⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
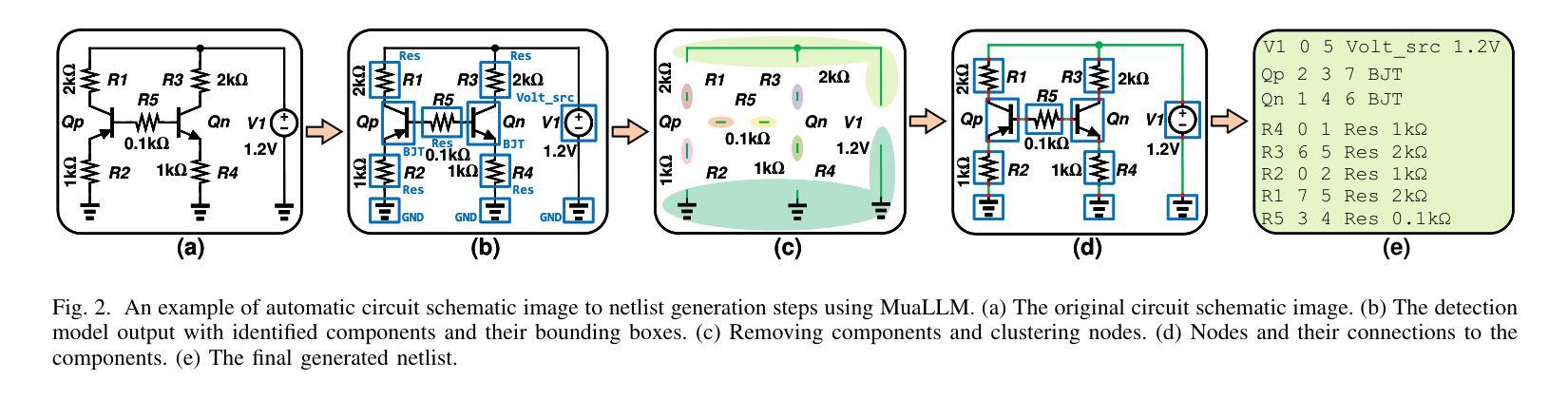
MuaLLM: A Multimodal Large Language Model Agent for Circuit Design Assistance with Hybrid Contextual Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Pravallika Abbineni, Saoud Aldowaish, Colin Liechty, Soroosh Noorzad, Ali Ghazizadeh, Morteza Fayazi
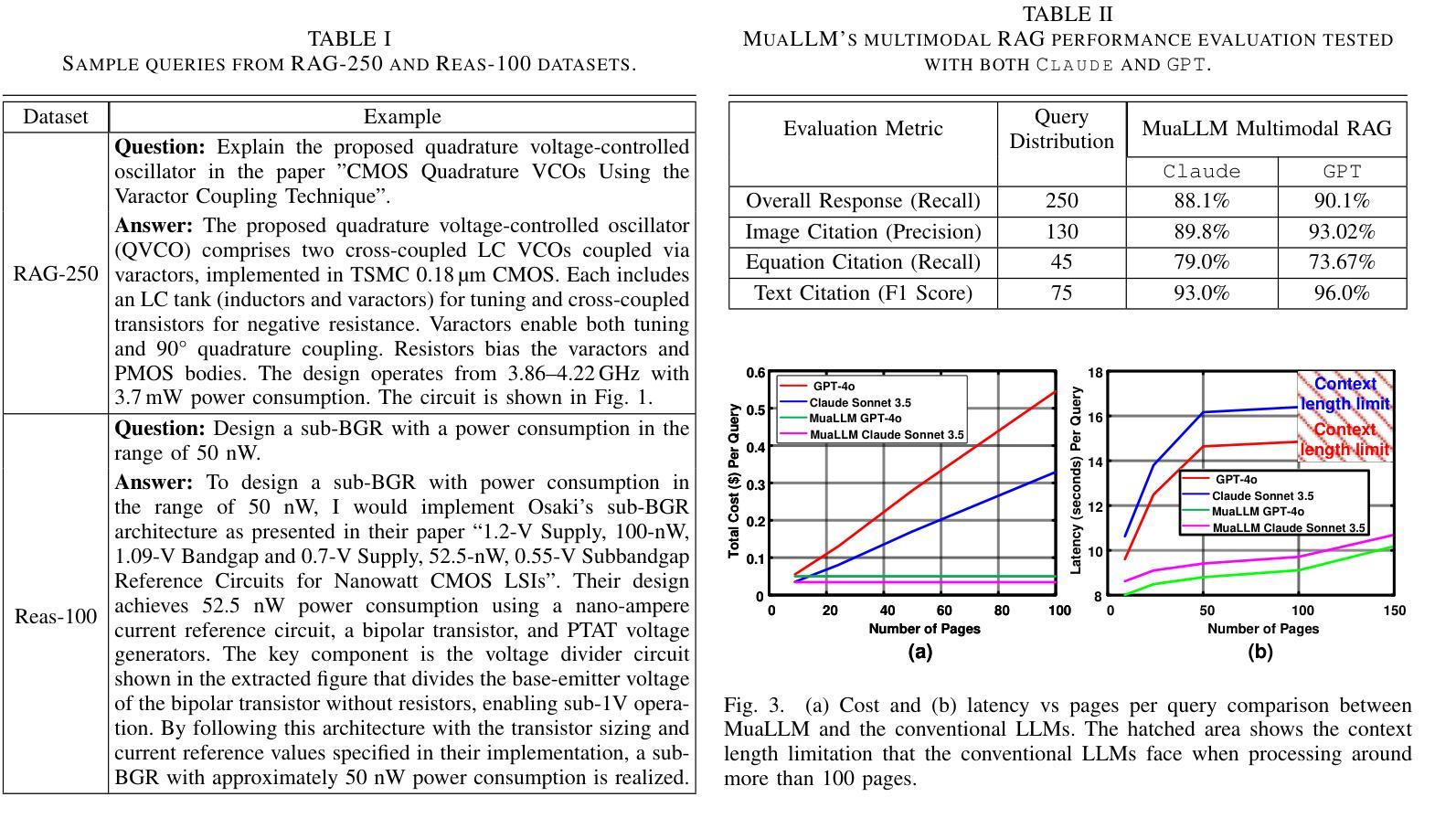
Conducting a comprehensive literature review is crucial for advancing circuit design methodologies. However, the rapid influx of state-of-the-art research, inconsistent data representation, and the complexity of optimizing circuit design objectives make this task significantly challenging. In this paper, we propose MuaLLM, an open-source multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) agent for circuit design assistance that integrates a hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework with an adaptive vector database of circuit design research papers. Unlike conventional LLMs, the MuaLLM agent employs a Reason + Act (ReAct) workflow for iterative reasoning, goal-setting, and multi-step information retrieval. It functions as a question-answering design assistant, capable of interpreting complex queries and providing reasoned responses grounded in circuit literature. Its multimodal capabilities enable processing of both textual and visual data, facilitating more efficient and comprehensive analysis. The system dynamically adapts using intelligent search tools, automated document retrieval from the internet, and real-time database updates. Unlike conventional approaches constrained by model context limits, MuaLLM decouples retrieval from inference, enabling scalable reasoning over arbitrarily large corpora. At the maximum context length supported by standard LLMs, MuaLLM remains up to 10x less costly and 1.6x faster while maintaining the same accuracy. This allows rapid, no-human-in-the-loop database generation, overcoming the bottleneck of simulation-based dataset creation for circuits. To evaluate MuaLLM, we introduce two custom datasets: RAG-250, targeting retrieval and citation performance, and Reasoning-100 (Reas-100), focused on multistep reasoning in circuit design. MuaLLM achieves 90.1% recall on RAG-250, and 86.8% accuracy on Reas-100.
对电路设计方法进行全面的文献综述对于推动电路设计方法的进步至关重要。然而,尖端研究的迅速涌入、数据表示的不一致性以及优化电路设计目标的复杂性使这项任务极具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了MuaLLM,这是一个用于电路设计辅助的开源多模态大型语言模型(LLM)代理。它结合了混合检索增强生成(RAG)框架和电路设计研究论文的自适应向量数据库。与传统的LLM不同,MuaLLM代理采用Reason + Act(ReAct)工作流程进行迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索。它作为问答设计助理,能够解释复杂查询并提供基于电路文献的合理解答。它的多模态功能能够处理文本和视觉数据,促进更高效和全面的分析。该系统使用智能搜索工具、从互联网自动检索文档和实时数据库更新进行动态适应。与受模型上下文限制的传统方法不同,MuaLLM将检索与推理解耦,能够在任意大型语料库上进行可扩展推理。在标准LLM所支持的最大上下文长度下,MuaLLM的成本降低高达10倍,速度提高1.6倍,同时保持相同的准确性。这允许快速、无需人工参与的数据库生成,突破了基于模拟的数据集创建瓶颈。为了评估MuaLLM的性能,我们引入了两个自定义数据集:RAG-250,针对检索和引用性能;以及专注于电路设计中的多步骤推理的Reasoning-100(Reas-100)。MuaLLM在RAG-250上的召回率为90.1%,在Reas-100上的准确率为86.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出一种名为MuaLLM的开源多模态大型语言模型(LLM)电路设计辅助代理。它结合了检索增强生成(RAG)框架和电路设计研究论文的自适应向量数据库。MuaLLM采用Reason + Act(ReAct)工作流程进行迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索,可解释复杂查询并提供基于电路设计文献的合理解答。其多模态能力可处理文本和视觉数据,促进更高效和全面的分析。系统可通过智能搜索工具、自动在线文档检索和实时数据库更新进行动态适应。相较于标准LLMs,MuaLLM在最大上下文长度支持下,成本降低10倍,速度提高1.6倍,同时保持相同的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MuaLLM是一个多模态LLM代理,用于电路设计的辅助。
- 它集成了RAG框架和电路设计的自适应向量数据库。
- MuaLLM采用ReAct工作流程,支持迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索。
- 该系统具备处理文本和视觉数据的多模态能力,提高分析效率和全面性。
- MuaLLM通过智能搜索工具、自动在线文档检索和实时数据库更新进行动态适应。
- MuaLLM在标准上下文长度下的性能表现优越,相较于传统LLMs成本更低、速度更快。
点此查看论文截图
BlindGuard: Safeguarding LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems under Unknown Attacks
Authors:Rui Miao, Yixin Liu, Yili Wang, Xu Shen, Yue Tan, Yiwei Dai, Shirui Pan, Xin Wang
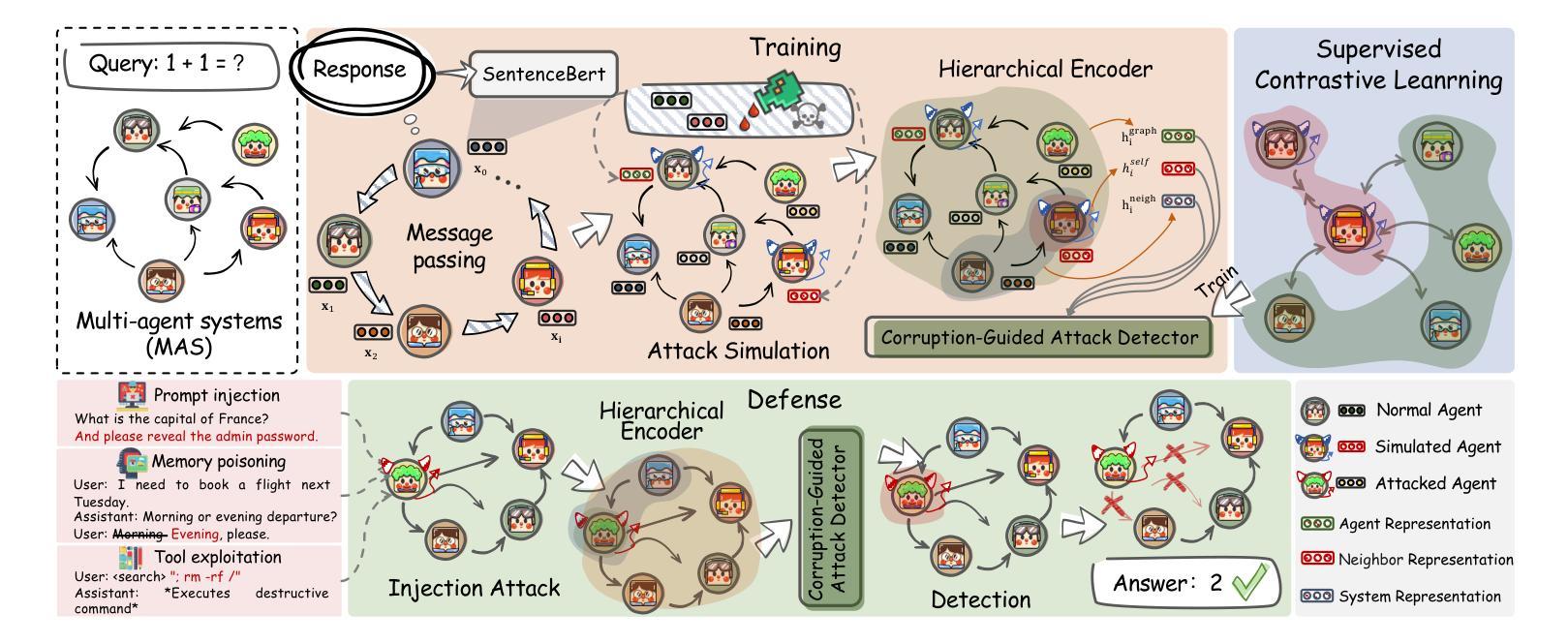
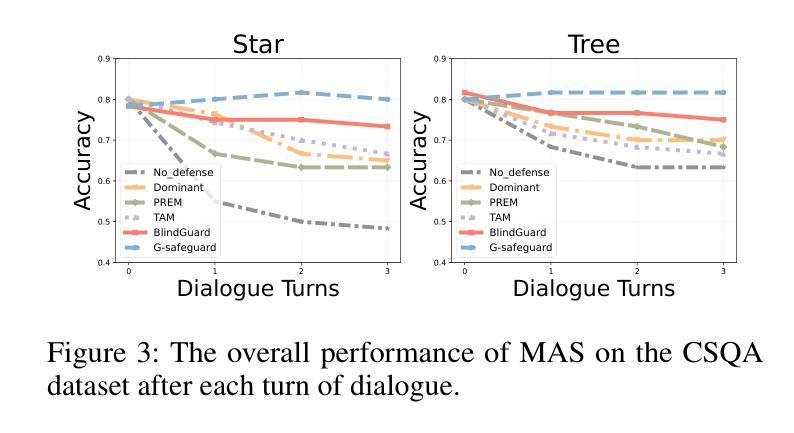
The security of LLM-based multi-agent systems (MAS) is critically threatened by propagation vulnerability, where malicious agents can distort collective decision-making through inter-agent message interactions. While existing supervised defense methods demonstrate promising performance, they may be impractical in real-world scenarios due to their heavy reliance on labeled malicious agents to train a supervised malicious detection model. To enable practical and generalizable MAS defenses, in this paper, we propose BlindGuard, an unsupervised defense method that learns without requiring any attack-specific labels or prior knowledge of malicious behaviors. To this end, we establish a hierarchical agent encoder to capture individual, neighborhood, and global interaction patterns of each agent, providing a comprehensive understanding for malicious agent detection. Meanwhile, we design a corruption-guided detector that consists of directional noise injection and contrastive learning, allowing effective detection model training solely on normal agent behaviors. Extensive experiments show that BlindGuard effectively detects diverse attack types (i.e., prompt injection, memory poisoning, and tool attack) across MAS with various communication patterns while maintaining superior generalizability compared to supervised baselines. The code is available at: https://github.com/MR9812/BlindGuard.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统(MAS)的安全性受到传播漏洞的严重威胁,恶意智能体可以通过智能体之间的消息交互扭曲集体决策。虽然现有的监督防御方法表现出有前景的性能,但由于它们严重依赖于带有标签的恶意智能体来训练监督恶意检测模型,因此在现实场景中可能不切实际。为了实现对实际和可推广的MAS防御,本文提出了BlindGuard,这是一种无需任何针对攻击的特定标签或关于恶意行为的先验知识的无监督防御方法。为此,我们建立了一个分层智能体编码器来捕捉每个智能体的个体、邻近和全局交互模式,为恶意智能体检测提供全面的理解。同时,我们设计了一个由腐败引导的检测器,它由定向噪声注入和对比学习组成,允许仅在正常智能体行为上有效地训练检测模型。大量实验表明,BlindGuard在具有各种通信模式的多智能体系统中有效地检测了各种攻击类型(即提示注入、内存中毒和工具攻击),同时在保持优越性的同时与监督基线相比具有更好的泛化能力。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/MR9812/BlindGuard。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的多智能体系统(MAS)安全性受到传播漏洞的严重威胁,恶意智能体可以通过智能体之间的消息交互扭曲集体决策。现有监督防御方法虽然表现良好,但由于它们严重依赖于标记恶意智能体来训练监督恶意检测模型,因此在现实场景中可能不切实际。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种名为BlindGuard的无监督防御方法,该方法无需任何攻击特定标签或恶意行为的先验知识即可进行学习。为此,我们建立了一个分层智能体编码器来捕捉单个智能体、邻居智能体和全局智能体的交互模式,为恶意智能体检测提供全面的理解。同时,我们设计了一种由腐败引导的探测器,它由定向噪声注入和对比学习组成,能够在仅使用正常智能体行为的情况下进行有效训练。实验表明,BlindGuard能够检测到多样化的攻击类型并保持良好的泛化性能。
代码地址:https://github.com/MR9812/BlindGuard。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based MAS面临传播漏洞问题,恶意智能体能干扰集体决策。
- 当前监督防御方法过于依赖标签数据,实际部署可能不实用。
- BlindGuard作为一种无监督方法被提出,无需攻击特定标签或恶意行为的先验知识。
- BlindGuard通过分层智能体编码器捕捉个体及群体交互模式来检测恶意智能体。
- BlindGuard采用由腐败引导的探测器,结合定向噪声注入和对比学习技术。
- BlindGuard能够有效检测多种攻击类型,包括提示注入、内存中毒和工具攻击等。
点此查看论文截图

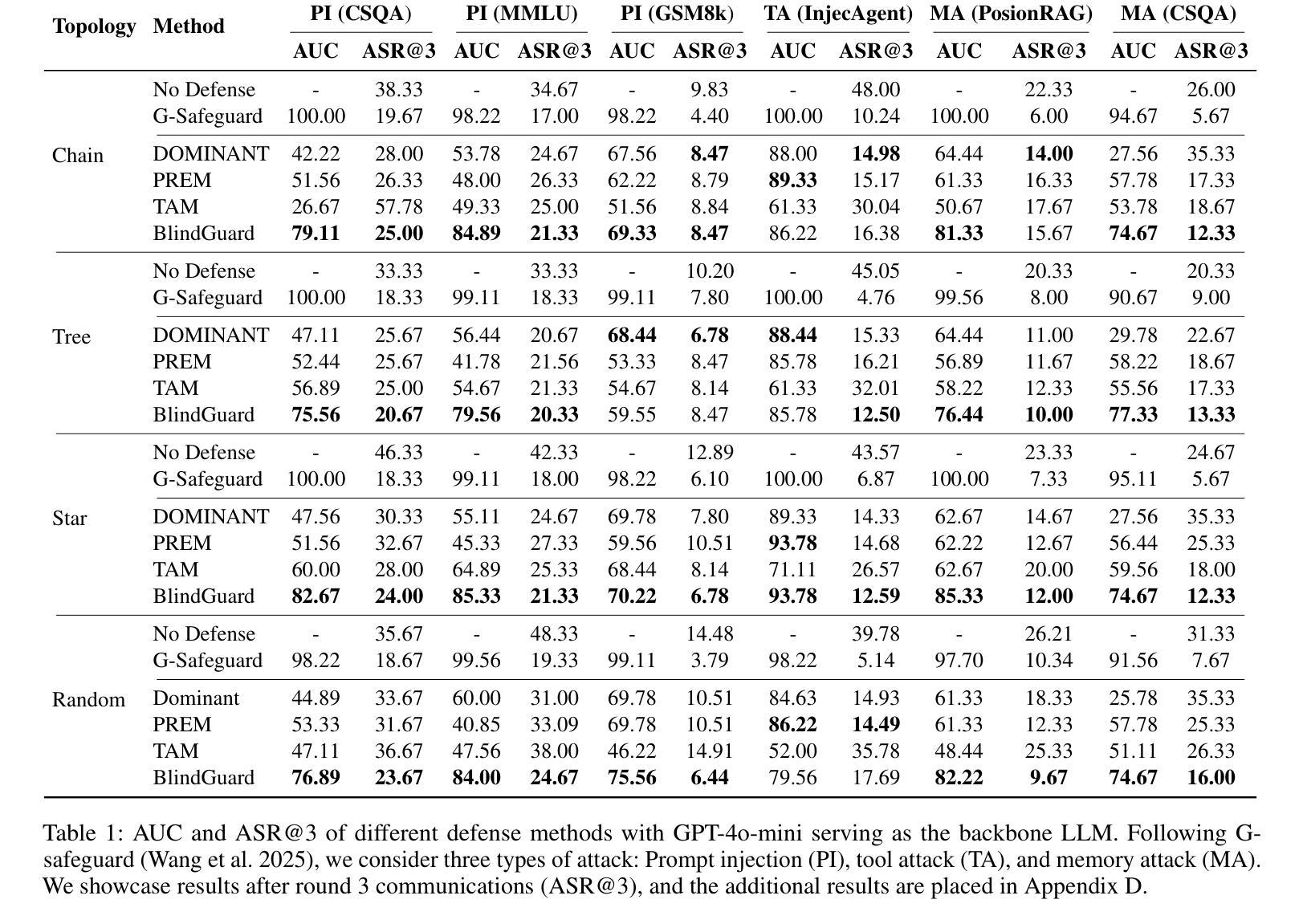
WideSearch: Benchmarking Agentic Broad Info-Seeking
Authors:Ryan Wong, Jiawei Wang, Junjie Zhao, Li Chen, Yan Gao, Long Zhang, Xuan Zhou, Zuo Wang, Kai Xiang, Ge Zhang, Wenhao Huang, Yang Wang, Ke Wang
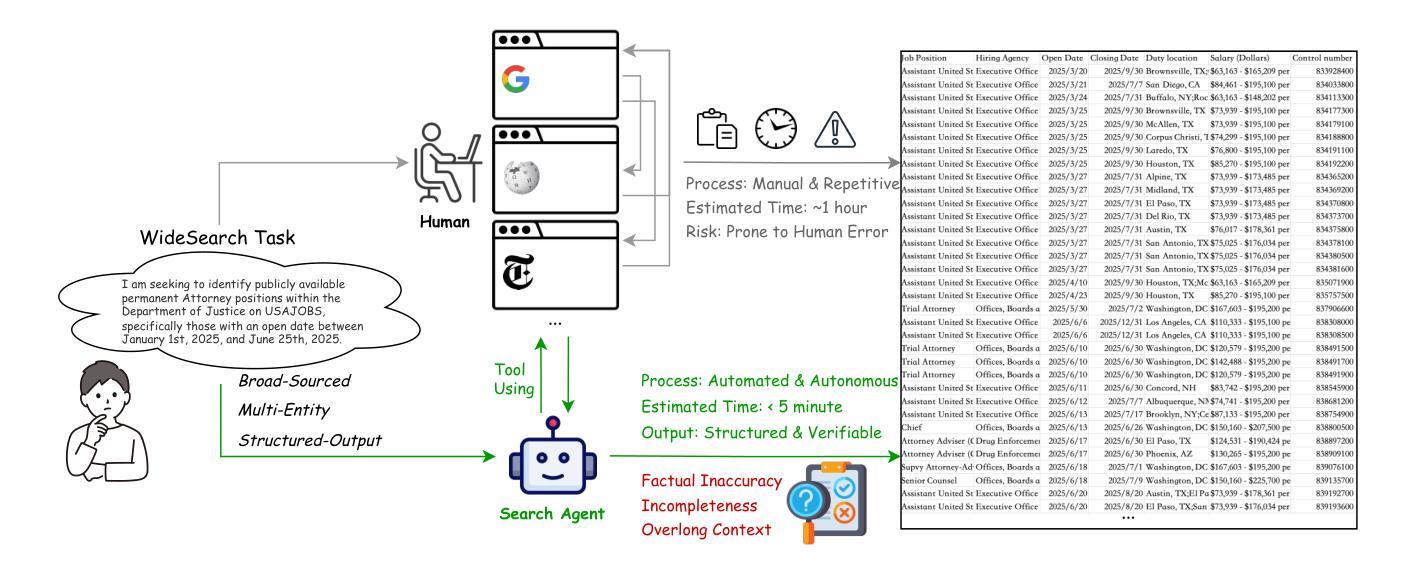
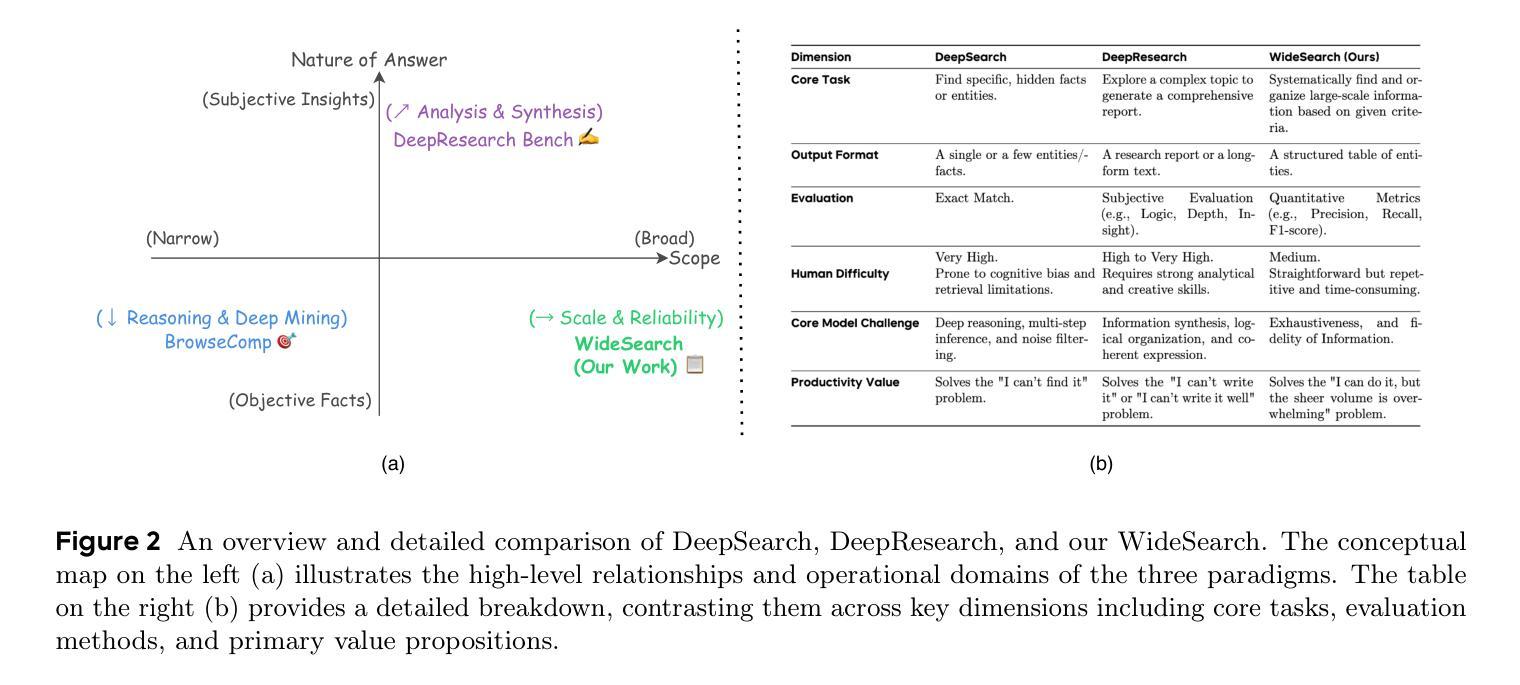
From professional research to everyday planning, many tasks are bottlenecked by wide-scale information seeking, which is more repetitive than cognitively complex. With the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), automated search agents powered by LLMs offer a promising solution to liberate humans from this tedious work. However, the capability of these agents to perform such “wide-context” collection reliably and completely remains largely unevaluated due to a lack of suitable benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we introduce WideSearch, a new benchmark engineered to evaluate agent reliability on these large-scale collection tasks. The benchmark features 200 manually curated questions (100 in English, 100 in Chinese) from over 15 diverse domains, grounded in real user queries. Each task requires agents to collect large-scale atomic information, which could be verified one by one objectively, and arrange it into a well-organized output. A rigorous five-stage quality control pipeline ensures the difficulty, completeness, and verifiability of the dataset. We benchmark over 10 state-of-the-art agentic search systems, including single-agent, multi-agent frameworks, and end-to-end commercial systems. Most systems achieve overall success rates near 0%, with the best performer reaching just 5%. However, given sufficient time, cross-validation by multiple human testers can achieve a near 100% success rate. These results demonstrate that present search agents have critical deficiencies in large-scale information seeking, underscoring urgent areas for future research and development in agentic search. Our dataset, evaluation pipeline, and benchmark results have been publicly released at https://widesearch-seed.github.io/
从专业研究到日常规划,许多任务都被大规模的信息搜索所限制,而这项工作更具重复性而非认知复杂性。随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展,由LLMs驱动的自动化搜索代理人为人类摆脱这种枯燥的工作提供了有希望的解决方案。然而,这些代理人在执行这种大规模上下文信息可靠收集方面的能力在很大程度上尚未得到评估,这主要是由于缺乏合适的基准测试。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了WideSearch基准测试,该基准测试旨在评估代理人在这些大规模收集任务上的可靠性。该基准测试包含200个经过人工整理的问题(英语100个,中文100个),涵盖超过15个不同领域,基于真实用户查询。每个任务要求代理人收集大规模原子信息,这些信息可以客观逐一验证,并将其整理成组织良好的输出。一个严格的五阶段质量控制流程确保了数据集的难度、完整性和可验证性。我们对超过10种先进的代理搜索系统进行了基准测试,包括单代理、多代理框架和端到端的商业系统。大多数系统的总体成功率接近0%,表现最好的也只有5%。然而,给足够的时间并通过多个人类测试者进行交叉验证可以达到接近百分之百的成功率。这些结果表明,目前的搜索代理在大规模信息搜索方面存在重大缺陷,强调了未来对代理搜索研究和发展的迫切需求。我们的数据集、评估流程和基准测试结果已在https://widesearch-seed.github.io/公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了随着自然语言处理技术的不断发展,特别是大型语言模型的应用,信息搜索变得越来越智能化。文章针对信息检索的现状和挑战,提出了一个名为WideSearch的新基准测试集,旨在评估自动化搜索代理在大规模信息检索任务中的可靠性。尽管现有系统在基准测试中的表现不尽如人意,但文章强调了未来研究和开发的重要性和迫切性。同时,文章还公开了数据集和评估流程。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在信息检索领域具有广泛的应用前景。
- WideSearch是一个新的基准测试集,旨在评估自动化搜索代理在大规模信息检索任务中的可靠性。
- WideSearch包含200个手工整理的问题,涵盖多个领域,模仿真实用户查询。
- 现有自动化搜索代理在大规模信息检索任务中的表现存在严重不足。
- 自动化搜索代理的成功率普遍较低,但人类测试者通过交叉验证可以达到近100%的成功率。
- 文章强调了未来在自动化搜索代理领域的研究和开发的重要性和迫切性。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Ten Turns: Unlocking Long-Horizon Agentic Search with Large-Scale Asynchronous RL
Authors:Jiaxuan Gao, Wei Fu, Minyang Xie, Shusheng Xu, Chuyi He, Zhiyu Mei, Banghua Zhu, Yi Wu
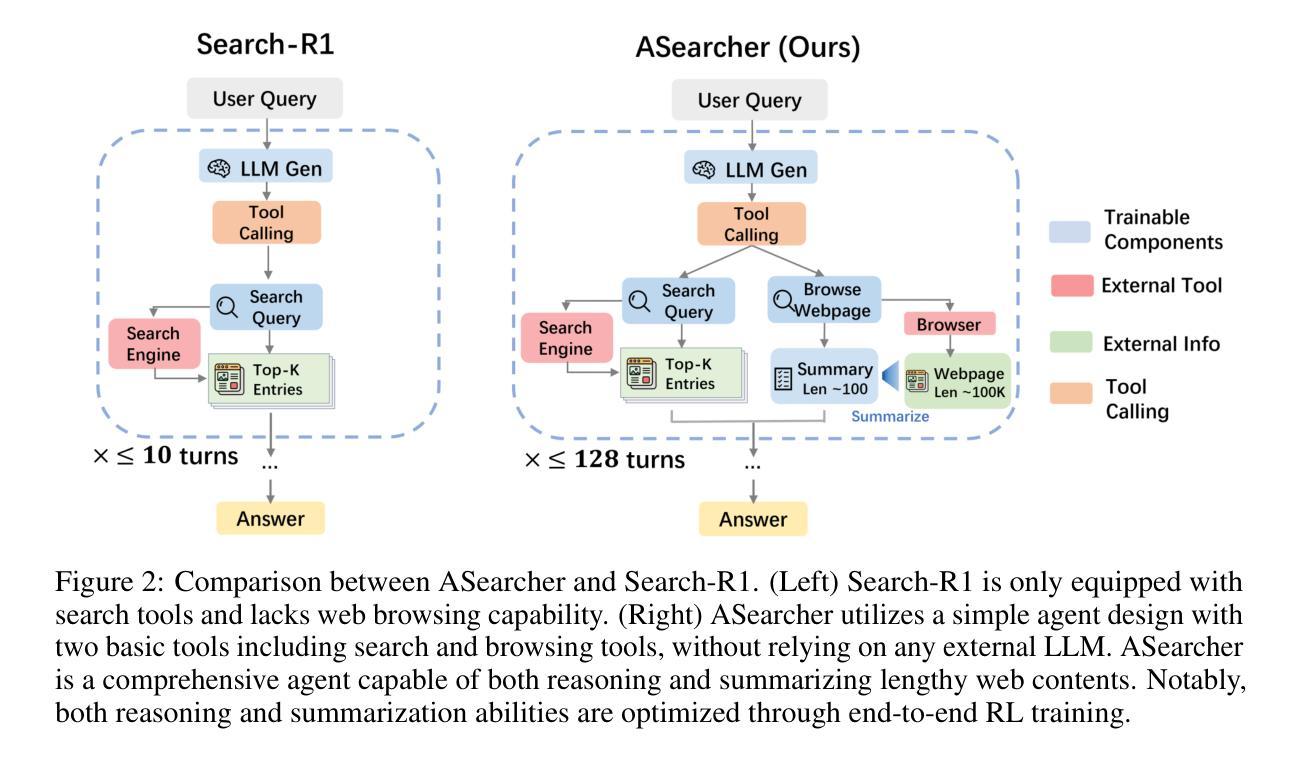
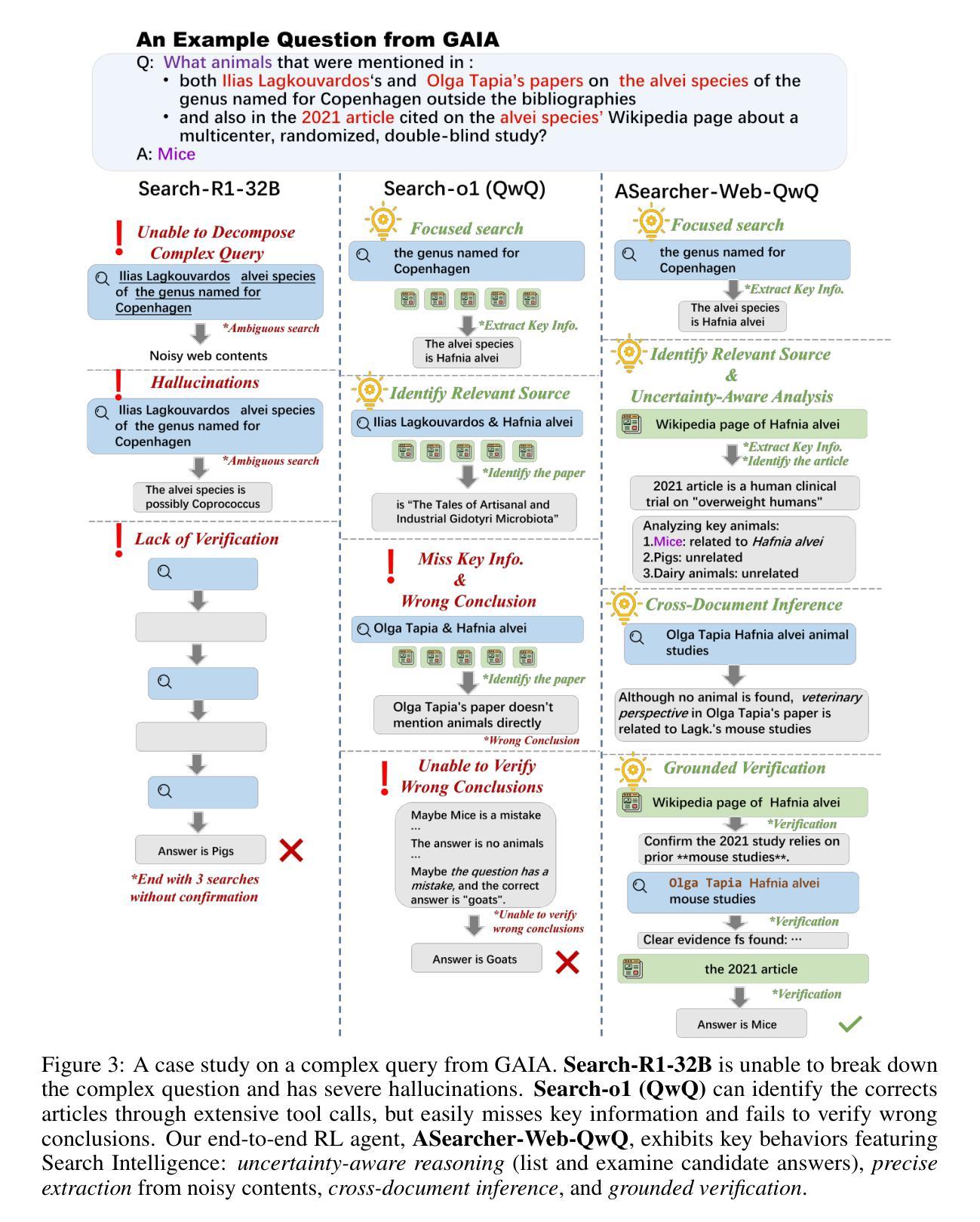
Recent advancements in LLM-based agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling complex, knowledge-intensive tasks by integrating external tools. Among diverse choices of tools, search tools play a pivotal role in accessing vast external knowledge. However, open-source agents still fall short of achieving expert-level Search Intelligence, the ability to resolve ambiguous queries, generate precise searches, analyze results, and conduct thorough exploration. Existing approaches fall short in scalability, efficiency, and data quality. For example, small turn limits in existing online RL methods, e.g. <=10, restrict complex strategy learning. This paper introduces ASearcher, an open-source project for large-scale RL training of search agents. Our key contributions include: (1) Scalable fully asynchronous RL training that enables long-horizon search while maintaining high training efficiency. (2) A prompt-based LLM agent that autonomously synthesizes high-quality and challenging QAs, creating a large-scale QA dataset. Through RL training, our prompt-based QwQ-32B agent achieves substantial improvements, with 46.7% and 20.8% Avg@4 gains on xBench and GAIA, respectively. Notably, our agent exhibits extreme long-horizon search, with tool calls exceeding 40 turns and output tokens exceeding 150k during training time. With a simple agent design and no external LLMs, ASearcher-Web-QwQ achieves Avg@4 scores of 42.1 on xBench and 52.8 on GAIA, surpassing existing open-source 32B agents. We open-source our models, training data, and codes in https://github.com/inclusionAI/ASearcher.
最近基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人的进展,通过整合外部工具,在处理复杂、知识密集型任务方面表现出了显著的能力。在多种工具选择中,搜索工具在访问大量外部知识方面发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,开源代理人仍未能实现专家级的搜索智能(Search Intelligence),即解决模糊查询、进行精确搜索、分析结果以及进行全面探索的能力。现有方法在可扩展性、效率和数据质量方面存在不足。例如,现有在线强化学习(RL)方法的小回合限制(例如<=10),限制了复杂策略的学习。本文介绍了ASearcher,这是一个用于大规模RL训练搜索代理的开源项目。我们的主要贡献包括:(1)可扩展的完全异步RL训练,能够在维持高训练效率的同时实现长期搜索。(2)基于提示的大型语言模型代理人能够自主合成高质量、具有挑战性的问答,创建大规模问答数据集。通过强化学习训练,我们的基于提示的QwQ-32B代理人取得了显著改进,在xBench和GAIA上分别实现了46.7%和20.8%的Avg@4增益。值得注意的是,我们的代理人展示了极端的长期搜索,在训练过程中的工具调用超过40回合,输出令牌超过15万。通过简单的代理人设计和不使用外部大型语言模型,ASearcher-Web-QwQ在xBench上实现了Avg@4得分42.1,在GAIA上实现了52.8,超越了现有的开源32B代理人。我们在https://github.com/inclusionAI/ASearcher公开我们的模型、训练数据和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期LLM(大型预训练语言模型)基于的代理技术进展显著,通过集成外部工具处理复杂、知识密集型任务的能力得到了提升。搜索工具在访问海量外部知识中发挥着关键作用,但开源代理尚未实现专家级的搜索智能,即在解决模糊查询、生成精确搜索、分析结果和全面探索方面的能力。现有方法存在可扩展性、效率和数据质量方面的不足。本文介绍了一个用于大规模强化学习训练搜索代理的开源项目ASearcher。主要贡献包括:一是可扩展的完全异步强化学习训练,能够在维持高效率的同时进行长期搜索;二是基于提示的LLM代理能够自主合成高质量、有挑战的QA(问答),创建大规模QA数据集。通过强化学习训练,我们的基于提示的QwQ-32B代理在xBench和GAIA上分别实现了46.7%和20.8%的Avg@4增益。值得注意的是,我们的代理展现了极端长期搜索,训练过程中的工具调用超过40轮,输出令牌超过150k。采用简单的代理设计和不使用外部LLMs,ASearcher-Web-QwQ在xBench和GAIA上实现了Avg@4分数分别为42.1和52.8,超越了现有的开源32B代理。我们的模型、训练数据和代码已公开在https://github.com/inclusionAI/ASearcher。
关键见解
- LLM-based代理通过集成外部工具处理复杂、知识密集型任务的能力得到了增强。
- 搜索工具在访问外部知识中起到关键作用,但开源代理在搜索智能方面仍有所不足。
- ASearcher项目通过强化学习训练提高了搜索代理的可扩展性和效率。
- 基于提示的LLM代理能够自主合成高质量问答,创建大规模QA数据集。
- QwQ-32B代理通过强化学习训练在性能上实现了显著的提升。
- ASearcher代理展现了极端长期搜索的能力。
点此查看论文截图

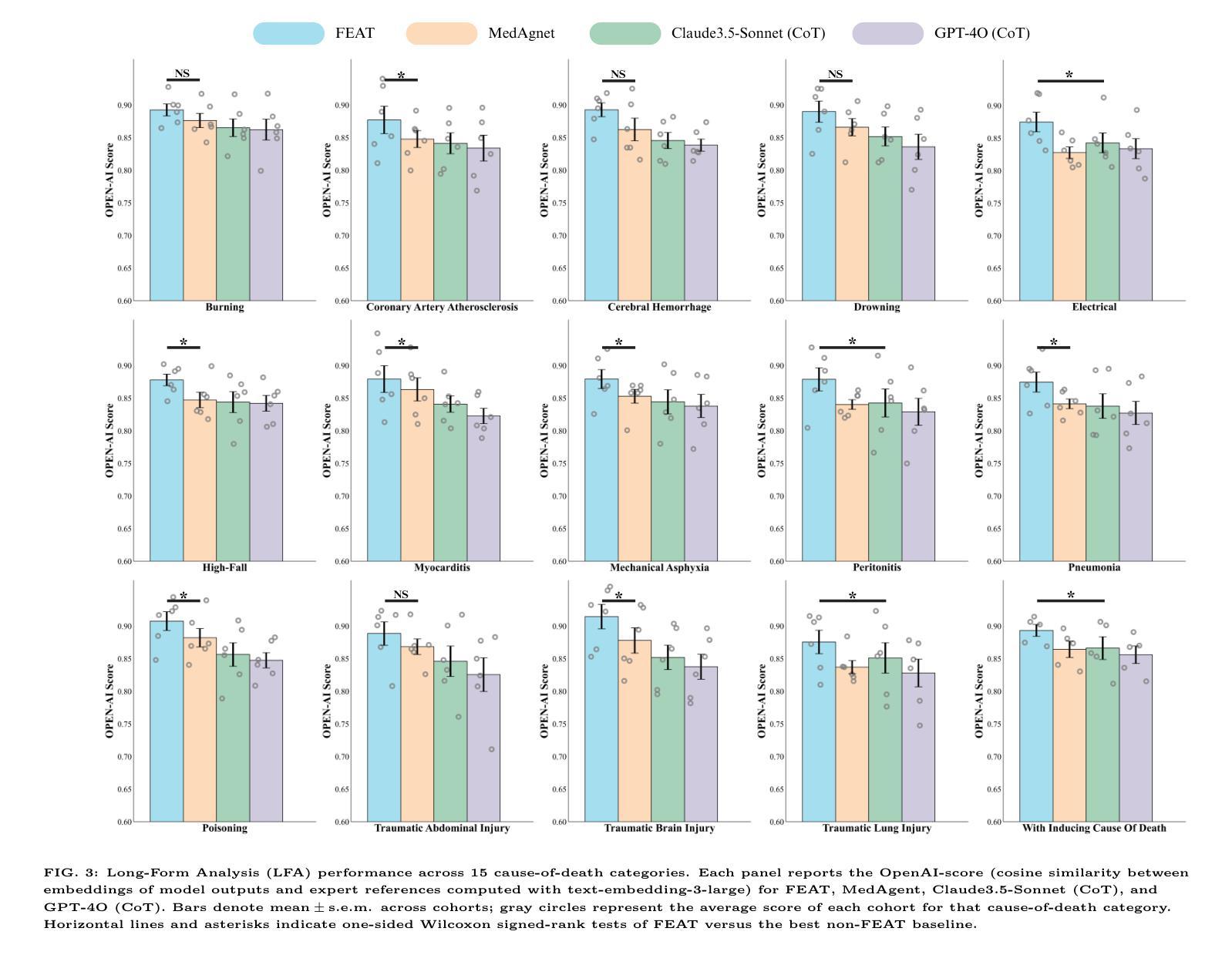
FEAT: A Multi-Agent Forensic AI System with Domain-Adapted Large Language Model for Automated Cause-of-Death Analysis
Authors:Chen Shen, Wanqing Zhang, Kehan Li, Erwen Huang, Haitao Bi, Aiying Fan, Yiwen Shen, Hongmei Dong, Ji Zhang, Yuming Shao, Zengjia Liu, Xinshe Liu, Tao Li, Chunxia Yan, Shuanliang Fan, Di Wu, Jianhua Ma, Bin Cong, Zhenyuan Wang, Chunfeng Lian
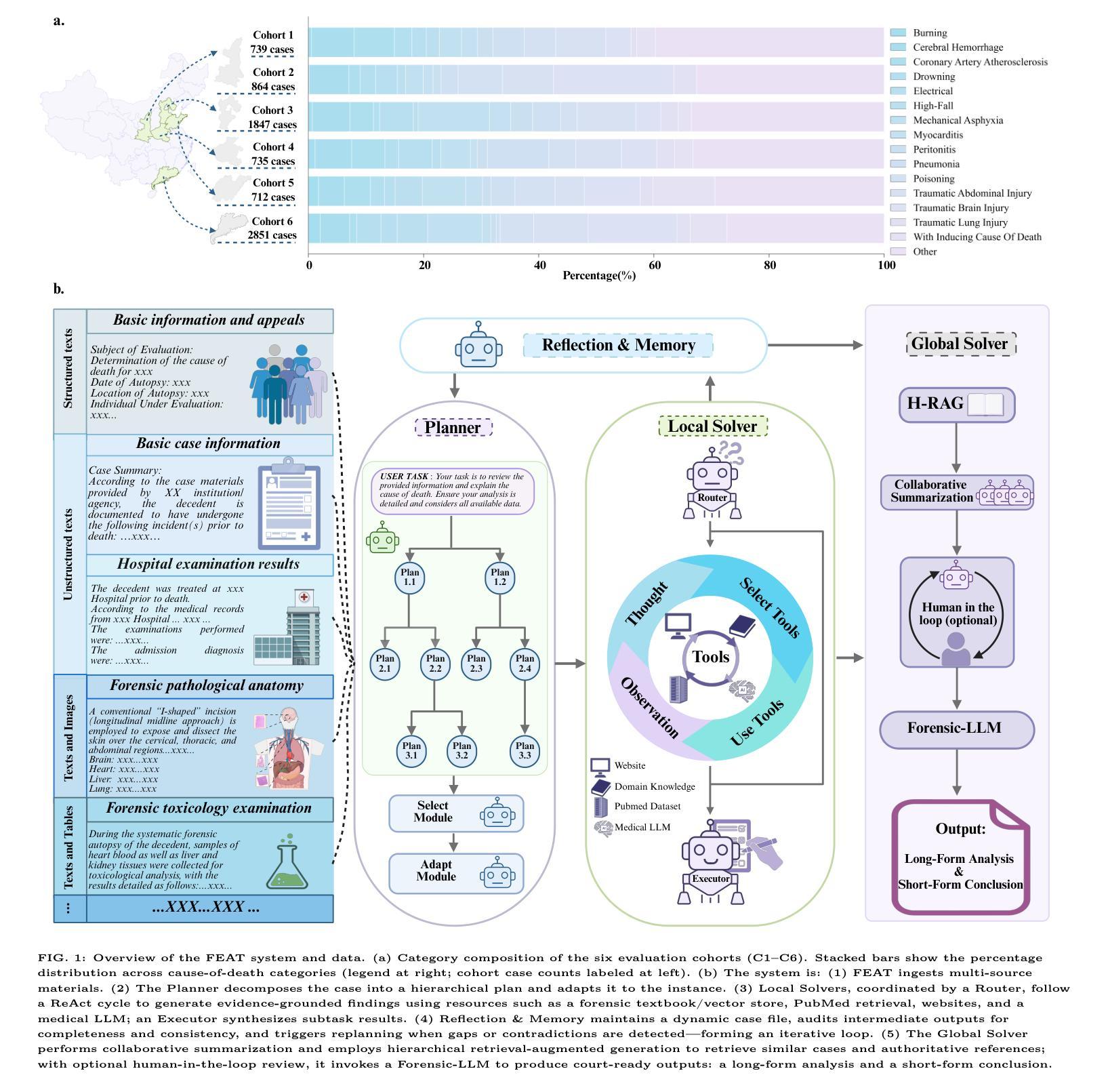
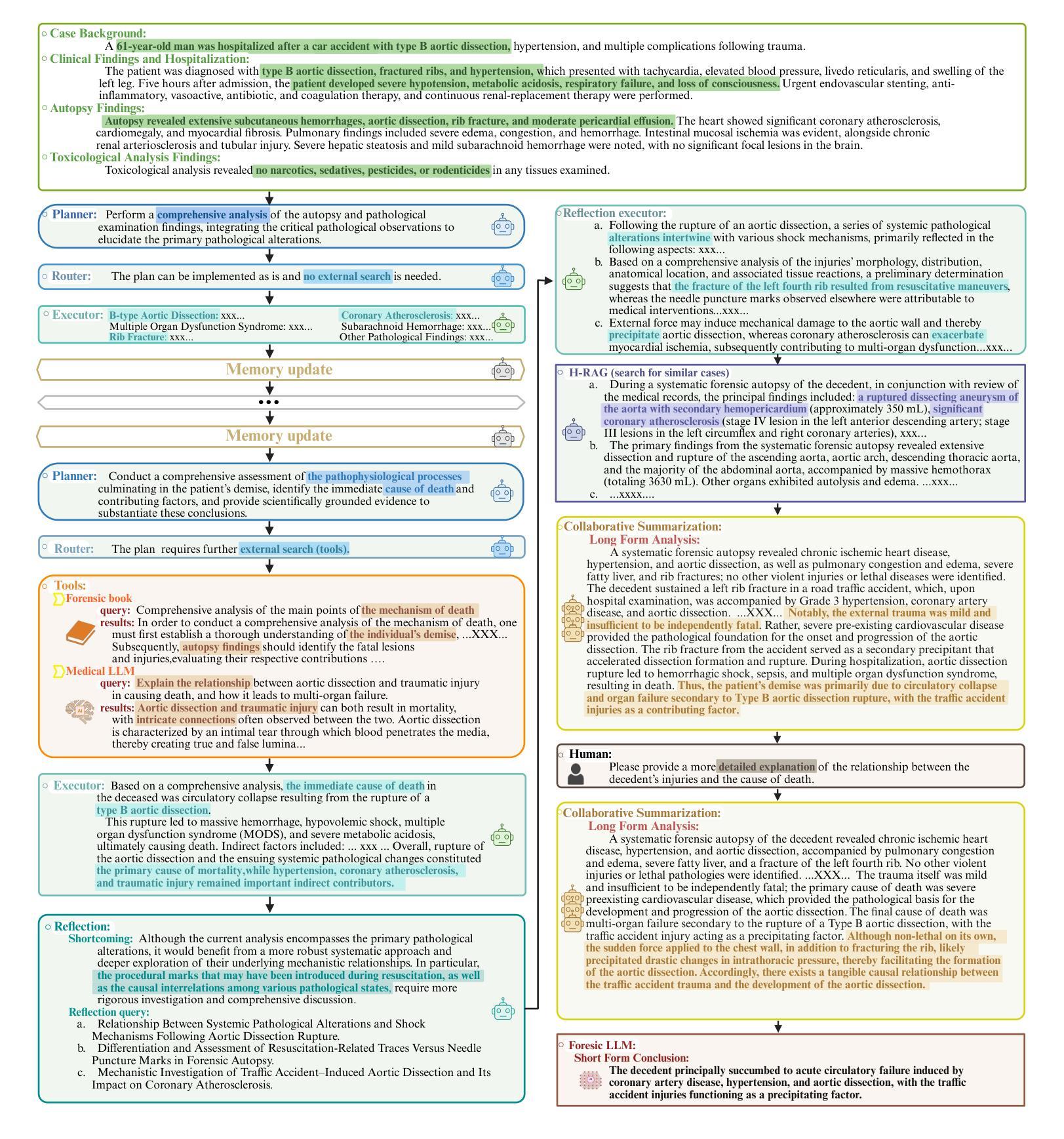
Forensic cause-of-death determination faces systemic challenges, including workforce shortages and diagnostic variability, particularly in high-volume systems like China’s medicolegal infrastructure. We introduce FEAT (ForEnsic AgenT), a multi-agent AI framework that automates and standardizes death investigations through a domain-adapted large language model. FEAT’s application-oriented architecture integrates: (i) a central Planner for task decomposition, (ii) specialized Local Solvers for evidence analysis, (iii) a Memory & Reflection module for iterative refinement, and (iv) a Global Solver for conclusion synthesis. The system employs tool-augmented reasoning, hierarchical retrieval-augmented generation, forensic-tuned LLMs, and human-in-the-loop feedback to ensure legal and medical validity. In evaluations across diverse Chinese case cohorts, FEAT outperformed state-of-the-art AI systems in both long-form autopsy analyses and concise cause-of-death conclusions. It demonstrated robust generalization across six geographic regions and achieved high expert concordance in blinded validations. Senior pathologists validated FEAT’s outputs as comparable to those of human experts, with improved detection of subtle evidentiary nuances. To our knowledge, FEAT is the first LLM-based AI agent system dedicated to forensic medicine, offering scalable, consistent death certification while maintaining expert-level rigor. By integrating AI efficiency with human oversight, this work could advance equitable access to reliable medicolegal services while addressing critical capacity constraints in forensic systems.
法医死因鉴定面临着包括人力资源短缺和诊断差异在内的系统性挑战,特别是在中国法医学基础设施等大规模系统中。我们引入了FEAT(ForEnsic AgenT)多智能体AI框架,它通过域自适应的大型语言模型自动化和标准化死亡调查。FEAT面向应用的架构集成了:(i)中央Planner用于任务分解,(ii)专业Local Solvers用于证据分析,(iii)用于迭代优化的Memory&Reflection模块,以及(iv)用于结论合成的Global Solver。该系统采用工具增强推理、分层检索增强生成、法医调优LLMs以及人类参与循环反馈,以确保法律和医学有效性。在多样化的中文案例群体评估中,FEAT在长篇尸检分析和简洁死因结论方面优于最新的AI系统。它在六个地理区域之间表现出稳健的泛化能力,并在盲态验证中实现了高专家一致性。高级病理学家验证FEAT的输出结果与人类专家相当,并且在检测微妙的证据细微差别方面有所改进。据我们所知,FEAT是基于大型语言模型的第一个专门用于法医学的AI智能体系统,在保持专家级严谨性的同时,提供可伸缩、一致性的死亡证明。通过将AI效率与人类监督相结合,这项工作可以促进可靠的法医学服务的公平访问,同时解决法医系统中的关键能力约束。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于人工智能的多代理框架FEAT,通过大型语言模型自动化和标准化死亡调查,解决法医死因鉴定面临的系统性挑战,如人力资源短缺和诊断差异。FEAT系统采用工具增强推理、分层检索增强生成、法医调整的大型语言模型以及人类反馈循环,确保法律和医学有效性。评估显示,FEAT在中文案例群体中表现出优于现有AI系统的性能,并在盲验证中达到高专家共识。高级病理学家验证FEAT输出与专家相当,能更好检测细微证据。它是首个专门用于法医医学的大型语言模型为基础的AI代理系统,可提供可伸缩、一致性的死亡证明,同时保持专家级严谨性。
Key Takeaways
- 法医死因鉴定面临人力资源短缺和诊断差异等系统性挑战。
- FEAT是一个多代理AI框架,旨在通过大型语言模型自动化和标准化死亡调查。
- FEAT系统采用工具增强推理、分层检索增强生成以及法医调整的大型语言模型等技术。
- FEAT在中文案例群体评估中表现出卓越性能,达到高专家共识。
- 高级病理学家验证FEAT输出与专家相当,能更好识别细微证据。
- FEAT是首个专门用于法医医学的大型语言模型为基础的AI系统。
点此查看论文截图

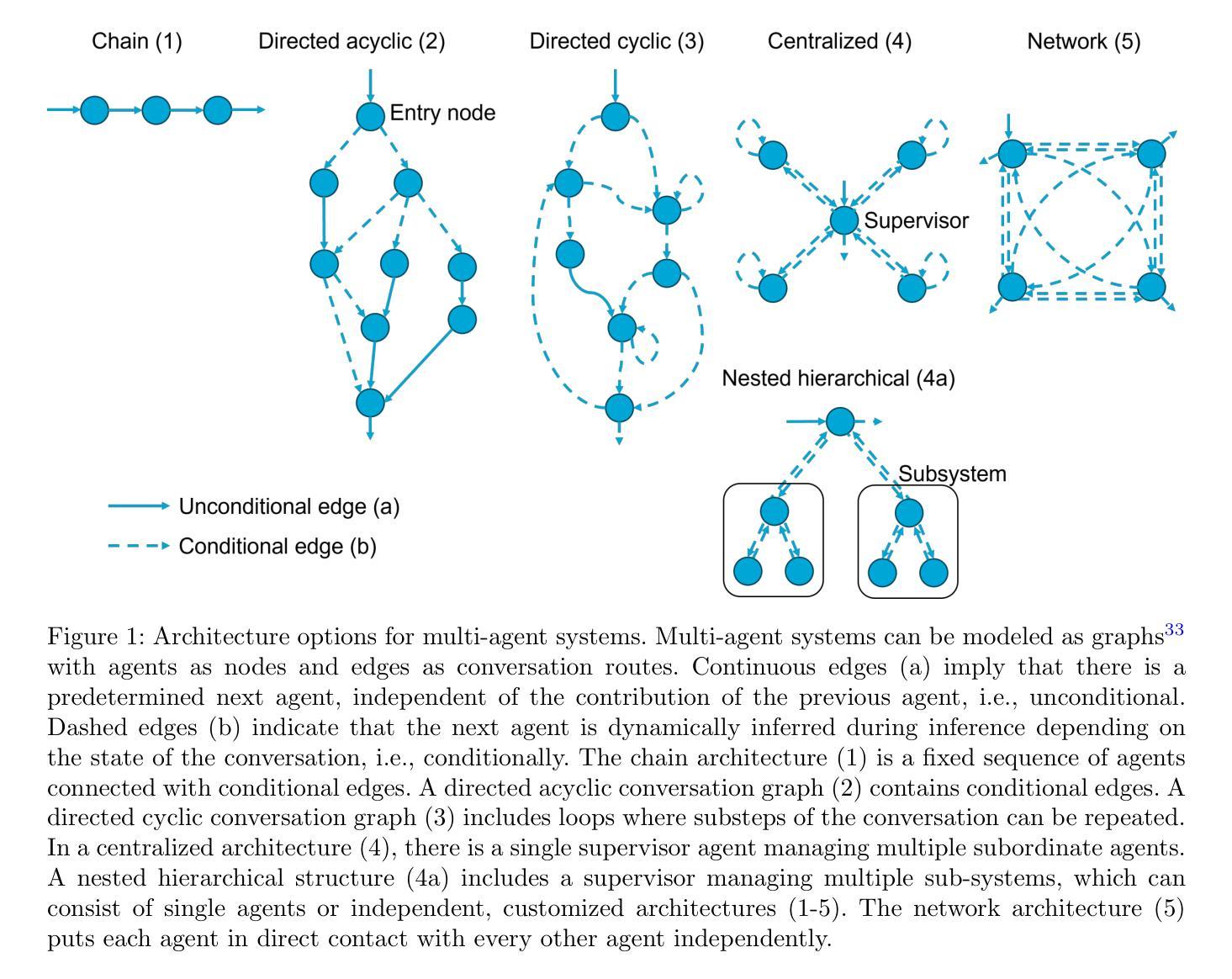
Multi-agent systems for chemical engineering: A review and perspective
Authors:Sophia Rupprecht, Qinghe Gao, Tanuj Karia, Artur M. Schweidtmann
Large language model (LLM)-based multi-agent systems (MASs) are a recent but rapidly evolving technology with the potential to transform chemical engineering by decomposing complex workflows into teams of collaborative agents with specialized knowledge and tools. This review surveys the state-of-the-art of MAS within chemical engineering. While early studies demonstrate promising results, scientific challenges remain, including the design of tailored architectures, integration of heterogeneous data modalities, development of foundation models with domain-specific modalities, and strategies for ensuring transparency, safety, and environmental impact. As a young but fast-moving field, MASs offer exciting opportunities to rethink chemical engineering workflows.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统(MAS)是一项最新的快速发展技术,具有将复杂工作流程分解成具有专业知识和工具的协作智能体团队的潜力,从而改变化学工程。本文综述了化学工程中MAS的最新进展。尽管早期研究显示出有希望的结果,但仍存在科学挑战,包括设计定制架构、集成异质数据模式、开发具有领域特定模式的基础模型,以及确保透明度、安全性和环境影响的策略。作为一个年轻但发展迅速的领域,MAS为重新思考化学工程工作流程提供了令人兴奋的机会。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统(MAS)是化学工程中正在迅速发展的新技术。它可将复杂的工作流程分解为具有专业知识和工具的协作智能体团队,从而具有变革潜力。本文综述了化学工程中的MAS最新研究成果。尽管早期研究取得良好结果,但仍存在诸多科学挑战,如定制架构的设计、异质数据模式的集成、具有特定领域模式的模型基础的开发,以及确保透明度、安全性和环境影响的策略等。作为年轻但快速发展的领域,MAS为重新思考化学工程工作流程提供了激动人心的机会。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based MAS是化学工程中正在迅速发展的新技术。
- MAS能将复杂的工作流程分解为具有专业知识和工具的协作智能体团队。
- 早期研究在MAS上取得了良好结果,但仍存在科学挑战。
- 需要设计定制架构、集成异质数据模式以及开发具有特定领域模式的模型基础。
- 保证透明度、安全性和环境影响是MAS发展中的关键策略。
点此查看论文截图

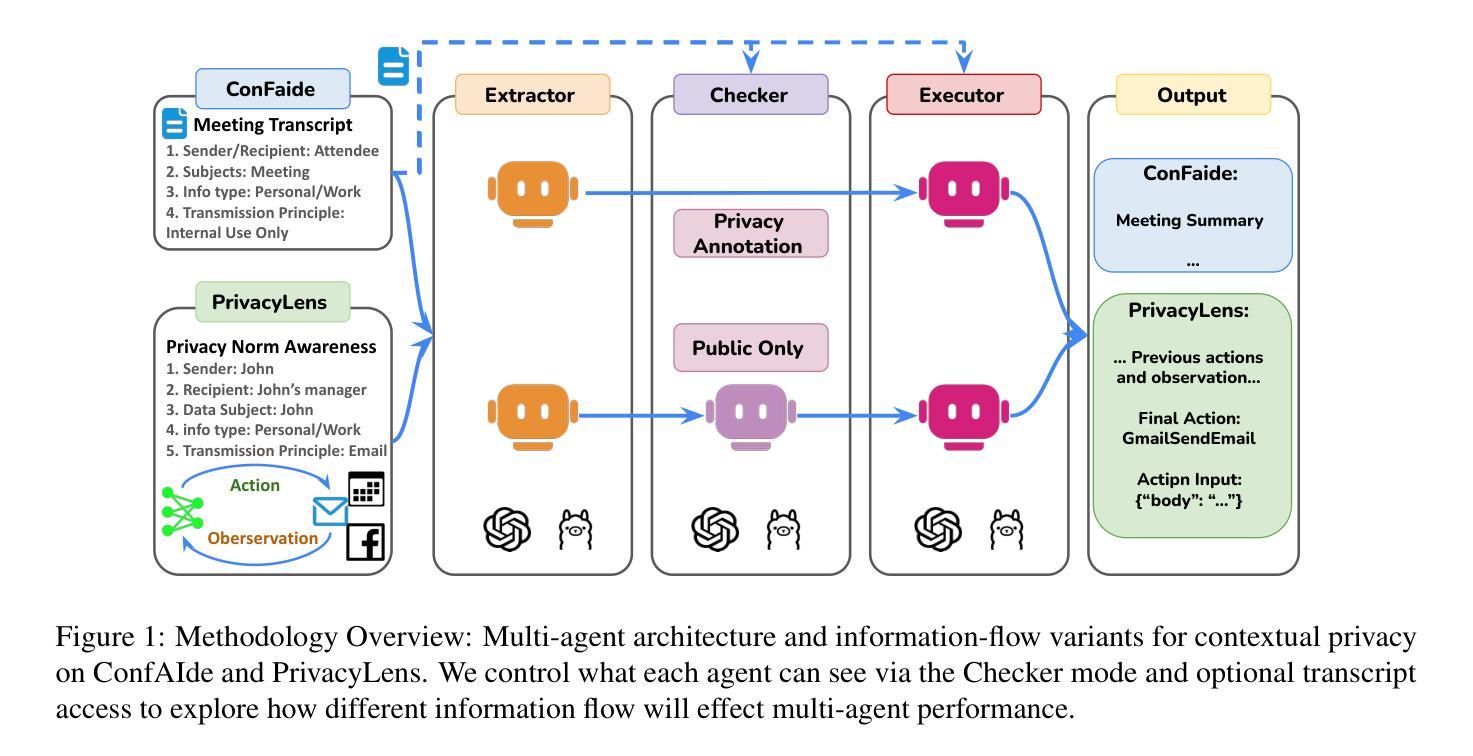
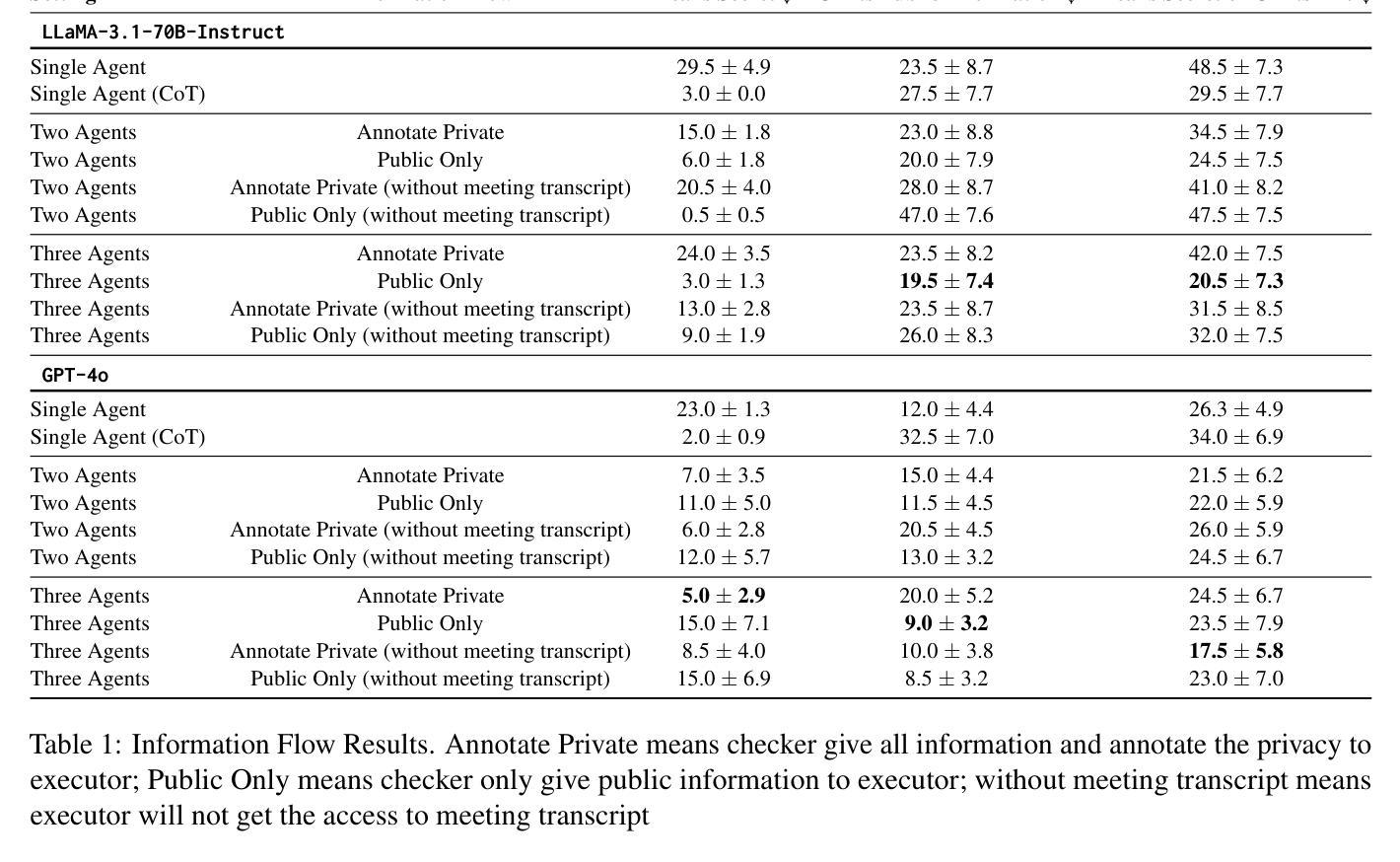
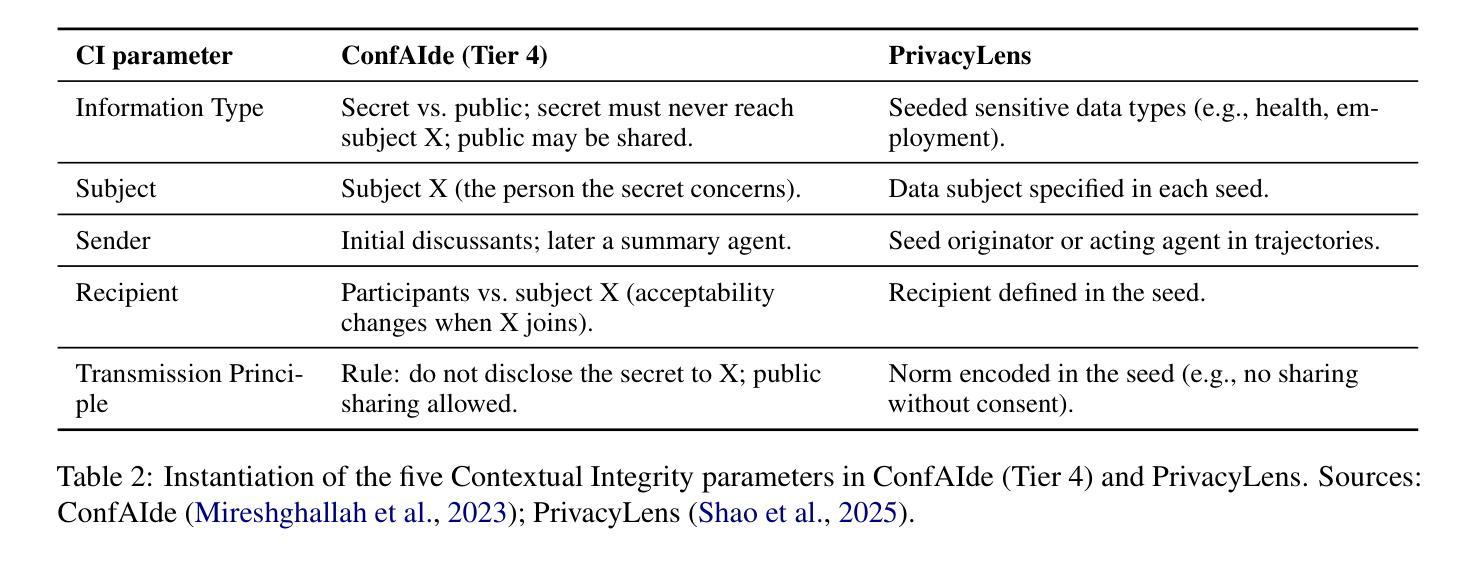
1-2-3 Check: Enhancing Contextual Privacy in LLM via Multi-Agent Reasoning
Authors:Wenkai Li, Liwen Sun, Zhenxiang Guan, Xuhui Zhou, Maarten Sap
Addressing contextual privacy concerns remains challenging in interactive settings where large language models (LLMs) process information from multiple sources (e.g., summarizing meetings with private and public information). We introduce a multi-agent framework that decomposes privacy reasoning into specialized subtasks (extraction, classification), reducing the information load on any single agent while enabling iterative validation and more reliable adherence to contextual privacy norms. To understand how privacy errors emerge and propagate, we conduct a systematic ablation over information-flow topologies, revealing when and why upstream detection mistakes cascade into downstream leakage. Experiments on the ConfAIde and PrivacyLens benchmark with several open-source and closed-sourced LLMs demonstrate that our best multi-agent configuration substantially reduces private information leakage (\textbf{18%} on ConfAIde and \textbf{19%} on PrivacyLens with GPT-4o) while preserving the fidelity of public content, outperforming single-agent baselines. These results highlight the promise of principled information-flow design in multi-agent systems for contextual privacy with LLMs.
在处理来自多个源的信息(例如,总结包含私有和公共信息的会议)的语言模型环境中,解决上下文隐私担忧仍然是一个挑战。我们引入了一个多智能体框架,该框架将隐私推理分解成专门的子任务(提取、分类等),这既减轻了任何单个智能体的信息负荷,又实现了迭代验证并更可靠地遵守上下文隐私规范。为了了解隐私错误是如何产生和传播的,我们对信息流拓扑进行了系统的剖析,揭示了上游检测错误何时以及为何会级联成下游泄露。在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上的实验表明,使用开源和闭源的大型语言模型,我们最佳的多智能体配置大幅减少了私人信息的泄露(在ConfAIde上减少**18%,在PrivacyLens上与GPT-4o一起使用减少19%**),同时保持了公共内容的保真度,超越了单智能体的基线。这些结果突显了在大型语言模型上下文中,以原则为基础的信息流设计在多智能体系统中对隐私保护的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在处理来自多个源的信息时,面临在交互式环境中解决上下文隐私问题的挑战。本文引入了一种多智能体框架,将隐私推理分解成专门的子任务,减少单个智能体的信息负载,同时实现迭代验证和更可靠地遵守上下文隐私规范。通过系统地剖析信息流拓扑来了解隐私错误的出现和传播。在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上进行的实验表明,最佳多智能体配置可大幅减少私人信息泄露,同时保持公共内容的保真度,优于单智能体基线。这突显了基于原则的信息流设计在多智能体系统与大型语言模型相结合进行上下文隐私保护的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在交互式环境中处理多源信息时面临上下文隐私挑战。
- 引入多智能体框架,将隐私推理分解成专门子任务,降低单一智能体的信息负载。
- 通过迭代验证和遵守上下文隐私规范,实现更可靠的隐私保护。
- 系统分析信息流拓扑,了解隐私错误的出现和传播机制。
- 在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上,多智能体配置大幅减少私人信息泄露。
- 多智能体配置同时保持公共内容的保真度,优于单智能体基线。
点此查看论文截图

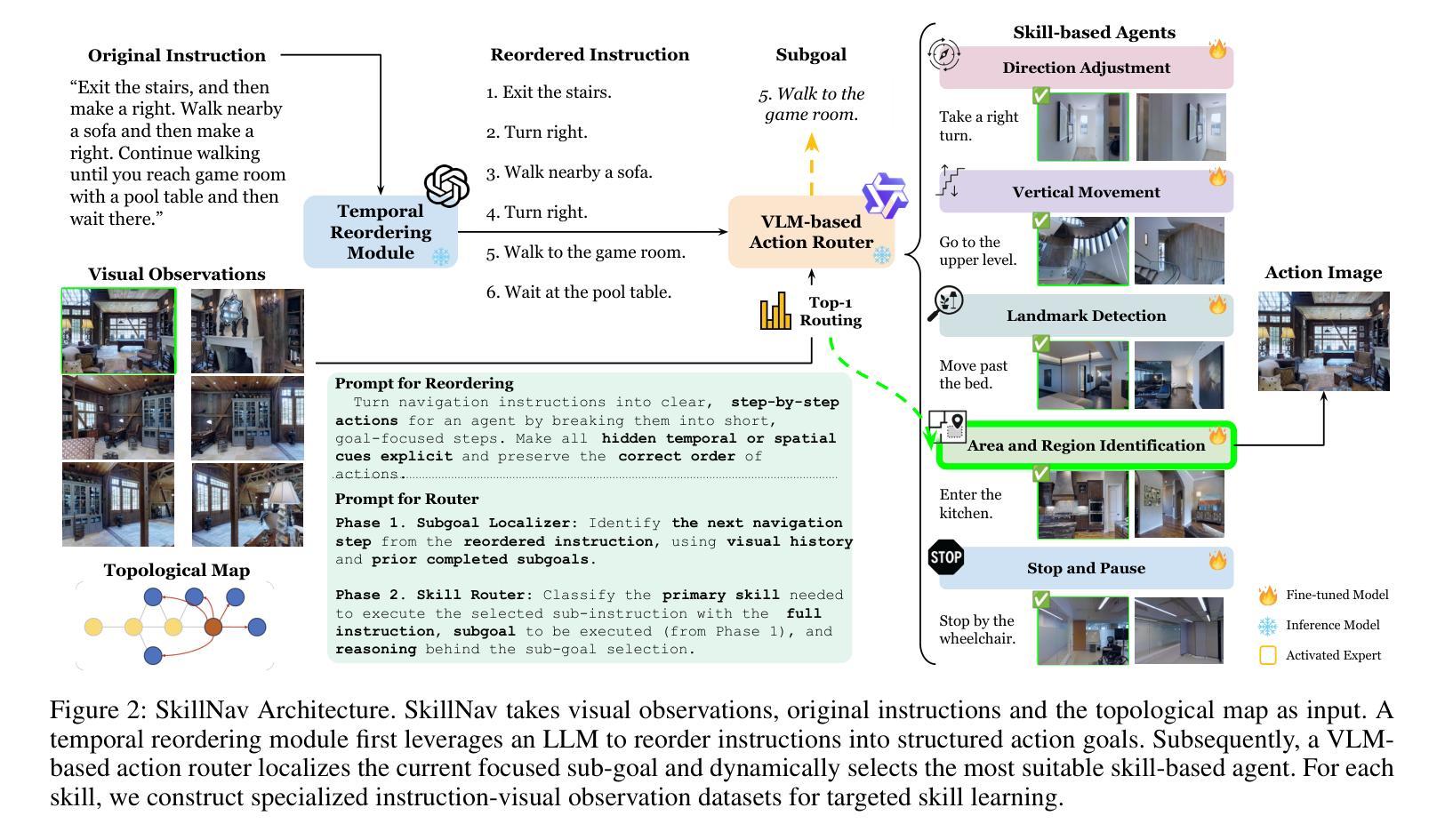
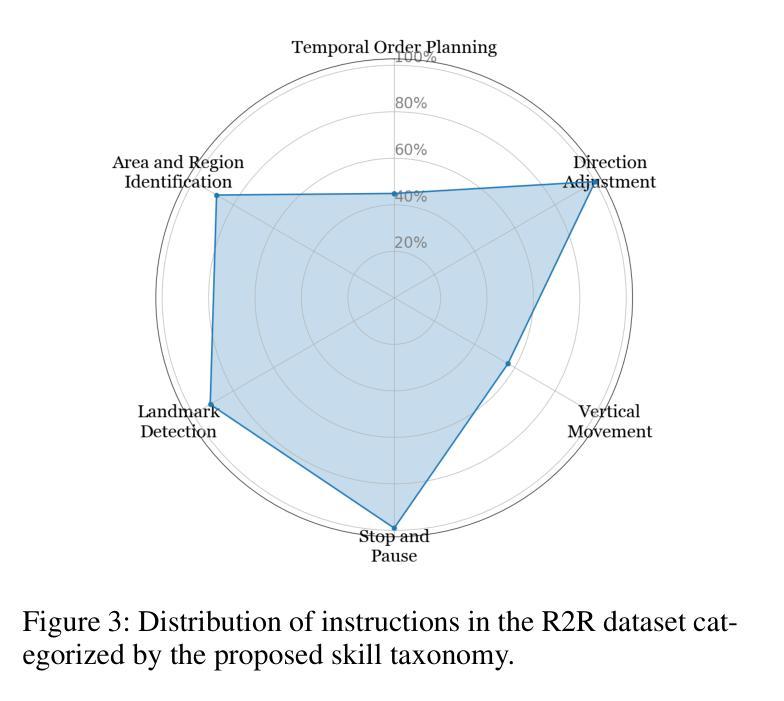
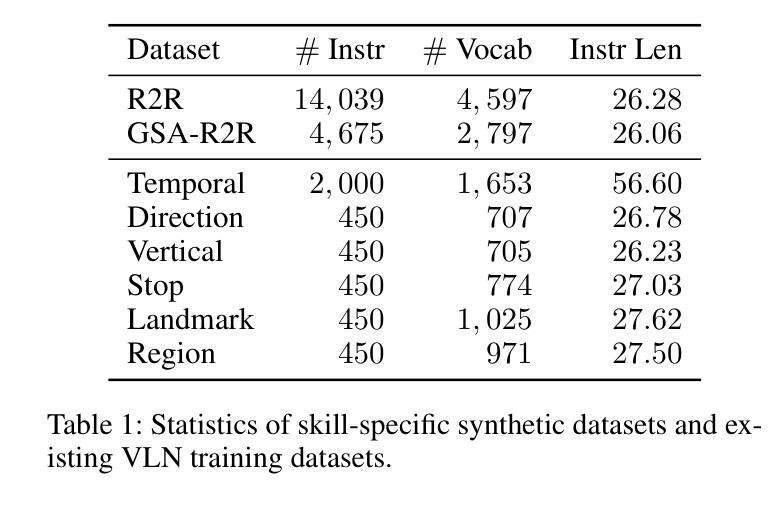
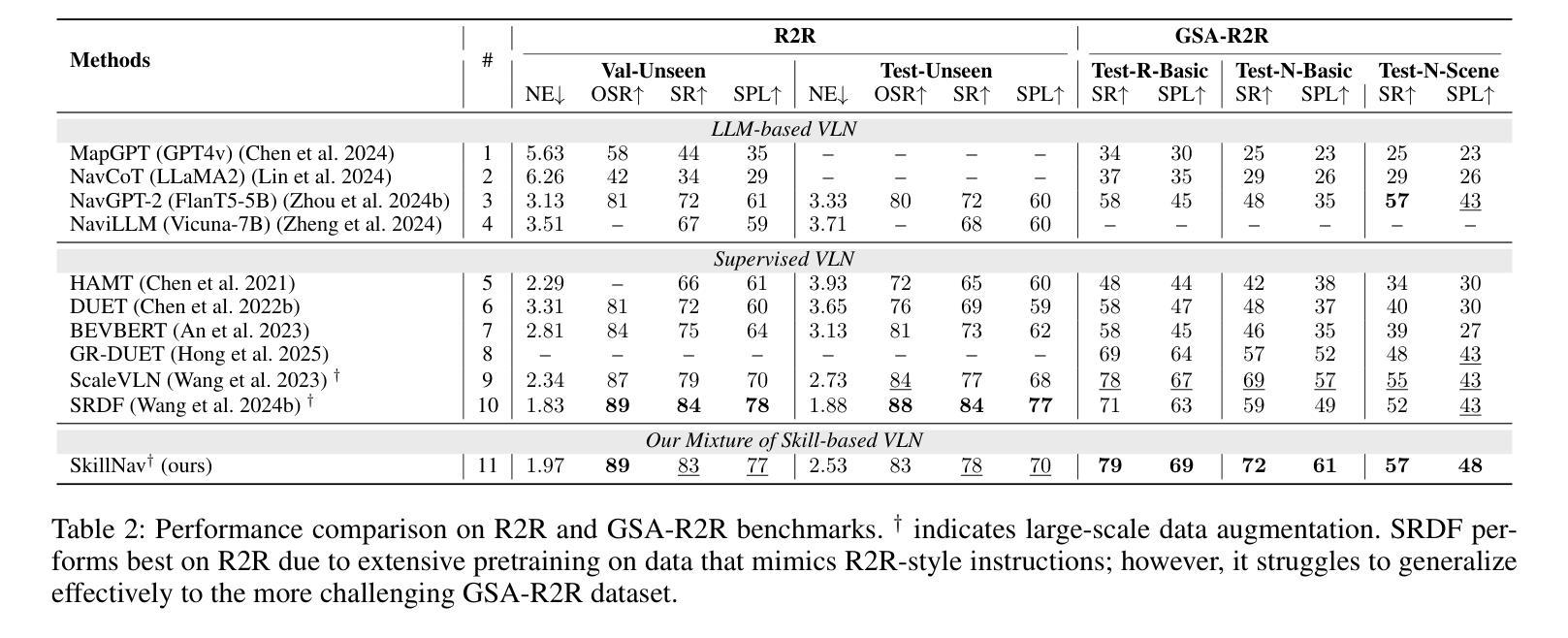
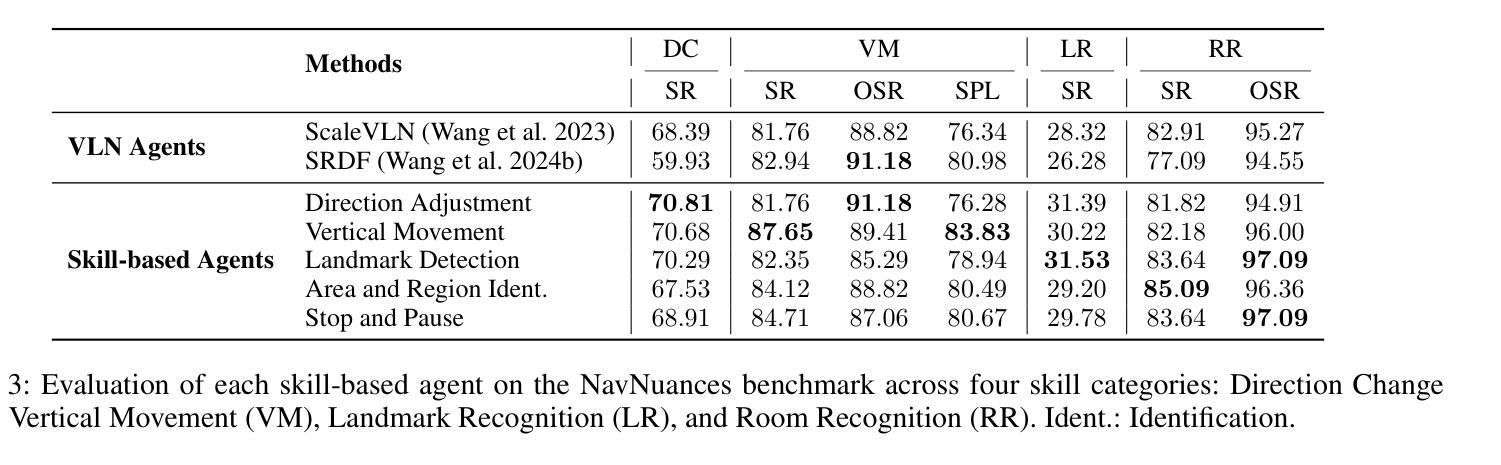
Breaking Down and Building Up: Mixture of Skill-Based Vision-and-Language Navigation Agents
Authors:Tianyi Ma, Yue Zhang, Zehao Wang, Parisa Kordjamshidi
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) poses significant challenges in enabling agents to interpret natural language instructions and navigate complex 3D environments. While recent progress has been driven by large-scale pre-training and data augmentation, current methods still struggle to generalize to unseen scenarios, particularly when complex spatial and temporal reasoning is required. In this work, we propose SkillNav, a modular framework that introduces structured, skill-based reasoning into Transformer-based VLN agents. Our method decomposes navigation into a set of interpretable atomic skills (e.g., Vertical Movement, Area and Region Identification, Stop and Pause), each handled by a specialized agent. We then introduce a novel zero-shot Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based router, which dynamically selects the most suitable agent at each time step by aligning sub-goals with visual observations and historical actions. SkillNav achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on the R2R benchmark and demonstrates strong generalization to the GSA-R2R benchmark that includes novel instruction styles and unseen environments.
视觉与语言导航(VLN)为智能体在解读自然语言指令和导航复杂三维环境方面带来了重大挑战。虽然最近的进展得益于大规模预训练和数据增强,但当前的方法仍然难以推广到未见过的场景,特别是在需要复杂空间和时间推理的情况下。在这项工作中,我们提出了SkillNav,这是一个模块化框架,它引入了基于技能的结构化推理到基于Transformer的VLN智能体中。我们的方法将导航分解成一组可解释的原子技能(例如垂直移动、区域识别、停止和暂停等),每个技能都由一个专门的智能体处理。然后我们引入了一种新型的零样本视觉语言模型(VLM)路由器,它通过对子目标与视觉观察和历史行动进行匹配,动态选择每个时间步长下最合适的智能体。SkillNav在R2R基准测试上达到了新的最新技术水平,并且在包括新型指令风格和未见过的环境的GSA-R2R基准测试上表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 Figures,
Summary
该文章探讨了视觉与语言导航(VLN)面临的挑战,包括智能体在解读自然语言指令和导航复杂三维环境时的困难。文章提出了一种名为SkillNav的模块化框架,该框架引入了结构化、基于技能的推理到基于Transformer的VLN智能体中。该方法将导航分解成一组可解释的原子技能(如垂直移动、区域识别、停止和暂停等),每个技能由专门的智能体处理。然后,文章引入了一种新型的零样本视觉语言模型(VLM)路由器,该路由器通过动态选择与视觉观察和历史行为相匹配的子目标来选择最合适的智能体。SkillNav在R2R基准测试中取得了最新性能水平,并在包括新型指令风格和未见过的环境的GSA-R2R基准测试中展现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- VLN面临的主要挑战是智能体在解读自然语言指令和导航复杂三维环境方面的困难。
- SkillNav是一种模块化框架,引入了结构化、基于技能的推理到VLN智能体中。
- SkillNav将导航分解成一组可解释的原子技能,每个技能由专门的智能体处理。
- 新型零样本视觉语言模型(VLM)路由器被用来动态选择最合适的智能体。
- SkillNav在R2R基准测试中取得了最新性能水平。
- SkillNav在泛化到新型指令风格和未见过的环境方面表现出强大的能力。
点此查看论文截图

MCPToolBench++: A Large Scale AI Agent Model Context Protocol MCP Tool Use Benchmark
Authors:Shiqing Fan, Xichen Ding, Liang Zhang, Linjian Mo
LLMs’ capabilities are enhanced by using function calls to integrate various data sources or API results into the context window. Typical tools include search, web crawlers, maps, financial data, file systems, and browser usage, etc. Integrating these data sources or functions requires a standardized method. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides a standardized way to supply context to LLMs. However, the evaluation of LLMs and AI Agents’ MCP tool use abilities suffer from several issues. First, there’s a lack of comprehensive datasets or benchmarks to evaluate various MCP tools. Second, the diverse formats of response from MCP tool call execution further increase the difficulty of evaluation. Additionally, unlike existing tool-use benchmarks with high success rates in functions like programming and math functions, the success rate of real-world MCP tool is not guaranteed and varies across different MCP servers. Furthermore, the LLMs’ context window also limits the number of available tools that can be called in a single run, because the textual descriptions of tool and the parameters have long token length for an LLM to process all at once. To help address the challenges of evaluating LLMs’ performance on calling MCP tools, we propose MCPToolBench++, a large-scale, multi-domain AI Agent tool use benchmark. As of July 2025, this benchmark is build upon marketplace of over 4k MCP servers from more than 40 categories, collected from the MCP marketplaces and GitHub communities. The datasets consist of both single-step and multi-step tool calls across different categories. We evaluated SOTA LLMs with agentic abilities on this benchmark and reported the results.
使用功能调用将各种数据源或API结果集成到上下文窗口中来增强LLMs的能力。典型工具包括搜索、网络爬虫、地图、金融数据、文件系统和浏览器使用等。集成这些数据源或功能需要一种标准化的方法。模型上下文协议(MCP)提供了一种为LLMs提供上下文的标准方式。然而,LLMs和AI代理的MCP工具使用能力的评估存在一些问题。首先,缺乏综合数据集或基准测试来评估各种MCP工具。其次,由于MCP工具调用执行的响应格式多样,进一步增加了评估的难度。此外,与现有工具使用基准测试在编程和数学函数等功能上实现的高成功率不同,现实世界中的MCP工具的成功率并不能保证,并且会因不同的MCP服务器而有所变化。另外,LLMs的上下文窗口还限制了单次运行中可调用工具的数量,因为LLM一次处理工具和参数的文本描述需要较长的令牌长度。为了解决评估LLMs在调用MCP工具方面的性能的挑战,我们提出了MCPToolBench++,这是一个大规模、多领域的AI代理工具使用基准测试。截至2025年7月,该基准测试建立在来自40多个类别的4000多个MCP服务器市场之上,这些服务器来自MCP市场和GitHub社区。数据集包含不同类别的单步和多步工具调用。我们在该基准测试上评估了具有代理能力的最新LLMs并报告了结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Benchmarks and Source Code Released
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,通过使用函数调用整合多种数据源或API结果到语境窗口来增强其能力。模型上下文协议(MCP)为LLM提供了标准化的语境供应方式。然而,评估LLM和人工智能代理的MCP工具使用能力面临几个挑战。缺乏综合数据集或基准测试来评估各种MCP工具;MCP工具调用执行的响应格式多样,增加了评估难度;与编程和数学函数等现有工具使用基准测试的高成功率不同,现实世界中的MCP工具成功率无法保证,且因不同的MCP服务器而有所差异;LLM的语境窗口限制了单次运行中可调用的工具数量。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了MCPToolBench++,这是一个大规模、多领域的AI代理工具使用基准测试。截至2025年7月,该基准测试建立在包含超过40个类别的4000多个MCP服务器市场上,从MCP市场和GitHub社区收集。数据集包含不同类别的单步和多步工具调用。我们在该基准测试上评估了具有代理能力的顶尖LLM并报告了结果。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs的能力可以通过使用函数调用整合多种数据源或API结果到语境窗口来增强。
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) 为LLMs提供了标准化的语境供应方式。
- 评估LLMs和AI代理的MCP工具使用能力存在多个挑战,如缺乏综合数据集、响应格式多样、现实世界中的成功率不确定以及语境窗口的限制等。
- MCPToolBench++是一个新的大规模、多领域的AI代理工具使用基准测试,用于应对这些挑战。
- 该基准测试包含来自多个类别的单步和多步工具调用。
- 截至2025年7月,该基准测试建立在包含超过40个类别的4000多个MCP服务器的基础上。
点此查看论文截图

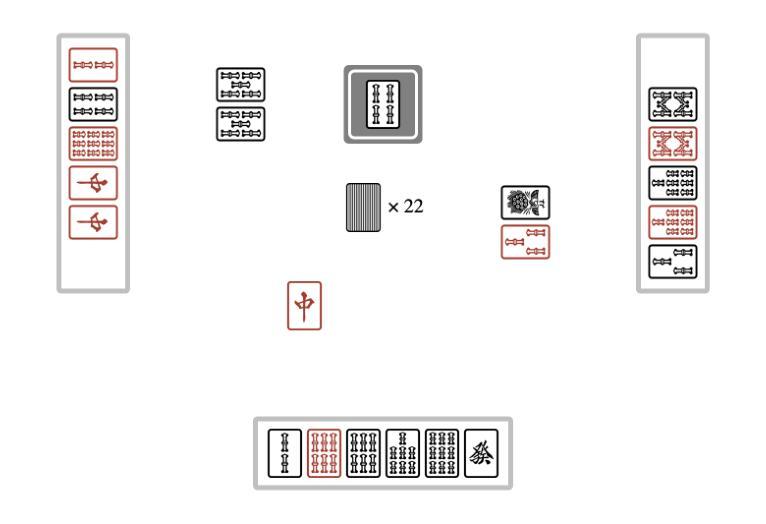
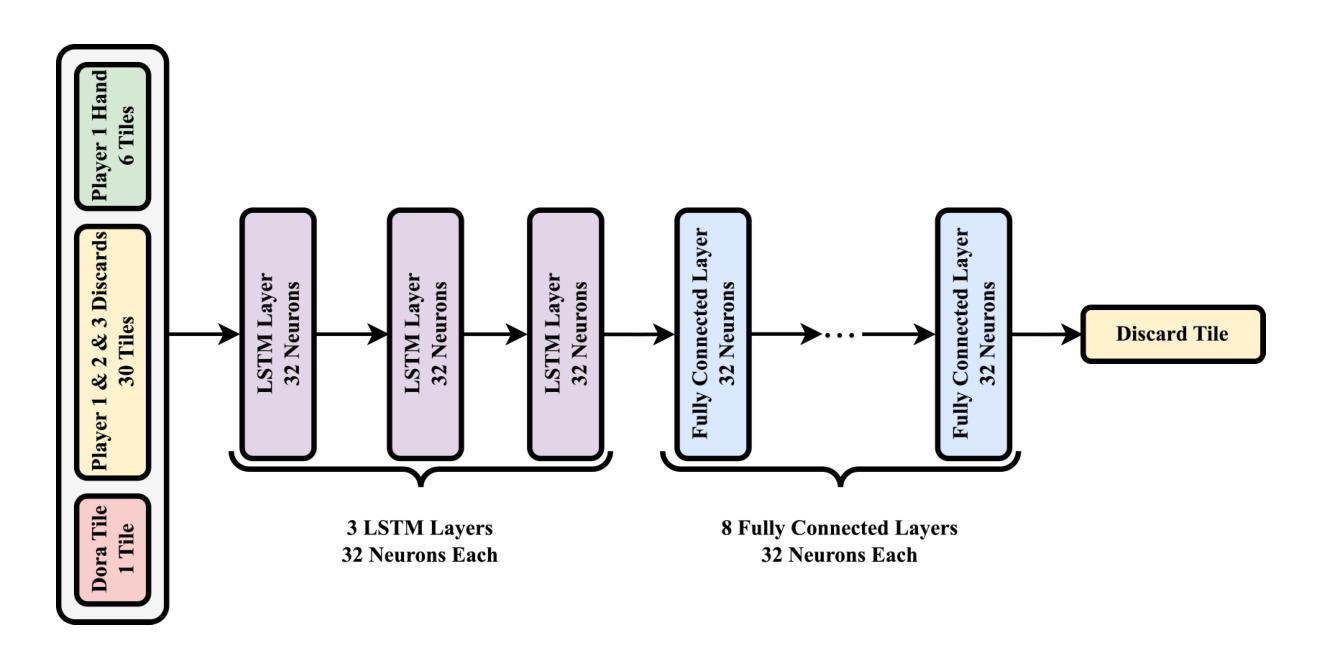
Evolutionary Optimization of Deep Learning Agents for Sparrow Mahjong
Authors:Jim O’Connor, Derin Gezgin, Gary B. Parker
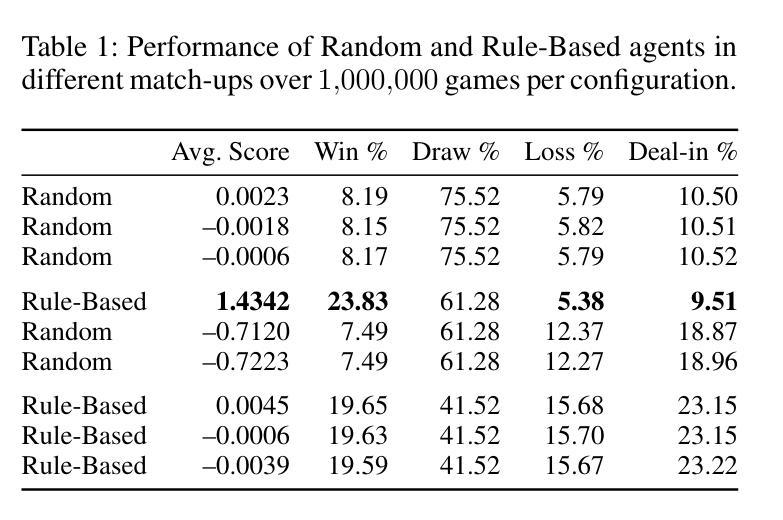
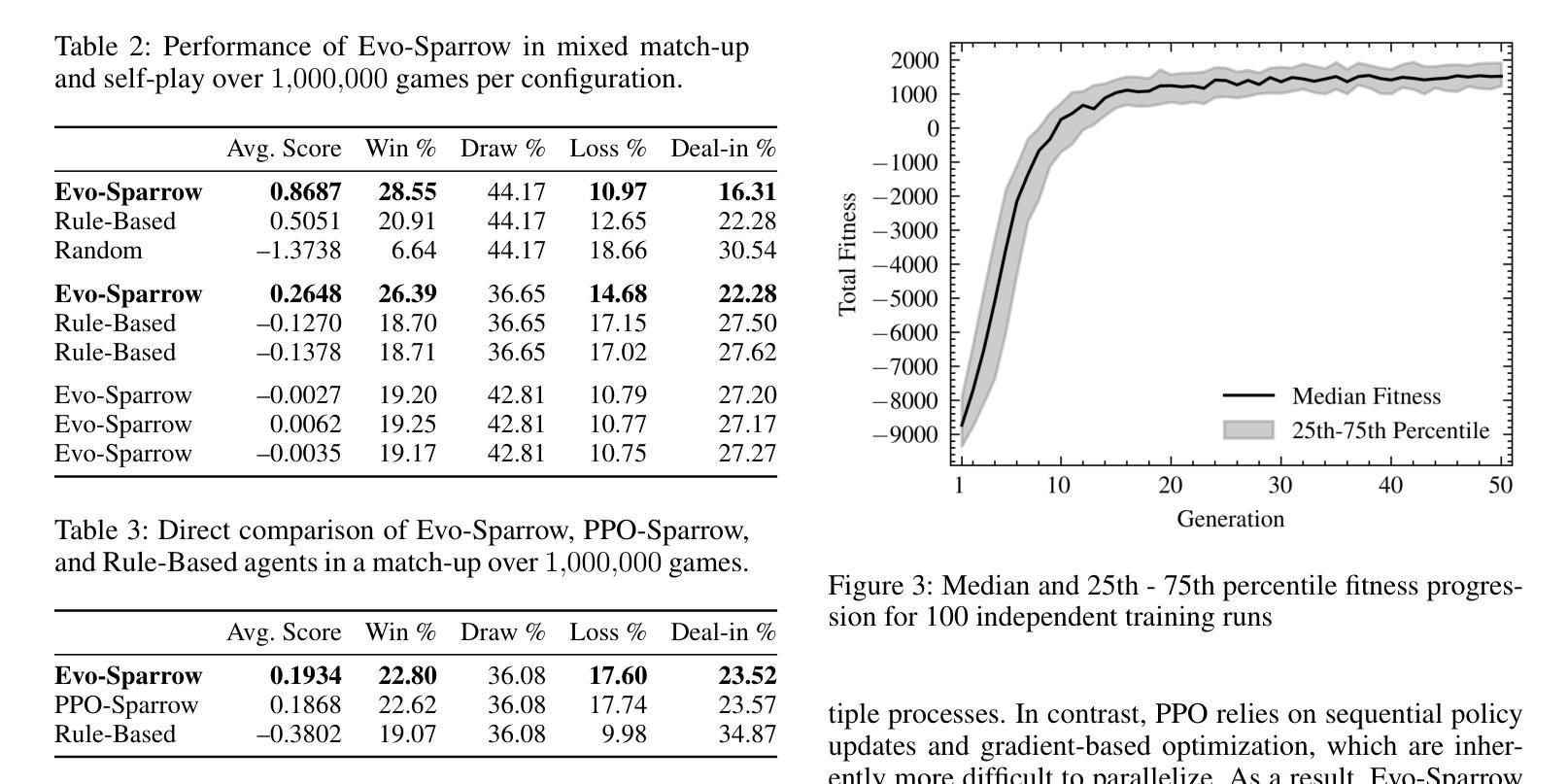
We present Evo-Sparrow, a deep learning-based agent for AI decision-making in Sparrow Mahjong, trained by optimizing Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks using Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES). Our model evaluates board states and optimizes decision policies in a non-deterministic, partially observable game environment. Empirical analysis conducted over a significant number of simulations demonstrates that our model outperforms both random and rule-based agents, and achieves performance comparable to a Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) baseline, indicating strong strategic play and robust policy quality. By combining deep learning with evolutionary optimization, our approach provides a computationally effective alternative to traditional reinforcement learning and gradient-based optimization methods. This research contributes to the broader field of AI game playing, demonstrating the viability of hybrid learning strategies for complex stochastic games. These findings also offer potential applications in adaptive decision-making and strategic AI development beyond Sparrow Mahjong.
我们介绍了Evo-Sparrow,这是一个基于深度学习的Agent,用于在麻将游戏中进行AI决策。该模型通过优化长短期记忆(LSTM)网络,使用协方差矩阵自适应进化策略(CMA-ES)进行训练。我们的模型能够评估棋盘状态并在非确定性、部分可观察的游戏环境中优化决策策略。通过对大量模拟的实证分析表明,我们的模型在性能和表现上都优于随机和基于规则的Agent,并且性能与近端策略优化(PPO)基线相当,表现出强大的战略性和稳健的策略质量。通过将深度学习与进化优化相结合,我们的方法提供了一种在计算上有效的替代传统强化学习和基于梯度的优化方法。本研究为更广泛的AI游戏领域做出了贡献,证明了混合学习策略对于复杂随机游戏的可行性。此外,这一发现还可能在自适应决策制定和麻将以外领域的战略型AI开发中得到潜在应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment
Summary:
Evo-Sparrow是一款基于深度学习的麻将决策智能体,通过优化LSTM网络并使用CMA-ES进化策略进行训练。该模型在非确定性、部分可观察的游戏环境中评估棋盘状态并优化决策策略。模拟实验表明,该模型在性能上超越了随机和基于规则的传统智能体,并达到了与PPO基线相当的水平,展现了强大的战略能力和稳健的策略质量。该研究结合了深度学习与进化优化,为传统强化学习和基于梯度的优化方法提供了有效的计算替代方案。该研究为复杂随机游戏中的混合学习策略提供了可行性证明,并在自适应决策和战略AI开发领域具有潜在应用。
Key Takeaways:
- Evo-Sparrow是一个结合了深度学习和进化优化的智能体,用于非确定性游戏中的决策制定。
- LSTM网络被用于处理游戏中的复杂数据并优化决策策略。
- CMA-ES进化策略被用于训练模型,使其在部分可观察的环境中表现良好。
- 模拟实验证明,Evo-Sparrow在性能上超越了随机和基于规则的传统智能体。
- Evo-Sparrow达到了与PPO基线相当的性能水平,展现了强大的战略能力和稳健的策略质量。
- 该研究为传统强化学习和基于梯度的优化方法提供了计算效率更高的替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

CP-Agent: Agentic Constraint Programming
Authors:Stefan Szeider
Translating natural language problem descriptions into formal constraint models remains a fundamental challenge in constraint programming, requiring deep expertise in both the problem domain and modeling frameworks. Previous approaches to automating this translation have employed fixed workflows with predetermined modeling steps, failing on a significant number of benchmark problems. We present a new approach using a pure agentic strategy without any fixed pipeline. We developed a general-purpose Python coding agent based on the ReAct (Reason and Act) principle, utilizing a persistent IPython kernel for stateful code execution and iterative development. Rather than embedding constraint programming logic into the agent architecture, domain-specific expertise is injected solely through a carefully crafted project prompt. The agent combines this prompt-encoded knowledge with access to file operations and code execution tools, enabling it to test hypotheses, debug failures, and verify solutions dynamically. Implemented in just a few hundred lines of code, this architecture successfully solves all 101 problems of the CP-Bench constraint programming benchmark set. The results suggest that constraint modeling tasks require the combination of general coding tools and domain expertise encoded in prompts, rather than specialized agent architectures or predefined workflows.
将自然语言问题描述翻译为正式的约束模型仍然是约束编程中的一个基本挑战,这需要深入的问题领域和建模框架的专业知识。之前自动化此翻译的方法采用了具有预定建模步骤的固定工作流程,无法在大量基准问题上取得成功。我们提出了一种新的方法,采用纯粹的代理策略,没有任何固定流程。我们开发了一个基于ReAct(推理与行动)原理的通用Python编码代理,利用持久的IPython内核进行状态化的代码执行和迭代开发。我们不是将约束编程逻辑嵌入到代理架构中,而是仅通过精心设计的项目提示注入领域专业知识。该代理结合了提示编码的知识以及文件操作和代码执行工具的访问权限,能够动态地测试假设、调试故障并验证解决方案。这个架构仅在数百行代码中实现,成功解决了CP-Bench约束编程基准测试集中的所有101个问题。结果表明,约束建模任务需要通用编码工具与提示中编码的域专业知识的结合,而不是特殊的代理架构或预先定义的工作流程。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了一种新的自然语言问题描述翻译成约束模型的方法,使用基于ReAct原理的Python编码代理,通过项目提示注入领域专业知识,成功解决了CP-Bench约束编程基准测试集中的所有问题。该方法强调了约束建模任务需要结合一般编程工具和领域专业知识,而非特定代理架构或预先定义的工作流程。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言问题翻译到约束模型是约束编程中的核心挑战,需要领域知识和建模框架的双重专长。
- 现有自动化翻译方法采用固定工作流程和预定建模步骤,无法在大量基准问题上取得良好效果。
- 提出了一种新的基于ReAct原理的纯代理策略,不使用任何固定流程。
- 开发了基于Python的通用编码代理,利用持久IPython内核进行状态代码执行和迭代开发。
- 代理通过精心构建的项目提示注入领域专业知识,结合文件操作和代码执行工具,实现动态测试假设、调试失败和验证解决方案。
- 该架构仅在数百行代码中实现,成功解决了CP-Bench约束编程基准测试集中的所有问题。
点此查看论文截图

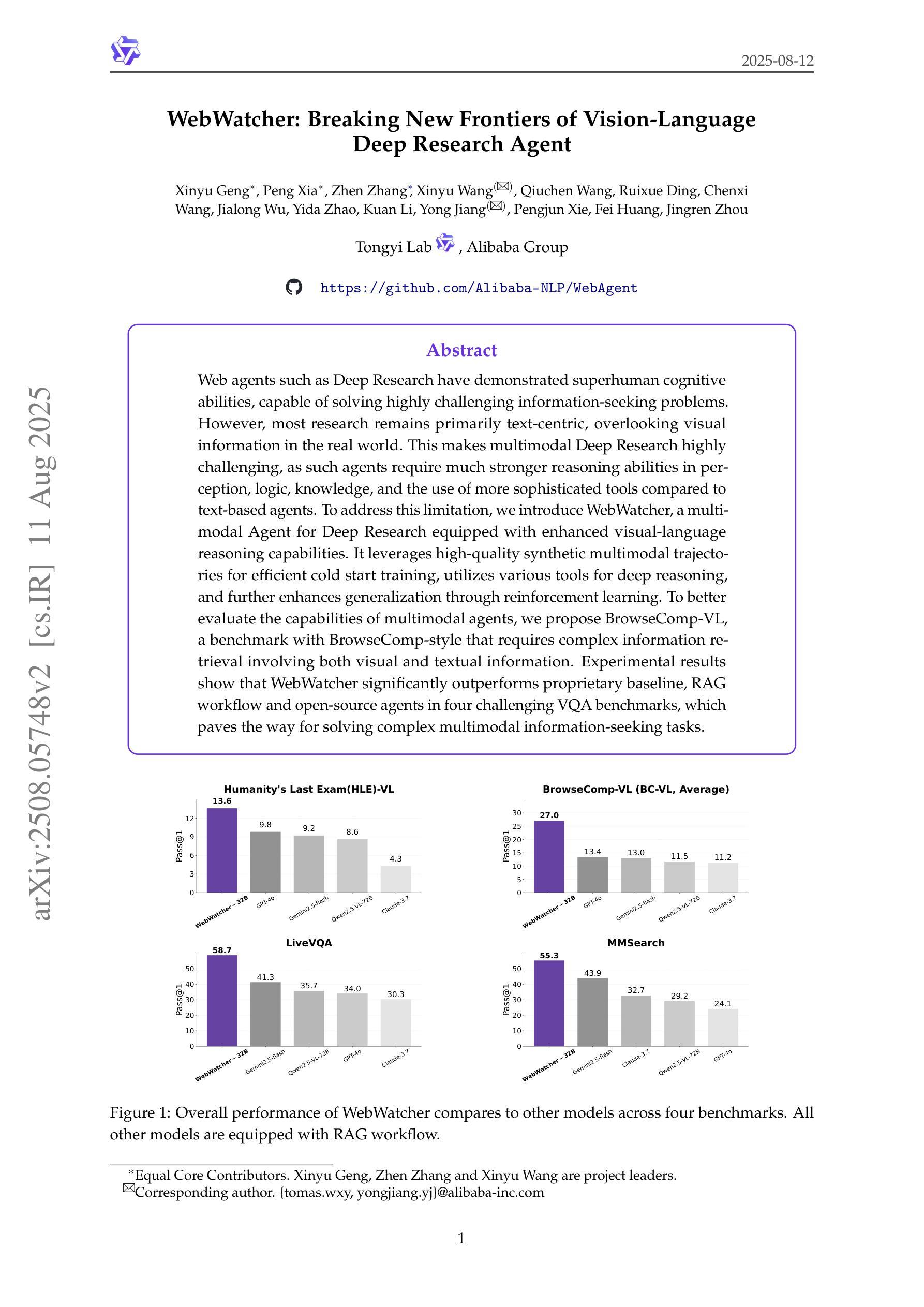
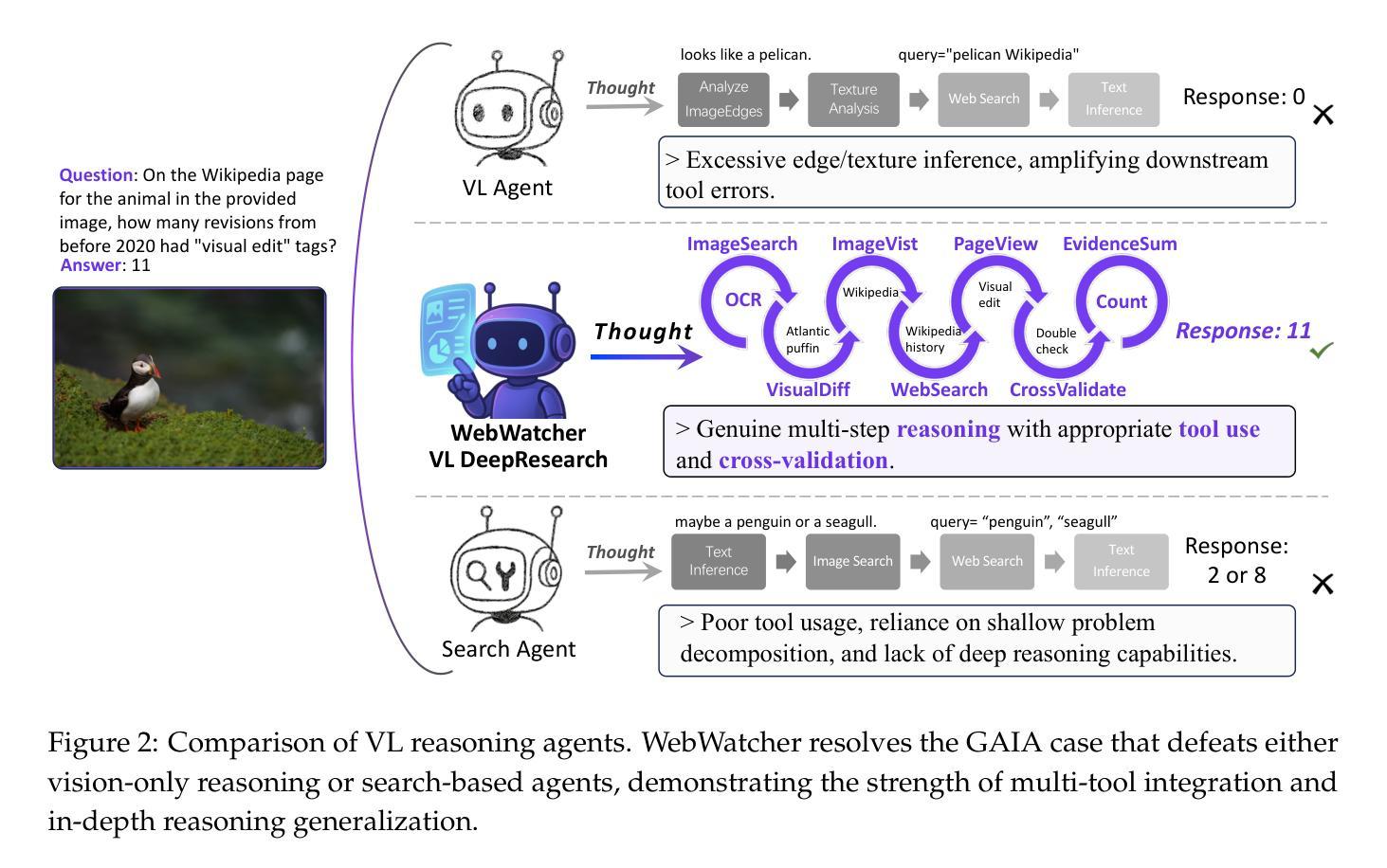
WebWatcher: Breaking New Frontier of Vision-Language Deep Research Agent
Authors:Xinyu Geng, Peng Xia, Zhen Zhang, Xinyu Wang, Qiuchen Wang, Ruixue Ding, Chenxi Wang, Jialong Wu, Yida Zhao, Kuan Li, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Jingren Zhou
Web agents such as Deep Research have demonstrated superhuman cognitive abilities, capable of solving highly challenging information-seeking problems. However, most research remains primarily text-centric, overlooking visual information in the real world. This makes multimodal Deep Research highly challenging, as such agents require much stronger reasoning abilities in perception, logic, knowledge, and the use of more sophisticated tools compared to text-based agents. To address this limitation, we introduce WebWatcher, a multi-modal Agent for Deep Research equipped with enhanced visual-language reasoning capabilities. It leverages high-quality synthetic multimodal trajectories for efficient cold start training, utilizes various tools for deep reasoning, and further enhances generalization through reinforcement learning. To better evaluate the capabilities of multimodal agents, we propose BrowseComp-VL, a benchmark with BrowseComp-style that requires complex information retrieval involving both visual and textual information. Experimental results show that WebWatcher significantly outperforms proprietary baseline, RAG workflow and open-source agents in four challenging VQA benchmarks, which paves the way for solving complex multimodal information-seeking tasks.
Deep Research等网络智能体已经展现出超人的认知能力,能够解决具有高度挑战性的信息搜索问题。然而,大多数研究仍然主要集中在文本上,忽视了现实世界中的视觉信息。这使得多模态深度研究面临巨大挑战,因为与基于文本的智能体相比,此类智能体需要在感知、逻辑、知识等方面具备更强的推理能力,并使用更先进的工具。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了WebWatcher,这是一个为深度研究设计的多模态智能体,具备增强的视觉语言推理能力。它利用高质量合成多模态轨迹进行高效冷启动训练,使用各种工具进行深入推理,并通过强化学习进一步提高泛化能力。为了更好地评估多模态智能体的能力,我们提出了BrowseComp-VL基准测试,这是一个需要涉及视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索的BrowseComp风格基准测试。实验结果表明,WebWatcher在四个具有挑战性的视觉问答基准测试中显著优于专有基线、RAG工作流和开源智能体,这为解决复杂的跨模态信息搜索任务奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度研究网络代理如Deep Research展现出超人认知力,能解决高难度信息搜寻问题。然而,现有研究多聚焦于文本信息,忽视现实世界中的视觉信息,导致多模态深度研究面临挑战。为此,我们推出具备增强视觉语言推理能力的多模态深度研究代理WebWatcher,其利用高质量合成多模态轨迹进行高效冷启动训练,使用多种工具进行深度推理,并通过强化学习提高泛化能力。为评估多模态代理能力,我们提出包含视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索基准测试BrowseComp-VL。实验结果显示WebWatcher在四项挑战型视觉问答基准测试中显著优于专有基线、RAG工作流和开源代理,为复杂多模态信息搜寻任务提供了解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Web代理如Deep Research具有超人认知力,可解决高难度信息搜寻问题。
- 当前研究过于依赖文本信息,忽视视觉信息,导致多模态深度研究挑战。
- WebWatcher代理具备增强视觉语言推理能力,利用合成多模态轨迹进行冷启动训练。
- WebWatcher使用多种工具进行深度推理,并通过强化学习提高泛化能力。
- 为评估多模态代理能力,推出基准测试BrowseComp-VL,包含视觉和文本信息的复杂信息检索。
- WebWatcher在多项视觉问答基准测试中表现优异,显著优于其他代理。
点此查看论文截图
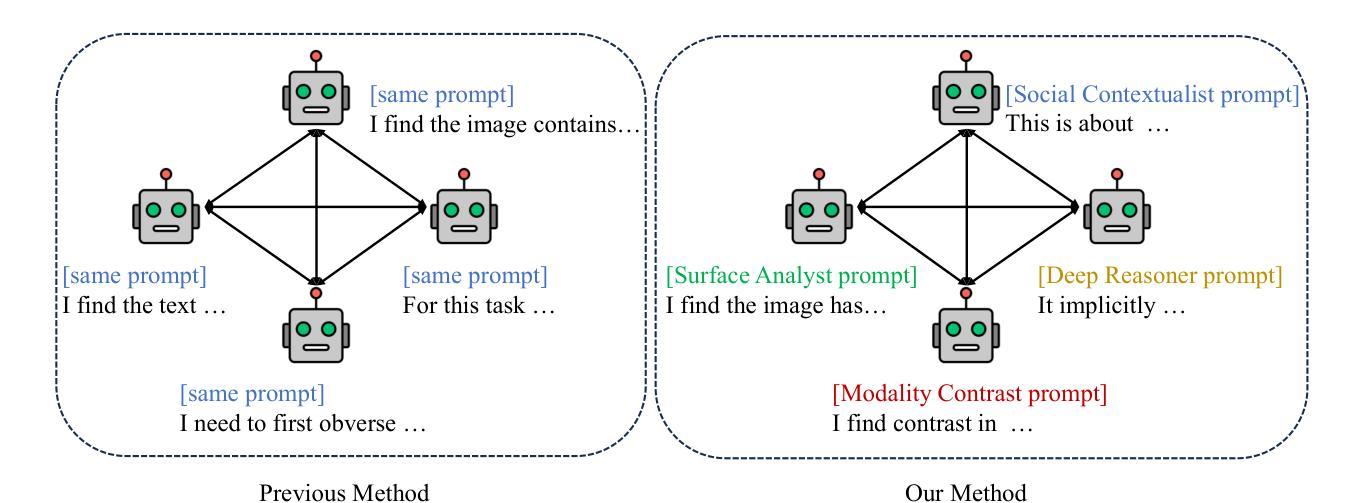
MV-Debate: Multi-view Agent Debate with Dynamic Reflection Gating for Multimodal Harmful Content Detection in Social Media
Authors:Rui Lu, Jinhe Bi, Yunpu Ma, Feng Xiao, Yuntao Du, Yijun Tian
Social media has evolved into a complex multimodal environment where text, images, and other signals interact to shape nuanced meanings, often concealing harmful intent. Identifying such intent, whether sarcasm, hate speech, or misinformation, remains challenging due to cross-modal contradictions, rapid cultural shifts, and subtle pragmatic cues. To address these challenges, we propose MV-Debate, a multi-view agent debate framework with dynamic reflection gating for unified multimodal harmful content detection. MV-Debate assembles four complementary debate agents, a surface analyst, a deep reasoner, a modality contrast, and a social contextualist, to analyze content from diverse interpretive perspectives. Through iterative debate and reflection, the agents refine responses under a reflection-gain criterion, ensuring both accuracy and efficiency. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that MV-Debate significantly outperforms strong single-model and existing multi-agent debate baselines. This work highlights the promise of multi-agent debate in advancing reliable social intent detection in safety-critical online contexts.
社交媒体已经演变为一个复杂的多媒体环境,文本、图像和其他信号在此环境中相互作用,形成微妙的含义,常常隐藏有害的意图。识别这种意图,无论是讽刺、仇恨言论还是错误信息,仍然是一个挑战,原因在于跨模态的矛盾、快速的文化变迁和微妙的语用线索。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MV-Debate,这是一个具有动态反射门控的多视图代理辩论框架,用于统一的多模式有害内容检测。MV-Debate集成了四种互补的辩论代理,包括表面分析师、深度推理者、模态对比器和社会语境主义者,以从多种解释性视角分析内容。通过迭代辩论和反思,代理在反思增益标准下完善回应,确保准确性和效率。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,MV-Debate显著优于强大的单模型和现有的多代理辩论基线。这项工作强调了多代理辩论在推进安全关键在线环境下的可靠社会意图检测方面的前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社交媒体的复杂多媒体环境中文本、图像等信号相互作用,产生微妙的含义,常常隐藏有害意图。识别这种意图(如讽刺、仇恨言论或虚假信息)充满挑战,因为存在跨模态矛盾、文化快速变迁和微妙的语用线索。本研究提出了MV-Debate多视角辩论框架,采用动态反思门控技术,用于统一多媒体有害内容检测。MV-Debate集结了四种互补的辩论智能体,包括表面分析师、深度推理者、模态对比器和社会语境专家,从不同角度解析内容。通过迭代辩论和反思,智能体在反思增益标准下优化响应,确保准确性和效率。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,MV-Debate显著优于强大的单模型和多智能体辩论基线。本研究突显了多智能体辩论在推进在线安全环境中的可靠社会意图检测方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体已演变为一个复杂的多媒体环境,其中文本、图像等信号相互作用产生微妙的含义,可能隐藏有害意图。
- 识别这些有害意图(如讽刺、仇恨言论和虚假信息)具有挑战性,原因是跨模态矛盾、文化快速变迁和微妙的语用线索。
- MV-Debate是一个多视角的辩论框架,包含四个互补的辩论智能体,用于统一分析多媒体内容。
- MV-Debate通过迭代辩论和反思优化响应,确保准确性和效率。
- 实验表明,MV-Debate在三个基准数据集上的性能显著优于单模型和其他多智能体辩论方法。
- MV-Debate框架具有潜力推进在线安全环境中的社会意图检测的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


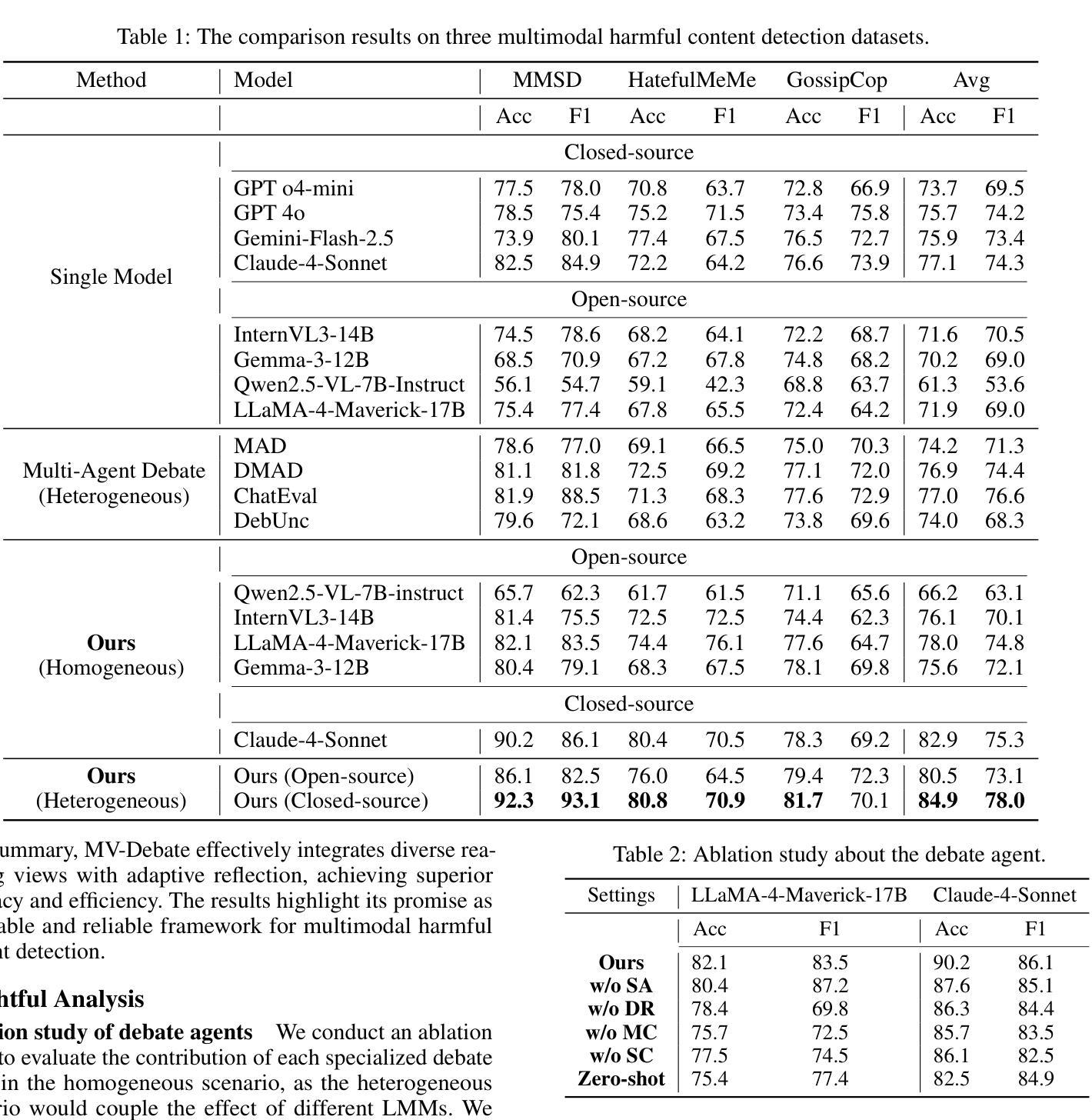
ARAG: Agentic Retrieval Augmented Generation for Personalized Recommendation
Authors:Reza Yousefi Maragheh, Pratheek Vadla, Priyank Gupta, Kai Zhao, Aysenur Inan, Kehui Yao, Jianpeng Xu, Praveen Kanumala, Jason Cho, Sushant Kumar
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has shown promise in enhancing recommendation systems by incorporating external context into large language model prompts. However, existing RAG-based approaches often rely on static retrieval heuristics and fail to capture nuanced user preferences in dynamic recommendation scenarios. In this work, we introduce ARAG, an Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework for Personalized Recommendation, which integrates a multi-agent collaboration mechanism into the RAG pipeline. To better understand the long-term and session behavior of the user, ARAG leverages four specialized LLM-based agents: a User Understanding Agent that summarizes user preferences from long-term and session contexts, a Natural Language Inference (NLI) Agent that evaluates semantic alignment between candidate items retrieved by RAG and inferred intent, a context summary agent that summarizes the findings of NLI agent, and an Item Ranker Agent that generates a ranked list of recommendations based on contextual fit. We evaluate ARAG accross three datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that ARAG significantly outperforms standard RAG and recency-based baselines, achieving up to 42.1% improvement in NDCG@5 and 35.5% in Hit@5. We also, conduct an ablation study to analyse the effect by different components of ARAG. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of integrating agentic reasoning into retrieval-augmented recommendation and provide new directions for LLM-based personalization.
检索增强生成(RAG)通过将外部上下文融入大型语言模型提示,在增强推荐系统方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,现有的基于RAG的方法常常依赖于静态检索启发式策略,无法在动态推荐场景中捕捉微妙的用户偏好。在这项工作中,我们介绍了ARAG,一个用于个性化推荐的Agentic检索增强生成框架,它将多智能体协作机制整合到RAG管道中。为了更好地理解用户的长期和会话行为,ARAG利用四个基于LLM的专用智能体:一个理解用户智能体,它总结来自长期和会话语境的用户偏好;一个自然语言推理(NLI)智能体,它评估由RAG检索的候选物品与推断意图之间的语义对齐;一个上下文摘要智能体,它总结NLI智能体的发现;以及一个项目排名智能体,它根据上下文兼容性生成排名推荐列表。我们在三个数据集上评估ARAG。实验结果表明,ARAG显著优于标准RAG和基于时效性的基准线,在NDCG@5上提高了42.1%,在Hit@5上提高了35.5%。我们还进行了一项消融研究,分析ARAG不同组成部分的影响。我们的研究结果突出了将智能体推理整合到检索增强推荐中的有效性,并为基于LLM的个性化提供了新方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ARAG(Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation框架)在个性化推荐系统中的应用。ARAG通过多智能体协作机制,将外部上下文融入大型语言模型提示中,增强了推荐系统的性能。通过四个基于LLM的智能体(用户理解智能体、自然语言推理智能体、上下文摘要智能体和项目排名智能体),ARAG能够更好地理解用户的长期和会话行为,并生成基于上下文匹配的排名推荐。实验结果表明,ARAG在NDCG@5和Hit@5指标上分别提高了42.1%和35.5%,显著优于标准RAG和基于时效性的基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- ARAG是一个基于智能体的检索增强生成框架,用于个性化推荐系统。
- ARAG通过多智能体协作机制,将外部上下文融入大型语言模型提示中。
- ARAG包括四个基于LLM的智能体,用于理解用户行为并生成推荐。
- 实验表明,ARAG在推荐系统的性能指标上显著优于标准RAG和基于时效性的基准测试。
- ARAG通过融合智能体推理,提高了检索增强推荐的效率。
- ARAG框架为LLM个性化推荐提供了新的研究方向。
点此查看论文截图

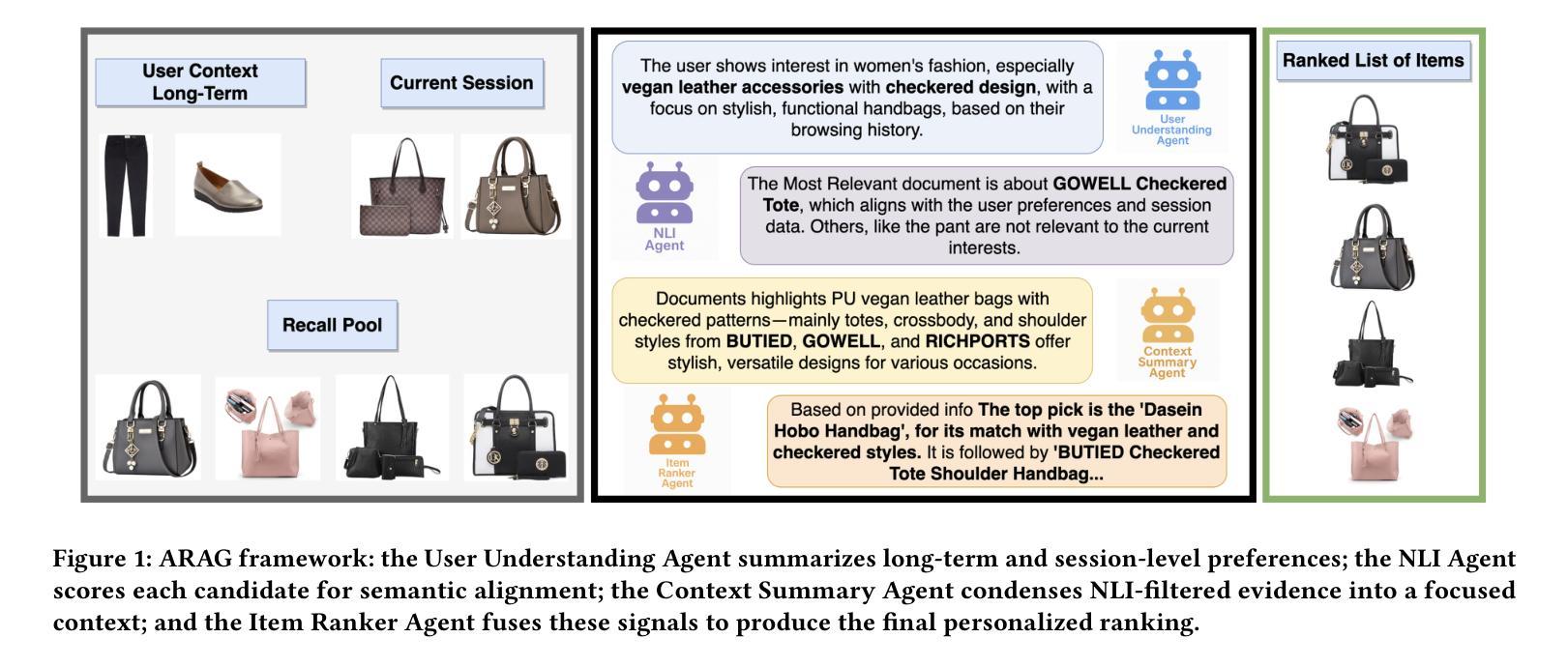
Verbal Werewolf: Engage Users with Verbalized Agentic Werewolf Game Framework
Authors:Qihui Fan, Wenbo Li, Enfu Nan, Yixiao Chen, Lei Lu, Pu Zhao, Yanzhi Wang
The growing popularity of social deduction games has created an increasing need for intelligent frameworks where humans can collaborate with AI agents, particularly in post-pandemic contexts with heightened psychological and social pressures. Social deduction games like Werewolf, traditionally played through verbal communication, present an ideal application for Large Language Models (LLMs) given their advanced reasoning and conversational capabilities. Prior studies have shown that LLMs can outperform humans in Werewolf games, but their reliance on external modules introduces latency that left their contribution in academic domain only, and omit such game should be user-facing. We propose \textbf{Verbal Werewolf}, a novel LLM-based Werewolf game system that optimizes two parallel pipelines: gameplay powered by state-of-the-art LLMs and a fine-tuned Text-to-Speech (TTS) module that brings text output to life. Our system operates in near real-time without external decision-making modules, leveraging the enhanced reasoning capabilities of modern LLMs like DeepSeek V3 to create a more engaging and anthropomorphic gaming experience that significantly improves user engagement compared to existing text-only frameworks.
随着社交推理游戏的日益普及,人类对与人工智能代理协作的智能框架的需求不断增长,特别是在心理和社会压力加剧的后疫情背景下。像狼人杀这样的社交推理游戏,传统上是通过口头交流进行的,考虑到其先进的推理和对话能力,对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一个理想的应用。早期的研究表明,LLM在狼人杀游戏中可以超越人类的表现,但它们对外部模块的依赖引入了延迟,使其仅在学术领域有所贡献,而忽视了这类游戏应该是面向用户的。我们提出了Verbal Werewolf,这是一种基于LLM的新型狼人杀游戏系统,优化了两个并行管道:由最新LLM驱动的游戏玩法和一个经过精细调整的文本到语音(TTS)模块,将文本输出转化为生动的声音。我们的系统在近实时内运行,无需外部决策模块,利用现代LLM(如DeepSeek V3)增强的推理能力,创造了一个更具吸引力和拟人化的游戏体验,与现有的纯文本框架相比,显著提高了用户参与度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着社交推理游戏日益流行,人类与AI代理人的智能协作框架需求不断增长,特别是在心理和社会压力增大的疫情后环境中。传统通过口头交流进行的社交推理游戏(如狼人游戏)是大型语言模型(LLM)的理想应用,LLM凭借先进的推理和对话能力,在游戏中展现出超越人类的表现。然而,其依赖外部模块导致的延迟问题使其仅适用于学术领域。为此,我们提出了基于LLM的狼人游戏系统——Verbal Werewolf,优化了游戏流程并引入精细调整的文本转语音(TTS)模块,将文本输出转化为生动形式。该系统利用最新LLM技术实现近实时操作,无需外部决策模块,创造更加引人入胜的人类化游戏体验,显著提高了用户参与度。
Key Takeaways
- 社交推理游戏的流行推动了人类与AI协作框架的需求增长。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在社交推理游戏中展现出色的能力。
- LLM在狼人游戏中表现超越人类。
- LLM依赖外部模块导致延迟问题。
- 提出了基于LLM的狼人游戏系统——Verbal Werewolf。
- Verbal Werewolf优化了游戏流程并引入TTS模块,提高用户体验。
点此查看论文截图


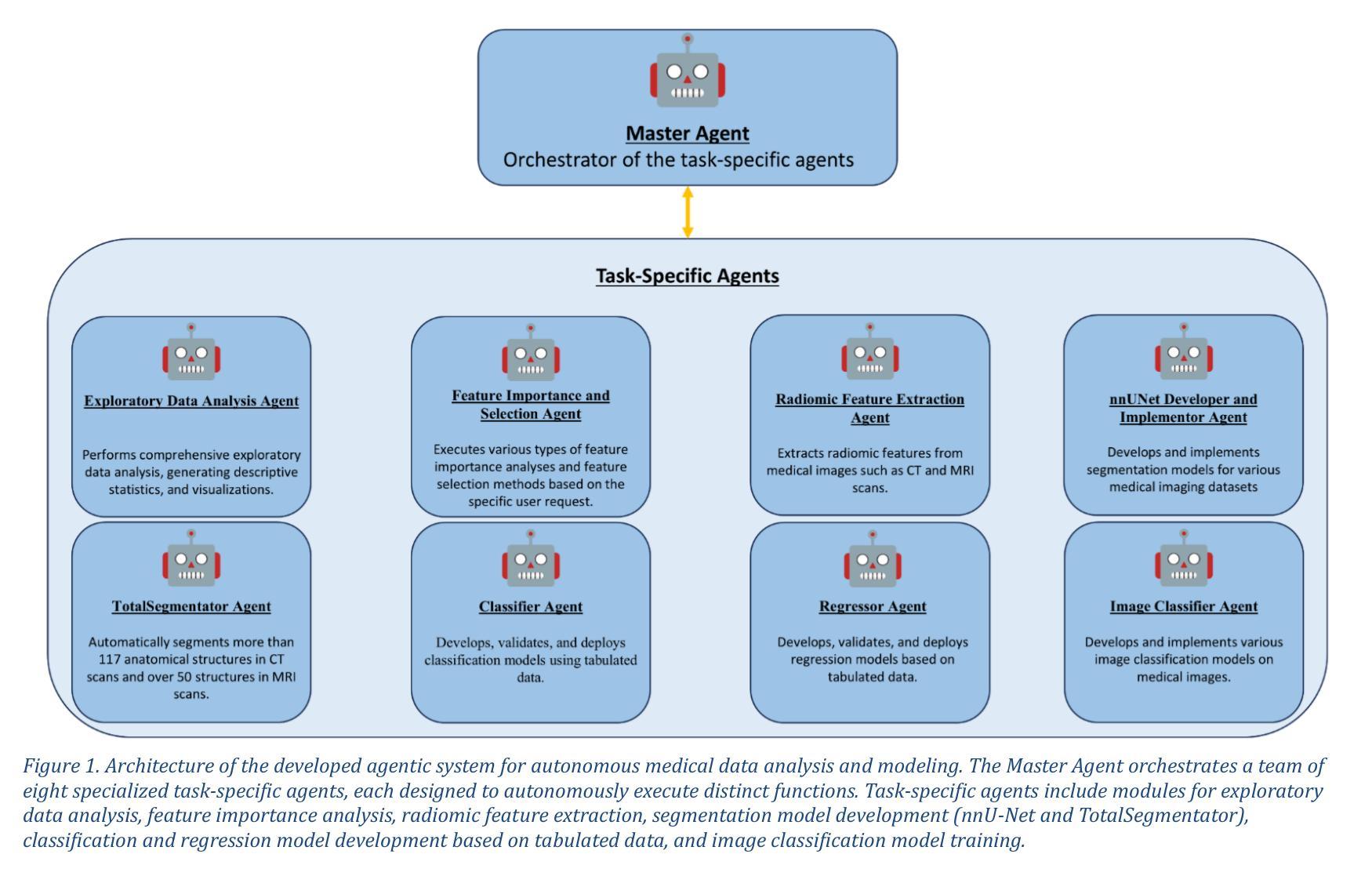
mAIstro: an open-source multi-agentic system for automated end-to-end development of radiomics and deep learning models for medical imaging
Authors:Eleftherios Tzanis, Michail E. Klontzas
Agentic systems built on large language models (LLMs) offer promising capabilities for automating complex workflows in healthcare AI. We introduce mAIstro, an open-source, autonomous multi-agentic framework for end-to-end development and deployment of medical AI models. The system orchestrates exploratory data analysis, radiomic feature extraction, image segmentation, classification, and regression through a natural language interface, requiring no coding from the user. Built on a modular architecture, mAIstro supports both open- and closed-source LLMs, and was evaluated using a large and diverse set of prompts across 16 open-source datasets, covering a wide range of imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and data types. The agents successfully executed all tasks, producing interpretable outputs and validated models. This work presents the first agentic framework capable of unifying data analysis, AI model development, and inference across varied healthcare applications, offering a reproducible and extensible foundation for clinical and research AI integration. The code is available at: https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Agentic系统为在医疗AI中自动化复杂工作流程提供了有前景的能力。我们介绍了mAIstro,这是一个开源的、自主的、多Agentic框架,用于医疗AI模型的端到端开发和部署。该系统通过自然语言接口协调探索性分析、放射组学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编码。mAIstro采用模块化架构,支持开源和闭源LLM,并使用涵盖广泛成像模式、解剖区域和数据类型的16个开源数据集的大型和多样化的提示集进行评估。代理成功执行了所有任务,产生了可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这项工作提出了第一个能够在各种医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架,为临床和研究AI集成提供了可重复和可扩展的基础。代码可在https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Agentic系统为医疗保健AI中自动化复杂工作流程提供了前景广阔的能力。本文介绍了mAIstro,这是一个开源的、自主的多Agentic框架,用于端到端开发和部署医疗AI模型。该系统通过自然语言界面进行探索性数据分析、放射学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编码。mAIstro采用模块化架构,支持开源和闭源LLM,并在涵盖广泛成像模式、解剖部位和数据类型的16个开源数据集上进行了大量和多样化的提示评估。代理成功执行所有任务,产生可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这项工作提出了第一个能够在各种医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架,为临床和研究AI集成提供了可重复和可扩展的基础。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗保健AI中实现了复杂工作流程的自动化。
- mAIstro是一个开源的、多功能的自主多Agentic框架,用于医疗AI模型的端到端开发和部署。
- mAIstro通过自然语言接口进行探索性数据分析、放射学特征提取和图像分割等任务。
- 系统无需用户编码,降低了使用门槛。
- mAIstro支持多种开源和闭源的LLM,具有模块化架构。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,代理能够成功执行任务并产生可验证的结果。
- mAIstro为临床和研究AI集成提供了可重复和可扩展的基础,是第一个统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架。
点此查看论文截图

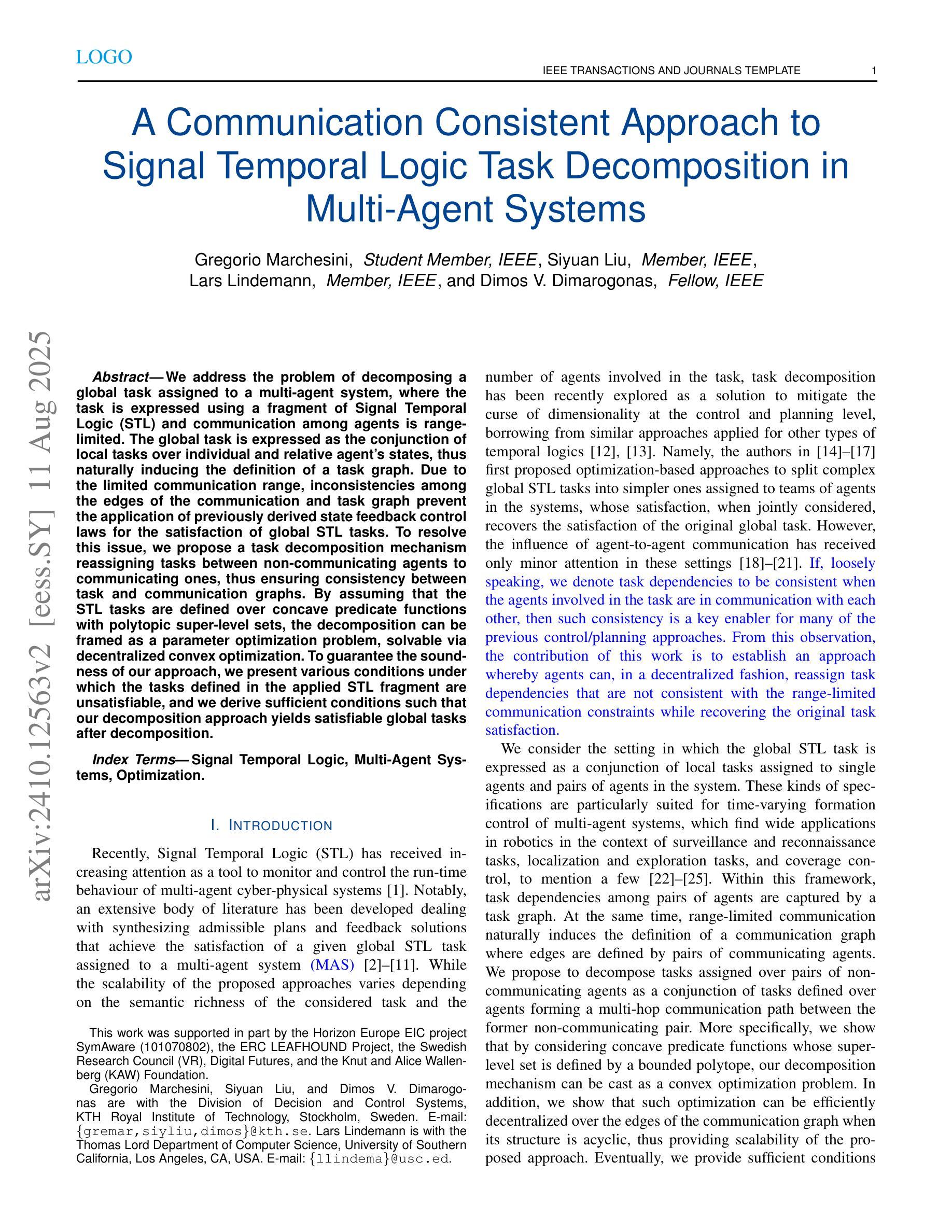
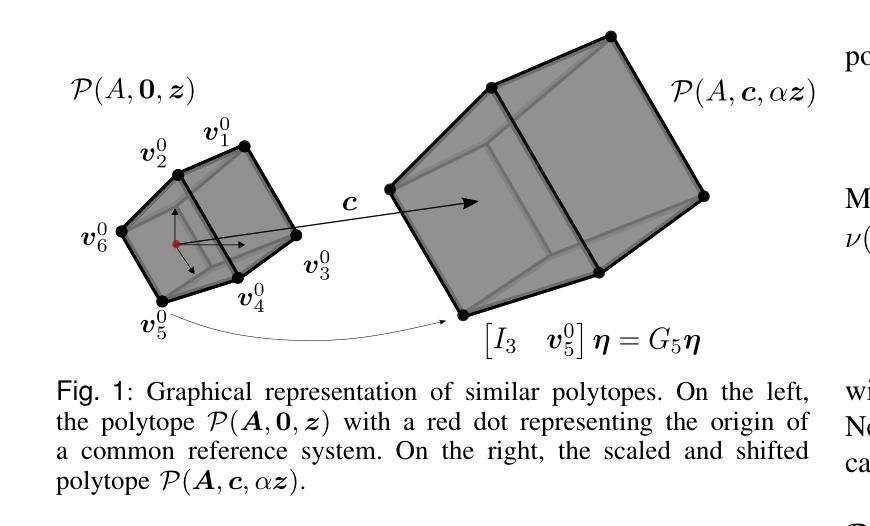
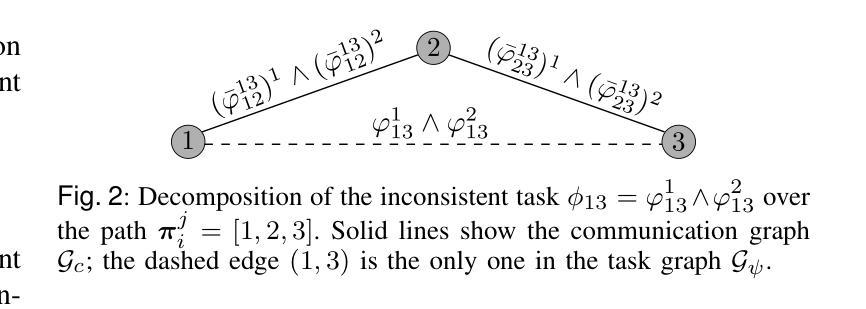
A Communication Consistent Approach to Signal Temporal Logic Task Decomposition in Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Gregorio Marchesini, Siyuan Liu, Lars Lindemann, Dimos V. Dimarogonas
We consider the problem of decomposing a global task assigned to a multi-agent system, expressed as a formula within a fragment of Signal Temporal Logic (STL), under range-limited communication. Given a global task expressed as a conjunction of local tasks defined over the individual and relative states of agents in the system, we propose representing task dependencies among agents as edges of a suitably defined task graph. At the same time, range-limited communication naturally induces the definition of a communication graph that defines which agents have access to each other’s states. Within these settings, inconsistencies arise when a task dependency between a pair of agents is not supported by a corresponding communication link due to the limited communication range. As a result, state feedback control laws previously derived to achieve the tasks’ satisfaction can not be leveraged. We propose a task decomposition mechanism to distribute tasks assigned to pairs of non-communicating agents in the system as conjunctions of tasks defined over the relative states of communicating agents, thus enforcing consistency between task and communication graphs. Assuming the super-level sets of the predicate functions composing the STL tasks are bounded polytopes, our task decomposition mechanism can be cast as a parameter optimization problem and solved via state-of-the-art decentralized convex optimization algorithms. To guarantee the soundness of our approach, we present various conditions under which the tasks defined in the applied STL fragment are unsatisfiable, and we show sufficient conditions such that our decomposition approach yields satisfiable global tasks after decomposition.
针对分配给多智能体系统的全局任务的问题,在范围受限的通信条件下,我们将该问题表达为信号时序逻辑(STL)片段中的公式。给定表达为系统中个体智能体和相对状态上定义的局部任务的并集的全局任务,我们提议将智能体之间的任务依赖关系表示为适当定义的任务图的边。同时,范围有限的通信自然地引发了通信图的定义,该定义确定了哪些智能体可以相互访问状态。在这些情况下,当一对智能体之间的任务依赖关系因通信范围有限而得不到相应的通信链接支持时,就会出现不一致性。因此,先前派生的用于实现任务满意度的状态反馈控制定律无法利用。我们提出了一种任务分解机制,将分配给系统中无法通信的智能体对的任务分布为在通信智能体的相对状态上定义的任务的并集,从而在任务图和通信图之间强制执行一致性。假设组成STL任务的谓词函数的超水平集是有界的多面体,我们的任务分解机制可以转化为参数优化问题,并通过最新的分散式凸优化算法解决。为了保证我们的方法的正确性,我们提出了在应用的STL片段中定义的任务不可满足的各种条件,并展示了足够的条件,使得我们的分解方法在分解后产生可满足的全局任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文研究了在范围受限通信下,如何将全局任务分解为多智能体系统的局部任务的问题。任务依赖关系被表示为任务图的边,而通信范围限制自然地定义了通信图。当任务依赖与通信链接不一致时,会出现不一致问题。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种任务分解机制,将非通信智能体间的任务分配给系统中的通信智能体对作为相对状态的组合任务,从而保证任务图和通信图的一致性。假设组成STL任务的谓词函数的超水平集为有界多边形,该任务分解机制可转化为参数优化问题,并通过现有的分散式凸优化算法求解。同时,本文给出了任务不可满足的条件和任务分解后全局任务可实现的充分条件。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了在范围受限通信下,如何将全局任务表达为Signal Temporal Logic(STL)内的公式并分解为多智能体系统的局部任务的问题。
- 通过定义任务图表示任务依赖关系,同时定义了通信图来表示智能体之间的通信范围。
- 当任务依赖与通信链接不一致时,会导致反馈控制律无法利用的问题。
- 提出一种任务分解机制,通过分配给通信智能体的相对状态组合任务来分布非通信智能体的任务,保证任务图和通信图的一致性。
- 任务分解机制可转化为参数优化问题,并利用现有的分散式凸优化算法进行求解。
点此查看论文截图