⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
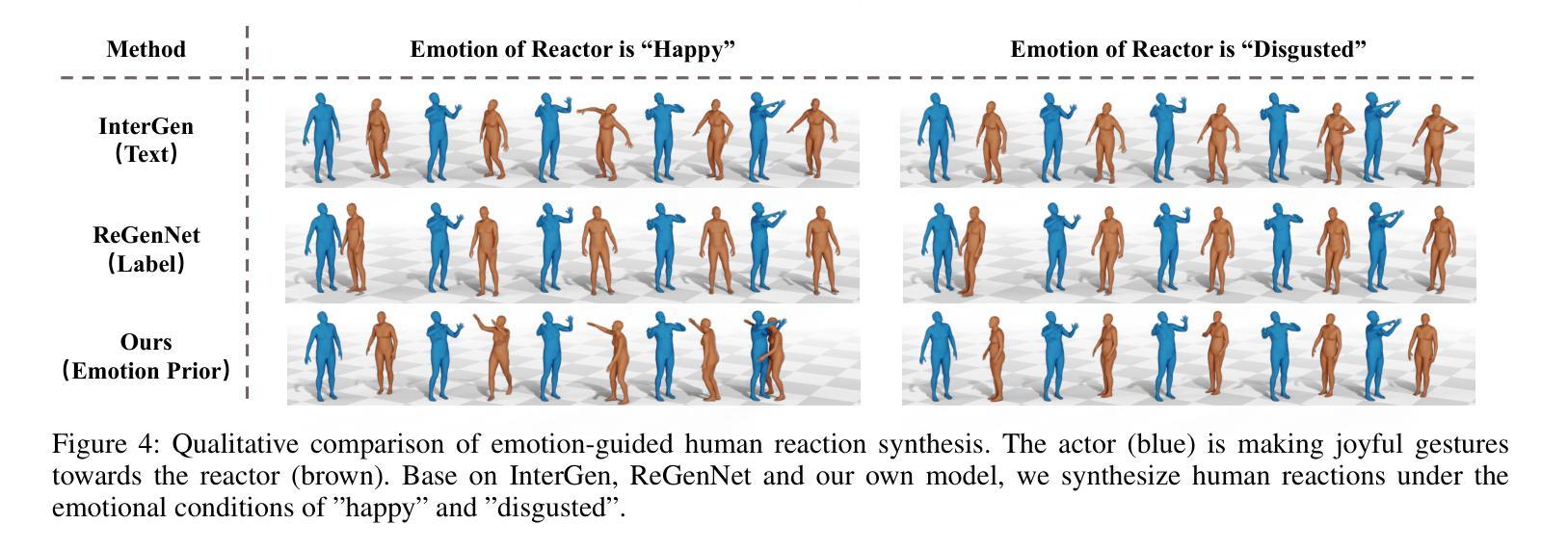
E-React: Towards Emotionally Controlled Synthesis of Human Reactions
Authors:Chen Zhu, Buzhen Huang, Zijing Wu, Binghui Zuo, Yangang Wang
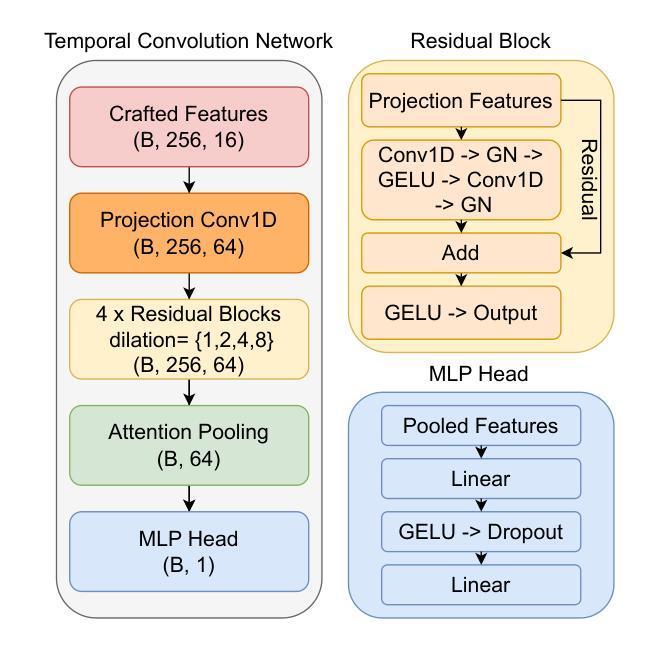
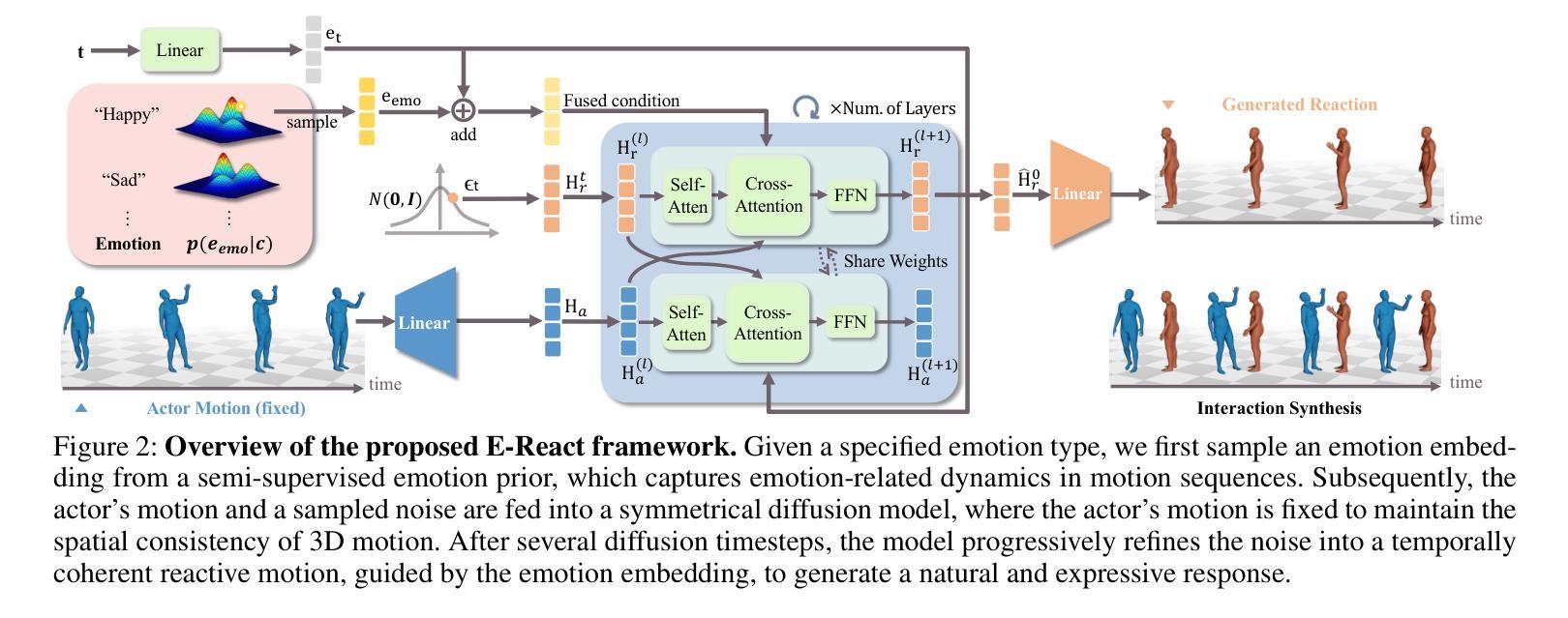
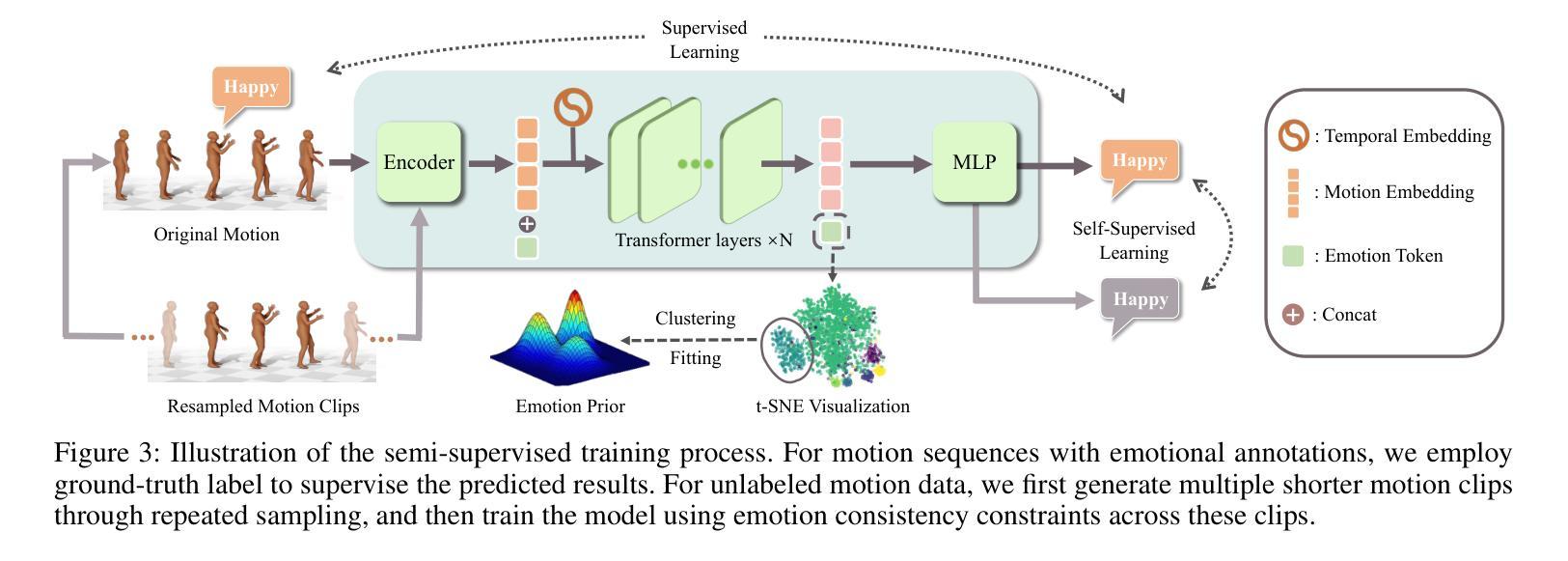
Emotion serves as an essential component in daily human interactions. Existing human motion generation frameworks do not consider the impact of emotions, which reduces naturalness and limits their application in interactive tasks, such as human reaction synthesis. In this work, we introduce a novel task: generating diverse reaction motions in response to different emotional cues. However, learning emotion representation from limited motion data and incorporating it into a motion generation framework remains a challenging problem. To address the above obstacles, we introduce a semi-supervised emotion prior in an actor-reactor diffusion model to facilitate emotion-driven reaction synthesis. Specifically, based on the observation that motion clips within a short sequence tend to share the same emotion, we first devise a semi-supervised learning framework to train an emotion prior. With this prior, we further train an actor-reactor diffusion model to generate reactions by considering both spatial interaction and emotional response. Finally, given a motion sequence of an actor, our approach can generate realistic reactions under various emotional conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms existing reaction generation methods. The code and data will be made publicly available at https://ereact.github.io/
情感在日常人际交往中扮演着至关重要的角色。现有的运动生成框架并没有考虑到情感的影响,这降低了自然性,并限制了它们在互动任务(如人类反应合成)中的应用。在这项工作中,我们引入了一项新任务:根据不同情绪线索生成多样化的反应动作。然而,从有限的运动数据中学习情感表示并将其纳入运动生成框架仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。为了克服上述障碍,我们在演员-反应器扩散模型中引入了半监督情感先验,以促进情感驱动的反应合成。具体来说,基于观察短时间内运动剪辑往往具有相同情感的发现,我们首先设计了一个半监督学习框架来训练情感先验。借助这个先验,我们进一步训练了一个演员-反应器扩散模型,通过考虑空间交互和情感反应来生成反应。最后,给定演员的某种动作序列,我们的方法可以在各种情绪条件下生成逼真的反应。实验结果表明,我们的模型优于现有的反应生成方法。[公开的代码和数据将在https://ereact.github.io/上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
情绪在日常人际交往中扮演着重要角色。现有的运动生成框架忽略了情绪的影响,降低了自然性,并限制了其在互动任务(如人类反应合成)中的应用。本研究引入了一项新任务:根据不同情绪线索生成多样化的反应动作。然而,从有限的运动数据中学习情感表征并将其纳入运动生成框架仍是一个挑战性问题。为解决上述难题,我们在actor-reactor扩散模型中引入半监督情感先验,促进情感驱动的反应合成。基于短序列内运动片段倾向于具有相同情感的观察,我们设计了一个半监督学习框架来训练情感先验。借助该先验,我们进一步训练了一个actor-reactor扩散模型,通过考虑空间交互和情感反应来生成反应。最终,给定演员的运动序列,我们的方法可以在各种情绪条件下生成逼真的反应。实验结果证明,我们的模型优于现有的反应生成方法。
Key Takeaways
- 情绪在日常人际交往中起重要作用,现有运动生成框架需考虑情绪影响以提高自然性和互动任务的实用性。
- 引入新任务:根据不同情绪线索生成多样化的反应动作。
- 从有限运动数据中学习情感表征并融入运动生成框架具挑战性。
- 提出在半监督学习框架下训练情感先验,促进情感驱动的反应合成。
- 利用短序列内运动片段的情感一致性来训练情感先验。
- 采用actor-reactor扩散模型,结合空间交互和情感反应生成反应。
点此查看论文截图

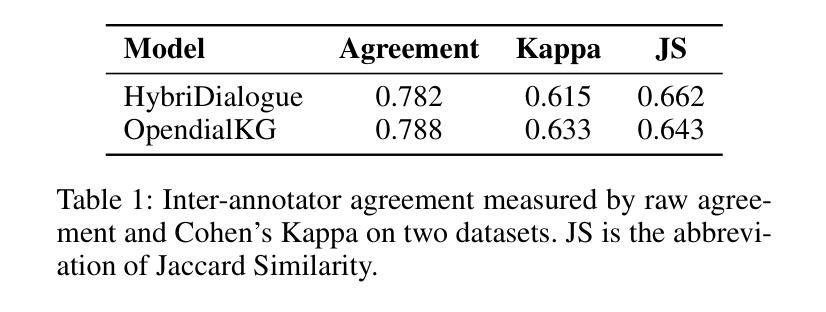
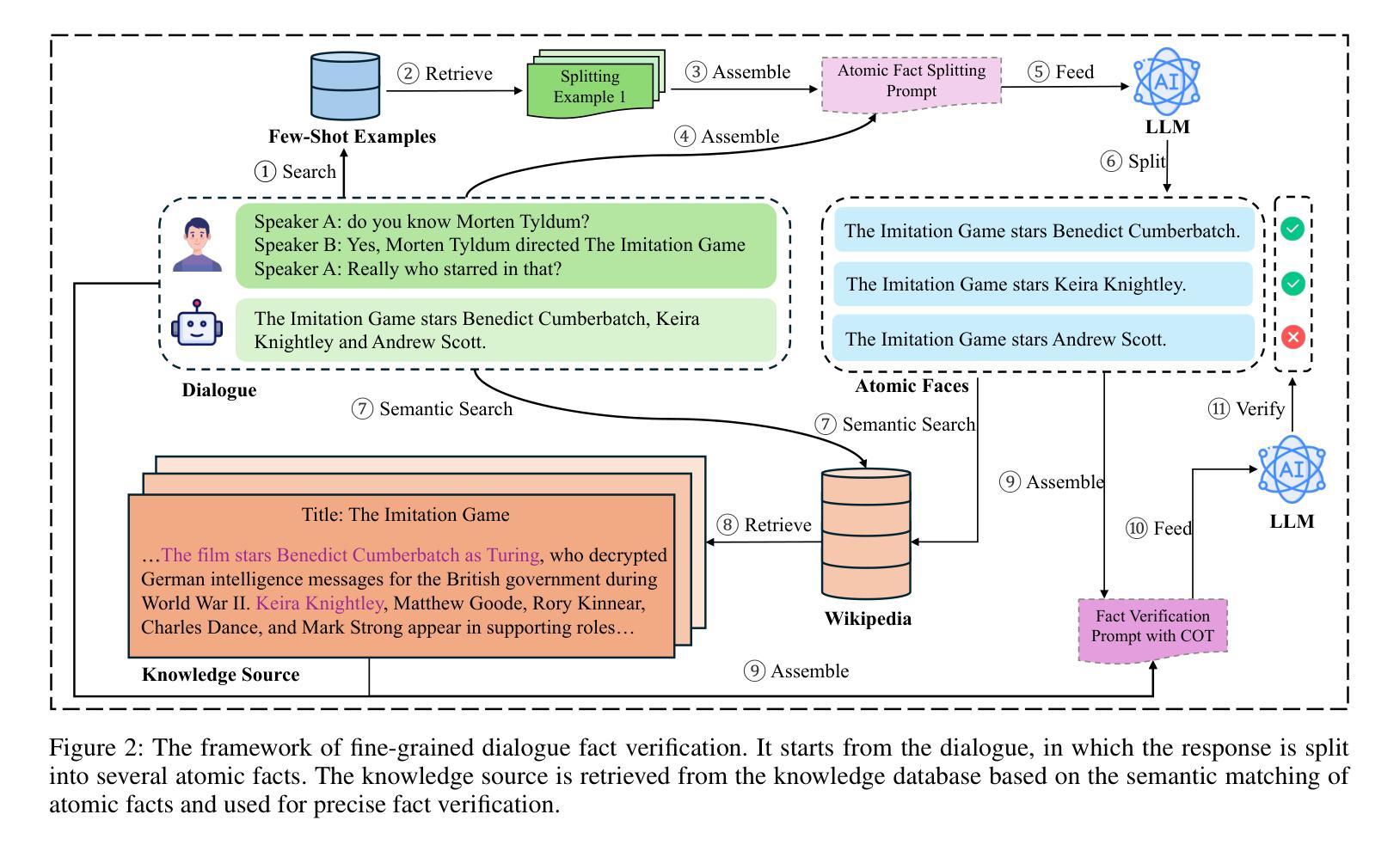
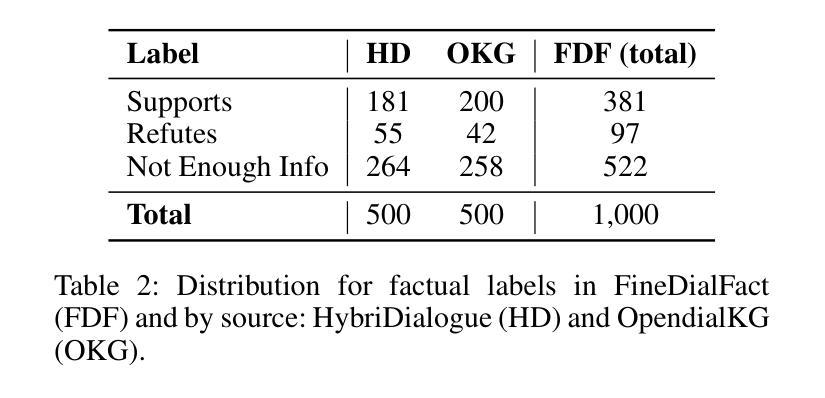
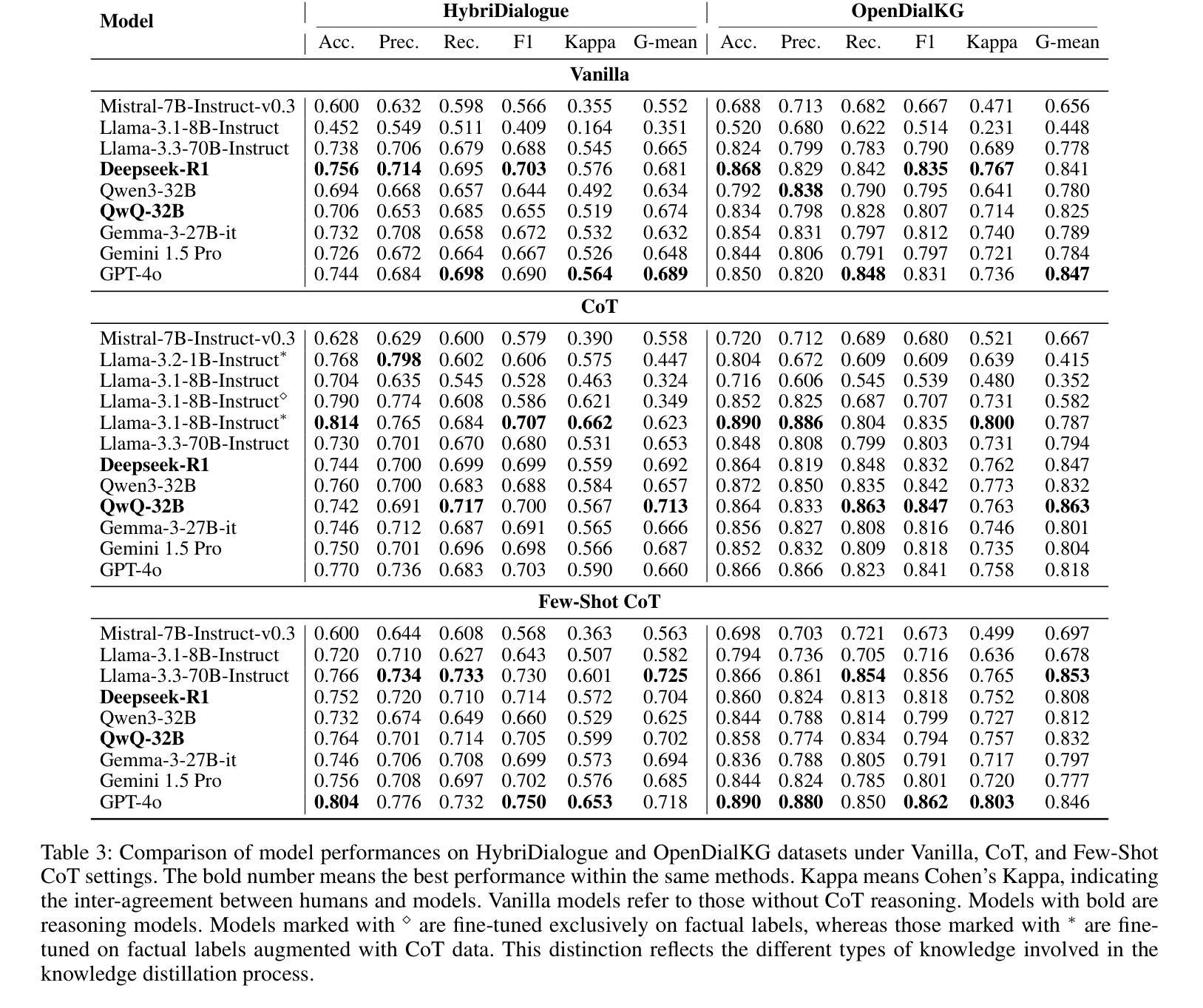
FineDialFact: A benchmark for Fine-grained Dialogue Fact Verification
Authors:Xiangyan Chen, Yufeng Li, Yujian Gan, Arkaitz Zubiaga, Matthew Purver
Large Language Models (LLMs) are known to produce hallucinations - factually incorrect or fabricated information - which poses significant challenges for many Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications, such as dialogue systems. As a result, detecting hallucinations has become a critical area of research. Current approaches to hallucination detection in dialogue systems primarily focus on verifying the factual consistency of generated responses. However, these responses often contain a mix of accurate, inaccurate or unverifiable facts, making one factual label overly simplistic and coarse-grained. In this paper, we introduce a benchmark, FineDialFact, for fine-grained dialogue fact verification, which involves verifying atomic facts extracted from dialogue responses. To support this, we construct a dataset based on publicly available dialogue datasets and evaluate it using various baseline methods. Experimental results demonstrate that methods incorporating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning can enhance performance in dialogue fact verification. Despite this, the best F1-score achieved on the HybriDialogue, an open-domain dialogue dataset, is only 0.75, indicating that the benchmark remains a challenging task for future research. Our dataset and code will be public on GitHub.
大型语言模型(LLMs)会产生幻觉——即事实上的错误或虚构的信息,这对许多自然语言处理(NLP)应用,如对话系统,构成了重大挑战。因此,检测幻觉已成为研究的关键领域。目前对话系统中检测幻觉的方法主要集中在验证生成响应的事实一致性上。然而,这些响应通常包含准确、不准确或无法验证的事实混合,使得单一的事实标签过于简单和粗糙。在本文中,我们介绍了一个精细对话事实验证的基准测试FineDialFact,它涉及验证从对话响应中提取的原子事实。为了支持这一点,我们在公开可用的对话数据集的基础上构建了一个数据集,并使用各种基准方法对其进行了评估。实验结果表明,采用链式思维(CoT)推理的方法可以提高对话事实验证的性能。尽管如此,在开放域对话数据集HybriDialogue上获得的最佳F1分数仅为0.75,这表明该基准测试仍然是未来研究的一个具有挑战性的任务。我们的数据集和代码将在GitHub上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)产生的幻觉(即事实错误或虚构信息)对自然语言处理(NLP)应用,如对话系统,构成了重大挑战。当前的研究主要集中在验证生成响应的事实一致性上进行幻觉检测,但这种方法过于简化且颗粒度较粗,因为响应中往往包含准确、不准确或无法验证的事实混合。本文介绍了一种精细颗粒度的对话事实验证基准测试FineDialFact,它涉及验证从对话响应中提取的原子事实。为了支持这一验证,我们在公开可用的对话数据集的基础上构建了一个数据集,并使用各种基准方法对其进行了评估。实验结果表明,采用链式思维(CoT)推理的方法可以提高对话事实验证的性能。尽管如此,在开放域对话数据集HybriDialogue上的最佳F1分数仅为0.75,表明该基准测试对未来研究仍具有挑战性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)产生的幻觉对自然语言处理(NLP)应用构成挑战。
- 当前幻觉检测的方法主要关注验证生成响应的事实一致性。
- 现有方法过于简化,不能处理响应中混合的准确、不准确或无法验证的事实。
- 引入了一种新的基准测试FineDialFact,用于精细颗粒度的对话事实验证。
- FineDialFact涉及验证从对话响应中提取的原子事实。
- 链式思维(CoT)推理方法能提高对话事实验证的性能。
点此查看论文截图