⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
ODYSSEY: Open-World Quadrupeds Exploration and Manipulation for Long-Horizon Tasks
Authors:Kaijun Wang, Liqin Lu, Mingyu Liu, Jianuo Jiang, Zeju Li, Bolin Zhang, Wancai Zheng, Xinyi Yu, Hao Chen, Chunhua Shen
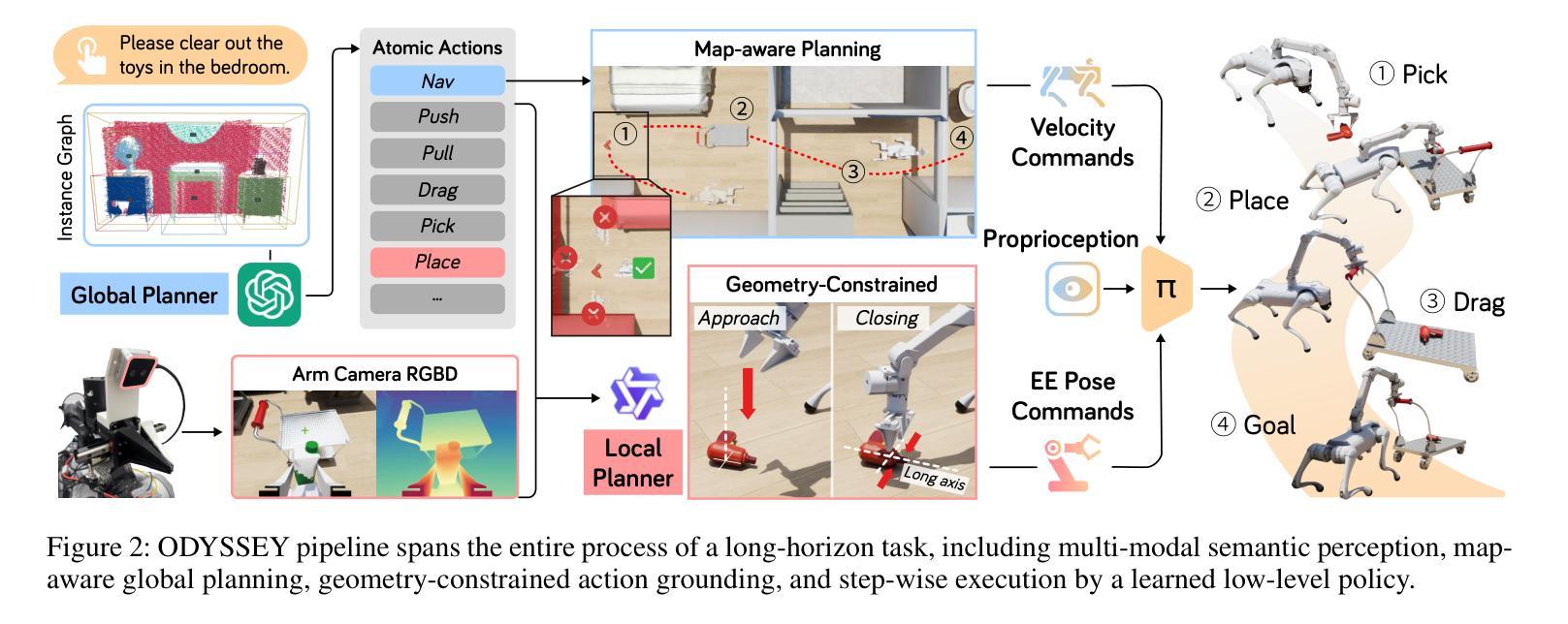
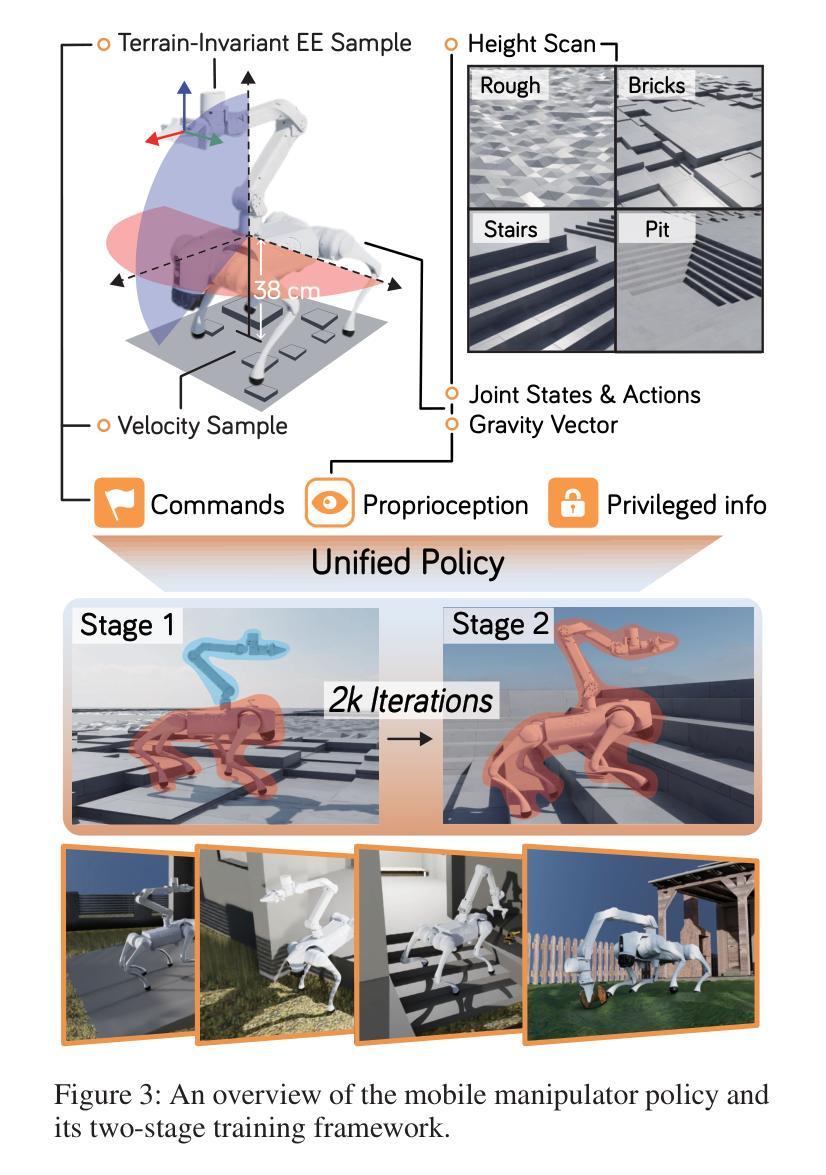
Language-guided long-horizon mobile manipulation has long been a grand challenge in embodied semantic reasoning, generalizable manipulation, and adaptive locomotion. Three fundamental limitations hinder progress: First, although large language models have improved spatial reasoning and task planning through semantic priors, existing implementations remain confined to tabletop scenarios, failing to address the constrained perception and limited actuation ranges of mobile platforms. Second, current manipulation strategies exhibit insufficient generalization when confronted with the diverse object configurations encountered in open-world environments. Third, while crucial for practical deployment, the dual requirement of maintaining high platform maneuverability alongside precise end-effector control in unstructured settings remains understudied. In this work, we present ODYSSEY, a unified mobile manipulation framework for agile quadruped robots equipped with manipulators, which seamlessly integrates high-level task planning with low-level whole-body control. To address the challenge of egocentric perception in language-conditioned tasks, we introduce a hierarchical planner powered by a vision-language model, enabling long-horizon instruction decomposition and precise action execution. At the control level, our novel whole-body policy achieves robust coordination across challenging terrains. We further present the first benchmark for long-horizon mobile manipulation, evaluating diverse indoor and outdoor scenarios. Through successful sim-to-real transfer, we demonstrate the system’s generalization and robustness in real-world deployments, underscoring the practicality of legged manipulators in unstructured environments. Our work advances the feasibility of generalized robotic assistants capable of complex, dynamic tasks. Our project page: https://kaijwang.github.io/odyssey.github.io/
语言引导的长期移动操作一直是语义理解、通用操作和自适应移动方面的一项重大挑战。存在三个基本局限性阻碍进展:首先,虽然大型语言模型通过语义先验改进了空间推理和任务规划,但现有实现仅限于桌面场景,无法解决移动平台的受限感知和有限的动作范围。其次,当前的操作策略在面对开放环境中遇到的各种对象配置时,泛化能力不足以应对。第三,虽然在实际部署中至关重要,但在非结构化环境中同时保持高平台机动性和精确末端执行器控制的双重要求在研究中仍然被忽视。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在基于语言的长期移动操纵方面,面临着诸多挑战,如语义理解、通用化操纵和自适应移动等。现有大型语言模型虽提升了空间推理和任务规划能力,但仍局限于桌面场景,难以解决移动平台感知受限和动作范围有限的问题。当前操纵策略在开放世界环境中面对多样化的对象配置时,其通用性不足。同时,在复杂、非结构化环境中,保持平台高度机动性和精确末端执行器控制的要求尚未得到充分研究。本研究提出ODYSSEY,一个用于敏捷四足机器人的统一移动操纵框架,配备操纵器,实现高级任务规划与低级全身控制的无缝集成。通过引入视觉语言模型的分层规划器,解决语言条件下的以自我为中心的感知挑战,实现长期指令分解和精确动作执行。在控制层面,我们的全新全身策略实现了复杂地形中的稳健协调。我们首次建立了长期移动操纵的基准测试,评估了多种室内和室外场景。通过成功的模拟到现实的转移,我们证明了系统在现实部署中的通用性和稳健性,强调了四肢操作器在非结构化环境中的实用性。本研究推动了通用机器人助手完成复杂动态任务的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 语言指导的长期移动操纵仍存在语义理解、通用化操纵和自适应移动等挑战。
- 现有大型语言模型在桌面场景外感知和动作范围方面的局限性。
- 当前操纵策略在开放世界环境中对象配置多样性面前的通用性不足。
- 移动平台高度机动性与精确末端执行器控制在复杂环境中的双重需求尚未得到充分研究。
- ODYSSEY框架实现了四足机器人的移动操纵,集成了任务规划和全身控制。
- 通过视觉语言模型分层规划器解决以自我为中心的感知挑战。
点此查看论文截图


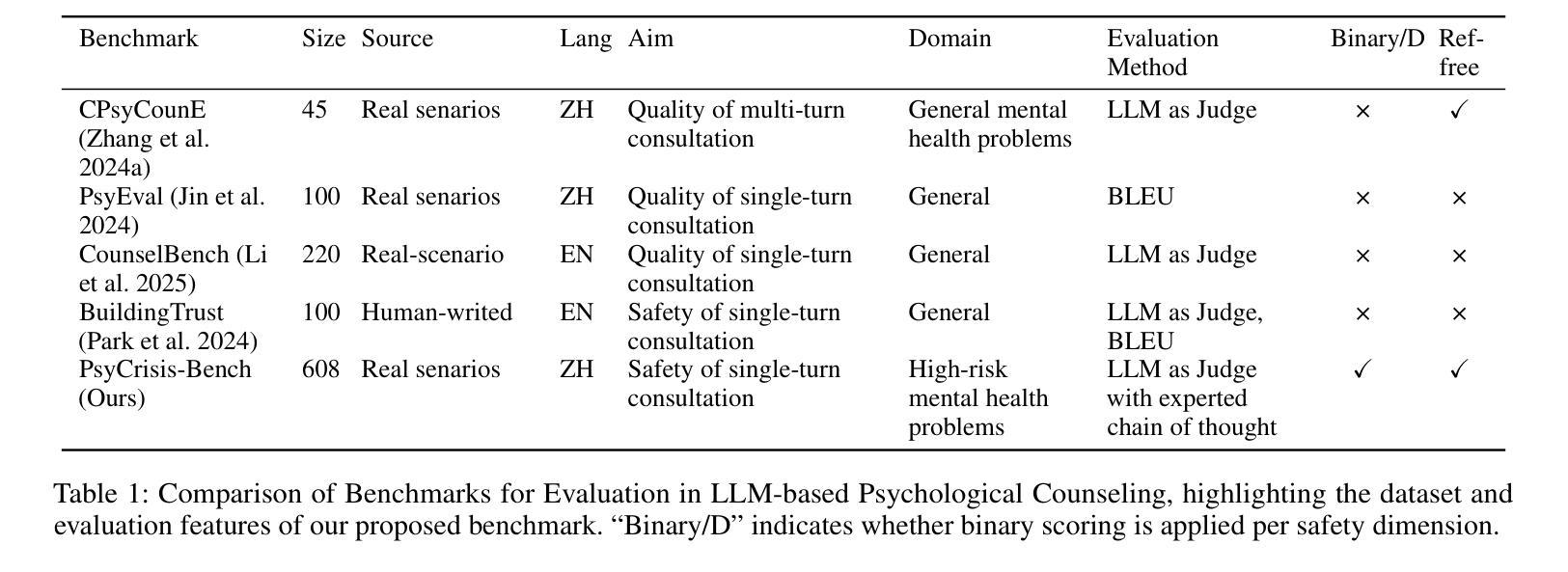
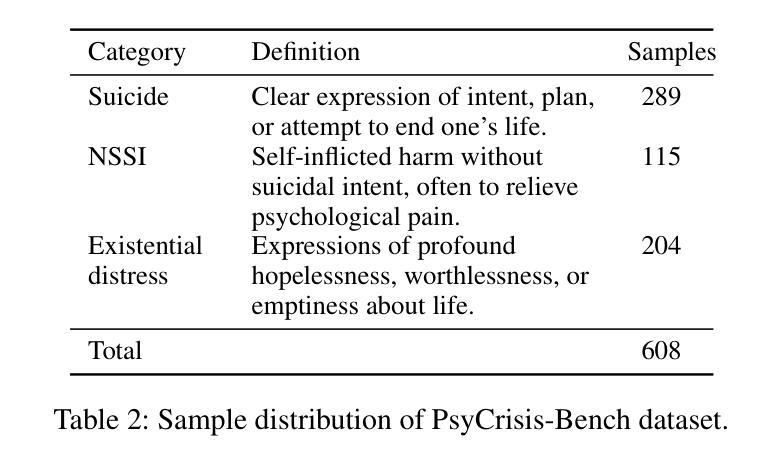
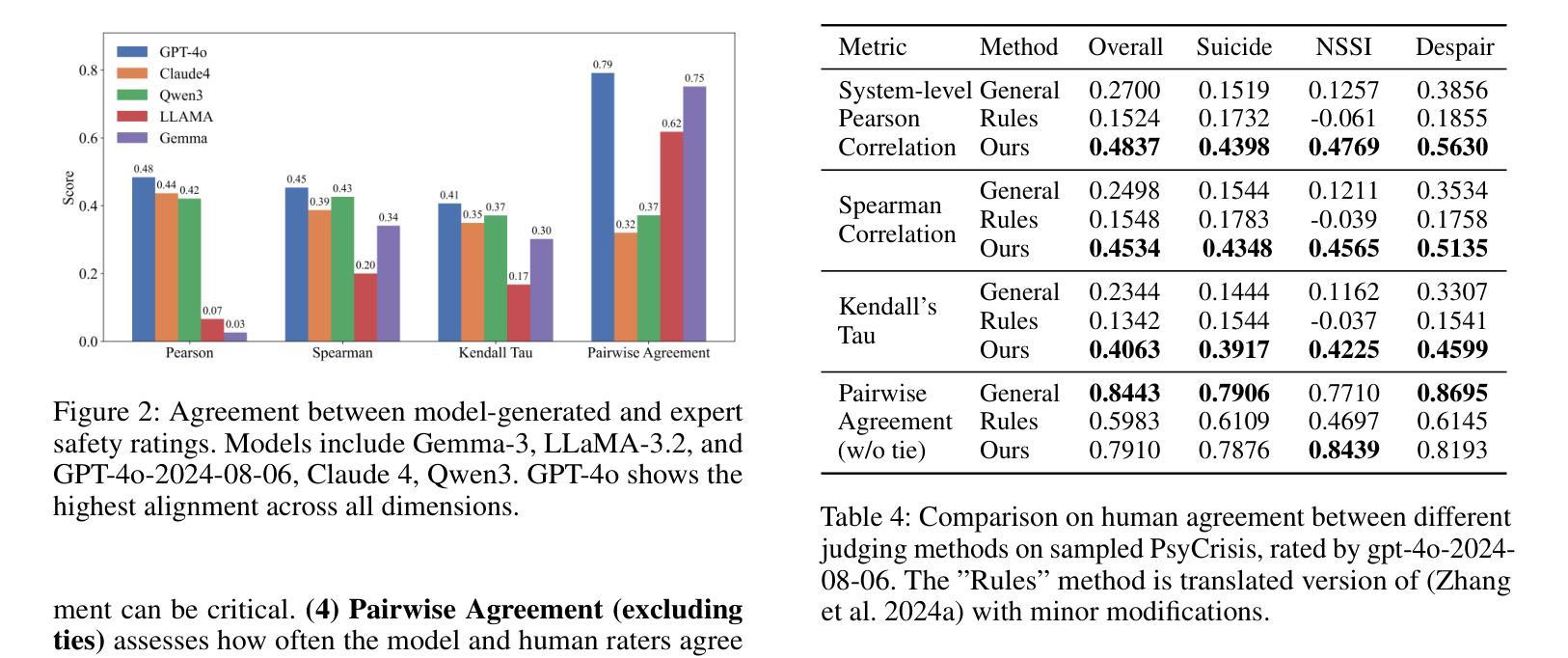
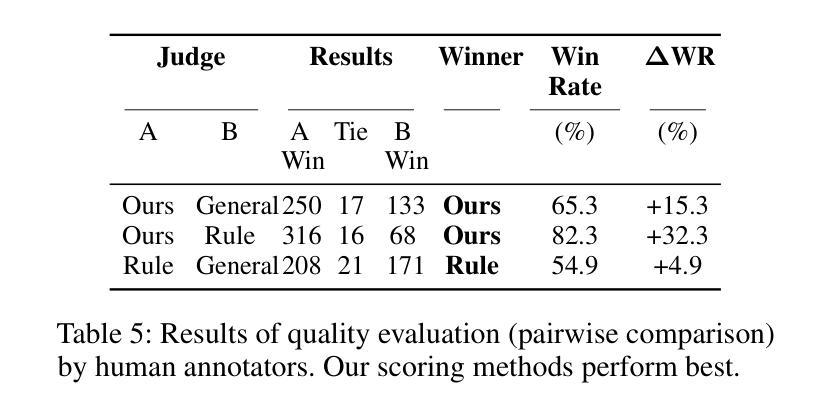
Exploring Safety Alignment Evaluation of LLMs in Chinese Mental Health Dialogues via LLM-as-Judge
Authors:Yunna Cai, Fan Wang, Haowei Wang, Kun Wang, Kailai Yang, Sophia Ananiadou, Moyan Li, Mingming Fan
Evaluating the safety alignment of LLM responses in high-risk mental health dialogues is particularly difficult due to missing gold-standard answers and the ethically sensitive nature of these interactions. To address this challenge, we propose PsyCrisis-Bench, a reference-free evaluation benchmark based on real-world Chinese mental health dialogues. It evaluates whether the model responses align with the safety principles defined by experts. Specifically designed for settings without standard references, our method adopts a prompt-based LLM-as-Judge approach that conducts in-context evaluation using expert-defined reasoning chains grounded in psychological intervention principles. We employ binary point-wise scoring across multiple safety dimensions to enhance the explainability and traceability of the evaluation. Additionally, we present a manually curated, high-quality Chinese-language dataset covering self-harm, suicidal ideation, and existential distress, derived from real-world online discourse. Experiments on 3600 judgments show that our method achieves the highest agreement with expert assessments and produces more interpretable evaluation rationales compared to existing approaches. Our dataset and evaluation tool are publicly available to facilitate further research.
评估高风险心理健康对话中LLM回答的安全一致性特别困难,这是由于缺乏金标准答案以及这些交互的伦理敏感性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了PsyCrisis-Bench,这是一个基于真实世界中文心理健康对话的参考自由评估基准。它评估模型响应是否与专家定义的安全原则一致。我们专为没有标准参考的设置设计的方法采用了基于提示的LLM-as-Judge方法,该方法使用专家定义的基于心理干预原则的推理链进行上下文评估。我们在多个安全维度上采用二进制点评分,以提高评估的可解释性和可追溯性。此外,我们还提供了一个手动整理的高质量中文数据集,涵盖自我伤害、自杀意念和存在性痛苦,来源于真实世界的在线话语。对3600次判断的实验表明,我们的方法与专家评估的契合度最高,与现有方法相比,能产生更可解释的评价理由。我们的数据集和评估工具公开可用,以促进进一步的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对高风险心理健康对话中LLM响应的安全对齐评估的挑战,并提出了PsyCrisis-Bench这一无参考评价的基准,基于真实世界的中文心理健康对话。它评价模型响应是否与专家定义的安全原则对齐。该方法采用基于提示的LLM-as-Judge方式进行上下文评价,使用专家定义的基于心理干预原理的推理链,并在多个安全维度上进行二元点级评分,以提高评价的解释性和可追溯性。此外,还提供了一个高质量的手动整理中文数据集,涵盖自我伤害、自杀意念和存在性焦虑等真实世界在线话语。实验表明,该方法与专家评估达到最高一致性,与现有方法相比,能产生更可解释的评价依据。
Key Takeaways
- 评估LLM在高风险心理健康对话中的安全响应是一项挑战,因为没有黄金标准答案和伦理敏感的交互。
- PsyCrisis-Bench是一个无参考评价的基准,基于真实世界的中文心理健康对话,用于评价模型响应是否符合安全原则。
- 采用基于提示的LLM-as-Judge方式进行上下文评价。
- 使用专家定义的基于心理干预原理的推理链进行安全维度的二元点级评分。
- 方法提高了评价的解释性和可追溯性。
- 提供了一个高质量的手动整理中文数据集,涵盖自我伤害、自杀意念和存在性焦虑等真实世界在线话语。
点此查看论文截图


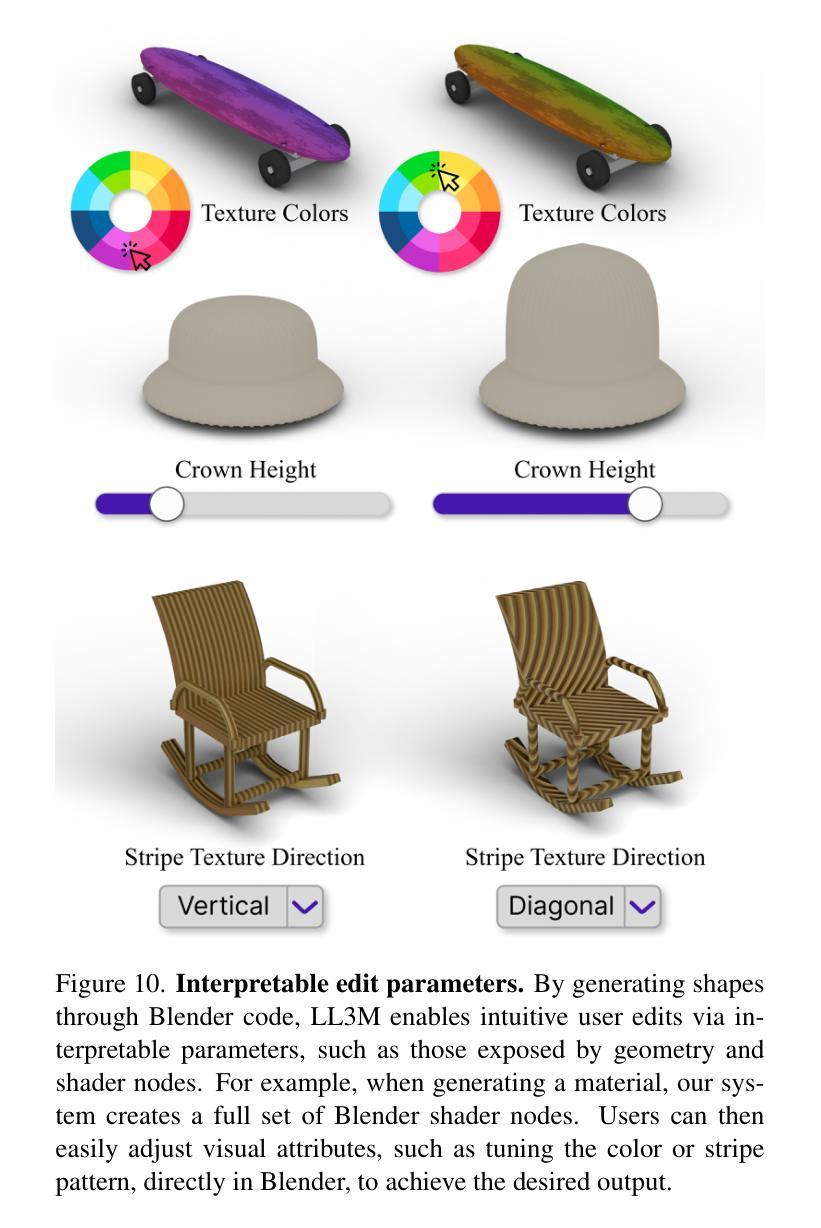
LL3M: Large Language 3D Modelers
Authors:Sining Lu, Guan Chen, Nam Anh Dinh, Itai Lang, Ari Holtzman, Rana Hanocka
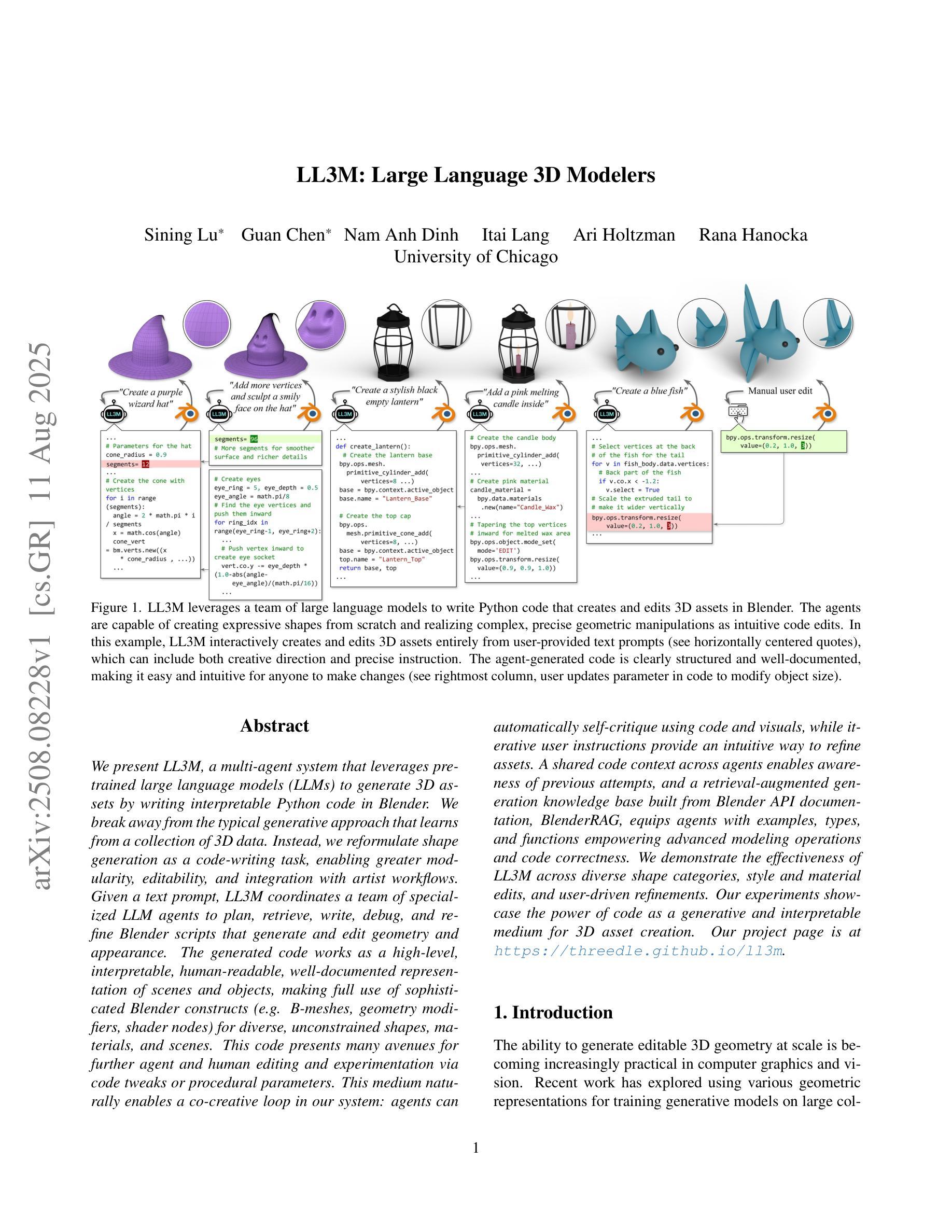
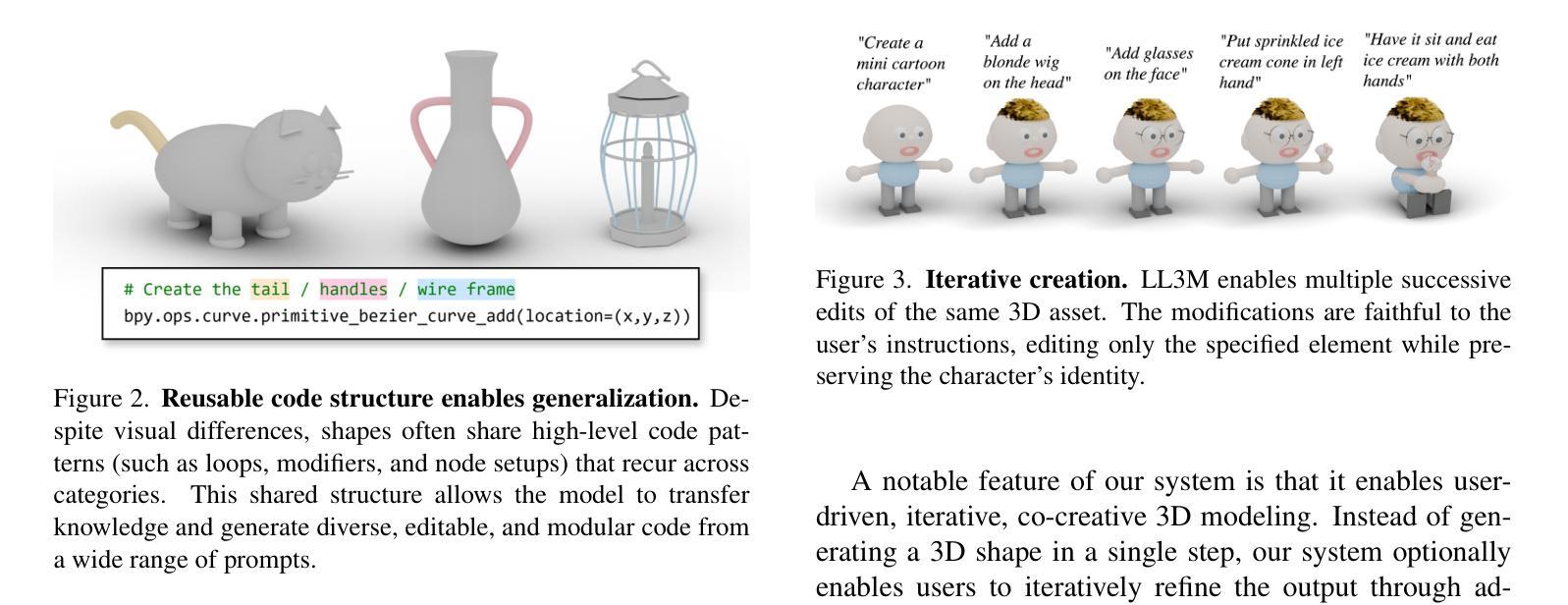
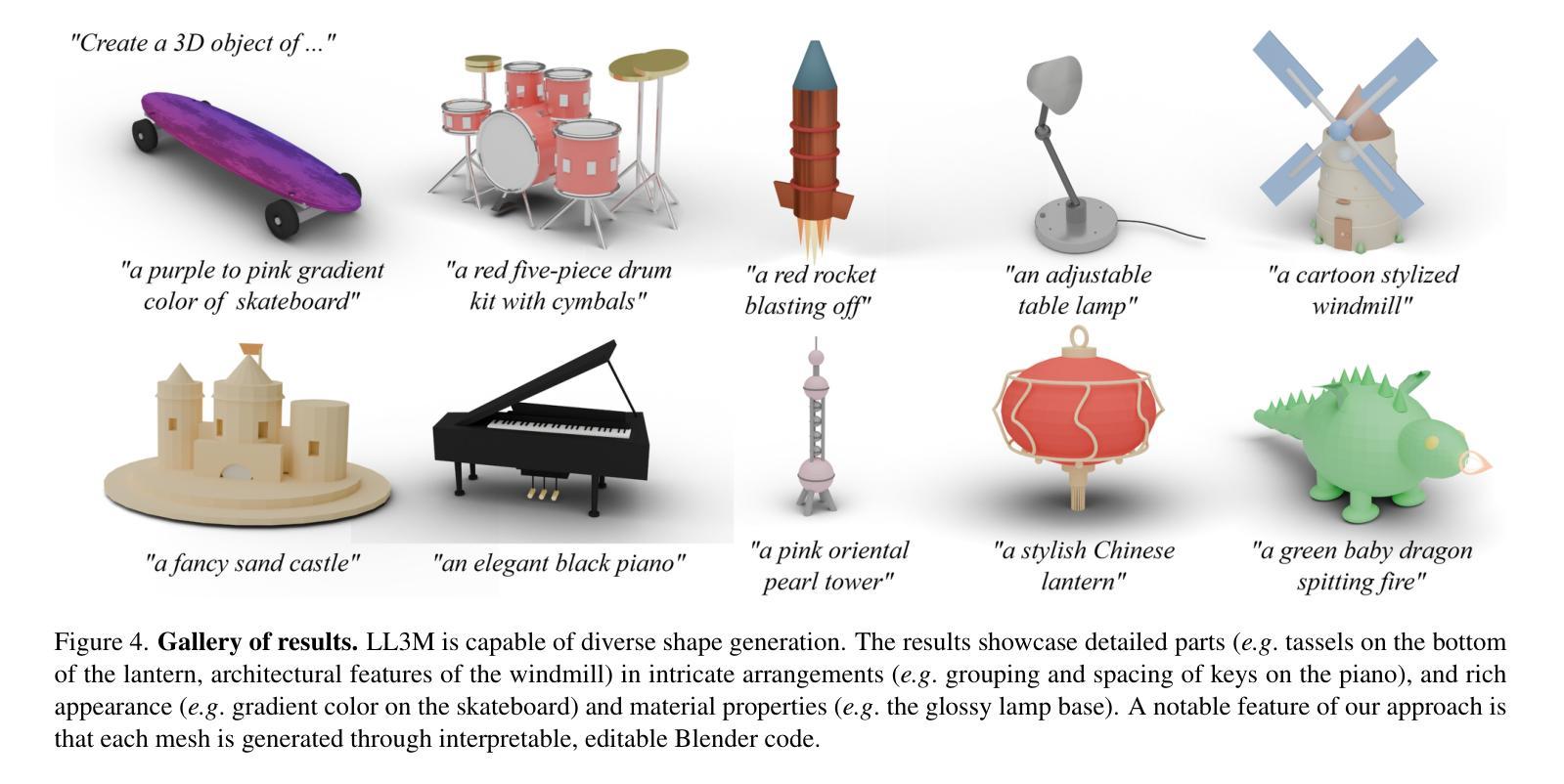
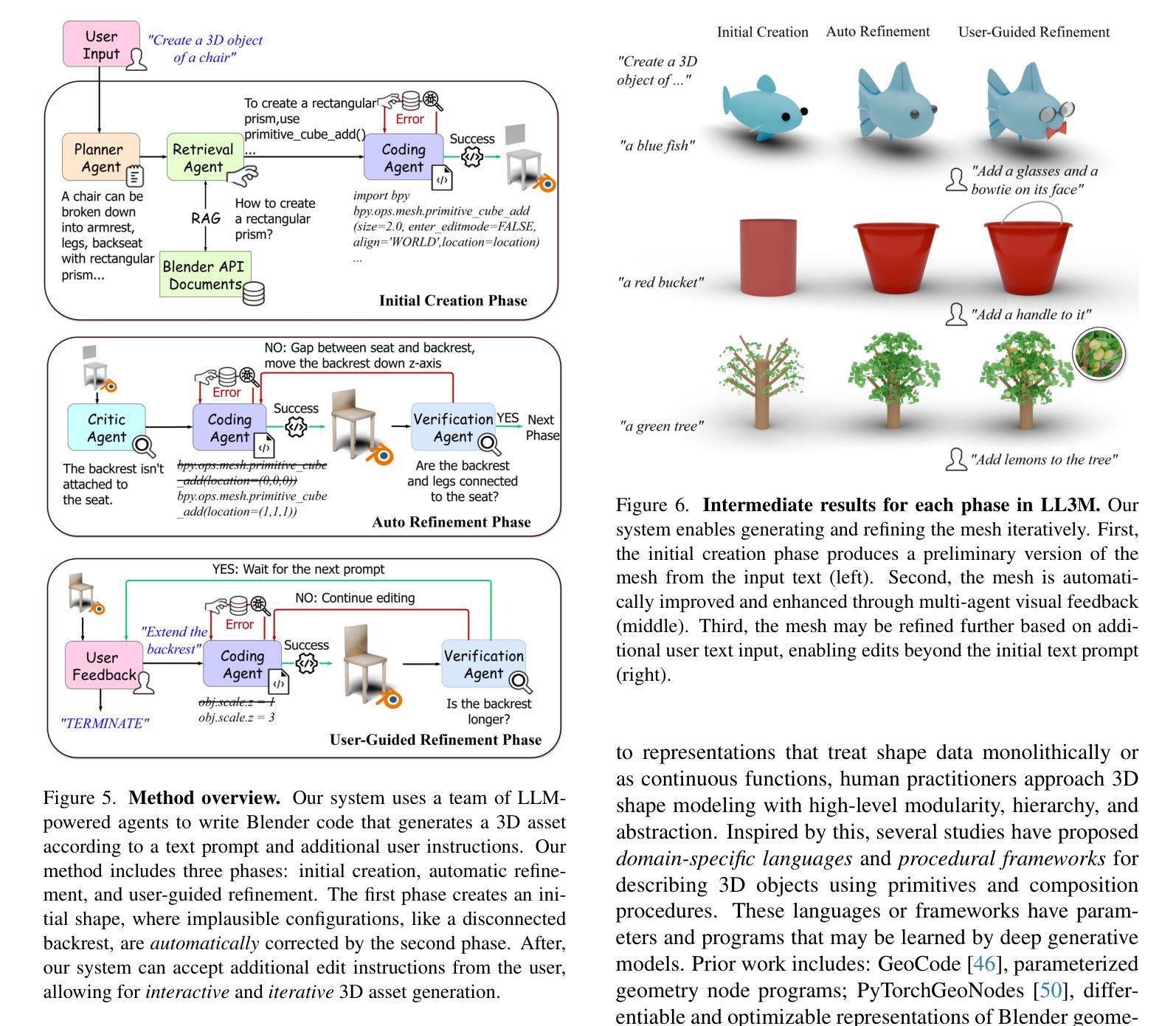
We present LL3M, a multi-agent system that leverages pretrained large language models (LLMs) to generate 3D assets by writing interpretable Python code in Blender. We break away from the typical generative approach that learns from a collection of 3D data. Instead, we reformulate shape generation as a code-writing task, enabling greater modularity, editability, and integration with artist workflows. Given a text prompt, LL3M coordinates a team of specialized LLM agents to plan, retrieve, write, debug, and refine Blender scripts that generate and edit geometry and appearance. The generated code works as a high-level, interpretable, human-readable, well-documented representation of scenes and objects, making full use of sophisticated Blender constructs (e.g. B-meshes, geometry modifiers, shader nodes) for diverse, unconstrained shapes, materials, and scenes. This code presents many avenues for further agent and human editing and experimentation via code tweaks or procedural parameters. This medium naturally enables a co-creative loop in our system: agents can automatically self-critique using code and visuals, while iterative user instructions provide an intuitive way to refine assets. A shared code context across agents enables awareness of previous attempts, and a retrieval-augmented generation knowledge base built from Blender API documentation, BlenderRAG, equips agents with examples, types, and functions empowering advanced modeling operations and code correctness. We demonstrate the effectiveness of LL3M across diverse shape categories, style and material edits, and user-driven refinements. Our experiments showcase the power of code as a generative and interpretable medium for 3D asset creation. Our project page is at https://threedle.github.io/ll3m.
我们介绍了LL3M,这是一个多智能体系统,它利用预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)通过编写可在Blender中解释的Python代码来生成3D资产。我们摒弃了从一组3D数据中学习的传统生成方法。相反,我们将形状生成重新定义为代码编写任务,从而实现更大的模块化、可编辑性和与艺术家工作流程的集成。给定文本提示,LL3M协调专业LLM智能体团队来规划、检索、编写、调试和精炼Blender脚本,以生成和编辑几何形状和外观。生成的代码作为场景和对象的高级、可解释、人类可读的良好文档表示,充分利用Blender的复杂结构(例如B网格、几何修饰符、着色器节点)来创建多样化的、无约束的形状、材质和场景。该代码为进一步的智能体和人类编辑和实验提供了许多途径,可以通过代码微调或程序参数进行调整。这种媒介自然地在我们系统中启用了协同创作循环:智能体可以使用代码和视觉效果自动进行自我批评,而迭代用户指令提供了一种完善资产直观方式。智能体之间的共享代码上下文使它们能够意识到之前的尝试,并且从Blender API文档构建的增强检索知识库BlenderRAG为智能体提供示例、类型和功能,支持高级建模操作和代码正确性。我们在各种形状类别、样式和材料编辑以及用户驱动的优化方面展示了LL3M的有效性。我们的实验展示了代码作为3D资产创建的可生成和可解释媒介的力量。我们的项目页面是https://threedle.github.io/ll3m。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our project page is at https://threedle.github.io/ll3m
Summary
LL3M是一个利用预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)生成三维资产的多智能体系统,它通过编写可在Blender中解释的Python代码来实现。与传统的从三维数据中学习的生成方法不同,LL3M将形状生成重新定义为代码编写任务,提高了模块化、可编辑性和与艺术家工作流程的集成度。通过文本提示,LL3M协调专业LLM智能体团队来规划、检索、编写、调试和优化Blender脚本,生成和编辑几何体和外观。生成的代码作为场景和对象的可解释、人类可读和有充分文档的高级表示形式,充分利用Blender的复杂结构来创建多样化的无约束形状、材质和场景。这为进一步的智能体和人类编辑以及通过代码微调或程序参数进行的实验提供了许多途径。这种媒介自然地在我们系统中启用了协同创作循环:智能体可以使用代码和视觉自动进行自我评价,而迭代用户指令为完善资产提供了一种直观的方式。智能体之间的共享代码上下文使它们能够意识到之前的尝试,而来自Blender API文档的检索增强生成知识库则为智能体提供了示例、类型和函数,支持高级建模操作和代码正确性。我们的实验展示了代码作为三维资产创建中生成和可解释媒介的力量。
Key Takeaways
- LL3M是一个利用大型语言模型生成三维资产的系统,通过编写Blender脚本实现。
- LL3M采用代码编写任务的方式,与传统从三维数据中学习的生成方法不同,强调模块化、可编辑性和与艺术家工作流程的集成。
- LL3M能够根据文本提示生成和编辑几何体和外观,生成的代码为场景和对象的高级、可解释、人类可读和有文档表示。
- 生成的代码利用Blender的复杂结构,可以创建多样化的无约束形状、材质和场景。
- LL3M系统中的智能体可以自动自我评价,并通过迭代用户指令进行资产完善。
- 智能体之间的共享代码上下文使它们能够意识到之前的尝试,而检索增强生成知识库则为智能体提供支持高级建模操作和代码正确性的资源。
点此查看论文截图


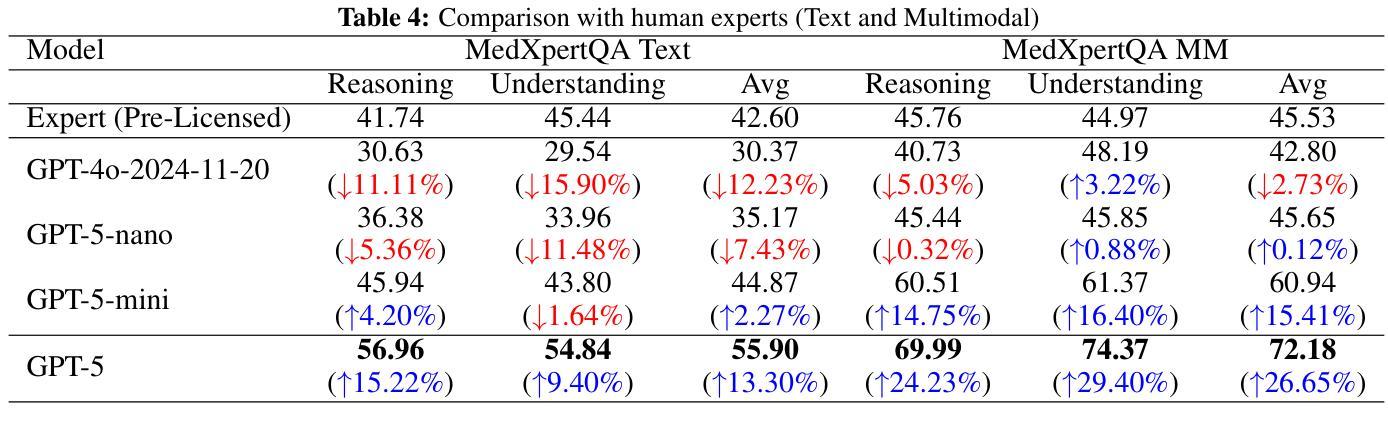
Capabilities of GPT-5 on Multimodal Medical Reasoning
Authors:Shansong Wang, Mingzhe Hu, Qiang Li, Mojtaba Safari, Xiaofeng Yang
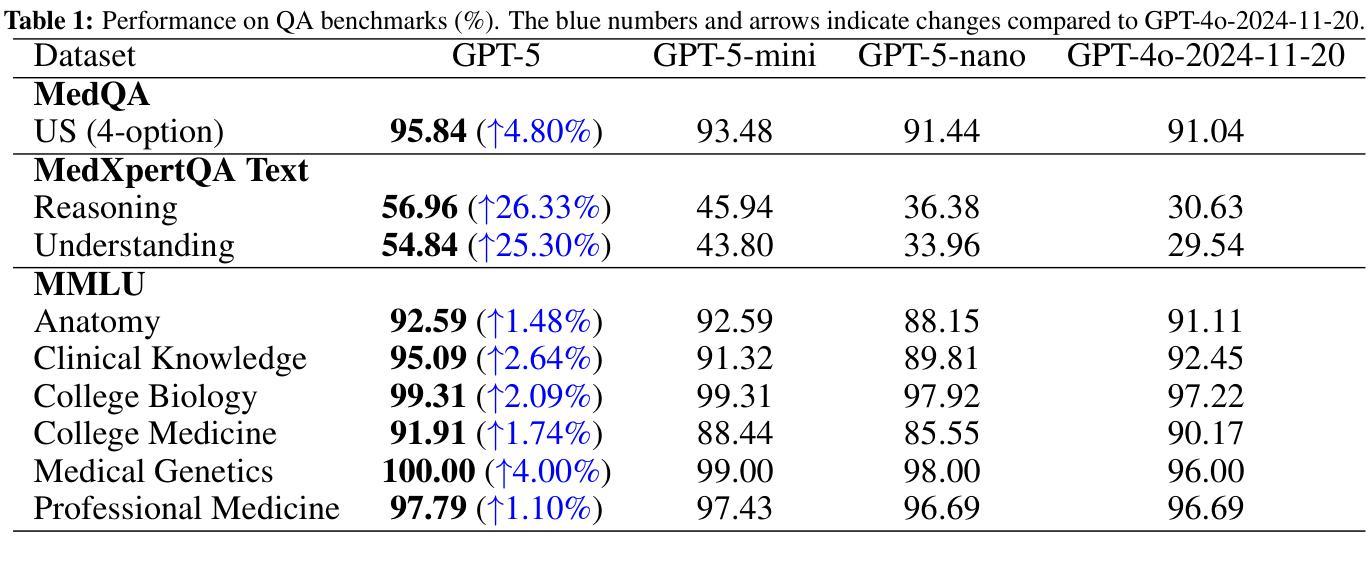
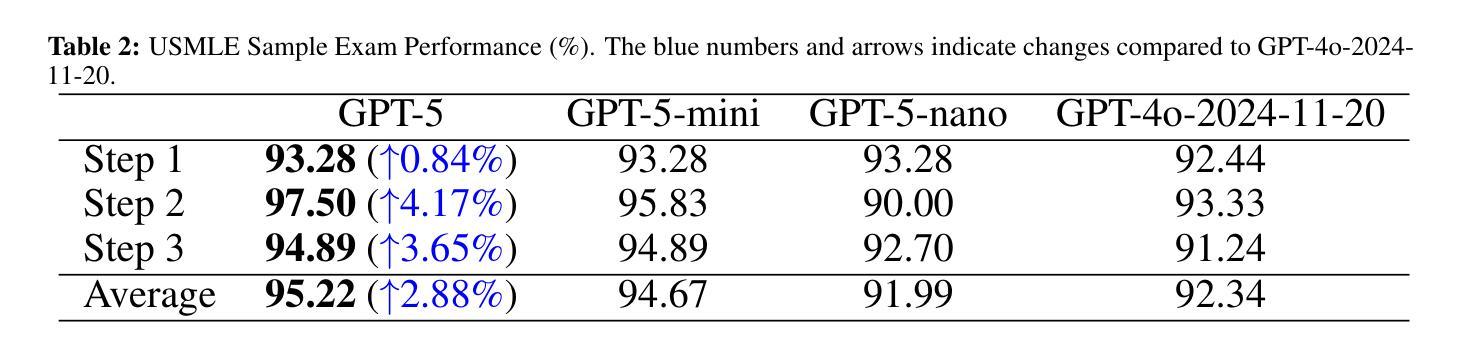
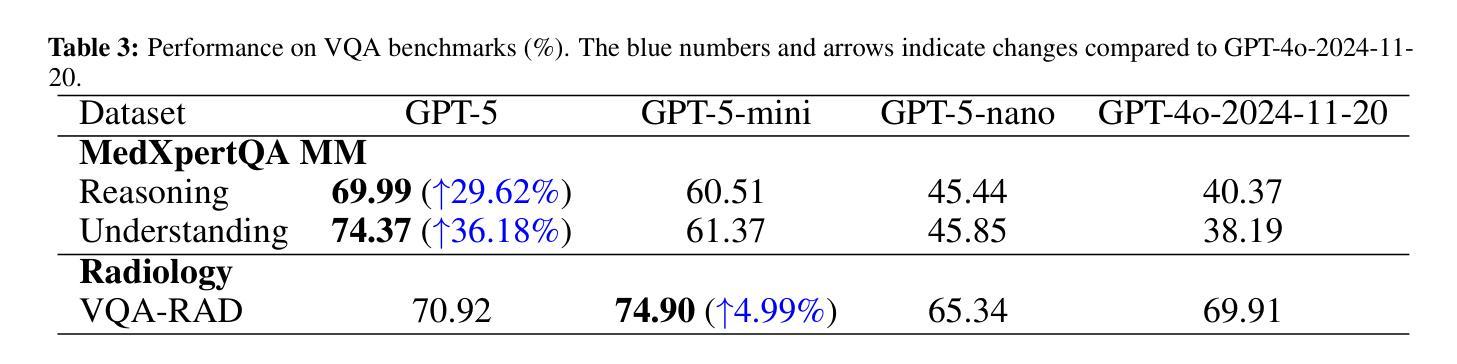
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled general-purpose systems to perform increasingly complex domain-specific reasoning without extensive fine-tuning. In the medical domain, decision-making often requires integrating heterogeneous information sources, including patient narratives, structured data, and medical images. This study positions GPT-5 as a generalist multimodal reasoner for medical decision support and systematically evaluates its zero-shot chain-of-thought reasoning performance on both text-based question answering and visual question answering tasks under a unified protocol. We benchmark GPT-5, GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano, and GPT-4o-2024-11-20 against standardized splits of MedQA, MedXpertQA (text and multimodal), MMLU medical subsets, USMLE self-assessment exams, and VQA-RAD. Results show that GPT-5 consistently outperforms all baselines, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy across all QA benchmarks and delivering substantial gains in multimodal reasoning. On MedXpertQA MM, GPT-5 improves reasoning and understanding scores by +29.62% and +36.18% over GPT-4o, respectively, and surpasses pre-licensed human experts by +24.23% in reasoning and +29.40% in understanding. In contrast, GPT-4o remains below human expert performance in most dimensions. A representative case study demonstrates GPT-5’s ability to integrate visual and textual cues into a coherent diagnostic reasoning chain, recommending appropriate high-stakes interventions. Our results show that, on these controlled multimodal reasoning benchmarks, GPT-5 moves from human-comparable to above human-expert performance. This improvement may substantially inform the design of future clinical decision-support systems.
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展使得通用系统能够在不需要广泛微调的情况下执行越来越复杂的特定领域推理。在医学领域,决策制定通常需要整合多种异质的信息来源,包括患者叙述、结构化数据和医学图像。本研究将GPT-5定位为医学决策支持的一般性多模式推理器,并在统一协议下,对其在基于文本的问题回答和视觉问题回答任务上的零起点思维链推理性能进行了系统评估。我们以MedQA、MedXpertQA(文本和多媒体)、MMLU医学子集、USMLE自我评估考试和VQA-RAD的标准分割为基准,对GPT-5、GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano以及GPT-4o-2024-11-20进行了评估。结果显示,GPT-5持续超越所有基线,在所有的问答基准测试中实现了最先进的准确性,并在多模式推理中取得了显著的提升。在MedXpertQA MM上,GPT-5的推理和理解分数分别比GPT-4o提高了+29.62%和+36.18%,并且其推理和理解的得分超过了预先授权的专家+24.23%和+29.40%。相比之下,GPT-4o在大多数维度上仍然低于人类专家的表现。一个典型的案例研究展示了GPT-5将视觉和文本线索整合到连贯的诊断推理链中的能力,并推荐了适当的高风险干预措施。我们的结果表明,在这些受控的多模式推理基准测试中,GPT-5的表现从与人类相当提升至超过人类专家。这一进步可能会为未来的临床决策支持系统提供重要信息参考。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展使得通用系统能够在不需要广泛微调的情况下执行越来越复杂的领域特定推理。本研究将GPT-5定位为医疗决策支持的一般性多模式推理器,并系统地评估其在统一协议下文本问题和视觉问题回答任务上的零射击链式思维推理性能。我们对GPT-5、GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano以及GPT-4o-2024-11-20进行了基准测试,与MedQA、MedXpertQA(文本和多模式)、MMLU医疗子集、USMLE自我评估考试和VQA-RAD的标准分割数据进行比较。结果表明,GPT-5始终优于所有基线,在问答基准测试中实现了最先进的准确性,并在多模式推理中取得了重大进展。在MedXpertQA MM上,GPT-5在推理和理解方面的得分分别比GPT-4o提高了+29.62%和+36.18%,并且超越了预先授权的人类专家在推理和理解方面的+24.23%和+29.40%。相比之下,GPT-4o在大多数维度上仍低于人类专家的性能。一个典型的案例研究表明,GPT-5能够整合视觉和文本线索,形成一个连贯的诊断推理链,推荐适当的高风险干预措施。我们的结果表明,在这些受控的多模式推理基准测试中,GPT-5的表现已从人类相当水平提升至超越人类专家。这一进步可能大大影响未来临床决策支持系统的设计。
关键见解
- LLM的最新进展使得通用系统在执行复杂的领域特定推理任务时表现出色,无需广泛微调。
- GPT-5被定位为医疗决策支持中的一般性多模式推理器,并进行了系统评估。
- GPT-5在多种标准化问答基准测试中表现出卓越性能,超越了许多基线模型。
- GPT-5在MedXpertQA上的表现优于GPT-4o和人类专家,显示出强大的推理和理解能力。
- GPT-5能够整合视觉和文本信息,形成连贯的诊断推理链。
- GPT-5在某些基准测试中的表现已超越人类专家,这可能对未来的临床决策支持系统产生重大影响。
点此查看论文截图



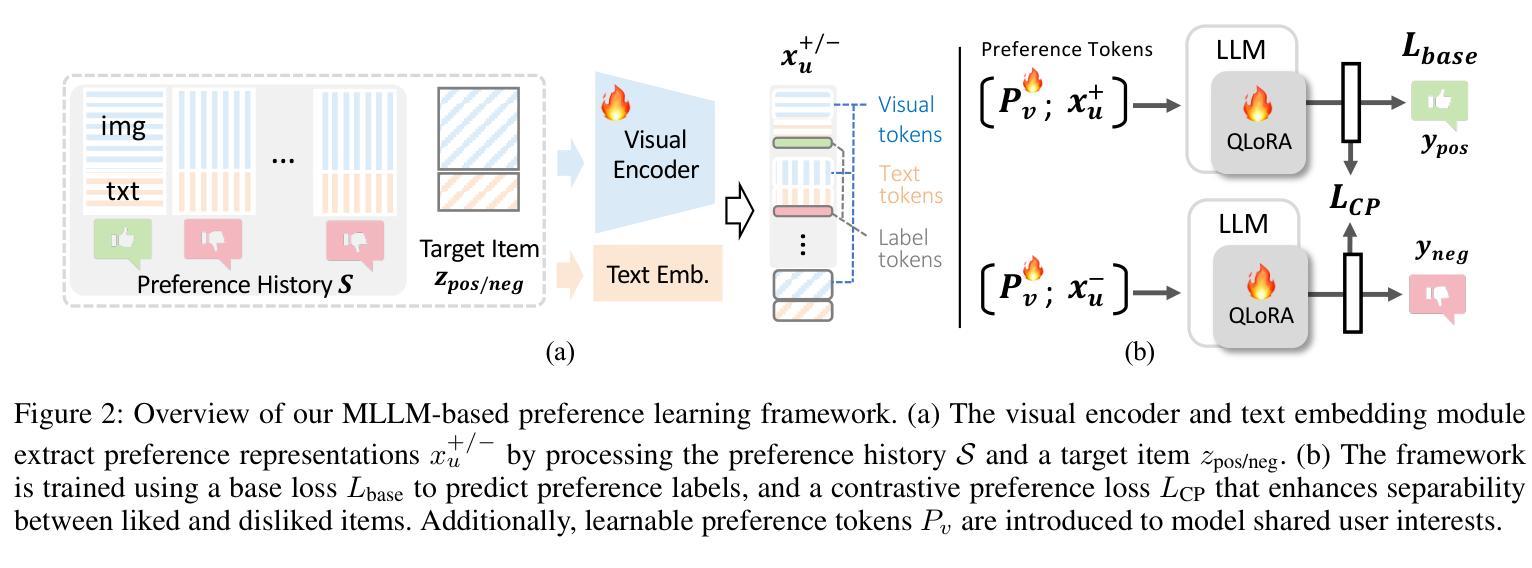
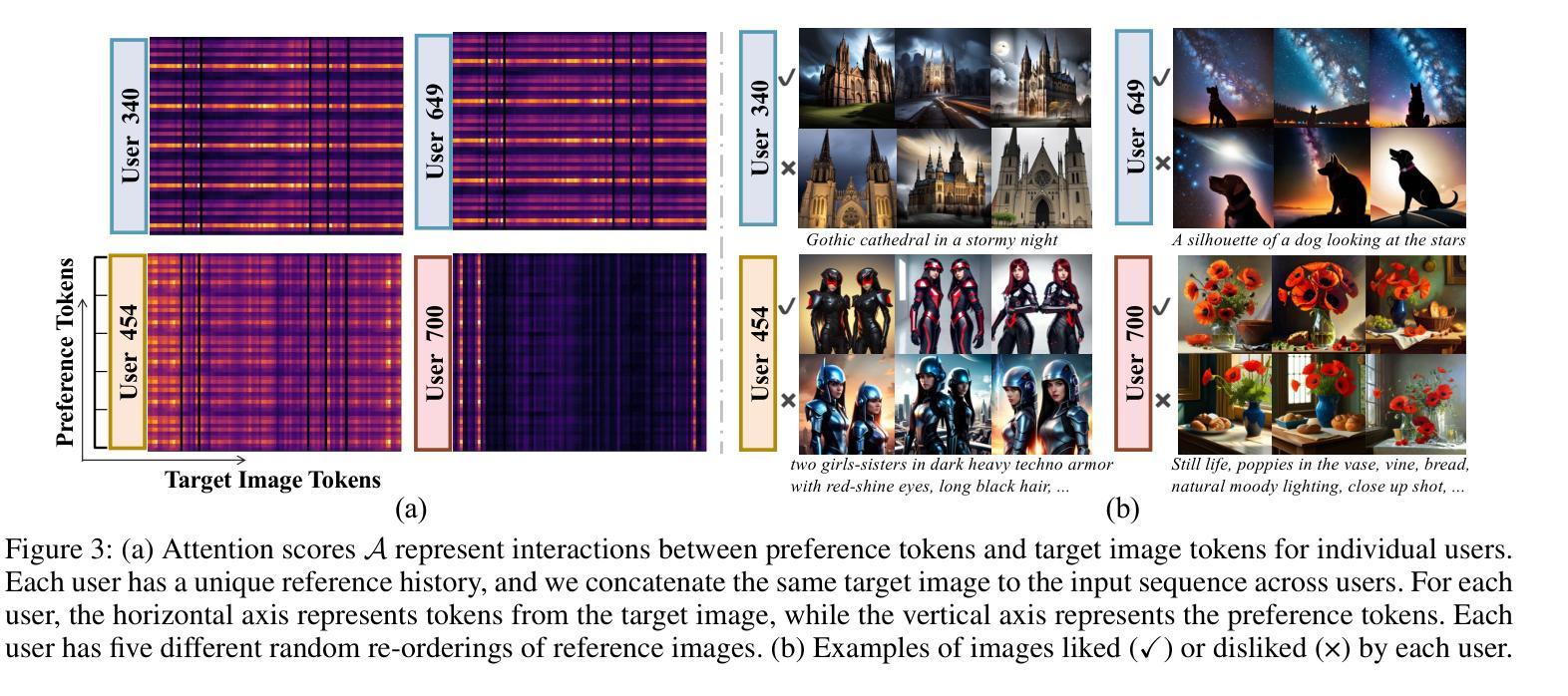
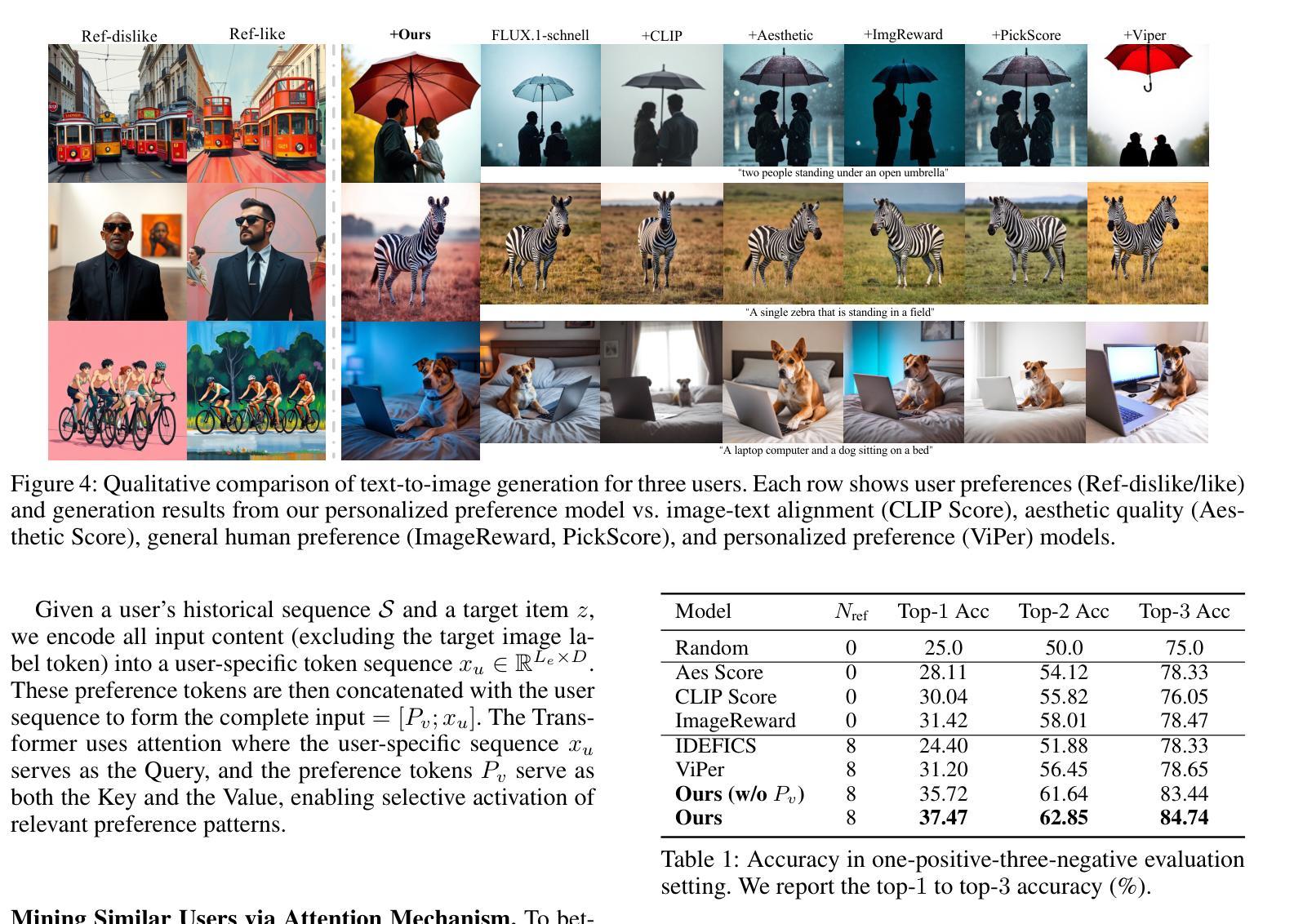
Learning User Preferences for Image Generation Model
Authors:Wenyi Mo, Ying Ba, Tianyu Zhang, Yalong Bai, Biye Li
User preference prediction requires a comprehensive and accurate understanding of individual tastes. This includes both surface-level attributes, such as color and style, and deeper content-related aspects, such as themes and composition. However, existing methods typically rely on general human preferences or assume static user profiles, often neglecting individual variability and the dynamic, multifaceted nature of personal taste. To address these limitations, we propose an approach built upon Multimodal Large Language Models, introducing contrastive preference loss and preference tokens to learn personalized user preferences from historical interactions. The contrastive preference loss is designed to effectively distinguish between user ‘’likes’’ and ‘’dislikes’’, while the learnable preference tokens capture shared interest representations among existing users, enabling the model to activate group-specific preferences and enhance consistency across similar users. Extensive experiments demonstrate our model outperforms other methods in preference prediction accuracy, effectively identifying users with similar aesthetic inclinations and providing more precise guidance for generating images that align with individual tastes. The project page is \texttt{https://learn-user-pref.github.io/}.
用户偏好预测需要对个人口味有全面准确的理解。这包括表面级别的属性,如颜色和风格,以及更深的内容相关方面,如主题和组成。然而,现有方法通常依赖于一般的人类偏好或假设用户配置文件是静态的,往往忽略了个人差异性以及个人口味的动态、多元性质。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于多模态大型语言模型的方法,引入对比偏好损失和偏好令牌,从历史交互中学习个性化用户偏好。对比偏好损失旨在有效区分用户“喜欢”和“不喜欢”的物品,而可学习的偏好令牌可以捕获现有用户之间的共享兴趣表示,使模型能够激活特定群体的偏好,并增强相似用户之间的一致性。大量实验表明,我们的模型在偏好预测准确性方面优于其他方法,能够识别具有相似审美倾向的用户,并为生成符合个人口味的图像提供更精确的指导。项目页面是[https://learn-user-pref.github.io/]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于用户多模态交互的大语言模型个性化偏好预测方法,结合了用户表面的属性喜好与深层次的内容偏好。引入对比偏好损失和个人偏好令牌,通过用户历史互动学习个性化偏好。对比偏好损失能区分用户的“喜欢”和“不喜欢”,而学习偏好令牌可捕获现有用户间的共享兴趣表示。此模型提高了预测准确率,能识别有相似审美倾向的用户,并为生成符合个人喜好的图像提供更精确指导。
Key Takeaways
- 用户偏好预测需要全面准确地了解个人口味,包括表面层次的属性和深层次的内容方面。
- 现有方法常常忽略个体差异性以及个人喜好的动态、多面性。
- 提出基于多模态大语言模型的解决方法,引入对比偏好损失以区分用户的“喜欢”和“不喜欢”。
- 引入学习偏好令牌,能够捕捉现有用户之间的共享兴趣表示,激活特定群体的偏好,并增强相似用户之间的一致性。
- 该模型在偏好预测准确性方面优于其他方法。
- 模型能够识别具有相似审美倾向的用户,为生成符合个人喜好的图像提供更精确指导。
点此查看论文截图

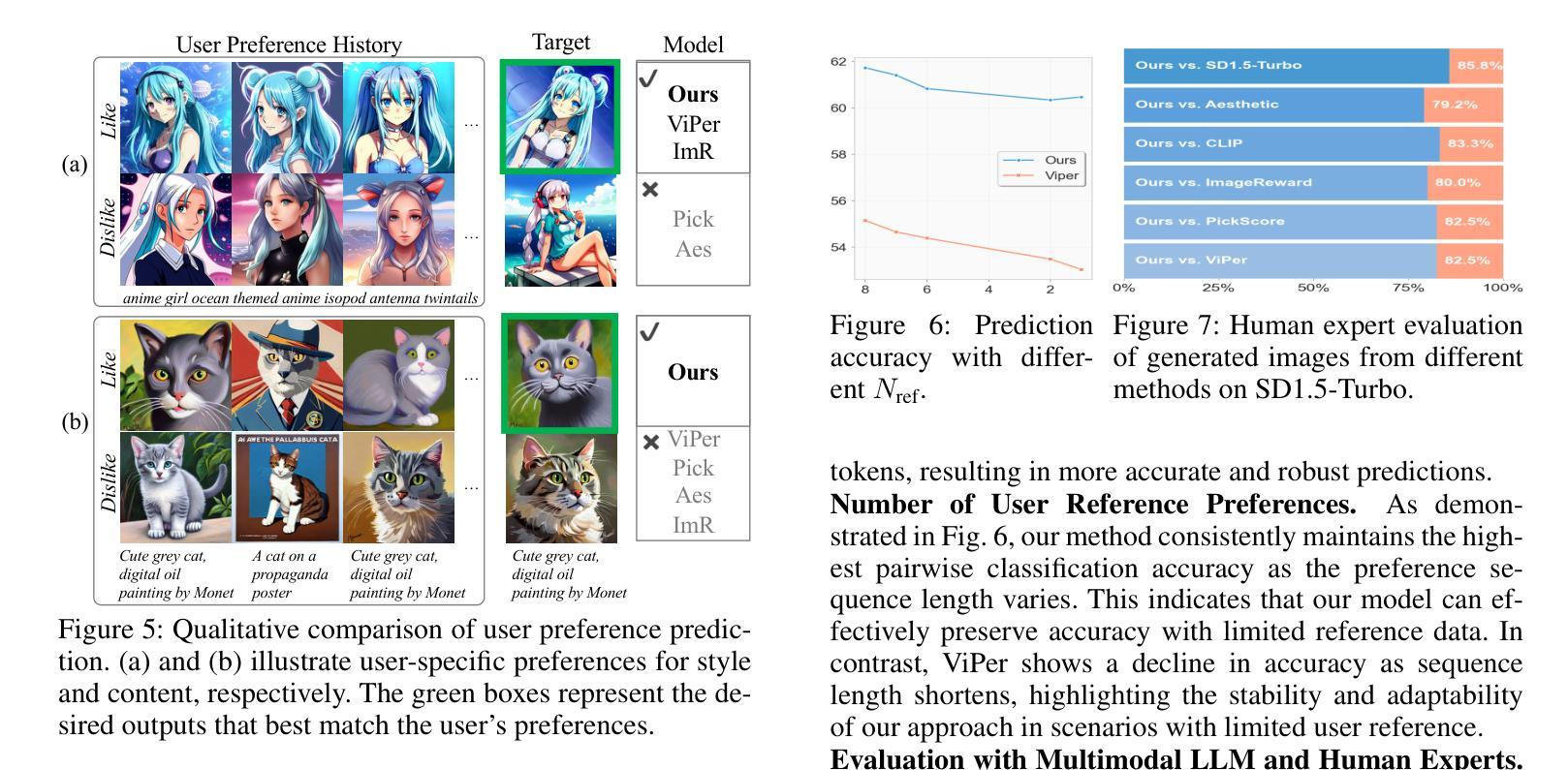

Efficient Speculative Decoding for Llama at Scale: Challenges and Solutions
Authors:Bangsheng Tang, Carl Chengyan Fu, Fei Kou, Grigory Sizov, Haoci Zhang, Jason Park, Jiawen Liu, Jie You, Qirui Yang, Sachin Mehta, Shengyong Cai, Xiaodong Wang, Xingyu Liu, Yunlu Li, Yanjun Zhou, Wei Wei, Zhiwei Zhao, Zixi Qi, Adolfo Victoria, Aya Ibrahim, Bram Wasti, Changkyu Kim, Daniel Haziza, Fei Sun, Giancarlo Delfin, Emily Guo, Jialin Ouyang, Jaewon Lee, Jianyu Huang, Jeremy Reizenstein, Lu Fang, Quinn Zhu, Ria Verma, Vlad Mihailescu, Xingwen Guo, Yan Cui, Ye Hu, Yejin Lee
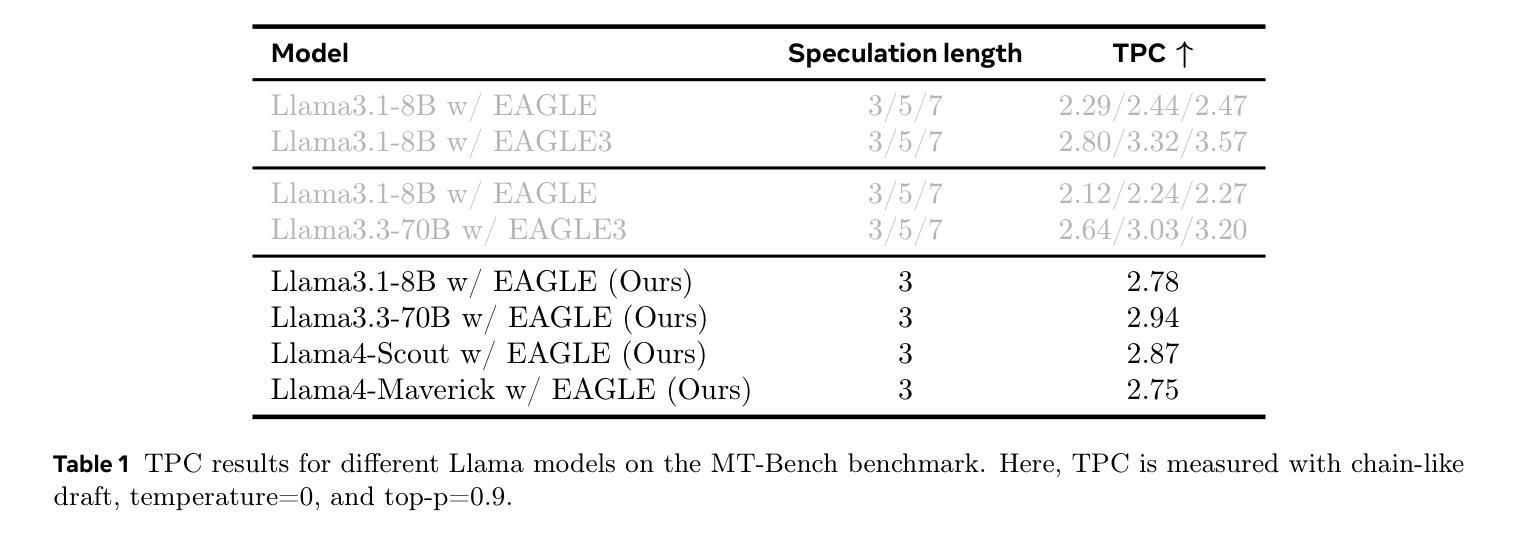
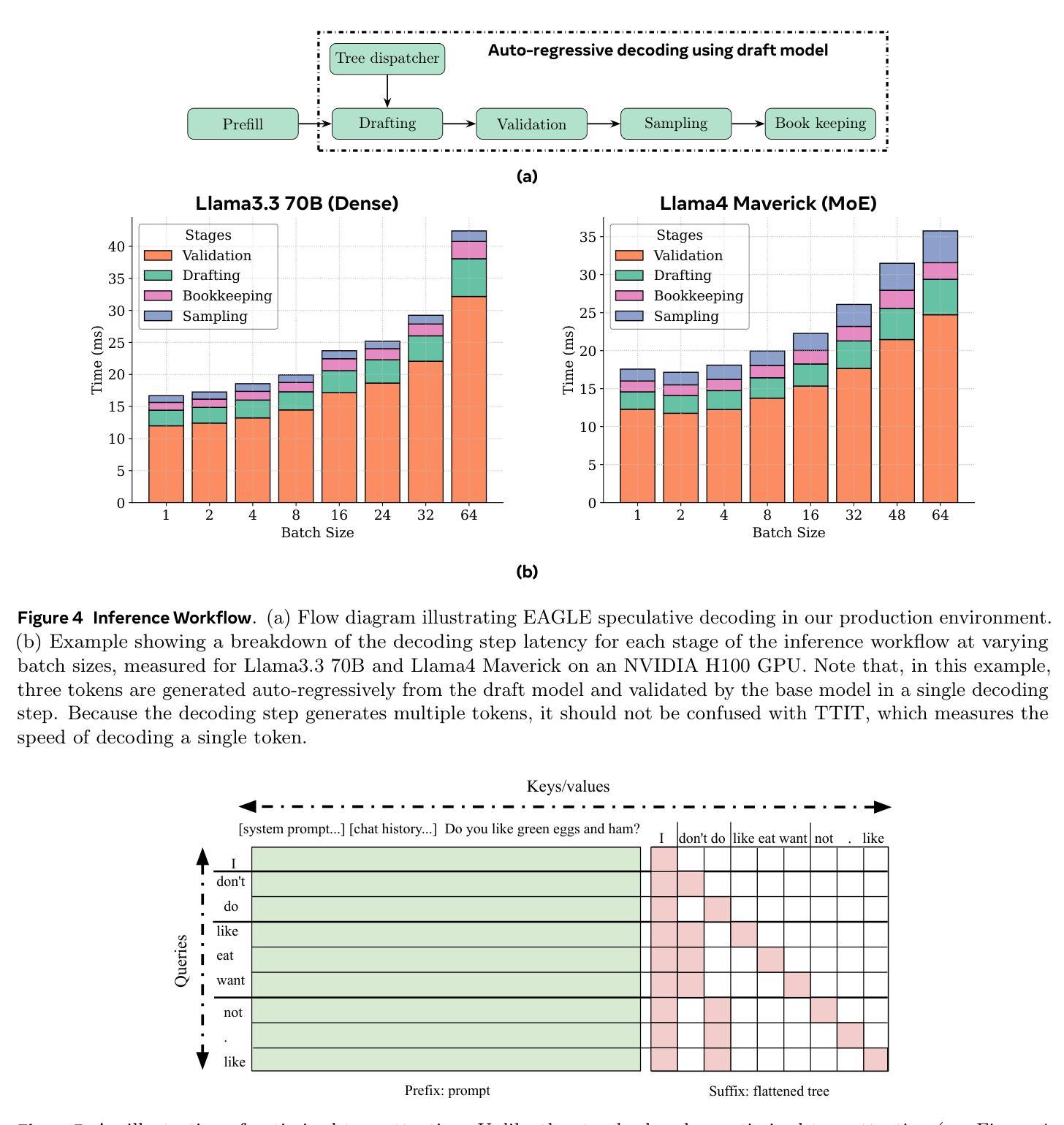
Speculative decoding is a standard method for accelerating the inference speed of large language models. However, scaling it for production environments poses several engineering challenges, including efficiently implementing different operations (e.g., tree attention and multi-round speculative decoding) on GPU. In this paper, we detail the training and inference optimization techniques that we have implemented to enable EAGLE-based speculative decoding at a production scale for Llama models. With these changes, we achieve a new state-of-the-art inference latency for Llama models. For example, Llama4 Maverick decodes at a speed of about 4 ms per token (with a batch size of one) on 8 NVIDIA H100 GPUs, which is 10% faster than the previously best known method. Furthermore, for EAGLE-based speculative decoding, our optimizations enable us to achieve a speed-up for large batch sizes between 1.4x and 2.0x at production scale.
推测解码是加速大型语言模型推理速度的一种标准方法。然而,将其扩展到生产环境面临许多工程挑战,包括在GPU上有效地实现不同操作(例如树状注意力和多轮推测解码)。在本文中,我们详细介绍了为应对生产规模下基于EAGLE的推测解码而实施的训练和推理优化技术。通过这些更改,我们为Llama模型实现了最新的推理延迟记录。例如,Llama4 Maverick在8个NVIDIA H100 GPU上实现了约每令牌4毫秒的解码速度(批处理大小为1),比已知的最佳方法快10%。此外,对于基于EAGLE的推测解码,我们的优化在生产规模下实现了大批量速度的1.4倍至2倍提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
大规模语言模型推理速度的提升通常采用投机解码这一标准方法。然而,在生产环境中实现规模化存在诸多工程挑战,特别是在GPU上有效实施不同操作(如树状注意力与多轮投机解码)。本文详细介绍了我们为Llama模型实现基于EAGLE的投机解码所进行的训练和推理优化技术。通过这些改进,Llama模型达到了业界领先的推理速度。例如,Llama4 Maverick在8个NVIDIA H100 GPU上实现了约每令牌4毫秒的解码速度(批处理大小为1),比已知的最佳方法快10%。此外,对于基于EAGLE的投机解码,我们的优化在生产规模下实现了对大规模批处理的加速,提速介于1.4倍至2倍之间。
Key Takeaways
- 投机型解码是用于加速大规模语言模型推理的标准方法。
- 生产环境中实现规模化投机解码面临诸多工程挑战。
- 本文介绍了针对Llama模型的训练和推理优化技术。
- 通过这些改进,Llama模型达到了新的业界领先的推理速度。
- Llama模型的优化能够在大规模批次下实现加速。
- 在基于EAGLE的投机解码中,优化技术显著提升了生产规模下的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Reinforcement Learning in Vision: A Survey
Authors:Weijia Wu, Chen Gao, Joya Chen, Kevin Qinghong Lin, Qingwei Meng, Yiming Zhang, Yuke Qiu, Hong Zhou, Mike Zheng Shou
Recent advances at the intersection of reinforcement learning (RL) and visual intelligence have enabled agents that not only perceive complex visual scenes but also reason, generate, and act within them. This survey offers a critical and up-to-date synthesis of the field. We first formalize visual RL problems and trace the evolution of policy-optimization strategies from RLHF to verifiable reward paradigms, and from Proximal Policy Optimization to Group Relative Policy Optimization. We then organize more than 200 representative works into four thematic pillars: multi-modal large language models, visual generation, unified model frameworks, and vision-language-action models. For each pillar we examine algorithmic design, reward engineering, benchmark progress, and we distill trends such as curriculum-driven training, preference-aligned diffusion, and unified reward modeling. Finally, we review evaluation protocols spanning set-level fidelity, sample-level preference, and state-level stability, and we identify open challenges that include sample efficiency, generalization, and safe deployment. Our goal is to provide researchers and practitioners with a coherent map of the rapidly expanding landscape of visual RL and to highlight promising directions for future inquiry. Resources are available at: https://github.com/weijiawu/Awesome-Visual-Reinforcement-Learning.
近期强化学习(RL)与视觉智能交叉领域的进展使得智能体不仅能够感知复杂的视觉场景,还能在这些场景中进行推理、生成和行动。这篇综述对该领域进行了批判性和最新的综合。我们首先正式提出视觉RL问题,并追溯策略优化策略从RLHF到可验证奖励范式的发展,以及从近端策略优化到群组相对策略优化的发展。然后,我们将超过200篇代表性作品整理为四个主题支柱:多模态大型语言模型、视觉生成、统一模型框架和视觉语言行动模型。对于每个支柱,我们研究了算法设计、奖励工程、基准进度,并总结了趋势,如课程驱动训练、偏好对齐扩散和统一奖励建模。最后,我们回顾了包括集合级保真度、样本级偏好和状态级稳定性的评估协议,并确定了开放挑战,包括样本效率、泛化和安全部署等。我们的目标是为研究人员和实践者提供视觉RL快速扩展景观的一致地图,并突出未来查询的有希望的方向。资源可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/weijiawu/Awesome-Visual-Reinforcement-Learning。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages
Summary
视觉强化学习(Visual RL)是强化学习与视觉智能的交叉点,近年来取得了重要进展。本文综述了该领域的研究进展,介绍了视觉RL问题的形式化定义,追踪了策略优化方法从RLHF到可验证奖励模式的演变,并整理了多模态大型语言模型、视觉生成、统一模型框架和视觉语言行动模型等四大支柱的研究工作。本文还探讨了算法设计、奖励工程、基准测试进展等趋势,并回顾了评估协议和开放挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉强化学习结合了强化学习与视觉智能,使智能体能够在复杂视觉场景中感知、推理、生成和行动。
- 本文形式化了视觉RL问题的定义,并追踪了策略优化方法的演变。
- 四大支柱的研究工作包括多模态大型语言模型、视觉生成、统一模型框架和视觉语言行动模型。
- 趋势包括课程驱动训练、偏好对齐扩散和统一奖励建模等。
- 评估协议包括集合级保真度、样本级偏好和状态级稳定性。
- 样本效率、泛化和安全部署是视觉强化学习的开放挑战。
点此查看论文截图

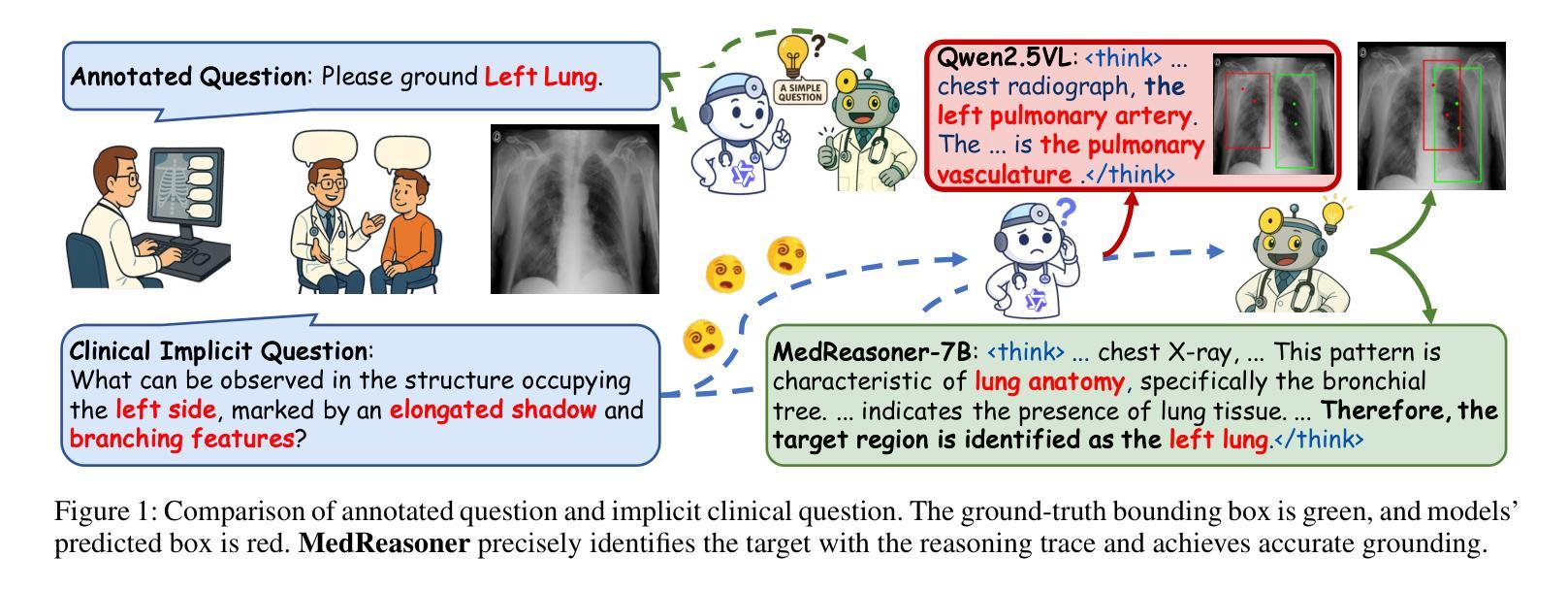
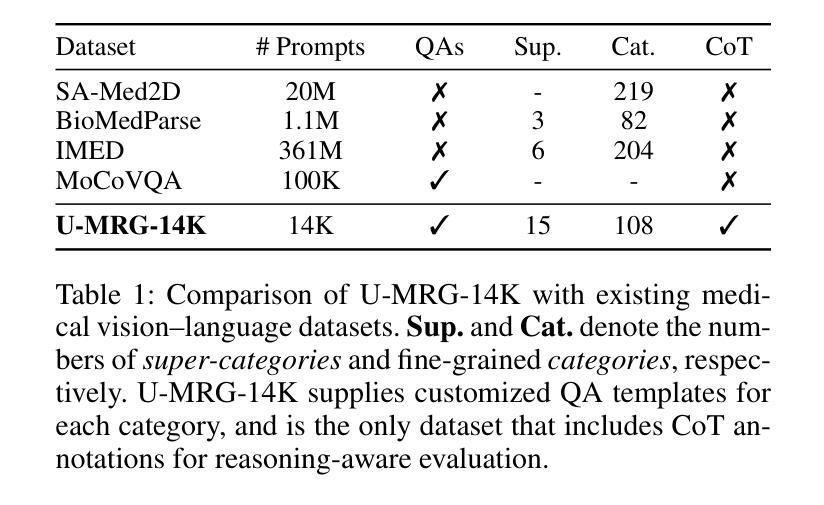
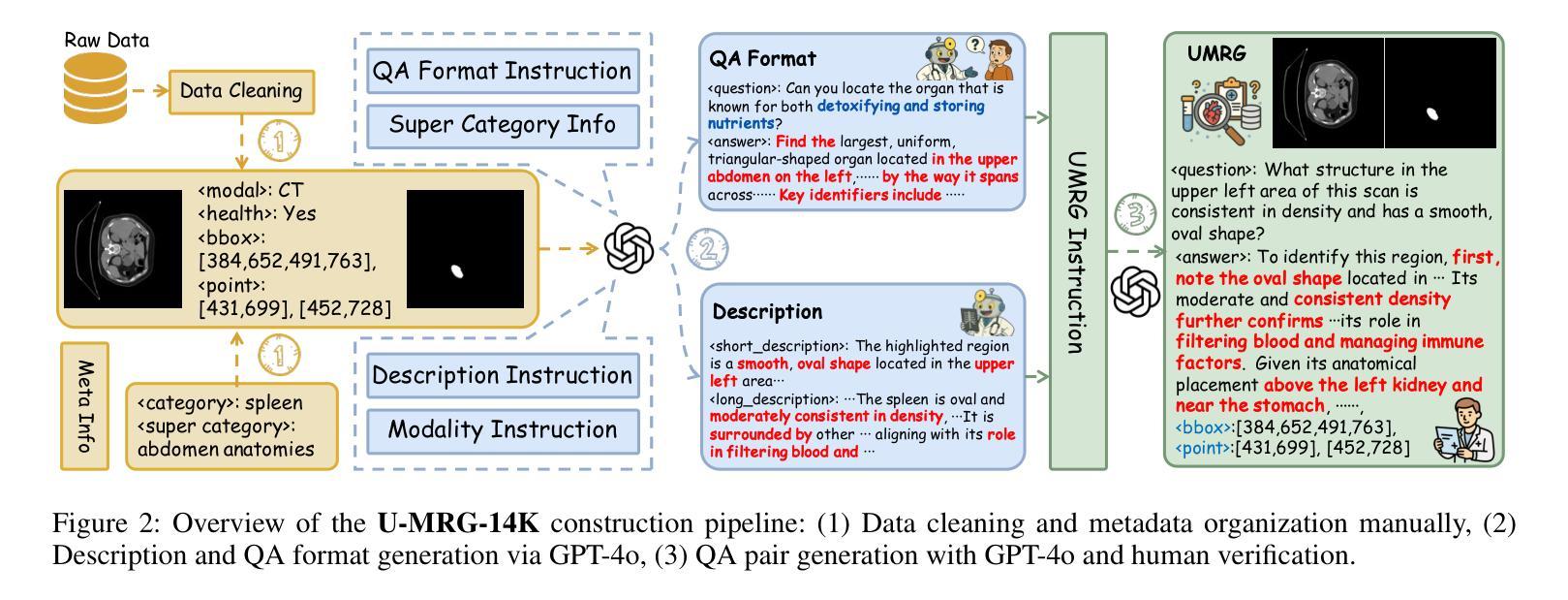
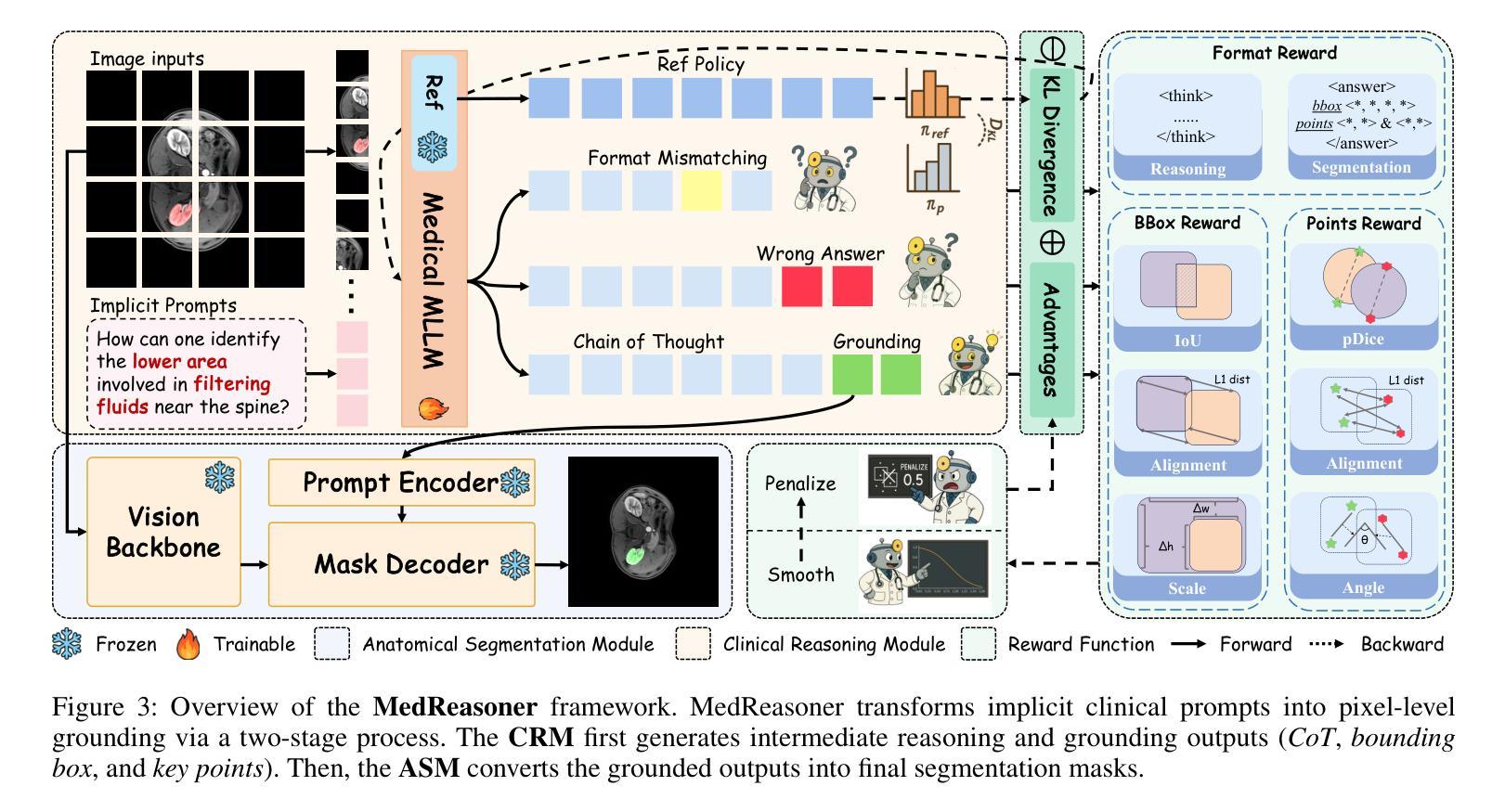
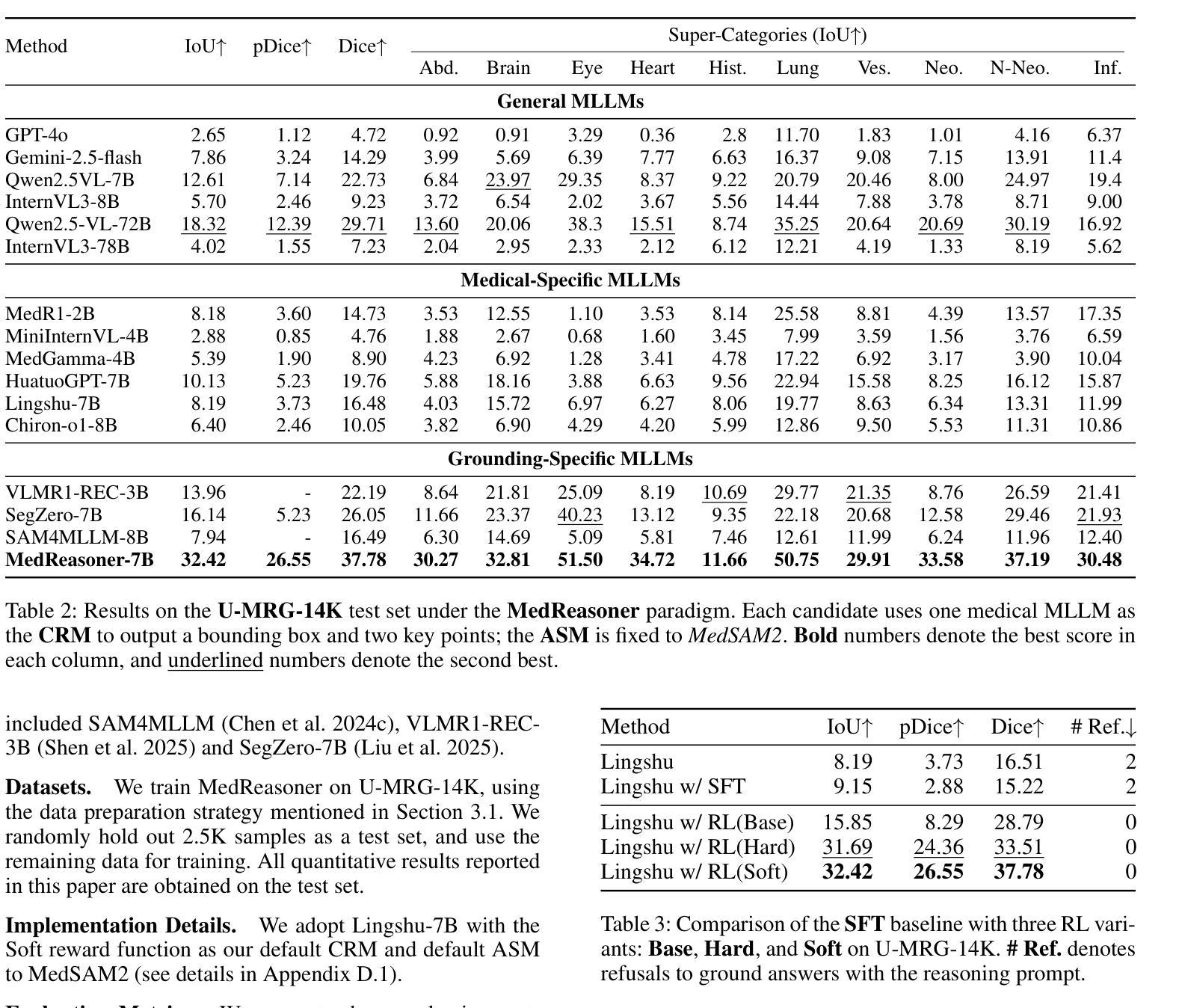
MedReasoner: Reinforcement Learning Drives Reasoning Grounding from Clinical Thought to Pixel-Level Precision
Authors:Zhonghao Yan, Muxi Diao, Yuxuan Yang, Jiayuan Xu, Kaizhou Zhang, Ruoyan Jing, Lele Yang, Yanxi Liu, Kongming Liang, Zhanyu Ma
Accurately grounding regions of interest (ROIs) is critical for diagnosis and treatment planning in medical imaging. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) combine visual perception with natural language, current medical-grounding pipelines still rely on supervised fine-tuning with explicit spatial hints, making them ill-equipped to handle the implicit queries common in clinical practice. This work makes three core contributions. We first define Unified Medical Reasoning Grounding (UMRG), a novel vision-language task that demands clinical reasoning and pixel-level grounding. Second, we release U-MRG-14K, a dataset of 14K samples featuring pixel-level masks alongside implicit clinical queries and reasoning traces, spanning 10 modalities, 15 super-categories, and 108 specific categories. Finally, we introduce MedReasoner, a modular framework that distinctly separates reasoning from segmentation: an MLLM reasoner is optimized with reinforcement learning, while a frozen segmentation expert converts spatial prompts into masks, with alignment achieved through format and accuracy rewards. MedReasoner achieves state-of-the-art performance on U-MRG-14K and demonstrates strong generalization to unseen clinical queries, underscoring the significant promise of reinforcement learning for interpretable medical grounding.
在医学成像的诊断和治疗计划制定中,准确地对感兴趣区域(ROIs)进行定位至关重要。虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了视觉感知与自然语言,但当前的医学定位流程仍依赖于具有明确空间提示的监督微调,因此难以应对临床实践中常见的隐含查询。本文作出三项核心贡献。首先,我们定义了统一医学推理定位(UMRG),这是一种新的视觉语言任务,要求进行临床推理和像素级定位。其次,我们发布了U-MRG-14K数据集,包含14K个样本,每个样本具有像素级掩膜、隐含的临床查询和推理轨迹,涵盖10种模态、15个超类别和108个特定类别。最后,我们推出了MedReasoner,这是一个模块化框架,将推理与分割区分开:MLLM推理器通过强化学习进行优化,而冻结的分割专家将空间提示转换为掩膜,通过格式和精度奖励实现对齐。MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K上达到了最先进的性能,并对未见过的临床查询表现出了强大的泛化能力,突显了强化学习在可解释的医学定位中的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages
Summary
基于医疗成像中的感兴趣区域(ROI)的准确定位对于诊断和治疗计划至关重要。当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了视觉感知和自然语言处理,但现有的医疗定位流程仍依赖于带有明确空间提示的监督微调,无法应对临床实践中的隐式查询。本研究提出了三项核心贡献。首先,定义了统一医学推理定位(UMRG)这一新型视觉语言任务,需要临床推理和像素级定位。其次,推出了包含超过1万个样本的U-MRG-14K数据集,数据集中的每个样本包含像素级蒙版和伴随的隐式临床查询及推理轨迹,涵盖十种模态、十五种超级类别和一百零八种特定类别。最后,推出了MedReasoner模块化框架,将推理与分割分离:使用强化学习优化MLLM推理器,冻结的分割专家将空间提示转换为蒙版,通过格式和准确性奖励实现对齐。MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现,并且对未见过的临床查询展现出强大的泛化能力,突显强化学习在可解释的医学定位方面的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 统一医学推理定位(UMRG)成为必要的新型视觉语言任务,因为它要求结合临床推理和像素级定位技术来处理复杂的医学成像数据。
- U-MRG-14K数据集填补了针对医学成像的隐式查询研究的空白,包含了丰富的样本数据和多样化的临床信息。
- MedReasoner模块化框架首次成功将推理与分割分离,提高了模型的灵活性和效率。
- 强化学习在MedReasoner中发挥了关键作用,使得模型能够更好地处理复杂的医学数据并提高其泛化能力。
- MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K数据集上取得了最先进的性能表现,验证了该框架的有效性和潜力。
- 当前的多模态大型语言模型在处理医学成像数据时仍然面临挑战,需要通过研究新的方法和策略来提高其性能。
点此查看论文截图

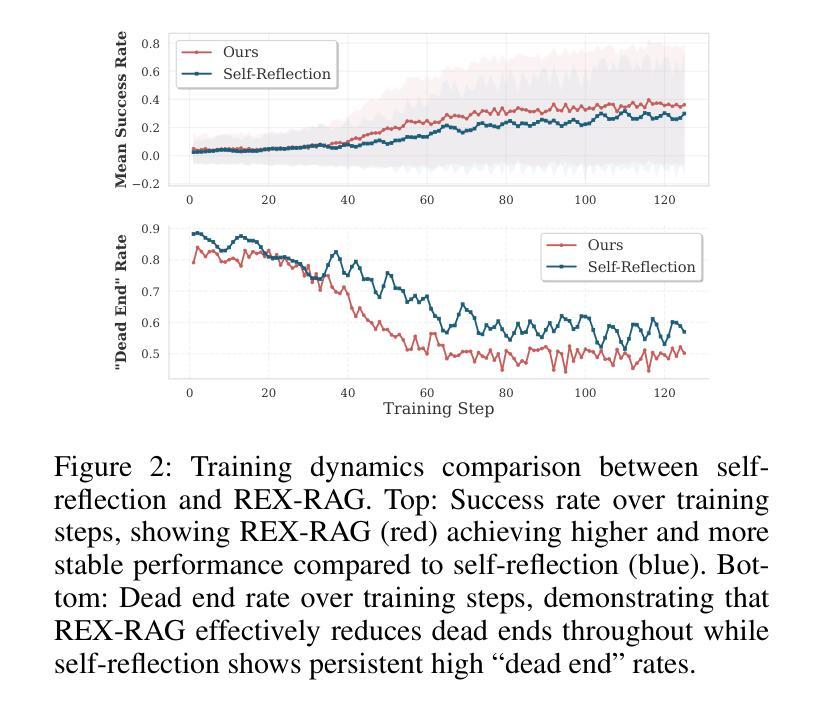
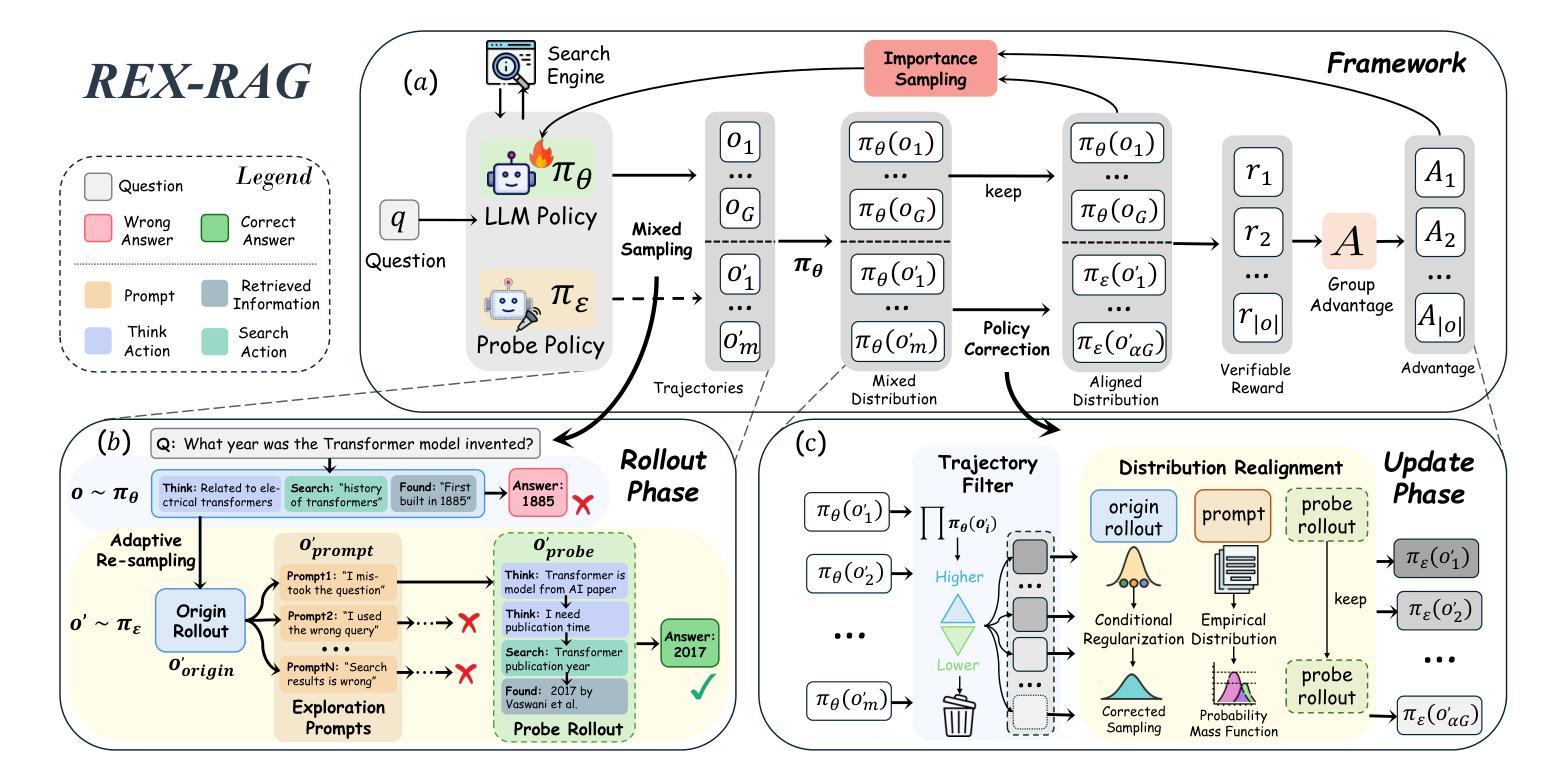
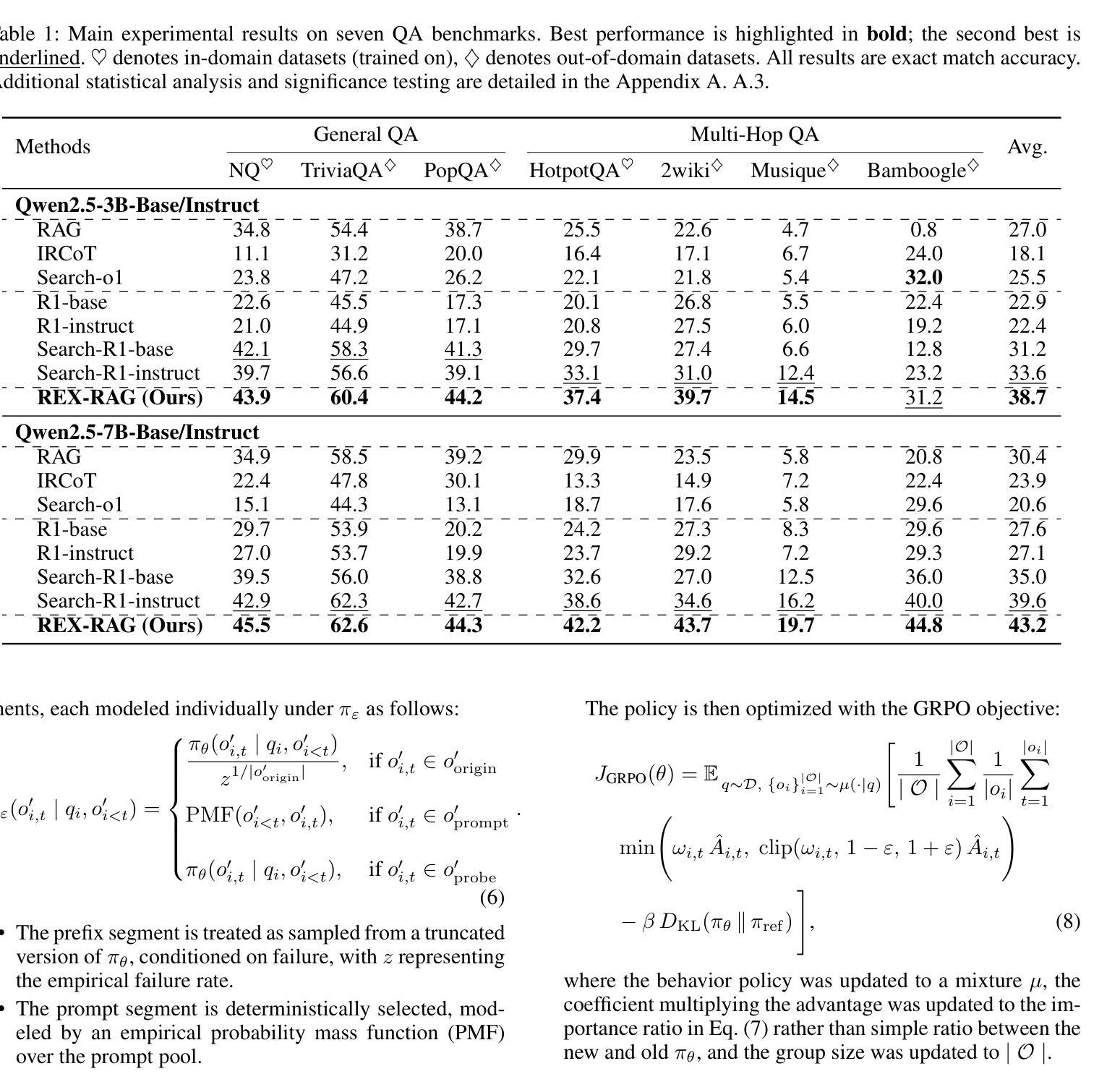
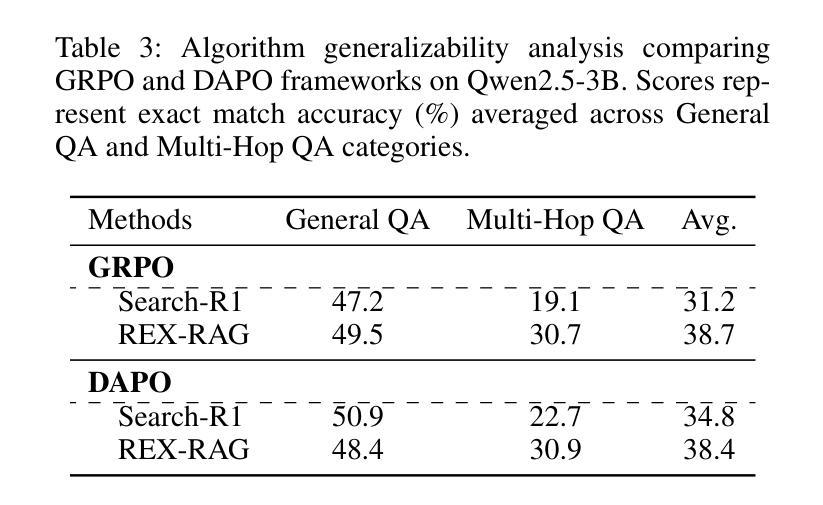
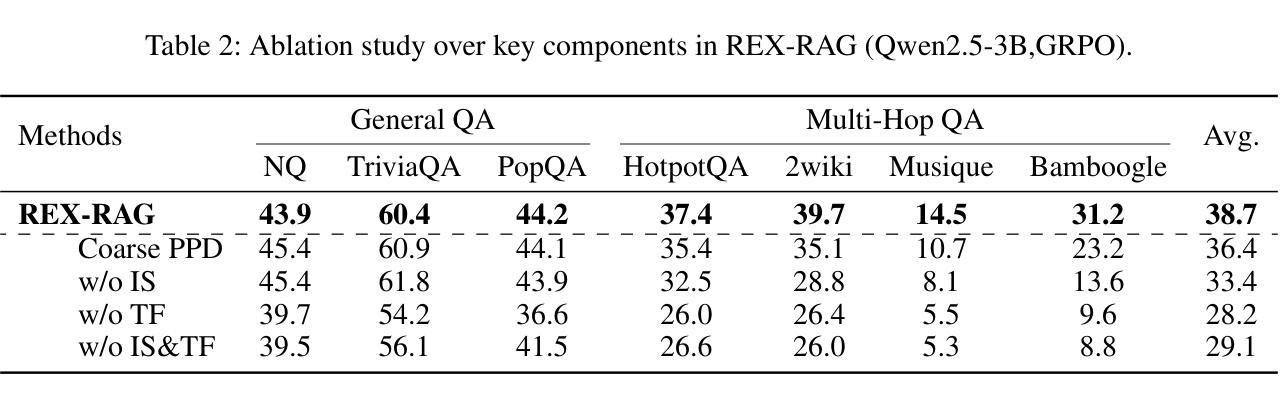
REX-RAG: Reasoning Exploration with Policy Correction in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Wentao Jiang, Xiang Feng, Zengmao Wang, Yong Luo, Pingbo Xu, Zhe Chen, Bo Du, Jing Zhang
Reinforcement learning (RL) is emerging as a powerful paradigm for enabling large language models (LLMs) to perform complex reasoning tasks. Recent advances indicate that integrating RL with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) allows LLMs to dynamically incorporate external knowledge, leading to more informed and robust decision making. However, we identify a critical challenge during policy-driven trajectory sampling: LLMs are frequently trapped in unproductive reasoning paths, which we refer to as “dead ends”, committing to overconfident yet incorrect conclusions. This severely hampers exploration and undermines effective policy optimization. To address this challenge, we propose REX-RAG (Reasoning Exploration with Policy Correction in Retrieval-Augmented Generation), a novel framework that explores alternative reasoning paths while maintaining rigorous policy learning through principled distributional corrections. Our approach introduces two key innovations: (1) Mixed Sampling Strategy, which combines a novel probe sampling method with exploratory prompts to escape dead ends; and (2) Policy Correction Mechanism, which employs importance sampling to correct distribution shifts induced by mixed sampling, thereby mitigating gradient estimation bias. We evaluate it on seven question-answering benchmarks, and the experimental results show that REX-RAG achieves average performance gains of 5.1% on Qwen2.5-3B and 3.6% on Qwen2.5-7B over strong baselines, demonstrating competitive results across multiple datasets. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/MiliLab/REX-RAG.
强化学习(RL)正成为一种强大的范式,使大型语言模型(LLM)能够执行复杂的推理任务。最近的进展表明,将RL与检索增强生成(RAG)相结合,可以使LLM动态地融入外部知识,从而实现更加明智和稳健的决策。然而,我们在政策驱动的轨迹采样过程中发现了一个关键挑战:LLM经常陷入不产生结果的推理路径,我们称之为“死胡同”,并导致过于自信且错误的结论。这严重阻碍了探索并破坏了有效的政策优化。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了REX-RAG(检索增强生成中的推理探索与政策校正),这是一个新的框架,能够在保持严格政策学习的情况下探索替代的推理路径,并通过原则性的分布校正来进行调整。我们的方法引入了两个关键的创新点:(1)混合采样策略,它将一种新的探针采样方法与探索性提示相结合,以逃离死胡同;(2)政策校正机制,它采用重要性采样来校正由混合采样引起的分布偏移,从而减轻梯度估计偏差。我们在七个问答基准测试上对其实验评估,实验结果表明,REX-RAG在Qwen2.5-3B上平均性能提升5.1%,在Qwen2.5-7B上相对于强大的基准测试平均提升3.6%,在多个数据集上取得了有竞争力的结果。代码已公开在https://github.com/MiliLab/REX-RAG。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 4 figures
Summary
强化学习(RL)与大语言模型(LLM)结合,可实现复杂推理任务。近期研究显示,将RL与检索增强生成(RAG)结合,可使LLMs动态融入外部知识,实现更明智和稳健的决策。然而,政策驱动轨迹采样存在挑战:LLMs易陷入无效推理路径(即“死胡同”),导致过度自信的错误结论。为解决此问题,我们提出REX-RAG框架,在检索增强生成中进行推理探索与策略修正。该框架引入两项关键创新:1)混合采样策略,结合新型探针采样方法与探索性提示以逃离死胡同;2)策略修正机制,采用重要性采样纠正混合采样引起的分布偏移,减轻梯度估计偏差。在七个问答基准测试集上的评估结果表明,REX-RAG在Qwen2.5-3B上平均性能提升5.1%,在Qwen2.5-7B上提升3.6%,相较于强基线具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)与大语言模型(LLM)结合可实现复杂推理任务。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)使LLMs能动态融入外部知识,实现更明智和稳健的决策。
- 政策驱动轨迹采样存在挑战,LLMs易陷入无效推理路径(即“死胡同”)。
- REX-RAG框架通过混合采样策略和策略修正机制解决此问题。
- 混合采样策略结合探针采样和探索性提示逃离死胡同。
- 策略修正机制采用重要性采样纠正分布偏移,减轻梯度估计偏差。
- REX-RAG在多个问答基准测试集上表现优异,平均性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

Data-Efficient Biomedical In-Context Learning: A Diversity-Enhanced Submodular Perspective
Authors:Jun Wang, Zaifu Zhan, Qixin Zhang, Mingquan Lin, Meijia Song, Rui Zhang
Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has leveraged their in-context learning (ICL) abilities to enable quick adaptation to unseen biomedical NLP tasks. By incorporating only a few input-output examples into prompts, LLMs can rapidly perform these new tasks. While the impact of these demonstrations on LLM performance has been extensively studied, most existing approaches prioritize representativeness over diversity when selecting examples from large corpora. To address this gap, we propose Dual-Div, a diversity-enhanced data-efficient framework for demonstration selection in biomedical ICL. Dual-Div employs a two-stage retrieval and ranking process: First, it identifies a limited set of candidate examples from a corpus by optimizing both representativeness and diversity (with optional annotation for unlabeled data). Second, it ranks these candidates against test queries to select the most relevant and non-redundant demonstrations. Evaluated on three biomedical NLP tasks (named entity recognition (NER), relation extraction (RE), and text classification (TC)) using LLaMA 3.1 and Qwen 2.5 for inference, along with three retrievers (BGE-Large, BMRetriever, MedCPT), Dual-Div consistently outperforms baselines-achieving up to 5% higher macro-F1 scores-while demonstrating robustness to prompt permutations and class imbalance. Our findings establish that diversity in initial retrieval is more critical than ranking-stage optimization, and limiting demonstrations to 3-5 examples maximizes performance efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展利用其上下文学习(ICL)能力,能够快速适应未见过的生物医学NLP任务。通过将在少数输入-输出示例融入提示中,LLM可以快速执行这些新任务。虽然这些演示对LLM性能的影响已经得到了广泛的研究,但现有大多数方法在选择例子时更侧重于代表性而非多样性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Dual-Div,这是一种用于生物医学ICL演示选择的增强多样性和数据高效的框架。Dual-Div采用两阶段检索和排名过程:首先,它通过优化代表性和多样性(未标记数据可进行可选注释)从语料库中确定一组有限的候选示例。其次,它根据测试查询对这些候选人进行排名,以选择最相关且非冗余的演示内容。通过LLaMA 3.1和Qwen 2.5进行推理,以及在三个生物医学NLP任务(命名实体识别(NER)、关系提取(RE)和文本分类(TC))上,与三种检索器(BGE-Large、BMRetriever、MedCPT)一起评估,Dual-Div始终优于基线,达到高达5%的宏观F1分数,同时显示出对提示排列和类别不平衡的稳健性。我们的研究结果表明,初始检索中的多样性比排名阶段的优化更为重要,将演示限制在3-5个示例内可以最大化性能效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生物医学自然语言处理(NLP)任务中展现出强大的上下文学习能力(ICL)。通过仅使用少量输入-输出示例作为提示,LLM可以快速适应新任务。尽管这些演示对LLM性能的影响已被广泛研究,但现有方法在选择示例时大多注重代表性而忽视多样性。为此,我们提出了Dual-Div框架,这是一个增强多样性的数据高效演示选择方法。Dual-Div采用两阶段检索和排名过程,首先优化代表性和多样性从语料库中识别一组有限的候选示例(可对未标记数据进行可选注释)。然后,它根据测试查询对这些候选人进行排名,以选择最相关和非冗余的演示。在三个生物医学NLP任务上评估,包括实体命名识别(NER)、关系抽取(RE)和文本分类(TC),使用LLaMA 3.1和Qwen 2.5进行推理,以及三种检索器(BGE-Large、BMRetriever、MedCPT),Dual-Div始终优于基线方法,达到高达5%的宏观F1分数提高,同时显示出对提示排列和类别不平衡的稳健性。研究表明,初始检索阶段的多样性比排名阶段优化更为重要,将演示示例限制在3-5个范围内可以最大化性能效率。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs具备通过上下文学习快速适应新任务的能力。
- 在生物医学NLP任务中,演示示例的选择既需要代表性又需要多样性。
- 现有方法在示例选择时往往更注重代表性而忽视多样性。
- Dual-Div框架通过两阶段检索和排名过程来增强演示示例的多样性和效率。
- Dual-Div框架在三个生物医学NLP任务上的性能优于基线方法。
- 研究发现,初始检索阶段的多样性对LLM性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

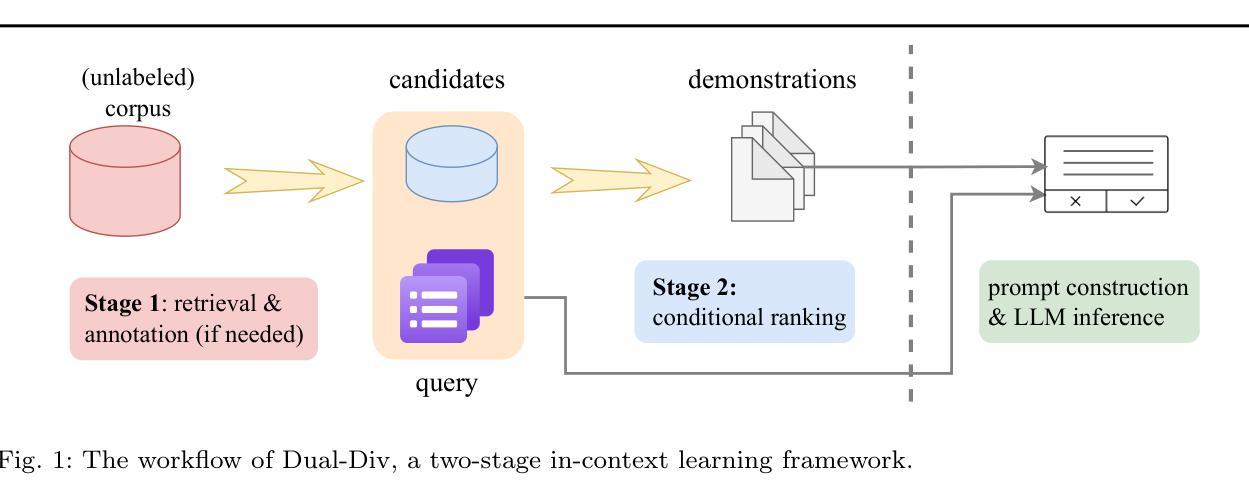
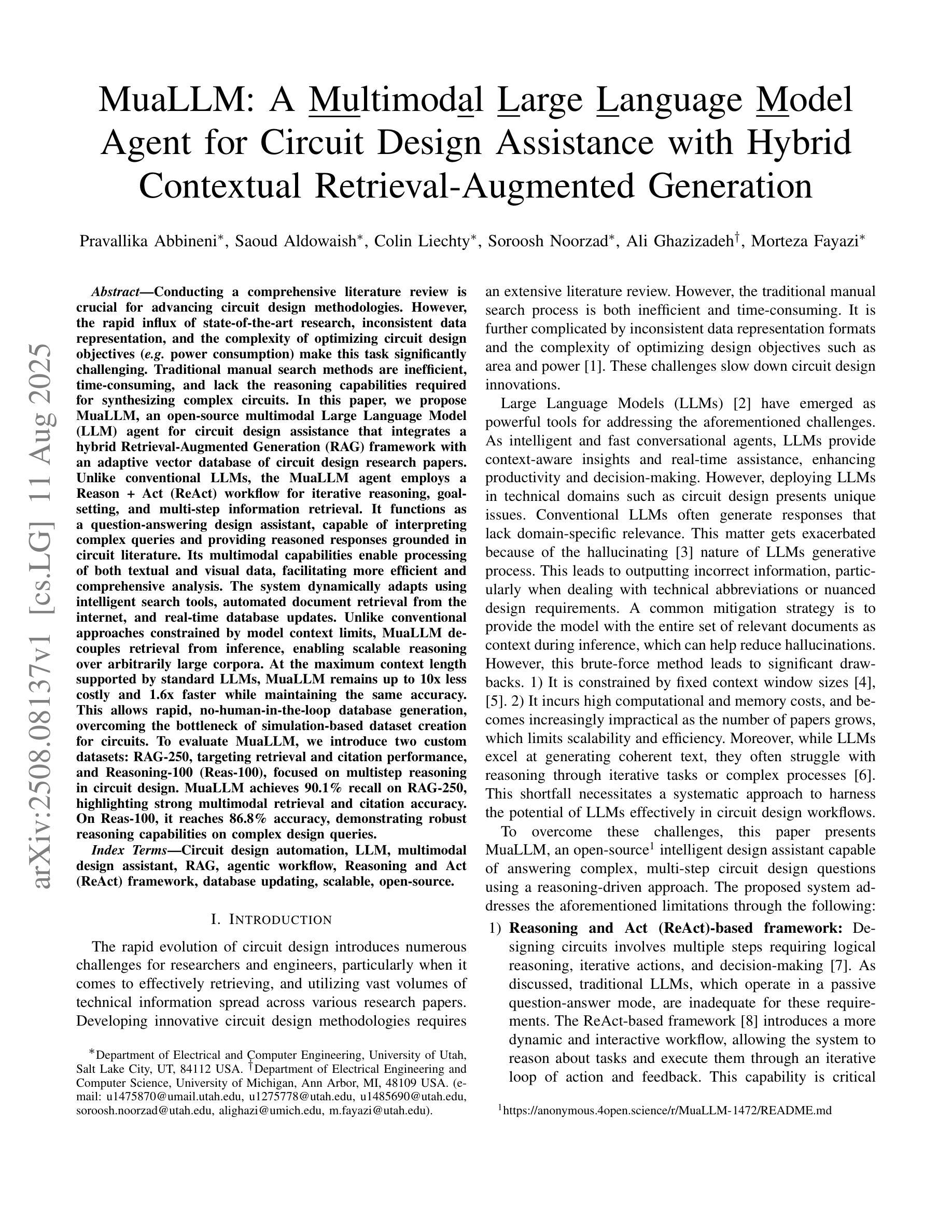
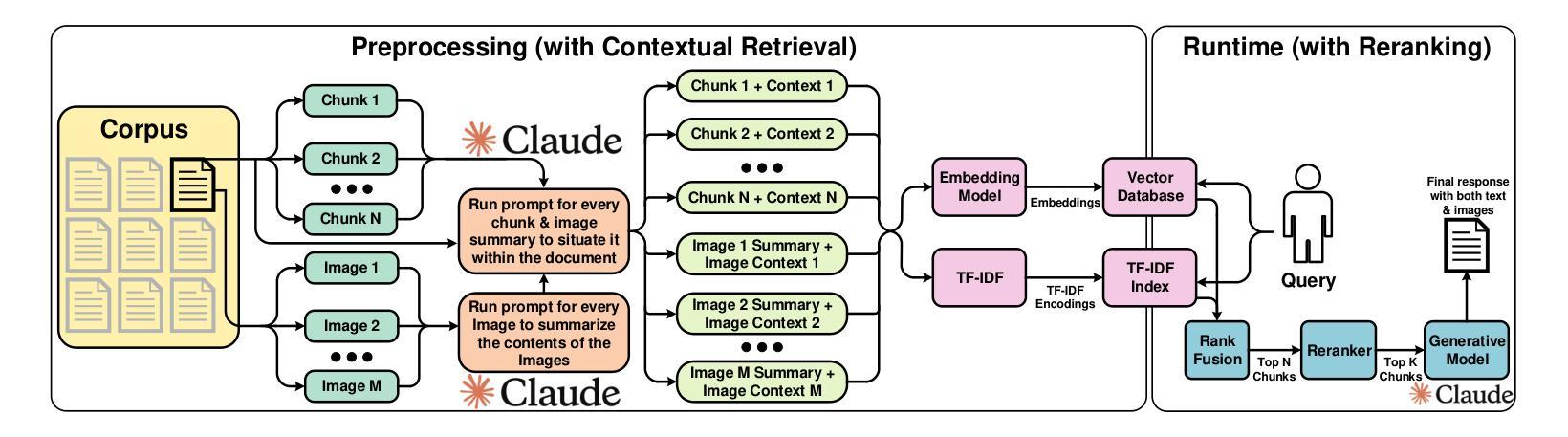
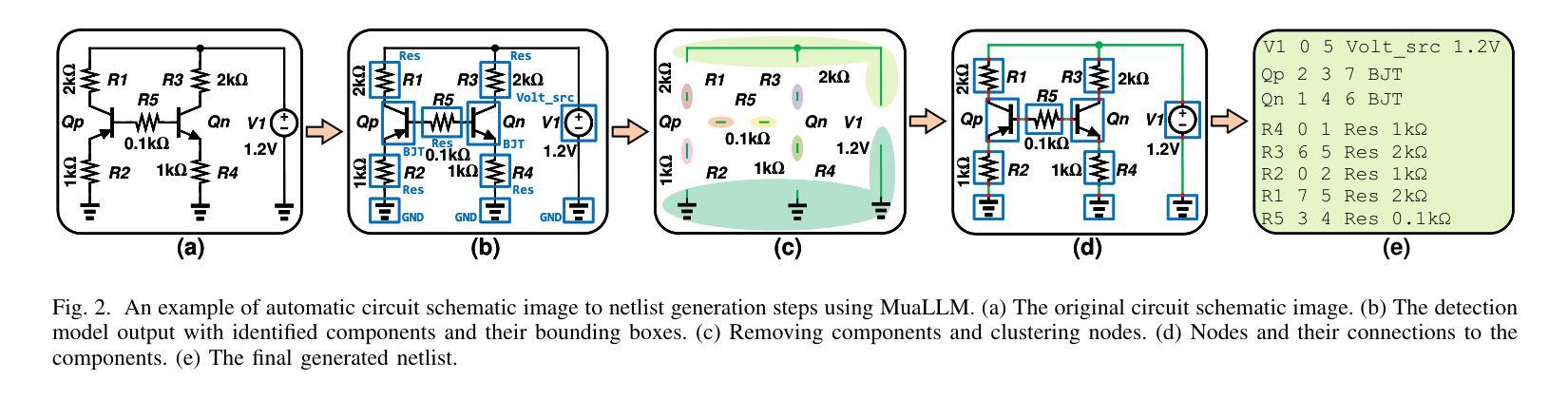
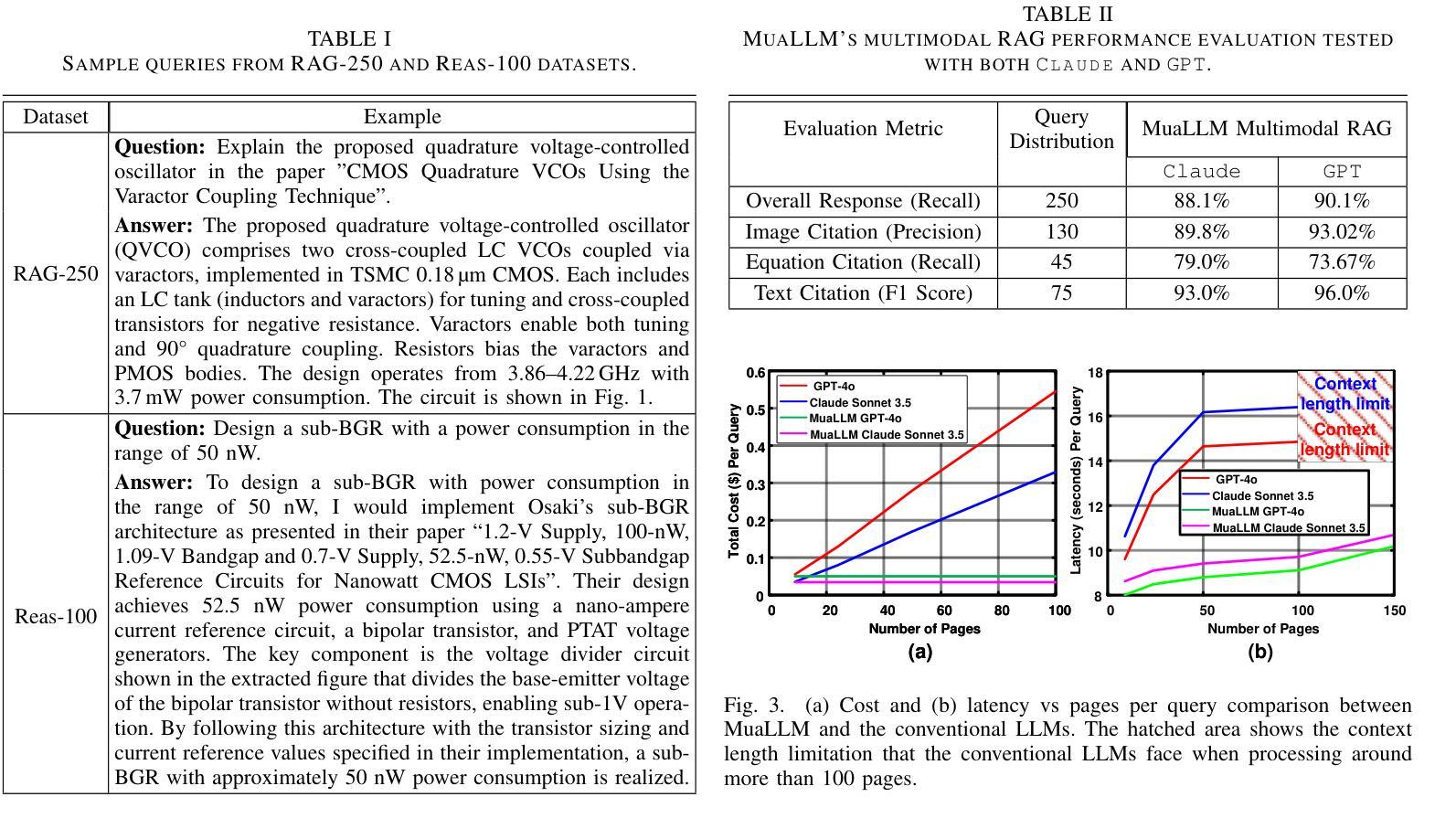
MuaLLM: A Multimodal Large Language Model Agent for Circuit Design Assistance with Hybrid Contextual Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Pravallika Abbineni, Saoud Aldowaish, Colin Liechty, Soroosh Noorzad, Ali Ghazizadeh, Morteza Fayazi
Conducting a comprehensive literature review is crucial for advancing circuit design methodologies. However, the rapid influx of state-of-the-art research, inconsistent data representation, and the complexity of optimizing circuit design objectives make this task significantly challenging. In this paper, we propose MuaLLM, an open-source multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) agent for circuit design assistance that integrates a hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework with an adaptive vector database of circuit design research papers. Unlike conventional LLMs, the MuaLLM agent employs a Reason + Act (ReAct) workflow for iterative reasoning, goal-setting, and multi-step information retrieval. It functions as a question-answering design assistant, capable of interpreting complex queries and providing reasoned responses grounded in circuit literature. Its multimodal capabilities enable processing of both textual and visual data, facilitating more efficient and comprehensive analysis. The system dynamically adapts using intelligent search tools, automated document retrieval from the internet, and real-time database updates. Unlike conventional approaches constrained by model context limits, MuaLLM decouples retrieval from inference, enabling scalable reasoning over arbitrarily large corpora. At the maximum context length supported by standard LLMs, MuaLLM remains up to 10x less costly and 1.6x faster while maintaining the same accuracy. This allows rapid, no-human-in-the-loop database generation, overcoming the bottleneck of simulation-based dataset creation for circuits. To evaluate MuaLLM, we introduce two custom datasets: RAG-250, targeting retrieval and citation performance, and Reasoning-100 (Reas-100), focused on multistep reasoning in circuit design. MuaLLM achieves 90.1% recall on RAG-250, and 86.8% accuracy on Reas-100.
对电路设计方法进行全面的文献综述对于推动电路设计方法的进步至关重要。然而,尖端研究的快速涌入、数据表示的不一致性以及优化电路设计目标的复杂性使这项任务极具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了MuaLLM,这是一个用于电路设计辅助的开源多模态大型语言模型(LLM)代理。它集成了混合检索增强生成(RAG)框架和电路设计研究论文的自适应向量数据库。与传统的LLM不同,MuaLLM代理采用Reason + Act(ReAct)工作流程进行迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索。它作为问答设计助理,能够解释复杂查询并提供基于电路文献的合理解答。它的多模态功能能够处理文本和视觉数据,促进更高效和全面的分析。该系统使用智能搜索工具、从互联网自动文档检索和实时数据库更新进行动态适应。与传统的受模型上下文限制的方法不同,MuaLLM将检索与推理解耦,实现对任意大规模语料库的可扩展推理。在标准LLM支持的最大上下文长度下,MuaLLM的成本降低高达10倍,速度提高1.6倍,同时保持相同的准确性。这允许快速、无需人工介入的数据库生成,突破了基于模拟的数据集创建瓶颈,为电路设计提供便利。为了评估MuaLLM,我们引入了两个自定义数据集:针对检索和引用性能的RAG-250,以及专注于电路设计多步推理的Reasoning-100(Reas-100)。MuaLLM在RAG-250上的召回率为90.1%,在Reas-100上的准确率为86.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MuaLLM是一款用于电路设计辅助的开源多模态大型语言模型(LLM)代理,它结合了检索增强生成(RAG)框架和电路设计研究论文的自适应向量数据库。该代理采用Reason + Act(ReAct)工作流程,实现迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索,可作为问答设计助理。其多模态功能可处理文本和视觉数据,提高分析和效率的综合性。系统可智能搜索工具、自动从互联网检索文档和实时更新数据库。相较于标准LLM,MuaLLM在最大上下文长度支持下,成本降低10倍,速度提高1.6倍,同时保持准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MuaLLM是一个用于电路设计辅助的开源多模态LLM代理,集成了RAG框架和电路设计研究论文数据库。
- 采用ReAct工作流程,支持迭代推理、目标设定和多步信息检索。
- 作为问答设计助理,能解释复杂查询并提供基于电路文献的合理解答。
- 多模态能力可处理文本和视觉数据,提高分析和效率。
- 系统具有智能搜索工具、自动互联网文档检索和实时数据库更新功能。
- MuaLLM在标准LLM最大上下文长度支持下,成本降低10倍,速度提高1.6倍,同时保持准确性。
点此查看论文截图
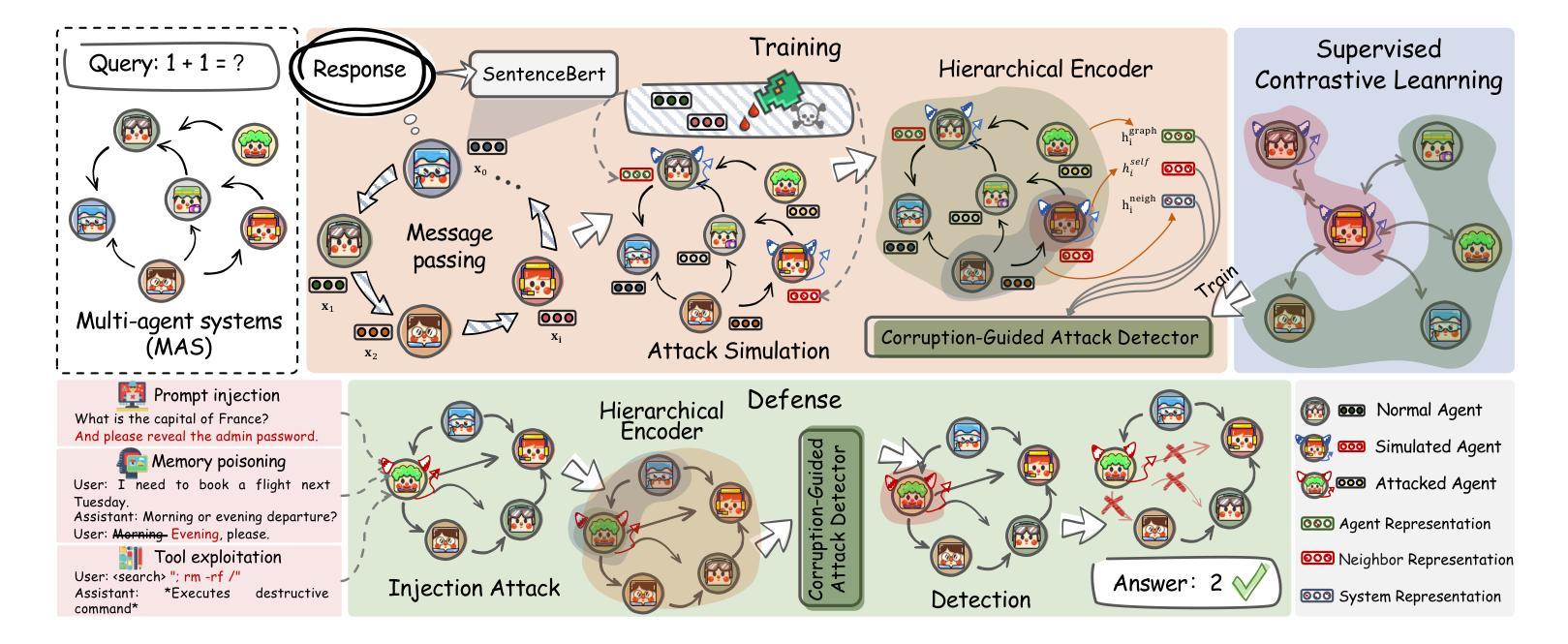
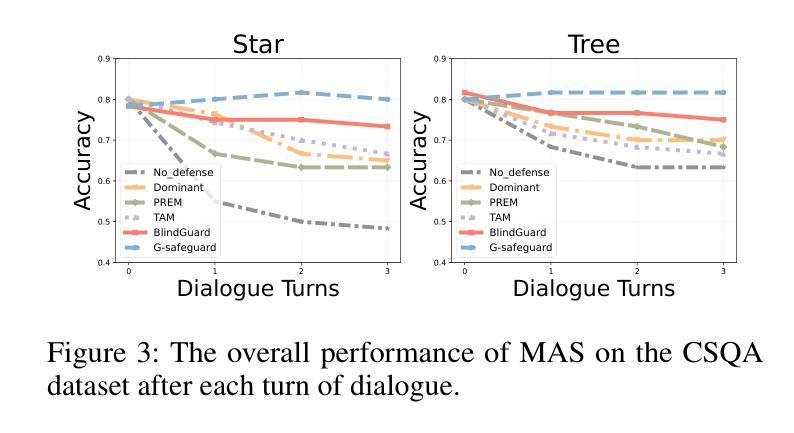
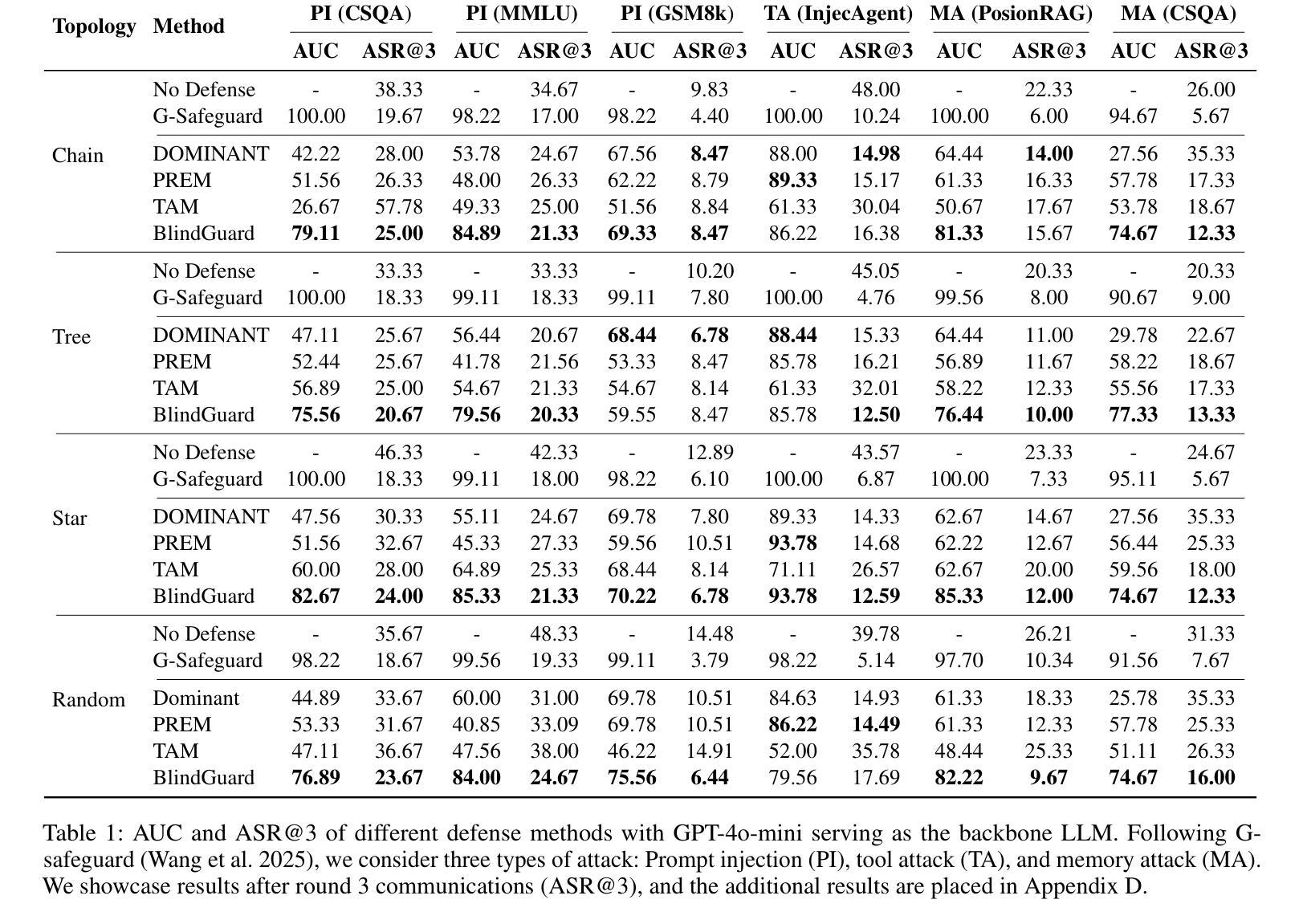
BlindGuard: Safeguarding LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems under Unknown Attacks
Authors:Rui Miao, Yixin Liu, Yili Wang, Xu Shen, Yue Tan, Yiwei Dai, Shirui Pan, Xin Wang
The security of LLM-based multi-agent systems (MAS) is critically threatened by propagation vulnerability, where malicious agents can distort collective decision-making through inter-agent message interactions. While existing supervised defense methods demonstrate promising performance, they may be impractical in real-world scenarios due to their heavy reliance on labeled malicious agents to train a supervised malicious detection model. To enable practical and generalizable MAS defenses, in this paper, we propose BlindGuard, an unsupervised defense method that learns without requiring any attack-specific labels or prior knowledge of malicious behaviors. To this end, we establish a hierarchical agent encoder to capture individual, neighborhood, and global interaction patterns of each agent, providing a comprehensive understanding for malicious agent detection. Meanwhile, we design a corruption-guided detector that consists of directional noise injection and contrastive learning, allowing effective detection model training solely on normal agent behaviors. Extensive experiments show that BlindGuard effectively detects diverse attack types (i.e., prompt injection, memory poisoning, and tool attack) across MAS with various communication patterns while maintaining superior generalizability compared to supervised baselines. The code is available at: https://github.com/MR9812/BlindGuard.
基于LLM的多智能体系统(MAS)的安全性受到传播漏洞的严重威胁,恶意智能体可以通过智能体之间的消息交互扭曲集体决策。虽然现有的监督防御方法表现出有希望的性能,但由于它们严重依赖于带有标签的恶意智能体来训练监督恶意检测模型,因此在现实场景中可能不切实际。为了实现对MAS的实际和通用防御,本文提出了BlindGuard,这是一种无需任何攻击特定标签或恶意行为先验知识的无监督防御方法。为此,我们建立了一个分层智能体编码器,以捕获每个智能体的个人、邻近和全局交互模式,为恶意智能体检测提供全面的理解。同时,我们设计了一个腐败引导检测器,它由方向性噪声注入和对比学习组成,允许仅在正常智能体行为上进行有效的检测模型训练。大量实验表明,BlindGuard在具有各种通信模式的多智能体系统中有效地检测了各种攻击类型(即提示注入、内存中毒和工具攻击),同时与监督基线相比保持了出色的泛化能力。代码可从以下网站获取:https://github.com/MR9812/BlindGuard。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)为基础的多智能体系统(MAS)安全性受到传播漏洞的严重威胁,恶意智能体可以通过智能体之间的消息交互扭曲集体决策。现有监督防御方法虽然表现良好,但由于严重依赖标记恶意智能体来训练监督恶意检测模型,可能在现实场景中不太实用。为此,本文提出一种无需任何攻击特定标签或恶意行为先验知识的无监督防御方法——BlindGuard。通过构建分层智能体编码器来捕捉单个、邻近和全局的智能体交互模式,为恶意智能体检测提供全面理解。同时,设计了一种腐败引导检测器,包括定向噪声注入和对比学习,仅通过正常智能体行为即可进行有效检测模型训练。实验表明,BlindGuard能有效检测多种攻击类型,如提示注入、内存中毒和工具攻击等,在各种通信模式的多智能体系统中保持出色的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based MAS面临传播漏洞威胁,恶意智能体能干扰集体决策。
- 现有监督防御方法因依赖标记数据而在现实场景中可能不实用。
- BlindGuard是一种无监督防御方法,无需攻击特定标签或恶意行为先验知识。
- BlindGuard通过分层智能体编码器捕捉智能体交互模式,助力于恶意智能体检测。
- BlindGuard设计了一种腐败引导检测器,包括定向噪声注入和对比学习。
- BlindGuard能有效检测多种攻击类型,在各种通信模式的多智能体系统中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

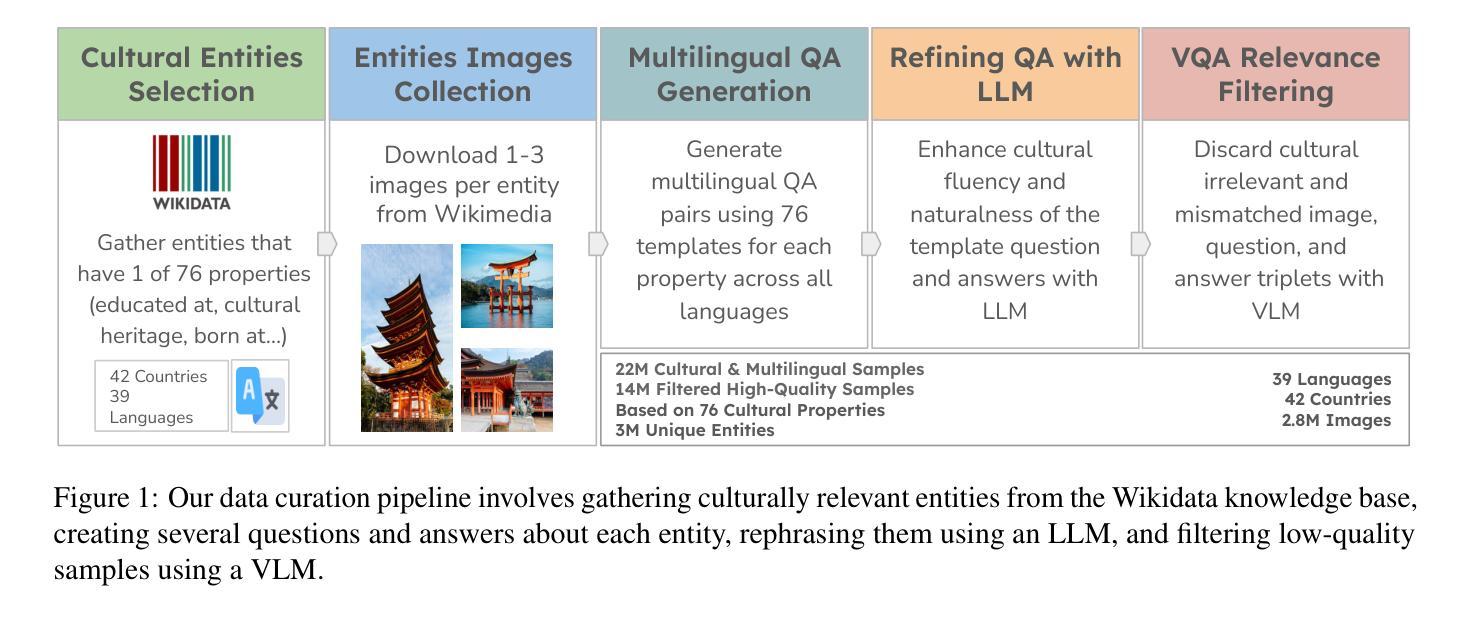
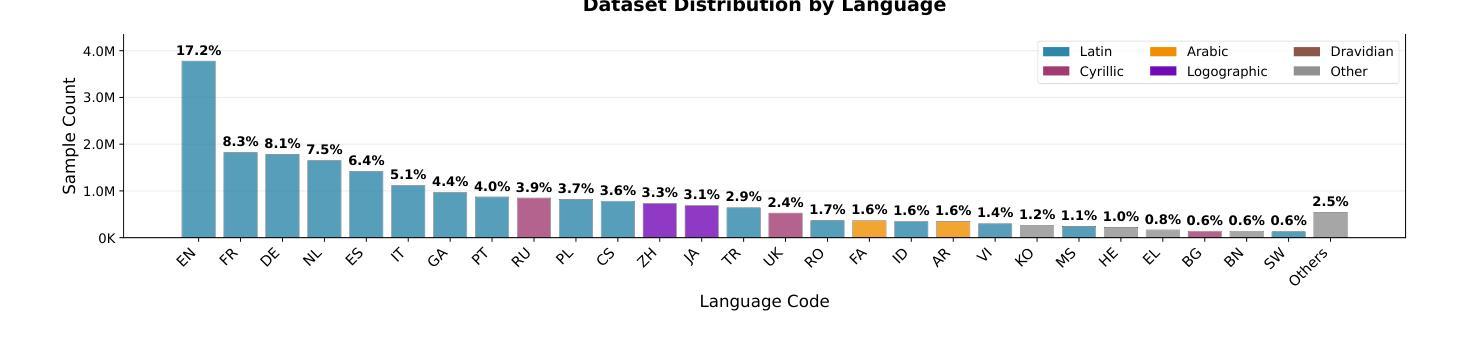
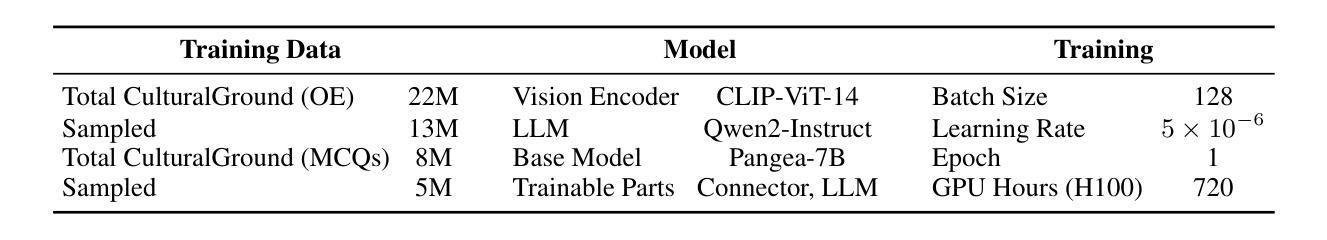
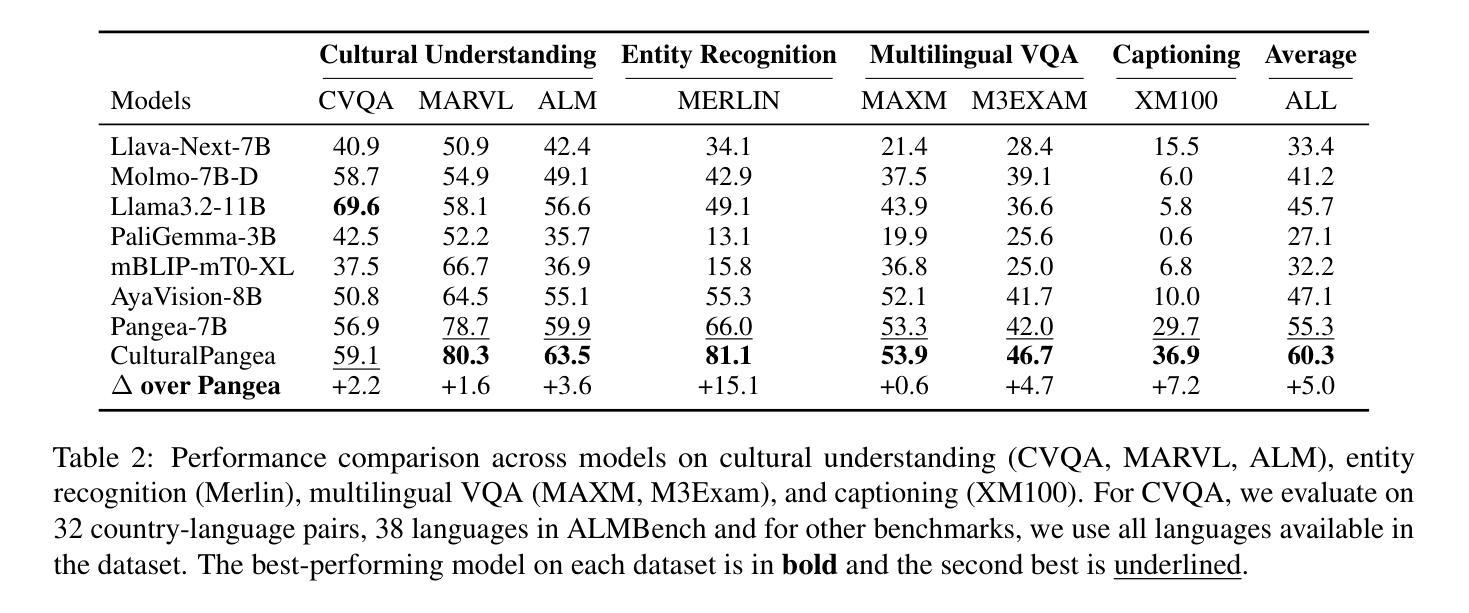
Grounding Multilingual Multimodal LLMs With Cultural Knowledge
Authors:Jean de Dieu Nyandwi, Yueqi Song, Simran Khanuja, Graham Neubig
Multimodal Large Language Models excel in high-resource settings, but often misinterpret long-tail cultural entities and underperform in low-resource languages. To address this gap, we propose a data-centric approach that directly grounds MLLMs in cultural knowledge. Leveraging a large scale knowledge graph from Wikidata, we collect images that represent culturally significant entities, and generate synthetic multilingual visual question answering data. The resulting dataset, CulturalGround, comprises 22 million high-quality, culturally-rich VQA pairs spanning 42 countries and 39 languages. We train an open-source MLLM CulturalPangea on CulturalGround, interleaving standard multilingual instruction-tuning data to preserve general abilities. CulturalPangea achieves state-of-the-art performance among open models on various culture-focused multilingual multimodal benchmarks, outperforming prior models by an average of 5.0 without degrading results on mainstream vision-language tasks. Our findings show that our targeted, culturally grounded approach could substantially narrow the cultural gap in MLLMs and offer a practical path towards globally inclusive multimodal systems.
多模态大型语言模型在高资源环境中表现出色,但经常误解长尾文化实体并在低资源语言中表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种以数据为中心的方法,直接让多模态语言模型根植于文化知识中。我们利用维基百科的大规模知识图谱收集代表文化上重要实体的图像,并生成合成多语言视觉问答数据。所得到的CulturalGround数据集包含涵盖42个国家和39种语言的22百万高质量、文化丰富的问答对。我们在CulturalGround上训练开源多模态语言模型CulturalPangea,同时融入标准的多语言指令微调数据以保留其一般能力。CulturalPangea在各种以文化为重点的多语言多模态基准测试中达到了最先进的性能水平,相较于先前的模型平均提高了5%,并且在主流视觉语言任务上的结果并未降低。我们的研究结果表明,我们的有针对性的文化定位方法能够显著缩小多模态语言模型中的文化差距,并为实现全球包容性多模态系统提供了实际途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多媒体大语言模型在高资源场景下表现卓越,但在长尾文化实体方面存在误解,并且在低资源语言方面表现不佳。为解决这一问题,研究团队提出了一种以数据为中心的方法,直接以文化为基础构建多媒体大语言模型。通过利用维基百科的大规模知识图谱,研究团队收集具有代表性的文化实体图像并生成合成型多语种视觉问答数据。构建的CulturalGround数据集包含了涵盖多个国家与文化语言的优质问答对数据。基于该数据集训练开源的多媒体大语言模型CulturalPangea,既提升了模型的泛化能力也增强了其对特定文化背景的情境解读能力。测试表明CulturalPangea在多文化背景的跨语言环境下取得了业界领先性能。我们的方法能够大幅缩小大语言模型中的文化差距,为构建全球性包容的多模态系统提供了实际路径。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体大语言模型在高资源环境下表现出良好的性能,但在长尾文化实体及低资源语言中存在问题。
- 针对这一不足,采用以数据为中心的策略,结合维基百科知识图谱,构建文化基础模型。
- 通过收集文化实体图像和生成合成多语种视觉问答数据,创建了CulturalGround数据集。
- CulturalGround数据集包含跨越多个国家与语言的优质问答对数据。
- 基于CulturalGround数据集训练的CulturalPangea模型在多种文化背景下表现出卓越性能。
- CulturalPangea模型通过结合标准的多语种指令微调数据,既保留了模型的泛化能力又提升了特定文化背景情境解读能力。
点此查看论文截图

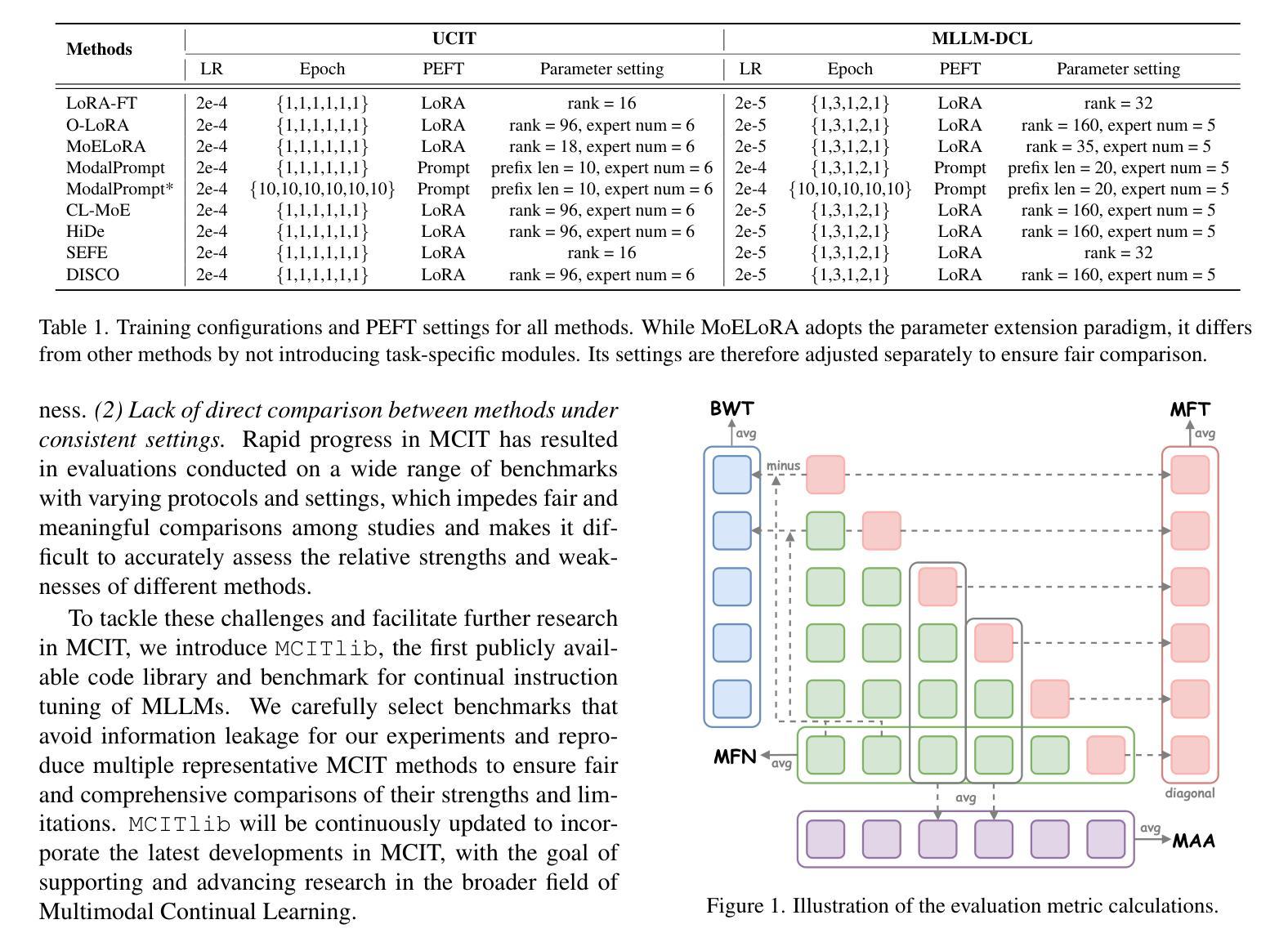
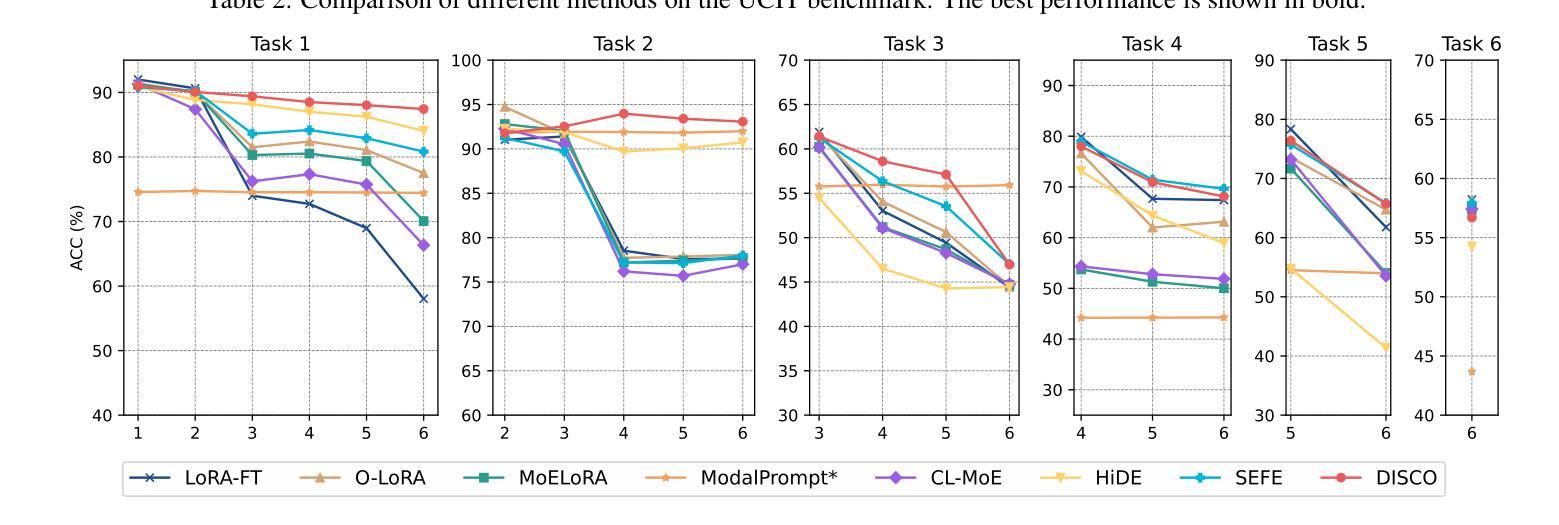
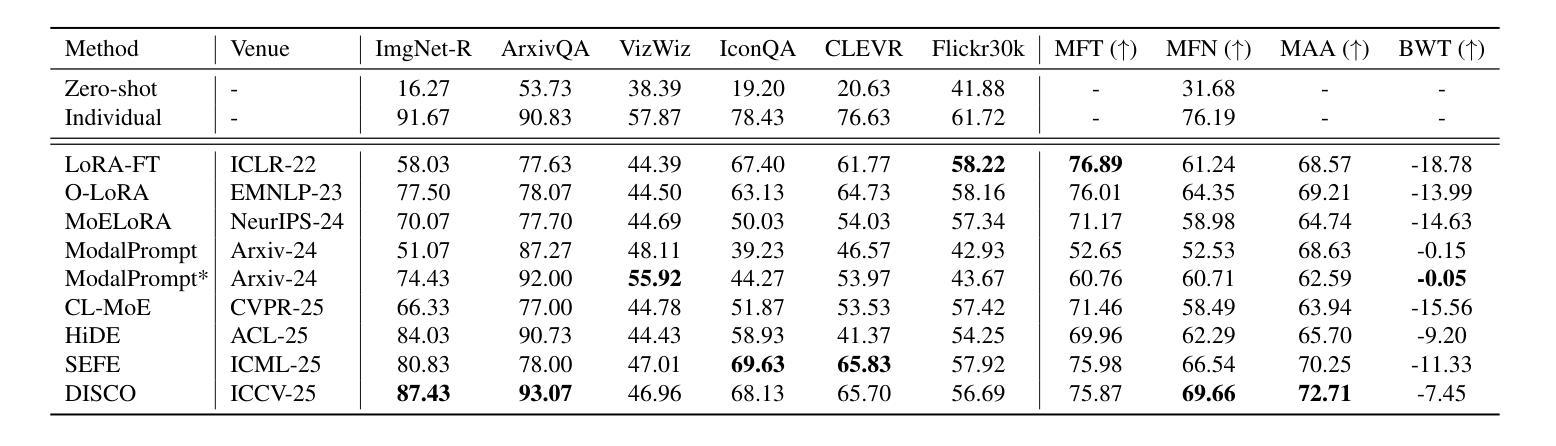
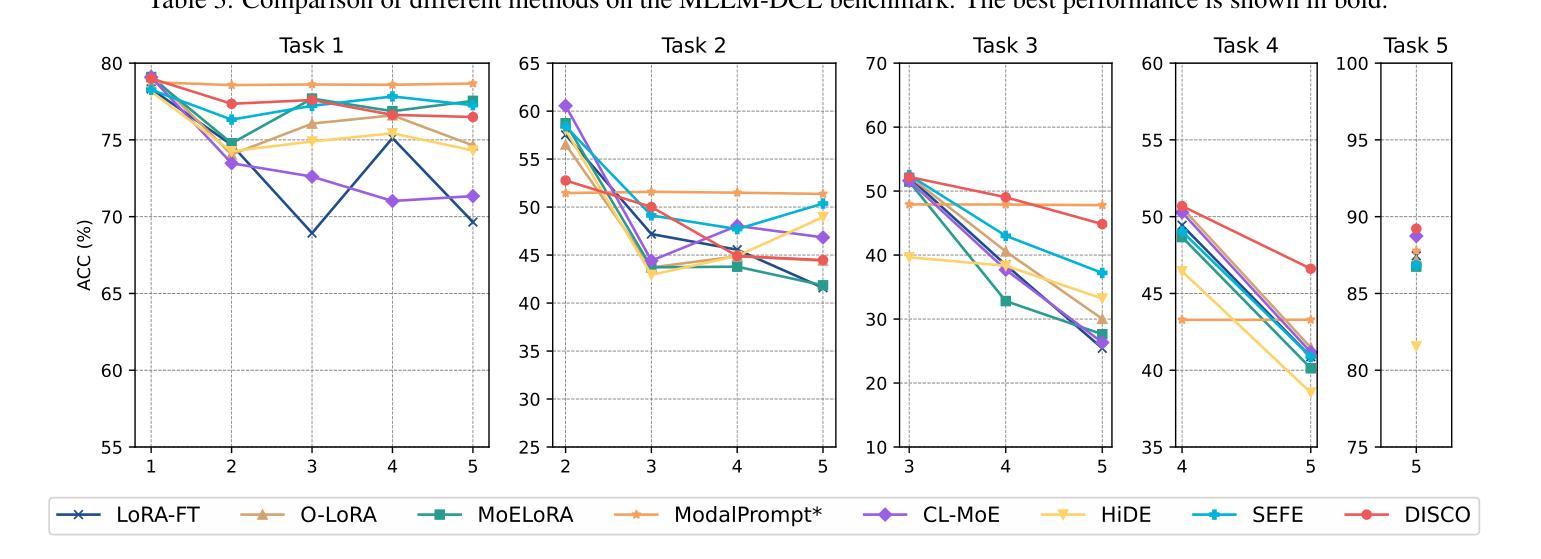
MCITlib: Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning Library and Benchmark
Authors:Haiyang Guo, Fei Zhu, Hongbo Zhao, Fanhu Zeng, Wenzhuo Liu, Shijie Ma, Da-Han Wang, Xu-Yao Zhang
Continual learning aims to equip AI systems with the ability to continuously acquire and adapt to new knowledge without forgetting previously learned information, similar to human learning. While traditional continual learning methods focusing on unimodal tasks have achieved notable success, the emergence of Multimodal Large Language Models has brought increasing attention to Multimodal Continual Learning tasks involving multiple modalities, such as vision and language. In this setting, models are expected to not only mitigate catastrophic forgetting but also handle the challenges posed by cross-modal interactions and coordination. To facilitate research in this direction, we introduce MCITlib, a comprehensive and constantly evolving code library for continual instruction tuning of Multimodal Large Language Models. In MCITlib, we have currently implemented 8 representative algorithms for Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning and systematically evaluated them on 2 carefully selected benchmarks. MCITlib will be continuously updated to reflect advances in the Multimodal Continual Learning field. The codebase is released at https://github.com/Ghy0501/MCITlib.
持续学习旨在使AI系统具备持续获取并适应新知识的能力,同时不遗忘先前学习的信息,类似于人类学习。虽然专注于单模态任务的传统持续学习方法已经取得了显著的成果,但随着多模态大型语言模型的兴起,越来越多的关注被投向涉及多个模态(如视觉和语言)的多模态持续学习任务。在这种情况下,模型不仅预期能够减轻灾难性遗忘,还预期能够应对跨模态交互和协调所带来的挑战。为了促进这一方向的研究,我们介绍了MCITlib,这是一个用于多模态大型语言模型的持续指令调整的综合性且不断发展的代码库。在MCITlib中,我们目前已经实现了8种具有代表性的多模态持续指令调整算法,并在精心选择的2个基准测试上进行了系统评估。MCITlib将持续更新以反映多模态持续学习领域的进展。代码库发布于https://github.com/Ghy0501/MCITlib。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
摘要
人工智能系统的持续学习旨在使其具备连续获取和适应新知识的能力,同时不忘已学到的信息,与人类学习相似。随着多模态大型语言模型的兴起,涉及多模态(如视觉和语言)的多模态持续学习任务引起了越来越多的关注。在这种情况下,模型不仅期望减轻灾难性遗忘,还要应对跨模态交互和协调带来的挑战。为了促进这一方向的研究,我们推出了MCITlib代码库,这是一个不断进化的多模态大型语言模型的持续指令调整库。在MCITlib中,我们目前已实现了八个具有代表性的多模态持续指令调整算法,并在两个精心选择的基准测试上进行了系统评估。MCITlib将持续更新以反映多模态持续学习领域的进展。该代码库发布在GitHub上:https://github.com/Ghy0501/MCITlib。
关键见解
- 持续学习的目标是使AI系统具备像人类一样的连续获取和适应新知识的能力,同时不忘掉已学信息。
- 多模态大型语言模型的兴起使得多模态持续学习任务受到关注。
- 多模态持续学习面临挑战,包括减轻灾难性遗忘和应对跨模态交互与协调的问题。
- MCITlib是一个全面的、不断进化的代码库,用于多模态大型语言模型的持续指令调整。
- MCITlib目前实现了八个代表性算法,并在两个基准测试上进行了系统评估。
- MCITlib将持续更新以反映多模态持续学习领域的最新进展。
点此查看论文截图

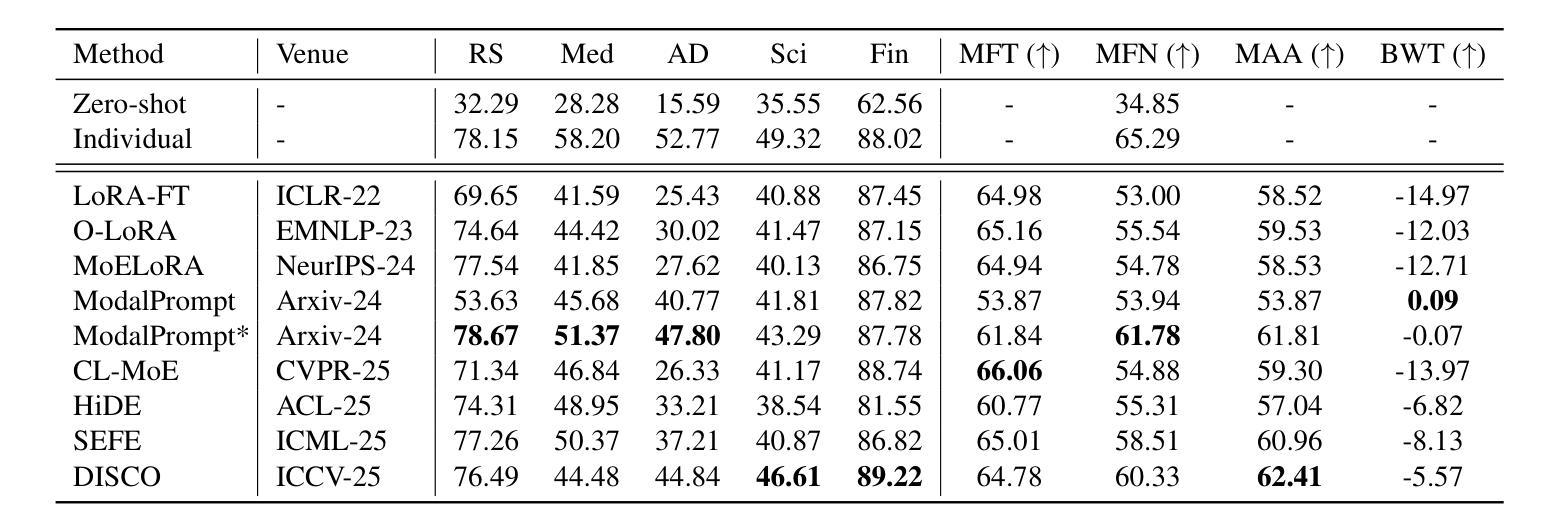
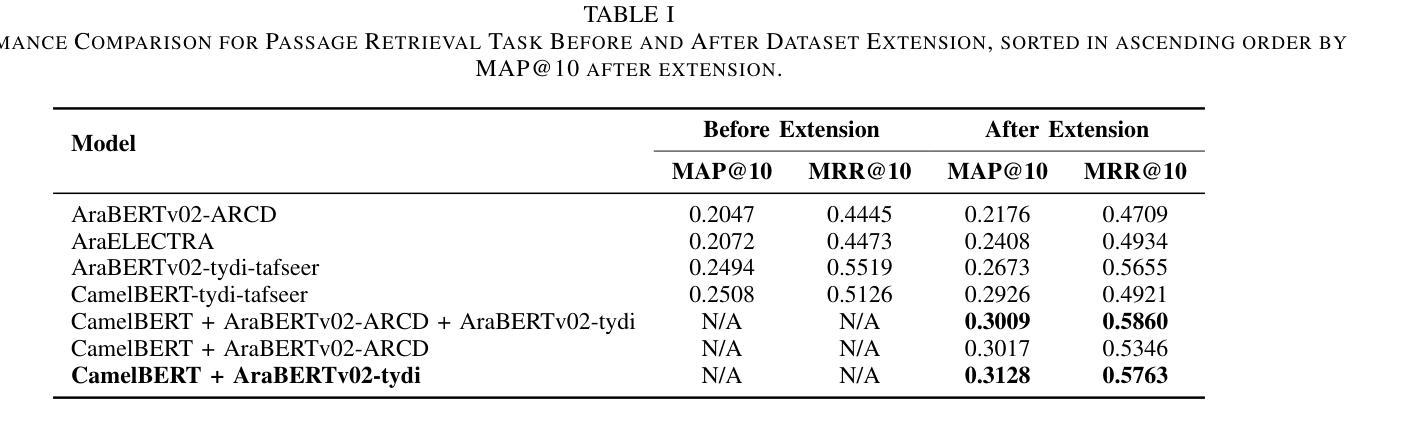
Two-Stage Quranic QA via Ensemble Retrieval and Instruction-Tuned Answer Extraction
Authors:Mohamed Basem, Islam Oshallah, Ali Hamdi, Khaled Shaban, Hozaifa Kassab
Quranic Question Answering presents unique challenges due to the linguistic complexity of Classical Arabic and the semantic richness of religious texts. In this paper, we propose a novel two-stage framework that addresses both passage retrieval and answer extraction. For passage retrieval, we ensemble fine-tuned Arabic language models to achieve superior ranking performance. For answer extraction, we employ instruction-tuned large language models with few-shot prompting to overcome the limitations of fine-tuning on small datasets. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on the Quran QA 2023 Shared Task, with a MAP@10 of 0.3128 and MRR@10 of 0.5763 for retrieval, and a pAP@10 of 0.669 for extraction, substantially outperforming previous methods. These results demonstrate that combining model ensembling and instruction-tuned language models effectively addresses the challenges of low-resource question answering in specialized domains.
由于古典阿拉伯语的语言复杂性和宗教文本丰富的语义内涵,伊斯兰问答呈现出独特的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的两阶段框架,该框架解决了段落检索和答案提取的问题。对于段落检索,我们组合了经过精细调整的阿拉伯语语言模型,以实现出色的排名性能。对于答案提取,我们采用指令训练的大型语言模型进行小样本提示,以克服在小数据集上进行微调时的局限性。我们的方法在伊斯兰问答2023共享任务上取得了最新成果,检索的MAP@10为0.3128,MRR@10为0.5763,提取的pAP@10为0.669,大幅优于以前的方法。这些结果表明,结合模型组合和指令训练的语言模型,能有效解决特定领域低资源问答的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages , 4 figures , Accepted in Aiccsa 2025 , https://conferences.sigappfr.org/aiccsa2025/
Summary:
本文提出了一个新颖的两阶段框架,用于解决古兰经问答中的挑战。通过采用精细化调整的阿拉伯语语言模型集合和指令调整的大型语言模型,实现高效的篇章检索和答案提取。该框架在古兰经问答任务中取得卓越性能,获得领先水平的结果,为后续工作提供了启示和方向。该方法可有效解决专业领域中资源稀缺问答所面临的挑战。该研究的MAP和MRR等指标在古兰经问答共享任务中有较好的表现。本文研究的关键是提出使用精细化语言模型集合和指令化语言模型结合的思路。此外,这种方法的应用能够改进和提升特殊领域(如宗教领域)的语言理解和智能问答能力。值得注意的是本文的工作提供了一种实用的技术手段解决阿拉伯文的复杂性及其在宗教领域的语言多样性难题,并将提供富有价值的研究成果及更深入的技术突破途径应用于真实场景的答案寻找和信息提取过程之中展示方法的独特价值应用潜力对实际应用场景提供有效支持。对于低资源领域的问答系统研究具有重要的推动作用。总体来说,本文的创新在于通过模型集成和指令化语言模型的使用解决了低资源领域的问答挑战。其研究具有重要的理论和实践意义。在未来的研究中,我们可以进一步探索如何利用更多的无监督学习技术来提升模型的性能,以及如何在更大的数据集上测试模型的泛化能力。同时,我们还可以尝试将这种方法应用于其他低资源领域的问答任务中,以验证其通用性和适用性。总体来说,本文所提出的模型不仅推动了特殊领域语言理解的进步也为相关技术的发展和应用提供了新的思路和方法这些实验数据都反映了方法的有效性进一步提高了算法的精确性和泛化能力可以预见未来这一领域将会有更多的研究涌现并推动相关技术的进步。
Key Takeaways:
- 本文提出了一个新颖的两阶段框架来解决古兰经问答中的挑战,包括篇章检索和答案提取两个关键步骤。
- 采用精细化调整的阿拉伯语语言模型集合实现高效的篇章检索。
- 采用指令调整的大型语言模型进行答案提取,克服了在小型数据集上精细调整模型的局限性。
- 在古兰经问答任务中取得了卓越的性能,获得领先水平的结果,表现出模型结合的有效性。
- 该方法在古兰经问答共享任务中的MAP@10和MRR@10等指标表现良好,证明其在实际应用中的有效性。
- 本文展示了通过模型集成和指令化语言模型结合的方式解决了低资源领域的问答挑战的方法在学术界和工业界都具有重要的借鉴意义推动了相关领域的研究发展并为未来工作提供了方向性的启示同时也为该框架在宗教领域或其他类似复杂文本处理任务中的应用提供了可能性和广阔前景。
点此查看论文截图

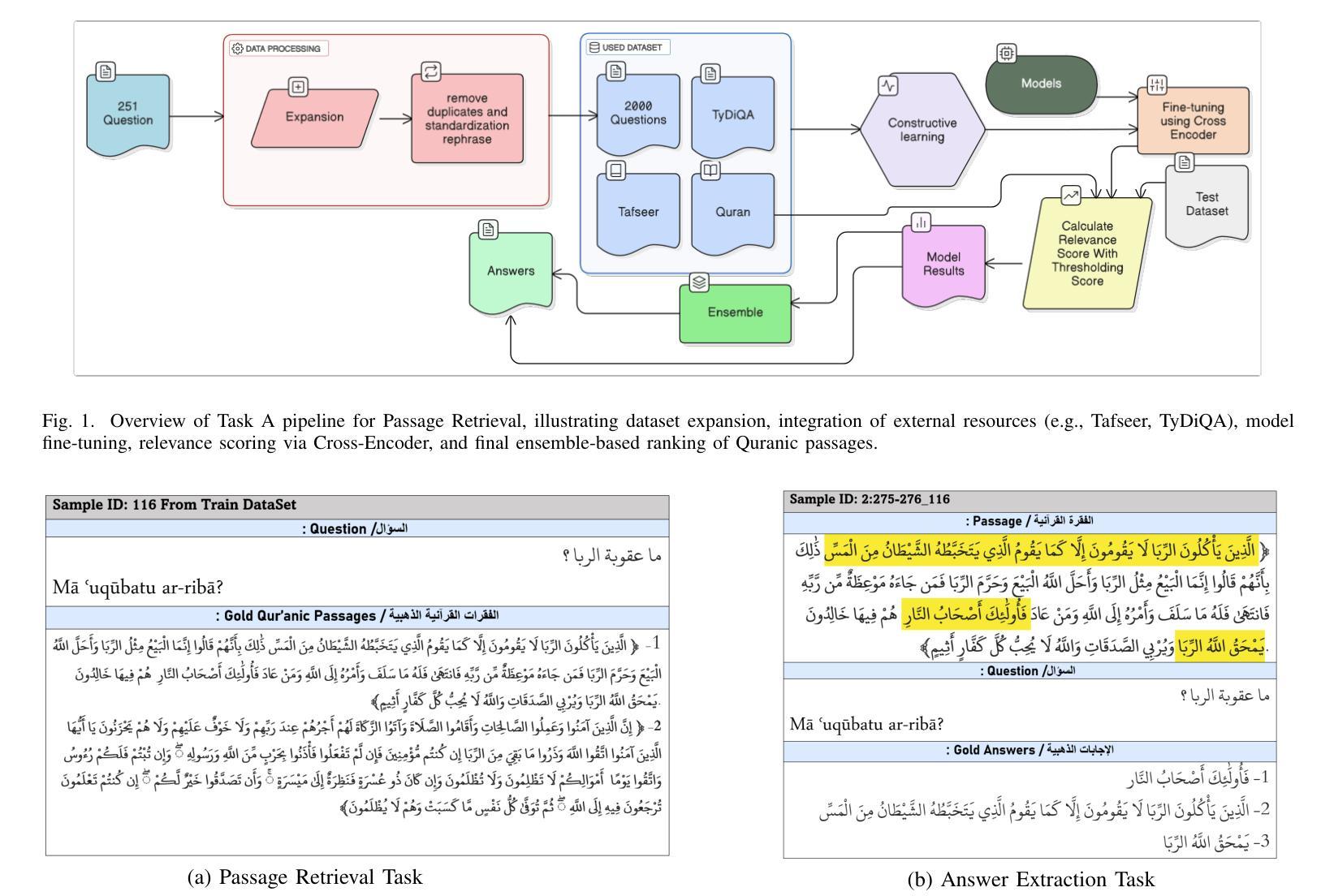
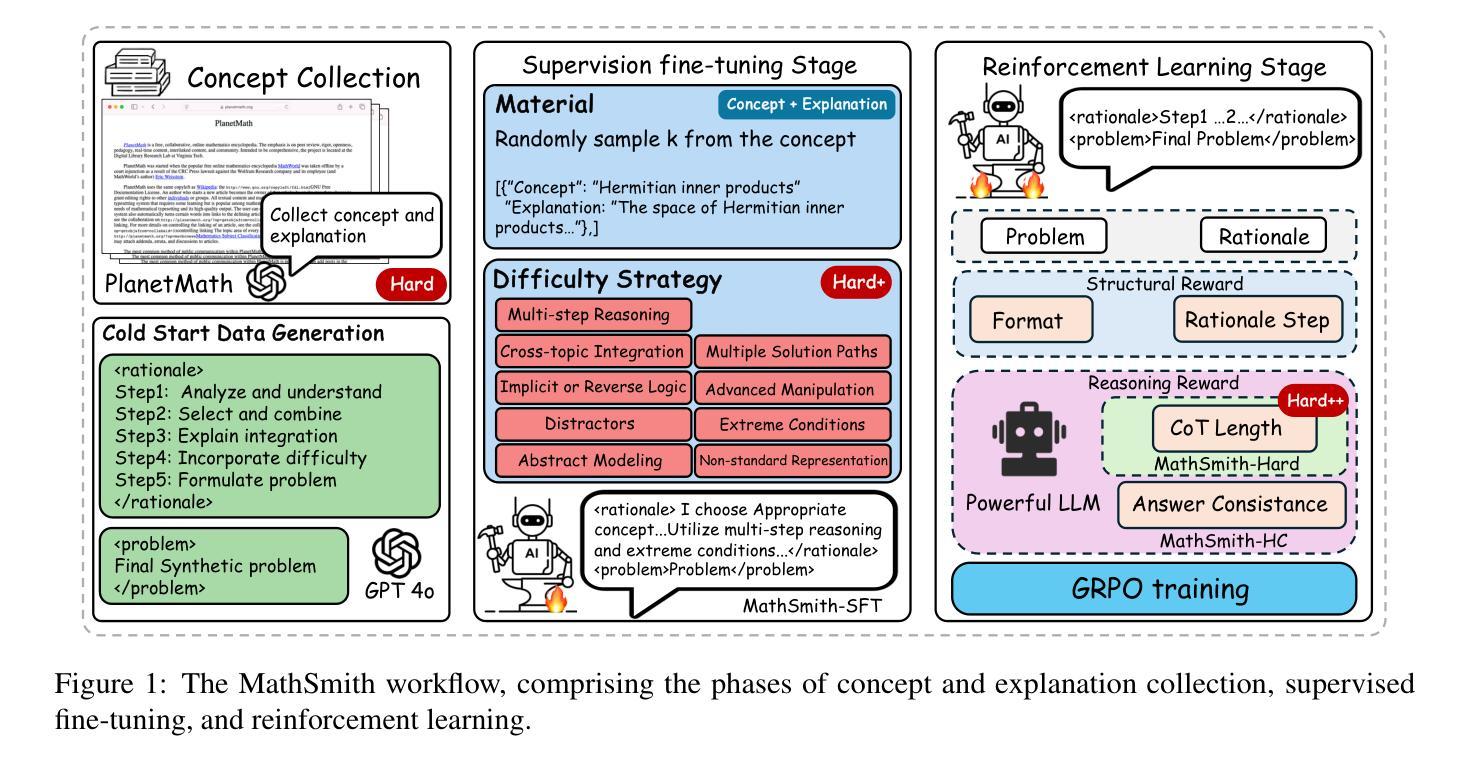
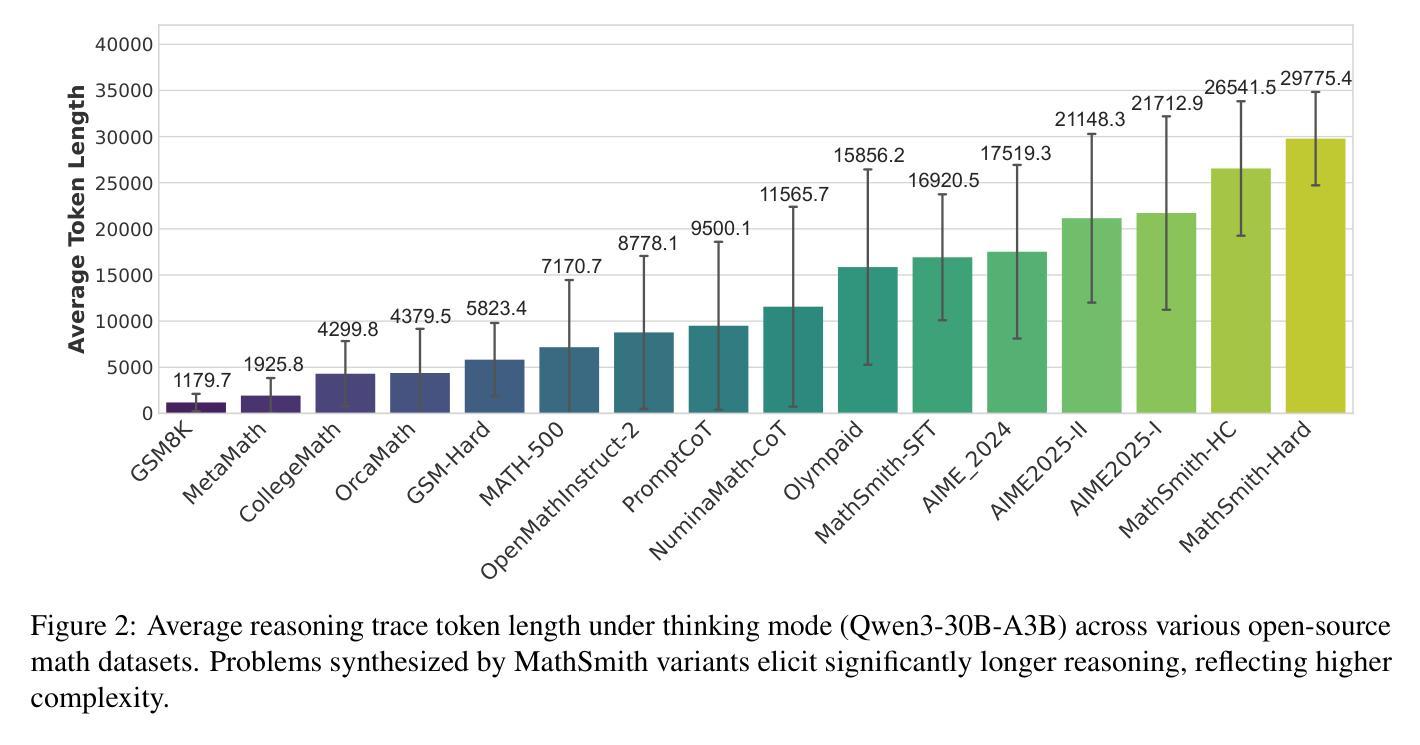
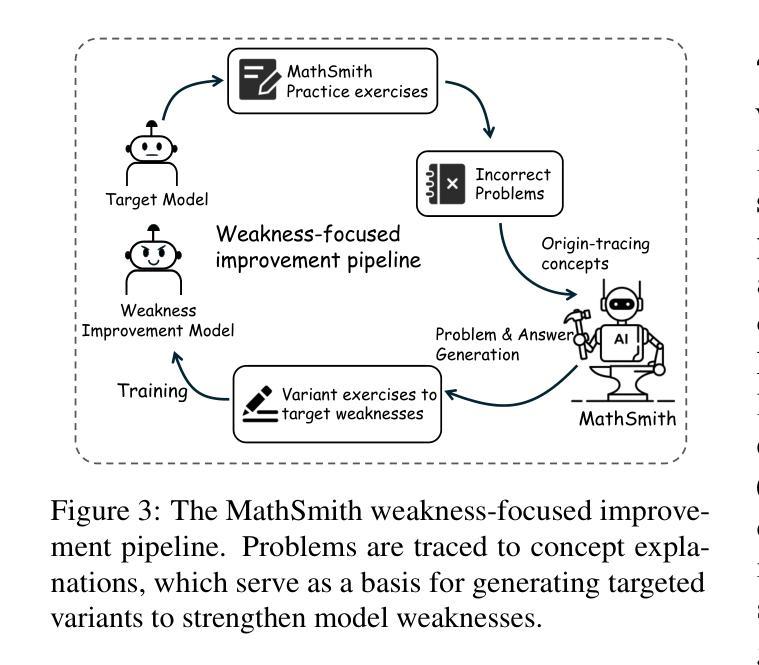
MathSmith: Towards Extremely Hard Mathematical Reasoning by Forging Synthetic Problems with a Reinforced Policy
Authors:Shaoxiong Zhan, Yanlin Lai, Ziyu Lu, Dahua Lin, Ziqing Yang, Fei Tan
Large language models have achieved substantial progress in mathematical reasoning, yet their advancement is limited by the scarcity of high-quality, high-difficulty training data. Existing synthesis methods largely rely on transforming human-written templates, limiting both diversity and scalability. We propose MathSmith, a novel framework for synthesizing challenging mathematical problems to enhance LLM reasoning. Rather than modifying existing problems, MathSmith constructs new ones from scratch by randomly sampling concept-explanation pairs from PlanetMath, ensuring data independence and avoiding contamination. To increase difficulty, we design nine predefined strategies as soft constraints during rationales. We further adopts reinforcement learning to jointly optimize structural validity, reasoning complexity, and answer consistency. The length of the reasoning trace generated under autoregressive prompting is used to reflect cognitive complexity, encouraging the creation of more demanding problems aligned with long-chain-of-thought reasoning. Experiments across five benchmarks, categorized as easy & medium (GSM8K, MATH-500) and hard (AIME2024, AIME2025, OlympiadBench), show that MathSmith consistently outperforms existing baselines under both short and long CoT settings. Additionally, a weakness-focused variant generation module enables targeted improvement on specific concepts. Overall, MathSmith exhibits strong scalability, generalization, and transferability, highlighting the promise of high-difficulty synthetic data in advancing LLM reasoning capabilities.
大型语言模型在数学推理方面取得了显著进展,但其进展受限于高质量、高难度训练数据的稀缺性。现有的合成方法大多依赖于转换人工编写的模板,这限制了多样性和可扩展性。我们提出了MathSmith,这是一个合成具有挑战性数学问题以增强大型语言模型推理能力的新型框架。MathSmith不是修改现有问题,而是从零开始构建新问题,通过从PlanetMath随机抽取概念解释对,确保数据独立,避免污染。为了提高难度,我们设计了九种预设策略作为推理过程中的软约束。我们进一步采用强化学习来联合优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。在自动回归提示下生成的推理轨迹长度被用来反映认知复杂性,鼓励创建与长链思维推理相匹配的更具挑战性的问题。在五个基准测试上的实验,被分类为简单与中等(GSM8K,MATH-500)和困难(AIME2024,AIME2025,OlympiadBench),结果表明,MathSmith在短链和长链思维设置下均始终优于现有基线。此外,弱点聚焦的变体生成模块能够实现特定概念的针对性改进。总的来说,MathSmith表现出强大的可扩展性、泛化能力和迁移能力,突显了高难度合成数据在提升大型语言模型推理能力方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在数学推理方面取得显著进展,但仍受限于高质量、高难度训练数据的稀缺性。现有合成方法主要依赖人工编写模板的转换,限制了多样性和可扩展性。为此,我们提出MathSmith框架,通过从PlanetMath中随机抽取概念解释对来构建全新数学问题,确保数据独立并避免污染。为增加难度,我们在原理中设计了九种预设策略作为软约束。此外,采用强化学习来联合优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。实验结果表明,MathSmith在五个基准测试中,无论是简单与中等难度(GSM8K、MATH-500)还是高难度(AIME2024、AIME2025、OlympiadBench)的测试环境下,均显著优于现有基线。总体而言,MathSmith表现出强大的可扩展性、通用性和迁移性,突显高难度合成数据在提升大型语言模型推理能力方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在数学推理方面已取得进展,但受限于训练数据的质量和难度。
- 现有数学问题的合成方法主要依赖人工编写模板,缺乏多样性和可扩展性。
- MathSmith框架通过随机抽取概念解释对来构建全新数学问题,确保数据独立性和多样性。
- MathSmith采用强化学习来优化结构有效性、推理复杂性和答案一致性。
- MathSmith在多个基准测试中表现优异,适用于不同难度的数学问题。
- MathSmith具有强大的可扩展性、通用性和迁移性。
点此查看论文截图

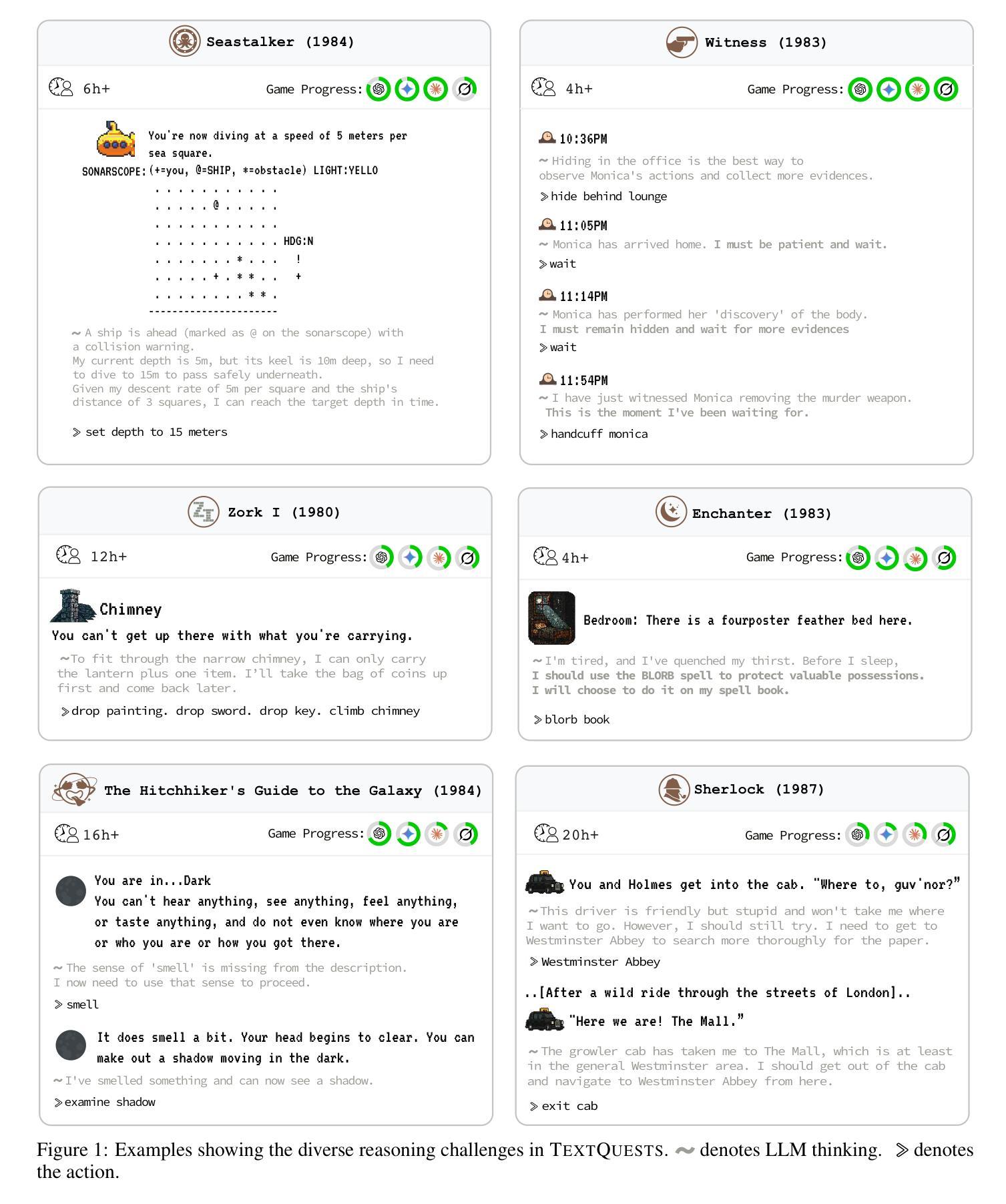
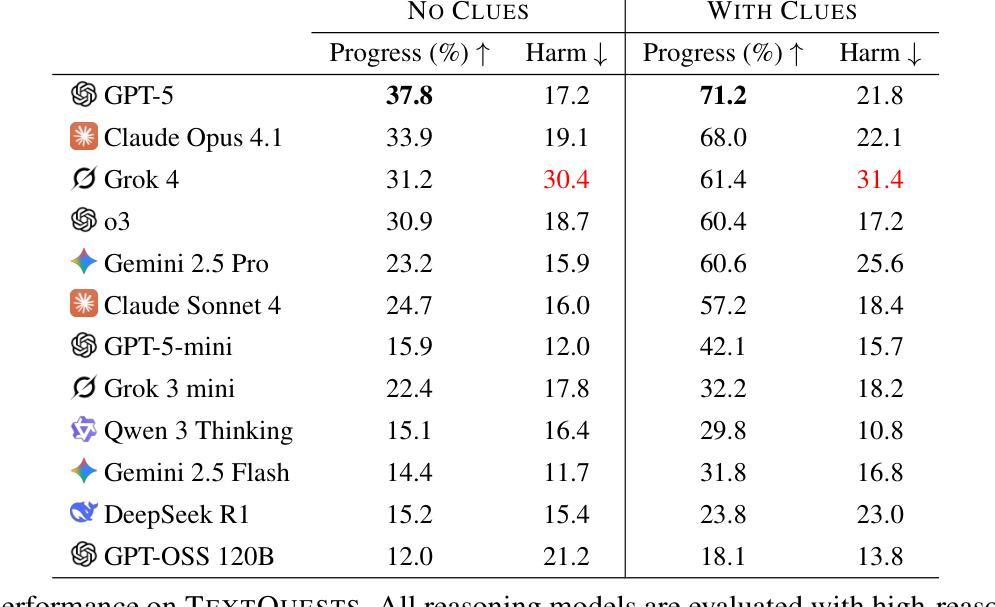
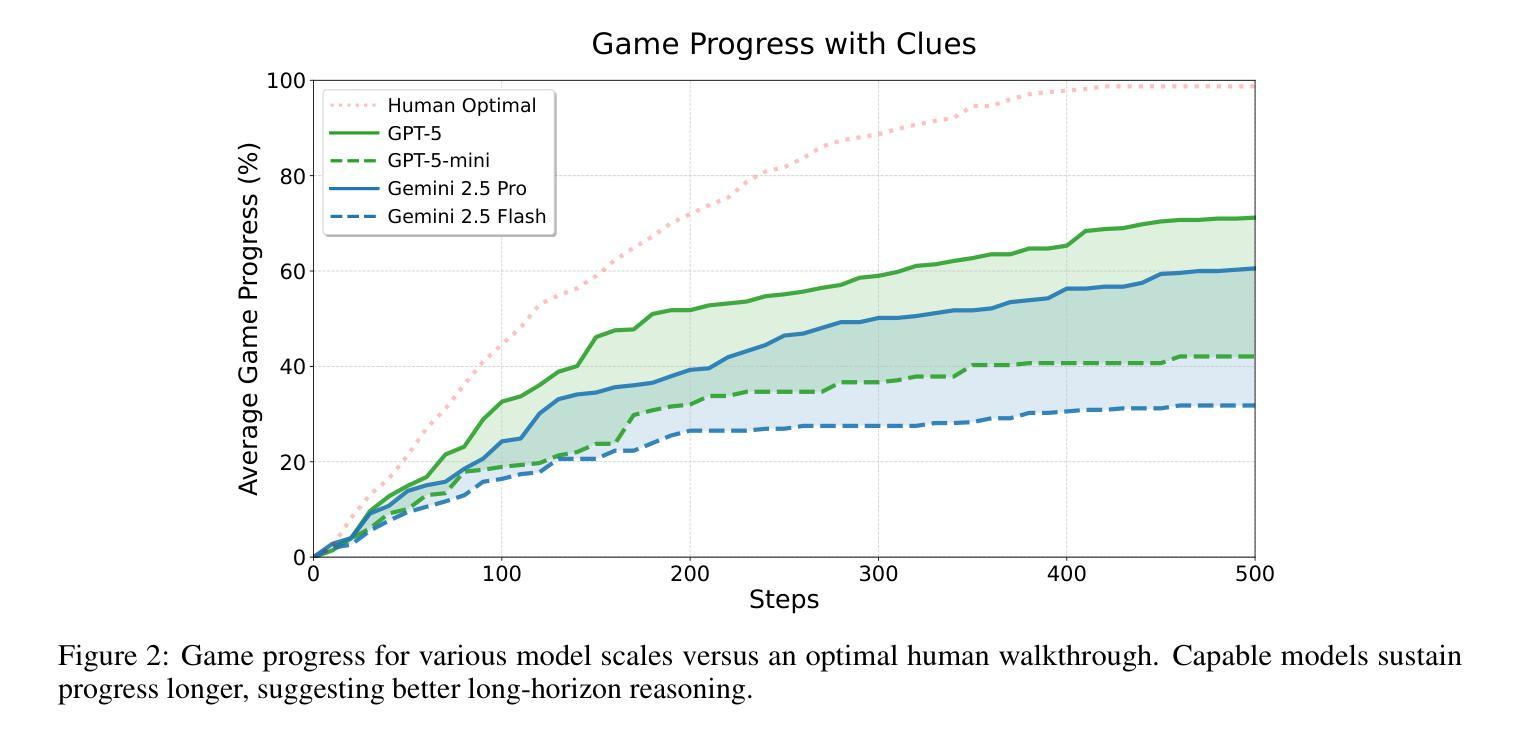
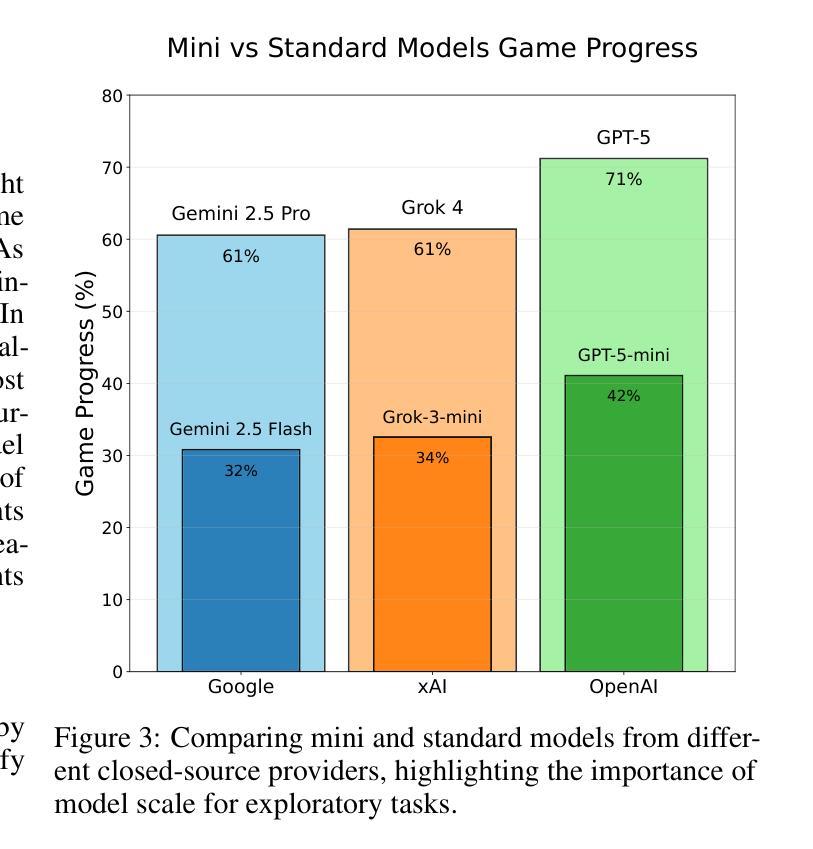
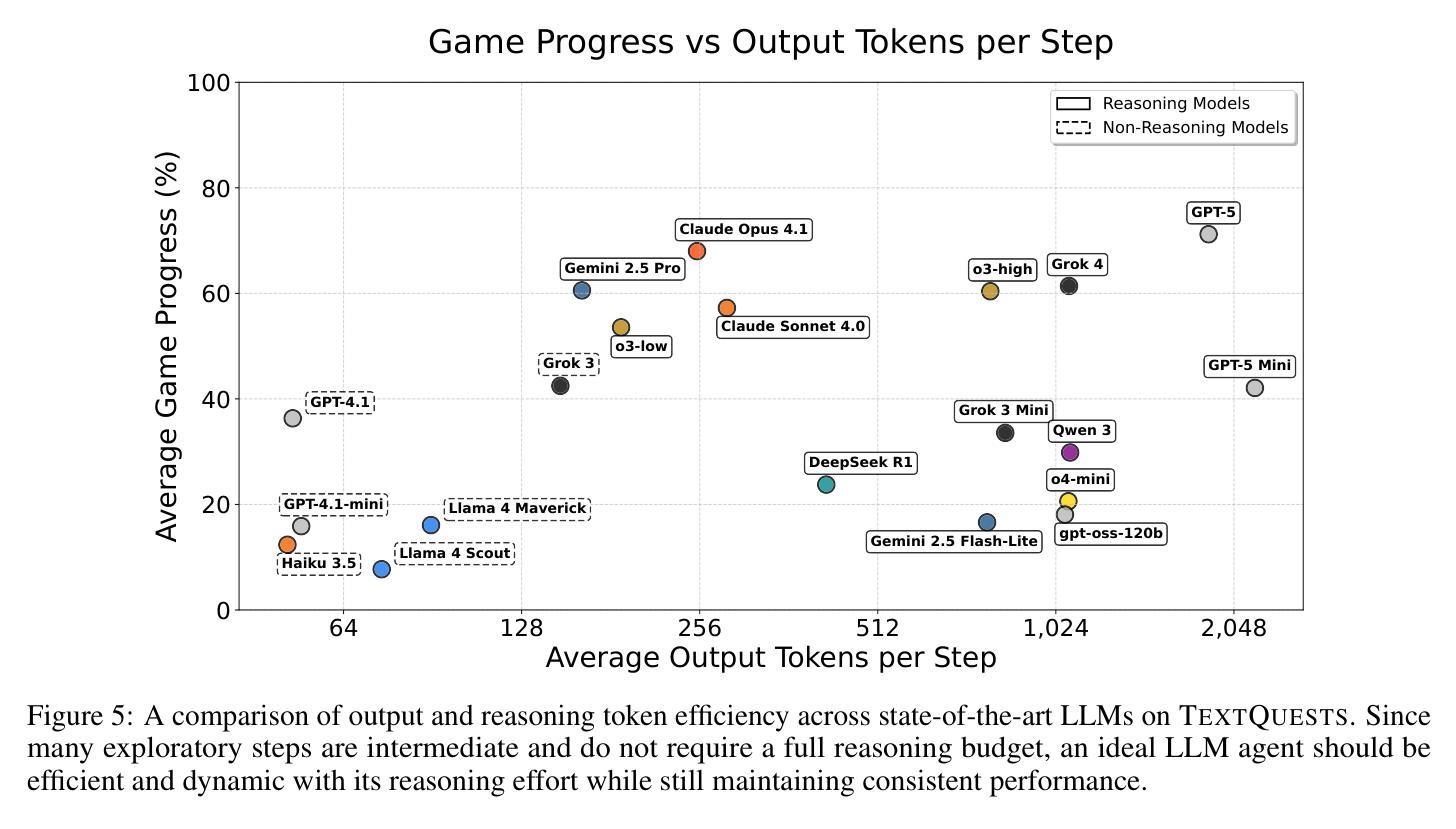
TextQuests: How Good are LLMs at Text-Based Video Games?
Authors:Long Phan, Mantas Mazeika, Andy Zou, Dan Hendrycks
Evaluating AI agents within complex, interactive environments that mirror real-world challenges is critical for understanding their practical capabilities. While existing agent benchmarks effectively assess skills like tool use or performance on structured tasks, they often do not fully capture an agent’s ability to operate autonomously in exploratory environments that demand sustained, self-directed reasoning over a long and growing context. To spur the development of agents capable of more robust intrinsic reasoning over long horizons, we introduce TextQuests, a benchmark based on the Infocom suite of interactive fiction games. These text-based adventures, which can take human players over 30 hours and require hundreds of precise actions to solve, serve as an effective proxy for evaluating AI agents on focused, stateful tasks. The benchmark is specifically designed to assess an LLM agent’s capacity for self-contained problem-solving by precluding the use of external tools, thereby focusing on intrinsic long-context reasoning capabilities in an exploratory environment characterized by the need for trial-and-error learning and sustained problem-solving within a single interactive session. We release TextQuests at https://textquests.ai.
评估在复杂、交互式环境中运行的AI代理,这些环境反映了现实世界的挑战,对于了解其实践能力至关重要。尽管现有的代理基准测试可以有效地评估工具使用或结构化任务上的技能,但它们通常不能完全捕捉到代理在探索环境中自主行动的能力,这些环境要求在一个不断发展和增长的背景下进行持续、自我导向的推理。为了促进能够在长期内具备更强内在推理能力的代理的发展,我们推出了基于Infocom系列交互式小说游戏的TextQuests基准测试。这些基于文本的挑战性冒险活动,可以让人类玩家花费超过30小时的时间,需要数百个精确的动作来解决。它可作为评估AI代理在专注、有状态任务上的有效代理。该基准测试专门设计用于评估LLM代理在禁止外部工具的情况下进行独立解决问题的能力,从而专注于探索环境中固有的长期上下文推理能力,这需要尝试和错误学习以及在单个交互式会话内持续解决问题的能力。我们在https://textquests.ai发布TextQuests。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
评估AI代理在模拟现实挑战的复杂交互环境中表现至关重要,以理解其实践能力。现有代理基准测试虽能有效评估工具使用或结构化任务上的技能,但往往无法全面捕捉代理在探索环境中自主行动的能力,这种环境需要长期持续的自导推理。为刺激开发能在长期视野中进行更稳健内在推理的代理,我们推出了基于Infocom交互式小说游戏系列的TextQuests基准测试。这些基于文本的挑战,人类玩家需要超过30小时和数百个精确动作来解决,可作为评估AI代理在专注、有状态任务上的能力的有效代理。该基准测试旨在评估LLM代理的自我解决问题的能力,禁止外部工具的使用,重点是在探索环境中内在长期上下文推理能力,这需要试错学习和单次互动会话中的持续问题解决能力。我们在https://textquests.ai发布TextQuests。
关键见解
- 评估AI代理在模拟现实挑战的复杂交互环境中的表现至关重要。
- 现有代理基准测试无法全面评估代理在探索环境中的自主行动能力。
- TextQuests基准测试基于Infocom交互式小说游戏,旨在评估AI代理的长期稳健内在推理能力。
- TextQuests基准测试通过禁止外部工具的使用,重点测试LLM代理的自我解决问题能力。
- 探索环境需要试错学习和单次互动会话中的持续问题解决能力。
- TextQuests为评估AI在处理复杂问题和任务时的实际能力提供了一个有效的平台。
点此查看论文截图


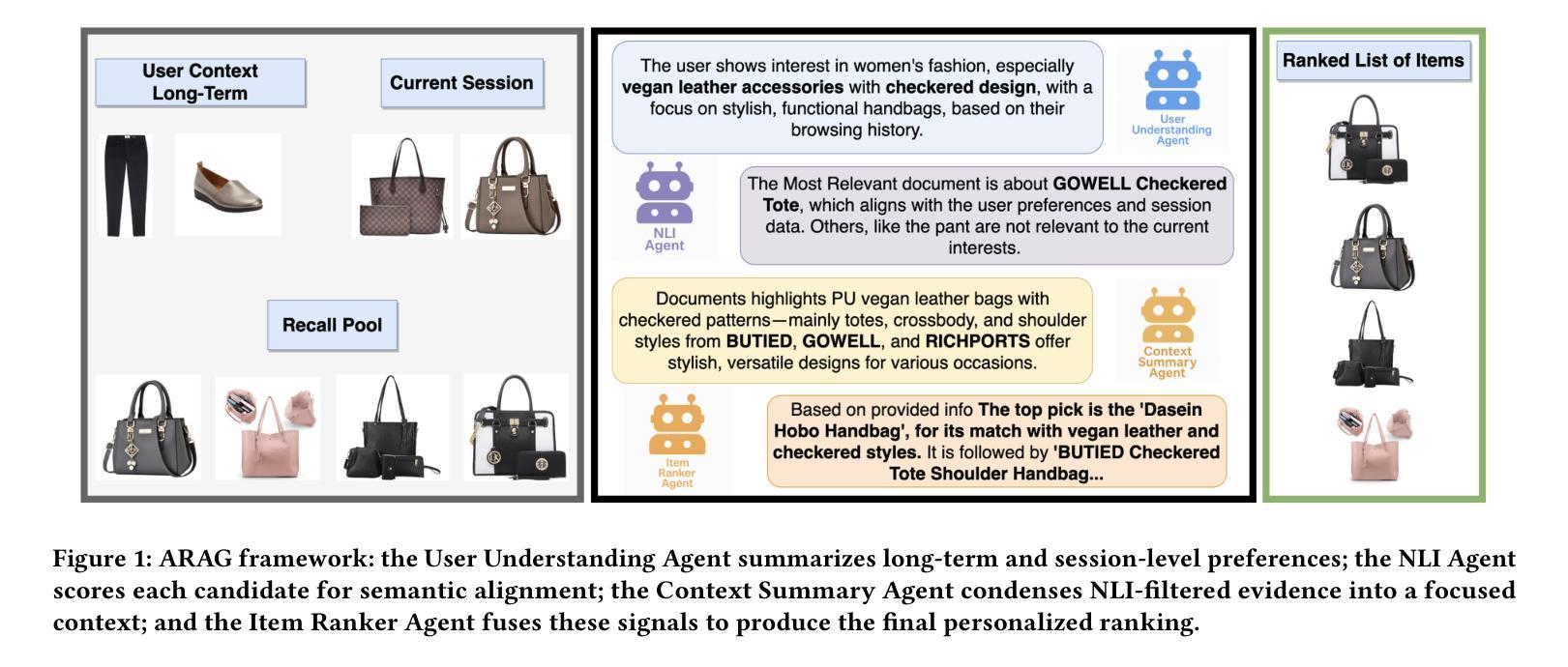
ARAG: Agentic Retrieval Augmented Generation for Personalized Recommendation
Authors:Reza Yousefi Maragheh, Pratheek Vadla, Priyank Gupta, Kai Zhao, Aysenur Inan, Kehui Yao, Jianpeng Xu, Praveen Kanumala, Jason Cho, Sushant Kumar
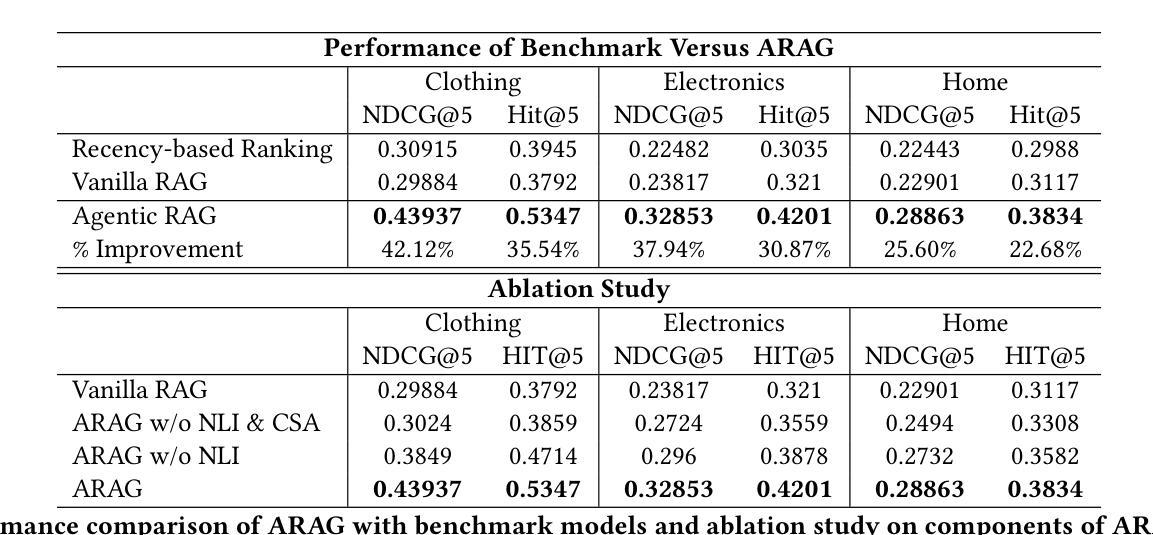
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has shown promise in enhancing recommendation systems by incorporating external context into large language model prompts. However, existing RAG-based approaches often rely on static retrieval heuristics and fail to capture nuanced user preferences in dynamic recommendation scenarios. In this work, we introduce ARAG, an Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework for Personalized Recommendation, which integrates a multi-agent collaboration mechanism into the RAG pipeline. To better understand the long-term and session behavior of the user, ARAG leverages four specialized LLM-based agents: a User Understanding Agent that summarizes user preferences from long-term and session contexts, a Natural Language Inference (NLI) Agent that evaluates semantic alignment between candidate items retrieved by RAG and inferred intent, a context summary agent that summarizes the findings of NLI agent, and an Item Ranker Agent that generates a ranked list of recommendations based on contextual fit. We evaluate ARAG accross three datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that ARAG significantly outperforms standard RAG and recency-based baselines, achieving up to 42.1% improvement in NDCG@5 and 35.5% in Hit@5. We also, conduct an ablation study to analyse the effect by different components of ARAG. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of integrating agentic reasoning into retrieval-augmented recommendation and provide new directions for LLM-based personalization.
检索增强生成(RAG)通过在大规模语言模型提示中融入外部上下文,在提升推荐系统方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,现有的基于RAG的方法往往依赖于静态检索启发式策略,无法捕捉到动态推荐场景中的微妙用户偏好。在这项工作中,我们引入了ARAG(个性化推荐的Agentic检索增强生成框架),它将多智能体协作机制集成到RAG管道中。为了更好地理解用户的长期和会话行为,ARAG采用了四个基于大规模语言模型的专用智能体:一个用户理解智能体,用于从长期和会话上下文中总结用户偏好;一个自然语言推理(NLI)智能体,用于评估由RAG检索到的候选项目和推断意图之间的语义对齐程度;一个上下文摘要智能体,用于总结NLI智能体的发现;以及一个项目排名智能体,根据上下文匹配度生成排名推荐列表。我们在三个数据集上评估了ARAG。实验结果表明,ARAG显著优于标准RAG和基于时效性的基准线,在NDCG@5上提高了42.1%,在Hit@5上提高了35.5%。我们还进行了一项消融研究,以分析ARAG不同组件的影响。我们的研究结果表明将智能体推理集成到检索增强推荐中的有效性,并为基于大规模语言模型的个性化推荐提供了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大语言模型(LLM)的Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG)在推荐系统中展现出潜力。然而,现有方法依赖静态检索启发式策略,无法捕捉动态推荐场景中的用户偏好细微差别。为此,本研究提出ARAG框架,通过集成多代理协作机制,改善RAG的性能。ARAG利用四个专门的大语言模型代理理解用户长期和会话行为,并通过评估候选项目和推断意图之间的语义对齐程度来生成个性化推荐。实验结果表明,ARAG显著优于标准RAG和基于时间的新颖性方法,其在NDCG@5上提升了42.1%,Hit@5上提升了35.5%。此研究为基于LLM的个人化推荐提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- ARAG框架通过集成多代理协作机制改进了基于大语言模型的检索增强生成方法(RAG)。
- ARAG使用四个专门的大语言模型代理:用户理解代理、自然语言推理(NLI)代理、上下文摘要代理和项目排名代理,以理解用户行为并生成个性化推荐。
- ARAG显著优于标准RAG和基于时间的新颖性方法,在NDCG@5和Hit@5等指标上有显著的提升。
- 实验结果证明了ARAG框架中每个组件的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Scaling Transformers for Discriminative Recommendation via Generative Pretraining
Authors:Chunqi Wang, Bingchao Wu, Zheng Chen, Lei Shen, Bing Wang, Xiaoyi Zeng
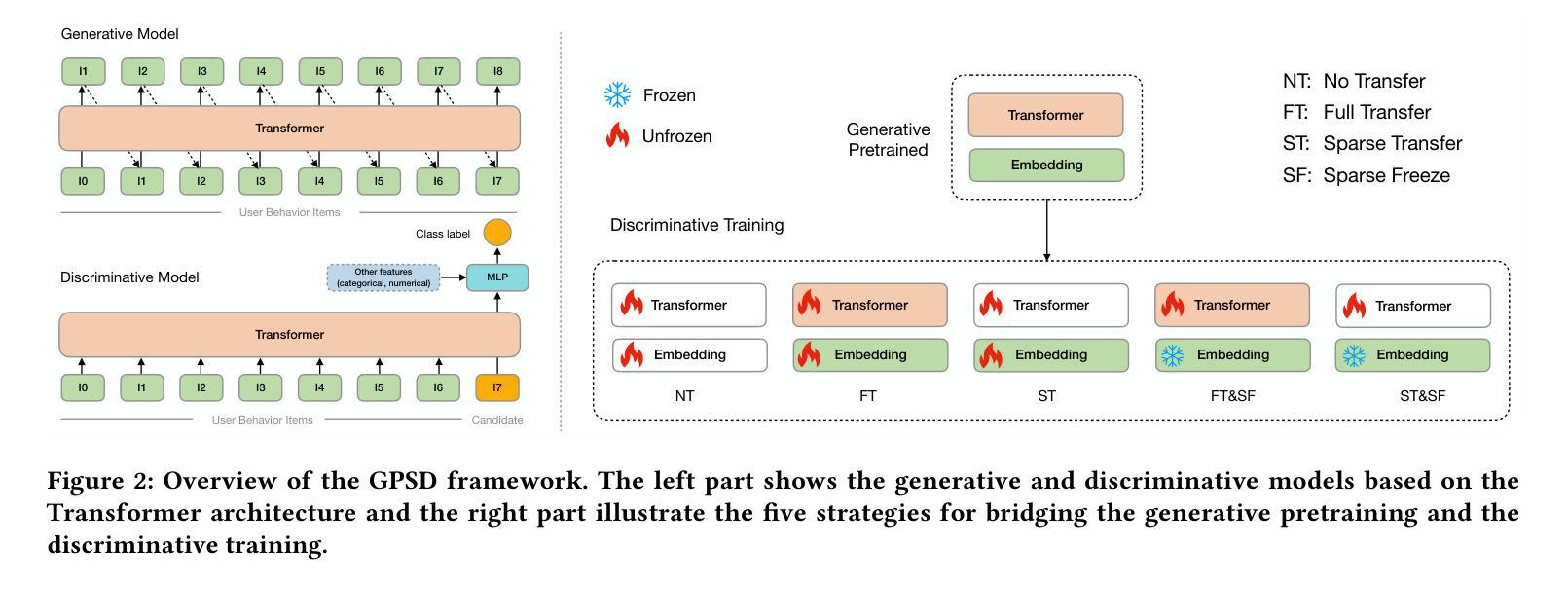
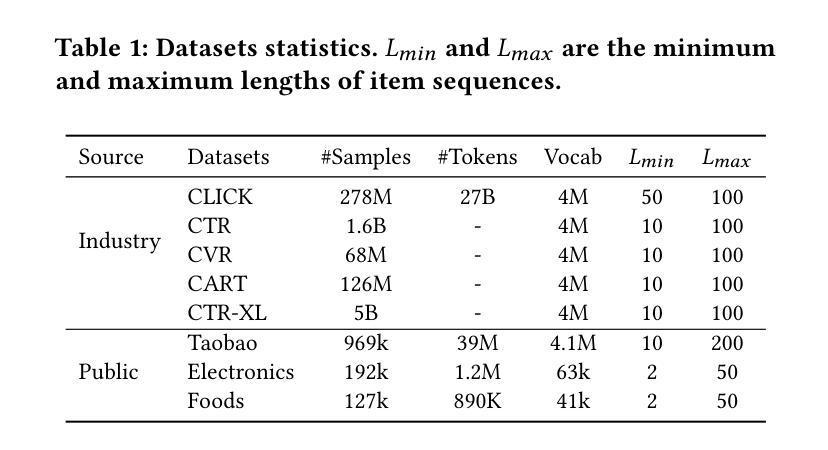
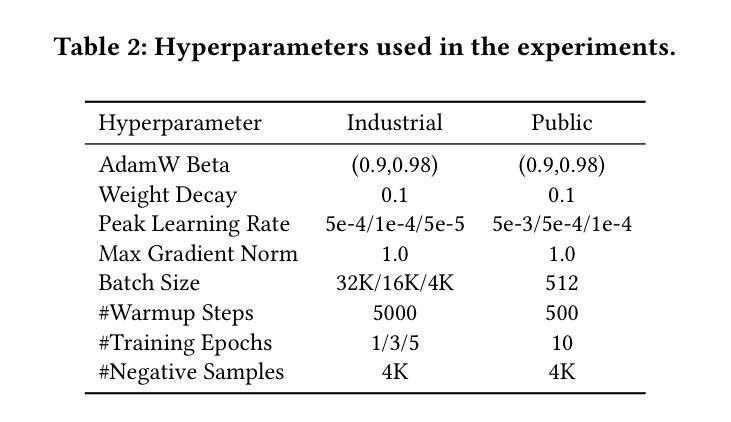
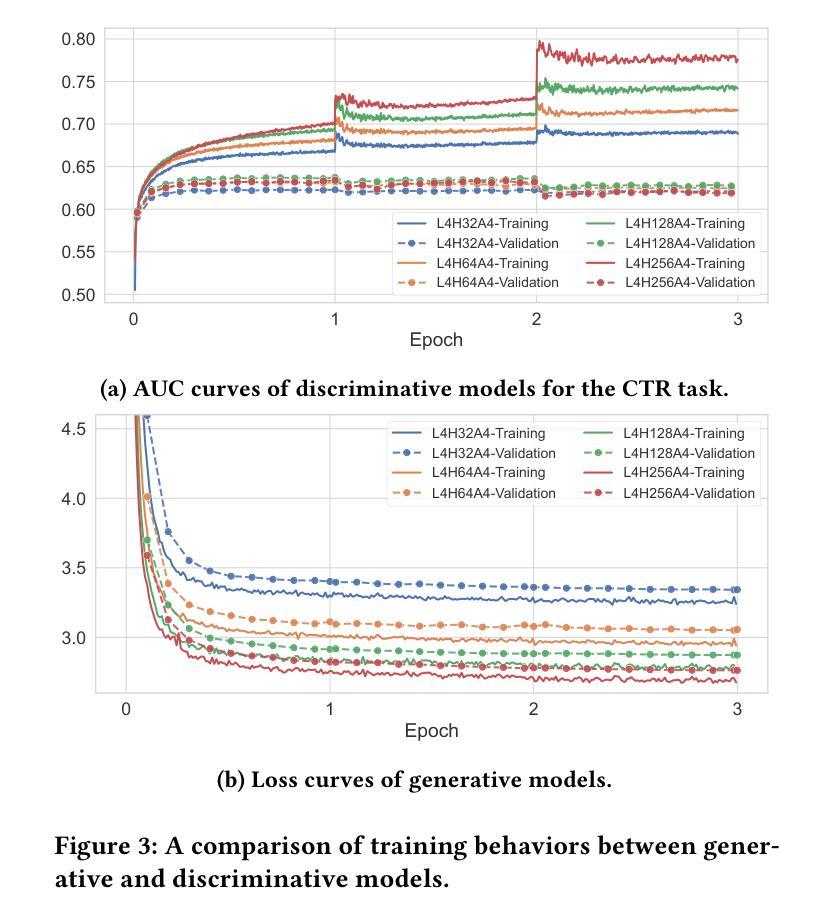
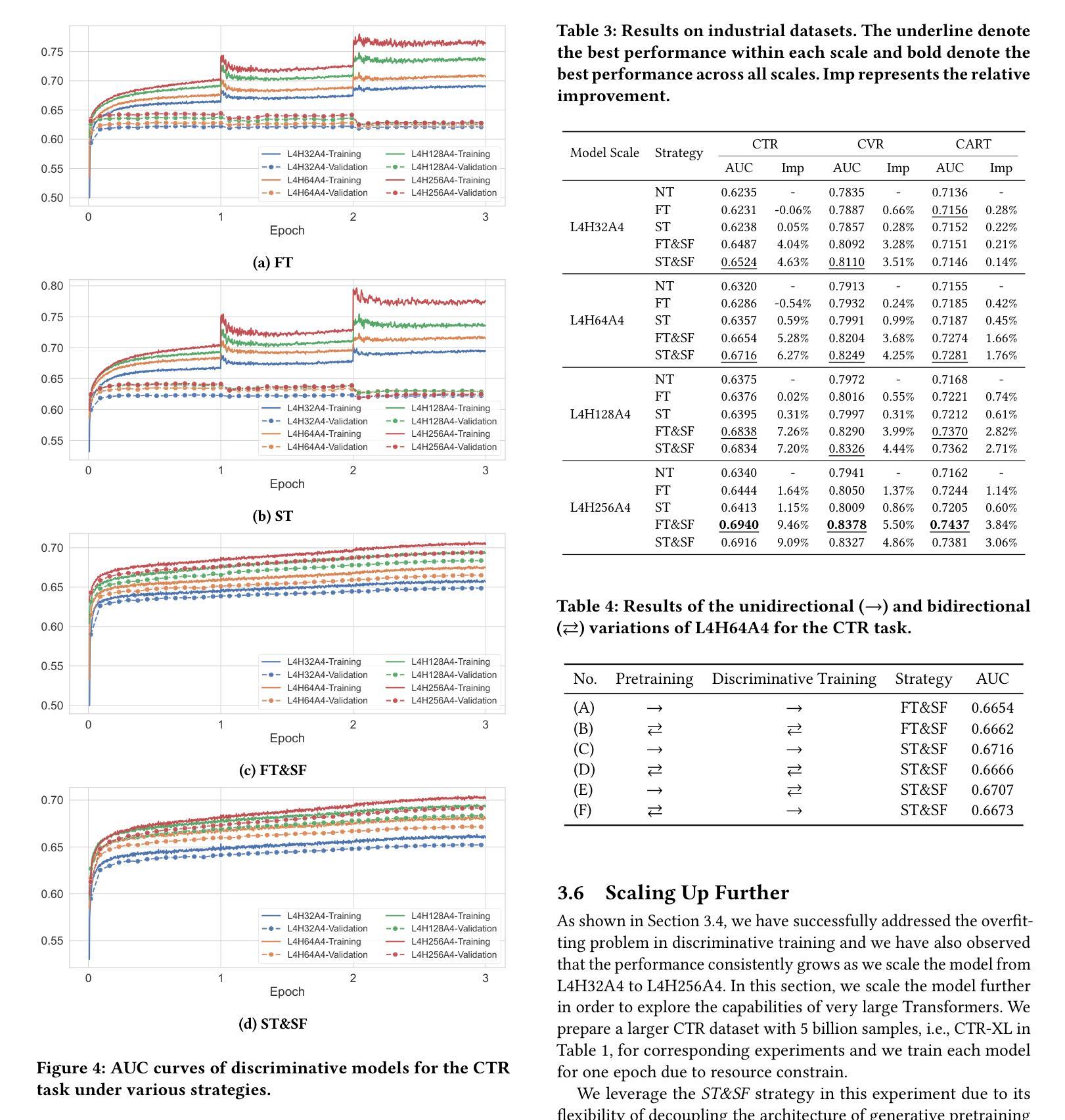
Discriminative recommendation tasks, such as CTR (click-through rate) and CVR (conversion rate) prediction, play critical roles in the ranking stage of large-scale industrial recommender systems. However, training a discriminative model encounters a significant overfitting issue induced by data sparsity. Moreover, this overfitting issue worsens with larger models, causing them to underperform smaller ones. To address the overfitting issue and enhance model scalability, we propose a framework named GPSD (\textbf{G}enerative \textbf{P}retraining for \textbf{S}calable \textbf{D}iscriminative Recommendation), drawing inspiration from generative training, which exhibits no evident signs of overfitting. GPSD leverages the parameters learned from a pretrained generative model to initialize a discriminative model, and subsequently applies a sparse parameter freezing strategy. Extensive experiments conducted on both industrial-scale and publicly available datasets demonstrate the superior performance of GPSD. Moreover, it delivers remarkable improvements in online A/B tests. GPSD offers two primary advantages: 1) it substantially narrows the generalization gap in model training, resulting in better test performance; and 2) it leverages the scalability of Transformers, delivering consistent performance gains as models are scaled up. Specifically, we observe consistent performance improvements as the model dense parameters scale from 13K to 0.3B, closely adhering to power laws. These findings pave the way for unifying the architectures of recommendation models and language models, enabling the direct application of techniques well-established in large language models to recommendation models. The code is available at https://github.com/chqiwang/gpsd-rec.
判别式推荐任务,如点击率(CTR)和转化率(CVR)预测,在大规模工业推荐系统的排序阶段起着至关重要的作用。然而,训练判别模型会遇到由数据稀疏引起的严重过拟合问题。而且,随着模型体积的增大,过拟合问题会恶化,导致模型性能不如较小的模型。为了解决过拟合问题并增强模型的可扩展性,我们提出了一种名为GPSD(面向可扩展判别推荐的生成预训练框架)的框架,该框架借鉴了生成式训练,几乎不会出现明显的过拟合迹象。GPSD利用从预训练的生成模型中学习的参数来初始化判别模型,随后应用稀疏参数冻结策略。在工业级和公开数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了GPSD的卓越性能。此外,它在在线A/B测试中取得了显著的改进。GPSD具有两个主要优势:1)它大大缩小了模型训练中的泛化差距,从而提高了测试性能;2)它利用Transformer的可扩展性,随着模型的规模扩大,性能持续提高。具体来说,我们观察到随着模型密集参数从13K扩展到0.3B,性能持续提高,这紧密遵循幂律。这些发现为统一推荐模型和语言模型的架构铺平了道路,使得大型语言模型中成熟的技术可以直接应用于推荐模型。代码可在https://github.com/chqiwang/gpsd-rec找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KDD’25
Summary
该文针对推荐系统中的过拟合问题提出了一种新的解决方案GPSD框架,利用生成式预训练为鉴别式推荐系统提供初始参数,并结合稀疏参数冻结策略来解决数据稀疏导致的过拟合问题。该框架在大型工业推荐系统和公开数据集上的实验表现出卓越性能,在线A/B测试也取得了显著改进。其主要优势在于缩小了模型训练中的泛化差距,并借助Transformer的可扩展性,随着模型规模的扩大,性能不断提升。该框架为推荐模型和语言模型的架构统一奠定了基础,使得语言模型中的技术可以直接应用于推荐模型。
Key Takeaways
- 鉴别式推荐任务在大型工业推荐系统中扮演重要角色,如CTR和CVR预测,但在数据稀疏场景下训练时存在严重的过拟合问题。
- GPSD框架结合生成式预训练解决了过拟合问题,提高了模型的泛化能力和可扩展性。
- GPSD框架利用生成式预训练模型参数初始化鉴别式模型,并采用稀疏参数冻结策略进一步优化性能。
- 在工业级和公开数据集上的实验验证了GPSD框架的优越性能。在线A/B测试也显示了显著的改进。
- GPSD框架的主要优势在于缩小了模型训练的泛化差距,并随着模型规模的扩大,性能持续提高。
- GPSD框架推动了推荐模型和语言模型的架构统一,使得语言模型的技术可以直接应用于推荐模型。
点此查看论文截图
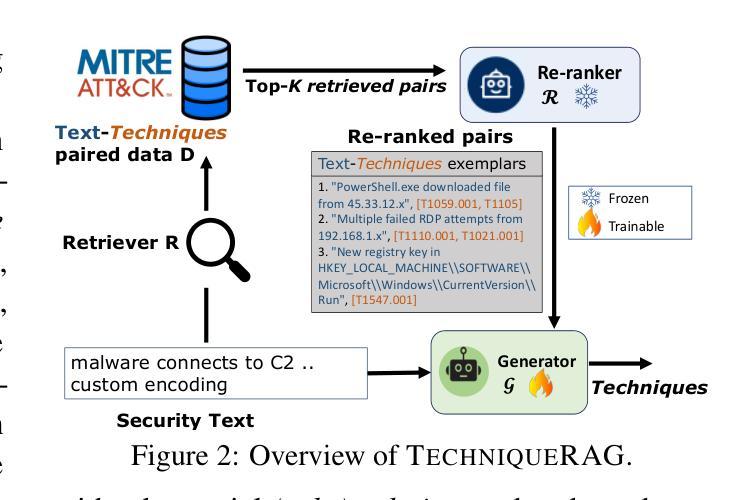
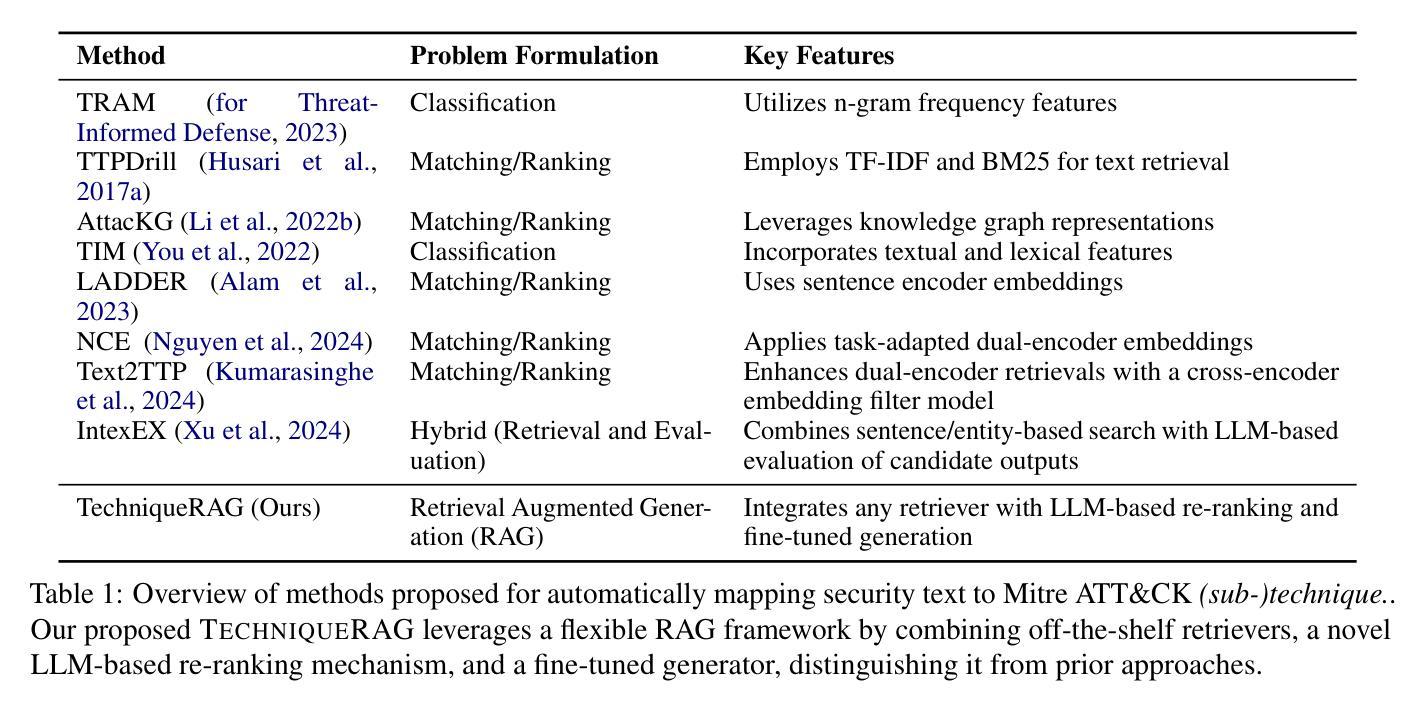
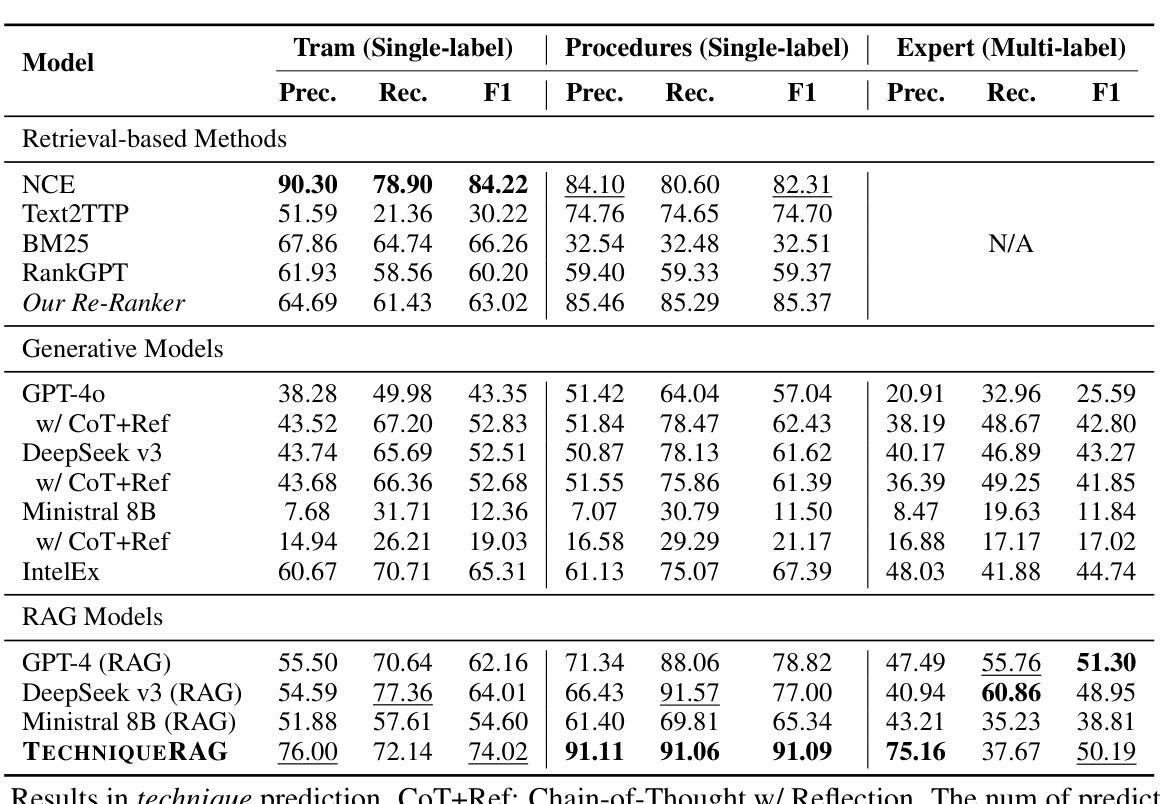
TechniqueRAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation for Adversarial Technique Annotation in Cyber Threat Intelligence Text
Authors:Ahmed Lekssays, Utsav Shukla, Husrev Taha Sencar, Md Rizwan Parvez
Accurately identifying adversarial techniques in security texts is critical for effective cyber defense. However, existing methods face a fundamental trade-off: they either rely on generic models with limited domain precision or require resource-intensive pipelines that depend on large labeled datasets and task-specific optimizations, such as custom hard-negative mining and denoising, resources rarely available in specialized domains. We propose TechniqueRAG, a domain-specific retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework that bridges this gap by integrating off-the-shelf retrievers, instruction-tuned LLMs, and minimal text-technique pairs. Our approach addresses data scarcity by fine-tuning only the generation component on limited in-domain examples, circumventing the need for resource-intensive retrieval training. While conventional RAG mitigates hallucination by coupling retrieval and generation, its reliance on generic retrievers often introduces noisy candidates, limiting domain-specific precision. To address this, we enhance retrieval quality and domain specificity through zero-shot LLM re-ranking, which explicitly aligns retrieved candidates with adversarial techniques. Experiments on multiple security benchmarks demonstrate that TechniqueRAG achieves state-of-the-art performance without extensive task-specific optimizations or labeled data, while comprehensive analysis provides further insights.
准确地识别安全文本中的对抗技术是有效网络防御的关键。然而,现有方法面临一个基本权衡:它们要么依赖于具有有限域精度的通用模型,要么需要依赖大量标记数据集和任务特定优化(如自定义的硬负样本挖掘和去噪)的资源密集型管道,这些资源在特定领域很少可用。我们提出了TechniqueRAG,这是一个域特定的检索增强生成(RAG)框架,它通过集成现成的检索器、指令调优的大型语言模型和少量的文本技术对来弥补这一差距。我们的方法通过仅对域内有限示例进行生成组件的微调来解决数据稀缺问题,从而避免了资源密集型的检索训练需求。虽然传统的RAG通过耦合检索和生成来缓解虚构问题,但它对通用检索器的依赖往往会引入嘈杂的候选对象,限制了域特定的精度。为了解决这一问题,我们通过零样本大型语言模型重新排序来提高检索质量和域特异性,这明确地使检索到的候选对象与对抗技术相匹配。在多个安全基准测试上的实验表明,TechniqueRAG在不进行大量特定任务优化或使用标记数据的情况下实现了最先进的性能,而综合分析则提供了进一步的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACL (Findings) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在安全文本中准确识别对抗性技术对于有效网络安全防御的重要性。现有方法存在通用性与精确度之间的权衡问题。本文提出了TechniqueRAG框架,通过集成现成的检索器、指令优化的大型语言模型(LLM)和少量的文本技术配对,以弥补这一差距。该框架解决了数据稀缺问题,只需对生成组件进行微调,而无需进行资源密集型的检索训练。实验证明,TechniqueRAG在不进行大量特定任务优化或使用标注数据的情况下,即可实现卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 准确识别安全文本中的对抗性技术对于有效网络安全防御至关重要。
- 现有方法面临通用性与精确度之间的权衡问题。
- TechniqueRAG框架通过集成现成的检索器、LLM和文本技术配对来解决这一问题。
- 该框架解决了数据稀缺问题,只需对生成组件进行微调。
- TechniqueRAG增强了检索质量和领域特异性,通过零样本LLM重新排序,明确将检索到的候选内容与对抗性技术对齐。
- 实验证明,TechniqueRAG在多个安全基准测试上实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图