⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
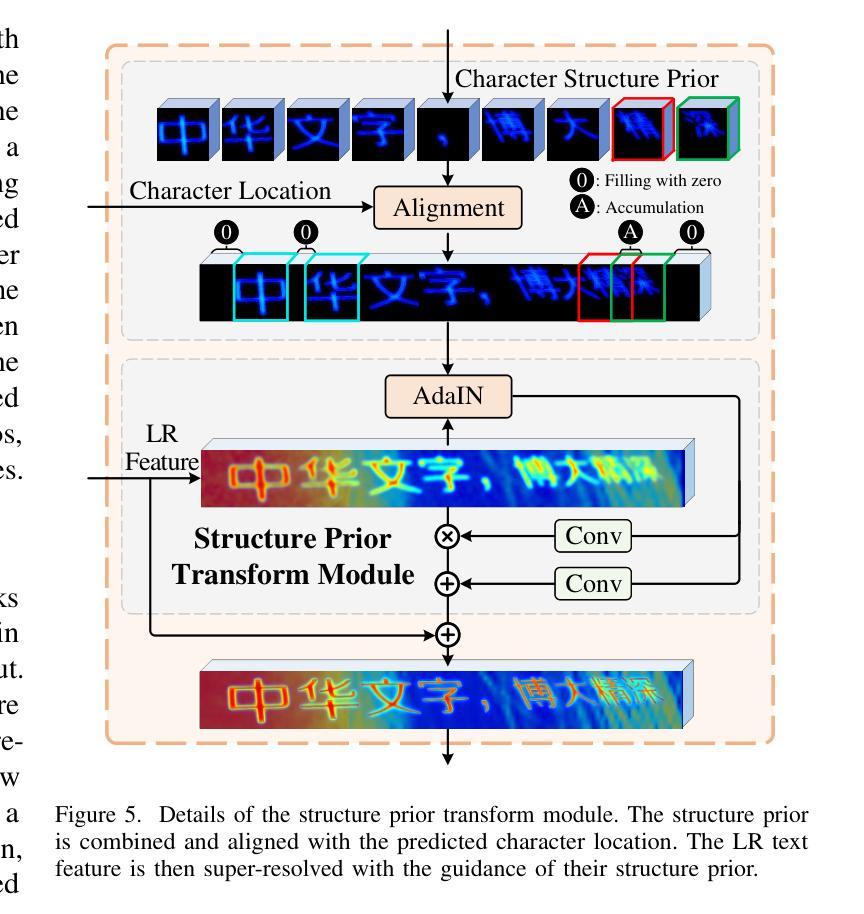
Enhanced Generative Structure Prior for Chinese Text Image Super-resolution
Authors:Xiaoming Li, Wangmeng Zuo, Chen Change Loy
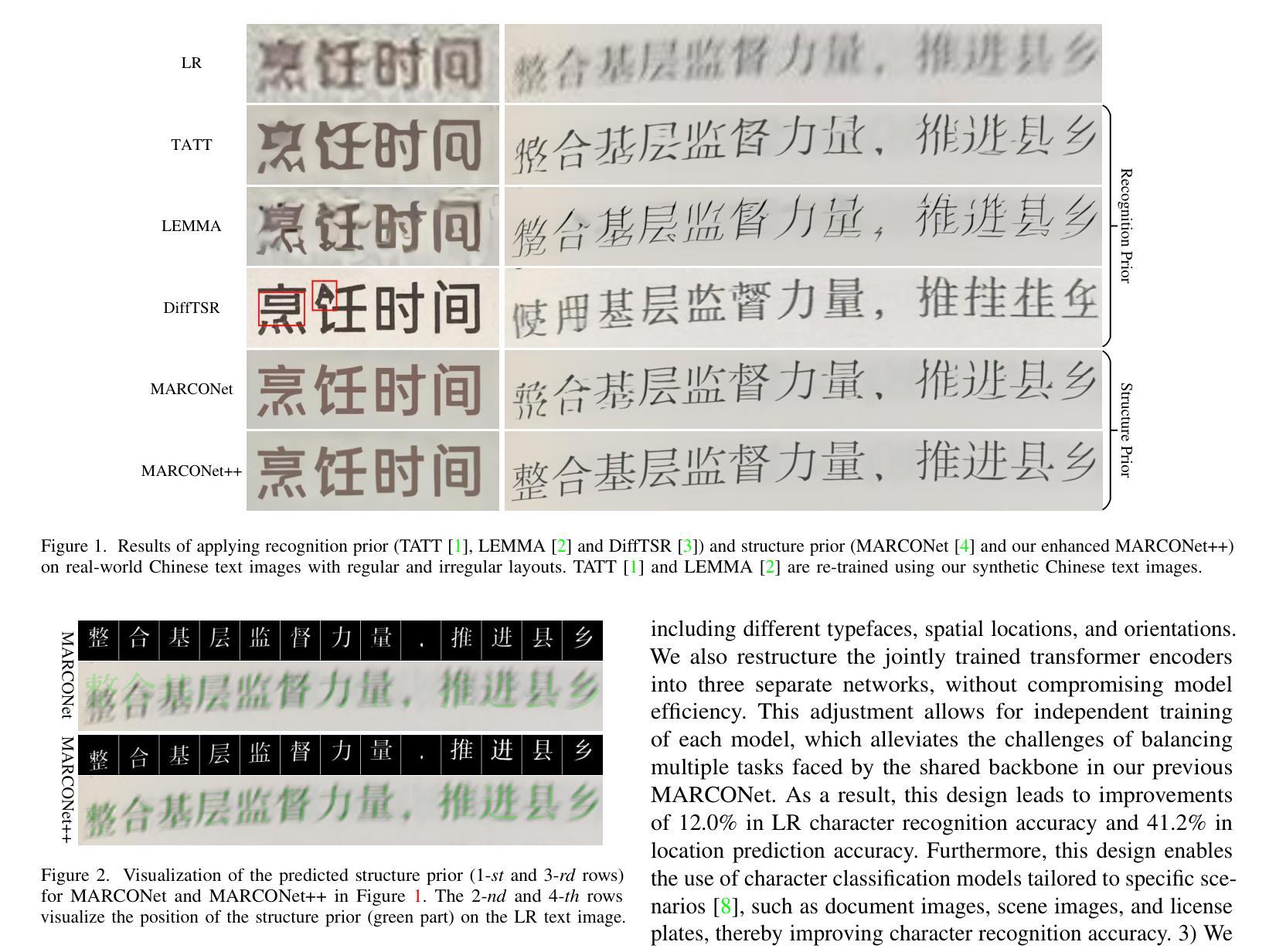
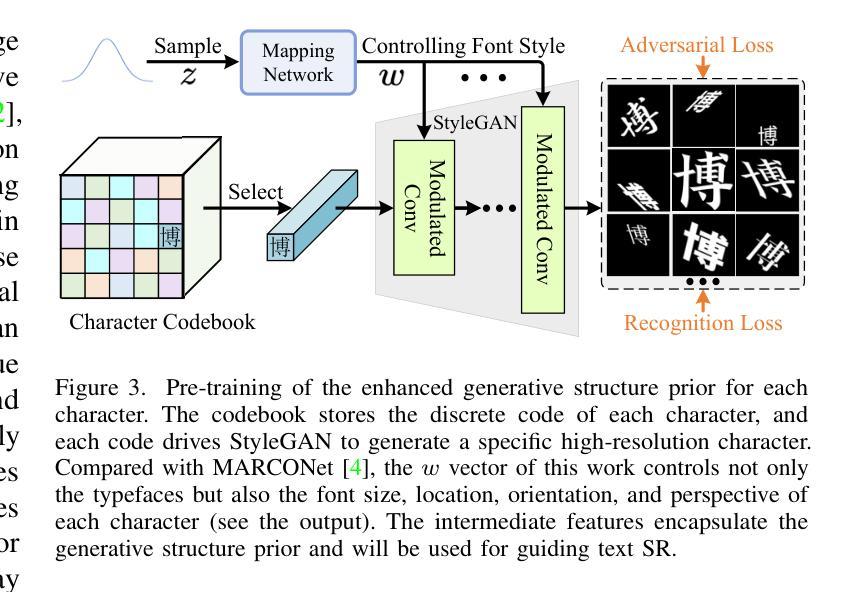
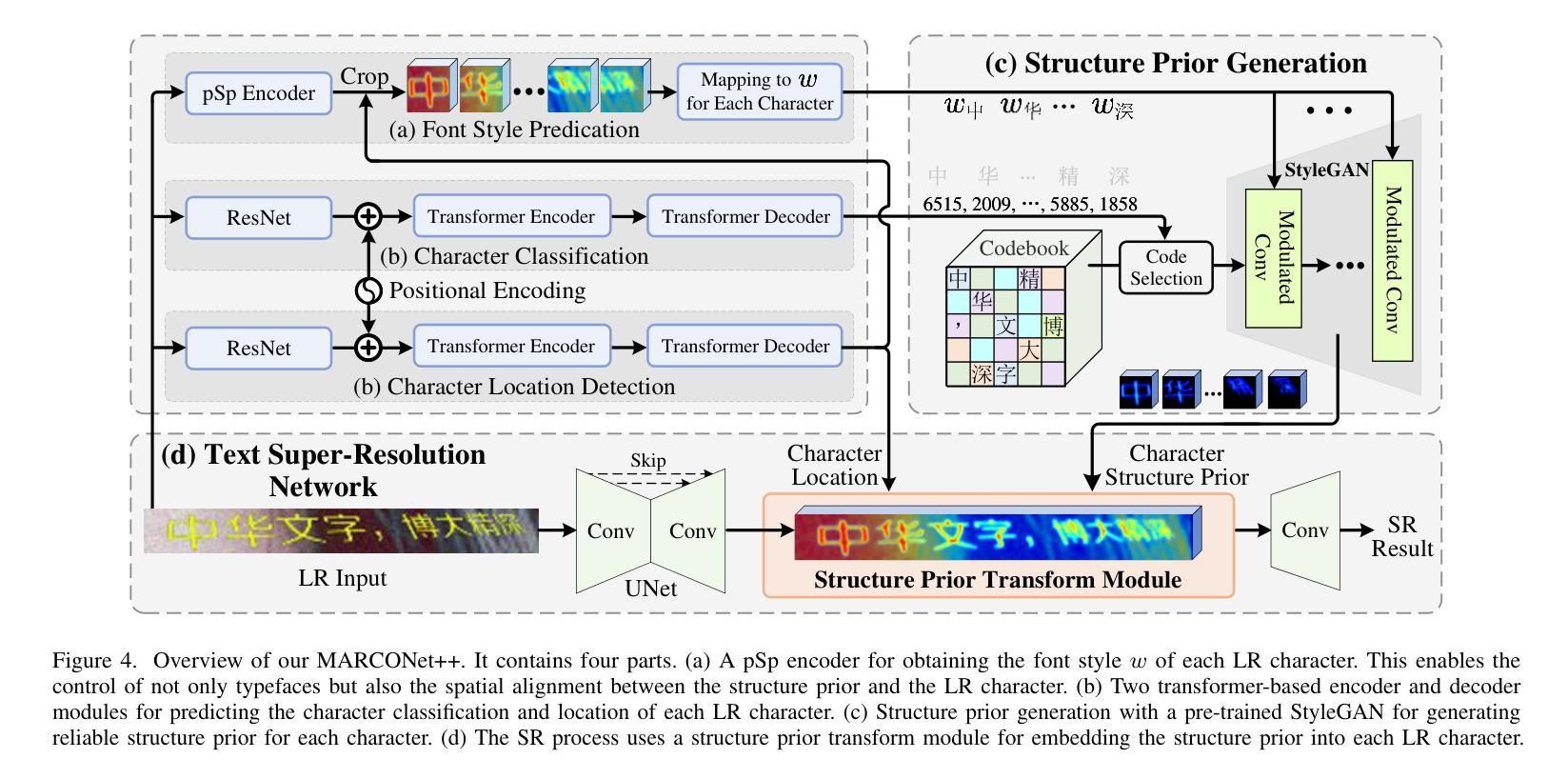
Faithful text image super-resolution (SR) is challenging because each character has a unique structure and usually exhibits diverse font styles and layouts. While existing methods primarily focus on English text, less attention has been paid to more complex scripts like Chinese. In this paper, we introduce a high-quality text image SR framework designed to restore the precise strokes of low-resolution (LR) Chinese characters. Unlike methods that rely on character recognition priors to regularize the SR task, we propose a novel structure prior that offers structure-level guidance to enhance visual quality. Our framework incorporates this structure prior within a StyleGAN model, leveraging its generative capabilities for restoration. To maintain the integrity of character structures while accommodating various font styles and layouts, we implement a codebook-based mechanism that restricts the generative space of StyleGAN. Each code in the codebook represents the structure of a specific character, while the vector $w$ in StyleGAN controls the character’s style, including typeface, orientation, and location. Through the collaborative interaction between the codebook and style, we generate a high-resolution structure prior that aligns with LR characters both spatially and structurally. Experiments demonstrate that this structure prior provides robust, character-specific guidance, enabling the accurate restoration of clear strokes in degraded characters, even for real-world LR Chinese text with irregular layouts. Our code and pre-trained models will be available at https://github.com/csxmli2016/MARCONetPlusPlus
文本图像超分辨率(SR)技术是一项挑战,因为每个字符都有独特的结构,并且通常呈现出不同的字体样式和布局。现有的方法主要集中在英文文本上,而对更复杂的脚本(如中文)关注较少。在本文中,我们介绍了一个高质量的文本图像SR框架,旨在恢复低分辨率(LR)中文字符的精确笔画。与依赖字符识别先验来规范SR任务的方法不同,我们提出了一种新的结构先验,它提供结构级别的指导以增强视觉质量。我们的框架将这种结构先验纳入StyleGAN模型中,利用其生成能力进行修复。为了保持字符结构的完整性,同时适应各种字体样式和布局,我们实现了一种基于代码本(codebook)的机制,限制了StyleGAN的生成空间。代码本中的每个代码代表一个特定字符的结构,而StyleGAN中的向量$w$则控制字符的风格,包括字体、方向和位置。通过代码本与风格的协同交互,我们生成了与低分辨率字符在空间上和结构上都对齐的高分辨率结构先验。实验表明,该结构先验提供了稳健的、针对字符的引导,能够准确恢复退化字符的清晰笔画,即使对于具有不规则布局的现实世界低分辨率中文文本也是如此。我们的代码和预先训练好的模型将在https://github.com/csxmli2016/MARCONetPlusPlus上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TPAMI
Summary
针对中文文本图像的超级分辨率(SR)恢复,现有方法主要集中在英文文本上,对于更复杂脚本如中文的关注度较低。本文介绍了一种针对低分辨率(LR)中文字符的精确笔画恢复的高质量文本图像SR框架。不同于依赖字符识别先验来规范SR任务的方法,本文提出了一种新型结构先验,为提升视觉质量提供结构层面的指导。该框架结合了StyleGAN模型的生成能力,通过结构先验进行恢复。为了保持字符结构的完整性并适应各种字体样式和布局,我们实现了一种基于代码簿的机制,限制了StyleGAN的生成空间。实验表明,该结构先验提供了稳健的字符特定指导,即使在具有不规则布局的真实世界LR中文文本中,也能准确恢复清晰的笔画。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种针对中文文本的超级分辨率恢复框架。
- 该框架旨在恢复低分辨率中文角色的精确笔画。
- 不同于依赖字符识别先验的方法,提出了一种新型结构先验。
- 结合StyleGAN模型的生成能力,通过结构先验进行恢复。
- 实现了一种基于代码簿的机制,以限制StyleGAN的生成空间并适应各种字体样式和布局。
- 结构先验通过提供字符特定的指导,能够准确恢复低分辨率中文文本的清晰笔画。
点此查看论文截图

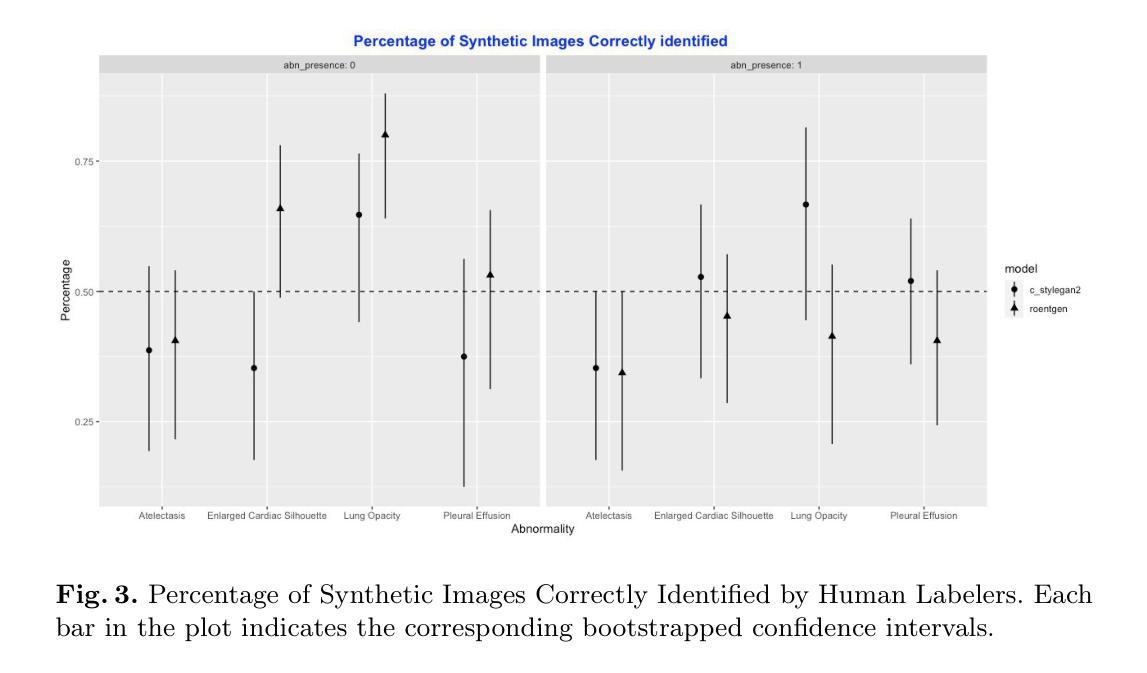
Perceptual Evaluation of GANs and Diffusion Models for Generating X-rays
Authors:Gregory Schuit, Denis Parra, Cecilia Besa
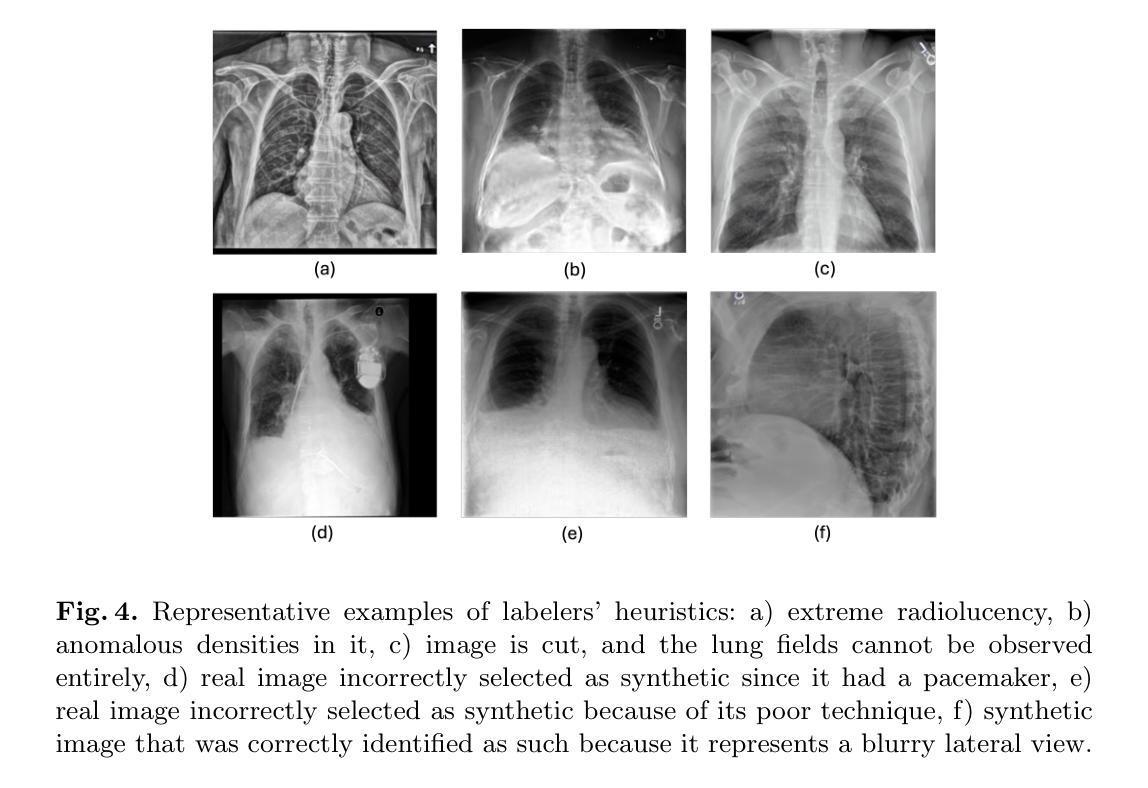
Generative image models have achieved remarkable progress in both natural and medical imaging. In the medical context, these techniques offer a potential solution to data scarcity-especially for low-prevalence anomalies that impair the performance of AI-driven diagnostic and segmentation tools. However, questions remain regarding the fidelity and clinical utility of synthetic images, since poor generation quality can undermine model generalizability and trust. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art generative models-Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs)-for synthesizing chest X-rays conditioned on four abnormalities: Atelectasis (AT), Lung Opacity (LO), Pleural Effusion (PE), and Enlarged Cardiac Silhouette (ECS). Using a benchmark composed of real images from the MIMIC-CXR dataset and synthetic images from both GANs and DMs, we conducted a reader study with three radiologists of varied experience. Participants were asked to distinguish real from synthetic images and assess the consistency between visual features and the target abnormality. Our results show that while DMs generate more visually realistic images overall, GANs can report better accuracy for specific conditions, such as absence of ECS. We further identify visual cues radiologists use to detect synthetic images, offering insights into the perceptual gaps in current models. These findings underscore the complementary strengths of GANs and DMs and point to the need for further refinement to ensure generative models can reliably augment training datasets for AI diagnostic systems.
生成图像模型在自然和医学影像方面都取得了显著的进步。在医学背景下,这些技术为解决数据稀缺问题提供了潜在的解决方案,特别是对于低发病率异常导致的AI驱动的诊断和分割工具性能下降问题。然而,关于合成图像的保真度和临床实用性仍存在疑问,因为生成质量差会影响模型的通用性和可信度。在这项研究中,我们评估了最先进的生成模型——生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在合成基于四种异常的胸部X射线图像方面的有效性:肺不张(AT)、肺实变(LO)、胸腔积液(PE)和心脏轮廓增大(ECS)。我们使用由MIMIC-CXR数据集的真实图像和GANs及DMs生成的合成图像组成的基准测试集,对三位不同经验的放射科医生进行了一项读者研究。参与者被要求区分真实图像和合成图像,并评估视觉特征与目标异常之间的一致性。我们的结果表明,虽然DMs总体上生成了更视觉真实的图像,但GANs在特定条件下的准确性更高,如ECS不存在的情况。我们还确定了放射科医生用来检测合成图像的视觉线索,这为我们提供了对当前模型感知差距的见解。这些发现突显了GANs和DMs的互补优势,并指出需要进一步改进,以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Workshop on Human-AI Collaboration at MICCAI 2025
Summary
该研究评估了最先进的生成模型——生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在合成胸X光片图像方面的表现,这些图像以四种异常状况为条件:肺不张、肺实变、胸膜积液和心脏轮廓增大。通过对比真实图像和合成图像,研究发现DMs生成的图像整体更逼真,而GANs在某些特定条件下的表现更准确。此外,还研究了放射科医生检测合成图像时使用的视觉线索。这一研究突显了GANs和DMs的互补优势,并指出了进一步提高模型精度和可靠性的必要性,以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
Key Takeaways
- GANs和DMs在医学图像合成上具有潜力,尤其在解决低发病率异常问题方面有助于增强AI诊断和分割工具的性能。
- DMs倾向于生成更逼真的图像,而GANs在某些特定异常检测方面表现更好。
- 视觉特征的逼真度和一致性对放射科医生评估图像真实性有影响。
- 放射科医生使用特定的视觉线索来检测合成图像,这揭示了当前模型的感知差距。
- GANs和DMs各有优势,未来需要进一步的改进以确保生成模型的可靠性。
- 生成模型在提高AI诊断系统的训练数据集方面有着广阔的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

CycleDiff: Cycle Diffusion Models for Unpaired Image-to-image Translation
Authors:Shilong Zou, Yuhang Huang, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
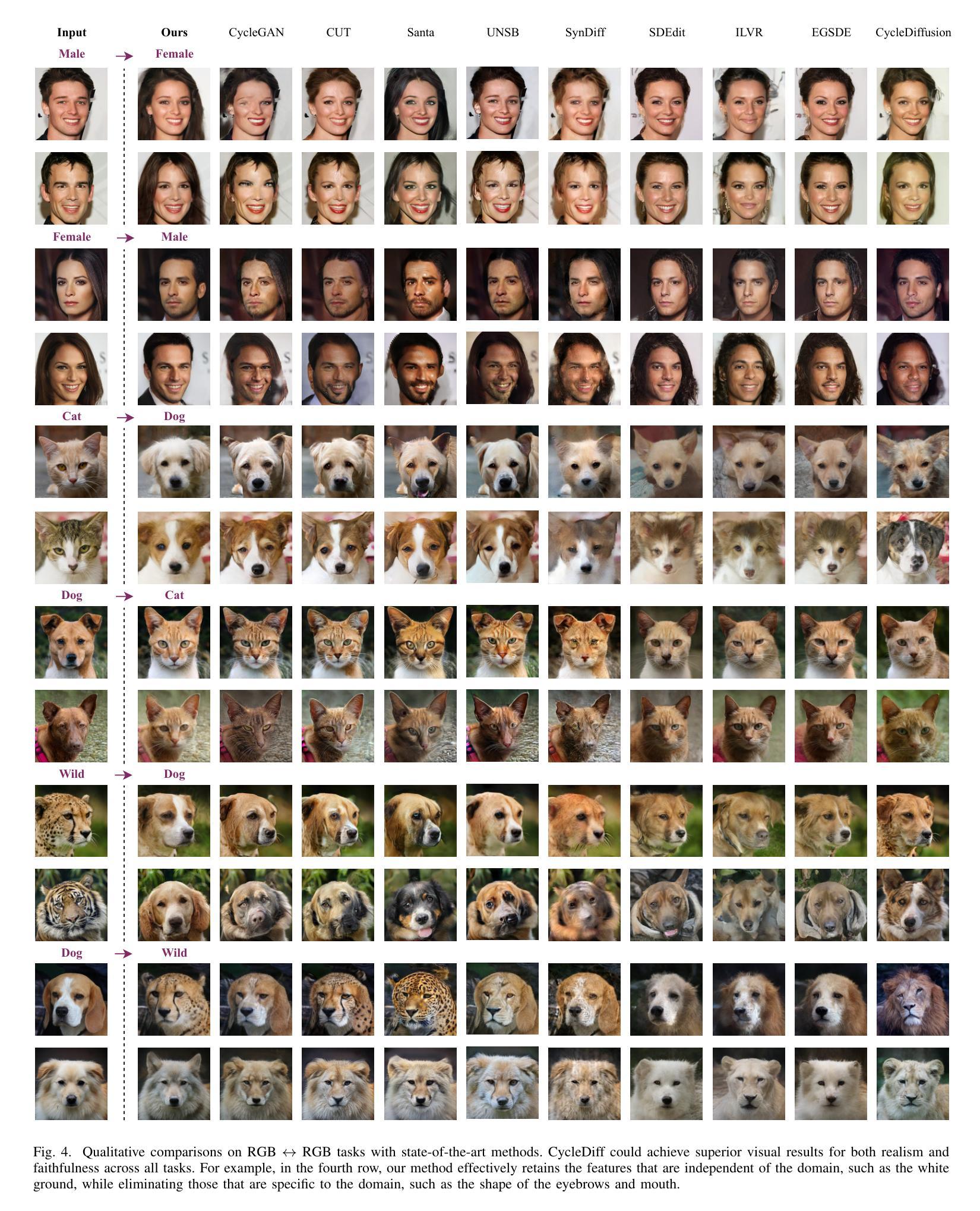
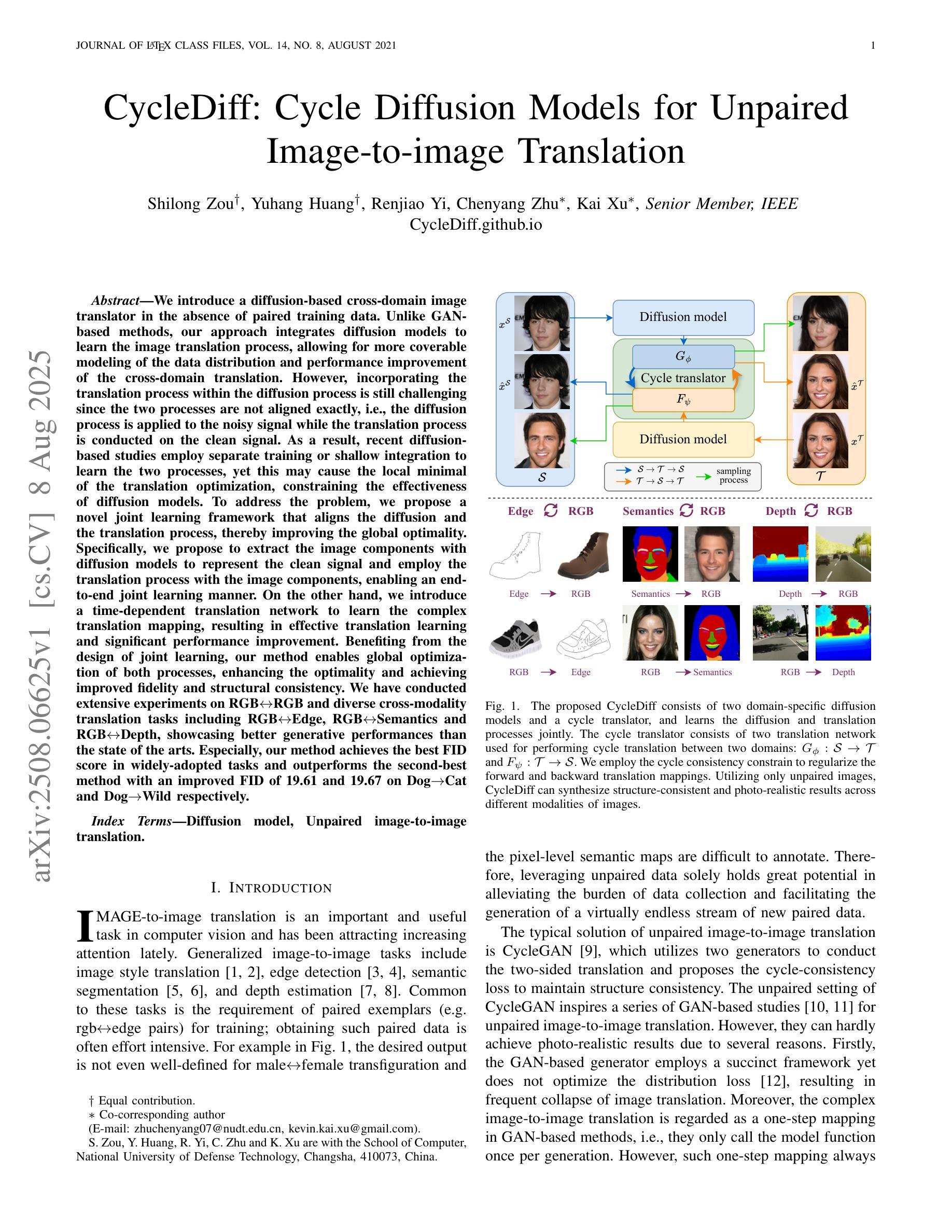
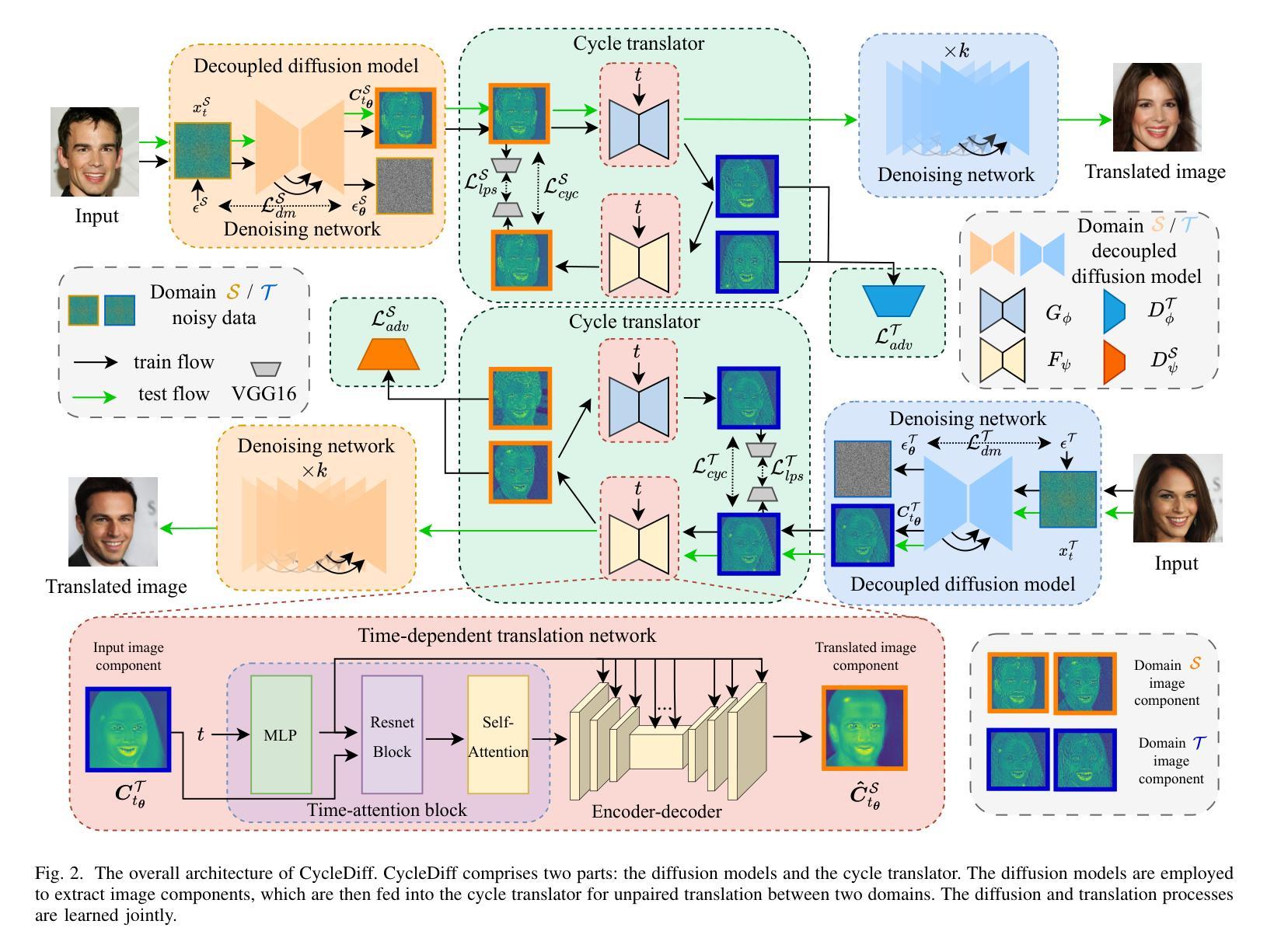
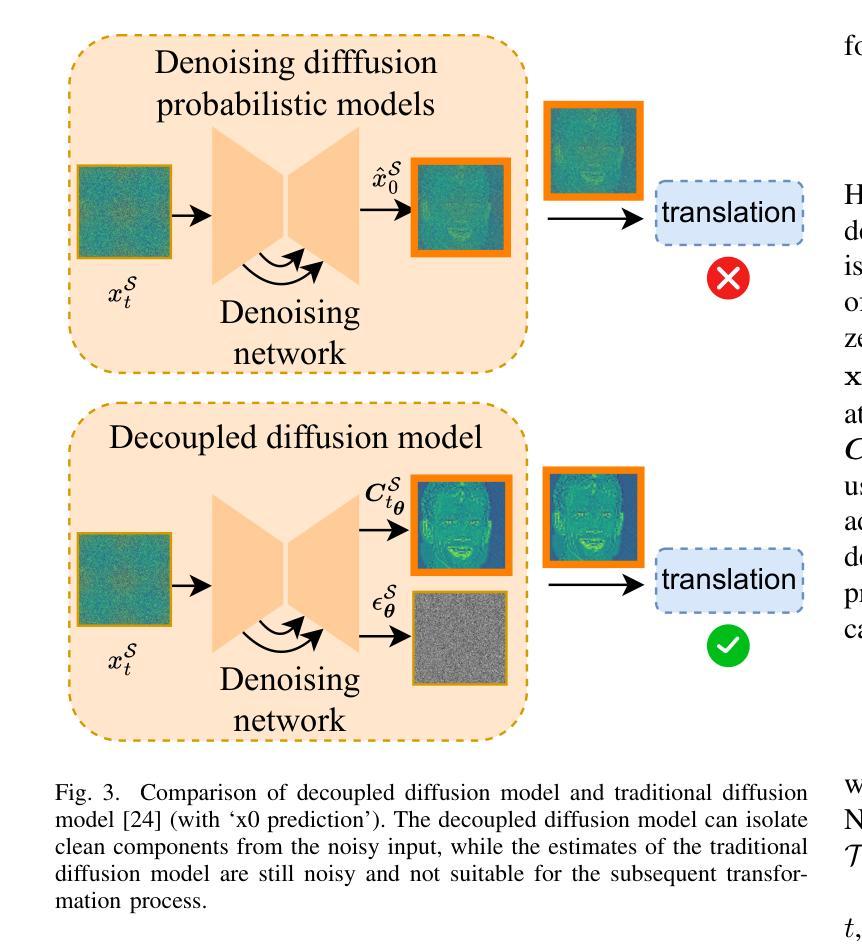
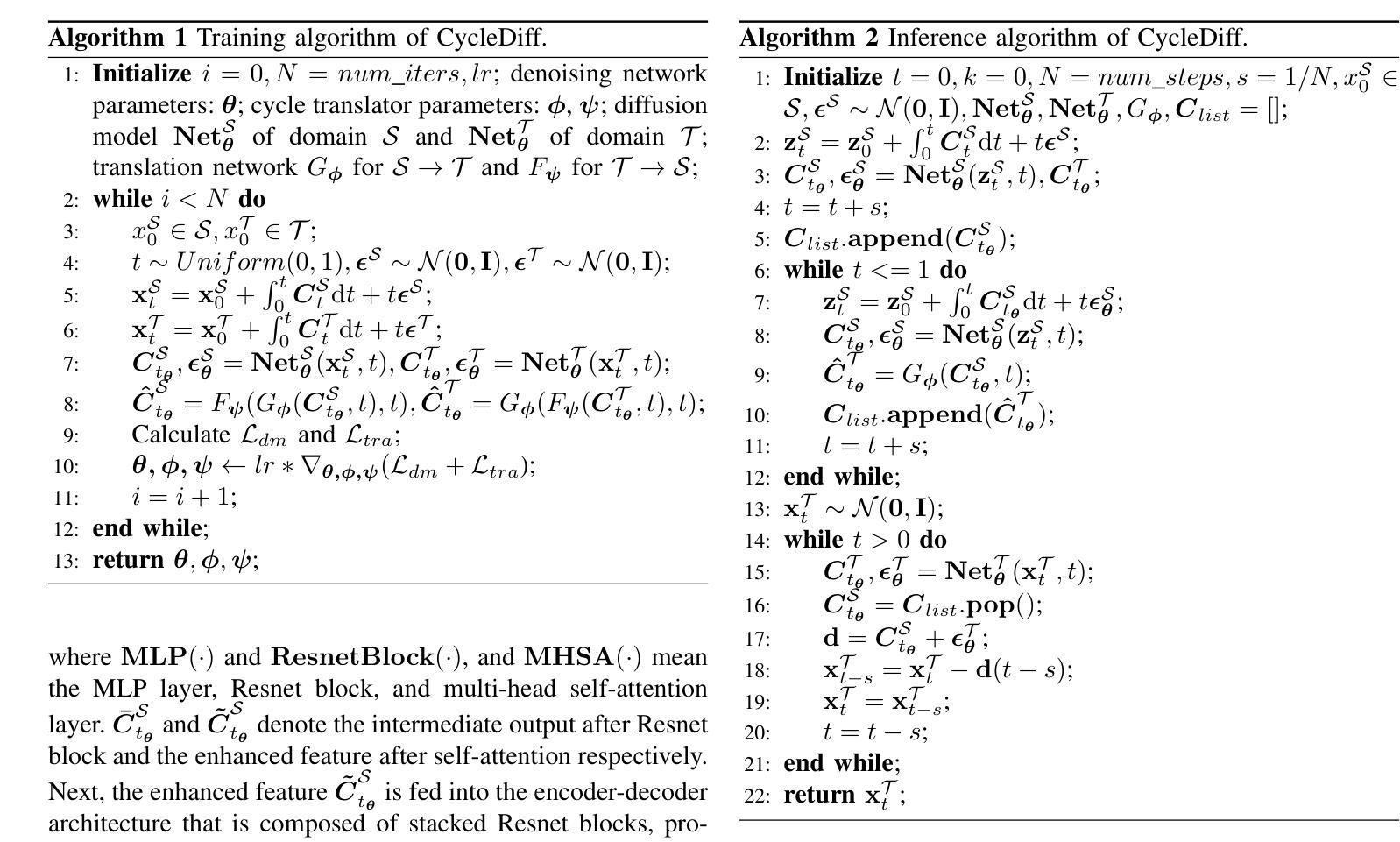
We introduce a diffusion-based cross-domain image translator in the absence of paired training data. Unlike GAN-based methods, our approach integrates diffusion models to learn the image translation process, allowing for more coverable modeling of the data distribution and performance improvement of the cross-domain translation. However, incorporating the translation process within the diffusion process is still challenging since the two processes are not aligned exactly, i.e., the diffusion process is applied to the noisy signal while the translation process is conducted on the clean signal. As a result, recent diffusion-based studies employ separate training or shallow integration to learn the two processes, yet this may cause the local minimal of the translation optimization, constraining the effectiveness of diffusion models. To address the problem, we propose a novel joint learning framework that aligns the diffusion and the translation process, thereby improving the global optimality. Specifically, we propose to extract the image components with diffusion models to represent the clean signal and employ the translation process with the image components, enabling an end-to-end joint learning manner. On the other hand, we introduce a time-dependent translation network to learn the complex translation mapping, resulting in effective translation learning and significant performance improvement. Benefiting from the design of joint learning, our method enables global optimization of both processes, enhancing the optimality and achieving improved fidelity and structural consistency. We have conducted extensive experiments on RGB$\leftrightarrow$RGB and diverse cross-modality translation tasks including RGB$\leftrightarrow$Edge, RGB$\leftrightarrow$Semantics and RGB$\leftrightarrow$Depth, showcasing better generative performances than the state of the arts.
我们引入了一种基于扩散的跨域图像转换器,无需配对训练数据。与基于GAN的方法不同,我们的方法结合了扩散模型来学习图像转换过程,实现了对数据分布的覆盖性建模以及跨域翻译的性能提升。然而,在扩散过程中融入翻译过程仍然具有挑战性,因为这两个过程并不完全对齐,即扩散过程应用于噪声信号,而翻译过程则在清洁信号上进行。因此,最近的基于扩散的研究采用单独训练或浅层集成来学习这两个过程,但这可能会导致翻译优化的局部最小值,限制扩散模型的有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型联合学习框架,对齐扩散和翻译过程,从而提高全局最优性。具体来说,我们提出使用扩散模型提取图像成分来表示清洁信号,并利用图像成分进行翻译过程,实现端到端的联合学习方式。另一方面,我们引入时间依赖翻译网络来学习复杂的翻译映射,实现有效的翻译学习和显著的性能提升。受益于联合学习设计,我们的方法使两个过程都能进行全局优化,提高了最优性和生成图像的保真度及结构一致性。我们在RGB→RGB和各种跨模态翻译任务(包括RGB→Edge、RGB→Semantics和RGB→Depth)上进行了大量实验,展现了比现有技术更好的生成性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究介绍了一种基于扩散的无配对训练数据交叉域图像翻译器。不同于基于GAN的方法,本研究将扩散模型融入图像翻译过程,实现对数据分布的更广泛建模和跨域翻译性能的改进。然而,将翻译过程融入扩散过程中仍存在挑战,因为这两个过程并不完全对齐。为解决这一问题,本研究提出一种新型联合学习框架,将扩散和翻译过程对齐,提高全局最优性。通过提取图像成分代表清洁信号,并采用翻译过程进行图像成分处理,实现端到端的联合学习方式。同时,引入时间依赖翻译网络学习复杂的翻译映射,有效提高翻译学习效果和性能。实验结果表明,该方法在RGB与RGB、RGB与边缘、RGB与语义以及RGB与深度等跨模态翻译任务上均表现出优异的生成性能。
关键见解
- 研究提出了一种基于扩散的无配对训练数据交叉域图像翻译方法。
- 整合扩散模型进行图像翻译,实现了更广泛的数据分布建模和性能提升。
- 面临将翻译过程融入扩散过程中的挑战,因两者不完全对齐。
- 提出一种新型联合学习框架,对齐扩散和翻译过程,提高全局最优性。
- 通过提取图像成分并采用翻译过程处理,实现端到端的联合学习方式。
- 引入时间依赖翻译网络,有效学习复杂翻译映射,提高翻译学习效果和性能。
- 在多种跨模态翻译任务上表现出优异的生成性能。
点此查看论文截图