⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
FineBadminton: A Multi-Level Dataset for Fine-Grained Badminton Video Understanding
Authors:Xusheng He, Wei Liu, Shanshan Ma, Qian Liu, Chenghao Ma, Jianlong Wu
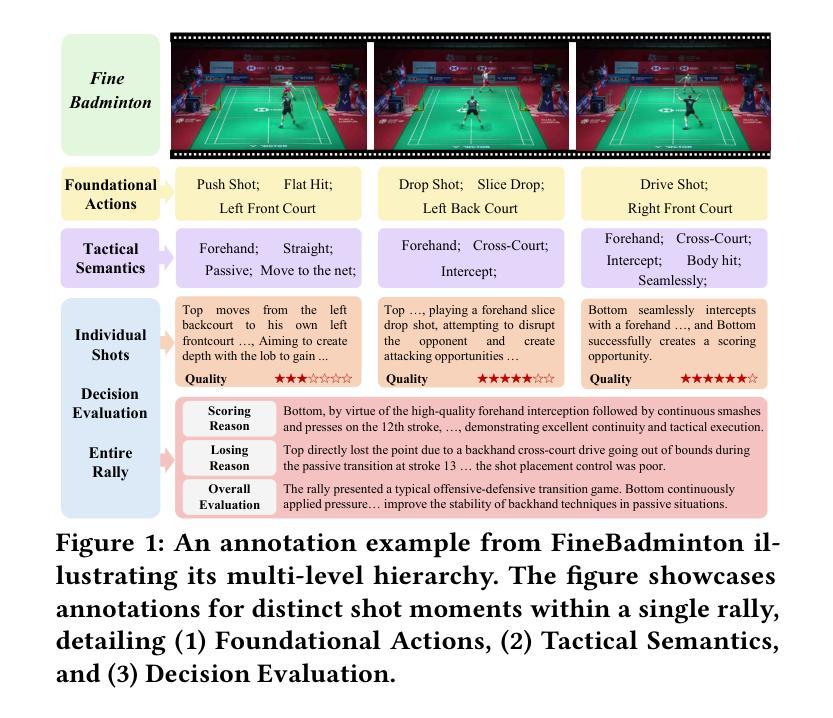
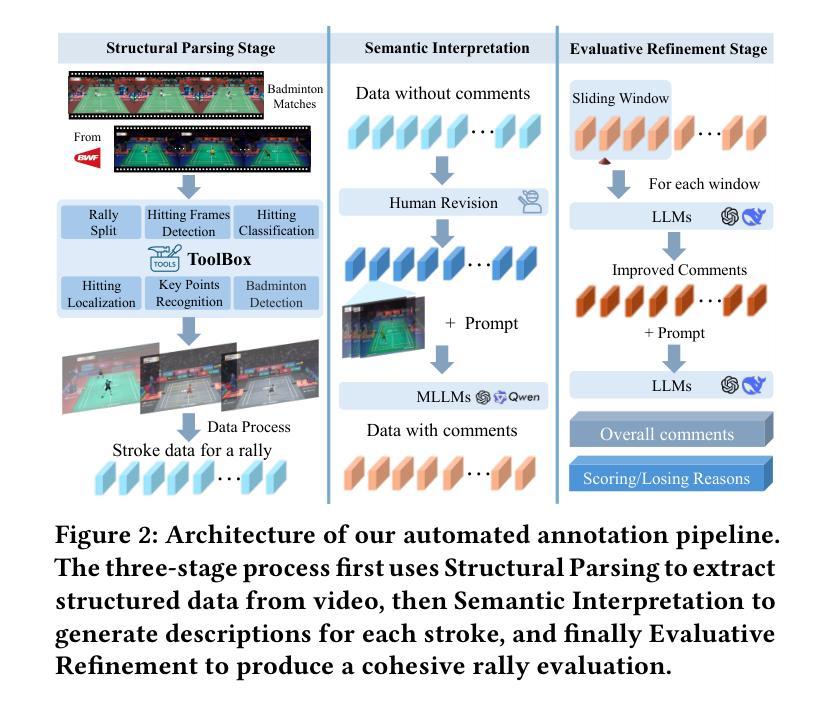
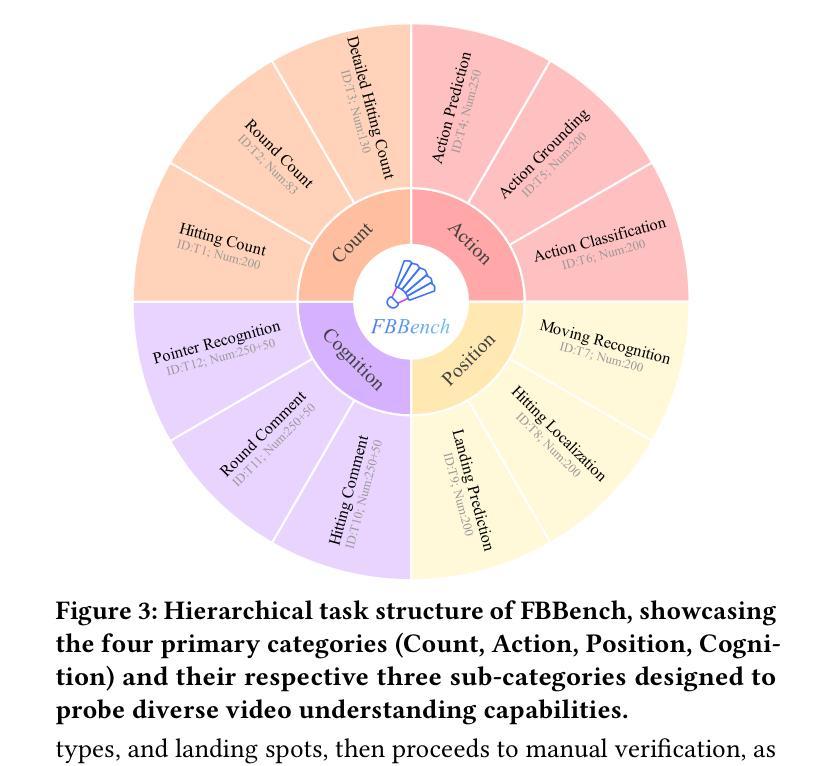
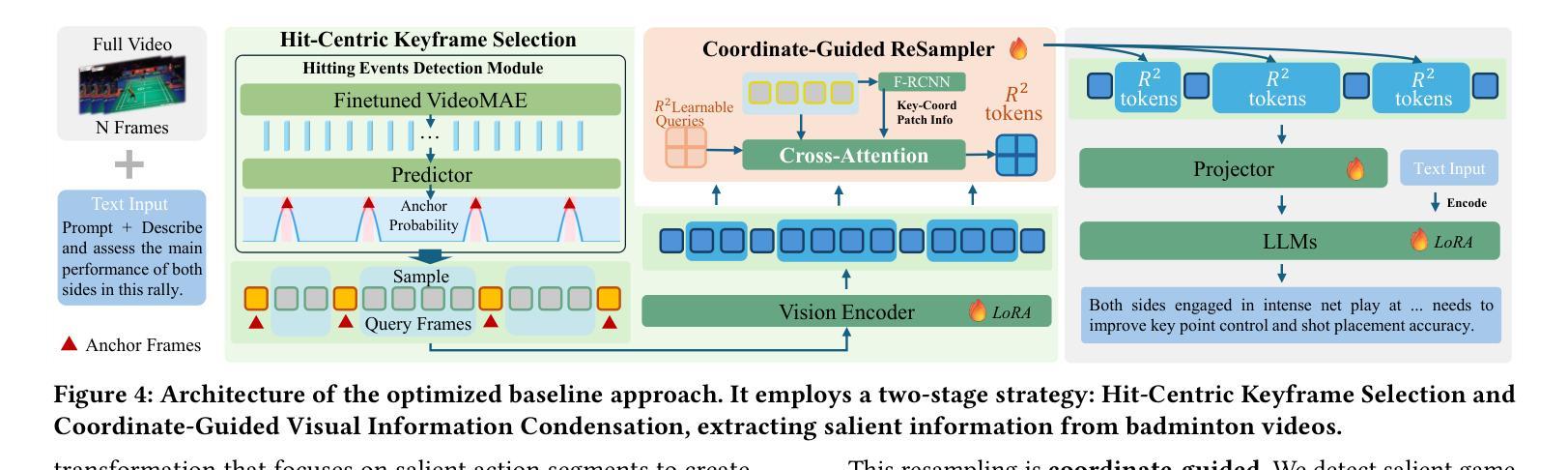
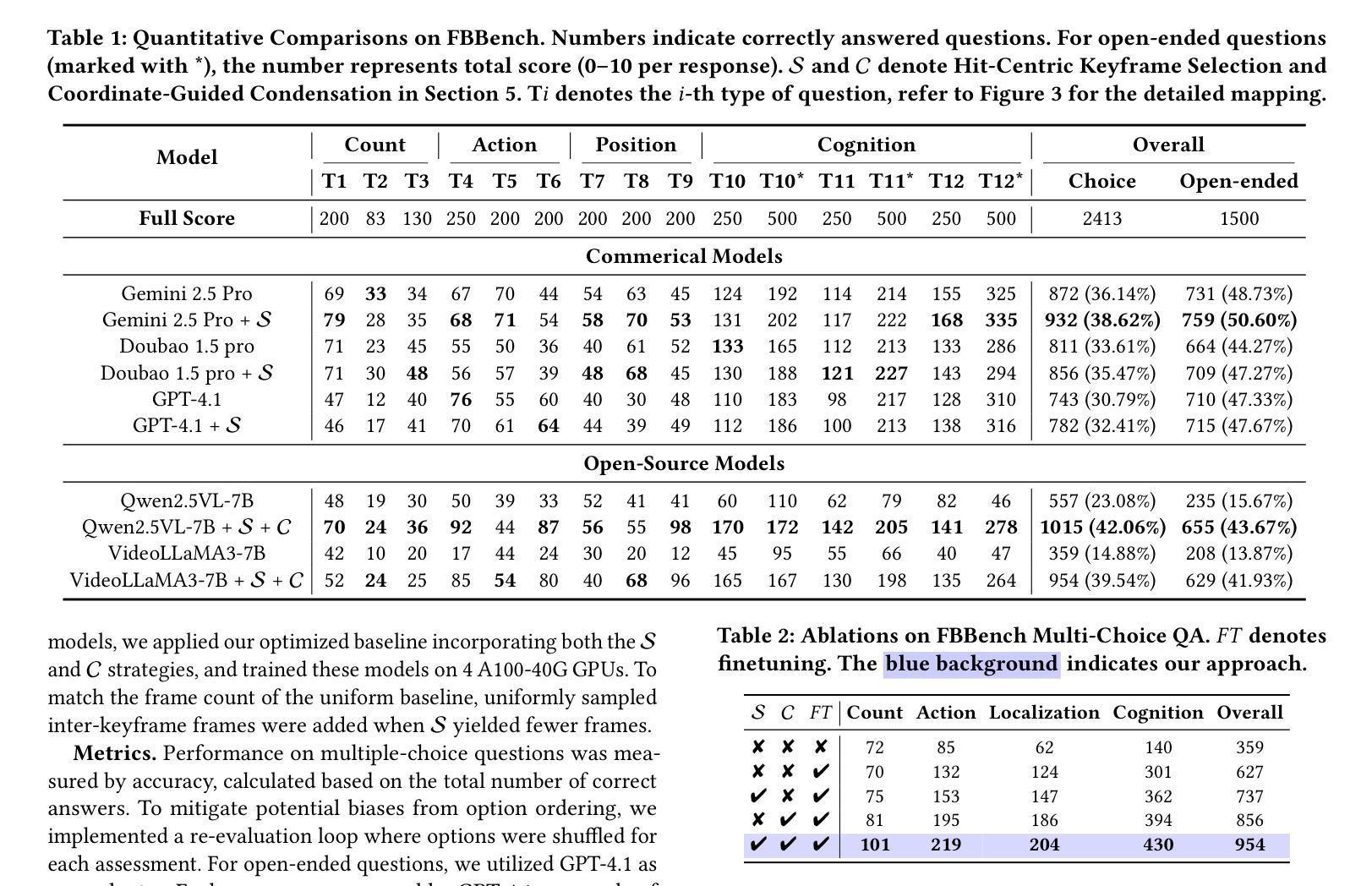
Fine-grained analysis of complex and high-speed sports like badminton presents a significant challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), despite their notable advancements in general video understanding. This difficulty arises primarily from the scarcity of datasets with sufficiently rich and domain-specific annotations. To bridge this gap, we introduce FineBadminton, a novel and large-scale dataset featuring a unique multi-level semantic annotation hierarchy (Foundational Actions, Tactical Semantics, and Decision Evaluation) for comprehensive badminton understanding. The construction of FineBadminton is powered by an innovative annotation pipeline that synergistically combines MLLM-generated proposals with human refinement. We also present FBBench, a challenging benchmark derived from FineBadminton, to rigorously evaluate MLLMs on nuanced spatio-temporal reasoning and tactical comprehension. Together, FineBadminton and FBBench provide a crucial ecosystem to catalyze research in fine-grained video understanding and advance the development of MLLMs in sports intelligence. Furthermore, we propose an optimized baseline approach incorporating Hit-Centric Keyframe Selection to focus on pivotal moments and Coordinate-Guided Condensation to distill salient visual information. The results on FBBench reveal that while current MLLMs still face significant challenges in deep sports video analysis, our proposed strategies nonetheless achieve substantial performance gains. The project homepage is available at https://finebadminton.github.io/FineBadminton/.
对羽毛球等复杂高速运动进行精细化的分析,对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来说是一个巨大的挑战。尽管其在一般视频理解方面取得了显著的进步,但这个困难主要源于缺乏足够丰富和特定领域的注释数据集。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了FineBadminton,这是一个新型的大规模数据集,具有独特的多层次语义注释层次结构(基础动作、战术语义和决策评估),以进行全面的羽毛球运动理解。FineBadminton的构建得益于创新的注释管道,该管道协同结合了MLLM生成的提案和人类精炼。我们还推出了由FineBadminton衍生的具有挑战性的基准测试FBBench,以严格评估MLLM在细微时空推理和战术理解方面的表现。总之,FineBadminton和FBBench共同提供了一个重要的生态系统,推动了精细视频理解和体育智能中MLLM的发展。此外,我们提出了一种优化的基线方法,结合了以命中为中心的关键帧选择和坐标引导浓缩策略,以专注于关键时刻并提炼显著视觉信息。在FBBench上的结果揭示,虽然当前MLLM在深度体育视频分析方面仍面临巨大挑战,但我们提出的策略仍然取得了实质性的性能提升。项目主页可在[https://finebadminton.github.io/FineBadminton/]访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对羽毛球这类复杂高速运动的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)所面临的挑战。为解决数据集中丰富、特定领域标注的缺乏问题,提出了FineBadminton数据集,具有独特的多层次语义标注层次结构,包括基础动作、战术语义和决策评估,以进行全面羽毛球理解。同时,结合MLLM生成的提案和人类精细修正的注释管道构建了该数据集。此外,还推出了源于FineBadminton的具有挑战性的基准测试FBBench,以严格评估MLLM在细微时空推理和战术理解方面的表现。本文提出的优化基线方法包括以击球为中心的关键帧选择和坐标引导浓缩策略,在FBBench上的结果展示了其性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在复杂高速运动如羽毛球的分析上仍面临挑战。
- 数据集缺乏丰富、特定领域的标注是这一挑战的主要原因。
- FineBadminton数据集具有多层次语义标注结构,旨在全面理解羽毛球。
- FineBadminton数据集的构建结合了MLLM生成的提案和人类精细修正的注释管道。
- FBBench是源于FineBadminton的基准测试,用于严格评估MLLM在细微时空推理和战术理解方面的性能。
- 提出的优化基线方法包括以击球为中心的关键帧选择和坐标引导浓缩策略。
点此查看论文截图

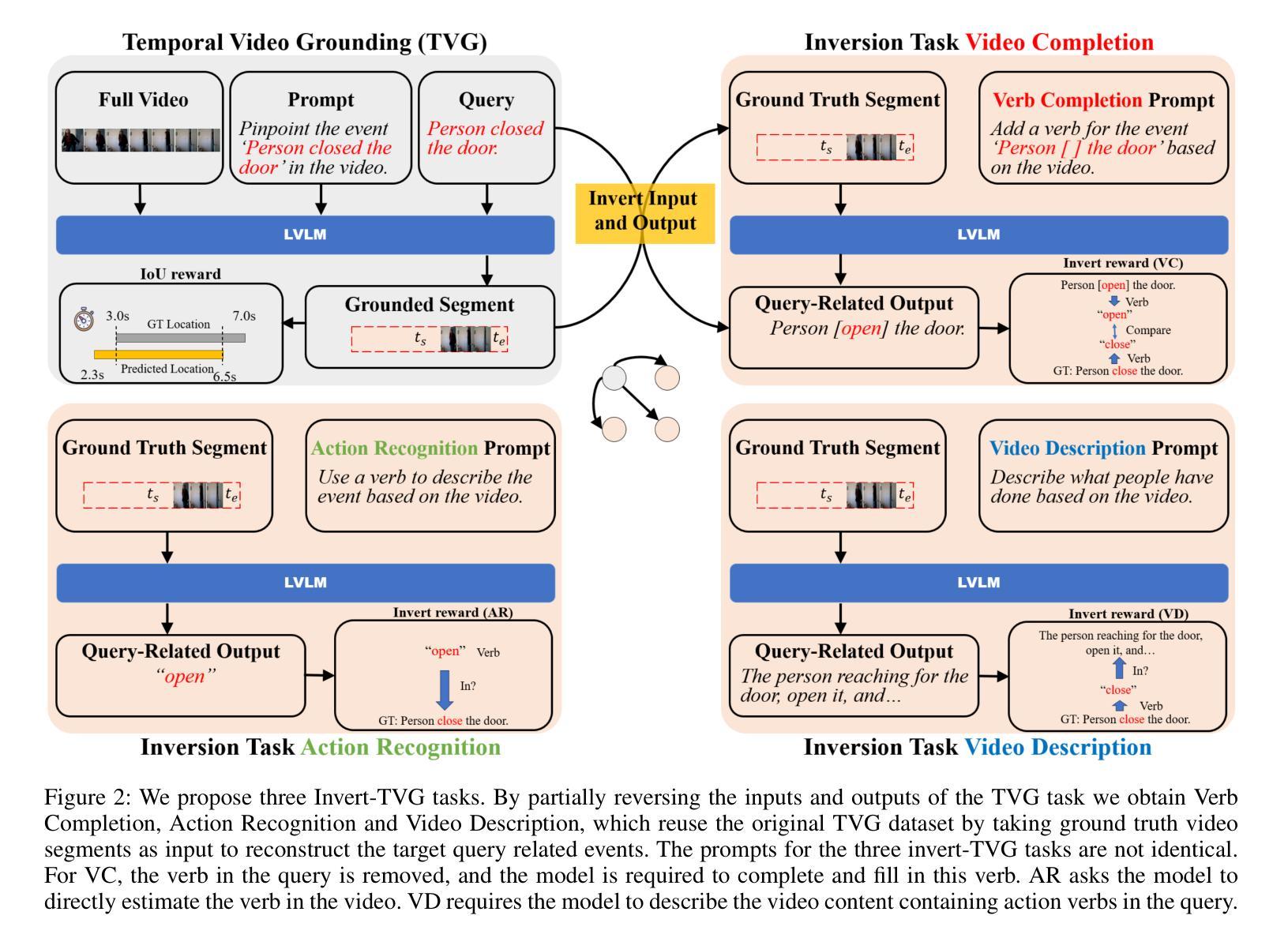
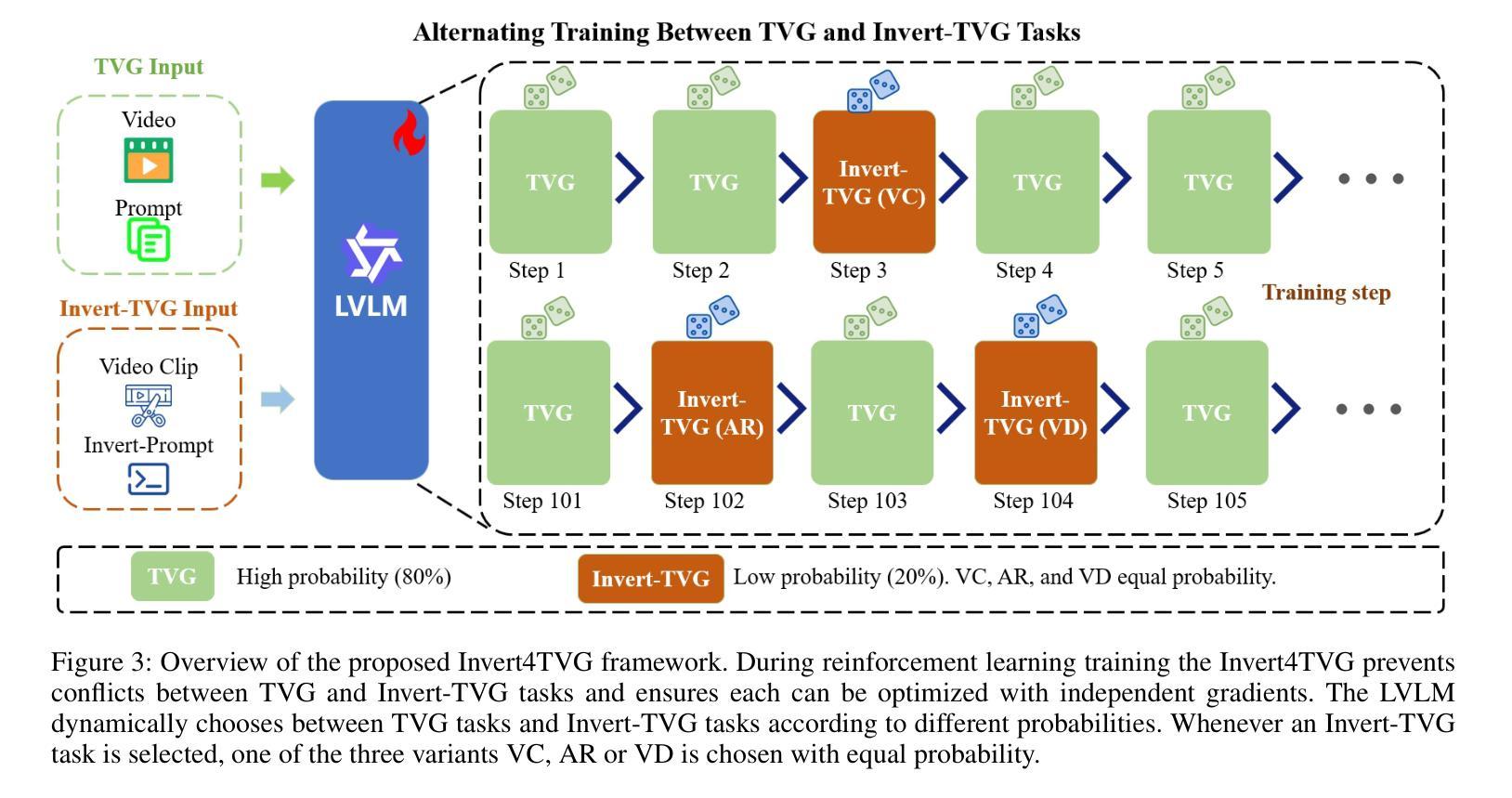
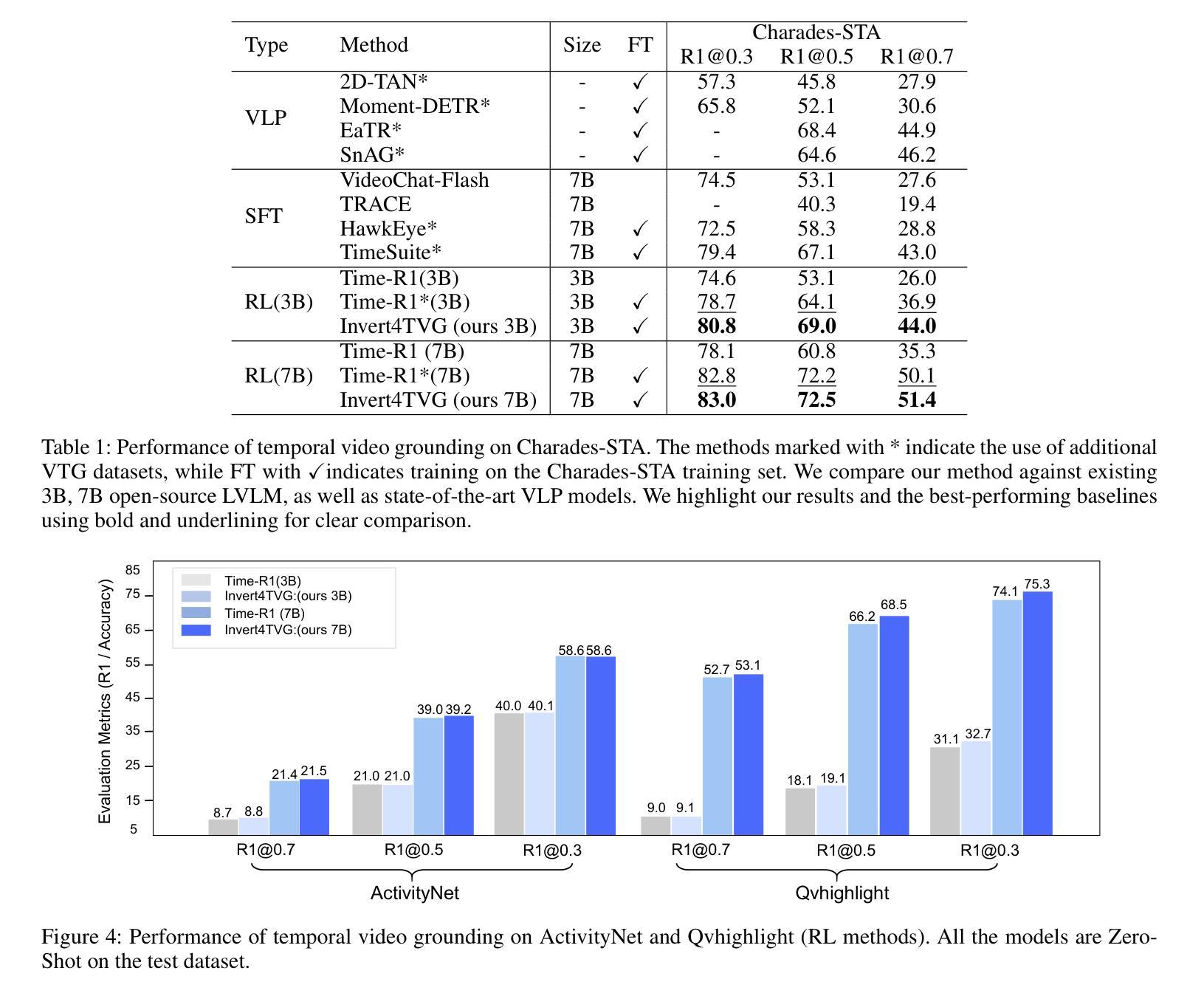
Invert4TVG: A Temporal Video Grounding Framework with Inversion Tasks for Enhanced Action Understanding
Authors:Zhaoyu Chen, Hongnan Lin, Yongwei Nie, Fei Ma, Xuemiao Xu, Fei Yu, Chengjiang Long
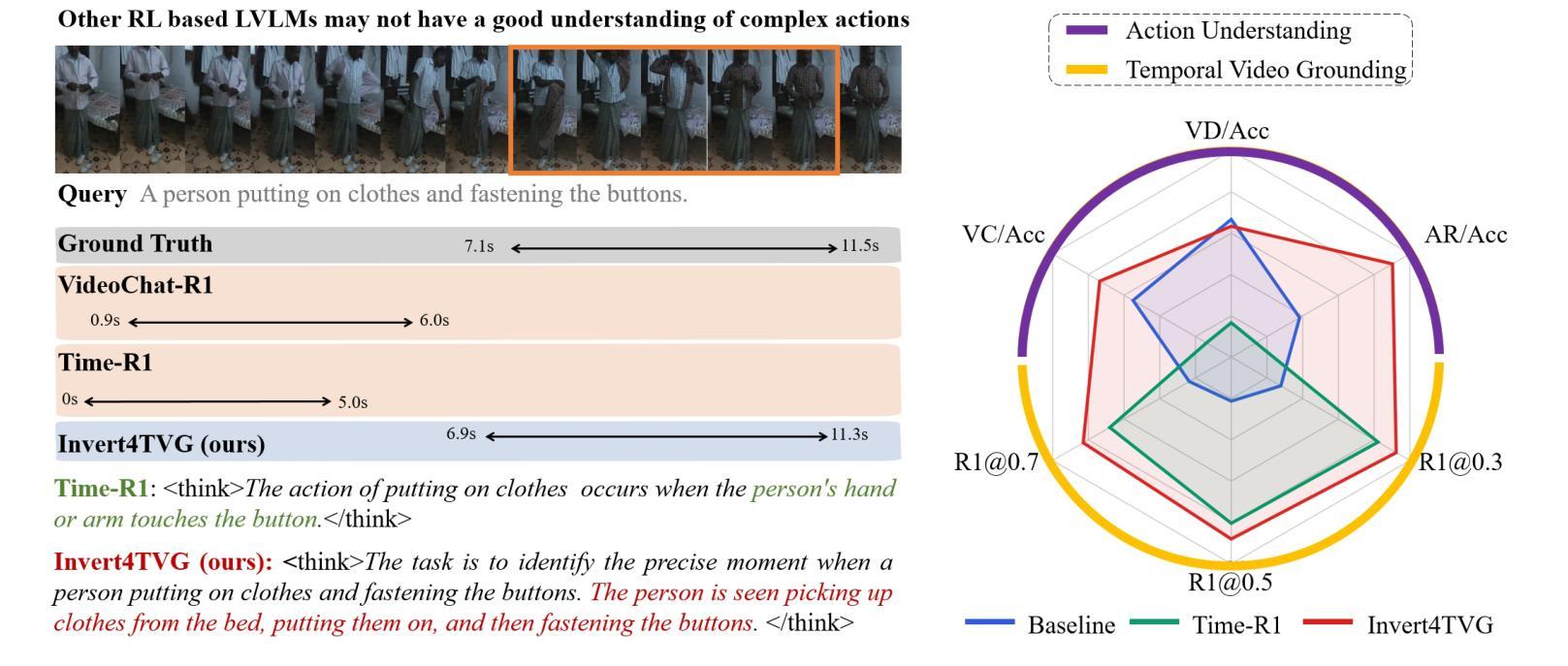
Temporal Video Grounding (TVG) seeks to localize video segments matching a given textual query. Current methods, while optimizing for high temporal Intersection-over-Union (IoU), often overfit to this metric, compromising semantic action understanding in the video and query, a critical factor for robust TVG. To address this, we introduce Inversion Tasks for TVG (Invert4TVG), a novel framework that enhances both localization accuracy and action understanding without additional data. Our approach leverages three inversion tasks derived from existing TVG annotations: (1) Verb Completion, predicting masked action verbs in queries from video segments; (2) Action Recognition, identifying query-described actions; and (3) Video Description, generating descriptions of video segments that explicitly embed query-relevant actions. These tasks, integrated with TVG via a reinforcement learning framework with well-designed reward functions, ensure balanced optimization of localization and semantics. Experiments show our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving a 7.1% improvement in R1@0.7 on Charades-STA for a 3B model compared to Time-R1. By inverting TVG to derive query-related actions from segments, our approach strengthens semantic understanding, significantly raising the ceiling of localization accuracy.
视频时序定位(TVG)旨在定位与给定文本查询匹配的视频片段。当前的方法虽然优化了高时序交并比(IoU),但往往过于依赖这一指标,牺牲了视频和查询中的语义动作理解,而这是实现稳健TVG的关键要素。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了TVG的倒置任务(Invert4TVG),这是一种新型框架,可以在不增加数据的情况下提高定位精度和动作理解。我们的方法利用现有TVG注释衍生出三个倒置任务:(1)动词补全,根据视频片段预测被掩盖的动作动词;(2)动作识别,识别查询描述的动作;(3)视频描述,生成明确嵌入查询相关动作的视频片段描述。这些任务通过与TVG结合的强化学习框架和精心设计的奖励函数,确保定位和语义的均衡优化。实验表明,我们的方法优于最新技术,在Charades-STA数据集上,相较于Time-R1,3B模型的R1@0.7提高了7.1%。通过倒置TVG从片段中推导出与查询相关的动作,我们的方法加强了语义理解,大大提高了定位精度的上限。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对时序视频定位(Temporal Video Grounding,TVG)任务的一种新方法——Invert4TVG。此方法旨在通过三个逆向任务强化视频段与查询文本的语义关联,同时提高定位精度。这些逆向任务包括动词补全、动作识别和视频描述。通过强化学习框架和精心设计奖励函数,该方法在Charades-STA数据集上实现了对最新技术的显著改进,特别是在R1@0.7指标上提高了7.1%。通过从视频段中导出与查询相关的动作,该方法强化了语义理解,显著提高了定位精度上限。
Key Takeaways
- 时序视频定位(TVG)旨在匹配给定文本查询的视频段。
- 当前方法过度优化IoU指标,可能影响对视频和查询的语义动作理解。
- Invert4TVG是一种新的框架,通过逆向任务增强定位精度和动作理解,无需额外数据。
- 三个逆向任务包括动词补全、动作识别和视频描述。
- 强化学习框架和奖励函数确保定位和语义的平衡优化。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在Charades-STA数据集上的R1@0.7指标优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

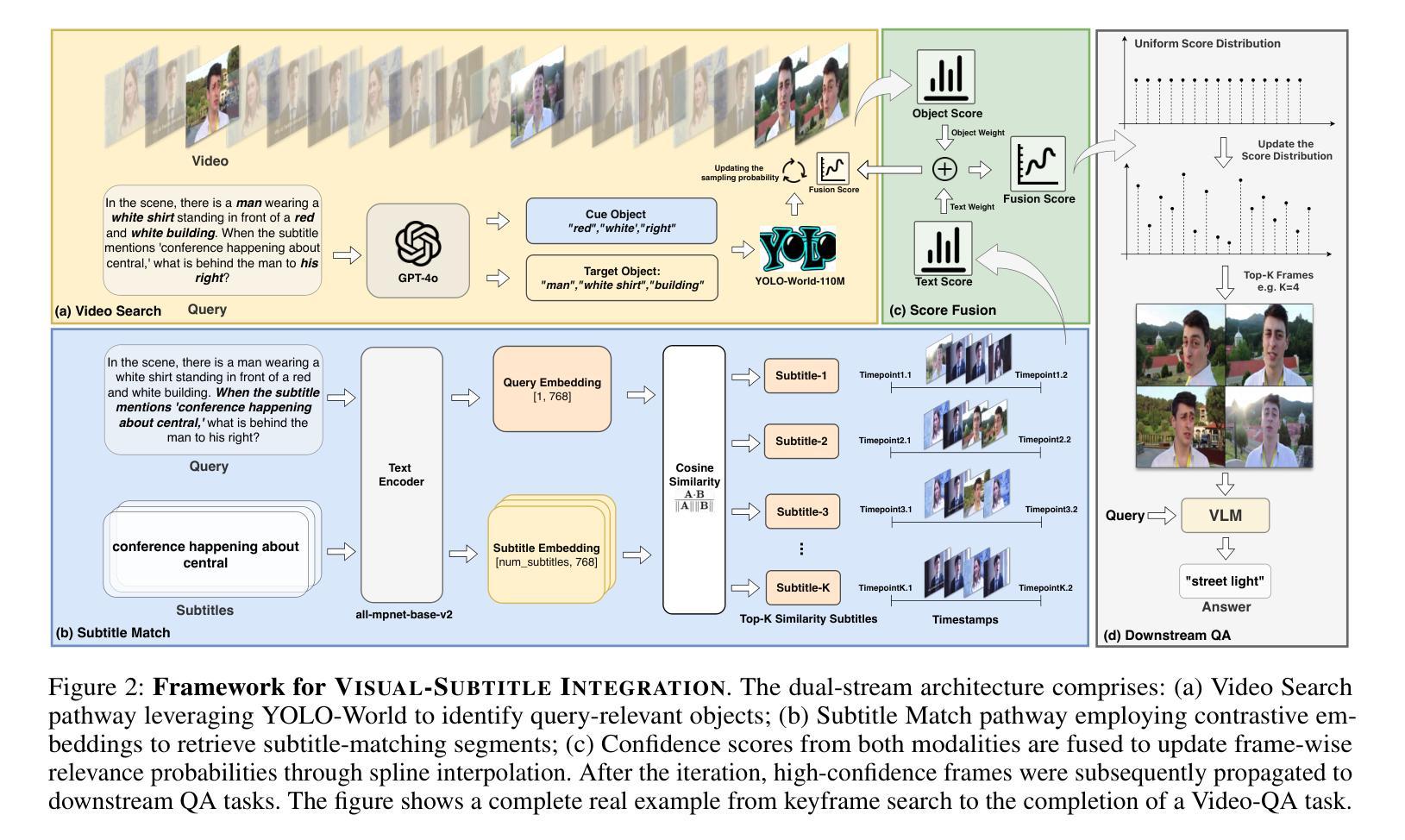
VSI: Visual Subtitle Integration for Keyframe Selection to enhance Long Video Understanding
Authors:Jianxiang He, Shaoguang Wang, Weiyu Guo, Meisheng Hong, Jungang Li, Yijie Xu, Ziyang Chen, Hui Xiong
Long video understanding presents a significant challenge to multimodal large language models (MLLMs) primarily due to the immense data scale. A critical and widely adopted strategy for making this task computationally tractable is keyframe retrieval, which seeks to identify a sparse set of video frames that are most salient to a given textual query. However, the efficacy of this approach is hindered by weak multimodal alignment between textual queries and visual content and fails to capture the complex temporal semantic information required for precise reasoning. To address this, we propose Visual-Subtitle Integeration(VSI), a multimodal keyframe search method that integrates subtitles, timestamps, and scene boundaries into a unified multimodal search process. The proposed method captures the visual information of video frames as well as the complementary textual information through a dual-stream search mechanism by Video Search Stream as well as Subtitle Match Stream, respectively, and improves the keyframe search accuracy through the interaction of the two search streams. Experimental results show that VSI achieve 40.00% key frame localization accuracy on the text-relevant subset of LongVideoBench and 68.48% accuracy on downstream long Video-QA tasks, surpassing competitive baselines by 20.35% and 15.79%, respectively. Furthermore, on the LongVideoBench, VSI achieved state-of-the-art(SOTA) in medium-to-long video-QA tasks, demonstrating the robustness and generalizability of the proposed multimodal search strategy.
长视频理解对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)提出了重大挑战,这主要是因为其数据量巨大。为了使这项任务在计算上可行,通常采用的关键策略是关键帧检索,它旨在识别给定文本查询中最显著的一组稀疏视频帧。然而,该方法的效力受到文本查询和视觉内容之间弱多模态对齐的阻碍,并且无法捕获用于精确推理所需的复杂时间语义信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了视觉字幕整合(VSI),这是一种多模态关键帧搜索方法,它将字幕、时间戳和场景边界整合到统一的多模态搜索过程中。该方法通过视频搜索流和字幕匹配流这两种双流搜索机制,分别捕获视频帧的视觉信息和互补的文本信息,并通过两个搜索流的交互提高关键帧搜索的准确性。实验结果表明,VSI在长视频基准测试文本相关子集上实现了关键帧定位精度为百分之四十,并且在下游长视频问答任务上的准确率为百分之六十八点四十八。与具有竞争力的基线相比,VSI分别提高了百分之二十三点三五和百分之十五点七九。此外,在LongVideoBench上,VSI在中长视频问答任务中达到了最佳水平,证明了所提出的多模态搜索策略的稳健性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,3 figures
Summary
针对长视频理解的多模态大型语言模型面临的挑战,提出了一种基于视觉字幕整合(VSI)的多模态关键帧搜索方法。该方法通过双流搜索机制,结合视频搜索流和字幕匹配流,提高了关键帧搜索的准确性。在LongVideoBench和长视频问答任务上的实验结果表明,VSI达到了卓越的性能,并实现了中等至长视频问答任务中的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 长视频理解对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)是一个重大挑战,主要因为数据规模庞大。
- 关键帧检索是应对这一挑战的一种常用策略,但其效果受到文本查询与视觉内容之间弱多模态对齐的限制。
- 提出的Visual-Subtitle Integration(VSI)方法通过结合字幕、时间戳和场景边界,进行多模态关键帧搜索。
- VSI采用双流搜索机制,包括视频搜索流和字幕匹配流,以提高关键帧搜索的准确性。
- 实验结果显示,VSI在LongVideoBench上的关键帧定位准确度较高,并在长视频问答任务中表现出卓越性能。
- VSI达到了先进性能,并在中等至长视频问答任务中实现了最佳效果。
点此查看论文截图



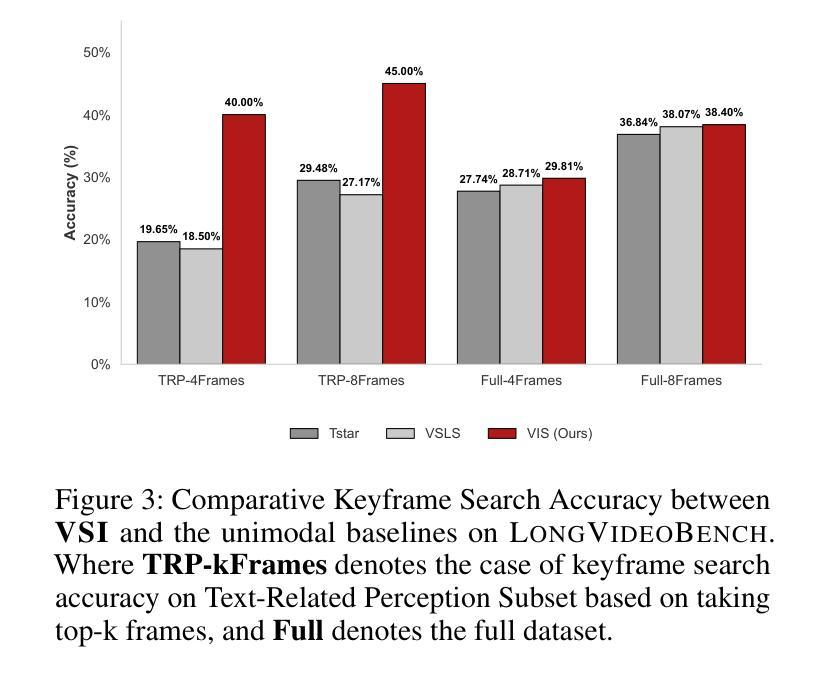
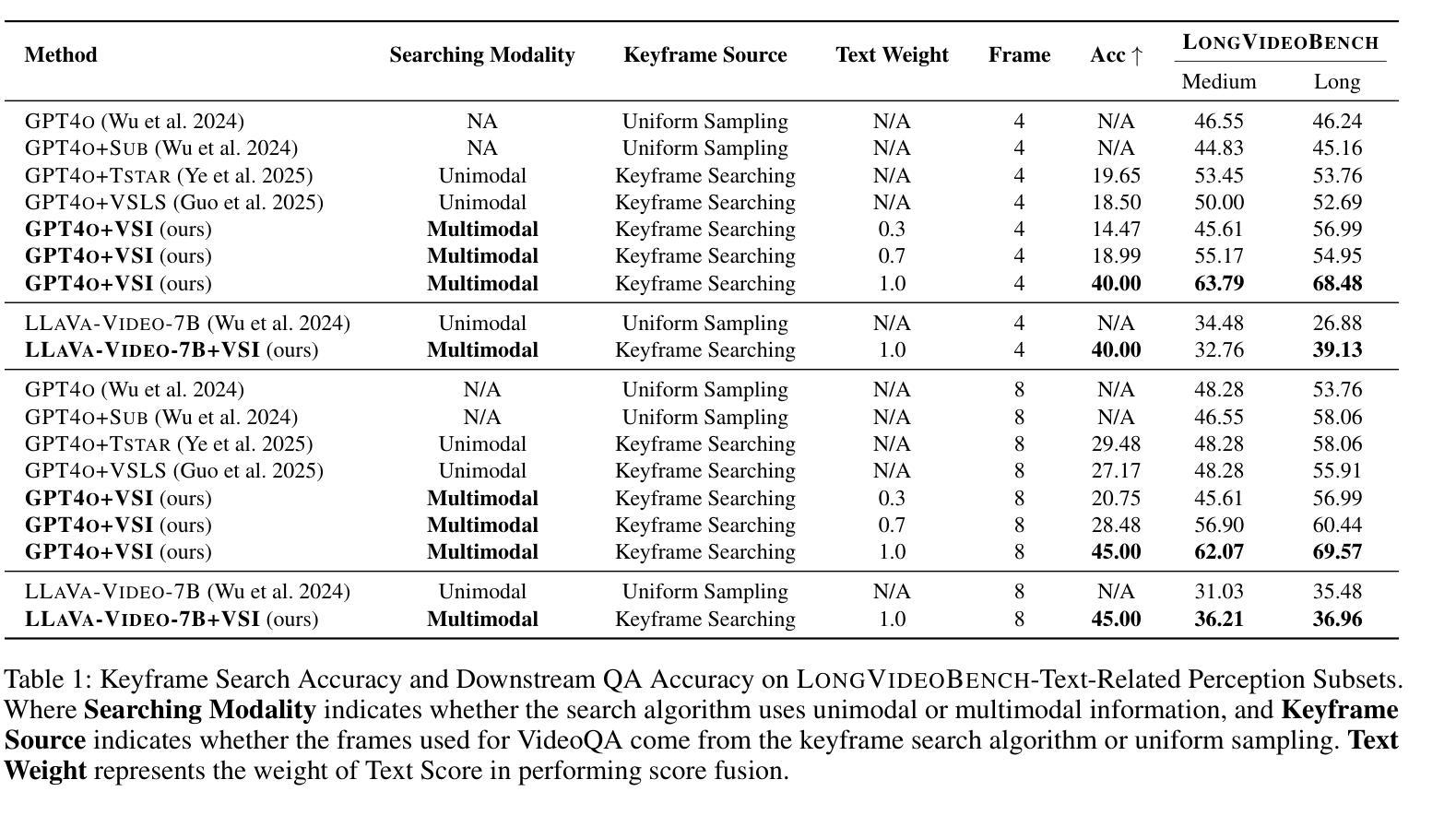
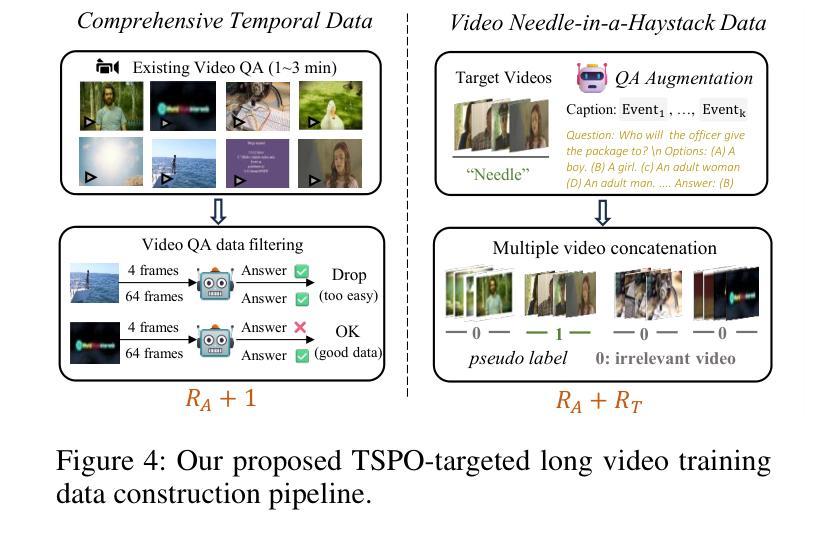
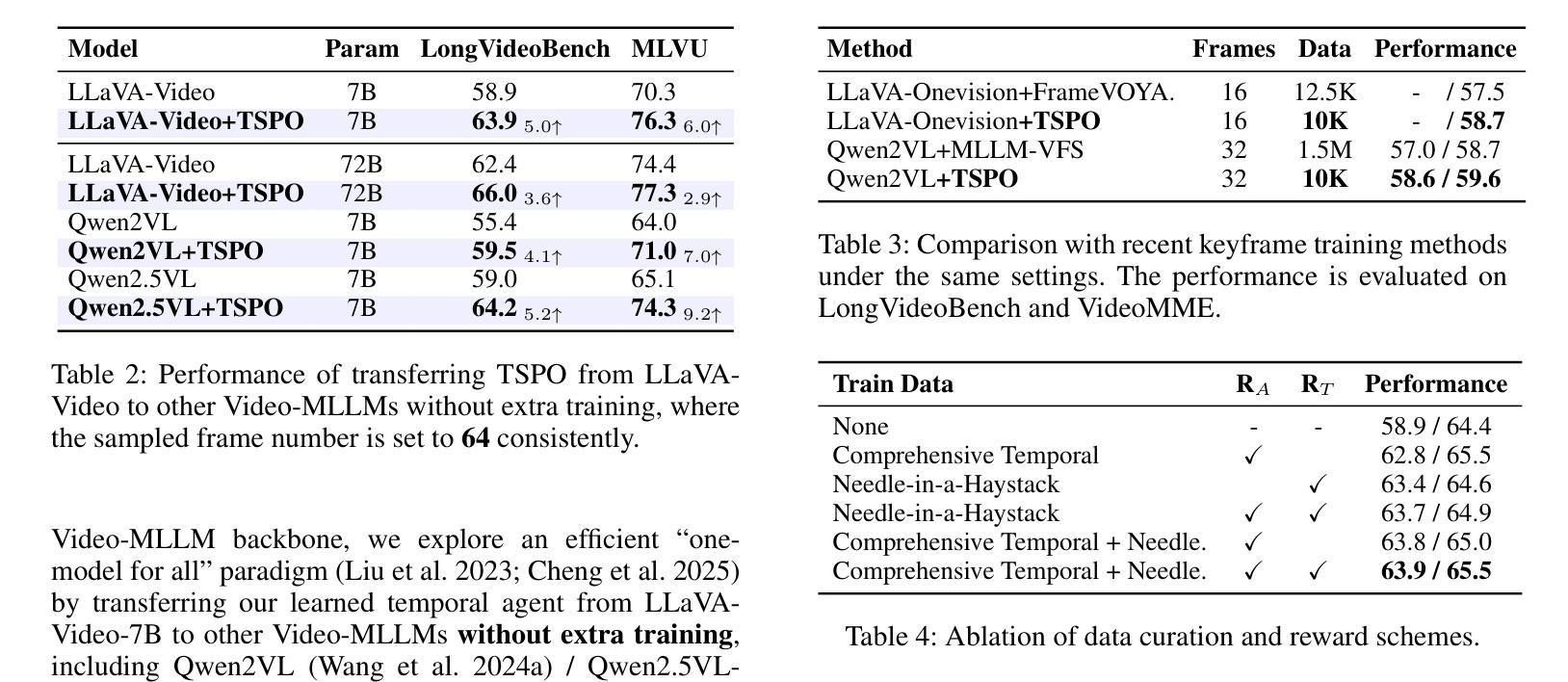
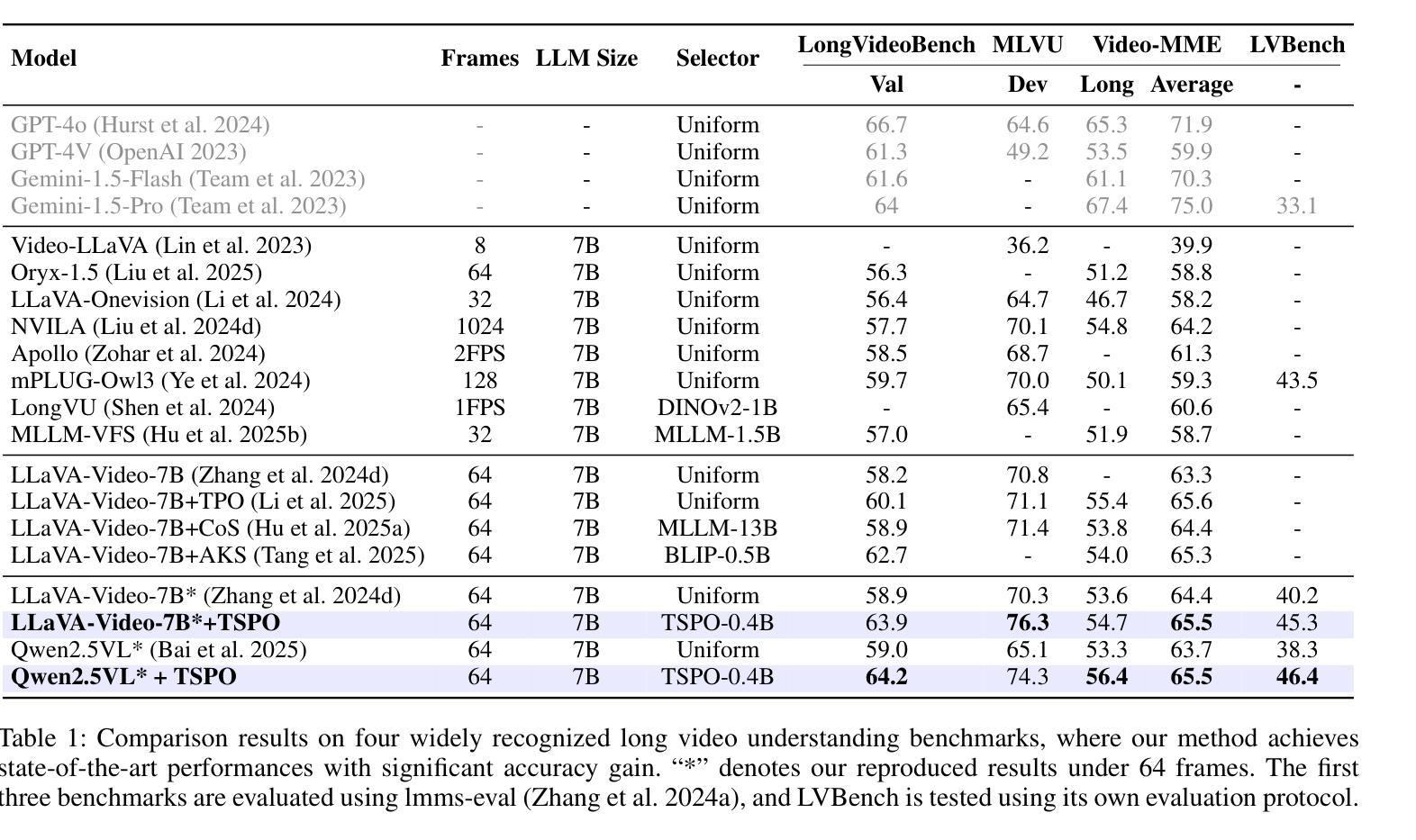
TSPO: Temporal Sampling Policy Optimization for Long-form Video Language Understanding
Authors:Canhui Tang, Zifan Han, Hongbo Sun, Sanping Zhou, Xuchong Zhang, Xin Wei, Ye Yuan, Huayu Zhang, Jinglin Xu, Hao Sun
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant progress in vision-language tasks, yet they still face challenges when processing long-duration video inputs. The limitation arises from MLLMs’ context limit and training costs, necessitating sparse frame sampling before feeding videos into MLLMs. However, building a trainable sampling method remains challenging due to the unsupervised and non-differentiable nature of sparse frame sampling in Video-MLLMs. To address these problems, we propose Temporal Sampling Policy Optimization (TSPO), advancing MLLMs’ long-form video-language understanding via reinforcement learning. Specifically, we first propose a trainable event-aware temporal agent, which captures event-query correlation for performing probabilistic keyframe selection. Then, we propose the TSPO reinforcement learning paradigm, which models keyframe selection and language generation as a joint decision-making process, enabling end-to-end group relative optimization for the temporal sampling policy. Furthermore, we propose a dual-style long video training data construction pipeline, balancing comprehensive temporal understanding and key segment localization. Finally, we incorporate rule-based answering accuracy and temporal locating reward mechanisms to optimize the temporal sampling policy. Comprehensive experiments show that our TSPO achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple long video understanding benchmarks, and shows transferable ability across different cutting-edge Video-MLLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/Hui-design/TSPO
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言任务中取得了显著进展,但在处理长时视频输入时仍面临挑战。这些限制源于MLLMs的上下文限制和训练成本,需要在将视频输入MLLMs之前进行稀疏帧采样。然而,构建可训练采样方法仍然具有挑战性,因为视频MLLMs中的稀疏帧采样具有无监督和不可微分的特性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出时序采样策略优化(TSPO),通过强化学习推进MLLMs对长格式视频语言的了解。具体来说,我们首先提出一个可训练的事件感知时序代理,用于捕捉事件查询相关性,以执行概率关键帧选择。然后,我们提出了TSPO强化学习范式,将关键帧选择和语言生成建模为联合决策过程,实现对时序采样策略端到端的群体相对优化。此外,我们提出了双风格长视频训练数据构建流程,平衡全面的时间理解和关键段落定位。最后,我们结合了基于规则的回答准确性和时间定位奖励机制,以优化时序采样策略。综合实验表明,我们的TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,并展示了在不同前沿视频MLLMs之间的可迁移能力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Hui-design/TSPO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型在处理长视频输入时面临挑战,由于上下文限制和训练成本,需对视频进行稀疏帧采样。提出一种基于强化学习的时序采样策略优化方法(TSPO),通过训练事件感知的时序代理和TSPO强化学习范式,实现长视频的语言理解。同时,构建了一种双风格长视频训练数据构建管道,平衡全面的时序理解和关键段定位。优化时序采样策略,通过规则回答准确率和时序定位奖励机制实现。实验表明,TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中达到最佳性能,并具备跨不同前沿视频-语言模型的迁移能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在处理长视频时存在挑战,主要受限于上下文和训练成本。
- 提出了基于强化学习的时序采样策略优化(TSPO)方法,解决视频-语言模型的稀疏帧采样问题。
- TSPO通过训练事件感知的时序代理和TSPO强化学习范式实现长视频的语言理解。
- 构建了双风格长视频训练数据构建管道,实现全面的时序理解和关键段定位平衡。
- 通过规则回答准确率和时序定位奖励机制优化时序采样策略。
- TSPO在多个长视频理解基准测试中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

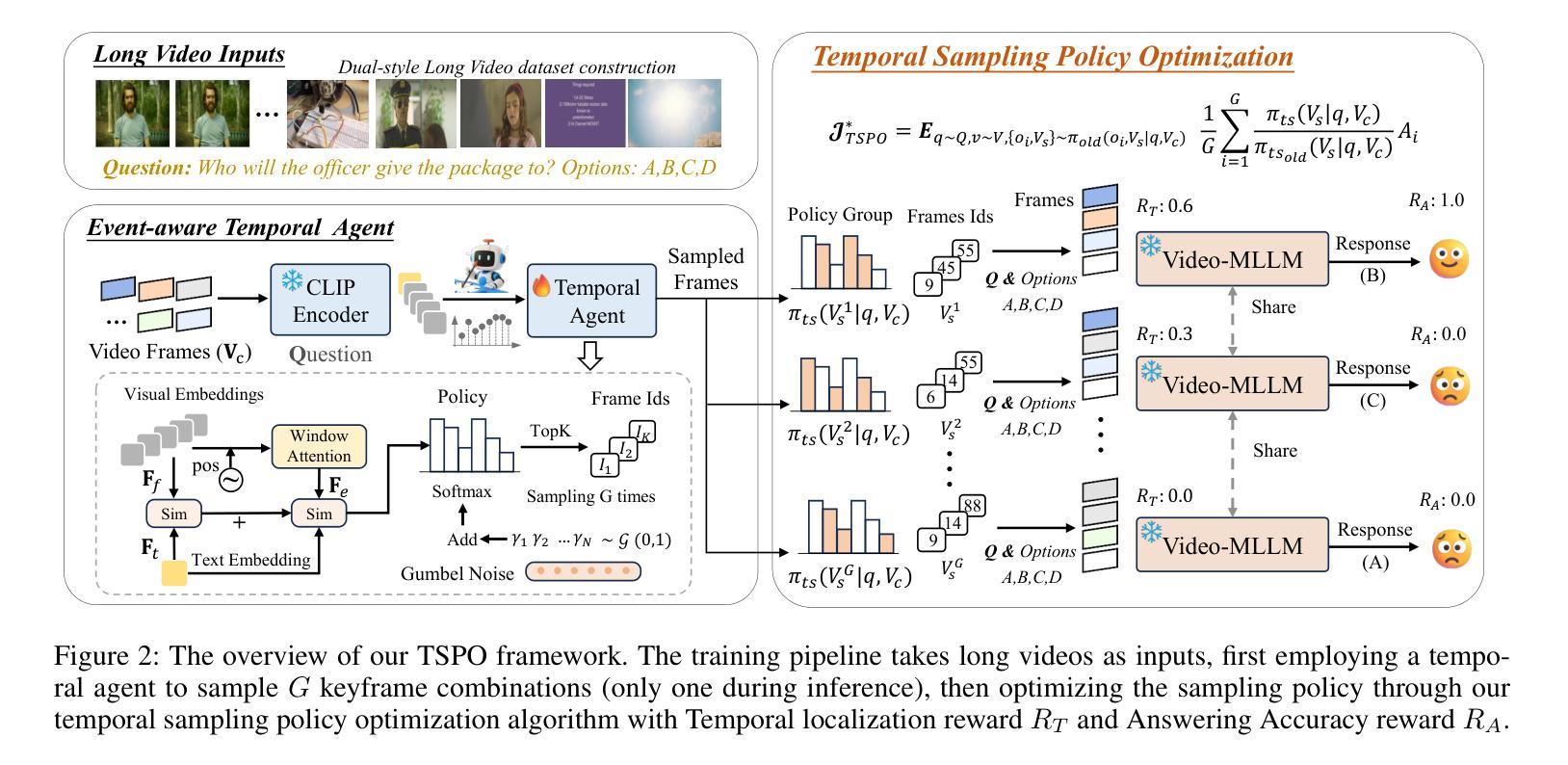
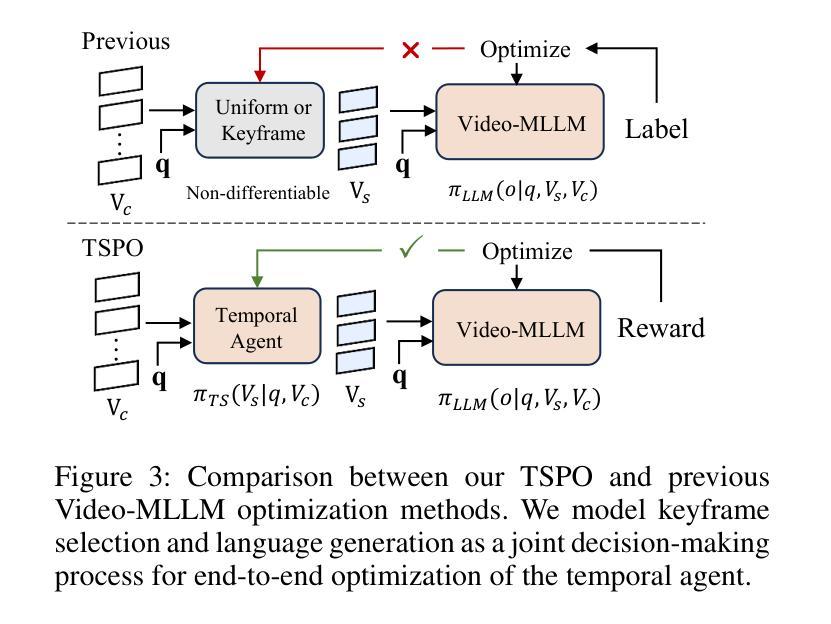
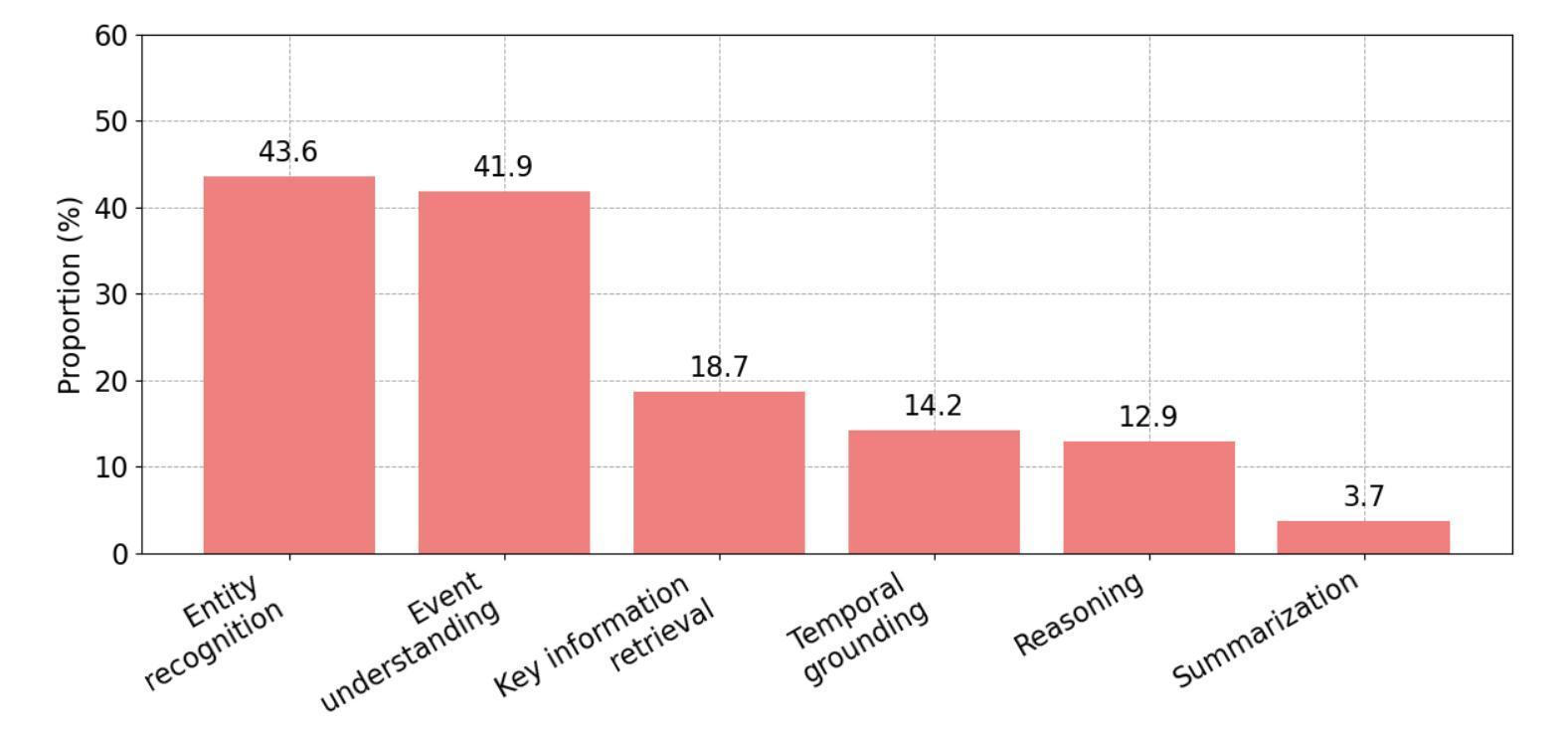
LVBench: An Extreme Long Video Understanding Benchmark
Authors:Weihan Wang, Zehai He, Wenyi Hong, Yean Cheng, Xiaohan Zhang, Ji Qi, Xiaotao Gu, Shiyu Huang, Bin Xu, Yuxiao Dong, Ming Ding, Jie Tang
Recent progress in multimodal large language models has markedly enhanced the understanding of short videos (typically under one minute), and several evaluation datasets have emerged accordingly. However, these advancements fall short of meeting the demands of real-world applications such as embodied intelligence for long-term decision-making, in-depth movie reviews and discussions, and live sports commentary, all of which require comprehension of long videos spanning several hours. To address this gap, we introduce LVBench, a benchmark specifically designed for long video understanding. Our dataset comprises publicly sourced videos and encompasses a diverse set of tasks aimed at long video comprehension and information extraction. LVBench is designed to challenge multimodal models to demonstrate long-term memory and extended comprehension capabilities. Our extensive evaluations reveal that current multimodal models still underperform on these demanding long video understanding tasks. Through LVBench, we aim to spur the development of more advanced models capable of tackling the complexities of long video comprehension. Our data and code are publicly available at: https://lvbench.github.io.
近期多模态大型语言模型的进展显著提高了对短视频(通常不到一分钟)的理解能力,并出现了几个相应的评估数据集。然而,这些进展还不足以满足现实世界应用的需求,如用于长期决策制定的嵌入式智能、深入的影评和讨论以及现场体育评论等,这些应用都需要理解长达数小时的长视频。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了LVBench,这是一个专门为长视频理解而设计的基准测试。我们的数据集包含公开来源的视频,涵盖了一系列旨在测试长视频理解和信息提取的任务。LVBench旨在挑战多模态模型,以展示其长期记忆和扩展理解能力。我们的广泛评估表明,当前的多模态模型在这些具有挑战性的长视频理解任务上表现仍然不足。通过LVBench,我们旨在促进更先进模型的发展,以应对长视频理解的复杂性。我们的数据和代码可在以下网址公开获取:https://lvbench.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对长视频理解的基准测试平台LVBench。该平台包含公开来源的视频,涵盖了一系列旨在测试长视频理解和信息提取的任务。LVBench旨在挑战多模态模型,展示其长期记忆和扩展理解能力。评估显示,当前多模态模型在这些任务上表现不佳,因此希望通过LVBench推动更先进模型的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在理解短视频方面取得了显著进步,但难以满足长视频理解需求。
- LVBench是一个专门设计用于长视频理解的基准测试平台。
- LVBench包含公开来源的视频,涵盖多种旨在测试长视频理解和信息提取的任务。
- LVBench旨在挑战多模态模型的长期记忆和扩展理解能力。
- 当前多模态模型在长视频理解任务上的表现仍然不足。
- LVBench的目标是推动更先进模型的发展,以应对长视频理解的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图


Video Understanding with Large Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Yunlong Tang, Jing Bi, Siting Xu, Luchuan Song, Susan Liang, Teng Wang, Daoan Zhang, Jie An, Jingyang Lin, Rongyi Zhu, Ali Vosoughi, Chao Huang, Zeliang Zhang, Pinxin Liu, Mingqian Feng, Feng Zheng, Jianguo Zhang, Ping Luo, Jiebo Luo, Chenliang Xu
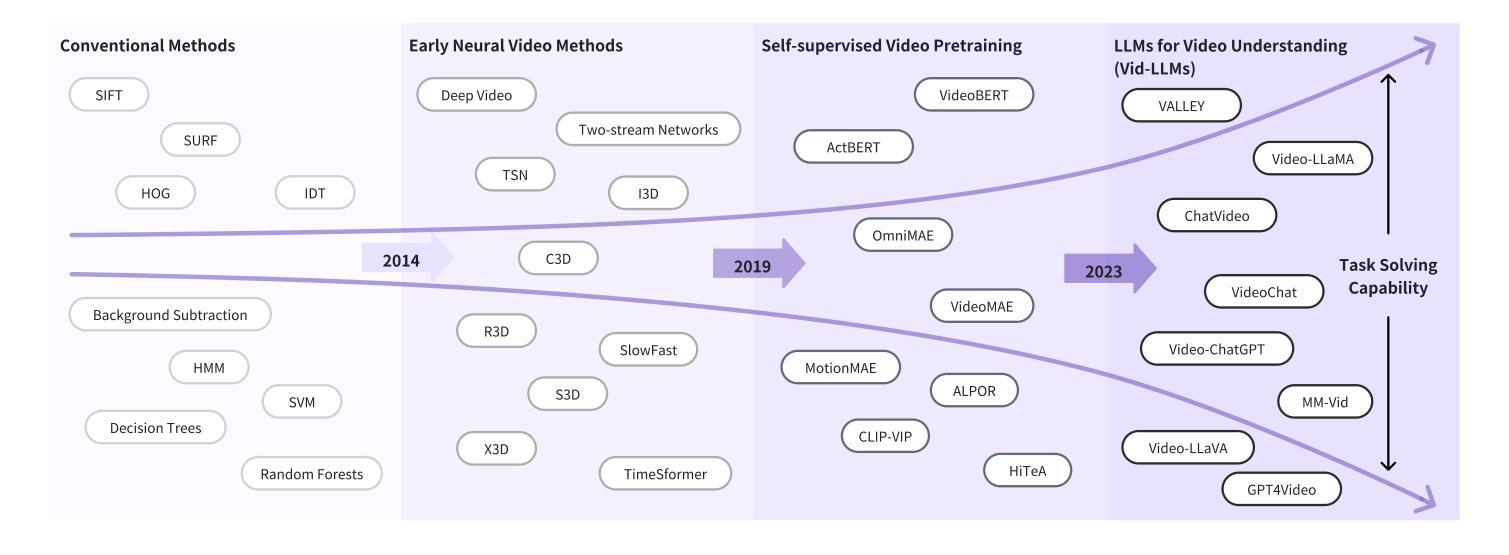
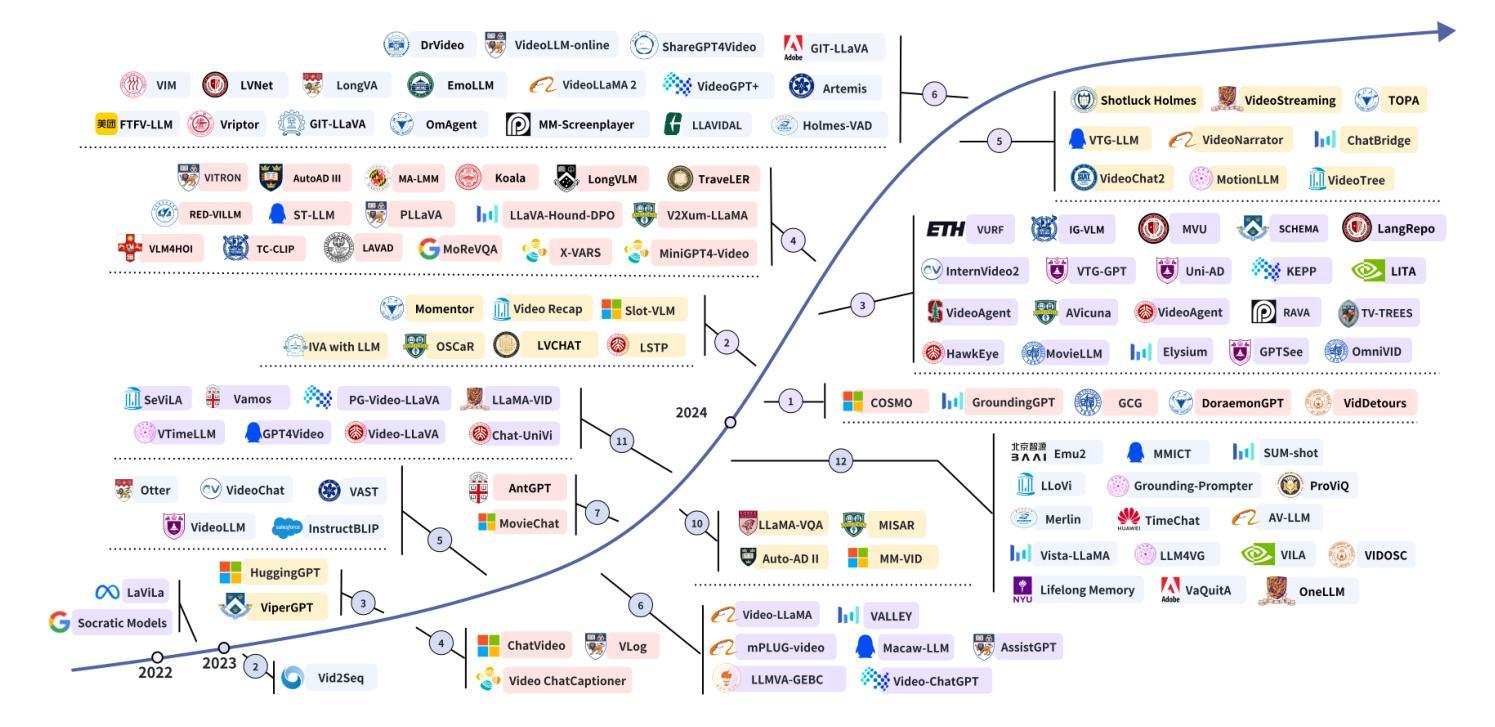
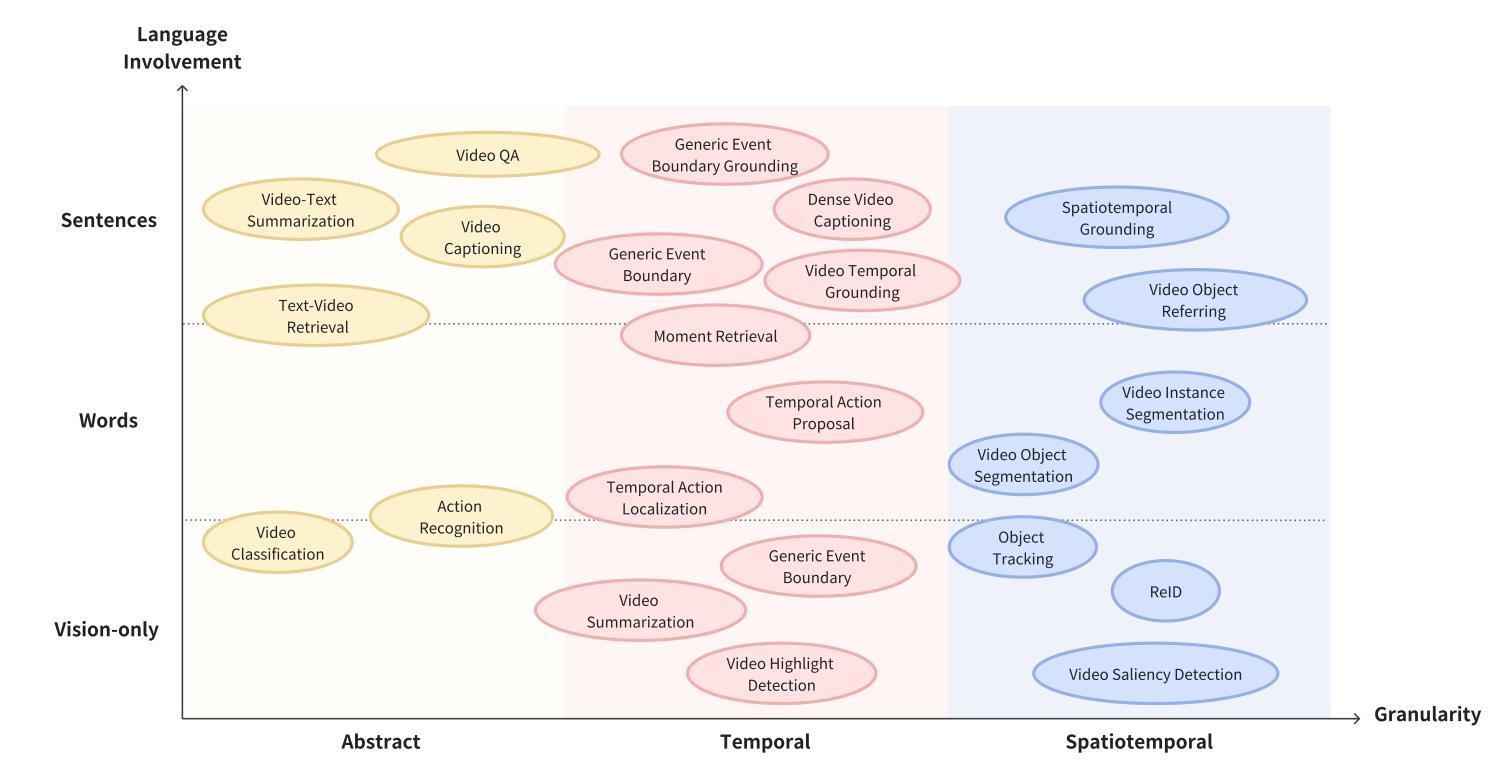
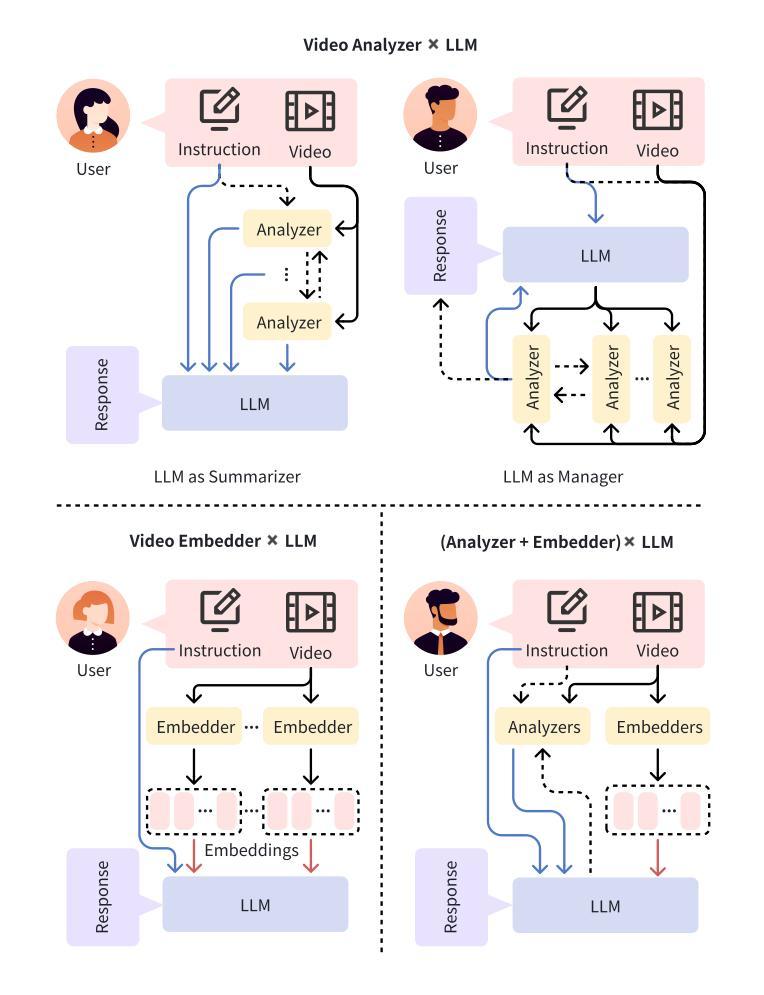
With the burgeoning growth of online video platforms and the escalating volume of video content, the demand for proficient video understanding tools has intensified markedly. Given the remarkable capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in language and multimodal tasks, this survey provides a detailed overview of recent advancements in video understanding that harness the power of LLMs (Vid-LLMs). The emergent capabilities of Vid-LLMs are surprisingly advanced, particularly their ability for open-ended multi-granularity (general, temporal, and spatiotemporal) reasoning combined with commonsense knowledge, suggesting a promising path for future video understanding. We examine the unique characteristics and capabilities of Vid-LLMs, categorizing the approaches into three main types: Video Analyzer x LLM, Video Embedder x LLM, and (Analyzer + Embedder) x LLM. Furthermore, we identify five sub-types based on the functions of LLMs in Vid-LLMs: LLM as Summarizer, LLM as Manager, LLM as Text Decoder, LLM as Regressor, and LLM as Hidden Layer. Furthermore, this survey presents a comprehensive study of the tasks, datasets, benchmarks, and evaluation methodologies for Vid-LLMs. Additionally, it explores the expansive applications of Vid-LLMs across various domains, highlighting their remarkable scalability and versatility in real-world video understanding challenges. Finally, it summarizes the limitations of existing Vid-LLMs and outlines directions for future research. For more information, readers are recommended to visit the repository at https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding.
随着在线视频平台的蓬勃发展和视频内容的不断增加,对熟练的视频理解工具的需求显著增加。鉴于大型语言模型(LLM)在语言和多媒体任务中的突出能力,这篇综述提供了关于如何利用LLM(视频LLM)的力量进行视频理解的最新进展的详细介绍。视频LLM的新兴能力令人惊讶地先进,尤其是它们结合常识知识进行的开放式多粒度(一般、时间和时空)推理能力,这为未来的视频理解指明了有希望的道路。我们研究了视频LLM的独特特征和功能,将方法分为三类:视频分析器xLLM、视频嵌入器xLLM和(分析器+嵌入器)xLLM。此外,我们根据LLM在视频LLM中的功能确定了五种亚型:LLM作为摘要器、LLM作为管理器、LLM作为文本解码器、LLM作为回归器和LLM作为隐藏层。此外,这篇综述还对视频LLM的任务、数据集、基准测试和评估方法进行了全面的研究。还探讨了视频LLM在各个领域的应用广泛性,突显了它们在现实世界的视频理解挑战中的出色可扩展性和通用性。最后,总结了现有视频LLM的局限性,并指出了未来研究的方向。更多信息请参阅https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding仓库。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT
Summary
基于在线视频平台的蓬勃发展和视频内容的快速增长,对熟练的视频理解工具的需求显著增加。本综述详细概述了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行视频理解的最新进展。Vid-LLMs的新兴能力令人惊讶地先进,特别是其结合常识知识进行开放式多粒度(一般、时间和时空)推理的能力,为未来的视频理解提供了充满希望的路径。
Key Takeaways
- 在线视频平台和视频内容的增长导致了对熟练视频理解工具的需求显著增加。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在视频理解方面表现出显著的能力。
- Vid-LLMs的新兴能力包括开放式的多粒度推理和结合常识知识。
- 视频理解的方法可以分类为三种主要类型:Video Analyzer x LLM、Video Embedder x LLM和(Analyzer + Embedder)x LLM。
- LLM在Vid-LLMs中的功能可以分为五种:总结器、管理器、文本解码器、回归器和隐藏层。
- Vid-LLMs的应用范围广泛,具有应对现实视频理解挑战的可扩展性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图