⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
GAPNet: A Lightweight Framework for Image and Video Salient Object Detection via Granularity-Aware Paradigm
Authors:Yu-Huan Wu, Wei Liu, Zi-Xuan Zhu, Zizhou Wang, Yong Liu, Liangli Zhen
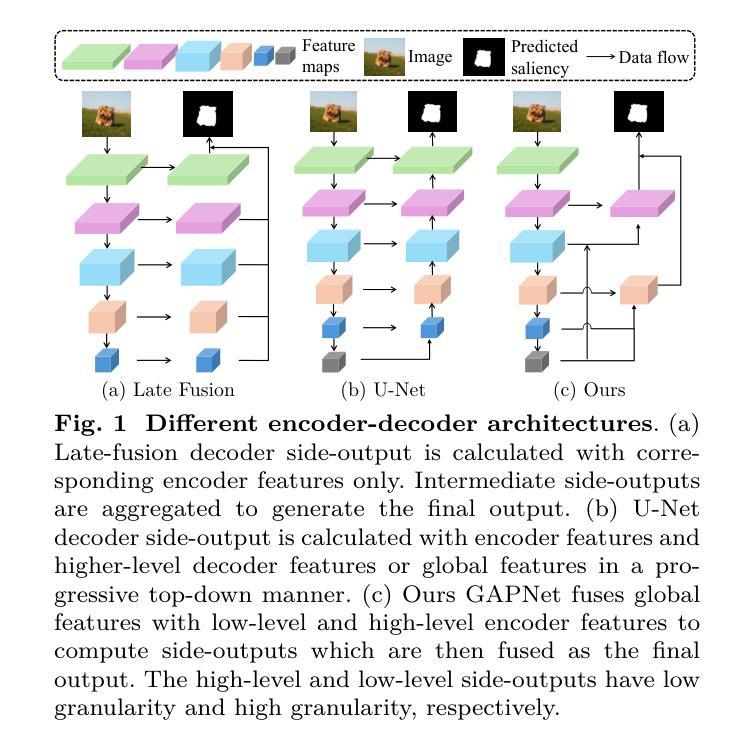
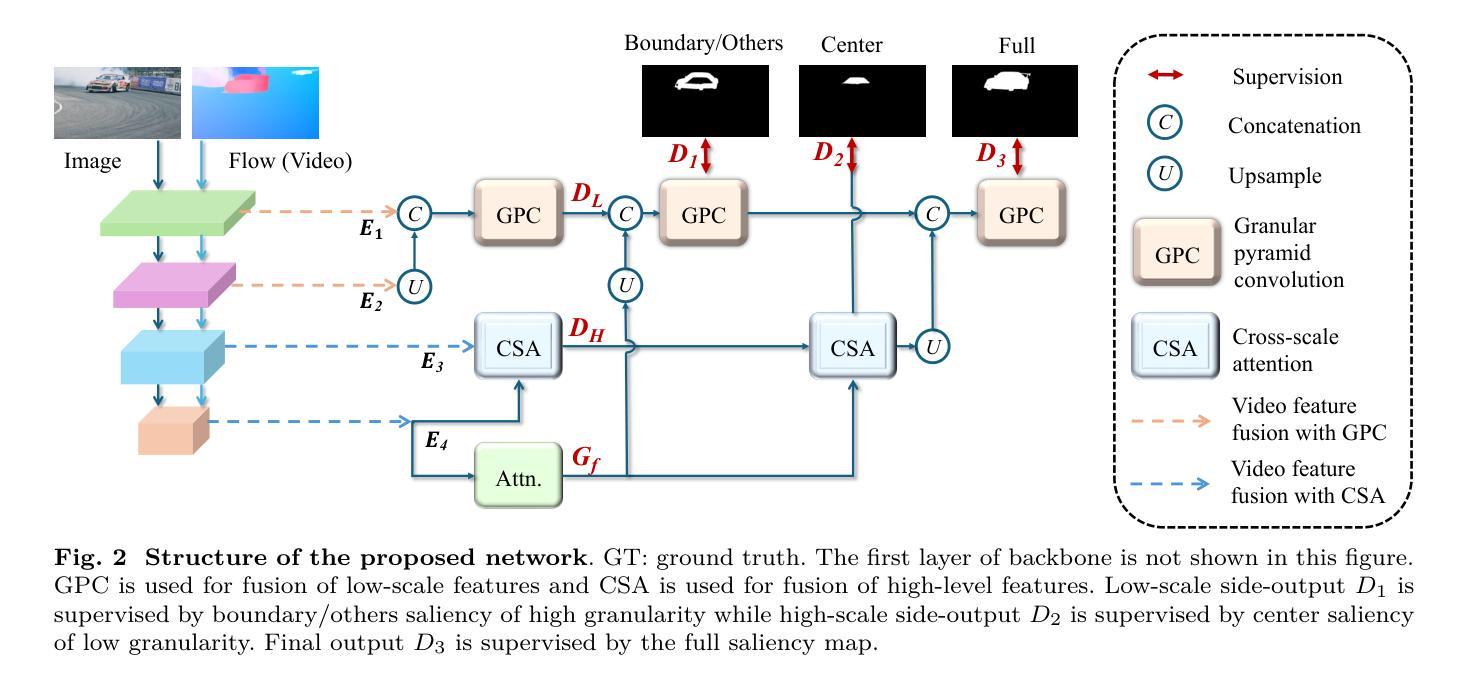
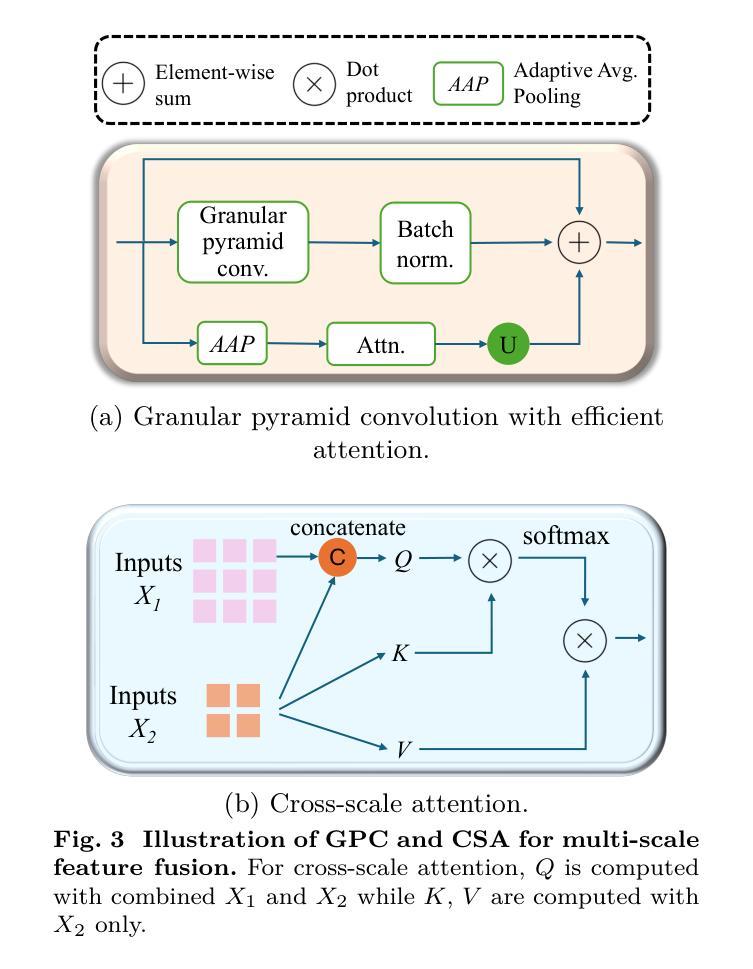
Recent salient object detection (SOD) models predominantly rely on heavyweight backbones, incurring substantial computational cost and hindering their practical application in various real-world settings, particularly on edge devices. This paper presents GAPNet, a lightweight network built on the granularity-aware paradigm for both image and video SOD. We assign saliency maps of different granularities to supervise the multi-scale decoder side-outputs: coarse object locations for high-level outputs and fine-grained object boundaries for low-level outputs. Specifically, our decoder is built with granularity-aware connections which fuse high-level features of low granularity and low-level features of high granularity, respectively. To support these connections, we design granular pyramid convolution (GPC) and cross-scale attention (CSA) modules for efficient fusion of low-scale and high-scale features, respectively. On top of the encoder, a self-attention module is built to learn global information, enabling accurate object localization with negligible computational cost. Unlike traditional U-Net-based approaches, our proposed method optimizes feature utilization and semantic interpretation while applying appropriate supervision at each processing stage. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method achieves a new state-of-the-art performance among lightweight image and video SOD models. Code is available at https://github.com/yuhuan-wu/GAPNet.
最近的显著目标检测(SOD)模型主要依赖于重量级的骨干网络,这产生了巨大的计算成本,并阻碍了它们在各种实际场景中的实际应用,特别是在边缘设备上。本文提出了GAPNet,一个基于粒度感知范式的轻量级网络,用于图像和视频SOD。我们为不同粒度的显著性图分配了监督多尺度解码器侧输出:高级输出用于粗略对象位置,低级输出用于精细对象边界。具体来说,我们的解码器是建立在一系列粒度感知连接上的,这些连接将粗粒度的高级特征和细粒度的低级特征分别融合。为了支持这些连接,我们设计了粒度金字塔卷积(GPC)和跨尺度注意力(CSA)模块,以有效地融合低尺度和高尺度特征。在编码器之上,建立了一个自注意力模块来学习全局信息,以极低的计算成本实现准确的对象定位。与传统的基于U-Net的方法不同,我们提出的方法优化了特征利用和语义解释,并在每个处理阶段应用了适当的监督。大量实验表明,该方法在轻量级图像和视频SOD模型中达到了最新的一流性能。代码可访问于https://github.com/yuhuan-wu/GAPNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables
Summary
超轻量级网络GAPNet被提出用于图像和视频显著性目标检测(SOD),其采用粒度感知范式,适用于边缘设备等实际应用场景。网络通过分配不同粒度的显著性图来监督多尺度解码器输出,并采用粒度感知连接融合高低级别的特征。此外,还设计了金字塔卷积和跨尺度注意力模块以实现高效的特征融合。实验表明,该方法在轻量级图像和视频SOD模型中取得了最新状态的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- GAPNet是一种超轻量级的网络模型,用于图像和视频显著性目标检测(SOD)。
- GAPNet采用粒度感知范式,旨在适应多种实际应用场景,特别是在边缘设备上。
- GAPNet通过分配不同粒度的显著性图来监督多尺度解码器输出,实现更精细的目标检测。
- GAPNet采用粒度感知连接融合高低级别的特征,提高特征利用率和语义解释能力。
- 网络设计包括金字塔卷积和跨尺度注意力模块,以实现高效的特征融合。
- GAPNet具有自我注意力模块,能够学习全局信息,从而实现准确的目标定位,同时计算成本低。
- 实验表明,GAPNet在轻量级图像和视频SOD模型中取得了最新性能的提升。
点此查看论文截图

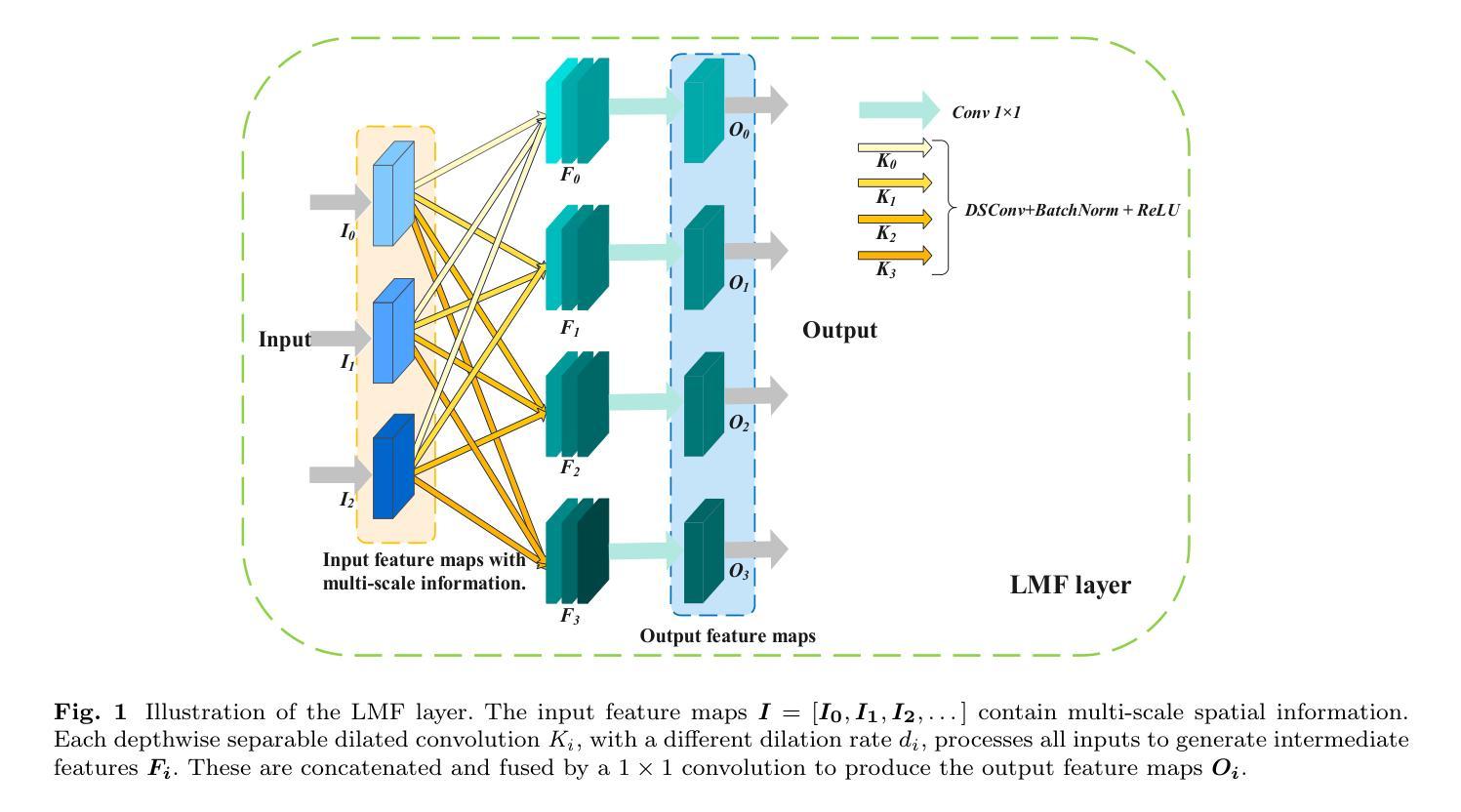
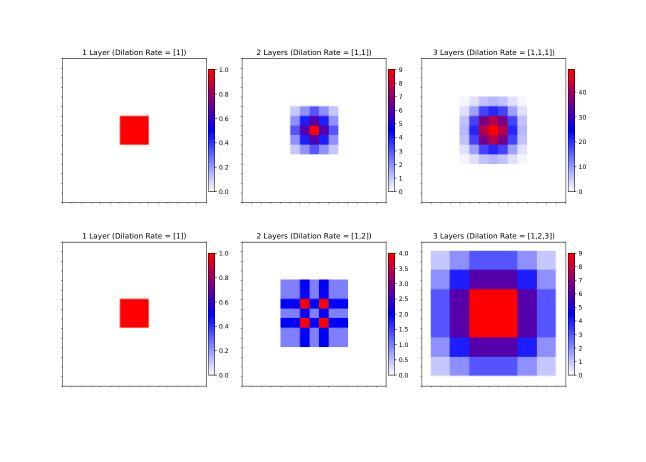
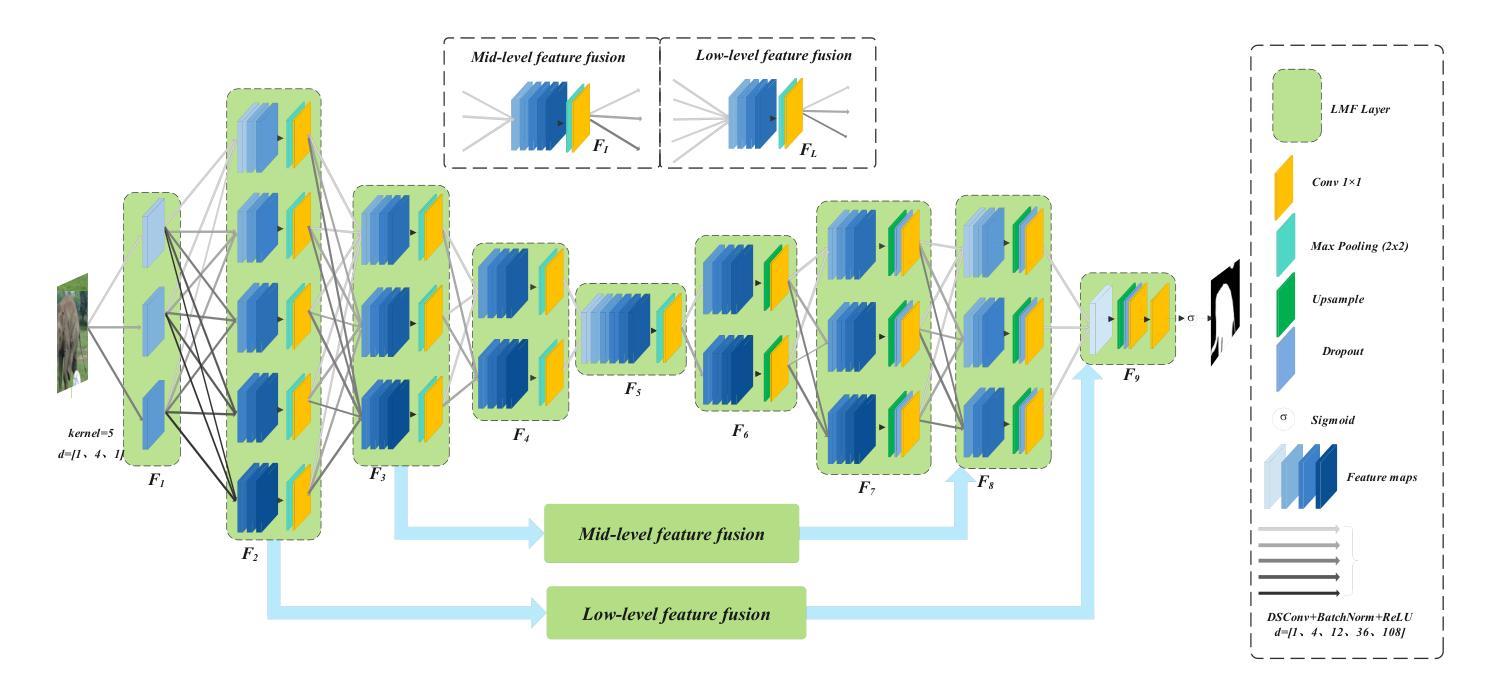
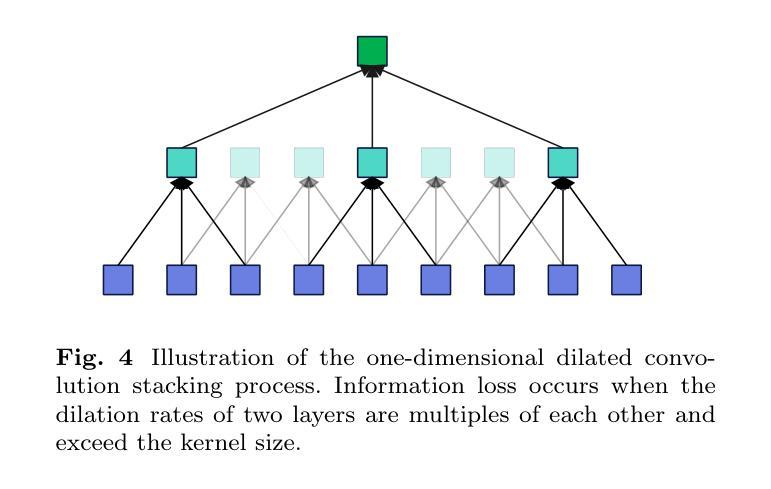
Lightweight Multi-Scale Feature Extraction with Fully Connected LMF Layer for Salient Object Detection
Authors:Yunpeng Shi, Lei Chen, Xiaolu Shen, Yanju Guo
In the domain of computer vision, multi-scale feature extraction is vital for tasks such as salient object detection. However, achieving this capability in lightweight networks remains challenging due to the trade-off between efficiency and performance. This paper proposes a novel lightweight multi-scale feature extraction layer, termed the LMF layer, which employs depthwise separable dilated convolutions in a fully connected structure. By integrating multiple LMF layers, we develop LMFNet, a lightweight network tailored for salient object detection. Our approach significantly reduces the number of parameters while maintaining competitive performance. Here, we show that LMFNet achieves state-of-the-art or comparable results on five benchmark datasets with only 0.81M parameters, outperforming several traditional and lightweight models in terms of both efficiency and accuracy. Our work not only addresses the challenge of multi-scale learning in lightweight networks but also demonstrates the potential for broader applications in image processing tasks. The related code files are available at https://github.com/Shi-Yun-peng/LMFNet
在计算机视觉领域,多尺度特征提取对于显著性目标检测等任务至关重要。然而,在轻量级网络中实现这种能力仍然具有挑战性,因为效率和性能之间存在权衡。本文提出了一种新型轻量级多尺度特征提取层,称为LMF层,它采用全连接结构中深度可分离的膨胀卷积。通过集成多个LMF层,我们开发出了针对显著性目标检测的轻量级网络LMFNet。我们的方法显著减少了参数数量,同时保持了竞争力。在这里,我们展示了LMFNet在五个基准数据集上实现了最前沿或相当的结果,仅有0.81M参数,在效率和准确性方面都优于几种传统和轻量级模型。我们的工作不仅解决了轻量级网络中的多尺度学习挑战,还展示了在图像处理任务中更广泛应用的潜力。相关代码文件可在https://github.com/Shi-Yun-peng/LMFNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为LMF层的轻量级多尺度特征提取层,采用深度可分离膨胀卷积在完全连接的结构中实现。通过集成多个LMF层,开发出针对显著性目标检测的轻量级网络LMFNet。该方法在减少参数数量的同时,保持了竞争力,实现了在五个基准数据集上的卓越性能或具有竞争力的结果,参数仅为0.81M。本文不仅解决了轻量级网络中的多尺度学习挑战,还展示了在图像处理任务中的潜在应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了名为LMF层的轻量级多尺度特征提取层。
- LMF层利用深度可分离膨胀卷积在完全连接的结构中实现。
- 通过集成多个LMF层,构建了轻量级网络LMFNet。
- LMFNet在显著性目标检测任务中实现了卓越性能或具有竞争力的结果。
- LMFNet的参数数量仅为0.81M,提高了效率。
- 与传统和轻量级模型相比,LMFNet在效率和准确性方面表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

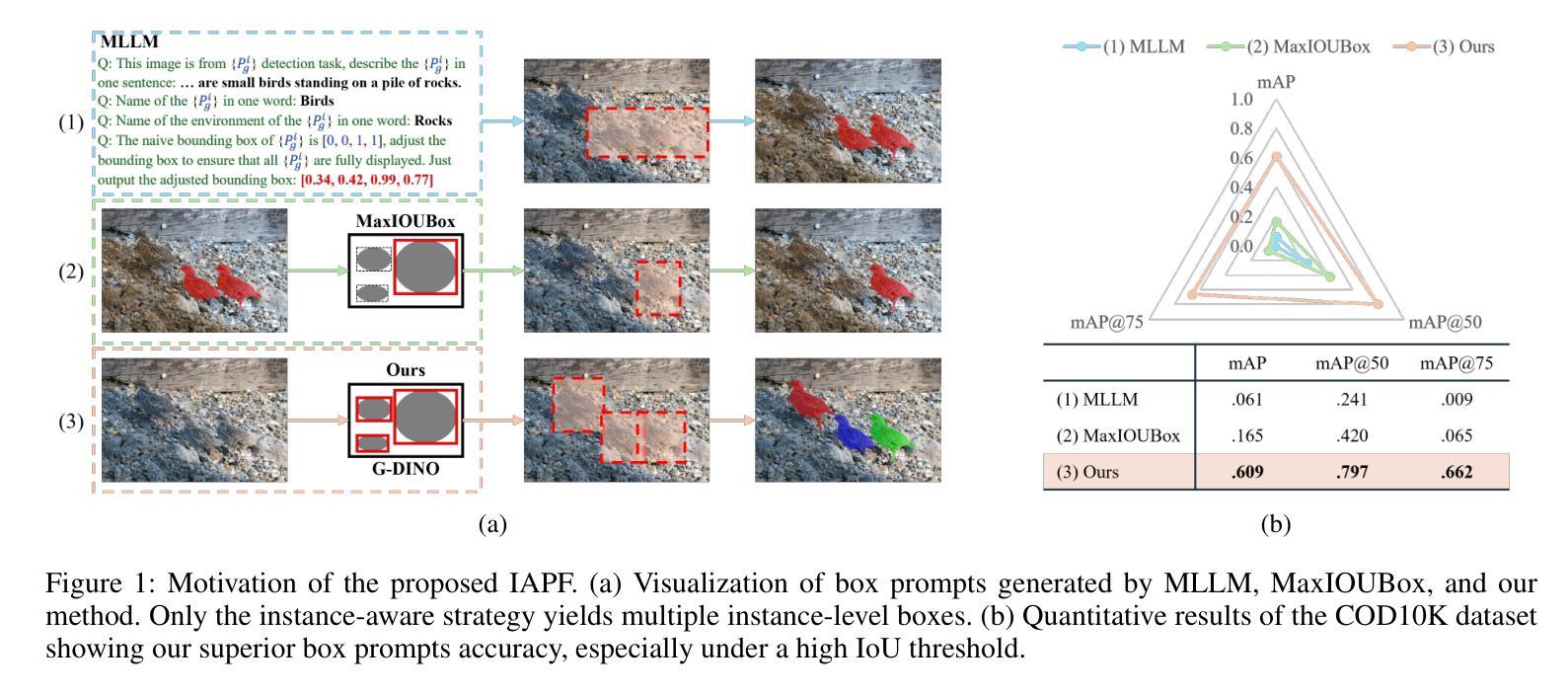
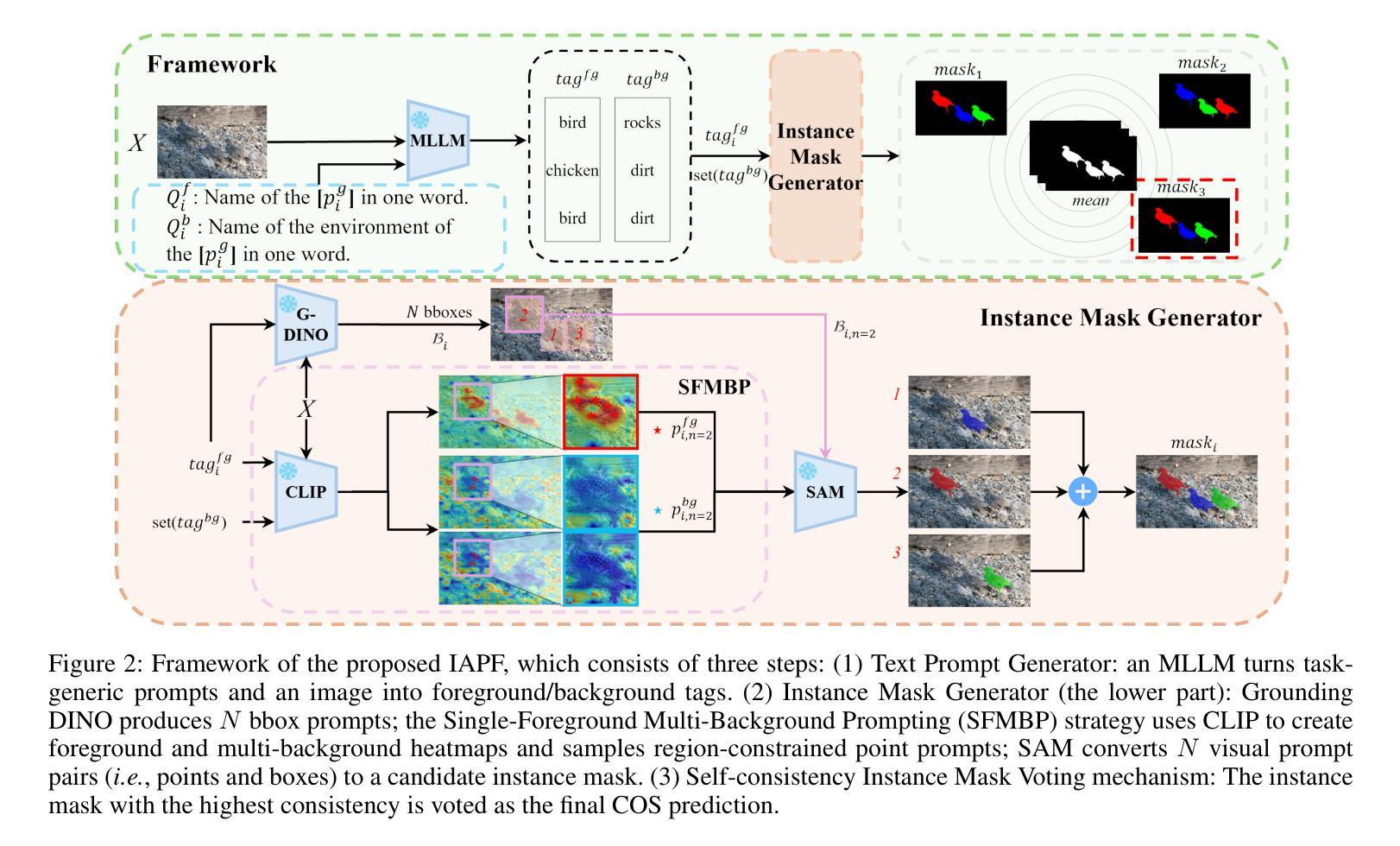
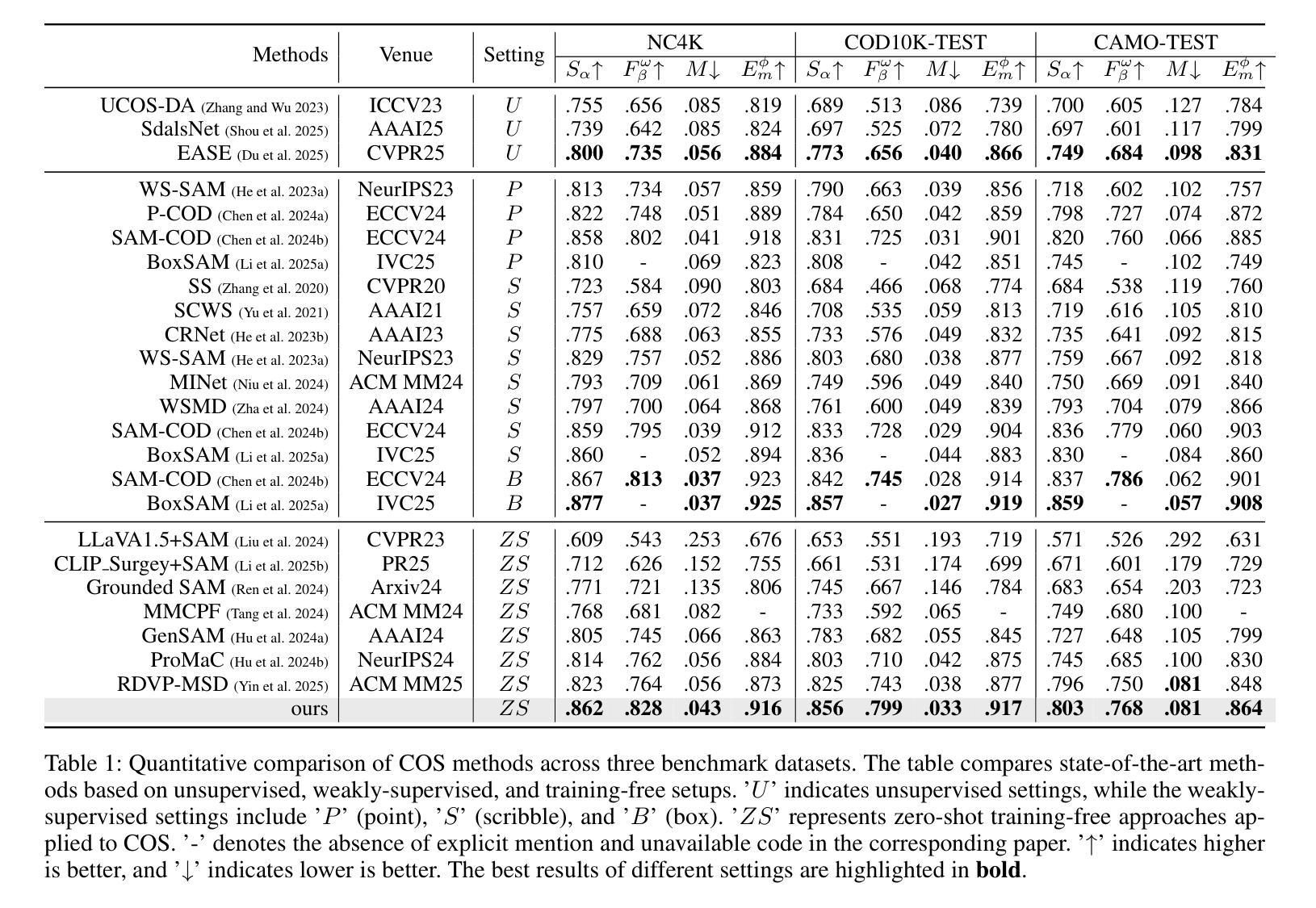
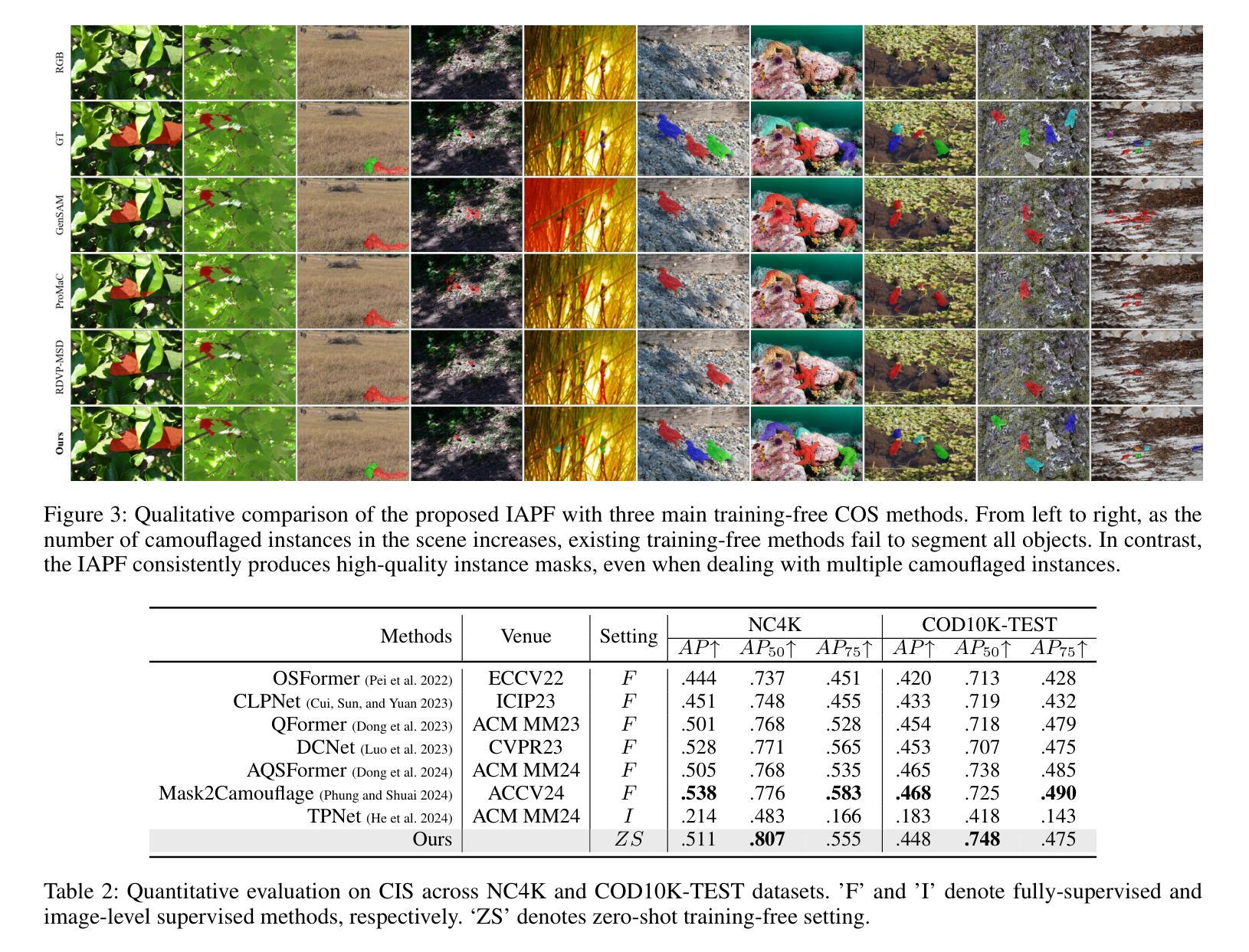
A Simple yet Powerful Instance-Aware Prompting Framework for Training-free Camouflaged Object Segmentation
Authors:Chao Yin, Jide Li, Xiaoqiang Li
Camouflaged Object Segmentation (COS) remains highly challenging due to the intrinsic visual similarity between target objects and their surroundings. While training-based COS methods achieve good performance, their performance degrades rapidly with increased annotation sparsity. To circumvent this limitation, recent studies have explored training-free COS methods, leveraging the Segment Anything Model (SAM) by automatically generating visual prompts from a single task-generic prompt (\textit{e.g.}, “\textit{camouflaged animal}”) uniformly applied across all test images. However, these methods typically produce only semantic-level visual prompts, causing SAM to output coarse semantic masks and thus failing to handle scenarios with multiple discrete camouflaged instances effectively. To address this critical limitation, we propose a simple yet powerful \textbf{I}nstance-\textbf{A}ware \textbf{P}rompting \textbf{F}ramework (IAPF), the first training-free COS pipeline that explicitly converts a task-generic prompt into fine-grained instance masks. Specifically, the IAPF comprises three steps: (1) Text Prompt Generator, utilizing task-generic queries to prompt a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) for generating image-specific foreground and background tags; (2) \textbf{Instance Mask Generator}, leveraging Grounding DINO to produce precise instance-level bounding box prompts, alongside the proposed Single-Foreground Multi-Background Prompting strategy to sample region-constrained point prompts within each box, enabling SAM to yield a candidate instance mask; (3) Self-consistency Instance Mask Voting, which selects the final COS prediction by identifying the candidate mask most consistent across multiple candidate instance masks. Extensive evaluations on standard COS benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed IAPF significantly surpasses existing state-of-the-art training-free COS methods.
隐蔽物体分割(COS)依然极具挑战性,因为目标物体与其周围环境之间固有的视觉相似性。基于训练的COS方法虽然取得了良好的性能,但随着标注稀疏性的增加,其性能会迅速下降。为了克服这一局限性,最近的研究探索了无训练COS方法,利用“任何物体分割模型”(SAM)通过自动从单一任务通用提示(例如“隐蔽动物”)生成视觉提示,并统一应用于所有测试图像。然而,这些方法通常只产生语义层面的视觉提示,导致SAM输出粗略的语义掩膜,因而无法有效地处理多个离散隐蔽实例场景。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了简单而强大的实例感知提示框架(IAPF),这是第一个无训练COS管道,能够显式地将任务通用提示转换为精细的实例掩膜。具体来说,IAPF包含三个步骤:(1)文本提示生成器,利用任务通用查询来提示多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)生成图像特定的前景和背景标签;(2)实例掩膜生成器,利用接地DINO生成精确的实例级边界框提示,以及提出的单前景多背景提示策略来在每个框内采样受区域约束的点提示,使SAM能够产生候选实例掩膜;(3)自洽实例掩膜投票,通过识别多个候选实例掩膜中最一致的候选掩膜来选择最终的COS预测。在标准COS基准测试上的广泛评估表明,所提出的IAPF显著超越了现有的最新无训练COS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
基于迷彩对象分割(COS)的挑战性,如目标对象与其周围环境之间的视觉相似性,训练型COS方法表现良好但在标注稀疏时性能迅速下降。为克服此限制,近期研究尝试无训练COS方法,利用通用提示自动产生视觉提示。然而,这些方法通常只产生语义级视觉提示,导致输出粗略语义掩膜,无法有效处理多个离散迷彩实例场景。为解决此问题,我们提出简单而强大的实例感知提示框架(IAPF),这是首个无需训练的COS管道,能将通用提示转化为精细实例掩膜。通过文本提示生成器、实例掩膜生成器和自我一致性实例掩膜投票三个步骤,IAPF显著超越了现有顶尖的无训练COS方法。
Key Takeaways
- 迷彩对象分割(COS)因目标对象与背景视觉相似性而具有挑战性。
- 训练型COS方法在标注稀疏时性能下降。
- 现有无训练COS方法通常只产生语义级视觉提示,导致输出粗略语义掩膜。
- 实例感知提示框架(IAPF)能将通用提示转化为精细实例掩膜。
- IAPF包括文本提示生成器、实例掩膜生成器和自我一致性实例掩膜投票三个关键步骤。
- IAPF通过精细处理多个离散迷彩实例场景,显著提高了COS的性能。
点此查看论文截图

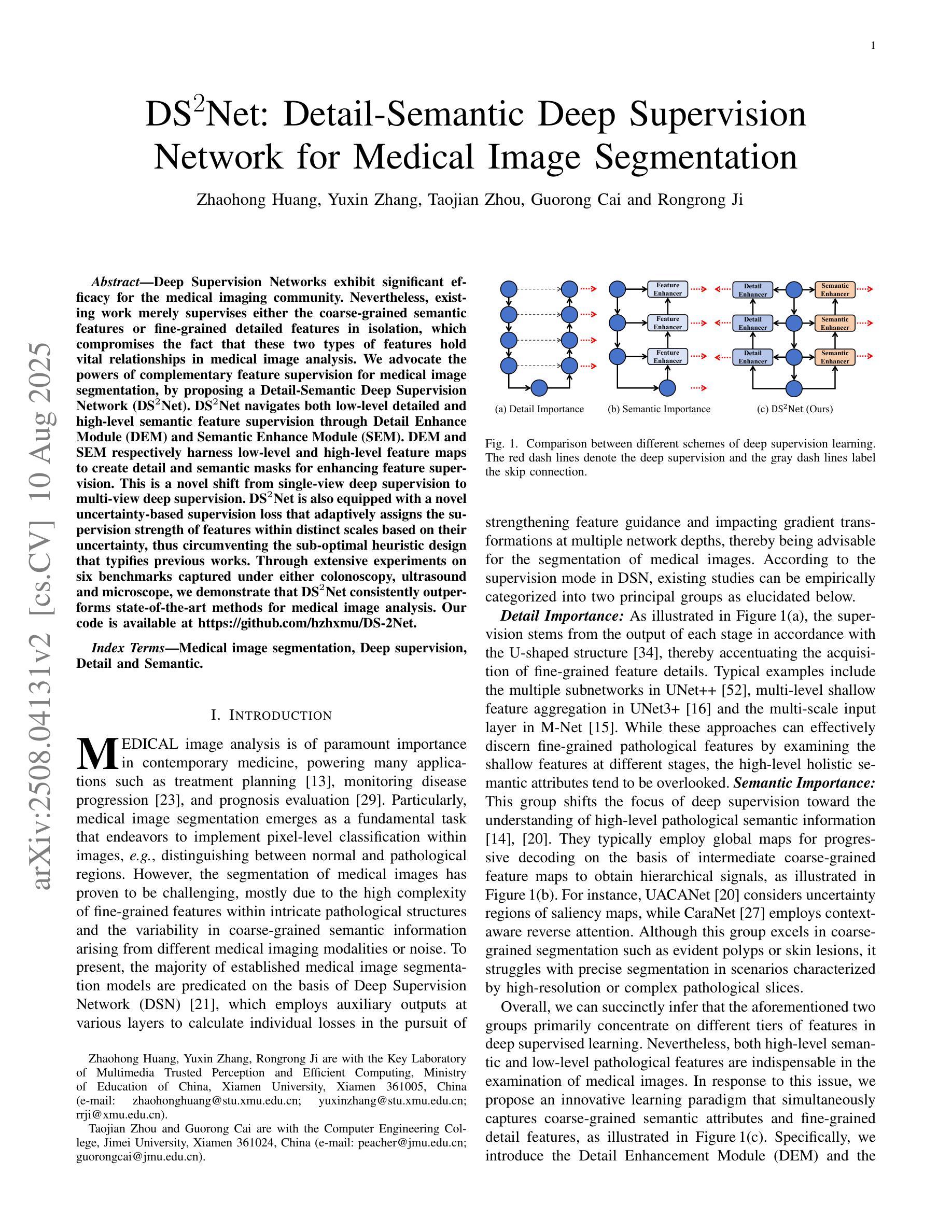
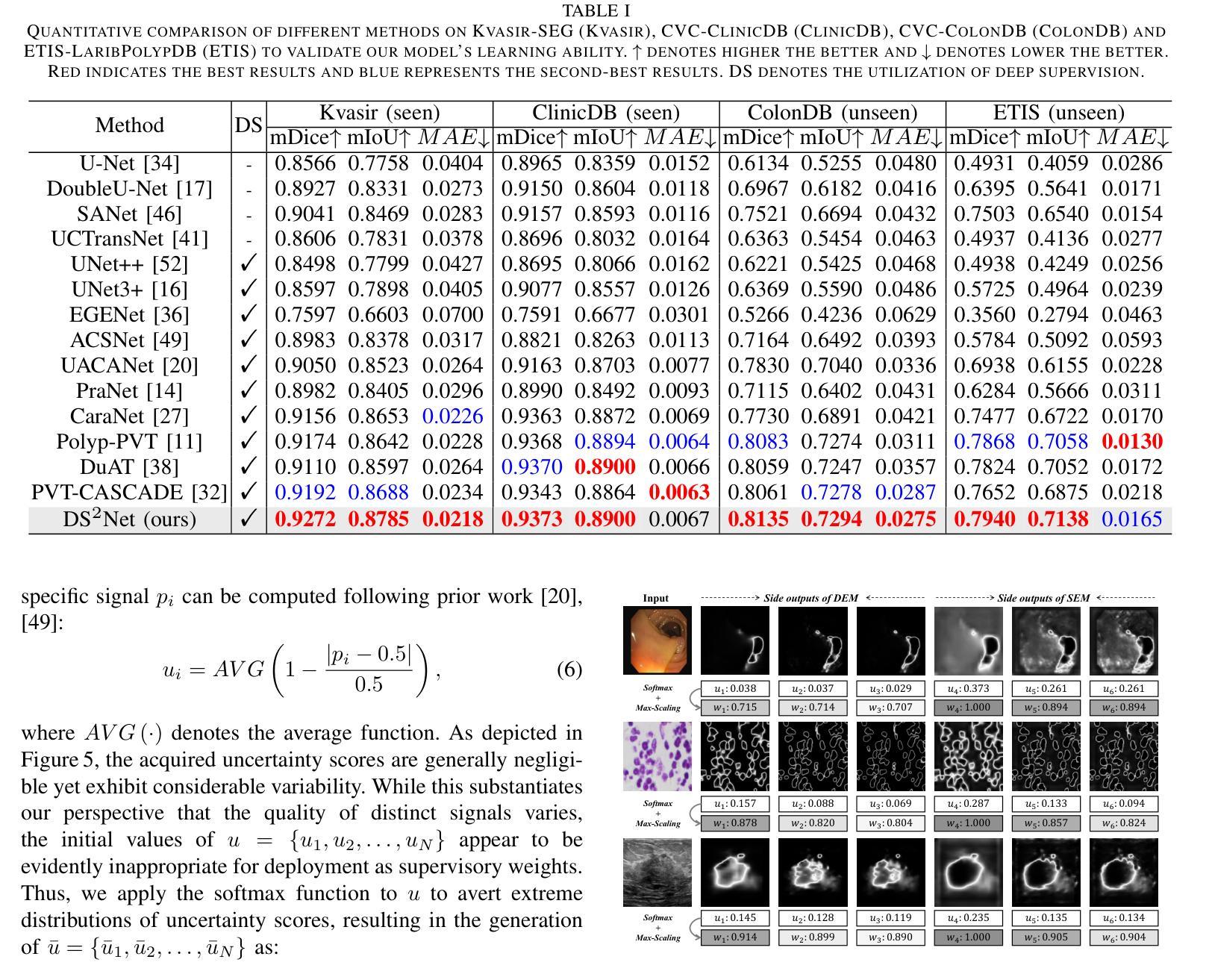
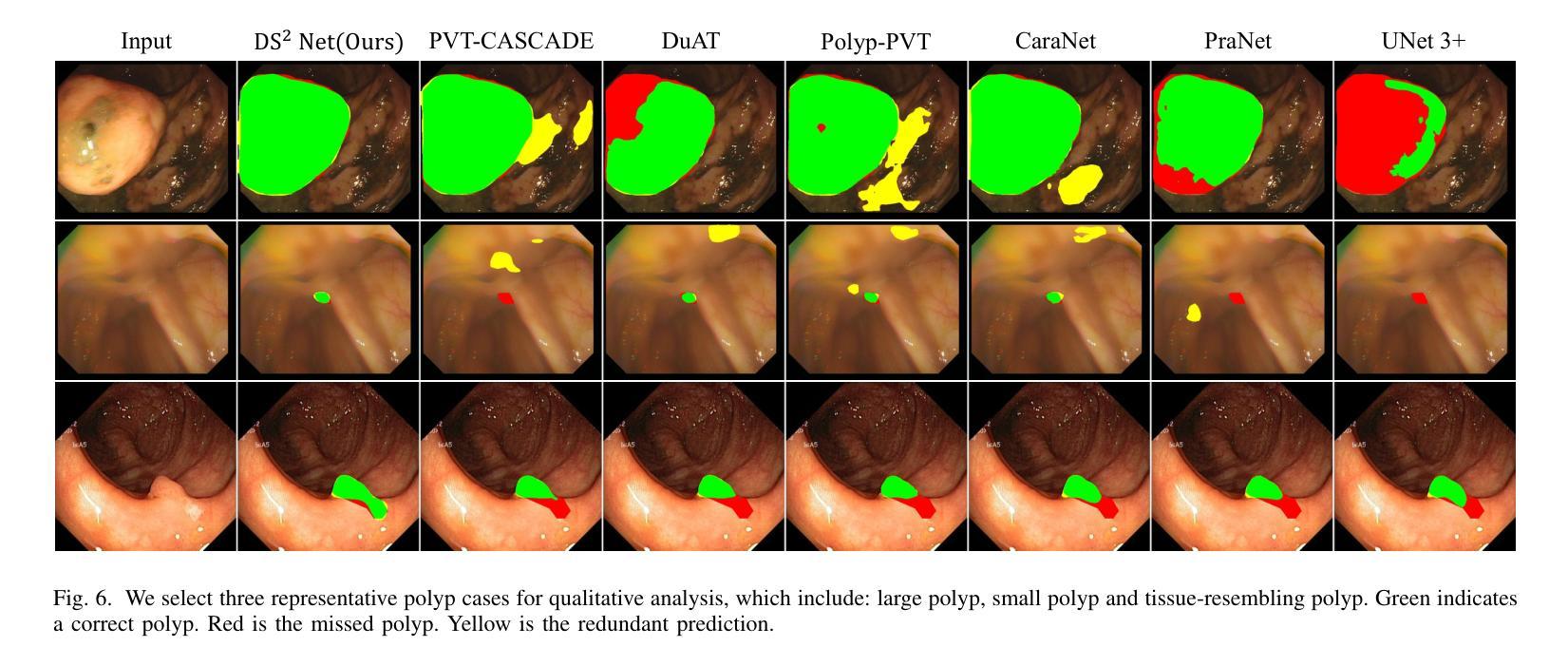
DS$^2$Net: Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhaohong Huang, Yuxin Zhang, Taojian Zhou, Guorong Cai, Rongrong Ji
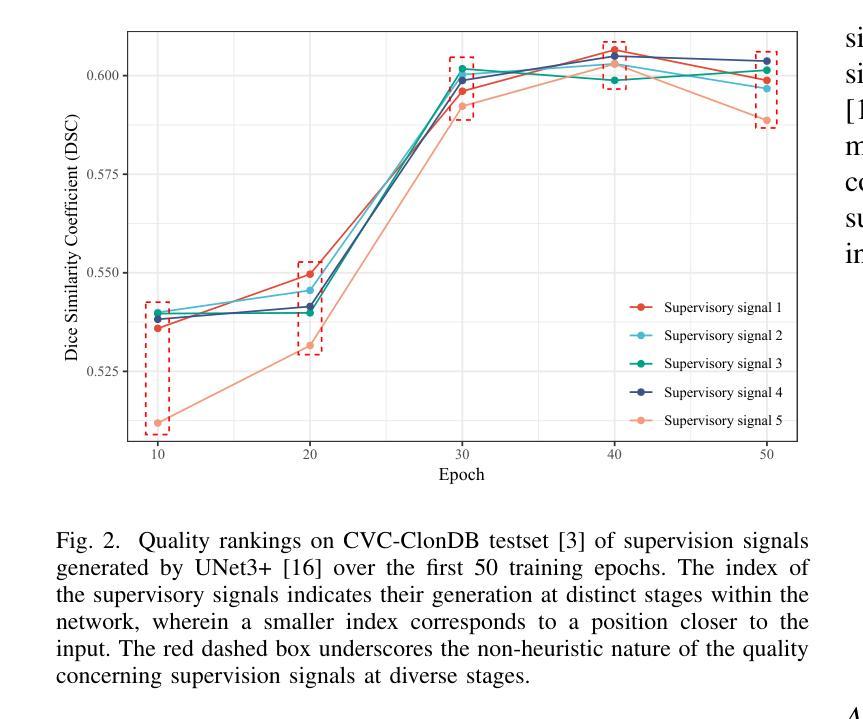
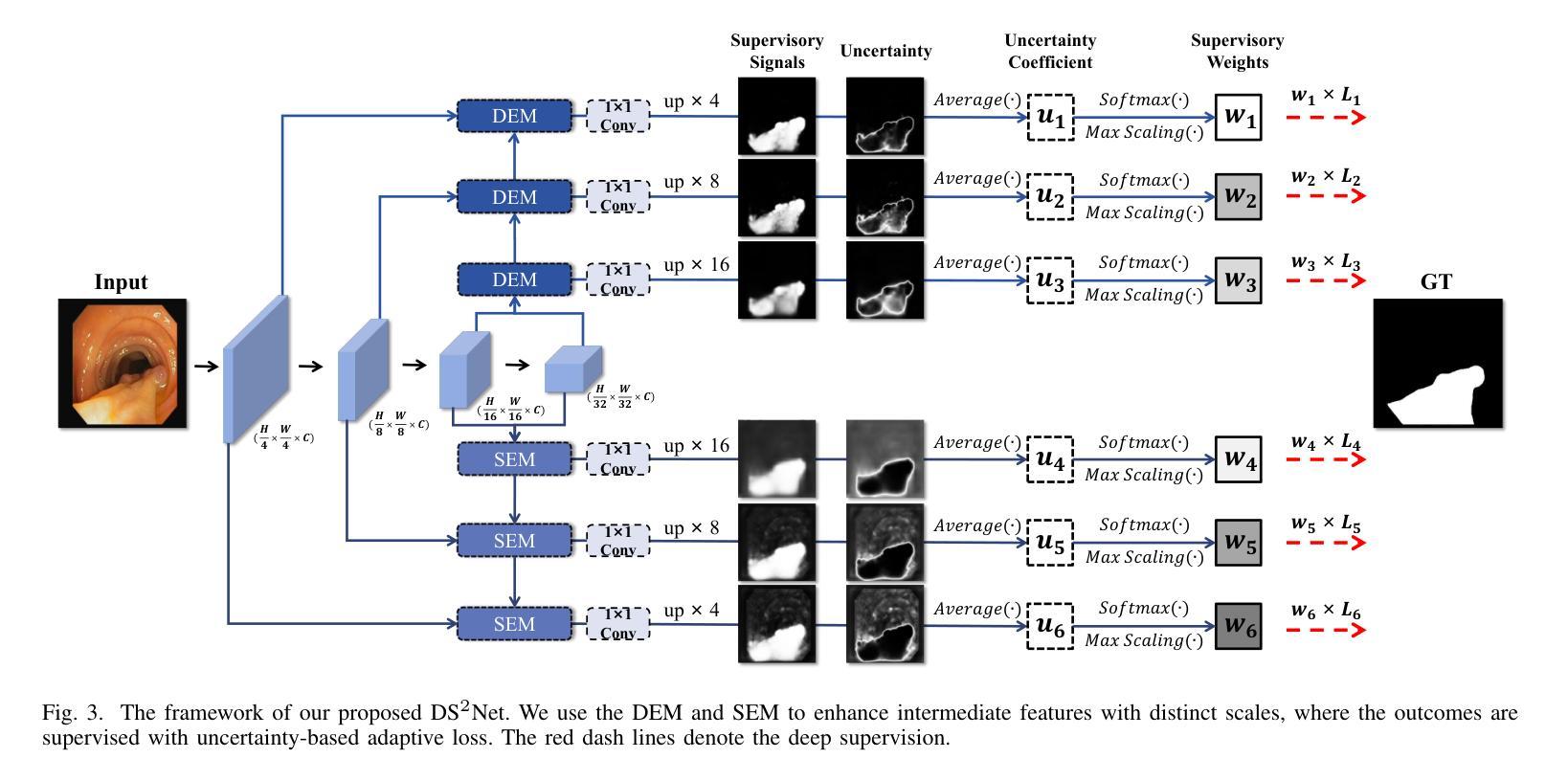
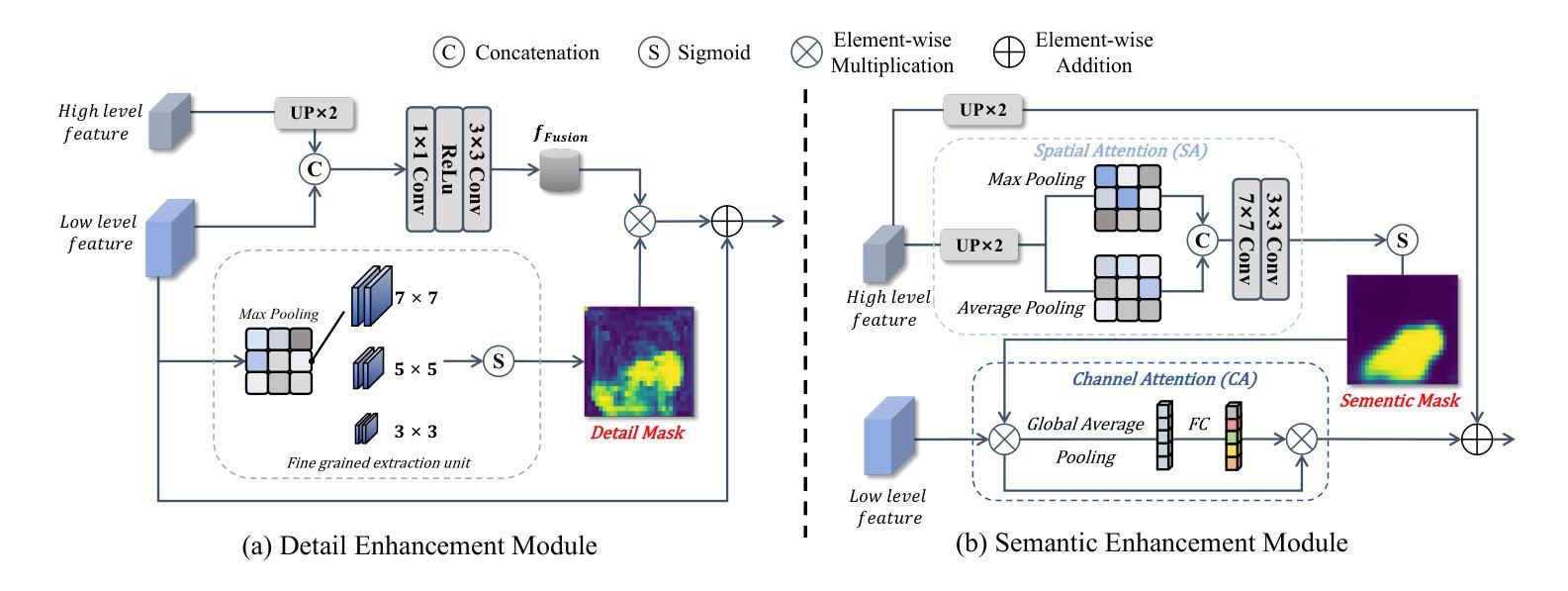
Deep Supervision Networks exhibit significant efficacy for the medical imaging community. Nevertheless, existing work merely supervises either the coarse-grained semantic features or fine-grained detailed features in isolation, which compromises the fact that these two types of features hold vital relationships in medical image analysis. We advocate the powers of complementary feature supervision for medical image segmentation, by proposing a Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network (DS$^2$Net). DS$^2$Net navigates both low-level detailed and high-level semantic feature supervision through Detail Enhance Module (DEM) and Semantic Enhance Module (SEM). DEM and SEM respectively harness low-level and high-level feature maps to create detail and semantic masks for enhancing feature supervision. This is a novel shift from single-view deep supervision to multi-view deep supervision. DS$^2$Net is also equipped with a novel uncertainty-based supervision loss that adaptively assigns the supervision strength of features within distinct scales based on their uncertainty, thus circumventing the sub-optimal heuristic design that typifies previous works. Through extensive experiments on six benchmarks captured under either colonoscopy, ultrasound and microscope, we demonstrate that DS$^2$Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for medical image analysis.
深度监督网络对医学影像界具有重要意义。然而,现有的工作只是对粗粒度的语义特征或精细的详细特征进行单独的监督,忽略了这两种特征在医学图像分析中存在着重要的关联。我们提倡对医学图像分割进行互补特征监督,为此提出了细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net)。DS$^2$Net通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)导航低级的详细特征和高级语义特征的监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低级和高级特征图创建细节和语义掩膜,以增强特征监督。这是一种从单视图深度监督到多视图深度监督的新转变。DS$^2$Net还配备了一种新型基于不确定性的监督损失,可以根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同规模的监督强度,从而避免了以前工作中典型的次优启发式设计。通过在结肠镜、超声和显微镜下的六个基准测试集上进行的大量实验,我们证明了DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度监督网络在医学影像领域表现出显著效果。然而,现有工作仅孤立地监督粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征,忽略了两者在医学图像分析中的紧密关系。本文提出一种细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net),通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)实现医学图像分割的互补特征监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低层次和高层次特征图创建细节和语义掩膜以增强特征监督,实现了从单视图深度监督到多视图深度监督的新转变。此外,DS$^2$Net还配备了基于不确定性监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度的特征监督强度,避免了以往工作中的次优启发式设计。在六个基准测试上的实验表明,DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度监督网络在医学成像领域效果显著。
- 当前研究忽视了粗粒度语义特征和细粒度详细特征之间的关系。
- 提出了细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net),结合了细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)。
- DS$^2$Net实现了从单视图到多视图深度监督的转变。
- DS$^2$Net配备了基于不确定性的监督损失,可自适应地分配不同尺度特征的监督强度。
- DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面性能卓越,优于现有最新方法。
点此查看论文截图
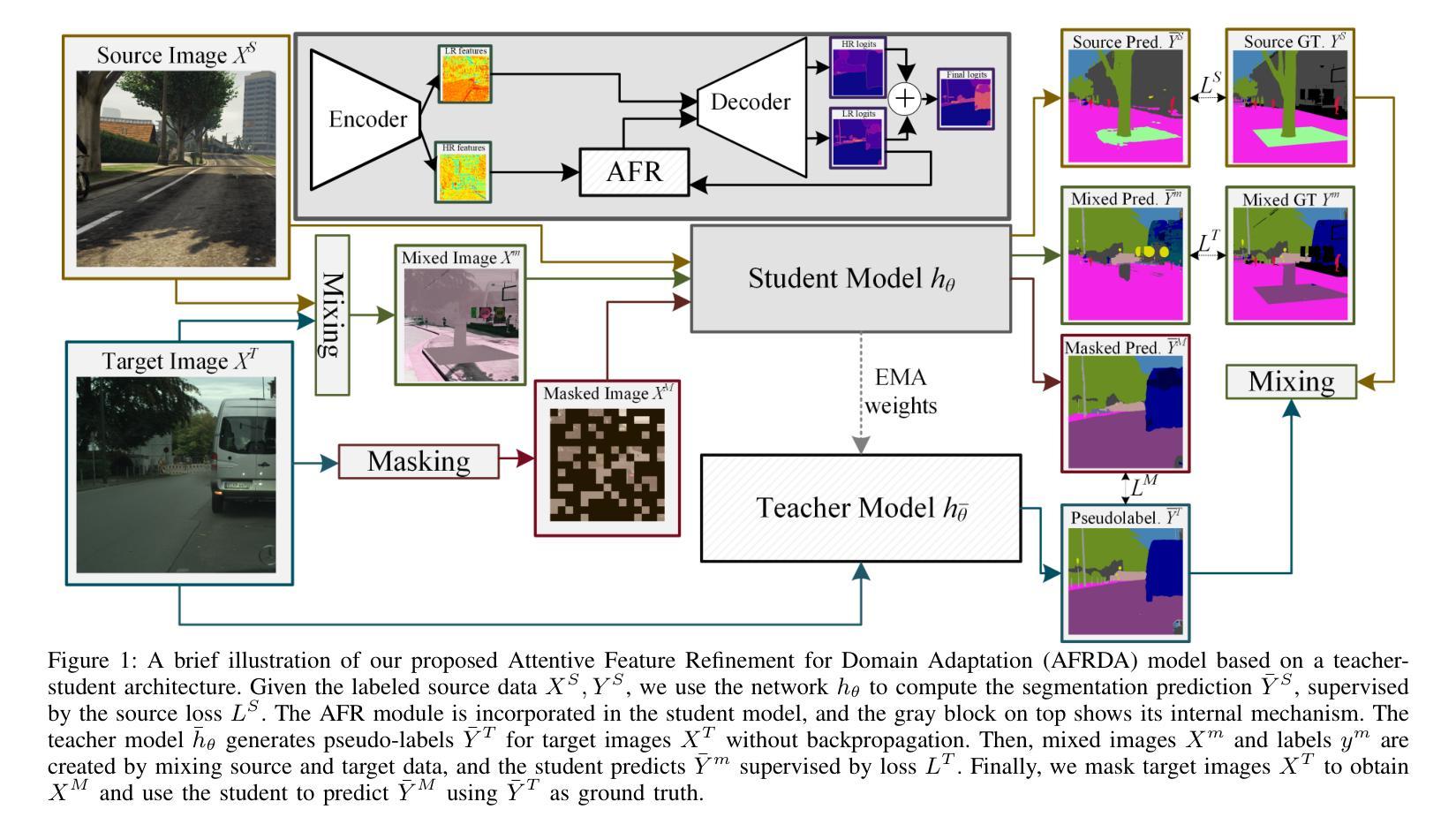
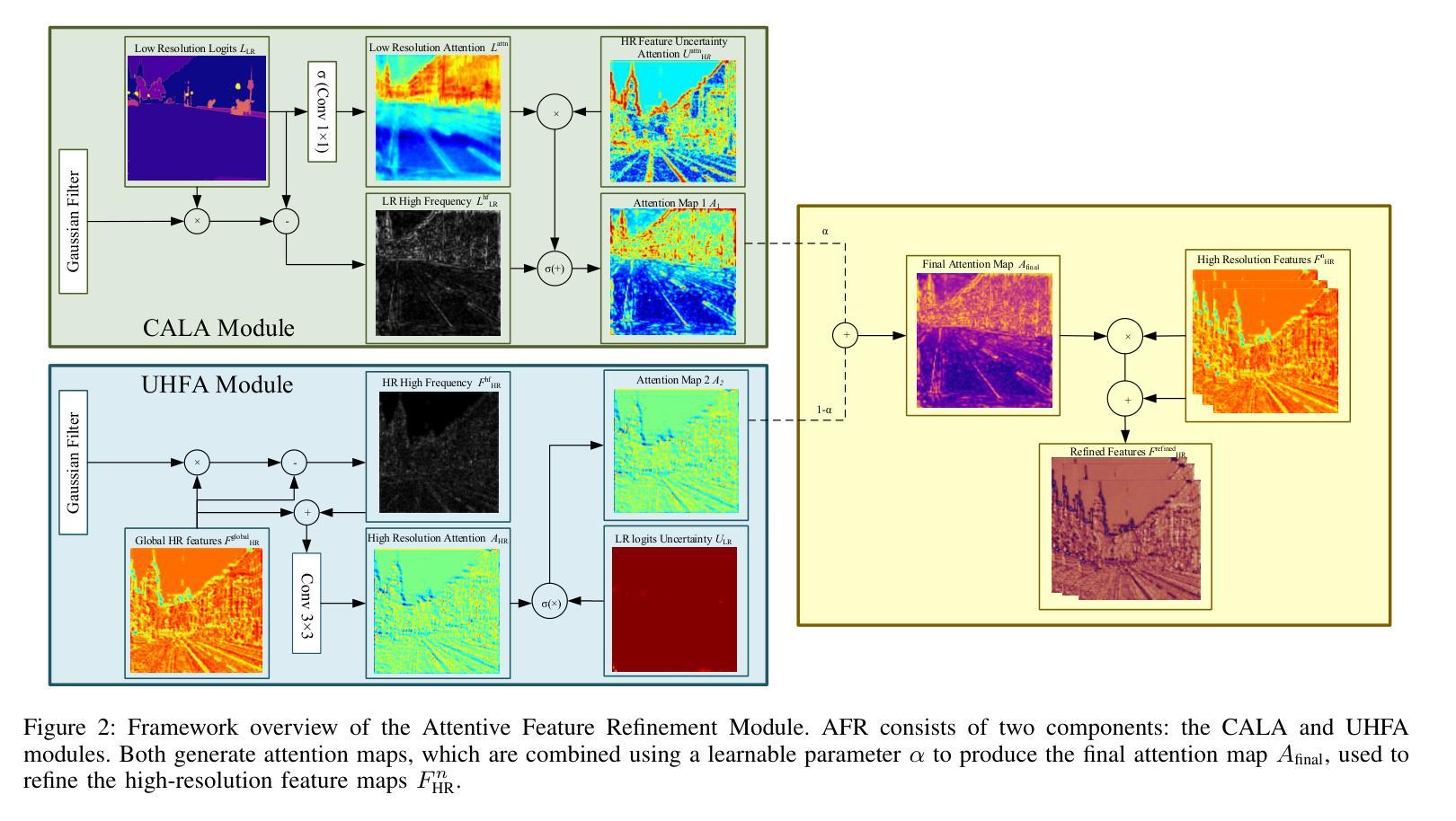
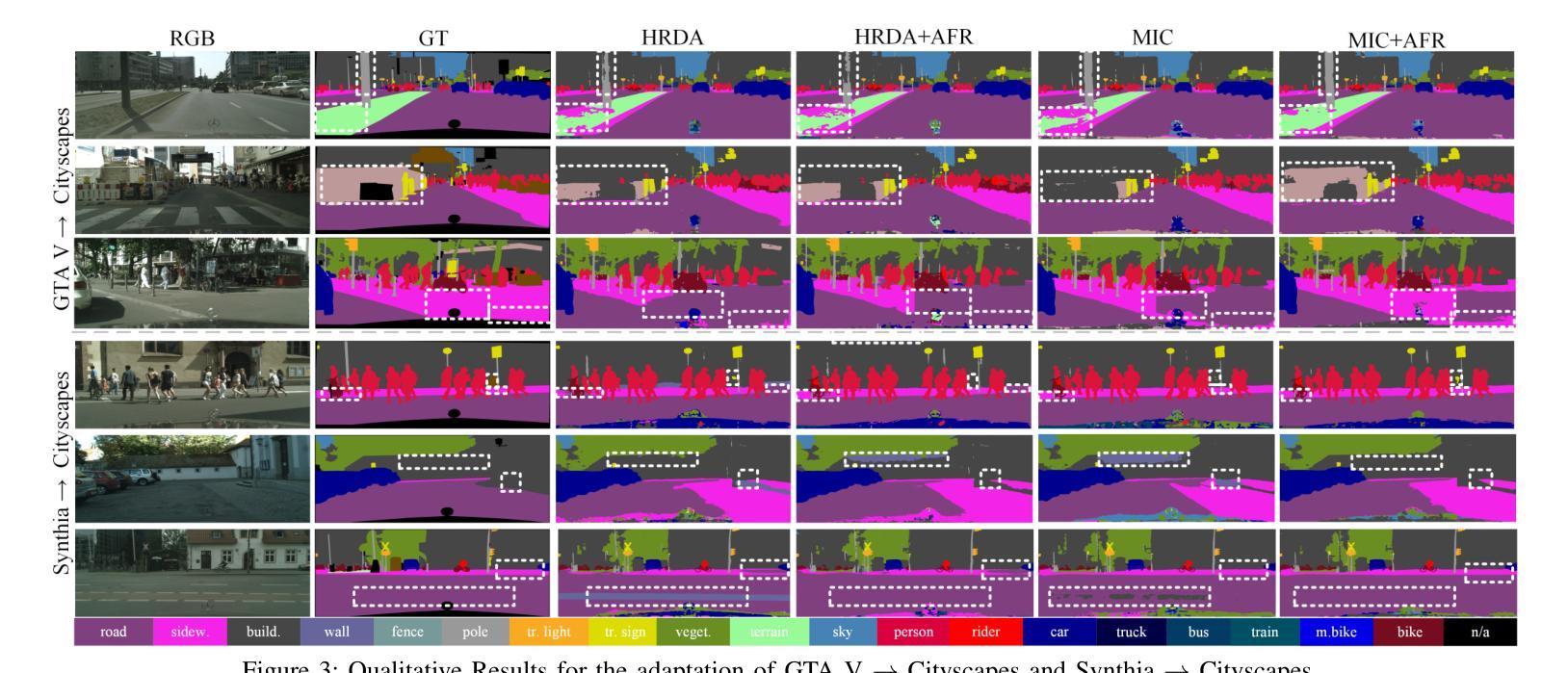
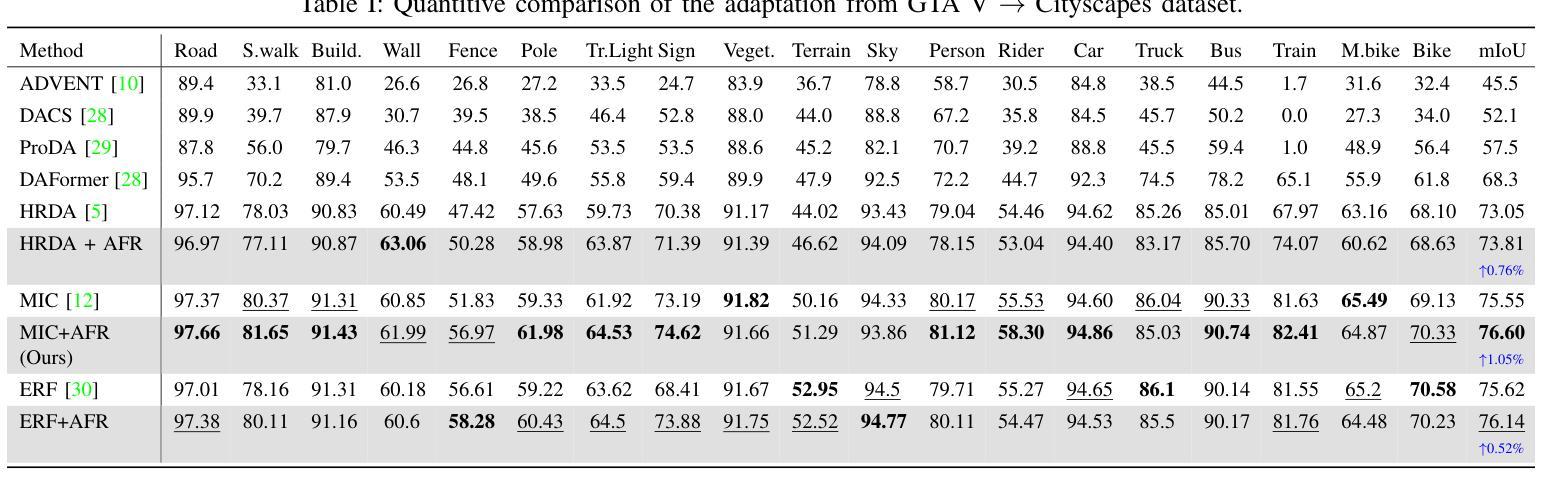
AFRDA: Attentive Feature Refinement for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Md. Al-Masrur Khan, Durgakant Pushp, Lantao Liu
In Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation (UDA-SS), a model is trained on labeled source domain data (e.g., synthetic images) and adapted to an unlabeled target domain (e.g., real-world images) without access to target annotations. Existing UDA-SS methods often struggle to balance fine-grained local details with global contextual information, leading to segmentation errors in complex regions. To address this, we introduce the Adaptive Feature Refinement (AFR) module, which enhances segmentation accuracy by refining highresolution features using semantic priors from low-resolution logits. AFR also integrates high-frequency components, which capture fine-grained structures and provide crucial boundary information, improving object delineation. Additionally, AFR adaptively balances local and global information through uncertaintydriven attention, reducing misclassifications. Its lightweight design allows seamless integration into HRDA-based UDA methods, leading to state-of-the-art segmentation performance. Our approach improves existing UDA-SS methods by 1.05% mIoU on GTA V –> Cityscapes and 1.04% mIoU on Synthia–>Cityscapes. The implementation of our framework is available at: https://github.com/Masrur02/AFRDA
在无需监督的领域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)中,模型会在标注的源域数据(例如,合成图像)上进行训练,并适应未标注的目标域(例如,真实世界图像),而无需访问目标注释。现有的UDA-SS方法往往难以平衡精细的局部细节和全局上下文信息,导致在复杂区域出现分割错误。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了自适应特征细化(AFR)模块,它通过利用低分辨率逻辑中的语义先验来细化高分辨率特征,从而提高分割准确性。AFR还集成了高频组件,这些组件可以捕捉精细结构并提供关键边界信息,从而改善对象轮廓。此外,AFR通过不确定性驱动的关注机制自适应地平衡局部和全局信息,减少误分类。其轻量级的设计可以无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法,实现最先进的分割性能。我们的方法在GTA V到Cityscapes和Synthia到Cityscapes的任务上分别提高了现有UDA-SS方法的1.05%和1.04%的mIoU。我们的框架实现可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/Masrur02/AFRDA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对无监督域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)中的模型在新领域适应性不足的问题,本文提出了自适应特征细化(AFR)模块。该模块通过利用低分辨率逻辑中的语义先验来优化高分辨率特征,并集成高频率组件以捕捉精细结构并提供关键边界信息,从而提高分割精度和对象轮廓清晰度。此外,通过不确定性驱动的注意力机制,AFR能够自适应地平衡局部和全局信息,减少误分类。其轻量级设计可无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法中,实现最先进的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- UDA-SS方法面临平衡局部细节和全局信息的挑战,导致复杂区域的分割错误。
- 引入AFR模块,通过利用低分辨率逻辑中的语义先验来优化高分辨率特征,提高分割精度。
- AFR集成高频率组件,捕捉精细结构并提供边界信息,改善对象轮廓清晰度。
- 通过不确定性驱动的注意力机制,AFR自适应平衡局部和全局信息。
- AFR设计轻量级,可无缝集成到基于HRDA的UDA方法中。
- 在GTA V到Cityscapes和Synthia到Cityscapes的测试中,该方法提高了现有UDA-SS方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

SARDet-100K: Towards Open-Source Benchmark and ToolKit for Large-Scale SAR Object Detection
Authors:Yuxuan Li, Xiang Li, Weijie Li, Qibin Hou, Li Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang
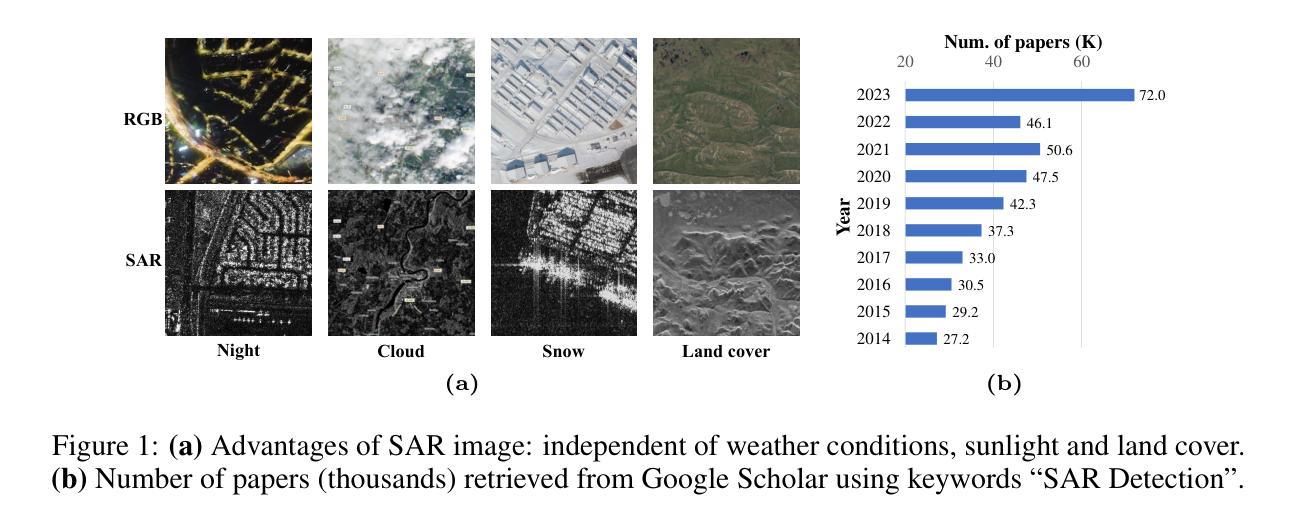
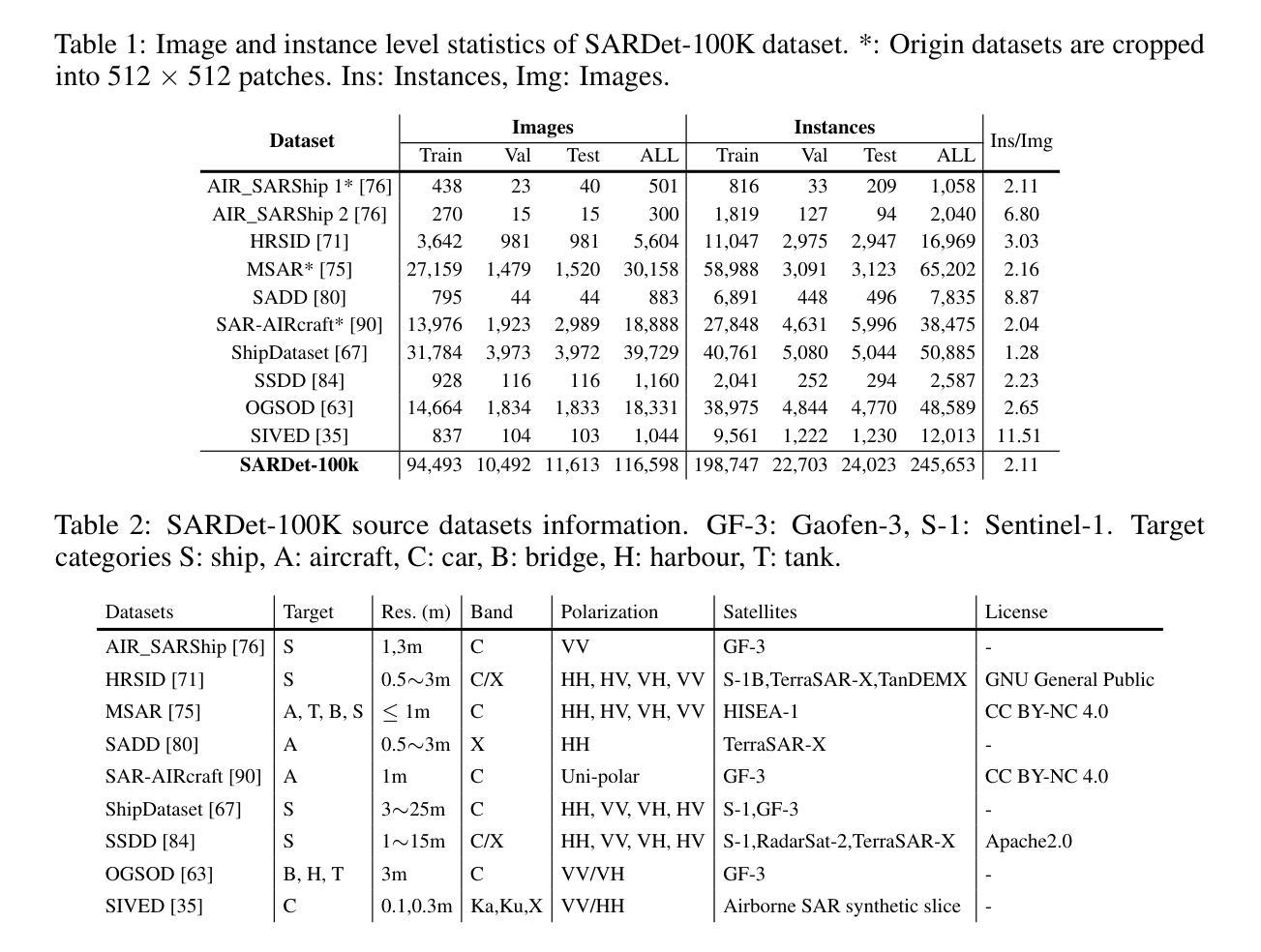
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) object detection has gained significant attention recently due to its irreplaceable all-weather imaging capabilities. However, this research field suffers from both limited public datasets (mostly comprising <2K images with only mono-category objects) and inaccessible source code. To tackle these challenges, we establish a new benchmark dataset and an open-source method for large-scale SAR object detection. Our dataset, SARDet-100K, is a result of intense surveying, collecting, and standardizing 10 existing SAR detection datasets, providing a large-scale and diverse dataset for research purposes. To the best of our knowledge, SARDet-100K is the first COCO-level large-scale multi-class SAR object detection dataset ever created. With this high-quality dataset, we conducted comprehensive experiments and uncovered a crucial challenge in SAR object detection: the substantial disparities between the pretraining on RGB datasets and finetuning on SAR datasets in terms of both data domain and model structure. To bridge these gaps, we propose a novel Multi-Stage with Filter Augmentation (MSFA) pretraining framework that tackles the problems from the perspective of data input, domain transition, and model migration. The proposed MSFA method significantly enhances the performance of SAR object detection models while demonstrating exceptional generalizability and flexibility across diverse models. This work aims to pave the way for further advancements in SAR object detection. The dataset and code is available at https://github.com/zcablii/SARDet_100K.
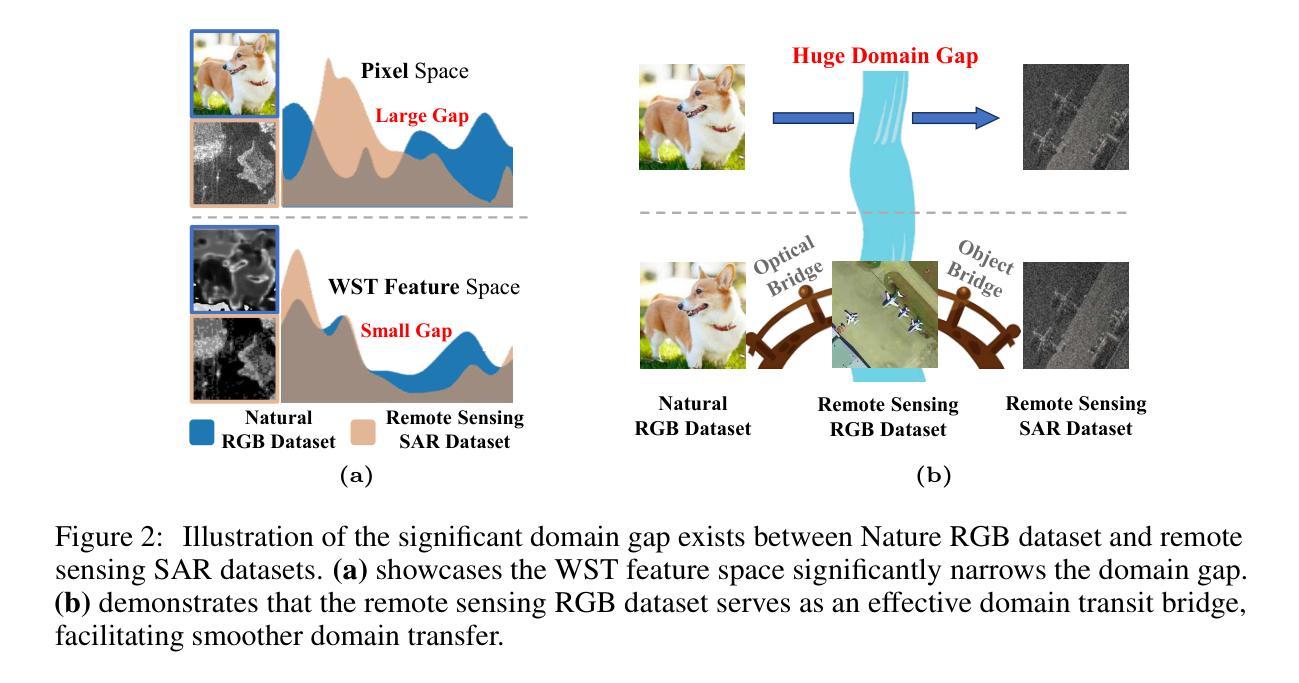
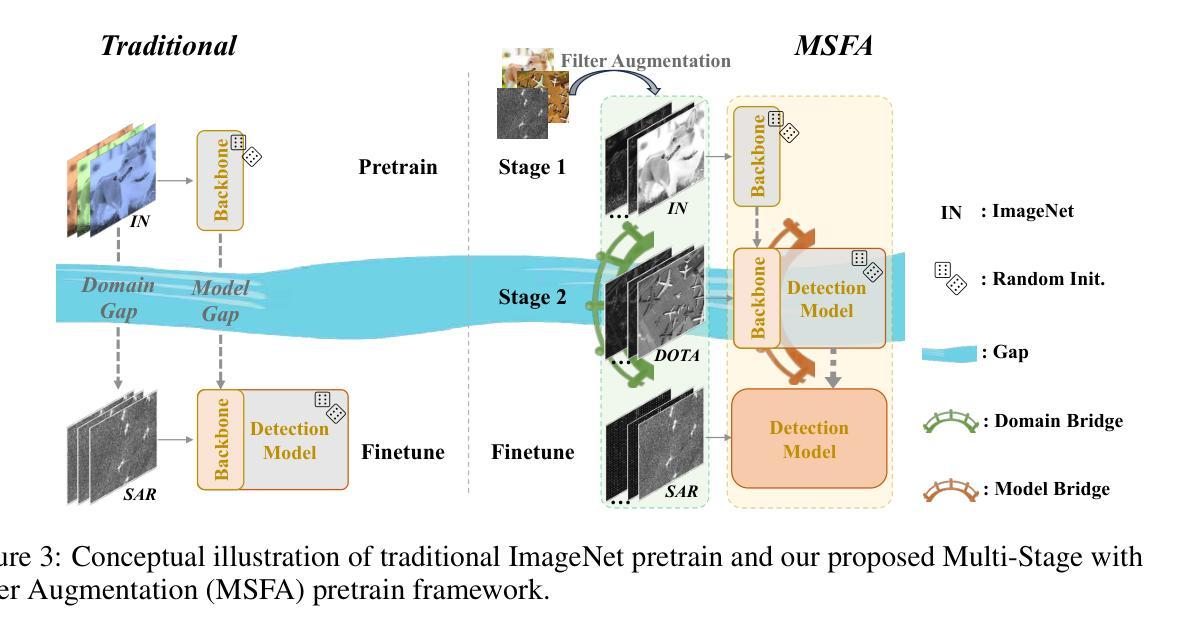
雷达合成孔径(SAR)目标检测由于其不可替代的全天候成像能力而最近备受关注。然而,此研究领域面临着公开数据集有限(大多包含少于2K图像且只有单类别目标)以及源代码无法访问的挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们建立了一个新的基准数据集和开源方法来进行大规模的SAR目标检测。我们的数据集SARDet-100K是对现有的十个SAR检测数据集的调查、收集与标准化后的结果,为研究工作提供了一个大规模且多样化的数据集。据我们所知,SARDet-100K是首个创建的COCO级别的大规模多类别SAR目标检测数据集。借助这个高质量的数据集,我们进行了全面的实验,并发现了SAR目标检测中的一个重要挑战:在RGB数据集上进行预训练和SAR数据集上进行微调时,数据域和模型结构方面存在的巨大差异。为了缩小这些差距,我们提出了新颖的多阶段滤波器增强(MSFA)预训练框架,从数据输入、域转换和模型迁移的角度解决问题。所提出的MSFA方法大大提高了SAR目标检测模型的性能,同时在不同的模型中表现出卓越的一般性和灵活性。这项工作旨在为SAR目标检测的进一步进展铺平道路。数据集和代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/zcablii/SARDet_100K。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at NeurIPS 2024. Spotlight. Project page: (https://github.com/zcablii/SARDet_100K)[https://github.com/zcablii/SARDet_100K]
Summary:近期合成孔径雷达(SAR)目标检测备受关注,但由于公开数据集有限且源代码不可访问,此领域面临挑战。为应对这些挑战,研究团队建立了新的基准数据集SARDet-100K,并提出了一种开放源方法用于大规模SAR目标检测。SARDet-100K是首个大规模多类SAR目标检测数据集。此外,研究还发现预训练和SAR数据集微调之间存在显著差距,为此提出了MSFA预训练框架。该框架从数据输入、域转换和模型迁移等角度解决了该问题,显著提高SAR目标检测模型的性能。数据集和代码可通过特定链接访问。
Key Takeaways:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR)目标检测因其在各种天气条件下的成像能力而受到关注。
- 公共数据集有限且主要为单一类别对象,使得研究面临挑战。
- 研究团队建立了新的基准数据集SARDet-100K,这是首个大规模多类SAR目标检测数据集。
- 预训练和SAR数据集微调之间存在显著差距。
- 为解决此问题,提出了MSFA预训练框架,从数据输入、域转换和模型迁移角度解决问题。
- MSFA方法显著提高了SAR目标检测模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图