⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
SPARSE Data, Rich Results: Few-Shot Semi-Supervised Learning via Class-Conditioned Image Translation
Authors:Guido Manni, Clemente Lauretti, Loredana Zollo, Paolo Soda
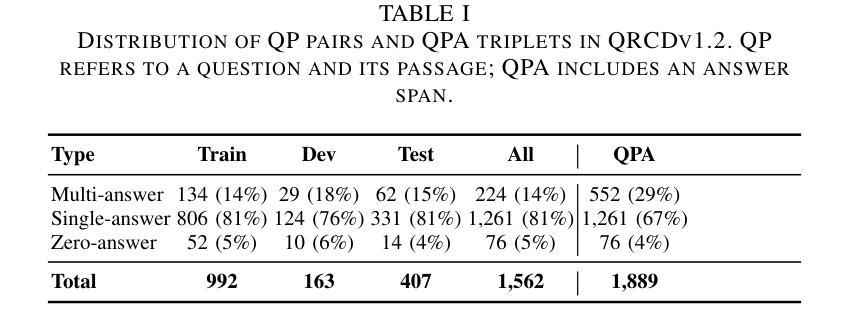
Deep learning has revolutionized medical imaging, but its effectiveness is severely limited by insufficient labeled training data. This paper introduces a novel GAN-based semi-supervised learning framework specifically designed for low labeled-data regimes, evaluated across settings with 5 to 50 labeled samples per class. Our approach integrates three specialized neural networks – a generator for class-conditioned image translation, a discriminator for authenticity assessment and classification, and a dedicated classifier – within a three-phase training framework. The method alternates between supervised training on limited labeled data and unsupervised learning that leverages abundant unlabeled images through image-to-image translation rather than generation from noise. We employ ensemble-based pseudo-labeling that combines confidence-weighted predictions from the discriminator and classifier with temporal consistency through exponential moving averaging, enabling reliable label estimation for unlabeled data. Comprehensive evaluation across eleven MedMNIST datasets demonstrates that our approach achieves statistically significant improvements over six state-of-the-art GAN-based semi-supervised methods, with particularly strong performance in the extreme 5-shot setting where the scarcity of labeled data is most challenging. The framework maintains its superiority across all evaluated settings (5, 10, 20, and 50 shots per class). Our approach offers a practical solution for medical imaging applications where annotation costs are prohibitive, enabling robust classification performance even with minimal labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE.
深度学习已经彻底改变了医学影像领域,但其有效性受到标注训练数据不足的严重限制。本文介绍了一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,该框架专门设计用于低标注数据情况。实验设置涵盖了每类5到50个标注样本的情况。我们的方法整合了三个专用神经网络——用于类别条件图像翻译的生成器、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及专用分类器——在一个三阶段训练框架中。该方法在有限的标注数据上进行监督训练,并通过图像到图像的翻译而不是从噪声生成来利用大量未标注图像进行无监督学习。我们采用基于集合的伪标签方法,将鉴别器和分类器的加权预测与通过指数移动平均实现的时序一致性相结合,为未标注数据提供可靠的标签估计。在11个MedMNIST数据集上的综合评估表明,我们的方法在六个最先进的基于GAN的半监督方法上实现了统计学上的显著改善,特别是在5个样本的极端设置中,标注数据的稀缺性最具挑战性。该框架在所有评估的设置(5、10、20和50个样本/类)中都保持其优越性。我们的方法为医学影像应用提供了实际解决方案,其中标注成本高昂,即使在少量标注数据的情况下也能实现稳健的分类性能。代码可用在:https://github.com/GuidoManni/SPARSE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医疗图像深度学习受限于标注数据不足的问题,本文提出一种基于GAN的半监督学习框架,用于低标注数据情况。框架包含三个神经网络,通过监督学习和无监督学习结合的方式训练,并在多个数据集上评估表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新的基于GAN的半监督学习框架,适用于医疗图像分类中标注数据不足的情况。
- 框架集成了三个神经网络:用于类别条件图像翻译的生成器、用于真实性和分类评估的鉴别器以及一个专门的分类器。
- 该方法采用三阶段训练框架,交替进行对有限标注数据的监督训练和通过图像到图像的翻译利用大量未标注数据的无监督学习。
- 采用了基于集合的伪标签方法,结合鉴别器和分类器的加权预测,并通过指数移动平均实现时间一致性,为未标注数据提供可靠的标签估计。
- 在多个MedMNIST数据集上的综合评估表明,该方法在六种最先进的GAN半监督方法中实现了统计上的显著改善,特别是在每类仅有5个样本的极端情况下。
- 该框架在所有评估设置中都保持了其优越性,包括每类5、10、20和50个样本的情况。
点此查看论文截图

Roll Your Eyes: Gaze Redirection via Explicit 3D Eyeball Rotation
Authors:YoungChan Choi, HengFei Wang, YiHua Cheng, Boeun Kim, Hyung Jin Chang, YoungGeun Choi, Sang-Il Choi
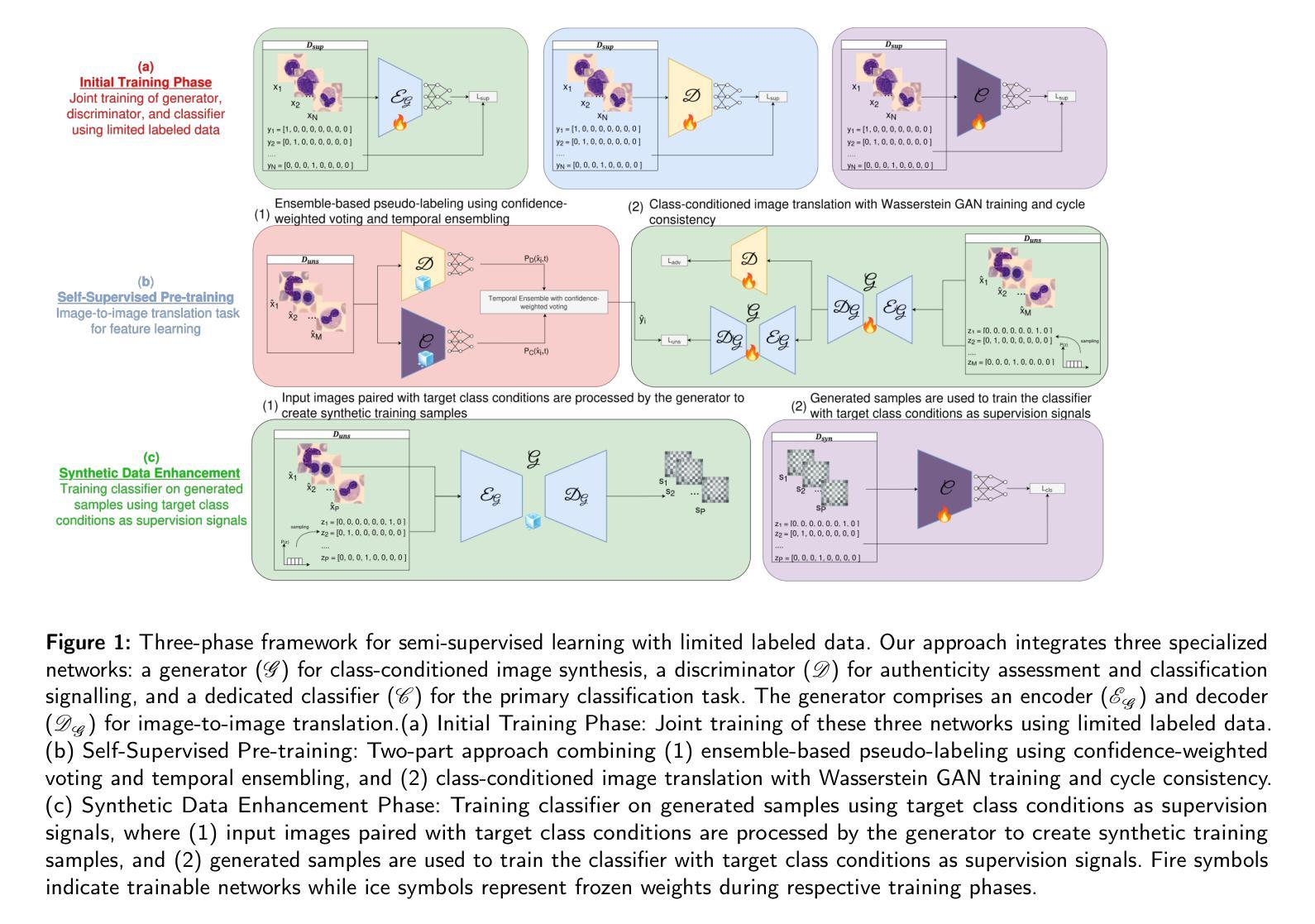
We propose a novel 3D gaze redirection framework that leverages an explicit 3D eyeball structure. Existing gaze redirection methods are typically based on neural radiance fields, which employ implicit neural representations via volume rendering. Unlike these NeRF-based approaches, where the rotation and translation of 3D representations are not explicitly modeled, we introduce a dedicated 3D eyeball structure to represent the eyeballs with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our method generates photorealistic images that faithfully reproduce the desired gaze direction by explicitly rotating and translating the 3D eyeball structure. In addition, we propose an adaptive deformation module that enables the replication of subtle muscle movements around the eyes. Through experiments conducted on the ETH-XGaze dataset, we demonstrate that our framework is capable of generating diverse novel gaze images, achieving superior image quality and gaze estimation accuracy compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
我们提出了一种新型的3D眼神重定向框架,该框架利用明确的3D眼球结构。现有的眼神重定向方法通常基于神经辐射场,通过体积渲染采用隐式神经表示。与这些基于NeRF的方法不同,后者没有明确地建模3D表示的旋转和平移,我们引入了一个专门的3D眼球结构,使用3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)来表示眼球。我们的方法生成了逼真的图像,通过明确地旋转和平移3D眼球结构,忠实地再现了期望的眼神方向。此外,我们提出了一种自适应变形模块,能够实现眼睛周围微妙肌肉运动的复制。在ETH-XGaze数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的框架能够生成多种新颖的眼神图像,与现有最先进的方法相比,图像质量和眼神估计精度更高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, ACM Multimeida 2025 accepted
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的三维目光重定向框架,该框架利用明确的3D眼球结构,通过三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)表示眼球。与传统的基于神经辐射场的方法不同,我们的方法能够明确地模拟三维表示的旋转和平移,生成真实感图像,准确地再现所需的目光方向。此外,我们还提出了一种自适应变形模块,可以复制眼睛周围微妙的肌肉运动。通过实验验证,我们的框架能够生成多种新颖的目光图像,相较于之前的最先进方法,具有更高的图像质量和目光估计准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于明确3D眼球结构的目光重定向框架。
- 采用三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)表示眼球。
- 能够显式模拟三维表示的旋转和平移。
- 生成真实感图像,准确再现目标目光方向。
- 引入自适应变形模块,模拟眼睛周围的微妙肌肉运动。
- 在ETH-XGaze数据集上进行了实验验证。
点此查看论文截图

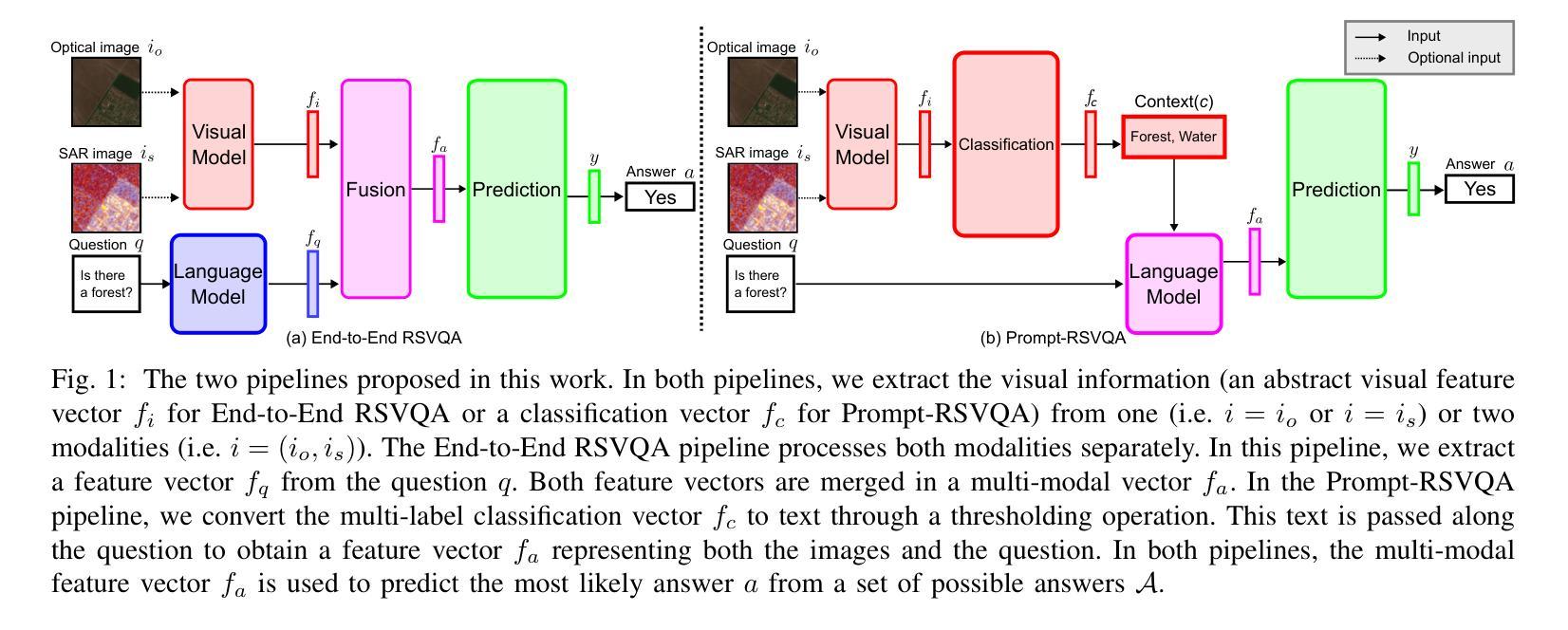
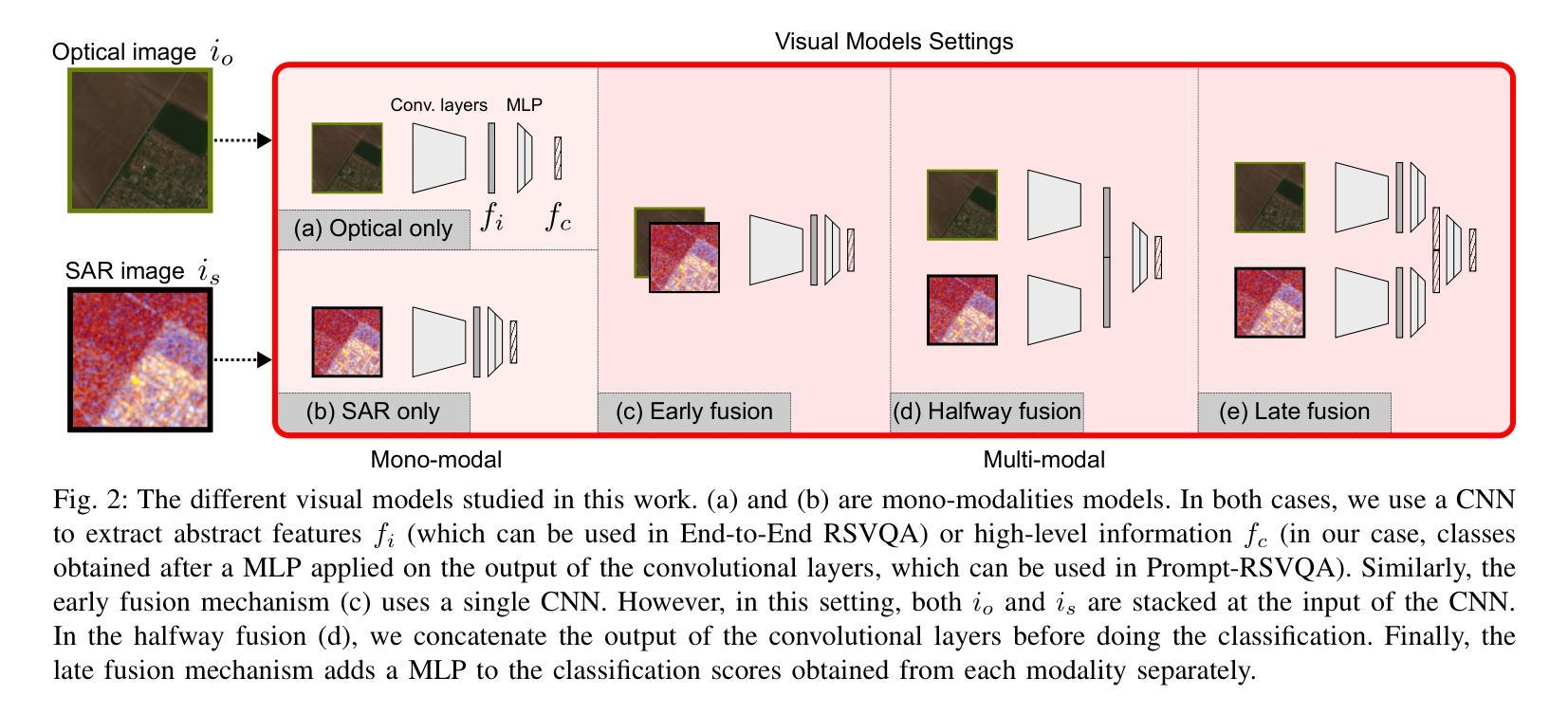
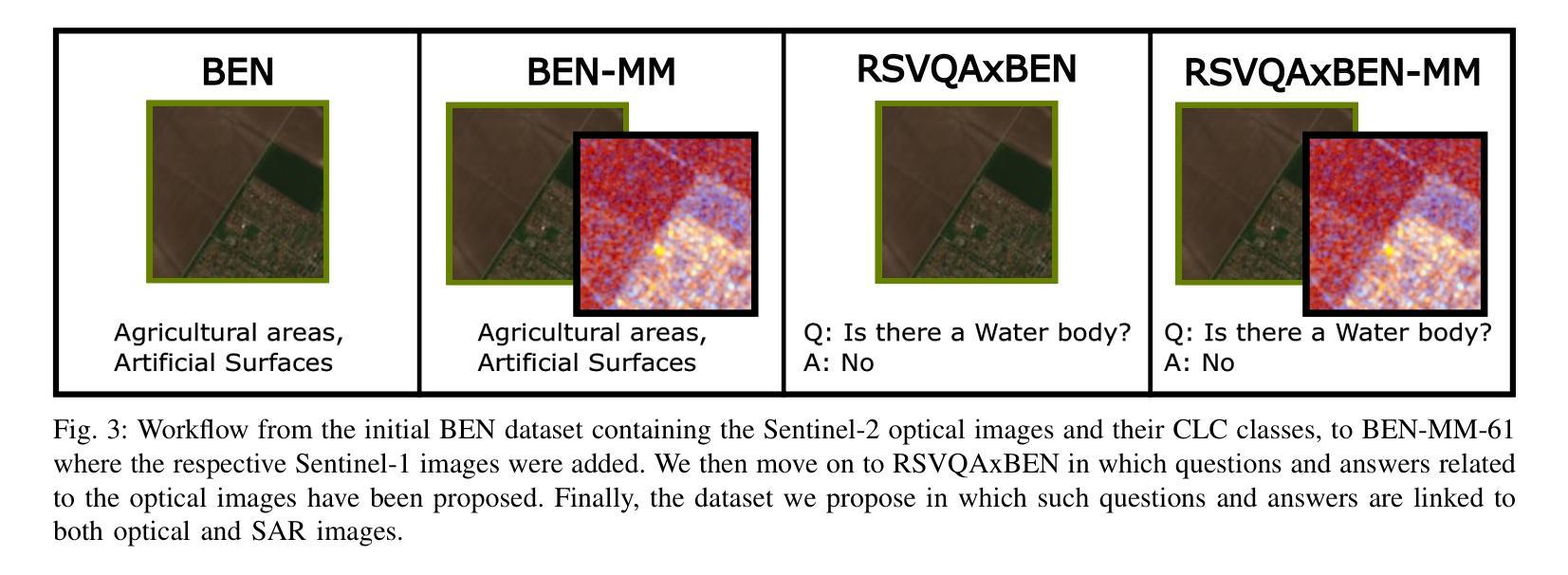
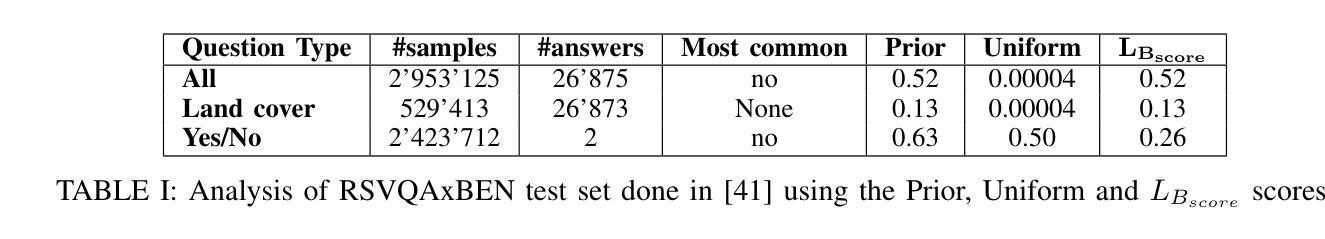
SAR Strikes Back: A New Hope for RSVQA
Authors:Lucrezia Tosato, Flora Weissgerber, Laurent Wendling, Sylvain Lobry
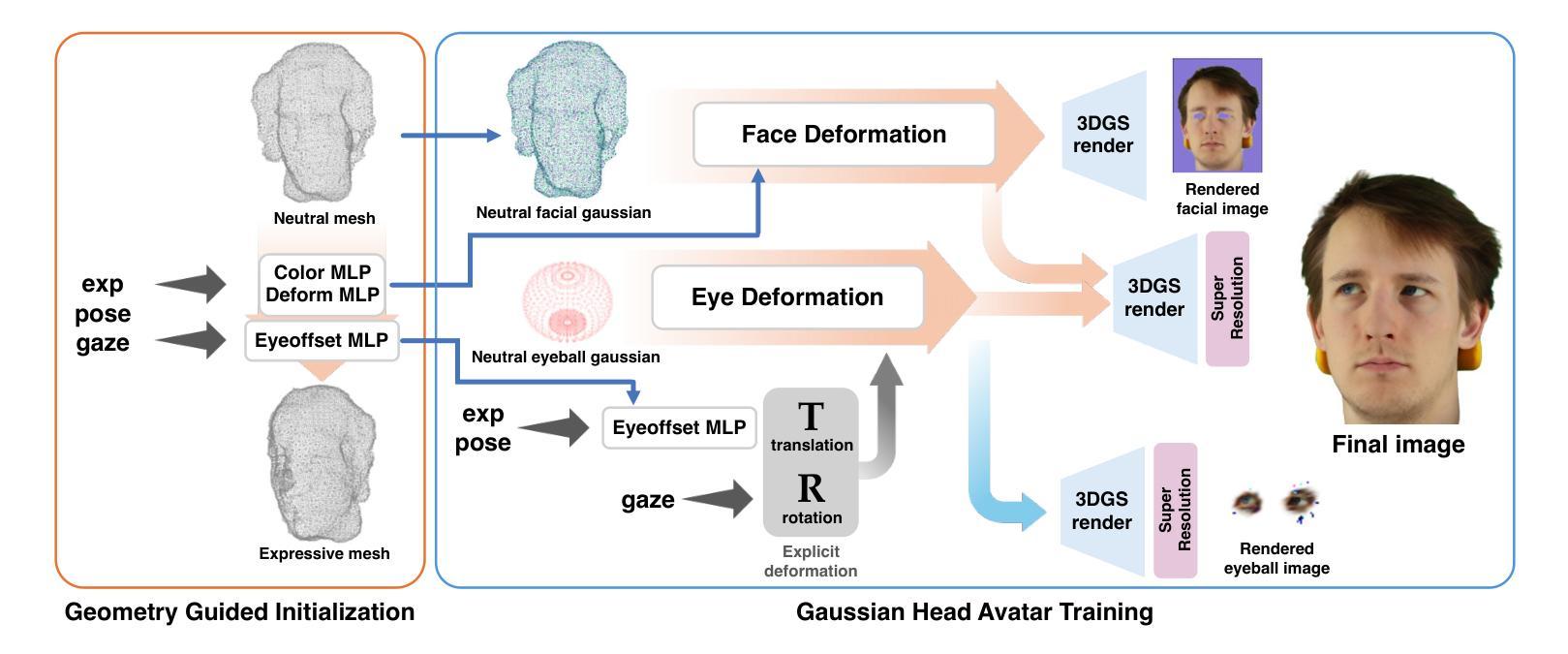
Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering (RSVQA) is a task that extracts information from satellite images to answer questions in natural language, aiding image interpretation. While several methods exist for optical images with varying spectral bands and resolutions, only recently have high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images been explored. SAR’s ability to operate in all weather conditions and capture electromagnetic features makes it a promising modality, yet no study has compared SAR and optical imagery in RSVQA or proposed effective fusion strategies. This work investigates how to integrate SAR data into RSVQA and how to best combine it with optical images. We present a dataset that enables SAR-based RSVQA and explore two pipelines for the task. The first is an end-to-end model, while the second is a two-stage framework: SAR information is first extracted and translated into text, which is then processed by a language model to produce the final answer. Our results show that the two-stage model performs better, improving accuracy by nearly 10% over the end-to-end approach. We also evaluate fusion strategies for combining SAR and optical data. A decision-level fusion yields the best results, with an F1-micro score of 75.00%, F1-average of 81.21%, and overall accuracy of 75.49% on the proposed dataset. SAR proves especially beneficial for questions related to specific land cover types, such as water areas, demonstrating its value as a complementary modality to optical imagery.
遥感视觉问答(RSVQA)是一项从卫星图像中提取信息并以自然语言回答问题,从而辅助图像解读的任务。虽然针对具有不同光谱波段和分辨率的光学图像存在多种方法,但高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像的研究仅在近期受到关注。SAR能够在所有天气条件下运行并捕捉电磁特征,使其成为有前途的模态,但在RSVQA中尚无将SAR和光学图像进行比较的研究,也没有提出有效的融合策略。本研究旨在探讨如何将SAR数据集成到RSVQA中,以及如何将其与光学图像最佳结合。我们提出了一个用于SAR数据的RSVQA数据集,并探索了两种用于该任务的管道。第一个是端到端模型,第二个是两阶段框架:首先提取SAR信息并将其翻译成文本,然后由语言模型处理以产生最终答案。我们的结果表明,两阶段模型的性能更好,其准确度比端到端方法提高了近10%。我们还评估了结合SAR和光学数据的融合策略。决策级融合效果最佳,在提出的数据集上,其微观F1分数为75.00%,平均F1分数为81.21%,总体准确率为75.49%。SAR对于涉及特定土地覆盖类型的问题(如水域)特别有益,证明了其作为光学图像的补充模态的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 13 pages, 6 figures
Summary
遥感视觉问答(RSVQA)能够从卫星图像中提取信息并以自然语言回答问题,有助于图像解读。虽然对于不同光谱波段和分辨率的光学图像存在多种方法,但近期才开始探索高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像的应用。SAR能够在所有天气条件下运行并捕捉电磁特征,因此是一种很有前景的模态。然而,目前尚未有研究比较SAR和光学图像在RSVQA中的表现或提出有效的融合策略。本研究旨在探讨如何将SAR数据融入RSVQA,并找到与光学图像的最佳结合方式。我们提供了用于SAR数据的RSVQA数据集,并探索了两种任务流程。一种是端到端模型,另一种是两阶段框架:首先提取SAR信息并转换为文本,然后通过语言模型处理产生最终答案。结果表明两阶段模型表现更佳,精度比端到端方法高出近10%。此外,我们评估了结合SAR和光学数据的融合策略。决策级融合表现最佳,在提出的数据集上达到了F1微观得分75%,F1平均得分81.21%,总体准确度为75.49%。SAR对于特定土地覆盖类型的问题特别有益,如水域等,证明了其作为光学图像的补充模态的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感视觉问答(RSVQA)能够从卫星图像中提取信息并回答自然语言问题。
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像在RSVQA中具有潜力,但目前研究尚处于初级阶段。
- SAR数据在多种天气条件下均可操作,并能捕捉电磁特征,具有价值。
- 研究比较了SAR和光学图像在RSVQA中的表现,提出两种任务流程模型。
- 两阶段模型比端到端模型表现更好,精度提高近10%。
- 决策级融合策略是结合SAR和光学数据的最佳方法,表现出较高的性能。
点此查看论文截图