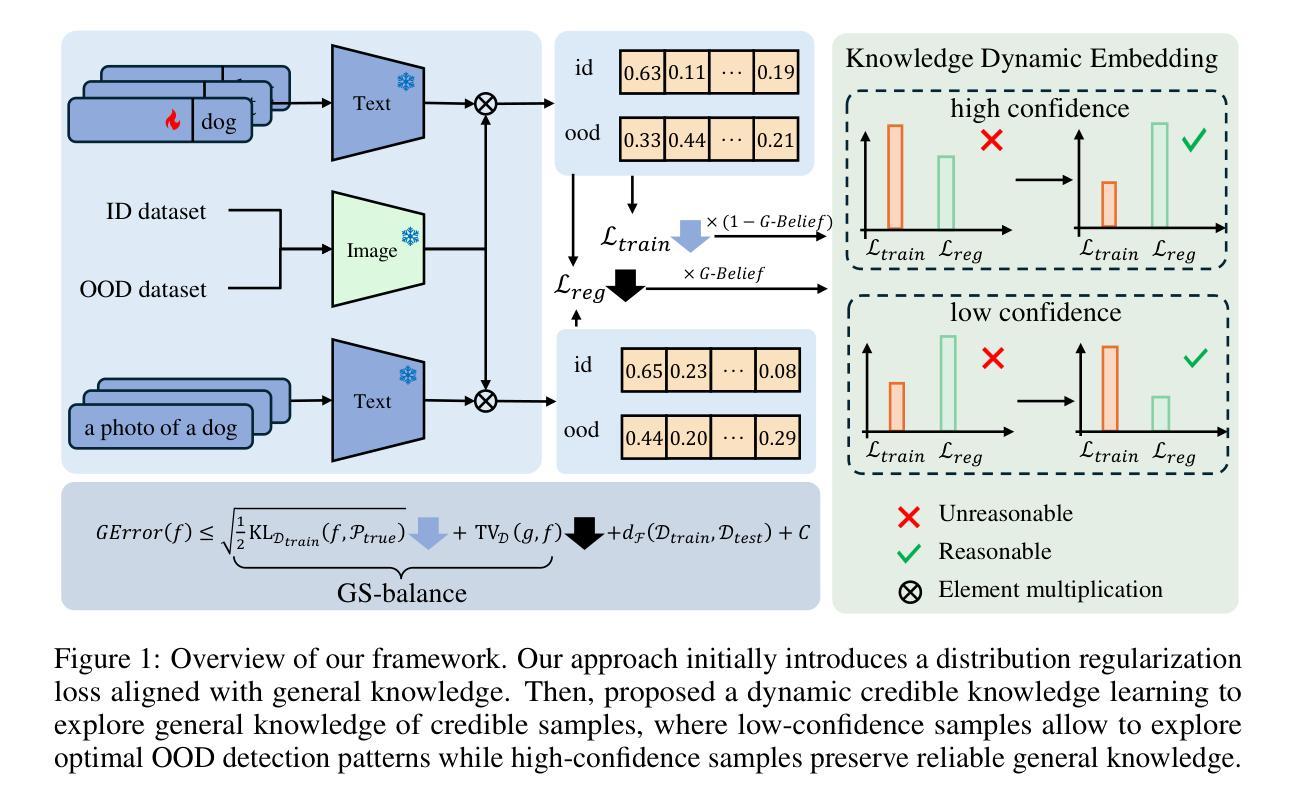
Generalized Few-Shot Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Pinxuan Li, Bing Cao, Changqing Zhang, Qinghua Hu
Few-shot Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection has emerged as a critical research direction in machine learning for practical deployment. Most existing Few-shot OOD detection methods suffer from insufficient generalization capability for the open world. Due to the few-shot learning paradigm, the OOD detection ability is often overfit to the limited training data itself, thus degrading the performance on generalized data and performing inconsistently across different scenarios. To address this challenge, we proposed a Generalized Few-shot OOD Detection (GOOD) framework, which empowers the general knowledge of the OOD detection model with an auxiliary General Knowledge Model (GKM), instead of directly learning from few-shot data. We proceed to reveal the few-shot OOD detection from a generalization perspective and theoretically derive the Generality-Specificity balance (GS-balance) for OOD detection, which provably reduces the upper bound of generalization error with a general knowledge model. Accordingly, we propose a Knowledge Dynamic Embedding (KDE) mechanism to adaptively modulate the guidance of general knowledge. KDE dynamically aligns the output distributions of the OOD detection model to the general knowledge model based on the Generalized Belief (G-Belief) of GKM, thereby boosting the GS-balance. Experiments on real-world OOD benchmarks demonstrate our superiority. Codes will be available.
少样本分布外(OOD)检测作为机器学习在实际部署中的关键研究方向已经出现。大多数现有的少样本OOD检测方法对于开放世界的泛化能力不足以应对挑战。由于少样本学习模式,OOD检测能力往往过度拟合有限的训练数据本身,从而在广义数据上的表现下降,并且在不同场景中的表现不一致。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了广义少样本OOD检测(GOOD)框架,该框架通过辅助通用知识模型(GKM)赋予OOD检测模型的通用知识,而不是直接从少量数据中学习。我们从泛化角度揭示少样本OOD检测,并理论上推导出OOD检测的泛化性-特异性平衡(GS-balance),使用通用知识模型可以证明降低泛化误差的上界。相应地,我们提出了知识动态嵌入(KDE)机制,以自适应地调节通用知识的指导。KDE基于GKM的广义信念(G-Belief)动态调整OOD检测模型的输出分布,以匹配通用知识模型,从而提高GS-balance。在真实世界的OOD基准测试上的实验证明了我们方法的优越性。相关代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了面向实际应用部署的机器学习领域中新兴的关键研究方向——Few-shot Out-of-Distribution(OOD)检测。现有方法普遍存在泛化能力不足的问题,导致在开放世界环境下表现不佳。针对此挑战,本文提出了Generalized Few-shot OOD Detection(GOOD)框架,借助辅助通用知识模型(GKM)为OOD检测模型赋予通用知识能力,而不是直接从少量数据中学习。本文还从泛化角度揭示了few-shot OOD检测,并理论上推导了用于减少泛化误差上界的Generality-Specificity平衡(GS-balance)。同时,提出了Knowledge Dynamic Embedding(KDE)机制,根据GKM的Generalized Belief自适应调整通用知识的指导,提升GS-balance。在真实世界的OOD基准测试上的实验证明了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot Out-of-Distribution (OOD) 检测是机器学习领域的重要研究方向,特别是在实际应用部署中。
- 现有方法存在泛化能力不足的问题,导致在开放世界环境下性能下降。
- 本文提出了Generalized Few-shot OOD Detection (GOOD) 框架,借助辅助通用知识模型(GKM)增强模型的泛化能力。
- 揭示了从泛化角度看待few-shot OOD检测,并推导了Generality-Specificity balance(GS-balance)以减少泛化误差上界。
- 提出了Knowledge Dynamic Embedding (KDE) 机制,根据GKM的Generalized Belief自适应调整通用知识的指导,增强模型的性能。
- 在真实世界的OOD基准测试上进行了实验验证,证明了所提方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

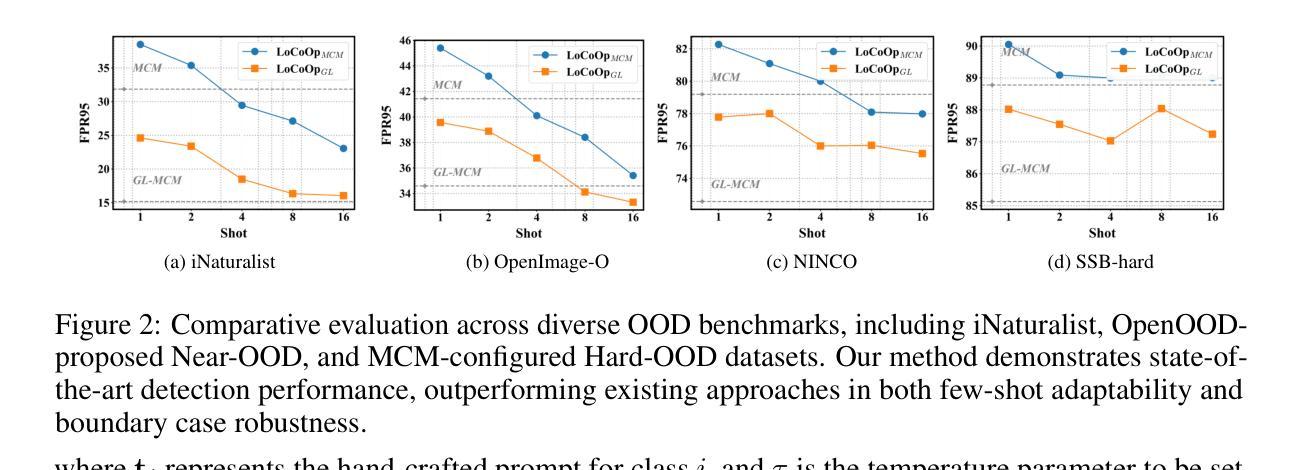
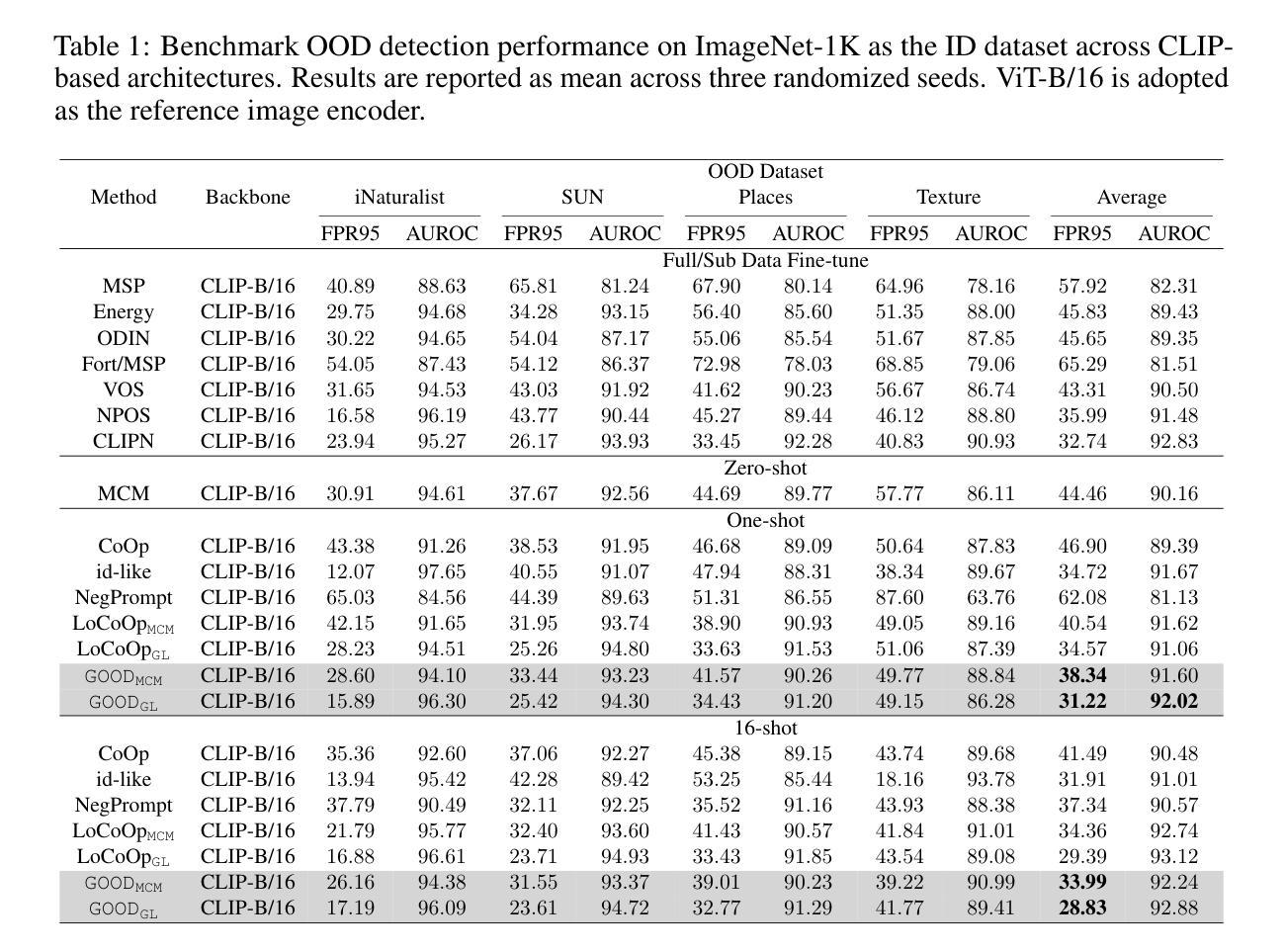
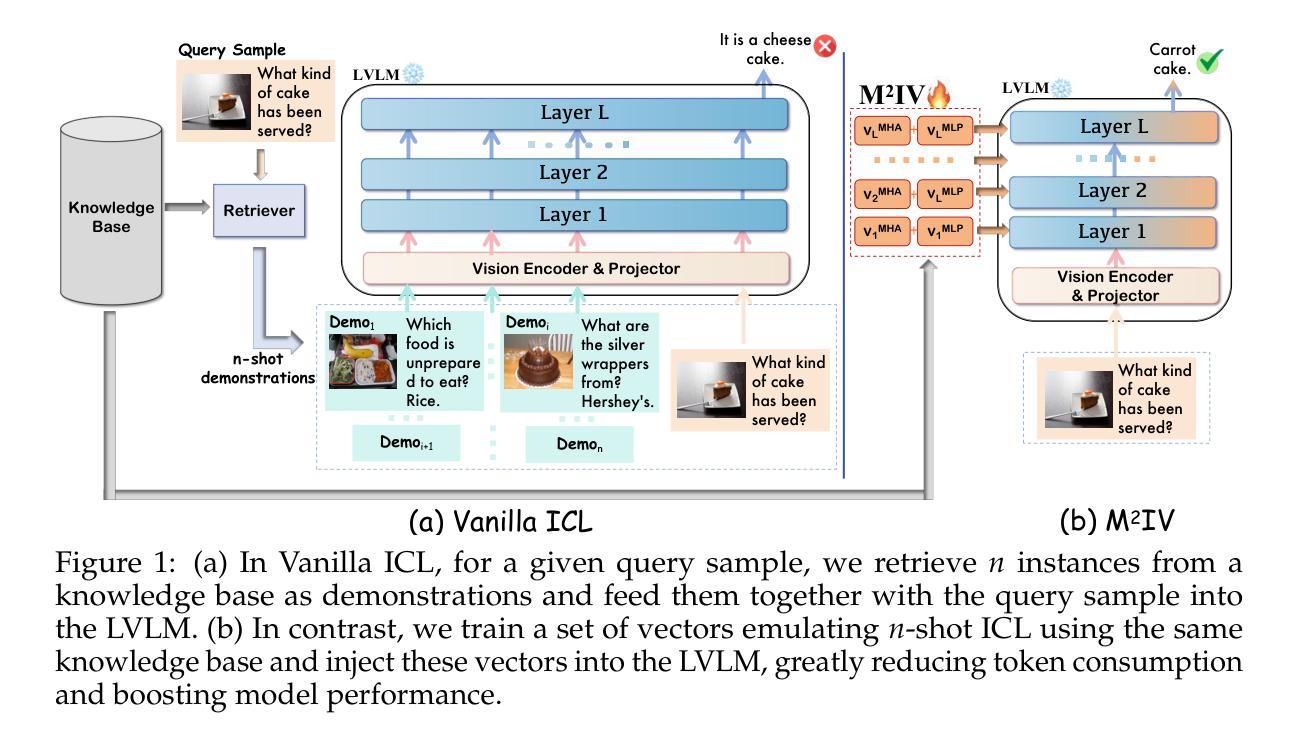
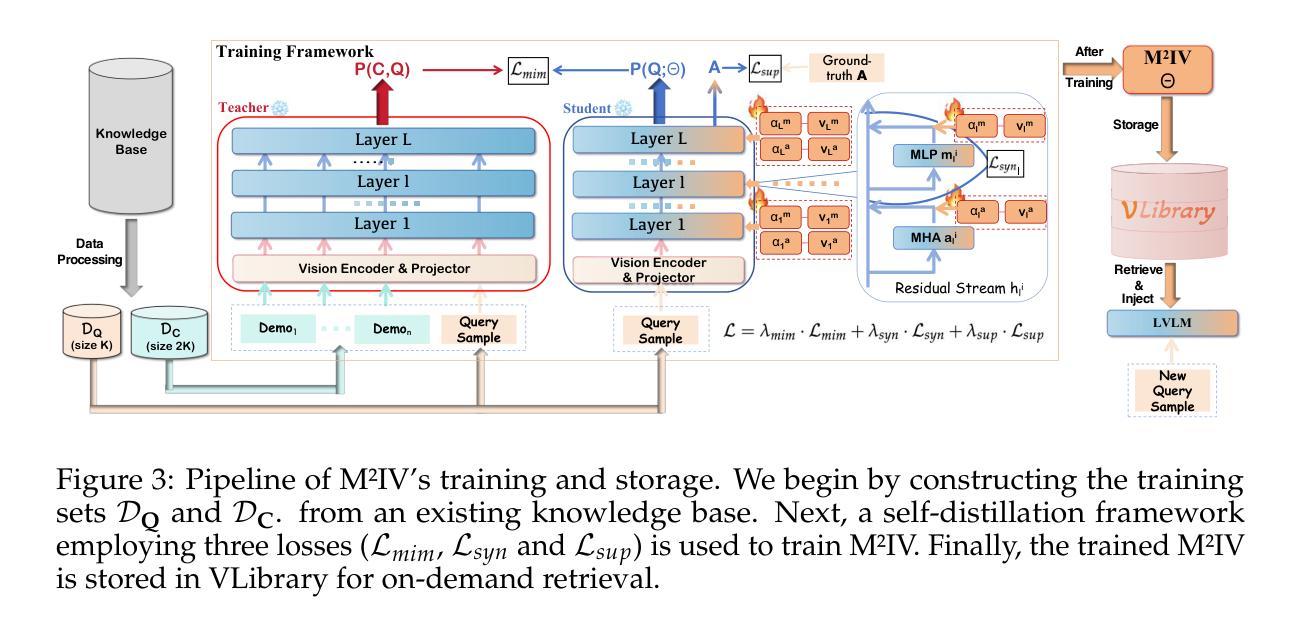
M$^2$IV: Towards Efficient and Fine-grained Multimodal In-Context Learning via Representation Engineering
Authors:Yanshu Li, Yi Cao, Hongyang He, Qisen Cheng, Xiang Fu, Xi Xiao, Tianyang Wang, Ruixiang Tang
Multimodal in-context learning (ICL) equips Large Vision-language Models (LVLMs) with the ability to adapt to new tasks via multiple user-provided demonstrations, without requiring any model parameter updates. However, its effectiveness is constrained by the token-intensive nature of multimodal inputs and the complexity of cross-modal few-shot reasoning, which together hinder LVLMs from extracting useful patterns from demonstrations. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{M$^2$IV}, a novel representation engineering approach that replaces explicit token-level demonstrations with a set of learnable Multimodal In-context Vectors directly injected into the residual streams of LVLMs. By analyzing the distinct roles of multi-head attention (MHA) and multi-layer perceptrons (MLP) in the ICL process, we design a training strategy that enables M$^2$IV to perform fine-grained semantic distillation and robust cross-modal representation learning. M$^2$IV not only improves performance across diverse tasks and LVLMs but also significantly reduces token overhead, enabling graceful scaling to many-shot scenarios. To further enhance usability, we introduce \textbf{VLibrary}, a repository that stores trained M$^2$IVs for flexible retrieval and injection. With VLibrary, users can steer pre-trained LVLMs in a customized manner that meets diverse requirements. Extensive experiments demonstrate that M$^2$IV consistently outperforms vanilla ICL and prior representation engineering baselines, achieving an average accuracy gain of 3.74% with substantial improvements in overall efficiency.
多模态上下文学习(ICL)使大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)能够通过多个用户提供的演示来适应新任务,而无需进行任何模型参数更新。然而,其有效性受到多模态输入中令牌密集性质和跨模态少量推理的复杂性的限制,这两者共同阻碍LVLMs从演示中提取有用的模式。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了\textbf{M$^2$IV},这是一种新型表示工程方法,它用一组可学习的多模态上下文向量替换显式令牌级演示,并直接注入LVLMs的残差流中。通过分析多头注意力(MHA)和多层感知器(MLP)在ICL过程中的不同作用,我们设计了一种训练策略,使M$^2$IV能够执行精细的语义蒸馏和稳健的跨模态表示学习。M$^2$IV不仅提高了不同任务和LVLMs的性能,而且大大降低了令牌开销,能够灵活地扩展到许多场景。为了进一步提高可用性,我们引入了\textbf{VLibrary},一个存储训练好的M$^2$IV的仓库,用于灵活检索和注入。借助VLibrary,用户可以以符合各种需求的方式引导预训练的LVLMs。大量实验表明,M$^2$IV始终优于普通ICL和先前的表示工程基线,在平均准确率上提高了3.74%,并且在总体效率上有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLM 2025, 30 pages, 10 figures, 16 tables
Summary
多模态上下文学习(ICL)通过用户提供的多个示范来使大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)适应新任务,无需更新任何模型参数。然而,其有效性受到多模态输入令牌密集和跨模态少样本推理的复杂性的限制,阻碍了LVLMs从演示中提取有用模式。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了M$^2$IV,这是一种新型表示工程方法,它用一组可学习的多模态上下文向量替换明确的令牌级演示,直接注入LVLMs的残差流中。通过分析和ICL过程中多头注意力(MHA)和多层感知器(MLP)的不同作用,我们设计了一种训练策略,使M$^2$IV能够进行精细的语义蒸馏和稳健的跨模态表示学习。M$^2$IV不仅提高了不同任务和LVLMs的性能,而且显著减少了令牌开销,实现平滑扩展至多实例场景。此外,我们引入了VLibrary存储库,用于存储训练好的M$^2$IV向量以供灵活检索和注入。用户可以利用VLibrary以符合各种需求的方式定制预训练的LVLMs。实验表明,M$^2$IV始终优于基本的ICL和先前的表示工程基线,平均准确度提高了3.74%,整体效率也大大提高。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态上下文学习(ICL)允许大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)通过用户提供的示范适应新任务,无需更新模型参数。
- M$^2$IV是一种新型表示工程方法,旨在解决多模态输入的令牌密集性和跨模态少样本推理的复杂性挑战。
- M$^2$IV通过引入多模态上下文向量来改进ICL,这些向量直接注入LVLMs的残差流中,提高了性能和效率。
- M$^2$IV结合了多头注意力(MHA)和多层感知器(MLP)的分析,实现了精细的语义蒸馏和跨模态表示学习。
- VLibrary是一个存储库,用于存储训练好的M$^2$IV向量,以便用户可以根据各种需求定制预训练的LVLMs。
- 实验表明,M$^2$IV在多个任务和LVLMs上的性能优于传统的ICL方法和表示工程基线。
点此查看论文截图