⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
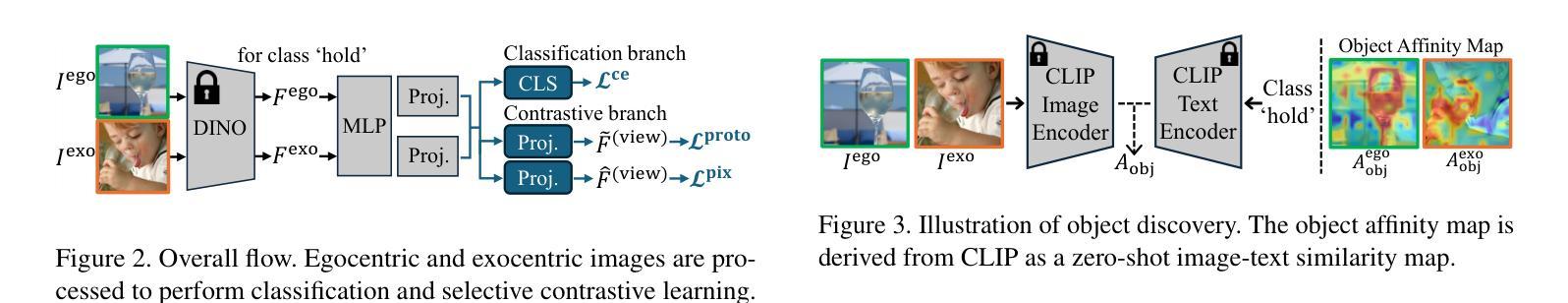
Selective Contrastive Learning for Weakly Supervised Affordance Grounding
Authors:WonJun Moon, Hyun Seok Seong, Jae-Pil Heo
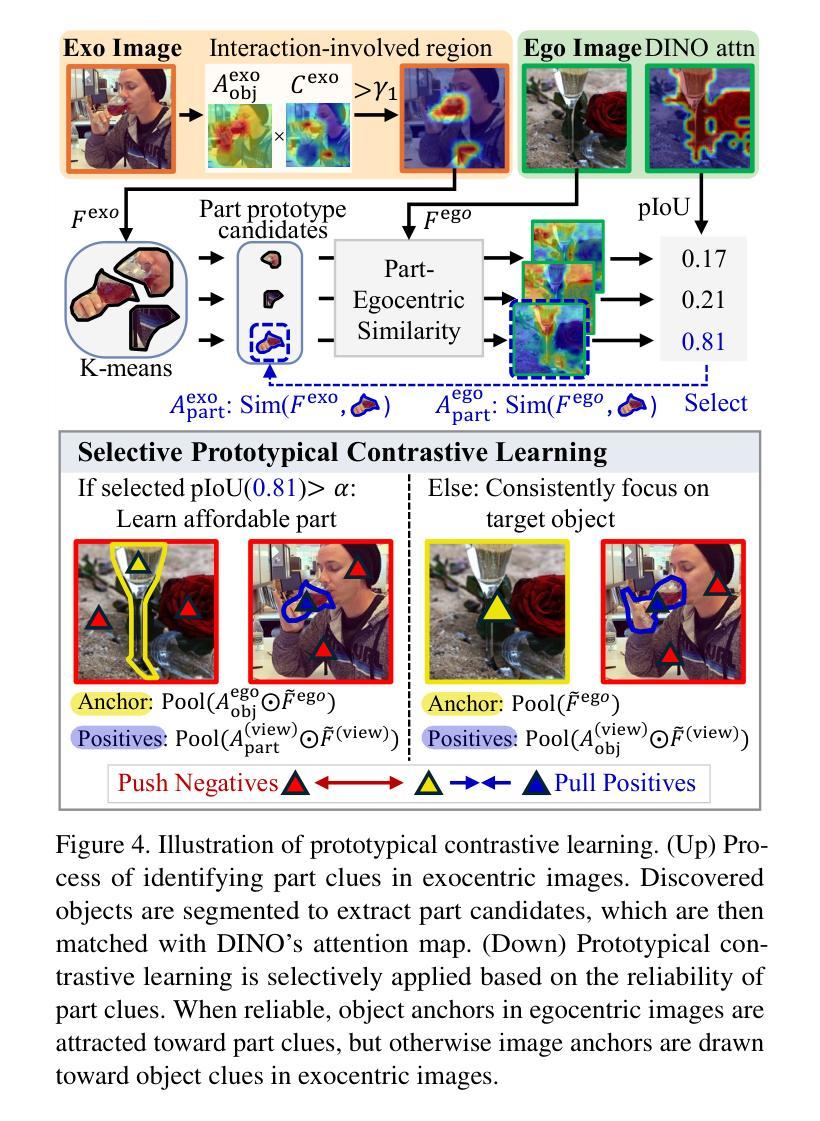
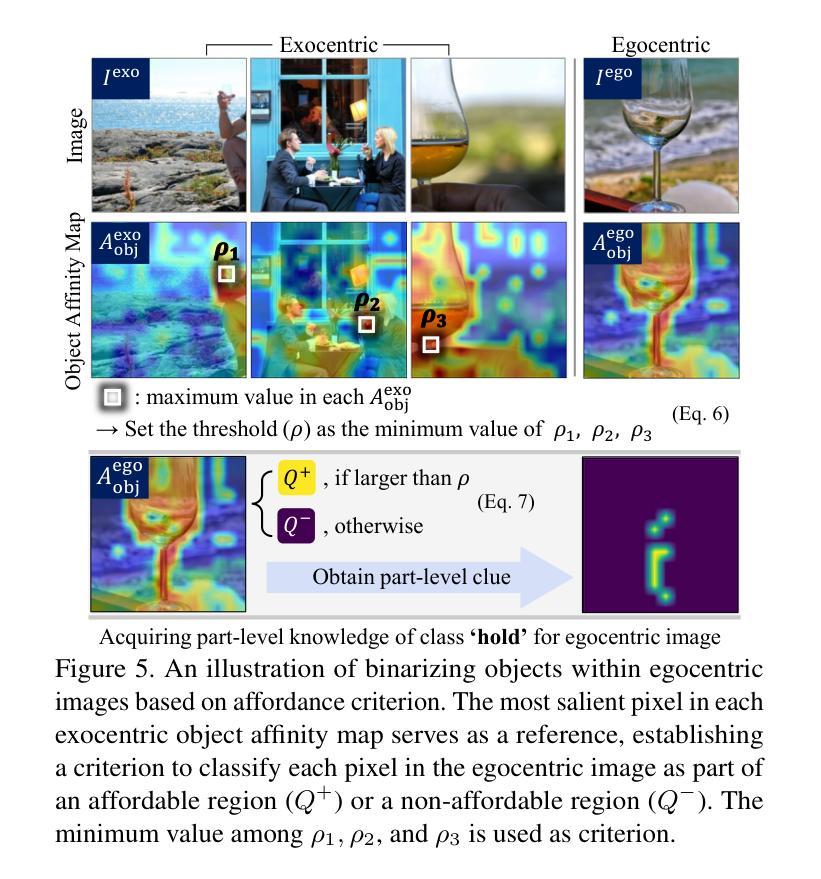
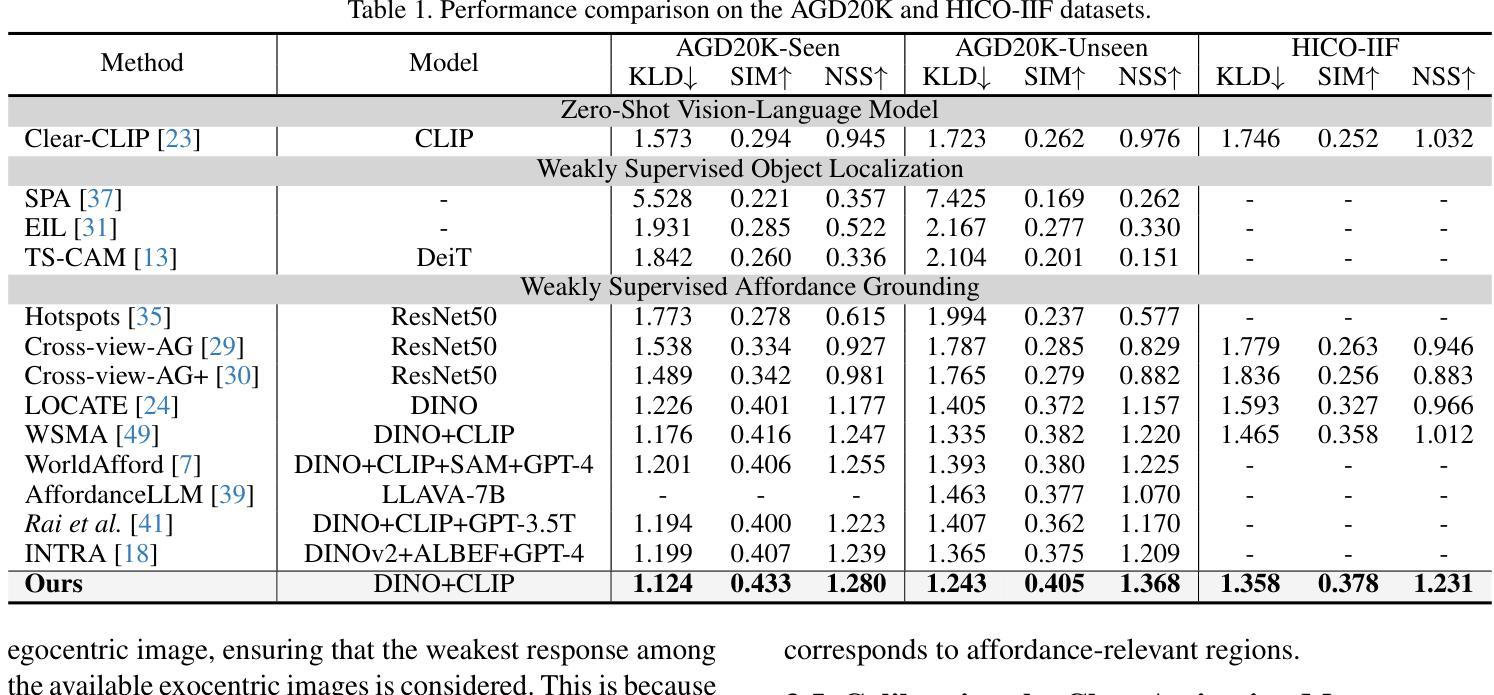
Facilitating an entity’s interaction with objects requires accurately identifying parts that afford specific actions. Weakly supervised affordance grounding (WSAG) seeks to imitate human learning from third-person demonstrations, where humans intuitively grasp functional parts without needing pixel-level annotations. To achieve this, grounding is typically learned using a shared classifier across images from different perspectives, along with distillation strategies incorporating part discovery process. However, since affordance-relevant parts are not always easily distinguishable, models primarily rely on classification, often focusing on common class-specific patterns that are unrelated to affordance. To address this limitation, we move beyond isolated part-level learning by introducing selective prototypical and pixel contrastive objectives that adaptively learn affordance-relevant cues at both the part and object levels, depending on the granularity of the available information. Initially, we find the action-associated objects in both egocentric (object-focused) and exocentric (third-person example) images by leveraging CLIP. Then, by cross-referencing the discovered objects of complementary views, we excavate the precise part-level affordance clues in each perspective. By consistently learning to distinguish affordance-relevant regions from affordance-irrelevant background context, our approach effectively shifts activation from irrelevant areas toward meaningful affordance cues. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Codes are available at github.com/hynnsk/SelectiveCL.
促进实体与物体的交互需要准确识别能够实现特定动作的部分。弱监督功能定位(WSAG)旨在模仿人类从第三人称演示中学习,人类能够直觉地把握功能部分而无需像素级的注释。为了实现这一点,通常通过在不同角度的图像中共享分类器来学习定位,同时使用包含部分发现过程的蒸馏策略。然而,由于功能相关的部分并不总是易于区分,模型主要依赖于分类,经常聚焦于与功能无关的通用类别特定模式。为了解决这一局限性,我们通过引入选择性原型和像素对比目标,超越了孤立的部分级别学习,这些目标可以自适应地学习部分和对象级别的功能相关线索,这取决于可用信息的粒度。首先,我们通过利用CLIP在自我中心(以对象为中心)和外向中心(第三人称示例)的图像中找到与动作相关的对象。然后,通过交叉引用不同视角的互补视图中的发现对象,我们挖掘出每个视角中精确的部分级别功能线索。通过持续学习区分功能相关区域和功能无关的背景上下文,我们的方法有效地将激活从无关区域转移到有意义的功能线索。实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在github.com/hynnsk/SelectiveCL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了通过引入选择性原型和像素对比目标,实现基于弱监督的交互动作识别方法。该方法在无需像素级标注的情况下,能够从第三人称演示中学习模仿人类交互行为,通过自适应学习在不同粒度下的动作相关线索来提升交互行为的识别精度。此外,通过挖掘不同视角中的互补信息,模型能够有效地挖掘出精确的动作相关区域线索。实验结果证明了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督下的动作相关部分识别是本文的核心问题。为了解决这个问题,引入了选择性原型和像素对比目标来适应性地学习动作相关的线索。
- 模型能够从第三人称演示中学习模仿人类交互行为,模仿的过程中使用了蒸馏策略和合并视角的方法来发掘精确的动作相关线索。
- 通过结合不同的图像视角(自我中心和第三人称视角),可以挖掘出不同视角中的互补信息。这对于更准确地识别动作相关区域非常重要。
点此查看论文截图

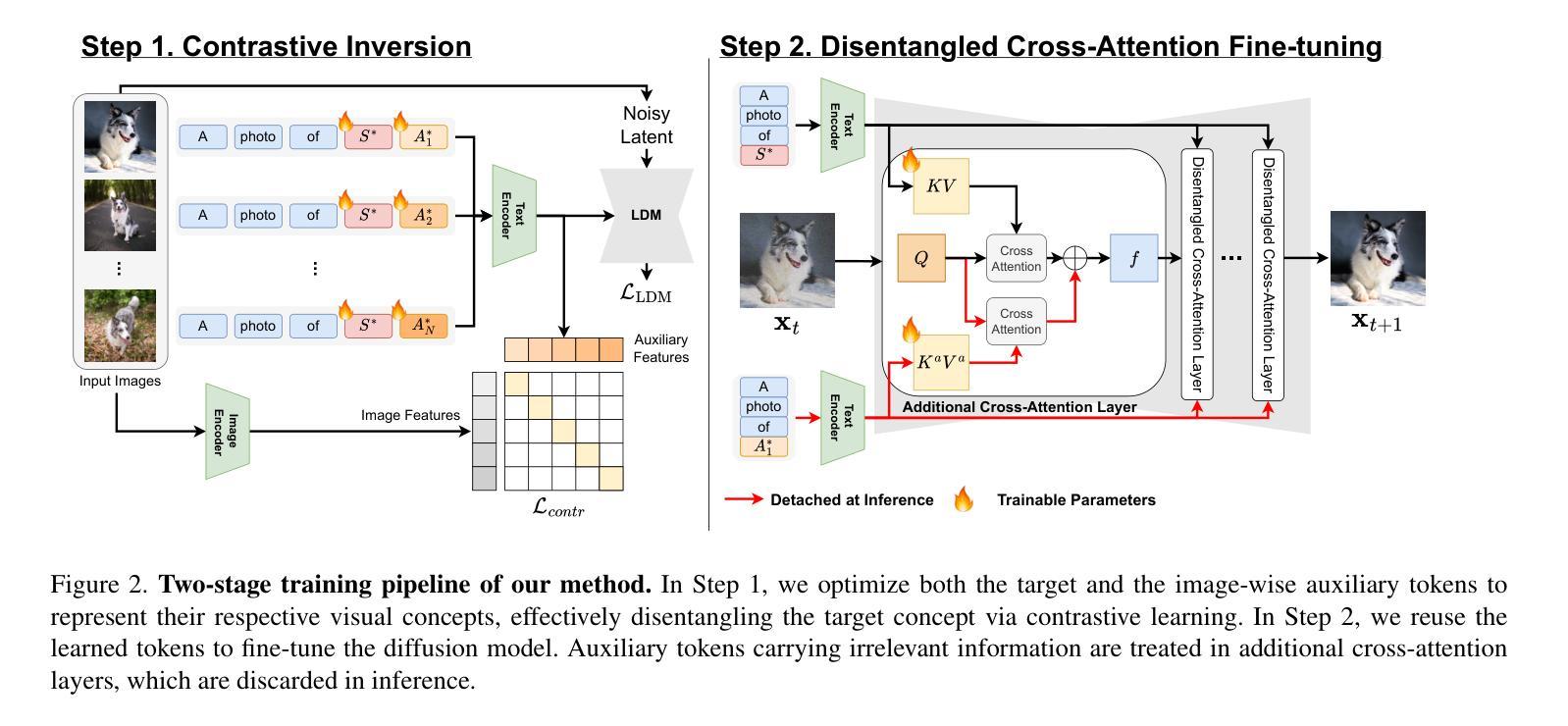
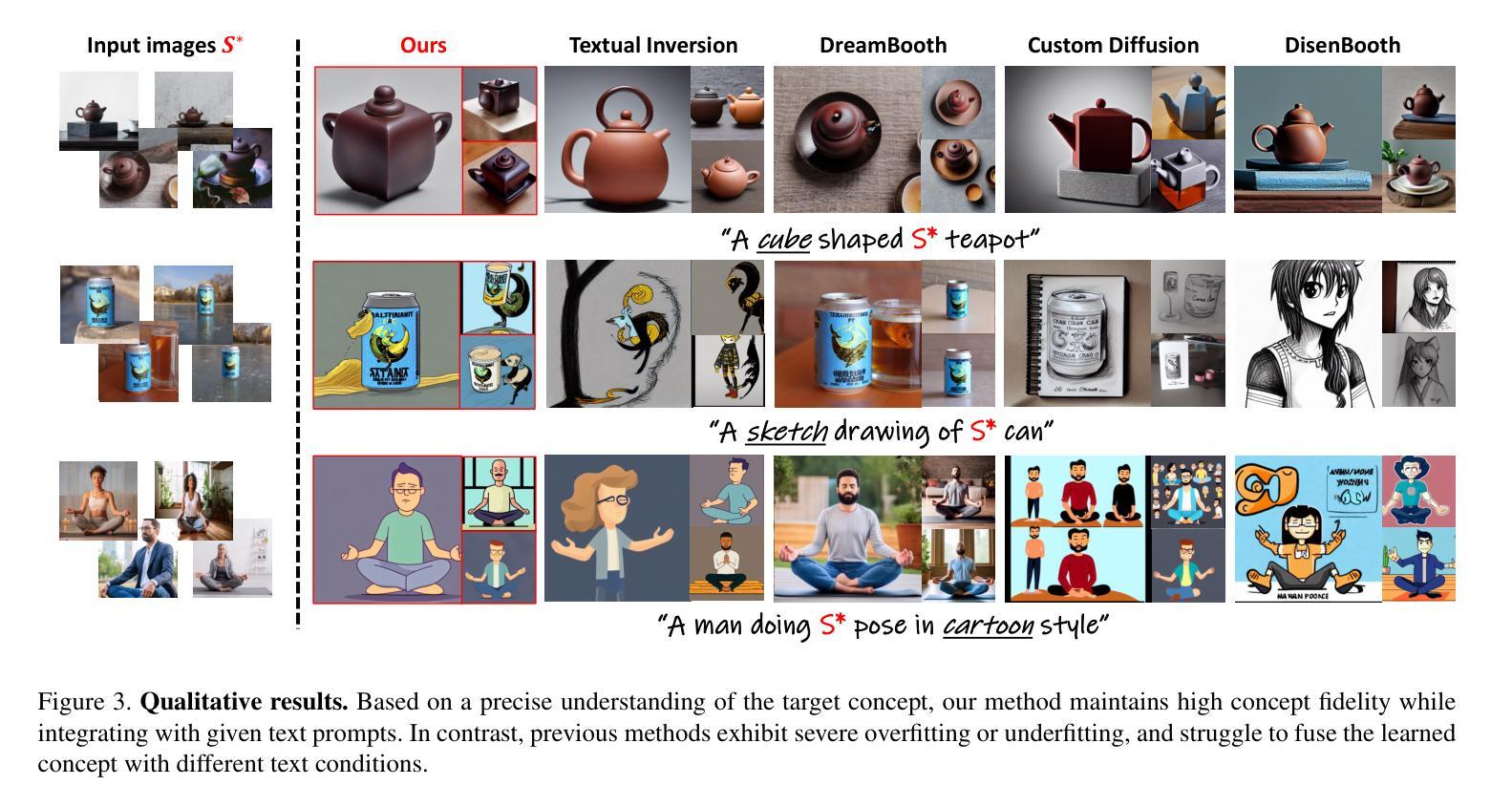
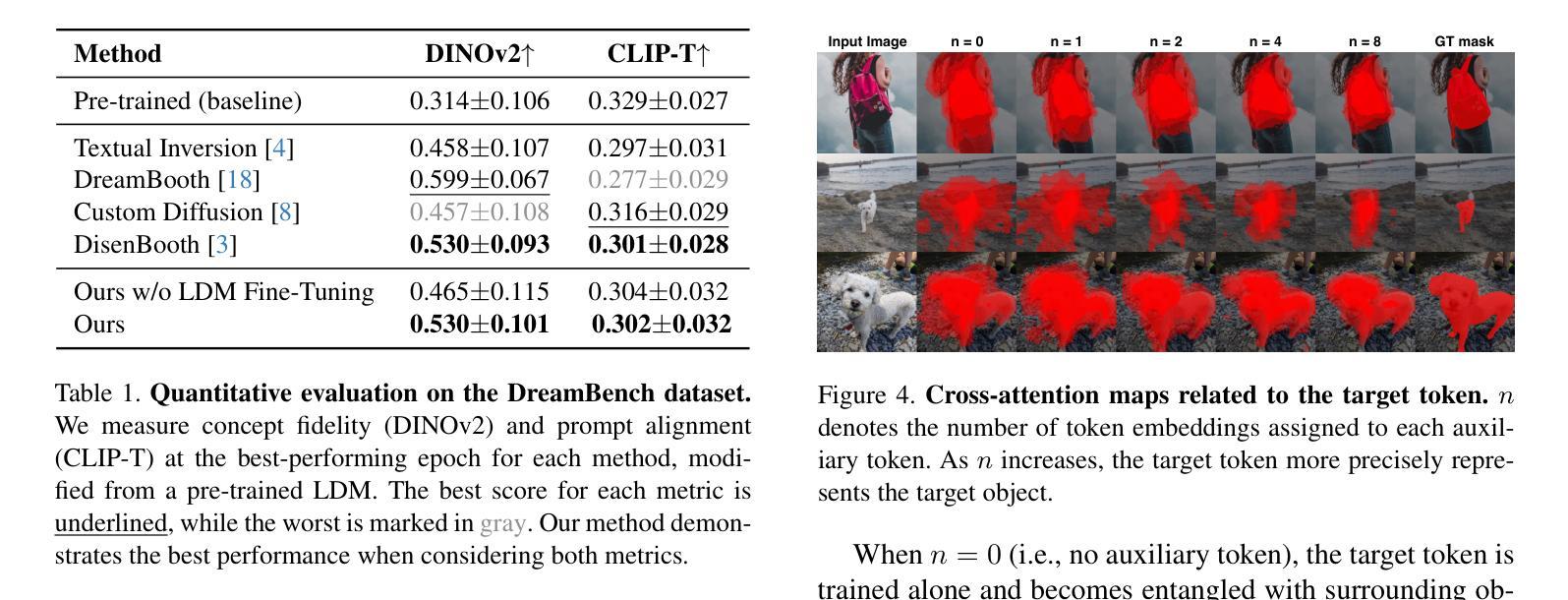
Comparison Reveals Commonality: Customized Image Generation through Contrastive Inversion
Authors:Minseo Kim, Minchan Kwon, Dongyeun Lee, Yunho Jeon, Junmo Kim
The recent demand for customized image generation raises a need for techniques that effectively extract the common concept from small sets of images. Existing methods typically rely on additional guidance, such as text prompts or spatial masks, to capture the common target concept. Unfortunately, relying on manually provided guidance can lead to incomplete separation of auxiliary features, which degrades generation quality.In this paper, we propose Contrastive Inversion, a novel approach that identifies the common concept by comparing the input images without relying on additional information. We train the target token along with the image-wise auxiliary text tokens via contrastive learning, which extracts the well-disentangled true semantics of the target. Then we apply disentangled cross-attention fine-tuning to improve concept fidelity without overfitting. Experimental results and analysis demonstrate that our method achieves a balanced, high-level performance in both concept representation and editing, outperforming existing techniques.
近期对定制图像生成的需求,催生了对从小规模图像集中有效提取共性概念的技术需求。现有方法通常依赖于额外的指导,如文本提示或空间蒙版,来捕获共同的目标概念。然而,依赖人工提供的指导可能会导致辅助特征分离不完全,从而降低了生成质量。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为“对比反转”(Contrastive Inversion)的新方法,它通过比较输入图像来识别共同概念,而无需依赖额外信息。我们通过对比学习训练目标标记和图像级的辅助文本标记,提取出目标对象的良好分离的真实语义。然后,我们应用解纠缠交叉注意力微调(disentangled cross-attention fine-tuning),以提高概念保真度,同时避免过度拟合。实验结果表明,我们的方法在概念表示和编辑方面都实现了平衡的高水平性能,优于现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 workshop (AI4CC)
Summary
本文提出一种名为Contrastive Inversion的新方法,通过比较输入图像来识别共同概念,无需额外信息。通过对比学习训练目标标记和图像级辅助文本标记,提取出目标物的良好分离语义。然后应用解纠缠交叉注意力微调来提高概念保真度,避免过拟合。实验结果分析表明,该方法在概念表示和编辑方面都实现了高水平的平衡性能,优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- Contrastive Inversion方法通过对比输入图像来识别共同概念,无需额外指导信息。
- 对比学习被用于训练目标标记和图像级辅助文本标记,以提取目标物的良好分离语义。
- 解纠缠交叉注意力微调用于提高概念保真度,避免过拟合。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在概念表示和编辑方面都表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法实现了高平衡水平性能,既关注概念识别又关注图像生成质量。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法在性能上有所超越。
点此查看论文截图