⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
MotionSwap
Authors:Om Patil, Jinesh Modi, Suryabha Mukhopadhyay, Meghaditya Giri, Chhavi Malhotra
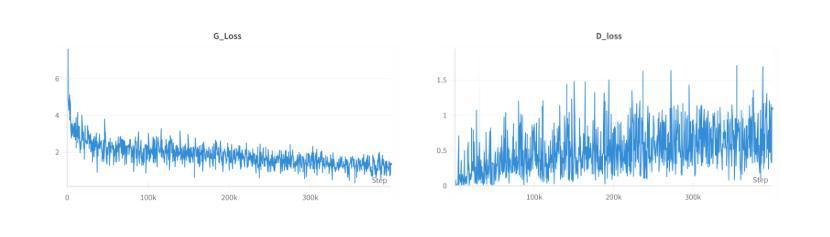
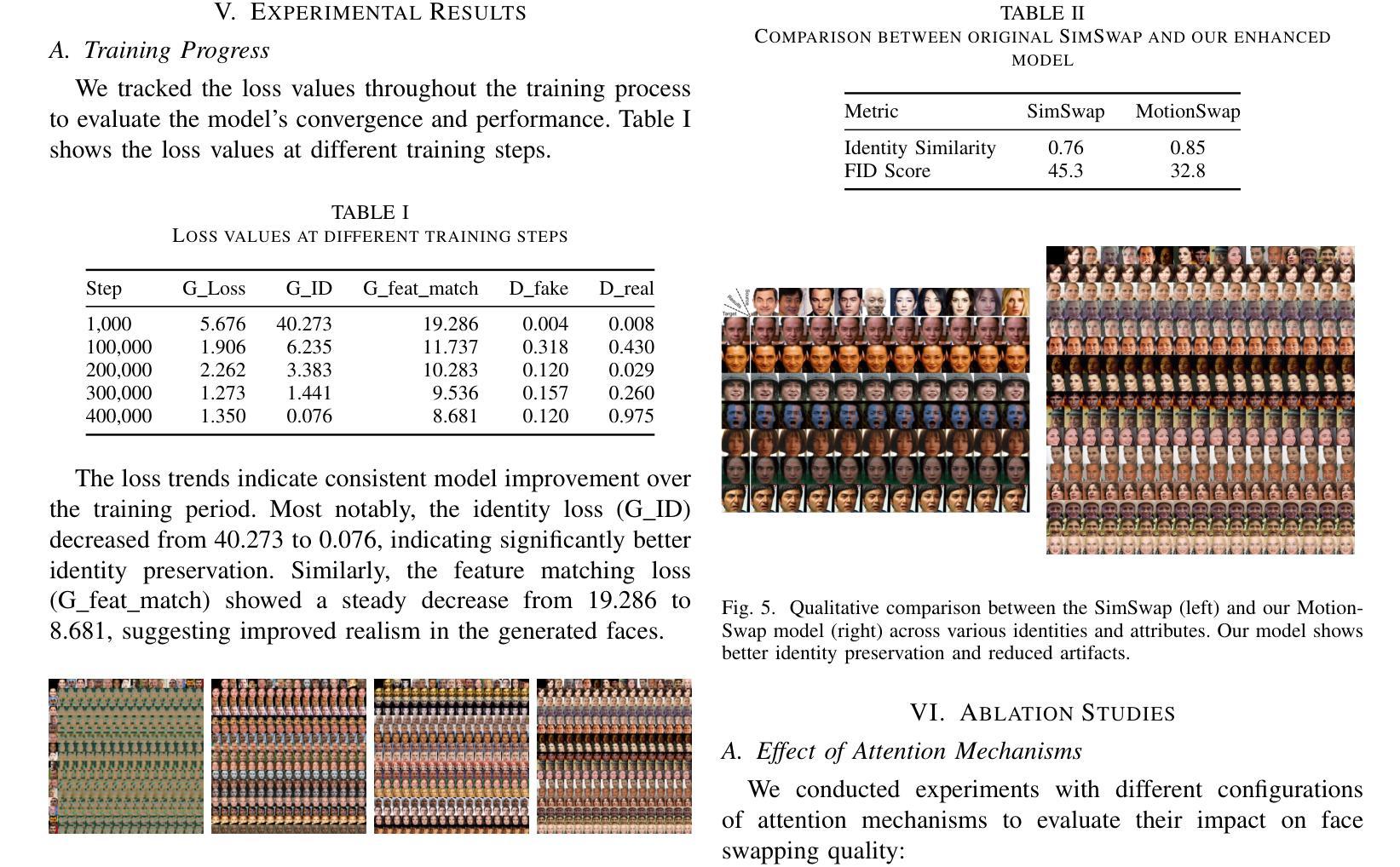
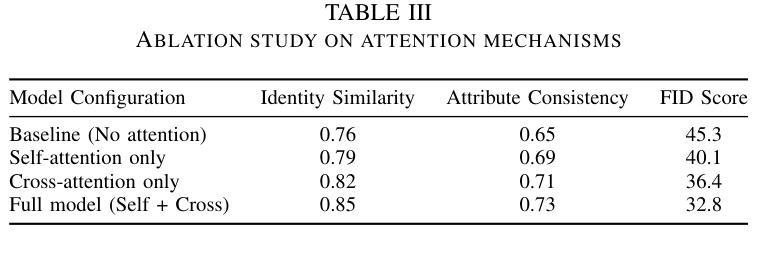
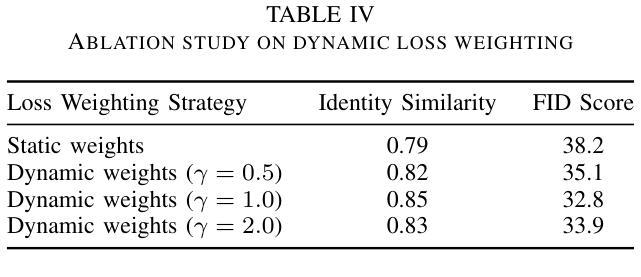
Face swapping technology has gained significant attention in both academic research and commercial applications. This paper presents our implementation and enhancement of SimSwap, an efficient framework for high fidelity face swapping. We introduce several improvements to the original model, including the integration of self and cross-attention mechanisms in the generator architecture, dynamic loss weighting, and cosine annealing learning rate scheduling. These enhancements lead to significant improvements in identity preservation, attribute consistency, and overall visual quality. Our experimental results, spanning 400,000 training iterations, demonstrate progressive improvements in generator and discriminator performance. The enhanced model achieves better identity similarity, lower FID scores, and visibly superior qualitative results compared to the baseline. Ablation studies confirm the importance of each architectural and training improvement. We conclude by identifying key future directions, such as integrating StyleGAN3, improving lip synchronization, incorporating 3D facial modeling, and introducing temporal consistency for video-based applications.
面部替换技术已在学术研究和商业应用中都受到了广泛关注。本文介绍了我们对SimSwap的实现和改进,SimSwap是一个高效的高保真面部替换框架。我们对原始模型进行了几项改进,包括在生成器架构中集成自注意力和交叉注意力机制、动态损失加权和余弦退火学习率调度。这些改进在身份保留、属性一致性和整体视觉质量方面取得了显著的改进。我们的实验结果跨越了40万次训练迭代,证明了生成器和鉴别器性能的逐步改进。增强型模型在身份相似性、FID得分方面取得了更好的表现,并且在定性结果上明显优于基线。消融研究证实了每种架构和训练改进的重要性。最后,我们确定了关键的未来方向,如集成StyleGAN3、改进唇同步、融入3D面部建模以及引入基于视频的时空一致性等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures, 5 tables. This is a student research submission from BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus. Our implementation enhances SimSwap with attention modules and dynamic training strategies
Summary
该论文介绍了SimSwap的实现和改进,这是一个高效的高保真度人脸替换框架。通过引入自注意力机制和交叉注意力机制、动态损失加权和余弦退火学习率调度等改进,提高了身份保留、属性一致性和整体视觉质量。实验结果显示,经过增强的模型在生成器和鉴别器性能上取得了渐进的改进,具有更好的身份相似性、更低的FID得分和明显的优质定性结果。
Key Takeaways
- 论文实现了SimSwap框架,用于高效的高保真度人脸替换。
- 引入了自注意力机制和交叉注意力机制,提高了生成器架构的性能。
- 通过动态损失加权和余弦退火学习率调度等改进,增强了模型的性能。
- 实验结果显示,改进后的模型在身份保留、属性一致性和整体视觉质量上取得了显著进步。
- 消融研究证实了每个架构和训练改进的重要性。
- 未来研究方向包括集成StyleGAN3、改善唇部同步、引入3D面部建模和实现视频应用的时序一致性。
点此查看论文截图

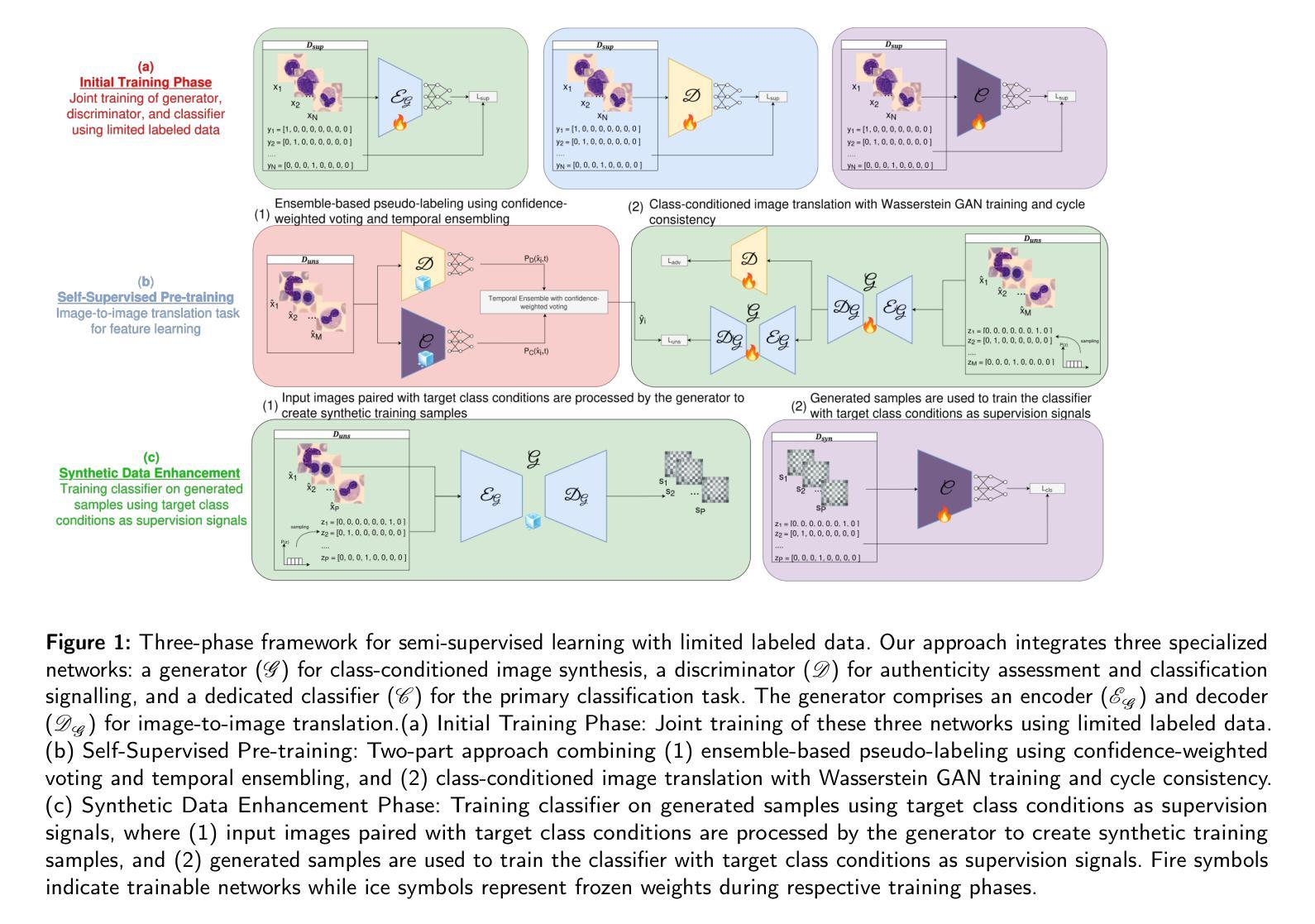
SPARSE Data, Rich Results: Few-Shot Semi-Supervised Learning via Class-Conditioned Image Translation
Authors:Guido Manni, Clemente Lauretti, Loredana Zollo, Paolo Soda
Deep learning has revolutionized medical imaging, but its effectiveness is severely limited by insufficient labeled training data. This paper introduces a novel GAN-based semi-supervised learning framework specifically designed for low labeled-data regimes, evaluated across settings with 5 to 50 labeled samples per class. Our approach integrates three specialized neural networks – a generator for class-conditioned image translation, a discriminator for authenticity assessment and classification, and a dedicated classifier – within a three-phase training framework. The method alternates between supervised training on limited labeled data and unsupervised learning that leverages abundant unlabeled images through image-to-image translation rather than generation from noise. We employ ensemble-based pseudo-labeling that combines confidence-weighted predictions from the discriminator and classifier with temporal consistency through exponential moving averaging, enabling reliable label estimation for unlabeled data. Comprehensive evaluation across eleven MedMNIST datasets demonstrates that our approach achieves statistically significant improvements over six state-of-the-art GAN-based semi-supervised methods, with particularly strong performance in the extreme 5-shot setting where the scarcity of labeled data is most challenging. The framework maintains its superiority across all evaluated settings (5, 10, 20, and 50 shots per class). Our approach offers a practical solution for medical imaging applications where annotation costs are prohibitive, enabling robust classification performance even with minimal labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE.
深度学习已经彻底改变了医学影像领域,但其有效性因缺乏标记的训练数据而受到严重限制。本文介绍了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,专为低标记数据场景设计,并在每类有5到50个标记样本的不同设置中进行评估。我们的方法将三个专用神经网络集成到一个三阶段训练框架中,包括用于类别条件图像翻译的发生器、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及一个专用分类器。该方法在有限的标记数据上进行监督训练,并在通过图像到图像的翻译而不是从噪声生成的无标签图像上进行无监督学习之间交替进行。我们采用基于集合的伪标签方法,将鉴别器和分类器的加权预测与通过指数移动平均实现的时序一致性相结合,为无标签数据提供可靠的标签估计。在包括十一个MedMNIST数据集的综合评估中,我们的方法实现了对六种最先进的基于GAN的半监督方法的统计显著性改进,特别是在极端5个样本的场景中,由于标记数据的稀缺性最具挑战性。该框架在所有评估设置(每类5个、10个、20个和50个样本)中都保持其优势。我们的方法为医学影像应用提供了实际解决方案,其中标注成本高昂,即使在标记数据极少的情况下也能实现稳健的分类性能。代码可在https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在深度学习应用于医学影像领域时,由于标注数据不足导致的局限性成为一大挑战。本文提出了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,适用于标注数据较少的场景。该框架结合了三种神经网络,包括用于类别条件图像转换的生成器、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及一个专门的分类器。通过在有限的标注数据和通过图像到图像的转换得到的无标签数据之间进行交替训练,该方法实现了可靠的未标注数据标签估计。在多个数据集上的评估表明,该方法相较于其他六种先进的半监督方法具有显著优势,特别是在仅有少量标注数据的极端情况下。框架在所有的评估设置中都表现出优越性。对于标注成本高昂的医学成像应用而言,这是一个实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,用于解决医学图像标注数据不足的问题。
- 框架结合了生成器、鉴别器和分类器三种神经网络。
- 该方法通过在有限的标注数据和通过图像到图像转换得到的无标签数据之间进行交替训练,提高了模型的性能。
- 通过集成基于伪标签的方法,结合鉴别器和分类器的加权预测以及通过指数移动平均实现的时序一致性,实现对未标注数据可靠标签的估计。
- 在多个数据集上的评估显示,该框架相较于其他先进方法具有显著优势,特别是在标注数据非常有限的极端情况下。
- 该框架适用于医学成像领域,为标注成本高昂的应用提供了实用解决方案。
点此查看论文截图