⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
Learning an Implicit Physics Model for Image-based Fluid Simulation
Authors:Emily Yue-Ting Jia, Jiageng Mao, Zhiyuan Gao, Yajie Zhao, Yue Wang
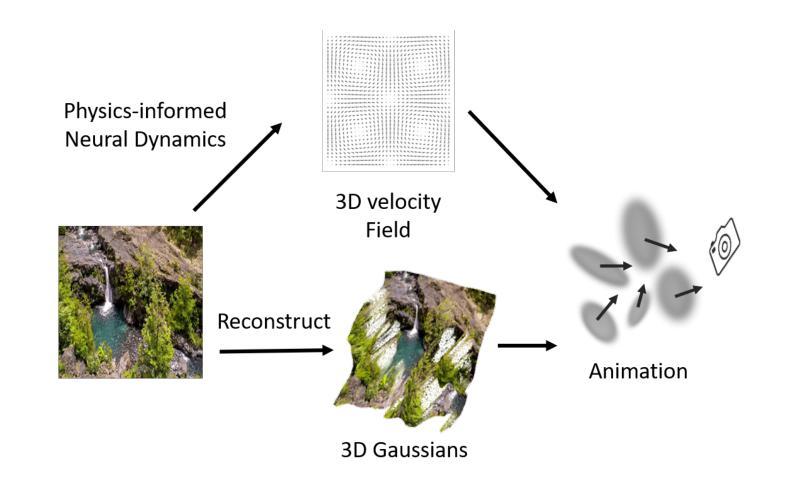
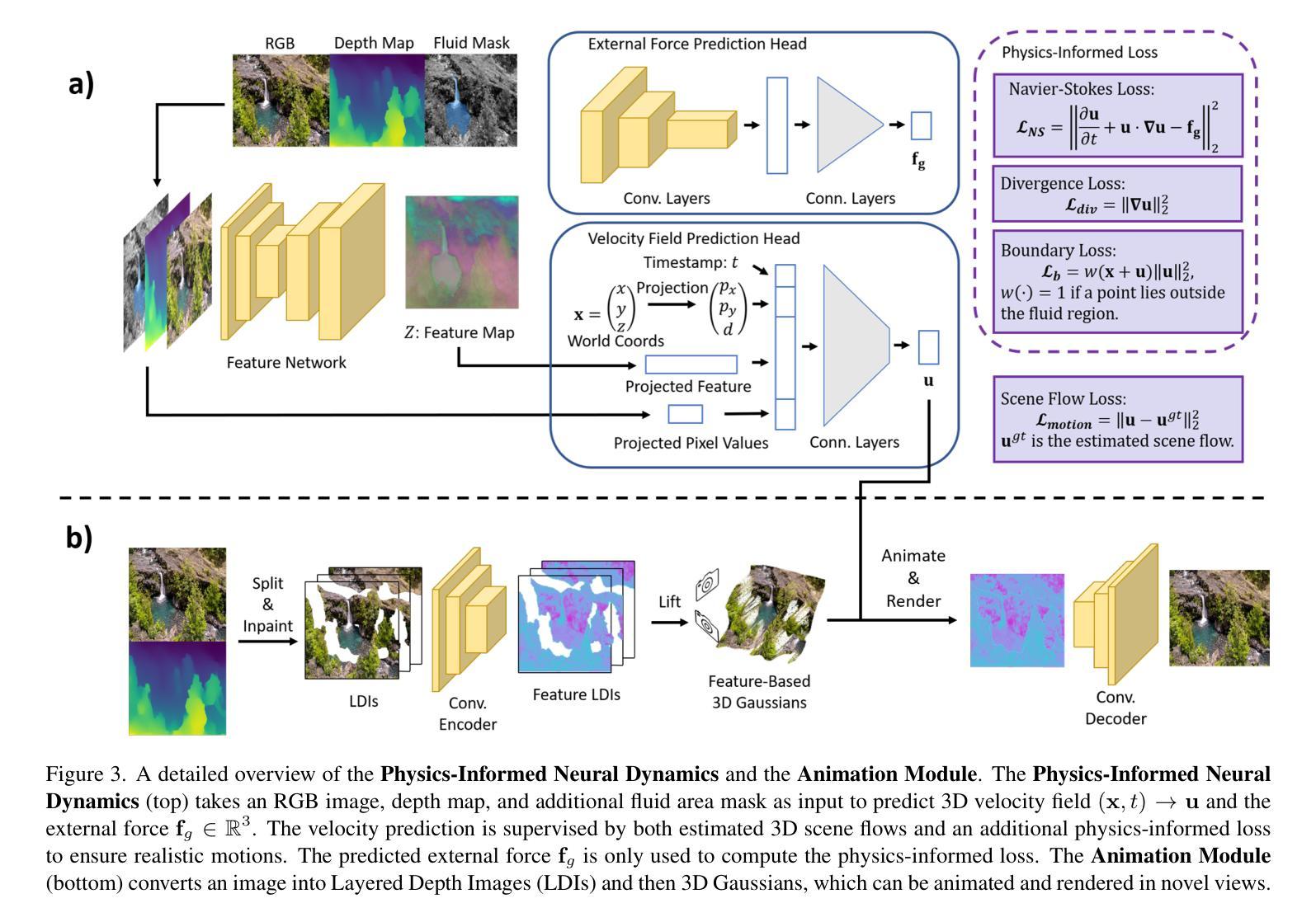
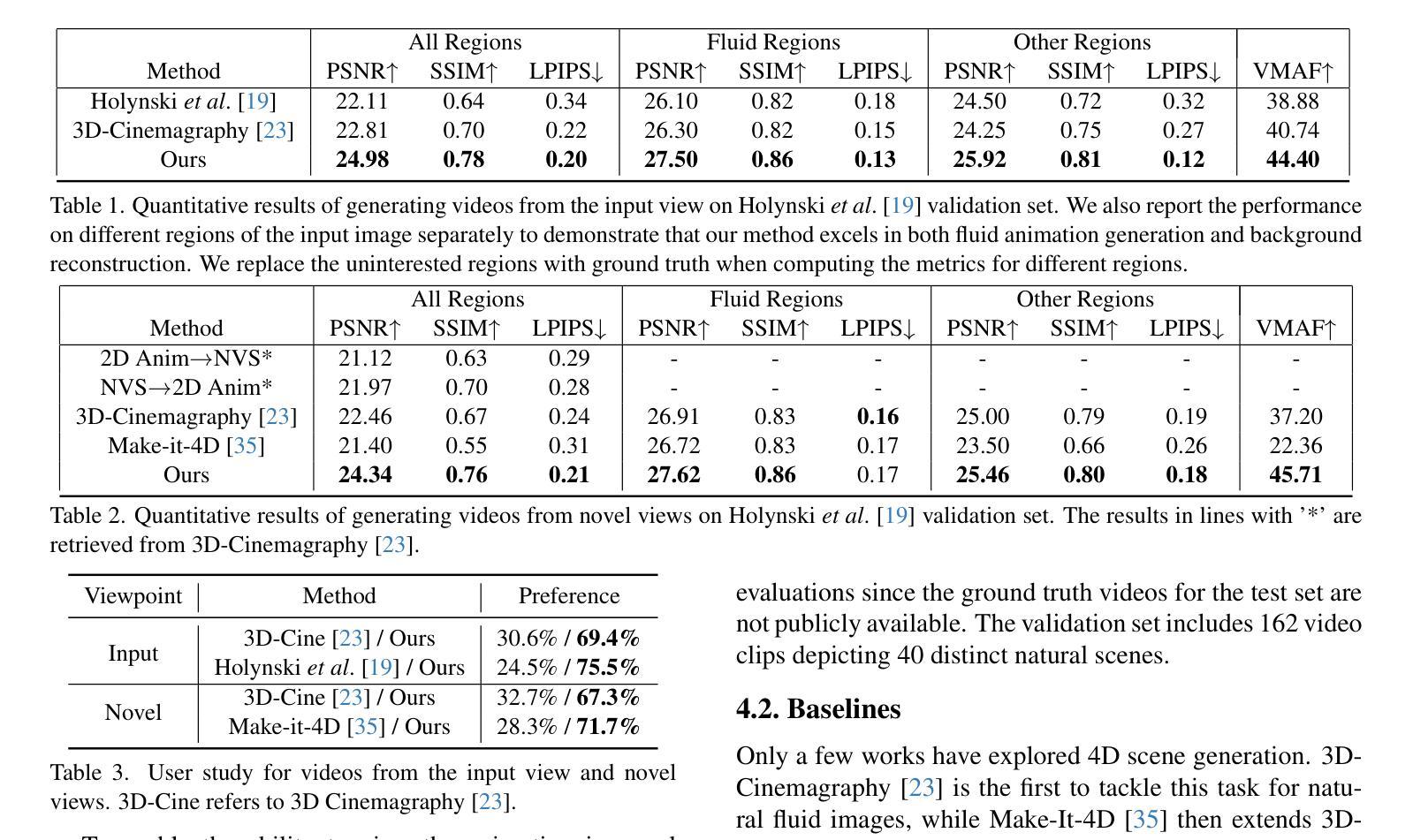
Humans possess an exceptional ability to imagine 4D scenes, encompassing both motion and 3D geometry, from a single still image. This ability is rooted in our accumulated observations of similar scenes and an intuitive understanding of physics. In this paper, we aim to replicate this capacity in neural networks, specifically focusing on natural fluid imagery. Existing methods for this task typically employ simplistic 2D motion estimators to animate the image, leading to motion predictions that often defy physical principles, resulting in unrealistic animations. Our approach introduces a novel method for generating 4D scenes with physics-consistent animation from a single image. We propose the use of a physics-informed neural network that predicts motion for each surface point, guided by a loss term derived from fundamental physical principles, including the Navier-Stokes equations. To capture appearance, we predict feature-based 3D Gaussians from the input image and its estimated depth, which are then animated using the predicted motions and rendered from any desired camera perspective. Experimental results highlight the effectiveness of our method in producing physically plausible animations, showcasing significant performance improvements over existing methods. Our project page is https://physfluid.github.io/ .
人类拥有从单一静态图像中想象出包含运动和3D几何的4D场景的特殊能力。这种能力源于我们对类似场景的累积观察和对物理的直观理解。在本文中,我们旨在在神经网络中复制这种能力,特别专注于自然流体图像。现有方法通常使用简单的2D运动估计器来使图像动画化,导致运动预测往往违背物理原理,从而产生不真实的动画。我们的方法引入了一种从单张图像生成具有物理一致性动画的4D场景的新方法。我们建议使用受物理启发的神经网络来预测每个表面点的运动,该网络受基本物理原理得出的损失项的指导,包括Navier-Stokes方程。为了捕捉外观,我们从输入图像和其估计的深度预测基于特征的3D高斯分布,然后使用预测的运动使其动画化,并从任何想要的相机角度进行渲染。实验结果突出了我们的方法在产生物理可行动画方面的有效性,展示了相较于现有方法的显著性能提升。我们的项目页面是https://physfluid.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨人类从单一静态图像中想象4D场景(包括运动和3D几何)的非凡能力,并提出一种在神经网络中复制这种能力的方法,特别关注自然流体图像。现有方法通常使用简单的2D运动估计器来驱动图像运动,导致预测的运动往往违背物理原则,产生不真实的动画。本文提出一种新型方法,利用物理信息神经网络预测每个表面点的运动,并通过基于Navier-Stokes方程等基础物理原理的损失函数进行引导。为了捕捉外观,我们从输入图像和其估计的深度预测特征化的3D高斯模型,然后使用预测的运动和任意期望的相机视角进行动画渲染。实验结果表明,该方法能生成物理上合理的动画,显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 人类具有从单一静态图像中想象4D场景(包括运动和3D几何)的非凡能力。
- 现有方法使用简单的2D运动估计器,导致预测的运动常常违背物理规律,产生不真实动画。
- 本文提出一种新型方法,使用物理信息神经网络预测每个表面点的运动。
- 预测的运动通过基于Navier-Stokes方程等基础物理原理的损失函数进行引导。
- 该方法可以预测特征化的3D高斯模型,捕捉图像外观。
- 预测的运动和任意期望的相机视角可用于动画渲染。
点此查看论文截图

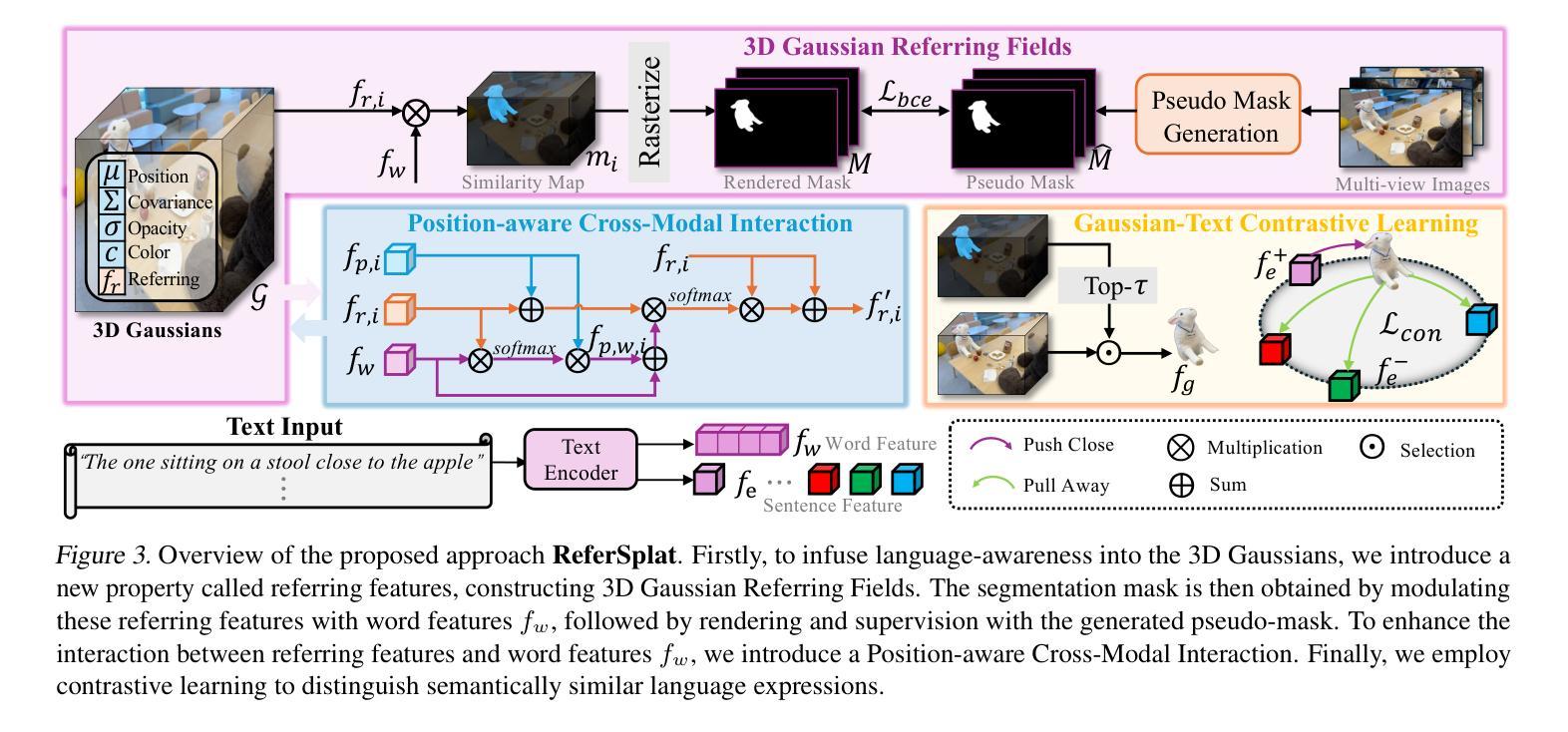
ReferSplat: Referring Segmentation in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Shuting He, Guangquan Jie, Changshuo Wang, Yun Zhou, Shuming Hu, Guanbin Li, Henghui Ding
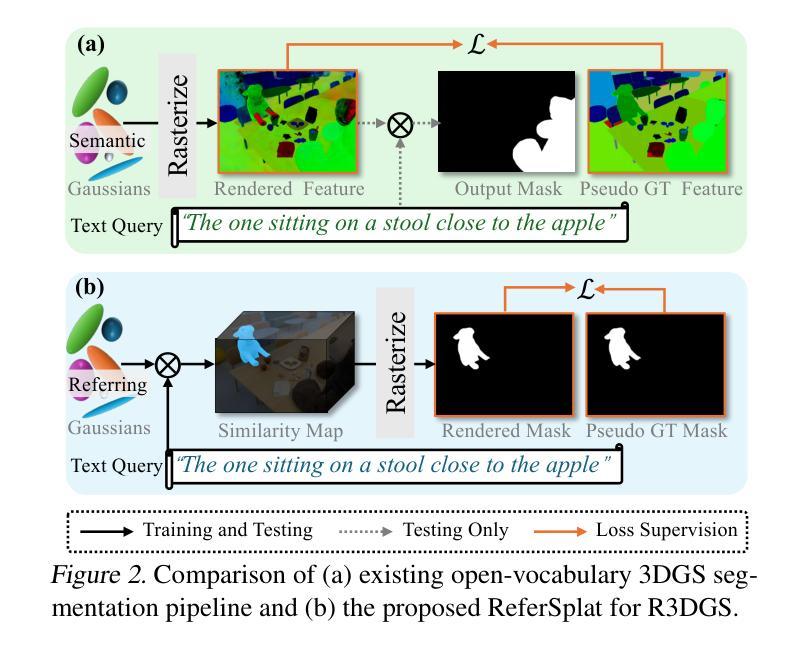
We introduce Referring 3D Gaussian Splatting Segmentation (R3DGS), a new task that aims to segment target objects in a 3D Gaussian scene based on natural language descriptions, which often contain spatial relationships or object attributes. This task requires the model to identify newly described objects that may be occluded or not directly visible in a novel view, posing a significant challenge for 3D multi-modal understanding. Developing this capability is crucial for advancing embodied AI. To support research in this area, we construct the first R3DGS dataset, Ref-LERF. Our analysis reveals that 3D multi-modal understanding and spatial relationship modeling are key challenges for R3DGS. To address these challenges, we propose ReferSplat, a framework that explicitly models 3D Gaussian points with natural language expressions in a spatially aware paradigm. ReferSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance on both the newly proposed R3DGS task and 3D open-vocabulary segmentation benchmarks. Dataset and code are available at https://github.com/heshuting555/ReferSplat.
我们介绍了基于自然语言描述的参照三维高斯喷射分割(R3DGS)这一新任务,该任务旨在根据包含空间关系或对象属性的自然语言描述来分割三维高斯场景中的目标对象。这一任务要求模型识别新描述的对象,这些对象可能在一个新视角中被遮挡或直接不可见,这为三维多模态理解带来了重大挑战。开发这种能力对于推动嵌入式人工智能的发展至关重要。为了支持这一领域的研究,我们构建了第一个R3DGS数据集Ref-LERF。我们的分析表明,三维多模态理解和空间关系建模是R3DGS的关键挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了ReferSplat框架,该框架采用空间感知范式显式地利用三维高斯点对自然语言表达式进行建模。ReferSplat在新提出的R3DGS任务和三维开放词汇分割基准测试上都达到了最先进的性能。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/heshuting555/ReferSplat获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Oral, Code: https://github.com/heshuting555/ReferSplat
Summary
本文介绍了一项新的任务——基于自然语言描述的3D高斯场景分割(R3DGS)。该任务旨在识别和分割在复杂环境中通过自然语言描述的目标物体,尤其关注语言中的空间关系和物体属性。为此,文章提出了首个R3DGS数据集Ref-LERF,并指出该领域的核心挑战在于多模态理解和空间关系建模。为解决这些挑战,文章提出了ReferSplat框架,通过明确建模高斯点与自然语言的空间关系达到卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍新的任务:基于自然语言描述的3D高斯场景分割(R3DGS)。
- R3DGS的目标是在复杂环境中识别和分割通过自然语言描述的目标物体。
- 自然语言描述中的空间关系和物体属性是完成任务的关键要素。
- 为支持该领域的研究,构建了首个R3DGS数据集Ref-LERF。
- 多模态理解和空间关系建模是完成R3DGS任务的核心挑战。
- 为解决这些挑战,提出了ReferSplat框架,其能明确建模高斯点与自然语言的空间关系。
点此查看论文截图

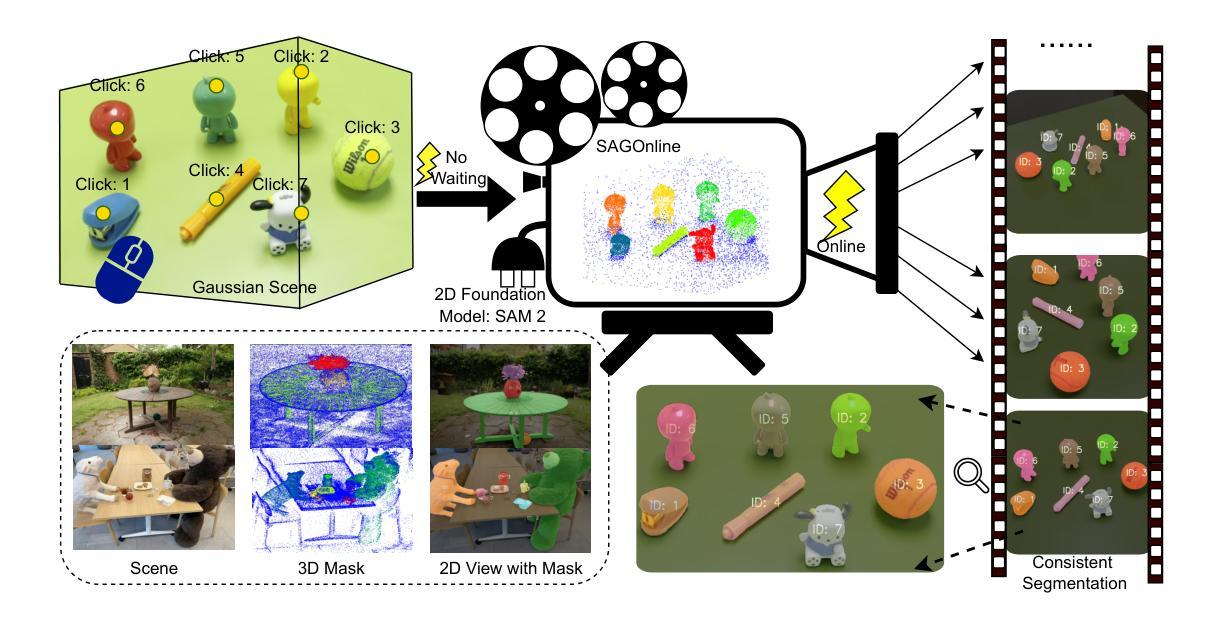
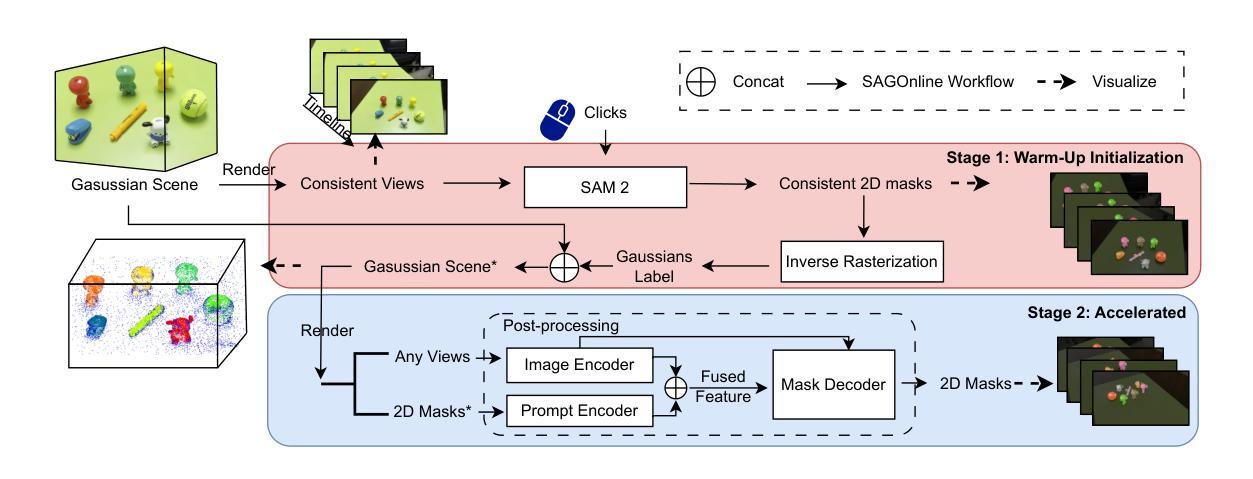
SAGOnline: Segment Any Gaussians Online
Authors:Wentao Sun, Quanyun Wu, Hanqing Xu, Kyle Gao, Zhengsen Xu, Yiping Chen, Dedong Zhang, Lingfei Ma, John S. Zelek, Jonathan Li
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for explicit 3D scene representation, yet achieving efficient and consistent 3D segmentation remains challenging. Current methods suffer from prohibitive computational costs, limited 3D spatial reasoning, and an inability to track multiple objects simultaneously. We present Segment Any Gaussians Online (SAGOnline), a lightweight and zero-shot framework for real-time 3D segmentation in Gaussian scenes that addresses these limitations through two key innovations: (1) a decoupled strategy that integrates video foundation models (e.g., SAM2) for view-consistent 2D mask propagation across synthesized views; and (2) a GPU-accelerated 3D mask generation and Gaussian-level instance labeling algorithm that assigns unique identifiers to 3D primitives, enabling lossless multi-object tracking and segmentation across views. SAGOnline achieves state-of-the-art performance on NVOS (92.7% mIoU) and Spin-NeRF (95.2% mIoU) benchmarks, outperforming Feature3DGS, OmniSeg3D-gs, and SA3D by 15–1500 times in inference speed (27 ms/frame). Qualitative results demonstrate robust multi-object segmentation and tracking in complex scenes. Our contributions include: (i) a lightweight and zero-shot framework for 3D segmentation in Gaussian scenes, (ii) explicit labeling of Gaussian primitives enabling simultaneous segmentation and tracking, and (iii) the effective adaptation of 2D video foundation models to the 3D domain. This work allows real-time rendering and 3D scene understanding, paving the way for practical AR/VR and robotic applications.
3D高斯展开(3DGS)已经成为一种强大的显式3D场景表示范式,但实现高效且一致的3D分割仍然具有挑战性。当前的方法存在计算成本高、3D空间推理有限、无法同时跟踪多个物体等缺点。我们提出了在线高斯分割任意物体(SAGOnline),这是一个用于高斯场景实时3D分割的轻量级零样本框架,通过两个关键创新解决了这些限制:(1)一种分离策略,集成了视频基础模型(例如SAM2),用于在合成视图之间进行一致的2D掩膜传播;(2)一个GPU加速的3D掩膜生成和高斯级别实例标记算法,该算法为3D基本元素分配唯一标识符,从而实现跨视图的无损多目标跟踪和分割。SAGOnline在NVOS(92.7% mIoU)和Spin-NeRF(95.2% mIoU)基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,相较于Feature3DGS、OmniSeg3D-gs和SA3D在推理速度上提升了15至1500倍(每秒处理帧数为每帧仅约需时27毫秒)。定性结果表明其在复杂场景中实现了稳健的多目标分割和跟踪。我们的贡献包括:(一)高斯场景下用于三维分割的轻量级零样本框架,(二)对高斯基本元素进行明确标记,以实现同时分割和跟踪,(三)有效适应二维视频基础模型到三维领域。这项工作为实时渲染和三维场景理解铺平了道路,为增强现实/虚拟现实和机器人应用等实用领域提供了可能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 10 figures
摘要
本文介绍了针对高斯场景实时三维分割的新型在线零点框架Segment Any Gaussians Online(SAGOnline)。该框架具有两项关键创新,即一项耦合策略与另一项针对视频基础的集成方法相结合。框架能在GPU上实现高效的运行速度和高斯级别实例的标签算法分配独特标识符进行三维元素分割,能够实现无损耗的多对象跟踪与不同视角分割。本文还包括贡献一:在简化三维场景的基础上开发新型高效零点框架进行高斯场景分割;贡献二:明确高斯元素标签,实现同时分割和跟踪;贡献三:有效适应二维视频基础模型到三维领域的广泛应用场景,且效率达到历史顶尖。本文主要结果促进高效实用渲染技术在虚拟现实及增强现实应用场景的运用和理解场景信息的普遍推广等AR和VR应用场景的应用与发展方向的研究和发展提供了启示和方向指导。这对于扩大应用行业及其真实感和场景的呈现无疑起到积极的推动作用。此外,该框架在NVOS和Spin-NeRF基准测试中表现优异,相对于其他模型如Feature3DGS等有着显著提升的推理速度(高达15倍至最高可达至150倍)。定量结果表明在复杂场景中多对象分割和跟踪的稳健性。因此,本文为实时渲染和三维场景理解开辟了新的道路。
关键见解
一、提出了一种新型的在线零点框架用于高斯场景的三维分割,实现了高效实时的分割性能。
二、通过明确高斯元素的标签,实现了同时分割和跟踪的功能,提高了多对象处理的效率。
点此查看论文截图

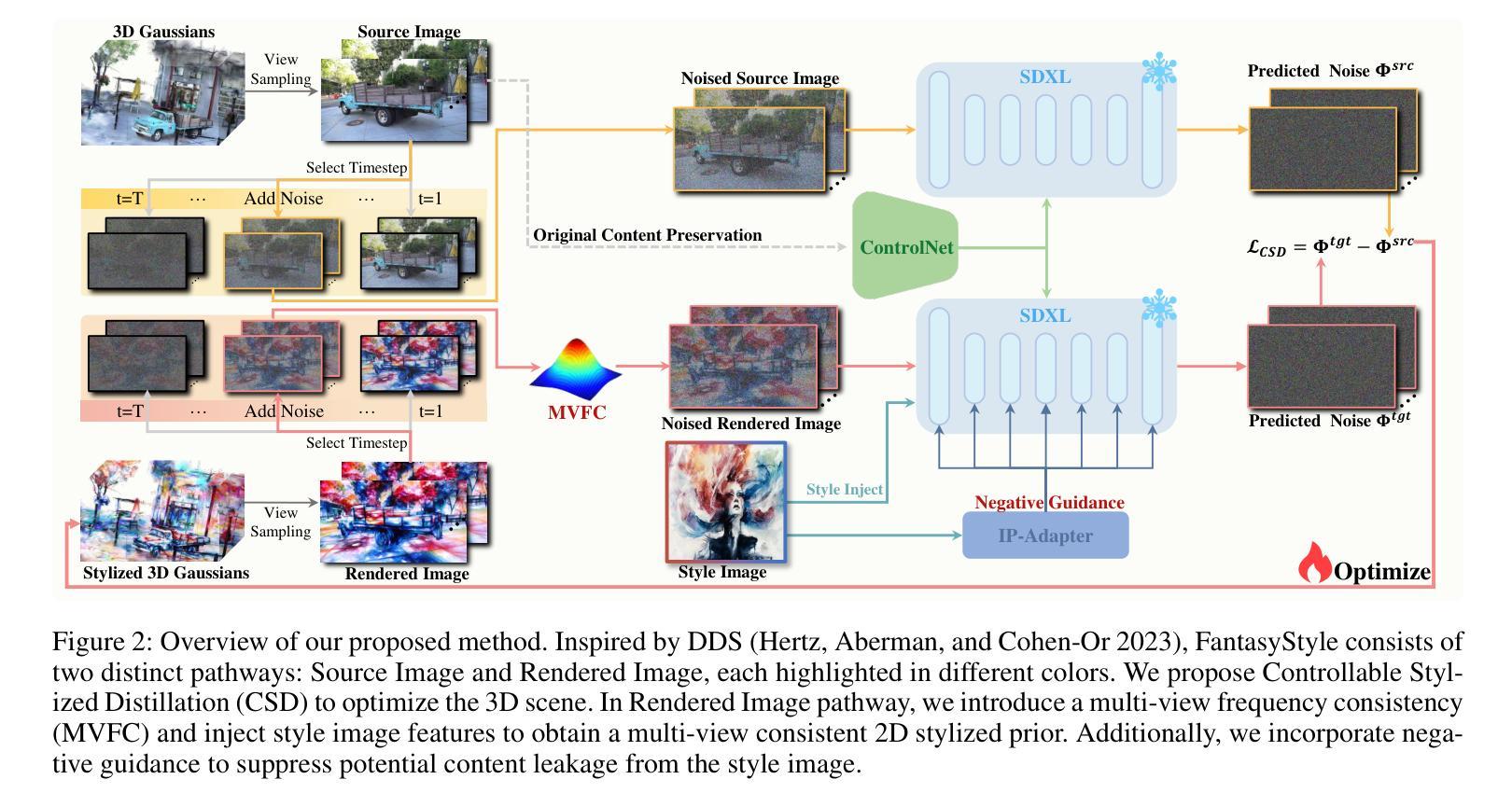
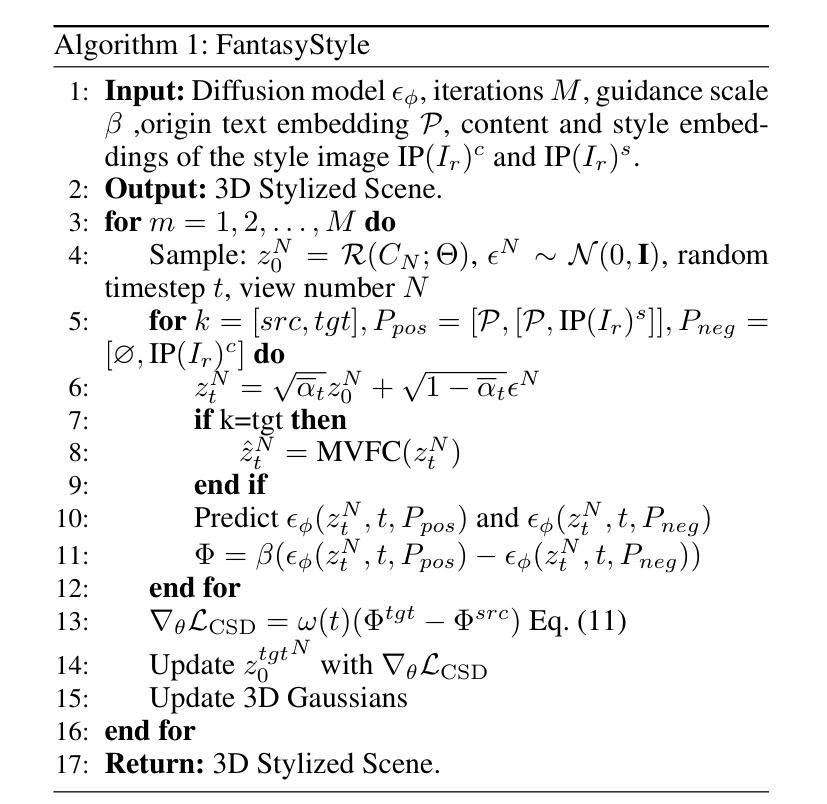
FantasyStyle: Controllable Stylized Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yitong Yang, Yinglin Wang, Changshuo Wang, Huajie Wang, Shuting He
The success of 3DGS in generative and editing applications has sparked growing interest in 3DGS-based style transfer. However, current methods still face two major challenges: (1) multi-view inconsistency often leads to style conflicts, resulting in appearance smoothing and distortion; and (2) heavy reliance on VGG features, which struggle to disentangle style and content from style images, often causing content leakage and excessive stylization. To tackle these issues, we introduce \textbf{FantasyStyle}, a 3DGS-based style transfer framework, and the first to rely entirely on diffusion model distillation. It comprises two key components: (1) \textbf{Multi-View Frequency Consistency}. We enhance cross-view consistency by applying a 3D filter to multi-view noisy latent, selectively reducing low-frequency components to mitigate stylized prior conflicts. (2) \textbf{Controllable Stylized Distillation}. To suppress content leakage from style images, we introduce negative guidance to exclude undesired content. In addition, we identify the limitations of Score Distillation Sampling and Delta Denoising Score in 3D style transfer and remove the reconstruction term accordingly. Building on these insights, we propose a controllable stylized distillation that leverages negative guidance to more effectively optimize the 3D Gaussians. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving higher stylization quality and visual realism across various scenes and styles.
3DGS在生成和编辑应用中的成功引发了基于3DGS的风格转换的日益增长的兴趣。然而,当前的方法仍然面临两大挑战:(1)多视图不一致性经常导致风格冲突,从而导致外观平滑和失真;(2)严重依赖VGG特征,其在从风格图像中分离风格和内容时遇到困难,经常导致内容泄露和过度风格化。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了\textbf{FantasyStyle},这是一个基于3DGS的风格转移框架,也是第一个完全依赖扩散模型蒸馏的框架。它包含两个关键组成部分:(1)\textbf{多视图频率一致性}。我们通过应用3D滤波器增强跨视图的一致性,对多视图噪声潜在进行选择性降低低频分量,以缓解风格化先验冲突。(2)\textbf{可控风格化蒸馏}。为了抑制来自风格图像的内容泄露,我们引入负引导来排除不需要的内容。此外,我们发现了3D风格转移中Score Distillation Sampling和Delta Denoising Score的局限性,并相应地删除了重建项。基于这些见解,我们提出了一种可控的风格化蒸馏,利用负引导更有效地优化3D高斯。大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最先进的方法,在各种场景和风格下实现更高的风格化质量和视觉真实性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于3DGS的风格转移框架FantasyStyle解决了现有方法的两大挑战:多视角不一致导致的风格冲突以及过度依赖VGG特征带来的内容泄露和过度风格化问题。它通过引入扩散模型蒸馏和两种关键技术——多视角频率一致性及可控风格化蒸馏,提高了跨视角一致性并有效抑制了内容泄露。实验证明,该方法在场景和风格方面均优于现有技术,提高了风格化的质量和视觉逼真度。
关键见解
- 基于3DGS的风格转移框架FantasyStyle旨在解决多视角不一致和过度依赖VGG特征导致的风格冲突和内容泄露问题。
- 多视角频率一致性技术通过应用3D滤波器增强跨视角一致性,减少低频频段以缓解风格化冲突。
- 可控风格化蒸馏通过引入负导向抑制内容泄露。此外,该研究指出了Score Distillation Sampling和Delta Denoising Score在3D风格转移中的局限性并进行了相应的改进。
点此查看论文截图



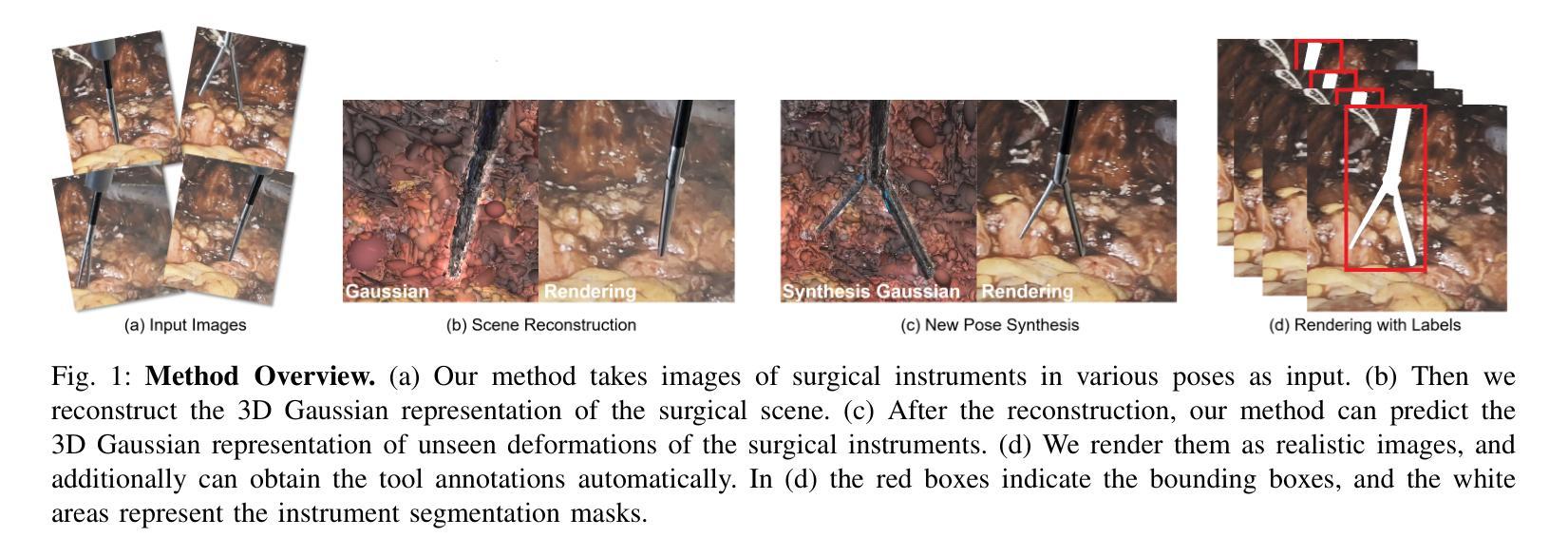
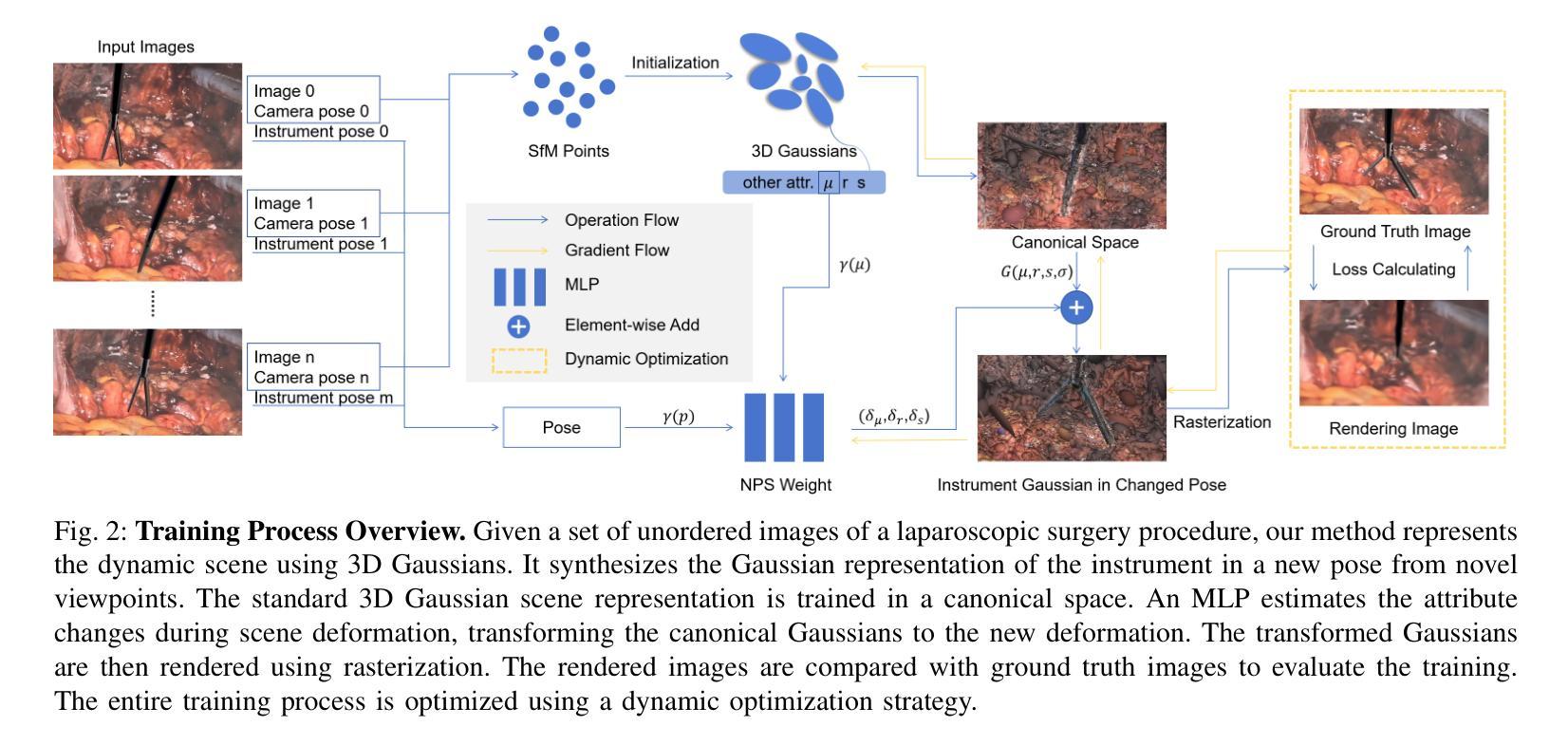
NeeCo: Image Synthesis of Novel Instrument States Based on Dynamic and Deformable 3D Gaussian Reconstruction
Authors:Tianle Zeng, Junlei Hu, Gerardo Loza Galindo, Sharib Ali, Duygu Sarikaya, Pietro Valdastri, Dominic Jones
Computer vision-based technologies significantly enhance surgical automation by advancing tool tracking, detection, and localization. However, Current data-driven approaches are data-voracious, requiring large, high-quality labeled image datasets, which limits their application in surgical data science. Our Work introduces a novel dynamic Gaussian Splatting technique to address the data scarcity in surgical image datasets. We propose a dynamic Gaussian model to represent dynamic surgical scenes, enabling the rendering of surgical instruments from unseen viewpoints and deformations with real tissue backgrounds. We utilize a dynamic training adjustment strategy to address challenges posed by poorly calibrated camera poses from real-world scenarios. Additionally, we propose a method based on dynamic Gaussians for automatically generating annotations for our synthetic data. For evaluation, we constructed a new dataset featuring seven scenes with 14,000 frames of tool and camera motion and tool jaw articulation, with a background of an ex-vivo porcine model. Using this dataset, we synthetically replicate the scene deformation from the ground truth data, allowing direct comparisons of synthetic image quality. Experimental results illustrate that our method generates photo-realistic labeled image datasets with the highest values in Peak-Signal-to-Noise Ratio (29.87). We further evaluate the performance of medical-specific neural networks trained on real and synthetic images using an unseen real-world image dataset. Our results show that the performance of models trained on synthetic images generated by the proposed method outperforms those trained with state-of-the-art standard data augmentation by 10%, leading to an overall improvement in model performances by nearly 15%.
基于计算机视觉的技术通过推动工具追踪、检测和定位,显著增强了手术的自动化程度。然而,当前的数据驱动方法需要大量的高质量标记图像数据集,这限制了它们在手术数据科学中的应用。我们的工作引入了一种新的动态高斯混合技术来解决手术图像数据集中数据稀缺的问题。我们提出一个动态高斯模型来表示动态手术场景,能够从未见过的视角和变形中呈现手术器械,并与真实组织背景相结合。我们采用动态训练调整策略,以解决由现实世界场景中相机姿态校准不良所带来的挑战。此外,我们还提出了一种基于动态高斯的方法,用于自动为我们合成的数据生成注释。为了进行评估,我们构建了一个新的数据集,包含七个场景,14000帧的工具和相机运动以及工具颚关节运动,背景是一个离体的猪模型。使用这个数据集,我们合成地复制了场景变形,与真实数据直接比较合成图像的质量。实验结果表明,我们的方法生成了具有最高峰值信号噪声比(29.87)的照片级真实标记图像数据集。我们进一步评估了使用真实和合成图像训练的医学专用神经网络在未见过的真实世界图像数据集上的性能。我们的结果表明,使用合成图像训练的模型性能优于使用最新标准数据增强的模型,提高了约10%,导致模型总体性能提高了近15%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 9 figures
摘要
基于计算机视觉的技术通过推进工具追踪、检测和定位来显著增强手术的自动化程度。然而,当前的数据驱动方法需要大量的高质量标记图像数据集,这限制了它们在手术数据科学中的应用。我们的工作引入了一种新的动态高斯涂布技术来解决手术图像数据集中数据缺乏的问题。我们提出一个动态高斯模型来表示动态手术场景,能够实现从未见过的视角和变形对手术器械进行渲染,并具有真实的组织背景。我们采用动态训练调整策略,以解决由现实世界场景中的相机姿势校准不良所带来的挑战。此外,我们还提出了一种基于动态高斯的方法,可以自动为我们合成的数据生成注释。为了评估,我们构建了一个新的数据集,包含七个场景,有14000帧的工具和相机运动以及工具关节运动的画面,背景是一个离体的猪模型。使用此数据集,我们合成地复制了场景变形从真实数据,允许直接比较合成图像的质量。实验结果表明,我们的方法生成了具有最高峰值信号噪声比(29.87)的照片级真实标记图像数据集。我们进一步评估了在真实和合成图像上训练的医疗专用神经网络在未见过的真实世界图像数据集上的性能。结果表明,由所提出方法生成的合成图像训练的模型性能比使用最新标准数据增强的模型高出10%,总体上提高了模型性能近15%。
要点
- 计算机视觉技术在手术自动化中扮演重要角色,但数据需求成为限制。
- 引入动态高斯涂布技术解决手术图像数据集中数据缺乏的问题。
- 提出动态高斯模型表示动态手术场景,能渲染手术器械并处理复杂的背景。
- 采用动态训练调整策略应对相机姿势校准的挑战。
- 自动生成合成数据的注释方法基于动态高斯。
- 构建新数据集进行评估,包含复杂手术场景和真实的猪模型背景。
点此查看论文截图

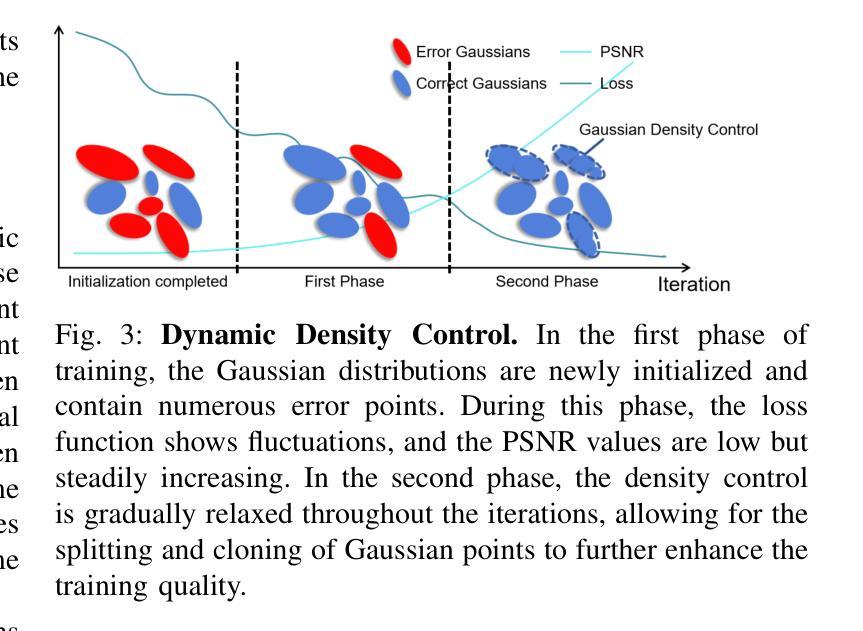
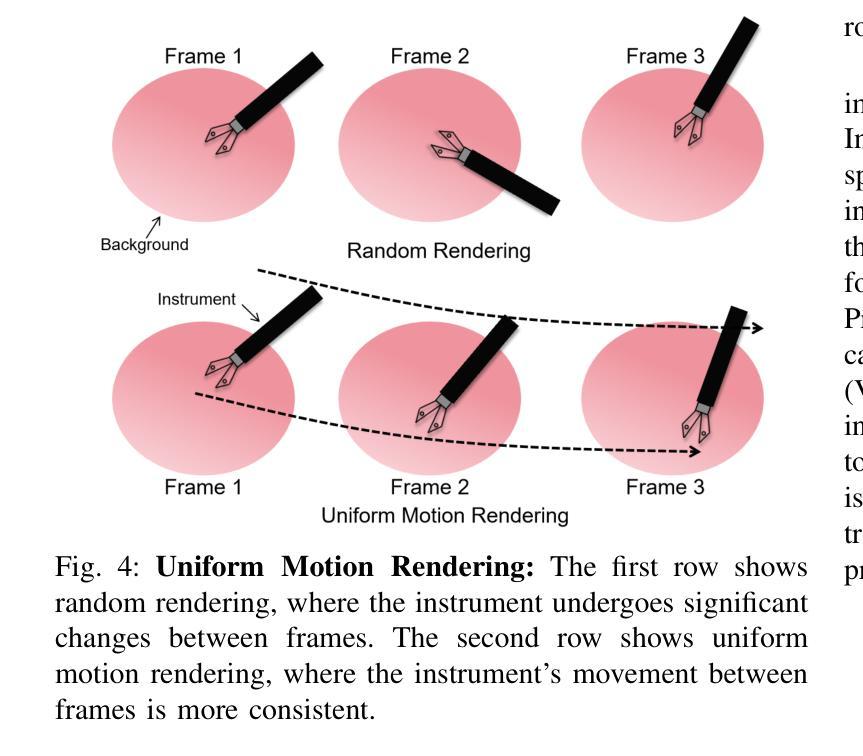
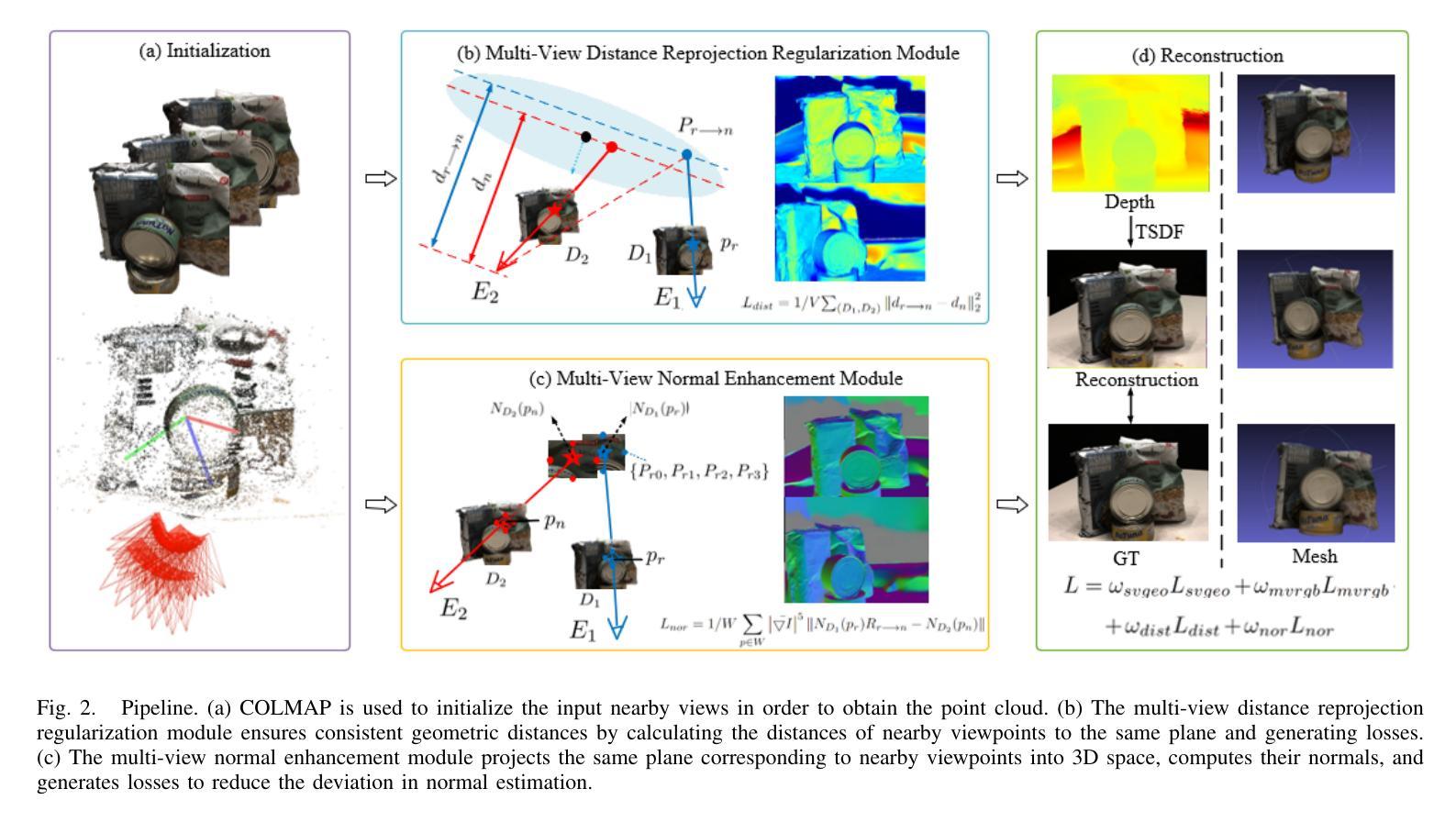
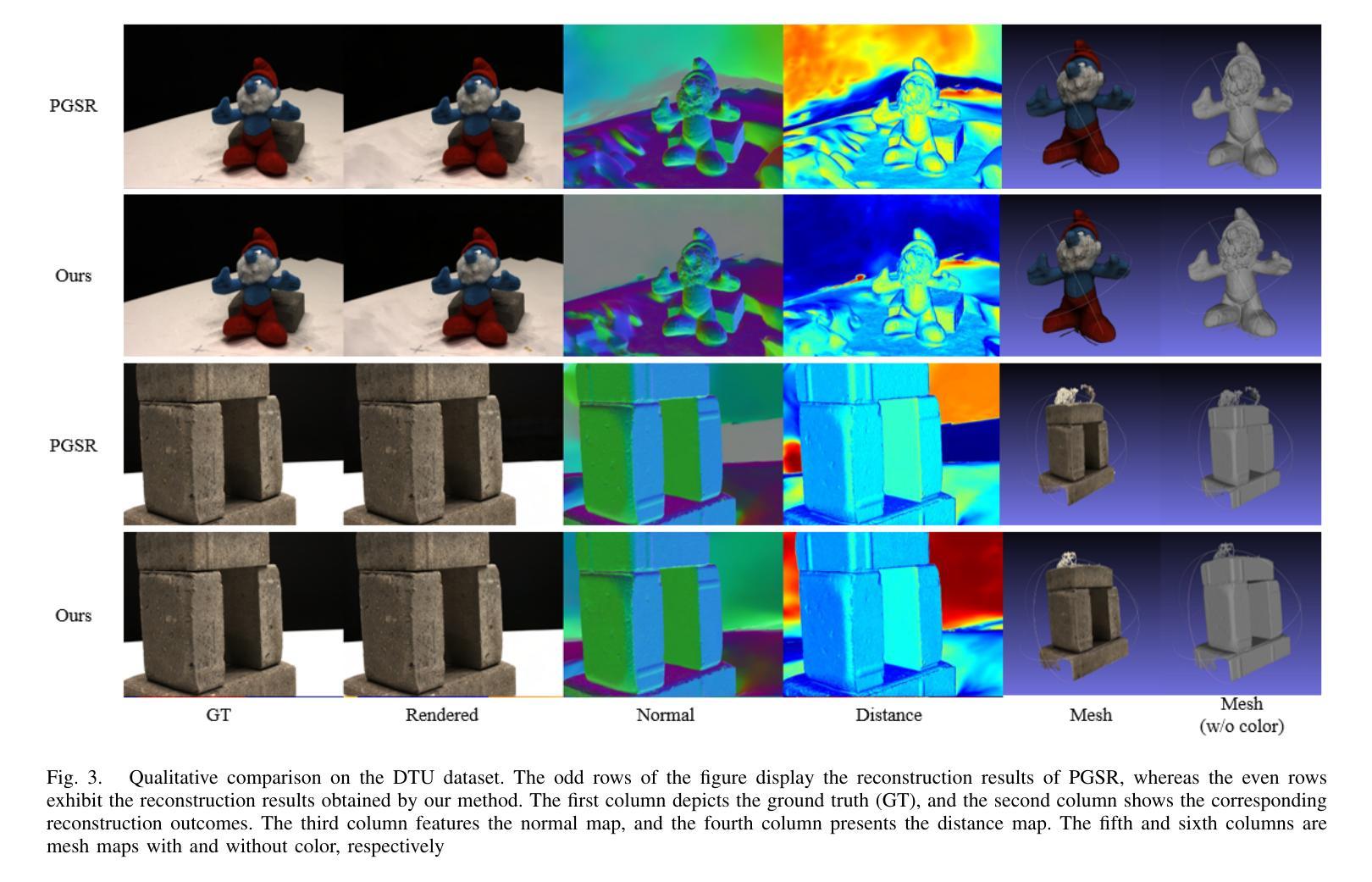
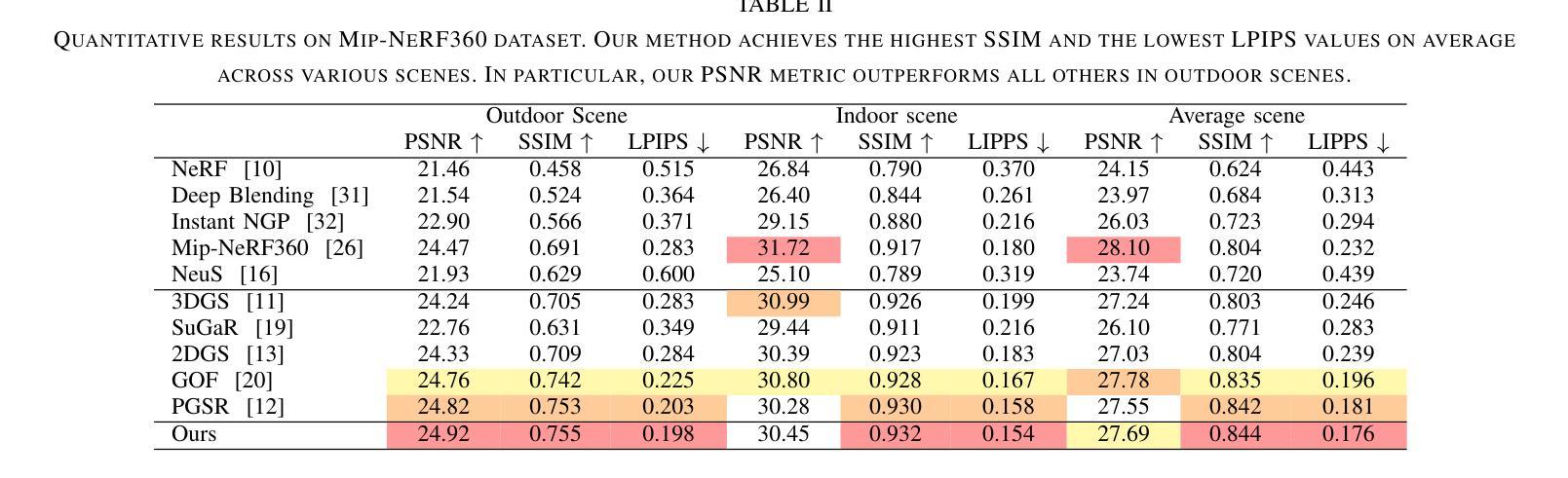
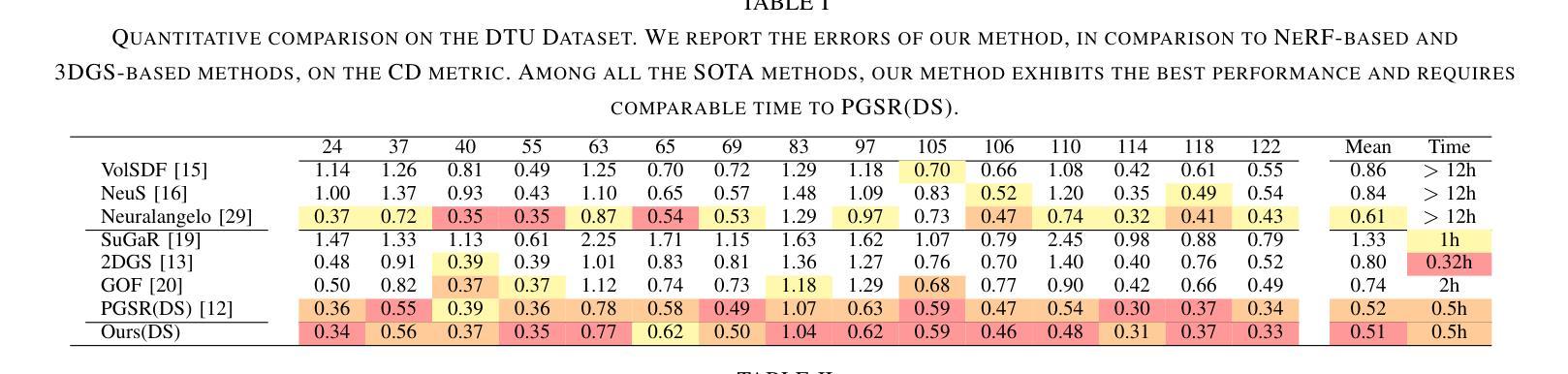
Multi-view Normal and Distance Guidance Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Bo Jia, Yanan Guo, Ying Chang, Benkui Zhang, Ying Xie, Kangning Du, Lin Cao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieves remarkable results in the field of surface reconstruction. However, when Gaussian normal vectors are aligned within the single-view projection plane, while the geometry appears reasonable in the current view, biases may emerge upon switching to nearby views. To address the distance and global matching challenges in multi-view scenes, we design multi-view normal and distance-guided Gaussian splatting. This method achieves geometric depth unification and high-accuracy reconstruction by constraining nearby depth maps and aligning 3D normals. Specifically, for the reconstruction of small indoor and outdoor scenes, we propose a multi-view distance reprojection regularization module that achieves multi-view Gaussian alignment by computing the distance loss between two nearby views and the same Gaussian surface. Additionally, we develop a multi-view normal enhancement module, which ensures consistency across views by matching the normals of pixel points in nearby views and calculating the loss. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the baseline in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, significantly enhancing the surface reconstruction capability of 3DGS.
3D高斯贴图(3DGS)在表面重建领域取得了显著成果。然而,当高斯法线向量在单视投影平面内对齐时,虽然在当前视角下几何结构看起来是合理的,但在切换到邻近视角时可能会出现偏差。为了解决多视角场景中的距离和全局匹配挑战,我们设计了多视角法线和距离引导的高斯贴图方法。通过约束邻近深度图并对齐3D法线,该方法实现了几何深度统一和高精度重建。具体来说,对于室内外小场景的重建,我们提出了多视角距离重投影正则化模块,通过计算两个邻近视角与同一高斯表面之间的距离损失,实现多视角高斯对齐。此外,我们还开发了一个多视角法线增强模块,通过匹配邻近视角中像素点的法线并计算损失,确保不同视角之间的一致性。大量的实验结果表明,我们的方法在定量和定性评估上都优于基线方法,显著提高了3DGS的表面重建能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IROS 2025
Summary
这篇关于三维高斯模板法(3DGS)的文章主要讨论了多视图重建的问题和解决方法。为提高表面重建的准确性,提出多视角正常和距离引导的高斯模板法,实现了深度统一和高精度重建。对于室内和室外小场景的重建,引入了多视角距离再投影正则化模块和多视角正常增强模块,取得了良好的多视角高斯对齐效果。此方法相较于基线方法在定量和定性评估上表现出更好的性能,显著提升了3DGS的表面重建能力。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文章的主要见解:
- 3DGS在多视角重建中存在距离和全局匹配挑战。
- 提出多视角正常和距离引导的高斯模板法,用于解决这些挑战。
- 通过约束邻近深度图和对齐三维正常向量实现几何深度统一和高精度重建。
- 针对室内和室外小场景的重建,引入多视角距离再投影正则化模块。
- 开发多视角正常增强模块,确保跨视图的一致性。
- 对比实验显示新方法在定量和定性评估上都优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图
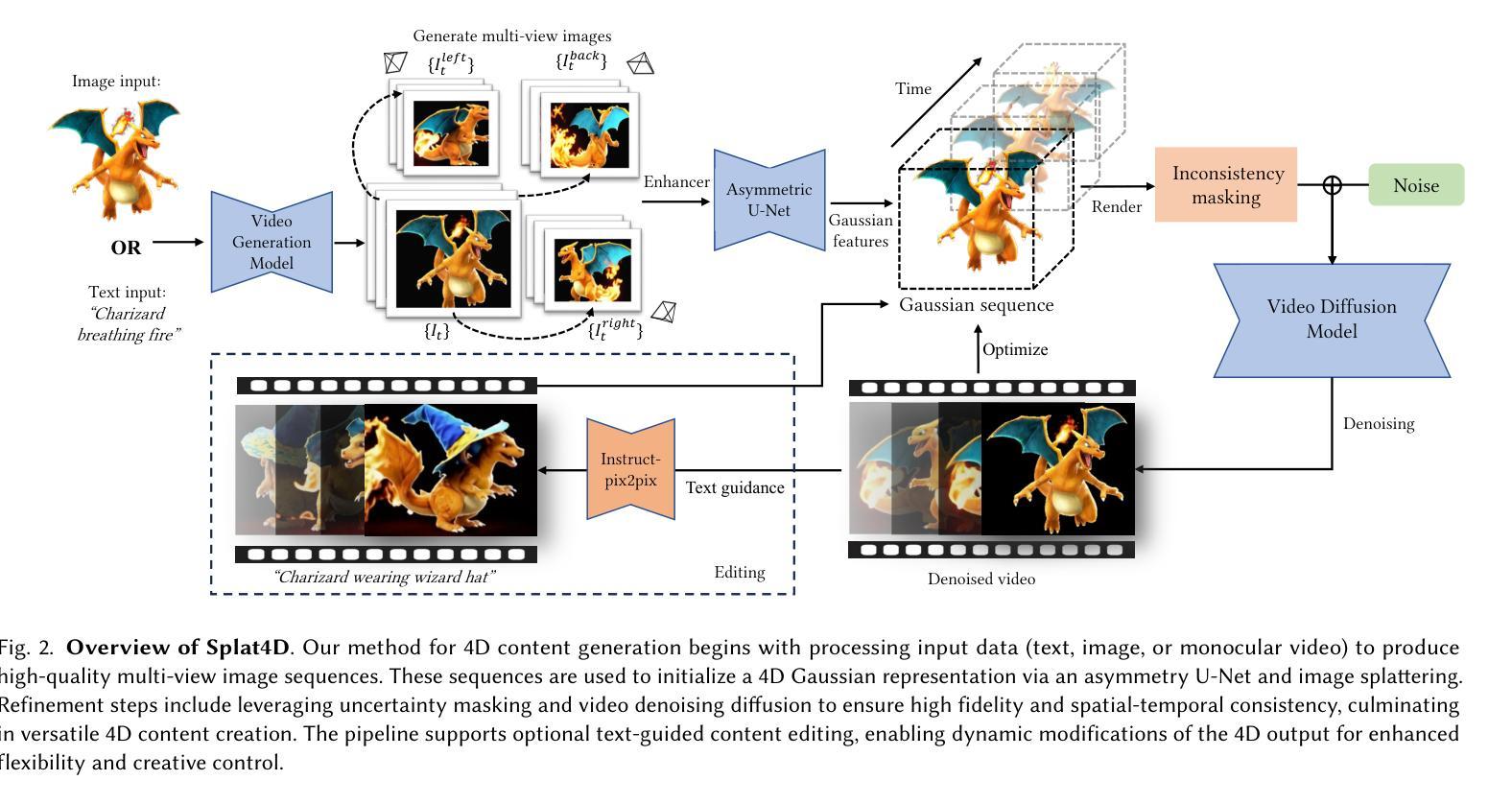
Splat4D: Diffusion-Enhanced 4D Gaussian Splatting for Temporally and Spatially Consistent Content Creation
Authors:Minghao Yin, Yukang Cao, Songyou Peng, Kai Han
Generating high-quality 4D content from monocular videos for applications such as digital humans and AR/VR poses challenges in ensuring temporal and spatial consistency, preserving intricate details, and incorporating user guidance effectively. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Splat4D, a novel framework enabling high-fidelity 4D content generation from a monocular video. Splat4D achieves superior performance while maintaining faithful spatial-temporal coherence by leveraging multi-view rendering, inconsistency identification, a video diffusion model, and an asymmetric U-Net for refinement. Through extensive evaluations on public benchmarks, Splat4D consistently demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various metrics, underscoring the efficacy of our approach. Additionally, the versatility of Splat4D is validated in various applications such as text/image conditioned 4D generation, 4D human generation, and text-guided content editing, producing coherent outcomes following user instructions.
从单目视频中生成高质量4D内容,用于数字人类和AR/VR等应用,在保障时间空间一致性、保留精细细节和有效融入用户指导方面面临挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了Splat4D,这是一个新型框架,能够从单目视频中生成高保真4D内容。Splat4D通过利用多视角渲染、不一致性识别、视频扩散模型以及用于精细化的不对称U-Net,在保持时空连贯性的同时实现了卓越性能。在公共基准测试上的广泛评估表明,Splat4D在各种指标上均表现出卓越的性能,凸显了我们的方法的有效性。此外,Splat4D的通用性在各种应用中得到了验证,如文本/图像控制的4D生成、4D人类生成和文本引导的内容编辑,能够根据用户的指令产生连贯的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了从单目视频中生成高质量4D内容所面临的挑战,包括确保时间性和空间性的一致性、保留细节以及有效地融入用户指导。为解决这些挑战,本文提出了Splat4D这一新型框架,该框架能够实现从单目视频的高保真4D内容生成。Splat4D通过利用多视角渲染、不一致性识别、视频扩散模型以及不对称U-Net进行精细化处理,取得了卓越的性能表现。在公共基准测试上的广泛评估证明了Splat4D在各种指标上的表现均达到业界领先,验证了其在文本/图像条件驱动的4D生成、4D人像生成以及文本引导的内容编辑等多种应用中的通用性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成高质量4D内容面临的挑战包括确保时间性和空间性的一致性、保留细节以及融入用户指导。
- Splat4D框架能够实现从单目视频的高保真4D内容生成。
- Splat4D利用多视角渲染、不一致性识别等技术实现卓越性能。
- Splat4D在公共基准测试上的表现达到业界领先。
- Splat4D具有多种应用,包括文本/图像条件驱动的4D生成、4D人像生成以及文本引导的内容编辑等。
- Splat4D能够产生连贯的结果,并遵循用户指导。
点此查看论文截图

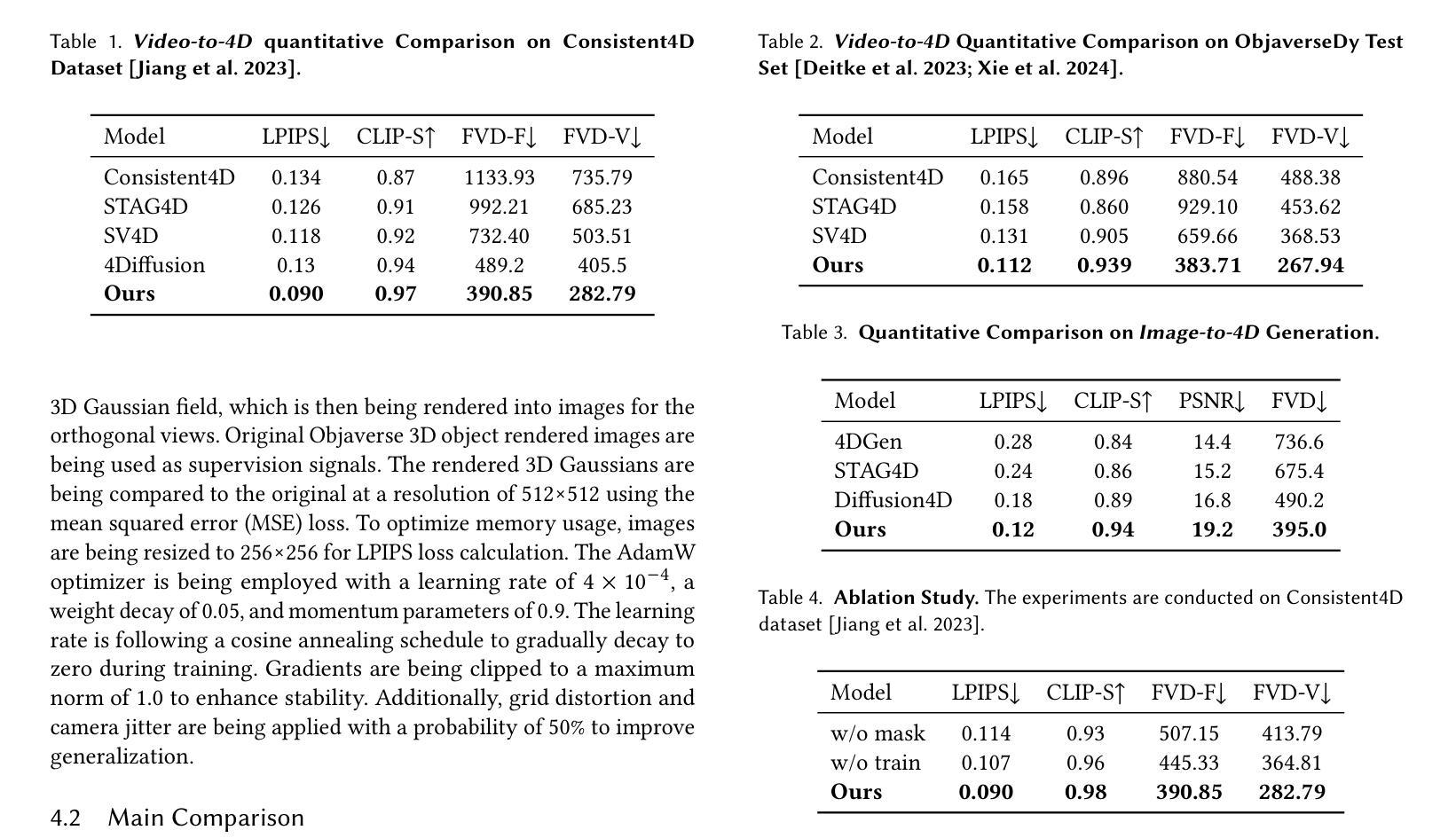
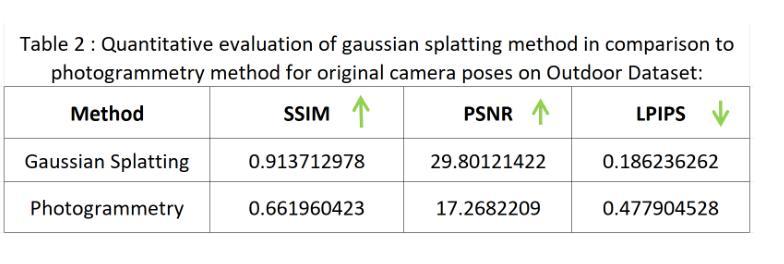
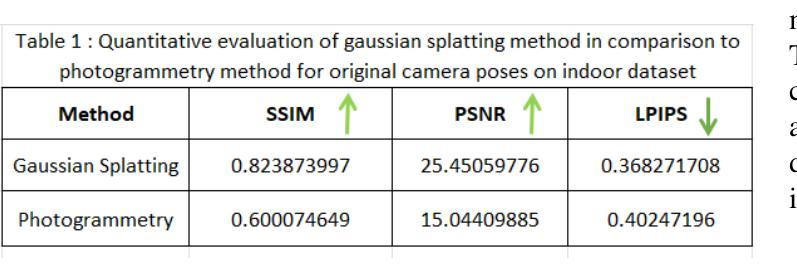
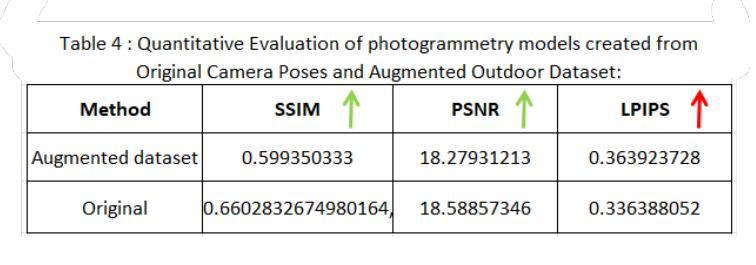
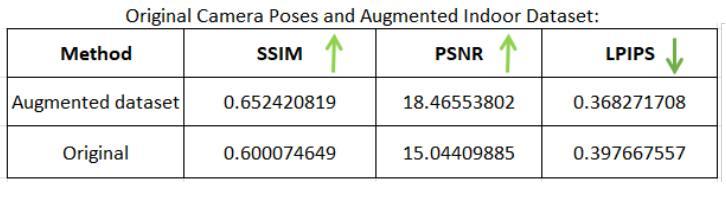
Novel View Synthesis with Gaussian Splatting: Impact on Photogrammetry Model Accuracy and Resolution
Authors:Pranav Chougule
In this paper, I present a comprehensive study comparing Photogrammetry and Gaussian Splatting techniques for 3D model reconstruction and view synthesis. I created a dataset of images from a real-world scene and constructed 3D models using both methods. To evaluate the performance, I compared the models using structural similarity index (SSIM), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS), and lp/mm resolution based on the USAF resolution chart. A significant contribution of this work is the development of a modified Gaussian Splatting repository, which I forked and enhanced to enable rendering images from novel camera poses generated in the Blender environment. This innovation allows for the synthesis of high-quality novel views, showcasing the flexibility and potential of Gaussian Splatting. My investigation extends to an augmented dataset that includes both original ground images and novel views synthesized via Gaussian Splatting. This augmented dataset was employed to generate a new photogrammetry model, which was then compared against the original photogrammetry model created using only the original images. The results demonstrate the efficacy of using Gaussian Splatting to generate novel high-quality views and its potential to improve photogrammetry-based 3D reconstructions. The comparative analysis highlights the strengths and limitations of both approaches, providing valuable information for applications in extended reality (XR), photogrammetry, and autonomous vehicle simulations. Code is available at https://github.com/pranavc2255/gaussian-splatting-novel-view-render.git.
在这篇论文中,我对摄影测量法和高斯贴图技术进行了全面的比较研究,这两种技术用于3D模型重建和视图合成。我从真实场景创建了一个图像数据集,并使用这两种方法构建了3D模型。为了评估性能,我使用结构相似性指数(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、学习感知图像块相似性(LPIPS)以及基于美国空军分辨率图的lp/mm分辨率对模型进行了比较。这项工作的一个重要贡献是开发了一个修改后的高斯贴图存储库,我对其进行了分叉并增强其功能,以呈现Blender环境中生成的新型相机姿态的图像。这一创新允许合成高质量的新型视图,展示了高斯贴图的灵活性和潜力。我的调查扩展到一个增强数据集,其中包括原始地面图像和通过高斯贴图合成的新型视图。这个增强数据集被用来生成一个新的摄影测量模型,然后将其与仅使用原始图像创建的原始摄影测量模型进行比较。结果表明,使用高斯贴图生成新型高质量视图的效用及其改善基于摄影测量的3D重建的潜力。比较分析突出了这两种方法的优势和局限性,为扩展现实(XR)、摄影测量和自动驾驶汽车模拟应用提供了有价值的信息。代码可在https://github.com/pranavc2255/gaussian-splatting-novel-view-render.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文对比研究了Photogrammetry和Gaussian Splatting技术在3D模型重建和视图合成方面的应用。作者创建了一个真实场景图像数据集,使用两种方法构建3D模型,并通过结构相似性指数(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、学习感知图像块相似性(LPIPS)和USAF分辨率图进行了模型评估。重要创新在于改进了Gaussian Splatting库,使其能够在Blender环境中生成的新相机姿态下渲染图像。该研究还扩展了数据集,包括原始地面图像和通过Gaussian Splatting合成的新视图,进一步对比了仅使用原始图像的摄影测量模型与采用合成视图的新型摄影测量模型的性能。结果表明,利用Gaussian Splatting生成新型高质量视图的有效性及其对摄影测量基于的3D重建的潜力。比较分析突出了两种方法的优点和局限性,为扩展现实(XR)、摄影测量和自动驾驶汽车模拟应用提供了有价值的信息。
Key Takeaways
- 论文对Photogrammetry和Gaussian Splatting技术进行了全面的比较研究。
- 作者创建了一个真实场景图像数据集,并使用两种方法构建3D模型。
- 通过多种指标评估了模型的性能,包括SSIM、PSNR、LPIPS和USAF分辨率图。
- 论文对Gaussian Splatting库进行了改进,可以在新相机姿态下生成高质量渲染图像。
- 研究还涉及扩展数据集的使用,包括原始地面图像和通过Gaussian Splatting技术合成的视图。
- 对比了仅使用原始图像的摄影测量模型与使用合成视图的新型摄影测量模型的性能差异。
点此查看论文截图





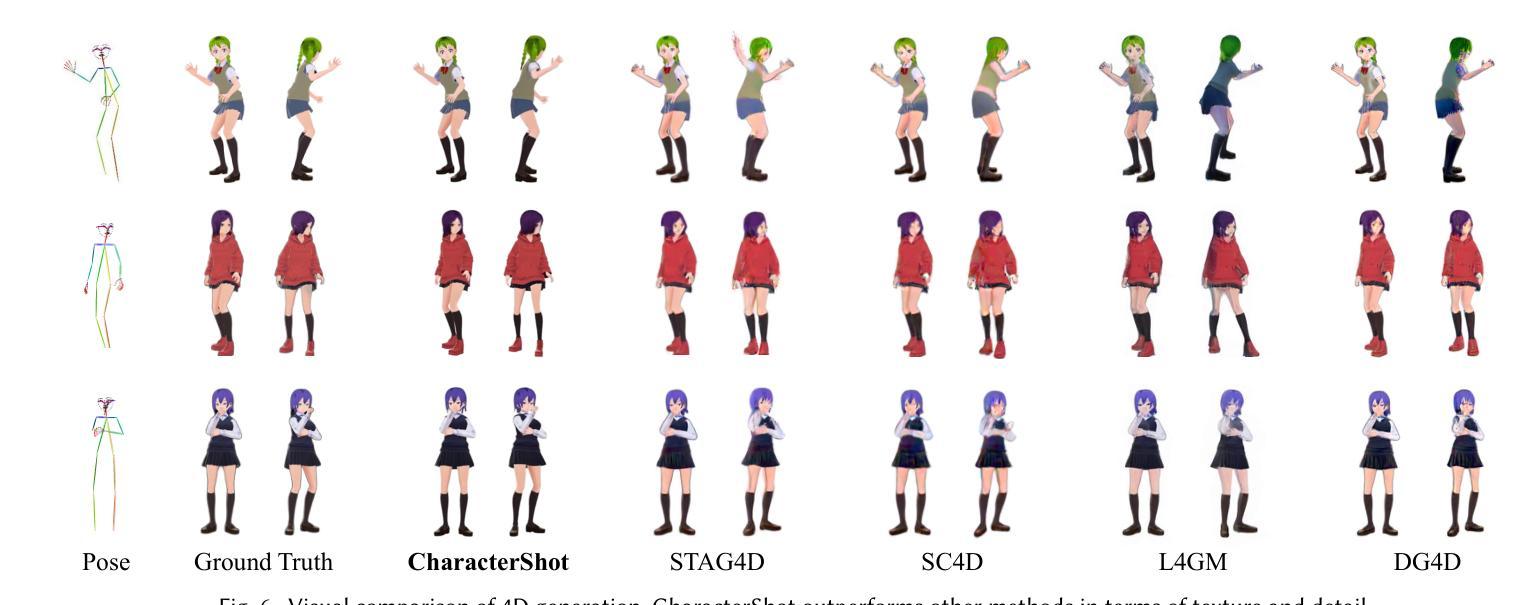
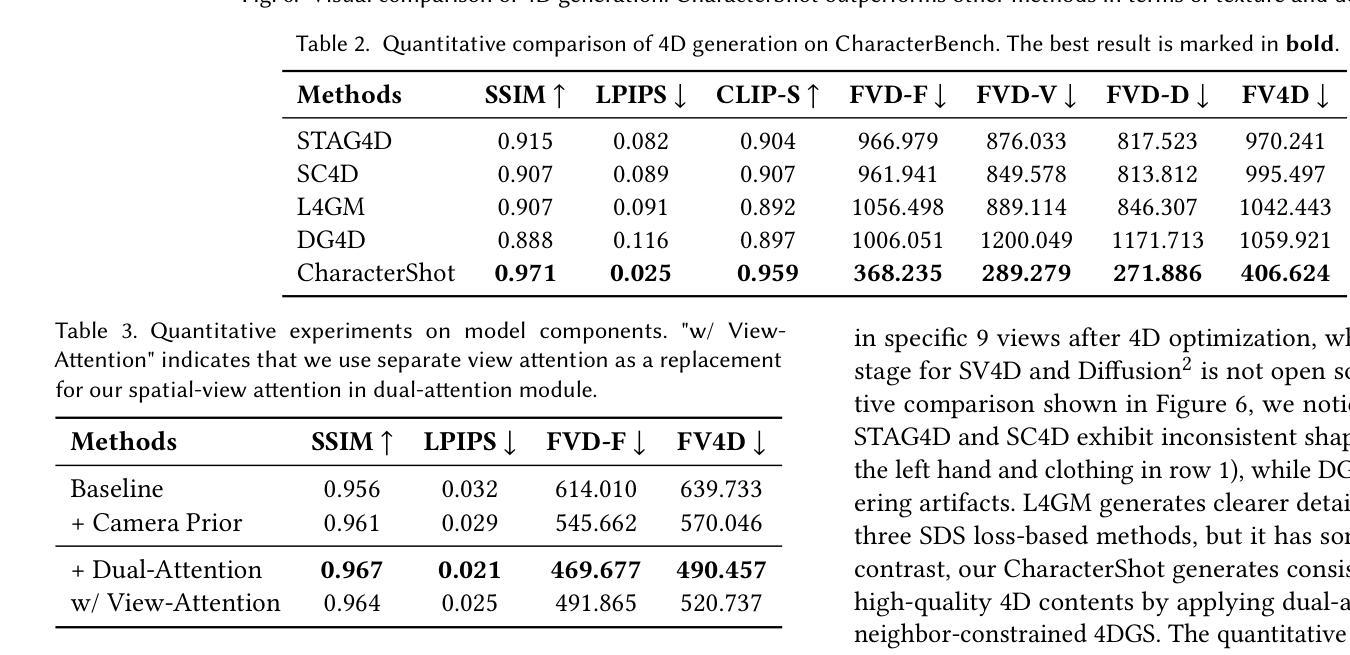
CharacterShot: Controllable and Consistent 4D Character Animation
Authors:Junyao Gao, Jiaxing Li, Wenran Liu, Yanhong Zeng, Fei Shen, Kai Chen, Yanan Sun, Cairong Zhao
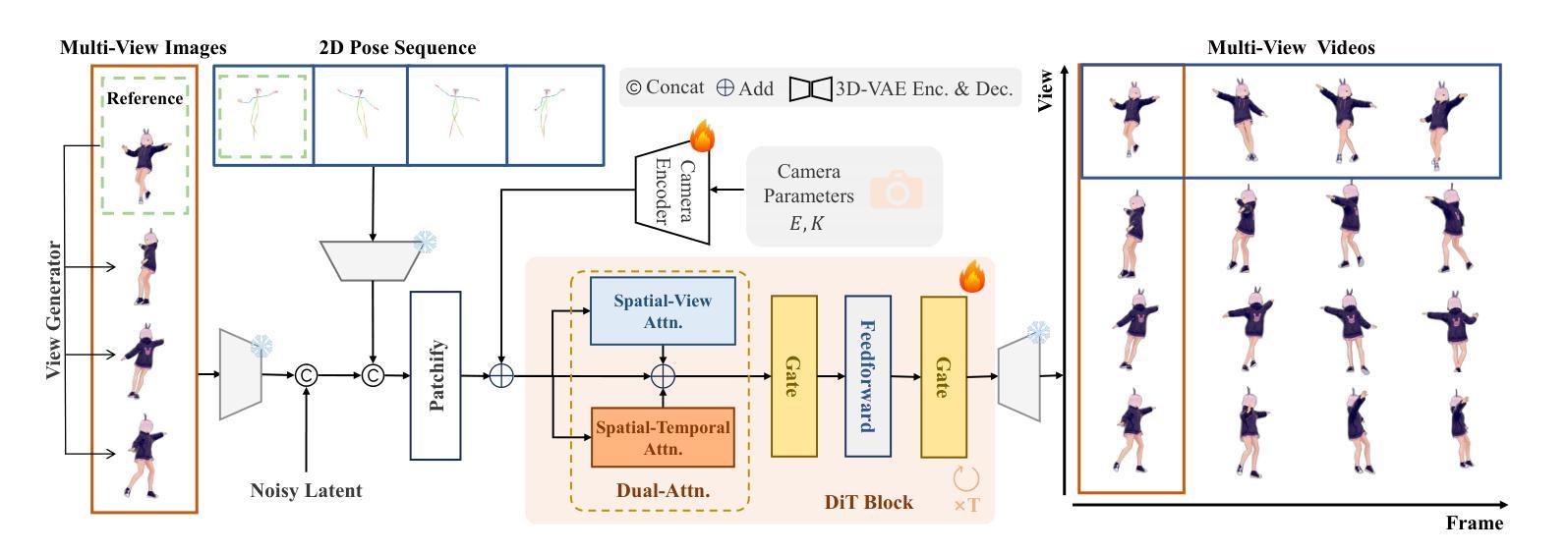
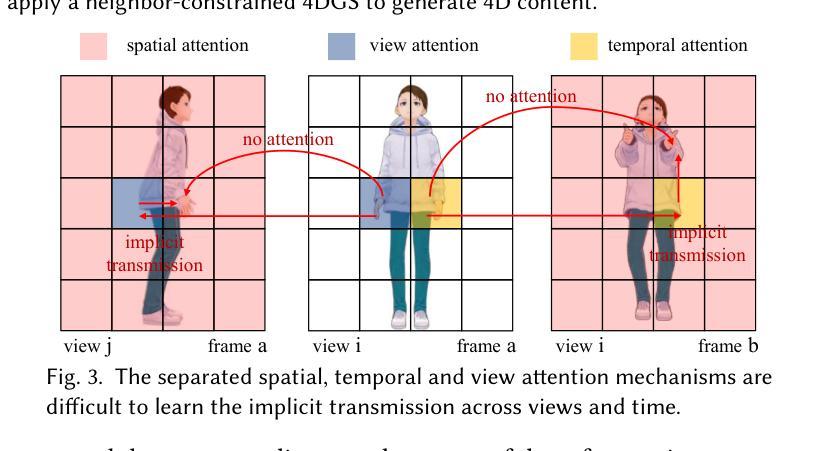
In this paper, we propose \textbf{CharacterShot}, a controllable and consistent 4D character animation framework that enables any individual designer to create dynamic 3D characters (i.e., 4D character animation) from a single reference character image and a 2D pose sequence. We begin by pretraining a powerful 2D character animation model based on a cutting-edge DiT-based image-to-video model, which allows for any 2D pose sequnce as controllable signal. We then lift the animation model from 2D to 3D through introducing dual-attention module together with camera prior to generate multi-view videos with spatial-temporal and spatial-view consistency. Finally, we employ a novel neighbor-constrained 4D gaussian splatting optimization on these multi-view videos, resulting in continuous and stable 4D character representations. Moreover, to improve character-centric performance, we construct a large-scale dataset Character4D, containing 13,115 unique characters with diverse appearances and motions, rendered from multiple viewpoints. Extensive experiments on our newly constructed benchmark, CharacterBench, demonstrate that our approach outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Code, models, and datasets will be publicly available at https://github.com/Jeoyal/CharacterShot.
本文中,我们提出了CharacterShot,这是一个可控且一致的4D角色动画框架,它允许任何个人设计师从单个参考角色图像和2D姿势序列中创建动态3D角色(即4D角色动画)。我们首先基于先进的DiT图像到视频模型的强大2D角色动画模型进行预训练,该模型允许任何2D姿势序列作为可控信号。然后我们通过引入双注意力模块和相机先验,将动画模型从2D提升到3D,生成具有时空和视空一致性的多视角视频。最后,我们在这些多视角视频上采用新型邻域约束的4D高斯点描优化方法,产生连续稳定的4D角色表示。此外,为了提升以角色为中心的性能,我们构建了一个大规模数据集Character4D,包含从多个视角渲染的具有不同外观和动作的独特角色图像共13,115张。在我们新构建的基准测试CharacterBench上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于当前最先进的算法。代码、模型和数据集将在https://github.com/Jeoyal/CharacterShot公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures. Code at https://github.com/Jeoyal/CharacterShot
Summary
本文提出了一个可控且一致的4D角色动画框架——CharacterShot。该框架允许设计师仅通过单个参考角色图像和2D姿态序列创建动态的3D角色(即4D角色动画)。通过基于先进的DiT图像到视频模型的2D角色动画模型进行预训练,引入双注意力模块和相机先验,将动画模型从2D提升到3D,生成具有时空和空视一致性的多视角视频。采用新型邻居约束的4D高斯喷涂优化技术,实现连续稳定的4D角色表示。此外,为提升角色为中心的性能,构建了大规模Character4D数据集,包含13,115个独特角色,具有多样化的外观和运动,从多个视角进行渲染。在全新构建的CharacterBench基准测试上的实验表明,该方法优于当前的最优方法。
Key Takeaways
- CharacterShot是一个4D角色动画框架,能从单一参考角色图像和2D姿态序列创建动态3D角色。
- 利用先进的DiT图像到视频模型进行2D角色动画模型的预训练,实现可控的2D姿态序列。
- 通过引入双注意力模块和相机先验,将动画模型从2D提升到3D。
- 生成具有时空和空视一致性的多视角视频。
- 采用邻居约束的4D高斯喷涂优化技术,确保4D角色表示的连续稳定性。
- 构建了大规模Character4D数据集,包含多样化外观和运动的独特角色。
点此查看论文截图


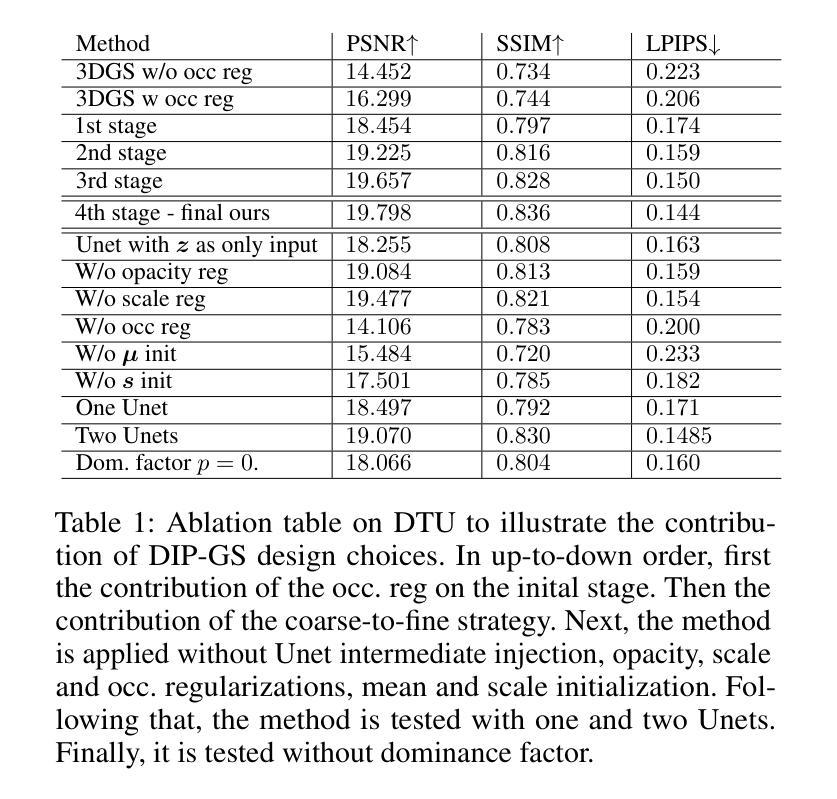
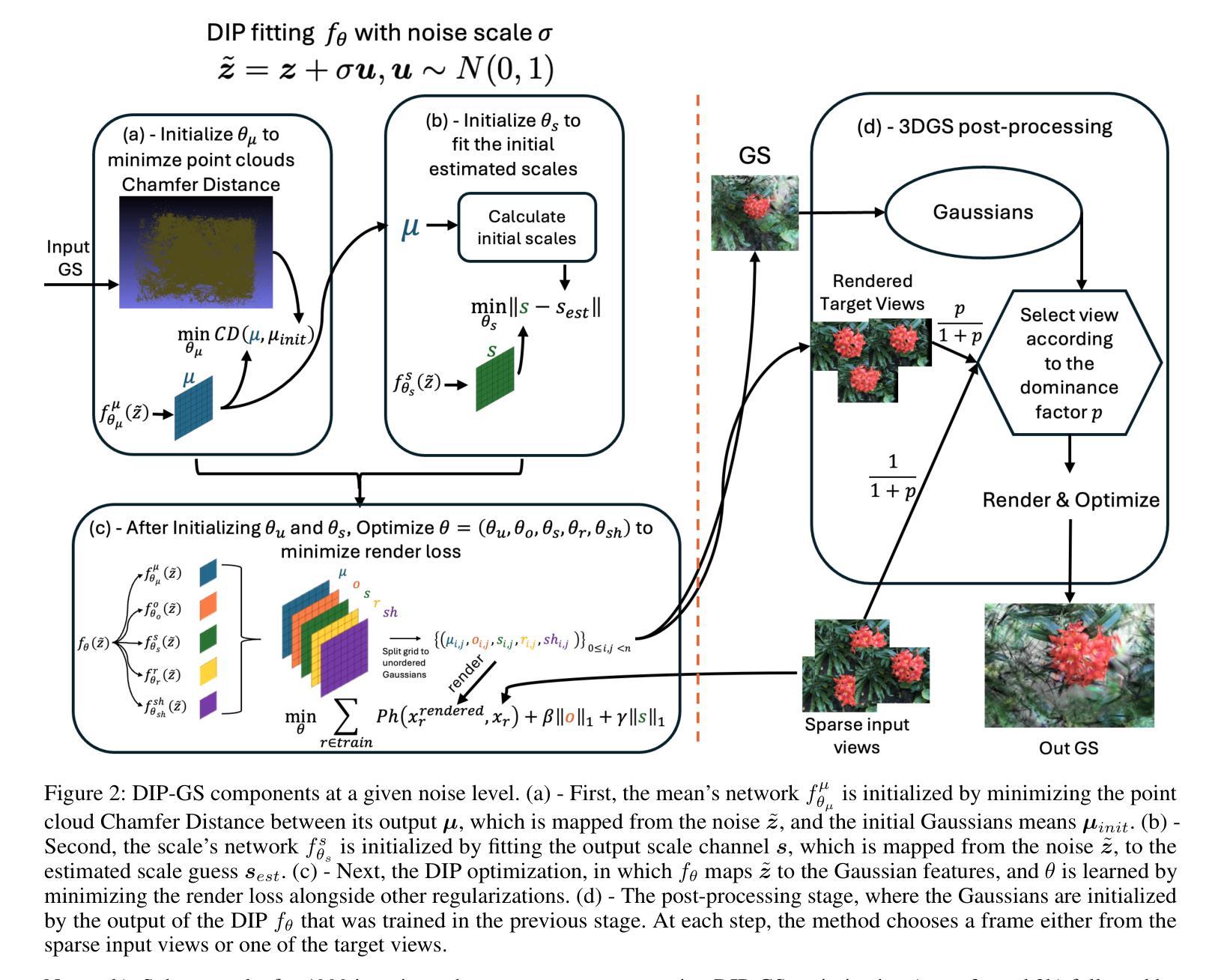
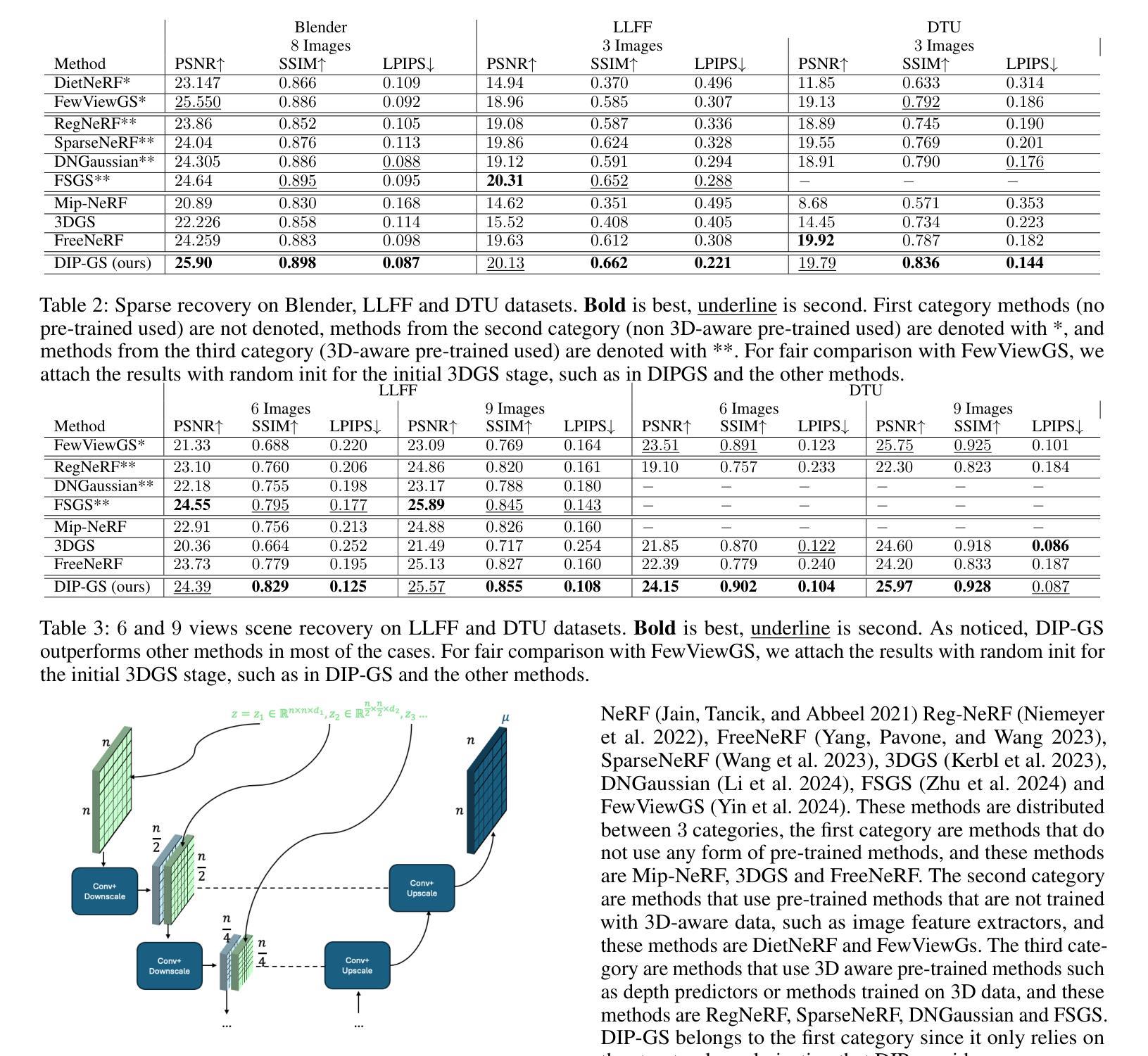
DIP-GS: Deep Image Prior For Gaussian Splatting Sparse View Recovery
Authors:Rajaei Khatib, Raja Giryes
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a leading 3D scene reconstruction method, obtaining high-quality reconstruction with real-time rendering runtime performance. The main idea behind 3DGS is to represent the scene as a collection of 3D gaussians, while learning their parameters to fit the given views of the scene. While achieving superior performance in the presence of many views, 3DGS struggles with sparse view reconstruction, where the input views are sparse and do not fully cover the scene and have low overlaps. In this paper, we propose DIP-GS, a Deep Image Prior (DIP) 3DGS representation. By using the DIP prior, which utilizes internal structure and patterns, with coarse-to-fine manner, DIP-based 3DGS can operate in scenarios where vanilla 3DGS fails, such as sparse view recovery. Note that our approach does not use any pre-trained models such as generative models and depth estimation, but rather relies only on the input frames. Among such methods, DIP-GS obtains state-of-the-art (SOTA) competitive results on various sparse-view reconstruction tasks, demonstrating its capabilities.
3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)是一种领先的3D场景重建方法,具有实时渲染运行时性能,并能获得高质量重建。3DGS的主要思想是将场景表示为3D高斯集合,同时学习其参数以适应场景的给定视图。虽然在多视图情况下表现优越,但3DGS在稀疏视图重建方面存在困难,即输入视图稀疏且不全面覆盖场景,重叠度较低。本文提出了DIP-GS,一种基于深度图像先验(DIP)的3DGS表示方法。通过使用DIP先验,利用内部结构模式和由粗到细的方式,基于DIP的3DGS可以在普通3DGS失败的情况下进行操作,如稀疏视图恢复。值得注意的是,我们的方法没有使用任何预训练模型,如生成模型和深度估计,而是仅依赖于输入帧。在这些方法中,DIP-GS在各种稀疏视图重建任务上取得了最先进的竞争结果,证明了其能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯展开技术(3DGS)的一种改进方法——DIP-GS。相较于传统三维重建方法,DIP-GS引入了一种称为深度图像先验(DIP)的新思路,无需依赖复杂的预训练模型即可在稀疏视图恢复场景中使用,以高还原度的重建质量和高效的渲染速度展示场景内容。在处理稀稀疏视图时具有出色表现。其在无密集视图的条件下重构场景中表现得尤为突出。此项技术代表了该领域最前沿的技术进展。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS作为前沿的三维重建技术,能够在实时渲染性能下实现高质量重建。
- 3DGS通过将场景表示为一系列三维高斯集合,通过拟合场景视图来学习参数。
- 在处理多个视图时表现优越,但在稀疏视图重建中面临挑战,如输入视图稀疏、不完全覆盖场景以及重叠度低等问题。
点此查看论文截图

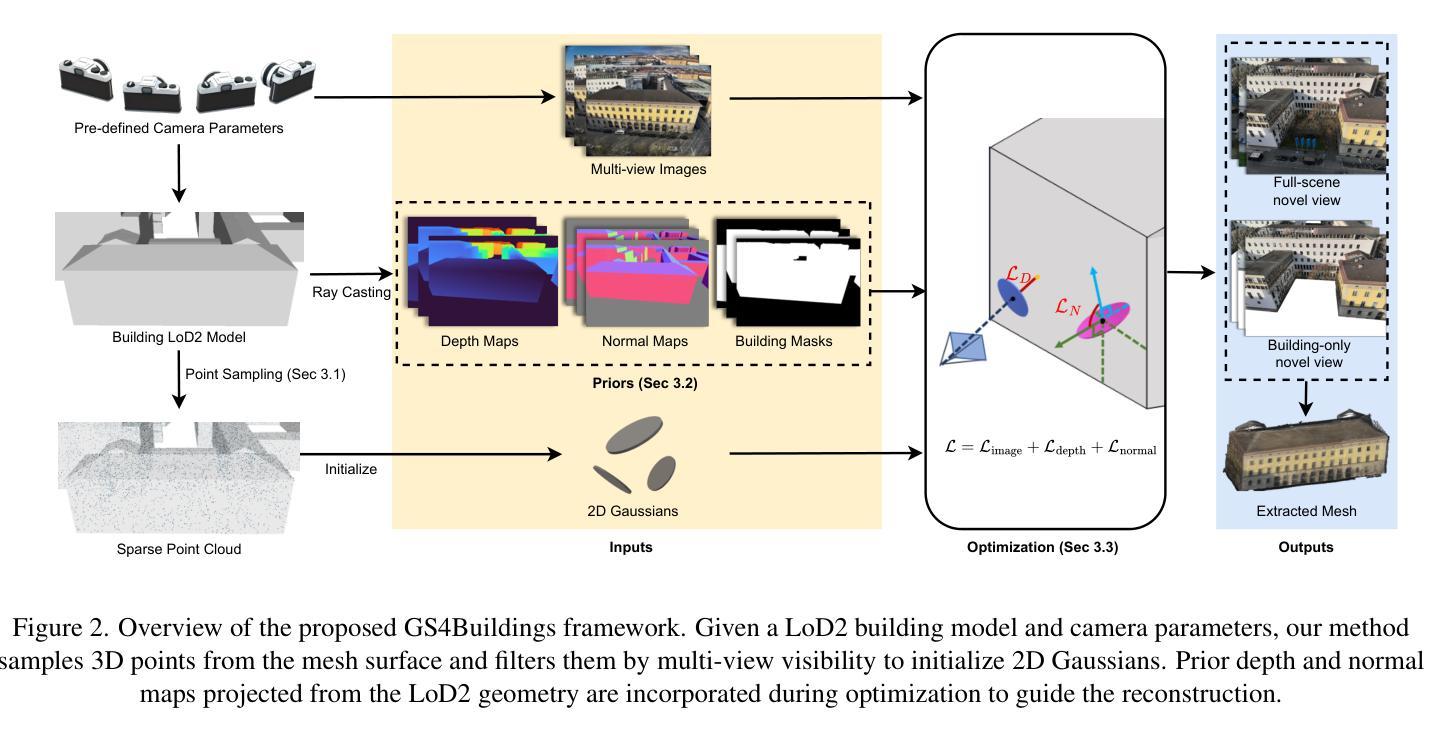
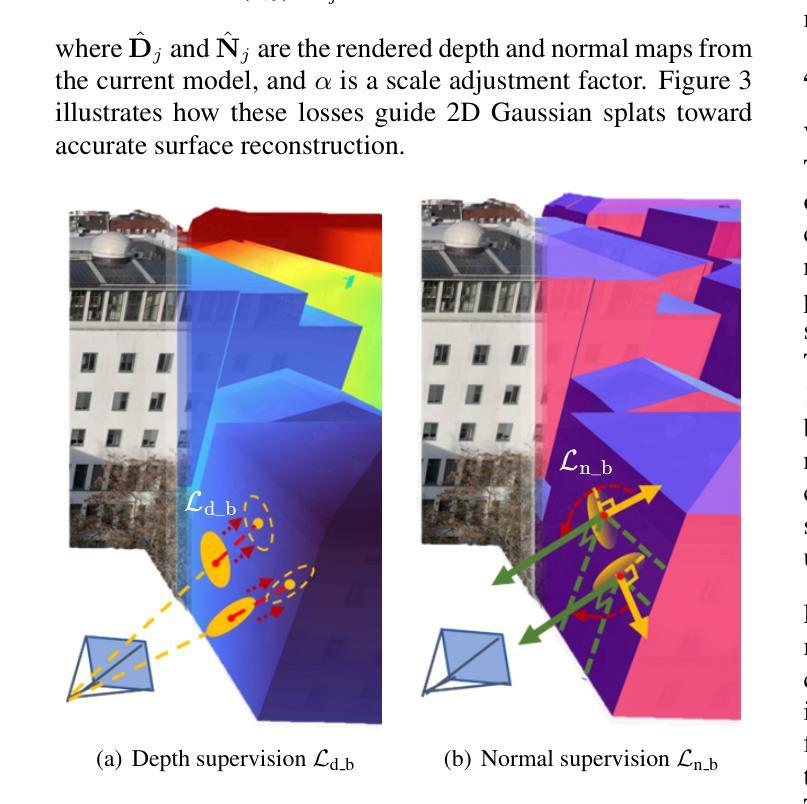
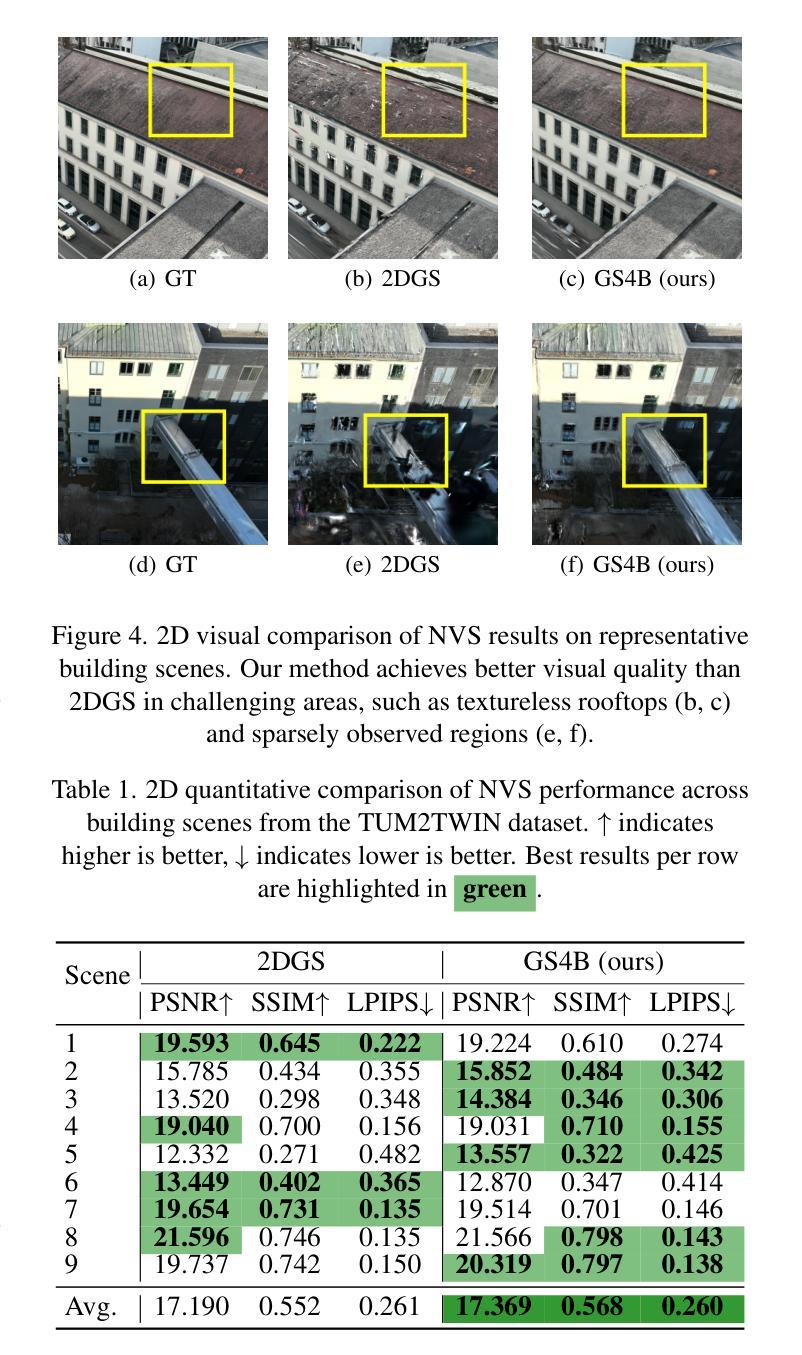
GS4Buildings: Prior-Guided Gaussian Splatting for 3D Building Reconstruction
Authors:Qilin Zhang, Olaf Wysocki, Boris Jutzi
Recent advances in Gaussian Splatting (GS) have demonstrated its effectiveness in photo-realistic rendering and 3D reconstruction. Among these, 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) is particularly suitable for surface reconstruction due to its flattened Gaussian representation and integrated normal regularization. However, its performance often degrades in large-scale and complex urban scenes with frequent occlusions, leading to incomplete building reconstructions. We propose GS4Buildings, a novel prior-guided Gaussian Splatting method leveraging the ubiquity of semantic 3D building models for robust and scalable building surface reconstruction. Instead of relying on traditional Structure-from-Motion (SfM) pipelines, GS4Buildings initializes Gaussians directly from low-level Level of Detail (LoD)2 semantic 3D building models. Moreover, we generate prior depth and normal maps from the planar building geometry and incorporate them into the optimization process, providing strong geometric guidance for surface consistency and structural accuracy. We also introduce an optional building-focused mode that limits reconstruction to building regions, achieving a 71.8% reduction in Gaussian primitives and enabling a more efficient and compact representation. Experiments on urban datasets demonstrate that GS4Buildings improves reconstruction completeness by 20.5% and geometric accuracy by 32.8%. These results highlight the potential of semantic building model integration to advance GS-based reconstruction toward real-world urban applications such as smart cities and digital twins. Our project is available: https://github.com/zqlin0521/GS4Buildings.
近期高斯混合技术(GS)的进步在光真实渲染和三维重建领域显示出其有效性。其中,二维高斯混合(2DGS)由于其扁平化高斯表示和集成正规化,特别适合用于表面重建。然而,它在处理大规模且复杂的城市场景时,经常遇到遮挡问题,导致建筑重建不完整。我们提出一种新型的先验引导高斯混合方法——GS4Buildings,该方法利用语义三维建筑模型的普遍性,实现稳健且可扩展的建筑表面重建。与传统的运动恢复结构(SfM)流程不同,GS4Buildings直接从低级别细节(LoD)2语义三维建筑模型初始化高斯分布。此外,我们从平面建筑几何生成先验深度图和正规图,并将其纳入优化流程,为表面一致性和结构准确性提供强大的几何指导。我们还引入了一种可选的建筑专注模式,将重建限制在建筑区域,实现了高斯原始数据71.8%的减少,使表示更加高效和紧凑。对城市数据集的实验表明,GS4Buildings提高了重建完整性20.5%和几何精度32.8%。这些结果凸显了语义建筑模型整合的潜力,推动了基于GS的重建技术向智慧城市和数字孪生等实际应用的发展。我们的项目可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/zqlin0521/GS4Buildings。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at ISPRS 3D GeoInfo & Smart Data, Smart Cities 2025, Kashiwa, Japan. To appear in the ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences
Summary
该文介绍了高斯融合(GS)在三维重建中的最新进展,特别是二维高斯融合(2DGS)在表面重建中的适用性。然而,在大规模、复杂的城市场景中,由于遮挡问题,其性能往往下降,导致建筑重建不完整。为此,文章提出了一种新的基于语义三维建筑模型的先验引导高斯融合方法GS4Buildings。该方法直接从低级别细节(LoD)的语义三维建筑模型初始化高斯,并生成先验深度图和法线图,融入优化过程,为表面一致性和结构准确性提供强有力的几何指导。实验表明,GS4Buildings能提高城市数据集重建的完整性和几何精度。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯融合(GS)在三维重建中有显著进展,尤其是二维高斯融合(2DGS)适用于表面重建。
- 在大规模、复杂的城市场景中,传统方法如结构从运动(SfM)管线在高斯融合中面临性能下降的问题。
- GS4Buildings是一种新的基于语义三维建筑模型的先验引导高斯融合方法,可提高建筑重建的鲁棒性和可扩展性。
- GS4Buildings直接从低级别细节(LoD)的语义三维建筑模型初始化高斯,增强了重建的准确性和效率。
- 通过生成先验深度图和法线图,融入优化过程,GS4Buildings为表面一致性和结构准确性提供强有力的几何指导。
- 实验表明,GS4Buildings能提高城市数据集重建的完整性和几何精度。
点此查看论文截图

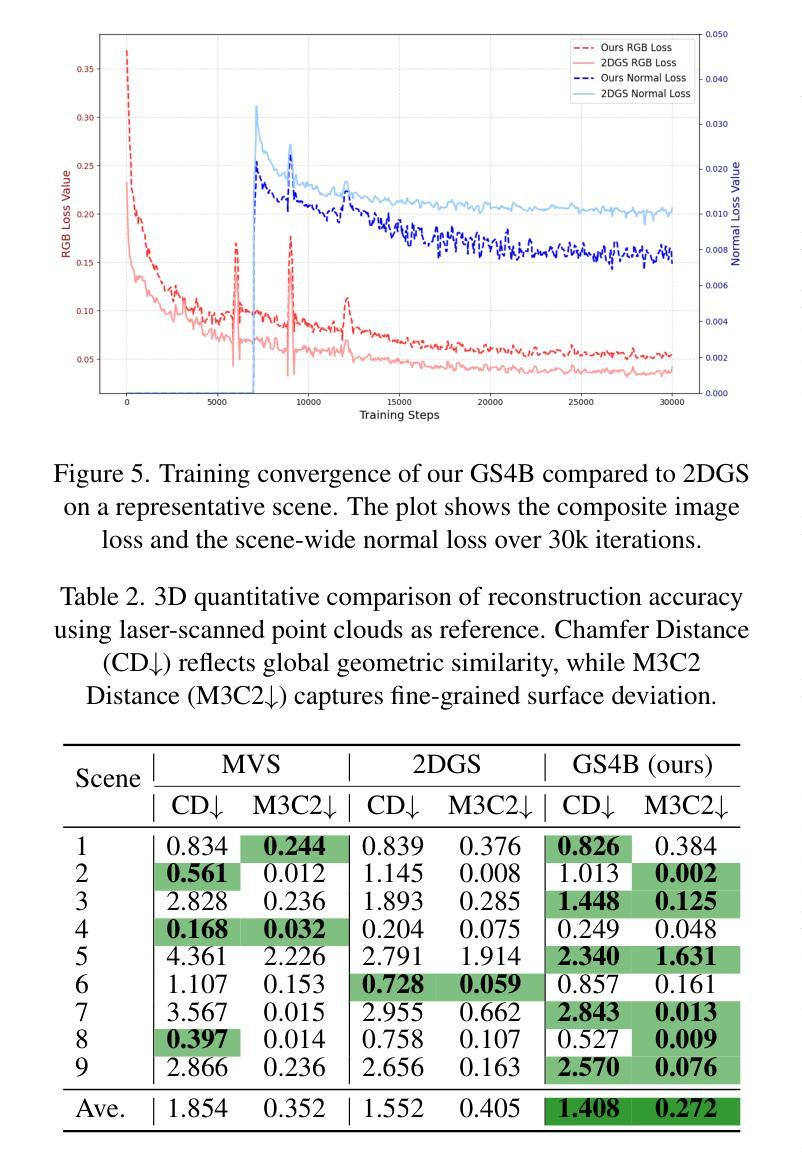
3D Gaussian Representations with Motion Trajectory Field for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Xuesong Li, Lars Petersson, Vivien Rolland
This paper addresses the challenge of novel-view synthesis and motion reconstruction of dynamic scenes from monocular video, which is critical for many robotic applications. Although Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have demonstrated remarkable success in rendering static scenes, extending them to reconstruct dynamic scenes remains challenging. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that combines 3DGS with a motion trajectory field, enabling precise handling of complex object motions and achieving physically plausible motion trajectories. By decoupling dynamic objects from static background, our method compactly optimizes the motion trajectory field. The approach incorporates time-invariant motion coefficients and shared motion trajectory bases to capture intricate motion patterns while minimizing optimization complexity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results in both novel-view synthesis and motion trajectory recovery from monocular video, advancing the capabilities of dynamic scene reconstruction.
本文旨在解决从单目视频中合成新视角和重建动态场景的挑战,这对于许多机器人应用至关重要。尽管神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯拼接(3DGS)在渲染静态场景方面取得了显著的成功,但它们扩展到重建动态场景仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖的方法,结合了三维高斯拼接和动态轨迹场,能够精确处理复杂物体的运动,实现物理合理的运动轨迹。通过将动态物体与静态背景解耦,我们的方法紧凑地优化了运动轨迹场。该方法结合了时间不变的动态系数和共享的运动轨迹基,能够捕捉复杂的运动模式,同时最小化优化复杂度。大量实验表明,我们的方法在单目视频的新视角合成和运动轨迹恢复方面取得了最先进的成果,提高了动态场景重建的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合3DGS和运动轨迹场的新方法,用于从单目视频中重建动态场景。该方法能够精确处理复杂物体运动,实现物理上可行的运动轨迹。通过解耦动态物体和静态背景,该方法能够紧凑地优化运动轨迹场,采用时间不变运动系数和共享运动轨迹基,以捕捉复杂的运动模式,同时降低优化复杂度。实验表明,该方法在单目视频的新视角合成和运动轨迹恢复方面均达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决了从单目视频中重建动态场景的挑战,这对于许多机器人应用至关重要。
- 引入了一种结合3DGS和运动轨迹场的新方法,以处理复杂的物体运动并实现物理上可行的运动轨迹。
- 通过解耦动态物体和静态背景,该方法能够紧凑地优化运动轨迹场。
- 采用时间不变运动系数和共享运动轨迹基来降低优化复杂度,同时捕捉复杂的运动模式。
- 该方法能够实现新视角合成和从单目视频中的运动轨迹恢复。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在动态场景重建方面达到领先水平。
- 该方法对未来机器人应用,如自动驾驶、智能监控等,具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

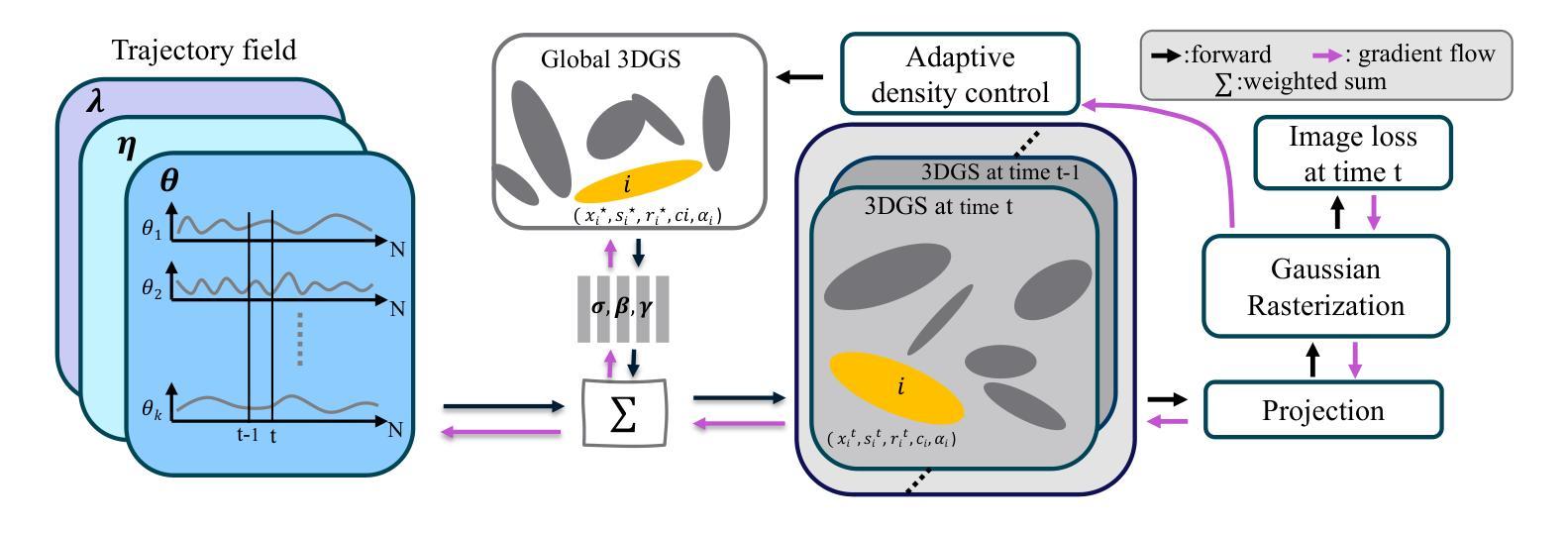
DexFruit: Dexterous Manipulation and Gaussian Splatting Inspection of Fruit
Authors:Aiden Swann, Alex Qiu, Matthew Strong, Angelina Zhang, Samuel Morstein, Kai Rayle, Monroe Kennedy III
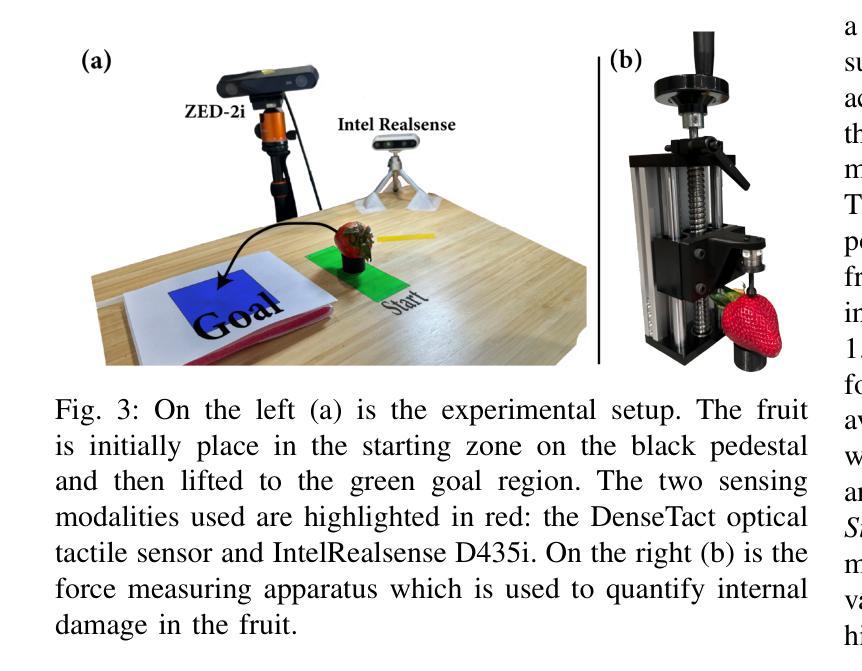
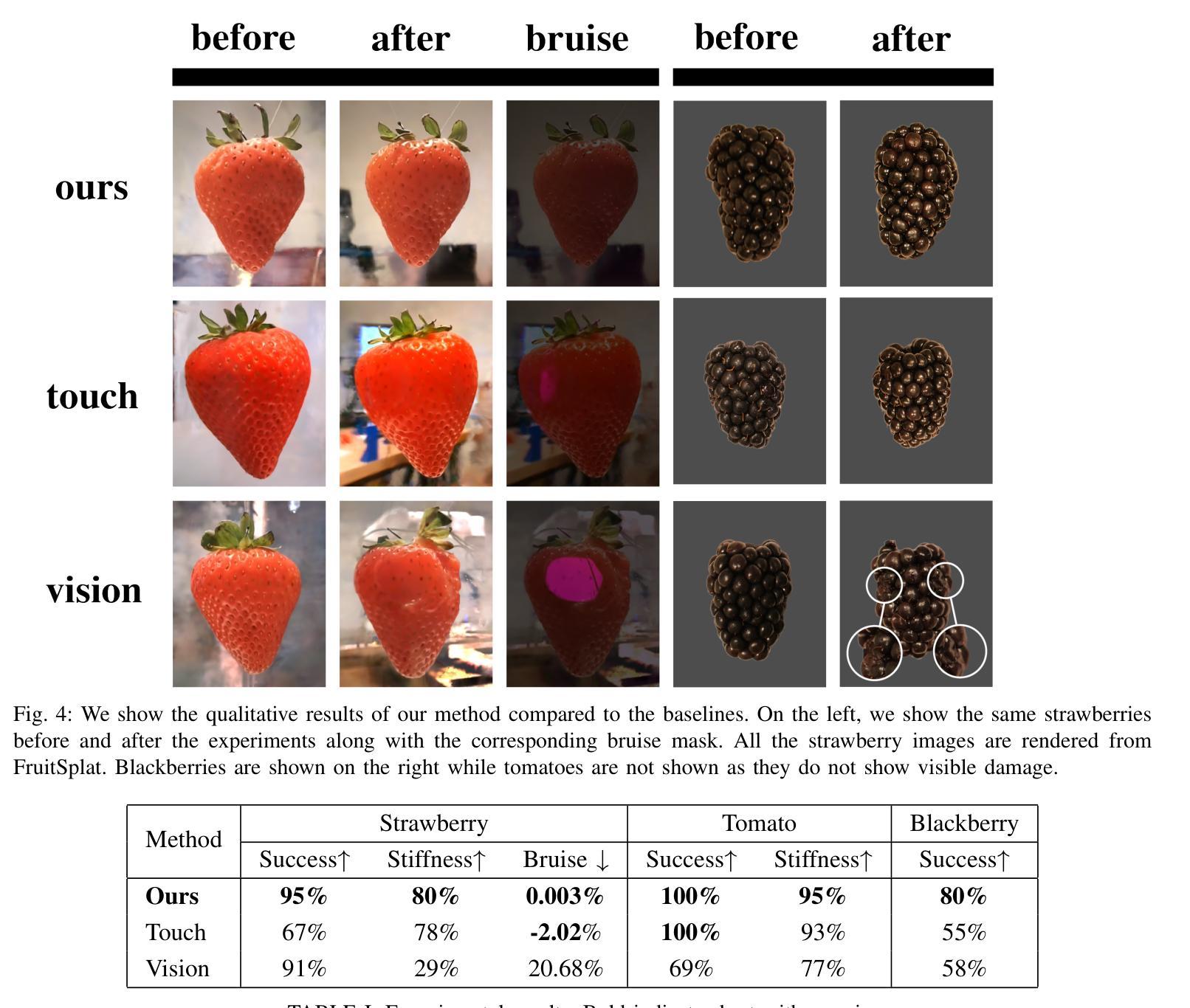
DexFruit is a robotic manipulation framework that enables gentle, autonomous handling of fragile fruit and precise evaluation of damage. Many fruits are fragile and prone to bruising, thus requiring humans to manually harvest them with care. In this work, we demonstrate by using optical tactile sensing, autonomous manipulation of fruit with minimal damage can be achieved. We show that our tactile informed diffusion policies outperform baselines in both reduced bruising and pick-and-place success rate across three fruits: strawberries, tomatoes, and blackberries. In addition, we introduce FruitSplat, a novel technique to represent and quantify visual damage in high-resolution 3D representation via 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Existing metrics for measuring damage lack quantitative rigor or require expensive equipment. With FruitSplat, we distill a 2D strawberry mask as well as a 2D bruise segmentation mask into the 3DGS representation. Furthermore, this representation is modular and general, compatible with any relevant 2D model. Overall, we demonstrate a 92% grasping policy success rate, up to a 20% reduction in visual bruising, and up to an 31% improvement in grasp success rate on challenging fruit compared to our baselines across our three tested fruits. We rigorously evaluate this result with over 630 trials. Please checkout our website at https://dex-fruit.github.io .
DexFruit是一个机器人操作框架,能够实现脆弱水果的轻柔自主处理和损伤的精确评估。许多水果是脆弱的,容易受损,因此需要人们小心地手工采摘它们。在这项工作中,我们通过使用光学触觉感应技术,展示了可以对水果进行自主操作,实现最小的损伤。我们证明,我们的触觉感知扩散策略在减少损伤和采摘放置成功率方面超过了基线标准。这项技术在草莓、番茄和黑莓这三种水果上得到了验证。此外,我们还推出了一种新型技术FruitSplat,它可以通过3D高斯喷涂技术(3DGS)以高分辨率的3D形式表示和量化视觉损伤。现有的损伤测量指标缺乏定量严谨性或需要昂贵的设备。借助FruitSplat,我们将一个二维草莓掩膜和一个二维淤血分割掩膜蒸馏到3DGS表示中。此外,这种表示是模块化和通用的,可以与任何相关的二维模型兼容。总的来说,我们实现了92%的抓取策略成功率,视觉淤血减少了高达20%,在具有挑战性的水果上与基线相比,抓取成功率提高了高达31%。我们对这一结果进行了超过630次的严格试验评价。请访问我们的网站https://dex-fruit.github.io了解更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
DexFruit框架实现了对脆弱水果的轻柔自主操控与损伤精确评估。通过光学触觉感知技术,实现了对草莓、番茄和覆盆子等三种水果的自主操控,减少了损伤并提高了拾取放置的成功率。此外,研究还引入了FruitSplat技术,通过3D高斯贴图(3DGS)以高分辨率3D形式呈现和量化视觉损伤。此技术可模块化并通用化,适用于任何相关2D模型。整体而言,研究实现了92%的抓取策略成功率,视觉损伤减少达20%,与基线相比在挑战性水果上抓取成功率提高达31%,经过超过630次试验的严格评估。
Key Takeaways
- DexFruit是一个用于操控脆弱水果的框架,能实现自主操控和损伤评估。
- 通过光学触觉感知技术,实现了对多种水果的自主操控,减少了损伤并提高拾取放置成功率。
- 引入FruitSplat技术,使用3D高斯贴图(3DGS)进行视觉损伤的精准呈现和量化。
- 此技术适用于任何相关2D模型并具有模块化特点。
- 研究达到了较高的抓取策略成功率,并显著减少了视觉损伤。
- 与基线相比,在挑战性水果上的抓取成功率显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

3DGS-VBench: A Comprehensive Video Quality Evaluation Benchmark for 3DGS Compression
Authors:Yuke Xing, William Gordon, Qi Yang, Kaifa Yang, Jiarui Wang, Yiling Xu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables real-time novel view synthesis with high visual fidelity, but its substantial storage requirements hinder practical deployment, prompting state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3DGS methods to incorporate compression modules. However, these 3DGS generative compression techniques introduce unique distortions lacking systematic quality assessment research. To this end, we establish 3DGS-VBench, a large-scale Video Quality Assessment (VQA) Dataset and Benchmark with 660 compressed 3DGS models and video sequences generated from 11 scenes across 6 SOTA 3DGS compression algorithms with systematically designed parameter levels. With annotations from 50 participants, we obtained MOS scores with outlier removal and validated dataset reliability. We benchmark 6 3DGS compression algorithms on storage efficiency and visual quality, and evaluate 15 quality assessment metrics across multiple paradigms. Our work enables specialized VQA model training for 3DGS, serving as a catalyst for compression and quality assessment research. The dataset is available at https://github.com/YukeXing/3DGS-VBench.
3D高斯混成(3DGS)能够以高视觉保真度实现实时新型视图合成,但其巨大的存储需求阻碍了实际应用部署,促使最先进的(SOTA)3DGS方法融入压缩模块。然而,这些3DGS生成压缩技术引入了独特的失真,缺乏系统的质量评估研究。为此,我们建立了大规模的Video Quality Assessment(视频质量评估,简称VQA)数据集和基准测试平台——3DGS-VBench,包含660个压缩的3DGS模型和由6种最先进3DGS压缩算法生成的视频序列,这些视频序列涵盖了11个场景并带有系统设计的参数级别。通过50名参与者的标注,我们获得了去除异常值后的平均意见分数(MOS),并验证了数据集可靠性。我们在存储效率和视觉质量方面对6种3DGS压缩算法进行了基准测试,并评估了跨多种范式的15种质量评估指标。我们的工作能够实现针对3DGS的专门化VQA模型训练,成为压缩和质量评估研究的催化剂。数据集可在https://github.com/YukeXing/3DGS-VBench获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种用于评估三维高斯融合(3DGS)压缩技术视频质量的大型数据集和基准测试。该数据集包含来自不同场景的压缩视频序列和模型,涵盖了多种先进的压缩算法。通过参与者评估和标注,建立了数据集可靠性。该研究有助于训练专门针对三维高斯融合的特殊视频质量评估模型,推动压缩技术与质量评估领域的研究进展。数据集可从链接获取:https://github.com/YukeXing/3DGS-VBench。
关键见解
- 3DGS可实现具有高质量视觉效果的实时新视角合成,但其大量存储需求限制了实际应用。因此,最新的方法融入了压缩模块。
- 现有研究缺少关于如何系统性地评估这种新的3DGS压缩技术所特有的扭曲的技术分析。这带来了需求进行专门的质量评估研究。
点此查看论文截图


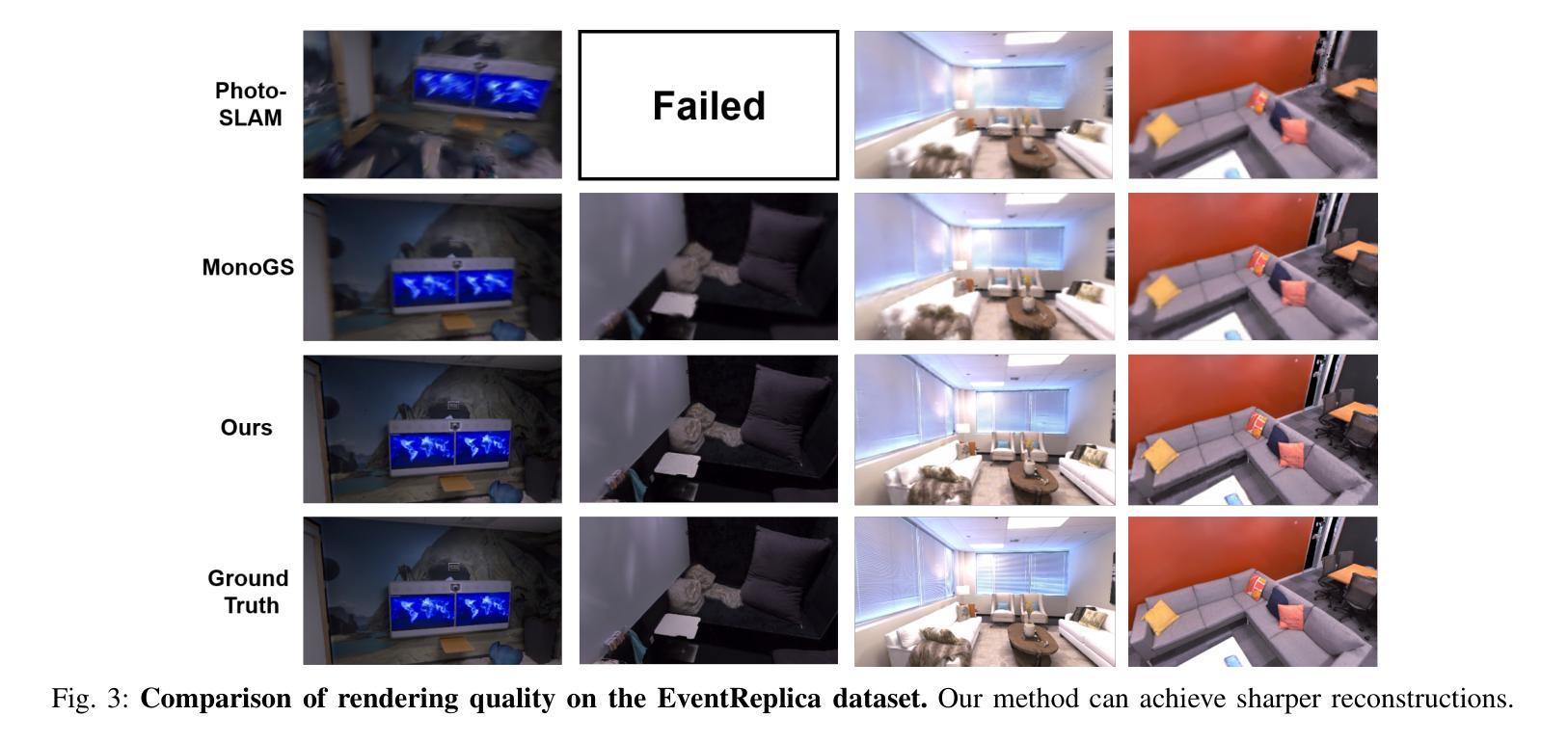
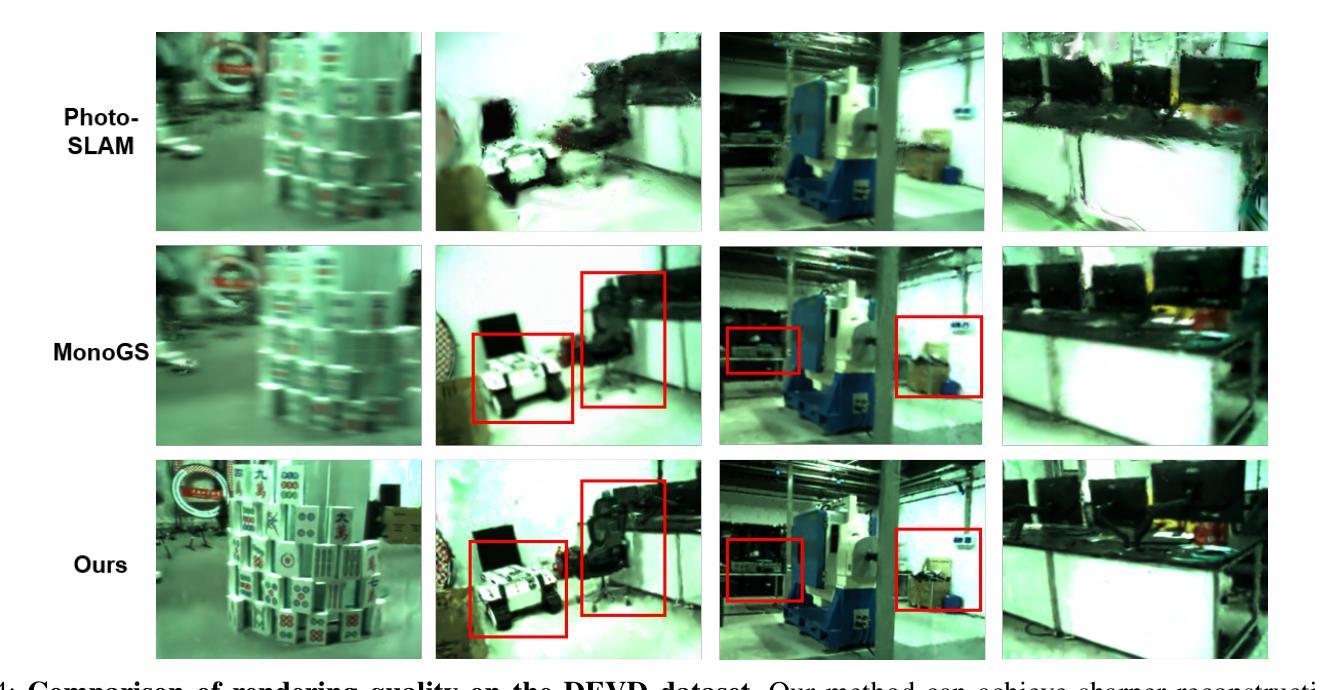
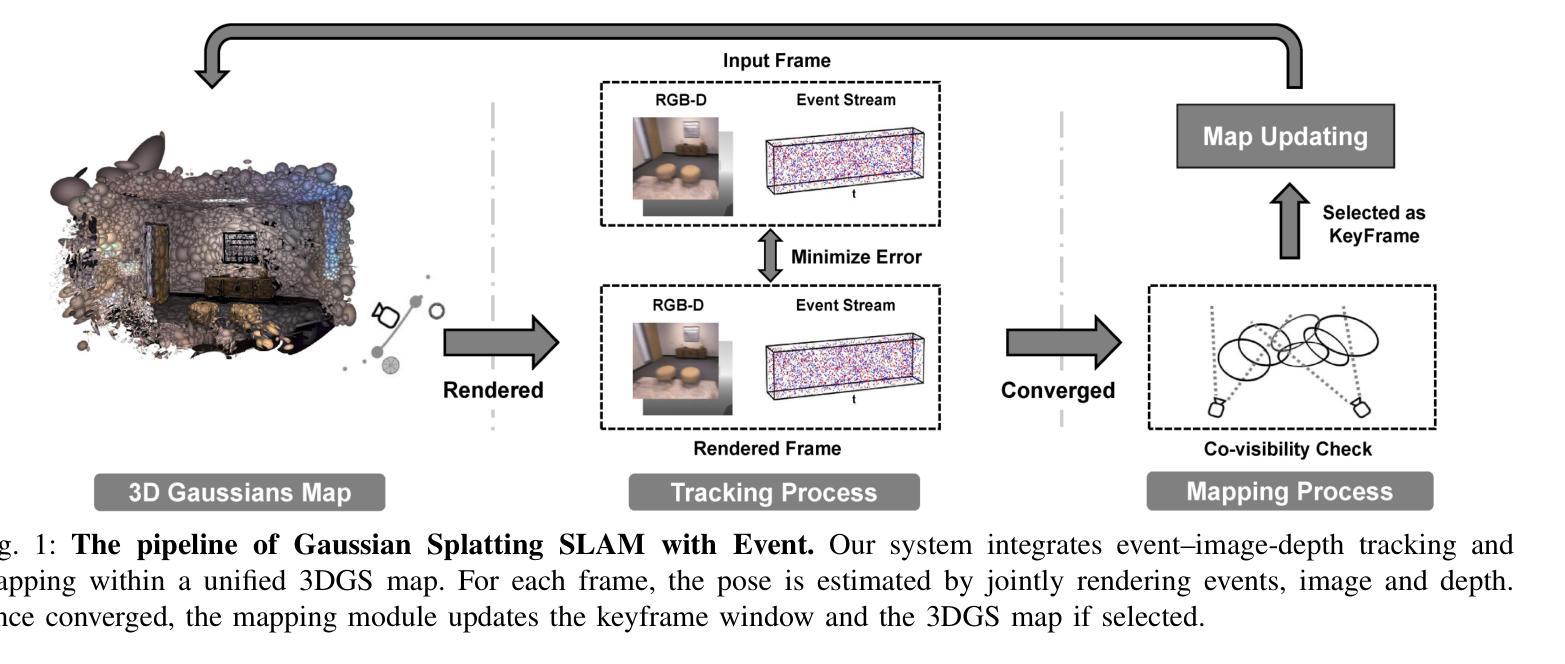
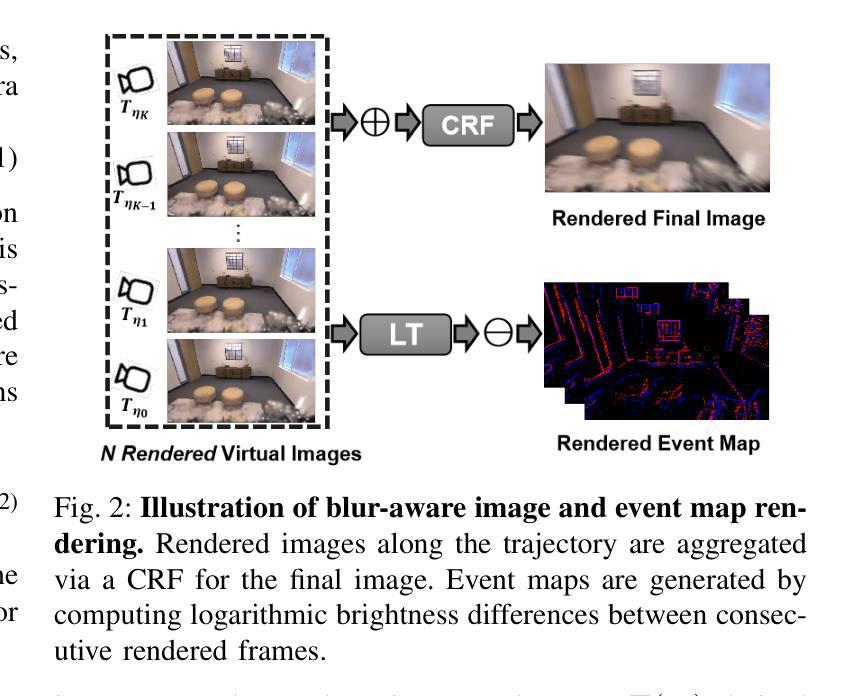
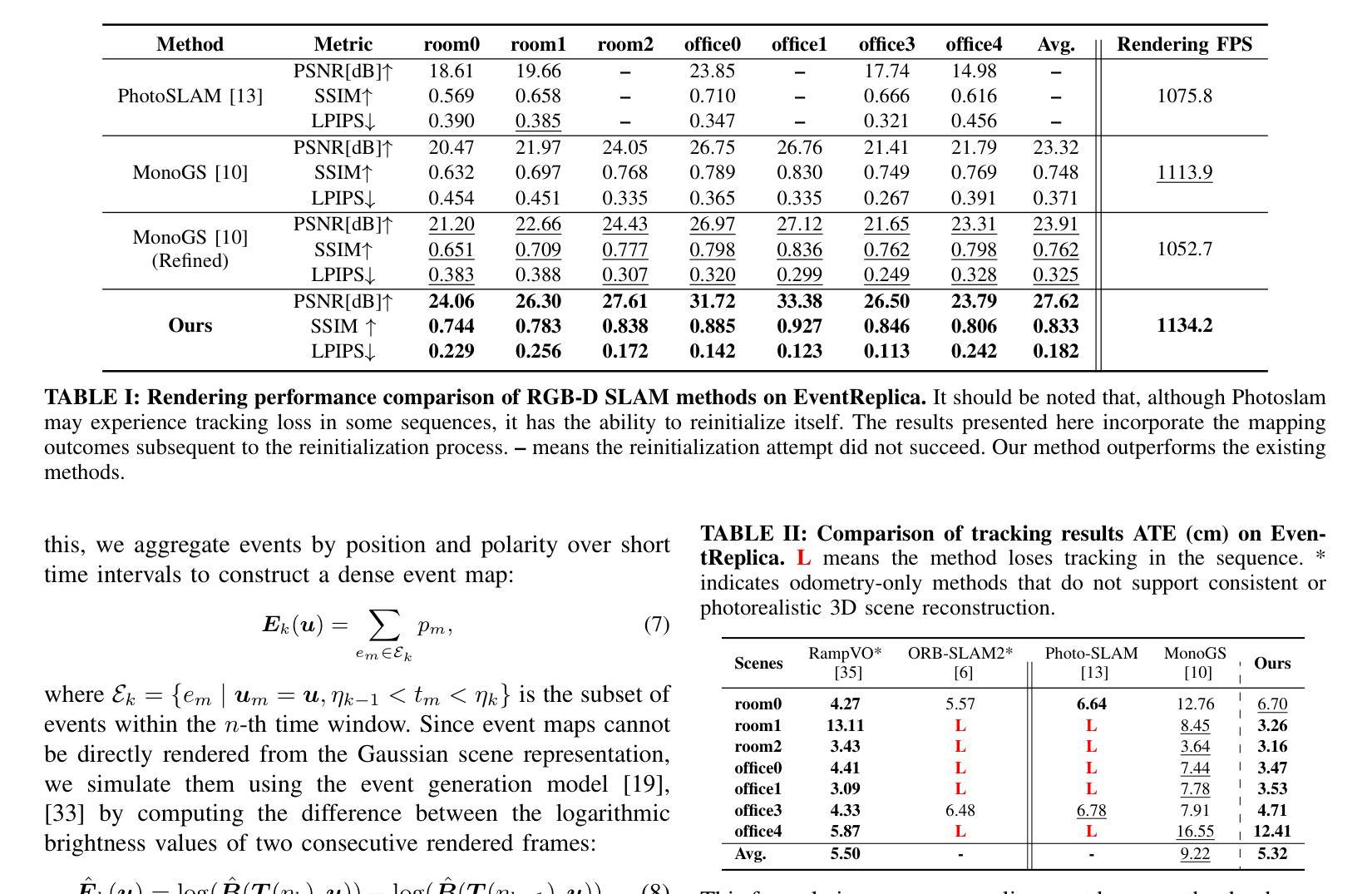
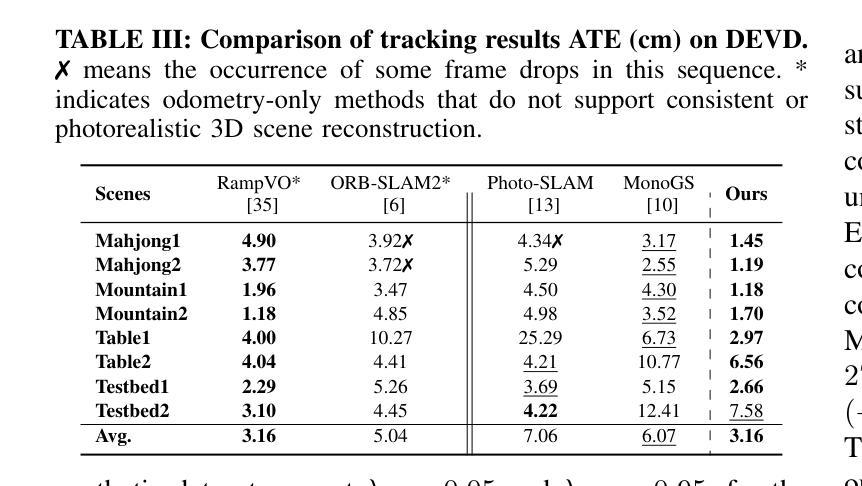
EGS-SLAM: RGB-D Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Events
Authors:Siyu Chen, Shenghai Yuan, Thien-Minh Nguyen, Zhuyu Huang, Chenyang Shi, Jin Jing, Lihua Xie
Gaussian Splatting SLAM (GS-SLAM) offers a notable improvement over traditional SLAM methods, enabling photorealistic 3D reconstruction that conventional approaches often struggle to achieve. However, existing GS-SLAM systems perform poorly under persistent and severe motion blur commonly encountered in real-world scenarios, leading to significantly degraded tracking accuracy and compromised 3D reconstruction quality. To address this limitation, we propose EGS-SLAM, a novel GS-SLAM framework that fuses event data with RGB-D inputs to simultaneously reduce motion blur in images and compensate for the sparse and discrete nature of event streams, enabling robust tracking and high-fidelity 3D Gaussian Splatting reconstruction. Specifically, our system explicitly models the camera’s continuous trajectory during exposure, supporting event- and blur-aware tracking and mapping on a unified 3D Gaussian Splatting scene. Furthermore, we introduce a learnable camera response function to align the dynamic ranges of events and images, along with a no-event loss to suppress ringing artifacts during reconstruction. We validate our approach on a new dataset comprising synthetic and real-world sequences with significant motion blur. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that EGS-SLAM consistently outperforms existing GS-SLAM systems in both trajectory accuracy and photorealistic 3D Gaussian Splatting reconstruction. The source code will be available at https://github.com/Chensiyu00/EGS-SLAM.
高斯融合SLAM(GS-SLAM)相较于传统SLAM方法在光幻真3D重建方面提供了显著的改进,而传统方法往往难以实现这一点。然而,现有GS-SLAM系统在现实场景中常见的持久性严重运动模糊情况下表现不佳,导致跟踪精度显著降低和3D重建质量受损。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了EGS-SLAM,这是一种新的GS-SLAM框架,它将事件数据与RGB-D输入融合,可同时减少图像中的运动模糊并补偿事件流的稀疏离散性质,从而实现稳健的跟踪和高保真度的3D高斯融合重建。具体来说,我们的系统显式建模相机曝光过程中的连续轨迹,支持事件和模糊感知的跟踪和映射在统一的3D高斯融合场景上。此外,我们引入了一个可学习的相机响应函数来对齐事件和图像的动态范围,以及无事件损失来抑制重建过程中的振铃伪影。我们在包含合成和真实序列的新数据集上验证了我们的方法,该数据集具有显著的运动模糊。大量实验结果表明,EGS-SLAM在轨迹准确性和光幻真3D高斯融合重建方面均优于现有GS-SLAM系统。源代码将在https://github.com/Chensiyu00/EGS-SLAM上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE RAL
Summary
GS-SLAM方法在真实世界场景中存在运动模糊问题,导致跟踪精度下降和3D重建质量受损。针对此问题,提出EGS-SLAM框架,融合事件数据和RGB-D输入,减少图像运动模糊,并补偿事件流的稀疏和离散性,实现稳健跟踪和高保真3D高斯喷溅重建。该框架显式建模相机曝光期间的连续轨迹,支持事件和模糊感知的跟踪和映射,并引入可学习的相机响应函数和对齐事件和图像动态范围的方法,以及无事件损失来抑制重建过程中的振铃伪影。
Key Takeaways
- GS-SLAM在真实场景中存在运动模糊问题。
- EGS-SLAM框架融合事件数据和RGB-D输入,减少图像运动模糊。
- EGS-SLAM补偿事件流的稀疏和离散性,实现稳健跟踪和高保真3D重建。
- 框架显式建模相机曝光期间的连续轨迹,支持事件和模糊感知的跟踪和映射。
- 引入可学习的相机响应函数,对齐事件和图像动态范围。
- 采用无事件损失抑制重建过程中的振铃伪影。
- 验证方法在新数据集上表现优异,包括合成和真实世界序列。
点此查看论文截图



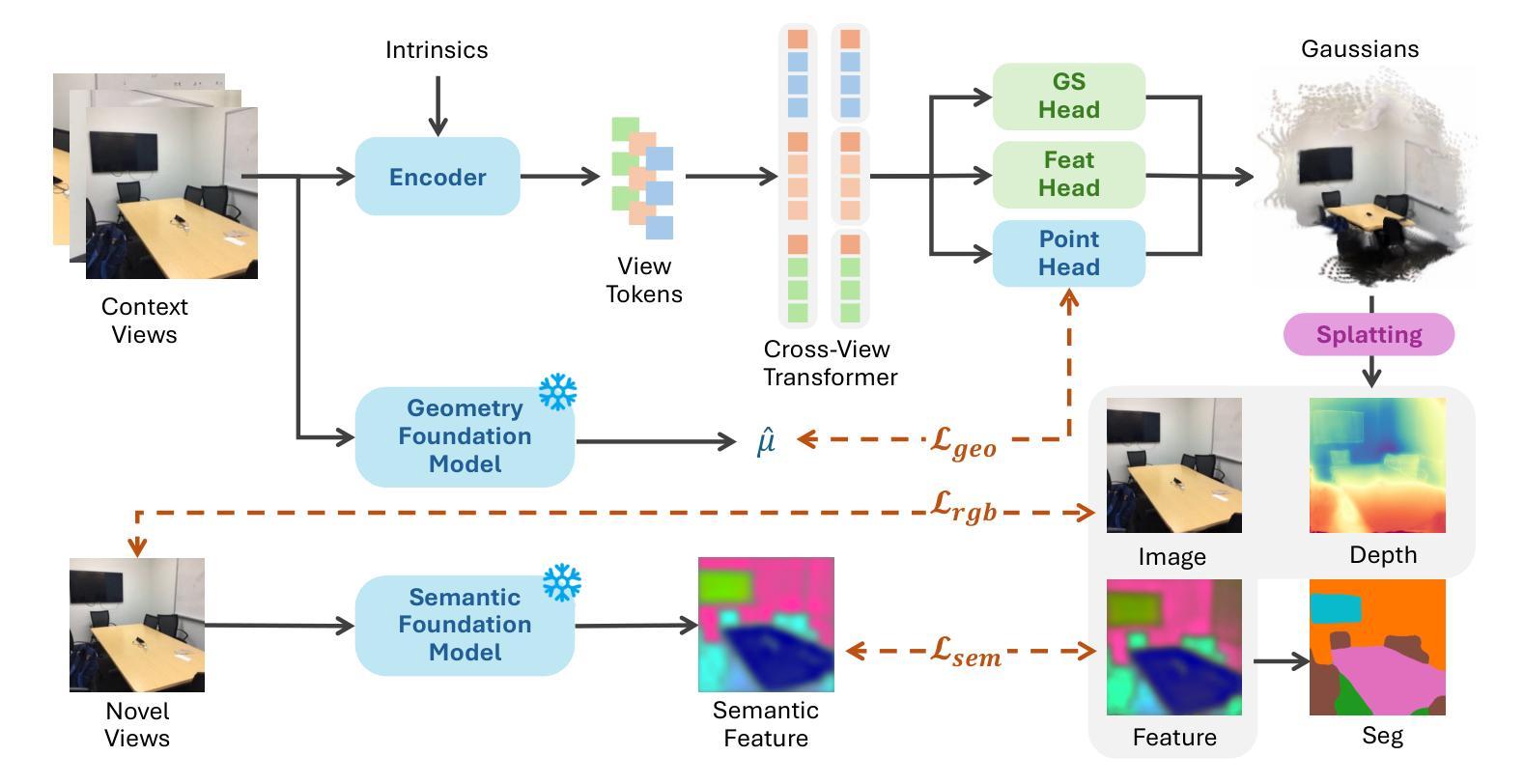
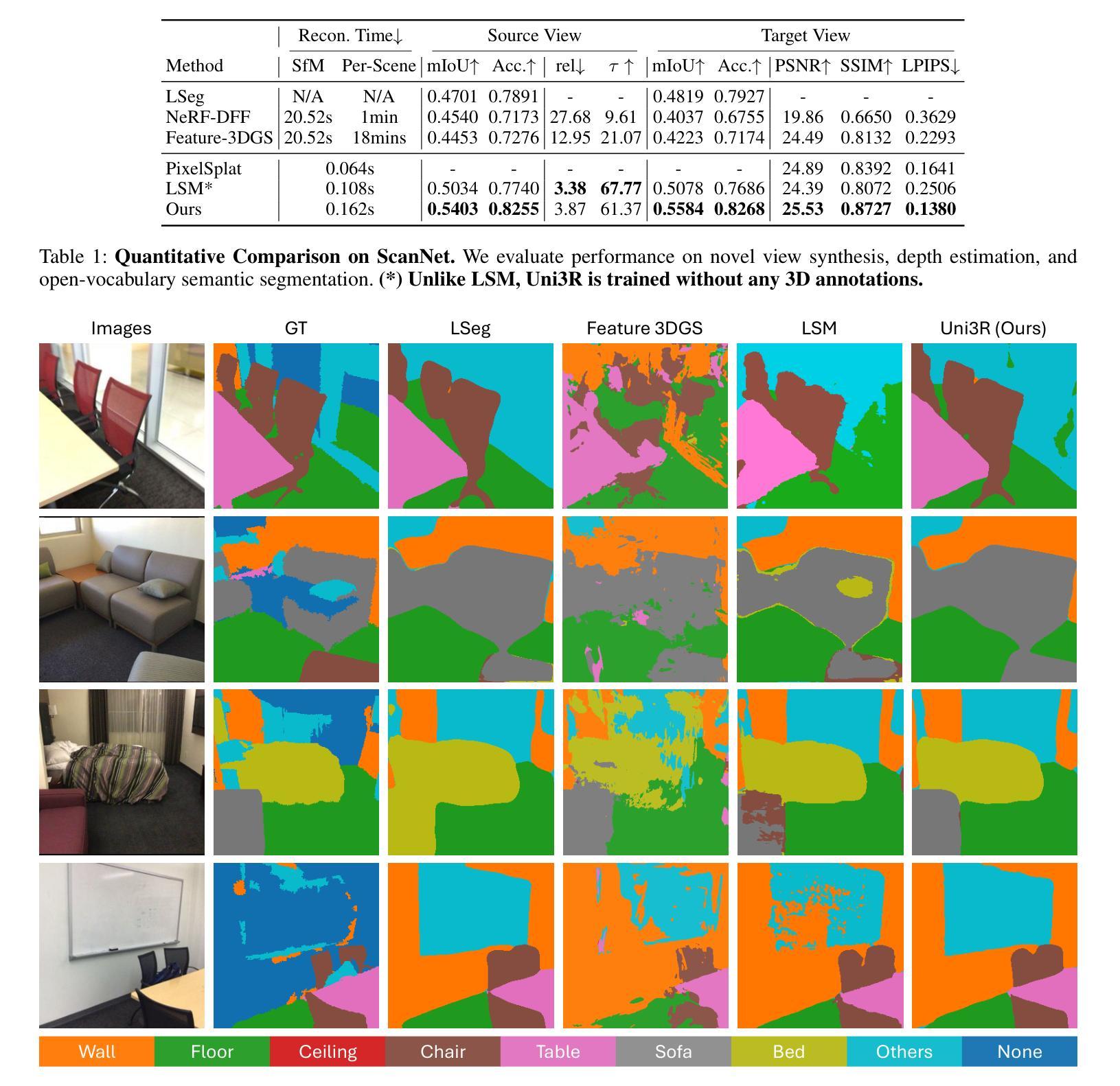
Uni3R: Unified 3D Reconstruction and Semantic Understanding via Generalizable Gaussian Splatting from Unposed Multi-View Images
Authors:Xiangyu Sun, Haoyi Jiang, Liu Liu, Seungtae Nam, Gyeongjin Kang, Xinjie Wang, Wei Sui, Zhizhong Su, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang, Eunbyung Park
Reconstructing and semantically interpreting 3D scenes from sparse 2D views remains a fundamental challenge in computer vision. Conventional methods often decouple semantic understanding from reconstruction or necessitate costly per-scene optimization, thereby restricting their scalability and generalizability. In this paper, we introduce Uni3R, a novel feed-forward framework that jointly reconstructs a unified 3D scene representation enriched with open-vocabulary semantics, directly from unposed multi-view images. Our approach leverages a Cross-View Transformer to robustly integrate information across arbitrary multi-view inputs, which then regresses a set of 3D Gaussian primitives endowed with semantic feature fields. This unified representation facilitates high-fidelity novel view synthesis, open-vocabulary 3D semantic segmentation, and depth prediction, all within a single, feed-forward pass. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Uni3R establishes a new state-of-the-art across multiple benchmarks, including 25.07 PSNR on RE10K and 55.84 mIoU on ScanNet. Our work signifies a novel paradigm towards generalizable, unified 3D scene reconstruction and understanding. The code is available at https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R.
从稀疏的二维视角重建和语义解释三维场景仍是计算机视觉领域的一个基本挑战。传统的方法常常将语义理解与重建解耦,或者需要昂贵的场景优化,从而限制了其可扩展性和通用性。在本文中,我们介绍了Uni3R,这是一种新型前馈框架,它直接从未定位的多视角图像中联合重建了丰富的开放词汇语义的统一三维场景表示。我们的方法利用跨视图变压器稳健地整合任意多视角输入的信息,然后回归一组带有语义特征场的三维高斯基元。这种统一表示有助于高保真度的新视角合成、开放词汇的3D语义分割和深度预测,所有这些都在单次前馈传递中完成。大量实验表明,Uni3R在多个基准测试中建立了新的最先进的性能,包括RE10K上的25.07 PSNR和ScanNet上的55.84 mIoU。我们的工作标志着朝着通用、统一的三维场景重建和理解的新范式。代码可在https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code is available at https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/Uni3R
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Uni3R的新型前馈框架,能够从无姿态的多视角图像直接重建统一且富含开放词汇语义的3D场景表示。该框架利用跨视图变压器稳健地整合任意多视角输入信息,然后回归一组带有语义特征场的3D高斯原始数据。这一统一表示有助于高保真新颖视图合成、开放词汇3D语义分割和深度预测,所有这些都可在单次前馈传递中完成。
Key Takeaways
- Uni3R是一个前馈框架,能够从稀疏的2D视角重建3D场景。
- 它联合了语义理解和场景重建,无需对每个场景进行优化。
- Uni3R利用跨视图变压器整合多视角信息。
- 该框架回归带有语义特征场的3D高斯原始数据,形成统一的场景表示。
- Uni3R支持高保真新颖视图合成、开放词汇3D语义分割和深度预测。
- 该方法在多个基准测试中达到最新水平,包括RE10K上的25.07 PSNR和ScanNet上的55.84 mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

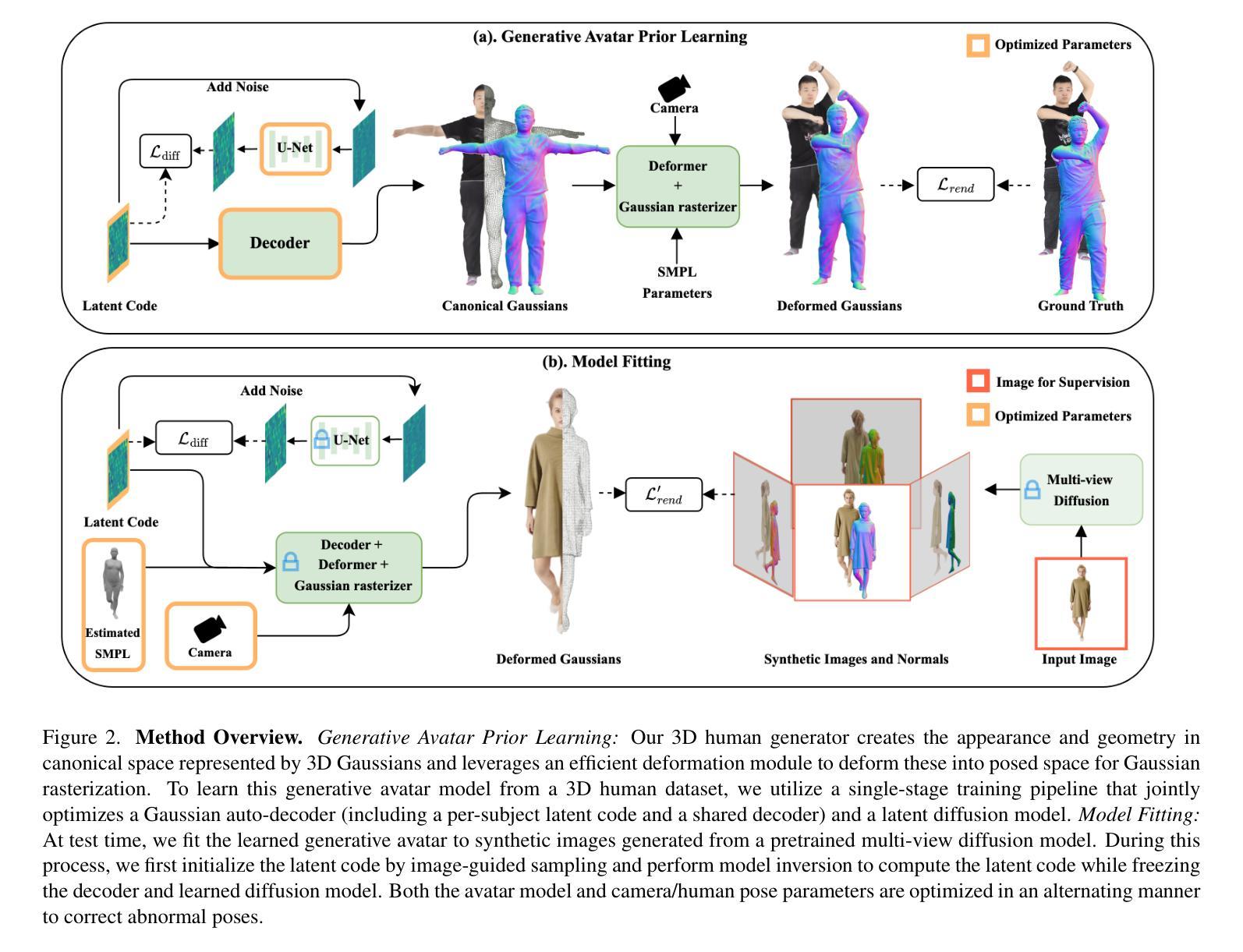
MoGA: 3D Generative Avatar Prior for Monocular Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction
Authors:Zijian Dong, Longteng Duan, Jie Song, Michael J. Black, Andreas Geiger
We present MoGA, a novel method to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D Gaussian avatars from a single-view image. The main challenge lies in inferring unseen appearance and geometric details while ensuring 3D consistency and realism. Most previous methods rely on 2D diffusion models to synthesize unseen views; however, these generated views are sparse and inconsistent, resulting in unrealistic 3D artifacts and blurred appearance. To address these limitations, we leverage a generative avatar model, that can generate diverse 3D avatars by sampling deformed Gaussians from a learned prior distribution. Due to limited 3D training data, such a 3D model alone cannot capture all image details of unseen identities. Consequently, we integrate it as a prior, ensuring 3D consistency by projecting input images into its latent space and enforcing additional 3D appearance and geometric constraints. Our novel approach formulates Gaussian avatar creation as model inversion by fitting the generative avatar to synthetic views from 2D diffusion models. The generative avatar provides an initialization for model fitting, enforces 3D regularization, and helps in refining pose. Experiments show that our method surpasses state-of-the-art techniques and generalizes well to real-world scenarios. Our Gaussian avatars are also inherently animatable. For code, see https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/.
我们提出了MoGA,这是一种从单视图图像重建高保真3D高斯头像的新方法。主要挑战在于推断出看不见的外观和几何细节,同时确保3D的一致性和真实性。大多数之前的方法依赖于2D扩散模型来合成未见的视图;然而,这些生成的视图是稀疏且不一致的,导致3D伪影不真实和外观模糊。为了解决这些局限性,我们利用生成头像模型,通过从学习的先验分布中采样变形高斯来生成各种3D头像。由于有限的3D训练数据,仅使用这样的3D模型无法捕获未见身份的所有图像细节。因此,我们将其整合为优先事项,通过将输入图像投影到其潜在空间并强制执行额外的3D外观和几何约束来确保3D的一致性。我们的新方法将高斯头像创建公式化为模型反转,通过将生成头像拟合到2D扩散模型的合成视图来实现。生成头像为模型拟合提供了初始化,强制执行3D正则化,并有助于细化姿态。实验表明,我们的方法超越了最先进的技术,并很好地推广到了现实世界场景。我们的高斯头像也是固有可动画的。有关代码,请参阅https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 (Highlight), Project Page: https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为MoGA的新方法,该方法能够从单一视角的图像重建出高保真度的3D高斯化身。MoGA通过利用生成化身模型来解决在推断隐藏的外观和几何细节时面临的挑战,确保3D一致性和真实性。该方法通过将生成化身模型作为先验,将输入图像投影到其潜在空间并施加额外的3D外观和几何约束,解决了现有方法生成视图稀疏且不一致的问题。MoGA将高斯化身创建公式化为模型反演问题,通过将生成化身拟合到来自二维扩散模型的合成视图来实现。实验表明,该方法超越了现有技术并在真实世界场景中具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- MoGA是一种从单一视角图像重建高保真3D高斯化身的新方法。
- 该方法主要挑战在于推断隐藏的外观和几何细节,同时确保3D一致性和真实性。
- MoGA利用生成化身模型来解决这个问题,该模型可以生成多样化的3D化身。
- MoGA通过将生成化身模型作为先验,解决了现有方法生成视图稀疏且不一致的问题。
- MoGA通过将高斯化身创建公式化为模型反演问题,实现了对二维扩散模型的合成视图的拟合。
- 实验表明MoGA在性能上超越了现有技术,并在真实世界场景中具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


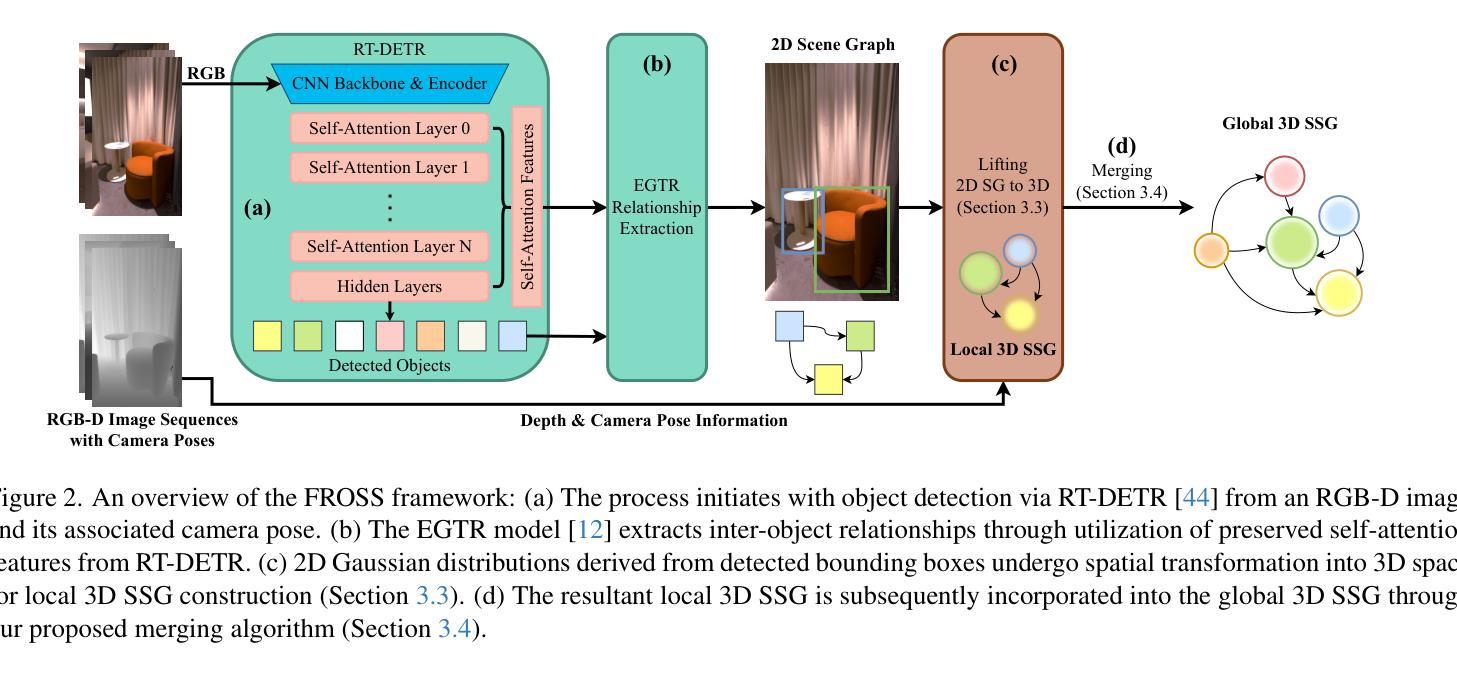
FROSS: Faster-than-Real-Time Online 3D Semantic Scene Graph Generation from RGB-D Images
Authors:Hao-Yu Hou, Chun-Yi Lee, Motoharu Sonogashira, Yasutomo Kawanishi
The ability to abstract complex 3D environments into simplified and structured representations is crucial across various domains. 3D semantic scene graphs (SSGs) achieve this by representing objects as nodes and their interrelationships as edges, facilitating high-level scene understanding. Existing methods for 3D SSG generation, however, face significant challenges, including high computational demands and non-incremental processing that hinder their suitability for real-time open-world applications. To address this issue, we propose FROSS (Faster-than-Real-Time Online 3D Semantic Scene Graph Generation), an innovative approach for online and faster-than-real-time 3D SSG generation that leverages the direct lifting of 2D scene graphs to 3D space and represents objects as 3D Gaussian distributions. This framework eliminates the dependency on precise and computationally-intensive point cloud processing. Furthermore, we extend the Replica dataset with inter-object relationship annotations, creating the ReplicaSSG dataset for comprehensive evaluation of FROSS. The experimental results from evaluations on ReplicaSSG and 3DSSG datasets show that FROSS can achieve superior performance while operating significantly faster than prior 3D SSG generation methods. Our implementation and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/Howardkhh/FROSS.
将复杂的三维环境抽象为简洁的结构化表示,在不同领域中都至关重要。三维语义场景图(SSG)通过以节点表示物体、以边表示它们之间的相互关系,来实现这一目的,从而促进对高级场景的理解。然而,现有的三维SSG生成方法面临重大挑战,包括计算需求高和非增量处理,这阻碍了它们在实时开放世界应用中的适用性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FROSS(实时三维语义场景图快速生成),这是一种创新的在线三维SSG快速生成方法,它利用二维场景图到三维空间的直接提升,并将物体表示为三维高斯分布。该框架消除了对精确且计算密集的点云处理的依赖。此外,我们扩展了Replica数据集,增加了物体间关系注释,创建了ReplicaSSG数据集,以便全面评估FROSS。在ReplicaSSG和3DSSG数据集上的评估实验结果表明,FROSS在性能上优于以前的三维SSG生成方法,同时运行速度更快。我们的实现和数据集可在https://github.com/Howardkhh/FROSS上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2025)
Summary
本文提出一种名为FROSS的快速在线三维语义场景图生成方法,通过将二维场景图直接提升到三维空间并用三维高斯分布表示物体,实现了在线、实时三维语义场景图的快速生成。该方法克服了现有三维SSG生成方法的计算量大和非增量处理的缺点,适用于实时开放世界应用。同时,扩展了Replica数据集,增加了物体间关系注释,创建了ReplicaSSG数据集用于全面评估FROSS性能。实验结果表明,FROSS在性能上优于其他三维SSG生成方法,且运行速度更快。
Key Takeaways
- 3D语义场景图(SSGs)在表示物体的节点及其相互关系边缘方面,促进了高级场景理解,广泛应用于不同领域。
- 现有3D SSG生成方法面临高计算需求和不适合实时开放世界应用的挑战。
- FROSS方法通过将二维场景图直接提升到三维空间并用三维高斯分布表示物体,实现了快速在线三维SSG生成。
- FROSS消除了对精确且计算密集的点云处理的依赖,显著提高了性能。
- 为全面评估FROSS性能,扩展了Replica数据集并创建了ReplicaSSG数据集。
- 实验结果表明,FROSS在性能上优于其他三维SSG生成方法。
点此查看论文截图


QuickSplat: Fast 3D Surface Reconstruction via Learned Gaussian Initialization
Authors:Yueh-Cheng Liu, Lukas Höllein, Matthias Nießner, Angela Dai
Surface reconstruction is fundamental to computer vision and graphics, enabling applications in 3D modeling, mixed reality, robotics, and more. Existing approaches based on volumetric rendering obtain promising results, but optimize on a per-scene basis, resulting in a slow optimization that can struggle to model under-observed or textureless regions. We introduce QuickSplat, which learns data-driven priors to generate dense initializations for 2D gaussian splatting optimization of large-scale indoor scenes. This provides a strong starting point for the reconstruction, which accelerates the convergence of the optimization and improves the geometry of flat wall structures. We further learn to jointly estimate the densification and update of the scene parameters during each iteration; our proposed densifier network predicts new Gaussians based on the rendering gradients of existing ones, removing the needs of heuristics for densification. Extensive experiments on large-scale indoor scene reconstruction demonstrate the superiority of our data-driven optimization. Concretely, we accelerate runtime by 8x, while decreasing depth errors by up to 48% in comparison to state of the art methods.
表面重建是计算机视觉和图形学的基础,在3D建模、混合现实、机器人技术等领域有着广泛的应用。现有的基于体积渲染的方法取得了有前景的结果,但它们是针对每个场景进行优化的,导致优化过程缓慢,难以对观测不足或无纹理的区域进行建模。我们推出了QuickSplat,它利用数据驱动先验知识生成大规模室内场景的2D高斯拼贴优化的密集初始化。这为重建提供了一个良好的起点,加速了优化的收敛,并改善了平面墙结构的几何形状。我们进一步学习在每次迭代期间联合估计场景的密集化和参数更新;我们提出的密度网络根据现有渲染梯度预测新的高斯分布,从而消除了启发式密集化的需求。大规模室内场景重建的广泛实验证明了我们数据驱动优化的优越性。具体来说,我们的方法将运行时速度提高了8倍,与最新技术相比,深度误差降低了高达48%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://liu115.github.io/quicksplat, Video: https://youtu.be/2IA_gnFvFG8
Summary
本文介绍了QuickSplat方法,该方法利用数据驱动先验生成大规模室内场景的密集初始化,用于2D高斯涂抹优化。此方法为重建提供了一个良好的起点,加速了优化的收敛,并改进了平面墙结构的几何形状。通过联合估计场景参数的密集和更新,提出的新型密度网络能够预测基于现有渲染梯度的新的高斯分布,无需密度启发式算法。实验证明,在大型室内场景重建中,数据驱动的优化方法具有优越性,运行时速度提高了8倍,深度误差降低了高达48%。
Key Takeaways
- QuickSplat方法利用数据驱动先验生成大规模室内场景的密集初始化,用于加速3D建模的2D高斯涂抹优化。
- 该方法提供了一个强大的起点,使优化过程更快收敛,并改进了平面墙结构的几何形状。
- 通过联合估计场景参数的密集和更新,提高了优化效率。
- 提出的密度网络能够预测新的高斯分布,基于现有渲染梯度的信息,无需额外的启发式算法。
- 实验结果显示,与现有方法相比,QuickSplat方法在运行时速度上提高了8倍。
- QuickSplat方法能够降低深度误差,其降低幅度高达48%。
点此查看论文截图

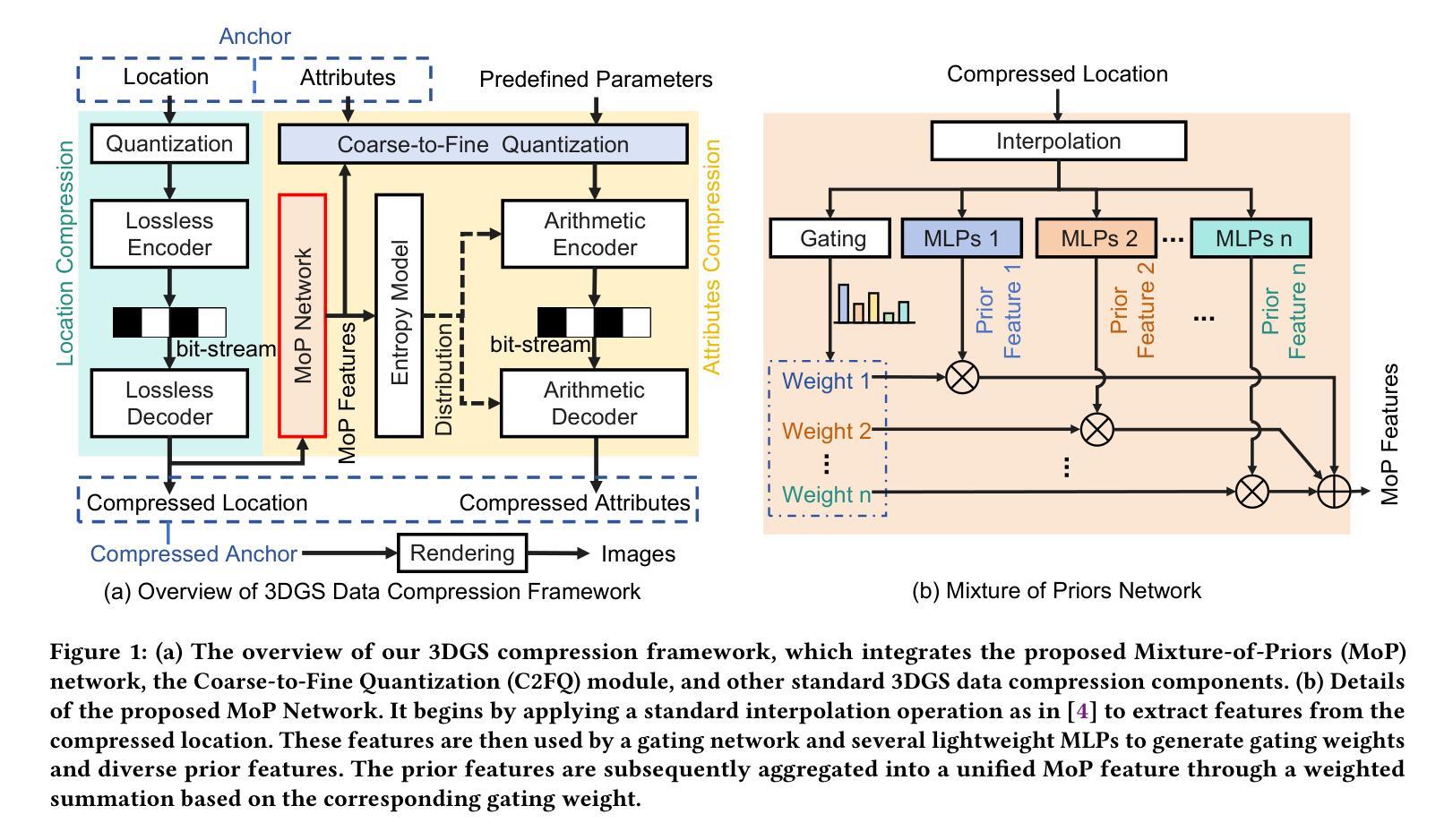
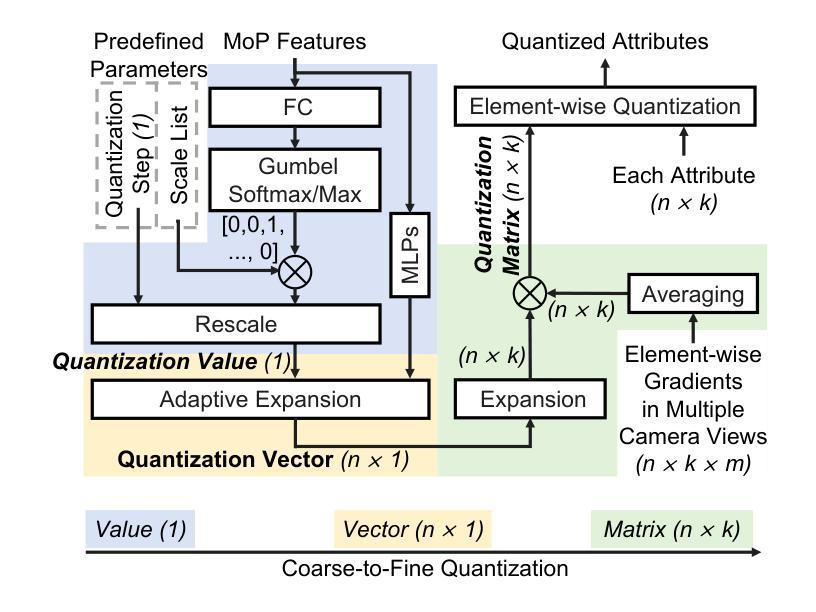
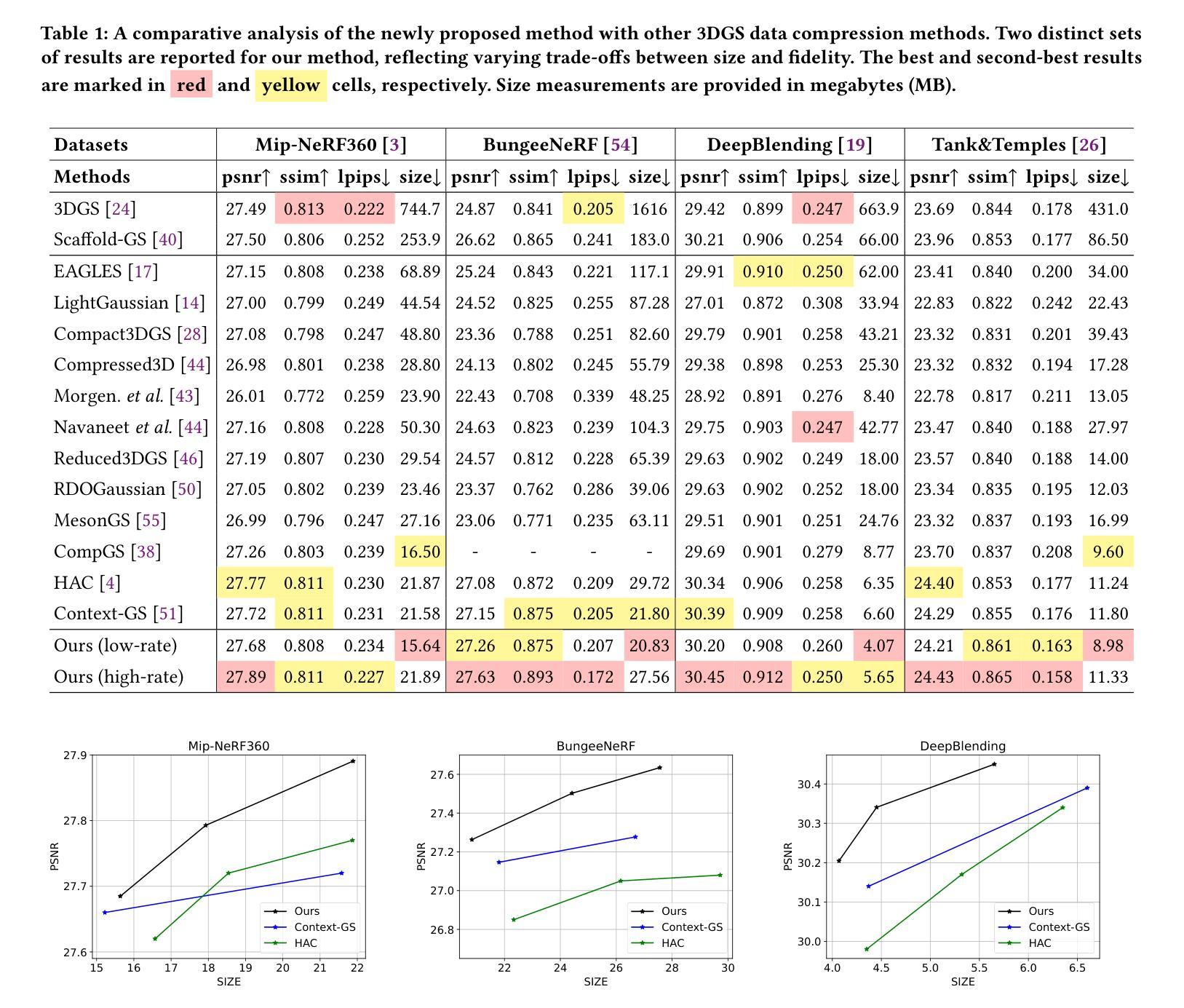
3D Gaussian Splatting Data Compression with Mixture of Priors
Authors:Lei Liu, Zhenghao Chen, Dong Xu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) data compression is crucial for enabling efficient storage and transmission in 3D scene modeling. However, its development remains limited due to inadequate entropy models and suboptimal quantization strategies for both lossless and lossy compression scenarios, where existing methods have yet to 1) fully leverage hyperprior information to construct robust conditional entropy models, and 2) apply fine-grained, element-wise quantization strategies for improved compression granularity. In this work, we propose a novel Mixture of Priors (MoP) strategy to simultaneously address these two challenges. Specifically, inspired by the Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) paradigm, our MoP approach processes hyperprior information through multiple lightweight MLPs to generate diverse prior features, which are subsequently integrated into the MoP feature via a gating mechanism. To enhance lossless compression, the resulting MoP feature is utilized as a hyperprior to improve conditional entropy modeling. Meanwhile, for lossy compression, we employ the MoP feature as guidance information in an element-wise quantization procedure, leveraging a prior-guided Coarse-to-Fine Quantization (C2FQ) strategy with a predefined quantization step value. Specifically, we expand the quantization step value into a matrix and adaptively refine it from coarse to fine granularity, guided by the MoP feature, thereby obtaining a quantization step matrix that facilitates element-wise quantization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed 3DGS data compression framework achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks, including Mip-NeRF360, BungeeNeRF, DeepBlending, and Tank&Temples.
3D高斯混合(3DGS)数据压缩对于实现三维场景建模中的高效存储和传输至关重要。然而,其开发仍然受限,因为在无损和有损压缩场景中,现有的熵模型不够充分,量化策略也不佳。现有方法尚未充分利用超先验信息来构建稳健的条件熵模型,并且未采用精细粒度的元素级量化策略来提高压缩粒度。针对这两个挑战,我们提出了一种新颖的先验混合(MoP)策略。具体来说,受到混合专家(MoE)范式的启发,我们的MoP方法通过多个轻量级MLP处理超先验信息,以生成多种先验特征,然后通过门控机制将这些特征集成到MoP特征中。为了提高无损压缩性能,我们将得到的MoP特征用作超先验信息,以改进条件熵建模。而对于有损压缩,我们将MoP特征用作元素级量化过程中的引导信息,采用受先验引导的粗细量化(C2FQ)策略及预设的量化步长值。具体来说,我们将量化步长值扩展为矩阵,并在MoP特征的引导下从粗到细粒度进行自适应细化,从而获得一个量化步长矩阵,以支持元素级量化。大量实验表明,我们提出的3DGS数据压缩框架在多个基准测试中达到了最先进的性能水平,包括Mip-NeRF360、BungeeNeRF、DeepBlending和Tank&Temples。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于三维高斯融合(3DGS)的数据压缩技术对于三维场景建模的重要性。针对现有方法的不足,如缺乏高效的熵模型和量化策略,本文提出了一种新颖的混合先验(MoP)策略来同时解决无损和有损压缩的问题。MoP策略利用多个轻量级MLP处理超先验信息生成多种先验特征,然后通过门控机制整合到MoP特征中。在无损压缩方面,使用MoP特征提高条件熵建模。对于有损压缩,将MoP特征用作引导信息进行元素级量化过程,并利用先验引导下的粗细量化策略获得自适应的量化步长矩阵。实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上取得了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS数据压缩对于高效存储和传输在3D场景建模中至关重要。
- 现有方法在无损和损失压缩场景中,由于缺乏高效的熵模型和量化策略而受到限制。
- 提出了一种新颖的混合先验(MoP)策略来改进条件熵建模和提高量化精度。
- MoP策略使用多个轻量级MLP处理超先验信息并整合到MoP特征中。
- MoP特征在无损压缩中用于提高条件熵建模,在损失压缩中用作引导信息来进行元素级量化。
点此查看论文截图