⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
SystolicAttention: Fusing FlashAttention within a Single Systolic Array
Authors:Jiawei Lin, Guokai Chen, Yuanlong Li, Thomas Bourgeat
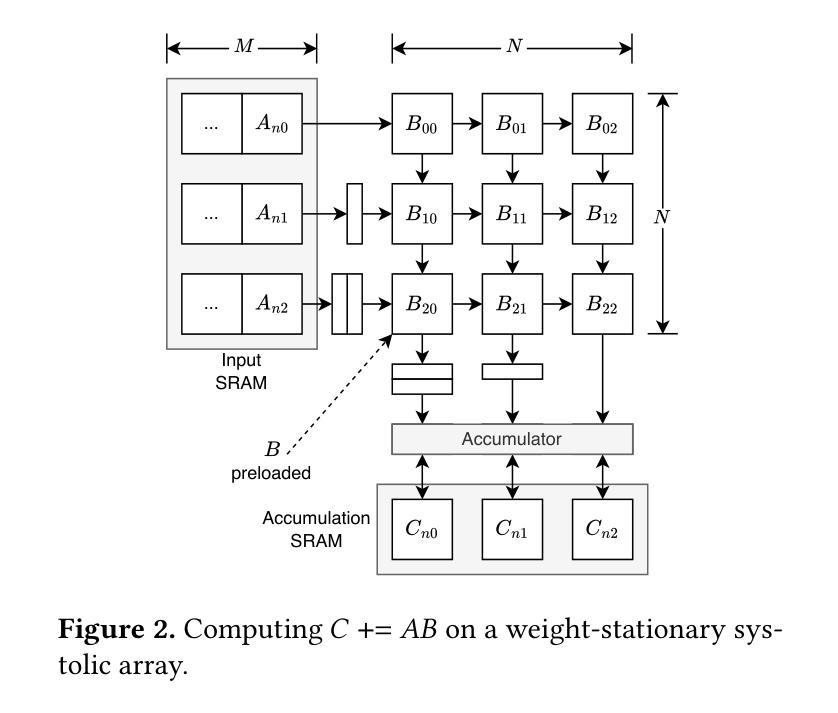
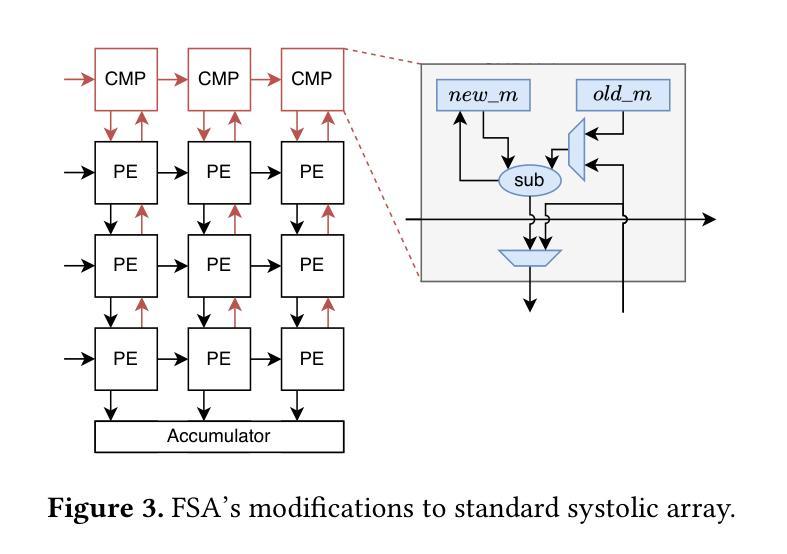
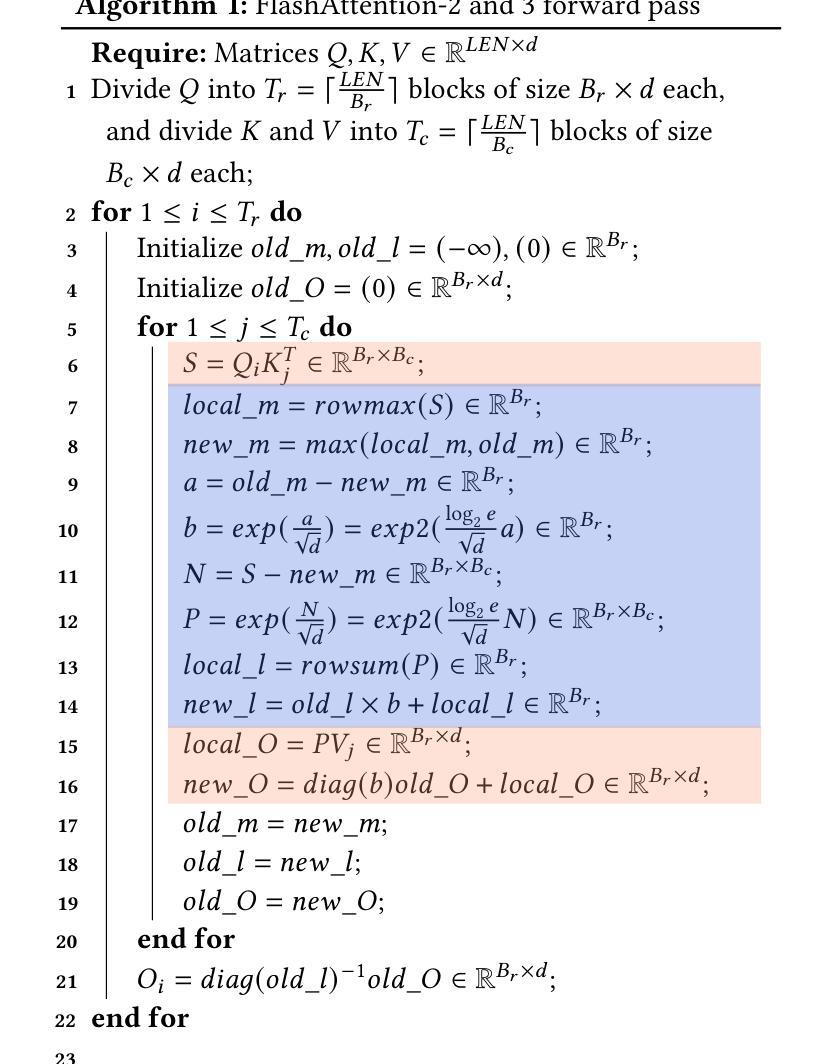
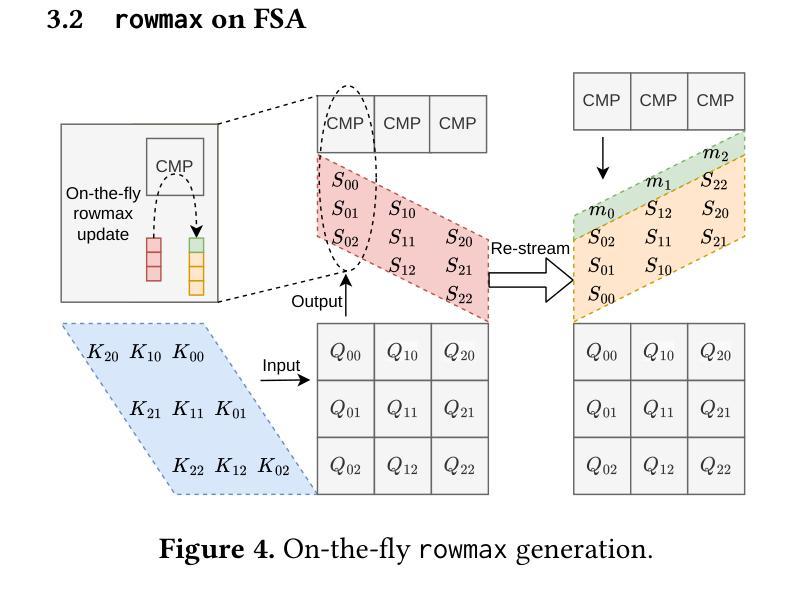
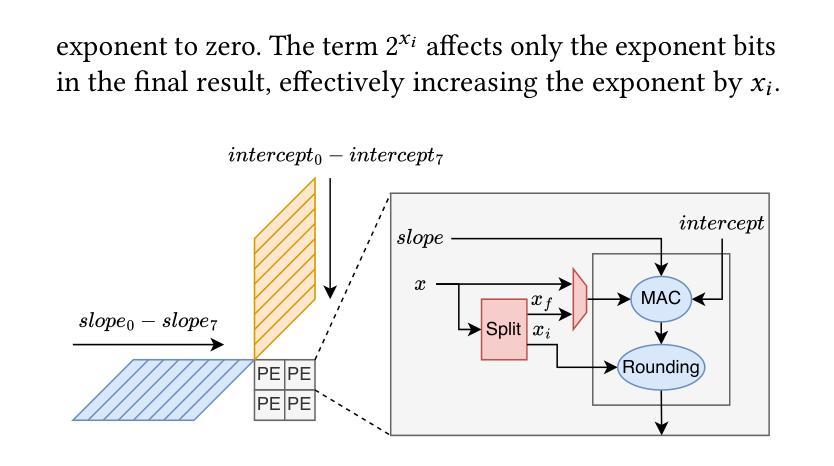
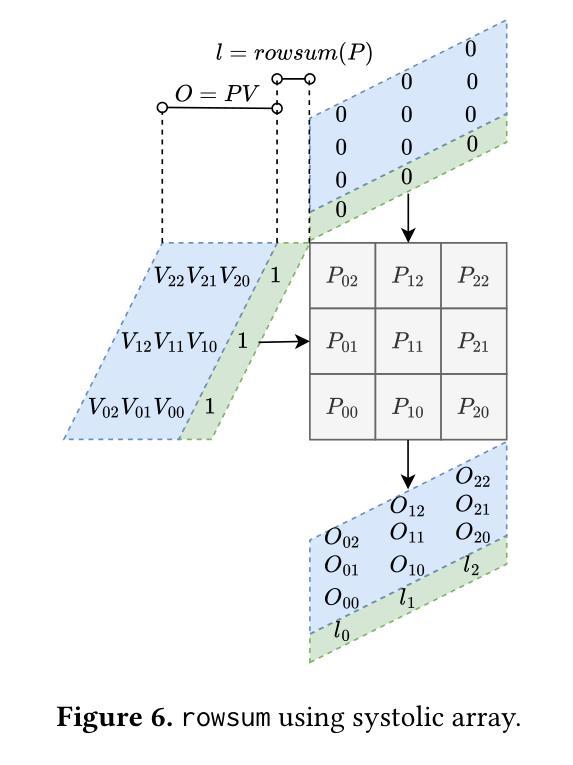
Transformer models rely heavily on scaled dot-product attention (SDPA), typically implemented using the FlashAttention algorithm. However, current systolic-array-based accelerators face significant challenges when executing FlashAttention. Systolic arrays achieve high utilization primarily for consecutive and large matrix multiplications, whereas FlashAttention requires frequent interleaving of matrix multiplications and softmax operations. The frequent data swaps between matrix multiplications on the systolic array and softmax operations on external units result in low array utilization. Moreover, when these computations run concurrently, the softmax stage contends with matrix multiplication for register file and SRAM ports, further degrading performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose FSA, an enhanced systolic array architecture that enables the FlashAttention algorithm to run entirely within a single systolic array, eliminating the need for external vector units. At the core of FSA is SystolicAttention, a novel scheduling algorithm that maps FlashAttention operations onto systolic arrays with fine-grained, element-wise overlap. This approach significantly improves array utilization while preserving the original floating-point operation order to maintain numerical stability. We implement FSA in synthesizable RTL and evaluate its performance against state-of-the-art commercial accelerators. Our results show that FSA achieves 1.77 and 4.83 times higher attention FLOPs/s utilization compared to AWS Neuron v2 and Google TPUv5e, respectively, with only 12% area overhead.
Transformer模型在很大程度上依赖于缩放点积注意力(SDPA),通常使用FlashAttention算法来实现。然而,当前的基于收缩阵列的加速器在执行FlashAttention时面临重大挑战。收缩阵列主要为了实现连续的、大规模的矩阵乘法而达到高利用率,而FlashAttention则需要频繁地交替进行矩阵乘法和Softmax操作。收缩阵列上矩阵乘法与外置单元上Softmax操作之间的频繁数据交换导致阵列利用率低。此外,当这些计算并行运行时,Softmax阶段与矩阵乘法竞争寄存器文件和SRAM端口,进一步降低性能。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了FSA,这是一种增强的收缩阵列架构,它能够让FlashAttention算法完全在一个单一的收缩阵列内运行,无需外部向量单元。FSA的核心是SystolicAttention,这是一种新型调度算法,它以细粒度、逐元素重叠的方式将FlashAttention操作映射到收缩阵列上。这种方法在保持原始浮点操作顺序以维持数值稳定性的同时,显著提高了阵列利用率。我们将FSA用可综合RTL实现,并对其性能进行了与最先进的商业加速器的评估。结果表明,FSA相对于AWS Neuron v2和Google TPUv5e分别实现了1.77和4.83倍的注意力FLOPs/s利用率提升,并且只有12%的面积开销。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了Transformer模型在采用FlashAttention算法实现缩放点积注意力(SDPA)时面临的挑战。针对systolic array架构在执行FlashAttention时利用率低的问题,提出了一种名为FSA的增强型systolic array架构。该架构通过引入SystolicAttention调度算法,实现了FlashAttention操作在systolic array上的精细粒度映射和元素级重叠,显著提高了阵列利用率并保持了数值稳定性。相较于现有的商业加速器,FSA实现了更高的注意力FLOPs/s利用率。
Key Takeaways:
- Transformer模型依赖FlashAttention算法实现缩放点积注意力(SDPA)。
- Systolic arrays面临执行FlashAttention时的挑战,主要表现为利用率不高。
- FSA架构旨在解决这一问题,通过增强systolic array实现在单个阵列上完全运行FlashAttention算法。
- FSA引入SystolicAttention调度算法,实现了精细粒度的操作映射和元素级重叠。
- FSA提高了阵列利用率,同时保持了数值稳定性。
- 相较于AWS Neuron v2和Google TPUv5e,FSA实现了更高的注意力FLOPs/s利用率。
点此查看论文截图