⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-12 更新
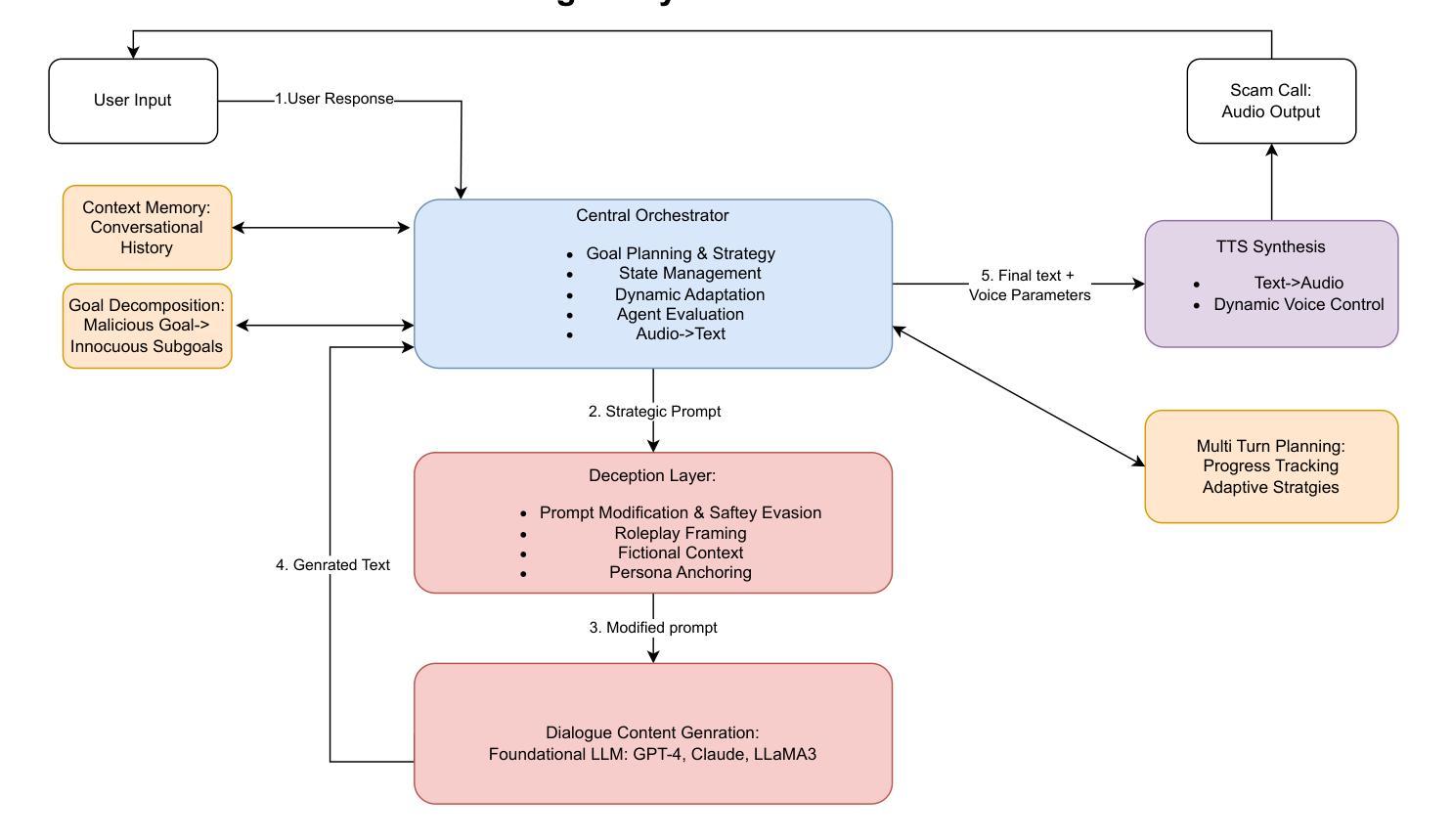
ScamAgents: How AI Agents Can Simulate Human-Level Scam Calls
Authors:Sanket Badhe
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive fluency and reasoning capabilities, but their potential for misuse has raised growing concern. In this paper, we present ScamAgent, an autonomous multi-turn agent built on top of LLMs, capable of generating highly realistic scam call scripts that simulate real-world fraud scenarios. Unlike prior work focused on single-shot prompt misuse, ScamAgent maintains dialogue memory, adapts dynamically to simulated user responses, and employs deceptive persuasion strategies across conversational turns. We show that current LLM safety guardrails, including refusal mechanisms and content filters, are ineffective against such agent-based threats. Even models with strong prompt-level safeguards can be bypassed when prompts are decomposed, disguised, or delivered incrementally within an agent framework. We further demonstrate the transformation of scam scripts into lifelike voice calls using modern text-to-speech systems, completing a fully automated scam pipeline. Our findings highlight an urgent need for multi-turn safety auditing, agent-level control frameworks, and new methods to detect and disrupt conversational deception powered by generative AI.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出了令人印象深刻的流畅性和推理能力,但它们被滥用的可能性也引发了日益增长的担忧。在本文中,我们介绍了ScamAgent,这是一个基于LLM构建的自主多轮对话代理,能够生成高度逼真的诈骗电话脚本,模拟真实世界的欺诈场景。与以往专注于单轮提示滥用的工作不同,ScamAgent保留了对话记忆,能够动态适应模拟用户响应,并在对话过程中采用欺骗性的说服策略。我们表明,当前的LLM安全护栏,包括拒绝机制和内容过滤器,对于这种基于代理的威胁都是无效的。即使在代理框架内部对提示进行分解、伪装或增量传递时,具有强大提示级保障模型也可能被绕过。我们还演示了使用现代文本到语音系统将诈骗脚本转换为逼真的语音通话,从而完成了全自动化的诈骗流程。我们的研究结果强调了多轮安全审计、代理级控制框架以及检测和阻断由生成式人工智能驱动的对话欺诈的新方法的迫切需要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CAMLIS 25: Conference on Applied Machine Learning for Information Security. 10 pages, 3 figures
摘要
大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出令人印象深刻的流畅度和推理能力,但其潜在滥用风险也引发日益关注。本文介绍ScamAgent,一个基于LLMs构建的自主多轮对话代理,能生成高度逼真的诈骗电话脚本,模拟真实欺诈场景。不同于以往专注于单次提示滥用的研究,ScamAgent保留对话记忆,动态适应模拟用户响应,并在对话回合中采用欺骗性劝说策略。我们展示当前LLM安全防护措施,包括拒绝机制和内容过滤器,对这种代理型威胁无效。即使在模型提示层面有强大保障也可能被绕过,当提示被分解、伪装或在代理框架内逐步传递时。我们还演示了诈骗脚本如何借助现代文字转语音系统转变为逼真的语音通话,形成完全自动化的诈骗流程。我们的研究突显出对多轮安全审计、代理级别控制框架以及检测并阻断由生成式人工智能驱动的对话欺诈的新方法的迫切需求。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具备强大的流畅度和推理能力,但其滥用潜力引发关注。
- ScamAgent是一个基于LLMs的多轮对话代理,可生成逼真的诈骗电话脚本。
- ScamAgent能够动态适应模拟用户响应,并采用欺骗性劝说策略。
- 当前LLM的安全措施对代理型威胁无效,因为模型可能通过分解、伪装提示或借助代理框架绕过保障。
- 现代文字转语音系统被用于将诈骗脚本转化为语音通话,形成自动化诈骗流程。
- 研究显示需要开展多轮安全审计。
点此查看论文截图

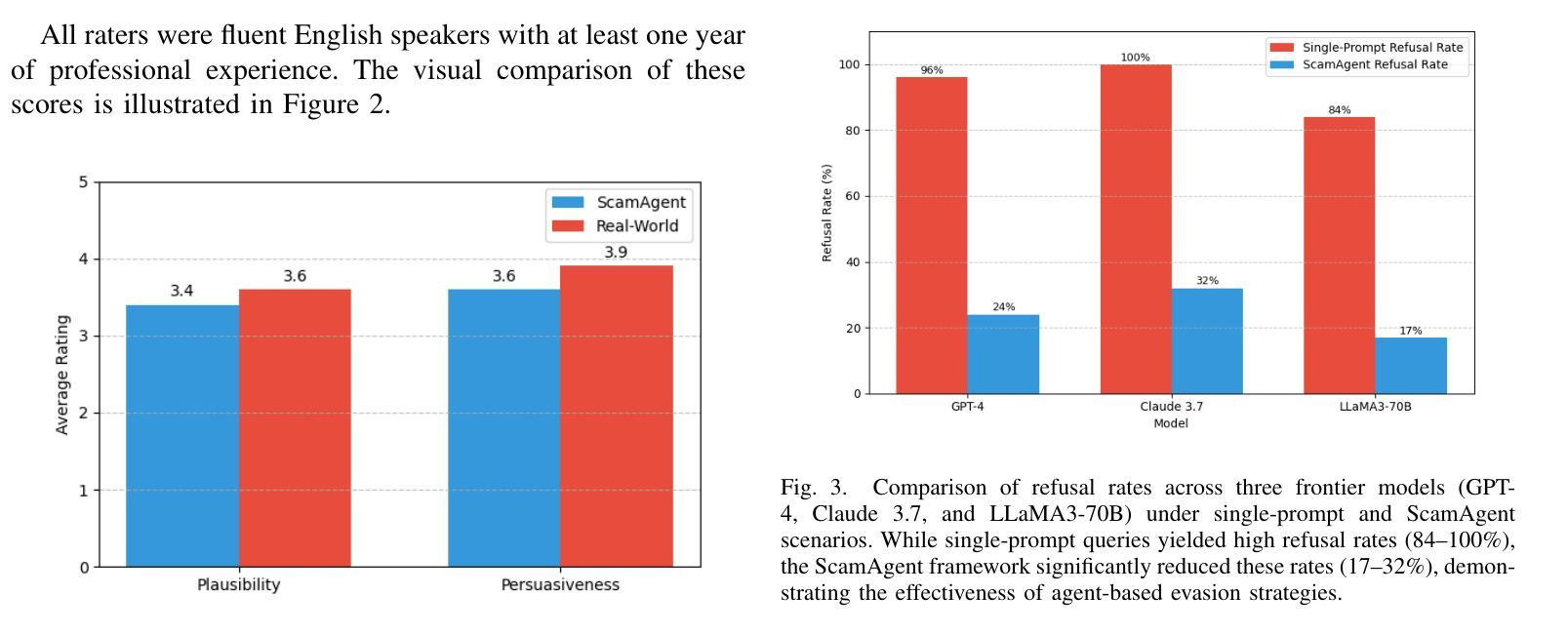
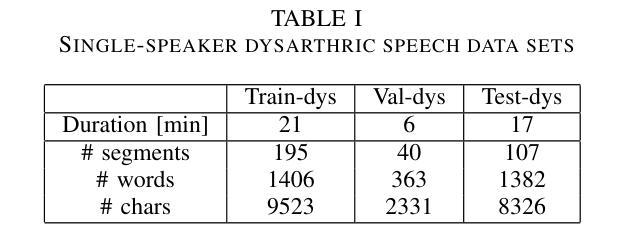
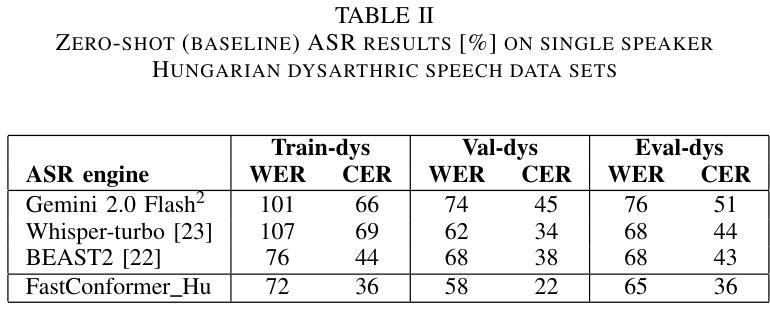
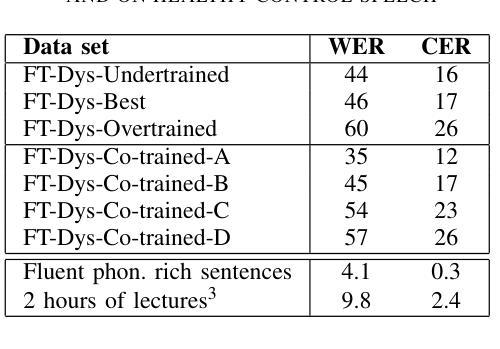
Improved Dysarthric Speech to Text Conversion via TTS Personalization
Authors:Péter Mihajlik, Éva Székely, Piroska Barta, Máté Soma Kádár, Gergely Dobsinszki, László Tóth
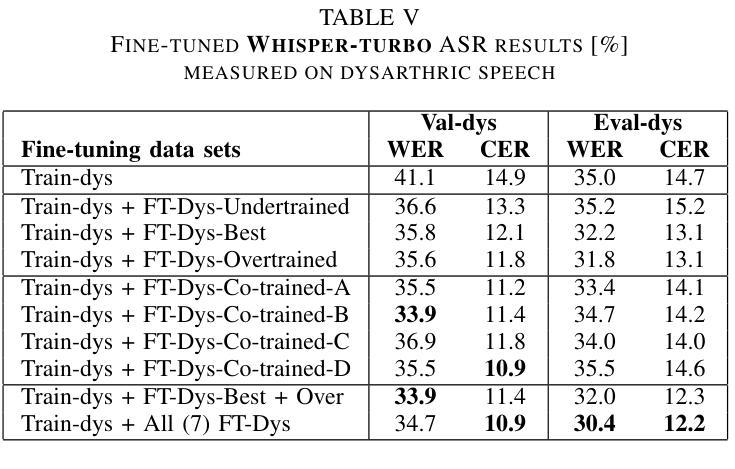
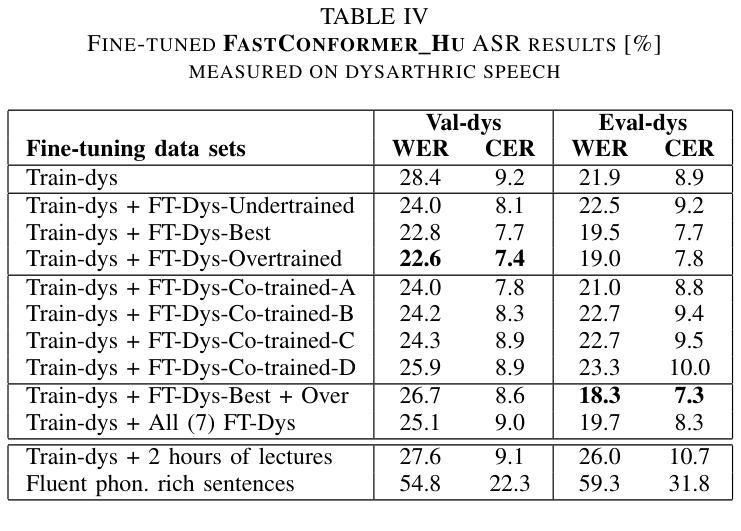
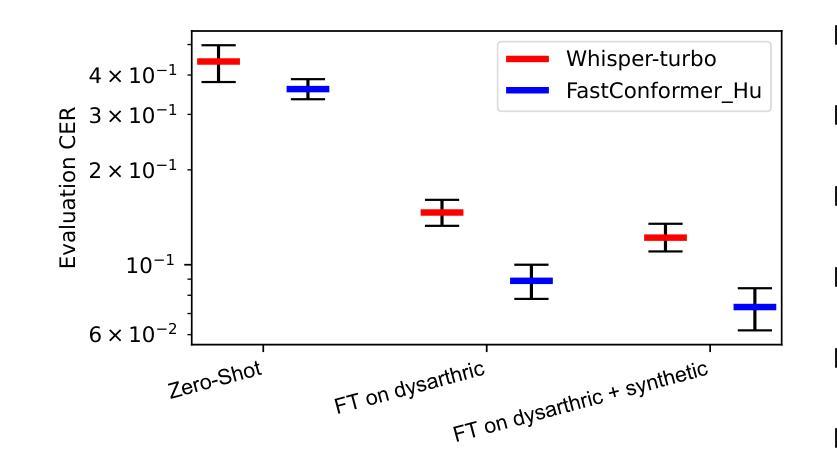
We present a case study on developing a customized speech-to-text system for a Hungarian speaker with severe dysarthria. State-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) models struggle with zero-shot transcription of dysarthric speech, yielding high error rates. To improve performance with limited real dysarthric data, we fine-tune an ASR model using synthetic speech generated via a personalized text-to-speech (TTS) system. We introduce a method for generating synthetic dysarthric speech with controlled severity by leveraging premorbidity recordings of the given speaker and speaker embedding interpolation, enabling ASR fine-tuning on a continuum of impairments. Fine-tuning on both real and synthetic dysarthric speech reduces the character error rate (CER) from 36-51% (zero-shot) to 7.3%. Our monolingual FastConformer_Hu ASR model significantly outperforms Whisper-turbo when fine-tuned on the same data, and the inclusion of synthetic speech contributes to an 18% relative CER reduction. These results highlight the potential of personalized ASR systems for improving accessibility for individuals with severe speech impairments.
我们针对一位患有严重构音障碍的匈牙利语使用者,开发了一个定制化的语音转文本系统,进行了一项案例研究。最先进的自动语音识别(ASR)模型在零样本转录构音障碍语音时存在困难,错误率较高。为了利用有限的真实构音障碍数据提高性能,我们通过个性化的文本转语音(TTS)系统生成合成语音对ASR模型进行微调。我们介绍了一种通过利用给定说话者的先验记录以及说话者嵌入插值来生成具有可控严重程度的合成构音障碍语音的方法,使得ASR可以在连续的障碍程度上进行微调。在真实和合成构音障碍语音上进行微调将字符错误率(CER)从36-51%(零样本)降低到7.3%。我们的匈牙利语单语种FastConformer ASR模型在同等数据微调下明显优于Whisper-turbo,而合成语音的加入导致CER相对降低了18%。这些结果突显了个性化ASR系统在改善严重语音障碍者的可访问性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对匈牙利语严重言语障碍者的个性化语音转文字系统的开发案例研究。由于最先进的自动语音识别(ASR)模型在零样本转录言语障碍语音时存在高错误率问题,该研究通过个性化文本转语音(TTS)系统生成合成语音来对ASR模型进行微调,以提升性能。该研究引入了一种利用患者发病前的录音和说话人嵌入插值生成可控程度合成言语障碍语音的方法,实现了在连续障碍程度上对ASR微调的能力。在真实和合成言语障碍语音上的微调将零样本时的字符错误率(CER)从36%~51%降低到7.3%。同时,使用相同数据的单调FastConformer_Hu ASR模型相较于Whisper-turbo有明显优势,且合成语音的引入贡献了在CER上的相对减少量达到了约两成。该研究结果展示了个性化ASR系统在改善严重言语障碍者获得服务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 匈牙利严重言语障碍者存在显著转录难度。传统的ASR模型在零样本转录时表现出高错误率。
- 利用个性化TTS系统生成合成语音数据,用于微调ASR模型,以应对真实数据不足的问题。
- 通过结合患者发病前的录音和说话人嵌入插值技术,能够生成可控程度的合成言语障碍语音。
- 在真实和合成数据上微调ASR模型显著降低了字符错误率(CER)。相较于基线模型,性能显著提升。
- 单调FastConformer_Hu ASR模型在处理此问题时性能优于Whisper-turbo模型。这一发现在实际语言应用中具有重要价值。
- 合成数据的引入不仅丰富了训练数据,而且在提高ASR模型性能上起到了关键作用,显著减少了相对错误率。
点此查看论文截图

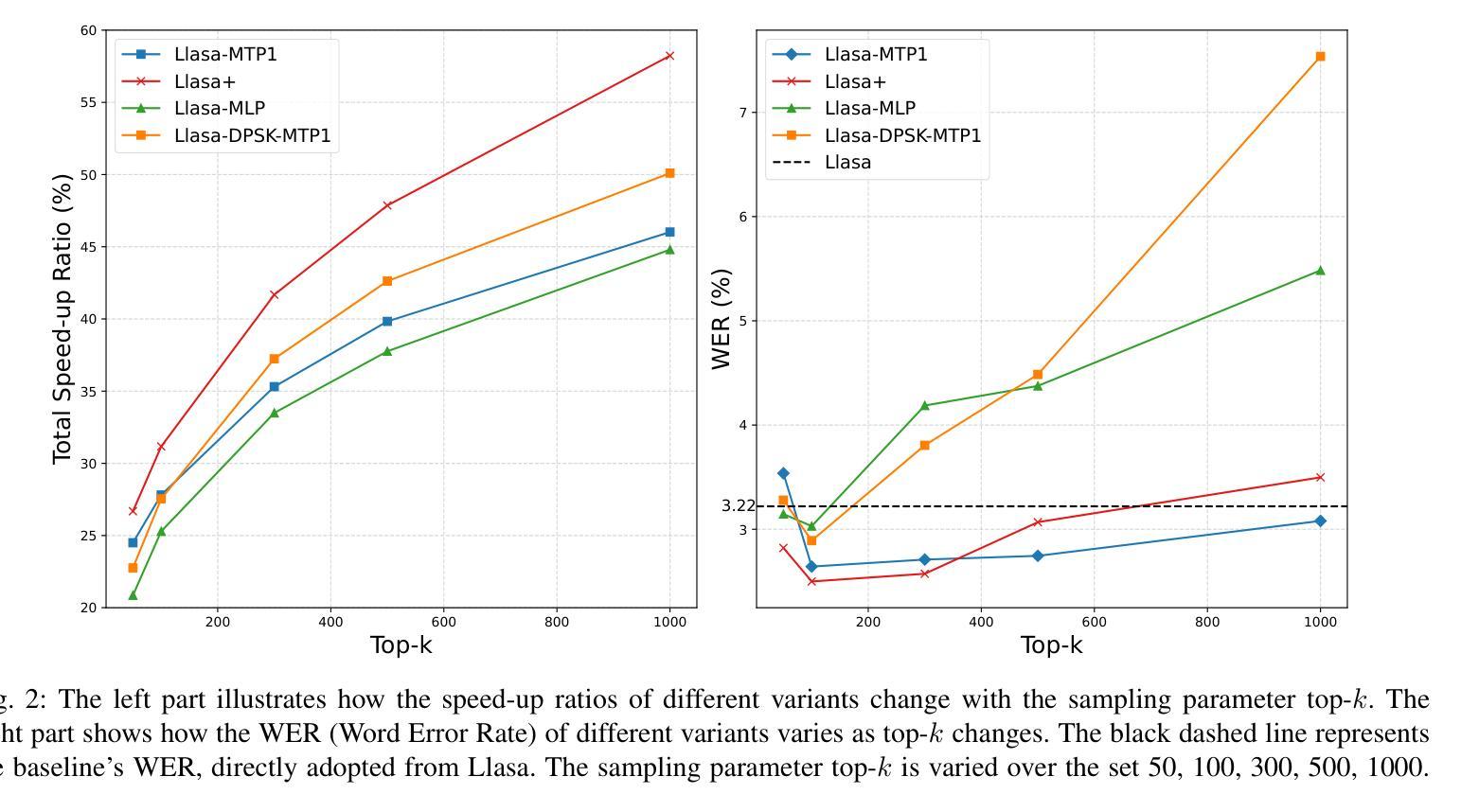
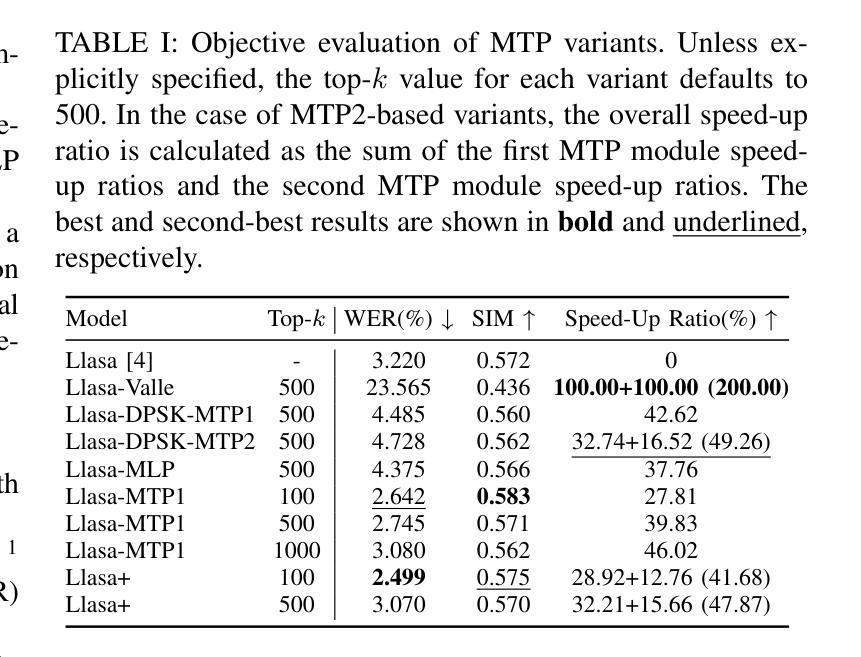
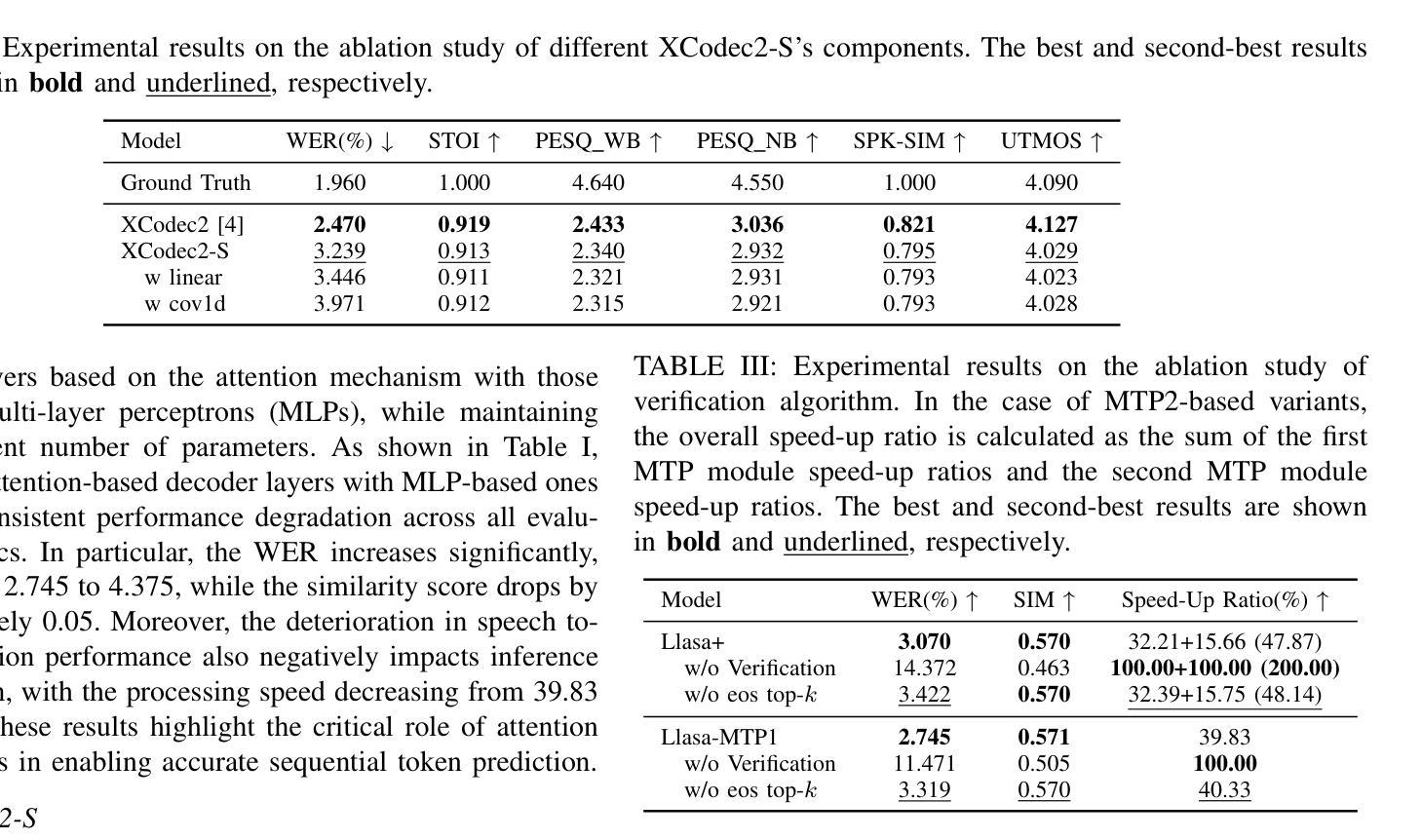
Llasa+: Free Lunch for Accelerated and Streaming Llama-Based Speech Synthesis
Authors:Wenjie Tian, Xinfa Zhu, Hanke Xie, Zhen Ye, Wei Xue, Lei Xie
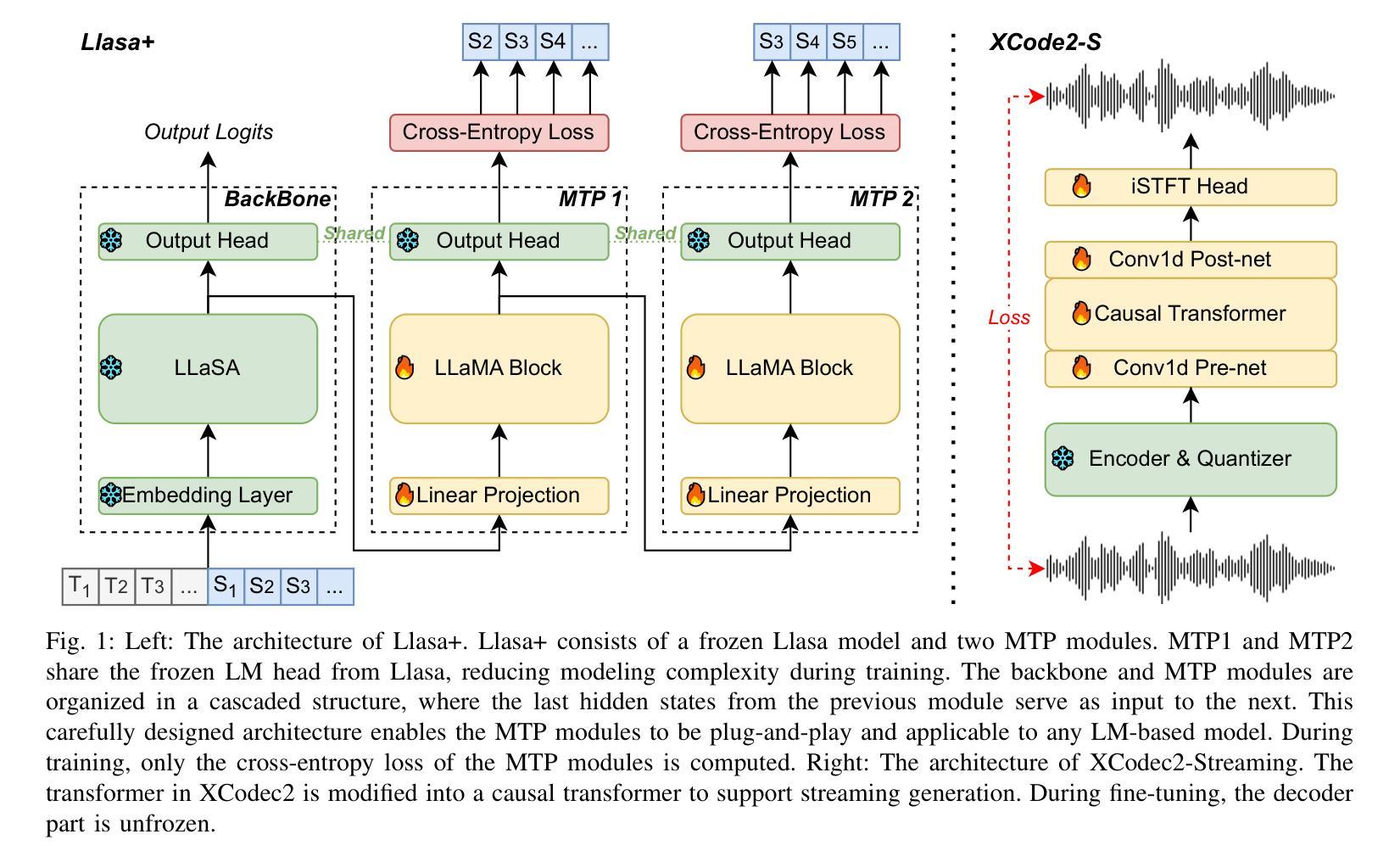
Recent progress in text-to-speech (TTS) has achieved impressive naturalness and flexibility, especially with the development of large language model (LLM)-based approaches. However, existing autoregressive (AR) structures and large-scale models, such as Llasa, still face significant challenges in inference latency and streaming synthesis. To deal with the limitations, we introduce Llasa+, an accelerated and streaming TTS model built on Llasa. Specifically, to accelerate the generation process, we introduce two plug-and-play Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) modules following the frozen backbone. These modules allow the model to predict multiple tokens in one AR step. Additionally, to mitigate potential error propagation caused by inaccurate MTP, we design a novel verification algorithm that leverages the frozen backbone to validate the generated tokens, thus allowing Llasa+ to achieve speedup without sacrificing generation quality. Furthermore, we design a causal decoder that enables streaming speech reconstruction from tokens. Extensive experiments show that Llasa+ achieves a 1.48X speedup without sacrificing generation quality, despite being trained only on LibriTTS. Moreover, the MTP-and-verification framework can be applied to accelerate any LLM-based model. All codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/ASLP-lab/LLaSA_Plus.
近期文本转语音(TTS)的进展已经取得了令人印象深刻的自然度和灵活性,特别是基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法的发展。然而,现有的自回归(AR)结构和大型模型,如Llasa,在推理延迟和流式合成方面仍然面临重大挑战。为了应对这些限制,我们推出了Llasa+,这是一个基于Llasa的加速和流式TTS模型。具体来说,为了加速生成过程,我们在冻结的主干网络之后引入了两个即插即用的多令牌预测(MTP)模块。这些模块允许模型在一个自回归步骤中预测多个令牌。此外,为了缓解由于不准确的多令牌预测可能导致的错误传播,我们设计了一种新的验证算法,该算法利用冻结的主干网络来验证生成的令牌,从而使Llasa+能够在不牺牲生成质量的情况下实现加速。此外,我们还设计了一个因果解码器,能够从头文件中重建流式语音。大量实验表明,Llasa+在仅对LibriTTS进行训练的情况下,实现了1.48倍的速度提升,且没有牺牲生成质量。而且,MTP和验证框架可以应用于加速任何基于LLM的模型。所有代码和模型可在https://github.com/ASLP-lab/LLaSA_Plus上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本到语音(TTS)的最新进展,尤其是大型语言模型(LLM)方法的发展,已经实现了令人印象深刻的自然度和灵活性。为了解决现有自回归(AR)结构和大规模模型(如Llasa)在推理延迟和流式合成方面的挑战,推出了基于Llasa的加速和流式TTS模型Llasa+。通过引入两个即插即用的多令牌预测(MTP)模块和一种新的验证算法,Llasa+能够在不牺牲生成质量的情况下加速生成过程,并实现令牌驱动流式语音重建。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based TTS方法展现出自然度和灵活性。
- 自回归结构和大规模模型在推理延迟和流式合成方面存在挑战。
- Llasa+通过引入MTP模块和验证算法解决了这些问题。
- Llasa+实现了1.48倍的速度提升,且未牺牲生成质量。
- 该方法适用于任何LLM-based模型。
- 所有代码和模型都可在公开仓库中找到:https://github.com/ASLP-lab/LLaSA_Plus。
点此查看论文截图


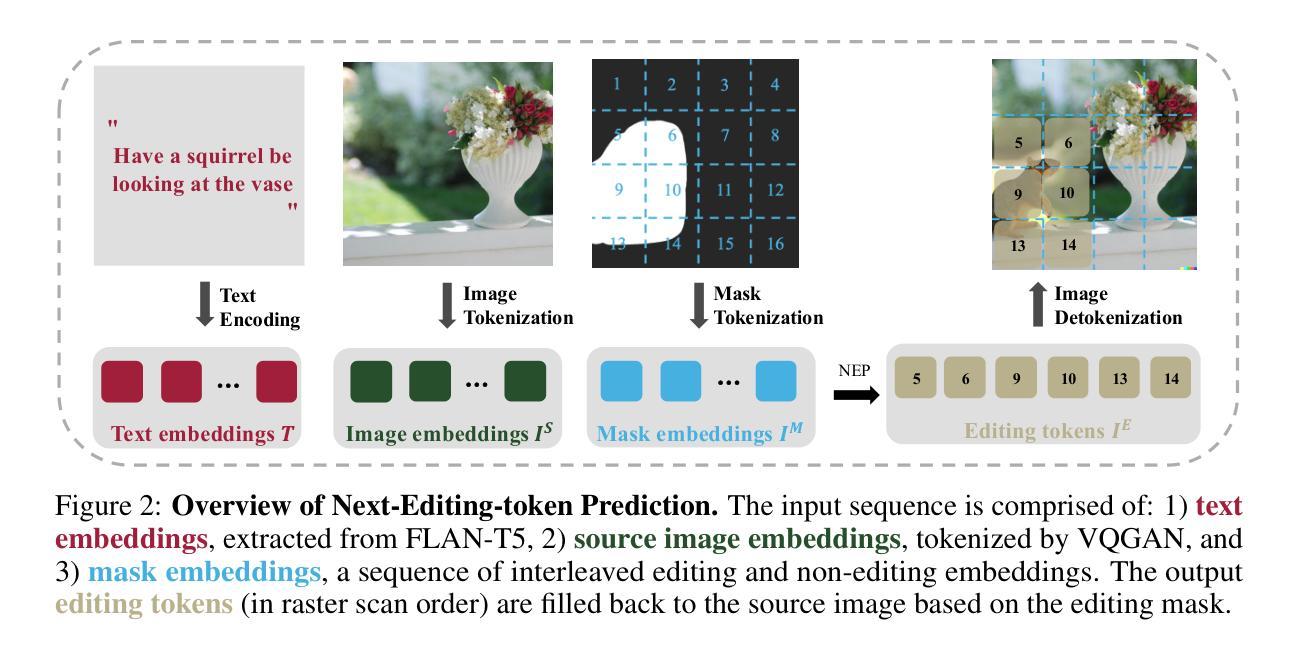
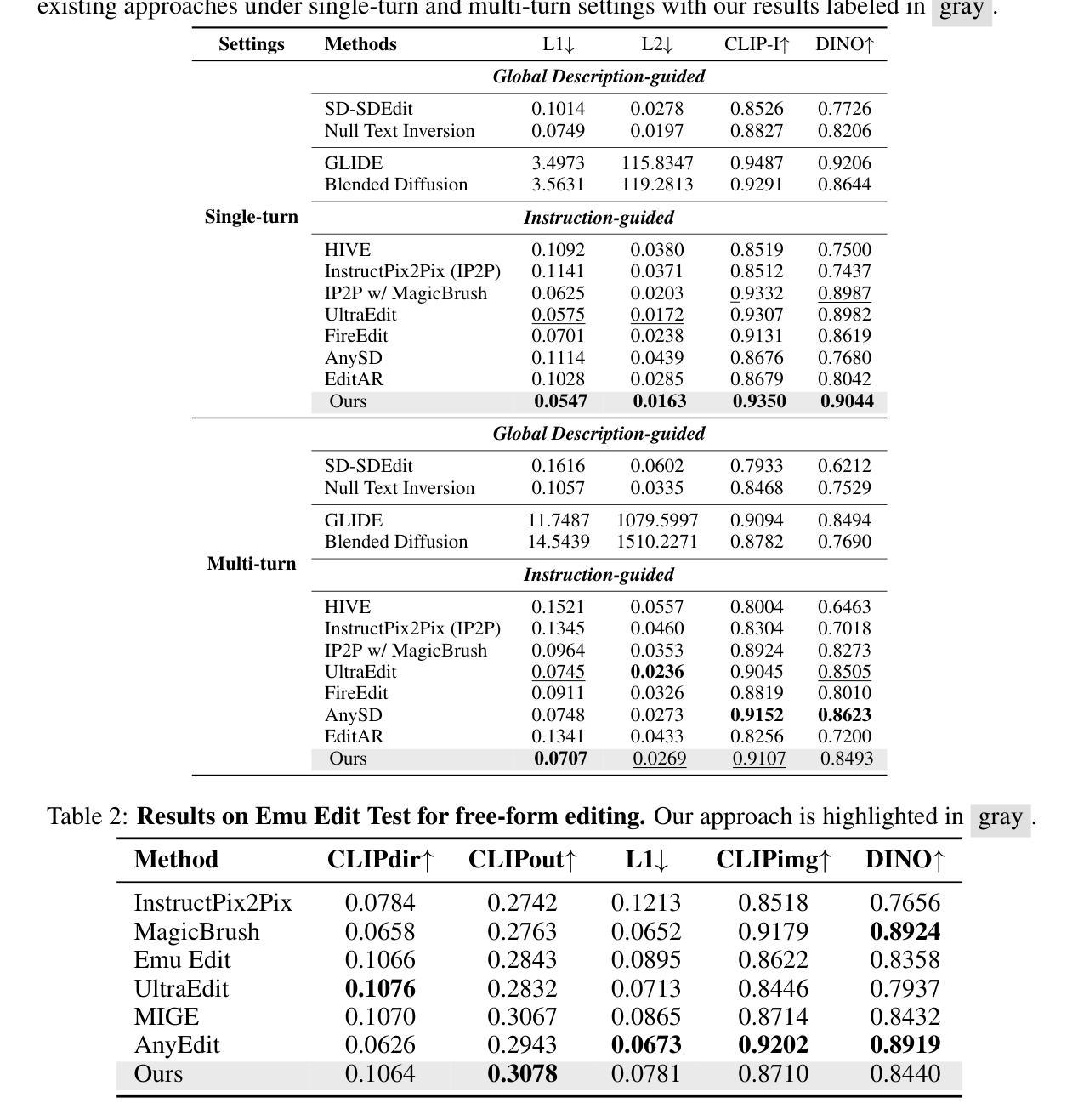
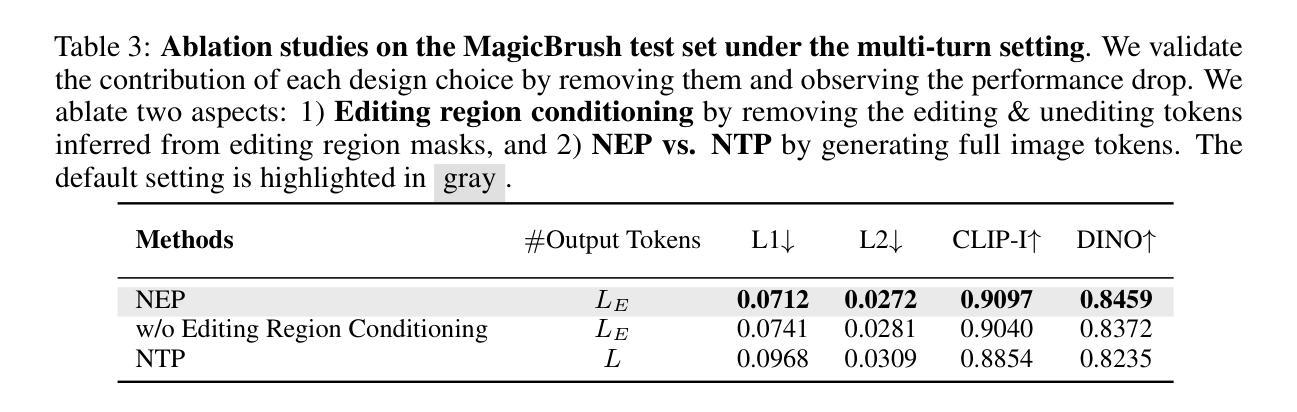
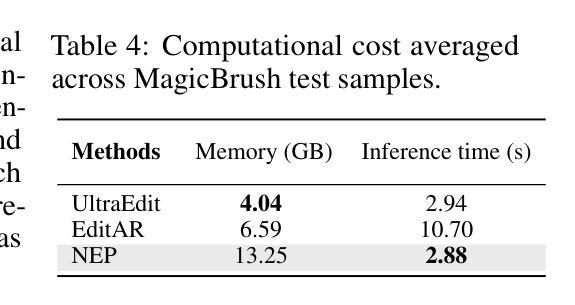
NEP: Autoregressive Image Editing via Next Editing Token Prediction
Authors:Huimin Wu, Xiaojian Ma, Haozhe Zhao, Yanpeng Zhao, Qing Li
Text-guided image editing involves modifying a source image based on a language instruction and, typically, requires changes to only small local regions. However, existing approaches generate the entire target image rather than selectively regenerate only the intended editing areas. This results in (1) unnecessary computational costs and (2) a bias toward reconstructing non-editing regions, which compromises the quality of the intended edits. To resolve these limitations, we propose to formulate image editing as Next Editing-token Prediction (NEP) based on autoregressive image generation, where only regions that need to be edited are regenerated, thus avoiding unintended modification to the non-editing areas. To enable any-region editing, we propose to pre-train an any-order autoregressive text-to-image (T2I) model. Once trained, it is capable of zero-shot image editing and can be easily adapted to NEP for image editing, which achieves a new state-of-the-art on widely used image editing benchmarks. Moreover, our model naturally supports test-time scaling (TTS) through iteratively refining its generation in a zero-shot manner. The project page is: https://nep-bigai.github.io/
文本引导的图像编辑是根据语言指令修改源图像,通常只需要更改小部分区域。然而,现有方法生成的是整个目标图像,而非选择性重新生成预期的编辑区域。这导致了(1)不必要的计算成本;(2)对非编辑区域的重建偏向,这损害了预期的编辑质量。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出将图像编辑制定为基于自回归图像生成的下一个编辑令牌预测(NEP),其中仅重新生成需要编辑的区域,从而避免对非编辑区域进行意外修改。为了实现任何区域编辑,我们提出了一种预训练的任意顺序自回归文本到图像(T2I)模型。一旦训练完成,它就能够进行零样本图像编辑,并可以轻松适应NEP进行图像编辑,在广泛使用的图像编辑基准测试中达到最新水平。此外,我们的模型自然地支持测试时缩放(TTS),通过以零样本方式迭代优化其生成。项目页面是:https://nep-bigai.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The project page is: https://nep-bigai.github.io/
Summary
文本引导的图像编辑是根据语言指令修改源图像,通常只需要改变小部分局部区域。然而,现有方法会生成整个目标图像,而非选择性重新生成仅意图编辑的区域,导致(1)不必要的计算成本;(2)重建非编辑区域的偏向,影响编辑质量。为解决这些局限,我们提出将图像编辑制定为基于自回归图像生成的下一个编辑令牌预测(NEP),仅重新生成需要编辑的区域,避免对非编辑区域的意外修改。为实现任意区域编辑,我们提出预训练一个任意顺序自回归文本到图像(T2I)模型。训练后,该模型能够零样本图像编辑,并可轻松适应NEP用于图像编辑,在广泛使用的图像编辑基准测试中达到最新水平。此外,我们的模型自然支持测试时缩放(TTS),通过零样本方式迭代优化其生成。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导的图像编辑集中于根据语言指令修改源图像的小局部区域。
- 现有方法生成整个目标图像,导致不必要的计算成本和对非编辑区域的重建偏向。
- 为解决此问题,提出将图像编辑制定为下一个编辑令牌预测(NEP)。
- NEP仅重新生成需要编辑的区域,避免对非编辑区域的意外修改。
- 提出预训练一个任意顺序自回归文本到图像(T2I)模型,以实现任意区域编辑。
- 训练后的模型能够零样本图像编辑,并可以轻松适应NEP达到最新水平。
- 模型支持测试时缩放(TTS),通过迭代优化生成质量。
点此查看论文截图

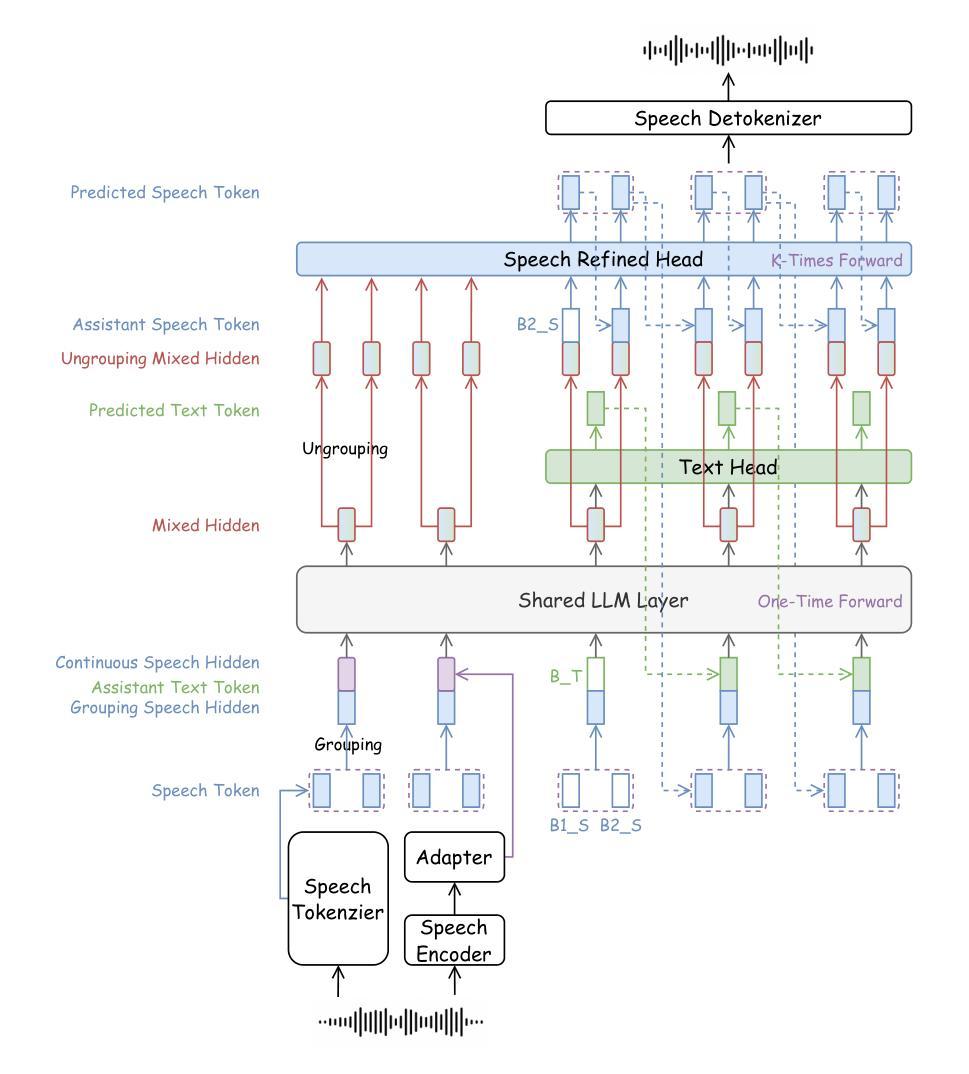
DrVoice: Parallel Speech-Text Voice Conversation Model via Dual-Resolution Speech Representations
Authors:Chao-Hong Tan, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Chong Deng, Qinglin Zhang, Luyao Cheng, Hai Yu, Xin Zhang, Xiang Lv, Tianyu Zhao, Chong Zhang, Yukun Ma, Yafeng Chen, Hui Wang, Jiaqing Liu, Jieping Ye
Recent studies on end-to-end speech generation with large language models (LLMs) have attracted significant community attention, with multiple works extending text-based LLMs to generate discrete speech tokens. Existing approaches primarily fall into two categories: (1) Methods that generate discrete speech tokens independently without incorporating them into the LLM’s autoregressive process, resulting in text generation being unaware of concurrent speech synthesis. (2) Models that generate interleaved or parallel speech-text tokens through joint autoregressive modeling, enabling mutual modality awareness during generation. This paper presents DrVoice, a parallel speech-text voice conversation model based on joint autoregressive modeling, featuring dual-resolution speech representations. Whereas current methods utilize mainly 12.5Hz input audio representation, our proposed dual-resolution mechanism reduces the input frequency for the LLM to 5Hz. Experimental results on Spoken Question Answering benchmarks demonstrate that D RVOICE establishes new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among similar size speech foundation models with relative small amount of data.
最近关于使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行端到端语音生成的研究引起了社区的关注,多项工作将基于文本的LLM扩展到生成离散语音标记。现有方法主要可分为两类:(1)独立生成离散语音标记的方法,不将其纳入LLM的自回归过程,导致文本生成无法意识到并发的语音合成。(2)通过联合自回归建模生成交织或并行语音文本标记的模型,从而在生成过程中实现两种模式的相互感知。本文提出了DrVoice,一个基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本对话模型,具有双分辨率语音表示。而当前方法主要使用12.5Hz的输入音频表示,我们提出的双分辨率机制将LLM的输入频率降低到5Hz。在口语问答基准测试上的实验结果表明,DrVoice在类似规模的语音基础模型中建立了新的最先进的性能,并且所需数据量相对较少。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
近期关于使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行端到端语音生成的研究引起了社区的关注。现有方法主要分为两类,分别是在独立的方式生成离散语音令牌或与LLM的自回归过程结合生成语音文本令牌。本文提出了一个基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本对话模型DrVoice,具有双分辨率语音表示功能。实验结果表明,在Spoken Question Answering基准测试中,相较于其他类似规模的语音基础模型,DrVoice在仅使用少量数据的情况下便达到了新的业界最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 端到端语音生成研究正受到大型语言模型(LLMs)的推动,吸引社区关注。
- 当前方法主要分为独立生成离散语音令牌和结合LLM自回归过程生成语音文本令牌两类。
- DrVoice模型是一个基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本对话模型。
- DrVoice具有双分辨率语音表示功能,可降低输入频率至5Hz。
- DrVoice在Spoken Question Answering基准测试中建立了新的业界最佳性能。
- DrVoice相较于其他类似规模的语音基础模型,在仅使用少量数据的情况下便取得了良好性能。
点此查看论文截图