⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
UltraAD: Fine-Grained Ultrasound Anomaly Classification via Few-Shot CLIP Adaptation
Authors:Yue Zhou, Yuan Bi, Wenjuan Tong, Wei Wang, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
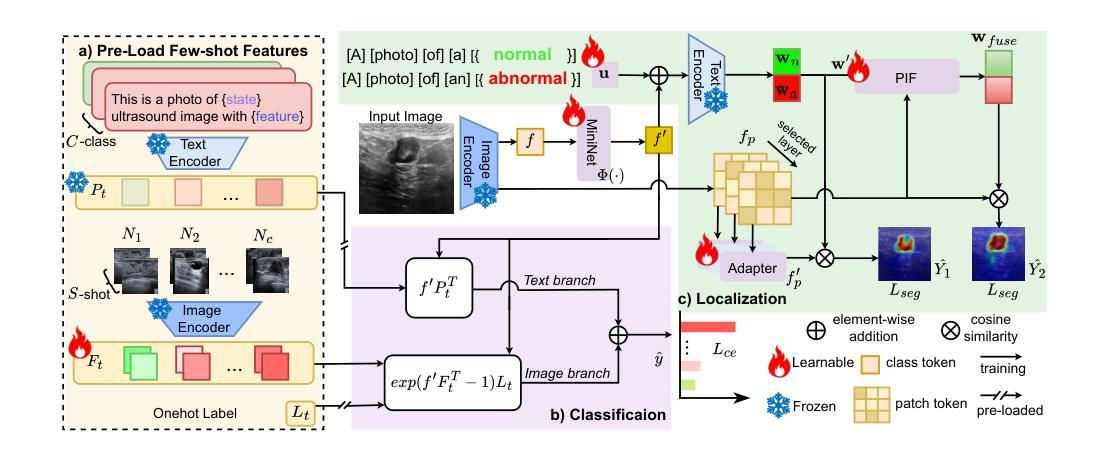
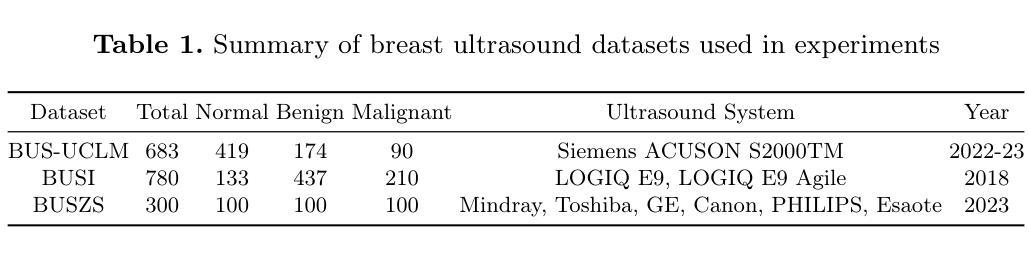
Precise anomaly detection in medical images is critical for clinical decision-making. While recent unsupervised or semi-supervised anomaly detection methods trained on large-scale normal data show promising results, they lack fine-grained differentiation, such as benign vs. malignant tumors. Additionally, ultrasound (US) imaging is highly sensitive to devices and acquisition parameter variations, creating significant domain gaps in the resulting US images. To address these challenges, we propose UltraAD, a vision-language model (VLM)-based approach that leverages few-shot US examples for generalized anomaly localization and fine-grained classification. To enhance localization performance, the image-level token of query visual prototypes is first fused with learnable text embeddings. This image-informed prompt feature is then further integrated with patch-level tokens, refining local representations for improved accuracy. For fine-grained classification, a memory bank is constructed from few-shot image samples and corresponding text descriptions that capture anatomical and abnormality-specific features. During training, the stored text embeddings remain frozen, while image features are adapted to better align with medical data. UltraAD has been extensively evaluated on three breast US datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both lesion localization and fine-grained medical classification. The code will be released upon acceptance.
医学图像中的精确异常检测对于临床决策至关重要。虽然最近基于大规模正常数据训练的监督或无监督异常检测方法显示出有希望的结果,但它们缺乏精细的区分度,如良性和恶性肿瘤。此外,超声(US)成像对设备和采集参数的变化高度敏感,导致超声图像中存在明显的领域差异。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了UltraAD,一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法,它利用少量超声样本进行通用异常定位和精细分类。为了提高定位性能,首先融合查询视觉原型的图像级令牌和可学习的文本嵌入。然后,将图像信息提示特征与补丁级令牌进一步集成,细化局部表示以提高准确性。对于精细分类,从少量图像样本和相应的文本描述中构建了一个内存银行,以捕获解剖结构和异常特定的特征。在训练过程中,存储的文本嵌入保持不变,而图像特征更好地适应医学数据。UltraAD在三个乳腺超声数据集上进行了广泛评估,在病灶定位和精细医学分类方面均优于最新方法。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的UltraAD方法,用于医学超声图像中的异常检测与精细分类。通过融合查询视觉原型与可学习文本嵌入,提高定位性能。利用少量超声图像样本及其文本描述构建记忆库,进行精细分类。在三个乳腺超声数据集上的实验表明,UltraAD在病灶定位和精细分类方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- UltraAD方法结合了视觉语言模型(VLM),用于医学超声图像中的异常检测与精细分类。
- 通过融合查询视觉原型与文本嵌入,提高异常定位性能。
- 利用少量超声图像样本及其文本描述构建记忆库,实现精细分类。
- 该方法提高了对医学超声图像中病灶的识别准确性。
- UltraAD在三个乳腺超声数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
- UltraAD具有广泛的应用前景,可用于提高医疗影像诊断的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图