⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
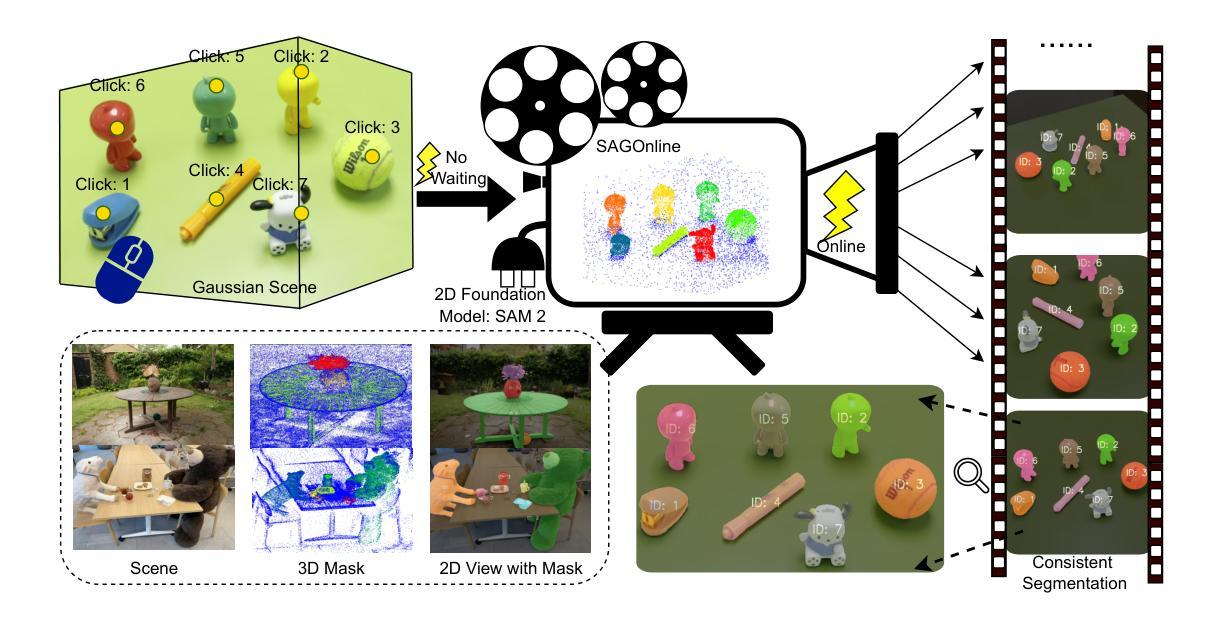
SAGOnline: Segment Any Gaussians Online
Authors:Wentao Sun, Quanyun Wu, Hanqing Xu, Kyle Gao, Zhengsen Xu, Yiping Chen, Dedong Zhang, Lingfei Ma, John S. Zelek, Jonathan Li
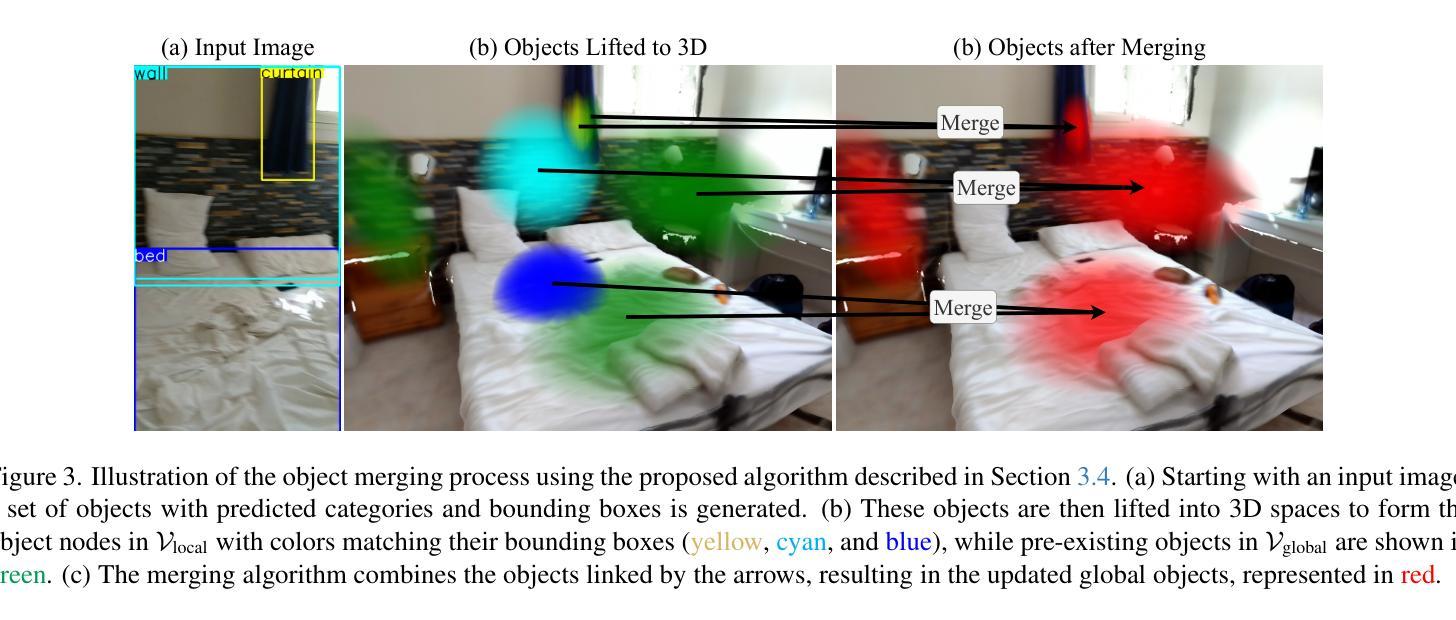
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for explicit 3D scene representation, yet achieving efficient and consistent 3D segmentation remains challenging. Current methods suffer from prohibitive computational costs, limited 3D spatial reasoning, and an inability to track multiple objects simultaneously. We present Segment Any Gaussians Online (SAGOnline), a lightweight and zero-shot framework for real-time 3D segmentation in Gaussian scenes that addresses these limitations through two key innovations: (1) a decoupled strategy that integrates video foundation models (e.g., SAM2) for view-consistent 2D mask propagation across synthesized views; and (2) a GPU-accelerated 3D mask generation and Gaussian-level instance labeling algorithm that assigns unique identifiers to 3D primitives, enabling lossless multi-object tracking and segmentation across views. SAGOnline achieves state-of-the-art performance on NVOS (92.7% mIoU) and Spin-NeRF (95.2% mIoU) benchmarks, outperforming Feature3DGS, OmniSeg3D-gs, and SA3D by 15–1500 times in inference speed (27 ms/frame). Qualitative results demonstrate robust multi-object segmentation and tracking in complex scenes. Our contributions include: (i) a lightweight and zero-shot framework for 3D segmentation in Gaussian scenes, (ii) explicit labeling of Gaussian primitives enabling simultaneous segmentation and tracking, and (iii) the effective adaptation of 2D video foundation models to the 3D domain. This work allows real-time rendering and 3D scene understanding, paving the way for practical AR/VR and robotic applications.
3D高斯延展(3DGS)已经成为一种强大的显式3D场景表示范式,但实现高效且一致的3D分割仍然具有挑战性。当前的方法存在计算成本高昂、3D空间推理有限、无法同时跟踪多个物体等缺点。我们提出了在线高斯任意分割(SAGOnline)框架,这是一种用于高斯场景的实时3D分割的轻量级零样本框架,通过两个关键创新解决了这些限制:(1)一种分离策略,集成了视频基础模型(例如SAM2),用于在合成视图之间进行视图一致的2D掩膜传播;(2)GPU加速的3D掩膜生成和高斯级别的实例标记算法,该算法为3D原始数据分配唯一标识符,从而实现跨视图的无损多目标跟踪和分割。SAGOnline在NVOS(92.7% mIoU)和Spin-NeRF(95.2% mIoU)基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在推理速度上比Feature3DGS、OmniSeg3D-gs和SA3D快15至1500倍(每秒处理帧数达到27毫秒)。定性结果证明了在复杂场景中实现多目标分割和跟踪的稳健性。我们的贡献包括:(i)用于高斯场景的实时3D分割的轻量级零样本框架,(ii)对高斯原始数据的显式标记,从而实现同时分割和跟踪,(iii)有效适应二维视频基础模型到三维领域。这项工作为实现实时渲染和三维场景理解铺平了道路,为增强现实/虚拟现实和机器人应用等实用领域提供了可能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维高斯场景中的实时分割问题,提出的在线分割任意高斯(SAGOnline)框架。该框架通过两项关键技术突破现有方法的限制:一是采用解耦策略,集成视频基础模型进行视图一致的二维掩膜传播;二是采用GPU加速的三维掩膜生成和高斯级别的实例标注算法,实现对三维原始数据的无损多目标跟踪和跨视图分割。SAGOnline在NVOS和Spin-NeRF基准测试中达到业界领先水平,推理速度比Feature3DGS、OmniSeg3D-gs和SA3D快15至1500倍,达到每帧27毫秒。该工作为实时渲染和三维场景理解铺平了道路,为AR/VR和机器人应用提供了可能。
Key Takeaways
- SAGOnline是一个针对高斯场景中的实时三维分割的轻量级零样本框架。
- 通过集成视频基础模型,实现视图一致的二维掩膜传播。
- 采用GPU加速的三维掩膜生成和高斯级别的实例标注算法,实现多目标跟踪和跨视图分割。
- SAGOnline在NVOS和Spin-NeRF基准测试中表现优异。
- 与其他方法相比,SAGOnline的推理速度显著提高。
- 该工作为实时渲染和三维场景理解提供了可能。
点此查看论文截图

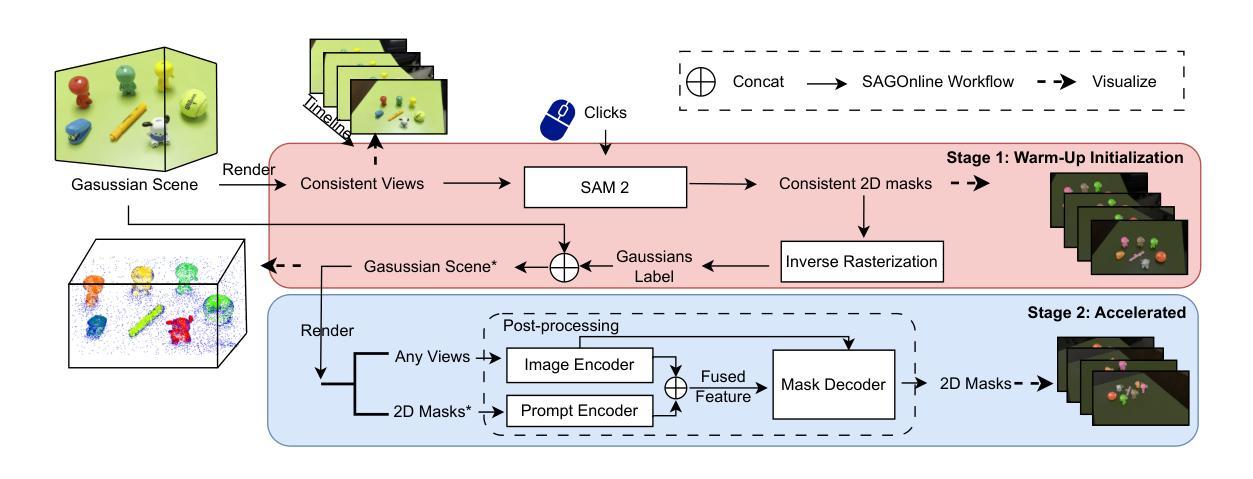
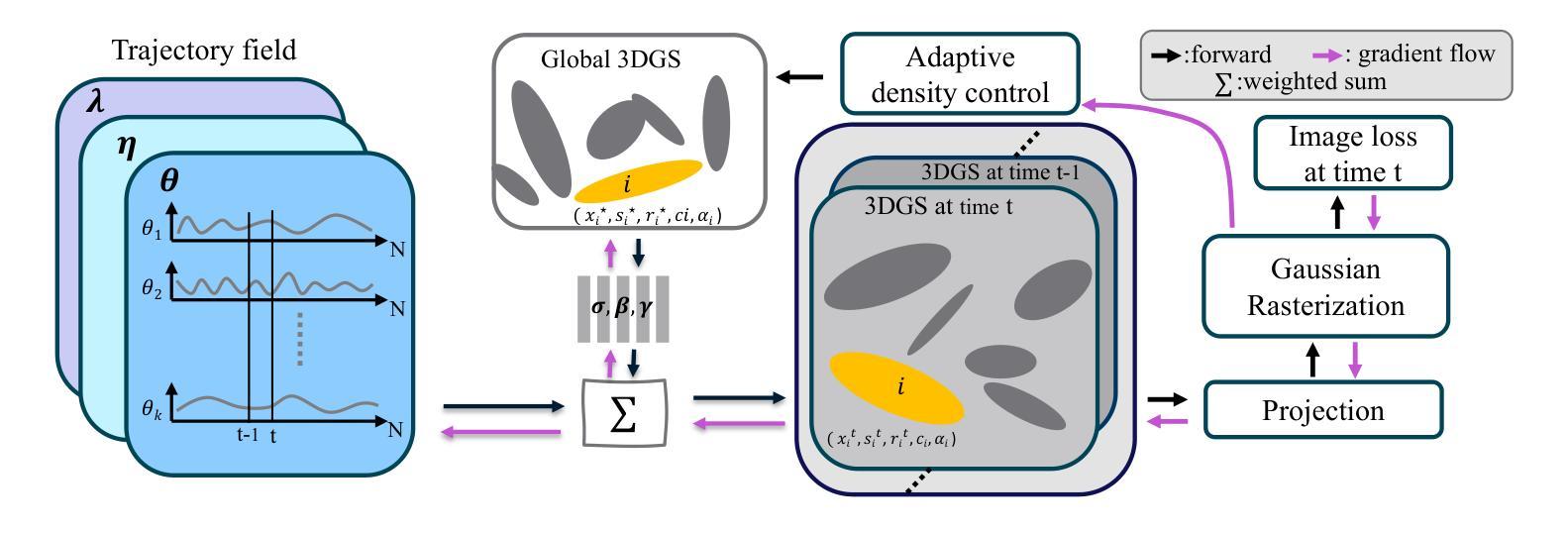
3D Gaussian Representations with Motion Trajectory Field for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Xuesong Li, Lars Petersson, Vivien Rolland
This paper addresses the challenge of novel-view synthesis and motion reconstruction of dynamic scenes from monocular video, which is critical for many robotic applications. Although Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have demonstrated remarkable success in rendering static scenes, extending them to reconstruct dynamic scenes remains challenging. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that combines 3DGS with a motion trajectory field, enabling precise handling of complex object motions and achieving physically plausible motion trajectories. By decoupling dynamic objects from static background, our method compactly optimizes the motion trajectory field. The approach incorporates time-invariant motion coefficients and shared motion trajectory bases to capture intricate motion patterns while minimizing optimization complexity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results in both novel-view synthesis and motion trajectory recovery from monocular video, advancing the capabilities of dynamic scene reconstruction.
本文应对了从单目视频中合成新视角和重建动态场景的挑战,这对于许多机器人应用至关重要。尽管神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯涂画(3DGS)在渲染静态场景方面取得了显著的成功,但它们扩展到重建动态场景仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种将3DGS与运动轨迹场相结合的新方法,能够精确处理复杂物体运动,并实现物理上可行的运动轨迹。通过将动态物体与静态背景解耦,我们的方法可以紧凑地优化运动轨迹场。该方法结合了时间不变的运动系数和共享的运动轨迹基础,以捕捉复杂的运动模式,同时最小化优化复杂度。大量实验表明,我们的方法在从新视角合成和从单目视频中恢复运动轨迹方面达到了最新水平,提高了动态场景重建的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种将3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)与运动轨迹场相结合的新方法,用于从单目视频中重建动态场景。该方法通过解耦动态物体与静态背景,优化运动轨迹场,并引入时间不变运动系数和共享运动轨迹基,以捕捉复杂的运动模式,同时降低优化复杂度。实验表明,该方法在单目视频的新视图合成和运动轨迹恢复方面达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了从单目视频中重建动态场景的挑战,这对于许多机器人应用至关重要。
- 引入了一种结合3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)和运动轨迹场的新方法。
- 通过解耦动态物体和静态背景,该方法能够紧凑地优化运动轨迹场。
- 引入时间不变运动系数和共享运动轨迹基,以捕捉复杂的运动模式。
- 方法降低了优化复杂度。
- 实验表明,该方法在新型视图合成和运动轨迹恢复方面达到了最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

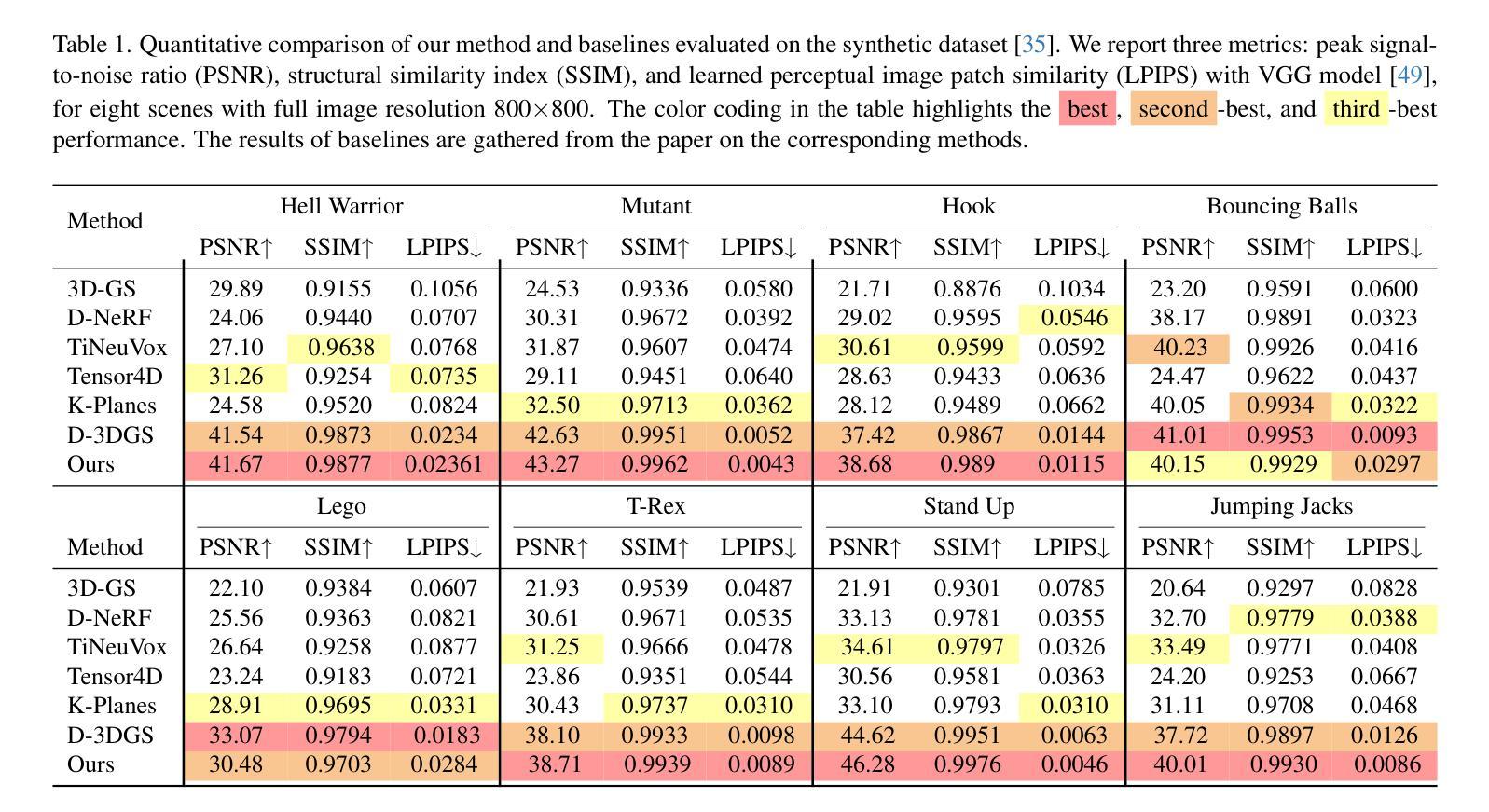
Perceptual Evaluation of GANs and Diffusion Models for Generating X-rays
Authors:Gregory Schuit, Denis Parra, Cecilia Besa
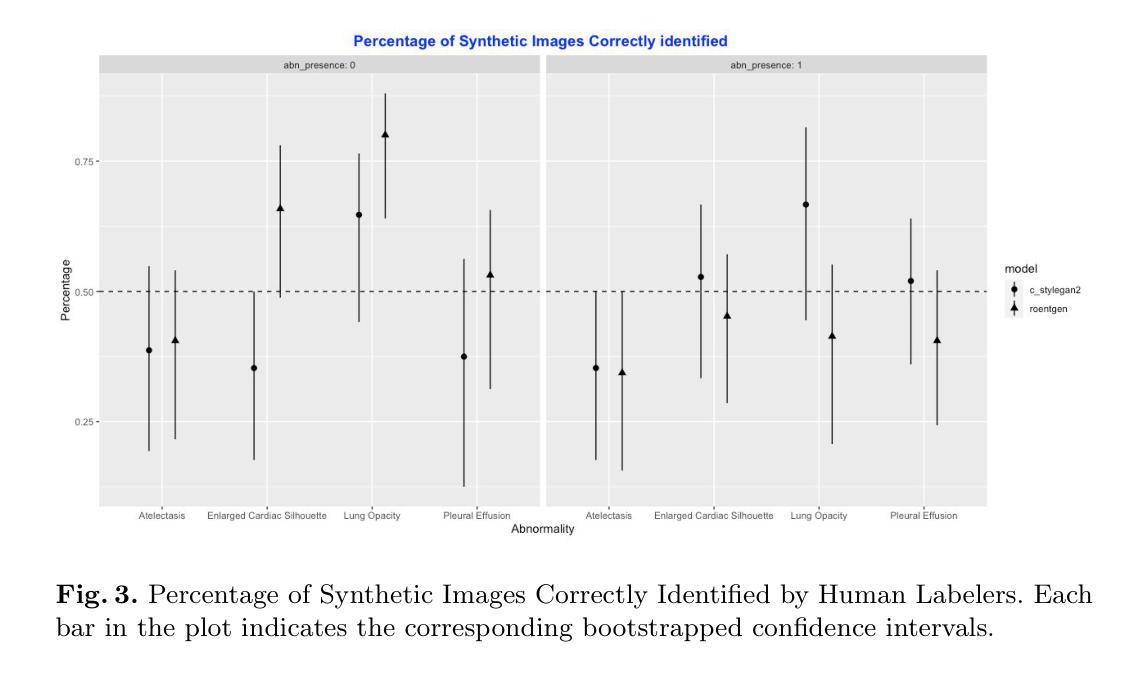
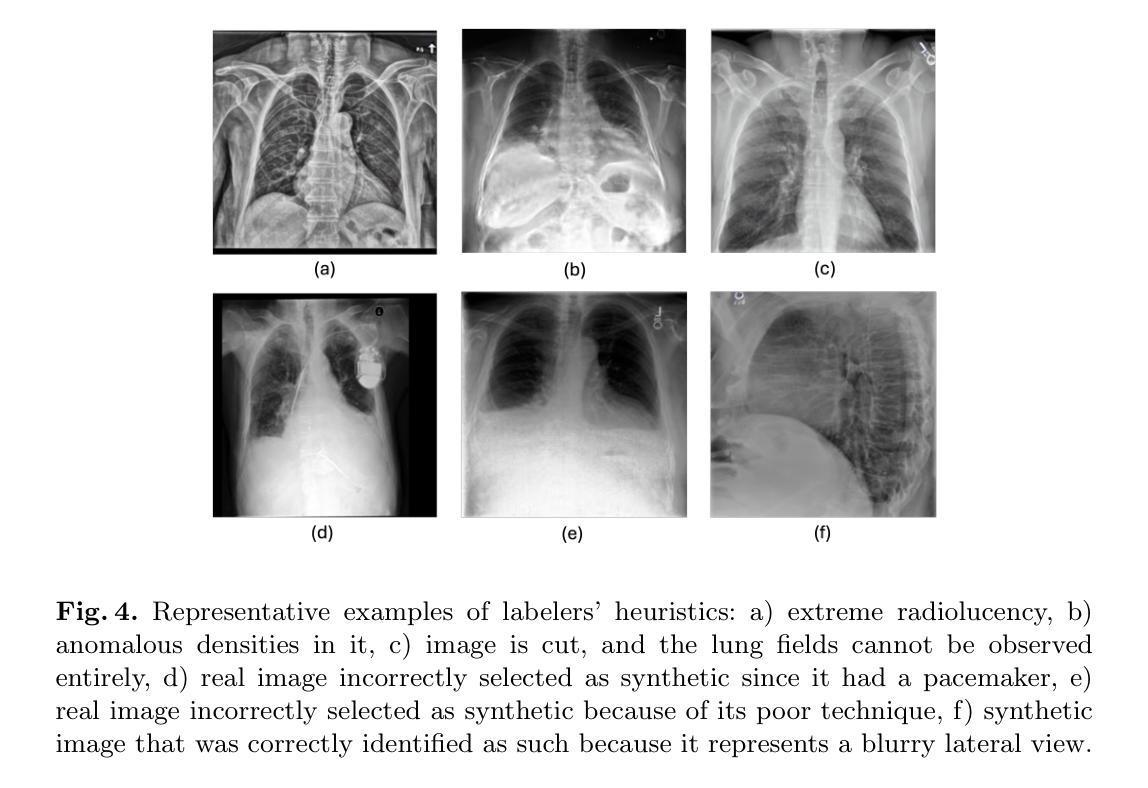
Generative image models have achieved remarkable progress in both natural and medical imaging. In the medical context, these techniques offer a potential solution to data scarcity-especially for low-prevalence anomalies that impair the performance of AI-driven diagnostic and segmentation tools. However, questions remain regarding the fidelity and clinical utility of synthetic images, since poor generation quality can undermine model generalizability and trust. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art generative models-Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs)-for synthesizing chest X-rays conditioned on four abnormalities: Atelectasis (AT), Lung Opacity (LO), Pleural Effusion (PE), and Enlarged Cardiac Silhouette (ECS). Using a benchmark composed of real images from the MIMIC-CXR dataset and synthetic images from both GANs and DMs, we conducted a reader study with three radiologists of varied experience. Participants were asked to distinguish real from synthetic images and assess the consistency between visual features and the target abnormality. Our results show that while DMs generate more visually realistic images overall, GANs can report better accuracy for specific conditions, such as absence of ECS. We further identify visual cues radiologists use to detect synthetic images, offering insights into the perceptual gaps in current models. These findings underscore the complementary strengths of GANs and DMs and point to the need for further refinement to ensure generative models can reliably augment training datasets for AI diagnostic systems.
在天然成像和医学影像领域,生成图像模型已经取得了显著的进步。在医学背景下,这些技术为解决数据稀缺问题提供了潜在解决方案,尤其是对于那些会降低AI诊断和分割工具性能的罕见异常。然而,关于合成图像的保真度和临床实用性仍存在疑问,因为生成质量差会损害模型的通用性和信任度。在这项研究中,我们评估了最先进的生成模型——生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在根据四种异常情况合成胸部X射线图像方面的有效性,这四种异常情况包括肺不张(AT)、肺实变(LO)、胸膜积液(PE)和心脏轮廓增大(ECS)。我们使用由MIMIC-CXR数据集的真实图像和GANs及DMs生成的合成图像组成的基准测试集,对三位不同经验的放射科医生进行了一项读者研究。参与者被要求区分真实和合成图像,并评估视觉特征与目标异常之间的一致性。我们的结果表明,总体而言,DMs生成了更为视觉真实的图像,但对于特定条件(如没有ECS的情况),GANs报告的准确性更高。我们还确定了放射科医生用来检测合成图像的视觉线索,这为我们了解当前模型中的感知差距提供了见解。这些发现强调了GANs和DMs的互补优势,并指出需要进一步改进以确保生成模型能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Workshop on Human-AI Collaboration at MICCAI 2025
Summary
该研究评估了先进生成模型在合成胸X光片上的表现,主要针对四种异常情况:肺不张、肺实变、胸腔积液和心脏轮廓增大。研究结果显示,扩散模型生成的图像整体视觉更真实,而生成对抗网络对某些特定条件的准确性更高。此外,该研究还识别了放射科医生用于检测合成图像的可视线索,强调了生成模型在AI诊断系统训练数据集扩充中的互补性和进一步优化的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成图像模型在自然和医学成像方面都取得了显著进展。
- 在医学背景下,生成模型为解决数据稀缺问题提供了潜在解决方案,特别是在低发病率异常情况下。
- 研究评估了GANs和DMs在合成胸X光片上的表现,涉及四种异常情况。
- 扩散模型生成的图像整体视觉更真实,而生成对抗网络在某些特定条件下的准确性更高。
- 放射科医生可以通过特定的视觉线索来区分合成图像和真实图像。
- 研究强调了生成模型的互补性和进一步优化的必要性,以确保它们能够可靠地增强AI诊断系统的训练数据集。
- 研究结果对于改进生成模型以及提高AI在医学图像分析中的性能具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

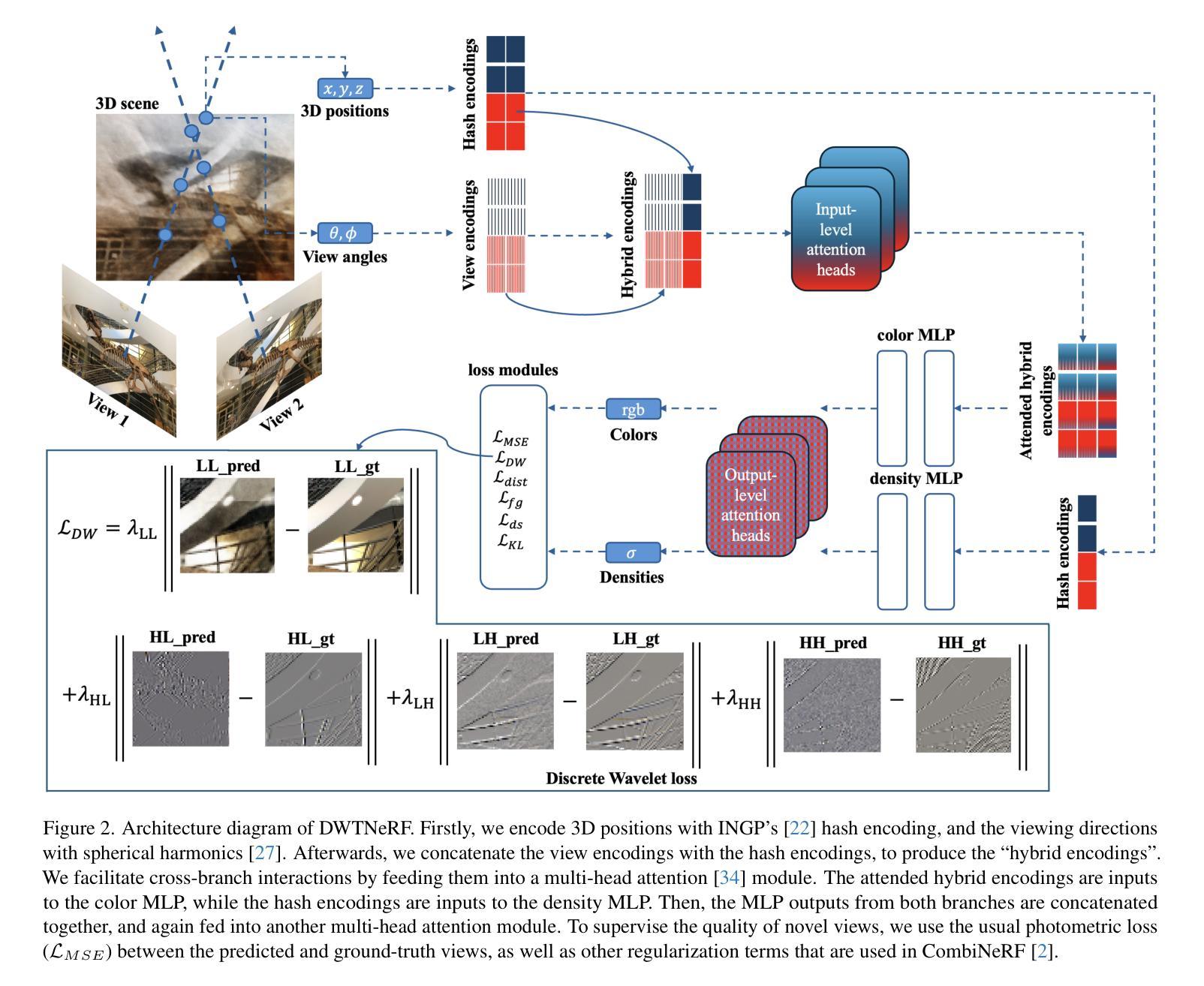
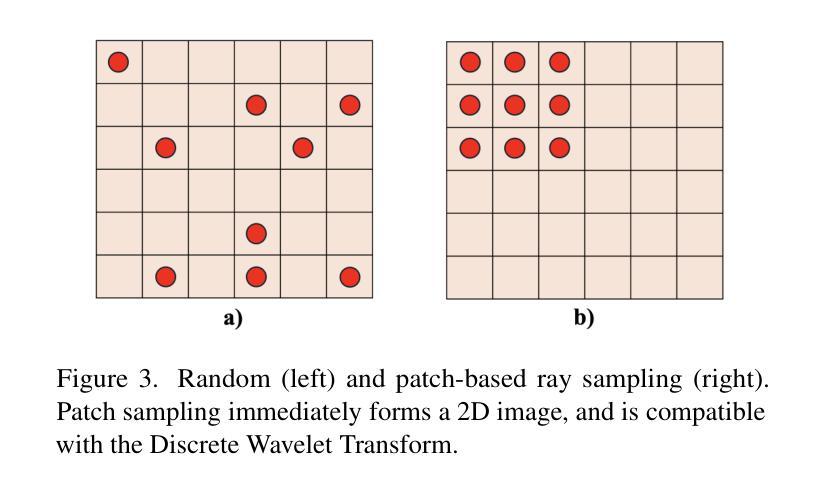
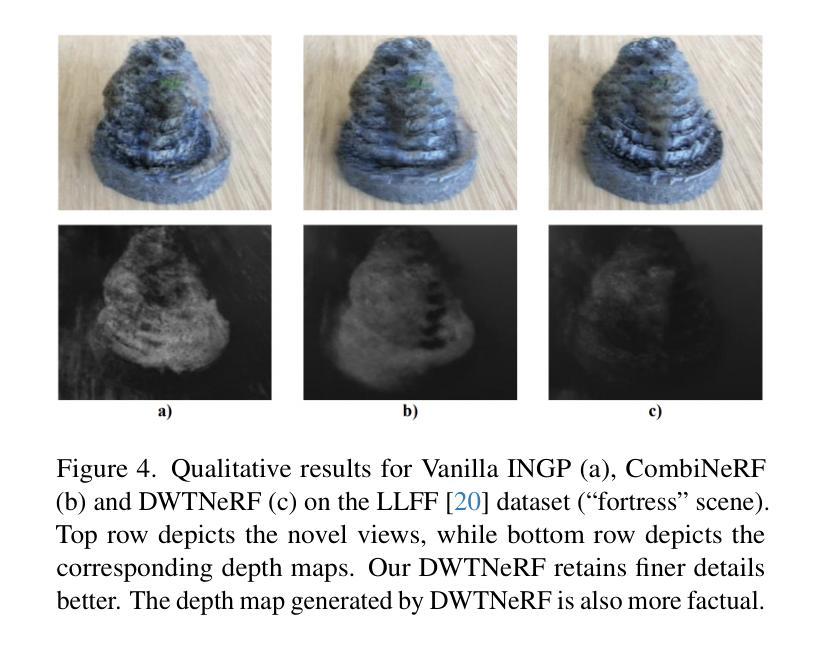
DWTNeRF: Boosting Few-shot Neural Radiance Fields via Discrete Wavelet Transform
Authors:Hung Nguyen, Blark Runfa Li, Truong Nguyen
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) has achieved superior performance in novel view synthesis and 3D scene representation, but its practical applications are hindered by slow convergence and reliance on dense training views. To this end, we present DWTNeRF, a unified framework based on Instant-NGP’s fast-training hash encoding. It is coupled with regularization terms designed for few-shot NeRF, which operates on sparse training views. Our DWTNeRF additionally includes a novel Discrete Wavelet loss that allows explicit prioritization of low frequencies directly in the training objective, reducing few-shot NeRF’s overfitting on high frequencies in earlier training stages. We also introduce a model-based approach, based on multi-head attention, that is compatible with INGP, which are sensitive to architectural changes. On the 3-shot LLFF benchmark, DWTNeRF outperforms Vanilla INGP by 15.07% in PSNR, 24.45% in SSIM and 36.30% in LPIPS. Our approach encourages a re-thinking of current few-shot approaches for fast-converging implicit representations like INGP or 3DGS.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在新型视图合成和3D场景表示方面取得了卓越的性能,但其实际应用受到了收敛速度慢和依赖密集训练视图的影响。为此,我们提出了DWTNeRF,一个基于Instant-NGP快速训练哈希编码的统一框架。它与针对少镜头NeRF设计的正则化项相结合,可在稀疏训练视图上运行。我们的DWTNeRF还包括一种新型的离散小波损失,允许在训练目标中直接明确优先低频,从而减少早期训练阶段中少镜头NeRF对高频的过拟合。我们还介绍了一种基于多头注意力的模型方法,该方法与INGP兼容,对架构变化敏感。在3镜头LLFF基准测试中,DWTNeRF在PSNR上较Vanilla INGP高出15.07%,在SSIM上高出24.45%,在LPIPS上高出36.30%。我们的方法鼓励对现有的快速收敛隐式表示方法(如INGP或3DGS)的少镜头方法进行重新思考。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于NeRF技术的新研究“DWTNeRF”推出了一种全新框架,用于实现快速训练NeRF模型并实现少量样本学习。它结合了Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码,并为稀疏训练视图设计了正则化术语。此外,DWTNeRF引入了一种新颖离散小波损失(Discrete Wavelet loss),直接针对训练目标显式强调低频优先级,从而减少早期训练阶段中对高频的过度拟合。该研究还在模型层面引入了基于多头注意力的方法,适用于对架构变动敏感的模型。DWTNeRF在3镜头LLFF基准测试中实现了优于普通INGP模型的显著表现。这启发我们对现有快速收敛隐式表示方法的重新思考。
Key Takeaways
- DWTNeRF是一个基于NeRF技术的统一框架,用于实现快速训练和稀疏样本学习。
- 它结合了Instant-NGP的快速训练哈希编码技术。
- 设计了正则化术语以适应稀疏训练视图。
- 引入了一种新颖离散小波损失(Discrete Wavelet loss),以减少早期训练阶段对高频的过度拟合。
- 在模型层面引入了基于多头注意力的方法,增强了模型的适应性。
- 在3镜头LLFF基准测试中表现优于普通模型。
点此查看论文截图