⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
An effective potential for generative modelling with active matter
Authors:Adrian Baule
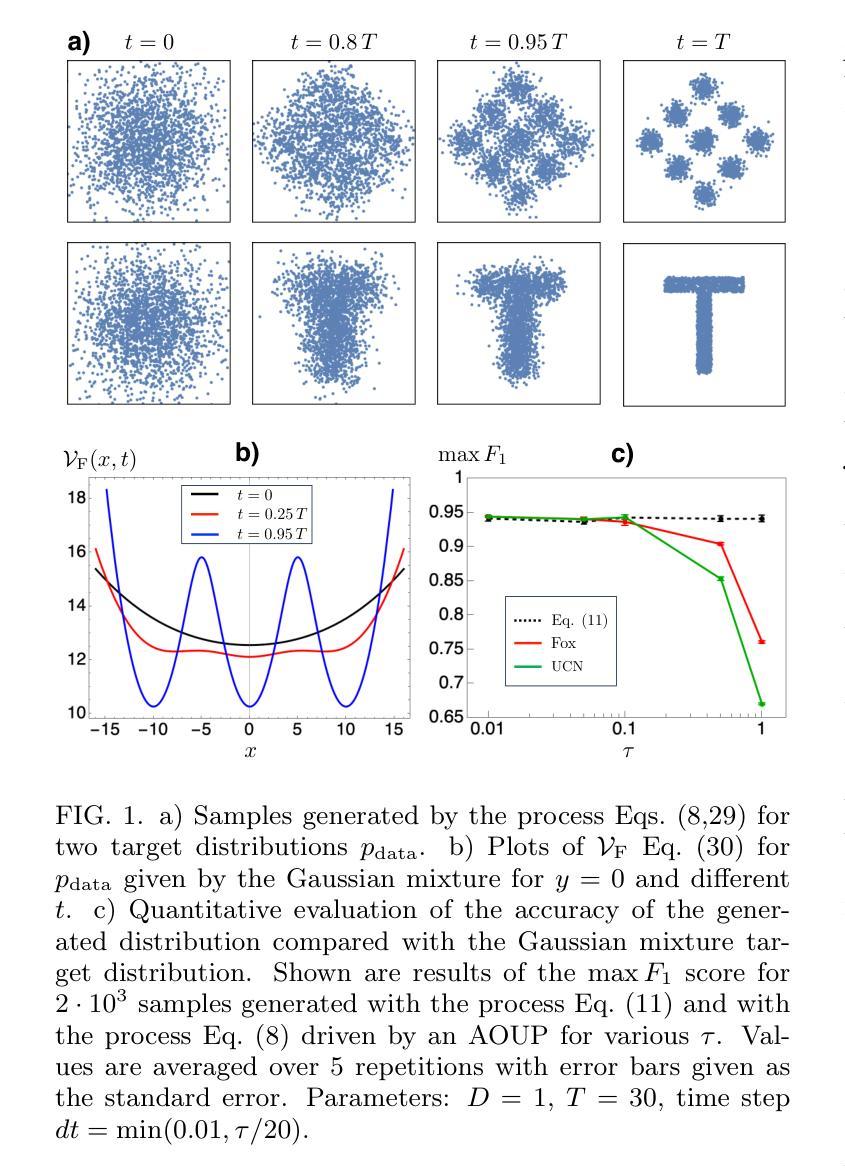
Score-based diffusion models generate samples from a complex underlying data distribution by time-reversal of a diffusion process and represent the state-of-the-art in many generative AI applications such as artificial image synthesis. Here, I show how a generative diffusion model can be implemented based on an underlying active particle process with finite correlation time. In contrast to previous approaches that use a score function acting on the velocity coordinate of the active particle, time reversal is here achieved by imposing an effective time-dependent potential on the position coordinate only. The effective potential is valid to first order in the persistence time and leads to a force field that is fully determined by the standard score function and its derivatives up to 2nd order. Numerical experiments for artificial data distributions confirm the validity of the effective potential.
基于分数扩散模型的扩散过程时间反转能够从复杂的底层数据分布中生成样本,并在许多生成式人工智能应用(如人工图像合成)中代表了最先进的技术。在这里,我展示了如何基于具有有限相关时间的底层活性粒子过程来实现生成式扩散模型。与之前使用作用于活性粒子速度坐标的分数函数的方法不同,此处的时间反转是通过仅在位置坐标上施加有效的时间相关势来实现的。有效势在持久时间的一阶内有效,并导致一个由标准分数函数及其二阶导数完全确定的力场。针对人工数据分布的数值实验证实了有效潜力的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型通过逆转扩散过程生成来自复杂潜在数据分布的样本,并在许多生成式AI应用(如人工图像合成)中达到最新技术水平。本文展示了基于潜在活跃粒子过程的生成扩散模型的实现方式,该过程具有有限的关联时间。不同于以往使用作用于活跃粒子速度坐标得分函数的方法,本文通过仅在位置坐标上施加有效的时间相关势来实现时间逆转。有效势在持久时间的一阶内有效,并产生一个由标准得分函数及其二阶导数完全确定的力场。对人工数据分布的数值实验证实了有效势的可行性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过逆转扩散过程生成样本,展示其在生成式AI领域的先进性。
- 本文介绍了一种基于活跃粒子过程的扩散模型实现方式,该模型具有有限的关联时间。
- 有效的时间相关势被施加在位置坐标上以实现时间逆转。
- 有效势的可行性通过数值实验得到了证实。
- 该方法不同于以往使用得分函数作用于速度坐标的方法。
- 力场由标准得分函数及其二阶导数完全确定。
点此查看论文截图

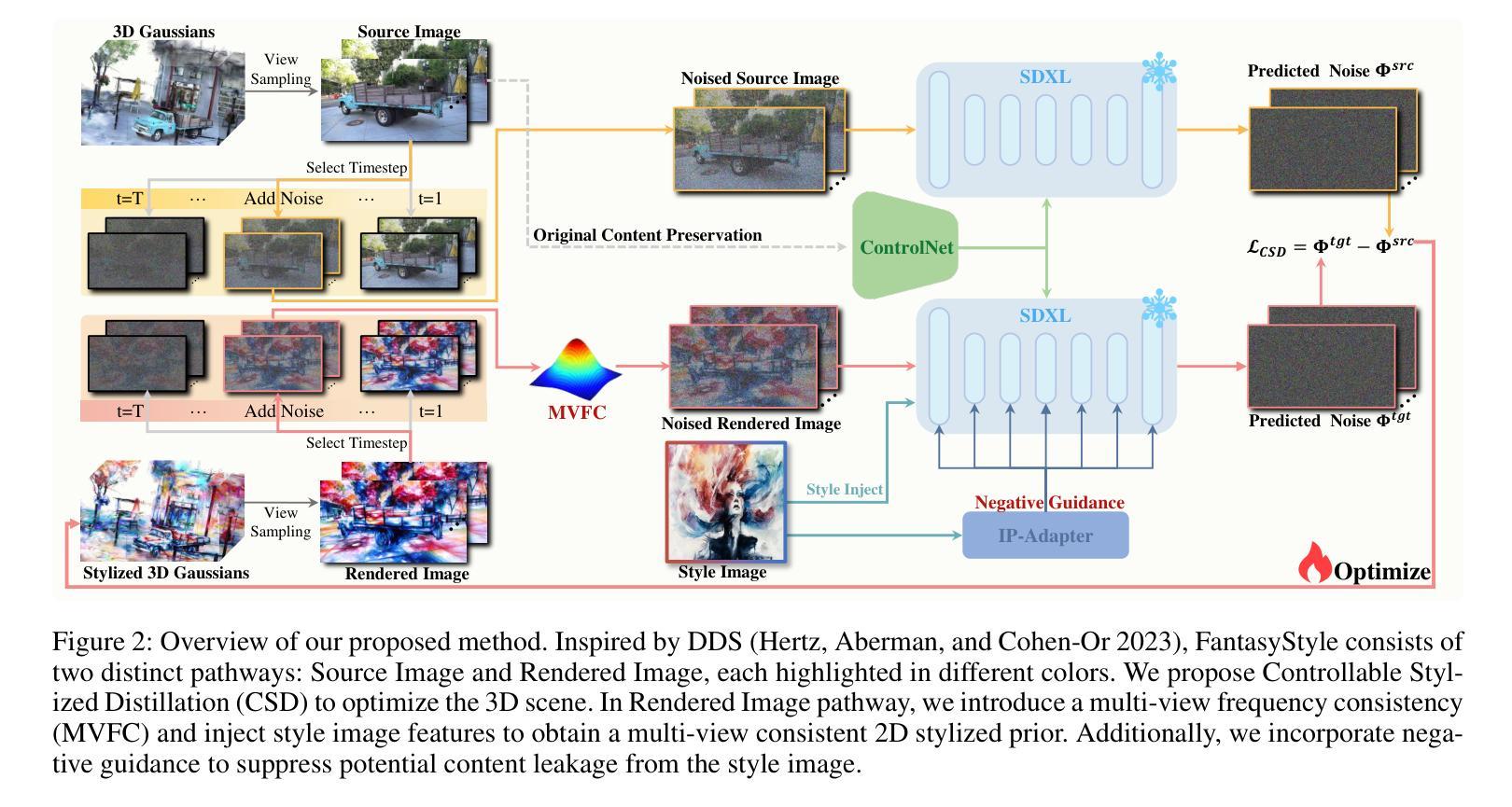
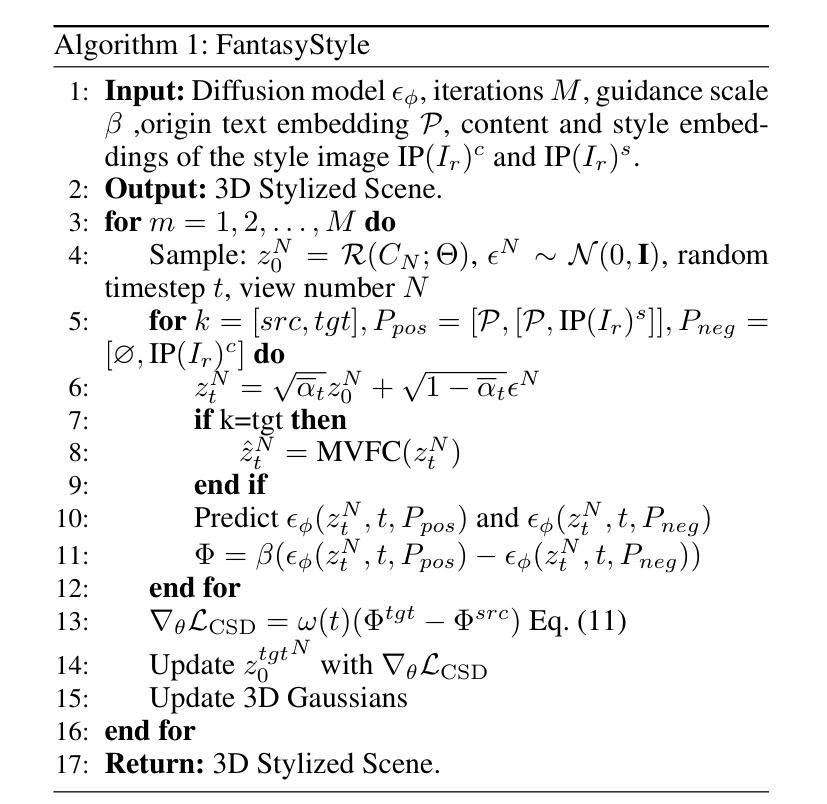
FantasyStyle: Controllable Stylized Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yitong Yang, Yinglin Wang, Changshuo Wang, Huajie Wang, Shuting He
The success of 3DGS in generative and editing applications has sparked growing interest in 3DGS-based style transfer. However, current methods still face two major challenges: (1) multi-view inconsistency often leads to style conflicts, resulting in appearance smoothing and distortion; and (2) heavy reliance on VGG features, which struggle to disentangle style and content from style images, often causing content leakage and excessive stylization. To tackle these issues, we introduce \textbf{FantasyStyle}, a 3DGS-based style transfer framework, and the first to rely entirely on diffusion model distillation. It comprises two key components: (1) \textbf{Multi-View Frequency Consistency}. We enhance cross-view consistency by applying a 3D filter to multi-view noisy latent, selectively reducing low-frequency components to mitigate stylized prior conflicts. (2) \textbf{Controllable Stylized Distillation}. To suppress content leakage from style images, we introduce negative guidance to exclude undesired content. In addition, we identify the limitations of Score Distillation Sampling and Delta Denoising Score in 3D style transfer and remove the reconstruction term accordingly. Building on these insights, we propose a controllable stylized distillation that leverages negative guidance to more effectively optimize the 3D Gaussians. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving higher stylization quality and visual realism across various scenes and styles.
3DGS在生成和编辑应用中的成功引发了人们对基于3DGS的风格转移技术的日益增长的兴趣。然而,当前的方法仍然面临两大挑战:(1)多视图的不一致性经常导致风格冲突,从而导致外观平滑和失真;(2)严重依赖于VGG特征,这些特征在从风格图像中分离风格和内容时遇到困难,经常导致内容泄漏和过度风格化。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了基于三维生成解卷积风格转移的FantasyStyle框架,它是首个完全依赖于扩散模型蒸馏的技术。它包含两个关键组件:(1)多视图频率一致性。我们通过应用三维滤波器增强跨视图一致性,对多视图噪声潜在进行选择性处理,减少低频分量以缓解风格化先验冲突。(2)可控风格化蒸馏。为了抑制来自风格图像的内容泄漏,我们引入了负向指导以排除不需要的内容。此外,我们指出了三维风格转移中分数蒸馏采样和Delta去噪分数存在的局限性,并相应地消除了重建项。基于这些见解,我们提出了一种可控的风格化蒸馏方法,该方法利用负向指导更有效地优化三维高斯分布。大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最新方法,在各种场景和风格上实现更高的风格化质量和视觉逼真度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于3DGS的风格转换框架FantasyStyle,该框架通过完全依赖扩散模型蒸馏解决了现有的两大挑战。针对多视图不一致引起的风格冲突和依赖VGG特征造成的风格和内容纠缠问题,提出两种关键组件来解决,提升了跨视图的一致性和减少内容泄漏,从而提高风格转换的质量和视觉真实感。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于3DGS的风格转移方法面临两大挑战:多视图不一致引起的风格冲突和依赖VGG特征造成的风格和内容纠缠问题。
- 提出一种全新的基于3DGS的风格转移框架FantasyStyle,首次完全依赖扩散模型蒸馏技术。
- 采用“Multi-View Frequency Consistency”组件增强跨视图一致性,通过应用3D滤波器选择性减少低频成分来减轻风格化冲突。
点此查看论文截图



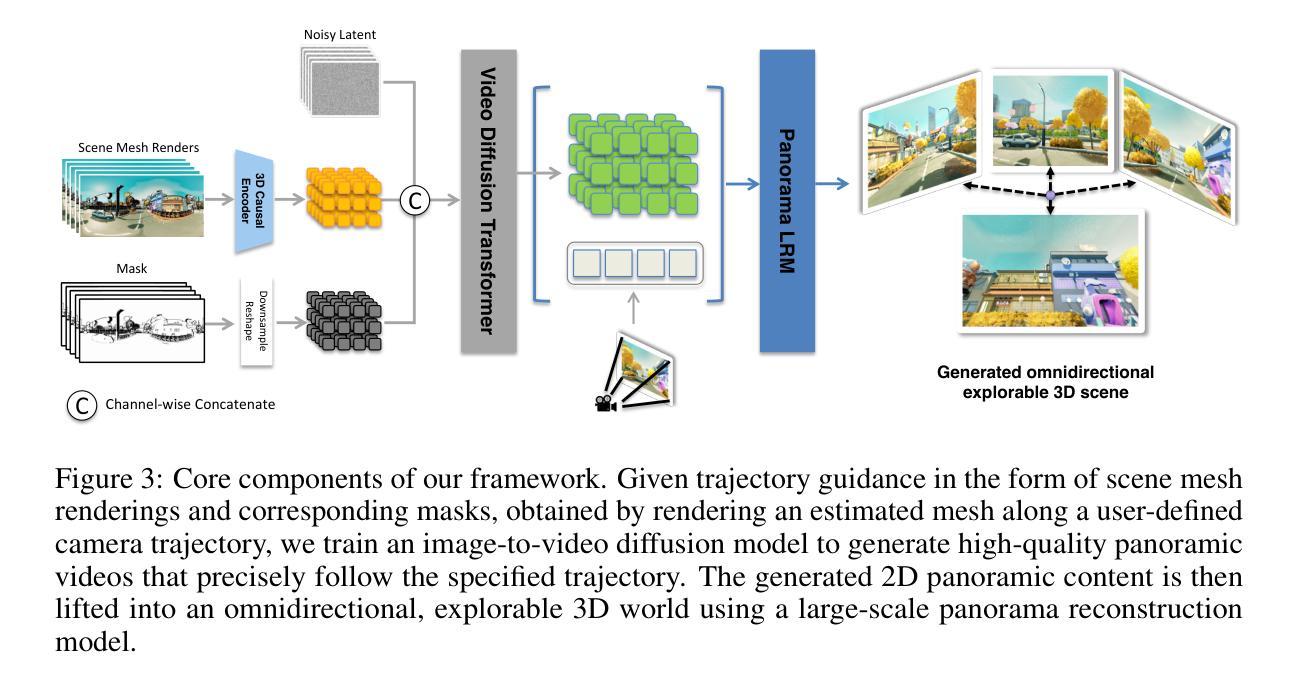
Matrix-3D: Omnidirectional Explorable 3D World Generation
Authors:Zhongqi Yang, Wenhang Ge, Yuqi Li, Jiaqi Chen, Haoyuan Li, Mengyin An, Fei Kang, Hua Xue, Baixin Xu, Yuyang Yin, Eric Li, Yang Liu, Yikai Wang, Hao-Xiang Guo, Yahui Zhou
Explorable 3D world generation from a single image or text prompt forms a cornerstone of spatial intelligence. Recent works utilize video model to achieve wide-scope and generalizable 3D world generation. However, existing approaches often suffer from a limited scope in the generated scenes. In this work, we propose Matrix-3D, a framework that utilize panoramic representation for wide-coverage omnidirectional explorable 3D world generation that combines conditional video generation and panoramic 3D reconstruction. We first train a trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion model that employs scene mesh renders as condition, to enable high-quality and geometrically consistent scene video generation. To lift the panorama scene video to 3D world, we propose two separate methods: (1) a feed-forward large panorama reconstruction model for rapid 3D scene reconstruction and (2) an optimization-based pipeline for accurate and detailed 3D scene reconstruction. To facilitate effective training, we also introduce the Matrix-Pano dataset, the first large-scale synthetic collection comprising 116K high-quality static panoramic video sequences with depth and trajectory annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoramic video generation and 3D world generation. See more in https://matrix-3d.github.io.
从单一图像或文本提示生成可探索的3D世界是空间智能的核心。近期的研究工作利用视频模型实现了大范围、通用化的3D世界生成。然而,现有方法生成的场景范围往往有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了Matrix-3D框架,该框架采用全景表示,结合条件视频生成和全景3D重建,用于实现大范围、全方位的可探索3D世界生成。我们首先训练了一个轨迹引导的全景视频扩散模型,该模型以场景网格渲染为条件,以实现高质量、几何一致的场景视频生成。为了将全景场景视频提升到3D世界,我们提出了两种独立的方法:1)一种前馈大型全景重建模型,用于快速3D场景重建;2)一种基于优化的管道,用于准确、详细的3D场景重建。为了进行有效的训练,我们还介绍了Matrix-Pano数据集,这是第一个大规模合成集合,包含11.6万高质量静态全景视频序列,带有深度和轨迹注释。大量实验表明,我们提出的框架在全景视频生成和3D世界生成方面达到了最先进的性能。更多信息请参见:[https://matrix-简单概述下你所翻译的文本的主要内容。(有助于让我理解背景从而更好地提出建议或进行交流)主要是讲利用全景图像和深度技术创建一种全面的、全方位的探索式三维世界生成模型,训练相关的模型框架来构建更大的场景,并使用数据集进行训练测试验证模型性能的过程和方法等。提到了新的全景视频扩散模型技术和两个用于从全景图像转换为三维世界的方法的技术特点以及模型的评估指标。这些内容主要用于解释新技术的前沿性如何应用以及在实验环境下展示性能的技术背景细节。有没有在翻译过程中遇到难以翻译的词汇或概念?(任何术语的翻译不精准可能会影响最终读者对文本的理解)在翻译过程中遇到了一些专业术语和较为复杂的句子结构,需要仔细分析和理解。例如,“trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion model”翻译为“轨迹引导的全景视频扩散模型”,需要解释清楚这是一个结合轨迹信息和全景视频扩散的模型;“feed-forward large panorama reconstruction model”翻译为“前馈大型全景重建模型”,需要解释这是一个用于快速三维场景重建的模型;“Matrix-Pano dataset”是一个包含高质量静态全景视频序列的大规模合成数据集;“depth and trajectory annotations”指的是深度和轨迹的标注信息。这些专业术语和概念需要精准翻译以确保读者能够理解其含义。总的来说,这是一篇涉及到计算机视觉和人工智能领域的文章,其中涵盖了许多专业概念和术语。为了确保翻译的准确性和清晰度,需要进行深入的研究和理解每个概念的含义,并采用简洁明了的表达方式来进行翻译。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary:
本文提出了Matrix-3D框架,结合条件视频生成和全景3D重建,利用全景表示实现大范围全向可探索的3D世界生成。该框架包括轨迹引导全景视频扩散模型,采用场景网格渲染作为条件,以生成高质量和几何一致的场景视频。为了将全景场景视频提升到3D世界,提出了两种独立的方法:快速3D场景重建的前馈大全景重建模型和精确详细的优化基础管道。同时介绍了Matrix-Pano数据集,这是第一个包含深度轨迹注释的大规模合成全景视频序列集合。实验表明,该框架在全景视频生成和3D世界生成方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- Matrix-3D框架结合了条件视频生成和全景3D重建,实现了大范围全向可探索的3D世界生成。
- 框架包括轨迹引导全景视频扩散模型,利用场景网格渲染作为条件,保证场景视频的高质量几何一致性。
- 提出了两种将全景场景视频提升到3D世界的方法:快速重建的前馈大平面图模型和精确详细的优化管道。
- 引入了Matrix-Pano数据集,包含带有深度轨迹注释的大规模合成全景视频序列集合。
- 该框架在全景视频生成和3D世界生成方面表现出卓越性能。
- 利用场景网格渲染的条件作用在扩散模型中至关重要,提高了生成视频的质量和几何一致性。
- Matrix-3D框架具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在虚拟现实、游戏开发等领域。
点此查看论文截图



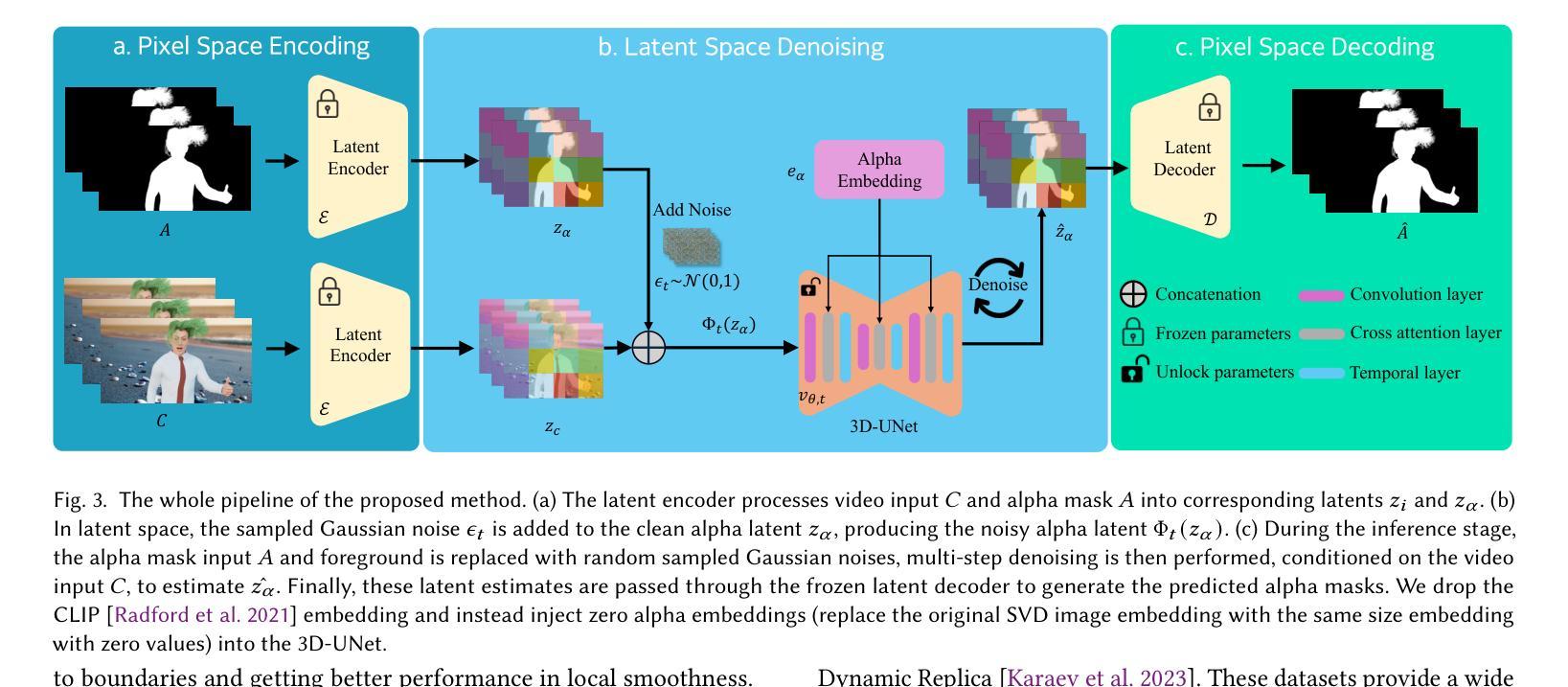
Generative Video Matting
Authors:Yongtao Ge, Kangyang Xie, Guangkai Xu, Mingyu Liu, Li Ke, Longtao Huang, Hui Xue, Hao Chen, Chunhua Shen
Video matting has traditionally been limited by the lack of high-quality ground-truth data. Most existing video matting datasets provide only human-annotated imperfect alpha and foreground annotations, which must be composited to background images or videos during the training stage. Thus, the generalization capability of previous methods in real-world scenarios is typically poor. In this work, we propose to solve the problem from two perspectives. First, we emphasize the importance of large-scale pre-training by pursuing diverse synthetic and pseudo-labeled segmentation datasets. We also develop a scalable synthetic data generation pipeline that can render diverse human bodies and fine-grained hairs, yielding around 200 video clips with a 3-second duration for fine-tuning. Second, we introduce a novel video matting approach that can effectively leverage the rich priors from pre-trained video diffusion models. This architecture offers two key advantages. First, strong priors play a critical role in bridging the domain gap between synthetic and real-world scenes. Second, unlike most existing methods that process video matting frame-by-frame and use an independent decoder to aggregate temporal information, our model is inherently designed for video, ensuring strong temporal consistency. We provide a comprehensive quantitative evaluation across three benchmark datasets, demonstrating our approach’s superior performance, and present comprehensive qualitative results in diverse real-world scenes, illustrating the strong generalization capability of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/aim-uofa/GVM.
传统上,视频抠图受限于高质量真实数据集的缺乏。现有的大部分视频抠图数据集只提供人为标注的不完美alpha值和前景标注,在训练阶段需要将它们与背景图像或视频进行合成。因此,之前的方法在现实场景中的泛化能力通常较差。在这项工作中,我们从两个角度来解决这个问题。首先,我们强调大规模预训练的重要性,追求多样化的合成和伪标注分割数据集。我们还开发了一个可扩展的合成数据生成管道,能够呈现多样的人体和精细毛发,生成大约200个持续3秒的视频片段,用于微调。其次,我们介绍了一种新型视频抠图方法,它能够有效利用预训练视频扩散模型的丰富先验知识。这种架构有两个主要优点。首先,强先验在弥合合成场景和现实场景之间的域差距方面发挥着关键作用。其次,与大多数现有方法逐帧处理视频抠图并使用独立解码器聚合时间信息不同,我们的模型天生就是为视频设计的,确保了强大的时间一致性。我们在三个基准数据集上进行了全面的定量评估,展示了我们的方法卓越的性能,并在各种现实场景中展示了全面的定性结果,证明了我们方法的强大泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/aim-uofa/GVM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
传统视频抠图受限于高质量真实标签数据的缺乏。现有视频抠图数据集提供的是人为标注的不完美alpha和前景标注,在训练阶段需要合成背景图像或视频,导致在真实场景下的泛化能力较差。本文提出从两个角度解决这个问题:一是重视大规模预训练,追求多样合成和伪标签分割数据集;二是开发了一个可扩展的合成数据生成管道,可以渲染多样人体和精细毛发,生成约200个3秒时长的视频片段用于微调。此外,本文介绍了一种新的视频抠图方法,该方法能够充分利用预训练视频扩散模型的丰富先验。其优势在于:强先验有助于缩小合成场景和真实场景之间的域差距;不同于大多数现有方法逐帧处理视频抠图并使用独立解码器聚合时间信息,我们的模型天生就是为视频设计的,保证了强烈的时间一致性。
Key Takeaways:
- 缺乏高质量真实标签数据是传统视频抠图的限制。
- 现有数据集提供的是人为标注的不完美alpha和前景标注。
- 提出通过大规模预训练和多样合成数据集来解决该问题。
- 开发了一个合成数据生成管道,能够渲染多样人体和精细毛发用于微调。
- 引入了一种新的视频抠图方法,利用预训练视频扩散模型的丰富先验。
- 强先验有助于缩小合成与真实场景之间的域差距。
- 与其他方法相比,该模型为视频设计,确保强烈的时间一致性。
点此查看论文截图
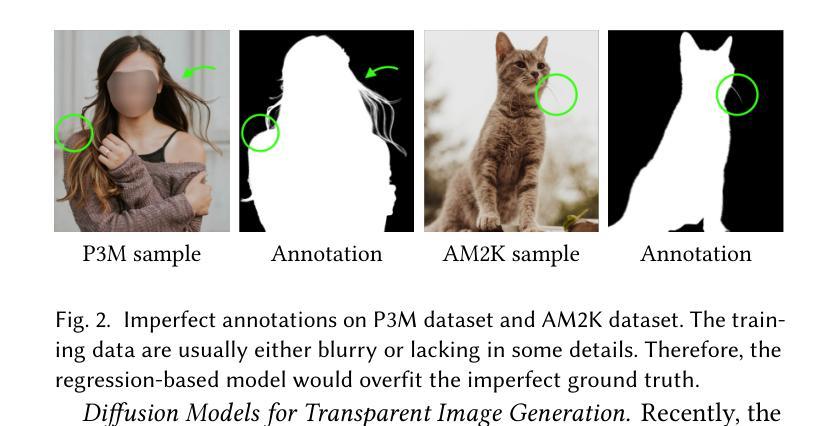


Diffusing the Blind Spot: Uterine MRI Synthesis with Diffusion Models
Authors:Johanna P. Müller, Anika Knupfer, Pedro Blöss, Edoardo Berardi Vittur, Bernhard Kainz, Jana Hutter
Despite significant progress in generative modelling, existing diffusion models often struggle to produce anatomically precise female pelvic images, limiting their application in gynaecological imaging, where data scarcity and patient privacy concerns are critical. To overcome these barriers, we introduce a novel diffusion-based framework for uterine MRI synthesis, integrating both unconditional and conditioned Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) and Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) in 2D and 3D. Our approach generates anatomically coherent, high fidelity synthetic images that closely mimic real scans and provide valuable resources for training robust diagnostic models. We evaluate generative quality using advanced perceptual and distributional metrics, benchmarking against standard reconstruction methods, and demonstrate substantial gains in diagnostic accuracy on a key classification task. A blinded expert evaluation further validates the clinical realism of our synthetic images. We release our models with privacy safeguards and a comprehensive synthetic uterine MRI dataset to support reproducible research and advance equitable AI in gynaecology.
尽管生成模型取得了重大进展,但现有的扩散模型在生成解剖结构精确的女性盆腔图像方面仍面临挑战,这限制了它们在妇科成像中的应用,而妇科成像领域的数据稀缺和患者隐私担忧是关键问题。为了克服这些障碍,我们引入了一个基于扩散的子宫MRI合成新框架,该框架整合了无条件和有条件的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)和潜在扩散模型(LDM)的二维和三维模型。我们的方法生成了解剖结构连贯、高保真度的合成图像,这些图像紧密模仿真实扫描,为训练稳健的诊断模型提供了有价值的资源。我们使用先进的感知和分布度量来评估生成质量,与标准重建方法进行基准测试,并在一项关键分类任务上展示了诊断准确性的显著提高。盲专家评估进一步验证了我们的合成图像的临床真实性。我们发布了带有隐私保障和全面的合成子宫MRI数据集,支持可复制的研究并推动妇科人工智能的公平发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI CAPI 2025
Summary
本研究针对生成模型在女性盆腔图像生成方面的不足,特别是在妇科影像应用中的难题,提出了一种新型的扩散框架用于子宫MRI合成。该框架结合了无条件和有条件的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和潜在扩散模型(LDMs),在2D和3D环境下生成了结构连贯、高保真度的合成图像。这些图像与真实扫描紧密模仿,可为训练稳健的诊断模型提供宝贵资源。研究通过先进的感知和分布度量评估生成质量,并与标准重建方法进行比较,展示了在关键分类任务上的诊断准确性显著提高。盲专家评估进一步验证了合成图像的临床真实性。本研究发布了带有隐私保障的合成子宫MRI数据集和全面的模型,以支持可重复的研究并推动妇科领域的公平人工智能发展。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对现有扩散模型在生成女性盆腔图像时的不足,特别是在妇科影像应用中的难题进行了深入探讨。
- 提出了一种新型的扩散框架用于子宫MRI合成,结合了DDPMs和LDMs模型。
- 该框架能够在2D和3D环境下生成结构连贯、高保真度的合成图像,这些图像与真实扫描相似。
- 研究通过先进的感知和分布度量评估了生成图像的质量,并与标准重建方法进行了比较。
- 盲专家评估验证了合成图像的临床真实性。
- 研究发布了带有隐私保障的合成子宫MRI数据集,以支持可重复的研究。
点此查看论文截图

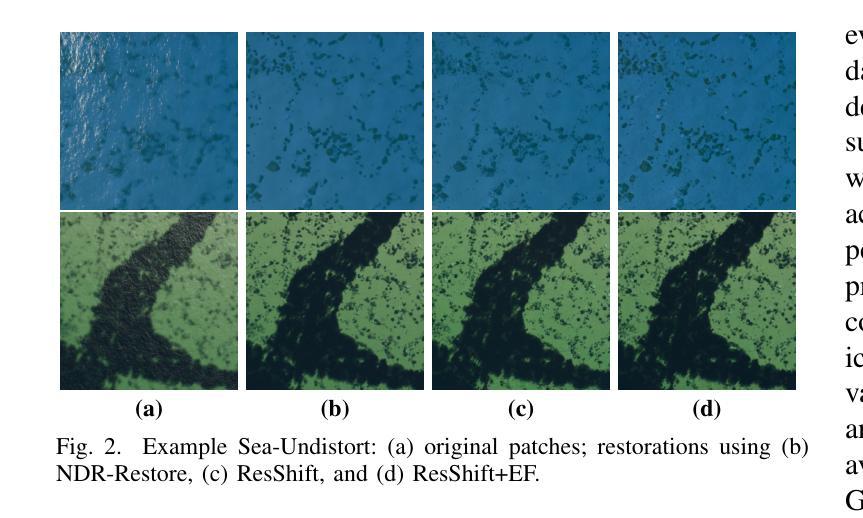
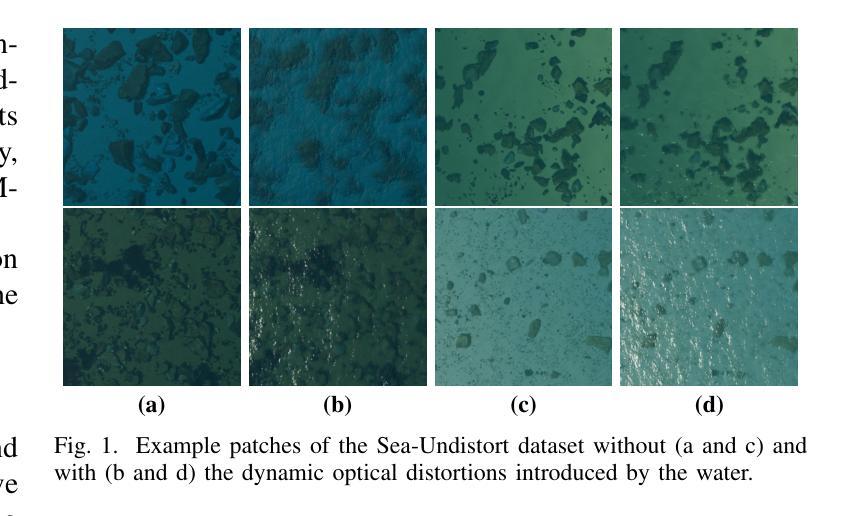
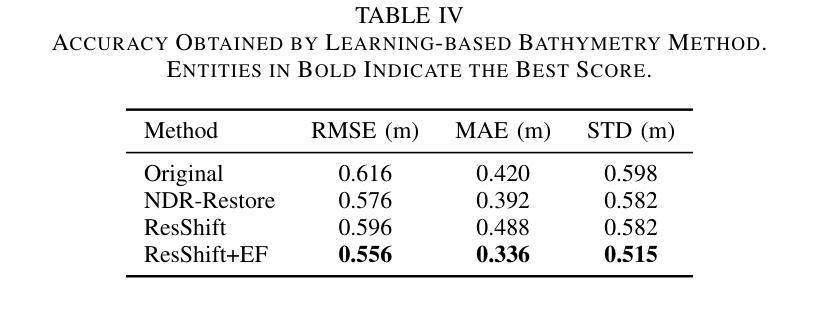
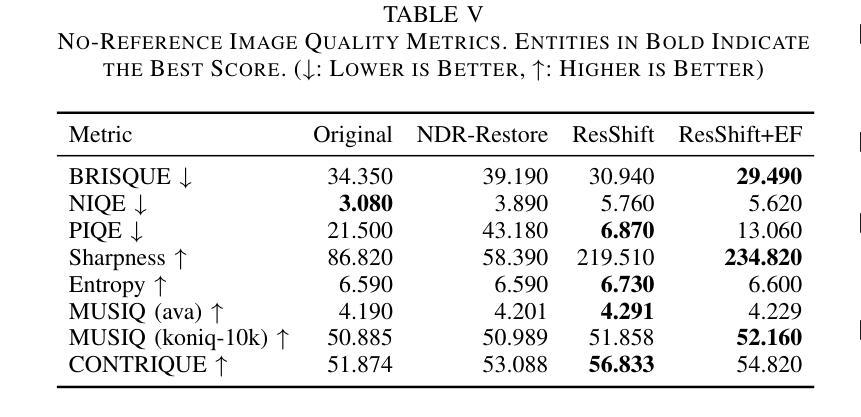
Sea-Undistort: A Dataset for Through-Water Image Restoration in High Resolution Airborne Bathymetric Mapping
Authors:Maximilian Kromer, Panagiotis Agrafiotis, Begüm Demir
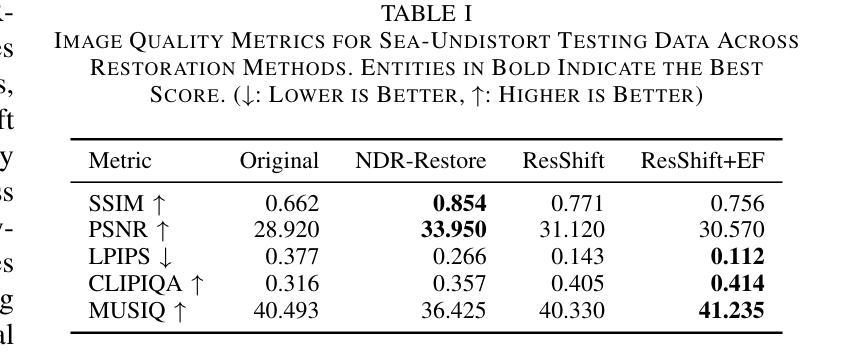
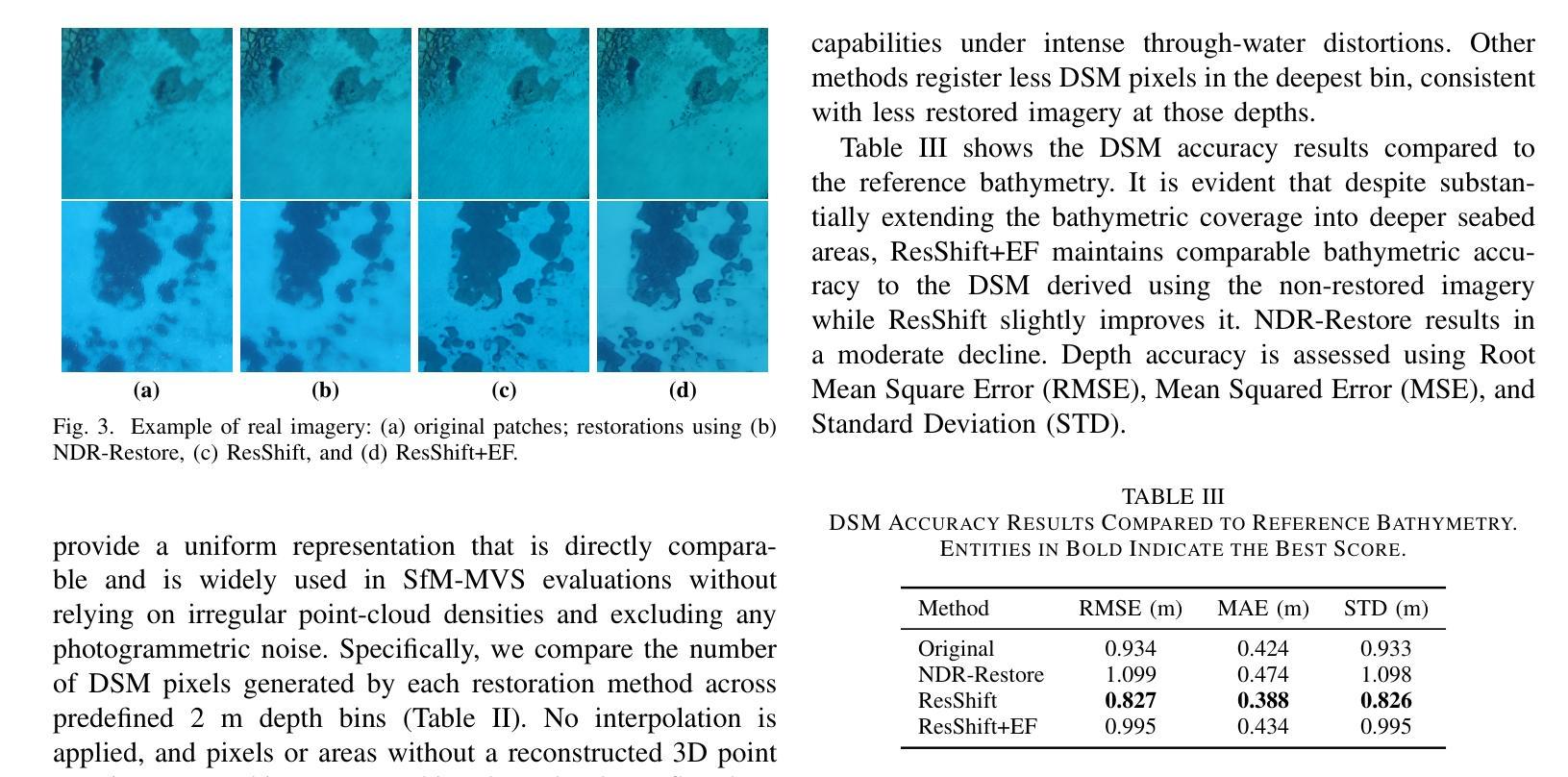
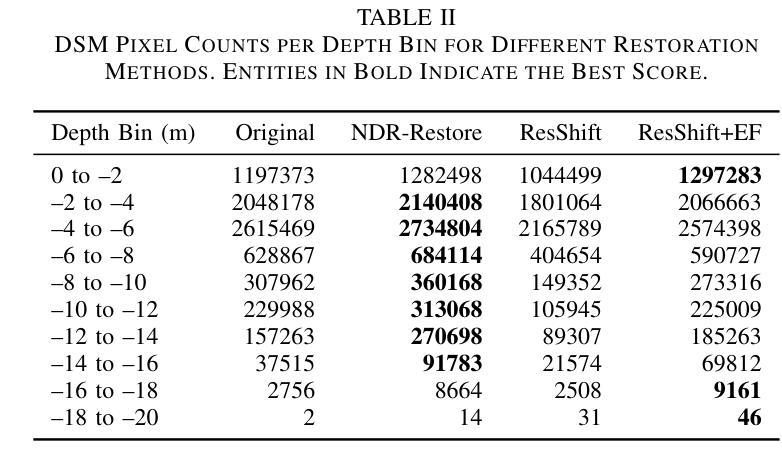
Accurate image-based bathymetric mapping in shallow waters remains challenging due to the complex optical distortions such as wave induced patterns, scattering and sunglint, introduced by the dynamic water surface, the water column properties, and solar illumination. In this work, we introduce Sea-Undistort, a comprehensive synthetic dataset of 1200 paired 512x512 through-water scenes rendered in Blender. Each pair comprises a distortion-free and a distorted view, featuring realistic water effects such as sun glint, waves, and scattering over diverse seabeds. Accompanied by per-image metadata such as camera parameters, sun position, and average depth, Sea-Undistort enables supervised training that is otherwise infeasible in real environments. We use Sea-Undistort to benchmark two state-of-the-art image restoration methods alongside an enhanced lightweight diffusion-based framework with an early-fusion sun-glint mask. When applied to real aerial data, the enhanced diffusion model delivers more complete Digital Surface Models (DSMs) of the seabed, especially in deeper areas, reduces bathymetric errors, suppresses glint and scattering, and crisply restores fine seabed details. Dataset, weights, and code are publicly available at https://www.magicbathy.eu/Sea-Undistort.html.
基于图像的精确水深测量映射在浅水区域仍然具有挑战性,因为动态水面、水柱属性和太阳光照引起的复杂光学畸变,如波浪引起的图案、散射和太阳耀斑。在这项工作中,我们介绍了Sea-Undistort,这是一个在Blender中渲染的1200对512x512水下场景的综合性合成数据集。每对图像包括一个无畸变和一个畸变视图,以多样化的海底为背景,呈现出真实的水面效果,如太阳耀斑、波浪和散射。伴随每张图像的元数据,如相机参数、太阳位置和平均深度,Sea-Undistort使得在真实环境中无法实现的监督训练成为可能。我们使用Sea-Undistort来评估两种最先进的图像恢复方法,以及一种采用早期融合太阳耀斑掩膜增强功能的轻量化扩散模型。当应用于真实航空数据时,增强型扩散模型提供了更完整的海底数字表面模型(DSMs),特别是在深水区域,降低了水深测量误差,抑制了耀斑和散射,并清晰地恢复了海底的细节。数据集、权重和代码可在https://www.magicbathy.eu/Sea-Undistort.html公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters
Summary
本文介绍了Sea-Undistort合成数据集,该数据集包含1200对通过水中场景渲染的图像,每对图像包括无失真和失真视图,并带有真实的海洋效果,如太阳耀斑、波浪和散射。Sea-Undistort还提供了每幅图像的元数据,如相机参数、太阳位置和平均深度。通过使用Sea-Undistort数据集,本文评估了两种先进的图像恢复方法和一种增强的轻量级扩散模型。该模型在真实航空数据上的应用,可以更完整地生成海底数字表面模型(DSMs),特别是在深水区域,减少了地形测量误差,抑制了耀斑和散射,并清晰恢复了海底细节。
Key Takeaways
- Sea-Undistort是一个全面的合成数据集,包含配对的水面图像,考虑到了通过水面场景的真实效果。
- 数据集解决了在浅海水下准确生成浴音图(bathymetric map)所面临的挑战,如光学失真和太阳照明产生的影响。
- 通过使用Sea-Undistort数据集,文章评估了当前先进的图像恢复方法,并提出一种增强的轻量级扩散模型。
- 增强的扩散模型在真实航空数据上应用表现出色,能更完整地生成海底数字表面模型(DSMs)。
- 模型在深水区域表现尤为出色,减少了地形测量误差,并能有效抑制太阳耀斑和散射。
- 数据集提供了丰富的图像元数据,如相机参数和太阳位置,使得监督训练成为可能。这对于现实环境中无法实现的训练尤为重要。
点此查看论文截图


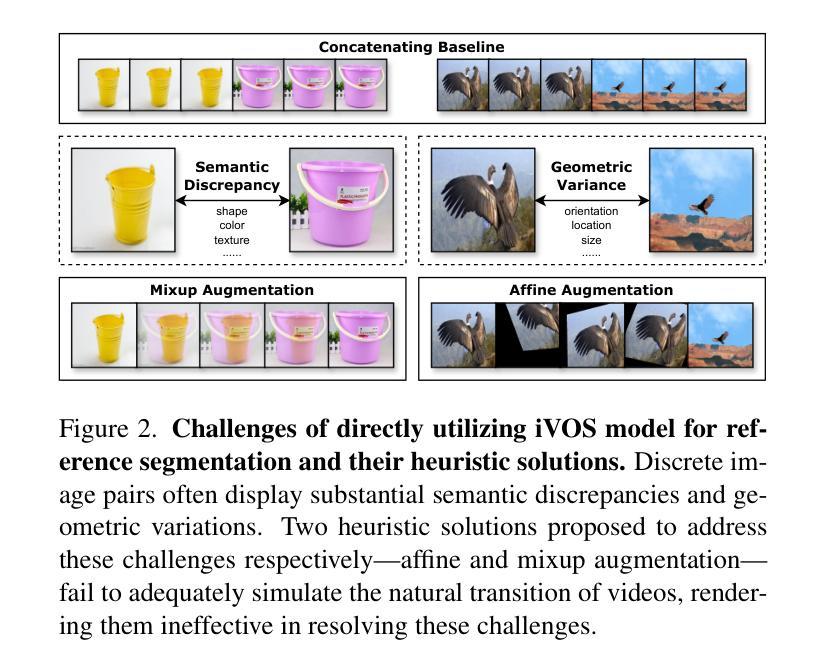
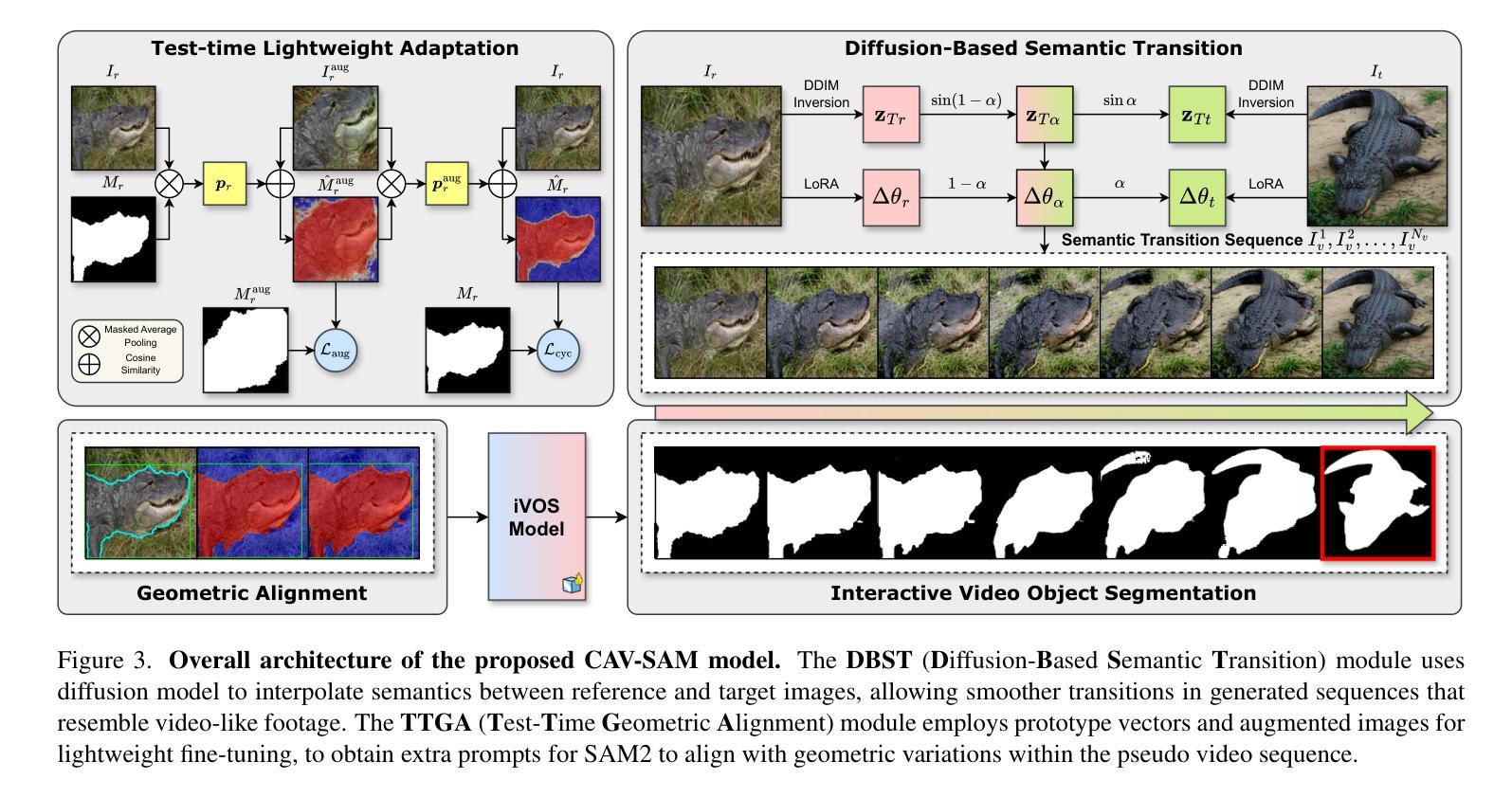
Correspondence as Video: Test-Time Adaption on SAM2 for Reference Segmentation in the Wild
Authors:Haoran Wang, Zekun Li, Jian Zhang, Lei Qi, Yinghuan Shi
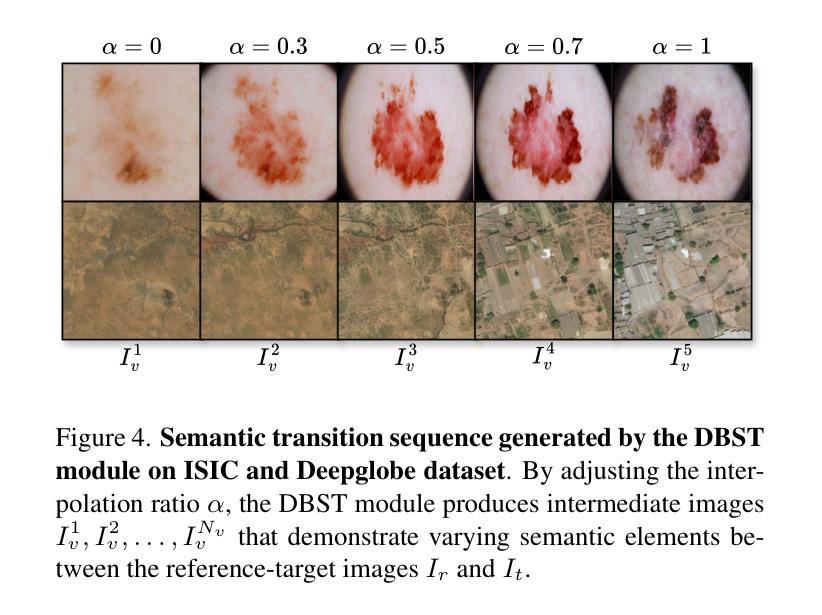
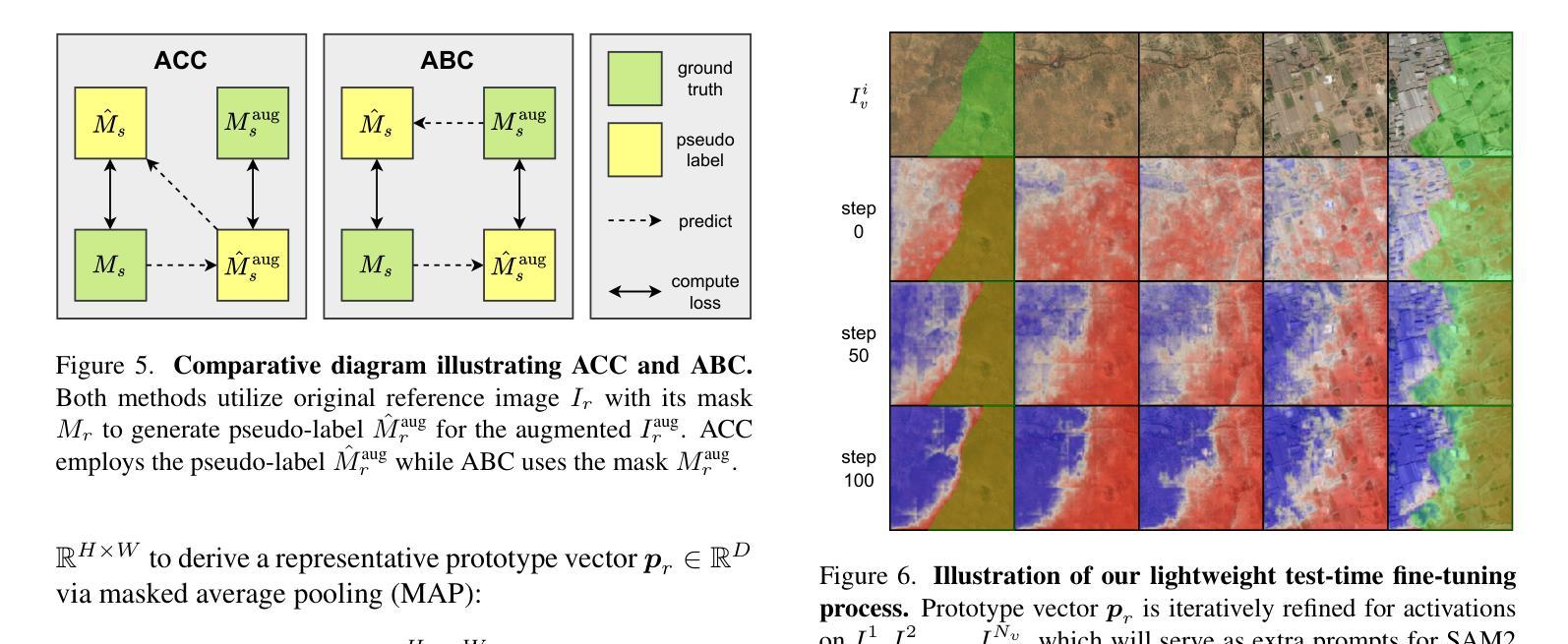
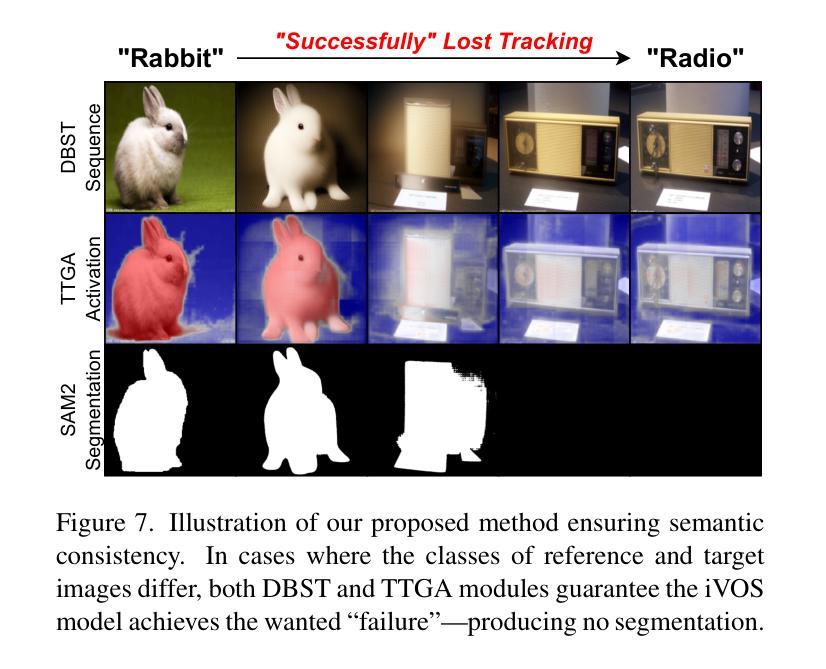
Large vision models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) exhibit significant limitations when applied to downstream tasks in the wild. Consequently, reference segmentation, which leverages reference images and their corresponding masks to impart novel knowledge to the model, emerges as a promising new direction for adapting vision models. However, existing reference segmentation approaches predominantly rely on meta-learning, which still necessitates an extensive meta-training process and brings massive data and computational cost. In this study, we propose a novel approach by representing the inherent correspondence between reference-target image pairs as a pseudo video. This perspective allows the latest version of SAM, known as SAM2, which is equipped with interactive video object segmentation (iVOS) capabilities, to be adapted to downstream tasks in a lightweight manner. We term this approach Correspondence As Video for SAM (CAV-SAM). CAV-SAM comprises two key modules: the Diffusion-Based Semantic Transition (DBST) module employs a diffusion model to construct a semantic transformation sequence, while the Test-Time Geometric Alignment (TTGA) module aligns the geometric changes within this sequence through test-time fine-tuning. We evaluated CAVSAM on widely-used datasets, achieving segmentation performance improvements exceeding 5% over SOTA methods. Implementation is provided in the supplementary materials.
大型视觉模型,如万物分割模型(SAM),在应用于实际下游任务时存在显著局限性。因此,利用参考图像及其对应掩膜给模型传授新知识的参考分割法,成为了适应视觉模型的有前途的新方向。然而,现有的参考分割方法主要依赖于元学习,这仍然需要大规模的元训练过程,并带来了大量的数据和计算成本。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新方法,通过将参考目标图像对之间的内在对应关系表示为伪视频。这个视角允许配备有交互式视频对象分割(iVOS)功能的SAM的最新版本,即SAM2,以轻便的方式适应下游任务。我们将这种方法称为SAM的对应关系视频(CAV-SAM)。CAV-SAM包含两个关键模块:扩散基础语义转换(DBST)模块利用扩散模型构建语义转换序列,而测试时间几何对齐(TTGA)模块则通过测试时的微调,对齐此序列中的几何变化。我们在广泛使用的数据集上评估了CAVSAM,其分割性能提高了超过5%,超过了最先进的方法。实现方法详见补充材料。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型视觉模型(如Segment Anything Model,SAM)在应用于实际下游任务时存在显著局限性。参考分割法利用参考图像及其遮罩向模型传授新知识,成为适应视觉模型的有前途的新方向。然而,现有参考分割方法主要依赖元学习,仍需大量元训练过程,带来巨大数据和计算成本。本研究提出一种新方法,将参考目标图像对之间的内在对应关系表示为伪视频。借助具有交互式视频对象分割(iVOS)功能的SAM最新版本(SAM2),以轻松适应下游任务。我们称这种方法为SAM的对应关系视频(CAV-SAM)。CAV-SAM包括两个关键模块:扩散基础语义转换(DBST)模块采用扩散模型构建语义转换序列,测试时间几何对齐(TTGA)模块通过测试时微调对齐此序列中的几何变化。我们在广泛使用的数据集上评估了CAV-SAM,其分割性能较最优方法提高了超过5%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型在下游任务应用中存在局限性。
- 参考分割法是一个新兴方向,通过参考图像和遮罩为模型引入新知识。
- 现有参考分割方法主要依赖元学习,需大量元训练,导致高成本和资源消耗。
- 本研究创新性地提出CAV-SAM方法,将参考图像对的对应关系表示为伪视频。
- CAV-SAM利用SAM2的iVOS功能,以更轻松的方式适应下游任务。
- CAV-SAM包含两个核心模块:DBST和TTGA,分别负责语义转换和几何对齐。
- 在广泛数据集上的评估显示,CAV-SAM的分割性能较最优方法有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

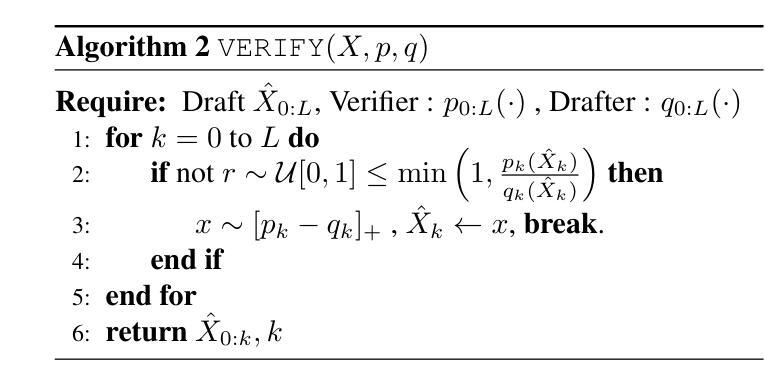
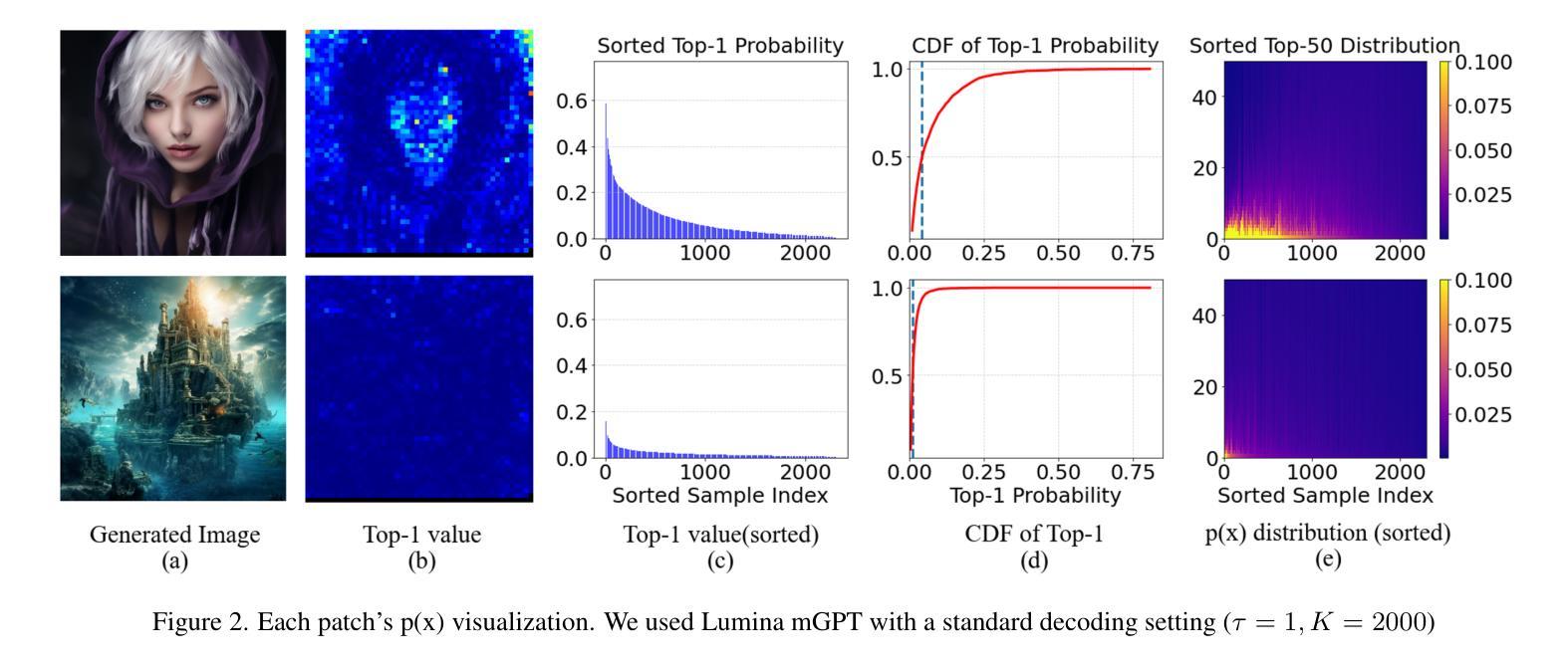
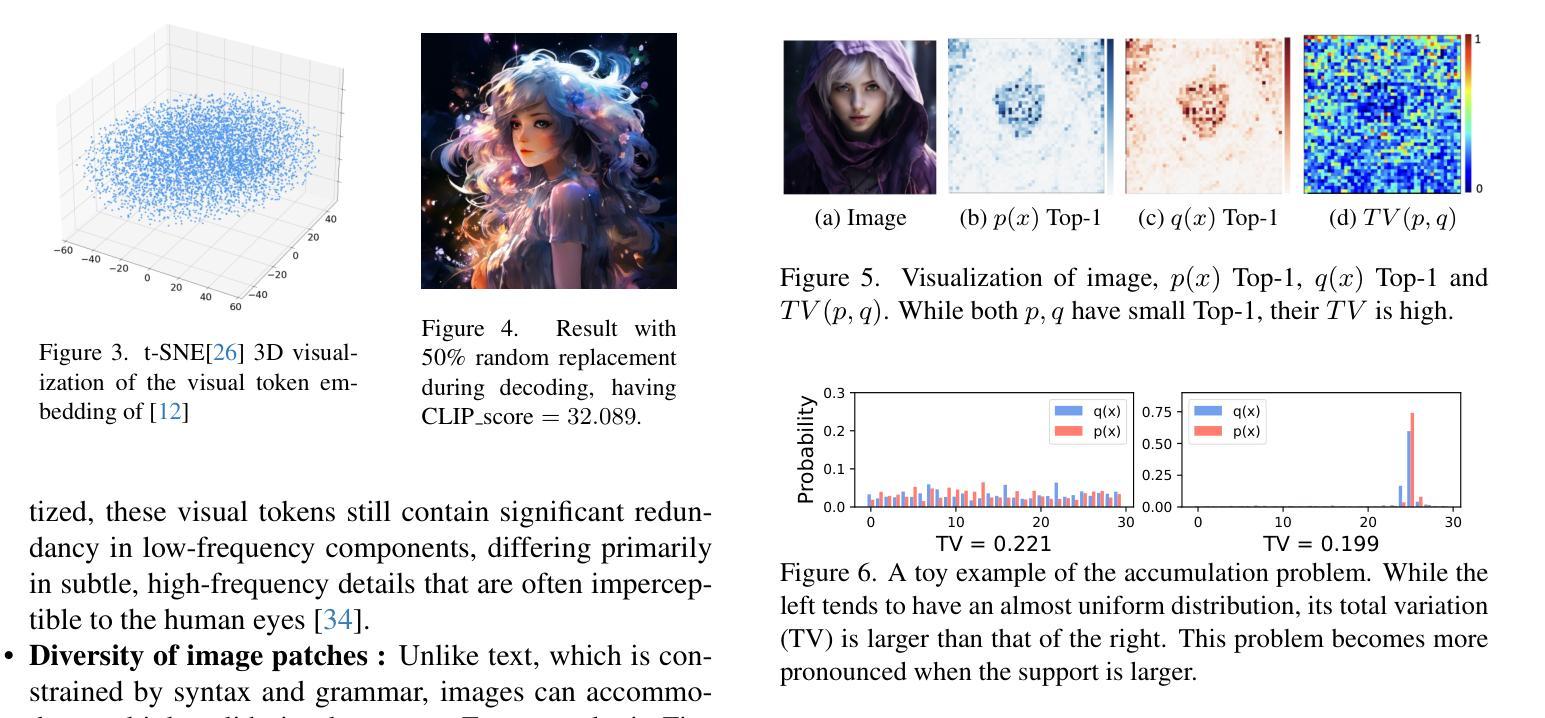
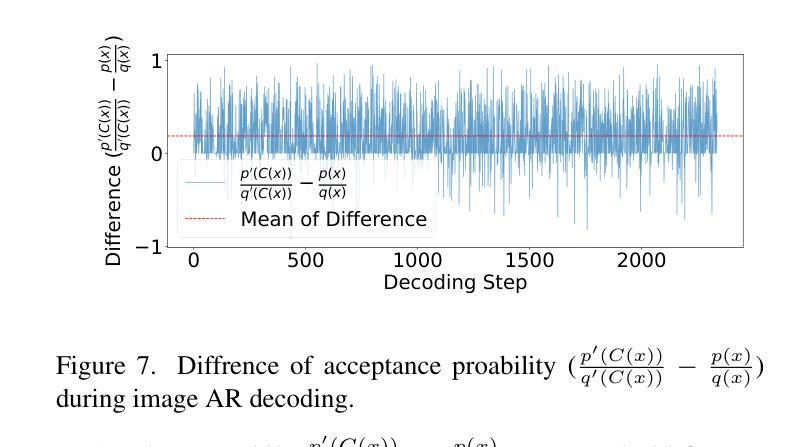
Grouped Speculative Decoding for Autoregressive Image Generation
Authors:Junhyuk So, Juncheol Shin, Hyunho Kook, Eunhyeok Park
Recently, autoregressive (AR) image models have demonstrated remarkable generative capabilities, positioning themselves as a compelling alternative to diffusion models. However, their sequential nature leads to long inference times, limiting their practical scalability. In this work, we introduce Grouped Speculative Decoding (GSD), a novel, training-free acceleration method for AR image models. While recent studies have explored Speculative Decoding (SD) as a means to speed up AR image generation, existing approaches either provide only modest acceleration or require additional training. Our in-depth analysis reveals a fundamental difference between language and image tokens: image tokens exhibit inherent redundancy and diversity, meaning multiple tokens can convey valid semantics. However, traditional SD methods are designed to accept only a single most-likely token, which fails to leverage this difference, leading to excessive false-negative rejections. To address this, we propose a new SD strategy that evaluates clusters of visually valid tokens rather than relying on a single target token. Additionally, we observe that static clustering based on embedding distance is ineffective, which motivates our dynamic GSD approach. Extensive experiments show that GSD accelerates AR image models by an average of 3.7x while preserving image quality-all without requiring any additional training. The source code is available at https://github.com/junhyukso/GSD
最近,自回归(AR)图像模型已经展现出显著的生成能力,成为扩散模型的有力替代方案。然而,它们的顺序性质导致推理时间较长,限制了其实践中的可扩展性。在这项工作中,我们引入了分组推测解码(GSD),这是一种用于AR图像模型的新型、无需训练的加速方法。虽然最近的研究已经探索了推测解码(SD)来加速AR图像生成,但现有方法要么只提供适度的加速,要么需要额外的训练。我们的深入分析揭示了语言令牌和图像令牌之间的根本差异:图像令牌具有固有的冗余性和多样性,意味着多个令牌可以传递有效的语义。然而,传统的SD方法被设计为仅接受一个最可能的令牌,这未能利用这种差异,导致过多的假阴性拒绝。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的SD策略,该策略评估视觉上有效令牌的集群,而不是依赖于单个目标令牌。此外,我们发现基于嵌入距离的静态聚类无效,这促使我们采用动态GSD方法。大量实验表明,GSD平均加速AR图像模型3.7倍,同时保持图像质量,而且无需任何额外的训练。源代码可在https://github.com/junhyukso/GSD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICCV 2025
Summary
近期,自回归(AR)图像模型的生成能力备受瞩目,成为扩散模型的强劲竞争对手。但其顺序性导致推理时间长,限制了实际应用的扩展性。本研究提出一种无需训练的加速方法——分组推测解码(GSD),用于加速AR图像模型。通过对语言与图像令牌的区别进行深入分析,发现图像令牌存在内在冗余和多样性。传统的推测解码方法设计接受单一的最高概率令牌,未能充分利用这种差异,导致过多的假阴性拒绝。因此,本研究提出一种新策略,评估视觉上有效的令牌群而非单一目标令牌。实验表明,GSD在加速AR图像模型的同时,保证了图像质量,无需任何额外训练。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归(AR)图像模型展现出强大的生成能力,但推理时间长,限制了实际应用。
- 分组推测解码(GSD)是一种新型的、无需训练的加速方法,用于提升AR图像模型的效率。
- 与现有研究相比,GSD能有效加速AR图像模型的推理过程,平均提速3.7倍。
- 语言与图像令牌存在显著区别,图像令牌具有内在冗余和多样性。
- 传统推测解码方法因设计缺陷导致过多的假阴性拒绝。
- GSD通过评估视觉上有效的令牌群而非单一目标令牌来克服这一缺陷。
点此查看论文截图

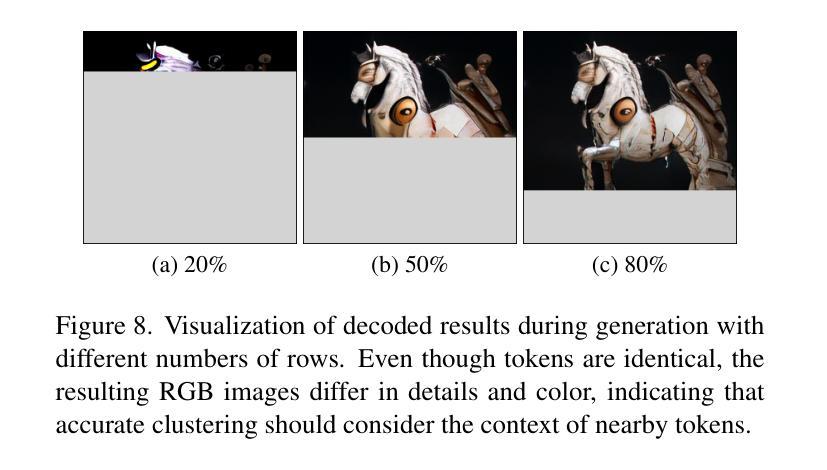

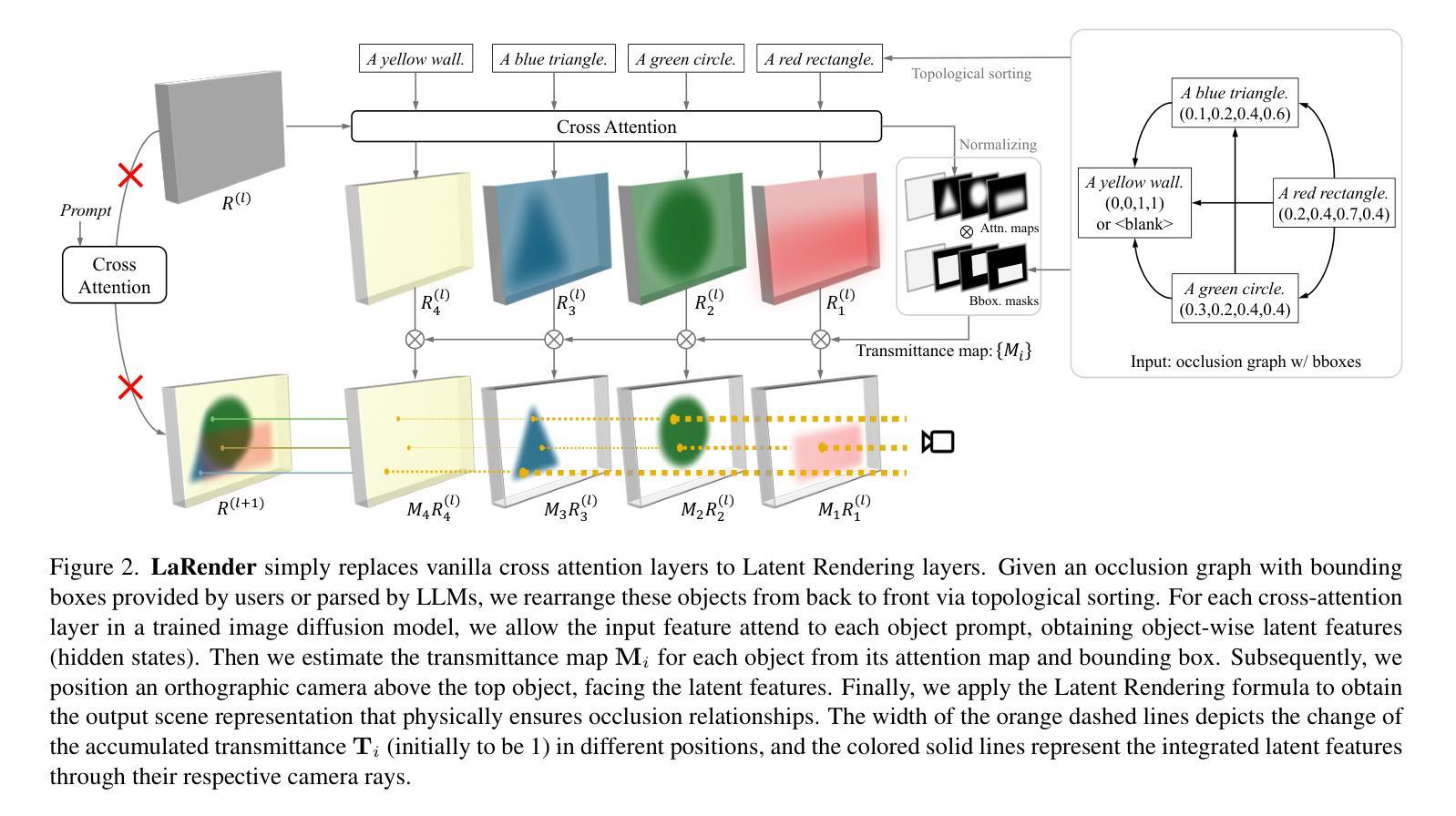
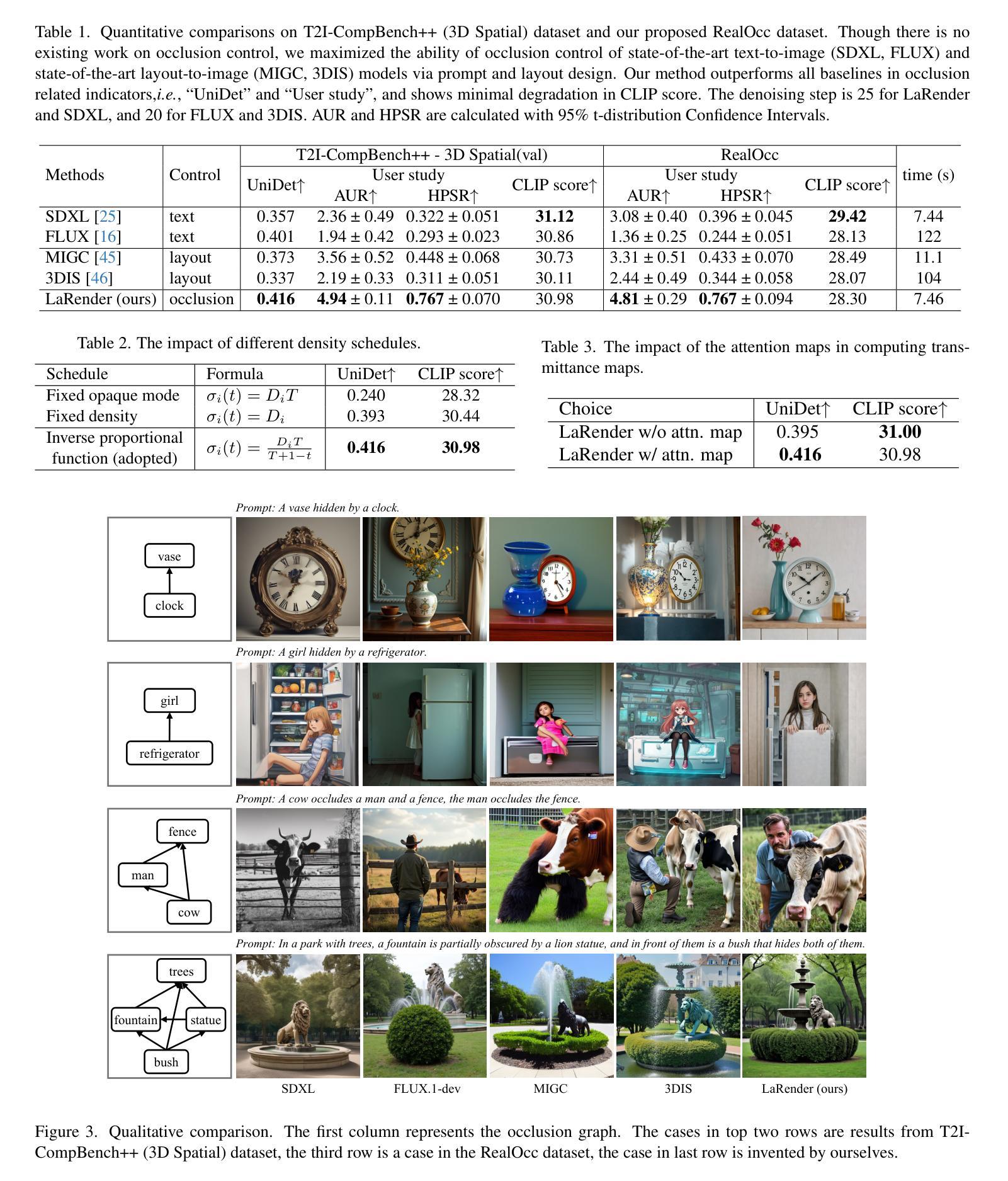
LaRender: Training-Free Occlusion Control in Image Generation via Latent Rendering
Authors:Xiaohang Zhan, Dingming Liu
We propose a novel training-free image generation algorithm that precisely controls the occlusion relationships between objects in an image. Existing image generation methods typically rely on prompts to influence occlusion, which often lack precision. While layout-to-image methods provide control over object locations, they fail to address occlusion relationships explicitly. Given a pre-trained image diffusion model, our method leverages volume rendering principles to “render” the scene in latent space, guided by occlusion relationships and the estimated transmittance of objects. This approach does not require retraining or fine-tuning the image diffusion model, yet it enables accurate occlusion control due to its physics-grounded foundation. In extensive experiments, our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of occlusion accuracy. Furthermore, we demonstrate that by adjusting the opacities of objects or concepts during rendering, our method can achieve a variety of effects, such as altering the transparency of objects, the density of mass (e.g., forests), the concentration of particles (e.g., rain, fog), the intensity of light, and the strength of lens effects, etc.
我们提出了一种无需训练即可生成图像的新算法,该算法可以精确控制图像中对象之间的遮挡关系。现有的图像生成方法通常依赖于提示来影响遮挡,但往往缺乏精度。虽然布局到图像的方法可以控制对象的位置,但它们无法明确处理遮挡关系。给定一个预训练的图像扩散模型,我们的方法利用体积渲染原理在潜在空间中“渲染”场景,由遮挡关系和估计的对象透射率来指导。这种方法不需要重新训练或微调图像扩散模型,但由于其基于物理的基础,它能够实现精确的遮挡控制。在广泛的实验中,我们的方法在遮挡精度方面显著优于现有方法。此外,我们证明,通过在渲染过程中调整对象的透明度或概念,我们的方法可以实现各种效果,如改变对象的透明度、物质密度(例如森林)、粒子浓度(例如雨、雾)、光线强度以及镜头效果强度等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025 (oral). Project page: https://xiaohangzhan.github.io/projects/larender/
摘要
本文提出了一种无需训练的图片生成算法,能够精确控制图像中物体之间的遮挡关系。现有的图片生成方法通常依赖提示来影响遮挡,这往往缺乏精确性。而我们的方法借助预训练的图片扩散模型,利用体积渲染原理在潜在空间“渲染”场景,由遮挡关系和物体透射率的估计来引导,无需对图片扩散模型进行再训练或微调。由于其物理基础,我们的方法能够实现精确的遮挡控制。在广泛的实验中,我们的方法在遮挡准确性方面显著优于现有方法。此外,我们还证明,通过在渲染过程中调整物体的透明度或概念,我们的方法可以实现各种效果,如改变物体的透明度、物体的密度(如森林)、粒子的浓度(如雨、雾)、光的强度以及镜头效果等。
要点
- 提出了一种新的无需训练的图片生成算法,精确控制图像中物体间的遮挡关系。
- 与依赖提示影响遮挡的现有方法相比,更具精确性。
- 利用体积渲染原理在潜在空间“渲染”场景,由遮挡关系和物体透射率估计引导。
- 不需要再训练或微调图片扩散模型。
- 在遮挡准确性方面显著优于现有方法。
- 通过调整渲染过程中的物体透明度或概念,可以实现多种效果。
- 该方法具有物理基础,能够实现更真实、更自然的图像生成。
点此查看论文截图

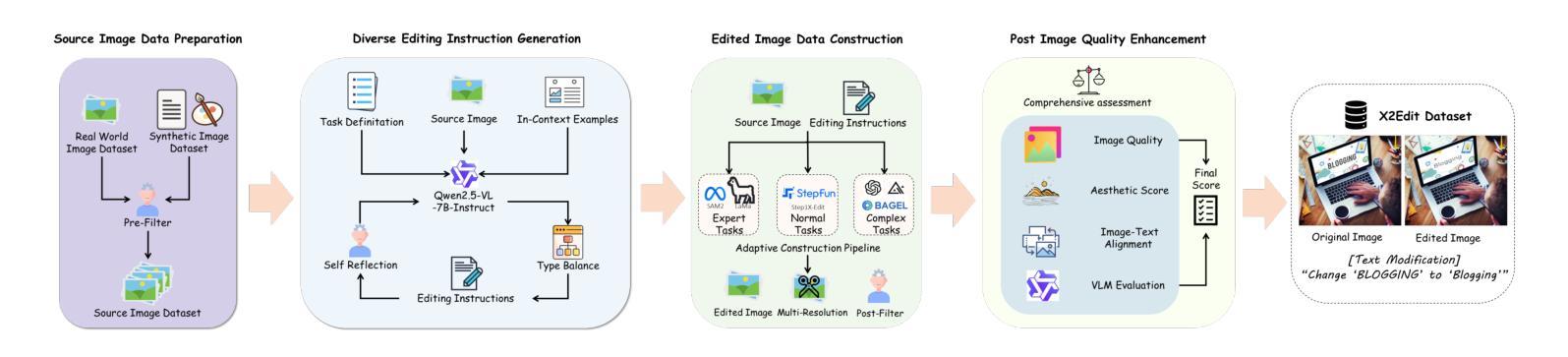
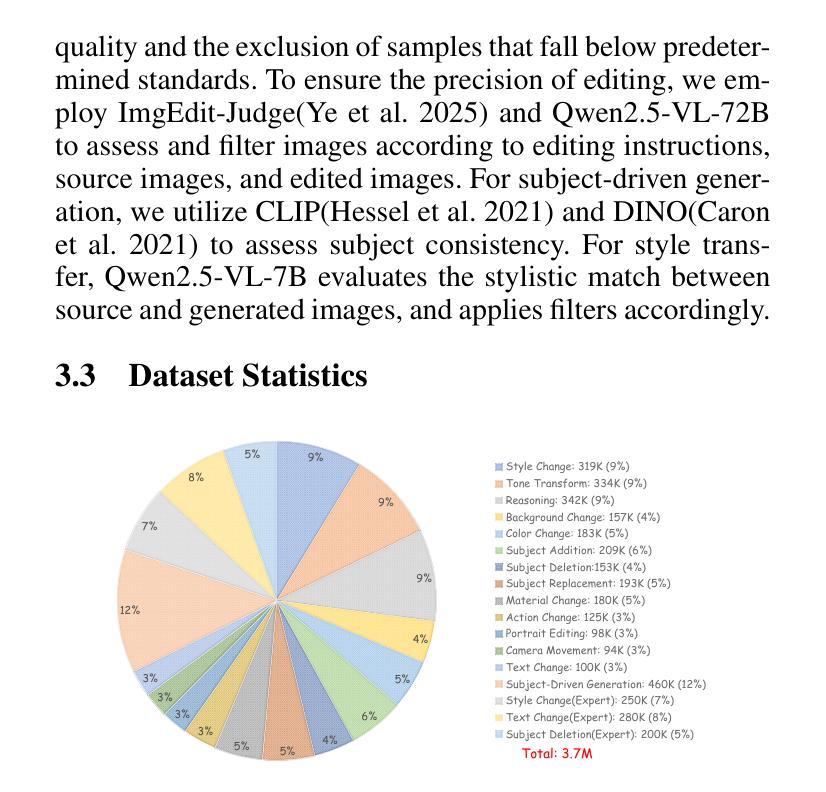
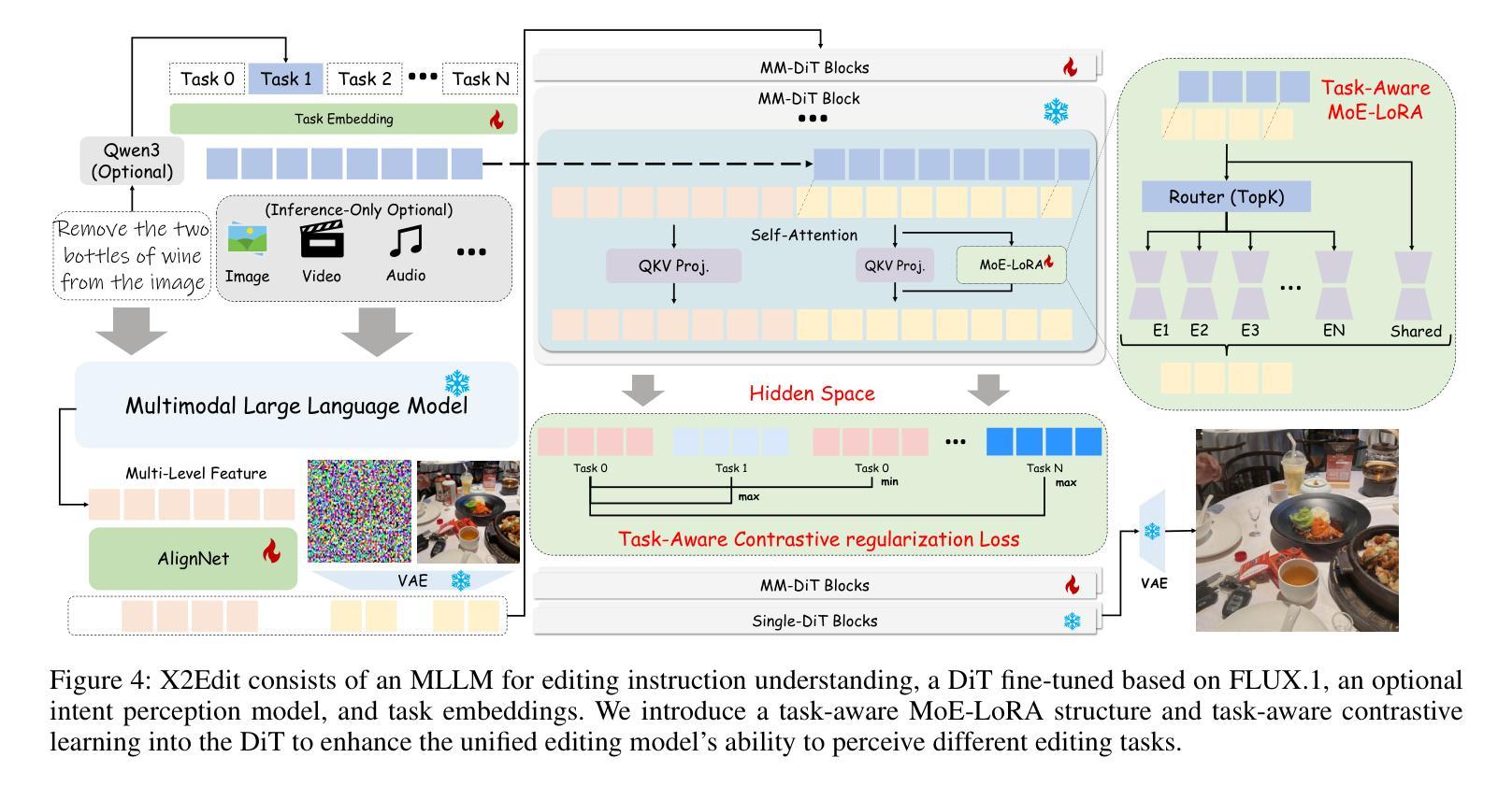
X2Edit: Revisiting Arbitrary-Instruction Image Editing through Self-Constructed Data and Task-Aware Representation Learning
Authors:Jian Ma, Xujie Zhu, Zihao Pan, Qirong Peng, Xu Guo, Chen Chen, Haonan Lu
Existing open-source datasets for arbitrary-instruction image editing remain suboptimal, while a plug-and-play editing module compatible with community-prevalent generative models is notably absent. In this paper, we first introduce the X2Edit Dataset, a comprehensive dataset covering 14 diverse editing tasks, including subject-driven generation. We utilize the industry-leading unified image generation models and expert models to construct the data. Meanwhile, we design reasonable editing instructions with the VLM and implement various scoring mechanisms to filter the data. As a result, we construct 3.7 million high-quality data with balanced categories. Second, to better integrate seamlessly with community image generation models, we design task-aware MoE-LoRA training based on FLUX.1, with only 8% of the parameters of the full model. To further improve the final performance, we utilize the internal representations of the diffusion model and define positive/negative samples based on image editing types to introduce contrastive learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the model’s editing performance is competitive among many excellent models. Additionally, the constructed dataset exhibits substantial advantages over existing open-source datasets. The open-source code, checkpoints, and datasets for X2Edit can be found at the following link: https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2Edit.
现有用于任意指令图像编辑的开源数据集仍然不够理想,而与社区流行生成模型兼容的即插即用编辑模块明显缺失。在本文中,我们首先介绍了X2Edit数据集,这是一个涵盖14种不同编辑任务的综合性数据集,包括主题驱动生成。我们利用行业领先的统一图像生成模型和专家模型来构建数据。同时,我们使用VLM设计合理的编辑指令,并实施各种评分机制来过滤数据。因此,我们构建了370万高质量数据,类别平衡。其次,为了更好地与社区图像生成模型无缝集成,我们基于FLUX设计了任务感知的MoE-LoRA训练。该训练仅占全模型的8%的参数。为了进一步提高最终性能,我们利用扩散模型的内部表示,根据图像编辑类型定义正负样本,引入对比学习。大量实验表明,该模型的编辑性能在众多优秀模型中具有竞争力。此外,构建的数据集在现有开源数据集上具有显著优势。X2Edit的开源代码、检查点和数据集可在以下链接中找到:https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2Edit。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2Edit
Summary
本文介绍了X2Edit数据集,该数据集包含14种不同的图像编辑任务,采用领先的统一图像生成模型和专家模型构建数据,并通过合理的设计编辑指令和评分机制,筛选出高质量的数据。为更好地与社区图像生成模型无缝集成,设计了一种基于MoE-LoRA的任务感知训练方案。通过对比学习提高模型性能,实验表明该模型在图像编辑任务上的性能具有竞争力,且所构建数据集优于现有开源数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 引入X2Edit数据集,包含14种图像编辑任务,数据全面。
- 采用领先的统一图像生成模型和专家模型构建数据。
- 通过合理的设计编辑指令和评分机制,筛选出高质量数据。
- 设计基于MoE-LoRA的任务感知训练方案,与社区图像生成模型无缝集成。
- 利用对比学习提高模型性能。
- 模型在图像编辑任务上的性能具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


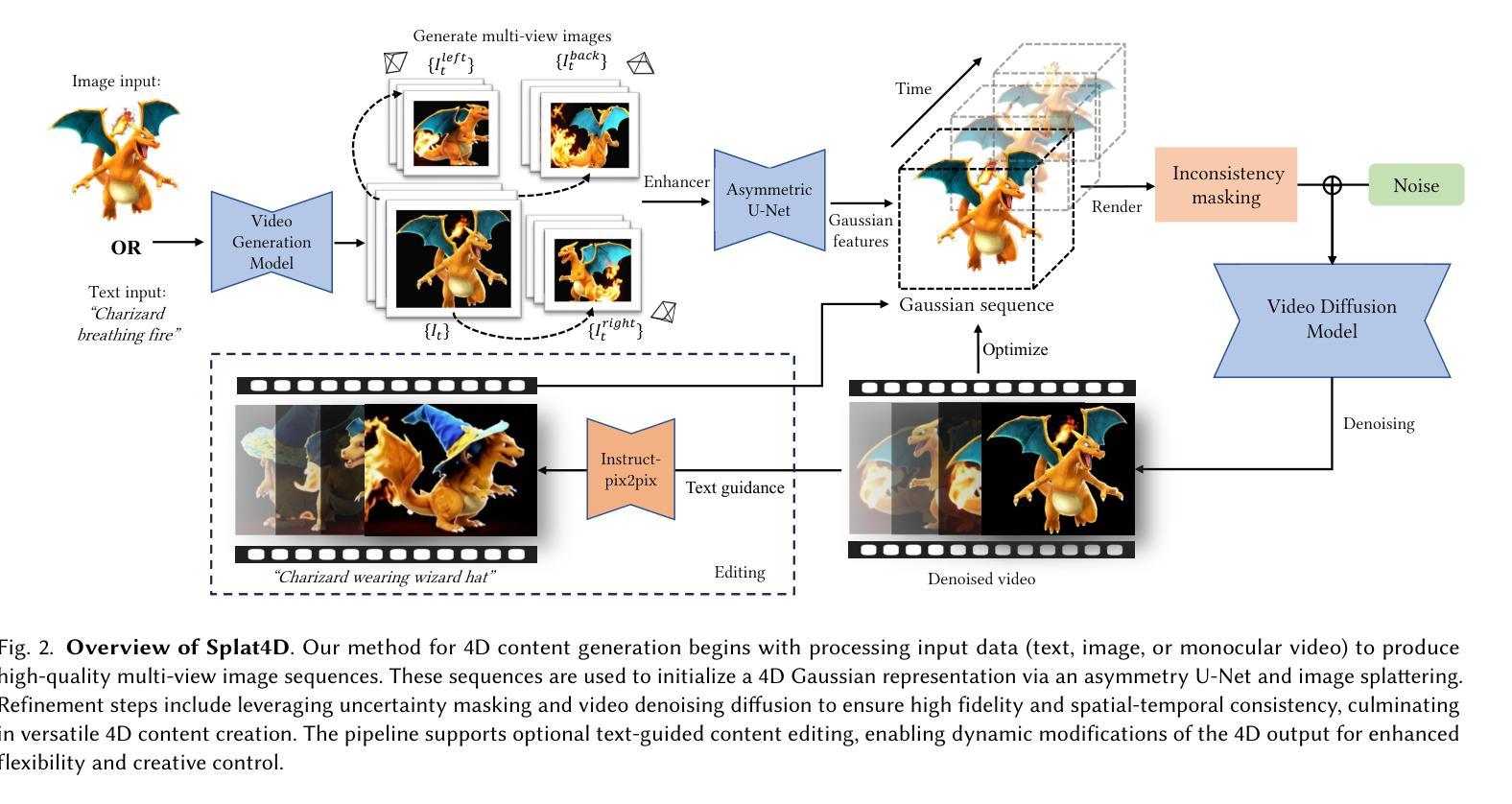
Splat4D: Diffusion-Enhanced 4D Gaussian Splatting for Temporally and Spatially Consistent Content Creation
Authors:Minghao Yin, Yukang Cao, Songyou Peng, Kai Han
Generating high-quality 4D content from monocular videos for applications such as digital humans and AR/VR poses challenges in ensuring temporal and spatial consistency, preserving intricate details, and incorporating user guidance effectively. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Splat4D, a novel framework enabling high-fidelity 4D content generation from a monocular video. Splat4D achieves superior performance while maintaining faithful spatial-temporal coherence by leveraging multi-view rendering, inconsistency identification, a video diffusion model, and an asymmetric U-Net for refinement. Through extensive evaluations on public benchmarks, Splat4D consistently demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various metrics, underscoring the efficacy of our approach. Additionally, the versatility of Splat4D is validated in various applications such as text/image conditioned 4D generation, 4D human generation, and text-guided content editing, producing coherent outcomes following user instructions.
从单目视频中生成高质量4D内容,用于数字人类和AR/VR等应用,在保障时间空间连贯性、保留细节以及有效融入用户指导方面面临挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了Splat4D,一个能够从单目视频中实现高保真4D内容生成的新型框架。Splat4D通过利用多视角渲染、不一致性识别、视频扩散模型以及用于精细化的不对称U-Net,在保持时空连贯性的同时实现了卓越性能。在公共基准测试上的广泛评估表明,Splat4D在各种指标上均表现出卓越的性能,凸显了我们的方法的有效性。此外,Splat4D的通用性在各种应用中得到了验证,如文本/图像条件驱动的4D生成、4D人类生成以及文本引导的内容编辑,能够根据用户指令产生连贯的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了从单目视频中生成高质量4D内容的新框架Splat4D。它通过多视角渲染、不一致性识别、视频扩散模型和不对称U-Net的精细处理,实现高性能的时空连贯性,同时保持高质量的空间细节。Splat4D在各种公共基准测试上的表现均优于其他方法,验证了其在文本/图像控制的4D生成、4D人类生成和文本引导的内容编辑等应用中的效能和灵活性。
Key Takeaways
- Splat4D框架能够从单目视频中生成高质量4D内容。
- 利用多视角渲染技术提高生成的连贯性和质量。
- 通过不一致性识别技术,确保生成的时空连贯性。
- 使用视频扩散模型,使得内容更加真实自然。
- 利用不对称U-Net进行精细处理,保留高质量的空间细节。
- Splat4D在多个公共基准测试中表现优越,展现了其卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

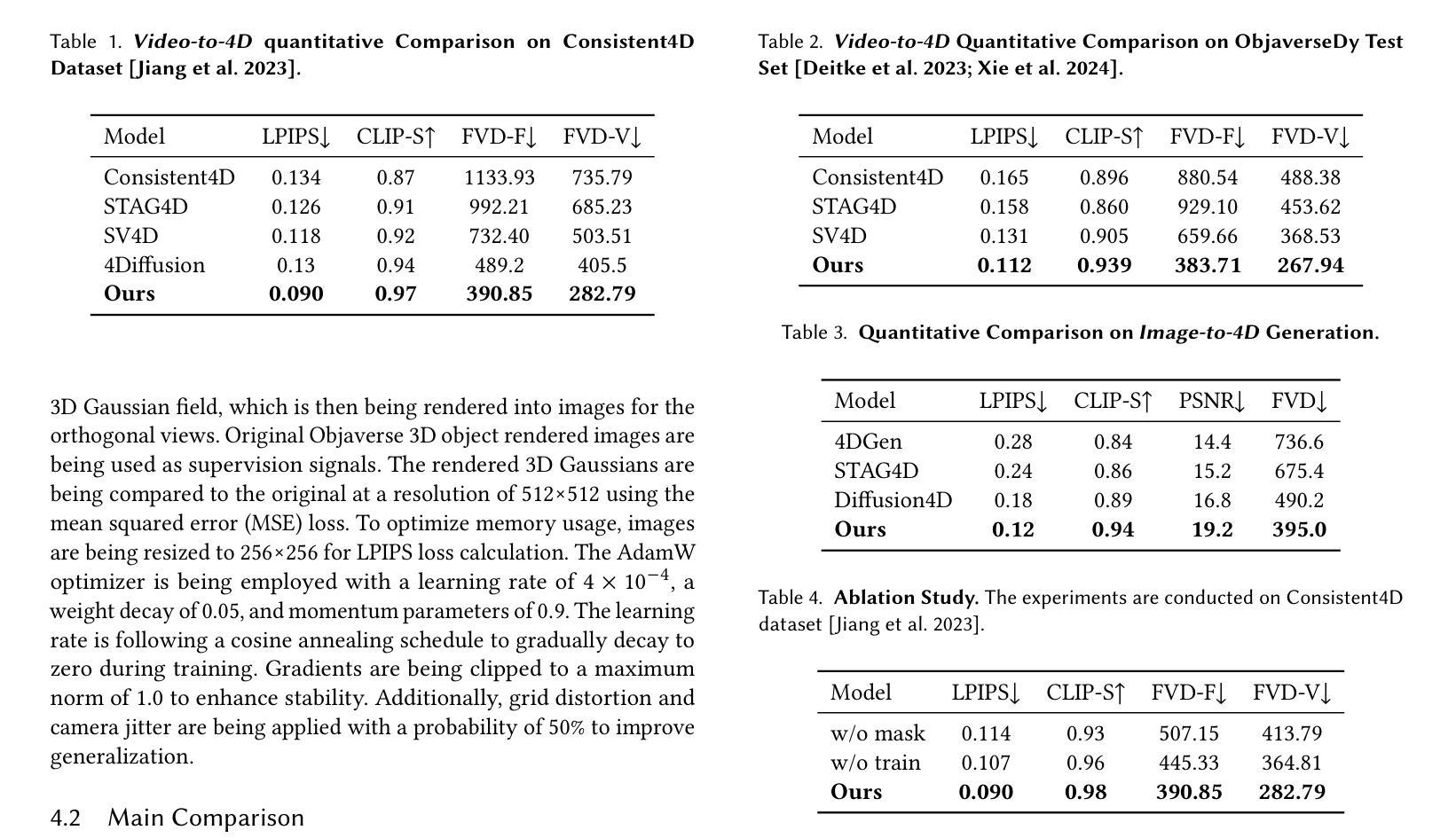
Exploring Multimodal Diffusion Transformers for Enhanced Prompt-based Image Editing
Authors:Joonghyuk Shin, Alchan Hwang, Yujin Kim, Daneul Kim, Jaesik Park
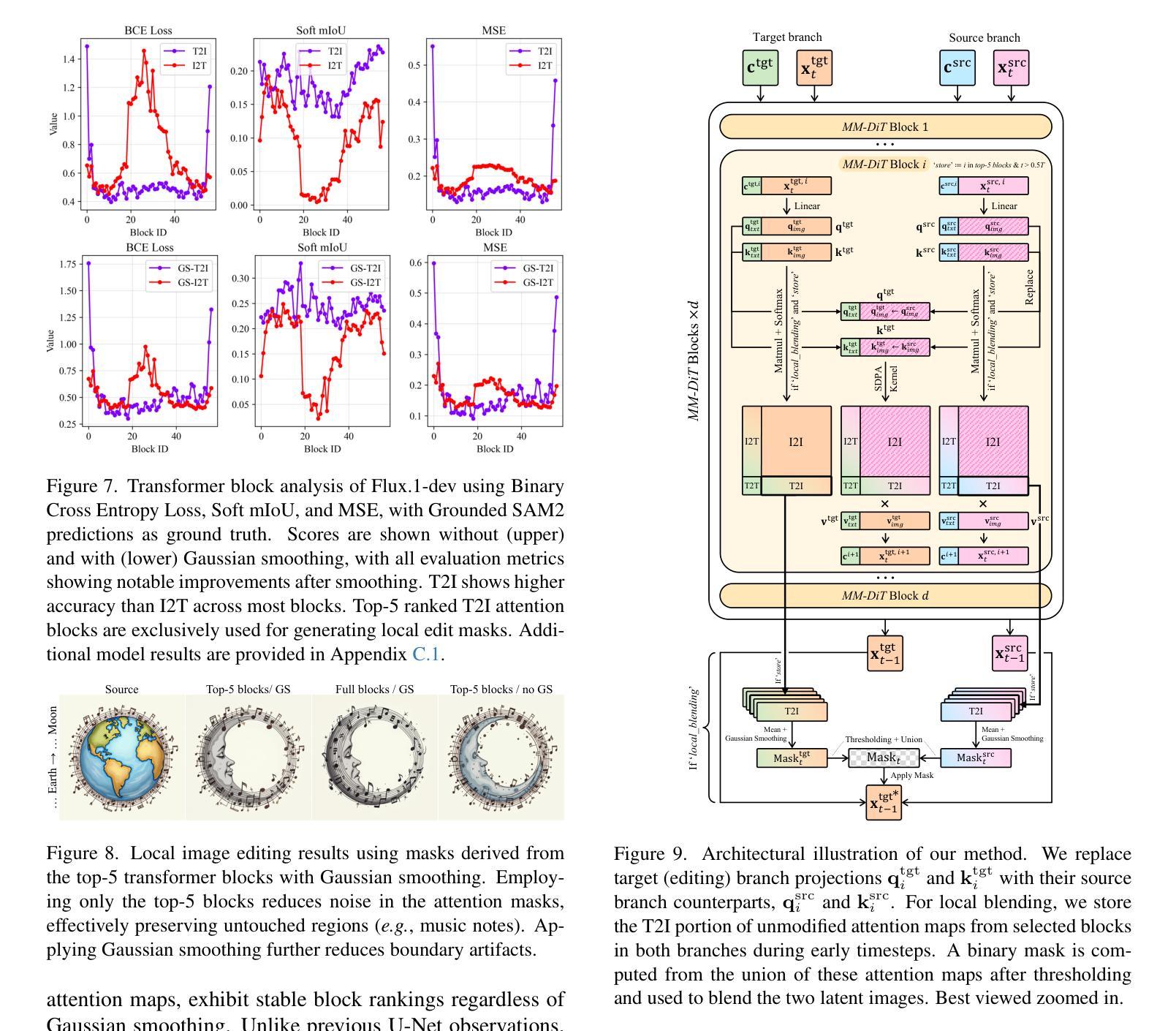
Transformer-based diffusion models have recently superseded traditional U-Net architectures, with multimodal diffusion transformers (MM-DiT) emerging as the dominant approach in state-of-the-art models like Stable Diffusion 3 and Flux.1. Previous approaches have relied on unidirectional cross-attention mechanisms, with information flowing from text embeddings to image latents. In contrast, MMDiT introduces a unified attention mechanism that concatenates input projections from both modalities and performs a single full attention operation, allowing bidirectional information flow between text and image branches. This architectural shift presents significant challenges for existing editing techniques. In this paper, we systematically analyze MM-DiT’s attention mechanism by decomposing attention matrices into four distinct blocks, revealing their inherent characteristics. Through these analyses, we propose a robust, prompt-based image editing method for MM-DiT that supports global to local edits across various MM-DiT variants, including few-step models. We believe our findings bridge the gap between existing U-Net-based methods and emerging architectures, offering deeper insights into MMDiT’s behavioral patterns.
基于Transformer的扩散模型最近已经取代了传统的U-Net架构,多模态扩散Transformer(MM-DiT)成为先进模型如Stable Diffusion 3和Flux的主导方法。之前的方法依赖于单向交叉注意力机制,信息从文本嵌入流向图像潜在表示。相比之下,MMDiT引入了一种统一注意力机制,该机制将来自两个模态的输入投影连接起来,并执行一次完整的注意力操作,允许文本和图像分支之间的双向信息流。这种架构的变化给现有的编辑技术带来了重大挑战。在本文中,我们通过将注意力矩阵分解为四个不同的块来系统地分析MM-DiT的注意力机制,揭示了它们的固有特性。通过这些分析,我们提出了一种针对MM-DiT的稳健提示式图像编辑方法,该方法支持各种MM-DiT变种(包括少步骤模型)进行全局到局部编辑。我们相信,我们的研究成果架起了现有U-Net方法和新兴架构之间的桥梁,为理解MMDiT的行为模式提供了更深入见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project webpage: https://joonghyuk.com/exploring-mmdit-web/
Summary
基于Transformer的扩散模型已逐渐取代传统U-Net架构,并在最新技术中占据主导地位,如Stable Diffusion 3和Flux。其中,多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)引入了一种统一注意力机制,允许文本和图像分支间的双向信息流。本文对MM-DiT的注意力机制进行了系统分析,并提出了一种针对MM-DiT的基于提示的图像编辑方法,支持全局到局部编辑。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer-based diffusion models have surpassed traditional U-Net architectures in state-of-the-art models like Stable Diffusion 3 and Flux.
- 多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)引入了统一注意力机制,允许文本和图像分支间的双向信息流。
- MM-DiT的注意力机制被分解为四个独立块进行系统分析。
- 对MM-DiT的注意力机制分析揭示了其内在特性。
- 提出了一种基于提示的图像编辑方法,适用于各种MM-DiT变体,包括少步骤模型。
- 该方法支持从全局到局部的图像编辑。
点此查看论文截图

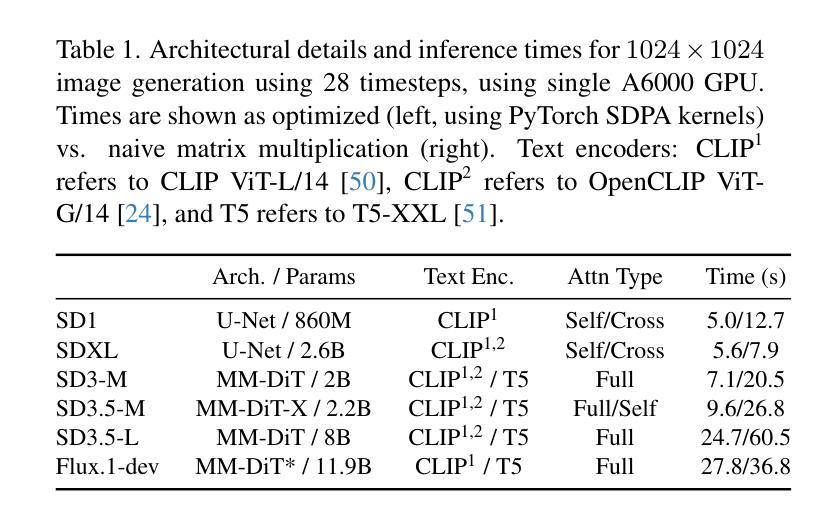
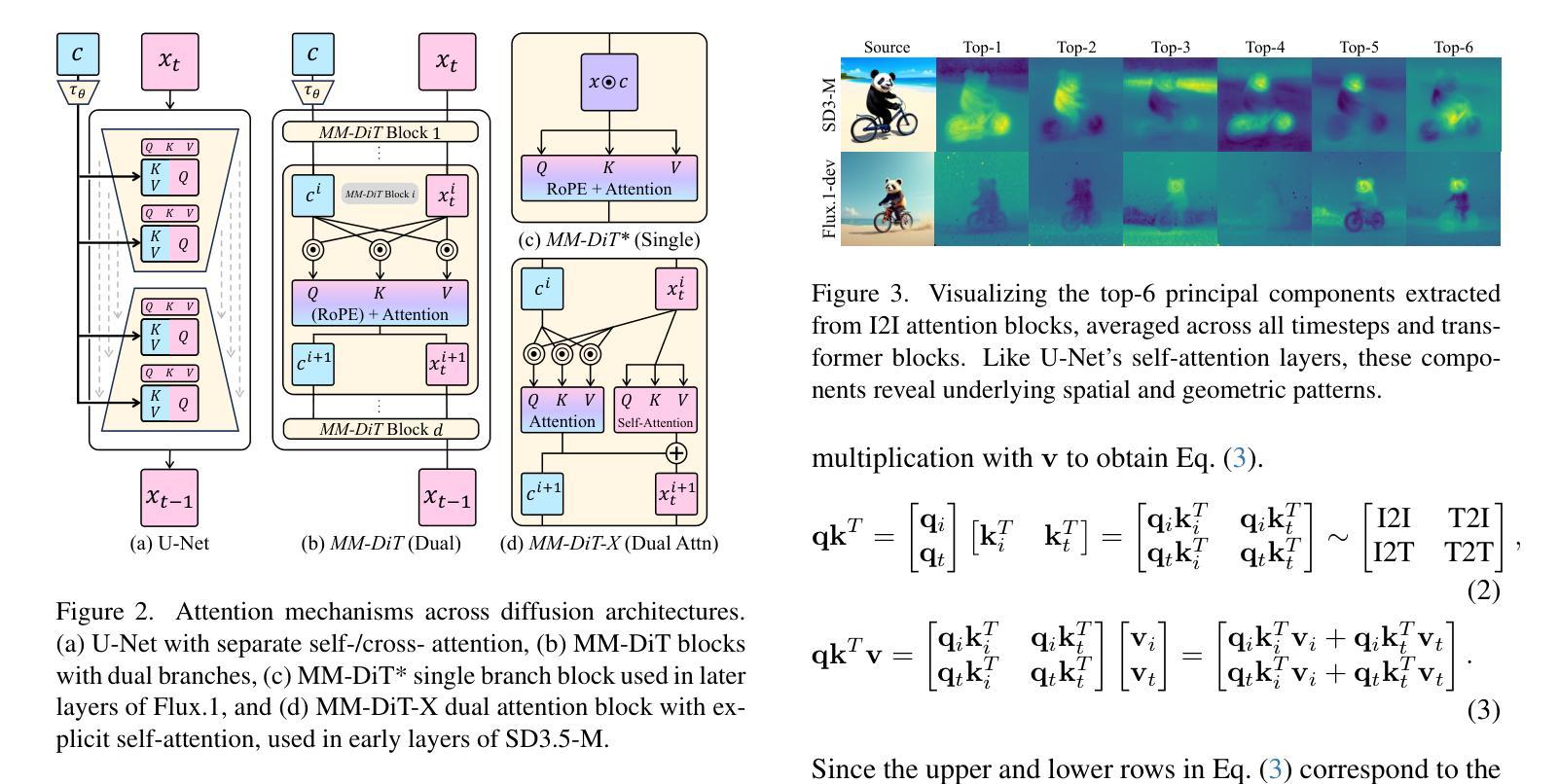
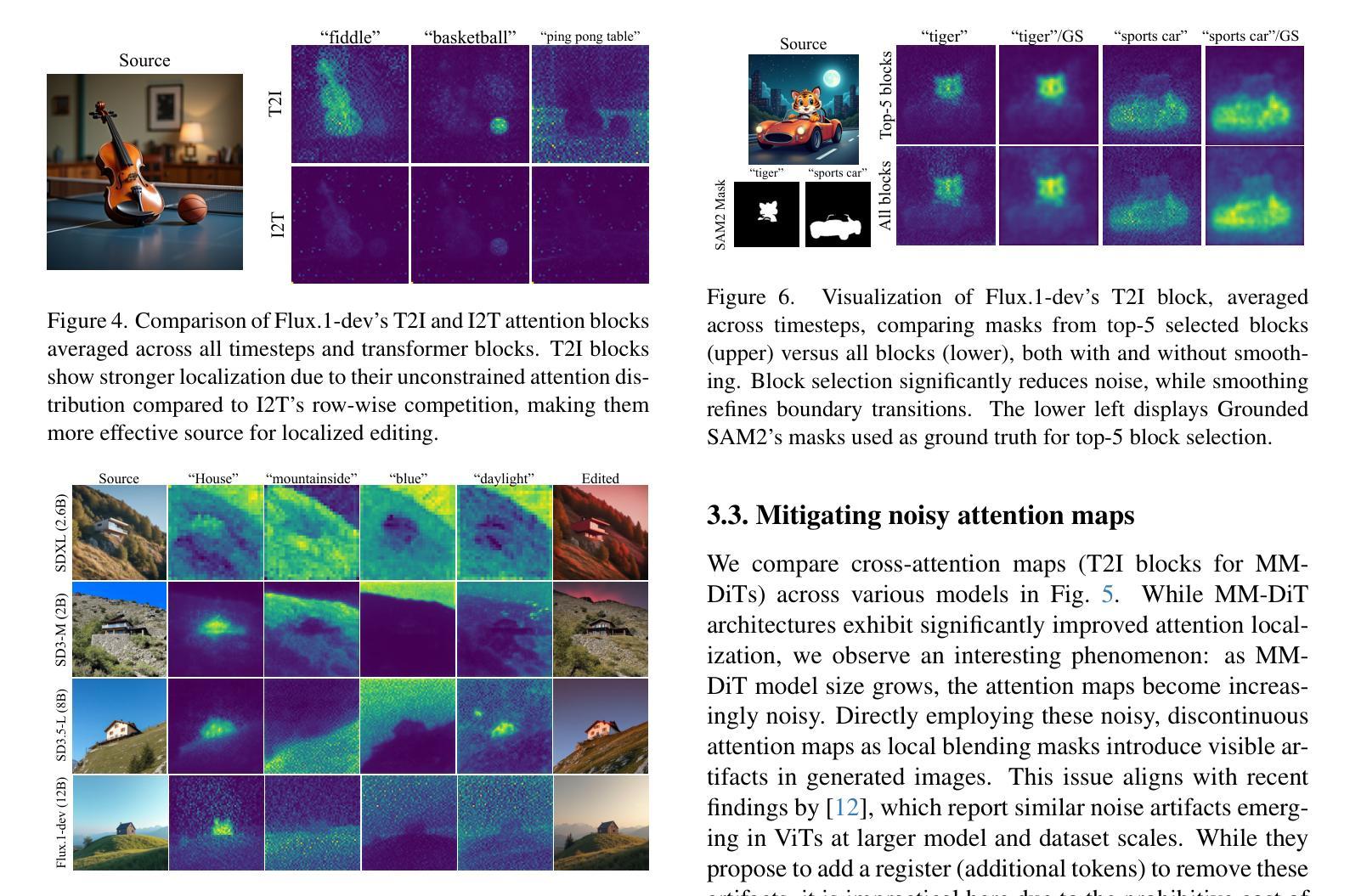

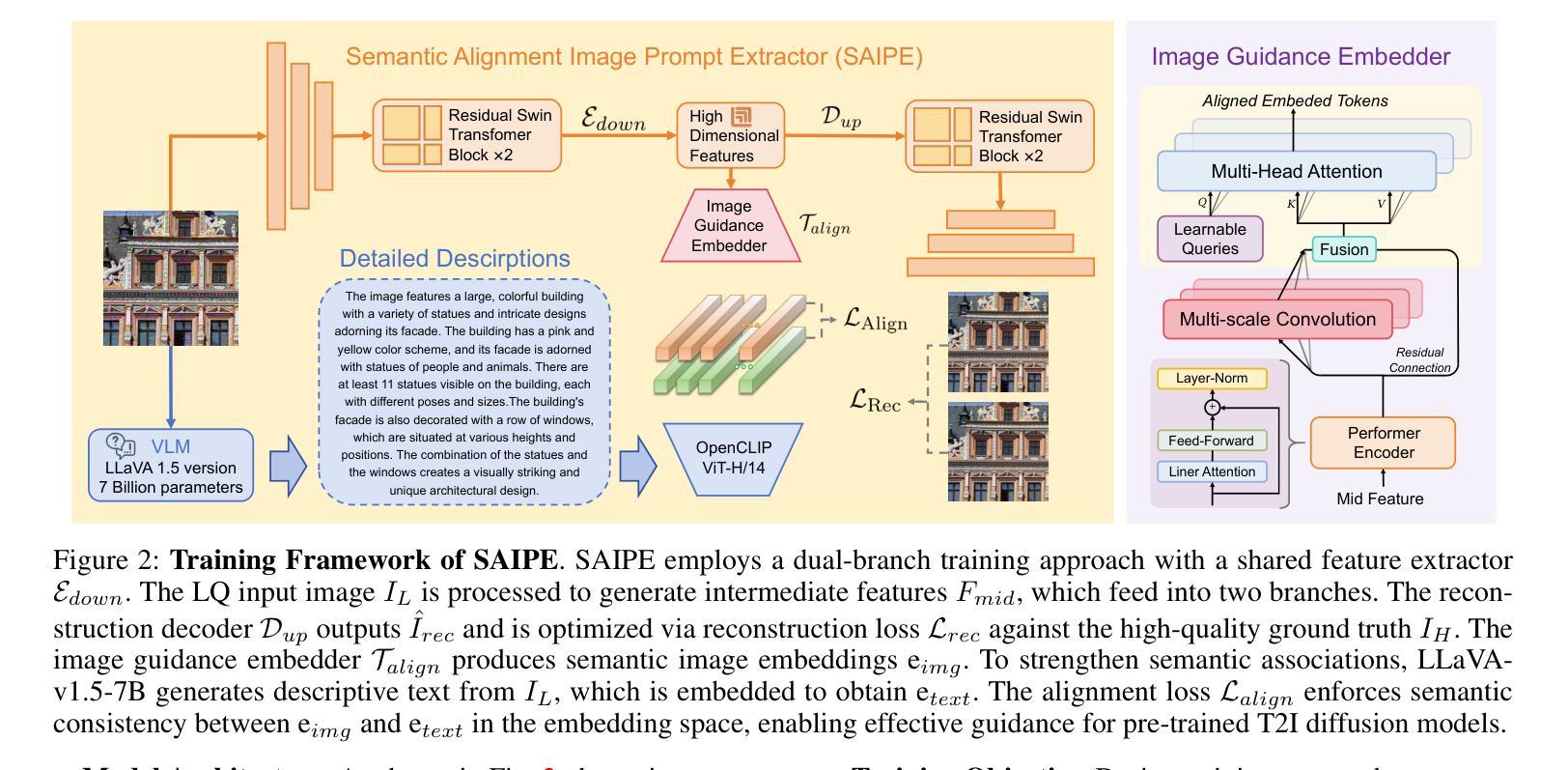
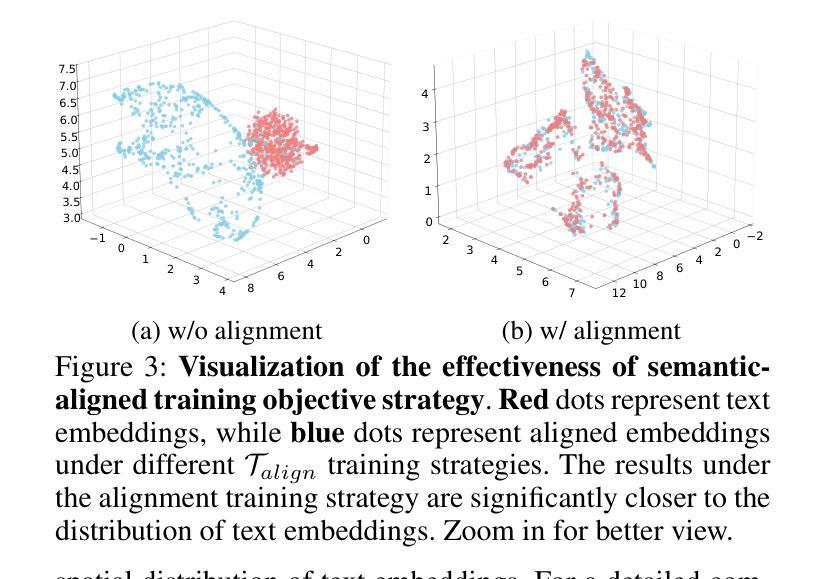
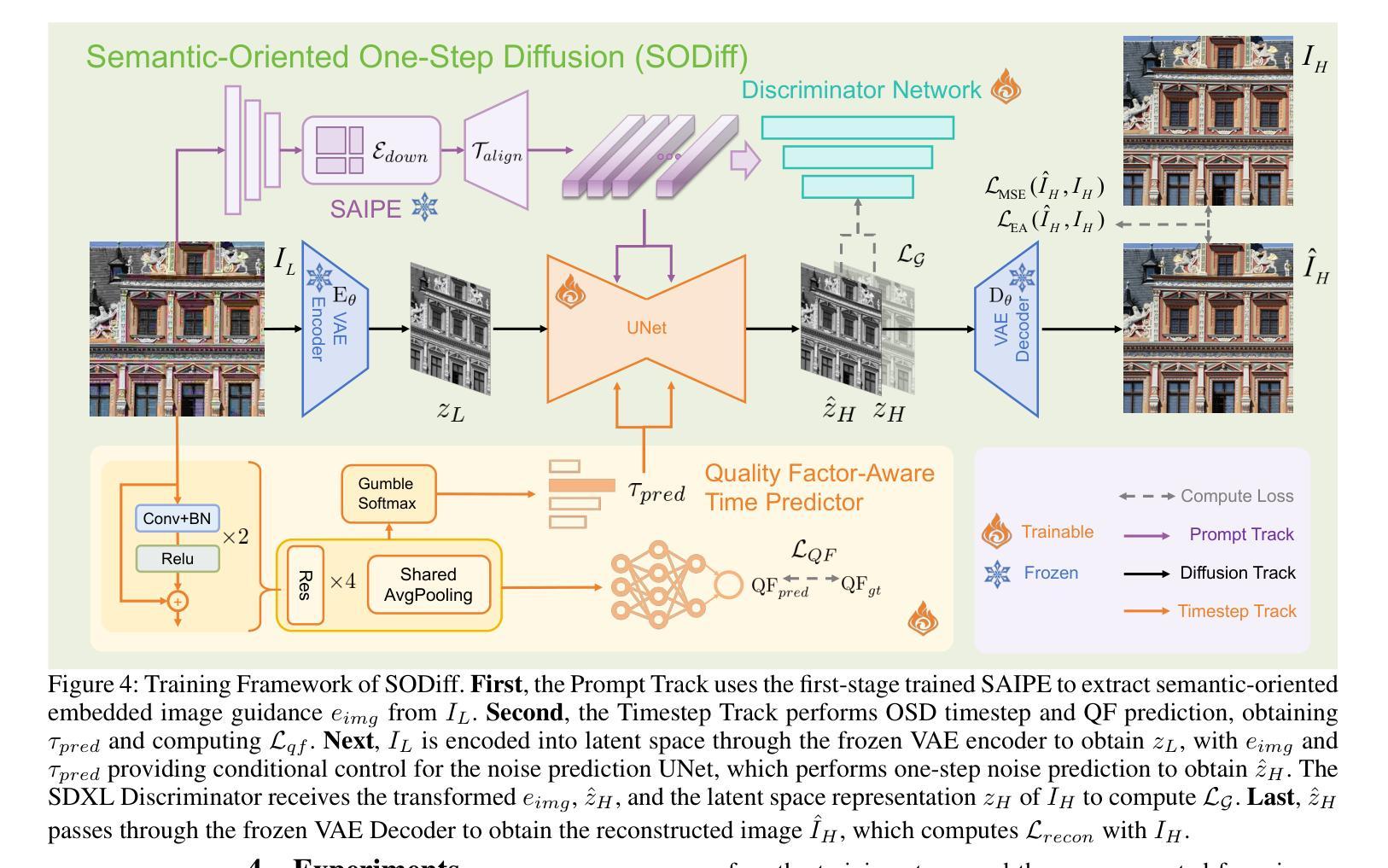
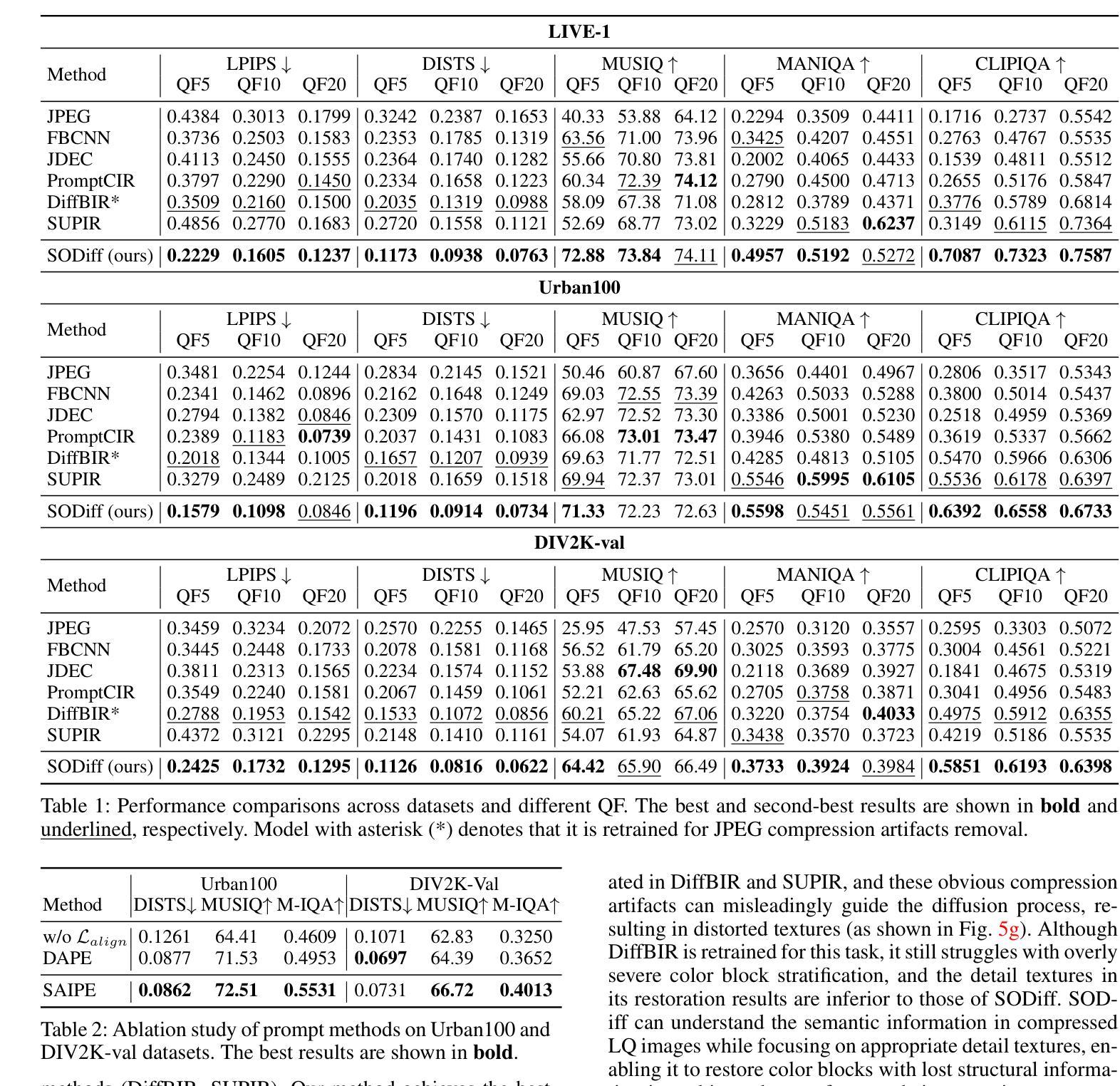
SODiff: Semantic-Oriented Diffusion Model for JPEG Compression Artifacts Removal
Authors:Tingyu Yang, Jue Gong, Jinpei Guo, Wenbo Li, Yong Guo, Yulun Zhang
JPEG, as a widely used image compression standard, often introduces severe visual artifacts when achieving high compression ratios. Although existing deep learning-based restoration methods have made considerable progress, they often struggle to recover complex texture details, resulting in over-smoothed outputs. To overcome these limitations, we propose SODiff, a novel and efficient semantic-oriented one-step diffusion model for JPEG artifacts removal. Our core idea is that effective restoration hinges on providing semantic-oriented guidance to the pre-trained diffusion model, thereby fully leveraging its powerful generative prior. To this end, SODiff incorporates a semantic-aligned image prompt extractor (SAIPE). SAIPE extracts rich features from low-quality (LQ) images and projects them into an embedding space semantically aligned with that of the text encoder. Simultaneously, it preserves crucial information for faithful reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose a quality factor-aware time predictor that implicitly learns the compression quality factor (QF) of the LQ image and adaptively selects the optimal denoising start timestep for the diffusion process. Extensive experimental results show that our SODiff outperforms recent leading methods in both visual quality and quantitative metrics. Code is available at: https://github.com/frakenation/SODiff
JPEG作为一种广泛使用的图像压缩标准,在达到高压缩比时往往会引入严重的视觉失真。尽管现有的基于深度学习的恢复方法已经取得了相当的进展,但它们通常难以恢复复杂的纹理细节,导致输出过于平滑。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了SODiff,这是一种用于去除JPEG失真的新颖且高效的一站式语义导向扩散模型。我们的核心理念是,有效的恢复取决于向预训练的扩散模型提供语义导向的引导,从而充分利用其强大的生成先验。为此,SODiff结合了语义对齐图像提示提取器(SAIPE)。SAIPE从低质量(LQ)图像中提取丰富的特征,并将其投影到与文本编码器语义对齐的嵌入空间中。同时,它保留了用于忠实重建的关键信息。此外,我们提出了一种质量因子感知时间预测器,该预测器能够隐性学习LQ图像的质量因子(QF),并自适应地选择扩散过程的最佳去噪开始时间步长。大量的实验结果表明,我们的SODiff在视觉质量和定量指标方面都优于最新的主流方法。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/frakenation/SODiff
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures. The code will be available at \url{https://github.com/frakenation/SODiff}
Summary
本文提出了一种新的针对JPEG压缩图像的高效语义导向扩散模型SODiff,用于去除JPEG压缩带来的视觉伪影。SODiff结合了语义对齐图像提示提取器(SAIPE),能够从低质量图像中提取丰富的特征,并将其投影到与文本编码器语义对齐的嵌入空间中。同时,SODiff还提出了一种质量因子感知的时间预测器,能够自适应地选择最佳去噪起始时间步长,以提高扩散过程的性能。实验结果表明,SODiff在视觉质量和定量指标方面均优于当前主流方法。
Key Takeaways
- SODiff是一种新的针对JPEG压缩伪影的语义导向扩散模型。
- SODiff结合了语义对齐图像提示提取器(SAIPE),能够从低质量图像中提取丰富的特征。
- SAIPE将提取的特征投影到与文本编码器语义对齐的嵌入空间中。
- SODiff提出了质量因子感知的时间预测器,能够自适应选择去噪起始时间步长。
- SODiff提高了扩散过程的性能。
- SODiff在视觉质量和定量指标方面优于当前主流方法。
点此查看论文截图

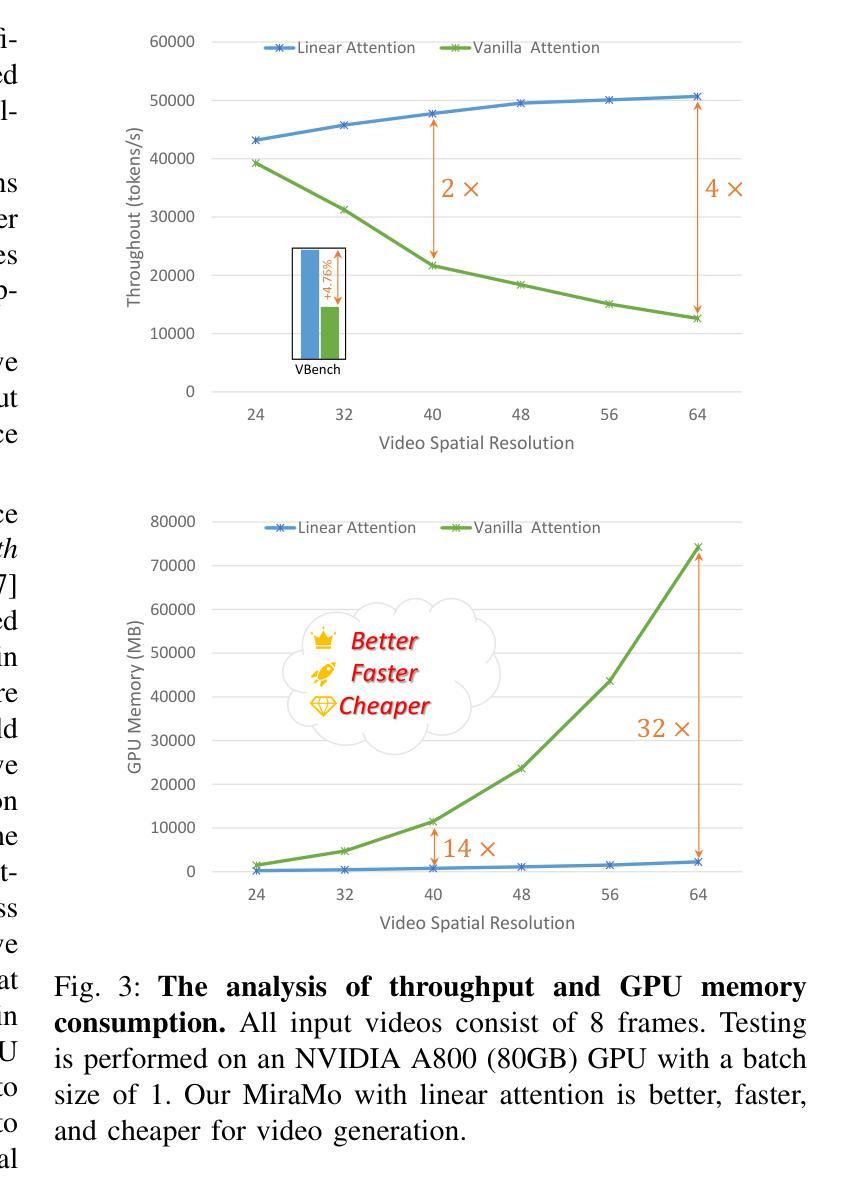
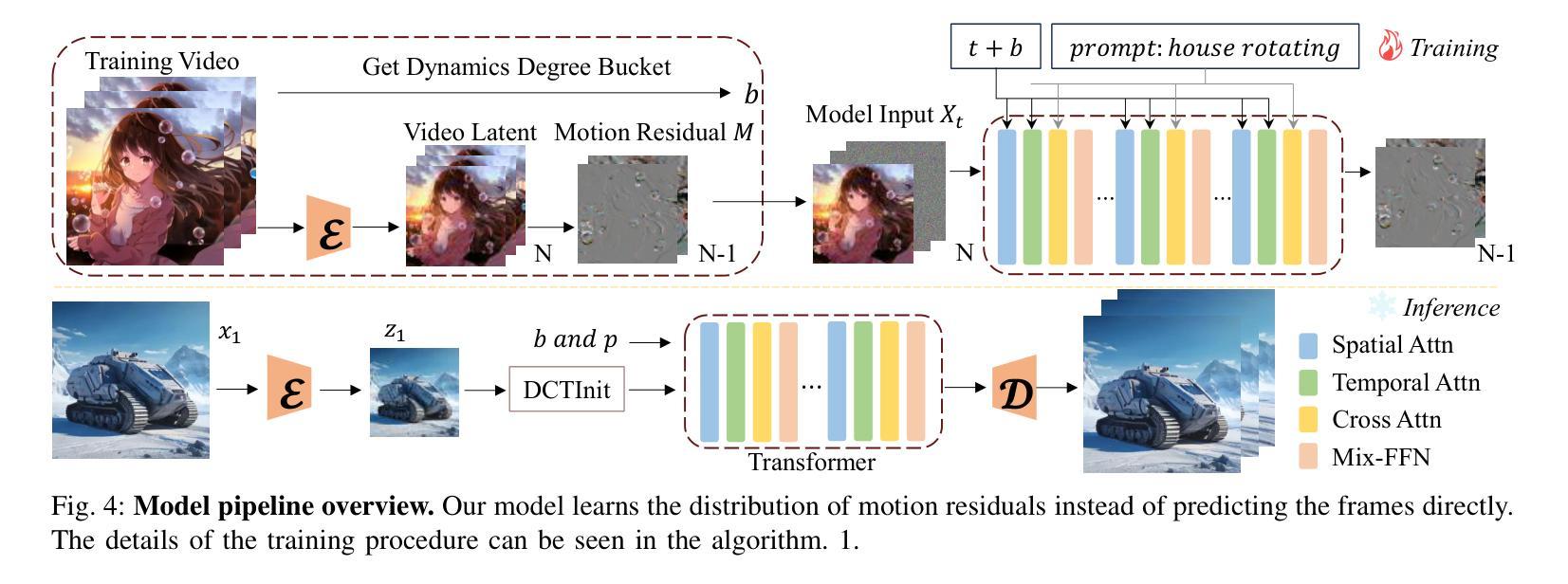
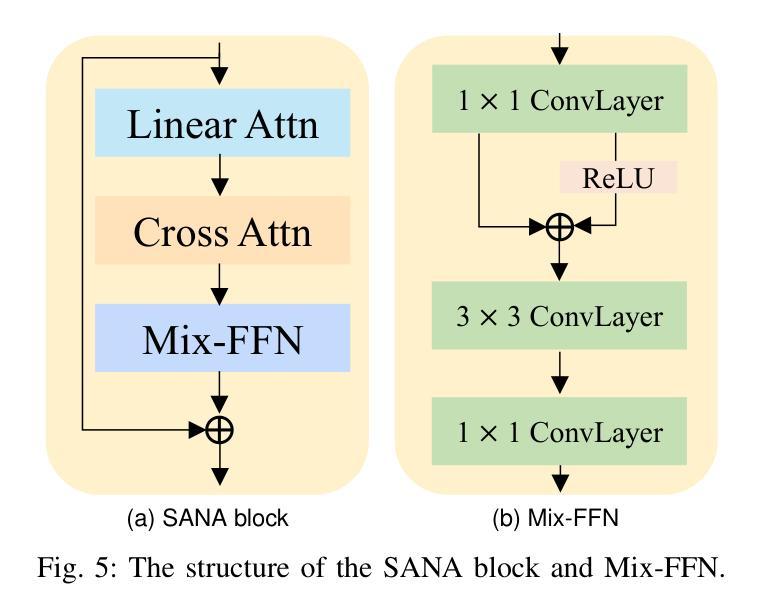
Consistent and Controllable Image Animation with Motion Linear Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Xin Ma, Yaohui Wang, Genyun Jia, Xinyuan Chen, Tien-Tsin Wong, Cunjian Chen
Image animation has seen significant progress, driven by the powerful generative capabilities of diffusion models. However, maintaining appearance consistency with static input images and mitigating abrupt motion transitions in generated animations remain persistent challenges. While text-to-video (T2V) generation has demonstrated impressive performance with diffusion transformer models, the image animation field still largely relies on U-Net-based diffusion models, which lag behind the latest T2V approaches. Moreover, the quadratic complexity of vanilla self-attention mechanisms in Transformers imposes heavy computational demands, making image animation particularly resource-intensive. To address these issues, we propose MiraMo, a framework designed to enhance efficiency, appearance consistency, and motion smoothness in image animation. Specifically, MiraMo introduces three key elements: (1) A foundational text-to-video architecture replacing vanilla self-attention with efficient linear attention to reduce computational overhead while preserving generation quality; (2) A novel motion residual learning paradigm that focuses on modeling motion dynamics rather than directly predicting frames, improving temporal consistency; and (3) A DCT-based noise refinement strategy during inference to suppress sudden motion artifacts, complemented by a dynamics control module to balance motion smoothness and expressiveness. Extensive experiments against state-of-the-art methods validate the superiority of MiraMo in generating consistent, smooth, and controllable animations with accelerated inference speed. Additionally, we demonstrate the versatility of MiraMo through applications in motion transfer and video editing tasks.
图像动画领域取得了显著的进步,这得益于扩散模型的强大生成能力。然而,保持与静态输入图像的外貌一致性,以及减轻生成动画中的突兀运动过渡,仍然是持续存在的挑战。尽管文本到视频(T2V)生成已经展示了扩散变压器模型的令人印象深刻的表现,但图像动画领域仍然主要依赖于基于U-Net的扩散模型,这些模型落后于最新的T2V方法。此外,Transformer中普通自注意力机制的二次复杂性带来了巨大的计算需求,使得图像动画特别耗费资源。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MiraMo,这是一个旨在提高图像动画的效率、外观一致性和运动平滑度的框架。具体来说,MiraMo引入了三个关键要素:1)一种基础文本到视频架构,用高效的线性注意力替换普通自注意力,以降低计算开销同时保持生成质量;2)一种新颖的运动残差学习范式,侧重于模拟运动动力学而不是直接预测帧,以提高时间一致性;3)一种基于DCT的推理过程中的噪声细化策略,抑制突然的运动伪影,辅以动力学控制模块来平衡运动的平滑度和表现力。与最先进的方法的大量实验验证了MiraMo在生成一致、平滑和可控的动画方面的优越性,同时加快了推理速度。此外,我们还通过运动转移和视频编辑任务的应用展示了MiraMo的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://maxin-cn.github.io/miramo_project
Summary
扩散模型在图像动画领域取得了显著进展,但保持与静态输入图像的外观一致性以及减轻生成动画中的突兀运动过渡仍是持续挑战。虽然文本到视频(T2V)生成已经展示了扩散变压器模型的令人印象深刻的表现,但图像动画领域仍然主要依赖于U-Net基础的扩散模型,这些模型落后于最新的T2V方法。为此,我们提出了MiraMo框架,旨在提高图像动画的效率、外观一致性和运动平滑度。它通过引入高效线性注意力机制、运动残差学习范式和DCT噪声推理策略,改善了计算开销、时间一致性和运动突兀问题。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像动画领域有重大进展,但存在外观一致性和运动过渡的持续性挑战。
- 文本到视频(T2V)生成已经取得显著进步,但图像动画领域仍主要依赖U-Net基础的扩散模型。
- MiraMo框架通过引入高效线性注意力机制,提高了计算效率并保持了生成质量。
- MiraMo引入了运动残差学习范式,专注于模拟运动动力学,提高了时间一致性。
- DCT噪声推理策略在推理过程中被用来抑制突然的运动伪影。
- MiraMo框架能够生成一致、平滑和可控的动画,并具有加速的推理速度。
点此查看论文截图


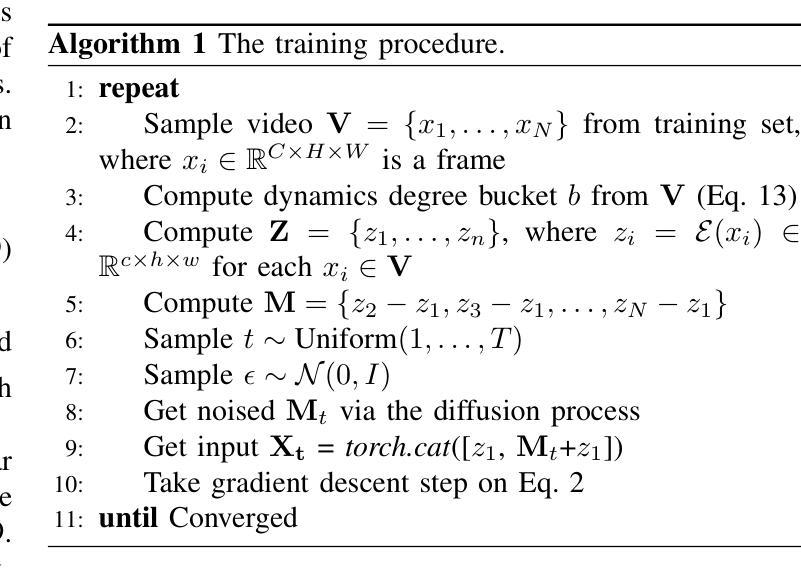
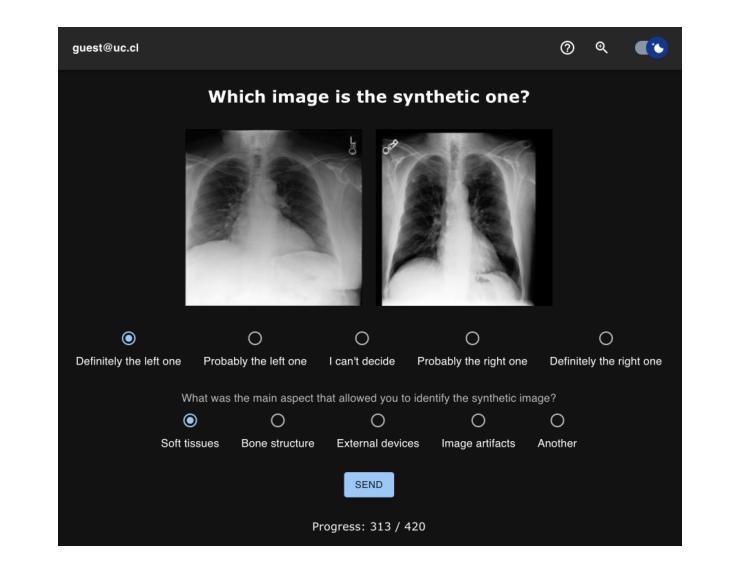
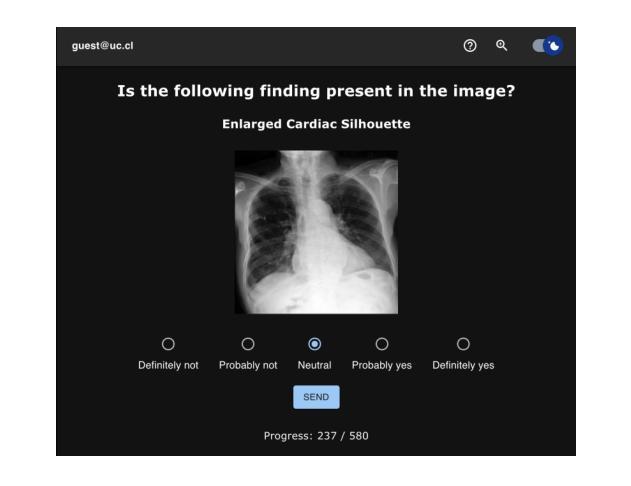
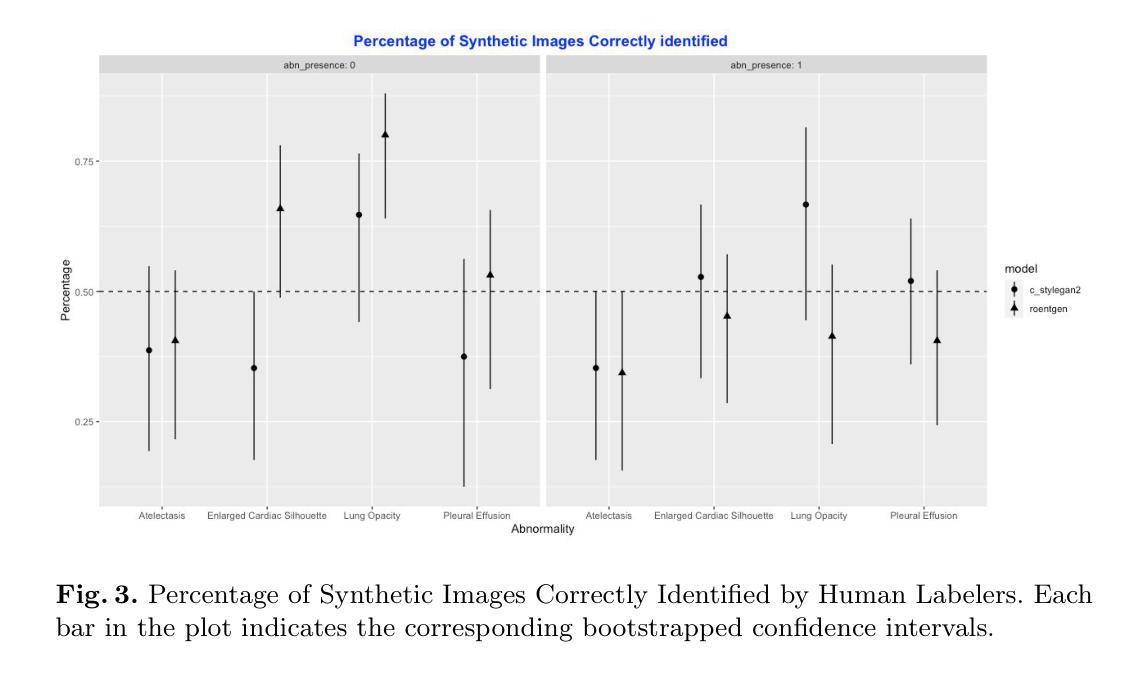
Perceptual Evaluation of GANs and Diffusion Models for Generating X-rays
Authors:Gregory Schuit, Denis Parra, Cecilia Besa
Generative image models have achieved remarkable progress in both natural and medical imaging. In the medical context, these techniques offer a potential solution to data scarcity-especially for low-prevalence anomalies that impair the performance of AI-driven diagnostic and segmentation tools. However, questions remain regarding the fidelity and clinical utility of synthetic images, since poor generation quality can undermine model generalizability and trust. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art generative models-Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs)-for synthesizing chest X-rays conditioned on four abnormalities: Atelectasis (AT), Lung Opacity (LO), Pleural Effusion (PE), and Enlarged Cardiac Silhouette (ECS). Using a benchmark composed of real images from the MIMIC-CXR dataset and synthetic images from both GANs and DMs, we conducted a reader study with three radiologists of varied experience. Participants were asked to distinguish real from synthetic images and assess the consistency between visual features and the target abnormality. Our results show that while DMs generate more visually realistic images overall, GANs can report better accuracy for specific conditions, such as absence of ECS. We further identify visual cues radiologists use to detect synthetic images, offering insights into the perceptual gaps in current models. These findings underscore the complementary strengths of GANs and DMs and point to the need for further refinement to ensure generative models can reliably augment training datasets for AI diagnostic systems.
生成图像模型在自然和医学影像方面都取得了显著的进步。在医疗背景下,这些技术为解决数据稀缺问题提供了潜在解决方案,尤其是针对那些低发病率异常导致的AI诊断和分割工具性能下降的问题。然而,关于合成图像的保真度和临床实用性仍存在疑问,因为生成质量差可能会损害模型的通用性和信任度。在这项研究中,我们评估了最先进的生成模型——生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在基于四种异常情况合成胸部X射线图像方面的有效性:肺不张(AT)、肺实变(LO)、胸膜积液(PE)和心脏轮廓增大(ECS)。我们使用来自MIMIC-CXR数据集的真实图像和来自GANs及DMs的合成图像组成的基准测试集,对三位不同经验的放射科医生进行了一项读者研究。参与者被要求区分真实和合成图像,并评估视觉特征与目标异常之间的一致性。我们的结果表明,虽然DMs总体上生成了更逼真的图像,但GANs在特定条件下的准确性更高,如ECS不存在的情况。我们还确定了放射科医生用来检测合成图像的可视线索,这为我们提供了对当前模型感知差距的见解。这些发现强调了GANs和DMs的互补优势,并指出需要进一步改进,以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Workshop on Human-AI Collaboration at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文研究了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在合成胸部X光片图像方面的表现,针对四种异常情况进行了评估:肺不张、肺实变、胸膜积液和心脏轮廓增大。研究发现,扩散模型生成的图像整体视觉更真实,而GANs在某些特定条件下的准确性更高。此外,通过读者研究识别了医生识别合成图像时使用的视觉线索,揭示了当前模型感知上的差距。研究表明,GANs和DMs各有优势,需要进一步改进以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 生成图像模型在自然和医学成像领域取得了显著进展,为解决数据稀缺问题提供了潜在解决方案,特别是在低发病率异常情况下。
- 扩散模型(DMs)生成的图像整体视觉更真实,而生成对抗网络(GANs)在某些特定异常情况下表现更好。
- 在区分真实和合成图像以及评估图像视觉特征与目标异常一致性方面,三位不同经验程度的放射科医生参与了读者研究。
- 读者研究揭示了医生识别合成图像时使用的视觉线索,突出了当前模型的感知差距。
- 研究结果强调了GANs和DMs的互补优势,指出了进一步改进的必要性,以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
- 文章使用MIMIC-CXR数据集进行基准测试,为评估生成模型在医学图像领域的性能提供了重要参考。
点此查看论文截图

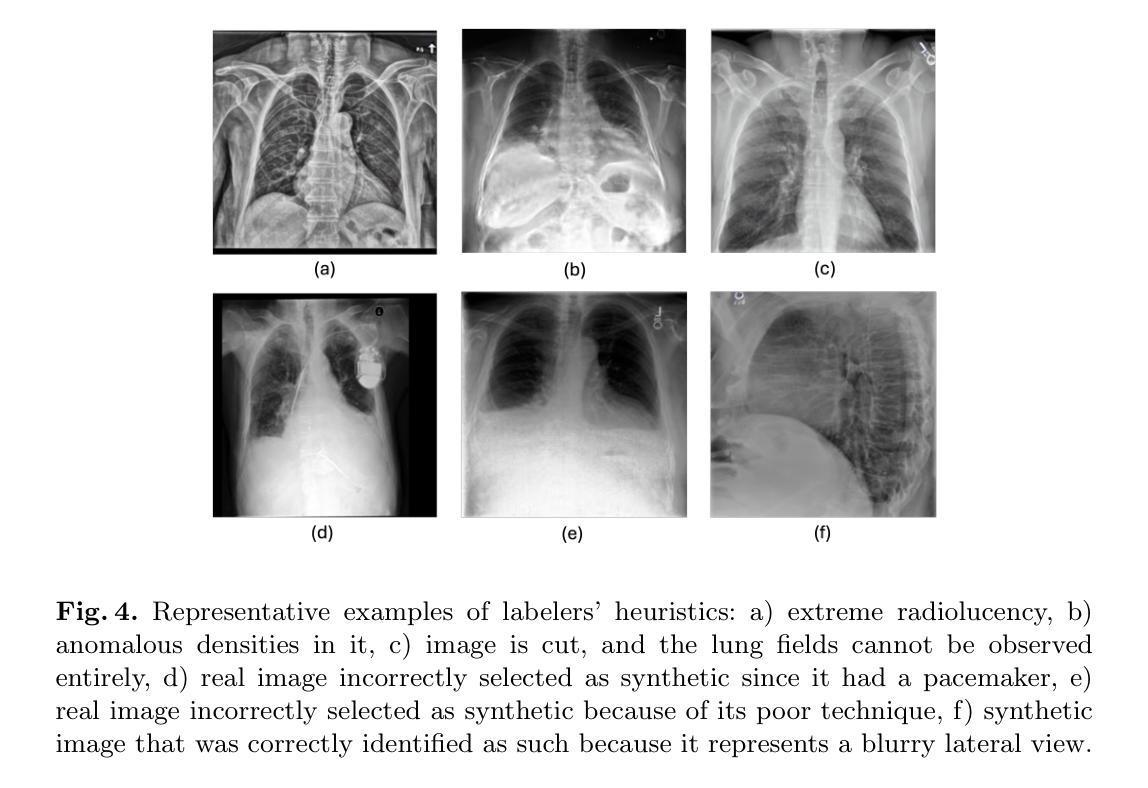
Spatio-Temporal Conditional Diffusion Models for Forecasting Future Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Masks Conditioned on Treatments
Authors:Gian Mario Favero, Ge Ya Luo, Nima Fathi, Justin Szeto, Douglas L. Arnold, Brennan Nichyporuk, Chris Pal, Tal Arbel
Image-based personalized medicine has the potential to transform healthcare, particularly for diseases that exhibit heterogeneous progression such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS). In this work, we introduce the first treatment-aware spatio-temporal diffusion model that is able to generate future masks demonstrating lesion evolution in MS. Our voxel-space approach incorporates multi-modal patient data, including MRI and treatment information, to forecast new and enlarging T2 (NET2) lesion masks at a future time point. Extensive experiments on a multi-centre dataset of 2131 patient 3D MRIs from randomized clinical trials for relapsing-remitting MS demonstrate that our generative model is able to accurately predict NET2 lesion masks for patients across six different treatments. Moreover, we demonstrate our model has the potential for real-world clinical applications through downstream tasks such as future lesion count and location estimation, binary lesion activity classification, and generating counterfactual future NET2 masks for several treatments with different efficacies. This work highlights the potential of causal, image-based generative models as powerful tools for advancing data-driven prognostics in MS.
基于图像的个性化医疗具有改变医疗保健的潜力,特别是在多发性硬化症(MS)等表现出异质进展的疾病中。在这项工作中,我们引入了第一个能生成未来掩码的时空扩散模型,这些掩码显示MS中的病灶演变。我们的体素空间方法结合了多模态患者数据,包括MRI和治疗信息,以预测未来某个时间点的新的和扩大的T2(NET2)病灶掩码。在来自复发缓解型MS随机临床试验的2131名患者的多中心数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的生成模型能够准确预测六种不同治疗方法下患者的NET2病灶掩码。此外,我们通过下游任务展示了我们的模型在现实临床应用中的潜力,如未来的病灶计数和位置估计、二元病灶活动分类以及为几种不同疗效的治疗生成反事实未来的NET2掩码。这项工作突出了因果、基于图像的生成模型作为推进MS数据驱动预后预测的强大工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025 (LMID Workshop)
Summary
本文介绍了首个治疗感知的时空扩散模型,该模型能够生成展示多发性硬化症(MS)病变演变的未来掩膜。通过结合多模态患者数据(包括MRI和治疗信息),该模型在随机临床试验的多中心数据集上进行了广泛实验,准确预测了六种不同治疗下患者的NET2病变掩膜。此外,该模型还展示了在下游任务(如未来病变计数和位置估计、二元病变活动分类以及为不同疗效的治疗生成反事实未来NET2掩膜)中的实际应用潜力,突显了因果图像生成模型在推进多发性硬化症数据驱动预后中的强大作用。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了首个治疗感知的时空扩散模型,用于生成展示多发性硬化症(MS)病变演变的未来掩膜。
- 通过结合多模态患者数据(包括MRI和治疗信息),在预测MS病变演变方面取得了显著成果。
- 模型在多个治疗下的患者数据上进行了广泛实验,准确预测了NET2病变掩膜。
- 模型展示了在下游任务中的实际应用潜力,包括未来病变计数和位置估计、二元病变活动分类等。
- 模型能够生成不同治疗下的反事实未来NET2掩膜,为临床决策提供支持。
- 本研究突显了因果图像生成模型在推进数据驱动的多发性硬化症预后中的重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

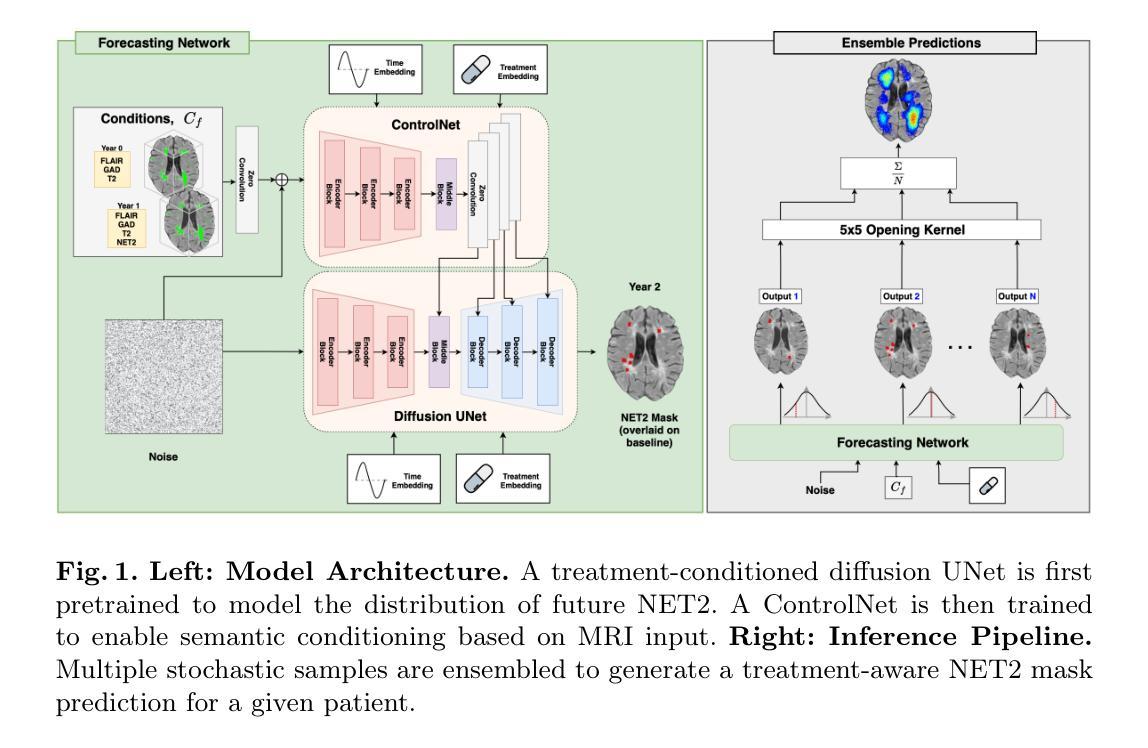
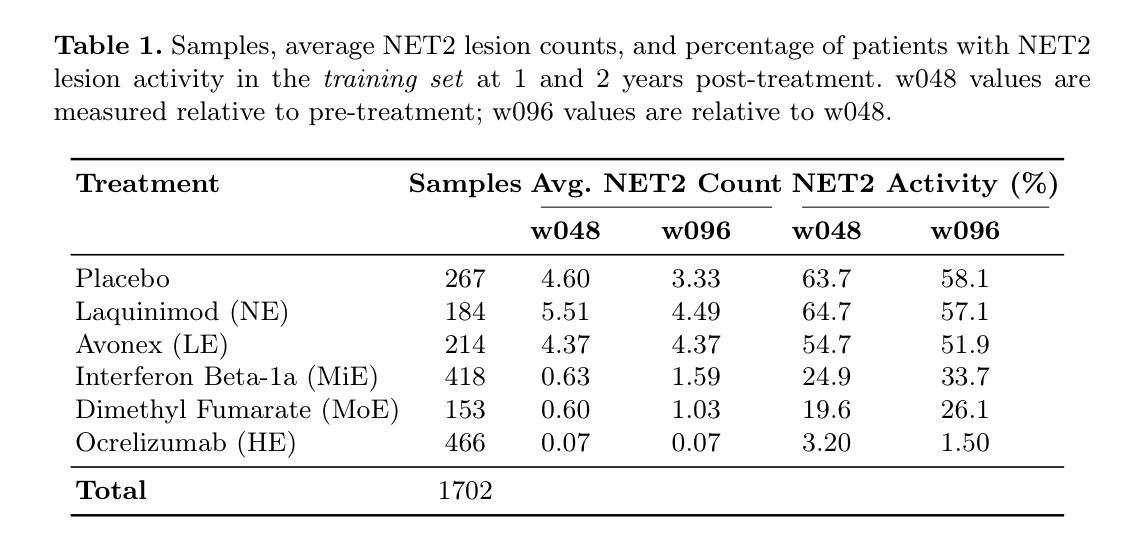
WeatherDiffusion: Weather-Guided Diffusion Model for Forward and Inverse Rendering
Authors:Yixin Zhu, Zuoliang Zhu, Miloš Hašan, Jian Yang, Jin Xie, Beibei Wang
Forward and inverse rendering have emerged as key techniques for enabling understanding and reconstruction in the context of autonomous driving (AD). However, complex weather and illumination pose great challenges to this task. The emergence of large diffusion models has shown promise in achieving reasonable results through learning from 2D priors, but these models are difficult to control and lack robustness. In this paper, we introduce WeatherDiffusion, a diffusion-based framework for forward and inverse rendering on AD scenes with various weather and lighting conditions. Our method enables authentic estimation of material properties, scene geometry, and lighting, and further supports controllable weather and illumination editing through the use of predicted intrinsic maps guided by text descriptions. We observe that different intrinsic maps should correspond to different regions of the original image. Based on this observation, we propose Intrinsic map-aware attention (MAA) to enable high-quality inverse rendering. Additionally, we introduce a synthetic dataset (\ie WeatherSynthetic) and a real-world dataset (\ie WeatherReal) for forward and inverse rendering on AD scenes with diverse weather and lighting. Extensive experiments show that our WeatherDiffusion outperforms state-of-the-art methods on several benchmarks. Moreover, our method demonstrates significant value in downstream tasks for AD, enhancing the robustness of object detection and image segmentation in challenging weather scenarios.
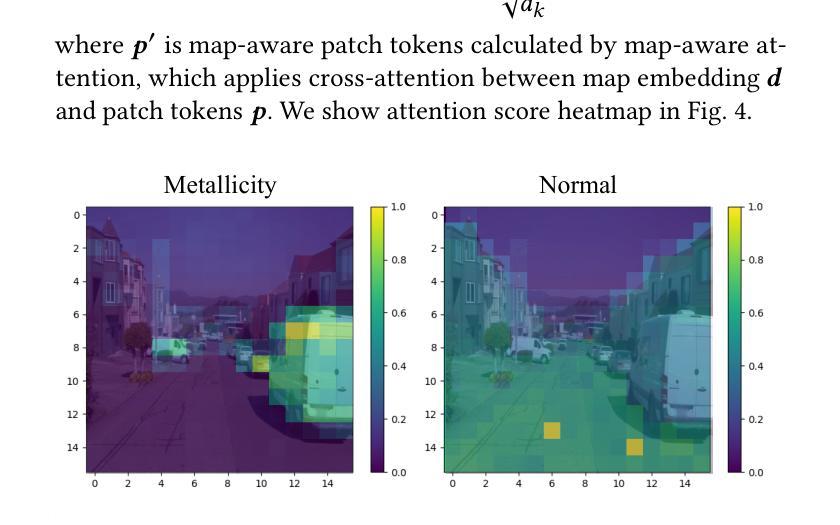
正向和逆向渲染技术在自动驾驶(AD)的上下文中已经成为实现理解和重建的关键技术。然而,复杂的天气和光照条件给这一任务带来了很大的挑战。大型扩散模型的兴起显示出通过学习二维先验知识实现合理结果的潜力,但这些模型难以控制和缺乏稳健性。在本文中,我们介绍了WeatherDiffusion,这是一个基于扩散的框架,用于在具有各种天气和光照条件的AD场景上进行正向和逆向渲染。我们的方法能够真实估计材料属性、场景几何和光照,并且进一步通过预测的固有地图和文本描述的支持来实现可控的天气和光照编辑。我们观察到不同的固有地图应该对应于原始图像的不同区域。基于这一观察,我们提出了固有地图感知注意力(MAA)以实现高质量的反向渲染。此外,我们还介绍了合成数据集(即WeatherSynthetic)和真实世界数据集(即WeatherReal),用于在具有各种天气和光照条件的AD场景上进行正向和逆向渲染。大量实验表明,我们的WeatherDiffusion在多个基准测试上超越了最先进的方法。而且,我们的方法在自动驾驶的下游任务中显示出显著的价值,提高了在具有挑战性的天气情况下对象检测和图像分割的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对自动驾驶(AD)场景中的天气和光照变化,采用扩散模型实现的渲染技术。文章提出了一个名为WeatherDiffusion的框架,结合了正向和逆向渲染技术,实现了在不同天气和光照条件下的场景重建。该框架可估算材质属性、场景几何结构和光照,并支持通过文本描述进行可控的天气和光照编辑。为提高逆向渲染质量,文章还提出了基于内在图谱感知的注意力机制(Intrinsic map-aware attention,MAA)。此外,文章介绍了合成数据集(WeatherSynthetic)和真实世界数据集(WeatherReal),并通过大量实验验证了WeatherDiffusion在多个基准测试上的优越性能,特别是在下游自动驾驶任务中的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了自动驾驶中天气和光照变化的挑战。
- 提出了一种名为WeatherDiffusion的扩散模型框架,用于应对不同天气和光照条件下的正向和逆向渲染。
- WeatherDiffusion可估算材质属性、场景几何结构和光照,并支持可控的天气和光照编辑。
- 提出基于内在图谱感知的注意力机制(MAA)以提高逆向渲染质量。
- 介绍了合成数据集(WeatherSynthetic)和真实世界数据集(WeatherReal)用于自动驾驶场景的渲染研究。
- 实验表明,WeatherDiffusion在多个基准测试上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图



MoGA: 3D Generative Avatar Prior for Monocular Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction
Authors:Zijian Dong, Longteng Duan, Jie Song, Michael J. Black, Andreas Geiger
We present MoGA, a novel method to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D Gaussian avatars from a single-view image. The main challenge lies in inferring unseen appearance and geometric details while ensuring 3D consistency and realism. Most previous methods rely on 2D diffusion models to synthesize unseen views; however, these generated views are sparse and inconsistent, resulting in unrealistic 3D artifacts and blurred appearance. To address these limitations, we leverage a generative avatar model, that can generate diverse 3D avatars by sampling deformed Gaussians from a learned prior distribution. Due to limited 3D training data, such a 3D model alone cannot capture all image details of unseen identities. Consequently, we integrate it as a prior, ensuring 3D consistency by projecting input images into its latent space and enforcing additional 3D appearance and geometric constraints. Our novel approach formulates Gaussian avatar creation as model inversion by fitting the generative avatar to synthetic views from 2D diffusion models. The generative avatar provides an initialization for model fitting, enforces 3D regularization, and helps in refining pose. Experiments show that our method surpasses state-of-the-art techniques and generalizes well to real-world scenarios. Our Gaussian avatars are also inherently animatable. For code, see https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/.
我们提出了MoGA这一新方法,可以从单视角图像重建高保真3D高斯头像。主要挑战在于推断出不可见的外观和几何细节,同时确保3D一致性和逼真性。之前的大多数方法都依赖于2D扩散模型来合成未见视图;然而,这些生成的视图稀疏且不一致,导致3D伪影和模糊的外观。为了解决这个问题,我们利用生成头像模型,通过从学习到的先验分布中采样变形高斯分布,可以生成多样化的3D头像。由于有限的3D训练数据,仅使用这样的3D模型无法捕获未见身份的所有图像细节。因此,我们将其整合为先验,通过将输入图像投影到其潜在空间并施加额外的3D外观和几何约束来确保3D一致性。我们的新方法将高斯头像创建表述为模型反演,通过将生成头像拟合到来自2D扩散模型的合成视图来实现。生成头像为模型拟合提供了初始化,强制实施3D正则化,并有助于优化姿态。实验表明,我们的方法超越了最先进的技术,并能很好地推广到现实世界场景。我们的高斯头像也具有内在的可动画性。有关代码,请参见https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 (Highlight), Project Page: https://zj-dong.github.io/MoGA/
Summary
MoGA方法能够从单视角图像重建高保真3D高斯化身。它通过结合生成化身模型和2D扩散模型,解决了之前方法生成的视图稀疏和不一致的问题,确保了3D一致性并呈现出更真实的视觉效果。实验表明,MoGA超越了当前的技术并很好地适应现实场景。其创建的Gaussian化身具有内在的可动画性。
Key Takeaways
- MoGA是一个能够从单视角图像重建高保真3D高斯化身的新方法。
- 该方法结合生成化身模型和2D扩散模型,解决了之前方法的视图稀疏和不一致问题。
- MoGA确保了3D一致性并呈现出更真实的视觉效果。
- MoGA通过模型拟合将生成化身作为初始化,并执行3D正则化以优化姿态。
- 该方法超越了当前技术并很好地适应现实场景。
- MoGA创建的Gaussian化身具有内在的可动画性。
点此查看论文截图


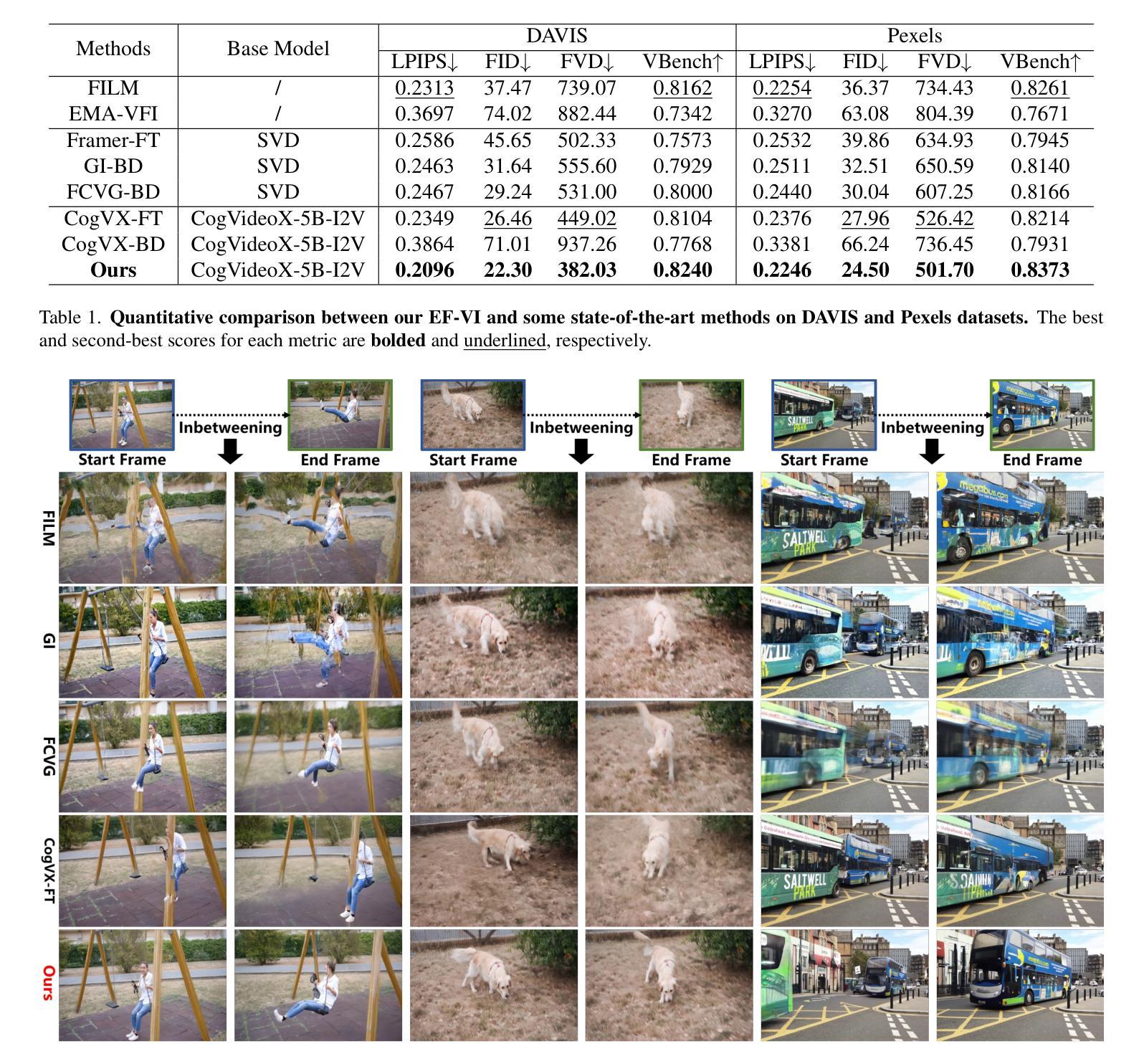
EF-VI: Enhancing End-Frame Injection for Video Inbetweening
Authors:Liuhan Chen, Xiaodong Cun, Xiaoyu Li, Xianyi He, Shenghai Yuan, Jie Chen, Ying Shan, Li Yuan
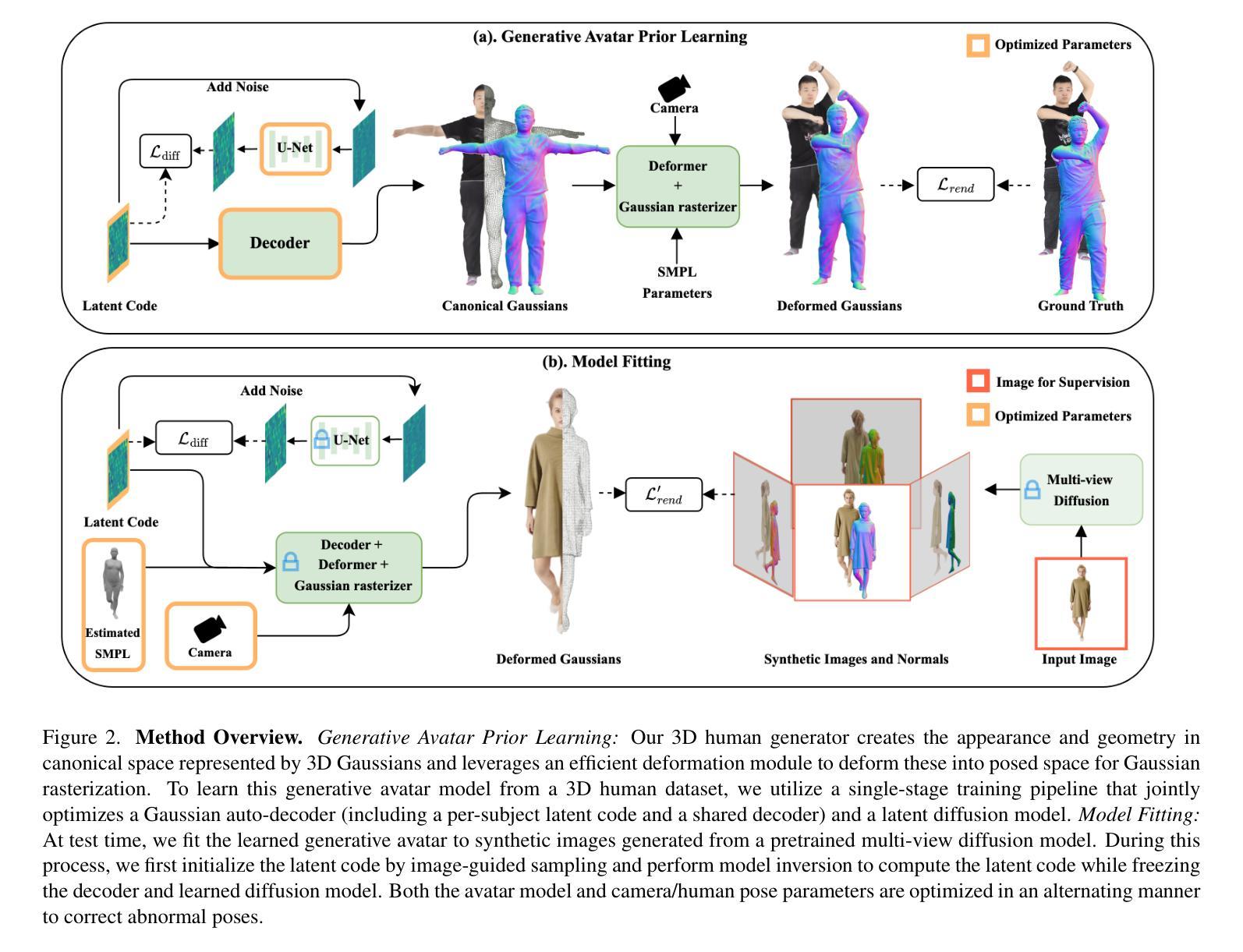
Video inbetweening aims to synthesize intermediate video sequences conditioned on the given start and end frames. Current state-of-the-art methods primarily extend large-scale pre-trained Image-to-Video Diffusion Models (I2V-DMs) by incorporating the end-frame condition via direct fine-tuning or temporally bidirectional sampling. However, the former results in a weak end-frame constraint, while the latter inevitably disrupts the input representation of video frames, leading to suboptimal performance. To improve the end-frame constraint while avoiding disruption of the input representation, we propose a novel video inbetweening framework specific to recent and more powerful transformer-based I2V-DMs, termed EF-VI. It efficiently strengthens the end-frame constraint by utilizing an enhanced injection. This is based on our proposed well-designed lightweight module, termed EF-Net, which encodes only the end frame and expands it into temporally adaptive frame-wise features injected into the I2V-DM. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our EF-VI compared with other baselines.
视频插帧旨在根据给定的起始帧和结束帧合成中间视频序列。当前最先进的方法主要是通过将结束帧条件融入大规模预训练的图像到视频扩散模型(I2V-DMs),通过直接微调或时间双向采样进行扩展。然而,前者导致结束帧约束较弱,而后者不可避免地破坏了视频帧的输入表示,导致性能不佳。为了加强结束帧的约束同时避免破坏输入表示,我们针对最新、更强大的基于transformer的I2V-DMs,提出了一种新型的视频插帧框架,称为EF-VI。它通过利用增强的注入来有效地加强结束帧的约束。这是基于我们提出的精心设计的小型模块EF-Net,它只编码结束帧并将其扩展为注入到I2V-DM中的时间自适应帧级特征。大量实验证明,我们的EF-VI与其他基线相比具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 11 figures
Summary
针对视频插帧问题,现有方法主要基于大型预训练图像到视频扩散模型(I2V-DM),但存在端帧约束不足和输入表示破坏的问题。我们提出了一种新的视频插帧框架EF-VI,它强化了端帧约束,同时避免了输入表示的破坏。该框架利用一个名为EF-Net的轻量级模块,仅对端帧进行编码,并扩展为时间适应性帧级特征,注入到I2V-DM中。
Key Takeaways
- 视频插帧的目标是合成给定起始和结束帧之间的中间视频序列。
- 当前先进的方法主要通过扩展预训练的图像到视频扩散模型(I2V-DM)来进行视频插帧。
- 现有方法存在端帧约束不足和输入表示破坏的问题。
- 我们提出的EF-VI框架旨在强化端帧约束,同时避免输入表示的破坏。
- EF-VI利用名为EF-Net的轻量级模块,仅对端帧进行编码,并转化为时间适应性帧级特征。
- EF-Net模块被注入到I2V-DM中,以提高效率并强化端帧约束。
点此查看论文截图

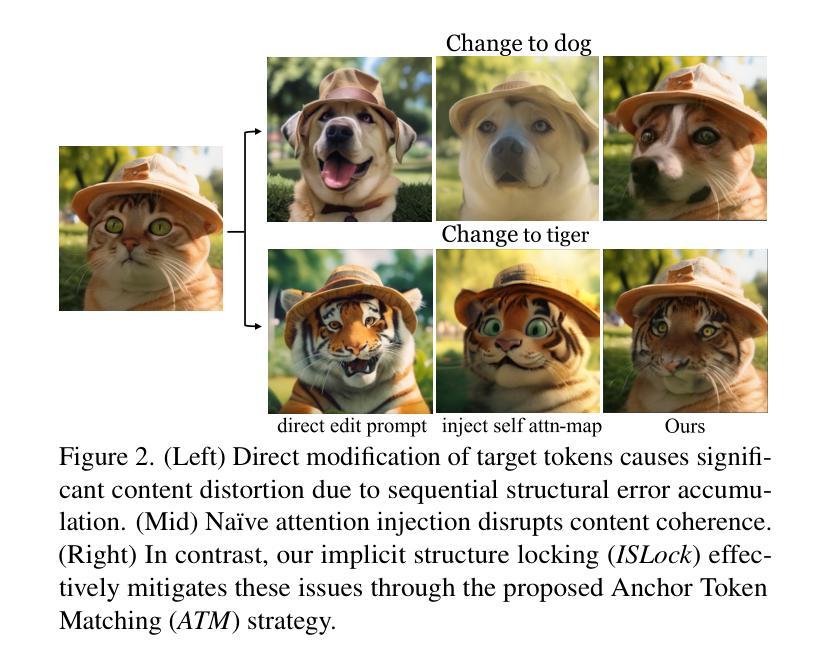
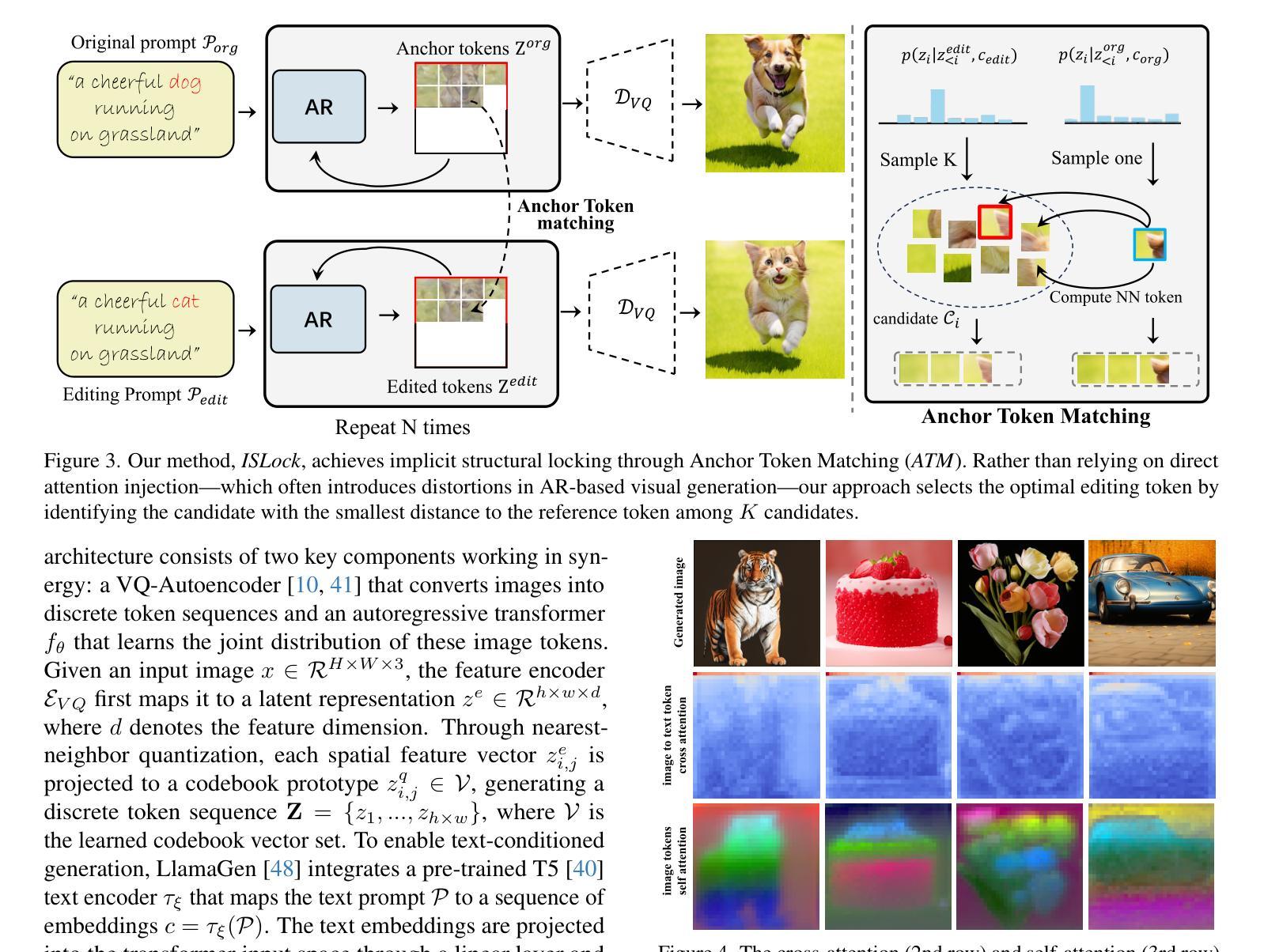
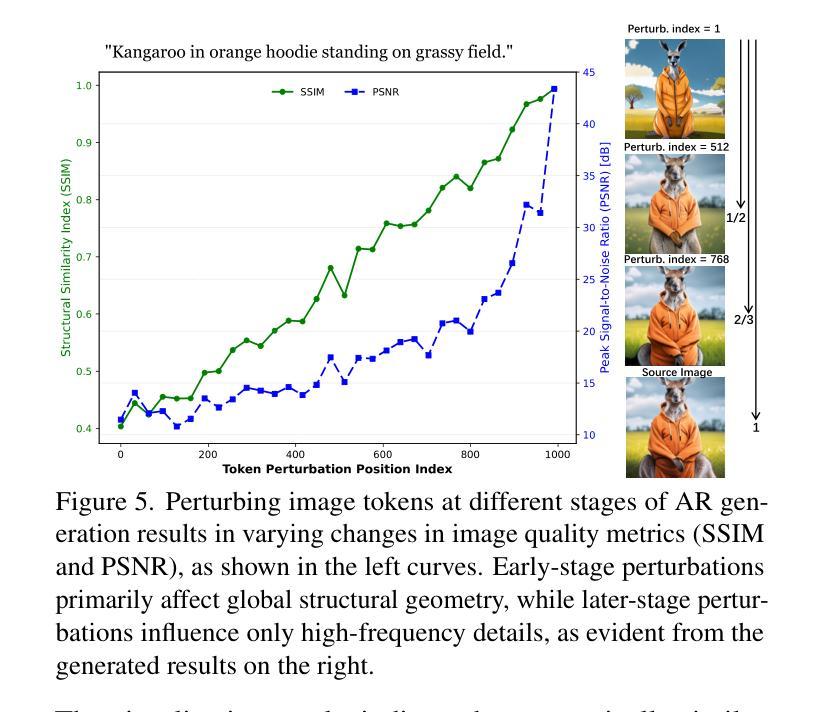
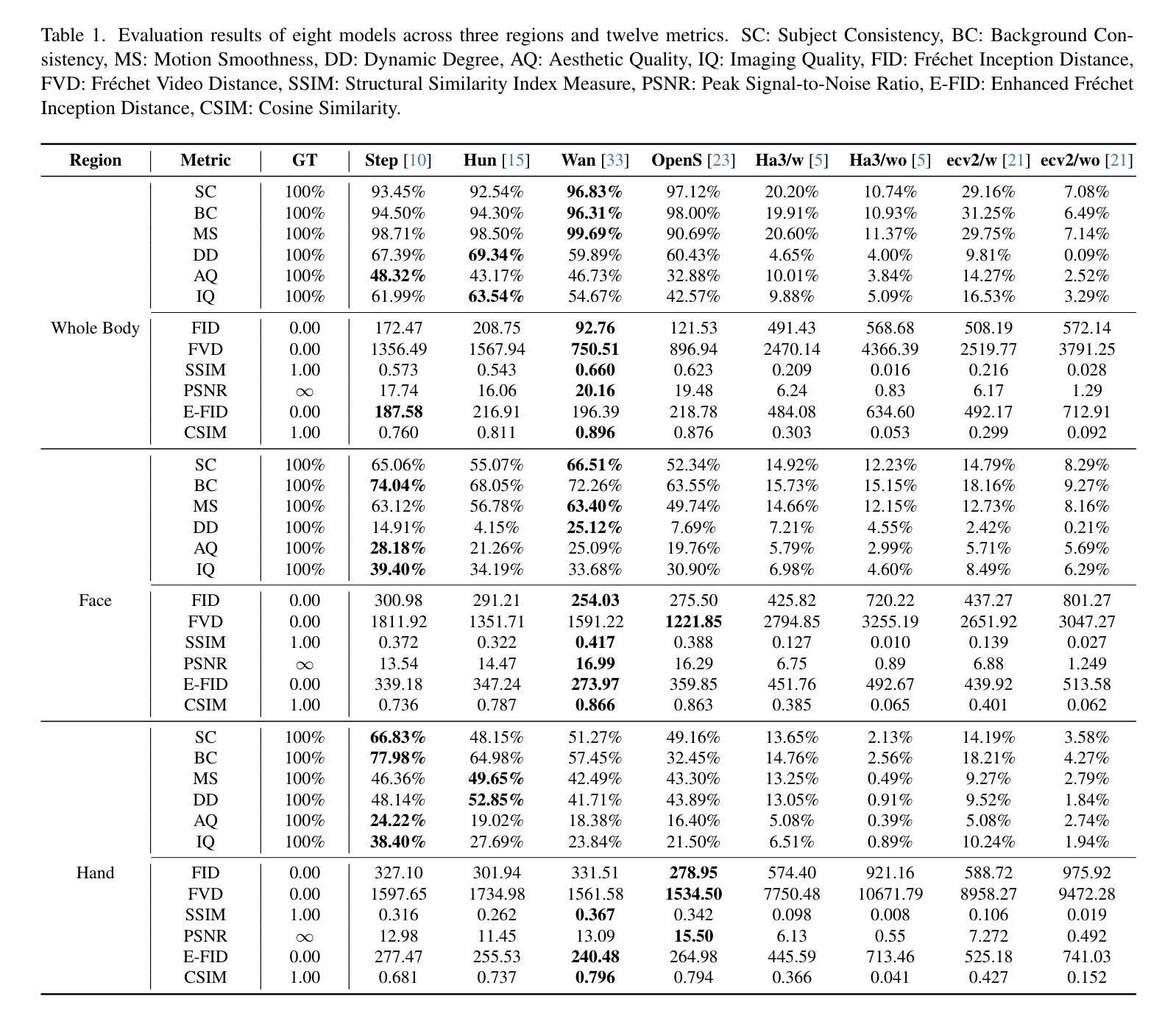
Anchor Token Matching: Implicit Structure Locking for Training-free AR Image Editing
Authors:Taihang Hu, Linxuan Li, Kai Wang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng
Text-to-image generation has seen groundbreaking advancements with diffusion models, enabling high-fidelity synthesis and precise image editing through cross-attention manipulation. Recently, autoregressive (AR) models have re-emerged as powerful alternatives, leveraging next-token generation to match diffusion models. However, existing editing techniques designed for diffusion models fail to translate directly to AR models due to fundamental differences in structural control. Specifically, AR models suffer from spatial poverty of attention maps and sequential accumulation of structural errors during image editing, which disrupt object layouts and global consistency. In this work, we introduce Implicit Structure Locking (ISLock), the first training-free editing strategy for AR visual models. Rather than relying on explicit attention manipulation or fine-tuning, ISLock preserves structural blueprints by dynamically aligning self-attention patterns with reference images through the Anchor Token Matching (ATM) protocol. By implicitly enforcing structural consistency in latent space, our method ISLock enables structure-aware editing while maintaining generative autonomy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ISLock achieves high-quality, structure-consistent edits without additional training and is superior or comparable to conventional editing techniques. Our findings pioneer the way for efficient and flexible AR-based image editing, further bridging the performance gap between diffusion and autoregressive generative models. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM
文本到图像生成领域在扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的推动下取得了突破性进展,通过跨注意力操纵(cross-attention manipulation)实现了高保真合成和精确图像编辑。近期,自回归(AR)模型作为强大的替代方案重新出现,利用下一代令牌生成(next-token generation)与扩散模型相匹配。然而,针对扩散模型设计的现有编辑技术无法直接应用于AR模型,因为它们在结构控制上存在根本差异。具体来说,AR模型存在注意力图的空间贫困问题(spatial poverty of attention maps)以及在图像编辑过程中序列累积的结构错误(sequential accumulation of structural errors),这破坏了对象布局和全局一致性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了无需训练的编辑策略——隐式结构锁定(ISLock),这是针对AR视觉模型的首个此类策略。ISLock不依赖于显式注意力操纵或微调,而是通过锚点令牌匹配(ATM)协议动态地将自我注意力模式与参考图像对齐,从而保留结构蓝图。通过在潜在空间中隐式强制执行结构一致性,我们的ISLock方法能够在保持生成自主性的同时进行结构感知编辑。大量实验表明,ISLock无需额外训练即可实现高质量、结构一致性的编辑,并且在传统编辑技术上具有优势或与之相当。我们的研究为高效、灵活的自回归(AR)图像编辑方式开辟了道路,进一步缩小了扩散模型和自回归生成模型之间的性能差距。代码将在https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025. Code will be released in https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM
Summary
扩散模型在文本转图像生成领域取得了突破性进展,能够实现高保真合成和通过跨注意力操纵精确图像编辑。近期,自回归(AR)模型作为强大的替代方法重新出现,利用下一代标记匹配扩散模型。然而,为扩散模型设计的编辑技术无法直接应用于AR模型,因为两者在结构控制上存在根本差异。AR模型面临注意力图的空间贫困和图像编辑中结构错误的顺序累积问题,会破坏对象布局和全局一致性。本研究提出无训练编辑策略——隐式结构锁定(ISLock),作为AR视觉模型的首创。ISLock通过动态对齐参考图像的自我注意力模式,借助锚标记匹配(ATM)协议,保留结构蓝图。通过在潜在空间中隐式强制执行结构一致性,ISLock能够在保持生成自主权的同时,实现结构感知编辑。实验证明,ISLock无需额外训练即可实现高质量、结构一致性的编辑,且优于或相当于传统编辑技术。这开辟了AR模型高效灵活图像编辑的先河,进一步缩小了扩散模型和自回归生成模型之间的性能差距。相关代码将公开在:https://github.com/hutaiHang/ATM。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本转图像生成中实现了高保真合成和精确编辑。
- 自回归(AR)模型作为强大的替代方法重新出现,利用下一代标记匹配扩散模型。
- AR模型在图像编辑中面临空间贫困和结构性错误的问题。
- 隐式结构锁定(ISLock)是无训练编辑策略,适用于AR视觉模型。
- ISLock通过动态对齐参考图像的自我注意力模式来保留结构蓝图。
- ISLock实现了结构感知编辑,且无需额外训练。
点此查看论文截图